User login
Severe Autoimmune Pancytopenia: An Unusual Presentation of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
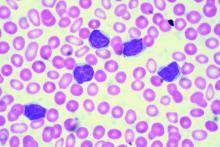
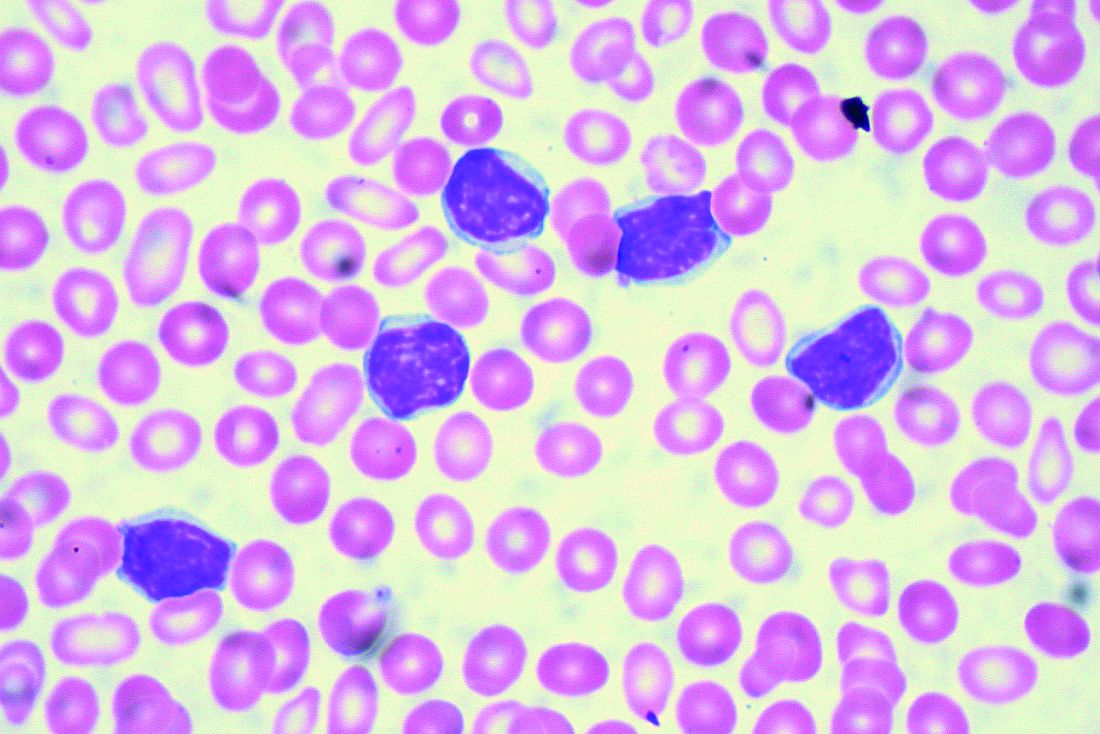
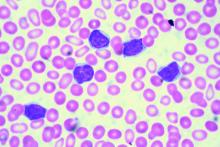
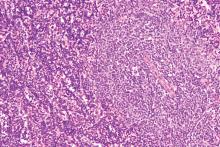
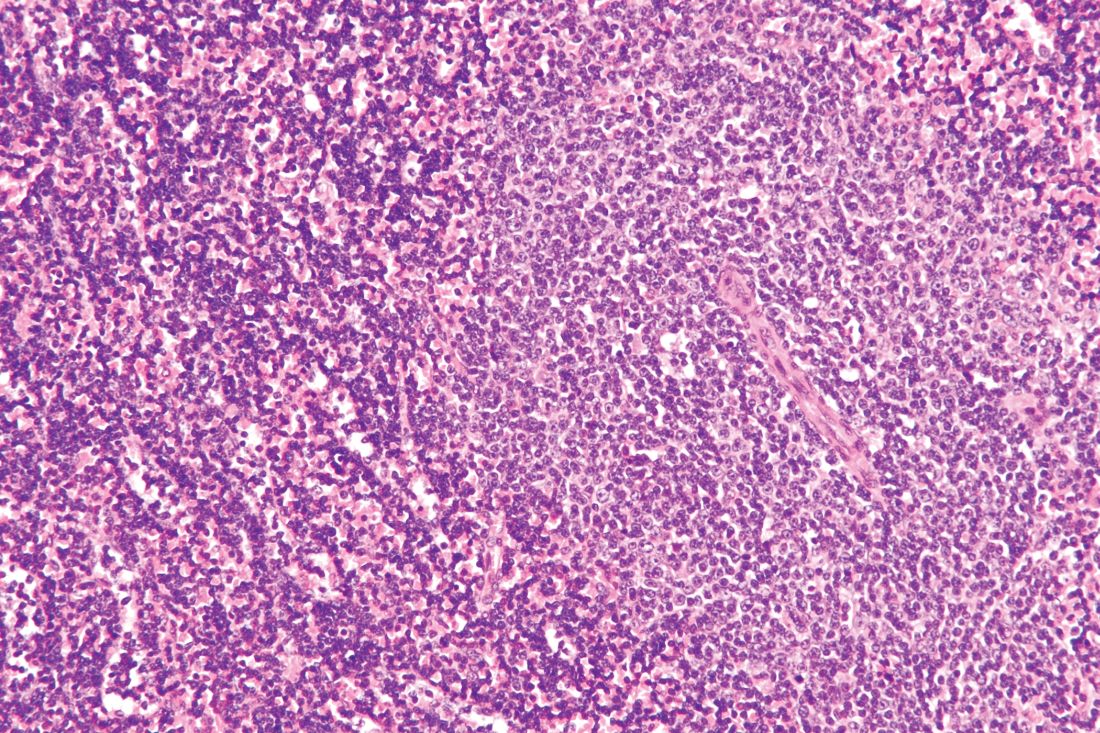
Case Report: A 61-year-old African American man presented to his PCP complaining of severe weakness and dyspnea with minimal exertion. The symptoms had begun about 6 weeks prior to the visit and had slowly worsened. The patient denied any bleeding, fever chills or sweats. He had a past, presumed history of ulcerative colitis, inactive, on no medications, as well as benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) without therapy. He denied any use of OTC’s; no drug or alcohol use. No risk factors for HIV. In the office he was noticed to be severely anemic with a Hgb of 2.5, on repeat was 2.7 gm/dL. Platelet count was 10 000/uL, confirmed on repeat CBC and examination of the smear. WBC was 4,500 with about 80% normal appearing lymphocytes. LDH was 143(wnl). A B12 level was low at 208, with an elevated MMA of 829. The patient was admitted for evaluation and transfusions. There were no petechiae or echymoses in the visible areas of the skin. The patient initially refused physical exam or any diagnostic procedures. A subsequent flow cytometric assay of his blood was consistent with CLL. Eventually a bone marrow aspirate and biopsy were performed. It showed a hypercellular bone marrow, with major decrease in all myeloid, erythroid and megakaryocytic elements which were replaced by population of mature, small lymphocytes, consistent with the diagnosis of CLL. In particular, histology was characterized by almost complete absence of megakaryocytes, leading to suspicion of an auto-immune component driving disease. The patient was started on pulse dexamethasone vitamin B12, and administered weekly anti-CD20 (Rituximab) for 4 doses. He was also started on eltrombopag and a BTK inhibitor (Ibrutinib) both of which he continues to take to date. His counts have slowly risen, and the patient continues to improve.
Discussion: Severe pancytopenia as a presentation of CLL is uncommon, perhaps in contrast to autoimmune cytopenias which are relatively common events during the lifecycle of patients with CLL and are thought to arise from antibody production by the normal BCells, in this setting of T-cell dysregulation. Given recent trends in the treatment of CLL with BTK inhibitors, which have been both used to treat, as well as believed to have caused auto-immune CLL complications it’s important to review the occurrence of cytopenias and how to manage them in this setting.
Case Report: A 61-year-old African American man presented to his PCP complaining of severe weakness and dyspnea with minimal exertion. The symptoms had begun about 6 weeks prior to the visit and had slowly worsened. The patient denied any bleeding, fever chills or sweats. He had a past, presumed history of ulcerative colitis, inactive, on no medications, as well as benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) without therapy. He denied any use of OTC’s; no drug or alcohol use. No risk factors for HIV. In the office he was noticed to be severely anemic with a Hgb of 2.5, on repeat was 2.7 gm/dL. Platelet count was 10 000/uL, confirmed on repeat CBC and examination of the smear. WBC was 4,500 with about 80% normal appearing lymphocytes. LDH was 143(wnl). A B12 level was low at 208, with an elevated MMA of 829. The patient was admitted for evaluation and transfusions. There were no petechiae or echymoses in the visible areas of the skin. The patient initially refused physical exam or any diagnostic procedures. A subsequent flow cytometric assay of his blood was consistent with CLL. Eventually a bone marrow aspirate and biopsy were performed. It showed a hypercellular bone marrow, with major decrease in all myeloid, erythroid and megakaryocytic elements which were replaced by population of mature, small lymphocytes, consistent with the diagnosis of CLL. In particular, histology was characterized by almost complete absence of megakaryocytes, leading to suspicion of an auto-immune component driving disease. The patient was started on pulse dexamethasone vitamin B12, and administered weekly anti-CD20 (Rituximab) for 4 doses. He was also started on eltrombopag and a BTK inhibitor (Ibrutinib) both of which he continues to take to date. His counts have slowly risen, and the patient continues to improve.
Discussion: Severe pancytopenia as a presentation of CLL is uncommon, perhaps in contrast to autoimmune cytopenias which are relatively common events during the lifecycle of patients with CLL and are thought to arise from antibody production by the normal BCells, in this setting of T-cell dysregulation. Given recent trends in the treatment of CLL with BTK inhibitors, which have been both used to treat, as well as believed to have caused auto-immune CLL complications it’s important to review the occurrence of cytopenias and how to manage them in this setting.
