User login
ASCO updates guidance on prophylaxis for adults with cancer-related immunosuppression
Fluoroquinolones are recommended for adults with cancer-related immunosuppression if they are at high risk of infection, according to an updated clinical practice guideline on antimicrobial prophylaxis.
By contrast, patients with solid tumors are not routinely recommended to receive antibiotic prophylaxis, according to the guideline, developed by the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) with the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA).
The guideline includes antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral prophylaxis recommendations, along with additional precautions such as hand hygiene that may reduce infection risk.
Released in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, the updated guidelines were developed by an expert panel cochaired by Christopher R. Flowers, MD of Emory University, Atlanta, and Randy A. Taplitz, MD of the University of California, San Diego, Health.
For the most part, the panel endorsed the previous ASCO recommendations, published in 2013. However, the panel considered six new high-quality studies and six new or updated meta-analyses to make modifications and add some new recommendations.
Fluoroquinolones, in the 2013 guideline, were recommended over trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole because of fewer adverse events leading to treatment discontinuation. Panelists for the new guidelines said they continued to support that recommendation, based on an updated literature review.
That review showed significant reductions in both febrile neutropenia incidence and all-cause mortality, not only for patients at high risk of febrile neutropenia or profound, protracted neutropenia but also for lower-risk patients with solid tumors, they said.
However, the benefits did not sufficiently outweigh the harms to justify recommending fluoroquinolone prophylaxis for all patients with solid tumors or lymphoma, according to the report from the expert panel.
Those harms could include antibiotic-associated adverse effects, emergence of resistance, and Clostridium difficile infections, they said.
Accordingly, they recommended fluoroquinolone prophylaxis for the high-risk patients, including most patients with acute myeloid leukemia/myelodysplastic syndromes (AML/MDS) or those undergoing hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT).
Similarly, the panel recommended that high-risk patients should receive antifungal prophylaxis with an oral triazole or parenteral echinocandin, while prophylaxis would not be routinely recommended for solid tumor patients.
By contrast, all patients undergoing chemotherapy for malignancy should receive yearly influenza vaccination with an inactivated quadrivalent vaccine, the panel said in its antiviral prophylaxis recommendations.
Family members, household contacts, and health care providers also should receive influenza vaccinations, said the panel, endorsing recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention that were also cited in the 2013 ASCO guidelines.
Health care workers should follow hand hygiene and respiratory hygiene/cough etiquette to reduce risk of pathogen transmission, the panel said, endorsing CDC recommendations cited in the previous guideline.
However, the panel said they recommend against interventions such as neutropenic diet, footwear exchange, nutritional supplements, and surgical masks.
“Evidence of clinical benefit is lacking” for those interventions, they said.
Participants in the expert panel disclosed potential conflicts of interest related to Merck, Chimerix, GlyPharma Therapeutic, Pfizer, Cidara Therapeutics, Celgene, Astellas Pharma, Gilead Sciences, and Allergan, among other entities.
SOURCE: Taplitz RA et al. J Clin Oncol. 2018 Sept 4. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.00374.
Fluoroquinolones are recommended for adults with cancer-related immunosuppression if they are at high risk of infection, according to an updated clinical practice guideline on antimicrobial prophylaxis.
By contrast, patients with solid tumors are not routinely recommended to receive antibiotic prophylaxis, according to the guideline, developed by the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) with the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA).
The guideline includes antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral prophylaxis recommendations, along with additional precautions such as hand hygiene that may reduce infection risk.
Released in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, the updated guidelines were developed by an expert panel cochaired by Christopher R. Flowers, MD of Emory University, Atlanta, and Randy A. Taplitz, MD of the University of California, San Diego, Health.
For the most part, the panel endorsed the previous ASCO recommendations, published in 2013. However, the panel considered six new high-quality studies and six new or updated meta-analyses to make modifications and add some new recommendations.
Fluoroquinolones, in the 2013 guideline, were recommended over trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole because of fewer adverse events leading to treatment discontinuation. Panelists for the new guidelines said they continued to support that recommendation, based on an updated literature review.
That review showed significant reductions in both febrile neutropenia incidence and all-cause mortality, not only for patients at high risk of febrile neutropenia or profound, protracted neutropenia but also for lower-risk patients with solid tumors, they said.
However, the benefits did not sufficiently outweigh the harms to justify recommending fluoroquinolone prophylaxis for all patients with solid tumors or lymphoma, according to the report from the expert panel.
Those harms could include antibiotic-associated adverse effects, emergence of resistance, and Clostridium difficile infections, they said.
Accordingly, they recommended fluoroquinolone prophylaxis for the high-risk patients, including most patients with acute myeloid leukemia/myelodysplastic syndromes (AML/MDS) or those undergoing hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT).
Similarly, the panel recommended that high-risk patients should receive antifungal prophylaxis with an oral triazole or parenteral echinocandin, while prophylaxis would not be routinely recommended for solid tumor patients.
By contrast, all patients undergoing chemotherapy for malignancy should receive yearly influenza vaccination with an inactivated quadrivalent vaccine, the panel said in its antiviral prophylaxis recommendations.
Family members, household contacts, and health care providers also should receive influenza vaccinations, said the panel, endorsing recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention that were also cited in the 2013 ASCO guidelines.
Health care workers should follow hand hygiene and respiratory hygiene/cough etiquette to reduce risk of pathogen transmission, the panel said, endorsing CDC recommendations cited in the previous guideline.
However, the panel said they recommend against interventions such as neutropenic diet, footwear exchange, nutritional supplements, and surgical masks.
“Evidence of clinical benefit is lacking” for those interventions, they said.
Participants in the expert panel disclosed potential conflicts of interest related to Merck, Chimerix, GlyPharma Therapeutic, Pfizer, Cidara Therapeutics, Celgene, Astellas Pharma, Gilead Sciences, and Allergan, among other entities.
SOURCE: Taplitz RA et al. J Clin Oncol. 2018 Sept 4. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.00374.
Fluoroquinolones are recommended for adults with cancer-related immunosuppression if they are at high risk of infection, according to an updated clinical practice guideline on antimicrobial prophylaxis.
By contrast, patients with solid tumors are not routinely recommended to receive antibiotic prophylaxis, according to the guideline, developed by the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) with the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA).
The guideline includes antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral prophylaxis recommendations, along with additional precautions such as hand hygiene that may reduce infection risk.
Released in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, the updated guidelines were developed by an expert panel cochaired by Christopher R. Flowers, MD of Emory University, Atlanta, and Randy A. Taplitz, MD of the University of California, San Diego, Health.
For the most part, the panel endorsed the previous ASCO recommendations, published in 2013. However, the panel considered six new high-quality studies and six new or updated meta-analyses to make modifications and add some new recommendations.
Fluoroquinolones, in the 2013 guideline, were recommended over trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole because of fewer adverse events leading to treatment discontinuation. Panelists for the new guidelines said they continued to support that recommendation, based on an updated literature review.
That review showed significant reductions in both febrile neutropenia incidence and all-cause mortality, not only for patients at high risk of febrile neutropenia or profound, protracted neutropenia but also for lower-risk patients with solid tumors, they said.
However, the benefits did not sufficiently outweigh the harms to justify recommending fluoroquinolone prophylaxis for all patients with solid tumors or lymphoma, according to the report from the expert panel.
Those harms could include antibiotic-associated adverse effects, emergence of resistance, and Clostridium difficile infections, they said.
Accordingly, they recommended fluoroquinolone prophylaxis for the high-risk patients, including most patients with acute myeloid leukemia/myelodysplastic syndromes (AML/MDS) or those undergoing hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT).
Similarly, the panel recommended that high-risk patients should receive antifungal prophylaxis with an oral triazole or parenteral echinocandin, while prophylaxis would not be routinely recommended for solid tumor patients.
By contrast, all patients undergoing chemotherapy for malignancy should receive yearly influenza vaccination with an inactivated quadrivalent vaccine, the panel said in its antiviral prophylaxis recommendations.
Family members, household contacts, and health care providers also should receive influenza vaccinations, said the panel, endorsing recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention that were also cited in the 2013 ASCO guidelines.
Health care workers should follow hand hygiene and respiratory hygiene/cough etiquette to reduce risk of pathogen transmission, the panel said, endorsing CDC recommendations cited in the previous guideline.
However, the panel said they recommend against interventions such as neutropenic diet, footwear exchange, nutritional supplements, and surgical masks.
“Evidence of clinical benefit is lacking” for those interventions, they said.
Participants in the expert panel disclosed potential conflicts of interest related to Merck, Chimerix, GlyPharma Therapeutic, Pfizer, Cidara Therapeutics, Celgene, Astellas Pharma, Gilead Sciences, and Allergan, among other entities.
SOURCE: Taplitz RA et al. J Clin Oncol. 2018 Sept 4. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.00374.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
Rituximab/lenalidomide similar to rituximab/chemotherapy for follicular lymphoma
Rituximab plus lenalidomide had efficacy similar to that of rituximab plus chemotherapy in treatment of follicular lymphoma, according to results from a phase 3 trial.
RELEVANCE (NCT01476787) was a multicenter, international, randomized, open-label trial designed to determine the superiority of rituximab/lenalidomide over rituximab/chemotherapy.
This trial randomized 1,030 patients with previously untreated follicular lymphoma to receive either rituximab plus lenalidomide (n = 513) or rituximab plus chemotherapy (n = 517) for 18 cycles; both groups then went on to receive rituximab maintenance therapy for 12 cycles. The total duration of treatment was 120 weeks. The median age of the combined groups was 59 years. The study was published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
One of the coprimary endpoints was complete response (confirmed or unconfirmed) by the end of the treatment period; the other was progression-free survival, which was planned to be assessed through three analyses, including two interim analyses, the first of which was reported in this study.
After a median follow-up of 37.9 months, the rates of coprimary endpoints were similar between the two groups. Complete response (confirmed or unconfirmed) was seen in 48% of the rituximab/lenalidomide group (95% confidence interval [CI], 44-53) and in 53% of the rituximab/chemotherapy group (95% CI, 49-57; P = .13). The hazard ratio for progression or death from any cause was 1.10 (95% CI, 0.85-1.43; P = .48).
