User login
Well-Designed IT Systems Essential to Healthcare Integration
David Lawrence, MD, retired head of the Kaiser Foundation health plan, says in a recent Information Week article that it will be “nearly impossible” to achieve the goals of healthcare integration without the connectivity of a well-designed health IT system.4 Dr. Lawrence was a member of a committee that authored the recent report Order from Chaos: Accelerating Care Integration for the Lucian Leape Institute at the National Patient Care Safety Foundation. Failures of coordination most often happen during the crucial information transfers that happen during care transitions, but there has not been enough attention to how important information technology could be to these transfers, Dr. Lawrence told the magazine. “It’s the really complex stuff where this becomes particularly critical,” he said.
The federal Office of Inspector General (OIG) took the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) to task in a November report for not having adequate oversight or safeguards for its EHR meaningful-use program.5 As a result, OIG described Medicare as “vulnerable” to fraud and abuse of incentive payments made to hospitals and health professionals, according to OIG. OIG recommends that CMS request and review supporting documentation for selected providers and issue guidance with specific examples of appropriate documentation. As of September 2012, CMS had paid out $4 billion in meaningful-use incentives to 1,400 hospitals and 82,000 professionals.
References
- Enguidanos S, Vesper E, Lorenz K. 30-day readmissions among seriously ill older adults. J Palliat Med. 2012;15(12):1356-1361.
- The Advisory Board Company. Mastering the cardiovascular care continuum: strategies for bridging divides among providers and across time. The Advisory Board Company website. Available at: http://www.advisory.com/Research/Cardiovascular-Roundtable/Studies/2012/Mastering-the-Cardiovascular-Care-Continuum. Accessed Jan. 8, 2013.
- Misky G, Carlson T, Klem P, et al. Development and implementation of a clinical care pathway for acute VTE reduces hospital utilization and cost at an urban tertiary care center [abstract]. J Hosp Med. 2012;7 Suppl 2:S66-S67.
- Versel N. Health IT holds key to better care integration. Information Week website. Available at: http://www.informationweek.com/healthcare/interoperability/health-it-holds-key-to-better-care-integ/240012443. Accessed Jan. 8, 2013.
- Office of Inspector General. Early Assessment Finds That CMS Faces Obstacles in Overseeing the Medicare EHR Incentive Program. Office of Inspector General website. Available at: https://oig.hhs.gov/oei/reports/oei-05-11-00250.asp. Accessed Jan. 8, 2013.
David Lawrence, MD, retired head of the Kaiser Foundation health plan, says in a recent Information Week article that it will be “nearly impossible” to achieve the goals of healthcare integration without the connectivity of a well-designed health IT system.4 Dr. Lawrence was a member of a committee that authored the recent report Order from Chaos: Accelerating Care Integration for the Lucian Leape Institute at the National Patient Care Safety Foundation. Failures of coordination most often happen during the crucial information transfers that happen during care transitions, but there has not been enough attention to how important information technology could be to these transfers, Dr. Lawrence told the magazine. “It’s the really complex stuff where this becomes particularly critical,” he said.
The federal Office of Inspector General (OIG) took the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) to task in a November report for not having adequate oversight or safeguards for its EHR meaningful-use program.5 As a result, OIG described Medicare as “vulnerable” to fraud and abuse of incentive payments made to hospitals and health professionals, according to OIG. OIG recommends that CMS request and review supporting documentation for selected providers and issue guidance with specific examples of appropriate documentation. As of September 2012, CMS had paid out $4 billion in meaningful-use incentives to 1,400 hospitals and 82,000 professionals.
References
- Enguidanos S, Vesper E, Lorenz K. 30-day readmissions among seriously ill older adults. J Palliat Med. 2012;15(12):1356-1361.
- The Advisory Board Company. Mastering the cardiovascular care continuum: strategies for bridging divides among providers and across time. The Advisory Board Company website. Available at: http://www.advisory.com/Research/Cardiovascular-Roundtable/Studies/2012/Mastering-the-Cardiovascular-Care-Continuum. Accessed Jan. 8, 2013.
- Misky G, Carlson T, Klem P, et al. Development and implementation of a clinical care pathway for acute VTE reduces hospital utilization and cost at an urban tertiary care center [abstract]. J Hosp Med. 2012;7 Suppl 2:S66-S67.
- Versel N. Health IT holds key to better care integration. Information Week website. Available at: http://www.informationweek.com/healthcare/interoperability/health-it-holds-key-to-better-care-integ/240012443. Accessed Jan. 8, 2013.
- Office of Inspector General. Early Assessment Finds That CMS Faces Obstacles in Overseeing the Medicare EHR Incentive Program. Office of Inspector General website. Available at: https://oig.hhs.gov/oei/reports/oei-05-11-00250.asp. Accessed Jan. 8, 2013.
David Lawrence, MD, retired head of the Kaiser Foundation health plan, says in a recent Information Week article that it will be “nearly impossible” to achieve the goals of healthcare integration without the connectivity of a well-designed health IT system.4 Dr. Lawrence was a member of a committee that authored the recent report Order from Chaos: Accelerating Care Integration for the Lucian Leape Institute at the National Patient Care Safety Foundation. Failures of coordination most often happen during the crucial information transfers that happen during care transitions, but there has not been enough attention to how important information technology could be to these transfers, Dr. Lawrence told the magazine. “It’s the really complex stuff where this becomes particularly critical,” he said.
The federal Office of Inspector General (OIG) took the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) to task in a November report for not having adequate oversight or safeguards for its EHR meaningful-use program.5 As a result, OIG described Medicare as “vulnerable” to fraud and abuse of incentive payments made to hospitals and health professionals, according to OIG. OIG recommends that CMS request and review supporting documentation for selected providers and issue guidance with specific examples of appropriate documentation. As of September 2012, CMS had paid out $4 billion in meaningful-use incentives to 1,400 hospitals and 82,000 professionals.
References
- Enguidanos S, Vesper E, Lorenz K. 30-day readmissions among seriously ill older adults. J Palliat Med. 2012;15(12):1356-1361.
- The Advisory Board Company. Mastering the cardiovascular care continuum: strategies for bridging divides among providers and across time. The Advisory Board Company website. Available at: http://www.advisory.com/Research/Cardiovascular-Roundtable/Studies/2012/Mastering-the-Cardiovascular-Care-Continuum. Accessed Jan. 8, 2013.
- Misky G, Carlson T, Klem P, et al. Development and implementation of a clinical care pathway for acute VTE reduces hospital utilization and cost at an urban tertiary care center [abstract]. J Hosp Med. 2012;7 Suppl 2:S66-S67.
- Versel N. Health IT holds key to better care integration. Information Week website. Available at: http://www.informationweek.com/healthcare/interoperability/health-it-holds-key-to-better-care-integ/240012443. Accessed Jan. 8, 2013.
- Office of Inspector General. Early Assessment Finds That CMS Faces Obstacles in Overseeing the Medicare EHR Incentive Program. Office of Inspector General website. Available at: https://oig.hhs.gov/oei/reports/oei-05-11-00250.asp. Accessed Jan. 8, 2013.
Hospitalists Get Answers to Tough Healthcare Questions
When it comes to Medicare, the Affordable Care Act, and a host of other healthcare-reform-related topics, hospitalists have lots of good questions, such as:
- When does the Physician Value-Based Payment Modifier (VBPM) take effect? And will I be included?
- Which primary-care services are covered by the increased Medicaid payments?
- Are hospitalists eligible to bill for Medicare’s new CPT Transitional Care Management (TCM) codes? (see “New Codes Bridge Billing Gap,”).
Now, SHM’s Public Policy Committee has answered all of the above—and many more—in a set of three “Frequently Asked Questions” documents available at www.hospitalmedicine.org/advocacy. Each document goes in-depth on the most cutting-edge policy issues that are top of mind for hospitalists and the hospitals they serve on these issues:
The Physician Value-Based Payment Modifier (VBPM): The VBPM seeks to connect cost and quality of services in order to begin reimbursement for the value, rather than the quantity, of care. It combines the quality measuring in the Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS), cost measures, and a payment adjustment for physicians. Measurement begins this year, and many hospitalists will be included.
Medicaid/Medicare parity regulation: On Nov. 1, 2012, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) released the final regulations implementing Section 1202 of the Affordable Care Act, which increases Medicaid payments for specified primary-care services to 100% of Medicare levels in 2013 and 2014.
New CPT Transitional Care Management (TCM) codes 99495-99496: CMS has created two new CPT Transitional Care Management (TCM) codes designed to improve care coordination and provide better incentives to ensure patients are seen in a physician’s office, rather than be at risk for readmission.
New Action: Getting Involved Just Got Easier
SHM’s Legislative Action Center also makes getting involved easier with a new grassroots outreach tool called Voter Voice. SHM’s first action alert on Voter Voice was sent to members in December. Hospitalists’ willingness to take a few minutes and contact their congressional leaders using Voter Voice increased SHM’s visibility to Congress by nearly five times compared with prior similar alerts.
Getting involved is easy and only takes a few seconds. You can use either your ZIP code to look up your members of Congress or search active legislation by keyword. SHM members can sign up for SHM Legislative Action Center alerts by entering their email address.
To download the new SHM advocacy FAQs or use the improved Legislative Action Center, visit www.hospitalmedicine.org/advocacy.
When it comes to Medicare, the Affordable Care Act, and a host of other healthcare-reform-related topics, hospitalists have lots of good questions, such as:
- When does the Physician Value-Based Payment Modifier (VBPM) take effect? And will I be included?
- Which primary-care services are covered by the increased Medicaid payments?
- Are hospitalists eligible to bill for Medicare’s new CPT Transitional Care Management (TCM) codes? (see “New Codes Bridge Billing Gap,”).
Now, SHM’s Public Policy Committee has answered all of the above—and many more—in a set of three “Frequently Asked Questions” documents available at www.hospitalmedicine.org/advocacy. Each document goes in-depth on the most cutting-edge policy issues that are top of mind for hospitalists and the hospitals they serve on these issues:
The Physician Value-Based Payment Modifier (VBPM): The VBPM seeks to connect cost and quality of services in order to begin reimbursement for the value, rather than the quantity, of care. It combines the quality measuring in the Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS), cost measures, and a payment adjustment for physicians. Measurement begins this year, and many hospitalists will be included.
Medicaid/Medicare parity regulation: On Nov. 1, 2012, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) released the final regulations implementing Section 1202 of the Affordable Care Act, which increases Medicaid payments for specified primary-care services to 100% of Medicare levels in 2013 and 2014.
New CPT Transitional Care Management (TCM) codes 99495-99496: CMS has created two new CPT Transitional Care Management (TCM) codes designed to improve care coordination and provide better incentives to ensure patients are seen in a physician’s office, rather than be at risk for readmission.
New Action: Getting Involved Just Got Easier
SHM’s Legislative Action Center also makes getting involved easier with a new grassroots outreach tool called Voter Voice. SHM’s first action alert on Voter Voice was sent to members in December. Hospitalists’ willingness to take a few minutes and contact their congressional leaders using Voter Voice increased SHM’s visibility to Congress by nearly five times compared with prior similar alerts.
Getting involved is easy and only takes a few seconds. You can use either your ZIP code to look up your members of Congress or search active legislation by keyword. SHM members can sign up for SHM Legislative Action Center alerts by entering their email address.
To download the new SHM advocacy FAQs or use the improved Legislative Action Center, visit www.hospitalmedicine.org/advocacy.
When it comes to Medicare, the Affordable Care Act, and a host of other healthcare-reform-related topics, hospitalists have lots of good questions, such as:
- When does the Physician Value-Based Payment Modifier (VBPM) take effect? And will I be included?
- Which primary-care services are covered by the increased Medicaid payments?
- Are hospitalists eligible to bill for Medicare’s new CPT Transitional Care Management (TCM) codes? (see “New Codes Bridge Billing Gap,”).
Now, SHM’s Public Policy Committee has answered all of the above—and many more—in a set of three “Frequently Asked Questions” documents available at www.hospitalmedicine.org/advocacy. Each document goes in-depth on the most cutting-edge policy issues that are top of mind for hospitalists and the hospitals they serve on these issues:
The Physician Value-Based Payment Modifier (VBPM): The VBPM seeks to connect cost and quality of services in order to begin reimbursement for the value, rather than the quantity, of care. It combines the quality measuring in the Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS), cost measures, and a payment adjustment for physicians. Measurement begins this year, and many hospitalists will be included.
Medicaid/Medicare parity regulation: On Nov. 1, 2012, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) released the final regulations implementing Section 1202 of the Affordable Care Act, which increases Medicaid payments for specified primary-care services to 100% of Medicare levels in 2013 and 2014.
New CPT Transitional Care Management (TCM) codes 99495-99496: CMS has created two new CPT Transitional Care Management (TCM) codes designed to improve care coordination and provide better incentives to ensure patients are seen in a physician’s office, rather than be at risk for readmission.
New Action: Getting Involved Just Got Easier
SHM’s Legislative Action Center also makes getting involved easier with a new grassroots outreach tool called Voter Voice. SHM’s first action alert on Voter Voice was sent to members in December. Hospitalists’ willingness to take a few minutes and contact their congressional leaders using Voter Voice increased SHM’s visibility to Congress by nearly five times compared with prior similar alerts.
Getting involved is easy and only takes a few seconds. You can use either your ZIP code to look up your members of Congress or search active legislation by keyword. SHM members can sign up for SHM Legislative Action Center alerts by entering their email address.
To download the new SHM advocacy FAQs or use the improved Legislative Action Center, visit www.hospitalmedicine.org/advocacy.
HMX Term of the Month: CMS 1500
Medical claim form established by CMS to submit paper claims to Medicare and Medicaid. Most commercial insurance carriers also require paper claims be submitted on CMS 1500s. The form is distinguished by its red ink.
Medical claim form established by CMS to submit paper claims to Medicare and Medicaid. Most commercial insurance carriers also require paper claims be submitted on CMS 1500s. The form is distinguished by its red ink.
Medical claim form established by CMS to submit paper claims to Medicare and Medicaid. Most commercial insurance carriers also require paper claims be submitted on CMS 1500s. The form is distinguished by its red ink.
New Codes Bridge Hospitals' Post-Discharge Billing Gap
In November 2012, the Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) finalized its 2013 physician fee schedule with two new transitional-care-management (TCM) codes, 99495 and 99496. These codes provide reimbursement for transitional-care services to patients for 30 days after hospital discharge. CMS estimates that two-thirds of the 10 million Medicare patients discharged annually from hospitals will have TCM services provided by an outpatient doctor. Why might hospitalists be interested in these outpatient codes? Read on.
As a post-discharge provider in a primary-care-based discharge clinic, I can say the new Medicare transitional codes read like our job description. Because I’ve worked in a post-discharge clinic for the past three years, I have learned that post-discharge care requires time and resource allocation beyond routine outpatient care. Because of the unique population we see, on average we bill at a higher level than the rest of the practice. Yet we, like all outpatient providers, remain constrained by the existing billing structure, which is intimately connected to physician face-to-face visits.
Here’s an illustration of a typical afternoon in the post-discharge clinic: A schizophrenic patient presents with renal failure, hypoglycemia, and confusion. Her home visiting nurse (VNA) administers her medications; the patient cannot tell you any of them. While you are calling the VNA to clarify her medications, trying to identify her healthcare proxy, and stopping her ACE inhibitor because her potassium is 5.6, the next patient arrives. She has end-stage liver disease and was recently in the hospital for liver failure, and now has worsening recurrent ascites. After clinic, you call interventional radiology to coordinate a therapeutic paracentesis and change diuretic doses after her labs return. Two weeks later, you arrange a repeat paracentesis, and subsequently a transition to comfort care in a hospice house. For this work, right now, you can at most bill a high-complexity office visit (99215), and the rest of the care coordination—by you, your nurse, or your administrative staff—is not compensated.
How Do the New Codes Work?
CMS created the new TCM codes to begin to change the outpatient fee schedule to emphasize primary care and care coordination for beneficiaries, particularly in the post-hospitalization period. The new TCM codes are a first step toward reimbursement for non-face-to-face activities, which are increasingly important in the evolving healthcare system.
The investment is estimated at more than $1 billion in 2013. The new codes are available to physicians, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, and other advanced-practice nurses only once within the 30 days after hospital discharge. During the 30 days after discharge, the two codes, 99495 and 99496, require a single face-to-face visit within seven days of discharge for the highest-risk patients and within 14 days of discharge for moderate-risk patients. The face-to-face visit is not billed separately. The codes also mandate telephone communication with the patient or caregiver within two business days of hospital discharge; the medical decision-making must be of either moderate or high complexity.
The average reimbursement for the codes will be $132.96 for 99495 and $231.11 for 99496, reflecting a higher wRVU than either hospital discharge day management or high-acuity outpatient visits. The code is billed at the end of the 30 days. The TCM code cannot be billed a second time if a patient is readmitted within the 30 days. Other E/M codes can be billed during the same time period for additional visits as necessary.
What’s the Impact on Hospitalists?
The new codes affect hospitalists in two ways. First, the hospitalists in the growing group of “transitionalists,” many of whom practice in outpatient clinics seeing patients after discharge, will be able to use these codes. As the codes require no pre-existing relationship with the patient, non-primary-care providers will be able to bill these codes, assuming that they fulfill the designated requirements. This concession enables hospitalists to fill a vital role for those patients who have inadequate access to immediate primary care post-hospitalization. It also provides a necessary bridge to appropriate primary care for those patients. This group of patients might be particularly vulnerable to adverse events, including hospital readmission, given their suboptimal connection with their primary-care providers.
Hospitalists who practice entirely as inpatient physicians will not be able to bill these new codes, but they will provide a valuable service to patients by helping identify the physicians who will provide their TCM and documenting this in the discharge documentation, already seen as a key element of discharge day management services.
Do These Codes Change the Business Case for Discharge Clinics?
Discharge clinics, either hospitalist-staffed or otherwise, have been actively discussed in the media in recent years.1 Even without these transitional codes, discharge clinics have arisen where primary-care access is limited and as a potential, but as yet unproven, solution to high readmission rates. Despite this proliferation, discharge clinics have not yet proven to be cost-effective.
Implementation of these codes could change the calculus for organizations considering dedicating resources to a discharge clinic. The new codes could make discharge clinics more financially viable by increasing the reimbursement for care that often requires more than 30 minutes. However, based on the experience in our clinic, the increased revenue accurately reflects the intensity of service necessary to coordinate care in the post-discharge period.
The time intensity of care already is obvious from the structure of established discharge clinics. Examples include the comprehensive care centers at HealthCare Partners in Southern California, where multidisciplinary visits average 90 minutes, or at our clinic at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston.2 While the visits in our clinic are less than half as long as those at HealthCare Partners, we are not including the time spent reviewing the discharge documentation, outstanding tests, and medication changes in advance of the visit, and the time spent after the visit, coordinating the patient’s care with visiting nurses and elder service agencies.3
What’s Next?