Case Report: A 61-year-old African American man presented to his PCP complaining of severe weakness and dyspnea with minimal exertion. The symptoms had begun about 6 weeks prior to the visit and had slowly worsened. The patient denied any bleeding, fever chills or sweats. He had a past, presumed history of ulcerative colitis, inactive, on no medications, as well as benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) without therapy. He denied any use of OTC’s; no drug or alcohol use. No risk factors for HIV. In the office he was noticed to be severely anemic with a Hgb of 2.5, on repeat was 2.7 gm/dL. Platelet count was 10 000/uL, confirmed on repeat CBC and examination of the smear. WBC was 4,500 with about 80% normal appearing lymphocytes. LDH was 143(wnl). A B12 level was low at 208, with an elevated MMA of 829. The patient was admitted for evaluation and transfusions. There were no petechiae or echymoses in the visible areas of the skin. The patient initially refused physical exam or any diagnostic procedures. A subsequent flow cytometric assay of his blood was consistent with CLL. Eventually a bone marrow aspirate and biopsy were performed. It showed a hypercellular bone marrow, with major decrease in all myeloid, erythroid and megakaryocytic elements which were replaced by population of mature, small lymphocytes, consistent with the diagnosis of CLL. In particular, histology was characterized by almost complete absence of megakaryocytes, leading to suspicion of an auto-immune component driving disease. The patient was started on pulse dexamethasone vitamin B12, and administered weekly anti-CD20 (Rituximab) for 4 doses. He was also started on eltrombopag and a BTK inhibitor (Ibrutinib) both of which he continues to take to date. His counts have slowly risen, and the patient continues to improve.
Discussion: Severe pancytopenia as a presentation of CLL is uncommon, perhaps in contrast to autoimmune cytopenias which are relatively common events during the lifecycle of patients with CLL and are thought to arise from antibody production by the normal BCells, in this setting of T-cell dysregulation. Given recent trends in the treatment of CLL with BTK inhibitors, which have been both used to treat, as well as believed to have caused auto-immune CLL complications it’s important to review the occurrence of cytopenias and how to manage them in this setting.
CK doesn’t seem to affect OS in CLL patients taking idelalisib
The presence of complex karyotype (CK) does not affect survival in patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who are treated with idelalisib, according to a new analysis.
Researchers analyzed data from two clinical trials of idelalisib, given alone or in combination with rituximab, and found no significant difference in overall survival (OS) between patients with and without CK.
Karl-Anton Kreuzer, MD, of the University of Cologne (Germany), and colleagues described these findings in a letter to Leukemia.
The researchers evaluated patients with previously treated CLL who were enrolled in a phase 3 trial and received either idelalisib plus rituximab or rituximab plus placebo. Patients from either treatment arm could enroll in an extension study of idelalisib monotherapy.
There were 220 patients randomized to idelalisib plus rituximab (n = 110) or placebo plus rituximab (n = 110) in the primary study, and 161 of these patients were enrolled in the extension study.
The final analysis included 120 patients who were successfully karyotyped – 63 from the idelalisib-rituximab arm and 57 from the placebo-rituximab arm. Less than half of patients in each arm were CK-positive – 41% (26/63) of the idelalisib arm and 42% (24/57) of the placebo arm.
The researchers wrote that baseline characteristics were “mostly balanced” between the CK-positive and CK-negative groups in each treatment arm. The only significant difference was that fewer CK-positive patients in the placebo arm had a creatinine clearance of 30-59 mL/min (P = .0324).
Results
There were no significant differences in outcomes between CK-positive and CK-negative patients who received idelalisib and rituximab. The overall response rate was 81% in CK-positive patients and 89% in CK-negative patients (P = .3509). The median progression-free survival was 20.9 months and 19.4 months, respectively (P = .5848).
The median OS was 28.3 months in the CK-positive group and 49.7 months in the CK-negative group (P = .2099). The copresence of CK and del(17p), TP53 mutation, or del(11q) didn’t significantly affect OS, the researchers noted.
Among all CK-positive patients, the median OS was 28.3 months in the idelalisib-rituximab arm and 9.2 months in the placebo-rituximab arm (P = .0412).
“Our analysis suggests that CK-positive patients treated with idelalisib/rituximab did not exhibit a significantly shortened survival compared with those who were CK negative,” the researchers wrote. “In addition, the primary beneficial effect of adding idelalisib to rituximab treatment in [relapsed/refractory] CLL patients with CK was reflected in OS prolongation compared to those who received only rituximab.”
The researchers noted that this study has limitations, so prospective clinical trials are needed to guide treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory CLL and CK.
Both trials of idelalisib were sponsored by Gilead. The researchers reported relationships, including employment, with Gilead and other companies. They also disclosed funding from the German government and from nonprofit organizations in Germany.
SOURCE: Kreuzer K-A et al. Leukemia. 2019 Aug 19. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0533-6.
The presence of complex karyotype (CK) does not affect survival in patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who are treated with idelalisib, according to a new analysis.
Researchers analyzed data from two clinical trials of idelalisib, given alone or in combination with rituximab, and found no significant difference in overall survival (OS) between patients with and without CK.
Karl-Anton Kreuzer, MD, of the University of Cologne (Germany), and colleagues described these findings in a letter to Leukemia.
The researchers evaluated patients with previously treated CLL who were enrolled in a phase 3 trial and received either idelalisib plus rituximab or rituximab plus placebo. Patients from either treatment arm could enroll in an extension study of idelalisib monotherapy.
There were 220 patients randomized to idelalisib plus rituximab (n = 110) or placebo plus rituximab (n = 110) in the primary study, and 161 of these patients were enrolled in the extension study.
The final analysis included 120 patients who were successfully karyotyped – 63 from the idelalisib-rituximab arm and 57 from the placebo-rituximab arm. Less than half of patients in each arm were CK-positive – 41% (26/63) of the idelalisib arm and 42% (24/57) of the placebo arm.
The researchers wrote that baseline characteristics were “mostly balanced” between the CK-positive and CK-negative groups in each treatment arm. The only significant difference was that fewer CK-positive patients in the placebo arm had a creatinine clearance of 30-59 mL/min (P = .0324).
Results
There were no significant differences in outcomes between CK-positive and CK-negative patients who received idelalisib and rituximab. The overall response rate was 81% in CK-positive patients and 89% in CK-negative patients (P = .3509). The median progression-free survival was 20.9 months and 19.4 months, respectively (P = .5848).
The median OS was 28.3 months in the CK-positive group and 49.7 months in the CK-negative group (P = .2099). The copresence of CK and del(17p), TP53 mutation, or del(11q) didn’t significantly affect OS, the researchers noted.
Among all CK-positive patients, the median OS was 28.3 months in the idelalisib-rituximab arm and 9.2 months in the placebo-rituximab arm (P = .0412).
“Our analysis suggests that CK-positive patients treated with idelalisib/rituximab did not exhibit a significantly shortened survival compared with those who were CK negative,” the researchers wrote. “In addition, the primary beneficial effect of adding idelalisib to rituximab treatment in [relapsed/refractory] CLL patients with CK was reflected in OS prolongation compared to those who received only rituximab.”
The researchers noted that this study has limitations, so prospective clinical trials are needed to guide treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory CLL and CK.
Both trials of idelalisib were sponsored by Gilead. The researchers reported relationships, including employment, with Gilead and other companies. They also disclosed funding from the German government and from nonprofit organizations in Germany.
SOURCE: Kreuzer K-A et al. Leukemia. 2019 Aug 19. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0533-6.
The presence of complex karyotype (CK) does not affect survival in patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who are treated with idelalisib, according to a new analysis.
Researchers analyzed data from two clinical trials of idelalisib, given alone or in combination with rituximab, and found no significant difference in overall survival (OS) between patients with and without CK.
Karl-Anton Kreuzer, MD, of the University of Cologne (Germany), and colleagues described these findings in a letter to Leukemia.
The researchers evaluated patients with previously treated CLL who were enrolled in a phase 3 trial and received either idelalisib plus rituximab or rituximab plus placebo. Patients from either treatment arm could enroll in an extension study of idelalisib monotherapy.
There were 220 patients randomized to idelalisib plus rituximab (n = 110) or placebo plus rituximab (n = 110) in the primary study, and 161 of these patients were enrolled in the extension study.
The final analysis included 120 patients who were successfully karyotyped – 63 from the idelalisib-rituximab arm and 57 from the placebo-rituximab arm. Less than half of patients in each arm were CK-positive – 41% (26/63) of the idelalisib arm and 42% (24/57) of the placebo arm.
The researchers wrote that baseline characteristics were “mostly balanced” between the CK-positive and CK-negative groups in each treatment arm. The only significant difference was that fewer CK-positive patients in the placebo arm had a creatinine clearance of 30-59 mL/min (P = .0324).
Results
There were no significant differences in outcomes between CK-positive and CK-negative patients who received idelalisib and rituximab. The overall response rate was 81% in CK-positive patients and 89% in CK-negative patients (P = .3509). The median progression-free survival was 20.9 months and 19.4 months, respectively (P = .5848).
The median OS was 28.3 months in the CK-positive group and 49.7 months in the CK-negative group (P = .2099). The copresence of CK and del(17p), TP53 mutation, or del(11q) didn’t significantly affect OS, the researchers noted.
Among all CK-positive patients, the median OS was 28.3 months in the idelalisib-rituximab arm and 9.2 months in the placebo-rituximab arm (P = .0412).
“Our analysis suggests that CK-positive patients treated with idelalisib/rituximab did not exhibit a significantly shortened survival compared with those who were CK negative,” the researchers wrote. “In addition, the primary beneficial effect of adding idelalisib to rituximab treatment in [relapsed/refractory] CLL patients with CK was reflected in OS prolongation compared to those who received only rituximab.”