In the subgroup analyses, the efficacy of rituximab plus chemotherapy was greater in low-risk patients (based on Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores) and in patients whose follicular lymphoma was Ann Arbor stage I or II, whereas efficacy of rituximab/lenalidomide was independent of prognostic factors.
Safety was the biggest area of difference, with some events being more common in one group than in the other. For example, cutaneous reactions, diarrhea, rash, and myalgia were more common with rituximab/lenalidomide treatment, whereas anemia, fatigue, nausea, and febrile neutropenia were more common with rituximab/chemotherapy treatment. Among grade 3 or 4 events, cutaneous reactions were more common with rituximab/lenalidomide, and grade 3 or 4 neutropenia was more common with rituximab/chemotherapy.
“Overall, both treatment groups showed good outcomes, and a median has not yet been reached for either progression-free survival or overall survival,” the study authors wrote.
The RELEVANCE trial was sponsored by Celgene and the Lymphoma Academic Research Organisation. The study authors reported various disclosures, including financial ties to Celgene.
SOURCE: Morschhauser F et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:934-47.
Rituximab plus lenalidomide had efficacy similar to that of rituximab plus chemotherapy in treatment of follicular lymphoma, according to results from a phase 3 trial.
RELEVANCE (NCT01476787) was a multicenter, international, randomized, open-label trial designed to determine the superiority of rituximab/lenalidomide over rituximab/chemotherapy.
This trial randomized 1,030 patients with previously untreated follicular lymphoma to receive either rituximab plus lenalidomide (n = 513) or rituximab plus chemotherapy (n = 517) for 18 cycles; both groups then went on to receive rituximab maintenance therapy for 12 cycles. The total duration of treatment was 120 weeks. The median age of the combined groups was 59 years. The study was published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
One of the coprimary endpoints was complete response (confirmed or unconfirmed) by the end of the treatment period; the other was progression-free survival, which was planned to be assessed through three analyses, including two interim analyses, the first of which was reported in this study.
After a median follow-up of 37.9 months, the rates of coprimary endpoints were similar between the two groups. Complete response (confirmed or unconfirmed) was seen in 48% of the rituximab/lenalidomide group (95% confidence interval [CI], 44-53) and in 53% of the rituximab/chemotherapy group (95% CI, 49-57; P = .13). The hazard ratio for progression or death from any cause was 1.10 (95% CI, 0.85-1.43; P = .48).
In the subgroup analyses, the efficacy of rituximab plus chemotherapy was greater in low-risk patients (based on Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores) and in patients whose follicular lymphoma was Ann Arbor stage I or II, whereas efficacy of rituximab/lenalidomide was independent of prognostic factors.
Safety was the biggest area of difference, with some events being more common in one group than in the other. For example, cutaneous reactions, diarrhea, rash, and myalgia were more common with rituximab/lenalidomide treatment, whereas anemia, fatigue, nausea, and febrile neutropenia were more common with rituximab/chemotherapy treatment. Among grade 3 or 4 events, cutaneous reactions were more common with rituximab/lenalidomide, and grade 3 or 4 neutropenia was more common with rituximab/chemotherapy.
“Overall, both treatment groups showed good outcomes, and a median has not yet been reached for either progression-free survival or overall survival,” the study authors wrote.
The RELEVANCE trial was sponsored by Celgene and the Lymphoma Academic Research Organisation. The study authors reported various disclosures, including financial ties to Celgene.
SOURCE: Morschhauser F et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:934-47.
Rituximab plus lenalidomide had efficacy similar to that of rituximab plus chemotherapy in treatment of follicular lymphoma, according to results from a phase 3 trial.
RELEVANCE (NCT01476787) was a multicenter, international, randomized, open-label trial designed to determine the superiority of rituximab/lenalidomide over rituximab/chemotherapy.
This trial randomized 1,030 patients with previously untreated follicular lymphoma to receive either rituximab plus lenalidomide (n = 513) or rituximab plus chemotherapy (n = 517) for 18 cycles; both groups then went on to receive rituximab maintenance therapy for 12 cycles. The total duration of treatment was 120 weeks. The median age of the combined groups was 59 years. The study was published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
One of the coprimary endpoints was complete response (confirmed or unconfirmed) by the end of the treatment period; the other was progression-free survival, which was planned to be assessed through three analyses, including two interim analyses, the first of which was reported in this study.
After a median follow-up of 37.9 months, the rates of coprimary endpoints were similar between the two groups. Complete response (confirmed or unconfirmed) was seen in 48% of the rituximab/lenalidomide group (95% confidence interval [CI], 44-53) and in 53% of the rituximab/chemotherapy group (95% CI, 49-57; P = .13). The hazard ratio for progression or death from any cause was 1.10 (95% CI, 0.85-1.43; P = .48).
In the subgroup analyses, the efficacy of rituximab plus chemotherapy was greater in low-risk patients (based on Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores) and in patients whose follicular lymphoma was Ann Arbor stage I or II, whereas efficacy of rituximab/lenalidomide was independent of prognostic factors.
Safety was the biggest area of difference, with some events being more common in one group than in the other. For example, cutaneous reactions, diarrhea, rash, and myalgia were more common with rituximab/lenalidomide treatment, whereas anemia, fatigue, nausea, and febrile neutropenia were more common with rituximab/chemotherapy treatment. Among grade 3 or 4 events, cutaneous reactions were more common with rituximab/lenalidomide, and grade 3 or 4 neutropenia was more common with rituximab/chemotherapy.
“Overall, both treatment groups showed good outcomes, and a median has not yet been reached for either progression-free survival or overall survival,” the study authors wrote.
The RELEVANCE trial was sponsored by Celgene and the Lymphoma Academic Research Organisation. The study authors reported various disclosures, including financial ties to Celgene.
SOURCE: Morschhauser F et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:934-47.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Complete responses were seen in 48% of rituximab/lenalidomide patients versus 53% in the rituximab/chemotherapy patients (P = .13).
Study details: A phase 3 superiority trial of 1,030 patients with previously untreated follicular lymphoma.
Disclosures: Celgene and the Lymphoma Academic Research Organization funded the study. The authors reported various disclosures, including financial ties to Celgene.
Source: Morschhauser F et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:934-47.
FDA approves ibrutinib with rituximab in Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia
The Food and Drug Administration has approved ibrutinib (Imbruvica) for use in combination with rituximab to treat adults with Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (WM).
Ibrutinib was approved for use as a single agent in adults with WM in January 2015.
The latest approval was supported by the phase 3 iNNOVATE trial, in which researchers compared ibrutinib plus rituximab to rituximab alone in patients with previously untreated or relapsed/refractory WM.
Results from iNNOVATE were presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology and simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2018;378:2399-2410).
The 30-month progression-free survival rates were 82% in the ibrutinib arm and 28% in the placebo arm. The median progression-free survival was not reached in the ibrutinib arm and was 20.3 months in the placebo arm (hazard ratio, 0.20; P less than .0001).
The 30-month overall survival rates were 94% in the ibrutinib arm and 92% in the placebo arm.
Grade 3 or higher treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) occurred in 60% of patients in the ibrutinib arm and 61% in the placebo arm. Serious AEs occurred in 43% and 33%, respectively. There were no fatal AEs in the ibrutinib arm and three in the rituximab arm.
Ibrutinib is jointly developed and commercialized by Pharmacyclics, an AbbVie company, and Janssen Biotech.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved ibrutinib (Imbruvica) for use in combination with rituximab to treat adults with Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (WM).
Ibrutinib was approved for use as a single agent in adults with WM in January 2015.
The latest approval was supported by the phase 3 iNNOVATE trial, in which researchers compared ibrutinib plus rituximab to rituximab alone in patients with previously untreated or relapsed/refractory WM.
Results from iNNOVATE were presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology and simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2018;378:2399-2410).
The 30-month progression-free survival rates were 82% in the ibrutinib arm and 28% in the placebo arm. The median progression-free survival was not reached in the ibrutinib arm and was 20.3 months in the placebo arm (hazard ratio, 0.20; P less than .0001).
The 30-month overall survival rates were 94% in the ibrutinib arm and 92% in the placebo arm.
Grade 3 or higher treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) occurred in 60% of patients in the ibrutinib arm and 61% in the placebo arm. Serious AEs occurred in 43% and 33%, respectively. There were no fatal AEs in the ibrutinib arm and three in the rituximab arm.
Ibrutinib is jointly developed and commercialized by Pharmacyclics, an AbbVie company, and Janssen Biotech.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved ibrutinib (Imbruvica) for use in combination with rituximab to treat adults with Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (WM).
Ibrutinib was approved for use as a single agent in adults with WM in January 2015.
The latest approval was supported by the phase 3 iNNOVATE trial, in which researchers compared ibrutinib plus rituximab to rituximab alone in patients with previously untreated or relapsed/refractory WM.
Results from iNNOVATE were presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology and simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2018;378:2399-2410).
The 30-month progression-free survival rates were 82% in the ibrutinib arm and 28% in the placebo arm. The median progression-free survival was not reached in the ibrutinib arm and was 20.3 months in the placebo arm (hazard ratio, 0.20; P less than .0001).
The 30-month overall survival rates were 94% in the ibrutinib arm and 92% in the placebo arm.
Grade 3 or higher treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) occurred in 60% of patients in the ibrutinib arm and 61% in the placebo arm. Serious AEs occurred in 43% and 33%, respectively. There were no fatal AEs in the ibrutinib arm and three in the rituximab arm.
Ibrutinib is jointly developed and commercialized by Pharmacyclics, an AbbVie company, and Janssen Biotech.
