User login
Official Newspaper of the American College of Surgeons
Open enrollment 2019: Busiest week so far at HealthCare.gov
but the weekly and cumulative totals for plans selected continued to run below last year’s levels, according to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.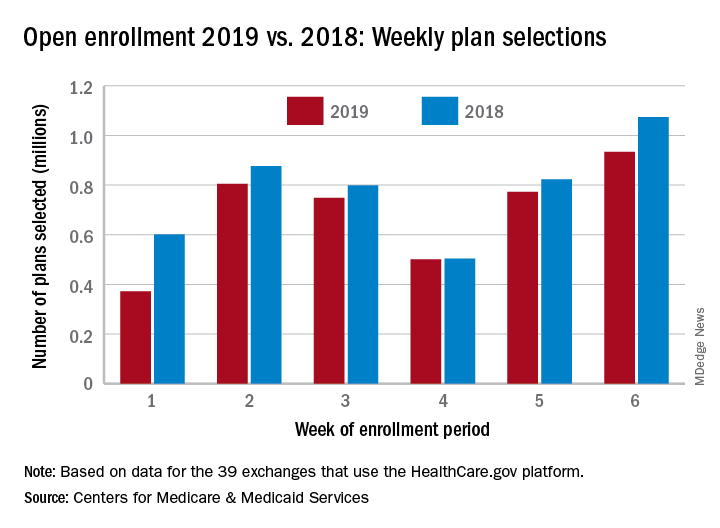
Over 934,000 plans were selected from Dec. 2 to Dec. 8, which puts the total at 4.13 million plans for the 2019 coverage year in the 39 states that use the HealthCare.gov platform, the CMS reported. Consumers renewing their coverage make up the majority of plans selected during week 6 (640,000) and cumulatively for the season (3.03 million), with new applications running at 295,000 for week 6 and 1.1 million overall.
Those numbers are down from last year, when 1.07 million plans (685,000 renewals and 389,000 new applications) were selected during week 6 of open enrollment for the 2018 coverage year, which brought the total for the season at the time to 4.68 million (3.30 million/1.38 million), CMS data show.
The deadline to enroll in a plan for 2019 is Dec. 15.
but the weekly and cumulative totals for plans selected continued to run below last year’s levels, according to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
Over 934,000 plans were selected from Dec. 2 to Dec. 8, which puts the total at 4.13 million plans for the 2019 coverage year in the 39 states that use the HealthCare.gov platform, the CMS reported. Consumers renewing their coverage make up the majority of plans selected during week 6 (640,000) and cumulatively for the season (3.03 million), with new applications running at 295,000 for week 6 and 1.1 million overall.
Those numbers are down from last year, when 1.07 million plans (685,000 renewals and 389,000 new applications) were selected during week 6 of open enrollment for the 2018 coverage year, which brought the total for the season at the time to 4.68 million (3.30 million/1.38 million), CMS data show.
The deadline to enroll in a plan for 2019 is Dec. 15.
but the weekly and cumulative totals for plans selected continued to run below last year’s levels, according to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
Over 934,000 plans were selected from Dec. 2 to Dec. 8, which puts the total at 4.13 million plans for the 2019 coverage year in the 39 states that use the HealthCare.gov platform, the CMS reported. Consumers renewing their coverage make up the majority of plans selected during week 6 (640,000) and cumulatively for the season (3.03 million), with new applications running at 295,000 for week 6 and 1.1 million overall.
Those numbers are down from last year, when 1.07 million plans (685,000 renewals and 389,000 new applications) were selected during week 6 of open enrollment for the 2018 coverage year, which brought the total for the season at the time to 4.68 million (3.30 million/1.38 million), CMS data show.
The deadline to enroll in a plan for 2019 is Dec. 15.
Brazil sees first live birth from deceased-donor uterus transplant
The healthy 2,550-g infant girl was born in December 2017 via a planned cesarean delivery at about 36 weeks’ gestation. Her mother, the transplant recipient, has congenital absence of the uterus from Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser (MRKH) syndrome. Removal of the transplanted uterus at the time of delivery allowed the woman to stop taking the immunosuppressive medications that she’d been on since the transplantation, which had been performed less than a year and a half previously.
The uterus had been retrieved from a 45-year-old donor who experienced a subarachnoid hemorrhage and subsequent brain death. The donor had three vaginal deliveries, and no history of reproductive issues or sexually transmitted infection, wrote Dani Ejzenberg, MD, and his colleagues at the University of São Paolo, Brazil.
The retrieval and transplantation procedures were done at the university’s hospital, in accordance with a research protocol approved by the university, a Brazilian national ethics committee, and the country’s national transplantation system. Thorough psychological evaluation was part of the research protocol, and the patient and her partner had monthly psychological counseling from therapists with expertise in transplant and fertility, wrote Dr. Ejzenberg and his colleagues.
In preparation for the transplantation, which occurred when the recipient was 32 years old, she had in vitro fertilization several months before the procedure. Eight “good-quality” blastocysts were retrieved and cryopreserved, said Dr. Ejzenberg and his coauthors. The recipient’s menstrual cycle resumed 37 days after transplantation, and one of the cryopreserved embryos was transferred about 7 months after the uterine transplantation procedure, resulting in the pregnancy.
The donor and recipient were matched only by ABO blood type, with no further tissue typing being done, wrote Dr. Ejzenberg and his colleagues. The immunosuppressive regimen paralleled that used in previous successful uterine transplantations from live donors in Sweden, with induction via 1 g intraoperative methylprednisolone and 1.5 mg/kg of thymoglobulin. Thereafter, the recipient received tacrolimus titrated to a trough of 8-10 ng/mL, along with mycophenolate mofetil 720 mg twice daily. Five months after her transplantation, the mycophenolate mofetil was replaced with 100 mg azathioprine and 10 mg prednisone daily, a regimen that she stayed on until cesarean delivery.
Broad-spectrum antibiotics, antifungals, and anthelmintics were administered during the patient’s hospital stay. Prophylactic antibiotics were continued for 6 months, and antiviral medication was given prophylactically for 3 months. The recipient had one episode of vaginal discharge, treated with antifungal medication, and one episode of pyelonephritis during pregnancy, treated during a brief inpatient stay.
Enoxaparin and aspirin were used for inpatient venous thromboembolism prophylaxis, and heparin and aspirin thereafter. Aspirin was discontinued at 34 weeks, and heparin the day before delivery.
Swedish and American teams involved in uterine transplantation are working to develop standardization of surgical techniques, immunosuppression protocol, and methods to monitor rejection.
However, pointed out Dr. Ejzenberg and his coauthors, some technical aspects were unique to the deceased donor transplantation. These included managing total ischemic time for the donor tissue because heart, liver, and kidney retrieval all were given priority.
One downstream effect of this was longer-than-expected procedure and anesthesia time for the recipient, because coordinating donor uterus retrieval and preparation of the surgical bed in the live recipient was tricky; surgery time was about 10.5 hours. Also, there was prolonged warm-ischemia time because six small-vessel anastomoses needed to be performed, wrote the investigators.
After reperfusion of the implanted uterus, there was brisk bleeding from a number of small vessels that had not been ligated on retrieval because of concerns about ischemic time. These were identified and sutured or cauterized, but the total estimated blood loss during the procedures was 1,200 mL, with most of that coming from the uterus, said Dr. Ejzenberg and his coauthors.
The donor uterus had a total of almost 8 hours of ischemic time, exceeding the previously published live donor maximum uterine ischemic time of 3 hours, 25 minutes. This experience can inform surgical teams considering future uterine transplantations.
Dr. Ejzenberg and his colleagues also said that they cast a broad net with immunosuppression, erring on the side of caution. With more experience may come the ability to scale back immunosuppressive regimens, they noted.
The explantation of the uterus and associated blood vessels after delivery afforded the opportunity for pathological examination of the uterus and other tissues, which showed no signs of rejection. The uterine arteries did have mild intimal fibrous hyperplasia that was likely related to the age of the donor, said Dr. Ejzenberg and his coauthors.
This successful completion of a deceased-donor uterine transplantation demonstrates the feasibility of accessing “a much wider potential donor population, as the numbers of people willing and committed to donate organs upon their own deaths are far larger than those of potential live donors,” wrote Dr. Ejzenberg and his colleagues. “Further incidental but substantial benefits of the use of deceased donors include lower costs and avoidance of live donors’ surgical risks.”
In 2011, a uterine transplantation from a deceased donor resulted in pregnancy, but ended in miscarriage.
Funding was provided by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo and the Hospital das Clínicas of University of São Paulo School of Medicine. Dr. Ejzenberg and his colleagues reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Ejzenberg D. et al. Lancet. 2018 Dec. doi: 10.1015/S0140-6736(18)31766-5.
Among the advances seen in this deceased-donor uterus transplant is a demonstration that ischemic time of nearly 8 hours – four times the average seen in live donation – does not preclude a successful transplantation.
Also, the timetable for transplantation seen here did not involve the year-long waiting period between transplantation and pregnancy that has been the norm in live uterine transplantation.
However, uterine transplantation, whether from a living or deceased donor, is still in its early stages. Among the many unsettled questions are whether live or deceased donor transplantations yield superior results. Additional technical aspects to be further studied include best surgical approach for the donor uterus, best anastomosis technique, and optimal immunosuppression and antimicrobial/antifungal/antiviral regimens.
Continued work needs to be done to standardize these and other aspects of the peri- and postoperative care of women undergoing uterine transplantation.
In addition, long-term tracking of children born from transplanted uteri is needed, so outcomes can be assessed over the lifespan.
Going forward, it could be that uterine transplantation may be offered to an expanded cohort of women, including those with bulky, nonoperable uterine fibroids, those who have received pelvic radiotherapy, and even those who have had multiple unexplained problems with implantation during fertility treatments. In all cases, researchers should work toward achieving the highest live birth rate at the lowest risk to donors and patients, while also working to make more organs available; establishing registries, and encouraging prospective registration and transparent reporting of uterus transplantation procedures.
Cesar Diaz-Garcia, MD, is medical director of IVI-London, and Antonio Pellicer, MD, is professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Valencia, Spain. These remarks were drawn from their editorial accompanying the report by Ejzenberg et al. (Lancet. 2018 Dec. doi: 10.1016/50140-6736(18)32106-8).
Among the advances seen in this deceased-donor uterus transplant is a demonstration that ischemic time of nearly 8 hours – four times the average seen in live donation – does not preclude a successful transplantation.
Also, the timetable for transplantation seen here did not involve the year-long waiting period between transplantation and pregnancy that has been the norm in live uterine transplantation.
However, uterine transplantation, whether from a living or deceased donor, is still in its early stages. Among the many unsettled questions are whether live or deceased donor transplantations yield superior results. Additional technical aspects to be further studied include best surgical approach for the donor uterus, best anastomosis technique, and optimal immunosuppression and antimicrobial/antifungal/antiviral regimens.
Continued work needs to be done to standardize these and other aspects of the peri- and postoperative care of women undergoing uterine transplantation.
In addition, long-term tracking of children born from transplanted uteri is needed, so outcomes can be assessed over the lifespan.
Going forward, it could be that uterine transplantation may be offered to an expanded cohort of women, including those with bulky, nonoperable uterine fibroids, those who have received pelvic radiotherapy, and even those who have had multiple unexplained problems with implantation during fertility treatments. In all cases, researchers should work toward achieving the highest live birth rate at the lowest risk to donors and patients, while also working to make more organs available; establishing registries, and encouraging prospective registration and transparent reporting of uterus transplantation procedures.
Cesar Diaz-Garcia, MD, is medical director of IVI-London, and Antonio Pellicer, MD, is professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Valencia, Spain. These remarks were drawn from their editorial accompanying the report by Ejzenberg et al. (Lancet. 2018 Dec. doi: 10.1016/50140-6736(18)32106-8).
Among the advances seen in this deceased-donor uterus transplant is a demonstration that ischemic time of nearly 8 hours – four times the average seen in live donation – does not preclude a successful transplantation.
Also, the timetable for transplantation seen here did not involve the year-long waiting period between transplantation and pregnancy that has been the norm in live uterine transplantation.
However, uterine transplantation, whether from a living or deceased donor, is still in its early stages. Among the many unsettled questions are whether live or deceased donor transplantations yield superior results. Additional technical aspects to be further studied include best surgical approach for the donor uterus, best anastomosis technique, and optimal immunosuppression and antimicrobial/antifungal/antiviral regimens.
Continued work needs to be done to standardize these and other aspects of the peri- and postoperative care of women undergoing uterine transplantation.
In addition, long-term tracking of children born from transplanted uteri is needed, so outcomes can be assessed over the lifespan.
Going forward, it could be that uterine transplantation may be offered to an expanded cohort of women, including those with bulky, nonoperable uterine fibroids, those who have received pelvic radiotherapy, and even those who have had multiple unexplained problems with implantation during fertility treatments. In all cases, researchers should work toward achieving the highest live birth rate at the lowest risk to donors and patients, while also working to make more organs available; establishing registries, and encouraging prospective registration and transparent reporting of uterus transplantation procedures.
Cesar Diaz-Garcia, MD, is medical director of IVI-London, and Antonio Pellicer, MD, is professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Valencia, Spain. These remarks were drawn from their editorial accompanying the report by Ejzenberg et al. (Lancet. 2018 Dec. doi: 10.1016/50140-6736(18)32106-8).