The researchers noted that this study has limitations, so prospective clinical trials are needed to guide treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory CLL and CK.
Both trials of idelalisib were sponsored by Gilead. The researchers reported relationships, including employment, with Gilead and other companies. They also disclosed funding from the German government and from nonprofit organizations in Germany.
SOURCE: Kreuzer K-A et al. Leukemia. 2019 Aug 19. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0533-6.
FROM LEUKEMIA
Calquence earns breakthrough designation for CLL monotherapy
The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor is already approved for the treatment of adults with mantle cell lymphoma who have received at least one prior therapy, and multiple trials are underway to evaluate the drug’s use in a variety of B-cell malignancies, according to the drug’s sponsor, AstraZeneca.
The current designation was based on preliminary results from two phase 3 trials – ELEVATE-TN and ASCEND. In the three-arm ELEVATE-TN trial, researchers evaluated acalabrutinib alone or in combination with obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated patients with CLL. In the two-arm ASCEND trial, previously treated patients with CLL were randomized to receive acalabrutinib monotherapy or the physician’s choice of either rituximab plus idelalisib or rituximab plus bendamustine.
Interim analyses of the two trials showed that acalabrutinib alone, or in combination, significantly improved progression-free survival without raising safety concerns.
Breakthrough therapy designation allows for an expedited review by the FDA for treatments aimed at treating serious conditions where there is preliminary clinical evidence showing a substantial improvement over an available therapy or a clinically significant endpoint.
The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor is already approved for the treatment of adults with mantle cell lymphoma who have received at least one prior therapy, and multiple trials are underway to evaluate the drug’s use in a variety of B-cell malignancies, according to the drug’s sponsor, AstraZeneca.
The current designation was based on preliminary results from two phase 3 trials – ELEVATE-TN and ASCEND. In the three-arm ELEVATE-TN trial, researchers evaluated acalabrutinib alone or in combination with obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated patients with CLL. In the two-arm ASCEND trial, previously treated patients with CLL were randomized to receive acalabrutinib monotherapy or the physician’s choice of either rituximab plus idelalisib or rituximab plus bendamustine.
Interim analyses of the two trials showed that acalabrutinib alone, or in combination, significantly improved progression-free survival without raising safety concerns.
Breakthrough therapy designation allows for an expedited review by the FDA for treatments aimed at treating serious conditions where there is preliminary clinical evidence showing a substantial improvement over an available therapy or a clinically significant endpoint.
The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor is already approved for the treatment of adults with mantle cell lymphoma who have received at least one prior therapy, and multiple trials are underway to evaluate the drug’s use in a variety of B-cell malignancies, according to the drug’s sponsor, AstraZeneca.
The current designation was based on preliminary results from two phase 3 trials – ELEVATE-TN and ASCEND. In the three-arm ELEVATE-TN trial, researchers evaluated acalabrutinib alone or in combination with obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated patients with CLL. In the two-arm ASCEND trial, previously treated patients with CLL were randomized to receive acalabrutinib monotherapy or the physician’s choice of either rituximab plus idelalisib or rituximab plus bendamustine.
Interim analyses of the two trials showed that acalabrutinib alone, or in combination, significantly improved progression-free survival without raising safety concerns.
Breakthrough therapy designation allows for an expedited review by the FDA for treatments aimed at treating serious conditions where there is preliminary clinical evidence showing a substantial improvement over an available therapy or a clinically significant endpoint.
Zanubrutinib may be poised to challenge ibrutinib for CLL
The Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor zanubrutinib appears safe and effective for patients with B-cell malignancies, according to results from a phase 1 trial.
Among patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), the overall response rate was 96.2%, reported Constantine Si Lun Tam, MD, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne and colleagues.
“Zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) is a highly specific next-generation BTK inhibitor with favorable oral bioavailability, as shown in preclinical studies,” the investigators wrote in Blood. “Compared with ibrutinib, zanubrutinib has shown greater selectivity for BTK and fewer off-target effects in multiple in vitro enzymatic and cell-based assays.”
The current, open-label trial involved 144 patients with B-cell malignancies. To determine optimal dosing, the investigators recruited 17 patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell malignancies who had received at least one prior therapy. The dose expansion part of the study assessed responses in multiple cohorts, including patients with CLL/SLL, mantle cell lymphoma, and Waldenström macroglobulinemia. The primary endpoints were safety and tolerability, including maximum tolerated dose. Efficacy findings were also reported.
During dose escalation, no dose-limiting toxicities were observed, so the highest dose – 320 mg once daily or 160 mg twice daily – was selected for further testing.
The investigators highlighted efficacy and safety findings from 94 patients with CLL/SLL who were involved in dose expansion. Although nearly one-quarter (23.4%) were treatment-naive, the median number of prior therapies was two, and some patients had high-risk features, such as adverse cytogenetics, including 19.1% with a TP53 mutation and 23.3% with a 17p deletion. After a median follow-up of 13.7 months, 94.7% of these patients were still undergoing treatment.
Out of the initial 94 patients with CLL/SLL, 78 were evaluable for efficacy. The overall response rate was 96.2%, including two (2.6%) complete responses, 63 (80.8%) partial responses, and 10 (12.8%) partial responses with lymphocytosis. The median progression-free survival had not been reached, and the 12-month estimated progression-free survival was 100%.
In regard to safety, the most common adverse events were contusion (35.1%), upper respiratory tract infection (33.0%), cough (25.5%), diarrhea (21.3%), fatigue (19.1%), back pain (14.9%), hematuria (14.9%), headache (13.8%), nausea (13.8%), rash (12.8%), arthralgia (11.7%), muscle spasms (11.7%), and urinary tract infection (10.6%).
A number of other adverse events were reported, although these occurred in less than 10% of patients.
More than one-third of patients (36.2%) experienced grade 3 or higher adverse events, with neutropenia being most common (6.4%), followed by pneumonia , hypertension, and anemia, which each occurred in 2.1% of patients, and less commonly, back pain, nausea, urinary tract infection, purpura, cellulitis, and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, which each occurred in 1.1% of patients.
“In this first-in-human study, zanubrutinib demonstrated encouraging activity in patients with relapsed/refractory and treatment-naive CLL/SLL, with good tolerability,” the investigators concluded. “Two ongoing randomized studies of zanubrutinib versus ibrutinib (NCT03053440 and NCT03734016) aim to determine whether consistent, continuous BTK blockade with a selective inhibitor results in fewer off-target effects and translates into improvements in disease control.”
The study was funded by BeiGene USA, which is developing the drug. The investigators reported relationships with the study sponsor, as well as Janssen, Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, and others.
SOURCE: Tam CSL et al. Blood. 2019 Jul 24. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019001160.
The Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor zanubrutinib appears safe and effective for patients with B-cell malignancies, according to results from a phase 1 trial.
Among patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), the overall response rate was 96.2%, reported Constantine Si Lun Tam, MD, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne and colleagues.
“Zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) is a highly specific next-generation BTK inhibitor with favorable oral bioavailability, as shown in preclinical studies,” the investigators wrote in Blood. “Compared with ibrutinib, zanubrutinib has shown greater selectivity for BTK and fewer off-target effects in multiple in vitro enzymatic and cell-based assays.”
The current, open-label trial involved 144 patients with B-cell malignancies. To determine optimal dosing, the investigators recruited 17 patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell malignancies who had received at least one prior therapy. The dose expansion part of the study assessed responses in multiple cohorts, including patients with CLL/SLL, mantle cell lymphoma, and Waldenström macroglobulinemia. The primary endpoints were safety and tolerability, including maximum tolerated dose. Efficacy findings were also reported.
During dose escalation, no dose-limiting toxicities were observed, so the highest dose – 320 mg once daily or 160 mg twice daily – was selected for further testing.
The investigators highlighted efficacy and safety findings from 94 patients with CLL/SLL who were involved in dose expansion. Although nearly one-quarter (23.4%) were treatment-naive, the median number of prior therapies was two, and some patients had high-risk features, such as adverse cytogenetics, including 19.1% with a TP53 mutation and 23.3% with a 17p deletion. After a median follow-up of 13.7 months, 94.7% of these patients were still undergoing treatment.
Out of the initial 94 patients with CLL/SLL, 78 were evaluable for efficacy. The overall response rate was 96.2%, including two (2.6%) complete responses, 63 (80.8%) partial responses, and 10 (12.8%) partial responses with lymphocytosis. The median progression-free survival had not been reached, and the 12-month estimated progression-free survival was 100%.
In regard to safety, the most common adverse events were contusion (35.1%), upper respiratory tract infection (33.0%), cough (25.5%), diarrhea (21.3%), fatigue (19.1%), back pain (14.9%), hematuria (14.9%), headache (13.8%), nausea (13.8%), rash (12.8%), arthralgia (11.7%), muscle spasms (11.7%), and urinary tract infection (10.6%).
A number of other adverse events were reported, although these occurred in less than 10% of patients.
More than one-third of patients (36.2%) experienced grade 3 or higher adverse events, with neutropenia being most common (6.4%), followed by pneumonia , hypertension, and anemia, which each occurred in 2.1% of patients, and less commonly, back pain, nausea, urinary tract infection, purpura, cellulitis, and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, which each occurred in 1.1% of patients.
“In this first-in-human study, zanubrutinib demonstrated encouraging activity in patients with relapsed/refractory and treatment-naive CLL/SLL, with good tolerability,” the investigators concluded. “Two ongoing randomized studies of zanubrutinib versus ibrutinib (NCT03053440 and NCT03734016) aim to determine whether consistent, continuous BTK blockade with a selective inhibitor results in fewer off-target effects and translates into improvements in disease control.”