Make The Diagnosis - September 2018
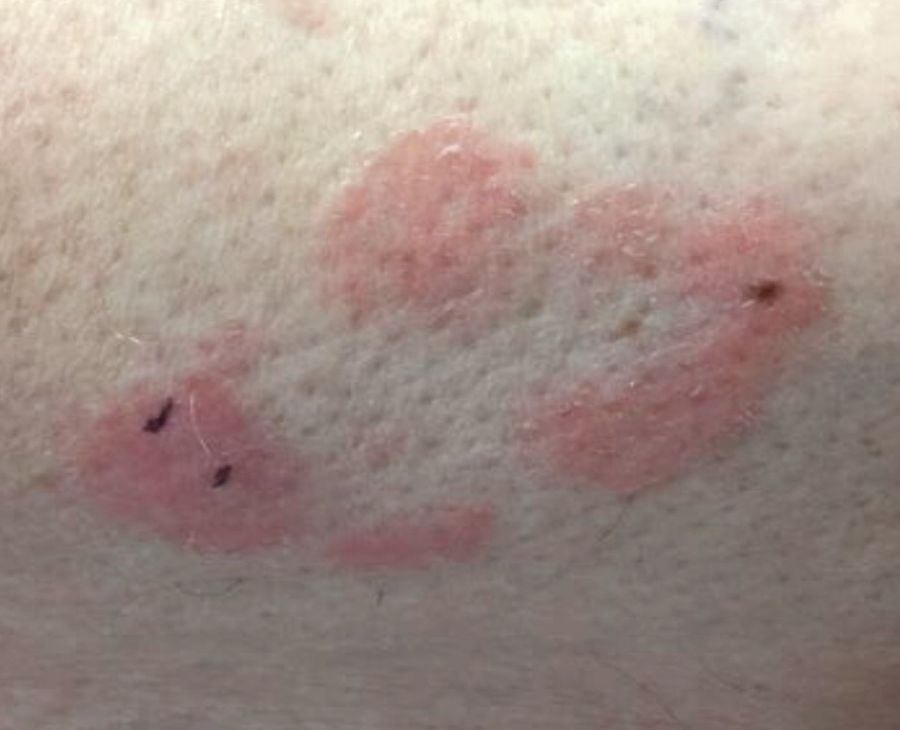
Some have postulated an infectious agent as the cause. Atopic dermatitis may confer an increased risk because of the chronic stimulation of T cells. Males are more commonly affected than females by a 2:1 ratio. A worse prognosis is associated with advanced age. Children and adolescents may be affected as well.
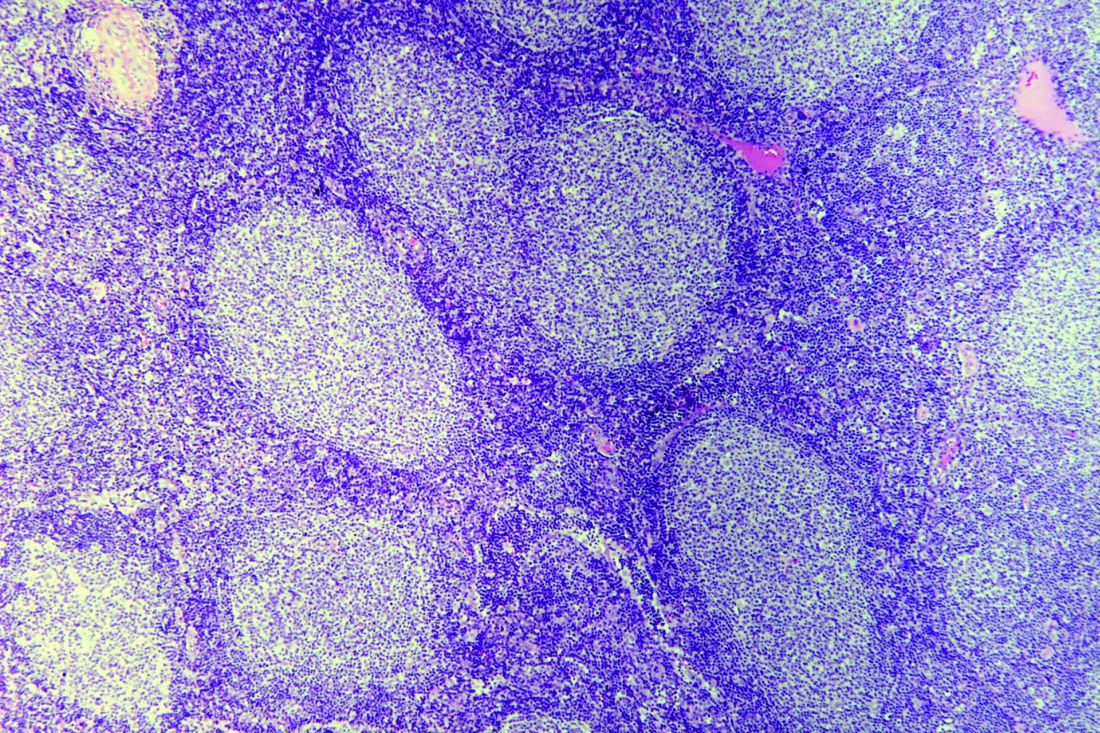
With mycosis fungoides, there are three main types of skin lesions: patch, plaque, and tumor. Patients will progress from patch to plaque to tumor stage in classic MF. Often, lesions begin as scaly, erythematous patches that resemble eczema. Because of the nonspecific nature of early lesions, the median duration from the onset of skin lesions to the diagnosis of MF is 4-6 years. Patch stage lesions may be pruritic or asymptomatic. Commonly, they present in non–sun-exposed areas, such as the buttocks. Annular, infiltrated, red-brown or violaceous plaques can develop, which represent malignant T-cell infiltration. Many patients never progress past the plaque stage. Tumor stage MF is more aggressive, with nodules that may undergo necrosis and ulceration.
The leukemic form of MF is Sézary syndrome. Patients present with pruritic erythroderma and lymphadenopathy. Nail dystrophy, scaling of palms and soles, and alopecia may be present. A peripheral blood smear reveals Sézary cells, which are large, hyperconvoluted lymphocytes. The count of Sézary cells is usually greater than 1000 cells/mm3.
Histology of early lesions may not be diagnostic for CTCL. Often, biopsies will be read as eczematous or psoriasiform for years before the diagnosis of MF is made. Classically, epidermotropism (single-cell exocytosis of lymphocytes into the epidermis) is present. Advanced stages may show a dense infiltrate of lymphocytes in the dermis. Groups of lymphocytes in the epidermis form Pautrier’s microabscesses. Mycosis cells may exhibit cerebriform nuclei. Neoplastic cells in MF are CD3+, CD4+, CD45RO+, CD8–. Tissue can be sent for T-cell gene rearrangement polymerase chain reaction. The presence of monoclonal T-cell gene receptor rearrangements can aid in the diagnosis of MF.
Treatment includes topical steroids, mechlorethamine (nitrogen mustard) or bexarotene gel, PUVA therapy, and narrow-band UVB light for limited and/or patch disease. Localized radiotherapy can be used for more resistant lesions. Topical therapies are preferred in the early stages in MF. Systemic treatments for patients who do not respond to local therapy, or in more advanced disease include methotrexate, interferon-alpha, oral bexarotene, denileukin diftitox, and combination chemotherapy. Photopheresis is reserved for erythrodermic disease.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
Some have postulated an infectious agent as the cause. Atopic dermatitis may confer an increased risk because of the chronic stimulation of T cells. Males are more commonly affected than females by a 2:1 ratio. A worse prognosis is associated with advanced age. Children and adolescents may be affected as well.
With mycosis fungoides, there are three main types of skin lesions: patch, plaque, and tumor. Patients will progress from patch to plaque to tumor stage in classic MF. Often, lesions begin as scaly, erythematous patches that resemble eczema. Because of the nonspecific nature of early lesions, the median duration from the onset of skin lesions to the diagnosis of MF is 4-6 years. Patch stage lesions may be pruritic or asymptomatic. Commonly, they present in non–sun-exposed areas, such as the buttocks. Annular, infiltrated, red-brown or violaceous plaques can develop, which represent malignant T-cell infiltration. Many patients never progress past the plaque stage. Tumor stage MF is more aggressive, with nodules that may undergo necrosis and ulceration.
The leukemic form of MF is Sézary syndrome. Patients present with pruritic erythroderma and lymphadenopathy. Nail dystrophy, scaling of palms and soles, and alopecia may be present. A peripheral blood smear reveals Sézary cells, which are large, hyperconvoluted lymphocytes. The count of Sézary cells is usually greater than 1000 cells/mm3.
Histology of early lesions may not be diagnostic for CTCL. Often, biopsies will be read as eczematous or psoriasiform for years before the diagnosis of MF is made. Classically, epidermotropism (single-cell exocytosis of lymphocytes into the epidermis) is present. Advanced stages may show a dense infiltrate of lymphocytes in the dermis. Groups of lymphocytes in the epidermis form Pautrier’s microabscesses. Mycosis cells may exhibit cerebriform nuclei. Neoplastic cells in MF are CD3+, CD4+, CD45RO+, CD8–. Tissue can be sent for T-cell gene rearrangement polymerase chain reaction. The presence of monoclonal T-cell gene receptor rearrangements can aid in the diagnosis of MF.
Treatment includes topical steroids, mechlorethamine (nitrogen mustard) or bexarotene gel, PUVA therapy, and narrow-band UVB light for limited and/or patch disease. Localized radiotherapy can be used for more resistant lesions. Topical therapies are preferred in the early stages in MF. Systemic treatments for patients who do not respond to local therapy, or in more advanced disease include methotrexate, interferon-alpha, oral bexarotene, denileukin diftitox, and combination chemotherapy. Photopheresis is reserved for erythrodermic disease.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
Some have postulated an infectious agent as the cause. Atopic dermatitis may confer an increased risk because of the chronic stimulation of T cells. Males are more commonly affected than females by a 2:1 ratio. A worse prognosis is associated with advanced age. Children and adolescents may be affected as well.
