User login
Finding the Best Match for MASLD Management
, according to the authors of clinical reviews who offered guidance on the pros and cons of resmetirom and semaglutide.
MASLD has become one of the most common causes of chronic liver disease due to the increased prevalence of diabetes, obesity, and other metabolic disorders, Joanne Lin, DO, an internist in the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at the University of California, San Francisco, and colleagues wrote, in a review published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology.
Its complexity makes MASLD challenging to manage. Metabolic, genetic, and environmental factors are involved in the disease, so patients require multidisciplinary and individualized care, Lin told GI & Hepatology News.
Weight loss, dietary changes, and exercise had long been the only treatment approach clinicians could offer patients. But the approval of two drugs — the thyroid hormone receptor-beta agonist resmetirom and the GLP-1 receptor agonist (RA) semaglutide — for patients whose MASLD has advanced to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) gives physicians new options for patients with severe disease.
In the review, published online before the official approval of semaglutide, Lin and colleagues proposed an algorithm to guide clinicians in choosing a pharmacological therapy for MASLD. “Resmetirom should be primarily used to reverse fibrosis for patients with MASLD and F2-F3 stages, while GLP-1 RAs are beneficial in managing metabolic comorbidities and weight loss in patients with MASLD,” the researchers concluded.
GLP-1 Power and Potential
In August 2025, the FDA approved semaglutide for MASH and cited evidence from the ESSENCE trial in its decision.
The ESSENCE study, published in The New England Journal of Medicine, showed significantly higher rates of resolution of steatohepatitis without worsening of fibrosis and reduction in liver fibrosis without worsening steatohepatitis in patients with MASH and moderate or advanced liver fibrosis who received 2.4 mg of once-weekly semaglutide compared with patients who received placebo.
The most common adverse events reported with GLP-1 RAs are gastrointestinal-related, including nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and constipation, and are mainly mild-to-moderate and dose dependent, Lin and colleagues noted in their review.
GLP-1s have some limitations, Lin said. “GLP-1s are great for weight loss and metabolic risk reduction, but studies are still ongoing to determine their effect on liver histology and reversing fibrosis/cirrhosis,” she said. Some patients seeking these medications also have trouble obtaining them because of their popularity for weight loss, she noted.
Resmetirom Shows Success
Resmetirom has demonstrated ability to target hepatocytes and increase the hepatic metabolism of lipids, Lin and colleagues wrote in their review.
Several trials have examined resmetirom as a treatment for MASH, notably the landmark MAESTRO-NASH study , a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of nearly 1000 adults with biopsy-confirmed MASH and stage F2 or F3 fibrosis, which was the basis for the FDA’s approval of the drug in 2024. In the study, 25.9% of the patients treated with 80 mg of resmetirom and 29.9% treated with 100 mg resmetirom achieved MASH resolution with no increase in fibrosis compared with 9.7% of patients treated with placebo. In addition, 24.2% of the patients in the 80-mg resmetirom group and 25.9% of those in the 100-mg resmetirom group achieved fibrosis improvement by at least one stage without worsening of MASLD activity scores compared with 14.2% of patients treated with placebo.
The most common reported side effects from resmetirom are diarrhea or constipation, nausea or vomiting, and abdominal pain.
“The limitations of resmetirom include the absence of validated predictors for individual patient response, and no societal guidelines are available to determine when to stop the medication if ineffective,” Lin told GI & Hepatology News. In addition, resmetirom is currently only recommended for a subset of patients with F2-F3 fibrosis, based on the existing trial, she said.
Other limitations include its high cost, which restricts access to the drug for some patients, and lack of long-term safety and efficacy data, Lin added.
Weighing the Options
Comparing the emerging agents in the context of MASLD/MASH is important to help clinicians understand how different patient populations respond and guide evidence-based treatment decisions, said Hazem Ayesh, MD, an endocrinologist at Deaconess Health System, Evansville, Indiana, in an interview.
“The choice of therapy should be individualized based on comorbidities,” said Ayesh, the lead author of a 2024 review published in Biomedicines that compared resmetirom, GLP-1 agonists, and fibroblast growth factor 21 analogs.
“For example, a GLP-1 receptor agonist may be more appropriate for patients with coexisting diabetes or obesity, while resmetirom may be better suited for patients with more advanced liver disease or minimal metabolic comorbidities,” he said.
GLP-1 RAs, such as semaglutide, offer benefits for diabetes, obesity, and metabolic dysfunction in patients with MASLD/MASH and may be more accessible and cost effective, Ayesh told GI & Hepatology News. However, some patients may experience gastrointestinal side effects or be unable to tolerate GLP-1 RAs, he noted.
By contrast, resmetirom may be preferable for patients with low BMI, advanced fibrosis, or an inability to tolerate GLP-1s, as resmetirom directly targets hepatic pathways involved in MASLD/MASH progression, Ayesh said.
Next Steps to Inform Practice
“More research is needed to validate noninvasive biomarkers to monitor response to these medications, determine predictors of efficacy, and evaluate the additive effects, safety, and drug-drug interactions of combination therapy,” Lin said.