Whether these codes lead to an increased interest in hospitalist-staffed discharge clinics or to primary-care development of robust transitional-care structures, these new codes will help focus resources and attention on increasing services, with the goal of improving patient care during a period of extreme vulnerability. This alone is something to be grateful for, whether you are a transitionalist, hospitalist, primary-care doctor, caregiver, or patient.
Dr. Doctoroff is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston and an instructor in medicine at Harvard Medical School. She is medical director of BIDMC’s Health Care Associates Post Discharge Clinic.
References
- Andrews M. Post-discharge clinics try to cut hospital readmissions by helping patients. Washington Post website. Available at: http://articles.washingtonpost.com/2011-12-19/national/35288219_1_readmissions-discharge-vulnerable-patients. Accessed Jan. 7, 2013.
- Feder JL. Predictive modeling and team care for high-need patients at HealthCare Partners. Health Aff (Millwood). 2011;30(3):416-418.
- Doctoroff L. Interval examination: establishment of a hospitalist-staffed discharge clinic. J Gen Intern Med. 2012;27(10):1377-1382.
In November 2012, the Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) finalized its 2013 physician fee schedule with two new transitional-care-management (TCM) codes, 99495 and 99496. These codes provide reimbursement for transitional-care services to patients for 30 days after hospital discharge. CMS estimates that two-thirds of the 10 million Medicare patients discharged annually from hospitals will have TCM services provided by an outpatient doctor. Why might hospitalists be interested in these outpatient codes? Read on.
As a post-discharge provider in a primary-care-based discharge clinic, I can say the new Medicare transitional codes read like our job description. Because I’ve worked in a post-discharge clinic for the past three years, I have learned that post-discharge care requires time and resource allocation beyond routine outpatient care. Because of the unique population we see, on average we bill at a higher level than the rest of the practice. Yet we, like all outpatient providers, remain constrained by the existing billing structure, which is intimately connected to physician face-to-face visits.
Here’s an illustration of a typical afternoon in the post-discharge clinic: A schizophrenic patient presents with renal failure, hypoglycemia, and confusion. Her home visiting nurse (VNA) administers her medications; the patient cannot tell you any of them. While you are calling the VNA to clarify her medications, trying to identify her healthcare proxy, and stopping her ACE inhibitor because her potassium is 5.6, the next patient arrives. She has end-stage liver disease and was recently in the hospital for liver failure, and now has worsening recurrent ascites. After clinic, you call interventional radiology to coordinate a therapeutic paracentesis and change diuretic doses after her labs return. Two weeks later, you arrange a repeat paracentesis, and subsequently a transition to comfort care in a hospice house. For this work, right now, you can at most bill a high-complexity office visit (99215), and the rest of the care coordination—by you, your nurse, or your administrative staff—is not compensated.
How Do the New Codes Work?
CMS created the new TCM codes to begin to change the outpatient fee schedule to emphasize primary care and care coordination for beneficiaries, particularly in the post-hospitalization period. The new TCM codes are a first step toward reimbursement for non-face-to-face activities, which are increasingly important in the evolving healthcare system.
The investment is estimated at more than $1 billion in 2013. The new codes are available to physicians, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, and other advanced-practice nurses only once within the 30 days after hospital discharge. During the 30 days after discharge, the two codes, 99495 and 99496, require a single face-to-face visit within seven days of discharge for the highest-risk patients and within 14 days of discharge for moderate-risk patients. The face-to-face visit is not billed separately. The codes also mandate telephone communication with the patient or caregiver within two business days of hospital discharge; the medical decision-making must be of either moderate or high complexity.
The average reimbursement for the codes will be $132.96 for 99495 and $231.11 for 99496, reflecting a higher wRVU than either hospital discharge day management or high-acuity outpatient visits. The code is billed at the end of the 30 days. The TCM code cannot be billed a second time if a patient is readmitted within the 30 days. Other E/M codes can be billed during the same time period for additional visits as necessary.
What’s the Impact on Hospitalists?
The new codes affect hospitalists in two ways. First, the hospitalists in the growing group of “transitionalists,” many of whom practice in outpatient clinics seeing patients after discharge, will be able to use these codes. As the codes require no pre-existing relationship with the patient, non-primary-care providers will be able to bill these codes, assuming that they fulfill the designated requirements. This concession enables hospitalists to fill a vital role for those patients who have inadequate access to immediate primary care post-hospitalization. It also provides a necessary bridge to appropriate primary care for those patients. This group of patients might be particularly vulnerable to adverse events, including hospital readmission, given their suboptimal connection with their primary-care providers.
Hospitalists who practice entirely as inpatient physicians will not be able to bill these new codes, but they will provide a valuable service to patients by helping identify the physicians who will provide their TCM and documenting this in the discharge documentation, already seen as a key element of discharge day management services.
Do These Codes Change the Business Case for Discharge Clinics?
Discharge clinics, either hospitalist-staffed or otherwise, have been actively discussed in the media in recent years.1 Even without these transitional codes, discharge clinics have arisen where primary-care access is limited and as a potential, but as yet unproven, solution to high readmission rates. Despite this proliferation, discharge clinics have not yet proven to be cost-effective.
Implementation of these codes could change the calculus for organizations considering dedicating resources to a discharge clinic. The new codes could make discharge clinics more financially viable by increasing the reimbursement for care that often requires more than 30 minutes. However, based on the experience in our clinic, the increased revenue accurately reflects the intensity of service necessary to coordinate care in the post-discharge period.
The time intensity of care already is obvious from the structure of established discharge clinics. Examples include the comprehensive care centers at HealthCare Partners in Southern California, where multidisciplinary visits average 90 minutes, or at our clinic at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston.2 While the visits in our clinic are less than half as long as those at HealthCare Partners, we are not including the time spent reviewing the discharge documentation, outstanding tests, and medication changes in advance of the visit, and the time spent after the visit, coordinating the patient’s care with visiting nurses and elder service agencies.3
What’s Next?
Whether these codes lead to an increased interest in hospitalist-staffed discharge clinics or to primary-care development of robust transitional-care structures, these new codes will help focus resources and attention on increasing services, with the goal of improving patient care during a period of extreme vulnerability. This alone is something to be grateful for, whether you are a transitionalist, hospitalist, primary-care doctor, caregiver, or patient.
Dr. Doctoroff is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston and an instructor in medicine at Harvard Medical School. She is medical director of BIDMC’s Health Care Associates Post Discharge Clinic.
References
- Andrews M. Post-discharge clinics try to cut hospital readmissions by helping patients. Washington Post website. Available at: http://articles.washingtonpost.com/2011-12-19/national/35288219_1_readmissions-discharge-vulnerable-patients. Accessed Jan. 7, 2013.
- Feder JL. Predictive modeling and team care for high-need patients at HealthCare Partners. Health Aff (Millwood). 2011;30(3):416-418.
- Doctoroff L. Interval examination: establishment of a hospitalist-staffed discharge clinic. J Gen Intern Med. 2012;27(10):1377-1382.
In November 2012, the Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) finalized its 2013 physician fee schedule with two new transitional-care-management (TCM) codes, 99495 and 99496. These codes provide reimbursement for transitional-care services to patients for 30 days after hospital discharge. CMS estimates that two-thirds of the 10 million Medicare patients discharged annually from hospitals will have TCM services provided by an outpatient doctor. Why might hospitalists be interested in these outpatient codes? Read on.
As a post-discharge provider in a primary-care-based discharge clinic, I can say the new Medicare transitional codes read like our job description. Because I’ve worked in a post-discharge clinic for the past three years, I have learned that post-discharge care requires time and resource allocation beyond routine outpatient care. Because of the unique population we see, on average we bill at a higher level than the rest of the practice. Yet we, like all outpatient providers, remain constrained by the existing billing structure, which is intimately connected to physician face-to-face visits.
Here’s an illustration of a typical afternoon in the post-discharge clinic: A schizophrenic patient presents with renal failure, hypoglycemia, and confusion. Her home visiting nurse (VNA) administers her medications; the patient cannot tell you any of them. While you are calling the VNA to clarify her medications, trying to identify her healthcare proxy, and stopping her ACE inhibitor because her potassium is 5.6, the next patient arrives. She has end-stage liver disease and was recently in the hospital for liver failure, and now has worsening recurrent ascites. After clinic, you call interventional radiology to coordinate a therapeutic paracentesis and change diuretic doses after her labs return. Two weeks later, you arrange a repeat paracentesis, and subsequently a transition to comfort care in a hospice house. For this work, right now, you can at most bill a high-complexity office visit (99215), and the rest of the care coordination—by you, your nurse, or your administrative staff—is not compensated.
How Do the New Codes Work?
CMS created the new TCM codes to begin to change the outpatient fee schedule to emphasize primary care and care coordination for beneficiaries, particularly in the post-hospitalization period. The new TCM codes are a first step toward reimbursement for non-face-to-face activities, which are increasingly important in the evolving healthcare system.
The investment is estimated at more than $1 billion in 2013. The new codes are available to physicians, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, and other advanced-practice nurses only once within the 30 days after hospital discharge. During the 30 days after discharge, the two codes, 99495 and 99496, require a single face-to-face visit within seven days of discharge for the highest-risk patients and within 14 days of discharge for moderate-risk patients. The face-to-face visit is not billed separately. The codes also mandate telephone communication with the patient or caregiver within two business days of hospital discharge; the medical decision-making must be of either moderate or high complexity.
The average reimbursement for the codes will be $132.96 for 99495 and $231.11 for 99496, reflecting a higher wRVU than either hospital discharge day management or high-acuity outpatient visits. The code is billed at the end of the 30 days. The TCM code cannot be billed a second time if a patient is readmitted within the 30 days. Other E/M codes can be billed during the same time period for additional visits as necessary.
What’s the Impact on Hospitalists?
The new codes affect hospitalists in two ways. First, the hospitalists in the growing group of “transitionalists,” many of whom practice in outpatient clinics seeing patients after discharge, will be able to use these codes. As the codes require no pre-existing relationship with the patient, non-primary-care providers will be able to bill these codes, assuming that they fulfill the designated requirements. This concession enables hospitalists to fill a vital role for those patients who have inadequate access to immediate primary care post-hospitalization. It also provides a necessary bridge to appropriate primary care for those patients. This group of patients might be particularly vulnerable to adverse events, including hospital readmission, given their suboptimal connection with their primary-care providers.
Hospitalists who practice entirely as inpatient physicians will not be able to bill these new codes, but they will provide a valuable service to patients by helping identify the physicians who will provide their TCM and documenting this in the discharge documentation, already seen as a key element of discharge day management services.
Do These Codes Change the Business Case for Discharge Clinics?
Discharge clinics, either hospitalist-staffed or otherwise, have been actively discussed in the media in recent years.1 Even without these transitional codes, discharge clinics have arisen where primary-care access is limited and as a potential, but as yet unproven, solution to high readmission rates. Despite this proliferation, discharge clinics have not yet proven to be cost-effective.
Implementation of these codes could change the calculus for organizations considering dedicating resources to a discharge clinic. The new codes could make discharge clinics more financially viable by increasing the reimbursement for care that often requires more than 30 minutes. However, based on the experience in our clinic, the increased revenue accurately reflects the intensity of service necessary to coordinate care in the post-discharge period.
The time intensity of care already is obvious from the structure of established discharge clinics. Examples include the comprehensive care centers at HealthCare Partners in Southern California, where multidisciplinary visits average 90 minutes, or at our clinic at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston.2 While the visits in our clinic are less than half as long as those at HealthCare Partners, we are not including the time spent reviewing the discharge documentation, outstanding tests, and medication changes in advance of the visit, and the time spent after the visit, coordinating the patient’s care with visiting nurses and elder service agencies.3
What’s Next?
Whether these codes lead to an increased interest in hospitalist-staffed discharge clinics or to primary-care development of robust transitional-care structures, these new codes will help focus resources and attention on increasing services, with the goal of improving patient care during a period of extreme vulnerability. This alone is something to be grateful for, whether you are a transitionalist, hospitalist, primary-care doctor, caregiver, or patient.
Dr. Doctoroff is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston and an instructor in medicine at Harvard Medical School. She is medical director of BIDMC’s Health Care Associates Post Discharge Clinic.
References
- Andrews M. Post-discharge clinics try to cut hospital readmissions by helping patients. Washington Post website. Available at: http://articles.washingtonpost.com/2011-12-19/national/35288219_1_readmissions-discharge-vulnerable-patients. Accessed Jan. 7, 2013.
- Feder JL. Predictive modeling and team care for high-need patients at HealthCare Partners. Health Aff (Millwood). 2011;30(3):416-418.
- Doctoroff L. Interval examination: establishment of a hospitalist-staffed discharge clinic. J Gen Intern Med. 2012;27(10):1377-1382.
ONLINE EXCLUSIVE: Billing Expert Explains Why Documentation, Education, and Feedback Are Crucial to Reimbursement
ONLINE EXCLUSIVE: CogentHMG hospitalist explains how hospitalists can prepare for Value-Based Purchasing at hospital, individual level
Click here to listen to Dr. Wright
Click here to listen to Dr. Wright
Click here to listen to Dr. Wright
12 Things Hospitalists Need to Know About Billing and Coding
Documentation, CPT codes, modifiers—it’s not glamorous, but it’s an integral part of a 21st-century physician’s job description. The Hospitalist queried more than a handful of billing and coding experts about the advice they would dispense to clinicians navigating the reimbursement maze.
“Physicians often do more than what is reflected in the documentation,” says Barb Pierce, CCS-P, ACS-EM, a national coding consultant based in West Des Moines, Iowa, and CODE-H faculty. “They can’t always bill for everything they do, but they certainly can document and code to obtain the appropriate levels of service.”
Meanwhile, hospitalists have to be careful they aren’t excessive in their billing practices. “The name of the game isn’t just to bill higher,” Pierce adds, “but to make sure that your documentation supports the service being billed, and Medicare is watching. They’re doing a lot of focused audits.”
Some hospitalists might opt for a lower level of service, suspecting they’re less likely to be audited. Other hospitalists might seek reimbursement for more of their time and efforts.
“You have both ends of the spectrum,” says Raemarie Jimenez, CPC, CPMA, CPC-I, CANPC, CRHC, director of education for AAPC, formerly known as the American Academy of Professional Coders. “There are a lot of factors that would go into why a provider would code something incorrectly.”
Here’s how to land somewhere in the middle.
1 Be thorough in documenting the initial hospital visit.
When selecting the level of service for an initial hospital visit, the documentation consists of three key components: history, physical examination, and medical decision-making. The history includes the chief complaint as well as the review of systems. This is “an inventory of the patient’s organ systems.” Both the complaint and the systems review are often incorporated in the history of present illness, says Mary Mulholland, MHA, BSN, RN, CPC, senior coding and education specialist in the Department of Medicine at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
A patient’s family history is commonly overlooked in a hospitalist’s notes, primarily when they know the patient from previous admissions for chronic diseases and when the family history will likely not have an impact on treatment. “If they do not document a complete review of systems or miss one of the histories, the service will definitely be down-coded,” Mulholland says, “no matter how complete the exam and medical decision-making documentation.”
2 Familiarize yourself with Medicare reimbursement rules in the state where you practice.
In some states, Medicare contractors require providers to document the status of each organ system reviewed individually. In other states, it’s acceptable to document a system review with pertinent findings, “whether positive or negative,” and the statement of “all other systems negative,” Mulholland says.
The auditor will give credit for the review based on the number of organ systems documented. “If you miss one system review, it will take down what otherwise would be a Level Three hospital admission to a Level One,” she says. “So there would be a significant financial impact.”
Medicare reimbursement for a Level Three initial visit in Mulholland’s area of practice—Philadelphia County in Pennsylvania—is $206.57, compared with $104.69 for a Level One. During this visit, each of the key components—history, exam, and medical decision-making—need to be documented completely for the provider to receive the highest level of reimbursement.
3 Ask about a patient’s social history.
Social history can be obtained by querying the patient about smoking, drug and alcohol use, his or her occupation, marital status, and type of living arrangement.
“Knowing the social history helps the hospitalist understand the home situation or social circumstances that may have contributed to the hospitalization or may complicate the discharge plan,” Mulholland says.
This is particularly important in decision-making that involves elderly patients. The clinician should “think down the road” as to where the patient will be discharged and if a social worker’s assistance will be needed. It’s about “seeing the whole patient,” she says, “not just the disease.”
4 Remember to include the actual diagnosis.
“As coders, we can see all the clinical indicators of a particular diagnosis,” says Kathryn DeVault, RHIA, CCS, CCS-P, a director at HIM Solutions at the American Health Management Association. However, “unless [physicians] write down the diagnosis, we can’t code it.”
Documents without a diagnosis are more common than one would expect. For example, if a patient has pain when urinating, the hospitalist typically orders a culture. If the result is positive, the hospitalist prescribes an antibiotic for the infection, and too often “the story ends there.” From experience, DeVault can decipher that the patient is being treated for a urinary tract infection, but she can’t assign a code without querying the physician. Hospitalists, she suggests, should try to “close the loop in their documentation.”
5 Be specific in your written assessment of the patient’s condition.
“The main thing that we see is missing documentation,” says Angie Comfort, RHIT, CCS, a director at HIM Solutions. For instance, if a hospitalist documents congestive heart failure, it’s important to indicate whether the condition is chronic or acute and systolic or diastolic.
In the case of a diabetic patient, the notes should specify the type of diabetes. Not doing so “could be a reimbursement-changer,” Comfort says. In contrast, documenting such specifics could result in higher reimbursement, especially if a patient has complications from Type 1 diabetes.
6 Note the severity of the patient’s case.
Hospitalists’ documentation doesn’t always capture everything they’re evaluating for patients. “I’ve seen notes to the extent of ‘patient doing well; waiting on test results,’” the AAPC’s Jimenez says. “If they’re doing certain tests, why are they doing them? What are they trying to diagnose for the patient? What treatment are they considering?”
The reasons for the tests need to be explained. When a provider is monitoring someone in the hospital, the documentation should elaborate on the patient’s response to a treatment, and whether the patient’s condition is better, stable, or worse. This information helps put the severity in perspective.
“A diabetic could be a diabetic out of control. It could be a diabetic who’s not responding or who has comorbidities,” Jimenez says. “No one diagnosis is the same for every patient.”