The healthy 2,550-g infant girl was born in December 2017 via a planned cesarean delivery at about 36 weeks’ gestation. Her mother, the transplant recipient, has congenital absence of the uterus from Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser (MRKH) syndrome. Removal of the transplanted uterus at the time of delivery allowed the woman to stop taking the immunosuppressive medications that she’d been on since the transplantation, which had been performed less than a year and a half previously.
The uterus had been retrieved from a 45-year-old donor who experienced a subarachnoid hemorrhage and subsequent brain death. The donor had three vaginal deliveries, and no history of reproductive issues or sexually transmitted infection, wrote Dani Ejzenberg, MD, and his colleagues at the University of São Paolo, Brazil.
The retrieval and transplantation procedures were done at the university’s hospital, in accordance with a research protocol approved by the university, a Brazilian national ethics committee, and the country’s national transplantation system. Thorough psychological evaluation was part of the research protocol, and the patient and her partner had monthly psychological counseling from therapists with expertise in transplant and fertility, wrote Dr. Ejzenberg and his colleagues.
In preparation for the transplantation, which occurred when the recipient was 32 years old, she had in vitro fertilization several months before the procedure. Eight “good-quality” blastocysts were retrieved and cryopreserved, said Dr. Ejzenberg and his coauthors. The recipient’s menstrual cycle resumed 37 days after transplantation, and one of the cryopreserved embryos was transferred about 7 months after the uterine transplantation procedure, resulting in the pregnancy.
The donor and recipient were matched only by ABO blood type, with no further tissue typing being done, wrote Dr. Ejzenberg and his colleagues. The immunosuppressive regimen paralleled that used in previous successful uterine transplantations from live donors in Sweden, with induction via 1 g intraoperative methylprednisolone and 1.5 mg/kg of thymoglobulin. Thereafter, the recipient received tacrolimus titrated to a trough of 8-10 ng/mL, along with mycophenolate mofetil 720 mg twice daily. Five months after her transplantation, the mycophenolate mofetil was replaced with 100 mg azathioprine and 10 mg prednisone daily, a regimen that she stayed on until cesarean delivery.
Broad-spectrum antibiotics, antifungals, and anthelmintics were administered during the patient’s hospital stay. Prophylactic antibiotics were continued for 6 months, and antiviral medication was given prophylactically for 3 months. The recipient had one episode of vaginal discharge, treated with antifungal medication, and one episode of pyelonephritis during pregnancy, treated during a brief inpatient stay.
Enoxaparin and aspirin were used for inpatient venous thromboembolism prophylaxis, and heparin and aspirin thereafter. Aspirin was discontinued at 34 weeks, and heparin the day before delivery.
Swedish and American teams involved in uterine transplantation are working to develop standardization of surgical techniques, immunosuppression protocol, and methods to monitor rejection.
However, pointed out Dr. Ejzenberg and his coauthors, some technical aspects were unique to the deceased donor transplantation. These included managing total ischemic time for the donor tissue because heart, liver, and kidney retrieval all were given priority.
One downstream effect of this was longer-than-expected procedure and anesthesia time for the recipient, because coordinating donor uterus retrieval and preparation of the surgical bed in the live recipient was tricky; surgery time was about 10.5 hours. Also, there was prolonged warm-ischemia time because six small-vessel anastomoses needed to be performed, wrote the investigators.
After reperfusion of the implanted uterus, there was brisk bleeding from a number of small vessels that had not been ligated on retrieval because of concerns about ischemic time. These were identified and sutured or cauterized, but the total estimated blood loss during the procedures was 1,200 mL, with most of that coming from the uterus, said Dr. Ejzenberg and his coauthors.
The donor uterus had a total of almost 8 hours of ischemic time, exceeding the previously published live donor maximum uterine ischemic time of 3 hours, 25 minutes. This experience can inform surgical teams considering future uterine transplantations.
Dr. Ejzenberg and his colleagues also said that they cast a broad net with immunosuppression, erring on the side of caution. With more experience may come the ability to scale back immunosuppressive regimens, they noted.
The explantation of the uterus and associated blood vessels after delivery afforded the opportunity for pathological examination of the uterus and other tissues, which showed no signs of rejection. The uterine arteries did have mild intimal fibrous hyperplasia that was likely related to the age of the donor, said Dr. Ejzenberg and his coauthors.
This successful completion of a deceased-donor uterine transplantation demonstrates the feasibility of accessing “a much wider potential donor population, as the numbers of people willing and committed to donate organs upon their own deaths are far larger than those of potential live donors,” wrote Dr. Ejzenberg and his colleagues. “Further incidental but substantial benefits of the use of deceased donors include lower costs and avoidance of live donors’ surgical risks.”
In 2011, a uterine transplantation from a deceased donor resulted in pregnancy, but ended in miscarriage.
Funding was provided by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo and the Hospital das Clínicas of University of São Paulo School of Medicine. Dr. Ejzenberg and his colleagues reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Ejzenberg D. et al. Lancet. 2018 Dec. doi: 10.1015/S0140-6736(18)31766-5.
The healthy 2,550-g infant girl was born in December 2017 via a planned cesarean delivery at about 36 weeks’ gestation. Her mother, the transplant recipient, has congenital absence of the uterus from Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser (MRKH) syndrome. Removal of the transplanted uterus at the time of delivery allowed the woman to stop taking the immunosuppressive medications that she’d been on since the transplantation, which had been performed less than a year and a half previously.
The uterus had been retrieved from a 45-year-old donor who experienced a subarachnoid hemorrhage and subsequent brain death. The donor had three vaginal deliveries, and no history of reproductive issues or sexually transmitted infection, wrote Dani Ejzenberg, MD, and his colleagues at the University of São Paolo, Brazil.
The retrieval and transplantation procedures were done at the university’s hospital, in accordance with a research protocol approved by the university, a Brazilian national ethics committee, and the country’s national transplantation system. Thorough psychological evaluation was part of the research protocol, and the patient and her partner had monthly psychological counseling from therapists with expertise in transplant and fertility, wrote Dr. Ejzenberg and his colleagues.
In preparation for the transplantation, which occurred when the recipient was 32 years old, she had in vitro fertilization several months before the procedure. Eight “good-quality” blastocysts were retrieved and cryopreserved, said Dr. Ejzenberg and his coauthors. The recipient’s menstrual cycle resumed 37 days after transplantation, and one of the cryopreserved embryos was transferred about 7 months after the uterine transplantation procedure, resulting in the pregnancy.
The donor and recipient were matched only by ABO blood type, with no further tissue typing being done, wrote Dr. Ejzenberg and his colleagues. The immunosuppressive regimen paralleled that used in previous successful uterine transplantations from live donors in Sweden, with induction via 1 g intraoperative methylprednisolone and 1.5 mg/kg of thymoglobulin. Thereafter, the recipient received tacrolimus titrated to a trough of 8-10 ng/mL, along with mycophenolate mofetil 720 mg twice daily. Five months after her transplantation, the mycophenolate mofetil was replaced with 100 mg azathioprine and 10 mg prednisone daily, a regimen that she stayed on until cesarean delivery.
Broad-spectrum antibiotics, antifungals, and anthelmintics were administered during the patient’s hospital stay. Prophylactic antibiotics were continued for 6 months, and antiviral medication was given prophylactically for 3 months. The recipient had one episode of vaginal discharge, treated with antifungal medication, and one episode of pyelonephritis during pregnancy, treated during a brief inpatient stay.
Enoxaparin and aspirin were used for inpatient venous thromboembolism prophylaxis, and heparin and aspirin thereafter. Aspirin was discontinued at 34 weeks, and heparin the day before delivery.
Swedish and American teams involved in uterine transplantation are working to develop standardization of surgical techniques, immunosuppression protocol, and methods to monitor rejection.
However, pointed out Dr. Ejzenberg and his coauthors, some technical aspects were unique to the deceased donor transplantation. These included managing total ischemic time for the donor tissue because heart, liver, and kidney retrieval all were given priority.
One downstream effect of this was longer-than-expected procedure and anesthesia time for the recipient, because coordinating donor uterus retrieval and preparation of the surgical bed in the live recipient was tricky; surgery time was about 10.5 hours. Also, there was prolonged warm-ischemia time because six small-vessel anastomoses needed to be performed, wrote the investigators.
After reperfusion of the implanted uterus, there was brisk bleeding from a number of small vessels that had not been ligated on retrieval because of concerns about ischemic time. These were identified and sutured or cauterized, but the total estimated blood loss during the procedures was 1,200 mL, with most of that coming from the uterus, said Dr. Ejzenberg and his coauthors.
The donor uterus had a total of almost 8 hours of ischemic time, exceeding the previously published live donor maximum uterine ischemic time of 3 hours, 25 minutes. This experience can inform surgical teams considering future uterine transplantations.
Dr. Ejzenberg and his colleagues also said that they cast a broad net with immunosuppression, erring on the side of caution. With more experience may come the ability to scale back immunosuppressive regimens, they noted.
The explantation of the uterus and associated blood vessels after delivery afforded the opportunity for pathological examination of the uterus and other tissues, which showed no signs of rejection. The uterine arteries did have mild intimal fibrous hyperplasia that was likely related to the age of the donor, said Dr. Ejzenberg and his coauthors.
This successful completion of a deceased-donor uterine transplantation demonstrates the feasibility of accessing “a much wider potential donor population, as the numbers of people willing and committed to donate organs upon their own deaths are far larger than those of potential live donors,” wrote Dr. Ejzenberg and his colleagues. “Further incidental but substantial benefits of the use of deceased donors include lower costs and avoidance of live donors’ surgical risks.”
In 2011, a uterine transplantation from a deceased donor resulted in pregnancy, but ended in miscarriage.
Funding was provided by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo and the Hospital das Clínicas of University of São Paulo School of Medicine. Dr. Ejzenberg and his colleagues reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Ejzenberg D. et al. Lancet. 2018 Dec. doi: 10.1015/S0140-6736(18)31766-5.
FROM THE LANCET
CABG surpasses PCI for diabetics out to 7.5 years
CHICAGO – Patients with diabetes who underwent coronary artery bypass grafting had significantly better survival than patients with diabetes who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention after a median 7.5 years of follow-up.

Those patients comprised about half the patients enrolled in the FREEDOM randomized trial.
Long-term follow-up was only possible for just under half the 1,900 patients with diabetes and multivessel coronary disease originally enrolled in FREEDOM, but when researchers combined the long-term results with the data collected in the original study that had a median 3.8-year follow-up, they found all-cause mortality occurred in 18.3% of the patients who underwent coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and in 24.3% of patients treated with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), a 6% absolute between-group difference that was statistically significant, Valentin Fuster, MD, said at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. This fully jibed with the primary FREEDOM results, which found after 5 years a statistically significant reduction in all-cause death with CABG, compared with PCI, and also a significant reduction in the study’s primary endpoint (a combination of all-cause death, MI, and stroke), which occurred in 18.7% of patients randomized to CABG and in 26.6% of those randomized to PCI (N Engl J Med. 2012 Dec 20;367[25]:2375-84).
The extended follow-up finding lent additional support to existing society recommendations that CABG is the preferred revascularization strategy for patients with diabetes and multivessel coronary disease, most recently from the European Society of Cardiology (Eur Heart J. 2018 Aug 25. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy394), said Dr. Fuster, professor of medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and director of Mount Sinai Heart in New York. A subgroup analysis of the extended follow-up also suggested that the survival benefit from CABG, compared with PCI, was especially strong among patients at or below the study’s median age of 63 years. In the younger subgroup survival among patients treated with CABG was twice as good as it was among patients treated with PCI.
Dr. Fuster noted that few data have been previously reported for survival rates beyond 5 years after revascularization. “This was a difficult study. Following patients for more than 5 years is hard,” he said. Concurrently with his report at the meeting the results also appeared online (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Nov 11. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.11.001).
The FREEDOM (Future Revascularization Evaluation in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: Optimal Management of Multivessel Disease) trial enrolled patients at 140 participating centers during 2005-2010. A total of 25 sites agreed to participate in the extended follow-up and could track 943 patients, 50% of the starting cohort of 1,900 and 89% of the patients originally enrolled at these 25 centers. Dr. Fuster stressed that the 957 patients not included in the follow-up had not been lost, but rather had been managed at sites that declined to participate in this additional study.
Dr. Fuster acknowledged that methods and hardware for PCI have changed since the study ran a decade ago, as have options for medical management. He also highlighted that the long-term follow-up results had no data on rates of MIs and strokes.
FREEDOM had no commercial funding. Dr. Fuster reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Fuster V et al. AHA 2018, Abstract 18609.
These extended results from the FREEDOM trial that followed many patients for 10 years or longer add to the consistent evidence base that supports coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) as the preferred revascularization strategy for patients with diabetes and multivessel coronary disease. The new findings support existing society guidelines that recommend CABG over percutaneous coronary intervention in these patients, most recently in the revascularization guidelines from the European Society of Cardiology (Eur Heart J. 2018 Aug 25. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy394). An update to the U.S. guidelines should appear in 2019.
Continued improvement of revascularization techniques, hardware, and medical management of patients with diabetes and multivessel coronary artery disease makes it challenging to apply the results of studies run in earlier eras to today’s practice. It is possible that continued evolution of coronary stent technology may reduce the differences in outcomes between bypass surgery and percutaneous coronary interventions, although this is less likely if much of CABG’s success relates to the protection it gives against new disease. Future comparisons of different approaches with revascularization will need to take into account the potential contribution of other procedures, other adverse outcomes aside from mortality during long-term follow-up, the consequences of incomplete revascularization, and the impact of new medications for treating diabetes that have been recently shown to also have cardiovascular disease effects. All these factors in concert will define the optimal approach to managing these patients.