The study was funded by BeiGene USA, which is developing the drug. The investigators reported relationships with the study sponsor, as well as Janssen, Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, and others.
SOURCE: Tam CSL et al. Blood. 2019 Jul 24. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019001160.
The Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor zanubrutinib appears safe and effective for patients with B-cell malignancies, according to results from a phase 1 trial.
Among patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), the overall response rate was 96.2%, reported Constantine Si Lun Tam, MD, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne and colleagues.
“Zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) is a highly specific next-generation BTK inhibitor with favorable oral bioavailability, as shown in preclinical studies,” the investigators wrote in Blood. “Compared with ibrutinib, zanubrutinib has shown greater selectivity for BTK and fewer off-target effects in multiple in vitro enzymatic and cell-based assays.”
The current, open-label trial involved 144 patients with B-cell malignancies. To determine optimal dosing, the investigators recruited 17 patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell malignancies who had received at least one prior therapy. The dose expansion part of the study assessed responses in multiple cohorts, including patients with CLL/SLL, mantle cell lymphoma, and Waldenström macroglobulinemia. The primary endpoints were safety and tolerability, including maximum tolerated dose. Efficacy findings were also reported.
During dose escalation, no dose-limiting toxicities were observed, so the highest dose – 320 mg once daily or 160 mg twice daily – was selected for further testing.
The investigators highlighted efficacy and safety findings from 94 patients with CLL/SLL who were involved in dose expansion. Although nearly one-quarter (23.4%) were treatment-naive, the median number of prior therapies was two, and some patients had high-risk features, such as adverse cytogenetics, including 19.1% with a TP53 mutation and 23.3% with a 17p deletion. After a median follow-up of 13.7 months, 94.7% of these patients were still undergoing treatment.
Out of the initial 94 patients with CLL/SLL, 78 were evaluable for efficacy. The overall response rate was 96.2%, including two (2.6%) complete responses, 63 (80.8%) partial responses, and 10 (12.8%) partial responses with lymphocytosis. The median progression-free survival had not been reached, and the 12-month estimated progression-free survival was 100%.
In regard to safety, the most common adverse events were contusion (35.1%), upper respiratory tract infection (33.0%), cough (25.5%), diarrhea (21.3%), fatigue (19.1%), back pain (14.9%), hematuria (14.9%), headache (13.8%), nausea (13.8%), rash (12.8%), arthralgia (11.7%), muscle spasms (11.7%), and urinary tract infection (10.6%).
A number of other adverse events were reported, although these occurred in less than 10% of patients.
More than one-third of patients (36.2%) experienced grade 3 or higher adverse events, with neutropenia being most common (6.4%), followed by pneumonia , hypertension, and anemia, which each occurred in 2.1% of patients, and less commonly, back pain, nausea, urinary tract infection, purpura, cellulitis, and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, which each occurred in 1.1% of patients.
“In this first-in-human study, zanubrutinib demonstrated encouraging activity in patients with relapsed/refractory and treatment-naive CLL/SLL, with good tolerability,” the investigators concluded. “Two ongoing randomized studies of zanubrutinib versus ibrutinib (NCT03053440 and NCT03734016) aim to determine whether consistent, continuous BTK blockade with a selective inhibitor results in fewer off-target effects and translates into improvements in disease control.”
The study was funded by BeiGene USA, which is developing the drug. The investigators reported relationships with the study sponsor, as well as Janssen, Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, and others.
SOURCE: Tam CSL et al. Blood. 2019 Jul 24. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019001160.
FROM BLOOD
ICYMI: Ibrutinib/rituximab combo improves CLL survival
Patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) aged 70 years or younger who received ibrutinib/rituximab therapy experienced significantly greater progression-free survival, compared with those who received standard chemotherapy with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (89.4% vs. 72.9% at 3 years; hazard ratio, 0.35; 95% confidence interval, 0.22-0.56; P less than .001), according to results from a randomized, phase 3 trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019;381:432-43).
We first reported on the results of this trial when they were presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology. Find our coverage at the link below.
Patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) aged 70 years or younger who received ibrutinib/rituximab therapy experienced significantly greater progression-free survival, compared with those who received standard chemotherapy with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (89.4% vs. 72.9% at 3 years; hazard ratio, 0.35; 95% confidence interval, 0.22-0.56; P less than .001), according to results from a randomized, phase 3 trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019;381:432-43).
We first reported on the results of this trial when they were presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology. Find our coverage at the link below.
Patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) aged 70 years or younger who received ibrutinib/rituximab therapy experienced significantly greater progression-free survival, compared with those who received standard chemotherapy with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (89.4% vs. 72.9% at 3 years; hazard ratio, 0.35; 95% confidence interval, 0.22-0.56; P less than .001), according to results from a randomized, phase 3 trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019;381:432-43).
We first reported on the results of this trial when they were presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology. Find our coverage at the link below.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
BTK mutations linked to CLL progression on ibrutinib
Mutations in Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) are associated with progression of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in patients taking ibrutinib, according to a new study.
Researchers analyzed a “real-life” cohort of CLL patients taking ibrutinib for about 3 years and found that patients with BTK mutations were significantly more likely to progress (P = .0005).
“Our findings support that mutational analysis should be considered in patients receiving ibrutinib who have residual clonal lymphocytosis, and that clinical trials are needed to evaluate whether patients with a BTK mutation may benefit from an early switch to another treatment,” wrote Anne Quinquenel, MD, PhD, of Hôpital Robert Debré, Université Reims (France) Champagne-Ardenne, and colleagues. Their report is in Blood.
The researchers studied 57 CLL patients who were still on ibrutinib after at least 3 years and provided fresh blood samples. The median time between the start of ibrutinib and sample collection was 3.5 years.
All 57 patients had minimal residual disease at baseline. Of the 55 patients with response data available, 48 had a partial response, and 7 had a partial response with lymphocytosis.
Mutational profiling was possible in 30 patients who had a CLL clone greater than or equal to 0.5 x 109/L.
BTK mutations were present in 17 of the 30 patients (57%). There were 20 BTK mutations in total, all were at C481, and 14 were at C481S.
The researchers also identified 15 patients with TP53 mutations and 4 patients with phospholipase Cg2 (PLCG2) mutations. All 4 patients with PLCG2 mutations also had a BTK mutation and a TP53 mutation.
However, there were no significant associations between BTK mutations and other mutations. BTK mutations were not associated with the number of previous therapies a patient received or the need for ibrutinib dose interruptions or reductions.
The researchers assessed CLL progression at median of 8.5 months from sample collection and found the presence of a BTK mutation was significantly associated with progression (P = .0005).
Of the 17 patients with a BTK mutation, 14 progressed with one case of Richter’s syndrome. Three patients who progressed were still on ibrutinib, nine patients received venetoclax, and two patients died without further treatment.
Of the 13 patients without BTK mutations, just two patients progressed. One patient died without further treatment, and the other received venetoclax.
The event-free survival was significantly shorter in patients with a BTK mutation than in those without (P = .0380), but there was no significant difference in overall survival.
This research was supported by Sunesis Pharmaceuticals and the Force Hemato (fonds de recherche clinique en hématologie) foundation. The researchers reported relationships with Janssen, Gilead, Roche, and AbbVie.
SOURCE: Quinquenel A et al. Blood. 2019 Jun 26. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000854.
Mutations in Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) are associated with progression of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in patients taking ibrutinib, according to a new study.
Researchers analyzed a “real-life” cohort of CLL patients taking ibrutinib for about 3 years and found that patients with BTK mutations were significantly more likely to progress (P = .0005).
“Our findings support that mutational analysis should be considered in patients receiving ibrutinib who have residual clonal lymphocytosis, and that clinical trials are needed to evaluate whether patients with a BTK mutation may benefit from an early switch to another treatment,” wrote Anne Quinquenel, MD, PhD, of Hôpital Robert Debré, Université Reims (France) Champagne-Ardenne, and colleagues. Their report is in Blood.
The researchers studied 57 CLL patients who were still on ibrutinib after at least 3 years and provided fresh blood samples. The median time between the start of ibrutinib and sample collection was 3.5 years.
All 57 patients had minimal residual disease at baseline. Of the 55 patients with response data available, 48 had a partial response, and 7 had a partial response with lymphocytosis.
Mutational profiling was possible in 30 patients who had a CLL clone greater than or equal to 0.5 x 109/L.
BTK mutations were present in 17 of the 30 patients (57%). There were 20 BTK mutations in total, all were at C481, and 14 were at C481S.
The researchers also identified 15 patients with TP53 mutations and 4 patients with phospholipase Cg2 (PLCG2) mutations. All 4 patients with PLCG2 mutations also had a BTK mutation and a TP53 mutation.
However, there were no significant associations between BTK mutations and other mutations. BTK mutations were not associated with the number of previous therapies a patient received or the need for ibrutinib dose interruptions or reductions.
The researchers assessed CLL progression at median of 8.5 months from sample collection and found the presence of a BTK mutation was significantly associated with progression (P = .0005).
Of the 17 patients with a BTK mutation, 14 progressed with one case of Richter’s syndrome. Three patients who progressed were still on ibrutinib, nine patients received venetoclax, and two patients died without further treatment.
Of the 13 patients without BTK mutations, just two patients progressed. One patient died without further treatment, and the other received venetoclax.
The event-free survival was significantly shorter in patients with a BTK mutation than in those without (P = .0380), but there was no significant difference in overall survival.
This research was supported by Sunesis Pharmaceuticals and the Force Hemato (fonds de recherche clinique en hématologie) foundation. The researchers reported relationships with Janssen, Gilead, Roche, and AbbVie.
SOURCE: Quinquenel A et al. Blood. 2019 Jun 26. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000854.
Mutations in Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) are associated with progression of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in patients taking ibrutinib, according to a new study.