—Mary Mulholland, MHA, BSN, RN, CPC, senior coding and education specialist, department of medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia
7 Indicate which aspect of the patient’s condition you are treating.
When multiple providers are involved in a hospitalized patient’s care, it’s important to document your specific role apart from the services rendered by specialists, Jimenez says. The codes billed must be supported by the documentation for each service. Many providers contribute to the inpatient documentation, so it must be clear what each clinician personally performs.
Only report the diagnosis you are treating or the diagnoses that affect the ones you are managing. If a specialist has been brought in to take over treatment for a specific condition, a hospitalist would not bill for that diagnosis code.

—Raemarie Jimenez, CPC, CPMA, CPC-I, CANPC, CRHC, director of education, AAPC Salt Lake City
8 Note your personal review of medical records and reports from other clinicians.
Hospitalists should document their review of lab data or radiology reports, discussion of the case with other providers, or collection of the history from someone other than the patient. It’s also helpful to document your personal review of any images, such as a chest X-ray or MRI. Examining the images yourself might lead to higher reimbursement, Mulholland says.
Providers also should note when they request or review old records, and they should include a short synopsis of the information obtained and how it contributed to the current treatment plan.
9 Learn the correct coding for patients being transferred.
A transfer can occur either from a different facility or from a hospital floor to a rehabilitation unit. Either way, the patient is seen twice in one day, with each visit covered by the same hospitalist practice.
“Both physicians often report a separate independent visit. However, because these services occurred on the same day, it is not appropriate to bill for two separate subsequent or initial hospital codes,” says Sherri Dumford, MBA, CHBME, director of operations and past president of the Healthcare Billing and Management Association. “Often what will happen is both services will be reported and get through the billing system. The second claim is just written off as a denied service, when, in fact, you could combine the elements of service of both visits and possibly bill for a single higher level of visit.”
10 Consider delegating to a coding expert.
While smaller hospitalist groups can turn to a coding consultant on an as-needed basis, larger groups might consider bringing a certified coder on staff. This person would inform physicians about proper coding, review their documentation, and “give real-time feedback,” Pierce says.
An internal audit would show if the documentation meets selected evaluation management codes. Also, it usually takes a coding professional to determine whether prolonged services are an option for the team on any given date of service. Someone would need to internally “add together” multiple services on one date to see if there is sufficient time documented to allow billing for these add-on codes, Pierce says. Similarly, critical-care time needs to be accumulated during a date of service.

