User login
Untreated Infertility Linked to Higher Risk for Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Disease After Childbirth
TOPLINE:
The association persists even after accounting for adverse pregnancy outcomes. Women who have experienced infertility without fertility treatment show a 25% higher risk for systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease (SARD) up to 9 years after delivery, compared with those without infertility.
METHODOLOGY:
- Population-based cohort study analyzed 568,053 singleton births among 465,078 women aged 18-50 years without pre-existing SARD in Ontario, Canada, from 2012 to 2021.
- Participants were categorized into four groups: No infertility with unassisted conception (88.0%), infertility without fertility treatment (9.2%), infertility with noninvasive fertility treatment (1.4%), and infertility with invasive fertility treatment (1.4%).
- Researchers used marginal structural Cox proportional hazards models to generate hazard ratios and 95% CIs, adjusting for sociodemographic characteristics, comorbidities, smoking, and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
- Analysis included a median follow-up duration of 6.5 years (interquartile range: 4-9 years) from delivery date until SARD diagnosis, death, loss of health insurance, or study end.
TAKEAWAY:
- The incidence rate of SARD was 12.5 per 10,000 person-years in women with untreated infertility, compared with 9.3 per 10,000 person-years in women without infertility.
- Women with untreated infertility showed an elevated risk for SARD (controlled direct effect hazard ratio [HR], 1.25; 95% CI, 1.12-1.40) even after accounting for adverse pregnancy outcomes.
- Neither noninvasive fertility treatment (total effect HR, 1.06; 95% CI, 0.79-1.42) nor invasive fertility treatment (total effect HR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.69-1.36) were associated with increased SARD risk.
- The association between untreated infertility and SARD persisted in analyses restricted to women aged < 38 years and in those without endometriosis or other autoimmune diseases.
IN PRACTICE:
“Future research efforts should seek to corroborate this association by infertility cause, with a focus on possible mechanisms related to ovulatory, ovarian, and sexual dysfunction. Greater health provider awareness of SARD symptoms and related gynecological issues that may present in women with infertility could facilitate earlier detection and treatment of SARD during the reproductive years,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Natalie V. Scime of the Department of Health and Society, University of Toronto Scarborough in Ontario, Canada. It was published online in Human Reproduction.
LIMITATIONS:
Exposure and outcome misclassification was possible due to the use of published algorithms in health administrative data with unknown or imperfect sensitivity and specificity. The researchers noted that individual-level social and lifestyle factors and underlying causes of infertility were not available, and thus, were not included in the analysis.
DISCLOSURES:
This research received funding through a Banting Postdoctoral Fellowship to Scime and Canada Research Chair to Hilary K. Brown (2019-00158), with support from ICES, funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Long-Term Care. One coauthor disclosed consulting for Celltrion, Werfen, Organon, MitogenDx, AstraZeneca, Mallinckrodt Canada, and GlaxoSmithKline. All other authors reported no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The association persists even after accounting for adverse pregnancy outcomes. Women who have experienced infertility without fertility treatment show a 25% higher risk for systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease (SARD) up to 9 years after delivery, compared with those without infertility.
METHODOLOGY:
- Population-based cohort study analyzed 568,053 singleton births among 465,078 women aged 18-50 years without pre-existing SARD in Ontario, Canada, from 2012 to 2021.
- Participants were categorized into four groups: No infertility with unassisted conception (88.0%), infertility without fertility treatment (9.2%), infertility with noninvasive fertility treatment (1.4%), and infertility with invasive fertility treatment (1.4%).
- Researchers used marginal structural Cox proportional hazards models to generate hazard ratios and 95% CIs, adjusting for sociodemographic characteristics, comorbidities, smoking, and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
- Analysis included a median follow-up duration of 6.5 years (interquartile range: 4-9 years) from delivery date until SARD diagnosis, death, loss of health insurance, or study end.
TAKEAWAY:
- The incidence rate of SARD was 12.5 per 10,000 person-years in women with untreated infertility, compared with 9.3 per 10,000 person-years in women without infertility.
- Women with untreated infertility showed an elevated risk for SARD (controlled direct effect hazard ratio [HR], 1.25; 95% CI, 1.12-1.40) even after accounting for adverse pregnancy outcomes.
- Neither noninvasive fertility treatment (total effect HR, 1.06; 95% CI, 0.79-1.42) nor invasive fertility treatment (total effect HR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.69-1.36) were associated with increased SARD risk.
- The association between untreated infertility and SARD persisted in analyses restricted to women aged < 38 years and in those without endometriosis or other autoimmune diseases.
IN PRACTICE:
“Future research efforts should seek to corroborate this association by infertility cause, with a focus on possible mechanisms related to ovulatory, ovarian, and sexual dysfunction. Greater health provider awareness of SARD symptoms and related gynecological issues that may present in women with infertility could facilitate earlier detection and treatment of SARD during the reproductive years,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Natalie V. Scime of the Department of Health and Society, University of Toronto Scarborough in Ontario, Canada. It was published online in Human Reproduction.
LIMITATIONS:
Exposure and outcome misclassification was possible due to the use of published algorithms in health administrative data with unknown or imperfect sensitivity and specificity. The researchers noted that individual-level social and lifestyle factors and underlying causes of infertility were not available, and thus, were not included in the analysis.
DISCLOSURES:
This research received funding through a Banting Postdoctoral Fellowship to Scime and Canada Research Chair to Hilary K. Brown (2019-00158), with support from ICES, funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Long-Term Care. One coauthor disclosed consulting for Celltrion, Werfen, Organon, MitogenDx, AstraZeneca, Mallinckrodt Canada, and GlaxoSmithKline. All other authors reported no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The association persists even after accounting for adverse pregnancy outcomes. Women who have experienced infertility without fertility treatment show a 25% higher risk for systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease (SARD) up to 9 years after delivery, compared with those without infertility.
METHODOLOGY:
- Population-based cohort study analyzed 568,053 singleton births among 465,078 women aged 18-50 years without pre-existing SARD in Ontario, Canada, from 2012 to 2021.
- Participants were categorized into four groups: No infertility with unassisted conception (88.0%), infertility without fertility treatment (9.2%), infertility with noninvasive fertility treatment (1.4%), and infertility with invasive fertility treatment (1.4%).
- Researchers used marginal structural Cox proportional hazards models to generate hazard ratios and 95% CIs, adjusting for sociodemographic characteristics, comorbidities, smoking, and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
- Analysis included a median follow-up duration of 6.5 years (interquartile range: 4-9 years) from delivery date until SARD diagnosis, death, loss of health insurance, or study end.
TAKEAWAY:
- The incidence rate of SARD was 12.5 per 10,000 person-years in women with untreated infertility, compared with 9.3 per 10,000 person-years in women without infertility.
- Women with untreated infertility showed an elevated risk for SARD (controlled direct effect hazard ratio [HR], 1.25; 95% CI, 1.12-1.40) even after accounting for adverse pregnancy outcomes.
- Neither noninvasive fertility treatment (total effect HR, 1.06; 95% CI, 0.79-1.42) nor invasive fertility treatment (total effect HR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.69-1.36) were associated with increased SARD risk.
- The association between untreated infertility and SARD persisted in analyses restricted to women aged < 38 years and in those without endometriosis or other autoimmune diseases.
IN PRACTICE:
“Future research efforts should seek to corroborate this association by infertility cause, with a focus on possible mechanisms related to ovulatory, ovarian, and sexual dysfunction. Greater health provider awareness of SARD symptoms and related gynecological issues that may present in women with infertility could facilitate earlier detection and treatment of SARD during the reproductive years,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Natalie V. Scime of the Department of Health and Society, University of Toronto Scarborough in Ontario, Canada. It was published online in Human Reproduction.
LIMITATIONS:
Exposure and outcome misclassification was possible due to the use of published algorithms in health administrative data with unknown or imperfect sensitivity and specificity. The researchers noted that individual-level social and lifestyle factors and underlying causes of infertility were not available, and thus, were not included in the analysis.
DISCLOSURES:
This research received funding through a Banting Postdoctoral Fellowship to Scime and Canada Research Chair to Hilary K. Brown (2019-00158), with support from ICES, funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Long-Term Care. One coauthor disclosed consulting for Celltrion, Werfen, Organon, MitogenDx, AstraZeneca, Mallinckrodt Canada, and GlaxoSmithKline. All other authors reported no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PET/CT Imaging Study Reveals Differing Views on How to Manage Incidental Findings
Disparate views on managing incidental imaging findings made during clinical research — particularly for unclear results — signal a need for standardized guidance, according to recent survey results.
Respondents were split on whether it was the site primary investigator’s responsibility to decide which incidental findings should be reported back to the patient, and the most commonly cited challenges included adequately explaining these findings and the follow-up required. These issues were most present when dealing with nonspecific incidental findings or findings of unclear importance, said lead author Jane S. Kang, MD, a bioethicist and associate professor of medicine in the Division of Rheumatology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York City.
“It can be difficult to have a clear approach” when it comes to these situations that are not black and white, and it is hard to get a clear answer, she said in an interview.
The survey included responses from investigators from the Treatments Against Rheumatoid Arthritis and Effect on 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET/CT (TARGET) trial, conducted between 2015 and 2021. The 24-week trial included patients from 28 centers in the United States to investigate how different disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs can reduce cardiovascular and joint inflammation, assessed via whole body FDG PET/CT. The survey was a planned substudy of the TARGET trial and is “the first study that examines researchers’ attitudes and beliefs regarding incidental research findings from whole body FDG PET/CT,” Kang and her coauthors wrote.
This news organization reported the main results of the TARGET trial in 2022.
Eighteen of the 28 site primary investigators (PIs) of the TARGET trial participated in the survey, which was published in Arthritis Care & Research in September 2024.
TARGET Trial Incidental Findings
The TARGET trial enrolled 159 patients, of whom 82% had at least one incidental finding and 62% had one or more FDG-avid incidental findings. There were 46 “clinically actionable findings” for 40 participants overall; the reading radiologists recommended additional imaging for 28 findings and specialist consultation or procedural evaluation for 15 findings.
Details on these incidental findings were presented in a poster at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR), held in Washington, DC.
The most common non–FDG-avid findings were pulmonary nodules, diverticulosis, cholelithiasis, sinus disease, and vascular calcifications. The most common FDG-avid findings were hypermetabolic lymphadenopathy, increased gastric/esophageal uptake, increased bowel uptake, and increased pharyngeal uptake.
In the related survey, 11 respondents (61%) said they returned any incidental findings to participants and 5 (28%) did not; the remaining 2 respondents did not know.
Across all study PIs, 22% felt that incidental findings were beneficial, 39% said they were potentially beneficial, and 11% said they were potentially detrimental. PIs that ranked incidental findings as potentially detrimental pointed to how these findings led to invasive additional testing.
“One of my subjects was found to have diverticulosis, which needed an invasive procedure to rule out malignancy,” one respondent wrote. “However, the subject had already had a colonoscopy months prior to the PET findings, which was still not deemed sufficient by the nuclear radiologist and GI consultant, so he had to have another colonoscopy, which was benign, but uncomfortable.”
Obligation to Return Findings
All investigators agreed that incidental findings should be shared with patients if they revealed a high-risk medical condition that can be treated; had important health implications such as premature death or substantial morbidity; and their health could be improved with proven preventive or therapeutic interventions.
There was more disagreement on whether to share that the FDG PET/CT revealed no findings or if the test revealed a finding without clear medical importance of which the research participant may not be aware.
An example of a less-specific finding could be something like increased FDG uptake in a particular area, like the bowel, Kang explained.
“The question is: What does that mean?” she said. “How do you interpret that?”
While some PIs might feel obligated to share all results with patients, sharing ambiguous incidental findings will likely not be helpful to the patient, said Arthur Caplan, PhD, of the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University (NYU) Grossman School of Medicine, New York City.
“Dealing in unknowns and uncertainties when you’re diagnosing doesn’t really do people very much good,” he said in an interview.
While most survey respondents said they were at least moderately obligated to disclose incidental research findings if a patient requests them, Caplan noted that it was ultimately the researchers’ decision.
“Patient preferences are something to take into account, but they’re not final. If the research team says, ‘we don’t know, it’s too uncertain, it’s too new,’ then I don’t think they have any obligation to return that [information],” he said. “You can’t tell somebody what you don’t understand.”
Conversely, the clearer the incidental finding, the stronger the obligation to share that information with research participants, he continued.
Need for a Standardized Approach
The TARGET study, like many research studies, left the management of incidental imaging findings to individual research sites and investigators.
It’s possible that different sites responded to these ambiguous clinical findings in different ways, Kang noted.
“If there’s a situation that’s difficult to interpret as it is, you can imagine that the resulting actions that may result from that can vary, too,” she said, which highlights the need for more specific and standardized guidance.
One way to approach this, Caplan noted, is establishing an agreed-upon approach for dealing with any incidental findings across all research sites before a study begins.
“If there is going to be a common study at many sites, then they should have a common response on what they are going to do,” he noted, and how they will share that information effectively with the research participants to ensure it’s understandable. However, in a lot of research studies, each site has its own approach.
“Right now, it’s all over the place and that shouldn’t be,” he said.
Institutional review boards (IRBs) could be one resource to help build detailed guidance on managing unclear incidental findings in future research, wrote Kang and coauthors.
“For incidental findings from whole body FDG PET/CT that are not clearly actionable or less straightforward, IRBs may consider requiring a certain level of follow-up for different categories or types of incidental findings or require that all incidental findings are reviewed by an independent group that would provide timely recommendations on the most appropriate return and management of those findings,” Kang and colleagues wrote. “With IRB guidance, very specific and detailed policies and procedures for returning and managing incidental findings should be established for every study, with consistency among the research sites of multicenter trials.”
The TARGET trial and survey were funded by a grant from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Kang reported receiving research funding from the National Institutes of Health and the Rheumatology Research Foundation. Caplan serves as a contributing author for this news organization and served on an independent bioethics panel for compassionate drug use that was funded by Johnson & Johnson through the NYU Grossman School of Medicine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Disparate views on managing incidental imaging findings made during clinical research — particularly for unclear results — signal a need for standardized guidance, according to recent survey results.
Respondents were split on whether it was the site primary investigator’s responsibility to decide which incidental findings should be reported back to the patient, and the most commonly cited challenges included adequately explaining these findings and the follow-up required. These issues were most present when dealing with nonspecific incidental findings or findings of unclear importance, said lead author Jane S. Kang, MD, a bioethicist and associate professor of medicine in the Division of Rheumatology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York City.
“It can be difficult to have a clear approach” when it comes to these situations that are not black and white, and it is hard to get a clear answer, she said in an interview.
The survey included responses from investigators from the Treatments Against Rheumatoid Arthritis and Effect on 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET/CT (TARGET) trial, conducted between 2015 and 2021. The 24-week trial included patients from 28 centers in the United States to investigate how different disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs can reduce cardiovascular and joint inflammation, assessed via whole body FDG PET/CT. The survey was a planned substudy of the TARGET trial and is “the first study that examines researchers’ attitudes and beliefs regarding incidental research findings from whole body FDG PET/CT,” Kang and her coauthors wrote.
This news organization reported the main results of the TARGET trial in 2022.
Eighteen of the 28 site primary investigators (PIs) of the TARGET trial participated in the survey, which was published in Arthritis Care & Research in September 2024.
TARGET Trial Incidental Findings
The TARGET trial enrolled 159 patients, of whom 82% had at least one incidental finding and 62% had one or more FDG-avid incidental findings. There were 46 “clinically actionable findings” for 40 participants overall; the reading radiologists recommended additional imaging for 28 findings and specialist consultation or procedural evaluation for 15 findings.
Details on these incidental findings were presented in a poster at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR), held in Washington, DC.
The most common non–FDG-avid findings were pulmonary nodules, diverticulosis, cholelithiasis, sinus disease, and vascular calcifications. The most common FDG-avid findings were hypermetabolic lymphadenopathy, increased gastric/esophageal uptake, increased bowel uptake, and increased pharyngeal uptake.
In the related survey, 11 respondents (61%) said they returned any incidental findings to participants and 5 (28%) did not; the remaining 2 respondents did not know.
Across all study PIs, 22% felt that incidental findings were beneficial, 39% said they were potentially beneficial, and 11% said they were potentially detrimental. PIs that ranked incidental findings as potentially detrimental pointed to how these findings led to invasive additional testing.
“One of my subjects was found to have diverticulosis, which needed an invasive procedure to rule out malignancy,” one respondent wrote. “However, the subject had already had a colonoscopy months prior to the PET findings, which was still not deemed sufficient by the nuclear radiologist and GI consultant, so he had to have another colonoscopy, which was benign, but uncomfortable.”
Obligation to Return Findings
All investigators agreed that incidental findings should be shared with patients if they revealed a high-risk medical condition that can be treated; had important health implications such as premature death or substantial morbidity; and their health could be improved with proven preventive or therapeutic interventions.
There was more disagreement on whether to share that the FDG PET/CT revealed no findings or if the test revealed a finding without clear medical importance of which the research participant may not be aware.
An example of a less-specific finding could be something like increased FDG uptake in a particular area, like the bowel, Kang explained.
“The question is: What does that mean?” she said. “How do you interpret that?”