Alice K. Jacobs, MD , is director of the cardiac catheterization laboratory at Boston Medical Center and a professor of medicine at Boston University. She has received research support from Abbott Vascular. She made these comments as designated discussant for the study.
These extended results from the FREEDOM trial that followed many patients for 10 years or longer add to the consistent evidence base that supports coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) as the preferred revascularization strategy for patients with diabetes and multivessel coronary disease. The new findings support existing society guidelines that recommend CABG over percutaneous coronary intervention in these patients, most recently in the revascularization guidelines from the European Society of Cardiology (Eur Heart J. 2018 Aug 25. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy394). An update to the U.S. guidelines should appear in 2019.
Continued improvement of revascularization techniques, hardware, and medical management of patients with diabetes and multivessel coronary artery disease makes it challenging to apply the results of studies run in earlier eras to today’s practice. It is possible that continued evolution of coronary stent technology may reduce the differences in outcomes between bypass surgery and percutaneous coronary interventions, although this is less likely if much of CABG’s success relates to the protection it gives against new disease. Future comparisons of different approaches with revascularization will need to take into account the potential contribution of other procedures, other adverse outcomes aside from mortality during long-term follow-up, the consequences of incomplete revascularization, and the impact of new medications for treating diabetes that have been recently shown to also have cardiovascular disease effects. All these factors in concert will define the optimal approach to managing these patients.
Alice K. Jacobs, MD , is director of the cardiac catheterization laboratory at Boston Medical Center and a professor of medicine at Boston University. She has received research support from Abbott Vascular. She made these comments as designated discussant for the study.
These extended results from the FREEDOM trial that followed many patients for 10 years or longer add to the consistent evidence base that supports coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) as the preferred revascularization strategy for patients with diabetes and multivessel coronary disease. The new findings support existing society guidelines that recommend CABG over percutaneous coronary intervention in these patients, most recently in the revascularization guidelines from the European Society of Cardiology (Eur Heart J. 2018 Aug 25. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy394). An update to the U.S. guidelines should appear in 2019.
Continued improvement of revascularization techniques, hardware, and medical management of patients with diabetes and multivessel coronary artery disease makes it challenging to apply the results of studies run in earlier eras to today’s practice. It is possible that continued evolution of coronary stent technology may reduce the differences in outcomes between bypass surgery and percutaneous coronary interventions, although this is less likely if much of CABG’s success relates to the protection it gives against new disease. Future comparisons of different approaches with revascularization will need to take into account the potential contribution of other procedures, other adverse outcomes aside from mortality during long-term follow-up, the consequences of incomplete revascularization, and the impact of new medications for treating diabetes that have been recently shown to also have cardiovascular disease effects. All these factors in concert will define the optimal approach to managing these patients.
Alice K. Jacobs, MD , is director of the cardiac catheterization laboratory at Boston Medical Center and a professor of medicine at Boston University. She has received research support from Abbott Vascular. She made these comments as designated discussant for the study.
CHICAGO – Patients with diabetes who underwent coronary artery bypass grafting had significantly better survival than patients with diabetes who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention after a median 7.5 years of follow-up.

Those patients comprised about half the patients enrolled in the FREEDOM randomized trial.
Long-term follow-up was only possible for just under half the 1,900 patients with diabetes and multivessel coronary disease originally enrolled in FREEDOM, but when researchers combined the long-term results with the data collected in the original study that had a median 3.8-year follow-up, they found all-cause mortality occurred in 18.3% of the patients who underwent coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and in 24.3% of patients treated with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), a 6% absolute between-group difference that was statistically significant, Valentin Fuster, MD, said at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. This fully jibed with the primary FREEDOM results, which found after 5 years a statistically significant reduction in all-cause death with CABG, compared with PCI, and also a significant reduction in the study’s primary endpoint (a combination of all-cause death, MI, and stroke), which occurred in 18.7% of patients randomized to CABG and in 26.6% of those randomized to PCI (N Engl J Med. 2012 Dec 20;367[25]:2375-84).
The extended follow-up finding lent additional support to existing society recommendations that CABG is the preferred revascularization strategy for patients with diabetes and multivessel coronary disease, most recently from the European Society of Cardiology (Eur Heart J. 2018 Aug 25. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy394), said Dr. Fuster, professor of medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and director of Mount Sinai Heart in New York. A subgroup analysis of the extended follow-up also suggested that the survival benefit from CABG, compared with PCI, was especially strong among patients at or below the study’s median age of 63 years. In the younger subgroup survival among patients treated with CABG was twice as good as it was among patients treated with PCI.
Dr. Fuster noted that few data have been previously reported for survival rates beyond 5 years after revascularization. “This was a difficult study. Following patients for more than 5 years is hard,” he said. Concurrently with his report at the meeting the results also appeared online (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Nov 11. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.11.001).
The FREEDOM (Future Revascularization Evaluation in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: Optimal Management of Multivessel Disease) trial enrolled patients at 140 participating centers during 2005-2010. A total of 25 sites agreed to participate in the extended follow-up and could track 943 patients, 50% of the starting cohort of 1,900 and 89% of the patients originally enrolled at these 25 centers. Dr. Fuster stressed that the 957 patients not included in the follow-up had not been lost, but rather had been managed at sites that declined to participate in this additional study.
Dr. Fuster acknowledged that methods and hardware for PCI have changed since the study ran a decade ago, as have options for medical management. He also highlighted that the long-term follow-up results had no data on rates of MIs and strokes.
FREEDOM had no commercial funding. Dr. Fuster reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Fuster V et al. AHA 2018, Abstract 18609.
CHICAGO – Patients with diabetes who underwent coronary artery bypass grafting had significantly better survival than patients with diabetes who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention after a median 7.5 years of follow-up.

Those patients comprised about half the patients enrolled in the FREEDOM randomized trial.
Long-term follow-up was only possible for just under half the 1,900 patients with diabetes and multivessel coronary disease originally enrolled in FREEDOM, but when researchers combined the long-term results with the data collected in the original study that had a median 3.8-year follow-up, they found all-cause mortality occurred in 18.3% of the patients who underwent coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and in 24.3% of patients treated with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), a 6% absolute between-group difference that was statistically significant, Valentin Fuster, MD, said at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. This fully jibed with the primary FREEDOM results, which found after 5 years a statistically significant reduction in all-cause death with CABG, compared with PCI, and also a significant reduction in the study’s primary endpoint (a combination of all-cause death, MI, and stroke), which occurred in 18.7% of patients randomized to CABG and in 26.6% of those randomized to PCI (N Engl J Med. 2012 Dec 20;367[25]:2375-84).
The extended follow-up finding lent additional support to existing society recommendations that CABG is the preferred revascularization strategy for patients with diabetes and multivessel coronary disease, most recently from the European Society of Cardiology (Eur Heart J. 2018 Aug 25. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy394), said Dr. Fuster, professor of medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and director of Mount Sinai Heart in New York. A subgroup analysis of the extended follow-up also suggested that the survival benefit from CABG, compared with PCI, was especially strong among patients at or below the study’s median age of 63 years. In the younger subgroup survival among patients treated with CABG was twice as good as it was among patients treated with PCI.
Dr. Fuster noted that few data have been previously reported for survival rates beyond 5 years after revascularization. “This was a difficult study. Following patients for more than 5 years is hard,” he said. Concurrently with his report at the meeting the results also appeared online (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Nov 11. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.11.001).
The FREEDOM (Future Revascularization Evaluation in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: Optimal Management of Multivessel Disease) trial enrolled patients at 140 participating centers during 2005-2010. A total of 25 sites agreed to participate in the extended follow-up and could track 943 patients, 50% of the starting cohort of 1,900 and 89% of the patients originally enrolled at these 25 centers. Dr. Fuster stressed that the 957 patients not included in the follow-up had not been lost, but rather had been managed at sites that declined to participate in this additional study.
Dr. Fuster acknowledged that methods and hardware for PCI have changed since the study ran a decade ago, as have options for medical management. He also highlighted that the long-term follow-up results had no data on rates of MIs and strokes.
FREEDOM had no commercial funding. Dr. Fuster reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Fuster V et al. AHA 2018, Abstract 18609.
REPORTING FROM THE AHA SCIENTIFIC SESSIONS
Key clinical point:
Major finding: After 7.5 years, mortality in the full FREEDOM cohort was 18% after coronary artery bypass grafting and 24% after percutaneous coronary intervention.
Study details: An extended follow-up of 943 of patients enrolled in FREEDOM, a randomized, multicenter trial.
Disclosures: FREEDOM had no commercial funding. Dr. Fuster reported no relevant disclosures.
Source: Fuster V et al. AHA 2018, Abstract 18609.
Study: Few physicians use telemedicine
Just 15% of U.S. physician practices report using telemedicine for patient care, with use of the technology varying widely by specialty.
Carol Kane, director of economic and health policy research, and Kurt Gillis, principal economist, both of the American Medical Association, evaluated the responses of 3,500 physicians about their telemedicine usage through data from the AMA’s 2016 Physician Practice Benchmark Survey. They took into account physicians’ specialty, age, sex, practice setting, and region, as well as the type of telemedicine services employed, if any.
In a research article published in Health Affairs, they found that in 2016, 15% of medical practices used telemedicine for patient interactions – including e-visits and store and forward services – while 11% used the technology to communicate with other health professionals.
Of the primary three telemedicine modalities, physicians used videoconferencing most often (13%), followed by store and forward of data (9%), and remote patient monitoring (7%).
Of specialists, 40% of radiologists, 28% of psychiatrists, and 24% of cardiologists used telemedicine for patient interactions, Ms. Kane and Mr. Gillis found. Emergency physicians were most likely to use telemedicine for interactions with other health professionals (39%), followed by pathologists (30%), and radiologists 26%). On the lower end of the spectrum, 6% of immunologists, 9% of ob.gyns., and 10% of general surgeons used telemedicine for patient care.
Remote patient monitoring was the least used telemedicine modality, with less than 10% of physicians in every broad specialty group using the service, with the exception of internal medicine subspecialties. Cardiologists reported the highest use of remote patient monitoring, followed by nephrologists.
Practice size and setting markedly influenced the practice of telemedicine. Use for patient interactions ranged from 8% among physicians in practices with one to four doctors to 27% among physician practices with at least 50 physicians. Similarly, telemedicine use between physicians and other health care professionals ranged from 4% among doctors in the smallest practice category to 23% in the largest practice category. Physicians in solo practice were less likely to use telemedicine for patient interactions than physicians in single- or multispecialty group practices.
Unsurprisingly, rural physicians were more likely to use telemedicine to consult with other doctors and to use video conferencing with patients than were physicians in metropolitan areas. No significant differences in telemedicine use were observed between physicians in states with parity laws. Such laws generally require that commercial insurers cover and reimburse for telemedicine services as they would for in-person services.
SOURCE: Kane et al. Health Affairs. 2018. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2018.05077.
Just 15% of U.S. physician practices report using telemedicine for patient care, with use of the technology varying widely by specialty.
Carol Kane, director of economic and health policy research, and Kurt Gillis, principal economist, both of the American Medical Association, evaluated the responses of 3,500 physicians about their telemedicine usage through data from the AMA’s 2016 Physician Practice Benchmark Survey. They took into account physicians’ specialty, age, sex, practice setting, and region, as well as the type of telemedicine services employed, if any.
In a research article published in Health Affairs, they found that in 2016, 15% of medical practices used telemedicine for patient interactions – including e-visits and store and forward services – while 11% used the technology to communicate with other health professionals.
Of the primary three telemedicine modalities, physicians used videoconferencing most often (13%), followed by store and forward of data (9%), and remote patient monitoring (7%).
Of specialists, 40% of radiologists, 28% of psychiatrists, and 24% of cardiologists used telemedicine for patient interactions, Ms. Kane and Mr. Gillis found. Emergency physicians were most likely to use telemedicine for interactions with other health professionals (39%), followed by pathologists (30%), and radiologists 26%). On the lower end of the spectrum, 6% of immunologists, 9% of ob.gyns., and 10% of general surgeons used telemedicine for patient care.
Remote patient monitoring was the least used telemedicine modality, with less than 10% of physicians in every broad specialty group using the service, with the exception of internal medicine subspecialties. Cardiologists reported the highest use of remote patient monitoring, followed by nephrologists.
Practice size and setting markedly influenced the practice of telemedicine. Use for patient interactions ranged from 8% among physicians in practices with one to four doctors to 27% among physician practices with at least 50 physicians. Similarly, telemedicine use between physicians and other health care professionals ranged from 4% among doctors in the smallest practice category to 23% in the largest practice category. Physicians in solo practice were less likely to use telemedicine for patient interactions than physicians in single- or multispecialty group practices.
Unsurprisingly, rural physicians were more likely to use telemedicine to consult with other doctors and to use video conferencing with patients than were physicians in metropolitan areas. No significant differences in telemedicine use were observed between physicians in states with parity laws. Such laws generally require that commercial insurers cover and reimburse for telemedicine services as they would for in-person services.
SOURCE: Kane et al. Health Affairs. 2018. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2018.05077.
Just 15% of U.S. physician practices report using telemedicine for patient care, with use of the technology varying widely by specialty.