—Barb Pierce, CCS-P, ACS-EM, national coding consultant, West Des Moines, Iowa
11 Indicate the number of minutes spent arranging for a patient’s discharge.
Discharging a patient involves various steps, says Peter Thompson, MD, chief of clinical operations at the Phoenix headquarters of Apogee Physicians, a hospitalist management company that employs about 750 hospitalists across the country. Hospitalists discuss the hospital stay with the patient and family members, prescribe medications, issue discharge recommendations, set up follow-up care, and coordinate with the case manager, specialists, and primary-care physician.
“It generally is one sequential event after the other,” lasting between 20 and 40 minutes and leading up to discharge, Thompson says. Reimbursement for a high-level discharge constitutes more than 30 minutes. However, without proper documentation, he cautions, the claim could be downgraded or denied.
12 Don’t forget to sign, date, and time your progress note.
Last but not least, when it comes to reimbursement, your signature really does matter.
“For an illegible signature, Medicare and the insurance companies have the option of not paying for the service,” Mulholland says. “They’re trying to establish or authenticate who provided the service.”
And they want to know when the hospitalist saw the patient, so it’s a good idea to indicate the exact time of your visit.
Susan Kreimer is a freelance medical writer in New York.
Documentation, CPT codes, modifiers—it’s not glamorous, but it’s an integral part of a 21st-century physician’s job description. The Hospitalist queried more than a handful of billing and coding experts about the advice they would dispense to clinicians navigating the reimbursement maze.
“Physicians often do more than what is reflected in the documentation,” says Barb Pierce, CCS-P, ACS-EM, a national coding consultant based in West Des Moines, Iowa, and CODE-H faculty. “They can’t always bill for everything they do, but they certainly can document and code to obtain the appropriate levels of service.”
Meanwhile, hospitalists have to be careful they aren’t excessive in their billing practices. “The name of the game isn’t just to bill higher,” Pierce adds, “but to make sure that your documentation supports the service being billed, and Medicare is watching. They’re doing a lot of focused audits.”
Some hospitalists might opt for a lower level of service, suspecting they’re less likely to be audited. Other hospitalists might seek reimbursement for more of their time and efforts.
“You have both ends of the spectrum,” says Raemarie Jimenez, CPC, CPMA, CPC-I, CANPC, CRHC, director of education for AAPC, formerly known as the American Academy of Professional Coders. “There are a lot of factors that would go into why a provider would code something incorrectly.”
Here’s how to land somewhere in the middle.
1 Be thorough in documenting the initial hospital visit.
When selecting the level of service for an initial hospital visit, the documentation consists of three key components: history, physical examination, and medical decision-making. The history includes the chief complaint as well as the review of systems. This is “an inventory of the patient’s organ systems.” Both the complaint and the systems review are often incorporated in the history of present illness, says Mary Mulholland, MHA, BSN, RN, CPC, senior coding and education specialist in the Department of Medicine at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
A patient’s family history is commonly overlooked in a hospitalist’s notes, primarily when they know the patient from previous admissions for chronic diseases and when the family history will likely not have an impact on treatment. “If they do not document a complete review of systems or miss one of the histories, the service will definitely be down-coded,” Mulholland says, “no matter how complete the exam and medical decision-making documentation.”
2 Familiarize yourself with Medicare reimbursement rules in the state where you practice.
In some states, Medicare contractors require providers to document the status of each organ system reviewed individually. In other states, it’s acceptable to document a system review with pertinent findings, “whether positive or negative,” and the statement of “all other systems negative,” Mulholland says.
The auditor will give credit for the review based on the number of organ systems documented. “If you miss one system review, it will take down what otherwise would be a Level Three hospital admission to a Level One,” she says. “So there would be a significant financial impact.”
Medicare reimbursement for a Level Three initial visit in Mulholland’s area of practice—Philadelphia County in Pennsylvania—is $206.57, compared with $104.69 for a Level One. During this visit, each of the key components—history, exam, and medical decision-making—need to be documented completely for the provider to receive the highest level of reimbursement.
3 Ask about a patient’s social history.
Social history can be obtained by querying the patient about smoking, drug and alcohol use, his or her occupation, marital status, and type of living arrangement.
“Knowing the social history helps the hospitalist understand the home situation or social circumstances that may have contributed to the hospitalization or may complicate the discharge plan,” Mulholland says.
This is particularly important in decision-making that involves elderly patients. The clinician should “think down the road” as to where the patient will be discharged and if a social worker’s assistance will be needed. It’s about “seeing the whole patient,” she says, “not just the disease.”
4 Remember to include the actual diagnosis.
“As coders, we can see all the clinical indicators of a particular diagnosis,” says Kathryn DeVault, RHIA, CCS, CCS-P, a director at HIM Solutions at the American Health Management Association. However, “unless [physicians] write down the diagnosis, we can’t code it.”
Documents without a diagnosis are more common than one would expect. For example, if a patient has pain when urinating, the hospitalist typically orders a culture. If the result is positive, the hospitalist prescribes an antibiotic for the infection, and too often “the story ends there.” From experience, DeVault can decipher that the patient is being treated for a urinary tract infection, but she can’t assign a code without querying the physician. Hospitalists, she suggests, should try to “close the loop in their documentation.”
5 Be specific in your written assessment of the patient’s condition.
“The main thing that we see is missing documentation,” says Angie Comfort, RHIT, CCS, a director at HIM Solutions. For instance, if a hospitalist documents congestive heart failure, it’s important to indicate whether the condition is chronic or acute and systolic or diastolic.
In the case of a diabetic patient, the notes should specify the type of diabetes. Not doing so “could be a reimbursement-changer,” Comfort says. In contrast, documenting such specifics could result in higher reimbursement, especially if a patient has complications from Type 1 diabetes.
6 Note the severity of the patient’s case.
Hospitalists’ documentation doesn’t always capture everything they’re evaluating for patients. “I’ve seen notes to the extent of ‘patient doing well; waiting on test results,’” the AAPC’s Jimenez says. “If they’re doing certain tests, why are they doing them? What are they trying to diagnose for the patient? What treatment are they considering?”
The reasons for the tests need to be explained. When a provider is monitoring someone in the hospital, the documentation should elaborate on the patient’s response to a treatment, and whether the patient’s condition is better, stable, or worse. This information helps put the severity in perspective.
“A diabetic could be a diabetic out of control. It could be a diabetic who’s not responding or who has comorbidities,” Jimenez says. “No one diagnosis is the same for every patient.”

—Mary Mulholland, MHA, BSN, RN, CPC, senior coding and education specialist, department of medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia
7 Indicate which aspect of the patient’s condition you are treating.
When multiple providers are involved in a hospitalized patient’s care, it’s important to document your specific role apart from the services rendered by specialists, Jimenez says. The codes billed must be supported by the documentation for each service. Many providers contribute to the inpatient documentation, so it must be clear what each clinician personally performs.
Only report the diagnosis you are treating or the diagnoses that affect the ones you are managing. If a specialist has been brought in to take over treatment for a specific condition, a hospitalist would not bill for that diagnosis code.

—Raemarie Jimenez, CPC, CPMA, CPC-I, CANPC, CRHC, director of education, AAPC Salt Lake City
8 Note your personal review of medical records and reports from other clinicians.
Hospitalists should document their review of lab data or radiology reports, discussion of the case with other providers, or collection of the history from someone other than the patient. It’s also helpful to document your personal review of any images, such as a chest X-ray or MRI. Examining the images yourself might lead to higher reimbursement, Mulholland says.
Providers also should note when they request or review old records, and they should include a short synopsis of the information obtained and how it contributed to the current treatment plan.
9 Learn the correct coding for patients being transferred.
A transfer can occur either from a different facility or from a hospital floor to a rehabilitation unit. Either way, the patient is seen twice in one day, with each visit covered by the same hospitalist practice.
“Both physicians often report a separate independent visit. However, because these services occurred on the same day, it is not appropriate to bill for two separate subsequent or initial hospital codes,” says Sherri Dumford, MBA, CHBME, director of operations and past president of the Healthcare Billing and Management Association. “Often what will happen is both services will be reported and get through the billing system. The second claim is just written off as a denied service, when, in fact, you could combine the elements of service of both visits and possibly bill for a single higher level of visit.”
10 Consider delegating to a coding expert.
While smaller hospitalist groups can turn to a coding consultant on an as-needed basis, larger groups might consider bringing a certified coder on staff. This person would inform physicians about proper coding, review their documentation, and “give real-time feedback,” Pierce says.
An internal audit would show if the documentation meets selected evaluation management codes. Also, it usually takes a coding professional to determine whether prolonged services are an option for the team on any given date of service. Someone would need to internally “add together” multiple services on one date to see if there is sufficient time documented to allow billing for these add-on codes, Pierce says. Similarly, critical-care time needs to be accumulated during a date of service.

—Barb Pierce, CCS-P, ACS-EM, national coding consultant, West Des Moines, Iowa
11 Indicate the number of minutes spent arranging for a patient’s discharge.
Discharging a patient involves various steps, says Peter Thompson, MD, chief of clinical operations at the Phoenix headquarters of Apogee Physicians, a hospitalist management company that employs about 750 hospitalists across the country. Hospitalists discuss the hospital stay with the patient and family members, prescribe medications, issue discharge recommendations, set up follow-up care, and coordinate with the case manager, specialists, and primary-care physician.
“It generally is one sequential event after the other,” lasting between 20 and 40 minutes and leading up to discharge, Thompson says. Reimbursement for a high-level discharge constitutes more than 30 minutes. However, without proper documentation, he cautions, the claim could be downgraded or denied.
12 Don’t forget to sign, date, and time your progress note.
Last but not least, when it comes to reimbursement, your signature really does matter.
“For an illegible signature, Medicare and the insurance companies have the option of not paying for the service,” Mulholland says. “They’re trying to establish or authenticate who provided the service.”
And they want to know when the hospitalist saw the patient, so it’s a good idea to indicate the exact time of your visit.
Susan Kreimer is a freelance medical writer in New York.
Documentation, CPT codes, modifiers—it’s not glamorous, but it’s an integral part of a 21st-century physician’s job description. The Hospitalist queried more than a handful of billing and coding experts about the advice they would dispense to clinicians navigating the reimbursement maze.
“Physicians often do more than what is reflected in the documentation,” says Barb Pierce, CCS-P, ACS-EM, a national coding consultant based in West Des Moines, Iowa, and CODE-H faculty. “They can’t always bill for everything they do, but they certainly can document and code to obtain the appropriate levels of service.”
Meanwhile, hospitalists have to be careful they aren’t excessive in their billing practices. “The name of the game isn’t just to bill higher,” Pierce adds, “but to make sure that your documentation supports the service being billed, and Medicare is watching. They’re doing a lot of focused audits.”
Some hospitalists might opt for a lower level of service, suspecting they’re less likely to be audited. Other hospitalists might seek reimbursement for more of their time and efforts.
“You have both ends of the spectrum,” says Raemarie Jimenez, CPC, CPMA, CPC-I, CANPC, CRHC, director of education for AAPC, formerly known as the American Academy of Professional Coders. “There are a lot of factors that would go into why a provider would code something incorrectly.”
Here’s how to land somewhere in the middle.
1 Be thorough in documenting the initial hospital visit.
When selecting the level of service for an initial hospital visit, the documentation consists of three key components: history, physical examination, and medical decision-making. The history includes the chief complaint as well as the review of systems. This is “an inventory of the patient’s organ systems.” Both the complaint and the systems review are often incorporated in the history of present illness, says Mary Mulholland, MHA, BSN, RN, CPC, senior coding and education specialist in the Department of Medicine at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
A patient’s family history is commonly overlooked in a hospitalist’s notes, primarily when they know the patient from previous admissions for chronic diseases and when the family history will likely not have an impact on treatment. “If they do not document a complete review of systems or miss one of the histories, the service will definitely be down-coded,” Mulholland says, “no matter how complete the exam and medical decision-making documentation.”
2 Familiarize yourself with Medicare reimbursement rules in the state where you practice.
In some states, Medicare contractors require providers to document the status of each organ system reviewed individually. In other states, it’s acceptable to document a system review with pertinent findings, “whether positive or negative,” and the statement of “all other systems negative,” Mulholland says.
The auditor will give credit for the review based on the number of organ systems documented. “If you miss one system review, it will take down what otherwise would be a Level Three hospital admission to a Level One,” she says. “So there would be a significant financial impact.”
Medicare reimbursement for a Level Three initial visit in Mulholland’s area of practice—Philadelphia County in Pennsylvania—is $206.57, compared with $104.69 for a Level One. During this visit, each of the key components—history, exam, and medical decision-making—need to be documented completely for the provider to receive the highest level of reimbursement.
3 Ask about a patient’s social history.
Social history can be obtained by querying the patient about smoking, drug and alcohol use, his or her occupation, marital status, and type of living arrangement.
“Knowing the social history helps the hospitalist understand the home situation or social circumstances that may have contributed to the hospitalization or may complicate the discharge plan,” Mulholland says.
This is particularly important in decision-making that involves elderly patients. The clinician should “think down the road” as to where the patient will be discharged and if a social worker’s assistance will be needed. It’s about “seeing the whole patient,” she says, “not just the disease.”
4 Remember to include the actual diagnosis.
“As coders, we can see all the clinical indicators of a particular diagnosis,” says Kathryn DeVault, RHIA, CCS, CCS-P, a director at HIM Solutions at the American Health Management Association. However, “unless [physicians] write down the diagnosis, we can’t code it.”
Documents without a diagnosis are more common than one would expect. For example, if a patient has pain when urinating, the hospitalist typically orders a culture. If the result is positive, the hospitalist prescribes an antibiotic for the infection, and too often “the story ends there.” From experience, DeVault can decipher that the patient is being treated for a urinary tract infection, but she can’t assign a code without querying the physician. Hospitalists, she suggests, should try to “close the loop in their documentation.”
5 Be specific in your written assessment of the patient’s condition.
“The main thing that we see is missing documentation,” says Angie Comfort, RHIT, CCS, a director at HIM Solutions. For instance, if a hospitalist documents congestive heart failure, it’s important to indicate whether the condition is chronic or acute and systolic or diastolic.
In the case of a diabetic patient, the notes should specify the type of diabetes. Not doing so “could be a reimbursement-changer,” Comfort says. In contrast, documenting such specifics could result in higher reimbursement, especially if a patient has complications from Type 1 diabetes.
6 Note the severity of the patient’s case.
Hospitalists’ documentation doesn’t always capture everything they’re evaluating for patients. “I’ve seen notes to the extent of ‘patient doing well; waiting on test results,’” the AAPC’s Jimenez says. “If they’re doing certain tests, why are they doing them? What are they trying to diagnose for the patient? What treatment are they considering?”
The reasons for the tests need to be explained. When a provider is monitoring someone in the hospital, the documentation should elaborate on the patient’s response to a treatment, and whether the patient’s condition is better, stable, or worse. This information helps put the severity in perspective.
“A diabetic could be a diabetic out of control. It could be a diabetic who’s not responding or who has comorbidities,” Jimenez says. “No one diagnosis is the same for every patient.”