While some PIs might feel obligated to share all results with patients, sharing ambiguous incidental findings will likely not be helpful to the patient, said Arthur Caplan, PhD, of the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University (NYU) Grossman School of Medicine, New York City.
“Dealing in unknowns and uncertainties when you’re diagnosing doesn’t really do people very much good,” he said in an interview.
While most survey respondents said they were at least moderately obligated to disclose incidental research findings if a patient requests them, Caplan noted that it was ultimately the researchers’ decision.
“Patient preferences are something to take into account, but they’re not final. If the research team says, ‘we don’t know, it’s too uncertain, it’s too new,’ then I don’t think they have any obligation to return that [information],” he said. “You can’t tell somebody what you don’t understand.”
Conversely, the clearer the incidental finding, the stronger the obligation to share that information with research participants, he continued.
Need for a Standardized Approach
The TARGET study, like many research studies, left the management of incidental imaging findings to individual research sites and investigators.
It’s possible that different sites responded to these ambiguous clinical findings in different ways, Kang noted.
“If there’s a situation that’s difficult to interpret as it is, you can imagine that the resulting actions that may result from that can vary, too,” she said, which highlights the need for more specific and standardized guidance.
One way to approach this, Caplan noted, is establishing an agreed-upon approach for dealing with any incidental findings across all research sites before a study begins.
“If there is going to be a common study at many sites, then they should have a common response on what they are going to do,” he noted, and how they will share that information effectively with the research participants to ensure it’s understandable. However, in a lot of research studies, each site has its own approach.
“Right now, it’s all over the place and that shouldn’t be,” he said.
Institutional review boards (IRBs) could be one resource to help build detailed guidance on managing unclear incidental findings in future research, wrote Kang and coauthors.
“For incidental findings from whole body FDG PET/CT that are not clearly actionable or less straightforward, IRBs may consider requiring a certain level of follow-up for different categories or types of incidental findings or require that all incidental findings are reviewed by an independent group that would provide timely recommendations on the most appropriate return and management of those findings,” Kang and colleagues wrote. “With IRB guidance, very specific and detailed policies and procedures for returning and managing incidental findings should be established for every study, with consistency among the research sites of multicenter trials.”
The TARGET trial and survey were funded by a grant from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Kang reported receiving research funding from the National Institutes of Health and the Rheumatology Research Foundation. Caplan serves as a contributing author for this news organization and served on an independent bioethics panel for compassionate drug use that was funded by Johnson & Johnson through the NYU Grossman School of Medicine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Disparate views on managing incidental imaging findings made during clinical research — particularly for unclear results — signal a need for standardized guidance, according to recent survey results.
Respondents were split on whether it was the site primary investigator’s responsibility to decide which incidental findings should be reported back to the patient, and the most commonly cited challenges included adequately explaining these findings and the follow-up required. These issues were most present when dealing with nonspecific incidental findings or findings of unclear importance, said lead author Jane S. Kang, MD, a bioethicist and associate professor of medicine in the Division of Rheumatology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York City.
“It can be difficult to have a clear approach” when it comes to these situations that are not black and white, and it is hard to get a clear answer, she said in an interview.
The survey included responses from investigators from the Treatments Against Rheumatoid Arthritis and Effect on 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET/CT (TARGET) trial, conducted between 2015 and 2021. The 24-week trial included patients from 28 centers in the United States to investigate how different disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs can reduce cardiovascular and joint inflammation, assessed via whole body FDG PET/CT. The survey was a planned substudy of the TARGET trial and is “the first study that examines researchers’ attitudes and beliefs regarding incidental research findings from whole body FDG PET/CT,” Kang and her coauthors wrote.
This news organization reported the main results of the TARGET trial in 2022.
Eighteen of the 28 site primary investigators (PIs) of the TARGET trial participated in the survey, which was published in Arthritis Care & Research in September 2024.
TARGET Trial Incidental Findings
The TARGET trial enrolled 159 patients, of whom 82% had at least one incidental finding and 62% had one or more FDG-avid incidental findings. There were 46 “clinically actionable findings” for 40 participants overall; the reading radiologists recommended additional imaging for 28 findings and specialist consultation or procedural evaluation for 15 findings.
Details on these incidental findings were presented in a poster at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR), held in Washington, DC.
The most common non–FDG-avid findings were pulmonary nodules, diverticulosis, cholelithiasis, sinus disease, and vascular calcifications. The most common FDG-avid findings were hypermetabolic lymphadenopathy, increased gastric/esophageal uptake, increased bowel uptake, and increased pharyngeal uptake.
In the related survey, 11 respondents (61%) said they returned any incidental findings to participants and 5 (28%) did not; the remaining 2 respondents did not know.
Across all study PIs, 22% felt that incidental findings were beneficial, 39% said they were potentially beneficial, and 11% said they were potentially detrimental. PIs that ranked incidental findings as potentially detrimental pointed to how these findings led to invasive additional testing.
“One of my subjects was found to have diverticulosis, which needed an invasive procedure to rule out malignancy,” one respondent wrote. “However, the subject had already had a colonoscopy months prior to the PET findings, which was still not deemed sufficient by the nuclear radiologist and GI consultant, so he had to have another colonoscopy, which was benign, but uncomfortable.”
Obligation to Return Findings
All investigators agreed that incidental findings should be shared with patients if they revealed a high-risk medical condition that can be treated; had important health implications such as premature death or substantial morbidity; and their health could be improved with proven preventive or therapeutic interventions.
There was more disagreement on whether to share that the FDG PET/CT revealed no findings or if the test revealed a finding without clear medical importance of which the research participant may not be aware.
An example of a less-specific finding could be something like increased FDG uptake in a particular area, like the bowel, Kang explained.
“The question is: What does that mean?” she said. “How do you interpret that?”
While some PIs might feel obligated to share all results with patients, sharing ambiguous incidental findings will likely not be helpful to the patient, said Arthur Caplan, PhD, of the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University (NYU) Grossman School of Medicine, New York City.
“Dealing in unknowns and uncertainties when you’re diagnosing doesn’t really do people very much good,” he said in an interview.
While most survey respondents said they were at least moderately obligated to disclose incidental research findings if a patient requests them, Caplan noted that it was ultimately the researchers’ decision.
“Patient preferences are something to take into account, but they’re not final. If the research team says, ‘we don’t know, it’s too uncertain, it’s too new,’ then I don’t think they have any obligation to return that [information],” he said. “You can’t tell somebody what you don’t understand.”
Conversely, the clearer the incidental finding, the stronger the obligation to share that information with research participants, he continued.
Need for a Standardized Approach
The TARGET study, like many research studies, left the management of incidental imaging findings to individual research sites and investigators.
It’s possible that different sites responded to these ambiguous clinical findings in different ways, Kang noted.
“If there’s a situation that’s difficult to interpret as it is, you can imagine that the resulting actions that may result from that can vary, too,” she said, which highlights the need for more specific and standardized guidance.
One way to approach this, Caplan noted, is establishing an agreed-upon approach for dealing with any incidental findings across all research sites before a study begins.
“If there is going to be a common study at many sites, then they should have a common response on what they are going to do,” he noted, and how they will share that information effectively with the research participants to ensure it’s understandable. However, in a lot of research studies, each site has its own approach.
“Right now, it’s all over the place and that shouldn’t be,” he said.
Institutional review boards (IRBs) could be one resource to help build detailed guidance on managing unclear incidental findings in future research, wrote Kang and coauthors.
“For incidental findings from whole body FDG PET/CT that are not clearly actionable or less straightforward, IRBs may consider requiring a certain level of follow-up for different categories or types of incidental findings or require that all incidental findings are reviewed by an independent group that would provide timely recommendations on the most appropriate return and management of those findings,” Kang and colleagues wrote. “With IRB guidance, very specific and detailed policies and procedures for returning and managing incidental findings should be established for every study, with consistency among the research sites of multicenter trials.”
The TARGET trial and survey were funded by a grant from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Kang reported receiving research funding from the National Institutes of Health and the Rheumatology Research Foundation. Caplan serves as a contributing author for this news organization and served on an independent bioethics panel for compassionate drug use that was funded by Johnson & Johnson through the NYU Grossman School of Medicine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ARTHRITIS CARE & RESEARCH
RA Assessment Via Automated Ultrasound Scanner With AI Saves Time, Performs as Well as Rheumatologists
WASHINGTON — A fully automated ultrasound scanning system combined with artificial intelligence–based disease activity scoring performed as well as expert rheumatologists in hand joint assessment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), new research found.
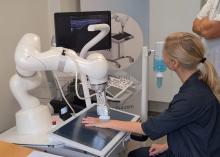
The system, made by a Danish company called ROPCA, comprises an ultrasound scanner called ARTHUR (RA Ultrasound Robot) that interacts directly with the patient and scans 11 joints per hand and a neural network–based software system, DIANA (Diagnosis Aid Network for RA), that evaluates the images and monitors RA activity.
The combined system classifies the degree of RA according to the joint European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR)–Outcome Measures in Rheumatology (OMERACT) standards for RA diagnosis. It received a CE Mark in Europe in 2022 and is currently in use in six rheumatology clinics in Denmark, Germany, Switzerland, and Austria, with more to come, ROPCA Co-founder and Chief Medical Officer Søren A. Just, MD, said in an interview.
“Automated systems could help rheumatologists in the early detection and monitoring of arthritis diseases. Systems can be placed or move in areas with insufficient rheumatological expertise,” Just said during a special late-breaker session presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
He said in an interview: “Currently, there are so many people referred and few and fewer rheumatologists. So we need to think differently. We need good automated assistants.” As a screening tool, the system can determine whether a person with hand pain has RA or just osteoarthritis “and also can give the patient an immediate answer, instead of waiting sometimes up to 6 months to get the information.”
Just, who is also a senior physician in the Department of Internal Medicine at Odense University Hospital in Denmark, said that his department is also using the system to assess flares in patients with established RA. “They can have a blood sample taken. They’re scanned by the robot, and you can see if there is any disease activity. But I think that screening of patients with joint pain is the beginning.”
Asked to comment, session moderator Gregory C. Gardner, MD, Emeritus Professor in the Division of Rheumatology at the University of Washington, Seattle, and a member of the ACR conference program committee, said in an interview “one of the reasons we chose to feature this abstract is because we’re interested in science at the convergence. We really thought this was a potential way to move the field forward for rheumatologists.”
Gardner said it’s an advantage that the patient could potentially have an ARTHUR scan with a DIANA report and get blood tests done prior to a visit with the rheumatologist. “It’s really time-consuming for a human to do these studies, so if you automate it, that’s a step forward in terms of having the data available for the rheumatologist to view and use sequentially to follow how patients are doing.”
When introducing Just’s presentation, Gardner called it “the coolest abstract of the meeting.”
Both DIANA and ARTHUR Performed At Least as Well as Human Rheumatologists
In the study, 30 patients with RA underwent two scans by ARTHUR, followed by a scan from a rheumatologist specialist in musculoskeletal ultrasound. The scans were sent to DIANA, who graded the images according to the Global OMERACT-EULAR Synovitis Score, as did the human rheumatologist.
A “ground truth” was established by another human expert who evaluated both ARTHUR’s and the other rheumatologist’s images, blinded to the scanning method. The image with the highest disease activity was deemed “ground truth,” and agreement with that was assessed for the two individual methods.
Just showed a video of a patient being scanned by ARTHUR. The machine verbally guided her through removing her jewelry, applying the gel, and placing her hand on the screen under the scanner. ARTHUR’s arm moved around on the patient’s hand, locating the best angles to take grayscale images and Doppler images and Doppler video. The scan takes 15-20 minutes, and the images are stored, Just said.
The study patients had a mean age of 65 years, and 23 of the 30 were men. Their average disease duration was 11 years, and mean Disease Activity Score in 28 joints using C-reactive protein was 3.86, indicating moderate disease. A majority (73%) of patients were taking disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, and about one third were taking biologics. ARTHUR scanned a total of 660 joints, and 564 scans were successful.
For repeatability between the two ARTHUR scans, percent exact agreement was 63% for synovial hypertrophy, 75% for Doppler activity, and 60% combined. Percent close (within a point) agreements were 93%, 94%, and 92%, respectively. Binary agreements as to whether the joint was healthy vs diseased were 88%, 91%, and 85%, respectively.
At the joint level, ARTHUR and DIANA’s percent exact agreement with ground truth was 49% for synovial hypertrophy, 63% for Doppler activity, and 48% combined. Binary agreements with disease vs healthy were 80%, 88%, and 78%, respectively.
The human rheumatologists scored very similarly. Percent exact agreement with ground truth was 51% for synovial hypertrophy, 64% for Doppler activity, and 50% combined. Percent close agreements were 94%, 94%, and 92%, respectively. And binary agreements with diseased vs healthy were 83%, 91%, and 80%, respectively.
At the patient level (all joints combined), ARTHUR and DIANA’s binary disease assessment of healthy vs disease showed agreement with the ground truth of 87% for synovial hypertrophy, 83% for Doppler activity, and 87% combined. Here, the rheumatologists scored lower, at 53%, 67%, and 60%, respectively.
“In this study, we think the precision of ARTHUR and DIANA was comparable to that of an experienced rheumatologist, at both the joint and patient level,” Just said.
Gardner pointed out another advantage of the system. “DIANA doesn’t get fatigued. ... With human reading, the precision may change based on the time of day or stress level. ... But with DIANA, you’re going to get consistent information.”
Just said that the Arthritis Foundation in Germany recently put ARTHUR and DIANA on a bus and took it to cities that lacked a rheumatologist. Patients lined up, answered a questionnaire, had blood drawn, and received their scans. A rheumatologist on the bus then interpreted the data and consulted with the individuals about their RA risk. “In the last trip, we screened 800 patients in 6 days. So there are definitely possibilities here.”
Just is co-owner of ROPCA. Gardner had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — A fully automated ultrasound scanning system combined with artificial intelligence–based disease activity scoring performed as well as expert rheumatologists in hand joint assessment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), new research found.
The system, made by a Danish company called ROPCA, comprises an ultrasound scanner called ARTHUR (RA Ultrasound Robot) that interacts directly with the patient and scans 11 joints per hand and a neural network–based software system, DIANA (Diagnosis Aid Network for RA), that evaluates the images and monitors RA activity.
The combined system classifies the degree of RA according to the joint European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR)–Outcome Measures in Rheumatology (OMERACT) standards for RA diagnosis. It received a CE Mark in Europe in 2022 and is currently in use in six rheumatology clinics in Denmark, Germany, Switzerland, and Austria, with more to come, ROPCA Co-founder and Chief Medical Officer Søren A. Just, MD, said in an interview.
“Automated systems could help rheumatologists in the early detection and monitoring of arthritis diseases. Systems can be placed or move in areas with insufficient rheumatological expertise,” Just said during a special late-breaker session presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
He said in an interview: “Currently, there are so many people referred and few and fewer rheumatologists. So we need to think differently. We need good automated assistants.” As a screening tool, the system can determine whether a person with hand pain has RA or just osteoarthritis “and also can give the patient an immediate answer, instead of waiting sometimes up to 6 months to get the information.”
Just, who is also a senior physician in the Department of Internal Medicine at Odense University Hospital in Denmark, said that his department is also using the system to assess flares in patients with established RA. “They can have a blood sample taken. They’re scanned by the robot, and you can see if there is any disease activity. But I think that screening of patients with joint pain is the beginning.”
Asked to comment, session moderator Gregory C. Gardner, MD, Emeritus Professor in the Division of Rheumatology at the University of Washington, Seattle, and a member of the ACR conference program committee, said in an interview “one of the reasons we chose to feature this abstract is because we’re interested in science at the convergence. We really thought this was a potential way to move the field forward for rheumatologists.”
Gardner said it’s an advantage that the patient could potentially have an ARTHUR scan with a DIANA report and get blood tests done prior to a visit with the rheumatologist. “It’s really time-consuming for a human to do these studies, so if you automate it, that’s a step forward in terms of having the data available for the rheumatologist to view and use sequentially to follow how patients are doing.”
When introducing Just’s presentation, Gardner called it “the coolest abstract of the meeting.”
Both DIANA and ARTHUR Performed At Least as Well as Human Rheumatologists
In the study, 30 patients with RA underwent two scans by ARTHUR, followed by a scan from a rheumatologist specialist in musculoskeletal ultrasound. The scans were sent to DIANA, who graded the images according to the Global OMERACT-EULAR Synovitis Score, as did the human rheumatologist.
A “ground truth” was established by another human expert who evaluated both ARTHUR’s and the other rheumatologist’s images, blinded to the scanning method. The image with the highest disease activity was deemed “ground truth,” and agreement with that was assessed for the two individual methods.
Just showed a video of a patient being scanned by ARTHUR. The machine verbally guided her through removing her jewelry, applying the gel, and placing her hand on the screen under the scanner. ARTHUR’s arm moved around on the patient’s hand, locating the best angles to take grayscale images and Doppler images and Doppler video. The scan takes 15-20 minutes, and the images are stored, Just said.
The study patients had a mean age of 65 years, and 23 of the 30 were men. Their average disease duration was 11 years, and mean Disease Activity Score in 28 joints using C-reactive protein was 3.86, indicating moderate disease. A majority (73%) of patients were taking disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, and about one third were taking biologics. ARTHUR scanned a total of 660 joints, and 564 scans were successful.