Carol Kane, director of economic and health policy research, and Kurt Gillis, principal economist, both of the American Medical Association, evaluated the responses of 3,500 physicians about their telemedicine usage through data from the AMA’s 2016 Physician Practice Benchmark Survey. They took into account physicians’ specialty, age, sex, practice setting, and region, as well as the type of telemedicine services employed, if any.
In a research article published in Health Affairs, they found that in 2016, 15% of medical practices used telemedicine for patient interactions – including e-visits and store and forward services – while 11% used the technology to communicate with other health professionals.
Of the primary three telemedicine modalities, physicians used videoconferencing most often (13%), followed by store and forward of data (9%), and remote patient monitoring (7%).
Of specialists, 40% of radiologists, 28% of psychiatrists, and 24% of cardiologists used telemedicine for patient interactions, Ms. Kane and Mr. Gillis found. Emergency physicians were most likely to use telemedicine for interactions with other health professionals (39%), followed by pathologists (30%), and radiologists 26%). On the lower end of the spectrum, 6% of immunologists, 9% of ob.gyns., and 10% of general surgeons used telemedicine for patient care.
Remote patient monitoring was the least used telemedicine modality, with less than 10% of physicians in every broad specialty group using the service, with the exception of internal medicine subspecialties. Cardiologists reported the highest use of remote patient monitoring, followed by nephrologists.
Practice size and setting markedly influenced the practice of telemedicine. Use for patient interactions ranged from 8% among physicians in practices with one to four doctors to 27% among physician practices with at least 50 physicians. Similarly, telemedicine use between physicians and other health care professionals ranged from 4% among doctors in the smallest practice category to 23% in the largest practice category. Physicians in solo practice were less likely to use telemedicine for patient interactions than physicians in single- or multispecialty group practices.
Unsurprisingly, rural physicians were more likely to use telemedicine to consult with other doctors and to use video conferencing with patients than were physicians in metropolitan areas. No significant differences in telemedicine use were observed between physicians in states with parity laws. Such laws generally require that commercial insurers cover and reimburse for telemedicine services as they would for in-person services.
SOURCE: Kane et al. Health Affairs. 2018. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2018.05077.
FROM HEALTH AFFAIRS
Key clinical point: Most U.S. physicians do not use telemedicine for patient care.
Major finding: In 2016, 15% of medical practices used telemedicine to treat patients, while 11% of practices used it to consult with other health professionals.
Study details: A study of 3,500 physicians and their responses to telemedicine questions through data from the American Medical Association’s 2016 Physician Practice Benchmark Survey
Disclosures: The researchers reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
Source: Kane C et al. Health Affairs. 2018. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2018.05077
NSAIDs can play major role in pre- and postoperative hysterectomy pain
LAS VEGAS – An ob.gyn. has some handy hysterectomy-related pain management tips for her colleagues: Don’t assume patients know how to titrate between NSAIDs and opioids after surgery. Consider neuropathic medications alone in patients undergoing minimally invasive hysterectomies. And
Sawsan As-Sanie, MD, MPH, director of the University of Michigan Endometriosis Center, Ann Arbor, offered these and other recommendations about hysterectomy-related pain at the Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium.
Try acetaminophen and an NSAID
In the preoperative period, a combination of acetaminophen (Tylenol) and an NSAID can provide significant postop relief, Dr. As-Sanie said.
She highlighted a 2010 systematic review of 21 studies that included 1,909 patients and found acetaminophen/NSAID combinations improved pain intensity by about 35% in positive studies when compared with either acetaminophen or NSAID alone. The painkiller combination was positive – more effective than a solo agent – in 85% of studies of combo versus acetaminophen alone and 64% of studies of combo versus NSAID alone (Anesth Analg. 2010 Apr 1;110[4]:1170-9).
Another study, she said, found that there’s no clear advantage to IV administration for acetaminophen if patients can take the drug orally (Can J Hosp Pharm. 2015 May-Jun;68[3]:238-47).
Consider gabapentin, but not postoperatively
Dr. As-Sanie pointed to a 2014 systematic review and meta-analysis that suggested the use of preoperative gabapentin in abdominal hysterectomy reduces pain and opioid use. However, adding postoperative doses of gabapentin, she said, don’t appear to produce a greater effect (Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Jun;123[6]:1221-9).
Consider neuropathics for minimally invasive hysterectomy
Two studies, one in 2004 and the other in 2008, suggest that gabapentin (on a postop basis) and pregabalin (perioperatively) can reduce postop opioid use. (Pregabalin also was linked to more adverse effects.) “Even if they’re having a little bit of pain, they’re using fewer opioids,” she said (Pain. 2004 Jul;110[1-2]:175-81; Pain. 2008 Jan;134[1-2]:106-12).
Educate patients about postop painkiller use
Don’t assume that patients know how to adjust their over-the-counter painkiller use after surgery, Dr. As-Sanie said at the meeting jointly provided by Global Academy for Medical Education and the University of Cincinnati. Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same company. “While we as physicians think that knowledge about the use of ibuprofen and Tylenol is something everyone should be born with, it’s not obvious to most patients and families.”
It’s important to teach patients to start with NSAIDs or Tylenol postoperatively, and if that doesn’t control pain, “you add opioids and use medications to control constipation as needed. As you recover, you reduce the amount of opioids first and then reduce the NSAIDs or Tylenol,” she said. “That education can be very helpful for the vast majority of patients, and it’s one of the most important things we can provide.”
Don’t over-prescribe opioids
For a 2017 study, Dr. As-Sanie and colleagues tracked hysterectomy patients and surveyed them about their postop opioid use. “When asked 2 weeks after surgery, most used far less than half of what they prescribed,” Dr. As-Sanie said. “If we gave them about 40 pills, they had between 13-15 pills left after the surgery on average. Nearly 50% didn’t use any of their medication” (Obstet Gynecol. 2017 Dec;130[6]:1261-8).
Dr. As-Sanie urged colleagues to remember the lesson of the rise of super-sized portions at fast-food restaurants: Give people more of something and they’ll eat (or use) more of it. And the reverse is true: “If you give people fewer pills, they will use fewer pills.”
Dr. As-Sanie highlighted the recommendations about opioid prescription levels for various surgical procedures, including different types of hysterectomies, at www.opioidprescribing.info. The recommendations are provided by the Michigan Opioid Prescribing Engagement Network. They’re designed for opioid-naive patients and suggest the lowest doses for vaginal hysterectomy and the highest for abdominal hysterectomy, with recommended doses for laparoscopic and robotic hysterectomy in between.
Dr. As-Sanie disclosed she is a consultant for AbbVie and Myovant.
LAS VEGAS – An ob.gyn. has some handy hysterectomy-related pain management tips for her colleagues: Don’t assume patients know how to titrate between NSAIDs and opioids after surgery. Consider neuropathic medications alone in patients undergoing minimally invasive hysterectomies. And
Sawsan As-Sanie, MD, MPH, director of the University of Michigan Endometriosis Center, Ann Arbor, offered these and other recommendations about hysterectomy-related pain at the Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium.
Try acetaminophen and an NSAID
In the preoperative period, a combination of acetaminophen (Tylenol) and an NSAID can provide significant postop relief, Dr. As-Sanie said.
She highlighted a 2010 systematic review of 21 studies that included 1,909 patients and found acetaminophen/NSAID combinations improved pain intensity by about 35% in positive studies when compared with either acetaminophen or NSAID alone. The painkiller combination was positive – more effective than a solo agent – in 85% of studies of combo versus acetaminophen alone and 64% of studies of combo versus NSAID alone (Anesth Analg. 2010 Apr 1;110[4]:1170-9).
Another study, she said, found that there’s no clear advantage to IV administration for acetaminophen if patients can take the drug orally (Can J Hosp Pharm. 2015 May-Jun;68[3]:238-47).
Consider gabapentin, but not postoperatively
Dr. As-Sanie pointed to a 2014 systematic review and meta-analysis that suggested the use of preoperative gabapentin in abdominal hysterectomy reduces pain and opioid use. However, adding postoperative doses of gabapentin, she said, don’t appear to produce a greater effect (Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Jun;123[6]:1221-9).
Consider neuropathics for minimally invasive hysterectomy
Two studies, one in 2004 and the other in 2008, suggest that gabapentin (on a postop basis) and pregabalin (perioperatively) can reduce postop opioid use. (Pregabalin also was linked to more adverse effects.) “Even if they’re having a little bit of pain, they’re using fewer opioids,” she said (Pain. 2004 Jul;110[1-2]:175-81; Pain. 2008 Jan;134[1-2]:106-12).
Educate patients about postop painkiller use
Don’t assume that patients know how to adjust their over-the-counter painkiller use after surgery, Dr. As-Sanie said at the meeting jointly provided by Global Academy for Medical Education and the University of Cincinnati. Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same company. “While we as physicians think that knowledge about the use of ibuprofen and Tylenol is something everyone should be born with, it’s not obvious to most patients and families.”
It’s important to teach patients to start with NSAIDs or Tylenol postoperatively, and if that doesn’t control pain, “you add opioids and use medications to control constipation as needed. As you recover, you reduce the amount of opioids first and then reduce the NSAIDs or Tylenol,” she said. “That education can be very helpful for the vast majority of patients, and it’s one of the most important things we can provide.”
Don’t over-prescribe opioids
For a 2017 study, Dr. As-Sanie and colleagues tracked hysterectomy patients and surveyed them about their postop opioid use. “When asked 2 weeks after surgery, most used far less than half of what they prescribed,” Dr. As-Sanie said. “If we gave them about 40 pills, they had between 13-15 pills left after the surgery on average. Nearly 50% didn’t use any of their medication” (Obstet Gynecol. 2017 Dec;130[6]:1261-8).
Dr. As-Sanie urged colleagues to remember the lesson of the rise of super-sized portions at fast-food restaurants: Give people more of something and they’ll eat (or use) more of it. And the reverse is true: “If you give people fewer pills, they will use fewer pills.”
Dr. As-Sanie highlighted the recommendations about opioid prescription levels for various surgical procedures, including different types of hysterectomies, at www.opioidprescribing.info. The recommendations are provided by the Michigan Opioid Prescribing Engagement Network. They’re designed for opioid-naive patients and suggest the lowest doses for vaginal hysterectomy and the highest for abdominal hysterectomy, with recommended doses for laparoscopic and robotic hysterectomy in between.
Dr. As-Sanie disclosed she is a consultant for AbbVie and Myovant.
LAS VEGAS – An ob.gyn. has some handy hysterectomy-related pain management tips for her colleagues: Don’t assume patients know how to titrate between NSAIDs and opioids after surgery. Consider neuropathic medications alone in patients undergoing minimally invasive hysterectomies. And
Sawsan As-Sanie, MD, MPH, director of the University of Michigan Endometriosis Center, Ann Arbor, offered these and other recommendations about hysterectomy-related pain at the Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium.
Try acetaminophen and an NSAID
In the preoperative period, a combination of acetaminophen (Tylenol) and an NSAID can provide significant postop relief, Dr. As-Sanie said.
She highlighted a 2010 systematic review of 21 studies that included 1,909 patients and found acetaminophen/NSAID combinations improved pain intensity by about 35% in positive studies when compared with either acetaminophen or NSAID alone. The painkiller combination was positive – more effective than a solo agent – in 85% of studies of combo versus acetaminophen alone and 64% of studies of combo versus NSAID alone (Anesth Analg. 2010 Apr 1;110[4]:1170-9).
Another study, she said, found that there’s no clear advantage to IV administration for acetaminophen if patients can take the drug orally (Can J Hosp Pharm. 2015 May-Jun;68[3]:238-47).
Consider gabapentin, but not postoperatively
Dr. As-Sanie pointed to a 2014 systematic review and meta-analysis that suggested the use of preoperative gabapentin in abdominal hysterectomy reduces pain and opioid use. However, adding postoperative doses of gabapentin, she said, don’t appear to produce a greater effect (Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Jun;123[6]:1221-9).
Consider neuropathics for minimally invasive hysterectomy
Two studies, one in 2004 and the other in 2008, suggest that gabapentin (on a postop basis) and pregabalin (perioperatively) can reduce postop opioid use. (Pregabalin also was linked to more adverse effects.) “Even if they’re having a little bit of pain, they’re using fewer opioids,” she said (Pain. 2004 Jul;110[1-2]:175-81; Pain. 2008 Jan;134[1-2]:106-12).
Educate patients about postop painkiller use
Don’t assume that patients know how to adjust their over-the-counter painkiller use after surgery, Dr. As-Sanie said at the meeting jointly provided by Global Academy for Medical Education and the University of Cincinnati. Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same company. “While we as physicians think that knowledge about the use of ibuprofen and Tylenol is something everyone should be born with, it’s not obvious to most patients and families.”
It’s important to teach patients to start with NSAIDs or Tylenol postoperatively, and if that doesn’t control pain, “you add opioids and use medications to control constipation as needed. As you recover, you reduce the amount of opioids first and then reduce the NSAIDs or Tylenol,” she said. “That education can be very helpful for the vast majority of patients, and it’s one of the most important things we can provide.”
Don’t over-prescribe opioids
For a 2017 study, Dr. As-Sanie and colleagues tracked hysterectomy patients and surveyed them about their postop opioid use. “When asked 2 weeks after surgery, most used far less than half of what they prescribed,” Dr. As-Sanie said. “If we gave them about 40 pills, they had between 13-15 pills left after the surgery on average. Nearly 50% didn’t use any of their medication” (Obstet Gynecol. 2017 Dec;130[6]:1261-8).