—Mary Mulholland, MHA, BSN, RN, CPC, senior coding and education specialist, department of medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia
7 Indicate which aspect of the patient’s condition you are treating.
When multiple providers are involved in a hospitalized patient’s care, it’s important to document your specific role apart from the services rendered by specialists, Jimenez says. The codes billed must be supported by the documentation for each service. Many providers contribute to the inpatient documentation, so it must be clear what each clinician personally performs.
Only report the diagnosis you are treating or the diagnoses that affect the ones you are managing. If a specialist has been brought in to take over treatment for a specific condition, a hospitalist would not bill for that diagnosis code.

—Raemarie Jimenez, CPC, CPMA, CPC-I, CANPC, CRHC, director of education, AAPC Salt Lake City
8 Note your personal review of medical records and reports from other clinicians.
Hospitalists should document their review of lab data or radiology reports, discussion of the case with other providers, or collection of the history from someone other than the patient. It’s also helpful to document your personal review of any images, such as a chest X-ray or MRI. Examining the images yourself might lead to higher reimbursement, Mulholland says.
Providers also should note when they request or review old records, and they should include a short synopsis of the information obtained and how it contributed to the current treatment plan.
9 Learn the correct coding for patients being transferred.
A transfer can occur either from a different facility or from a hospital floor to a rehabilitation unit. Either way, the patient is seen twice in one day, with each visit covered by the same hospitalist practice.
“Both physicians often report a separate independent visit. However, because these services occurred on the same day, it is not appropriate to bill for two separate subsequent or initial hospital codes,” says Sherri Dumford, MBA, CHBME, director of operations and past president of the Healthcare Billing and Management Association. “Often what will happen is both services will be reported and get through the billing system. The second claim is just written off as a denied service, when, in fact, you could combine the elements of service of both visits and possibly bill for a single higher level of visit.”
10 Consider delegating to a coding expert.
While smaller hospitalist groups can turn to a coding consultant on an as-needed basis, larger groups might consider bringing a certified coder on staff. This person would inform physicians about proper coding, review their documentation, and “give real-time feedback,” Pierce says.
An internal audit would show if the documentation meets selected evaluation management codes. Also, it usually takes a coding professional to determine whether prolonged services are an option for the team on any given date of service. Someone would need to internally “add together” multiple services on one date to see if there is sufficient time documented to allow billing for these add-on codes, Pierce says. Similarly, critical-care time needs to be accumulated during a date of service.

—Barb Pierce, CCS-P, ACS-EM, national coding consultant, West Des Moines, Iowa
11 Indicate the number of minutes spent arranging for a patient’s discharge.
Discharging a patient involves various steps, says Peter Thompson, MD, chief of clinical operations at the Phoenix headquarters of Apogee Physicians, a hospitalist management company that employs about 750 hospitalists across the country. Hospitalists discuss the hospital stay with the patient and family members, prescribe medications, issue discharge recommendations, set up follow-up care, and coordinate with the case manager, specialists, and primary-care physician.
“It generally is one sequential event after the other,” lasting between 20 and 40 minutes and leading up to discharge, Thompson says. Reimbursement for a high-level discharge constitutes more than 30 minutes. However, without proper documentation, he cautions, the claim could be downgraded or denied.
12 Don’t forget to sign, date, and time your progress note.
Last but not least, when it comes to reimbursement, your signature really does matter.
“For an illegible signature, Medicare and the insurance companies have the option of not paying for the service,” Mulholland says. “They’re trying to establish or authenticate who provided the service.”
And they want to know when the hospitalist saw the patient, so it’s a good idea to indicate the exact time of your visit.
Susan Kreimer is a freelance medical writer in New York.
Accountability Hits Home for Hospitalists
Russell Cowles III, MD, lead hospitalist at Bergan Mercy Medical Center in Omaha, Neb., recalls the shock on the faces of hospitalists who attended his presentation to SHM’s Nebraska Area chapter meeting last spring. Dr. Cowles and co-presenter Eric Rice, MD, MMM, SFHM, chapter president and assistant medical director of Alegent Creighton Hospital Medicine Services, were introducing their fellow hospitalists to a forthcoming Medicare initiative called the Physician Feedback/Value-Based Payment Modifier (VBPM) program.
“And everyone in the audience was completely stunned,” Dr. Cowles says. “They had never even dreamed that any of this would come down to the physician level.”
They’re not alone.
“Unless you work in administration or you’re leading a group, I don’t think very many people know this exists,” Dr. Cowles says. “Your average practicing physician, I think, has no clue that this measurement is going on behind the scenes.”
Authorized by the Affordable Care Act, the budget-neutral scheme ties future Medicare reimbursements to measures of quality and efficiency, and grades physicians on a curve. The Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS), in place since 2007, forms the foundation of the new program, with feedback arriving in the form of a Quality and Resource Use Report (QRUR), a confidential report card sent to providers. The VBPM program then uses those reports as the basis for a financial reward or penalty.
In principle, SHM and hospitalist leaders have supported the concept of quality measurements as a way to hold doctors more accountable and to help the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) take a more proactive role in improving quality of care while containing costs. And, in theory, HM leaders say hospitalists might be better able to adapt to the added responsibility of performance measurement and reporting due to their central role in the like-minded hospital value-based purchasing (VBP) program that began Oct. 1.
“If the expectation is that we will be involved in some of these initiatives and help the hospitals gain revenue, now we can actually see some dollars for those efforts,” says Julia Wright, MD, SFHM, FACP, president of the MidAtlantic Business Unit for Brentwood, Tenn.-based Cogent HMG. But the inverse is also true: If hospitals are going to have dollars at risk for performance, she says, CMS believes physicians should share in that risk as the providers of healthcare.
On that score, Dr. Rice says, hospitalists might have an advantage due to their focus on teamwork and their role in transitioning patients between inpatient and outpatient settings. In fact, he sees the VBPM as an “enormous opportunity” for hospitalists to demonstrate their leadership in helping to shape how organizations and institutions adapt to a quickly evolving healthcare environment.
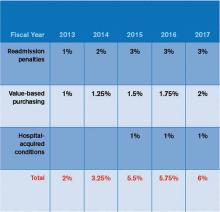
But first, hospitalists will need to fully engage. In 2010, CMS found that only about 1 in 4 eligible physicians were participating in the voluntary PQRS and earning a reporting bonus of what is now 0.5% of allowable Medicare charges (roughly $800 for the average hospitalist). The stakes will grow when the PQRS transforms into a negative incentive program in 2015, with a 1.5% penalty for doctors who do not meet its reporting requirements. In 2016 and thereafter, the assessed penalty grows to 2% (about $3,200 for the average hospitalist).
“I think the unfolding timeline has really provided the potential for lulling us into complacency and procrastination,” says Patrick Torcson, MD, MMM, FACP, SFHM, director of hospital medicine at St. Tammany Parish Hospital in Covington, La., and chair of SHM’s Performance Measurement and Reporting Committee.
According to CMS, “physician groups can avoid all negative adjustments simply by participating in the PQRS.” Nonparticipants, however, could get hit with a double whammy. With no quality data, CMS would have no way to assess groups’ performances and would automatically deduct an extra 1% of Medicare reimbursements under the VBPM program. For groups of 100 eligible providers or more, that combined PQRS-VBPM penalty could amount to 2.5% in 2015.
PQRS participants have more leeway and a smaller downside. Starting January 2015, eligible provider groups who meet the reporting requirements can choose either to have no adjustments at all or to compete in the VBPM program for a performance-based bonus or a penalty of 1%, based on cost and quality scores. In January 2017, the program is expected to expand to include all providers, whether in individual or group practice.
A Measure of Relevance
Based on the first QRURs, sent out in March 2012 to providers in four pilot states, SHM wrote a letter to CMS that offered a detailed analysis of several additional concerns. The society followed up with a second letter that provided a more expansive critique of the proposed 2013 Physician Fee Schedule.
One worry is whether the physician feedback/VBPM program has included enough performance measures that are relevant to hospitalists. A Public Policy column in The Hospitalist (“Metric Accountability,” November 2012, p. 18) counted only 10 PQRS measures that apply routinely to HM providers out of a list of more than 200. Even those 10 aren’t always applicable.
“I work at a teaching hospital that’s large enough to have a neurology program, so most acute-stroke patients are admitted by the neurologists,” says Gregory Seymann, MD, SFHM, chief of the division of hospital medicine at the University of California at San Diego and a member of SHM’s Performance Measurement and Reporting Committee. “Five of the 10 measures are related to stroke patients, but my group rarely admits stroke patients.” That means only five PQRS measures remain relevant to him.
On paper, the issue might be readily resolved by expanding the number of measures to better reflect HM responsibilities—such as four measures proposed by SHM that relate to transitions of care and medication reconciliation.

—Patrick Torcson, MD, MMM, FACP, SFHM, director, hospital medicine, St. Tammany Parish Hospital, Covington, La., chair, SHM’s Performance Measurement and Reporting Committee
Other groups, though, have their own ideas. A letter to CMS signed by 28 patient and healthcare payor groups calls for the elimination of almost two dozen PQRS measures deemed unnecessary, duplicative, or uninformative, and for the addition of nine others that might better assess patient outcomes and quality of care. Jennifer Eames Huff, director of the Consumer-Purchaser Disclosure Project at San Francisco-based Pacific Business Group on Health, one of the letter’s signatories, says some of those potential measures might be more applicable to hospitalists as well.
But therein lies the rub. Although process measures might not always be strong indicators of quality of care, the introduction of outcome measures often makes providers nervous, says Gary Young, JD, PhD, director of the Center for Health Policy and Healthcare Research at Northeastern University in Boston. “Most providers feel that their patients are sicker and more vulnerable to poorer outcomes, and they don’t want to be judged poorly because they have sicker patients,” he says. Reaching an agreement on the best collection of measures may require some intense negotiations, he says.