Researchers analyzed a “real-life” cohort of CLL patients taking ibrutinib for about 3 years and found that patients with BTK mutations were significantly more likely to progress (P = .0005).
“Our findings support that mutational analysis should be considered in patients receiving ibrutinib who have residual clonal lymphocytosis, and that clinical trials are needed to evaluate whether patients with a BTK mutation may benefit from an early switch to another treatment,” wrote Anne Quinquenel, MD, PhD, of Hôpital Robert Debré, Université Reims (France) Champagne-Ardenne, and colleagues. Their report is in Blood.
The researchers studied 57 CLL patients who were still on ibrutinib after at least 3 years and provided fresh blood samples. The median time between the start of ibrutinib and sample collection was 3.5 years.
All 57 patients had minimal residual disease at baseline. Of the 55 patients with response data available, 48 had a partial response, and 7 had a partial response with lymphocytosis.
Mutational profiling was possible in 30 patients who had a CLL clone greater than or equal to 0.5 x 109/L.
BTK mutations were present in 17 of the 30 patients (57%). There were 20 BTK mutations in total, all were at C481, and 14 were at C481S.
The researchers also identified 15 patients with TP53 mutations and 4 patients with phospholipase Cg2 (PLCG2) mutations. All 4 patients with PLCG2 mutations also had a BTK mutation and a TP53 mutation.
However, there were no significant associations between BTK mutations and other mutations. BTK mutations were not associated with the number of previous therapies a patient received or the need for ibrutinib dose interruptions or reductions.
The researchers assessed CLL progression at median of 8.5 months from sample collection and found the presence of a BTK mutation was significantly associated with progression (P = .0005).
Of the 17 patients with a BTK mutation, 14 progressed with one case of Richter’s syndrome. Three patients who progressed were still on ibrutinib, nine patients received venetoclax, and two patients died without further treatment.
Of the 13 patients without BTK mutations, just two patients progressed. One patient died without further treatment, and the other received venetoclax.
The event-free survival was significantly shorter in patients with a BTK mutation than in those without (P = .0380), but there was no significant difference in overall survival.
This research was supported by Sunesis Pharmaceuticals and the Force Hemato (fonds de recherche clinique en hématologie) foundation. The researchers reported relationships with Janssen, Gilead, Roche, and AbbVie.
SOURCE: Quinquenel A et al. Blood. 2019 Jun 26. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000854.
FROM BLOOD
Ibrutinib-venetoclax found highly active in hard-to-treat CLL
The strategy of simultaneously inhibiting proliferation and reactivating apoptosis can eradicate chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in a large share of patients, suggest results from the phase 2 CLARITY trial.
“Both ibrutinib and venetoclax are active in CLL with improved survival; however, as monotherapies, both currently are given until disease progression,” wrote Peter Hillmen, MBChB, PhD, St. James’s University Hospital, Leeds, England, and his colleagues.
In the single-arm, open-label trial, the investigators treated 53 patients with relapsed or refractory CLL with combination ibrutinib (Imbruvica), a small-molecule inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, and venetoclax (Venclexta), a small molecule inhibitor of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2. The primary endpoint was MRD negativity, defined as presence of fewer than one CLL cell in 10,000 leukocytes, after 12 months of combination therapy.
Results reported in the Journal of Clinical Oncology showed that the combination was highly active, with 53% of patients achieving MRD negativity in the blood and 36% achieving MRD negativity in the marrow.
Most patients, 89%, had a treatment response, and slightly more than half, 51%, achieved a complete remission. With a median 21.1-month follow-up, only a single patient experienced progression and all were still alive.
Adverse effects were generally manageable. Grade 3-4 adverse events of special interest included 34 cases of neutropenia and 1 case of biochemical tumor lysis syndrome that was managed by delaying venetoclax.
“We have demonstrated promising efficacy that indicates potent synergy between ibrutinib and venetoclax for inducing MRD-negative responses with manageable adverse effects,” the investigators wrote. “The observation that a significant proportion of patients experience MRD-negative remission indicates that this combination can be given for a limited period and then stopped after patients achieve a deep remission.”
Whether the combination leads to permanent disease eradication in certain patients is still unclear, the investigators added.
The trial was supported by Bloodwise under the Trials Acceleration Programme, by the National Institute for Health Research Leeds Clinical Research Facility, and by an unrestricted educational grant from Janssen-Cilag and AbbVie. Ibrutinib was provided free of charge by Janssen-Cilag, and venetoclax was provided free of charge by AbbVie. Dr. Hillman reported financial relationships with Janssen, AbbVie, Roche, Pharmacyclics, and Gilead Sciences.
SOURCE: Hillmen P et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jul 11. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00894.
The strategy of simultaneously inhibiting proliferation and reactivating apoptosis can eradicate chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in a large share of patients, suggest results from the phase 2 CLARITY trial.
“Both ibrutinib and venetoclax are active in CLL with improved survival; however, as monotherapies, both currently are given until disease progression,” wrote Peter Hillmen, MBChB, PhD, St. James’s University Hospital, Leeds, England, and his colleagues.
In the single-arm, open-label trial, the investigators treated 53 patients with relapsed or refractory CLL with combination ibrutinib (Imbruvica), a small-molecule inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, and venetoclax (Venclexta), a small molecule inhibitor of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2. The primary endpoint was MRD negativity, defined as presence of fewer than one CLL cell in 10,000 leukocytes, after 12 months of combination therapy.
Results reported in the Journal of Clinical Oncology showed that the combination was highly active, with 53% of patients achieving MRD negativity in the blood and 36% achieving MRD negativity in the marrow.
Most patients, 89%, had a treatment response, and slightly more than half, 51%, achieved a complete remission. With a median 21.1-month follow-up, only a single patient experienced progression and all were still alive.
Adverse effects were generally manageable. Grade 3-4 adverse events of special interest included 34 cases of neutropenia and 1 case of biochemical tumor lysis syndrome that was managed by delaying venetoclax.
“We have demonstrated promising efficacy that indicates potent synergy between ibrutinib and venetoclax for inducing MRD-negative responses with manageable adverse effects,” the investigators wrote. “The observation that a significant proportion of patients experience MRD-negative remission indicates that this combination can be given for a limited period and then stopped after patients achieve a deep remission.”
Whether the combination leads to permanent disease eradication in certain patients is still unclear, the investigators added.
The trial was supported by Bloodwise under the Trials Acceleration Programme, by the National Institute for Health Research Leeds Clinical Research Facility, and by an unrestricted educational grant from Janssen-Cilag and AbbVie. Ibrutinib was provided free of charge by Janssen-Cilag, and venetoclax was provided free of charge by AbbVie. Dr. Hillman reported financial relationships with Janssen, AbbVie, Roche, Pharmacyclics, and Gilead Sciences.
SOURCE: Hillmen P et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jul 11. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00894.
The strategy of simultaneously inhibiting proliferation and reactivating apoptosis can eradicate chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in a large share of patients, suggest results from the phase 2 CLARITY trial.
“Both ibrutinib and venetoclax are active in CLL with improved survival; however, as monotherapies, both currently are given until disease progression,” wrote Peter Hillmen, MBChB, PhD, St. James’s University Hospital, Leeds, England, and his colleagues.
In the single-arm, open-label trial, the investigators treated 53 patients with relapsed or refractory CLL with combination ibrutinib (Imbruvica), a small-molecule inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, and venetoclax (Venclexta), a small molecule inhibitor of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2. The primary endpoint was MRD negativity, defined as presence of fewer than one CLL cell in 10,000 leukocytes, after 12 months of combination therapy.
Results reported in the Journal of Clinical Oncology showed that the combination was highly active, with 53% of patients achieving MRD negativity in the blood and 36% achieving MRD negativity in the marrow.
Most patients, 89%, had a treatment response, and slightly more than half, 51%, achieved a complete remission. With a median 21.1-month follow-up, only a single patient experienced progression and all were still alive.
Adverse effects were generally manageable. Grade 3-4 adverse events of special interest included 34 cases of neutropenia and 1 case of biochemical tumor lysis syndrome that was managed by delaying venetoclax.
“We have demonstrated promising efficacy that indicates potent synergy between ibrutinib and venetoclax for inducing MRD-negative responses with manageable adverse effects,” the investigators wrote. “The observation that a significant proportion of patients experience MRD-negative remission indicates that this combination can be given for a limited period and then stopped after patients achieve a deep remission.”
Whether the combination leads to permanent disease eradication in certain patients is still unclear, the investigators added.
The trial was supported by Bloodwise under the Trials Acceleration Programme, by the National Institute for Health Research Leeds Clinical Research Facility, and by an unrestricted educational grant from Janssen-Cilag and AbbVie. Ibrutinib was provided free of charge by Janssen-Cilag, and venetoclax was provided free of charge by AbbVie. Dr. Hillman reported financial relationships with Janssen, AbbVie, Roche, Pharmacyclics, and Gilead Sciences.
SOURCE: Hillmen P et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jul 11. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00894.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
How to recognize pediatric leukemia cutis
Researchers have characterized the clinical presentation, progression, and prognosis of leukemia cutis in a pediatric population, according to findings from a retrospective case series.
“To our knowledge, this is the largest reported case series of pediatric leukemia cutis,” wrote Elena Corina Andriescu of the University of Texas, Houston, and colleagues. The results were published in Pediatric Dermatology.
The study included 31 children with histologically confirmed leukemia cutis at one of two pediatric institutions. The researchers reviewed medical records to distinguish common features among patients.
Various clinical data, including disease subtype, related symptoms, management, and prognosis, were collected from January 1993 to March 2014. The children in the case series ranged in age up to 19 years with a median age at diagnosis of 26.8 months.