Dr. As-Sanie urged colleagues to remember the lesson of the rise of super-sized portions at fast-food restaurants: Give people more of something and they’ll eat (or use) more of it. And the reverse is true: “If you give people fewer pills, they will use fewer pills.”
Dr. As-Sanie highlighted the recommendations about opioid prescription levels for various surgical procedures, including different types of hysterectomies, at www.opioidprescribing.info. The recommendations are provided by the Michigan Opioid Prescribing Engagement Network. They’re designed for opioid-naive patients and suggest the lowest doses for vaginal hysterectomy and the highest for abdominal hysterectomy, with recommended doses for laparoscopic and robotic hysterectomy in between.
Dr. As-Sanie disclosed she is a consultant for AbbVie and Myovant.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM PAGS
Uterine volume, fibroid diameter predict robotic myomectomy duration
LAS VEGAS – It would be nice if surgeons could know beforehand how long robotic laparoscopic myomectomies will take, according to Peter Movilla, MD, a minimally invasive gynecologic surgery fellow at Newton (Mass.) Wellesley Hospital.
Best guesses are sometimes wrong, and it’s not uncommon for robotic cases to go longer than expected, especially when they have to be converted to an open approach.
Among other problems, going long backs up operating room (OR)scheduling and makes families impatient. Also, if it was known beforehand that a robotic case might take 5 hours, patients could be offered a quicker open procedure, especially if they are not good candidates for prolonged pneumoperitoneum.
After a case went past 6 hours at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), when Dr. Movilla was an ob.gyn. resident, he wanted to find a better way.
“I saw that we were not the best at guessing how long these surgeries were going to take, and thought maybe we could make prediction a little better by [incorporating] preoperative factors” in a structured way. “I wanted to create something that would give us an answer of how long it will take,” he said at a meeting sponsored by AAGL.
So he and his colleagues reviewed 126 robot-assisted laparoscopic myomectomies at UCSF. The mean operative time from skin incision to closure was 213 minutes, mean specimen weight 264.4 g, mean dominant fibroid diameter 8.5 cm, and mean number of fibroids removed 2.5. Four cases (3%) were converted to open laparotomy.
The team divided the cases by how long they took; 20% were under 3 hours, 70% took 3-5 hours; and 10% went over 5 hours. “Five hours is a long time to be in the OR,” especially when a case could have been done open, Dr. Movilla said.
Length of surgery correlated with 7 of the 21 preoperative factors considered on multivariate logistic regression. Cases tended to be longer in younger women and in women with diabetes, and when surgeons had less experience. There was a trend toward longer cases with higher body mass indices, but it was not statistically significant.
Having three or more fibroids on preoperative imaging and a larger number of fibroids over 3 cm were predictive of operations longer than 3 hours. However, the strongest predictors of long cases were uterine volume and the diameter of the largest fibroid, a mean of 532.4 cm3 and 8.8 cm, respectively, in cases over 5 hours. Posterior and intramural fibroids also increased operative time, but, again, the trends were not statistically significant.
The team put it all together in a risk calculator they tested against their subjects’ actual surgery times. The model tended to underestimate very short and very long cases at either end of the curve, but overall the fit was “not too bad,” and the more cases that are added to the model, the more accurate it will get, Dr. Movilla said.
There was no external funding for the work, and Dr. Movilla had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Movilla P et al. 2018 AAGL Global Congress, Abstract 69.
LAS VEGAS – It would be nice if surgeons could know beforehand how long robotic laparoscopic myomectomies will take, according to Peter Movilla, MD, a minimally invasive gynecologic surgery fellow at Newton (Mass.) Wellesley Hospital.
Best guesses are sometimes wrong, and it’s not uncommon for robotic cases to go longer than expected, especially when they have to be converted to an open approach.
Among other problems, going long backs up operating room (OR)scheduling and makes families impatient. Also, if it was known beforehand that a robotic case might take 5 hours, patients could be offered a quicker open procedure, especially if they are not good candidates for prolonged pneumoperitoneum.
After a case went past 6 hours at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), when Dr. Movilla was an ob.gyn. resident, he wanted to find a better way.
“I saw that we were not the best at guessing how long these surgeries were going to take, and thought maybe we could make prediction a little better by [incorporating] preoperative factors” in a structured way. “I wanted to create something that would give us an answer of how long it will take,” he said at a meeting sponsored by AAGL.
So he and his colleagues reviewed 126 robot-assisted laparoscopic myomectomies at UCSF. The mean operative time from skin incision to closure was 213 minutes, mean specimen weight 264.4 g, mean dominant fibroid diameter 8.5 cm, and mean number of fibroids removed 2.5. Four cases (3%) were converted to open laparotomy.
The team divided the cases by how long they took; 20% were under 3 hours, 70% took 3-5 hours; and 10% went over 5 hours. “Five hours is a long time to be in the OR,” especially when a case could have been done open, Dr. Movilla said.
Length of surgery correlated with 7 of the 21 preoperative factors considered on multivariate logistic regression. Cases tended to be longer in younger women and in women with diabetes, and when surgeons had less experience. There was a trend toward longer cases with higher body mass indices, but it was not statistically significant.
Having three or more fibroids on preoperative imaging and a larger number of fibroids over 3 cm were predictive of operations longer than 3 hours. However, the strongest predictors of long cases were uterine volume and the diameter of the largest fibroid, a mean of 532.4 cm3 and 8.8 cm, respectively, in cases over 5 hours. Posterior and intramural fibroids also increased operative time, but, again, the trends were not statistically significant.
The team put it all together in a risk calculator they tested against their subjects’ actual surgery times. The model tended to underestimate very short and very long cases at either end of the curve, but overall the fit was “not too bad,” and the more cases that are added to the model, the more accurate it will get, Dr. Movilla said.
There was no external funding for the work, and Dr. Movilla had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Movilla P et al. 2018 AAGL Global Congress, Abstract 69.
LAS VEGAS – It would be nice if surgeons could know beforehand how long robotic laparoscopic myomectomies will take, according to Peter Movilla, MD, a minimally invasive gynecologic surgery fellow at Newton (Mass.) Wellesley Hospital.
Best guesses are sometimes wrong, and it’s not uncommon for robotic cases to go longer than expected, especially when they have to be converted to an open approach.
Among other problems, going long backs up operating room (OR)scheduling and makes families impatient. Also, if it was known beforehand that a robotic case might take 5 hours, patients could be offered a quicker open procedure, especially if they are not good candidates for prolonged pneumoperitoneum.
After a case went past 6 hours at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), when Dr. Movilla was an ob.gyn. resident, he wanted to find a better way.
“I saw that we were not the best at guessing how long these surgeries were going to take, and thought maybe we could make prediction a little better by [incorporating] preoperative factors” in a structured way. “I wanted to create something that would give us an answer of how long it will take,” he said at a meeting sponsored by AAGL.
So he and his colleagues reviewed 126 robot-assisted laparoscopic myomectomies at UCSF. The mean operative time from skin incision to closure was 213 minutes, mean specimen weight 264.4 g, mean dominant fibroid diameter 8.5 cm, and mean number of fibroids removed 2.5. Four cases (3%) were converted to open laparotomy.
The team divided the cases by how long they took; 20% were under 3 hours, 70% took 3-5 hours; and 10% went over 5 hours. “Five hours is a long time to be in the OR,” especially when a case could have been done open, Dr. Movilla said.
Length of surgery correlated with 7 of the 21 preoperative factors considered on multivariate logistic regression. Cases tended to be longer in younger women and in women with diabetes, and when surgeons had less experience. There was a trend toward longer cases with higher body mass indices, but it was not statistically significant.
Having three or more fibroids on preoperative imaging and a larger number of fibroids over 3 cm were predictive of operations longer than 3 hours. However, the strongest predictors of long cases were uterine volume and the diameter of the largest fibroid, a mean of 532.4 cm3 and 8.8 cm, respectively, in cases over 5 hours. Posterior and intramural fibroids also increased operative time, but, again, the trends were not statistically significant.
The team put it all together in a risk calculator they tested against their subjects’ actual surgery times. The model tended to underestimate very short and very long cases at either end of the curve, but overall the fit was “not too bad,” and the more cases that are added to the model, the more accurate it will get, Dr. Movilla said.
There was no external funding for the work, and Dr. Movilla had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Movilla P et al. 2018 AAGL Global Congress, Abstract 69.
REPORTING FROM AAGL GLOBAL CONGRESS
Key clinical point: A calculator is in the works to predict exactly how long robotic myomectomies will take.
Major finding: a mean of 532.4 cm3 and 8.8 cm, respectively, in cases over 5 hours.
Study details: Review of 126 cases.
Disclosures: There was no external funding, and Dr. Movilla had no disclosures.
Source: Movilla P et al. 2018 AAGL Global Congress, Abstract 69.
Gynecologic surgery insufflation pressure: Less is more
LAS VEGAS – performed at a single center by the same surgeon, said researchers at New York University (NYU) Medical Center.
Each incremental drop in abdominal insufflation pressure “improved intraoperative and postoperative clinical outcomes” with “faster postoperative recovery times, decreased immediate postoperative pain, and improved intraoperative respiratory parameters, without increasing duration of surgery or blood loss,” said investigator Christine Foley, MD, formerly at NYU, and now a minimally-invasive gynecologic surgery fellow at the University of Pittsburgh.
An abdominal insufflation pressure of 10 mm Hg or less was the sweet spot, she said at the meeting sponsored by AAGL.
The general surgery literature recommends operating at the lowest possible abdominal insufflation pressure to reduce postoperative pain, and that recommendation has been incorporated into enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) protocols. Gynecologic surgeons have not routinely followed suit, she noted. “Surgeons should consider operating at lower insufflation pressures to improve patient outcomes and PACU [postanesthesia care unit] utilization. Further research is warranted to determine if lower pressures ... should be included in ERAS protocols” for gynecologic surgery.
There’s not much in the way of data on insufflation pressures in robotic gynecologic surgery. What has been published suggests, as in general surgery, less postop pain, but at the cost of impaired visualization and greater blood loss. At the moment, robotic cases are often done at insufflation pressures above 12 mm Hg.
To get a better grasp of the issue, Dr. Foley and her team reviewed 196 hysterectomies, 275 myomectomies, and 127 endometriosis surgeries at NYU, all performed robotically by the same surgeon for benign indications. Ninety-nine cases were at 15 mm Hg; 100 at 12 mm Hg; 99 at 10 mm Hg, and 300 at 8 mm Hg.
The study did not address why the surgeon opted for different pressures in different cases. The body mass index was a mean of 27 kg/m2, and patient age was about 40 years, in all four pressure groups. There were trends for higher pressures with hysterectomies and lower pressures for endometriosis, but also considerable crossover, with more than 40% of the hysterectomies performed at 8 mm Hg, and almost 10% of the endometriosis cases done at 15 mm Hg.
Across the board, patients did better at lower pressures. Each drop in insufflation pressure correlated with a significant decrease in the initial pain score in the PACU (5.9 out of 10 points at 15 mm Hg, 5.4 at 12 mm Hg, 4.4 at 10 mm Hg, and 3.8 at 8 mm Hg, P less than .0001); lower pressures also correlated with shorter PACU stays (449 minutes, 467 minutes, 351 minutes, and 317 minutes, P less than .0001).
Surgery duration was a mean of 70 minutes across all four groups. Estimated blood loss was 114 mL at 15 mm Hg, 97.4 mL at 12 mm Hg, 127 mL 10 mm Hg, and 78.4 mL at 8 mm HG; the differences were not statistically significant. Maximum PACU pain levels favored lower pressures, and lower pressures correlated with significantly lower peak inspiratory pressures and tidal volumes.
The results argue for operating at the lowest possible pressure, Dr. Foley said, but she and her team did not address how their outcomes might have been influenced by the type of surgery the women had.
There was no external funding for the study. Dr. Foley had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Foley C et al. 2018 AAGL Global Congress, Abstract 23.
LAS VEGAS – performed at a single center by the same surgeon, said researchers at New York University (NYU) Medical Center.
Each incremental drop in abdominal insufflation pressure “improved intraoperative and postoperative clinical outcomes” with “faster postoperative recovery times, decreased immediate postoperative pain, and improved intraoperative respiratory parameters, without increasing duration of surgery or blood loss,” said investigator Christine Foley, MD, formerly at NYU, and now a minimally-invasive gynecologic surgery fellow at the University of Pittsburgh.
An abdominal insufflation pressure of 10 mm Hg or less was the sweet spot, she said at the meeting sponsored by AAGL.
The general surgery literature recommends operating at the lowest possible abdominal insufflation pressure to reduce postoperative pain, and that recommendation has been incorporated into enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) protocols. Gynecologic surgeons have not routinely followed suit, she noted. “Surgeons should consider operating at lower insufflation pressures to improve patient outcomes and PACU [postanesthesia care unit] utilization. Further research is warranted to determine if lower pressures ... should be included in ERAS protocols” for gynecologic surgery.
There’s not much in the way of data on insufflation pressures in robotic gynecologic surgery. What has been published suggests, as in general surgery, less postop pain, but at the cost of impaired visualization and greater blood loss. At the moment, robotic cases are often done at insufflation pressures above 12 mm Hg.