–Win Whitcomb, MD, MHM, medical director of healthcare quality, Baystate Medical Center, Springfield, Mass.
Fairer Comparisons
Dr. Cowles cites two de-identified QRURs received by Alegent Creighton Health back in March—one for a hospitalist and one for an office-based general internist—to illustrate another major concern shared by many HM providers. The reports broke down each doctor’s relative healthcare contributions, using predetermined percentages of the total care and costs to conclude whether that doctor directed, influenced, or contributed to a patient’s care.
Hospitalists, by the nature of their jobs, seldom direct the care of any patient. But because their influence or contribution is almost always within the inpatient environment, HM providers account for proportionately higher costs than office-based physicians. The result can be a rather ugly curve: For healthcare costs incurred, the general internist was at the 65th percentile, while the hospitalist was at the 96th percentile.
The point, Dr. Cowles says, is that hospitalists and clinic-based physicians see patients with remarkably different acuities. “We just need to make sure that we’re comparing apples to apples, that you’re going to compare someone who sees a high-acuity patient with someone else who sees a high-acuity patient,” he says.
One silver lining could be increased momentum toward establishing HM as its own Medicare-recognized specialty. Hospitalist leaders who say the process is likely to be difficult but not impossible cite the successful effort to win recognition of HM as a focused practice by the American Board of Internal Medicine.
“We’re going to have to think outside the box in terms of working toward an identifier for hospitalists,” says Win Whitcomb, MD, MHM, medical director of healthcare quality at Baystate Medical Center in Springfield, Mass., and a member of SHM’s Performance and Measurement Reporting Committee. “But that’s going to happen—it’s not a matter of if, it’s a matter of when and how.”
As one potential interim solution, SHM has suggested a self-identification designation by which hospitalists would distinguish themselves from the larger, general internal-medicine category and thereby avoid unfair comparisons.
A Question of Attribution
Of the concerns raised by SHM, the question of attribution might be among the thorniest. Dr. Young says the “big-time issue” is pitting many consumer groups, payors, and employers against healthcare providers. The consumer groups want accountability at the individual provider level, while the providers strongly prefer group accountability, setting up a major clash over how responsibility will be parceled out.
Hospitalists have been taught to embrace responsibility while viewing healthcare delivery as a team sport. And the contributions of individual HM providers aren’t easily untangled. “If somebody has a bad outcome and they’ve been under the care of three different hospitalists, it’s virtually impossible to attribute that outcome to one of those three hospitalists,” Dr. Whitcomb says. “We really need to think about attribution differently, and it’s going to need to be across groups of hospitalists.”
SHM has suggested that CMS include an option for group rather than individual evaluation. “You’re just making it explicit that you can’t assign some of these measures to individual physicians. We can assign some of these measures to groups,” Dr. Whitcomb says.

—Julia Wright, MD, SFHM, FACP, president, MidAtlantic Business Unit, Cogent HMG, Brentwood, Tenn.
In its 2013 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule final rule, CMS opted to alter the doctor comparison methodology used for upcoming QRURs and the 2015 application of the VBPM. The agency also agreed to consider hospitalists’ concerns about fair attribution, relevant measures, and proper designation as it develops future proposals. Regardless of how those issues are ironed out, Dr. Torcson says, it’s clear to him that sitting on the sidelines is no longer an option for any physician group. Nor is it acceptable “to say this won’t work for me. We’re having to come up with proactive proposals for what will work to be part of the CMS quality agenda.”
SHM’s thorough analysis and realistic feedback, he says, has been well received by Medicare officials, raising hopes that many of the remaining differences can be resolved. “I am very confident that self-reporting or self-nomination as a hospitalist is going to be in place by the time those negative incentives kick in,” Dr. Torcson says. “And I’m also very confident that we’re going to have other, very creative options for quality measurement and performance reporting.”
One idea under consideration by CMS would allow hospitalists or other doctors to designate their hospitals’ quality data as a surrogate measure of their own performance. “I think that’s going to be a really great option for hospitalists who self-nominate,” Dr. Torcson says.
For many hospitalists, the option would effectively get around the issue of individual versus group attribution and instead align doctors’ fates with that of their institutions. SHM, Dr. Torcson says, has endorsed the proposal and offered to work with CMS to help institute it. He’s also confident that the reporting requirements for multiple, overlapping CMS programs will be more streamlined over time.
Some health professionals believe that hospitals and doctors already are devoting too much time and energy to measuring and recording the proliferating set of mandatory metrics. But Dr. Whitcomb says payors and patients are unlikely to have much sympathy.
“We as a profession are accountable to society at large. And that argument, that there are too many measurements and that we shouldn’t be held accountable as physicians for our performance, is a nonstarter when you’re trying to explain that to consumers,” he says. “The status quo is not tenable, and so it’s going to be a long journey and we need to be able to move in that direction.”
Bryn Nelson is a freelance medical writer in Seattle.
Russell Cowles III, MD, lead hospitalist at Bergan Mercy Medical Center in Omaha, Neb., recalls the shock on the faces of hospitalists who attended his presentation to SHM’s Nebraska Area chapter meeting last spring. Dr. Cowles and co-presenter Eric Rice, MD, MMM, SFHM, chapter president and assistant medical director of Alegent Creighton Hospital Medicine Services, were introducing their fellow hospitalists to a forthcoming Medicare initiative called the Physician Feedback/Value-Based Payment Modifier (VBPM) program.
“And everyone in the audience was completely stunned,” Dr. Cowles says. “They had never even dreamed that any of this would come down to the physician level.”
They’re not alone.
“Unless you work in administration or you’re leading a group, I don’t think very many people know this exists,” Dr. Cowles says. “Your average practicing physician, I think, has no clue that this measurement is going on behind the scenes.”
Authorized by the Affordable Care Act, the budget-neutral scheme ties future Medicare reimbursements to measures of quality and efficiency, and grades physicians on a curve. The Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS), in place since 2007, forms the foundation of the new program, with feedback arriving in the form of a Quality and Resource Use Report (QRUR), a confidential report card sent to providers. The VBPM program then uses those reports as the basis for a financial reward or penalty.
In principle, SHM and hospitalist leaders have supported the concept of quality measurements as a way to hold doctors more accountable and to help the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) take a more proactive role in improving quality of care while containing costs. And, in theory, HM leaders say hospitalists might be better able to adapt to the added responsibility of performance measurement and reporting due to their central role in the like-minded hospital value-based purchasing (VBP) program that began Oct. 1.
“If the expectation is that we will be involved in some of these initiatives and help the hospitals gain revenue, now we can actually see some dollars for those efforts,” says Julia Wright, MD, SFHM, FACP, president of the MidAtlantic Business Unit for Brentwood, Tenn.-based Cogent HMG. But the inverse is also true: If hospitals are going to have dollars at risk for performance, she says, CMS believes physicians should share in that risk as the providers of healthcare.
On that score, Dr. Rice says, hospitalists might have an advantage due to their focus on teamwork and their role in transitioning patients between inpatient and outpatient settings. In fact, he sees the VBPM as an “enormous opportunity” for hospitalists to demonstrate their leadership in helping to shape how organizations and institutions adapt to a quickly evolving healthcare environment.
But first, hospitalists will need to fully engage. In 2010, CMS found that only about 1 in 4 eligible physicians were participating in the voluntary PQRS and earning a reporting bonus of what is now 0.5% of allowable Medicare charges (roughly $800 for the average hospitalist). The stakes will grow when the PQRS transforms into a negative incentive program in 2015, with a 1.5% penalty for doctors who do not meet its reporting requirements. In 2016 and thereafter, the assessed penalty grows to 2% (about $3,200 for the average hospitalist).
“I think the unfolding timeline has really provided the potential for lulling us into complacency and procrastination,” says Patrick Torcson, MD, MMM, FACP, SFHM, director of hospital medicine at St. Tammany Parish Hospital in Covington, La., and chair of SHM’s Performance Measurement and Reporting Committee.
According to CMS, “physician groups can avoid all negative adjustments simply by participating in the PQRS.” Nonparticipants, however, could get hit with a double whammy. With no quality data, CMS would have no way to assess groups’ performances and would automatically deduct an extra 1% of Medicare reimbursements under the VBPM program. For groups of 100 eligible providers or more, that combined PQRS-VBPM penalty could amount to 2.5% in 2015.
PQRS participants have more leeway and a smaller downside. Starting January 2015, eligible provider groups who meet the reporting requirements can choose either to have no adjustments at all or to compete in the VBPM program for a performance-based bonus or a penalty of 1%, based on cost and quality scores. In January 2017, the program is expected to expand to include all providers, whether in individual or group practice.
A Measure of Relevance
Based on the first QRURs, sent out in March 2012 to providers in four pilot states, SHM wrote a letter to CMS that offered a detailed analysis of several additional concerns. The society followed up with a second letter that provided a more expansive critique of the proposed 2013 Physician Fee Schedule.
One worry is whether the physician feedback/VBPM program has included enough performance measures that are relevant to hospitalists. A Public Policy column in The Hospitalist (“Metric Accountability,” November 2012, p. 18) counted only 10 PQRS measures that apply routinely to HM providers out of a list of more than 200. Even those 10 aren’t always applicable.
“I work at a teaching hospital that’s large enough to have a neurology program, so most acute-stroke patients are admitted by the neurologists,” says Gregory Seymann, MD, SFHM, chief of the division of hospital medicine at the University of California at San Diego and a member of SHM’s Performance Measurement and Reporting Committee. “Five of the 10 measures are related to stroke patients, but my group rarely admits stroke patients.” That means only five PQRS measures remain relevant to him.
On paper, the issue might be readily resolved by expanding the number of measures to better reflect HM responsibilities—such as four measures proposed by SHM that relate to transitions of care and medication reconciliation.

—Patrick Torcson, MD, MMM, FACP, SFHM, director, hospital medicine, St. Tammany Parish Hospital, Covington, La., chair, SHM’s Performance Measurement and Reporting Committee
Other groups, though, have their own ideas. A letter to CMS signed by 28 patient and healthcare payor groups calls for the elimination of almost two dozen PQRS measures deemed unnecessary, duplicative, or uninformative, and for the addition of nine others that might better assess patient outcomes and quality of care. Jennifer Eames Huff, director of the Consumer-Purchaser Disclosure Project at San Francisco-based Pacific Business Group on Health, one of the letter’s signatories, says some of those potential measures might be more applicable to hospitalists as well.
But therein lies the rub. Although process measures might not always be strong indicators of quality of care, the introduction of outcome measures often makes providers nervous, says Gary Young, JD, PhD, director of the Center for Health Policy and Healthcare Research at Northeastern University in Boston. “Most providers feel that their patients are sicker and more vulnerable to poorer outcomes, and they don’t want to be judged poorly because they have sicker patients,” he says. Reaching an agreement on the best collection of measures may require some intense negotiations, he says.

–Win Whitcomb, MD, MHM, medical director of healthcare quality, Baystate Medical Center, Springfield, Mass.
Fairer Comparisons
Dr. Cowles cites two de-identified QRURs received by Alegent Creighton Health back in March—one for a hospitalist and one for an office-based general internist—to illustrate another major concern shared by many HM providers. The reports broke down each doctor’s relative healthcare contributions, using predetermined percentages of the total care and costs to conclude whether that doctor directed, influenced, or contributed to a patient’s care.
Hospitalists, by the nature of their jobs, seldom direct the care of any patient. But because their influence or contribution is almost always within the inpatient environment, HM providers account for proportionately higher costs than office-based physicians. The result can be a rather ugly curve: For healthcare costs incurred, the general internist was at the 65th percentile, while the hospitalist was at the 96th percentile.
The point, Dr. Cowles says, is that hospitalists and clinic-based physicians see patients with remarkably different acuities. “We just need to make sure that we’re comparing apples to apples, that you’re going to compare someone who sees a high-acuity patient with someone else who sees a high-acuity patient,” he says.
One silver lining could be increased momentum toward establishing HM as its own Medicare-recognized specialty. Hospitalist leaders who say the process is likely to be difficult but not impossible cite the successful effort to win recognition of HM as a focused practice by the American Board of Internal Medicine.
“We’re going to have to think outside the box in terms of working toward an identifier for hospitalists,” says Win Whitcomb, MD, MHM, medical director of healthcare quality at Baystate Medical Center in Springfield, Mass., and a member of SHM’s Performance and Measurement Reporting Committee. “But that’s going to happen—it’s not a matter of if, it’s a matter of when and how.”
As one potential interim solution, SHM has suggested a self-identification designation by which hospitalists would distinguish themselves from the larger, general internal-medicine category and thereby avoid unfair comparisons.
A Question of Attribution
Of the concerns raised by SHM, the question of attribution might be among the thorniest. Dr. Young says the “big-time issue” is pitting many consumer groups, payors, and employers against healthcare providers. The consumer groups want accountability at the individual provider level, while the providers strongly prefer group accountability, setting up a major clash over how responsibility will be parceled out.
Hospitalists have been taught to embrace responsibility while viewing healthcare delivery as a team sport. And the contributions of individual HM providers aren’t easily untangled. “If somebody has a bad outcome and they’ve been under the care of three different hospitalists, it’s virtually impossible to attribute that outcome to one of those three hospitalists,” Dr. Whitcomb says. “We really need to think about attribution differently, and it’s going to need to be across groups of hospitalists.”
SHM has suggested that CMS include an option for group rather than individual evaluation. “You’re just making it explicit that you can’t assign some of these measures to individual physicians. We can assign some of these measures to groups,” Dr. Whitcomb says.