Studies are needed to determine both medications’ effects on patients with advanced fibrosis/cirrhosis and special populations, such as individuals with advanced renal disease or posttransplant patients, she added. More studies are expected to inform clinical practice and proper guidelines for the treatment of MASLD, as has been the case with chronic diseases such as hypertension and diabetes, Lin said.
Long-term safety and efficacy data are critical, as most trials of the newly approved medications have had relatively short follow-up periods of approximately 1 year, Ayesh said. “We need real-world evidence and longitudinal studies spanning 3-5 years to confirm sustained efficacy and safety,” he said. Research on cost effectiveness and health-system impacts will be essential to guide policy and ensure equitable access to the medications, he added.
The study by Lin and colleagues received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Ayesh had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to the authors of clinical reviews who offered guidance on the pros and cons of resmetirom and semaglutide.
MASLD has become one of the most common causes of chronic liver disease due to the increased prevalence of diabetes, obesity, and other metabolic disorders, Joanne Lin, DO, an internist in the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at the University of California, San Francisco, and colleagues wrote, in a review published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology.
Its complexity makes MASLD challenging to manage. Metabolic, genetic, and environmental factors are involved in the disease, so patients require multidisciplinary and individualized care, Lin told GI & Hepatology News.
Weight loss, dietary changes, and exercise had long been the only treatment approach clinicians could offer patients. But the approval of two drugs — the thyroid hormone receptor-beta agonist resmetirom and the GLP-1 receptor agonist (RA) semaglutide — for patients whose MASLD has advanced to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) gives physicians new options for patients with severe disease.
In the review, published online before the official approval of semaglutide, Lin and colleagues proposed an algorithm to guide clinicians in choosing a pharmacological therapy for MASLD. “Resmetirom should be primarily used to reverse fibrosis for patients with MASLD and F2-F3 stages, while GLP-1 RAs are beneficial in managing metabolic comorbidities and weight loss in patients with MASLD,” the researchers concluded.
GLP-1 Power and Potential
In August 2025, the FDA approved semaglutide for MASH and cited evidence from the ESSENCE trial in its decision.
The ESSENCE study, published in The New England Journal of Medicine, showed significantly higher rates of resolution of steatohepatitis without worsening of fibrosis and reduction in liver fibrosis without worsening steatohepatitis in patients with MASH and moderate or advanced liver fibrosis who received 2.4 mg of once-weekly semaglutide compared with patients who received placebo.
The most common adverse events reported with GLP-1 RAs are gastrointestinal-related, including nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and constipation, and are mainly mild-to-moderate and dose dependent, Lin and colleagues noted in their review.
GLP-1s have some limitations, Lin said. “GLP-1s are great for weight loss and metabolic risk reduction, but studies are still ongoing to determine their effect on liver histology and reversing fibrosis/cirrhosis,” she said. Some patients seeking these medications also have trouble obtaining them because of their popularity for weight loss, she noted.
Resmetirom Shows Success
Resmetirom has demonstrated ability to target hepatocytes and increase the hepatic metabolism of lipids, Lin and colleagues wrote in their review.
Several trials have examined resmetirom as a treatment for MASH, notably the landmark MAESTRO-NASH study , a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of nearly 1000 adults with biopsy-confirmed MASH and stage F2 or F3 fibrosis, which was the basis for the FDA’s approval of the drug in 2024. In the study, 25.9% of the patients treated with 80 mg of resmetirom and 29.9% treated with 100 mg resmetirom achieved MASH resolution with no increase in fibrosis compared with 9.7% of patients treated with placebo. In addition, 24.2% of the patients in the 80-mg resmetirom group and 25.9% of those in the 100-mg resmetirom group achieved fibrosis improvement by at least one stage without worsening of MASLD activity scores compared with 14.2% of patients treated with placebo.
The most common reported side effects from resmetirom are diarrhea or constipation, nausea or vomiting, and abdominal pain.
“The limitations of resmetirom include the absence of validated predictors for individual patient response, and no societal guidelines are available to determine when to stop the medication if ineffective,” Lin told GI & Hepatology News. In addition, resmetirom is currently only recommended for a subset of patients with F2-F3 fibrosis, based on the existing trial, she said.
Other limitations include its high cost, which restricts access to the drug for some patients, and lack of long-term safety and efficacy data, Lin added.
Weighing the Options
Comparing the emerging agents in the context of MASLD/MASH is important to help clinicians understand how different patient populations respond and guide evidence-based treatment decisions, said Hazem Ayesh, MD, an endocrinologist at Deaconess Health System, Evansville, Indiana, in an interview.
“The choice of therapy should be individualized based on comorbidities,” said Ayesh, the lead author of a 2024 review published in Biomedicines that compared resmetirom, GLP-1 agonists, and fibroblast growth factor 21 analogs.
“For example, a GLP-1 receptor agonist may be more appropriate for patients with coexisting diabetes or obesity, while resmetirom may be better suited for patients with more advanced liver disease or minimal metabolic comorbidities,” he said.