To get a better grasp of the issue, Dr. Foley and her team reviewed 196 hysterectomies, 275 myomectomies, and 127 endometriosis surgeries at NYU, all performed robotically by the same surgeon for benign indications. Ninety-nine cases were at 15 mm Hg; 100 at 12 mm Hg; 99 at 10 mm Hg, and 300 at 8 mm Hg.
The study did not address why the surgeon opted for different pressures in different cases. The body mass index was a mean of 27 kg/m2, and patient age was about 40 years, in all four pressure groups. There were trends for higher pressures with hysterectomies and lower pressures for endometriosis, but also considerable crossover, with more than 40% of the hysterectomies performed at 8 mm Hg, and almost 10% of the endometriosis cases done at 15 mm Hg.
Across the board, patients did better at lower pressures. Each drop in insufflation pressure correlated with a significant decrease in the initial pain score in the PACU (5.9 out of 10 points at 15 mm Hg, 5.4 at 12 mm Hg, 4.4 at 10 mm Hg, and 3.8 at 8 mm Hg, P less than .0001); lower pressures also correlated with shorter PACU stays (449 minutes, 467 minutes, 351 minutes, and 317 minutes, P less than .0001).
Surgery duration was a mean of 70 minutes across all four groups. Estimated blood loss was 114 mL at 15 mm Hg, 97.4 mL at 12 mm Hg, 127 mL 10 mm Hg, and 78.4 mL at 8 mm HG; the differences were not statistically significant. Maximum PACU pain levels favored lower pressures, and lower pressures correlated with significantly lower peak inspiratory pressures and tidal volumes.
The results argue for operating at the lowest possible pressure, Dr. Foley said, but she and her team did not address how their outcomes might have been influenced by the type of surgery the women had.
There was no external funding for the study. Dr. Foley had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Foley C et al. 2018 AAGL Global Congress, Abstract 23.
LAS VEGAS – performed at a single center by the same surgeon, said researchers at New York University (NYU) Medical Center.
Each incremental drop in abdominal insufflation pressure “improved intraoperative and postoperative clinical outcomes” with “faster postoperative recovery times, decreased immediate postoperative pain, and improved intraoperative respiratory parameters, without increasing duration of surgery or blood loss,” said investigator Christine Foley, MD, formerly at NYU, and now a minimally-invasive gynecologic surgery fellow at the University of Pittsburgh.
An abdominal insufflation pressure of 10 mm Hg or less was the sweet spot, she said at the meeting sponsored by AAGL.
The general surgery literature recommends operating at the lowest possible abdominal insufflation pressure to reduce postoperative pain, and that recommendation has been incorporated into enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) protocols. Gynecologic surgeons have not routinely followed suit, she noted. “Surgeons should consider operating at lower insufflation pressures to improve patient outcomes and PACU [postanesthesia care unit] utilization. Further research is warranted to determine if lower pressures ... should be included in ERAS protocols” for gynecologic surgery.
There’s not much in the way of data on insufflation pressures in robotic gynecologic surgery. What has been published suggests, as in general surgery, less postop pain, but at the cost of impaired visualization and greater blood loss. At the moment, robotic cases are often done at insufflation pressures above 12 mm Hg.
To get a better grasp of the issue, Dr. Foley and her team reviewed 196 hysterectomies, 275 myomectomies, and 127 endometriosis surgeries at NYU, all performed robotically by the same surgeon for benign indications. Ninety-nine cases were at 15 mm Hg; 100 at 12 mm Hg; 99 at 10 mm Hg, and 300 at 8 mm Hg.
The study did not address why the surgeon opted for different pressures in different cases. The body mass index was a mean of 27 kg/m2, and patient age was about 40 years, in all four pressure groups. There were trends for higher pressures with hysterectomies and lower pressures for endometriosis, but also considerable crossover, with more than 40% of the hysterectomies performed at 8 mm Hg, and almost 10% of the endometriosis cases done at 15 mm Hg.
Across the board, patients did better at lower pressures. Each drop in insufflation pressure correlated with a significant decrease in the initial pain score in the PACU (5.9 out of 10 points at 15 mm Hg, 5.4 at 12 mm Hg, 4.4 at 10 mm Hg, and 3.8 at 8 mm Hg, P less than .0001); lower pressures also correlated with shorter PACU stays (449 minutes, 467 minutes, 351 minutes, and 317 minutes, P less than .0001).
Surgery duration was a mean of 70 minutes across all four groups. Estimated blood loss was 114 mL at 15 mm Hg, 97.4 mL at 12 mm Hg, 127 mL 10 mm Hg, and 78.4 mL at 8 mm HG; the differences were not statistically significant. Maximum PACU pain levels favored lower pressures, and lower pressures correlated with significantly lower peak inspiratory pressures and tidal volumes.
The results argue for operating at the lowest possible pressure, Dr. Foley said, but she and her team did not address how their outcomes might have been influenced by the type of surgery the women had.
There was no external funding for the study. Dr. Foley had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Foley C et al. 2018 AAGL Global Congress, Abstract 23.
REPORTING FROM AAGL GLOBAL CONGRESS
Key clinical point: Lower insufflation pressures were associated with improved patient outcomes and reduced PACU use.
Major finding: There was a significant decrease in initial postop pain score with each incremental drop in insufflation pressure (5.9 out of 10 points at 15 mm Hg, 5.4 at 12 mm Hg; 4.4 at 10 mm Hg, and 3.8 at 8 mm Hg, P less than .0001).
Study details: Review of 598 robotic gynecologic procedures done at New York University by the same surgeon.
Disclosures: There was no external funding for the study. The presenter did not have any relevant financial disclosures.
Source: Foley C et al. 2018 AAGL Global Congress, Abstract 23.
Gap in care: Female patients with incontinence
LAS VEGAS – A pelvic surgeon brought a bold message to a gathering of gynecologists: There’s a great gap in American care for pelvic floor disorders such as urinary incontinence, and they’re the right physicians to make a difference by treating these common conditions.
“There are never going to be enough specialists to deal with these problems. This is a natural progression for many of you,” said urogynecologist and pelvic surgeon Mickey M. Karram, MD, in a joint presentation at the Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium. In fact, he said, “there’s so much disease out there to fix that you may become more overwhelmed.”
Dr. Karram, who has offices in Cincinnati, Beverly Hills, and Orange County, Calif., spoke about female urinary incontinence with obstetrician-gynecologist Beri M. Ridgeway, MD, of Cleveland Clinic. They offered these tips:
Test for stress incontinence
Dr. Karram recommends using a “quick and easy” cystometrogram (CMG) test to “corroborate or refute what the patient thinks is going on” in regard to urinary function. “With this simple test, you’ll get a clear understanding of sensation [to urinate] and of what their fullness and capacity numbers are,” he said. And if you have the patient cough or strain during the test, “you should be able to duplicate a sign of stress incontinence 90% of the time.”
If patients don’t leak when they take this test, there may be another problem such as overactive bladder, a condition that can’t be duplicated via the test, he said.
Ask the right questions
When it comes to identifying when they have urinary difficulties, some patients “say yes to every question we ask,” said Dr. Ridgeway, and they may not be able to distinguish between urgency and leakage.
A better approach is to ask women to provide specific examples of when they have continence issues, she said. It’s also useful to ask patients about what bothers them the most if they have multiple symptoms: Is it urgency (“Gotta go; gotta go”)? Leakage during certain situations like coughing and laughing? “That helps me decide how to go about treating them first and foremost,” she said. “It doesn’t mean you won’t treat both [problems], but it really gives you a reference point of where to start.”
Research suggests that women tend to be more bothered by urge incontinence than stress incontinence, she said, because they can regulate their activities or avoid the stress form.
Beware of acute incontinence cases
“If a woman walks in and says ‘Everything was great until a week or two ago, but now I’m living in pads,’ it could be a fecal impaction or a pelvic mass,” Dr. Karram said at the meeting jointly provided by Global Academy for Medical Education and the University of Cincinnati. Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same company.
Discuss the many treatment options
In some cases of incontinence, Dr. Ridgeway said she’ll mention “the array of treatment options, such as pelvic floor physical therapy, bladder retraining, vaginal estrogen, medications, and Botox.”
She added: “I explain that we’ll work together, and sometimes it will take a couple tries, or we’ll try a couple things at once.”
Dr. Ridgeway disclosed consulting for Coloplast and serving as an independent contractor (legal) for Ethicon. Dr. Karram disclosed speaking for Allergan, Astellas Pharma, Coloplast, and Cynosure/Hologic; consulting for Coloplast and Cynosure/Hologic; and receiving royalties from BihlerMed.
LAS VEGAS – A pelvic surgeon brought a bold message to a gathering of gynecologists: There’s a great gap in American care for pelvic floor disorders such as urinary incontinence, and they’re the right physicians to make a difference by treating these common conditions.
“There are never going to be enough specialists to deal with these problems. This is a natural progression for many of you,” said urogynecologist and pelvic surgeon Mickey M. Karram, MD, in a joint presentation at the Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium. In fact, he said, “there’s so much disease out there to fix that you may become more overwhelmed.”
Dr. Karram, who has offices in Cincinnati, Beverly Hills, and Orange County, Calif., spoke about female urinary incontinence with obstetrician-gynecologist Beri M. Ridgeway, MD, of Cleveland Clinic. They offered these tips:
Test for stress incontinence
Dr. Karram recommends using a “quick and easy” cystometrogram (CMG) test to “corroborate or refute what the patient thinks is going on” in regard to urinary function. “With this simple test, you’ll get a clear understanding of sensation [to urinate] and of what their fullness and capacity numbers are,” he said. And if you have the patient cough or strain during the test, “you should be able to duplicate a sign of stress incontinence 90% of the time.”
If patients don’t leak when they take this test, there may be another problem such as overactive bladder, a condition that can’t be duplicated via the test, he said.
Ask the right questions
When it comes to identifying when they have urinary difficulties, some patients “say yes to every question we ask,” said Dr. Ridgeway, and they may not be able to distinguish between urgency and leakage.
A better approach is to ask women to provide specific examples of when they have continence issues, she said. It’s also useful to ask patients about what bothers them the most if they have multiple symptoms: Is it urgency (“Gotta go; gotta go”)? Leakage during certain situations like coughing and laughing? “That helps me decide how to go about treating them first and foremost,” she said. “It doesn’t mean you won’t treat both [problems], but it really gives you a reference point of where to start.”
Research suggests that women tend to be more bothered by urge incontinence than stress incontinence, she said, because they can regulate their activities or avoid the stress form.
Beware of acute incontinence cases
“If a woman walks in and says ‘Everything was great until a week or two ago, but now I’m living in pads,’ it could be a fecal impaction or a pelvic mass,” Dr. Karram said at the meeting jointly provided by Global Academy for Medical Education and the University of Cincinnati. Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same company.
Discuss the many treatment options
In some cases of incontinence, Dr. Ridgeway said she’ll mention “the array of treatment options, such as pelvic floor physical therapy, bladder retraining, vaginal estrogen, medications, and Botox.”
She added: “I explain that we’ll work together, and sometimes it will take a couple tries, or we’ll try a couple things at once.”
Dr. Ridgeway disclosed consulting for Coloplast and serving as an independent contractor (legal) for Ethicon. Dr. Karram disclosed speaking for Allergan, Astellas Pharma, Coloplast, and Cynosure/Hologic; consulting for Coloplast and Cynosure/Hologic; and receiving royalties from BihlerMed.
LAS VEGAS – A pelvic surgeon brought a bold message to a gathering of gynecologists: There’s a great gap in American care for pelvic floor disorders such as urinary incontinence, and they’re the right physicians to make a difference by treating these common conditions.
“There are never going to be enough specialists to deal with these problems. This is a natural progression for many of you,” said urogynecologist and pelvic surgeon Mickey M. Karram, MD, in a joint presentation at the Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium. In fact, he said, “there’s so much disease out there to fix that you may become more overwhelmed.”
Dr. Karram, who has offices in Cincinnati, Beverly Hills, and Orange County, Calif., spoke about female urinary incontinence with obstetrician-gynecologist Beri M. Ridgeway, MD, of Cleveland Clinic. They offered these tips:
Test for stress incontinence
Dr. Karram recommends using a “quick and easy” cystometrogram (CMG) test to “corroborate or refute what the patient thinks is going on” in regard to urinary function. “With this simple test, you’ll get a clear understanding of sensation [to urinate] and of what their fullness and capacity numbers are,” he said. And if you have the patient cough or strain during the test, “you should be able to duplicate a sign of stress incontinence 90% of the time.”
If patients don’t leak when they take this test, there may be another problem such as overactive bladder, a condition that can’t be duplicated via the test, he said.
Ask the right questions
When it comes to identifying when they have urinary difficulties, some patients “say yes to every question we ask,” said Dr. Ridgeway, and they may not be able to distinguish between urgency and leakage.
A better approach is to ask women to provide specific examples of when they have continence issues, she said. It’s also useful to ask patients about what bothers them the most if they have multiple symptoms: Is it urgency (“Gotta go; gotta go”)? Leakage during certain situations like coughing and laughing? “That helps me decide how to go about treating them first and foremost,” she said. “It doesn’t mean you won’t treat both [problems], but it really gives you a reference point of where to start.”
Research suggests that women tend to be more bothered by urge incontinence than stress incontinence, she said, because they can regulate their activities or avoid the stress form.