—Julia Wright, MD, SFHM, FACP, president, MidAtlantic Business Unit, Cogent HMG, Brentwood, Tenn.
In its 2013 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule final rule, CMS opted to alter the doctor comparison methodology used for upcoming QRURs and the 2015 application of the VBPM. The agency also agreed to consider hospitalists’ concerns about fair attribution, relevant measures, and proper designation as it develops future proposals. Regardless of how those issues are ironed out, Dr. Torcson says, it’s clear to him that sitting on the sidelines is no longer an option for any physician group. Nor is it acceptable “to say this won’t work for me. We’re having to come up with proactive proposals for what will work to be part of the CMS quality agenda.”
SHM’s thorough analysis and realistic feedback, he says, has been well received by Medicare officials, raising hopes that many of the remaining differences can be resolved. “I am very confident that self-reporting or self-nomination as a hospitalist is going to be in place by the time those negative incentives kick in,” Dr. Torcson says. “And I’m also very confident that we’re going to have other, very creative options for quality measurement and performance reporting.”
One idea under consideration by CMS would allow hospitalists or other doctors to designate their hospitals’ quality data as a surrogate measure of their own performance. “I think that’s going to be a really great option for hospitalists who self-nominate,” Dr. Torcson says.
For many hospitalists, the option would effectively get around the issue of individual versus group attribution and instead align doctors’ fates with that of their institutions. SHM, Dr. Torcson says, has endorsed the proposal and offered to work with CMS to help institute it. He’s also confident that the reporting requirements for multiple, overlapping CMS programs will be more streamlined over time.
Some health professionals believe that hospitals and doctors already are devoting too much time and energy to measuring and recording the proliferating set of mandatory metrics. But Dr. Whitcomb says payors and patients are unlikely to have much sympathy.
“We as a profession are accountable to society at large. And that argument, that there are too many measurements and that we shouldn’t be held accountable as physicians for our performance, is a nonstarter when you’re trying to explain that to consumers,” he says. “The status quo is not tenable, and so it’s going to be a long journey and we need to be able to move in that direction.”
Bryn Nelson is a freelance medical writer in Seattle.
Russell Cowles III, MD, lead hospitalist at Bergan Mercy Medical Center in Omaha, Neb., recalls the shock on the faces of hospitalists who attended his presentation to SHM’s Nebraska Area chapter meeting last spring. Dr. Cowles and co-presenter Eric Rice, MD, MMM, SFHM, chapter president and assistant medical director of Alegent Creighton Hospital Medicine Services, were introducing their fellow hospitalists to a forthcoming Medicare initiative called the Physician Feedback/Value-Based Payment Modifier (VBPM) program.
“And everyone in the audience was completely stunned,” Dr. Cowles says. “They had never even dreamed that any of this would come down to the physician level.”
They’re not alone.
“Unless you work in administration or you’re leading a group, I don’t think very many people know this exists,” Dr. Cowles says. “Your average practicing physician, I think, has no clue that this measurement is going on behind the scenes.”
Authorized by the Affordable Care Act, the budget-neutral scheme ties future Medicare reimbursements to measures of quality and efficiency, and grades physicians on a curve. The Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS), in place since 2007, forms the foundation of the new program, with feedback arriving in the form of a Quality and Resource Use Report (QRUR), a confidential report card sent to providers. The VBPM program then uses those reports as the basis for a financial reward or penalty.
In principle, SHM and hospitalist leaders have supported the concept of quality measurements as a way to hold doctors more accountable and to help the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) take a more proactive role in improving quality of care while containing costs. And, in theory, HM leaders say hospitalists might be better able to adapt to the added responsibility of performance measurement and reporting due to their central role in the like-minded hospital value-based purchasing (VBP) program that began Oct. 1.
“If the expectation is that we will be involved in some of these initiatives and help the hospitals gain revenue, now we can actually see some dollars for those efforts,” says Julia Wright, MD, SFHM, FACP, president of the MidAtlantic Business Unit for Brentwood, Tenn.-based Cogent HMG. But the inverse is also true: If hospitals are going to have dollars at risk for performance, she says, CMS believes physicians should share in that risk as the providers of healthcare.
On that score, Dr. Rice says, hospitalists might have an advantage due to their focus on teamwork and their role in transitioning patients between inpatient and outpatient settings. In fact, he sees the VBPM as an “enormous opportunity” for hospitalists to demonstrate their leadership in helping to shape how organizations and institutions adapt to a quickly evolving healthcare environment.
But first, hospitalists will need to fully engage. In 2010, CMS found that only about 1 in 4 eligible physicians were participating in the voluntary PQRS and earning a reporting bonus of what is now 0.5% of allowable Medicare charges (roughly $800 for the average hospitalist). The stakes will grow when the PQRS transforms into a negative incentive program in 2015, with a 1.5% penalty for doctors who do not meet its reporting requirements. In 2016 and thereafter, the assessed penalty grows to 2% (about $3,200 for the average hospitalist).
“I think the unfolding timeline has really provided the potential for lulling us into complacency and procrastination,” says Patrick Torcson, MD, MMM, FACP, SFHM, director of hospital medicine at St. Tammany Parish Hospital in Covington, La., and chair of SHM’s Performance Measurement and Reporting Committee.
According to CMS, “physician groups can avoid all negative adjustments simply by participating in the PQRS.” Nonparticipants, however, could get hit with a double whammy. With no quality data, CMS would have no way to assess groups’ performances and would automatically deduct an extra 1% of Medicare reimbursements under the VBPM program. For groups of 100 eligible providers or more, that combined PQRS-VBPM penalty could amount to 2.5% in 2015.
PQRS participants have more leeway and a smaller downside. Starting January 2015, eligible provider groups who meet the reporting requirements can choose either to have no adjustments at all or to compete in the VBPM program for a performance-based bonus or a penalty of 1%, based on cost and quality scores. In January 2017, the program is expected to expand to include all providers, whether in individual or group practice.
A Measure of Relevance
Based on the first QRURs, sent out in March 2012 to providers in four pilot states, SHM wrote a letter to CMS that offered a detailed analysis of several additional concerns. The society followed up with a second letter that provided a more expansive critique of the proposed 2013 Physician Fee Schedule.
One worry is whether the physician feedback/VBPM program has included enough performance measures that are relevant to hospitalists. A Public Policy column in The Hospitalist (“Metric Accountability,” November 2012, p. 18) counted only 10 PQRS measures that apply routinely to HM providers out of a list of more than 200. Even those 10 aren’t always applicable.
“I work at a teaching hospital that’s large enough to have a neurology program, so most acute-stroke patients are admitted by the neurologists,” says Gregory Seymann, MD, SFHM, chief of the division of hospital medicine at the University of California at San Diego and a member of SHM’s Performance Measurement and Reporting Committee. “Five of the 10 measures are related to stroke patients, but my group rarely admits stroke patients.” That means only five PQRS measures remain relevant to him.
On paper, the issue might be readily resolved by expanding the number of measures to better reflect HM responsibilities—such as four measures proposed by SHM that relate to transitions of care and medication reconciliation.

—Patrick Torcson, MD, MMM, FACP, SFHM, director, hospital medicine, St. Tammany Parish Hospital, Covington, La., chair, SHM’s Performance Measurement and Reporting Committee
Other groups, though, have their own ideas. A letter to CMS signed by 28 patient and healthcare payor groups calls for the elimination of almost two dozen PQRS measures deemed unnecessary, duplicative, or uninformative, and for the addition of nine others that might better assess patient outcomes and quality of care. Jennifer Eames Huff, director of the Consumer-Purchaser Disclosure Project at San Francisco-based Pacific Business Group on Health, one of the letter’s signatories, says some of those potential measures might be more applicable to hospitalists as well.
But therein lies the rub. Although process measures might not always be strong indicators of quality of care, the introduction of outcome measures often makes providers nervous, says Gary Young, JD, PhD, director of the Center for Health Policy and Healthcare Research at Northeastern University in Boston. “Most providers feel that their patients are sicker and more vulnerable to poorer outcomes, and they don’t want to be judged poorly because they have sicker patients,” he says. Reaching an agreement on the best collection of measures may require some intense negotiations, he says.

–Win Whitcomb, MD, MHM, medical director of healthcare quality, Baystate Medical Center, Springfield, Mass.
Fairer Comparisons
Dr. Cowles cites two de-identified QRURs received by Alegent Creighton Health back in March—one for a hospitalist and one for an office-based general internist—to illustrate another major concern shared by many HM providers. The reports broke down each doctor’s relative healthcare contributions, using predetermined percentages of the total care and costs to conclude whether that doctor directed, influenced, or contributed to a patient’s care.
Hospitalists, by the nature of their jobs, seldom direct the care of any patient. But because their influence or contribution is almost always within the inpatient environment, HM providers account for proportionately higher costs than office-based physicians. The result can be a rather ugly curve: For healthcare costs incurred, the general internist was at the 65th percentile, while the hospitalist was at the 96th percentile.
The point, Dr. Cowles says, is that hospitalists and clinic-based physicians see patients with remarkably different acuities. “We just need to make sure that we’re comparing apples to apples, that you’re going to compare someone who sees a high-acuity patient with someone else who sees a high-acuity patient,” he says.
One silver lining could be increased momentum toward establishing HM as its own Medicare-recognized specialty. Hospitalist leaders who say the process is likely to be difficult but not impossible cite the successful effort to win recognition of HM as a focused practice by the American Board of Internal Medicine.
“We’re going to have to think outside the box in terms of working toward an identifier for hospitalists,” says Win Whitcomb, MD, MHM, medical director of healthcare quality at Baystate Medical Center in Springfield, Mass., and a member of SHM’s Performance and Measurement Reporting Committee. “But that’s going to happen—it’s not a matter of if, it’s a matter of when and how.”
As one potential interim solution, SHM has suggested a self-identification designation by which hospitalists would distinguish themselves from the larger, general internal-medicine category and thereby avoid unfair comparisons.
A Question of Attribution
Of the concerns raised by SHM, the question of attribution might be among the thorniest. Dr. Young says the “big-time issue” is pitting many consumer groups, payors, and employers against healthcare providers. The consumer groups want accountability at the individual provider level, while the providers strongly prefer group accountability, setting up a major clash over how responsibility will be parceled out.
Hospitalists have been taught to embrace responsibility while viewing healthcare delivery as a team sport. And the contributions of individual HM providers aren’t easily untangled. “If somebody has a bad outcome and they’ve been under the care of three different hospitalists, it’s virtually impossible to attribute that outcome to one of those three hospitalists,” Dr. Whitcomb says. “We really need to think about attribution differently, and it’s going to need to be across groups of hospitalists.”
SHM has suggested that CMS include an option for group rather than individual evaluation. “You’re just making it explicit that you can’t assign some of these measures to individual physicians. We can assign some of these measures to groups,” Dr. Whitcomb says.