GLP-1 RAs, such as semaglutide, offer benefits for diabetes, obesity, and metabolic dysfunction in patients with MASLD/MASH and may be more accessible and cost effective, Ayesh told GI & Hepatology News. However, some patients may experience gastrointestinal side effects or be unable to tolerate GLP-1 RAs, he noted.
By contrast, resmetirom may be preferable for patients with low BMI, advanced fibrosis, or an inability to tolerate GLP-1s, as resmetirom directly targets hepatic pathways involved in MASLD/MASH progression, Ayesh said.
Next Steps to Inform Practice
“More research is needed to validate noninvasive biomarkers to monitor response to these medications, determine predictors of efficacy, and evaluate the additive effects, safety, and drug-drug interactions of combination therapy,” Lin said.
Studies are needed to determine both medications’ effects on patients with advanced fibrosis/cirrhosis and special populations, such as individuals with advanced renal disease or posttransplant patients, she added. More studies are expected to inform clinical practice and proper guidelines for the treatment of MASLD, as has been the case with chronic diseases such as hypertension and diabetes, Lin said.
Long-term safety and efficacy data are critical, as most trials of the newly approved medications have had relatively short follow-up periods of approximately 1 year, Ayesh said. “We need real-world evidence and longitudinal studies spanning 3-5 years to confirm sustained efficacy and safety,” he said. Research on cost effectiveness and health-system impacts will be essential to guide policy and ensure equitable access to the medications, he added.
The study by Lin and colleagues received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Ayesh had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to the authors of clinical reviews who offered guidance on the pros and cons of resmetirom and semaglutide.
MASLD has become one of the most common causes of chronic liver disease due to the increased prevalence of diabetes, obesity, and other metabolic disorders, Joanne Lin, DO, an internist in the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at the University of California, San Francisco, and colleagues wrote, in a review published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology.
Its complexity makes MASLD challenging to manage. Metabolic, genetic, and environmental factors are involved in the disease, so patients require multidisciplinary and individualized care, Lin told GI & Hepatology News.
Weight loss, dietary changes, and exercise had long been the only treatment approach clinicians could offer patients. But the approval of two drugs — the thyroid hormone receptor-beta agonist resmetirom and the GLP-1 receptor agonist (RA) semaglutide — for patients whose MASLD has advanced to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) gives physicians new options for patients with severe disease.
In the review, published online before the official approval of semaglutide, Lin and colleagues proposed an algorithm to guide clinicians in choosing a pharmacological therapy for MASLD. “Resmetirom should be primarily used to reverse fibrosis for patients with MASLD and F2-F3 stages, while GLP-1 RAs are beneficial in managing metabolic comorbidities and weight loss in patients with MASLD,” the researchers concluded.
GLP-1 Power and Potential
In August 2025, the FDA approved semaglutide for MASH and cited evidence from the ESSENCE trial in its decision.
The ESSENCE study, published in The New England Journal of Medicine, showed significantly higher rates of resolution of steatohepatitis without worsening of fibrosis and reduction in liver fibrosis without worsening steatohepatitis in patients with MASH and moderate or advanced liver fibrosis who received 2.4 mg of once-weekly semaglutide compared with patients who received placebo.
The most common adverse events reported with GLP-1 RAs are gastrointestinal-related, including nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and constipation, and are mainly mild-to-moderate and dose dependent, Lin and colleagues noted in their review.
GLP-1s have some limitations, Lin said. “GLP-1s are great for weight loss and metabolic risk reduction, but studies are still ongoing to determine their effect on liver histology and reversing fibrosis/cirrhosis,” she said. Some patients seeking these medications also have trouble obtaining them because of their popularity for weight loss, she noted.
Resmetirom Shows Success
Resmetirom has demonstrated ability to target hepatocytes and increase the hepatic metabolism of lipids, Lin and colleagues wrote in their review.
Several trials have examined resmetirom as a treatment for MASH, notably the landmark MAESTRO-NASH study , a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of nearly 1000 adults with biopsy-confirmed MASH and stage F2 or F3 fibrosis, which was the basis for the FDA’s approval of the drug in 2024. In the study, 25.9% of the patients treated with 80 mg of resmetirom and 29.9% treated with 100 mg resmetirom achieved MASH resolution with no increase in fibrosis compared with 9.7% of patients treated with placebo. In addition, 24.2% of the patients in the 80-mg resmetirom group and 25.9% of those in the 100-mg resmetirom group achieved fibrosis improvement by at least one stage without worsening of MASLD activity scores compared with 14.2% of patients treated with placebo.
The most common reported side effects from resmetirom are diarrhea or constipation, nausea or vomiting, and abdominal pain.
“The limitations of resmetirom include the absence of validated predictors for individual patient response, and no societal guidelines are available to determine when to stop the medication if ineffective,” Lin told GI & Hepatology News. In addition, resmetirom is currently only recommended for a subset of patients with F2-F3 fibrosis, based on the existing trial, she said.
Other limitations include its high cost, which restricts access to the drug for some patients, and lack of long-term safety and efficacy data, Lin added.