With mycosis fungoides, there are three main types of skin lesions: patch, plaque, and tumor. Patients will progress from patch to plaque to tumor stage in classic MF. Often, lesions begin as scaly, erythematous patches that resemble eczema. Because of the nonspecific nature of early lesions, the median duration from the onset of skin lesions to the diagnosis of MF is 4-6 years. Patch stage lesions may be pruritic or asymptomatic. Commonly, they present in non–sun-exposed areas, such as the buttocks. Annular, infiltrated, red-brown or violaceous plaques can develop, which represent malignant T-cell infiltration. Many patients never progress past the plaque stage. Tumor stage MF is more aggressive, with nodules that may undergo necrosis and ulceration.
The leukemic form of MF is Sézary syndrome. Patients present with pruritic erythroderma and lymphadenopathy. Nail dystrophy, scaling of palms and soles, and alopecia may be present. A peripheral blood smear reveals Sézary cells, which are large, hyperconvoluted lymphocytes. The count of Sézary cells is usually greater than 1000 cells/mm3.
Histology of early lesions may not be diagnostic for CTCL. Often, biopsies will be read as eczematous or psoriasiform for years before the diagnosis of MF is made. Classically, epidermotropism (single-cell exocytosis of lymphocytes into the epidermis) is present. Advanced stages may show a dense infiltrate of lymphocytes in the dermis. Groups of lymphocytes in the epidermis form Pautrier’s microabscesses. Mycosis cells may exhibit cerebriform nuclei. Neoplastic cells in MF are CD3+, CD4+, CD45RO+, CD8–. Tissue can be sent for T-cell gene rearrangement polymerase chain reaction. The presence of monoclonal T-cell gene receptor rearrangements can aid in the diagnosis of MF.
Treatment includes topical steroids, mechlorethamine (nitrogen mustard) or bexarotene gel, PUVA therapy, and narrow-band UVB light for limited and/or patch disease. Localized radiotherapy can be used for more resistant lesions. Topical therapies are preferred in the early stages in MF. Systemic treatments for patients who do not respond to local therapy, or in more advanced disease include methotrexate, interferon-alpha, oral bexarotene, denileukin diftitox, and combination chemotherapy. Photopheresis is reserved for erythrodermic disease.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
New chronic lymphocytic leukemia guidelines from the UK
Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab are recommended as initial therapy for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia who do not have TP53 disruption, according to new guidelines from the British Society for Haematology.
The guidelines update the 2012 recommendations on chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) to include “significant” developments in treatment. They were published in the British Journal of Haematology.
Anna H. Schuh, MD, of the department of oncology at the University of Oxford (England), and her coauthors noted that, while these guidelines apply to treatments available outside clinical trials, wherever possible patients with CLL should be treated within the clinical trial setting.
While recommending fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab as first-line therapy, the guideline authors acknowledged that the combination of bendamustine and rituximab is an acceptable alternative for patients who could not take the triple therapy because of comorbidities such as advanced age, renal impairment, or issues with marrow capacity.
Similarly, less-fit patients could also be considered for chlorambucil-obinutuzumab or chlorambucil-ofatumumab combinations.
All patients diagnosed with CLL should be tested for TP53 deletions and mutations before each line of therapy, the guideline committee recommended. TP53 disruption makes chemoimmunotherapy ineffective because of either a deletion of chromosome 17p or a mutation in the TP53 gene. However, there is compelling evidence for the efficacy of ibrutinib in these patients, or idelalisib and rituximab for those with cardiac disease or receiving vitamin K antagonists.
With respect to maintenance therapy, the guidelines noted that this was not routinely recommended in CLL as “it is unclear to what extent the progression-free survival benefit is offset by long-term toxicity.”
Patients who are refractory to chemoimmunotherapy, who have relapsed, or who cannot be retreated with chemoimmunotherapy should be treated with idelalisib with rituximab or ibrutinib monotherapy, the guidelines suggested.
“Deciding whether ibrutinib or idelalisib with rituximab is most appropriate for an individual patient depends on a range of factors, including toxicity profile and convenience of delivery,” the authors wrote. However, they noted that the value of adding bendamustine to either option was unclear as research had not shown significant, associated gains in median progression-free survival.
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation should be considered as a treatment option for patients who have either failed chemotherapy, have a TP53 disruption and have not responded to B-cell receptor signaling pathway inhibitors such as ibrutinib, or have a Richter transformation.
The guidelines also addressed the issue of autoimmune cytopenias, which occur in 5%-10% of patients with CLL and can actually precede the diagnosis of CLL in about 9% of cases.
In patients where autoimmune cytopenia is the dominant clinical feature, they should be treated with corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin, or rituximab. However, for patients where the cytopenia is triggered by CLL therapy, the guidelines recommended halting treatment and beginning immunosuppression.
The guideline development was supported by the British Society for Haematology. The UK CLL Forum is a registered charity that receives funding from a number of pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Schuh AH et al. Br J Haematol. 2018 Jul 15. doi: 10.1111/bjh.15460.
Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab are recommended as initial therapy for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia who do not have TP53 disruption, according to new guidelines from the British Society for Haematology.
The guidelines update the 2012 recommendations on chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) to include “significant” developments in treatment. They were published in the British Journal of Haematology.
Anna H. Schuh, MD, of the department of oncology at the University of Oxford (England), and her coauthors noted that, while these guidelines apply to treatments available outside clinical trials, wherever possible patients with CLL should be treated within the clinical trial setting.
While recommending fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab as first-line therapy, the guideline authors acknowledged that the combination of bendamustine and rituximab is an acceptable alternative for patients who could not take the triple therapy because of comorbidities such as advanced age, renal impairment, or issues with marrow capacity.
Similarly, less-fit patients could also be considered for chlorambucil-obinutuzumab or chlorambucil-ofatumumab combinations.
All patients diagnosed with CLL should be tested for TP53 deletions and mutations before each line of therapy, the guideline committee recommended. TP53 disruption makes chemoimmunotherapy ineffective because of either a deletion of chromosome 17p or a mutation in the TP53 gene. However, there is compelling evidence for the efficacy of ibrutinib in these patients, or idelalisib and rituximab for those with cardiac disease or receiving vitamin K antagonists.
With respect to maintenance therapy, the guidelines noted that this was not routinely recommended in CLL as “it is unclear to what extent the progression-free survival benefit is offset by long-term toxicity.”
Patients who are refractory to chemoimmunotherapy, who have relapsed, or who cannot be retreated with chemoimmunotherapy should be treated with idelalisib with rituximab or ibrutinib monotherapy, the guidelines suggested.
“Deciding whether ibrutinib or idelalisib with rituximab is most appropriate for an individual patient depends on a range of factors, including toxicity profile and convenience of delivery,” the authors wrote. However, they noted that the value of adding bendamustine to either option was unclear as research had not shown significant, associated gains in median progression-free survival.
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation should be considered as a treatment option for patients who have either failed chemotherapy, have a TP53 disruption and have not responded to B-cell receptor signaling pathway inhibitors such as ibrutinib, or have a Richter transformation.
The guidelines also addressed the issue of autoimmune cytopenias, which occur in 5%-10% of patients with CLL and can actually precede the diagnosis of CLL in about 9% of cases.
In patients where autoimmune cytopenia is the dominant clinical feature, they should be treated with corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin, or rituximab. However, for patients where the cytopenia is triggered by CLL therapy, the guidelines recommended halting treatment and beginning immunosuppression.
The guideline development was supported by the British Society for Haematology. The UK CLL Forum is a registered charity that receives funding from a number of pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Schuh AH et al. Br J Haematol. 2018 Jul 15. doi: 10.1111/bjh.15460.
Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab are recommended as initial therapy for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia who do not have TP53 disruption, according to new guidelines from the British Society for Haematology.
The guidelines update the 2012 recommendations on chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) to include “significant” developments in treatment. They were published in the British Journal of Haematology.
Anna H. Schuh, MD, of the department of oncology at the University of Oxford (England), and her coauthors noted that, while these guidelines apply to treatments available outside clinical trials, wherever possible patients with CLL should be treated within the clinical trial setting.
While recommending fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab as first-line therapy, the guideline authors acknowledged that the combination of bendamustine and rituximab is an acceptable alternative for patients who could not take the triple therapy because of comorbidities such as advanced age, renal impairment, or issues with marrow capacity.
Similarly, less-fit patients could also be considered for chlorambucil-obinutuzumab or chlorambucil-ofatumumab combinations.
All patients diagnosed with CLL should be tested for TP53 deletions and mutations before each line of therapy, the guideline committee recommended. TP53 disruption makes chemoimmunotherapy ineffective because of either a deletion of chromosome 17p or a mutation in the TP53 gene. However, there is compelling evidence for the efficacy of ibrutinib in these patients, or idelalisib and rituximab for those with cardiac disease or receiving vitamin K antagonists.
With respect to maintenance therapy, the guidelines noted that this was not routinely recommended in CLL as “it is unclear to what extent the progression-free survival benefit is offset by long-term toxicity.”
Patients who are refractory to chemoimmunotherapy, who have relapsed, or who cannot be retreated with chemoimmunotherapy should be treated with idelalisib with rituximab or ibrutinib monotherapy, the guidelines suggested.
“Deciding whether ibrutinib or idelalisib with rituximab is most appropriate for an individual patient depends on a range of factors, including toxicity profile and convenience of delivery,” the authors wrote. However, they noted that the value of adding bendamustine to either option was unclear as research had not shown significant, associated gains in median progression-free survival.
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation should be considered as a treatment option for patients who have either failed chemotherapy, have a TP53 disruption and have not responded to B-cell receptor signaling pathway inhibitors such as ibrutinib, or have a Richter transformation.
The guidelines also addressed the issue of autoimmune cytopenias, which occur in 5%-10% of patients with CLL and can actually precede the diagnosis of CLL in about 9% of cases.
In patients where autoimmune cytopenia is the dominant clinical feature, they should be treated with corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin, or rituximab. However, for patients where the cytopenia is triggered by CLL therapy, the guidelines recommended halting treatment and beginning immunosuppression.
The guideline development was supported by the British Society for Haematology. The UK CLL Forum is a registered charity that receives funding from a number of pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Schuh AH et al. Br J Haematol. 2018 Jul 15. doi: 10.1111/bjh.15460.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF HAEMATOLOGY
Key clinical point:
Major finding: All patients diagnosed with CLL should be tested for TP53 disruption.