After analysis, the researchers reported that the magnitude and morphology of disease lesions differed among pediatric patients, with the most common sites being the lower extremities and head. The most common morphologies were nodules and papules. Additionally, the researchers found that lesions were often erythematous, violaceous, or both colors.
The majority of patients (65%) presented with concomitant systemic leukemia and leukemia cutis. The most common types of leukemia associated with the skin condition were acute myeloid leukemia (in 74% of cases) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (in 16% of cases). The researchers saw no significant differences in leukemia cutis morphology or distribution based on the leukemia diagnosis.
“Most cases of leukemia cutis arose during initial leukemia episodes, rather than with relapsed leukemia,” they added.
Because of an insufficiency of specific genetic data, investigators were unable to make prognostic inferences in the majority of participants.
Two key limitations of the study were the small sample size and retrospective design. As a result, the investigators were unable to prospectively classify skin findings in a systematic manner. Despite these limitations, the authors noted that these findings add to the present knowledge of leukemia cutis in pediatric patients.
“Importantly, the presence of [leukemia cutis] changed the management of systemic leukemia in one‐third of patients,” the researchers wrote. “The potential for major changes in treatment plans such as adding radiation therapy and deferring hematopoietic stem cell transplantation underscores the importance of diagnosing [leukemia cutis].”
No funding sources were reported. The authors did not report conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Andriescu EC et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019 Jul 5. doi: 10.1111/pde.13864.
Researchers have characterized the clinical presentation, progression, and prognosis of leukemia cutis in a pediatric population, according to findings from a retrospective case series.
“To our knowledge, this is the largest reported case series of pediatric leukemia cutis,” wrote Elena Corina Andriescu of the University of Texas, Houston, and colleagues. The results were published in Pediatric Dermatology.
The study included 31 children with histologically confirmed leukemia cutis at one of two pediatric institutions. The researchers reviewed medical records to distinguish common features among patients.
Various clinical data, including disease subtype, related symptoms, management, and prognosis, were collected from January 1993 to March 2014. The children in the case series ranged in age up to 19 years with a median age at diagnosis of 26.8 months.
After analysis, the researchers reported that the magnitude and morphology of disease lesions differed among pediatric patients, with the most common sites being the lower extremities and head. The most common morphologies were nodules and papules. Additionally, the researchers found that lesions were often erythematous, violaceous, or both colors.
The majority of patients (65%) presented with concomitant systemic leukemia and leukemia cutis. The most common types of leukemia associated with the skin condition were acute myeloid leukemia (in 74% of cases) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (in 16% of cases). The researchers saw no significant differences in leukemia cutis morphology or distribution based on the leukemia diagnosis.
“Most cases of leukemia cutis arose during initial leukemia episodes, rather than with relapsed leukemia,” they added.
Because of an insufficiency of specific genetic data, investigators were unable to make prognostic inferences in the majority of participants.
Two key limitations of the study were the small sample size and retrospective design. As a result, the investigators were unable to prospectively classify skin findings in a systematic manner. Despite these limitations, the authors noted that these findings add to the present knowledge of leukemia cutis in pediatric patients.
“Importantly, the presence of [leukemia cutis] changed the management of systemic leukemia in one‐third of patients,” the researchers wrote. “The potential for major changes in treatment plans such as adding radiation therapy and deferring hematopoietic stem cell transplantation underscores the importance of diagnosing [leukemia cutis].”
No funding sources were reported. The authors did not report conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Andriescu EC et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019 Jul 5. doi: 10.1111/pde.13864.
Researchers have characterized the clinical presentation, progression, and prognosis of leukemia cutis in a pediatric population, according to findings from a retrospective case series.
“To our knowledge, this is the largest reported case series of pediatric leukemia cutis,” wrote Elena Corina Andriescu of the University of Texas, Houston, and colleagues. The results were published in Pediatric Dermatology.
The study included 31 children with histologically confirmed leukemia cutis at one of two pediatric institutions. The researchers reviewed medical records to distinguish common features among patients.
Various clinical data, including disease subtype, related symptoms, management, and prognosis, were collected from January 1993 to March 2014. The children in the case series ranged in age up to 19 years with a median age at diagnosis of 26.8 months.
After analysis, the researchers reported that the magnitude and morphology of disease lesions differed among pediatric patients, with the most common sites being the lower extremities and head. The most common morphologies were nodules and papules. Additionally, the researchers found that lesions were often erythematous, violaceous, or both colors.
The majority of patients (65%) presented with concomitant systemic leukemia and leukemia cutis. The most common types of leukemia associated with the skin condition were acute myeloid leukemia (in 74% of cases) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (in 16% of cases). The researchers saw no significant differences in leukemia cutis morphology or distribution based on the leukemia diagnosis.
“Most cases of leukemia cutis arose during initial leukemia episodes, rather than with relapsed leukemia,” they added.
Because of an insufficiency of specific genetic data, investigators were unable to make prognostic inferences in the majority of participants.
Two key limitations of the study were the small sample size and retrospective design. As a result, the investigators were unable to prospectively classify skin findings in a systematic manner. Despite these limitations, the authors noted that these findings add to the present knowledge of leukemia cutis in pediatric patients.
“Importantly, the presence of [leukemia cutis] changed the management of systemic leukemia in one‐third of patients,” the researchers wrote. “The potential for major changes in treatment plans such as adding radiation therapy and deferring hematopoietic stem cell transplantation underscores the importance of diagnosing [leukemia cutis].”
No funding sources were reported. The authors did not report conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Andriescu EC et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019 Jul 5. doi: 10.1111/pde.13864.
FROM PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY
Acalabrutinib extends PFS in advanced CLL
AMSTERDAM – For patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), monotherapy with the Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor acalabrutinib (Calquence) was associated with better progression-free survival and a more tolerable safety profile than rituximab combined with either idelalisib (Zydelig) or bendamustine, an interim analysis from the phase 3 ASCEND trial showed.
Among 310 patients with previously treated CLL followed for a median of 16.1 months, the primary endpoint of median progression-free survival (PFS), as assessed by independent reviewers, had not been reached for patients treated with acalabrutinib, compared with 16.5 months for patients treated with idelalisib and rituximab (IdR) or bendamustine and rituximab (BR), reported Paolo Ghia, MD, PhD, from Università Vita-Salute San Raffaele in Milan.
“We show that acalabrutinib improved progression-free survival across all groups, including those with high-risk features,” he said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
Acalabrutinib is approved in the United States for treatment of mantle cell lymphoma that has progressed on at least one prior therapy. It has been shown in preclinical studies to be more selective for BTK than the first-in-class agent ibrutinib (Imbruvica), with less off-target kinase inhibition, Dr. Ghia said.
ASCEND was designed to see whether acalabrutinib monotherapy could offer superior PFS to IdR or BR in patients with CLL who had progressed or were refractory to at least one prior line of therapy.
Patients were randomly assigned, with 155 patients in each arm, to either acalabrutinib 100 mg orally twice daily or the investigator’s choice of either idelalisib 150 mg orally twice daily plus IV rituximab at an initial dose of 375 mg/m2, followed by up to seven doses at 500 mg/m2 delivered every 2 weeks for four infusions, then every 4 weeks for the remaining three infusions or IV bendamustine 70 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 of each cycle, plus rituximab at the 375 mg/m2 dose on day 1 for the first cycle, followed by 500 mg/m2 for up to six total cycles.
Dr. Ghia presented results of an interim analysis planned for when two-thirds of the predicted PFS events (approximately 79) had occurred.
The baseline patient characteristics were generally similar, with a median age of 68 years in the acalabrutinib arm and 67 years in the comparison arm. Almost half of all patients in each arm had bulky disease, defined as 5 cm or greater. The majority of patients had two or more prior lines of therapy.
The primary endpoint of PFS as assessed by independent review favored acalabrutinib, with a hazard ratio of 0.31 (P less than .0001). Results were similar when acalabrutinib was compared with each of the regimens in the comparison arm (HR, 0.29 vs. IdR, 0.36 vs. BR; P less than .001 for each comparison).
Acalabrutinib was also superior in patients with high-risk cytogenetic features, compared with the other two regimens combined (HR, 0.27; P less than .001).
The benefit of the BTK inhibitor was consistent across all subgroups, including age, sex, performance status, Rai stage at screening, bulky/nonbulky disease, number of prior therapies, presence or absence of deletion 17p or TP53 mutation, mutated or unmutated immunoglobulin heavy chain, and complex/noncomplex karyotype.
Reviewer-assessed objective response rates were similar, occurring in 81% of patients on acalabrutinib and 76% of patients on other regimens.
There were no complete responses in the acalabrutinib arm, compared with two complete responses in the comparison arm. The majority of responses in each arm were partial responses (81% and 74%, respectively).
The median duration of response was not reached with acalabrutinib, compared with 13.6 months with the other therapies (HR, 0.33; P less than .0001).
In all, 85% of patients on acalabrutinib had a response lasting at least 12 months, compared with 60% of patients on the other regimens. There was no difference in overall survival at the 16.1-month median follow-up.
Adverse events of any grade occurred in 94% of patients on acalabrutinib, 99% on IdR, and 80% on BR; the respective incidences of serious adverse events were 29%, 56%, and 26%. Grade 3-4 adverse events occurred in 45%, 86%, and 43% of patients, respectively.
There were 13 treatment-related deaths. Six deaths in the acalabrutinib arm were caused by brain neoplasm, cachexia, cerebral ischemia, malignant lung tumor, neuroendocrine carcinoma, and sepsis. Five deaths among IdR-treated patients included chronic heart failure, cardiopulmonary disease, interstitial lung disease, MI, and pseudomonal pneumonia. Two deaths in BR-treated patients were attributed to acute cardiac failure and a gastric neoplasm.
The results show that “acalabrutinib has demonstrated efficacy in previously untreated and relapsed/refractory CLL and may be considered as an option in the future treatment paradigm,” Dr. Ghia said.