Weighing the Options
Comparing the emerging agents in the context of MASLD/MASH is important to help clinicians understand how different patient populations respond and guide evidence-based treatment decisions, said Hazem Ayesh, MD, an endocrinologist at Deaconess Health System, Evansville, Indiana, in an interview.
“The choice of therapy should be individualized based on comorbidities,” said Ayesh, the lead author of a 2024 review published in Biomedicines that compared resmetirom, GLP-1 agonists, and fibroblast growth factor 21 analogs.
“For example, a GLP-1 receptor agonist may be more appropriate for patients with coexisting diabetes or obesity, while resmetirom may be better suited for patients with more advanced liver disease or minimal metabolic comorbidities,” he said.
GLP-1 RAs, such as semaglutide, offer benefits for diabetes, obesity, and metabolic dysfunction in patients with MASLD/MASH and may be more accessible and cost effective, Ayesh told GI & Hepatology News. However, some patients may experience gastrointestinal side effects or be unable to tolerate GLP-1 RAs, he noted.
By contrast, resmetirom may be preferable for patients with low BMI, advanced fibrosis, or an inability to tolerate GLP-1s, as resmetirom directly targets hepatic pathways involved in MASLD/MASH progression, Ayesh said.
Next Steps to Inform Practice
“More research is needed to validate noninvasive biomarkers to monitor response to these medications, determine predictors of efficacy, and evaluate the additive effects, safety, and drug-drug interactions of combination therapy,” Lin said.
Studies are needed to determine both medications’ effects on patients with advanced fibrosis/cirrhosis and special populations, such as individuals with advanced renal disease or posttransplant patients, she added. More studies are expected to inform clinical practice and proper guidelines for the treatment of MASLD, as has been the case with chronic diseases such as hypertension and diabetes, Lin said.
Long-term safety and efficacy data are critical, as most trials of the newly approved medications have had relatively short follow-up periods of approximately 1 year, Ayesh said. “We need real-world evidence and longitudinal studies spanning 3-5 years to confirm sustained efficacy and safety,” he said. Research on cost effectiveness and health-system impacts will be essential to guide policy and ensure equitable access to the medications, he added.
The study by Lin and colleagues received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Ayesh had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Vaping Increases Peptic Ulcer Disease Risk
PHOENIX — , a cross-sectional study found.
The study also found increased risk of PUD among former users of e-cigarettes, reported Albert E. Ohrin, MBChB, MHS, of Ascension Saint Agnes Hospital, Baltimore, Maryland, who presented the study here at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting.
While cigarette smoking is a known risk factor for PUD, there was little in the literature investigating whether vaping has a similar risk profile, said Ohrin, a first-year internal medicine resident. He told GI & Hepatology News he found e-cigarette users on Reddit discussing worsening PUD and decided to investigate further, especially since vaping is so popular among young people.
E-cigarettes are the most-used tobacco product among middle and high school students. The National Youth Tobacco Survey in the US reported that 1.6 million students (5.9%) vaped in 2024, a decline from 7.7% in 2023. And the number of adults using e-cigarettes is increasing, according to the US CDC. In 2023, 6.5% of adults over age 18 used e-cigarettes, up from 3.7% in 2020.
Ohrin and colleagues conducted a cross-sectional analysis of adults enrolled in the National Institutes of Health All of Us Research Program. Participants self-reported e-cigarette use. PUD was defined using validated electronic health record diagnosis codes.
Among the 371,398 participants, 29,373 (8%) reported using e-cigarettes, including 21,277 current users and 8096 former users. E-cigarette users were significantly younger (mean age 45.3 vs 59.3 years; P < .001), more likely to be female, and more likely to report lower education and income (P < .001).
Current e-cigarette users had 27% higher odds of PUD (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.27; 95% CI, 1.12-1.45), compared to never-users. This was greater than the risk with traditional combustible cigarettes (aOR, 1.19) that was seen in the study.
Former e-cig users had 13% higher odds (aOR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.04-1.24) compared to never-users, and any e-cigarette use was associated with higher odds of PUD (aOR, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.09-1.26) compared to never-use.
Use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (aOR, 2.15) and having gastroesophageal reflux disease (aOR, 4.45) presented the most significant PUD risk.
Ohrin said he and his colleagues were surprised to see that people who had stopped using e-cigarettes still had higher odds of PUD, although he pointed out that the researchers did not know the frequency of use or how long users had stopped.
“Now that we know there’s an association, we are going to do more studies on e-cigarettes” to see what the potential harms are, especially on the gastrointestinal system, he told GI & Hepatology News.
“One of the things we are looking to elicit is — is there a dose response?” he said, noting it would take a prospective trial to determine that effect.
‘Opens a Door’ to Looking at the GI System
Laura Crotty Alexander, MD, a professor of medicine and associate division chief of pulmonary, critical care, sleep medicine, and physiology at the University of California, San Diego, said she found the study novel and interesting.
“It’s the first I’ve heard of an association between e-cigarette vaping and peptic ulcer disease,” said Crotty Alexander, who has studied the health effects of e-cigarettes for a decade.