Study details: A guideline developed by the British Society for Haematology offering recommendations for CLL treatment outside clinical trials.
Disclosures: The guideline development was supported by the British Society for Haematology. The UK CLL Forum is a registered charity that receives funding from a number of pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Schuh AH et al. Br J Haematol. 2018 Jul 15. doi: 10.1111/bjh.15460.
Insurance is a matter of life or death for lymphoma patients
Having health insurance can mean the difference between life and death for patients with follicular lymphoma, suggest results of a study showing that patients with private health insurance had nearly twofold better survival outcomes than patients without insurance or those who were covered by Medicare or Medicaid.
A review of records on more than 43,000 patients with follicular lymphoma (FL) in a national cancer registry showed that, compared with patients under age 65 with private insurance, the hazard ratios (HR) for death among patients in the same age bracket with either no insurance, Medicaid, or Medicare were, respectively, 1.96, 1.83, and 1.96 (P less than .0001 for each comparison).
“Our study finds that insurance status contributes to survival disparities in FL. Future studies on outcomes in FL should include insurance status as an important predictor,” Christopher R. Flowers, MD, of Emory University in Atlanta and his colleagues wrote in Blood.
“Further research on prognosis for FL should examine the impact of public policy, such as the passage of the [Affordable Care Act], on FL outcomes, as well as examine other factors that influence access to care, such as individual-level socioeconomic status, regular primary care visits, access to prescription medications, and care affordability,” they added.
The investigators noted that earlier research found that patients with Medicaid or no insurance were more likely than privately-insured patients to be diagnosed with cancers at advanced stages, and that some patients with aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphomas have been shown to have insurance-related disparities in treatments and outcomes.
To see whether the same could be true for patients with indolent-histology lymphomas such as FL, they extracted data from the National Cancer Database, a nationwide hospital-based cancer registry sponsored jointly by the American College of Surgeons and the American Cancer Society.
They identified a total of 43,648 patients aged 18 years or older who were diagnosed with FL from 2004 through 2014. They looked at both patients 18-64 years and those 65 years and older to account for changes in insurance with Medicare eligibility.
Overall survival among patients younger than age 65 was significantly worse for patients with public insurance (Medicaid or Medicare) or no insurance in Cox proportional hazard models controlling for available data on sociodemographic factors and prognostic indicators.
However, compared with patients aged 65 and older with private insurance, only patients with Medicare as their sole source of insurance had significantly worse overall survival (HR, 1.28; P less than .0001).
Patients who were uninsured or had Medicaid were more likely than others to have lower socioeconomic status, present with advanced-stage disease, have systemic symptoms, and have multiple comorbidities that persisted after controlling for known sociodemographic and prognostic factors.
The investigators found that, among patients under age 65, those with a comorbidity score of 1 had an HR for death of 1.71, compared with patients with no comorbidities, and that patients with a score of 2 or greater had a HR of 3.1 (P less than .0001 for each comparison).
“The findings of the study indicate that improving access to affordable, quality health care may reduce disparities in survival for those currently lacking coverage,” the investigators wrote.
The study was supported by Emory University, the National Institutes of Health, and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Dr. Flowers reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Spectrum, Celgene, and several other companies. The other authors reported having nothing to disclose.
SOURCE: Goldstein JS et al. Blood. 2018 Jul 24. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-03-839035.
Having health insurance can mean the difference between life and death for patients with follicular lymphoma, suggest results of a study showing that patients with private health insurance had nearly twofold better survival outcomes than patients without insurance or those who were covered by Medicare or Medicaid.
A review of records on more than 43,000 patients with follicular lymphoma (FL) in a national cancer registry showed that, compared with patients under age 65 with private insurance, the hazard ratios (HR) for death among patients in the same age bracket with either no insurance, Medicaid, or Medicare were, respectively, 1.96, 1.83, and 1.96 (P less than .0001 for each comparison).
“Our study finds that insurance status contributes to survival disparities in FL. Future studies on outcomes in FL should include insurance status as an important predictor,” Christopher R. Flowers, MD, of Emory University in Atlanta and his colleagues wrote in Blood.
“Further research on prognosis for FL should examine the impact of public policy, such as the passage of the [Affordable Care Act], on FL outcomes, as well as examine other factors that influence access to care, such as individual-level socioeconomic status, regular primary care visits, access to prescription medications, and care affordability,” they added.
The investigators noted that earlier research found that patients with Medicaid or no insurance were more likely than privately-insured patients to be diagnosed with cancers at advanced stages, and that some patients with aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphomas have been shown to have insurance-related disparities in treatments and outcomes.
To see whether the same could be true for patients with indolent-histology lymphomas such as FL, they extracted data from the National Cancer Database, a nationwide hospital-based cancer registry sponsored jointly by the American College of Surgeons and the American Cancer Society.
They identified a total of 43,648 patients aged 18 years or older who were diagnosed with FL from 2004 through 2014. They looked at both patients 18-64 years and those 65 years and older to account for changes in insurance with Medicare eligibility.
Overall survival among patients younger than age 65 was significantly worse for patients with public insurance (Medicaid or Medicare) or no insurance in Cox proportional hazard models controlling for available data on sociodemographic factors and prognostic indicators.
However, compared with patients aged 65 and older with private insurance, only patients with Medicare as their sole source of insurance had significantly worse overall survival (HR, 1.28; P less than .0001).
Patients who were uninsured or had Medicaid were more likely than others to have lower socioeconomic status, present with advanced-stage disease, have systemic symptoms, and have multiple comorbidities that persisted after controlling for known sociodemographic and prognostic factors.
The investigators found that, among patients under age 65, those with a comorbidity score of 1 had an HR for death of 1.71, compared with patients with no comorbidities, and that patients with a score of 2 or greater had a HR of 3.1 (P less than .0001 for each comparison).
“The findings of the study indicate that improving access to affordable, quality health care may reduce disparities in survival for those currently lacking coverage,” the investigators wrote.
The study was supported by Emory University, the National Institutes of Health, and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Dr. Flowers reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Spectrum, Celgene, and several other companies. The other authors reported having nothing to disclose.
SOURCE: Goldstein JS et al. Blood. 2018 Jul 24. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-03-839035.
Having health insurance can mean the difference between life and death for patients with follicular lymphoma, suggest results of a study showing that patients with private health insurance had nearly twofold better survival outcomes than patients without insurance or those who were covered by Medicare or Medicaid.
A review of records on more than 43,000 patients with follicular lymphoma (FL) in a national cancer registry showed that, compared with patients under age 65 with private insurance, the hazard ratios (HR) for death among patients in the same age bracket with either no insurance, Medicaid, or Medicare were, respectively, 1.96, 1.83, and 1.96 (P less than .0001 for each comparison).
“Our study finds that insurance status contributes to survival disparities in FL. Future studies on outcomes in FL should include insurance status as an important predictor,” Christopher R. Flowers, MD, of Emory University in Atlanta and his colleagues wrote in Blood.
“Further research on prognosis for FL should examine the impact of public policy, such as the passage of the [Affordable Care Act], on FL outcomes, as well as examine other factors that influence access to care, such as individual-level socioeconomic status, regular primary care visits, access to prescription medications, and care affordability,” they added.
The investigators noted that earlier research found that patients with Medicaid or no insurance were more likely than privately-insured patients to be diagnosed with cancers at advanced stages, and that some patients with aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphomas have been shown to have insurance-related disparities in treatments and outcomes.
To see whether the same could be true for patients with indolent-histology lymphomas such as FL, they extracted data from the National Cancer Database, a nationwide hospital-based cancer registry sponsored jointly by the American College of Surgeons and the American Cancer Society.
They identified a total of 43,648 patients aged 18 years or older who were diagnosed with FL from 2004 through 2014. They looked at both patients 18-64 years and those 65 years and older to account for changes in insurance with Medicare eligibility.
Overall survival among patients younger than age 65 was significantly worse for patients with public insurance (Medicaid or Medicare) or no insurance in Cox proportional hazard models controlling for available data on sociodemographic factors and prognostic indicators.
However, compared with patients aged 65 and older with private insurance, only patients with Medicare as their sole source of insurance had significantly worse overall survival (HR, 1.28; P less than .0001).
Patients who were uninsured or had Medicaid were more likely than others to have lower socioeconomic status, present with advanced-stage disease, have systemic symptoms, and have multiple comorbidities that persisted after controlling for known sociodemographic and prognostic factors.
The investigators found that, among patients under age 65, those with a comorbidity score of 1 had an HR for death of 1.71, compared with patients with no comorbidities, and that patients with a score of 2 or greater had a HR of 3.1 (P less than .0001 for each comparison).
“The findings of the study indicate that improving access to affordable, quality health care may reduce disparities in survival for those currently lacking coverage,” the investigators wrote.
The study was supported by Emory University, the National Institutes of Health, and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Dr. Flowers reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Spectrum, Celgene, and several other companies. The other authors reported having nothing to disclose.
SOURCE: Goldstein JS et al. Blood. 2018 Jul 24. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-03-839035.
FROM BLOOD
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The risk for death among patients under age 65 with no insurance, Medicaid, or Medicare was nearly twice that of similar patients with private health insurance.
Study details: Review of data on 43,648 patients with follicular lymphoma in the National Cancer Database.
Disclosures: The study was supported by Emory University, the National Institutes of Health, and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Dr. Flowers reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Spectrum, Celgene, and several other companies. The other authors reported having nothing to disclose.
Source: Goldstein JS et al. Blood. 2018 Jul 24. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-03-839035.
Late mortality risk after childhood BMT is substantial, persistent
Children who undergo allogeneic blood or marrow transplantation (BMT) remain at an elevated risk of premature death even 25 years after the procedure, results of large, retrospective cohort study suggest.
Despite a significant decrease over several decades, the risk of all-cause mortality remained elevated, compared with the general population, according to this study of individuals who had BMT performed in childhood between 1974 and 2010.