Acalabrutinib monotherapy is currently being compared with ibrutinib monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory CLL; in addition, the phase 3 ELEVATE-TN study investigating acalabrutinib in combination with obinutuzumab (Gazyva) versus obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil has reached its primary PFS endpoint and will be reported soon, Dr. Ghia said.
The ASCEND trial is sponsored by Acerta Pharma; AstraZeneca holds majority shares in the company. Dr. Ghia reported consulting fees and honoraria from AstraZeneca and other companies, and research funding from several different companies.
SOURCE: Ghia P et al. EHA Congress, Abstract LB2606.
AMSTERDAM – For patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), monotherapy with the Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor acalabrutinib (Calquence) was associated with better progression-free survival and a more tolerable safety profile than rituximab combined with either idelalisib (Zydelig) or bendamustine, an interim analysis from the phase 3 ASCEND trial showed.
Among 310 patients with previously treated CLL followed for a median of 16.1 months, the primary endpoint of median progression-free survival (PFS), as assessed by independent reviewers, had not been reached for patients treated with acalabrutinib, compared with 16.5 months for patients treated with idelalisib and rituximab (IdR) or bendamustine and rituximab (BR), reported Paolo Ghia, MD, PhD, from Università Vita-Salute San Raffaele in Milan.
“We show that acalabrutinib improved progression-free survival across all groups, including those with high-risk features,” he said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
Acalabrutinib is approved in the United States for treatment of mantle cell lymphoma that has progressed on at least one prior therapy. It has been shown in preclinical studies to be more selective for BTK than the first-in-class agent ibrutinib (Imbruvica), with less off-target kinase inhibition, Dr. Ghia said.
ASCEND was designed to see whether acalabrutinib monotherapy could offer superior PFS to IdR or BR in patients with CLL who had progressed or were refractory to at least one prior line of therapy.
Patients were randomly assigned, with 155 patients in each arm, to either acalabrutinib 100 mg orally twice daily or the investigator’s choice of either idelalisib 150 mg orally twice daily plus IV rituximab at an initial dose of 375 mg/m2, followed by up to seven doses at 500 mg/m2 delivered every 2 weeks for four infusions, then every 4 weeks for the remaining three infusions or IV bendamustine 70 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 of each cycle, plus rituximab at the 375 mg/m2 dose on day 1 for the first cycle, followed by 500 mg/m2 for up to six total cycles.
Dr. Ghia presented results of an interim analysis planned for when two-thirds of the predicted PFS events (approximately 79) had occurred.
The baseline patient characteristics were generally similar, with a median age of 68 years in the acalabrutinib arm and 67 years in the comparison arm. Almost half of all patients in each arm had bulky disease, defined as 5 cm or greater. The majority of patients had two or more prior lines of therapy.
The primary endpoint of PFS as assessed by independent review favored acalabrutinib, with a hazard ratio of 0.31 (P less than .0001). Results were similar when acalabrutinib was compared with each of the regimens in the comparison arm (HR, 0.29 vs. IdR, 0.36 vs. BR; P less than .001 for each comparison).
Acalabrutinib was also superior in patients with high-risk cytogenetic features, compared with the other two regimens combined (HR, 0.27; P less than .001).
The benefit of the BTK inhibitor was consistent across all subgroups, including age, sex, performance status, Rai stage at screening, bulky/nonbulky disease, number of prior therapies, presence or absence of deletion 17p or TP53 mutation, mutated or unmutated immunoglobulin heavy chain, and complex/noncomplex karyotype.
Reviewer-assessed objective response rates were similar, occurring in 81% of patients on acalabrutinib and 76% of patients on other regimens.
There were no complete responses in the acalabrutinib arm, compared with two complete responses in the comparison arm. The majority of responses in each arm were partial responses (81% and 74%, respectively).
The median duration of response was not reached with acalabrutinib, compared with 13.6 months with the other therapies (HR, 0.33; P less than .0001).
In all, 85% of patients on acalabrutinib had a response lasting at least 12 months, compared with 60% of patients on the other regimens. There was no difference in overall survival at the 16.1-month median follow-up.
Adverse events of any grade occurred in 94% of patients on acalabrutinib, 99% on IdR, and 80% on BR; the respective incidences of serious adverse events were 29%, 56%, and 26%. Grade 3-4 adverse events occurred in 45%, 86%, and 43% of patients, respectively.
There were 13 treatment-related deaths. Six deaths in the acalabrutinib arm were caused by brain neoplasm, cachexia, cerebral ischemia, malignant lung tumor, neuroendocrine carcinoma, and sepsis. Five deaths among IdR-treated patients included chronic heart failure, cardiopulmonary disease, interstitial lung disease, MI, and pseudomonal pneumonia. Two deaths in BR-treated patients were attributed to acute cardiac failure and a gastric neoplasm.
The results show that “acalabrutinib has demonstrated efficacy in previously untreated and relapsed/refractory CLL and may be considered as an option in the future treatment paradigm,” Dr. Ghia said.
Acalabrutinib monotherapy is currently being compared with ibrutinib monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory CLL; in addition, the phase 3 ELEVATE-TN study investigating acalabrutinib in combination with obinutuzumab (Gazyva) versus obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil has reached its primary PFS endpoint and will be reported soon, Dr. Ghia said.
The ASCEND trial is sponsored by Acerta Pharma; AstraZeneca holds majority shares in the company. Dr. Ghia reported consulting fees and honoraria from AstraZeneca and other companies, and research funding from several different companies.
SOURCE: Ghia P et al. EHA Congress, Abstract LB2606.
AMSTERDAM – For patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), monotherapy with the Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor acalabrutinib (Calquence) was associated with better progression-free survival and a more tolerable safety profile than rituximab combined with either idelalisib (Zydelig) or bendamustine, an interim analysis from the phase 3 ASCEND trial showed.
Among 310 patients with previously treated CLL followed for a median of 16.1 months, the primary endpoint of median progression-free survival (PFS), as assessed by independent reviewers, had not been reached for patients treated with acalabrutinib, compared with 16.5 months for patients treated with idelalisib and rituximab (IdR) or bendamustine and rituximab (BR), reported Paolo Ghia, MD, PhD, from Università Vita-Salute San Raffaele in Milan.
“We show that acalabrutinib improved progression-free survival across all groups, including those with high-risk features,” he said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
Acalabrutinib is approved in the United States for treatment of mantle cell lymphoma that has progressed on at least one prior therapy. It has been shown in preclinical studies to be more selective for BTK than the first-in-class agent ibrutinib (Imbruvica), with less off-target kinase inhibition, Dr. Ghia said.
ASCEND was designed to see whether acalabrutinib monotherapy could offer superior PFS to IdR or BR in patients with CLL who had progressed or were refractory to at least one prior line of therapy.
Patients were randomly assigned, with 155 patients in each arm, to either acalabrutinib 100 mg orally twice daily or the investigator’s choice of either idelalisib 150 mg orally twice daily plus IV rituximab at an initial dose of 375 mg/m2, followed by up to seven doses at 500 mg/m2 delivered every 2 weeks for four infusions, then every 4 weeks for the remaining three infusions or IV bendamustine 70 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 of each cycle, plus rituximab at the 375 mg/m2 dose on day 1 for the first cycle, followed by 500 mg/m2 for up to six total cycles.
Dr. Ghia presented results of an interim analysis planned for when two-thirds of the predicted PFS events (approximately 79) had occurred.
The baseline patient characteristics were generally similar, with a median age of 68 years in the acalabrutinib arm and 67 years in the comparison arm. Almost half of all patients in each arm had bulky disease, defined as 5 cm or greater. The majority of patients had two or more prior lines of therapy.
The primary endpoint of PFS as assessed by independent review favored acalabrutinib, with a hazard ratio of 0.31 (P less than .0001). Results were similar when acalabrutinib was compared with each of the regimens in the comparison arm (HR, 0.29 vs. IdR, 0.36 vs. BR; P less than .001 for each comparison).
Acalabrutinib was also superior in patients with high-risk cytogenetic features, compared with the other two regimens combined (HR, 0.27; P less than .001).
The benefit of the BTK inhibitor was consistent across all subgroups, including age, sex, performance status, Rai stage at screening, bulky/nonbulky disease, number of prior therapies, presence or absence of deletion 17p or TP53 mutation, mutated or unmutated immunoglobulin heavy chain, and complex/noncomplex karyotype.
Reviewer-assessed objective response rates were similar, occurring in 81% of patients on acalabrutinib and 76% of patients on other regimens.
There were no complete responses in the acalabrutinib arm, compared with two complete responses in the comparison arm. The majority of responses in each arm were partial responses (81% and 74%, respectively).
The median duration of response was not reached with acalabrutinib, compared with 13.6 months with the other therapies (HR, 0.33; P less than .0001).
In all, 85% of patients on acalabrutinib had a response lasting at least 12 months, compared with 60% of patients on the other regimens. There was no difference in overall survival at the 16.1-month median follow-up.
Adverse events of any grade occurred in 94% of patients on acalabrutinib, 99% on IdR, and 80% on BR; the respective incidences of serious adverse events were 29%, 56%, and 26%. Grade 3-4 adverse events occurred in 45%, 86%, and 43% of patients, respectively.
There were 13 treatment-related deaths. Six deaths in the acalabrutinib arm were caused by brain neoplasm, cachexia, cerebral ischemia, malignant lung tumor, neuroendocrine carcinoma, and sepsis. Five deaths among IdR-treated patients included chronic heart failure, cardiopulmonary disease, interstitial lung disease, MI, and pseudomonal pneumonia. Two deaths in BR-treated patients were attributed to acute cardiac failure and a gastric neoplasm.