Beware of acute incontinence cases
“If a woman walks in and says ‘Everything was great until a week or two ago, but now I’m living in pads,’ it could be a fecal impaction or a pelvic mass,” Dr. Karram said at the meeting jointly provided by Global Academy for Medical Education and the University of Cincinnati. Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same company.
Discuss the many treatment options
In some cases of incontinence, Dr. Ridgeway said she’ll mention “the array of treatment options, such as pelvic floor physical therapy, bladder retraining, vaginal estrogen, medications, and Botox.”
She added: “I explain that we’ll work together, and sometimes it will take a couple tries, or we’ll try a couple things at once.”
Dr. Ridgeway disclosed consulting for Coloplast and serving as an independent contractor (legal) for Ethicon. Dr. Karram disclosed speaking for Allergan, Astellas Pharma, Coloplast, and Cynosure/Hologic; consulting for Coloplast and Cynosure/Hologic; and receiving royalties from BihlerMed.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM PAGS
When is it appropriate to remove ovaries in hysterectomy?
LAS VEGAS – The removal of both ovaries during hysterectomy – bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (BSO) – has declined sharply in popularity as physicians have become more aware of its risks.
Still, “we’re still seeing a relatively high rate of inappropriate BSO,” Amanda Nickles Fader, MD, said, despite “the many benefits of ovarian conservation. Strong consideration should be made for maintaining normal ovaries in premenopausal women who are not at higher genetic risk of ovarian cancer.”
Dr. Nickles Fader, director of the Kelly gynecologic oncology service and the director of the center for rare gynecologic cancers at Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, who spoke at the Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium, urged gynecologists to understand the data about ovarian conservation in hysterectomy and carefully counsel patients.
“We can counsel patients with 100% certainty that BSO absolutely reduces ovarian and fallopian tube cancer rates. That’s a given,” she said. “Women get very excited about that, but you’ve got to be careful to counsel them about the flip side: The overall benefit may not be there when you consider the other morbidity and mortality that may occur because of this removal.”
As she noted, multiple retrospective, prospective, and observational studies have linked ovary removal to a variety of heightened risks, especially on the cardiac front. She highlighted a 2009 study of nearly 30,000 nurses who’d undergone hysterectomy for benign disease, about which the authors wrote that, “compared with ovarian conservation, bilateral oophorectomy at the time of hysterectomy for benign disease is associated with a decreased risk of breast and ovarian cancer but an increased risk of all-cause mortality, fatal and nonfatal coronary heart disease, and lung cancer.” No age group gained a survival benefit from oophorectomy (Obstet Gynecol. 2009 May;113[5]:1027-37 ).
Meanwhile, over the past decade, the “pendulum has swung” toward ovary conservation, at least in premenopausal women, Dr. Nickles Fader said at the meeting jointly provided by Global Academy for Medical Education and the University of Cincinnati. Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same company.
A 2016 analysis of health statistics in five U.S. Eastern and Midwestern states found that, rates of hospital-based, hysterectomy-alone procedures grew by 15% from 2005 to 2013, while rates of oophorectomy alone and hysterectomy/oophorectomy combination procedures declined by 12% and 29%, respectively.
Still, Dr. Nickles Fader said, as many as 60% of hysterectomies are still performed in conjunction with oophorectomy.
Ovary removal, of course, can be appropriate when patients are at risk of ovarian cancer. Hereditary ovarian cancer accounts for up to 25% of epithelial ovarian cancer, she said, and research suggests that risk-reducing surgery is an effective preventative approach when high-penetrance genes are present. However, the value of the surgery is less clear in regard to moderate-penetrance genes.
Dr. Nickles Fader pointed to guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network that specify genes and syndromes that should trigger risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy, hysterectomy, or hysterectomy and risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy after childbirth.
Researchers are exploring salpingectomy – fallopian tube removal – as a possible replacement for oophorectomy. Dr. Nickles Fader highlighted a small pilot study published in 2018 that reported “BRCA mutation carriers who underwent bilateral salpingectomy had no intraoperative complications, were satisfied with their procedure choice, and had decreased cancer worry and anxiety after the procedure.”
Moving forward, she said, research will provide more insight into preventative options such as removing fallopian tubes alone instead of ovaries. “We’re starting to learn, and will probably know in the next 10-15 years, whether oophorectomy is necessary for all high-risk and moderate-risk women or if we can get away with removing their tubes and giving them the maximal health benefits of ovarian conservation.”
Dr. Nickles Fader reported consulting for Ethicon Endosurgery.
LAS VEGAS – The removal of both ovaries during hysterectomy – bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (BSO) – has declined sharply in popularity as physicians have become more aware of its risks.
Still, “we’re still seeing a relatively high rate of inappropriate BSO,” Amanda Nickles Fader, MD, said, despite “the many benefits of ovarian conservation. Strong consideration should be made for maintaining normal ovaries in premenopausal women who are not at higher genetic risk of ovarian cancer.”
Dr. Nickles Fader, director of the Kelly gynecologic oncology service and the director of the center for rare gynecologic cancers at Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, who spoke at the Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium, urged gynecologists to understand the data about ovarian conservation in hysterectomy and carefully counsel patients.
“We can counsel patients with 100% certainty that BSO absolutely reduces ovarian and fallopian tube cancer rates. That’s a given,” she said. “Women get very excited about that, but you’ve got to be careful to counsel them about the flip side: The overall benefit may not be there when you consider the other morbidity and mortality that may occur because of this removal.”
As she noted, multiple retrospective, prospective, and observational studies have linked ovary removal to a variety of heightened risks, especially on the cardiac front. She highlighted a 2009 study of nearly 30,000 nurses who’d undergone hysterectomy for benign disease, about which the authors wrote that, “compared with ovarian conservation, bilateral oophorectomy at the time of hysterectomy for benign disease is associated with a decreased risk of breast and ovarian cancer but an increased risk of all-cause mortality, fatal and nonfatal coronary heart disease, and lung cancer.” No age group gained a survival benefit from oophorectomy (Obstet Gynecol. 2009 May;113[5]:1027-37 ).
Meanwhile, over the past decade, the “pendulum has swung” toward ovary conservation, at least in premenopausal women, Dr. Nickles Fader said at the meeting jointly provided by Global Academy for Medical Education and the University of Cincinnati. Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same company.
A 2016 analysis of health statistics in five U.S. Eastern and Midwestern states found that, rates of hospital-based, hysterectomy-alone procedures grew by 15% from 2005 to 2013, while rates of oophorectomy alone and hysterectomy/oophorectomy combination procedures declined by 12% and 29%, respectively.
Still, Dr. Nickles Fader said, as many as 60% of hysterectomies are still performed in conjunction with oophorectomy.
Ovary removal, of course, can be appropriate when patients are at risk of ovarian cancer. Hereditary ovarian cancer accounts for up to 25% of epithelial ovarian cancer, she said, and research suggests that risk-reducing surgery is an effective preventative approach when high-penetrance genes are present. However, the value of the surgery is less clear in regard to moderate-penetrance genes.
Dr. Nickles Fader pointed to guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network that specify genes and syndromes that should trigger risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy, hysterectomy, or hysterectomy and risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy after childbirth.
Researchers are exploring salpingectomy – fallopian tube removal – as a possible replacement for oophorectomy. Dr. Nickles Fader highlighted a small pilot study published in 2018 that reported “BRCA mutation carriers who underwent bilateral salpingectomy had no intraoperative complications, were satisfied with their procedure choice, and had decreased cancer worry and anxiety after the procedure.”
Moving forward, she said, research will provide more insight into preventative options such as removing fallopian tubes alone instead of ovaries. “We’re starting to learn, and will probably know in the next 10-15 years, whether oophorectomy is necessary for all high-risk and moderate-risk women or if we can get away with removing their tubes and giving them the maximal health benefits of ovarian conservation.”
Dr. Nickles Fader reported consulting for Ethicon Endosurgery.
LAS VEGAS – The removal of both ovaries during hysterectomy – bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (BSO) – has declined sharply in popularity as physicians have become more aware of its risks.
Still, “we’re still seeing a relatively high rate of inappropriate BSO,” Amanda Nickles Fader, MD, said, despite “the many benefits of ovarian conservation. Strong consideration should be made for maintaining normal ovaries in premenopausal women who are not at higher genetic risk of ovarian cancer.”
Dr. Nickles Fader, director of the Kelly gynecologic oncology service and the director of the center for rare gynecologic cancers at Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, who spoke at the Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium, urged gynecologists to understand the data about ovarian conservation in hysterectomy and carefully counsel patients.
“We can counsel patients with 100% certainty that BSO absolutely reduces ovarian and fallopian tube cancer rates. That’s a given,” she said. “Women get very excited about that, but you’ve got to be careful to counsel them about the flip side: The overall benefit may not be there when you consider the other morbidity and mortality that may occur because of this removal.”
As she noted, multiple retrospective, prospective, and observational studies have linked ovary removal to a variety of heightened risks, especially on the cardiac front. She highlighted a 2009 study of nearly 30,000 nurses who’d undergone hysterectomy for benign disease, about which the authors wrote that, “compared with ovarian conservation, bilateral oophorectomy at the time of hysterectomy for benign disease is associated with a decreased risk of breast and ovarian cancer but an increased risk of all-cause mortality, fatal and nonfatal coronary heart disease, and lung cancer.” No age group gained a survival benefit from oophorectomy (Obstet Gynecol. 2009 May;113[5]:1027-37 ).
Meanwhile, over the past decade, the “pendulum has swung” toward ovary conservation, at least in premenopausal women, Dr. Nickles Fader said at the meeting jointly provided by Global Academy for Medical Education and the University of Cincinnati. Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same company.
A 2016 analysis of health statistics in five U.S. Eastern and Midwestern states found that, rates of hospital-based, hysterectomy-alone procedures grew by 15% from 2005 to 2013, while rates of oophorectomy alone and hysterectomy/oophorectomy combination procedures declined by 12% and 29%, respectively.
Still, Dr. Nickles Fader said, as many as 60% of hysterectomies are still performed in conjunction with oophorectomy.
Ovary removal, of course, can be appropriate when patients are at risk of ovarian cancer. Hereditary ovarian cancer accounts for up to 25% of epithelial ovarian cancer, she said, and research suggests that risk-reducing surgery is an effective preventative approach when high-penetrance genes are present. However, the value of the surgery is less clear in regard to moderate-penetrance genes.
Dr. Nickles Fader pointed to guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network that specify genes and syndromes that should trigger risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy, hysterectomy, or hysterectomy and risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy after childbirth.
Researchers are exploring salpingectomy – fallopian tube removal – as a possible replacement for oophorectomy. Dr. Nickles Fader highlighted a small pilot study published in 2018 that reported “BRCA mutation carriers who underwent bilateral salpingectomy had no intraoperative complications, were satisfied with their procedure choice, and had decreased cancer worry and anxiety after the procedure.”
Moving forward, she said, research will provide more insight into preventative options such as removing fallopian tubes alone instead of ovaries. “We’re starting to learn, and will probably know in the next 10-15 years, whether oophorectomy is necessary for all high-risk and moderate-risk women or if we can get away with removing their tubes and giving them the maximal health benefits of ovarian conservation.”
Dr. Nickles Fader reported consulting for Ethicon Endosurgery.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM PAGS
Parental leave for residents pales in comparison to that of faculty physicians
Leave policies for residents who become new parents are uneven, oft-ignored by training boards, and provide less time off than similar policies for faculty physicians. Those were the findings of a pair of research letters published in JAMA.
Kirti Magudia, MD, of the department of radiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston and her colleagues reviewed childbearing and family leave policies for 15 graduate medical education (GME)–sponsoring institutions, all of which were affiliated with the top 12 U.S. medical schools. Though all 12 schools provided paid childbearing or family leave for faculty physicians, only 8 of the 15 did so for residents (JAMA. 2018 Dec 11;320[22)]:2372-4).
In programs that did provide leave, the average of 6.6 weeks of paid total maternity leave for residents was less than the 8.6 weeks faculty receive. Both are considerably less than proscribed by the Family and Medical Leave Act, which requires large employers to provide 12 weeks of unpaid leave, but only after 12 months of employment.
The research focused on only institutional policies for paid leave; unpaid leave and state policies may extend the average, and departments may offer leave that goes beyond specific policies, Dr. Magudia and her colleagues noted.
Changes in the residency population make now the right time for establishing consistent family leave policies, Dr. Magudia said in an interview. “We have people starting training later; we have more female trainees. And with the Match system, you’re not in control of exactly where you’re going. You may not have a support system where you end up, and a lot of the top training institutions are in high cost-of-living areas. All of those things together can make trainees especially vulnerable, and because trainees are temporary employees, changing policies to benefit them is very challenging.
“Wellness is a huge issue in medicine, and at large in society,” she said. “Making sure people have adequate parental leave goes a long way toward reducing stress levels and helping them cope with normal life transitions. We want to take steps that promote success among a diverse community of physicians; we want to retain as many people in the field as possible, and we want them to feel supported.”
Beyond asking all GME-sponsoring institutions to adopt parental leave policies, Dr. Magudia believes trainees must be better informed. “It should be clear to training program applicants what the policies are at those institutions,” she said. “That information is extremely difficult to obtain, as we’ve discovered. You can imagine that, if you are the applicant, it can be difficult to ask about those policies during the interview process because it may affect how things turn out.”
“If we can see changes like these made in the near future,” she added, “we will be in a good place.”