Previous studies have shown that nicotine itself can drive an increase in gastric acid production and decrease healing, which can contribute to PUD, Crotty Alexander told GI & Hepatology News. With combustible cigarettes, it is thought that “the larger drivers of that association are the other things in tobacco smoke, such as tar and carbon monoxide and a million other horrible chemicals,” she said.
Crotty Alexander and her colleagues have conducted studies in vitro and in mice that show that e-cigarette aerosols are irritants and cause oxidative stress, which can drive PUD.
While many studies have shown vaping impacts various organs, Ohrin’s study “opens a door” to start looking at the gastrointestinal system, she said.
The study is also a signal to clinicians to “take an accurate inhalant history,” which means asking about vaping, she added.
Ohrin and Crotty Alexander reported no conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHOENIX — , a cross-sectional study found.
The study also found increased risk of PUD among former users of e-cigarettes, reported Albert E. Ohrin, MBChB, MHS, of Ascension Saint Agnes Hospital, Baltimore, Maryland, who presented the study here at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting.
While cigarette smoking is a known risk factor for PUD, there was little in the literature investigating whether vaping has a similar risk profile, said Ohrin, a first-year internal medicine resident. He told GI & Hepatology News he found e-cigarette users on Reddit discussing worsening PUD and decided to investigate further, especially since vaping is so popular among young people.
E-cigarettes are the most-used tobacco product among middle and high school students. The National Youth Tobacco Survey in the US reported that 1.6 million students (5.9%) vaped in 2024, a decline from 7.7% in 2023. And the number of adults using e-cigarettes is increasing, according to the US CDC. In 2023, 6.5% of adults over age 18 used e-cigarettes, up from 3.7% in 2020.
Ohrin and colleagues conducted a cross-sectional analysis of adults enrolled in the National Institutes of Health All of Us Research Program. Participants self-reported e-cigarette use. PUD was defined using validated electronic health record diagnosis codes.
Among the 371,398 participants, 29,373 (8%) reported using e-cigarettes, including 21,277 current users and 8096 former users. E-cigarette users were significantly younger (mean age 45.3 vs 59.3 years; P < .001), more likely to be female, and more likely to report lower education and income (P < .001).
Current e-cigarette users had 27% higher odds of PUD (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.27; 95% CI, 1.12-1.45), compared to never-users. This was greater than the risk with traditional combustible cigarettes (aOR, 1.19) that was seen in the study.
Former e-cig users had 13% higher odds (aOR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.04-1.24) compared to never-users, and any e-cigarette use was associated with higher odds of PUD (aOR, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.09-1.26) compared to never-use.
Use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (aOR, 2.15) and having gastroesophageal reflux disease (aOR, 4.45) presented the most significant PUD risk.
Ohrin said he and his colleagues were surprised to see that people who had stopped using e-cigarettes still had higher odds of PUD, although he pointed out that the researchers did not know the frequency of use or how long users had stopped.
“Now that we know there’s an association, we are going to do more studies on e-cigarettes” to see what the potential harms are, especially on the gastrointestinal system, he told GI & Hepatology News.
“One of the things we are looking to elicit is — is there a dose response?” he said, noting it would take a prospective trial to determine that effect.
‘Opens a Door’ to Looking at the GI System
Laura Crotty Alexander, MD, a professor of medicine and associate division chief of pulmonary, critical care, sleep medicine, and physiology at the University of California, San Diego, said she found the study novel and interesting.
“It’s the first I’ve heard of an association between e-cigarette vaping and peptic ulcer disease,” said Crotty Alexander, who has studied the health effects of e-cigarettes for a decade.
Previous studies have shown that nicotine itself can drive an increase in gastric acid production and decrease healing, which can contribute to PUD, Crotty Alexander told GI & Hepatology News. With combustible cigarettes, it is thought that “the larger drivers of that association are the other things in tobacco smoke, such as tar and carbon monoxide and a million other horrible chemicals,” she said.
Crotty Alexander and her colleagues have conducted studies in vitro and in mice that show that e-cigarette aerosols are irritants and cause oxidative stress, which can drive PUD.
While many studies have shown vaping impacts various organs, Ohrin’s study “opens a door” to start looking at the gastrointestinal system, she said.
The study is also a signal to clinicians to “take an accurate inhalant history,” which means asking about vaping, she added.
Ohrin and Crotty Alexander reported no conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHOENIX — , a cross-sectional study found.
The study also found increased risk of PUD among former users of e-cigarettes, reported Albert E. Ohrin, MBChB, MHS, of Ascension Saint Agnes Hospital, Baltimore, Maryland, who presented the study here at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting.
While cigarette smoking is a known risk factor for PUD, there was little in the literature investigating whether vaping has a similar risk profile, said Ohrin, a first-year internal medicine resident. He told GI & Hepatology News he found e-cigarette users on Reddit discussing worsening PUD and decided to investigate further, especially since vaping is so popular among young people.
E-cigarettes are the most-used tobacco product among middle and high school students. The National Youth Tobacco Survey in the US reported that 1.6 million students (5.9%) vaped in 2024, a decline from 7.7% in 2023. And the number of adults using e-cigarettes is increasing, according to the US CDC. In 2023, 6.5% of adults over age 18 used e-cigarettes, up from 3.7% in 2020.