For repeatability between the two ARTHUR scans, percent exact agreement was 63% for synovial hypertrophy, 75% for Doppler activity, and 60% combined. Percent close (within a point) agreements were 93%, 94%, and 92%, respectively. Binary agreements as to whether the joint was healthy vs diseased were 88%, 91%, and 85%, respectively.
At the joint level, ARTHUR and DIANA’s percent exact agreement with ground truth was 49% for synovial hypertrophy, 63% for Doppler activity, and 48% combined. Binary agreements with disease vs healthy were 80%, 88%, and 78%, respectively.
The human rheumatologists scored very similarly. Percent exact agreement with ground truth was 51% for synovial hypertrophy, 64% for Doppler activity, and 50% combined. Percent close agreements were 94%, 94%, and 92%, respectively. And binary agreements with diseased vs healthy were 83%, 91%, and 80%, respectively.
At the patient level (all joints combined), ARTHUR and DIANA’s binary disease assessment of healthy vs disease showed agreement with the ground truth of 87% for synovial hypertrophy, 83% for Doppler activity, and 87% combined. Here, the rheumatologists scored lower, at 53%, 67%, and 60%, respectively.
“In this study, we think the precision of ARTHUR and DIANA was comparable to that of an experienced rheumatologist, at both the joint and patient level,” Just said.
Gardner pointed out another advantage of the system. “DIANA doesn’t get fatigued. ... With human reading, the precision may change based on the time of day or stress level. ... But with DIANA, you’re going to get consistent information.”
Just said that the Arthritis Foundation in Germany recently put ARTHUR and DIANA on a bus and took it to cities that lacked a rheumatologist. Patients lined up, answered a questionnaire, had blood drawn, and received their scans. A rheumatologist on the bus then interpreted the data and consulted with the individuals about their RA risk. “In the last trip, we screened 800 patients in 6 days. So there are definitely possibilities here.”
Just is co-owner of ROPCA. Gardner had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — A fully automated ultrasound scanning system combined with artificial intelligence–based disease activity scoring performed as well as expert rheumatologists in hand joint assessment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), new research found.
The system, made by a Danish company called ROPCA, comprises an ultrasound scanner called ARTHUR (RA Ultrasound Robot) that interacts directly with the patient and scans 11 joints per hand and a neural network–based software system, DIANA (Diagnosis Aid Network for RA), that evaluates the images and monitors RA activity.
The combined system classifies the degree of RA according to the joint European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR)–Outcome Measures in Rheumatology (OMERACT) standards for RA diagnosis. It received a CE Mark in Europe in 2022 and is currently in use in six rheumatology clinics in Denmark, Germany, Switzerland, and Austria, with more to come, ROPCA Co-founder and Chief Medical Officer Søren A. Just, MD, said in an interview.
“Automated systems could help rheumatologists in the early detection and monitoring of arthritis diseases. Systems can be placed or move in areas with insufficient rheumatological expertise,” Just said during a special late-breaker session presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
He said in an interview: “Currently, there are so many people referred and few and fewer rheumatologists. So we need to think differently. We need good automated assistants.” As a screening tool, the system can determine whether a person with hand pain has RA or just osteoarthritis “and also can give the patient an immediate answer, instead of waiting sometimes up to 6 months to get the information.”
Just, who is also a senior physician in the Department of Internal Medicine at Odense University Hospital in Denmark, said that his department is also using the system to assess flares in patients with established RA. “They can have a blood sample taken. They’re scanned by the robot, and you can see if there is any disease activity. But I think that screening of patients with joint pain is the beginning.”
Asked to comment, session moderator Gregory C. Gardner, MD, Emeritus Professor in the Division of Rheumatology at the University of Washington, Seattle, and a member of the ACR conference program committee, said in an interview “one of the reasons we chose to feature this abstract is because we’re interested in science at the convergence. We really thought this was a potential way to move the field forward for rheumatologists.”
Gardner said it’s an advantage that the patient could potentially have an ARTHUR scan with a DIANA report and get blood tests done prior to a visit with the rheumatologist. “It’s really time-consuming for a human to do these studies, so if you automate it, that’s a step forward in terms of having the data available for the rheumatologist to view and use sequentially to follow how patients are doing.”
When introducing Just’s presentation, Gardner called it “the coolest abstract of the meeting.”
Both DIANA and ARTHUR Performed At Least as Well as Human Rheumatologists
In the study, 30 patients with RA underwent two scans by ARTHUR, followed by a scan from a rheumatologist specialist in musculoskeletal ultrasound. The scans were sent to DIANA, who graded the images according to the Global OMERACT-EULAR Synovitis Score, as did the human rheumatologist.
A “ground truth” was established by another human expert who evaluated both ARTHUR’s and the other rheumatologist’s images, blinded to the scanning method. The image with the highest disease activity was deemed “ground truth,” and agreement with that was assessed for the two individual methods.
Just showed a video of a patient being scanned by ARTHUR. The machine verbally guided her through removing her jewelry, applying the gel, and placing her hand on the screen under the scanner. ARTHUR’s arm moved around on the patient’s hand, locating the best angles to take grayscale images and Doppler images and Doppler video. The scan takes 15-20 minutes, and the images are stored, Just said.
The study patients had a mean age of 65 years, and 23 of the 30 were men. Their average disease duration was 11 years, and mean Disease Activity Score in 28 joints using C-reactive protein was 3.86, indicating moderate disease. A majority (73%) of patients were taking disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, and about one third were taking biologics. ARTHUR scanned a total of 660 joints, and 564 scans were successful.
For repeatability between the two ARTHUR scans, percent exact agreement was 63% for synovial hypertrophy, 75% for Doppler activity, and 60% combined. Percent close (within a point) agreements were 93%, 94%, and 92%, respectively. Binary agreements as to whether the joint was healthy vs diseased were 88%, 91%, and 85%, respectively.
At the joint level, ARTHUR and DIANA’s percent exact agreement with ground truth was 49% for synovial hypertrophy, 63% for Doppler activity, and 48% combined. Binary agreements with disease vs healthy were 80%, 88%, and 78%, respectively.
The human rheumatologists scored very similarly. Percent exact agreement with ground truth was 51% for synovial hypertrophy, 64% for Doppler activity, and 50% combined. Percent close agreements were 94%, 94%, and 92%, respectively. And binary agreements with diseased vs healthy were 83%, 91%, and 80%, respectively.
At the patient level (all joints combined), ARTHUR and DIANA’s binary disease assessment of healthy vs disease showed agreement with the ground truth of 87% for synovial hypertrophy, 83% for Doppler activity, and 87% combined. Here, the rheumatologists scored lower, at 53%, 67%, and 60%, respectively.
“In this study, we think the precision of ARTHUR and DIANA was comparable to that of an experienced rheumatologist, at both the joint and patient level,” Just said.
Gardner pointed out another advantage of the system. “DIANA doesn’t get fatigued. ... With human reading, the precision may change based on the time of day or stress level. ... But with DIANA, you’re going to get consistent information.”
Just said that the Arthritis Foundation in Germany recently put ARTHUR and DIANA on a bus and took it to cities that lacked a rheumatologist. Patients lined up, answered a questionnaire, had blood drawn, and received their scans. A rheumatologist on the bus then interpreted the data and consulted with the individuals about their RA risk. “In the last trip, we screened 800 patients in 6 days. So there are definitely possibilities here.”
Just is co-owner of ROPCA. Gardner had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACR 2024
Cancer Mortality Not Higher for Patients With Autoimmune Disease on Checkpoint Inhibitors
WASHINGTON — Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy does not increase mortality in people with preexisting autoimmune diseases, new research has found.
Results from a large database analysis of patients with and without autoimmune diseases suggest it is safe to treat them with ICI if they develop a cancer for which it is indicated, Greg Challener, MD, a postdoctoral fellow at the Rheumatology and Allergy Clinical Epidemiology Research Center, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said at the American College of Rheumatology 2024 Annual Meeting.
“One message is that, when rheumatologists are asked by oncologists about patients with rheumatoid arthritis or vasculitis or other autoimmune diseases and whether it’s safe to treat them with immune checkpoint inhibitors, this result provides some evidence that it probably is safe…. Checkpoint inhibitors are really incredible drugs, and they’ve improved mortality for a lot of cancers, particularly melanoma, and so I think there should be a pretty high threshold for us to say a patient shouldn’t receive them because of an autoimmune condition,” he told this news organization.
Another implication, Challener said, is that people with autoimmune diseases shouldn’t routinely be excluded from clinical trials of ICIs. Currently they are excluded because of concerns about exacerbation of underlying autoimmunity, possible interference between the ICI and the immunosuppressive drugs used to treat the autoimmune condition, and a theoretical risk for serious adverse events.
“Clinical trials are continuing to exclude these patients, and they paint with a very broad brush anyone with underlying autoimmunity ... I’m hoping that that changes. I don’t think there’s a great evidence base to support that practice, and it’s unfortunate that patients with underlying autoimmune diseases are excluded from important studies,” Challener said.
Asked to comment, session moderator Matlock Jeffries, MD, director of the Arthritis Research Unit at the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation, Oklahoma City, told this news organization that he agrees the data are generally reassuring. “If one of our patients gets cancer and their oncologist wants to use a checkpoint inhibitor, we’d obviously still monitor them for complications, but we wouldn’t automatically assume the combination of a checkpoint inhibitor and autoimmune disease would increase their mortality.”
No Difference in Mortality for Those With and Without Autoimmune Disease
Challener and colleagues used administrative health data from the TriNetX Diamond network of 92 US healthcare sites with 212 million patients. All patients included in the study were receiving anti-programmed death protein 1/programmed death ligand 1 to treat malignancies involving the skin, lung/bronchus, digestive organs, or urinary tract. The study population also had at least one rheumatologic, gastrointestinal, neurologic, dermatologic, or endocrine autoimmune disease.
Propensity score matching between those with and without autoimmune disease was performed for about 100 covariates. Prior to the matching, the autoimmune disease group had significantly higher rates of cardiovascular and other comorbidities. The matching yielded 23,714 individuals with autoimmune disease and the same number without who had similar demographics and comorbidity rates, as well as malignancy type, alcohol/tobacco use, and medication use.
At a median follow-up of 250 days, the risk for mortality prior to propensity matching was 40.0% in the autoimmune disease group and 38.1% for those without, a significant difference with hazard ratio 1.07 (95% CI, 1.05-1.10). But after the matching, the difference was no longer significant: 39.8% vs 40.2%, respectively (0.97, 0.94-1.00).
The Kaplan-Meier curves for survival probability for those with or without autoimmune disease were nearly superimposed, showing no difference up to 1600 days. An analysis of just the patients with rheumatic diseases yielded similar results, Challener said.
Some Caveats About the Data
Jeffries, who is also an associate professor of medicine at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, and the Oklahoma VA, said he would like to see additional data on outcomes, both for the autoimmune conditions and the cancers. Challener said there are plans to look at other hard endpoints such as myocardial infarction and end-stage renal disease, but that the database is limited.
Both Challener and Jeffries also cautioned that the reassurance may not apply to patients with active disease.
“One thing this research doesn’t address is whether active autoimmune disease might have a different outcome compared to more kind of quiet disease…. If you have a patient who has extremely active rheumatoid arthritis or extremely active giant cell arthritis, for instance, I think that could be more challenging. I would be frightened to put a patient with really active GCA on pembrolizumab or say that it’s safe without their disease being controlled. But for someone who has well-controlled disease or minimally active disease, this is very reassuring,” Challener told this news organization.
“I think this may also be important in that it’s a good argument to tell the drug companies to include autoimmune patients in these trials so we can get better data,” Jeffries said.
Challener and Jeffries had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy does not increase mortality in people with preexisting autoimmune diseases, new research has found.
Results from a large database analysis of patients with and without autoimmune diseases suggest it is safe to treat them with ICI if they develop a cancer for which it is indicated, Greg Challener, MD, a postdoctoral fellow at the Rheumatology and Allergy Clinical Epidemiology Research Center, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said at the American College of Rheumatology 2024 Annual Meeting.
“One message is that, when rheumatologists are asked by oncologists about patients with rheumatoid arthritis or vasculitis or other autoimmune diseases and whether it’s safe to treat them with immune checkpoint inhibitors, this result provides some evidence that it probably is safe…. Checkpoint inhibitors are really incredible drugs, and they’ve improved mortality for a lot of cancers, particularly melanoma, and so I think there should be a pretty high threshold for us to say a patient shouldn’t receive them because of an autoimmune condition,” he told this news organization.
Another implication, Challener said, is that people with autoimmune diseases shouldn’t routinely be excluded from clinical trials of ICIs. Currently they are excluded because of concerns about exacerbation of underlying autoimmunity, possible interference between the ICI and the immunosuppressive drugs used to treat the autoimmune condition, and a theoretical risk for serious adverse events.
“Clinical trials are continuing to exclude these patients, and they paint with a very broad brush anyone with underlying autoimmunity ... I’m hoping that that changes. I don’t think there’s a great evidence base to support that practice, and it’s unfortunate that patients with underlying autoimmune diseases are excluded from important studies,” Challener said.
Asked to comment, session moderator Matlock Jeffries, MD, director of the Arthritis Research Unit at the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation, Oklahoma City, told this news organization that he agrees the data are generally reassuring. “If one of our patients gets cancer and their oncologist wants to use a checkpoint inhibitor, we’d obviously still monitor them for complications, but we wouldn’t automatically assume the combination of a checkpoint inhibitor and autoimmune disease would increase their mortality.”
No Difference in Mortality for Those With and Without Autoimmune Disease
Challener and colleagues used administrative health data from the TriNetX Diamond network of 92 US healthcare sites with 212 million patients. All patients included in the study were receiving anti-programmed death protein 1/programmed death ligand 1 to treat malignancies involving the skin, lung/bronchus, digestive organs, or urinary tract. The study population also had at least one rheumatologic, gastrointestinal, neurologic, dermatologic, or endocrine autoimmune disease.
Propensity score matching between those with and without autoimmune disease was performed for about 100 covariates. Prior to the matching, the autoimmune disease group had significantly higher rates of cardiovascular and other comorbidities. The matching yielded 23,714 individuals with autoimmune disease and the same number without who had similar demographics and comorbidity rates, as well as malignancy type, alcohol/tobacco use, and medication use.
At a median follow-up of 250 days, the risk for mortality prior to propensity matching was 40.0% in the autoimmune disease group and 38.1% for those without, a significant difference with hazard ratio 1.07 (95% CI, 1.05-1.10). But after the matching, the difference was no longer significant: 39.8% vs 40.2%, respectively (0.97, 0.94-1.00).
The Kaplan-Meier curves for survival probability for those with or without autoimmune disease were nearly superimposed, showing no difference up to 1600 days. An analysis of just the patients with rheumatic diseases yielded similar results, Challener said.
Some Caveats About the Data
Jeffries, who is also an associate professor of medicine at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, and the Oklahoma VA, said he would like to see additional data on outcomes, both for the autoimmune conditions and the cancers. Challener said there are plans to look at other hard endpoints such as myocardial infarction and end-stage renal disease, but that the database is limited.
Both Challener and Jeffries also cautioned that the reassurance may not apply to patients with active disease.
“One thing this research doesn’t address is whether active autoimmune disease might have a different outcome compared to more kind of quiet disease…. If you have a patient who has extremely active rheumatoid arthritis or extremely active giant cell arthritis, for instance, I think that could be more challenging. I would be frightened to put a patient with really active GCA on pembrolizumab or say that it’s safe without their disease being controlled. But for someone who has well-controlled disease or minimally active disease, this is very reassuring,” Challener told this news organization.
“I think this may also be important in that it’s a good argument to tell the drug companies to include autoimmune patients in these trials so we can get better data,” Jeffries said.
Challener and Jeffries had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy does not increase mortality in people with preexisting autoimmune diseases, new research has found.
Results from a large database analysis of patients with and without autoimmune diseases suggest it is safe to treat them with ICI if they develop a cancer for which it is indicated, Greg Challener, MD, a postdoctoral fellow at the Rheumatology and Allergy Clinical Epidemiology Research Center, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said at the American College of Rheumatology 2024 Annual Meeting.
“One message is that, when rheumatologists are asked by oncologists about patients with rheumatoid arthritis or vasculitis or other autoimmune diseases and whether it’s safe to treat them with immune checkpoint inhibitors, this result provides some evidence that it probably is safe…. Checkpoint inhibitors are really incredible drugs, and they’ve improved mortality for a lot of cancers, particularly melanoma, and so I think there should be a pretty high threshold for us to say a patient shouldn’t receive them because of an autoimmune condition,” he told this news organization.
Another implication, Challener said, is that people with autoimmune diseases shouldn’t routinely be excluded from clinical trials of ICIs. Currently they are excluded because of concerns about exacerbation of underlying autoimmunity, possible interference between the ICI and the immunosuppressive drugs used to treat the autoimmune condition, and a theoretical risk for serious adverse events.
“Clinical trials are continuing to exclude these patients, and they paint with a very broad brush anyone with underlying autoimmunity ... I’m hoping that that changes. I don’t think there’s a great evidence base to support that practice, and it’s unfortunate that patients with underlying autoimmune diseases are excluded from important studies,” Challener said.