“These findings emphasize the need for lifelong follow-up care after allogeneic BMT performed in childhood,” reported Anna Sällfors Holmqvist, MD, PhD, of the department of clinical sciences at Skåne University Hospital, Lund University, Sweden, and her associates.
, Dr. Holmqvist and her colleagues reported in JAMA Oncology.
Their retrospective analysis included 1,388 individuals who lived at least 2 years after allogeneic BMT performed in childhood at one of three centers: the University of Alabama at Birmingham; the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis; and City of Hope, Duarte, Calif.
There were 295 deaths over a median of 14.9 years of follow-up, for an overall survival rate of 79.3% at 20 years after BMT, reported Dr. Holmqvist and her associates. The three leading causes of death were infection or chronic graft-versus-host disease in 49.6% of cases, primary disease in 24.6%, and later malignancies in 18.4%.
Relative to the general population, the cohort had a 14.4-fold increased risk of premature death (95% confidence interval, 12.8-16.1), compared with the general population. Relative mortality was highest 2-5 years after BMT and dropped substantially after that but remained elevated – even 25 years or more after the procedure, the investigators noted.
Mortality decreased significantly over the 3 decades evaluated in this study. The rate of all-cause, 10-year cumulative mortality was 18.9% before 1990, 12.9% from 1990 to 1999, and 11.0% from 2000 to 2010 (P = .002).
That decrease in cumulative mortality over time could not be explained by changes in transplant practice over those three time periods, according to results of a mediation analysis performed by Dr. Holmqvist and her associates.
That finding suggests that unmeasured variables might underlie the decrease in late mortality, the investigators said.
Those unmeasured variables might include supportive care strategies, management of chronic graft-versus-host disease, or improved patient selection, they noted.
Dr. Holmqvist and her associates cited as one limitation their reliance on death certificates for causes of death. In addition, the causes of death for 51 of the 295 deceased patients were lacking.
The study was supported in part by grants from the National Cancer Institute, the Leukemia Lymphoma Society, and the Swedish Childhood Cancer Foundation. Dr. Holmqvist and her associates reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Holmqvist AS et al. JAMA Oncol. 2018 Jul 26. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.2453.
Children who undergo allogeneic blood or marrow transplantation (BMT) remain at an elevated risk of premature death even 25 years after the procedure, results of large, retrospective cohort study suggest.
Despite a significant decrease over several decades, the risk of all-cause mortality remained elevated, compared with the general population, according to this study of individuals who had BMT performed in childhood between 1974 and 2010.
“These findings emphasize the need for lifelong follow-up care after allogeneic BMT performed in childhood,” reported Anna Sällfors Holmqvist, MD, PhD, of the department of clinical sciences at Skåne University Hospital, Lund University, Sweden, and her associates.
, Dr. Holmqvist and her colleagues reported in JAMA Oncology.
Their retrospective analysis included 1,388 individuals who lived at least 2 years after allogeneic BMT performed in childhood at one of three centers: the University of Alabama at Birmingham; the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis; and City of Hope, Duarte, Calif.
There were 295 deaths over a median of 14.9 years of follow-up, for an overall survival rate of 79.3% at 20 years after BMT, reported Dr. Holmqvist and her associates. The three leading causes of death were infection or chronic graft-versus-host disease in 49.6% of cases, primary disease in 24.6%, and later malignancies in 18.4%.
Relative to the general population, the cohort had a 14.4-fold increased risk of premature death (95% confidence interval, 12.8-16.1), compared with the general population. Relative mortality was highest 2-5 years after BMT and dropped substantially after that but remained elevated – even 25 years or more after the procedure, the investigators noted.
Mortality decreased significantly over the 3 decades evaluated in this study. The rate of all-cause, 10-year cumulative mortality was 18.9% before 1990, 12.9% from 1990 to 1999, and 11.0% from 2000 to 2010 (P = .002).
That decrease in cumulative mortality over time could not be explained by changes in transplant practice over those three time periods, according to results of a mediation analysis performed by Dr. Holmqvist and her associates.
That finding suggests that unmeasured variables might underlie the decrease in late mortality, the investigators said.
Those unmeasured variables might include supportive care strategies, management of chronic graft-versus-host disease, or improved patient selection, they noted.
Dr. Holmqvist and her associates cited as one limitation their reliance on death certificates for causes of death. In addition, the causes of death for 51 of the 295 deceased patients were lacking.
The study was supported in part by grants from the National Cancer Institute, the Leukemia Lymphoma Society, and the Swedish Childhood Cancer Foundation. Dr. Holmqvist and her associates reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Holmqvist AS et al. JAMA Oncol. 2018 Jul 26. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.2453.
Children who undergo allogeneic blood or marrow transplantation (BMT) remain at an elevated risk of premature death even 25 years after the procedure, results of large, retrospective cohort study suggest.
Despite a significant decrease over several decades, the risk of all-cause mortality remained elevated, compared with the general population, according to this study of individuals who had BMT performed in childhood between 1974 and 2010.
“These findings emphasize the need for lifelong follow-up care after allogeneic BMT performed in childhood,” reported Anna Sällfors Holmqvist, MD, PhD, of the department of clinical sciences at Skåne University Hospital, Lund University, Sweden, and her associates.
, Dr. Holmqvist and her colleagues reported in JAMA Oncology.
Their retrospective analysis included 1,388 individuals who lived at least 2 years after allogeneic BMT performed in childhood at one of three centers: the University of Alabama at Birmingham; the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis; and City of Hope, Duarte, Calif.
There were 295 deaths over a median of 14.9 years of follow-up, for an overall survival rate of 79.3% at 20 years after BMT, reported Dr. Holmqvist and her associates. The three leading causes of death were infection or chronic graft-versus-host disease in 49.6% of cases, primary disease in 24.6%, and later malignancies in 18.4%.
Relative to the general population, the cohort had a 14.4-fold increased risk of premature death (95% confidence interval, 12.8-16.1), compared with the general population. Relative mortality was highest 2-5 years after BMT and dropped substantially after that but remained elevated – even 25 years or more after the procedure, the investigators noted.
Mortality decreased significantly over the 3 decades evaluated in this study. The rate of all-cause, 10-year cumulative mortality was 18.9% before 1990, 12.9% from 1990 to 1999, and 11.0% from 2000 to 2010 (P = .002).
That decrease in cumulative mortality over time could not be explained by changes in transplant practice over those three time periods, according to results of a mediation analysis performed by Dr. Holmqvist and her associates.
That finding suggests that unmeasured variables might underlie the decrease in late mortality, the investigators said.
Those unmeasured variables might include supportive care strategies, management of chronic graft-versus-host disease, or improved patient selection, they noted.
Dr. Holmqvist and her associates cited as one limitation their reliance on death certificates for causes of death. In addition, the causes of death for 51 of the 295 deceased patients were lacking.
The study was supported in part by grants from the National Cancer Institute, the Leukemia Lymphoma Society, and the Swedish Childhood Cancer Foundation. Dr. Holmqvist and her associates reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Holmqvist AS et al. JAMA Oncol. 2018 Jul 26. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.2453.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Key clinical point: Individuals undergoing allogeneic blood or marrow transplantation (BMT) in childhood require careful follow-up for many years because of a persistent elevated risk of premature death.
Major finding: Risk of premature death was increased 14.4-fold, compared with the general population (95% confidence interval, 12.8-16.1).
Study details: A retrospective cohort study including 1,388 individuals living 2 years or more after allogeneic BMT performed in childhood.
Disclosures: The study was supported in part by grants from the National Cancer Institute, the Leukemia Lymphoma Society, and the Swedish Childhood Cancer Foundation. Dr. Holmqvist and her coauthors reported no conflicts of interest.
Source: Holmqvist AS et al. JAMA Oncol. 2018 Jul 26. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.2453.
Rituximab reduces risk of follicular lymphoma transformation
Rituximab-based chemotherapy can significantly reduce the risk of transformation of follicular lymphoma (FL) from an indolent to an aggressive histology, such as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, results of a retrospective pooled analysis have suggested.
“Despite the intrinsic limitations related to the retrospective nature of our study, we confirmed that the cumulative hazard of histological transformation as a first event in follicular lymphoma can be reduced significantly by introducing rituximab to a backbone therapy. Moreover, our data also confirm that histological transformation still has an adverse effect on patient outcome, although it is less catastrophic than the pre-rituximab regimens,” they wrote in the Lancet Haematology.
These investigators, from 11 cooperative groups or institutions across Europe, pooled data on patients aged 18 years and older who had a histologically confirmed diagnosis of grade 1, 2, or 3a FL between Jan. 2, 1997, and Dec. 20, 2013.
They defined histologic transformation as a biopsy-proven aggressive lymphoma that occurred as a first event after first-line therapy.
Data on a total of 8,116 patients were available for analysis; 509 of these patients had had histologic transformations. After a median follow-up of 87 months, the 10-year cumulative hazard for all patients was 7.7%. The 10-year cumulative hazard – one of two primary endpoints – was 5.2% for patients who had received any rituximab versus 8.7% for those who did not, which translated into a hazard ratio of 0.73 (P = .004).
Among patients who received rituximab during induction only, the 10-year cumulative hazard was 5.9%, and it was 3.6% among those who received rituximab during induction and maintenance phases of treatment. This difference translated into a HR of 0.55 (P = .003).
The benefit of rituximab induction and maintenance – compared with induction only – held up in a multivariate analysis controlling for age at diagnosis, sex, FLIPI (Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index) score, active surveillance vs. treatment, and FL grade (HR, 0.55; P = .016).
There were 287 deaths among the 509 patients with transformation, resulting in a 10-year survival after transformation of 32%.
The 5-year survival after transformation was 38% for patients who were not exposed to rituximab, 42% for patients who received induction rituximab, and 43% for those who received both induction and maintenance rituximab, but the differences between the three groups were not statistically significant.
“More comprehensive knowledge of the biological risk factors for follicular lymphoma transformation and the molecular pathways involved is likely to help clinicians make more accurate prognostic assessments and also inform the potential usefulness of novel drugs for the treatment of follicular lymphoma,” the researchers wrote.