Ohrin and colleagues conducted a cross-sectional analysis of adults enrolled in the National Institutes of Health All of Us Research Program. Participants self-reported e-cigarette use. PUD was defined using validated electronic health record diagnosis codes.
Among the 371,398 participants, 29,373 (8%) reported using e-cigarettes, including 21,277 current users and 8096 former users. E-cigarette users were significantly younger (mean age 45.3 vs 59.3 years; P < .001), more likely to be female, and more likely to report lower education and income (P < .001).
Current e-cigarette users had 27% higher odds of PUD (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.27; 95% CI, 1.12-1.45), compared to never-users. This was greater than the risk with traditional combustible cigarettes (aOR, 1.19) that was seen in the study.
Former e-cig users had 13% higher odds (aOR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.04-1.24) compared to never-users, and any e-cigarette use was associated with higher odds of PUD (aOR, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.09-1.26) compared to never-use.
Use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (aOR, 2.15) and having gastroesophageal reflux disease (aOR, 4.45) presented the most significant PUD risk.
Ohrin said he and his colleagues were surprised to see that people who had stopped using e-cigarettes still had higher odds of PUD, although he pointed out that the researchers did not know the frequency of use or how long users had stopped.
“Now that we know there’s an association, we are going to do more studies on e-cigarettes” to see what the potential harms are, especially on the gastrointestinal system, he told GI & Hepatology News.
“One of the things we are looking to elicit is — is there a dose response?” he said, noting it would take a prospective trial to determine that effect.
‘Opens a Door’ to Looking at the GI System
Laura Crotty Alexander, MD, a professor of medicine and associate division chief of pulmonary, critical care, sleep medicine, and physiology at the University of California, San Diego, said she found the study novel and interesting.
“It’s the first I’ve heard of an association between e-cigarette vaping and peptic ulcer disease,” said Crotty Alexander, who has studied the health effects of e-cigarettes for a decade.
Previous studies have shown that nicotine itself can drive an increase in gastric acid production and decrease healing, which can contribute to PUD, Crotty Alexander told GI & Hepatology News. With combustible cigarettes, it is thought that “the larger drivers of that association are the other things in tobacco smoke, such as tar and carbon monoxide and a million other horrible chemicals,” she said.
Crotty Alexander and her colleagues have conducted studies in vitro and in mice that show that e-cigarette aerosols are irritants and cause oxidative stress, which can drive PUD.
While many studies have shown vaping impacts various organs, Ohrin’s study “opens a door” to start looking at the gastrointestinal system, she said.
The study is also a signal to clinicians to “take an accurate inhalant history,” which means asking about vaping, she added.
Ohrin and Crotty Alexander reported no conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACG 2025
Helping Veterans Ease Into Civilian Life
What does a successful military-to-civilian transition look like? How do we know if a veteran is sinking, treading water, or swimming? Two recent studies by the Penn State University Clearinghouse for Military Family Readiness sought to answer to those questions and more while determining how and when is the right time to step in to help a veteran in need.
The research analyzed The Veterans Metrics Initiative data (TVMI). This longitudinal study surveyed 9566 men and women who left active duty in 2016 over 3 years, answering questions about deployment histories, adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) and exposure to combat. They also reported whether they had symptoms related to anxiety and depression.
The TVMI study found that ACEs predicted poor outcomes early on and when combined with warfare experience dramatically increased the likelihood of mental health issues, including posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety, and depression; moral injury impacted adjustment to civilian life (the degree varied by gender); and, many veterans have a “growth outlook” as a result of a trauma or crisis they experienced.
The TVMI study found that almost all veterans use transition resources in the first 2 years after military separation. Beyond that, however, those in high-risk categories (eg, PTSD and cumulative trauma experiences) need continued support. This may come in the form of a universal screener and linking it to a navigation infrastructure (eg, AmericaServes), “thereby identifying risk factors early and providing targeted supports, interventions, and components.”
Veterans often face a series of simultaneous challenges as they return to civilian life. Among them include getting used to family and friends again, finding jobs, losing their military identity, structure, and perhaps leaving military friends behind. In addition, veterans are likely dealing with physical and mental health challenges, which can significantly influence how well they readjust to civilian life and lead to inconsistency experiences for each individual.
A 2019 survey from the Pew Research Center found about 40% of veterans who suffered from PTSD said they frequently had difficulty dealing with the lack of structure in civilian life, compared with 5% of those who do not have PTSD. Another survey cited a large majority (78%) of pre-9/11 veterans said their readjustment was very or somewhat easy. However, 26% said adjusting to civilian life was difficult.
In 2011, 4 variables were identified that predicted easy civilian life re-entry: being an officer; having a consistently clear understanding of the missions while in the service; being a college graduate; and, for post-9/11 veterans, attending religious services frequently. Six variables were associated with a diminished probability of an easy transition: having had a traumatic experience; being seriously injured; serving in the post-9/11 era; serving in a combat zone; serving with someone who was killed or injured; and, for post-9/11 veterans, being married while in the service.