—Julia Wright, MD, SFHM, FACP, president, MidAtlantic Business Unit, Cogent HMG, Brentwood, Tenn.
In its 2013 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule final rule, CMS opted to alter the doctor comparison methodology used for upcoming QRURs and the 2015 application of the VBPM. The agency also agreed to consider hospitalists’ concerns about fair attribution, relevant measures, and proper designation as it develops future proposals. Regardless of how those issues are ironed out, Dr. Torcson says, it’s clear to him that sitting on the sidelines is no longer an option for any physician group. Nor is it acceptable “to say this won’t work for me. We’re having to come up with proactive proposals for what will work to be part of the CMS quality agenda.”
SHM’s thorough analysis and realistic feedback, he says, has been well received by Medicare officials, raising hopes that many of the remaining differences can be resolved. “I am very confident that self-reporting or self-nomination as a hospitalist is going to be in place by the time those negative incentives kick in,” Dr. Torcson says. “And I’m also very confident that we’re going to have other, very creative options for quality measurement and performance reporting.”
One idea under consideration by CMS would allow hospitalists or other doctors to designate their hospitals’ quality data as a surrogate measure of their own performance. “I think that’s going to be a really great option for hospitalists who self-nominate,” Dr. Torcson says.
For many hospitalists, the option would effectively get around the issue of individual versus group attribution and instead align doctors’ fates with that of their institutions. SHM, Dr. Torcson says, has endorsed the proposal and offered to work with CMS to help institute it. He’s also confident that the reporting requirements for multiple, overlapping CMS programs will be more streamlined over time.
Some health professionals believe that hospitals and doctors already are devoting too much time and energy to measuring and recording the proliferating set of mandatory metrics. But Dr. Whitcomb says payors and patients are unlikely to have much sympathy.
“We as a profession are accountable to society at large. And that argument, that there are too many measurements and that we shouldn’t be held accountable as physicians for our performance, is a nonstarter when you’re trying to explain that to consumers,” he says. “The status quo is not tenable, and so it’s going to be a long journey and we need to be able to move in that direction.”
Bryn Nelson is a freelance medical writer in Seattle.
Win Whitcomb: Hospitalists Central to Helping Hospitals Meet Performance Goals, Avoid Financial Penalities
After a long wait, the time where quality really matters to the finance department has arrived. Why? Because now a lot of money is on the line based on hospitals’ ability to demonstrate performance on quality, patient safety, and patient satisfaction measures. And there is no physician group more central to the hospital’s performance on these measures than hospitalists.
To make this point, I will discuss the financial implications of three programs that are part of the Affordable Care Act: hospital value-based purchasing (HVBP), readmission penalties, and hospital-acquired conditions (HACs). Although many have found fault with these programs, especially the ones that only penalize hospitals (HACs and readmissions*), the dollars at risk can represent a new business case for hospitalist programs. High-performing hospitalist programs can positively impact their institution’s income statement.
In October 2012, readmissions penalties and VBP payments/penalties went into effect. In October 2014, a 1% penalty for groups in the worst-performing quartile in the HACs will be in force. Taken together, as Table 1 demonstrates, the total payments at risk will grow such that by fiscal-year 2017, 6% of a hospital’s inpatient payments from Medicare will be at risk. To put this in perspective, Table 2 models the dollars at risk for each of the five years beginning in 2013 for the three programs in a hypothetical, 327-bed hospital. While the risk in 2013 is a modest $1.7 million, by 2017, this hospital has more than $5 million at risk.
So where should hospitalists be focusing their efforts with these three programs and the monies that accompany them? First, for those designing incentive compensation for hospitalists, the incentives should address the applicable elements of these programs. Second, the components of VBP will evolve. For example, 2013 VPB payments are based on 70% process measures (a subset of the core measure set for heart failure, myocardial infarction, pneumonia, and surgery) and 30% patient satisfaction measures. In 2015, VBP will add such outcomes measures as central-line-associated bloodstream infections, catheter UTIs, mortality rates, and the new efficiency measure, Medicare spending per beneficiary. Third, readmissions penalties, while encompassing heart failure, myocardial infarction, and pneumonia for fiscal-year 2013 payments, will expand in fiscal-year 2015 to include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, coronary artery bypass grafting, percutaneous coronary intervention, and other vascular conditions.
While all this can be hard to keep track of, not to mention address in the course of daily patient care, I suggest hospitalists set the following priorities to enable high performance for their hospitals under these programs:
- Catheter UTIs. Work with nursing, the ED, and other areas to ensure that catheters are indicated, insertion is sterile, there is a mechanism for their prompt removal, specimens are collected and handled appropriately, and that “present on admission” is documented if appropriate.
- Central-line-associated bloodstream infections. Ensure your hospital has the systems in place to support the central-line insertion bundle, and that the bundle elements are followed and documented.
- Readmissions. Focus on heart failure, pneumonia, myocardial infarction, and COPD; work with nursing and case management to identify those at high risk for readmission; perform targeted interventions based on that risk (e.g. palliative care or clinical pharmacy consultation); prioritize medication reconciliation; provide timely communication of discharge summary to the next provider of care; and contact the patient soon after discharge to ensure they are following their plan of care.
- Patient satisfaction. Have a system for high performance on the questions comprising the “doctor communication” domain. These are “How often did doctors treat you with courtesy and respect/listen carefully to you/explain things in a way you could understand?”
Medicare’s Message
Clearly, the financial impacts of hospital quality, satisfaction, and safety are growing, conveying the message from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) that quality matters, making a business case for quality. Our focus as leaders in hospital systems improvement will only sharpen as we see hospital payments increasingly affected as a direct consequence of our efforts. If that doesn’t get the attention of the finance department, what will?
Dr. Whitcomb is medical director of healthcare quality at Baystate Medical Center in Springfield, Mass. He is a co-founder and past president of SHM. Email him at [email protected].
After a long wait, the time where quality really matters to the finance department has arrived. Why? Because now a lot of money is on the line based on hospitals’ ability to demonstrate performance on quality, patient safety, and patient satisfaction measures. And there is no physician group more central to the hospital’s performance on these measures than hospitalists.
To make this point, I will discuss the financial implications of three programs that are part of the Affordable Care Act: hospital value-based purchasing (HVBP), readmission penalties, and hospital-acquired conditions (HACs). Although many have found fault with these programs, especially the ones that only penalize hospitals (HACs and readmissions*), the dollars at risk can represent a new business case for hospitalist programs. High-performing hospitalist programs can positively impact their institution’s income statement.
In October 2012, readmissions penalties and VBP payments/penalties went into effect. In October 2014, a 1% penalty for groups in the worst-performing quartile in the HACs will be in force. Taken together, as Table 1 demonstrates, the total payments at risk will grow such that by fiscal-year 2017, 6% of a hospital’s inpatient payments from Medicare will be at risk. To put this in perspective, Table 2 models the dollars at risk for each of the five years beginning in 2013 for the three programs in a hypothetical, 327-bed hospital. While the risk in 2013 is a modest $1.7 million, by 2017, this hospital has more than $5 million at risk.
So where should hospitalists be focusing their efforts with these three programs and the monies that accompany them? First, for those designing incentive compensation for hospitalists, the incentives should address the applicable elements of these programs. Second, the components of VBP will evolve. For example, 2013 VPB payments are based on 70% process measures (a subset of the core measure set for heart failure, myocardial infarction, pneumonia, and surgery) and 30% patient satisfaction measures. In 2015, VBP will add such outcomes measures as central-line-associated bloodstream infections, catheter UTIs, mortality rates, and the new efficiency measure, Medicare spending per beneficiary. Third, readmissions penalties, while encompassing heart failure, myocardial infarction, and pneumonia for fiscal-year 2013 payments, will expand in fiscal-year 2015 to include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, coronary artery bypass grafting, percutaneous coronary intervention, and other vascular conditions.
While all this can be hard to keep track of, not to mention address in the course of daily patient care, I suggest hospitalists set the following priorities to enable high performance for their hospitals under these programs:
- Catheter UTIs. Work with nursing, the ED, and other areas to ensure that catheters are indicated, insertion is sterile, there is a mechanism for their prompt removal, specimens are collected and handled appropriately, and that “present on admission” is documented if appropriate.
- Central-line-associated bloodstream infections. Ensure your hospital has the systems in place to support the central-line insertion bundle, and that the bundle elements are followed and documented.
- Readmissions. Focus on heart failure, pneumonia, myocardial infarction, and COPD; work with nursing and case management to identify those at high risk for readmission; perform targeted interventions based on that risk (e.g. palliative care or clinical pharmacy consultation); prioritize medication reconciliation; provide timely communication of discharge summary to the next provider of care; and contact the patient soon after discharge to ensure they are following their plan of care.
- Patient satisfaction. Have a system for high performance on the questions comprising the “doctor communication” domain. These are “How often did doctors treat you with courtesy and respect/listen carefully to you/explain things in a way you could understand?”
Medicare’s Message
Clearly, the financial impacts of hospital quality, satisfaction, and safety are growing, conveying the message from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) that quality matters, making a business case for quality. Our focus as leaders in hospital systems improvement will only sharpen as we see hospital payments increasingly affected as a direct consequence of our efforts. If that doesn’t get the attention of the finance department, what will?
Dr. Whitcomb is medical director of healthcare quality at Baystate Medical Center in Springfield, Mass. He is a co-founder and past president of SHM. Email him at [email protected].
After a long wait, the time where quality really matters to the finance department has arrived. Why? Because now a lot of money is on the line based on hospitals’ ability to demonstrate performance on quality, patient safety, and patient satisfaction measures. And there is no physician group more central to the hospital’s performance on these measures than hospitalists.
To make this point, I will discuss the financial implications of three programs that are part of the Affordable Care Act: hospital value-based purchasing (HVBP), readmission penalties, and hospital-acquired conditions (HACs). Although many have found fault with these programs, especially the ones that only penalize hospitals (HACs and readmissions*), the dollars at risk can represent a new business case for hospitalist programs. High-performing hospitalist programs can positively impact their institution’s income statement.
In October 2012, readmissions penalties and VBP payments/penalties went into effect. In October 2014, a 1% penalty for groups in the worst-performing quartile in the HACs will be in force. Taken together, as Table 1 demonstrates, the total payments at risk will grow such that by fiscal-year 2017, 6% of a hospital’s inpatient payments from Medicare will be at risk. To put this in perspective, Table 2 models the dollars at risk for each of the five years beginning in 2013 for the three programs in a hypothetical, 327-bed hospital. While the risk in 2013 is a modest $1.7 million, by 2017, this hospital has more than $5 million at risk.
So where should hospitalists be focusing their efforts with these three programs and the monies that accompany them? First, for those designing incentive compensation for hospitalists, the incentives should address the applicable elements of these programs. Second, the components of VBP will evolve. For example, 2013 VPB payments are based on 70% process measures (a subset of the core measure set for heart failure, myocardial infarction, pneumonia, and surgery) and 30% patient satisfaction measures. In 2015, VBP will add such outcomes measures as central-line-associated bloodstream infections, catheter UTIs, mortality rates, and the new efficiency measure, Medicare spending per beneficiary. Third, readmissions penalties, while encompassing heart failure, myocardial infarction, and pneumonia for fiscal-year 2013 payments, will expand in fiscal-year 2015 to include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, coronary artery bypass grafting, percutaneous coronary intervention, and other vascular conditions.
While all this can be hard to keep track of, not to mention address in the course of daily patient care, I suggest hospitalists set the following priorities to enable high performance for their hospitals under these programs:
- Catheter UTIs. Work with nursing, the ED, and other areas to ensure that catheters are indicated, insertion is sterile, there is a mechanism for their prompt removal, specimens are collected and handled appropriately, and that “present on admission” is documented if appropriate.
- Central-line-associated bloodstream infections. Ensure your hospital has the systems in place to support the central-line insertion bundle, and that the bundle elements are followed and documented.
- Readmissions. Focus on heart failure, pneumonia, myocardial infarction, and COPD; work with nursing and case management to identify those at high risk for readmission; perform targeted interventions based on that risk (e.g. palliative care or clinical pharmacy consultation); prioritize medication reconciliation; provide timely communication of discharge summary to the next provider of care; and contact the patient soon after discharge to ensure they are following their plan of care.
- Patient satisfaction. Have a system for high performance on the questions comprising the “doctor communication” domain. These are “How often did doctors treat you with courtesy and respect/listen carefully to you/explain things in a way you could understand?”
Medicare’s Message
Clearly, the financial impacts of hospital quality, satisfaction, and safety are growing, conveying the message from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) that quality matters, making a business case for quality. Our focus as leaders in hospital systems improvement will only sharpen as we see hospital payments increasingly affected as a direct consequence of our efforts. If that doesn’t get the attention of the finance department, what will?
Dr. Whitcomb is medical director of healthcare quality at Baystate Medical Center in Springfield, Mass. He is a co-founder and past president of SHM. Email him at [email protected].
Value-Based Purchasing Model for Medicare Reimbursement Extends to Physicians
What: The program, authorized by 2010’s Affordable Care Act, extends CMS’ concept of value-based purchasing to the individual physician level. That means a portion of doctors’ Medicare reimbursements will be contingent on scores designed to measure the quality and efficiency of the healthcare they deliver.
How: The program is designed to be budget-neutral, meaning that doctors will be graded on a curve; some will lose a percentage of Medicare reimbursements, while others will gain increased payments. A prerequisite for any bonus will be participation in the Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS), which carries its own nonparticipation penalties. The PQRS forms the core of the program, with a beefed-up Physician Compare website and the Physician Feedback Program providing public and private report cards, respectively. The latter will consist of confidential Quality and Resource Use Reports (QRURs), based on information from Medicare claims and the PQRS.
Who: At first, the VBPM program will apply to groups of 100 or more eligible professionals, currently defined as physicians, practitioners, and therapists. By 2017, however, all physicians will participate. Those in rural practices, critical-access hospitals, and federally qualified health centers are exempt; ACO participants are exempt for 2015 and 2016.
What: The program, authorized by 2010’s Affordable Care Act, extends CMS’ concept of value-based purchasing to the individual physician level. That means a portion of doctors’ Medicare reimbursements will be contingent on scores designed to measure the quality and efficiency of the healthcare they deliver.
How: The program is designed to be budget-neutral, meaning that doctors will be graded on a curve; some will lose a percentage of Medicare reimbursements, while others will gain increased payments. A prerequisite for any bonus will be participation in the Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS), which carries its own nonparticipation penalties. The PQRS forms the core of the program, with a beefed-up Physician Compare website and the Physician Feedback Program providing public and private report cards, respectively. The latter will consist of confidential Quality and Resource Use Reports (QRURs), based on information from Medicare claims and the PQRS.
Who: At first, the VBPM program will apply to groups of 100 or more eligible professionals, currently defined as physicians, practitioners, and therapists. By 2017, however, all physicians will participate. Those in rural practices, critical-access hospitals, and federally qualified health centers are exempt; ACO participants are exempt for 2015 and 2016.
What: The program, authorized by 2010’s Affordable Care Act, extends CMS’ concept of value-based purchasing to the individual physician level. That means a portion of doctors’ Medicare reimbursements will be contingent on scores designed to measure the quality and efficiency of the healthcare they deliver.
How: The program is designed to be budget-neutral, meaning that doctors will be graded on a curve; some will lose a percentage of Medicare reimbursements, while others will gain increased payments. A prerequisite for any bonus will be participation in the Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS), which carries its own nonparticipation penalties. The PQRS forms the core of the program, with a beefed-up Physician Compare website and the Physician Feedback Program providing public and private report cards, respectively. The latter will consist of confidential Quality and Resource Use Reports (QRURs), based on information from Medicare claims and the PQRS.
Who: At first, the VBPM program will apply to groups of 100 or more eligible professionals, currently defined as physicians, practitioners, and therapists. By 2017, however, all physicians will participate. Those in rural practices, critical-access hospitals, and federally qualified health centers are exempt; ACO participants are exempt for 2015 and 2016.