Asked to comment, session moderator Matlock Jeffries, MD, director of the Arthritis Research Unit at the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation, Oklahoma City, told this news organization that he agrees the data are generally reassuring. “If one of our patients gets cancer and their oncologist wants to use a checkpoint inhibitor, we’d obviously still monitor them for complications, but we wouldn’t automatically assume the combination of a checkpoint inhibitor and autoimmune disease would increase their mortality.”
No Difference in Mortality for Those With and Without Autoimmune Disease
Challener and colleagues used administrative health data from the TriNetX Diamond network of 92 US healthcare sites with 212 million patients. All patients included in the study were receiving anti-programmed death protein 1/programmed death ligand 1 to treat malignancies involving the skin, lung/bronchus, digestive organs, or urinary tract. The study population also had at least one rheumatologic, gastrointestinal, neurologic, dermatologic, or endocrine autoimmune disease.
Propensity score matching between those with and without autoimmune disease was performed for about 100 covariates. Prior to the matching, the autoimmune disease group had significantly higher rates of cardiovascular and other comorbidities. The matching yielded 23,714 individuals with autoimmune disease and the same number without who had similar demographics and comorbidity rates, as well as malignancy type, alcohol/tobacco use, and medication use.
At a median follow-up of 250 days, the risk for mortality prior to propensity matching was 40.0% in the autoimmune disease group and 38.1% for those without, a significant difference with hazard ratio 1.07 (95% CI, 1.05-1.10). But after the matching, the difference was no longer significant: 39.8% vs 40.2%, respectively (0.97, 0.94-1.00).
The Kaplan-Meier curves for survival probability for those with or without autoimmune disease were nearly superimposed, showing no difference up to 1600 days. An analysis of just the patients with rheumatic diseases yielded similar results, Challener said.
Some Caveats About the Data
Jeffries, who is also an associate professor of medicine at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, and the Oklahoma VA, said he would like to see additional data on outcomes, both for the autoimmune conditions and the cancers. Challener said there are plans to look at other hard endpoints such as myocardial infarction and end-stage renal disease, but that the database is limited.
Both Challener and Jeffries also cautioned that the reassurance may not apply to patients with active disease.
“One thing this research doesn’t address is whether active autoimmune disease might have a different outcome compared to more kind of quiet disease…. If you have a patient who has extremely active rheumatoid arthritis or extremely active giant cell arthritis, for instance, I think that could be more challenging. I would be frightened to put a patient with really active GCA on pembrolizumab or say that it’s safe without their disease being controlled. But for someone who has well-controlled disease or minimally active disease, this is very reassuring,” Challener told this news organization.
“I think this may also be important in that it’s a good argument to tell the drug companies to include autoimmune patients in these trials so we can get better data,” Jeffries said.
Challener and Jeffries had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACR 2024
Successful Phase 3 Vagus Nerve Stimulation Trial May Open Up New Therapeutic Avenue in RA
WASHINGTON — An implantable vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) device effectively treats moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in patients who had previously failed at least one biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (b/tsDMARD), according to results from a phase 3 trial.
Of the 242 patients in the RESET-RA study, all received the VNS device implant but were blinded as to whether the device was turned on. At 12 weeks, 35.2% of patients receiving daily stimulation achieved 20% improvement in American College of Rheumatology response criteria (ACR20) compared with 24.2% of those with an inactive device. The response was more pronounced among patients with exposure to only one prior b/tsDMARD. A greater proportion of patients in the overall treatment group also reached low disease activity or remission compared with those who did not receive stimulation.
The research was presented as a late-breaking poster at the ACR 2024 Annual Meeting.
“This is a particularly tough-to-treat patient population, since the patients enrolled were considered refractory to biologic therapy,” said Elena Schiopu, MD, professor of medicine in the Division of Rheumatology and director of clinical trials at the Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University. More than one third of patients in the study had tried three or more b/tsDMARDs prior to the study. “I’m pretty excited about these results,” she added. Schiopu was a RESET-RA institutional principal investigator and enrolled two patients in the trial.
These positive results are a first for VNS treatment in rheumatic diseases. Previous studies demonstrating the potential therapeutic effect of this implant approach have largely been open-label, proof-of-concept, or pilot studies. Noninvasive, wearable stimulation devices have also shown promise in open-label studies; however, a sham-controlled trial published in 2023 showed that transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation on the ear was no more effective than placebo.
But How Does It Work?
The device, developed by SetPoint Medical in Valencia, California, is about the size of a multivitamin and implanted in an outpatient setting. During the 45-minute procedure, surgeons isolate the vagus nerve on the left side of the neck and place the nerve stimulator with a silicone positioning pod to hold it in place.
The device is programmed to deliver stimulation for 1 minute every day and needs charging for only 10 minutes once a week, which is done remotely with a necklace.
The device takes advantage of the vagus nerve’s anti-inflammatory properties, stimulating the nerve to help regulate an overactive immune system of someone with RA, explained David Chernoff, MD, Setpoint Medical’s chief medical officer.
“We’re recapitulating what nature has developed over millions of years, which is the nexus between the brain and the immune system, which happens to be mediated by the vagus nerve,” he told Medscape Medical News.
This novel VNS approach also does not have the same immunosuppressive safety concerns as drugs commonly used to treat RA, he said.
“We’re able to adjust the amount of inflammation, but we don’t cause the host defense issues” that are present with some of these drugs, he continued.
SetPoint Medical’s pilot study of the device in 14 patients showed promising results. Five of 10 patients randomly assigned to active VNS over 12 weeks showed clinical improvements, measured by 28-joint Disease Activity Score based on C-reactive protein (DAS28-CRP) and the Clinical Disease Activity Index. In the remaining four patients who received sham stimulation — where the device was implanted but not activated — there were no clinical disease improvements.
RESET-RA Details
The most recent, much larger phase 3 study enrolled patients from 41 sites in the United States. Patients were on average 56 years old and had a body mass index of 30; 86% were women. A total of 39% had previously tried one b/tsDMARD, 22% had tried two, and 39% had tried three or more. Patients, on average, had 15 tender joints and 10 swollen joints. Patients discontinued their prior b/tsDMARD before the procedure and remained on conventional DMARDS during the trial, including methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, and sulfasalazine.
The researchers randomly assigned patients 1:1 to active (treatment) or nonactive (control) stimulation.
“The perception of stimulation varies from patient to patient, which itself is helpful in blinding as there is no expected perception of whether or how stimulation will be felt,” Chernoff explained. The 1-minute stimulation was scheduled in the early hours of the morning, when a patient typically would be asleep, he said.
Patients were excluded from the analysis if they were rescued by steroids or b/tsDMARDs through week 12. After week 12, the control group was switched to stimulation and efficacy was reassessed at week 24.
Higher ACR20 Response Rate, Lower Disease Activity
Beyond meeting the primary endpoint of ACR20 response, patients on the active stimulation group showed lower disease activity at week 12. Compared with 15.8% of patients in the control group, 27% of those in the treatment group achieved a DAS28-CRP ≤ 3.2.
The active stimulation was particularly effective in patients who had experience with only one prior b/tsDMARD. In this subset of patients, 44.2% in the treatment group achieved ACR20 compared with 19.0% in the control group.
During this sham-controlled trial period, 13.1% of patients in the treatment group and 18.3% of patients in the control group reported an adverse event (AE) related to the procedure or device, most commonly vocal cord paresis or dysphonia. In the treatment group, 8.2% reported stimulation-related AEs, most commonly mild/moderate pain that was managed by adjusting the stimulation level.
Serious adverse events (SAEs) were relatively rare, with four treatment-related SAEs across both study groups. No AEs led to study discontinuation through week 24.
The 12-week results mirror those of the initial Humira and Enbrel trials in the late 1990s and early 2000s, Schiopu said, although in those trials, the patients were naive to biologics, and some were naive to methotrexate. A more appropriate comparison, she said, would be biologic-experienced populations.
At week 24, the percentage of patients achieving ACR20 further increased to 51.5% in the treatment group and to 53.1% in the previous control group who were now crossed over to active stimulation. In this secondary period, patients could add any additional therapies like steroids or b/tsDMARDs. At 24 weeks, 81% of patients remained on stimulation without needing additional medication, beyond their continued background DMARDs.
The results also show “a continuum of improvement over time,” Schiopu said, where response rates climbed through week 24.
Schiopu is particularly excited about the potential to use this stimulation device in older patients, who have perhaps been on immunosuppressant drugs for decades.
“Aside from being chronically immunosuppressed, their immune system is more tired [due to age],” she said. With VNS therapies like SetPoint’s, “we could offer [these patients] a lesser immunosuppressive alternative that is still immune-modular enough to manage their RA.”
Schiopu is a consultant for Johnson & Johnson and reported receiving research funding for serving as an institutional principal investigator for SetPoint, Galapagos, Johnson & Johnson, Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, argenx, EMD Serono, Priovant, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Zena Pharmaceuticals, and Horizon/Amgen.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — An implantable vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) device effectively treats moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in patients who had previously failed at least one biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (b/tsDMARD), according to results from a phase 3 trial.
Of the 242 patients in the RESET-RA study, all received the VNS device implant but were blinded as to whether the device was turned on. At 12 weeks, 35.2% of patients receiving daily stimulation achieved 20% improvement in American College of Rheumatology response criteria (ACR20) compared with 24.2% of those with an inactive device. The response was more pronounced among patients with exposure to only one prior b/tsDMARD. A greater proportion of patients in the overall treatment group also reached low disease activity or remission compared with those who did not receive stimulation.
The research was presented as a late-breaking poster at the ACR 2024 Annual Meeting.
“This is a particularly tough-to-treat patient population, since the patients enrolled were considered refractory to biologic therapy,” said Elena Schiopu, MD, professor of medicine in the Division of Rheumatology and director of clinical trials at the Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University. More than one third of patients in the study had tried three or more b/tsDMARDs prior to the study. “I’m pretty excited about these results,” she added. Schiopu was a RESET-RA institutional principal investigator and enrolled two patients in the trial.
These positive results are a first for VNS treatment in rheumatic diseases. Previous studies demonstrating the potential therapeutic effect of this implant approach have largely been open-label, proof-of-concept, or pilot studies. Noninvasive, wearable stimulation devices have also shown promise in open-label studies; however, a sham-controlled trial published in 2023 showed that transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation on the ear was no more effective than placebo.
But How Does It Work?
The device, developed by SetPoint Medical in Valencia, California, is about the size of a multivitamin and implanted in an outpatient setting. During the 45-minute procedure, surgeons isolate the vagus nerve on the left side of the neck and place the nerve stimulator with a silicone positioning pod to hold it in place.
The device is programmed to deliver stimulation for 1 minute every day and needs charging for only 10 minutes once a week, which is done remotely with a necklace.
The device takes advantage of the vagus nerve’s anti-inflammatory properties, stimulating the nerve to help regulate an overactive immune system of someone with RA, explained David Chernoff, MD, Setpoint Medical’s chief medical officer.
“We’re recapitulating what nature has developed over millions of years, which is the nexus between the brain and the immune system, which happens to be mediated by the vagus nerve,” he told Medscape Medical News.
This novel VNS approach also does not have the same immunosuppressive safety concerns as drugs commonly used to treat RA, he said.
“We’re able to adjust the amount of inflammation, but we don’t cause the host defense issues” that are present with some of these drugs, he continued.
SetPoint Medical’s pilot study of the device in 14 patients showed promising results. Five of 10 patients randomly assigned to active VNS over 12 weeks showed clinical improvements, measured by 28-joint Disease Activity Score based on C-reactive protein (DAS28-CRP) and the Clinical Disease Activity Index. In the remaining four patients who received sham stimulation — where the device was implanted but not activated — there were no clinical disease improvements.
RESET-RA Details
The most recent, much larger phase 3 study enrolled patients from 41 sites in the United States. Patients were on average 56 years old and had a body mass index of 30; 86% were women. A total of 39% had previously tried one b/tsDMARD, 22% had tried two, and 39% had tried three or more. Patients, on average, had 15 tender joints and 10 swollen joints. Patients discontinued their prior b/tsDMARD before the procedure and remained on conventional DMARDS during the trial, including methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, and sulfasalazine.
The researchers randomly assigned patients 1:1 to active (treatment) or nonactive (control) stimulation.
“The perception of stimulation varies from patient to patient, which itself is helpful in blinding as there is no expected perception of whether or how stimulation will be felt,” Chernoff explained. The 1-minute stimulation was scheduled in the early hours of the morning, when a patient typically would be asleep, he said.
Patients were excluded from the analysis if they were rescued by steroids or b/tsDMARDs through week 12. After week 12, the control group was switched to stimulation and efficacy was reassessed at week 24.
Higher ACR20 Response Rate, Lower Disease Activity
Beyond meeting the primary endpoint of ACR20 response, patients on the active stimulation group showed lower disease activity at week 12. Compared with 15.8% of patients in the control group, 27% of those in the treatment group achieved a DAS28-CRP ≤ 3.2.
The active stimulation was particularly effective in patients who had experience with only one prior b/tsDMARD. In this subset of patients, 44.2% in the treatment group achieved ACR20 compared with 19.0% in the control group.
During this sham-controlled trial period, 13.1% of patients in the treatment group and 18.3% of patients in the control group reported an adverse event (AE) related to the procedure or device, most commonly vocal cord paresis or dysphonia. In the treatment group, 8.2% reported stimulation-related AEs, most commonly mild/moderate pain that was managed by adjusting the stimulation level.
Serious adverse events (SAEs) were relatively rare, with four treatment-related SAEs across both study groups. No AEs led to study discontinuation through week 24.
The 12-week results mirror those of the initial Humira and Enbrel trials in the late 1990s and early 2000s, Schiopu said, although in those trials, the patients were naive to biologics, and some were naive to methotrexate. A more appropriate comparison, she said, would be biologic-experienced populations.
At week 24, the percentage of patients achieving ACR20 further increased to 51.5% in the treatment group and to 53.1% in the previous control group who were now crossed over to active stimulation. In this secondary period, patients could add any additional therapies like steroids or b/tsDMARDs. At 24 weeks, 81% of patients remained on stimulation without needing additional medication, beyond their continued background DMARDs.
The results also show “a continuum of improvement over time,” Schiopu said, where response rates climbed through week 24.
Schiopu is particularly excited about the potential to use this stimulation device in older patients, who have perhaps been on immunosuppressant drugs for decades.
“Aside from being chronically immunosuppressed, their immune system is more tired [due to age],” she said. With VNS therapies like SetPoint’s, “we could offer [these patients] a lesser immunosuppressive alternative that is still immune-modular enough to manage their RA.”
Schiopu is a consultant for Johnson & Johnson and reported receiving research funding for serving as an institutional principal investigator for SetPoint, Galapagos, Johnson & Johnson, Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, argenx, EMD Serono, Priovant, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Zena Pharmaceuticals, and Horizon/Amgen.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — An implantable vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) device effectively treats moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in patients who had previously failed at least one biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (b/tsDMARD), according to results from a phase 3 trial.
Of the 242 patients in the RESET-RA study, all received the VNS device implant but were blinded as to whether the device was turned on. At 12 weeks, 35.2% of patients receiving daily stimulation achieved 20% improvement in American College of Rheumatology response criteria (ACR20) compared with 24.2% of those with an inactive device. The response was more pronounced among patients with exposure to only one prior b/tsDMARD. A greater proportion of patients in the overall treatment group also reached low disease activity or remission compared with those who did not receive stimulation.
The research was presented as a late-breaking poster at the ACR 2024 Annual Meeting.
“This is a particularly tough-to-treat patient population, since the patients enrolled were considered refractory to biologic therapy,” said Elena Schiopu, MD, professor of medicine in the Division of Rheumatology and director of clinical trials at the Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University. More than one third of patients in the study had tried three or more b/tsDMARDs prior to the study. “I’m pretty excited about these results,” she added. Schiopu was a RESET-RA institutional principal investigator and enrolled two patients in the trial.
These positive results are a first for VNS treatment in rheumatic diseases. Previous studies demonstrating the potential therapeutic effect of this implant approach have largely been open-label, proof-of-concept, or pilot studies. Noninvasive, wearable stimulation devices have also shown promise in open-label studies; however, a sham-controlled trial published in 2023 showed that transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation on the ear was no more effective than placebo.
But How Does It Work?
The device, developed by SetPoint Medical in Valencia, California, is about the size of a multivitamin and implanted in an outpatient setting. During the 45-minute procedure, surgeons isolate the vagus nerve on the left side of the neck and place the nerve stimulator with a silicone positioning pod to hold it in place.
The device is programmed to deliver stimulation for 1 minute every day and needs charging for only 10 minutes once a week, which is done remotely with a necklace.
The device takes advantage of the vagus nerve’s anti-inflammatory properties, stimulating the nerve to help regulate an overactive immune system of someone with RA, explained David Chernoff, MD, Setpoint Medical’s chief medical officer.
“We’re recapitulating what nature has developed over millions of years, which is the nexus between the brain and the immune system, which happens to be mediated by the vagus nerve,” he told Medscape Medical News.
This novel VNS approach also does not have the same immunosuppressive safety concerns as drugs commonly used to treat RA, he said.
“We’re able to adjust the amount of inflammation, but we don’t cause the host defense issues” that are present with some of these drugs, he continued.