The probabilities of an easy re-entry dropped from 82% for those who did not experience a traumatic event to 56% for those who did—the largest change noted in the 2011 study.
The second Penn State study evaluated a model framework with a lifespan development perspective. The study surveyed veterans on their self-reported satisfaction or symptoms in 7 domains of well-being: employment, education, financial, legal problems, social, physical health, and mental health. Within 3 months of separation , 41% of respondents fell into the “problematic” category for the mental health domain. However, by 30 to 33 months postseparation, this proportion dropped to 34%. During the same period, the proportion of veterans in the at risk category increased from 28% at Wave 1 to 37% at Wave 6. About 30% of veterans fell into the successful category for symptoms across the 3 examined waves. Almost 60% were in the successful category across the 3 time points.
Both Penn State studies emphasize the importance of viewing veterans as individuals on their own timelines.
“These findings underscore that the transition to civilian life is not a single moment, but a process influenced by experiences across the life span,” said Mary M. Mitchell, research professor at the Clearinghouse and lead author on the predictors study. “By following veterans over 3 years, we were able to see how patterns emerge that would be invisible in a one-time survey.”
Current conceptualization “assumes that there are commonalities across veterans when evaluating the success of the transition to civilian life,” according to the authors of the framework study. “However, each veteran likely has his or her view of what a successful transition constitutes, and he or she may weigh domains differently when considering his or her own transition.”
The research highlights the need to find ways to encourage veterans to seek help—and not just in the first year, which is often the most stressful. The Pew Research Center survey identified a “significant break from the past,” in that nearly 70% of post-9/11 veterans said their superiors made them feel comfortable about seeking help with emotional issues resulting from their military service.
However, ≤ 8% veterans in the TVMI study used any health programs, even when they screened positive for mental health problems. Veterans who did use counseling services, however, improved their depression symptoms. Engaging veterans at various time points could help keep mental health problems from worsening during—and beyond—the transition.
What does a successful military-to-civilian transition look like? How do we know if a veteran is sinking, treading water, or swimming? Two recent studies by the Penn State University Clearinghouse for Military Family Readiness sought to answer to those questions and more while determining how and when is the right time to step in to help a veteran in need.
The research analyzed The Veterans Metrics Initiative data (TVMI). This longitudinal study surveyed 9566 men and women who left active duty in 2016 over 3 years, answering questions about deployment histories, adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) and exposure to combat. They also reported whether they had symptoms related to anxiety and depression.
The TVMI study found that ACEs predicted poor outcomes early on and when combined with warfare experience dramatically increased the likelihood of mental health issues, including posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety, and depression; moral injury impacted adjustment to civilian life (the degree varied by gender); and, many veterans have a “growth outlook” as a result of a trauma or crisis they experienced.
The TVMI study found that almost all veterans use transition resources in the first 2 years after military separation. Beyond that, however, those in high-risk categories (eg, PTSD and cumulative trauma experiences) need continued support. This may come in the form of a universal screener and linking it to a navigation infrastructure (eg, AmericaServes), “thereby identifying risk factors early and providing targeted supports, interventions, and components.”
Veterans often face a series of simultaneous challenges as they return to civilian life. Among them include getting used to family and friends again, finding jobs, losing their military identity, structure, and perhaps leaving military friends behind. In addition, veterans are likely dealing with physical and mental health challenges, which can significantly influence how well they readjust to civilian life and lead to inconsistency experiences for each individual.
A 2019 survey from the Pew Research Center found about 40% of veterans who suffered from PTSD said they frequently had difficulty dealing with the lack of structure in civilian life, compared with 5% of those who do not have PTSD. Another survey cited a large majority (78%) of pre-9/11 veterans said their readjustment was very or somewhat easy. However, 26% said adjusting to civilian life was difficult.
In 2011, 4 variables were identified that predicted easy civilian life re-entry: being an officer; having a consistently clear understanding of the missions while in the service; being a college graduate; and, for post-9/11 veterans, attending religious services frequently. Six variables were associated with a diminished probability of an easy transition: having had a traumatic experience; being seriously injured; serving in the post-9/11 era; serving in a combat zone; serving with someone who was killed or injured; and, for post-9/11 veterans, being married while in the service.
The probabilities of an easy re-entry dropped from 82% for those who did not experience a traumatic event to 56% for those who did—the largest change noted in the 2011 study.
The second Penn State study evaluated a model framework with a lifespan development perspective. The study surveyed veterans on their self-reported satisfaction or symptoms in 7 domains of well-being: employment, education, financial, legal problems, social, physical health, and mental health. Within 3 months of separation , 41% of respondents fell into the “problematic” category for the mental health domain. However, by 30 to 33 months postseparation, this proportion dropped to 34%. During the same period, the proportion of veterans in the at risk category increased from 28% at Wave 1 to 37% at Wave 6. About 30% of veterans fell into the successful category for symptoms across the 3 examined waves. Almost 60% were in the successful category across the 3 time points.