The study was funded by the European Lymphoma Institute and other research groups. The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Federico M et al. Lancet Haematol. 2018 Jul 4. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(18)30090-5.
Rituximab-based chemotherapy can significantly reduce the risk of transformation of follicular lymphoma (FL) from an indolent to an aggressive histology, such as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, results of a retrospective pooled analysis have suggested.
“Despite the intrinsic limitations related to the retrospective nature of our study, we confirmed that the cumulative hazard of histological transformation as a first event in follicular lymphoma can be reduced significantly by introducing rituximab to a backbone therapy. Moreover, our data also confirm that histological transformation still has an adverse effect on patient outcome, although it is less catastrophic than the pre-rituximab regimens,” they wrote in the Lancet Haematology.
These investigators, from 11 cooperative groups or institutions across Europe, pooled data on patients aged 18 years and older who had a histologically confirmed diagnosis of grade 1, 2, or 3a FL between Jan. 2, 1997, and Dec. 20, 2013.
They defined histologic transformation as a biopsy-proven aggressive lymphoma that occurred as a first event after first-line therapy.
Data on a total of 8,116 patients were available for analysis; 509 of these patients had had histologic transformations. After a median follow-up of 87 months, the 10-year cumulative hazard for all patients was 7.7%. The 10-year cumulative hazard – one of two primary endpoints – was 5.2% for patients who had received any rituximab versus 8.7% for those who did not, which translated into a hazard ratio of 0.73 (P = .004).
Among patients who received rituximab during induction only, the 10-year cumulative hazard was 5.9%, and it was 3.6% among those who received rituximab during induction and maintenance phases of treatment. This difference translated into a HR of 0.55 (P = .003).
The benefit of rituximab induction and maintenance – compared with induction only – held up in a multivariate analysis controlling for age at diagnosis, sex, FLIPI (Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index) score, active surveillance vs. treatment, and FL grade (HR, 0.55; P = .016).
There were 287 deaths among the 509 patients with transformation, resulting in a 10-year survival after transformation of 32%.
The 5-year survival after transformation was 38% for patients who were not exposed to rituximab, 42% for patients who received induction rituximab, and 43% for those who received both induction and maintenance rituximab, but the differences between the three groups were not statistically significant.
“More comprehensive knowledge of the biological risk factors for follicular lymphoma transformation and the molecular pathways involved is likely to help clinicians make more accurate prognostic assessments and also inform the potential usefulness of novel drugs for the treatment of follicular lymphoma,” the researchers wrote.
The study was funded by the European Lymphoma Institute and other research groups. The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Federico M et al. Lancet Haematol. 2018 Jul 4. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(18)30090-5.
Rituximab-based chemotherapy can significantly reduce the risk of transformation of follicular lymphoma (FL) from an indolent to an aggressive histology, such as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, results of a retrospective pooled analysis have suggested.
“Despite the intrinsic limitations related to the retrospective nature of our study, we confirmed that the cumulative hazard of histological transformation as a first event in follicular lymphoma can be reduced significantly by introducing rituximab to a backbone therapy. Moreover, our data also confirm that histological transformation still has an adverse effect on patient outcome, although it is less catastrophic than the pre-rituximab regimens,” they wrote in the Lancet Haematology.
These investigators, from 11 cooperative groups or institutions across Europe, pooled data on patients aged 18 years and older who had a histologically confirmed diagnosis of grade 1, 2, or 3a FL between Jan. 2, 1997, and Dec. 20, 2013.
They defined histologic transformation as a biopsy-proven aggressive lymphoma that occurred as a first event after first-line therapy.
Data on a total of 8,116 patients were available for analysis; 509 of these patients had had histologic transformations. After a median follow-up of 87 months, the 10-year cumulative hazard for all patients was 7.7%. The 10-year cumulative hazard – one of two primary endpoints – was 5.2% for patients who had received any rituximab versus 8.7% for those who did not, which translated into a hazard ratio of 0.73 (P = .004).
Among patients who received rituximab during induction only, the 10-year cumulative hazard was 5.9%, and it was 3.6% among those who received rituximab during induction and maintenance phases of treatment. This difference translated into a HR of 0.55 (P = .003).
The benefit of rituximab induction and maintenance – compared with induction only – held up in a multivariate analysis controlling for age at diagnosis, sex, FLIPI (Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index) score, active surveillance vs. treatment, and FL grade (HR, 0.55; P = .016).
There were 287 deaths among the 509 patients with transformation, resulting in a 10-year survival after transformation of 32%.
The 5-year survival after transformation was 38% for patients who were not exposed to rituximab, 42% for patients who received induction rituximab, and 43% for those who received both induction and maintenance rituximab, but the differences between the three groups were not statistically significant.
“More comprehensive knowledge of the biological risk factors for follicular lymphoma transformation and the molecular pathways involved is likely to help clinicians make more accurate prognostic assessments and also inform the potential usefulness of novel drugs for the treatment of follicular lymphoma,” the researchers wrote.
The study was funded by the European Lymphoma Institute and other research groups. The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Federico M et al. Lancet Haematol. 2018 Jul 4. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(18)30090-5.
FROM THE LANCET HAEMATOLOGY
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The 10-year cumulative hazard of histologic transformation was 5.2% for patients who had received rituximab and 8.7% for those who had not.
Study details: Retrospective pooled analysis of 8,116 patients with FL, 509 of whom had transformation over a 10-year period.
Disclosures: The study was funded by Associazione Angela Serra per la Ricerca sul Cancro, European Lymphoma Institute, European Hematology Association Lymphoma Group, Fondazione Italiana Linfomi, and the Spanish Group of Lymphoma and Bone Marrow Transplantation. The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
Source: Federico M et al. Lancet Haematol. 2018 Jul 4. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(18)30090-5.
Combo treatment under review for Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia
by the Food and Drug Administration.
Ibrutinib, a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is already approved as a single agent for WM. The addition of rituximab to the indication is based on positive results from the phase 3 INNOVATE study. In particular, the trial showed a superior progression-free survival rate at 30 months for the ibrutinib-rituximab combination at 82%, compared with placebo plus rituximab at 28% (N Engl J Med. 2018;378:2399-410).
The study’s lead investigator, Meletios A. Dimopoulos, MD, called the combination a “new standard of care” for WM at the recent annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Ibrutinib, marketed as Imbruvica, is jointly developed and commercialized by Pharmacyclics and Janssen Biotech.
by the Food and Drug Administration.
Ibrutinib, a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is already approved as a single agent for WM. The addition of rituximab to the indication is based on positive results from the phase 3 INNOVATE study. In particular, the trial showed a superior progression-free survival rate at 30 months for the ibrutinib-rituximab combination at 82%, compared with placebo plus rituximab at 28% (N Engl J Med. 2018;378:2399-410).
The study’s lead investigator, Meletios A. Dimopoulos, MD, called the combination a “new standard of care” for WM at the recent annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Ibrutinib, marketed as Imbruvica, is jointly developed and commercialized by Pharmacyclics and Janssen Biotech.
by the Food and Drug Administration.
Ibrutinib, a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is already approved as a single agent for WM. The addition of rituximab to the indication is based on positive results from the phase 3 INNOVATE study. In particular, the trial showed a superior progression-free survival rate at 30 months for the ibrutinib-rituximab combination at 82%, compared with placebo plus rituximab at 28% (N Engl J Med. 2018;378:2399-410).
The study’s lead investigator, Meletios A. Dimopoulos, MD, called the combination a “new standard of care” for WM at the recent annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Ibrutinib, marketed as Imbruvica, is jointly developed and commercialized by Pharmacyclics and Janssen Biotech.
Is CLL chemoimmunotherapy dead? Not yet
CHICAGO – Chemoimmunotherapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia is on the way out, but there’s one scenario where it still plays a key role, according to one leukemia expert.
That scenario is not in relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), where the use of fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) may be hard to justify today. Data supporting use of FCR in relapsed CLL show a median progression-free survival (PFS) of about 21 months, Susan M. O’Brien, MD, of the University of California, Irvine, said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. There is also data for bendamustine-rituximab retreatment showing a median event-free survival of about 15 months, she added.
By contrast, the 5-year follow-up data for the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib in the relapsed/refractory setting shows a median PFS of 52 months, which is “extraordinary,” given that the patients had a median of four prior regimens, Dr. O’Brien said.
Similarly, recently published results from the randomized, phase 3 MURANO study of venetoclax plus rituximab in relapsed/refractory CLL showed that median PFS was not reached at a median follow-up of 23.8 months, versus a median of 17 months for the bendamustine-rituximab comparison arm (N Engl J Med. 2018;378[12]:1107-20).
“Thanks to the MURANO study, we likely will have an expanded label for venetoclax that includes the combination of venetoclax and rituximab,” Dr. O’Brien said. “I think it’s quite clear that either of these is dramatically better than what you get with retreatment with chemotherapy, so I personally don’t think there is a role for chemoimmunotherapy in the relapsed patient.”
On June 8, 2018, the Food and Drug Administration granted regular approval for venetoclax for patients with CLL or small lymphocytic lymphoma, with or without 17p deletion, who have received at least one prior therapy. The FDA also approved its use in combination with rituximab.*
But frontline CLL treatment is currently a little bit more complicated, Dr. O’Brien said.
Recent studies show favorable long-term outcomes with FCR frontline therapy in the immunoglobulin heavy chain variable gene (IgHV) –mutated subgroup of patients, she noted.
The longest follow-up comes from a study from investigators at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, published in 2016. In that study, the 12.8-year PFS was 53.9% for IgHV-mutated patients, versus just 8.7% for patients with unmutated IgHV. Of the IgHV-mutated group, more than half achieved minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity after treatment (Blood. 2016 Jan 21; 127[3]: 303-9).
“I’m going to go out on a limb and I’m going to suggest that I think there is a cure fraction here,” Dr. O’Brien said. “On the other hand, if there’s not a cure fraction and they’re going to relapse after 17 years, that’s a pretty attractive endpoint, even if it’s not a cure fraction.”