SetPoint Medical’s pilot study of the device in 14 patients showed promising results. Five of 10 patients randomly assigned to active VNS over 12 weeks showed clinical improvements, measured by 28-joint Disease Activity Score based on C-reactive protein (DAS28-CRP) and the Clinical Disease Activity Index. In the remaining four patients who received sham stimulation — where the device was implanted but not activated — there were no clinical disease improvements.
RESET-RA Details
The most recent, much larger phase 3 study enrolled patients from 41 sites in the United States. Patients were on average 56 years old and had a body mass index of 30; 86% were women. A total of 39% had previously tried one b/tsDMARD, 22% had tried two, and 39% had tried three or more. Patients, on average, had 15 tender joints and 10 swollen joints. Patients discontinued their prior b/tsDMARD before the procedure and remained on conventional DMARDS during the trial, including methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, and sulfasalazine.
The researchers randomly assigned patients 1:1 to active (treatment) or nonactive (control) stimulation.
“The perception of stimulation varies from patient to patient, which itself is helpful in blinding as there is no expected perception of whether or how stimulation will be felt,” Chernoff explained. The 1-minute stimulation was scheduled in the early hours of the morning, when a patient typically would be asleep, he said.
Patients were excluded from the analysis if they were rescued by steroids or b/tsDMARDs through week 12. After week 12, the control group was switched to stimulation and efficacy was reassessed at week 24.
Higher ACR20 Response Rate, Lower Disease Activity
Beyond meeting the primary endpoint of ACR20 response, patients on the active stimulation group showed lower disease activity at week 12. Compared with 15.8% of patients in the control group, 27% of those in the treatment group achieved a DAS28-CRP ≤ 3.2.
The active stimulation was particularly effective in patients who had experience with only one prior b/tsDMARD. In this subset of patients, 44.2% in the treatment group achieved ACR20 compared with 19.0% in the control group.
During this sham-controlled trial period, 13.1% of patients in the treatment group and 18.3% of patients in the control group reported an adverse event (AE) related to the procedure or device, most commonly vocal cord paresis or dysphonia. In the treatment group, 8.2% reported stimulation-related AEs, most commonly mild/moderate pain that was managed by adjusting the stimulation level.
Serious adverse events (SAEs) were relatively rare, with four treatment-related SAEs across both study groups. No AEs led to study discontinuation through week 24.
The 12-week results mirror those of the initial Humira and Enbrel trials in the late 1990s and early 2000s, Schiopu said, although in those trials, the patients were naive to biologics, and some were naive to methotrexate. A more appropriate comparison, she said, would be biologic-experienced populations.
At week 24, the percentage of patients achieving ACR20 further increased to 51.5% in the treatment group and to 53.1% in the previous control group who were now crossed over to active stimulation. In this secondary period, patients could add any additional therapies like steroids or b/tsDMARDs. At 24 weeks, 81% of patients remained on stimulation without needing additional medication, beyond their continued background DMARDs.
The results also show “a continuum of improvement over time,” Schiopu said, where response rates climbed through week 24.
Schiopu is particularly excited about the potential to use this stimulation device in older patients, who have perhaps been on immunosuppressant drugs for decades.
“Aside from being chronically immunosuppressed, their immune system is more tired [due to age],” she said. With VNS therapies like SetPoint’s, “we could offer [these patients] a lesser immunosuppressive alternative that is still immune-modular enough to manage their RA.”
Schiopu is a consultant for Johnson & Johnson and reported receiving research funding for serving as an institutional principal investigator for SetPoint, Galapagos, Johnson & Johnson, Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, argenx, EMD Serono, Priovant, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Zena Pharmaceuticals, and Horizon/Amgen.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACR 2024
Difficult-to-Treat RA Still Develops Often Despite Early Switch From Methotrexate
TOPLINE:
Early escalation to biologic therapies after failure of treat-to-target with methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) does not significantly reduce the risk for the development of difficult-to-treat RA.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective analysis including 722 patients with new-onset RA (mean age, 60 years; 72% women) who were identified from a cohort at the IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo University Hospital in Italy and followed-up for at least 3 years after diagnosis.
- Patients were initially treated with methotrexate, with escalation to biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARDs) in case they did not reach the therapeutic target.
- Follow-up for patients who started b/tsDMARDs occurred every 2 months for the first 6 months, then every 4 months, with a target of achieving low disease activity (28-joint disease activity score, < 3.2).
- The effectiveness of each DMARD was evaluated using drug survival rates, and the development of difficult-to-treat RA was assessed using the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology criteria.
TAKEAWAY:
- The retention rate of the first b/tsDMARD dropped from 72.3% at 12 months to 41.6% at 60 months, indicating a decline in treatment persistence over time.
- Early escalation to biologic therapies did not significantly reduce the risk for difficult-to-treat RA, with 29% patients meeting the criteria after a median follow-up period of 72.6 months.
- Patients with higher disease activity and a higher number of swollen joints at the start of biologic therapy were more likely to develop treatment resistance.
- Shorter disease duration at the start of treatment with b/tsDMARDs, a greater number of swollen joints, worse pain scores, and autoantibody-negative status were identified as independent predictors of difficult-to-treat RA.
IN PRACTICE:
“Early implementation of treatment after failure of treat-to-target with MTX [methotrexate] may not prevent the development of D2T [difficult-to-treat] in patients with RA,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Bernardo D’Onofrio, MD, and Ludovico De Stefano, MD, Department of Internal Medicine and Therapeutics, University of Pavia, in Italy. It was published online November 8, 2024, in Arthritis Research & Therapy.
LIMITATIONS:
The escalation to b/tsDMARDs was not strictly guided by disease activity scores, potentially reflecting clinical practice. Additionally, the study did not account for socioeconomic factors or adherence, which may have influenced treatment outcomes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by a grant from the IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo Foundation. One author reported receiving grants/research support and personal fees and two authors reported receiving personal fees from various pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Early escalation to biologic therapies after failure of treat-to-target with methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) does not significantly reduce the risk for the development of difficult-to-treat RA.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective analysis including 722 patients with new-onset RA (mean age, 60 years; 72% women) who were identified from a cohort at the IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo University Hospital in Italy and followed-up for at least 3 years after diagnosis.
- Patients were initially treated with methotrexate, with escalation to biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARDs) in case they did not reach the therapeutic target.
- Follow-up for patients who started b/tsDMARDs occurred every 2 months for the first 6 months, then every 4 months, with a target of achieving low disease activity (28-joint disease activity score, < 3.2).
- The effectiveness of each DMARD was evaluated using drug survival rates, and the development of difficult-to-treat RA was assessed using the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology criteria.
TAKEAWAY:
- The retention rate of the first b/tsDMARD dropped from 72.3% at 12 months to 41.6% at 60 months, indicating a decline in treatment persistence over time.
- Early escalation to biologic therapies did not significantly reduce the risk for difficult-to-treat RA, with 29% patients meeting the criteria after a median follow-up period of 72.6 months.
- Patients with higher disease activity and a higher number of swollen joints at the start of biologic therapy were more likely to develop treatment resistance.
- Shorter disease duration at the start of treatment with b/tsDMARDs, a greater number of swollen joints, worse pain scores, and autoantibody-negative status were identified as independent predictors of difficult-to-treat RA.
IN PRACTICE:
“Early implementation of treatment after failure of treat-to-target with MTX [methotrexate] may not prevent the development of D2T [difficult-to-treat] in patients with RA,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Bernardo D’Onofrio, MD, and Ludovico De Stefano, MD, Department of Internal Medicine and Therapeutics, University of Pavia, in Italy. It was published online November 8, 2024, in Arthritis Research & Therapy.
LIMITATIONS:
The escalation to b/tsDMARDs was not strictly guided by disease activity scores, potentially reflecting clinical practice. Additionally, the study did not account for socioeconomic factors or adherence, which may have influenced treatment outcomes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by a grant from the IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo Foundation. One author reported receiving grants/research support and personal fees and two authors reported receiving personal fees from various pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Early escalation to biologic therapies after failure of treat-to-target with methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) does not significantly reduce the risk for the development of difficult-to-treat RA.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective analysis including 722 patients with new-onset RA (mean age, 60 years; 72% women) who were identified from a cohort at the IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo University Hospital in Italy and followed-up for at least 3 years after diagnosis.
- Patients were initially treated with methotrexate, with escalation to biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARDs) in case they did not reach the therapeutic target.
- Follow-up for patients who started b/tsDMARDs occurred every 2 months for the first 6 months, then every 4 months, with a target of achieving low disease activity (28-joint disease activity score, < 3.2).
- The effectiveness of each DMARD was evaluated using drug survival rates, and the development of difficult-to-treat RA was assessed using the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology criteria.
TAKEAWAY:
- The retention rate of the first b/tsDMARD dropped from 72.3% at 12 months to 41.6% at 60 months, indicating a decline in treatment persistence over time.
- Early escalation to biologic therapies did not significantly reduce the risk for difficult-to-treat RA, with 29% patients meeting the criteria after a median follow-up period of 72.6 months.
- Patients with higher disease activity and a higher number of swollen joints at the start of biologic therapy were more likely to develop treatment resistance.
- Shorter disease duration at the start of treatment with b/tsDMARDs, a greater number of swollen joints, worse pain scores, and autoantibody-negative status were identified as independent predictors of difficult-to-treat RA.
IN PRACTICE:
“Early implementation of treatment after failure of treat-to-target with MTX [methotrexate] may not prevent the development of D2T [difficult-to-treat] in patients with RA,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Bernardo D’Onofrio, MD, and Ludovico De Stefano, MD, Department of Internal Medicine and Therapeutics, University of Pavia, in Italy. It was published online November 8, 2024, in Arthritis Research & Therapy.
LIMITATIONS:
The escalation to b/tsDMARDs was not strictly guided by disease activity scores, potentially reflecting clinical practice. Additionally, the study did not account for socioeconomic factors or adherence, which may have influenced treatment outcomes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by a grant from the IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo Foundation. One author reported receiving grants/research support and personal fees and two authors reported receiving personal fees from various pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Holding RA, SpA Drugs Did Not Improve Antibody Response to COVID Vaccine
WASHINGTON — There is no benefit to interrupting treatment with many of the available targeted synthetic or biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or spondyloarthritis (SpA) at the time of a repeat COVID-19 vaccine dose, new research found.
In the multicenter, randomized controlled COVID Vaccine Response (COVER) trial of 577 patients with RA or SpA taking either abatacept, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, interleukin (IL)–17 inhibitors, or tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, holding those drugs for 2 weeks at the time of COVID-19 vaccination supplemental doses didn’t improve antibody response to the vaccine but did lead to disease flares. Most participants had significant antibody responses to the vaccine, regardless of whether their medication had been held or continued, Jeffrey R. Curtis, MD, the Harbert-Ball Professor of Medicine, Epidemiology, and Computer Science at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
Guidelines issued by ACR in 2023 recommended holding abatacept for the COVID vaccine but said that “the task force failed to reach consensus” on whether or not to temporarily interrupt the other medications following primary vaccination or supplemental/booster dosing.
Curtis, who was an author on those guidelines, said in an interview, “to date, we haven’t known whether it might be a good idea to hold certain drugs at the time patients receive their next dose of the COVID vaccine. ... That’s because without direct evidence, you have people trading opinions based on extrapolated data.”
The inability to measure cell-mediated immunity and only humoral (ie, antibody-based) immunity is a limitation in COVER. “Nevertheless, based on what we know now, it isn’t advisable to hold any of the four drug classes that we studied at the time patients receive their next COVID vaccine dose. This finding is in contrast to data from a different trial showing that holding methotrexate for 2 weeks does appear to help in response to COVID-19 vaccination, as well as influenza vaccine,” Curtis said.
Asked to comment, session moderator Elena Myasoedova, MD, PhD, consultant rheumatologist and director of the Inflammatory Arthritis Clinic at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, said in an interview: “This has been an area of clinical uncertainty. It raises a lot of questions from patients and from physicians alike as to whether or not to hold the medication because the implications are flares, and that’s impactful for patients. Patients care about their RA status and how it is controlled, and if there is no difference, then there is no reason to change the medication regimen.”
To Hold or Not to Hold: COVER Shows It Makes Little Difference to Vaccine Response
In COVER, 128 patients were taking abatacept, 96 IL-17 inhibitors, 237 JAK inhibitors, and 116 TNF inhibitors. The study was conducted within 30 sites of the Excellence Network in Rheumatology, a rheumatology practice–based research network launched in 2021. Participants were identified and enrolled at clinic visits immediately prior to receiving their COVID-19 boosters (in routine settings).
All had previously received two or more doses of the mRNA vaccines made by Pfizer or Moderna. Blood was drawn, and they were randomized 1:1 to either continue or hold their disease medication for 2 weeks following the booster. Blood was collected again at 6 weeks post vaccine.
Anti–receptor-binding domain (RBD) IgG antibody titers increased significantly in all drug categories across both study arms, with no differences between the hold vs continue medication groups, even after adjustments for age, sex, body mass index, methotrexate use, steroid use, and time from booster to measurement. All groups also showed increases in geometric mean fold rise of more than 3%.
Subgroup analyses showed no major differences between antibody responses in the hold vs continue groups. The anti-RBD IgG response was lower for abatacept and JAK inhibitors than for the other two drugs, but there was still no significant benefit to holding them for 2 weeks post vaccination.
Holding Drugs Leads to Disease Flares
On the flip side, there were significant differences between the two groups in their responses to the question: “Did you experience any flare or worsening of your autoimmune disease following your recent COVID-19 booster dose?” Overall, 27% of the hold group responded that they had, compared with just 13% of the continue group (P < .05). This difference was greatest in the JAK inhibitor group (33% vs 9%; P < .05).
Among those reporting flares or worsening disease, both the severity and the duration of the flares were about the same. “Interestingly, the duration is beyond a week for the majority of patients. The reason that’s important is, any symptoms that are so-called flare might simply be reactogenicity symptoms, and that might be confused for flare or disease worsening, but you see that a majority of patients actually have those symptoms extending beyond the week. Most of them are worsening in arthritis, as you might expect,” Curtis said in his presentation.
Asked what they did about the flare, only a minority of patients reported contacting a healthcare provider. In all, 68% of the hold group and 78% of the continue group took no action. That’s good in the sense that most of the flares weren’t severe, but it has implications for research, Curtis pointed out.
“A lot of times in the vaccine literature, people do retrospective chart review by looking to see what the doctor said as to whether the patient had a flare. And what this would tell you is patients may be reporting a lot of flares that their doctor doesn’t know anything about. So if you really want to know whether people are having a flare, even a mild flare, you really have to collect prospective data.”
COVID is Not the Last Pandemic
“These results are reassuring, although I think we need a bit more data on abatacept,” Myasoedova said, adding, “I was also interested in the outcomes, such as severe infections, that actually happened to these patients. What we see in the labs in their immune response is one thing, but then also important is what actually evolves in terms of the outcomes, especially with abatacept.”
Overall, she said, “I think it’s reassuring and definitely informs clinical practice going forward. But then probably we’ll learn more. What we’re hearing is COVID is not the last pandemic.”
The COVER trial receives support from AbbVie, BMS, Eli Lilly, Novartis, and Pfizer. Curtis has received research grants and consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, GSK, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, and UCB. Myasoedova has no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — There is no benefit to interrupting treatment with many of the available targeted synthetic or biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or spondyloarthritis (SpA) at the time of a repeat COVID-19 vaccine dose, new research found.
In the multicenter, randomized controlled COVID Vaccine Response (COVER) trial of 577 patients with RA or SpA taking either abatacept, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, interleukin (IL)–17 inhibitors, or tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, holding those drugs for 2 weeks at the time of COVID-19 vaccination supplemental doses didn’t improve antibody response to the vaccine but did lead to disease flares. Most participants had significant antibody responses to the vaccine, regardless of whether their medication had been held or continued, Jeffrey R. Curtis, MD, the Harbert-Ball Professor of Medicine, Epidemiology, and Computer Science at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
Guidelines issued by ACR in 2023 recommended holding abatacept for the COVID vaccine but said that “the task force failed to reach consensus” on whether or not to temporarily interrupt the other medications following primary vaccination or supplemental/booster dosing.
Curtis, who was an author on those guidelines, said in an interview, “to date, we haven’t known whether it might be a good idea to hold certain drugs at the time patients receive their next dose of the COVID vaccine. ... That’s because without direct evidence, you have people trading opinions based on extrapolated data.”
The inability to measure cell-mediated immunity and only humoral (ie, antibody-based) immunity is a limitation in COVER. “Nevertheless, based on what we know now, it isn’t advisable to hold any of the four drug classes that we studied at the time patients receive their next COVID vaccine dose. This finding is in contrast to data from a different trial showing that holding methotrexate for 2 weeks does appear to help in response to COVID-19 vaccination, as well as influenza vaccine,” Curtis said.
Asked to comment, session moderator Elena Myasoedova, MD, PhD, consultant rheumatologist and director of the Inflammatory Arthritis Clinic at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, said in an interview: “This has been an area of clinical uncertainty. It raises a lot of questions from patients and from physicians alike as to whether or not to hold the medication because the implications are flares, and that’s impactful for patients. Patients care about their RA status and how it is controlled, and if there is no difference, then there is no reason to change the medication regimen.”