The results show that “acalabrutinib has demonstrated efficacy in previously untreated and relapsed/refractory CLL and may be considered as an option in the future treatment paradigm,” Dr. Ghia said.
Acalabrutinib monotherapy is currently being compared with ibrutinib monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory CLL; in addition, the phase 3 ELEVATE-TN study investigating acalabrutinib in combination with obinutuzumab (Gazyva) versus obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil has reached its primary PFS endpoint and will be reported soon, Dr. Ghia said.
The ASCEND trial is sponsored by Acerta Pharma; AstraZeneca holds majority shares in the company. Dr. Ghia reported consulting fees and honoraria from AstraZeneca and other companies, and research funding from several different companies.
SOURCE: Ghia P et al. EHA Congress, Abstract LB2606.
REPORTING FROM EHA CONGRESS
Ibrutinib tops chlorambucil against CLL
AMSTERDAM – After 5 years, a large majority of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with front-line ibrutinib (Imbruvica) have not experienced disease progression, and the median progression-free survival has still not been reached, long-term follow-up from the RESONATE-2 shows.
The 5-year estimated progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 70% for patients who had been randomized to receive ibrutinib monotherapy, compared with 12% for patients randomized to chlorambucil, reported Alessandra Tedeschi, MD, from Azienda Ospedaliera Niguarda Ca’ Granda in Milan.
Ibrutinib was also associated with a halving of risk for death, compared with chlorambucil, she said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
“Importantly, the rate of progression during ibrutinib treatment was very low; only 8 – that is, 6% of patients” – experienced disease progression while receiving ibrutinib, she noted.
In the RESONATE-2 (PCYC-1115) trial, investigators enrolled 269 adults aged 65 years and older with previously untreated CLL/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). Patients at the younger end of the age range (65-69 years) had to have comorbidities that would have made them ineligible for the FCR chemotherapy regimen (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab). Additionally, patients with the deleterious 17p deletion were excluded.
Patients were stratified by performance status and Rai stage and then randomized to receive either ibrutinib 420 mg once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity (136 patients) or chlorambucil 0.5 mg/kg to a maximum of 0.8 mg/kg for up to 12 cycles (133 patients). The trial also had an extension study for patients who had disease progression as confirmed by an independent review committee or who had completed the RESONATE-2 trial. Of the 133 patients in the chlorambucil arm, 76 (57% of the intention-to-treat population) were crossed over to ibrutinib following disease progression.
The median duration of ibrutinib treatment was 57.1 months, with 73% of patients being on it for more than 3 years, 65% for more than 4 years, and 27% for more than 5 years. As of the data cutoff, 79 patients (58%) were continuing with ibrutinib on study.
At 5 years, 70% of ibrutinib-treated patients and 12% of chlorambucil-treated patients were estimated to be progression-free and alive (hazard ratio for PFS with ibrutinib 0.146 (95% confidence interval, 0.10-0.22). The benefit of ibrutinib was consistent for patients with high-risk genomic features, including the 11q deletion and unmutated immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable genes.
Estimated 5-year overall survival was also better with ibrutinib, at 83% vs. 68% (hazard ratio, 0.45; 95% CI, 0.266-0.761).
The most common grade 3 or greater adverse events occurring with ibrutinib were neutropenia (13%), pneumonia (12%), hypertension (8%), anemia (7%), hyponatremia (6%), atrial fibrillation (5%), and cataract (5%). The rates of most adverse events decreased over time, and dose reductions because of adverse events also diminished over time, from 5% of patients in the first year down to zero in years 4 through 5.
Patients responded to subsequent CLL therapies following ibrutinib discontinuation, including chemoimmunotherapy and other kinase inhibitors, Dr. Tedeschi said.
The trial was sponsored by Pharmacyclics with collaboration from Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Tedeschi reported advisory board activities with Janssen, AbbVie, and BeiGene.
SOURCE: Tedeschi A et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S107.
AMSTERDAM – After 5 years, a large majority of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with front-line ibrutinib (Imbruvica) have not experienced disease progression, and the median progression-free survival has still not been reached, long-term follow-up from the RESONATE-2 shows.
The 5-year estimated progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 70% for patients who had been randomized to receive ibrutinib monotherapy, compared with 12% for patients randomized to chlorambucil, reported Alessandra Tedeschi, MD, from Azienda Ospedaliera Niguarda Ca’ Granda in Milan.
Ibrutinib was also associated with a halving of risk for death, compared with chlorambucil, she said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
“Importantly, the rate of progression during ibrutinib treatment was very low; only 8 – that is, 6% of patients” – experienced disease progression while receiving ibrutinib, she noted.
In the RESONATE-2 (PCYC-1115) trial, investigators enrolled 269 adults aged 65 years and older with previously untreated CLL/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). Patients at the younger end of the age range (65-69 years) had to have comorbidities that would have made them ineligible for the FCR chemotherapy regimen (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab). Additionally, patients with the deleterious 17p deletion were excluded.
Patients were stratified by performance status and Rai stage and then randomized to receive either ibrutinib 420 mg once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity (136 patients) or chlorambucil 0.5 mg/kg to a maximum of 0.8 mg/kg for up to 12 cycles (133 patients). The trial also had an extension study for patients who had disease progression as confirmed by an independent review committee or who had completed the RESONATE-2 trial. Of the 133 patients in the chlorambucil arm, 76 (57% of the intention-to-treat population) were crossed over to ibrutinib following disease progression.
The median duration of ibrutinib treatment was 57.1 months, with 73% of patients being on it for more than 3 years, 65% for more than 4 years, and 27% for more than 5 years. As of the data cutoff, 79 patients (58%) were continuing with ibrutinib on study.
At 5 years, 70% of ibrutinib-treated patients and 12% of chlorambucil-treated patients were estimated to be progression-free and alive (hazard ratio for PFS with ibrutinib 0.146 (95% confidence interval, 0.10-0.22). The benefit of ibrutinib was consistent for patients with high-risk genomic features, including the 11q deletion and unmutated immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable genes.
Estimated 5-year overall survival was also better with ibrutinib, at 83% vs. 68% (hazard ratio, 0.45; 95% CI, 0.266-0.761).
The most common grade 3 or greater adverse events occurring with ibrutinib were neutropenia (13%), pneumonia (12%), hypertension (8%), anemia (7%), hyponatremia (6%), atrial fibrillation (5%), and cataract (5%). The rates of most adverse events decreased over time, and dose reductions because of adverse events also diminished over time, from 5% of patients in the first year down to zero in years 4 through 5.
Patients responded to subsequent CLL therapies following ibrutinib discontinuation, including chemoimmunotherapy and other kinase inhibitors, Dr. Tedeschi said.
The trial was sponsored by Pharmacyclics with collaboration from Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Tedeschi reported advisory board activities with Janssen, AbbVie, and BeiGene.
SOURCE: Tedeschi A et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S107.
AMSTERDAM – After 5 years, a large majority of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with front-line ibrutinib (Imbruvica) have not experienced disease progression, and the median progression-free survival has still not been reached, long-term follow-up from the RESONATE-2 shows.
The 5-year estimated progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 70% for patients who had been randomized to receive ibrutinib monotherapy, compared with 12% for patients randomized to chlorambucil, reported Alessandra Tedeschi, MD, from Azienda Ospedaliera Niguarda Ca’ Granda in Milan.
Ibrutinib was also associated with a halving of risk for death, compared with chlorambucil, she said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
“Importantly, the rate of progression during ibrutinib treatment was very low; only 8 – that is, 6% of patients” – experienced disease progression while receiving ibrutinib, she noted.
In the RESONATE-2 (PCYC-1115) trial, investigators enrolled 269 adults aged 65 years and older with previously untreated CLL/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). Patients at the younger end of the age range (65-69 years) had to have comorbidities that would have made them ineligible for the FCR chemotherapy regimen (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab). Additionally, patients with the deleterious 17p deletion were excluded.
Patients were stratified by performance status and Rai stage and then randomized to receive either ibrutinib 420 mg once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity (136 patients) or chlorambucil 0.5 mg/kg to a maximum of 0.8 mg/kg for up to 12 cycles (133 patients). The trial also had an extension study for patients who had disease progression as confirmed by an independent review committee or who had completed the RESONATE-2 trial. Of the 133 patients in the chlorambucil arm, 76 (57% of the intention-to-treat population) were crossed over to ibrutinib following disease progression.
The median duration of ibrutinib treatment was 57.1 months, with 73% of patients being on it for more than 3 years, 65% for more than 4 years, and 27% for more than 5 years. As of the data cutoff, 79 patients (58%) were continuing with ibrutinib on study.
At 5 years, 70% of ibrutinib-treated patients and 12% of chlorambucil-treated patients were estimated to be progression-free and alive (hazard ratio for PFS with ibrutinib 0.146 (95% confidence interval, 0.10-0.22). The benefit of ibrutinib was consistent for patients with high-risk genomic features, including the 11q deletion and unmutated immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable genes.
Estimated 5-year overall survival was also better with ibrutinib, at 83% vs. 68% (hazard ratio, 0.45; 95% CI, 0.266-0.761).
The most common grade 3 or greater adverse events occurring with ibrutinib were neutropenia (13%), pneumonia (12%), hypertension (8%), anemia (7%), hyponatremia (6%), atrial fibrillation (5%), and cataract (5%). The rates of most adverse events decreased over time, and dose reductions because of adverse events also diminished over time, from 5% of patients in the first year down to zero in years 4 through 5.
Patients responded to subsequent CLL therapies following ibrutinib discontinuation, including chemoimmunotherapy and other kinase inhibitors, Dr. Tedeschi said.
The trial was sponsored by Pharmacyclics with collaboration from Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Tedeschi reported advisory board activities with Janssen, AbbVie, and BeiGene.
SOURCE: Tedeschi A et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S107.
REPORTING FROM EHA CONGRESS