In the second study, Briony K. Varda, MD, of the department of urology at Boston Children’s Hospital, and her colleagues also noted the complications of balancing parental leave with training requirements from specialty boards. They compared leave policies among American Board of Medical Specialty member organizations and found that less than half specifically mentioned parental leave for resident physicians (JAMA. 2018 Dec 11;320[22]:2374-7).
Dr. Varda and her colleagues reviewed the websites of 24 ABMS boards to determine their leave policies; 22 had policies but only 11 cited parental leave as an option for residents. Twenty boards have time-based training requirements and allow for a median of 6 weeks leave for any reason; none of the boards had a specific policy for parental leave. In addition, only eight boards had “explicit and clear clarifying language” that would allow program directors to seek exemptions for their residents.
Though limitations like not detecting all available policies – and a subjective evaluation of the policies that were reviewed – could have impacted their study, the coauthors reiterated that the median of 6 weeks leave is less than the average leave for faculty physicians. They also emphasized the detriments associated with inadequate parental leave, including delayed childbearing, use of assisted reproduction technology, and difficulty breastfeeding.
Dr. Varda underlined the issues that arise for program directors, who “must weigh potentially conflicting factors such as adhering to board and institutional policies, maintaining adequate clinical service coverage, considering precedent within the program, and ensuring that resident physicians are well trained.” To balance the needs of all involved “novel approaches such as use of competency-based rather than time-based training milestones” to determine certification eligibility and, in return, lessen the stresses for new-parent residents, she noted.
The researchers disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Magudia K et al. JAMA. 2018 Dec 11;320[22)]:2372-4; Varda B et al. JAMA. 2018 Dec 11;320[22]:2374-7.
Recent data by Magudia et al. have highlighted the fact that family leave policies supporting parents during medical training are widely inconsistent and in many instances do not exist. Where trainee policies do exist, benefits are routinely less robust than those of permanent faculty who receive on average 30% more paid leave time. Stratifying physician wellness needs by training status seems to be a misplaced approach.
It is not only the medical field which sees inconsistencies in the way family leave is allocated for different types of jobs. Millions of Americans receive no time off after birth or adoption, at a time when corporate America offers elite benefits for child care. In medicine, however, there is an expectation that paid family leave should be the norm, perhaps because of our mission to improve the quality of health care.
Of course, there are valid distinctions between faculty and trainees: faculty are more permanent, are more professionally differentiated and accomplished than trainees, have greater responsibilities, and are recruited for their expertise. Arguably, faculty deserve better compensation than trainees.
But the importance of parental leave transcends the routine benefits arguments. There is something more universal about how we value parenting. Parental leave policies benefit the health of parent and child, increase career satisfaction, and improve retention. The process of birth or adoption, ensuing fatigue, family bonding needs, and life-restructuring will challenge all parents regardless of career status.
Awareness of the inadequacies of parental leave policies is the first step in remedying the disparities in support for our trainees. Establishing an equal and adequate family leave policy for physicians at any stage is consistent with the goal of success and well-being for us all.
Laurel Fisher, MD, AGAF, professor of clinical internal medicine, division of gastroenterology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. She reports no conflicts of interest.
Recent data by Magudia et al. have highlighted the fact that family leave policies supporting parents during medical training are widely inconsistent and in many instances do not exist. Where trainee policies do exist, benefits are routinely less robust than those of permanent faculty who receive on average 30% more paid leave time. Stratifying physician wellness needs by training status seems to be a misplaced approach.
It is not only the medical field which sees inconsistencies in the way family leave is allocated for different types of jobs. Millions of Americans receive no time off after birth or adoption, at a time when corporate America offers elite benefits for child care. In medicine, however, there is an expectation that paid family leave should be the norm, perhaps because of our mission to improve the quality of health care.
Of course, there are valid distinctions between faculty and trainees: faculty are more permanent, are more professionally differentiated and accomplished than trainees, have greater responsibilities, and are recruited for their expertise. Arguably, faculty deserve better compensation than trainees.
But the importance of parental leave transcends the routine benefits arguments. There is something more universal about how we value parenting. Parental leave policies benefit the health of parent and child, increase career satisfaction, and improve retention. The process of birth or adoption, ensuing fatigue, family bonding needs, and life-restructuring will challenge all parents regardless of career status.
Awareness of the inadequacies of parental leave policies is the first step in remedying the disparities in support for our trainees. Establishing an equal and adequate family leave policy for physicians at any stage is consistent with the goal of success and well-being for us all.
Laurel Fisher, MD, AGAF, professor of clinical internal medicine, division of gastroenterology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. She reports no conflicts of interest.
Recent data by Magudia et al. have highlighted the fact that family leave policies supporting parents during medical training are widely inconsistent and in many instances do not exist. Where trainee policies do exist, benefits are routinely less robust than those of permanent faculty who receive on average 30% more paid leave time. Stratifying physician wellness needs by training status seems to be a misplaced approach.
It is not only the medical field which sees inconsistencies in the way family leave is allocated for different types of jobs. Millions of Americans receive no time off after birth or adoption, at a time when corporate America offers elite benefits for child care. In medicine, however, there is an expectation that paid family leave should be the norm, perhaps because of our mission to improve the quality of health care.
Of course, there are valid distinctions between faculty and trainees: faculty are more permanent, are more professionally differentiated and accomplished than trainees, have greater responsibilities, and are recruited for their expertise. Arguably, faculty deserve better compensation than trainees.
But the importance of parental leave transcends the routine benefits arguments. There is something more universal about how we value parenting. Parental leave policies benefit the health of parent and child, increase career satisfaction, and improve retention. The process of birth or adoption, ensuing fatigue, family bonding needs, and life-restructuring will challenge all parents regardless of career status.
Awareness of the inadequacies of parental leave policies is the first step in remedying the disparities in support for our trainees. Establishing an equal and adequate family leave policy for physicians at any stage is consistent with the goal of success and well-being for us all.
Laurel Fisher, MD, AGAF, professor of clinical internal medicine, division of gastroenterology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. She reports no conflicts of interest.
Leave policies for residents who become new parents are uneven, oft-ignored by training boards, and provide less time off than similar policies for faculty physicians. Those were the findings of a pair of research letters published in JAMA.
Kirti Magudia, MD, of the department of radiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston and her colleagues reviewed childbearing and family leave policies for 15 graduate medical education (GME)–sponsoring institutions, all of which were affiliated with the top 12 U.S. medical schools. Though all 12 schools provided paid childbearing or family leave for faculty physicians, only 8 of the 15 did so for residents (JAMA. 2018 Dec 11;320[22)]:2372-4).
In programs that did provide leave, the average of 6.6 weeks of paid total maternity leave for residents was less than the 8.6 weeks faculty receive. Both are considerably less than proscribed by the Family and Medical Leave Act, which requires large employers to provide 12 weeks of unpaid leave, but only after 12 months of employment.
The research focused on only institutional policies for paid leave; unpaid leave and state policies may extend the average, and departments may offer leave that goes beyond specific policies, Dr. Magudia and her colleagues noted.
Changes in the residency population make now the right time for establishing consistent family leave policies, Dr. Magudia said in an interview. “We have people starting training later; we have more female trainees. And with the Match system, you’re not in control of exactly where you’re going. You may not have a support system where you end up, and a lot of the top training institutions are in high cost-of-living areas. All of those things together can make trainees especially vulnerable, and because trainees are temporary employees, changing policies to benefit them is very challenging.
“Wellness is a huge issue in medicine, and at large in society,” she said. “Making sure people have adequate parental leave goes a long way toward reducing stress levels and helping them cope with normal life transitions. We want to take steps that promote success among a diverse community of physicians; we want to retain as many people in the field as possible, and we want them to feel supported.”
Beyond asking all GME-sponsoring institutions to adopt parental leave policies, Dr. Magudia believes trainees must be better informed. “It should be clear to training program applicants what the policies are at those institutions,” she said. “That information is extremely difficult to obtain, as we’ve discovered. You can imagine that, if you are the applicant, it can be difficult to ask about those policies during the interview process because it may affect how things turn out.”
“If we can see changes like these made in the near future,” she added, “we will be in a good place.”
In the second study, Briony K. Varda, MD, of the department of urology at Boston Children’s Hospital, and her colleagues also noted the complications of balancing parental leave with training requirements from specialty boards. They compared leave policies among American Board of Medical Specialty member organizations and found that less than half specifically mentioned parental leave for resident physicians (JAMA. 2018 Dec 11;320[22]:2374-7).
Dr. Varda and her colleagues reviewed the websites of 24 ABMS boards to determine their leave policies; 22 had policies but only 11 cited parental leave as an option for residents. Twenty boards have time-based training requirements and allow for a median of 6 weeks leave for any reason; none of the boards had a specific policy for parental leave. In addition, only eight boards had “explicit and clear clarifying language” that would allow program directors to seek exemptions for their residents.
Though limitations like not detecting all available policies – and a subjective evaluation of the policies that were reviewed – could have impacted their study, the coauthors reiterated that the median of 6 weeks leave is less than the average leave for faculty physicians. They also emphasized the detriments associated with inadequate parental leave, including delayed childbearing, use of assisted reproduction technology, and difficulty breastfeeding.
Dr. Varda underlined the issues that arise for program directors, who “must weigh potentially conflicting factors such as adhering to board and institutional policies, maintaining adequate clinical service coverage, considering precedent within the program, and ensuring that resident physicians are well trained.” To balance the needs of all involved “novel approaches such as use of competency-based rather than time-based training milestones” to determine certification eligibility and, in return, lessen the stresses for new-parent residents, she noted.
The researchers disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Magudia K et al. JAMA. 2018 Dec 11;320[22)]:2372-4; Varda B et al. JAMA. 2018 Dec 11;320[22]:2374-7.
Leave policies for residents who become new parents are uneven, oft-ignored by training boards, and provide less time off than similar policies for faculty physicians. Those were the findings of a pair of research letters published in JAMA.
Kirti Magudia, MD, of the department of radiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston and her colleagues reviewed childbearing and family leave policies for 15 graduate medical education (GME)–sponsoring institutions, all of which were affiliated with the top 12 U.S. medical schools. Though all 12 schools provided paid childbearing or family leave for faculty physicians, only 8 of the 15 did so for residents (JAMA. 2018 Dec 11;320[22)]:2372-4).
In programs that did provide leave, the average of 6.6 weeks of paid total maternity leave for residents was less than the 8.6 weeks faculty receive. Both are considerably less than proscribed by the Family and Medical Leave Act, which requires large employers to provide 12 weeks of unpaid leave, but only after 12 months of employment.
The research focused on only institutional policies for paid leave; unpaid leave and state policies may extend the average, and departments may offer leave that goes beyond specific policies, Dr. Magudia and her colleagues noted.
Changes in the residency population make now the right time for establishing consistent family leave policies, Dr. Magudia said in an interview. “We have people starting training later; we have more female trainees. And with the Match system, you’re not in control of exactly where you’re going. You may not have a support system where you end up, and a lot of the top training institutions are in high cost-of-living areas. All of those things together can make trainees especially vulnerable, and because trainees are temporary employees, changing policies to benefit them is very challenging.
“Wellness is a huge issue in medicine, and at large in society,” she said. “Making sure people have adequate parental leave goes a long way toward reducing stress levels and helping them cope with normal life transitions. We want to take steps that promote success among a diverse community of physicians; we want to retain as many people in the field as possible, and we want them to feel supported.”
Beyond asking all GME-sponsoring institutions to adopt parental leave policies, Dr. Magudia believes trainees must be better informed. “It should be clear to training program applicants what the policies are at those institutions,” she said. “That information is extremely difficult to obtain, as we’ve discovered. You can imagine that, if you are the applicant, it can be difficult to ask about those policies during the interview process because it may affect how things turn out.”
“If we can see changes like these made in the near future,” she added, “we will be in a good place.”
In the second study, Briony K. Varda, MD, of the department of urology at Boston Children’s Hospital, and her colleagues also noted the complications of balancing parental leave with training requirements from specialty boards. They compared leave policies among American Board of Medical Specialty member organizations and found that less than half specifically mentioned parental leave for resident physicians (JAMA. 2018 Dec 11;320[22]:2374-7).
Dr. Varda and her colleagues reviewed the websites of 24 ABMS boards to determine their leave policies; 22 had policies but only 11 cited parental leave as an option for residents. Twenty boards have time-based training requirements and allow for a median of 6 weeks leave for any reason; none of the boards had a specific policy for parental leave. In addition, only eight boards had “explicit and clear clarifying language” that would allow program directors to seek exemptions for their residents.
Though limitations like not detecting all available policies – and a subjective evaluation of the policies that were reviewed – could have impacted their study, the coauthors reiterated that the median of 6 weeks leave is less than the average leave for faculty physicians. They also emphasized the detriments associated with inadequate parental leave, including delayed childbearing, use of assisted reproduction technology, and difficulty breastfeeding.
Dr. Varda underlined the issues that arise for program directors, who “must weigh potentially conflicting factors such as adhering to board and institutional policies, maintaining adequate clinical service coverage, considering precedent within the program, and ensuring that resident physicians are well trained.” To balance the needs of all involved “novel approaches such as use of competency-based rather than time-based training milestones” to determine certification eligibility and, in return, lessen the stresses for new-parent residents, she noted.
The researchers disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Magudia K et al. JAMA. 2018 Dec 11;320[22)]:2372-4; Varda B et al. JAMA. 2018 Dec 11;320[22]:2374-7.
FROM JAMA