To Hold or Not to Hold: COVER Shows It Makes Little Difference to Vaccine Response
In COVER, 128 patients were taking abatacept, 96 IL-17 inhibitors, 237 JAK inhibitors, and 116 TNF inhibitors. The study was conducted within 30 sites of the Excellence Network in Rheumatology, a rheumatology practice–based research network launched in 2021. Participants were identified and enrolled at clinic visits immediately prior to receiving their COVID-19 boosters (in routine settings).
All had previously received two or more doses of the mRNA vaccines made by Pfizer or Moderna. Blood was drawn, and they were randomized 1:1 to either continue or hold their disease medication for 2 weeks following the booster. Blood was collected again at 6 weeks post vaccine.
Anti–receptor-binding domain (RBD) IgG antibody titers increased significantly in all drug categories across both study arms, with no differences between the hold vs continue medication groups, even after adjustments for age, sex, body mass index, methotrexate use, steroid use, and time from booster to measurement. All groups also showed increases in geometric mean fold rise of more than 3%.
Subgroup analyses showed no major differences between antibody responses in the hold vs continue groups. The anti-RBD IgG response was lower for abatacept and JAK inhibitors than for the other two drugs, but there was still no significant benefit to holding them for 2 weeks post vaccination.
Holding Drugs Leads to Disease Flares
On the flip side, there were significant differences between the two groups in their responses to the question: “Did you experience any flare or worsening of your autoimmune disease following your recent COVID-19 booster dose?” Overall, 27% of the hold group responded that they had, compared with just 13% of the continue group (P < .05). This difference was greatest in the JAK inhibitor group (33% vs 9%; P < .05).
Among those reporting flares or worsening disease, both the severity and the duration of the flares were about the same. “Interestingly, the duration is beyond a week for the majority of patients. The reason that’s important is, any symptoms that are so-called flare might simply be reactogenicity symptoms, and that might be confused for flare or disease worsening, but you see that a majority of patients actually have those symptoms extending beyond the week. Most of them are worsening in arthritis, as you might expect,” Curtis said in his presentation.
Asked what they did about the flare, only a minority of patients reported contacting a healthcare provider. In all, 68% of the hold group and 78% of the continue group took no action. That’s good in the sense that most of the flares weren’t severe, but it has implications for research, Curtis pointed out.
“A lot of times in the vaccine literature, people do retrospective chart review by looking to see what the doctor said as to whether the patient had a flare. And what this would tell you is patients may be reporting a lot of flares that their doctor doesn’t know anything about. So if you really want to know whether people are having a flare, even a mild flare, you really have to collect prospective data.”
COVID is Not the Last Pandemic
“These results are reassuring, although I think we need a bit more data on abatacept,” Myasoedova said, adding, “I was also interested in the outcomes, such as severe infections, that actually happened to these patients. What we see in the labs in their immune response is one thing, but then also important is what actually evolves in terms of the outcomes, especially with abatacept.”
Overall, she said, “I think it’s reassuring and definitely informs clinical practice going forward. But then probably we’ll learn more. What we’re hearing is COVID is not the last pandemic.”
The COVER trial receives support from AbbVie, BMS, Eli Lilly, Novartis, and Pfizer. Curtis has received research grants and consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, GSK, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, and UCB. Myasoedova has no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — There is no benefit to interrupting treatment with many of the available targeted synthetic or biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or spondyloarthritis (SpA) at the time of a repeat COVID-19 vaccine dose, new research found.
In the multicenter, randomized controlled COVID Vaccine Response (COVER) trial of 577 patients with RA or SpA taking either abatacept, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, interleukin (IL)–17 inhibitors, or tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, holding those drugs for 2 weeks at the time of COVID-19 vaccination supplemental doses didn’t improve antibody response to the vaccine but did lead to disease flares. Most participants had significant antibody responses to the vaccine, regardless of whether their medication had been held or continued, Jeffrey R. Curtis, MD, the Harbert-Ball Professor of Medicine, Epidemiology, and Computer Science at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
Guidelines issued by ACR in 2023 recommended holding abatacept for the COVID vaccine but said that “the task force failed to reach consensus” on whether or not to temporarily interrupt the other medications following primary vaccination or supplemental/booster dosing.
Curtis, who was an author on those guidelines, said in an interview, “to date, we haven’t known whether it might be a good idea to hold certain drugs at the time patients receive their next dose of the COVID vaccine. ... That’s because without direct evidence, you have people trading opinions based on extrapolated data.”
The inability to measure cell-mediated immunity and only humoral (ie, antibody-based) immunity is a limitation in COVER. “Nevertheless, based on what we know now, it isn’t advisable to hold any of the four drug classes that we studied at the time patients receive their next COVID vaccine dose. This finding is in contrast to data from a different trial showing that holding methotrexate for 2 weeks does appear to help in response to COVID-19 vaccination, as well as influenza vaccine,” Curtis said.
Asked to comment, session moderator Elena Myasoedova, MD, PhD, consultant rheumatologist and director of the Inflammatory Arthritis Clinic at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, said in an interview: “This has been an area of clinical uncertainty. It raises a lot of questions from patients and from physicians alike as to whether or not to hold the medication because the implications are flares, and that’s impactful for patients. Patients care about their RA status and how it is controlled, and if there is no difference, then there is no reason to change the medication regimen.”
To Hold or Not to Hold: COVER Shows It Makes Little Difference to Vaccine Response
In COVER, 128 patients were taking abatacept, 96 IL-17 inhibitors, 237 JAK inhibitors, and 116 TNF inhibitors. The study was conducted within 30 sites of the Excellence Network in Rheumatology, a rheumatology practice–based research network launched in 2021. Participants were identified and enrolled at clinic visits immediately prior to receiving their COVID-19 boosters (in routine settings).
All had previously received two or more doses of the mRNA vaccines made by Pfizer or Moderna. Blood was drawn, and they were randomized 1:1 to either continue or hold their disease medication for 2 weeks following the booster. Blood was collected again at 6 weeks post vaccine.
Anti–receptor-binding domain (RBD) IgG antibody titers increased significantly in all drug categories across both study arms, with no differences between the hold vs continue medication groups, even after adjustments for age, sex, body mass index, methotrexate use, steroid use, and time from booster to measurement. All groups also showed increases in geometric mean fold rise of more than 3%.
Subgroup analyses showed no major differences between antibody responses in the hold vs continue groups. The anti-RBD IgG response was lower for abatacept and JAK inhibitors than for the other two drugs, but there was still no significant benefit to holding them for 2 weeks post vaccination.
Holding Drugs Leads to Disease Flares
On the flip side, there were significant differences between the two groups in their responses to the question: “Did you experience any flare or worsening of your autoimmune disease following your recent COVID-19 booster dose?” Overall, 27% of the hold group responded that they had, compared with just 13% of the continue group (P < .05). This difference was greatest in the JAK inhibitor group (33% vs 9%; P < .05).
Among those reporting flares or worsening disease, both the severity and the duration of the flares were about the same. “Interestingly, the duration is beyond a week for the majority of patients. The reason that’s important is, any symptoms that are so-called flare might simply be reactogenicity symptoms, and that might be confused for flare or disease worsening, but you see that a majority of patients actually have those symptoms extending beyond the week. Most of them are worsening in arthritis, as you might expect,” Curtis said in his presentation.
Asked what they did about the flare, only a minority of patients reported contacting a healthcare provider. In all, 68% of the hold group and 78% of the continue group took no action. That’s good in the sense that most of the flares weren’t severe, but it has implications for research, Curtis pointed out.
“A lot of times in the vaccine literature, people do retrospective chart review by looking to see what the doctor said as to whether the patient had a flare. And what this would tell you is patients may be reporting a lot of flares that their doctor doesn’t know anything about. So if you really want to know whether people are having a flare, even a mild flare, you really have to collect prospective data.”
COVID is Not the Last Pandemic
“These results are reassuring, although I think we need a bit more data on abatacept,” Myasoedova said, adding, “I was also interested in the outcomes, such as severe infections, that actually happened to these patients. What we see in the labs in their immune response is one thing, but then also important is what actually evolves in terms of the outcomes, especially with abatacept.”
Overall, she said, “I think it’s reassuring and definitely informs clinical practice going forward. But then probably we’ll learn more. What we’re hearing is COVID is not the last pandemic.”
The COVER trial receives support from AbbVie, BMS, Eli Lilly, Novartis, and Pfizer. Curtis has received research grants and consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, GSK, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, and UCB. Myasoedova has no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACR 2024
Fertility Improved With Treat-to-Target Approach in Rheumatoid Arthritis
WASHINGTON — Women with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) experience improved fertility when treated using a treat-to-target (T2T) approach aimed at remission, according to a new research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
In the study, more than half the women following this T2T approach were able to conceive within 3 months, which is “nearly equal to the general population,” said presenter and senior author Radboud Dolhain, MD, PhD, who heads the Department of Rheumatology at Erasmus University Medical Center in Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
Compared with 10%-15% of the general population, as many as 42% of patients with RA are not able to get pregnant within 1 year of unprotected intercourse.
“For people who are thinking about pregnancy or want to plan for pregnancy, talking with them about the importance of making sure their RA is well-treated is an essential aspect,” said Mehret Birru Talabi, MD, PhD, director of the Women’s and Reproductive Health Rheumatology Clinic at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center in Pennsylvania. She was not involved with the research.
“This is a nice, relatively large study that’s demonstrating [that] if you actually treat the patient and treat them effectively, their time to pregnancy is lower,” she said.
Study Details
The analysis compared time to pregnancy between two cohorts of women with RA who aimed to become pregnant. Women were, on average, around 32 years old in both groups, and nearly 60% had not been pregnant before.
The first cohort was part of the Pregnancy-Induced Amelioration of RA (PARA) study, conducted by Erasmus University Medical Center from 2002 to 2010, in which patients were treated by their own rheumatologists with standard of care at the time. Of the 245 women included, 36% were on no medication, and one fourth were taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). One third of patients were prescribed sulfasalazine, 6% were on hydroxychloroquine, and 4% were prescribed a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor. Of the PARA patients prescribed prednisone, about half used a dose > 7.5 mg/d.
The second cohort was part of the Preconception Counseling in Active RA (PreCARA) study, conducted at Erasmus University Medical Center from 2012 to 2023. PreCARA patients were treated with the T2T approach aimed at remission/low disease activity and avoiding use of NSAIDs and high-dose prednisone (> 7.5 mg/d). Of the 215 women in the cohort, 69% were on sulfasalazine, 65% were on hydroxychloroquine, 53% were taking a TNF inhibitor, 45% took prednisone, and 13% took NSAIDs. For patients prescribed prednisone, 75% used a daily dose ≤ 7.5 mg/d. Only six patients were not taking any medication.
In the preconception period, the median Disease Activity Score in 28 joints using C-reactive protein was 2.33 in the PreCARA cohort and 3.84 in the PARA cohort.
The median time to pregnancy was 84 days in the PreCARA cohort, compared with 196 days in the PARA cohort. Compared with 42% of women in the PARA cohort, less than a quarter of women in the PreCARA cohort did not conceive within 1 year of trying. There was no difference between the two groups in the use of assisted reproductive techniques.
In an additional analysis, Dolhain and colleagues found that time to pregnancy in the PreCARA cohort was most associated with maternal age and nulliparity.
“You also will find [this association] in every cohort in time to pregnancy, and it underscores the robustness of our data,” Dolhain said. “We didn’t find any association [with time to pregnancy] anymore with disease activity, the use of NSAIDs, and the use of prednisone.”
Study ‘Will Make Patients Feel More Confident in Their Decisions’
Discussions about continuing medication before and during pregnancy can be a “tension point” for some patients, Talabi said, and these types of studies provide further evidence to reassure patients that this approach can help them reach their reproductive goals.
The study is “very clinically translatable, where you can show [patients] the benefit of continuing their medications” in the preconception period and during pregnancy, added Catherine Sims, MD, a rheumatologist at Duke Health in Durham, North Carolina, who is focused on reproductive rheumatology and preventive health.
“What we try to drive home is that the health of the mother directly translates to the health of the pregnancy and that includes medications, and that is okay because now we have shown that pregnancies are safe while taking these medications,” she said. “I think [this study] will make patients feel more confident in their decisions, which is a big, important piece of it.”
Sims is a consultant for Amgen and conducted research funded by GlaxoSmithKline. Dolhain and Talabi had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — Women with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) experience improved fertility when treated using a treat-to-target (T2T) approach aimed at remission, according to a new research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
In the study, more than half the women following this T2T approach were able to conceive within 3 months, which is “nearly equal to the general population,” said presenter and senior author Radboud Dolhain, MD, PhD, who heads the Department of Rheumatology at Erasmus University Medical Center in Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
Compared with 10%-15% of the general population, as many as 42% of patients with RA are not able to get pregnant within 1 year of unprotected intercourse.
“For people who are thinking about pregnancy or want to plan for pregnancy, talking with them about the importance of making sure their RA is well-treated is an essential aspect,” said Mehret Birru Talabi, MD, PhD, director of the Women’s and Reproductive Health Rheumatology Clinic at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center in Pennsylvania. She was not involved with the research.
“This is a nice, relatively large study that’s demonstrating [that] if you actually treat the patient and treat them effectively, their time to pregnancy is lower,” she said.
Study Details
The analysis compared time to pregnancy between two cohorts of women with RA who aimed to become pregnant. Women were, on average, around 32 years old in both groups, and nearly 60% had not been pregnant before.
The first cohort was part of the Pregnancy-Induced Amelioration of RA (PARA) study, conducted by Erasmus University Medical Center from 2002 to 2010, in which patients were treated by their own rheumatologists with standard of care at the time. Of the 245 women included, 36% were on no medication, and one fourth were taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). One third of patients were prescribed sulfasalazine, 6% were on hydroxychloroquine, and 4% were prescribed a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor. Of the PARA patients prescribed prednisone, about half used a dose > 7.5 mg/d.
The second cohort was part of the Preconception Counseling in Active RA (PreCARA) study, conducted at Erasmus University Medical Center from 2012 to 2023. PreCARA patients were treated with the T2T approach aimed at remission/low disease activity and avoiding use of NSAIDs and high-dose prednisone (> 7.5 mg/d). Of the 215 women in the cohort, 69% were on sulfasalazine, 65% were on hydroxychloroquine, 53% were taking a TNF inhibitor, 45% took prednisone, and 13% took NSAIDs. For patients prescribed prednisone, 75% used a daily dose ≤ 7.5 mg/d. Only six patients were not taking any medication.
In the preconception period, the median Disease Activity Score in 28 joints using C-reactive protein was 2.33 in the PreCARA cohort and 3.84 in the PARA cohort.
The median time to pregnancy was 84 days in the PreCARA cohort, compared with 196 days in the PARA cohort. Compared with 42% of women in the PARA cohort, less than a quarter of women in the PreCARA cohort did not conceive within 1 year of trying. There was no difference between the two groups in the use of assisted reproductive techniques.
In an additional analysis, Dolhain and colleagues found that time to pregnancy in the PreCARA cohort was most associated with maternal age and nulliparity.
“You also will find [this association] in every cohort in time to pregnancy, and it underscores the robustness of our data,” Dolhain said. “We didn’t find any association [with time to pregnancy] anymore with disease activity, the use of NSAIDs, and the use of prednisone.”
Study ‘Will Make Patients Feel More Confident in Their Decisions’
Discussions about continuing medication before and during pregnancy can be a “tension point” for some patients, Talabi said, and these types of studies provide further evidence to reassure patients that this approach can help them reach their reproductive goals.
The study is “very clinically translatable, where you can show [patients] the benefit of continuing their medications” in the preconception period and during pregnancy, added Catherine Sims, MD, a rheumatologist at Duke Health in Durham, North Carolina, who is focused on reproductive rheumatology and preventive health.
“What we try to drive home is that the health of the mother directly translates to the health of the pregnancy and that includes medications, and that is okay because now we have shown that pregnancies are safe while taking these medications,” she said. “I think [this study] will make patients feel more confident in their decisions, which is a big, important piece of it.”
Sims is a consultant for Amgen and conducted research funded by GlaxoSmithKline. Dolhain and Talabi had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — Women with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) experience improved fertility when treated using a treat-to-target (T2T) approach aimed at remission, according to a new research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
In the study, more than half the women following this T2T approach were able to conceive within 3 months, which is “nearly equal to the general population,” said presenter and senior author Radboud Dolhain, MD, PhD, who heads the Department of Rheumatology at Erasmus University Medical Center in Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
Compared with 10%-15% of the general population, as many as 42% of patients with RA are not able to get pregnant within 1 year of unprotected intercourse.
“For people who are thinking about pregnancy or want to plan for pregnancy, talking with them about the importance of making sure their RA is well-treated is an essential aspect,” said Mehret Birru Talabi, MD, PhD, director of the Women’s and Reproductive Health Rheumatology Clinic at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center in Pennsylvania. She was not involved with the research.
“This is a nice, relatively large study that’s demonstrating [that] if you actually treat the patient and treat them effectively, their time to pregnancy is lower,” she said.
Study Details
The analysis compared time to pregnancy between two cohorts of women with RA who aimed to become pregnant. Women were, on average, around 32 years old in both groups, and nearly 60% had not been pregnant before.