Clinical practice guidelines now recognize IgHV mutation status as an important marker that should be obtained when deciding on treatment, Dr. O’Brien noted.
For unmutated patients, the RESONATE-2 trial showed that ibrutinib was superior to chlorambucil in older patients, many of whom had comorbid conditions. In the 3-year update, median PFS was approximately 15 months for chlorambucil, while for ibrutinib the median PFS was “nowhere near” being reached, Dr. O’Brien said.
Those data may not be so relevant for fit, unmutated patients, and two randomized trials comparing FCR with bendamustine and rituximab have yet to report data. However, one recent cross-trial comparison found fairly overlapping survival curves for the two chemoimmunotherapy approaches.
Dr. O’Brien said she would put older patients with comorbidities on ibrutinib if a clinical trial was not available, and for fit, unmutated patients, while more data are needed, she would also use ibrutinib. However, patient preference sometimes tips the scale in favor of FCR.
“The discussions sometimes are quite long about whether the patient should opt to take ibrutinib or FCR,” Dr. O’Brien said. “The last patient I had that discussion with elected to take FCR. When I asked him why, he said because he liked the idea of being finished in six cycles, off all therapy, and hopefully in remission.”
While Dr. O’Brien said she views chemoimmunotherapy as still relevant in IgHV-mutated patients, eventually it will go away, she concluded. Toward that end, there is considerable interest in venetoclax plus ibrutinib, a combination that, in early reports, has yielded very encouraging MRD results in first-line CLL.
“We have no long-term data, but very, very exciting MRD negativity data,” Dr. O’Brien said.
Dr. O’Brien reported relationships with Abbvie, Amgen, Celgene, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Pfizer, Pharmacyclics, Sunesis Pharmaceuticals, and others.
*This story was updated 6/25/2018.
CHICAGO – Chemoimmunotherapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia is on the way out, but there’s one scenario where it still plays a key role, according to one leukemia expert.
That scenario is not in relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), where the use of fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) may be hard to justify today. Data supporting use of FCR in relapsed CLL show a median progression-free survival (PFS) of about 21 months, Susan M. O’Brien, MD, of the University of California, Irvine, said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. There is also data for bendamustine-rituximab retreatment showing a median event-free survival of about 15 months, she added.
By contrast, the 5-year follow-up data for the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib in the relapsed/refractory setting shows a median PFS of 52 months, which is “extraordinary,” given that the patients had a median of four prior regimens, Dr. O’Brien said.
Similarly, recently published results from the randomized, phase 3 MURANO study of venetoclax plus rituximab in relapsed/refractory CLL showed that median PFS was not reached at a median follow-up of 23.8 months, versus a median of 17 months for the bendamustine-rituximab comparison arm (N Engl J Med. 2018;378[12]:1107-20).
“Thanks to the MURANO study, we likely will have an expanded label for venetoclax that includes the combination of venetoclax and rituximab,” Dr. O’Brien said. “I think it’s quite clear that either of these is dramatically better than what you get with retreatment with chemotherapy, so I personally don’t think there is a role for chemoimmunotherapy in the relapsed patient.”
On June 8, 2018, the Food and Drug Administration granted regular approval for venetoclax for patients with CLL or small lymphocytic lymphoma, with or without 17p deletion, who have received at least one prior therapy. The FDA also approved its use in combination with rituximab.*
But frontline CLL treatment is currently a little bit more complicated, Dr. O’Brien said.
Recent studies show favorable long-term outcomes with FCR frontline therapy in the immunoglobulin heavy chain variable gene (IgHV) –mutated subgroup of patients, she noted.
The longest follow-up comes from a study from investigators at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, published in 2016. In that study, the 12.8-year PFS was 53.9% for IgHV-mutated patients, versus just 8.7% for patients with unmutated IgHV. Of the IgHV-mutated group, more than half achieved minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity after treatment (Blood. 2016 Jan 21; 127[3]: 303-9).
“I’m going to go out on a limb and I’m going to suggest that I think there is a cure fraction here,” Dr. O’Brien said. “On the other hand, if there’s not a cure fraction and they’re going to relapse after 17 years, that’s a pretty attractive endpoint, even if it’s not a cure fraction.”
Clinical practice guidelines now recognize IgHV mutation status as an important marker that should be obtained when deciding on treatment, Dr. O’Brien noted.
For unmutated patients, the RESONATE-2 trial showed that ibrutinib was superior to chlorambucil in older patients, many of whom had comorbid conditions. In the 3-year update, median PFS was approximately 15 months for chlorambucil, while for ibrutinib the median PFS was “nowhere near” being reached, Dr. O’Brien said.
Those data may not be so relevant for fit, unmutated patients, and two randomized trials comparing FCR with bendamustine and rituximab have yet to report data. However, one recent cross-trial comparison found fairly overlapping survival curves for the two chemoimmunotherapy approaches.
Dr. O’Brien said she would put older patients with comorbidities on ibrutinib if a clinical trial was not available, and for fit, unmutated patients, while more data are needed, she would also use ibrutinib. However, patient preference sometimes tips the scale in favor of FCR.
“The discussions sometimes are quite long about whether the patient should opt to take ibrutinib or FCR,” Dr. O’Brien said. “The last patient I had that discussion with elected to take FCR. When I asked him why, he said because he liked the idea of being finished in six cycles, off all therapy, and hopefully in remission.”
While Dr. O’Brien said she views chemoimmunotherapy as still relevant in IgHV-mutated patients, eventually it will go away, she concluded. Toward that end, there is considerable interest in venetoclax plus ibrutinib, a combination that, in early reports, has yielded very encouraging MRD results in first-line CLL.
“We have no long-term data, but very, very exciting MRD negativity data,” Dr. O’Brien said.
Dr. O’Brien reported relationships with Abbvie, Amgen, Celgene, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Pfizer, Pharmacyclics, Sunesis Pharmaceuticals, and others.
*This story was updated 6/25/2018.
CHICAGO – Chemoimmunotherapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia is on the way out, but there’s one scenario where it still plays a key role, according to one leukemia expert.
That scenario is not in relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), where the use of fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) may be hard to justify today. Data supporting use of FCR in relapsed CLL show a median progression-free survival (PFS) of about 21 months, Susan M. O’Brien, MD, of the University of California, Irvine, said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. There is also data for bendamustine-rituximab retreatment showing a median event-free survival of about 15 months, she added.
By contrast, the 5-year follow-up data for the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib in the relapsed/refractory setting shows a median PFS of 52 months, which is “extraordinary,” given that the patients had a median of four prior regimens, Dr. O’Brien said.
Similarly, recently published results from the randomized, phase 3 MURANO study of venetoclax plus rituximab in relapsed/refractory CLL showed that median PFS was not reached at a median follow-up of 23.8 months, versus a median of 17 months for the bendamustine-rituximab comparison arm (N Engl J Med. 2018;378[12]:1107-20).
“Thanks to the MURANO study, we likely will have an expanded label for venetoclax that includes the combination of venetoclax and rituximab,” Dr. O’Brien said. “I think it’s quite clear that either of these is dramatically better than what you get with retreatment with chemotherapy, so I personally don’t think there is a role for chemoimmunotherapy in the relapsed patient.”
On June 8, 2018, the Food and Drug Administration granted regular approval for venetoclax for patients with CLL or small lymphocytic lymphoma, with or without 17p deletion, who have received at least one prior therapy. The FDA also approved its use in combination with rituximab.*
But frontline CLL treatment is currently a little bit more complicated, Dr. O’Brien said.
Recent studies show favorable long-term outcomes with FCR frontline therapy in the immunoglobulin heavy chain variable gene (IgHV) –mutated subgroup of patients, she noted.
The longest follow-up comes from a study from investigators at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, published in 2016. In that study, the 12.8-year PFS was 53.9% for IgHV-mutated patients, versus just 8.7% for patients with unmutated IgHV. Of the IgHV-mutated group, more than half achieved minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity after treatment (Blood. 2016 Jan 21; 127[3]: 303-9).
“I’m going to go out on a limb and I’m going to suggest that I think there is a cure fraction here,” Dr. O’Brien said. “On the other hand, if there’s not a cure fraction and they’re going to relapse after 17 years, that’s a pretty attractive endpoint, even if it’s not a cure fraction.”
Clinical practice guidelines now recognize IgHV mutation status as an important marker that should be obtained when deciding on treatment, Dr. O’Brien noted.
For unmutated patients, the RESONATE-2 trial showed that ibrutinib was superior to chlorambucil in older patients, many of whom had comorbid conditions. In the 3-year update, median PFS was approximately 15 months for chlorambucil, while for ibrutinib the median PFS was “nowhere near” being reached, Dr. O’Brien said.
Those data may not be so relevant for fit, unmutated patients, and two randomized trials comparing FCR with bendamustine and rituximab have yet to report data. However, one recent cross-trial comparison found fairly overlapping survival curves for the two chemoimmunotherapy approaches.
Dr. O’Brien said she would put older patients with comorbidities on ibrutinib if a clinical trial was not available, and for fit, unmutated patients, while more data are needed, she would also use ibrutinib. However, patient preference sometimes tips the scale in favor of FCR.
“The discussions sometimes are quite long about whether the patient should opt to take ibrutinib or FCR,” Dr. O’Brien said. “The last patient I had that discussion with elected to take FCR. When I asked him why, he said because he liked the idea of being finished in six cycles, off all therapy, and hopefully in remission.”
While Dr. O’Brien said she views chemoimmunotherapy as still relevant in IgHV-mutated patients, eventually it will go away, she concluded. Toward that end, there is considerable interest in venetoclax plus ibrutinib, a combination that, in early reports, has yielded very encouraging MRD results in first-line CLL.
“We have no long-term data, but very, very exciting MRD negativity data,” Dr. O’Brien said.
Dr. O’Brien reported relationships with Abbvie, Amgen, Celgene, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Pfizer, Pharmacyclics, Sunesis Pharmaceuticals, and others.
*This story was updated 6/25/2018.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ASCO 2018