The first cohort was part of the Pregnancy-Induced Amelioration of RA (PARA) study, conducted by Erasmus University Medical Center from 2002 to 2010, in which patients were treated by their own rheumatologists with standard of care at the time. Of the 245 women included, 36% were on no medication, and one fourth were taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). One third of patients were prescribed sulfasalazine, 6% were on hydroxychloroquine, and 4% were prescribed a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor. Of the PARA patients prescribed prednisone, about half used a dose > 7.5 mg/d.
The second cohort was part of the Preconception Counseling in Active RA (PreCARA) study, conducted at Erasmus University Medical Center from 2012 to 2023. PreCARA patients were treated with the T2T approach aimed at remission/low disease activity and avoiding use of NSAIDs and high-dose prednisone (> 7.5 mg/d). Of the 215 women in the cohort, 69% were on sulfasalazine, 65% were on hydroxychloroquine, 53% were taking a TNF inhibitor, 45% took prednisone, and 13% took NSAIDs. For patients prescribed prednisone, 75% used a daily dose ≤ 7.5 mg/d. Only six patients were not taking any medication.
In the preconception period, the median Disease Activity Score in 28 joints using C-reactive protein was 2.33 in the PreCARA cohort and 3.84 in the PARA cohort.
The median time to pregnancy was 84 days in the PreCARA cohort, compared with 196 days in the PARA cohort. Compared with 42% of women in the PARA cohort, less than a quarter of women in the PreCARA cohort did not conceive within 1 year of trying. There was no difference between the two groups in the use of assisted reproductive techniques.
In an additional analysis, Dolhain and colleagues found that time to pregnancy in the PreCARA cohort was most associated with maternal age and nulliparity.
“You also will find [this association] in every cohort in time to pregnancy, and it underscores the robustness of our data,” Dolhain said. “We didn’t find any association [with time to pregnancy] anymore with disease activity, the use of NSAIDs, and the use of prednisone.”
Study ‘Will Make Patients Feel More Confident in Their Decisions’
Discussions about continuing medication before and during pregnancy can be a “tension point” for some patients, Talabi said, and these types of studies provide further evidence to reassure patients that this approach can help them reach their reproductive goals.
The study is “very clinically translatable, where you can show [patients] the benefit of continuing their medications” in the preconception period and during pregnancy, added Catherine Sims, MD, a rheumatologist at Duke Health in Durham, North Carolina, who is focused on reproductive rheumatology and preventive health.
“What we try to drive home is that the health of the mother directly translates to the health of the pregnancy and that includes medications, and that is okay because now we have shown that pregnancies are safe while taking these medications,” she said. “I think [this study] will make patients feel more confident in their decisions, which is a big, important piece of it.”
Sims is a consultant for Amgen and conducted research funded by GlaxoSmithKline. Dolhain and Talabi had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACR 2024
Expanded Ultrasound Use in RA, New Technology Spur Updated Guidance
WASHINGTON — After more than a decade, the American College of Rheumatology has developed new draft guidance for the use of musculoskeletal ultrasound (MSUS) to help with diagnosis, monitoring, and prognosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Though not yet finalized, the statements that came out of a first round of committee voting were unveiled at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
The committee was charged with updating the 2012 recommendations on using MSUS in rheumatology clinical practice, explained Veena K. Ranganath, MD, professor of clinical medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, and director of their Rheumatology Fellowship Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Training Program.
More than 30,000 articles on MSUS and any arthritis have been published since 2012, and there have been significant advances and improvements in technology as well as more widespread education and use in rheumatologic clinical practice, Ranganath said.
“There’s also been advancements in therapeutic agents and therapeutic strategies in use of these medications in rheumatoid arthritis,” Ranganath said. “We all know that the patient of today is very different than the patient of 10 years ago or 20 years ago, so this really impacts the clinical questions we ask of how we need to incorporate musculoskeletal ultrasound into our rheumatology clinical practice.”
The process of developing the guidance involved determining key domains and then relevant clinical questions for ultrasonography using the PICO model (patient/population, intervention, comparison, and outcomes). Evidence came from a review of relevant literature published since 1993 in PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Database. A panel of 11 experts voted on the quality of the evidence as being moderate or strong for 33 statements, rejecting three that had no consensus. The committee will hold another round of voting before the guidance is published.
Erin Arnold, MD, a rheumatologist at Arnold Arthritis & Rheumatology in Skokie, Illinois, said in an interview she believes the new guidance will be “tremendously helpful,” particularly in getting “everybody on the same page” with similar practices and helping enhance diagnosis and response to therapy.
Having used MSUS for over 20 years, Arnold said watching it evolve and seeing “this type of manuscript being put together as a resource for physicians who are taking care of inflammatory arthritis is exciting.”
“There’s not a single way we really can assess disease activity in our patients, and so having a composite of things that you’re looking at really enhances our ability to understand people’s pain,” Arnold said.
“When you have a patient in front of you that is in so much pain but doesn’t have any active inflammation, it’s hard to want to further put them at risk with more medication,” she said. “It’s so meaningful to be able to have a conversation about ... what are other complementary interventions? How are they sleeping? How are they eating? What are they taking as far as supplements? What are they doing to decrease that kind of fear and fight-or-flight response that often can drive some of our pain?”
Use of MSUS for Diagnosis Confirmation and Treatment Decisions
Gurjit S. Kaeley, MBBS, professor of medicine, division chief of rheumatology and clinical immunology, and medical director of the Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Program at the University of Florida College of Medicine, Jacksonville, reviewed the final statements for MSUS use with RA.
He said there was strong consensus that adding MSUS to clinical examination can aid diagnosis of early RA in patients with suspected RA, particularly with detection of synovitis, tenosynovitis, and erosions. There was moderate consensus that MSUS detection of tenosynovitis could predict later development of RA.
“Furthermore, erosions do have a predictive prognostic value in telling us that these patients need more attention and more urgent attention to getting urgent care with disease-modifying medications,” Kaeley said. “Ultrasound scanning for bone erosions on a few target joints was found to be feasible in literature and provides information not available with clinical examination. Furthermore, ultrasound is more sensitive than plain radiography for the detection of erosions.”
Moderate consensus supported a cutoff of at least 2 mm for erosions when using MSUS for diagnostic purposes.
Strong consensus supported using MSUS of the wrist, second and third metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints, and second and third interphalangeal (PIP) joints to aid early RA diagnosis, with moderate consensus that cutoffs of least 2 grayscale (GS) or at least 1 GS with at least 1 power Doppler (PD) at the joint level supports both an RA diagnosis and, in patients already diagnosed with RA, a positive joint.
“Grayscale-only definitions were included since equipment may not have sensitive Doppler,” Kaeley said.
Strong consensus supported scanning only a reduced set of representative or symptomatic joints to monitor disease activity with MSUS.
Inflammatory Signs, Disease Progression, and Flares
There was also strong consensus for using MSUS in patients with established RA and comorbidities to help distinguish between RA-related inflammation versus inflammation from other conditions, such as gout or calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease, or versus non–RA-related pain, such as that from fibromyalgia.
Patients with fibromyalgia, for example, “tend to have more steroid exposure and a high prevalence of biologic use because the composite disease scores tend to overestimate disease activity, especially when compared to ultrasound assessment,” Kaeley said.
Moderate consensus supported using MSUS in patients with established RA to objectively evaluate inflammation so as to eliminate age-related bias.
While MSUS signs of synovitis had only moderate consensus to be associated with radiographic progression and decline in patient-reported outcomes for patients with early RA, consensus was strong for this association in patients with established RA.
In terms of predicting disease progression with MSUS monitoring of RA disease activity, moderate consensus supported scanning the wrists and MCPs and PIPs of the hands and using the dorsal view. Kaeley emphasized that ultrasound is a clinical tool that should be used to answer a clinical question, so the sonographer or clinician needs to provide guidance on the areas to be scanned.
Multiple standardized scoring systems exist for predicting RA disease progression, but there is no consensus on which is the most effective, and there is only moderate consensus about the validity of using dichotomous scoring with an established cutoff for a positive joint.
The combination of MSUS with clinical examination appears to be more effective at confirming RA flares than using only clinical examination, and in certain patients with established RA, MSUS may provide insights into subclinical disease activity to help maintain remission and/or potentially guide treatment decisions, “especially when coming across de-escalation therapy decisions,” Kaeley said.
Despite the negative results of treat-to-target trials that tested MSUS as a routine tool in all patients, the committee achieved strong consensus on the potential value of using MSUS in early RA to clarify clinical status and/or help achieve low disease activity or remission in certain patient populations, “such as those with patient/provider discordance or difficult physical examinations,” Kaeley said.
Therapy Response, Remission, and Shared Decision-Making
Moderate consensus supported acknowledgment that using MSUS to assess response to therapy could be affected by obesity and that MSUS can distinguish active synovitis symptoms from other pain sources in difficult-to-treat RA.
In patients with established RA, the feasibility of scanning the wrists, MCPs, PIPs, and relevant symptomatic joints for remission evaluation received moderate consensus. Meanwhile, strong consensus supported the idea that increasing the number of joints scanned with MSUS could increase the certainty of the patient having achieved remission, though the guidance acknowledges that “this must be balanced against the feasibility within the context of clinical care.”
For confirming RA remission via MSUS, strong consensus supported using GS and PD synovitis and tenosynovitis findings. But consensus was moderate for using the combination of no PD signal and minimal synovial hypertrophy to define ultrasonographic remission and for the use of MSUS detection of subclinical inflammation to predict higher flare rates for those in clinical remission.
The committee moderately agreed that MSUS can enhance patient engagement and understanding of their disease to support personalized treatment decisions, such as adjusting disease-modifying antirheumatic drug regimens.
Finally, the committee broadly agreed that “the integration of musculoskeletal ultrasound presents significant advantages in shared decision-making between healthcare providers and patients,” Kaeley said. “Ultrasound, especially with Doppler technique, provides critical insights into disease activity and structural changes not always apparent during standard examination.”
Arnold said she particularly appreciated that the committee, rather than prescribing a specific exam, opted to be more generalizable so that people use the guidance in the context that makes the most sense for them clinically. She said it’s an incredible tool, without excluding the importance of a patient’s labs and physical examination.
“It’s helped us make diagnoses in patients who were difficult to diagnose. It’s helped us to understand response to therapy or no response to therapy,” she said. “It makes me question all the studies that I see done on medications where they’re not looking at some type of advanced imaging.”
No external funding was noted for the development of the guidance. Ranganath has reported receiving research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Mallinckrodt. Kaeley has reported receiving research funding from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead/Galapagos, Janssen, and Novartis. Arnold had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — After more than a decade, the American College of Rheumatology has developed new draft guidance for the use of musculoskeletal ultrasound (MSUS) to help with diagnosis, monitoring, and prognosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Though not yet finalized, the statements that came out of a first round of committee voting were unveiled at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
The committee was charged with updating the 2012 recommendations on using MSUS in rheumatology clinical practice, explained Veena K. Ranganath, MD, professor of clinical medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, and director of their Rheumatology Fellowship Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Training Program.
More than 30,000 articles on MSUS and any arthritis have been published since 2012, and there have been significant advances and improvements in technology as well as more widespread education and use in rheumatologic clinical practice, Ranganath said.
“There’s also been advancements in therapeutic agents and therapeutic strategies in use of these medications in rheumatoid arthritis,” Ranganath said. “We all know that the patient of today is very different than the patient of 10 years ago or 20 years ago, so this really impacts the clinical questions we ask of how we need to incorporate musculoskeletal ultrasound into our rheumatology clinical practice.”
The process of developing the guidance involved determining key domains and then relevant clinical questions for ultrasonography using the PICO model (patient/population, intervention, comparison, and outcomes). Evidence came from a review of relevant literature published since 1993 in PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Database. A panel of 11 experts voted on the quality of the evidence as being moderate or strong for 33 statements, rejecting three that had no consensus. The committee will hold another round of voting before the guidance is published.
Erin Arnold, MD, a rheumatologist at Arnold Arthritis & Rheumatology in Skokie, Illinois, said in an interview she believes the new guidance will be “tremendously helpful,” particularly in getting “everybody on the same page” with similar practices and helping enhance diagnosis and response to therapy.
Having used MSUS for over 20 years, Arnold said watching it evolve and seeing “this type of manuscript being put together as a resource for physicians who are taking care of inflammatory arthritis is exciting.”
“There’s not a single way we really can assess disease activity in our patients, and so having a composite of things that you’re looking at really enhances our ability to understand people’s pain,” Arnold said.
“When you have a patient in front of you that is in so much pain but doesn’t have any active inflammation, it’s hard to want to further put them at risk with more medication,” she said. “It’s so meaningful to be able to have a conversation about ... what are other complementary interventions? How are they sleeping? How are they eating? What are they taking as far as supplements? What are they doing to decrease that kind of fear and fight-or-flight response that often can drive some of our pain?”
Use of MSUS for Diagnosis Confirmation and Treatment Decisions
Gurjit S. Kaeley, MBBS, professor of medicine, division chief of rheumatology and clinical immunology, and medical director of the Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Program at the University of Florida College of Medicine, Jacksonville, reviewed the final statements for MSUS use with RA.
He said there was strong consensus that adding MSUS to clinical examination can aid diagnosis of early RA in patients with suspected RA, particularly with detection of synovitis, tenosynovitis, and erosions. There was moderate consensus that MSUS detection of tenosynovitis could predict later development of RA.
“Furthermore, erosions do have a predictive prognostic value in telling us that these patients need more attention and more urgent attention to getting urgent care with disease-modifying medications,” Kaeley said. “Ultrasound scanning for bone erosions on a few target joints was found to be feasible in literature and provides information not available with clinical examination. Furthermore, ultrasound is more sensitive than plain radiography for the detection of erosions.”
Moderate consensus supported a cutoff of at least 2 mm for erosions when using MSUS for diagnostic purposes.
Strong consensus supported using MSUS of the wrist, second and third metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints, and second and third interphalangeal (PIP) joints to aid early RA diagnosis, with moderate consensus that cutoffs of least 2 grayscale (GS) or at least 1 GS with at least 1 power Doppler (PD) at the joint level supports both an RA diagnosis and, in patients already diagnosed with RA, a positive joint.
“Grayscale-only definitions were included since equipment may not have sensitive Doppler,” Kaeley said.
Strong consensus supported scanning only a reduced set of representative or symptomatic joints to monitor disease activity with MSUS.
Inflammatory Signs, Disease Progression, and Flares
There was also strong consensus for using MSUS in patients with established RA and comorbidities to help distinguish between RA-related inflammation versus inflammation from other conditions, such as gout or calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease, or versus non–RA-related pain, such as that from fibromyalgia.
Patients with fibromyalgia, for example, “tend to have more steroid exposure and a high prevalence of biologic use because the composite disease scores tend to overestimate disease activity, especially when compared to ultrasound assessment,” Kaeley said.
Moderate consensus supported using MSUS in patients with established RA to objectively evaluate inflammation so as to eliminate age-related bias.
While MSUS signs of synovitis had only moderate consensus to be associated with radiographic progression and decline in patient-reported outcomes for patients with early RA, consensus was strong for this association in patients with established RA.
In terms of predicting disease progression with MSUS monitoring of RA disease activity, moderate consensus supported scanning the wrists and MCPs and PIPs of the hands and using the dorsal view. Kaeley emphasized that ultrasound is a clinical tool that should be used to answer a clinical question, so the sonographer or clinician needs to provide guidance on the areas to be scanned.
Multiple standardized scoring systems exist for predicting RA disease progression, but there is no consensus on which is the most effective, and there is only moderate consensus about the validity of using dichotomous scoring with an established cutoff for a positive joint.
The combination of MSUS with clinical examination appears to be more effective at confirming RA flares than using only clinical examination, and in certain patients with established RA, MSUS may provide insights into subclinical disease activity to help maintain remission and/or potentially guide treatment decisions, “especially when coming across de-escalation therapy decisions,” Kaeley said.
Despite the negative results of treat-to-target trials that tested MSUS as a routine tool in all patients, the committee achieved strong consensus on the potential value of using MSUS in early RA to clarify clinical status and/or help achieve low disease activity or remission in certain patient populations, “such as those with patient/provider discordance or difficult physical examinations,” Kaeley said.
Therapy Response, Remission, and Shared Decision-Making
Moderate consensus supported acknowledgment that using MSUS to assess response to therapy could be affected by obesity and that MSUS can distinguish active synovitis symptoms from other pain sources in difficult-to-treat RA.
In patients with established RA, the feasibility of scanning the wrists, MCPs, PIPs, and relevant symptomatic joints for remission evaluation received moderate consensus. Meanwhile, strong consensus supported the idea that increasing the number of joints scanned with MSUS could increase the certainty of the patient having achieved remission, though the guidance acknowledges that “this must be balanced against the feasibility within the context of clinical care.”
For confirming RA remission via MSUS, strong consensus supported using GS and PD synovitis and tenosynovitis findings. But consensus was moderate for using the combination of no PD signal and minimal synovial hypertrophy to define ultrasonographic remission and for the use of MSUS detection of subclinical inflammation to predict higher flare rates for those in clinical remission.
The committee moderately agreed that MSUS can enhance patient engagement and understanding of their disease to support personalized treatment decisions, such as adjusting disease-modifying antirheumatic drug regimens.
Finally, the committee broadly agreed that “the integration of musculoskeletal ultrasound presents significant advantages in shared decision-making between healthcare providers and patients,” Kaeley said. “Ultrasound, especially with Doppler technique, provides critical insights into disease activity and structural changes not always apparent during standard examination.”
Arnold said she particularly appreciated that the committee, rather than prescribing a specific exam, opted to be more generalizable so that people use the guidance in the context that makes the most sense for them clinically. She said it’s an incredible tool, without excluding the importance of a patient’s labs and physical examination.
“It’s helped us make diagnoses in patients who were difficult to diagnose. It’s helped us to understand response to therapy or no response to therapy,” she said. “It makes me question all the studies that I see done on medications where they’re not looking at some type of advanced imaging.”
No external funding was noted for the development of the guidance. Ranganath has reported receiving research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Mallinckrodt. Kaeley has reported receiving research funding from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead/Galapagos, Janssen, and Novartis. Arnold had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — After more than a decade, the American College of Rheumatology has developed new draft guidance for the use of musculoskeletal ultrasound (MSUS) to help with diagnosis, monitoring, and prognosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Though not yet finalized, the statements that came out of a first round of committee voting were unveiled at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
The committee was charged with updating the 2012 recommendations on using MSUS in rheumatology clinical practice, explained Veena K. Ranganath, MD, professor of clinical medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, and director of their Rheumatology Fellowship Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Training Program.
More than 30,000 articles on MSUS and any arthritis have been published since 2012, and there have been significant advances and improvements in technology as well as more widespread education and use in rheumatologic clinical practice, Ranganath said.
“There’s also been advancements in therapeutic agents and therapeutic strategies in use of these medications in rheumatoid arthritis,” Ranganath said. “We all know that the patient of today is very different than the patient of 10 years ago or 20 years ago, so this really impacts the clinical questions we ask of how we need to incorporate musculoskeletal ultrasound into our rheumatology clinical practice.”
The process of developing the guidance involved determining key domains and then relevant clinical questions for ultrasonography using the PICO model (patient/population, intervention, comparison, and outcomes). Evidence came from a review of relevant literature published since 1993 in PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Database. A panel of 11 experts voted on the quality of the evidence as being moderate or strong for 33 statements, rejecting three that had no consensus. The committee will hold another round of voting before the guidance is published.
Erin Arnold, MD, a rheumatologist at Arnold Arthritis & Rheumatology in Skokie, Illinois, said in an interview she believes the new guidance will be “tremendously helpful,” particularly in getting “everybody on the same page” with similar practices and helping enhance diagnosis and response to therapy.
Having used MSUS for over 20 years, Arnold said watching it evolve and seeing “this type of manuscript being put together as a resource for physicians who are taking care of inflammatory arthritis is exciting.”
“There’s not a single way we really can assess disease activity in our patients, and so having a composite of things that you’re looking at really enhances our ability to understand people’s pain,” Arnold said.
“When you have a patient in front of you that is in so much pain but doesn’t have any active inflammation, it’s hard to want to further put them at risk with more medication,” she said. “It’s so meaningful to be able to have a conversation about ... what are other complementary interventions? How are they sleeping? How are they eating? What are they taking as far as supplements? What are they doing to decrease that kind of fear and fight-or-flight response that often can drive some of our pain?”
Use of MSUS for Diagnosis Confirmation and Treatment Decisions
Gurjit S. Kaeley, MBBS, professor of medicine, division chief of rheumatology and clinical immunology, and medical director of the Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Program at the University of Florida College of Medicine, Jacksonville, reviewed the final statements for MSUS use with RA.
He said there was strong consensus that adding MSUS to clinical examination can aid diagnosis of early RA in patients with suspected RA, particularly with detection of synovitis, tenosynovitis, and erosions. There was moderate consensus that MSUS detection of tenosynovitis could predict later development of RA.
“Furthermore, erosions do have a predictive prognostic value in telling us that these patients need more attention and more urgent attention to getting urgent care with disease-modifying medications,” Kaeley said. “Ultrasound scanning for bone erosions on a few target joints was found to be feasible in literature and provides information not available with clinical examination. Furthermore, ultrasound is more sensitive than plain radiography for the detection of erosions.”
Moderate consensus supported a cutoff of at least 2 mm for erosions when using MSUS for diagnostic purposes.
Strong consensus supported using MSUS of the wrist, second and third metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints, and second and third interphalangeal (PIP) joints to aid early RA diagnosis, with moderate consensus that cutoffs of least 2 grayscale (GS) or at least 1 GS with at least 1 power Doppler (PD) at the joint level supports both an RA diagnosis and, in patients already diagnosed with RA, a positive joint.
“Grayscale-only definitions were included since equipment may not have sensitive Doppler,” Kaeley said.
Strong consensus supported scanning only a reduced set of representative or symptomatic joints to monitor disease activity with MSUS.
Inflammatory Signs, Disease Progression, and Flares
There was also strong consensus for using MSUS in patients with established RA and comorbidities to help distinguish between RA-related inflammation versus inflammation from other conditions, such as gout or calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease, or versus non–RA-related pain, such as that from fibromyalgia.
Patients with fibromyalgia, for example, “tend to have more steroid exposure and a high prevalence of biologic use because the composite disease scores tend to overestimate disease activity, especially when compared to ultrasound assessment,” Kaeley said.
Moderate consensus supported using MSUS in patients with established RA to objectively evaluate inflammation so as to eliminate age-related bias.
While MSUS signs of synovitis had only moderate consensus to be associated with radiographic progression and decline in patient-reported outcomes for patients with early RA, consensus was strong for this association in patients with established RA.
In terms of predicting disease progression with MSUS monitoring of RA disease activity, moderate consensus supported scanning the wrists and MCPs and PIPs of the hands and using the dorsal view. Kaeley emphasized that ultrasound is a clinical tool that should be used to answer a clinical question, so the sonographer or clinician needs to provide guidance on the areas to be scanned.
Multiple standardized scoring systems exist for predicting RA disease progression, but there is no consensus on which is the most effective, and there is only moderate consensus about the validity of using dichotomous scoring with an established cutoff for a positive joint.
The combination of MSUS with clinical examination appears to be more effective at confirming RA flares than using only clinical examination, and in certain patients with established RA, MSUS may provide insights into subclinical disease activity to help maintain remission and/or potentially guide treatment decisions, “especially when coming across de-escalation therapy decisions,” Kaeley said.
Despite the negative results of treat-to-target trials that tested MSUS as a routine tool in all patients, the committee achieved strong consensus on the potential value of using MSUS in early RA to clarify clinical status and/or help achieve low disease activity or remission in certain patient populations, “such as those with patient/provider discordance or difficult physical examinations,” Kaeley said.
Therapy Response, Remission, and Shared Decision-Making
Moderate consensus supported acknowledgment that using MSUS to assess response to therapy could be affected by obesity and that MSUS can distinguish active synovitis symptoms from other pain sources in difficult-to-treat RA.
In patients with established RA, the feasibility of scanning the wrists, MCPs, PIPs, and relevant symptomatic joints for remission evaluation received moderate consensus. Meanwhile, strong consensus supported the idea that increasing the number of joints scanned with MSUS could increase the certainty of the patient having achieved remission, though the guidance acknowledges that “this must be balanced against the feasibility within the context of clinical care.”
For confirming RA remission via MSUS, strong consensus supported using GS and PD synovitis and tenosynovitis findings. But consensus was moderate for using the combination of no PD signal and minimal synovial hypertrophy to define ultrasonographic remission and for the use of MSUS detection of subclinical inflammation to predict higher flare rates for those in clinical remission.
The committee moderately agreed that MSUS can enhance patient engagement and understanding of their disease to support personalized treatment decisions, such as adjusting disease-modifying antirheumatic drug regimens.
Finally, the committee broadly agreed that “the integration of musculoskeletal ultrasound presents significant advantages in shared decision-making between healthcare providers and patients,” Kaeley said. “Ultrasound, especially with Doppler technique, provides critical insights into disease activity and structural changes not always apparent during standard examination.”
Arnold said she particularly appreciated that the committee, rather than prescribing a specific exam, opted to be more generalizable so that people use the guidance in the context that makes the most sense for them clinically. She said it’s an incredible tool, without excluding the importance of a patient’s labs and physical examination.
“It’s helped us make diagnoses in patients who were difficult to diagnose. It’s helped us to understand response to therapy or no response to therapy,” she said. “It makes me question all the studies that I see done on medications where they’re not looking at some type of advanced imaging.”
No external funding was noted for the development of the guidance. Ranganath has reported receiving research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Mallinckrodt. Kaeley has reported receiving research funding from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead/Galapagos, Janssen, and Novartis. Arnold had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACR 2024
Onset of Rheumatoid Arthritis Presaged by Changes in Gut Microbiome
TOPLINE:
Individuals at an increased risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis (RA) have a unique gut microbial composition, characterized by a notable increase in certain strains of Prevotella bacteria. These changes begin approximately 10 months prior to the onset of RA.
METHODOLOGY:
- In this cross-sectional and longitudinal observational study, researchers aimed to identify microbial associations in the early stages of RA, focusing specifically on Prevotellaceae strains.
- The cross-sectional analysis assessed the gut microbiome profiles of 124 individuals at risk of developing RA, 7 patients with newly diagnosed RA, and 22 healthy control individuals free of musculoskeletal symptoms at five different time points over a period of 15 months; 30 patients progressed to RA during the study period.
- The longitudinal analysis was performed in 19 individuals at risk of developing RA, of whom 5 progressed to the condition.
- The risk of developing RA was identified by the presence of anti–cyclic citrullinated protein (anti-CCP) antibodies and the onset of musculoskeletal pain in the preceding 3 months.
- Gut microbiome taxonomic alterations were investigated using 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing and confirmed with shotgun metagenomic DNA sequencing of 49 samples.
TAKEAWAY:
- Gut microbial diversity, particularly alpha diversity, was notably reduced in CCP+ individuals at risk of developing RA vs healthy control individuals (P = .012). Recognized risk factors for RA development such as the presence of rheumatoid factor antibodies and the human leukocyte antigen shared epitope, were significantly linked to diminished gut microbial diversity, in addition to steroid use.
- A specific Prevotellaceae strain (ASV2058) was found to be overabundant in CCP+ individuals at risk of developing RA and in those newly diagnosed with the condition but not in healthy control individuals. Further analysis showed that enrichment and depletion of three and five strains of Prevotellaceae, respectively, were associated with the progression to RA in CCP+ individuals.
- CCP+ individuals who progressed to RA were found to have substantial fluctuations in gut microbiome profiles around 10 months before clinical diagnosis; however, these profiles were relatively stable 10-15 months before the onset of RA, suggesting that changes in the microbiome occur at a later stage.
- Patients with new-onset RA were found to have distinct metabolic shifts, particularly in pathways related to amino acid and energy metabolism.
IN PRACTICE:
“Individuals at risk of RA harbor a distinctive gut microbial composition, including but not limited to an overabundance of Prevotellaceae species. This microbial signature is consistent and correlates with traditional RA risk factors,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Christopher M. Rooney, MD, PhD, University of Leeds in England. It was published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The small longitudinal sample size and lack of a 1:1 longitudinal comparison between CCP+ individuals at risk for RA and healthy control individuals were major limitations of this study. The new-onset RA cohort was heterogeneous, reflecting the practical constraints of recruitment from standard care clinics. Integrated transcriptomic or metabolomic data were unavailable, restricting interpretation to potential rather than confirmed metabolic activity.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by personal fellowships received by the lead author from Versus Arthritis, Leeds Cares, and a National Institute for Health Research Clinical Lectureship. Some authors disclosed receiving grants, funding, consulting fees, or honoraria from various pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Individuals at an increased risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis (RA) have a unique gut microbial composition, characterized by a notable increase in certain strains of Prevotella bacteria. These changes begin approximately 10 months prior to the onset of RA.
METHODOLOGY:
- In this cross-sectional and longitudinal observational study, researchers aimed to identify microbial associations in the early stages of RA, focusing specifically on Prevotellaceae strains.
- The cross-sectional analysis assessed the gut microbiome profiles of 124 individuals at risk of developing RA, 7 patients with newly diagnosed RA, and 22 healthy control individuals free of musculoskeletal symptoms at five different time points over a period of 15 months; 30 patients progressed to RA during the study period.
- The longitudinal analysis was performed in 19 individuals at risk of developing RA, of whom 5 progressed to the condition.
- The risk of developing RA was identified by the presence of anti–cyclic citrullinated protein (anti-CCP) antibodies and the onset of musculoskeletal pain in the preceding 3 months.
- Gut microbiome taxonomic alterations were investigated using 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing and confirmed with shotgun metagenomic DNA sequencing of 49 samples.
TAKEAWAY:
- Gut microbial diversity, particularly alpha diversity, was notably reduced in CCP+ individuals at risk of developing RA vs healthy control individuals (P = .012). Recognized risk factors for RA development such as the presence of rheumatoid factor antibodies and the human leukocyte antigen shared epitope, were significantly linked to diminished gut microbial diversity, in addition to steroid use.
- A specific Prevotellaceae strain (ASV2058) was found to be overabundant in CCP+ individuals at risk of developing RA and in those newly diagnosed with the condition but not in healthy control individuals. Further analysis showed that enrichment and depletion of three and five strains of Prevotellaceae, respectively, were associated with the progression to RA in CCP+ individuals.
- CCP+ individuals who progressed to RA were found to have substantial fluctuations in gut microbiome profiles around 10 months before clinical diagnosis; however, these profiles were relatively stable 10-15 months before the onset of RA, suggesting that changes in the microbiome occur at a later stage.
- Patients with new-onset RA were found to have distinct metabolic shifts, particularly in pathways related to amino acid and energy metabolism.
IN PRACTICE:
“Individuals at risk of RA harbor a distinctive gut microbial composition, including but not limited to an overabundance of Prevotellaceae species. This microbial signature is consistent and correlates with traditional RA risk factors,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Christopher M. Rooney, MD, PhD, University of Leeds in England. It was published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The small longitudinal sample size and lack of a 1:1 longitudinal comparison between CCP+ individuals at risk for RA and healthy control individuals were major limitations of this study. The new-onset RA cohort was heterogeneous, reflecting the practical constraints of recruitment from standard care clinics. Integrated transcriptomic or metabolomic data were unavailable, restricting interpretation to potential rather than confirmed metabolic activity.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by personal fellowships received by the lead author from Versus Arthritis, Leeds Cares, and a National Institute for Health Research Clinical Lectureship. Some authors disclosed receiving grants, funding, consulting fees, or honoraria from various pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Individuals at an increased risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis (RA) have a unique gut microbial composition, characterized by a notable increase in certain strains of Prevotella bacteria. These changes begin approximately 10 months prior to the onset of RA.
METHODOLOGY:
- In this cross-sectional and longitudinal observational study, researchers aimed to identify microbial associations in the early stages of RA, focusing specifically on Prevotellaceae strains.
- The cross-sectional analysis assessed the gut microbiome profiles of 124 individuals at risk of developing RA, 7 patients with newly diagnosed RA, and 22 healthy control individuals free of musculoskeletal symptoms at five different time points over a period of 15 months; 30 patients progressed to RA during the study period.
- The longitudinal analysis was performed in 19 individuals at risk of developing RA, of whom 5 progressed to the condition.
- The risk of developing RA was identified by the presence of anti–cyclic citrullinated protein (anti-CCP) antibodies and the onset of musculoskeletal pain in the preceding 3 months.
- Gut microbiome taxonomic alterations were investigated using 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing and confirmed with shotgun metagenomic DNA sequencing of 49 samples.
TAKEAWAY:
- Gut microbial diversity, particularly alpha diversity, was notably reduced in CCP+ individuals at risk of developing RA vs healthy control individuals (P = .012). Recognized risk factors for RA development such as the presence of rheumatoid factor antibodies and the human leukocyte antigen shared epitope, were significantly linked to diminished gut microbial diversity, in addition to steroid use.
- A specific Prevotellaceae strain (ASV2058) was found to be overabundant in CCP+ individuals at risk of developing RA and in those newly diagnosed with the condition but not in healthy control individuals. Further analysis showed that enrichment and depletion of three and five strains of Prevotellaceae, respectively, were associated with the progression to RA in CCP+ individuals.
- CCP+ individuals who progressed to RA were found to have substantial fluctuations in gut microbiome profiles around 10 months before clinical diagnosis; however, these profiles were relatively stable 10-15 months before the onset of RA, suggesting that changes in the microbiome occur at a later stage.
- Patients with new-onset RA were found to have distinct metabolic shifts, particularly in pathways related to amino acid and energy metabolism.
IN PRACTICE:
“Individuals at risk of RA harbor a distinctive gut microbial composition, including but not limited to an overabundance of Prevotellaceae species. This microbial signature is consistent and correlates with traditional RA risk factors,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Christopher M. Rooney, MD, PhD, University of Leeds in England. It was published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The small longitudinal sample size and lack of a 1:1 longitudinal comparison between CCP+ individuals at risk for RA and healthy control individuals were major limitations of this study. The new-onset RA cohort was heterogeneous, reflecting the practical constraints of recruitment from standard care clinics. Integrated transcriptomic or metabolomic data were unavailable, restricting interpretation to potential rather than confirmed metabolic activity.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by personal fellowships received by the lead author from Versus Arthritis, Leeds Cares, and a National Institute for Health Research Clinical Lectureship. Some authors disclosed receiving grants, funding, consulting fees, or honoraria from various pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.