Both Penn State studies emphasize the importance of viewing veterans as individuals on their own timelines.
“These findings underscore that the transition to civilian life is not a single moment, but a process influenced by experiences across the life span,” said Mary M. Mitchell, research professor at the Clearinghouse and lead author on the predictors study. “By following veterans over 3 years, we were able to see how patterns emerge that would be invisible in a one-time survey.”
Current conceptualization “assumes that there are commonalities across veterans when evaluating the success of the transition to civilian life,” according to the authors of the framework study. “However, each veteran likely has his or her view of what a successful transition constitutes, and he or she may weigh domains differently when considering his or her own transition.”
The research highlights the need to find ways to encourage veterans to seek help—and not just in the first year, which is often the most stressful. The Pew Research Center survey identified a “significant break from the past,” in that nearly 70% of post-9/11 veterans said their superiors made them feel comfortable about seeking help with emotional issues resulting from their military service.
However, ≤ 8% veterans in the TVMI study used any health programs, even when they screened positive for mental health problems. Veterans who did use counseling services, however, improved their depression symptoms. Engaging veterans at various time points could help keep mental health problems from worsening during—and beyond—the transition.
What does a successful military-to-civilian transition look like? How do we know if a veteran is sinking, treading water, or swimming? Two recent studies by the Penn State University Clearinghouse for Military Family Readiness sought to answer to those questions and more while determining how and when is the right time to step in to help a veteran in need.
The research analyzed The Veterans Metrics Initiative data (TVMI). This longitudinal study surveyed 9566 men and women who left active duty in 2016 over 3 years, answering questions about deployment histories, adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) and exposure to combat. They also reported whether they had symptoms related to anxiety and depression.
The TVMI study found that ACEs predicted poor outcomes early on and when combined with warfare experience dramatically increased the likelihood of mental health issues, including posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety, and depression; moral injury impacted adjustment to civilian life (the degree varied by gender); and, many veterans have a “growth outlook” as a result of a trauma or crisis they experienced.
The TVMI study found that almost all veterans use transition resources in the first 2 years after military separation. Beyond that, however, those in high-risk categories (eg, PTSD and cumulative trauma experiences) need continued support. This may come in the form of a universal screener and linking it to a navigation infrastructure (eg, AmericaServes), “thereby identifying risk factors early and providing targeted supports, interventions, and components.”
Veterans often face a series of simultaneous challenges as they return to civilian life. Among them include getting used to family and friends again, finding jobs, losing their military identity, structure, and perhaps leaving military friends behind. In addition, veterans are likely dealing with physical and mental health challenges, which can significantly influence how well they readjust to civilian life and lead to inconsistency experiences for each individual.
A 2019 survey from the Pew Research Center found about 40% of veterans who suffered from PTSD said they frequently had difficulty dealing with the lack of structure in civilian life, compared with 5% of those who do not have PTSD. Another survey cited a large majority (78%) of pre-9/11 veterans said their readjustment was very or somewhat easy. However, 26% said adjusting to civilian life was difficult.
In 2011, 4 variables were identified that predicted easy civilian life re-entry: being an officer; having a consistently clear understanding of the missions while in the service; being a college graduate; and, for post-9/11 veterans, attending religious services frequently. Six variables were associated with a diminished probability of an easy transition: having had a traumatic experience; being seriously injured; serving in the post-9/11 era; serving in a combat zone; serving with someone who was killed or injured; and, for post-9/11 veterans, being married while in the service.
The probabilities of an easy re-entry dropped from 82% for those who did not experience a traumatic event to 56% for those who did—the largest change noted in the 2011 study.
The second Penn State study evaluated a model framework with a lifespan development perspective. The study surveyed veterans on their self-reported satisfaction or symptoms in 7 domains of well-being: employment, education, financial, legal problems, social, physical health, and mental health. Within 3 months of separation , 41% of respondents fell into the “problematic” category for the mental health domain. However, by 30 to 33 months postseparation, this proportion dropped to 34%. During the same period, the proportion of veterans in the at risk category increased from 28% at Wave 1 to 37% at Wave 6. About 30% of veterans fell into the successful category for symptoms across the 3 examined waves. Almost 60% were in the successful category across the 3 time points.
Both Penn State studies emphasize the importance of viewing veterans as individuals on their own timelines.
“These findings underscore that the transition to civilian life is not a single moment, but a process influenced by experiences across the life span,” said Mary M. Mitchell, research professor at the Clearinghouse and lead author on the predictors study. “By following veterans over 3 years, we were able to see how patterns emerge that would be invisible in a one-time survey.”
Current conceptualization “assumes that there are commonalities across veterans when evaluating the success of the transition to civilian life,” according to the authors of the framework study. “However, each veteran likely has his or her view of what a successful transition constitutes, and he or she may weigh domains differently when considering his or her own transition.”
The research highlights the need to find ways to encourage veterans to seek help—and not just in the first year, which is often the most stressful. The Pew Research Center survey identified a “significant break from the past,” in that nearly 70% of post-9/11 veterans said their superiors made them feel comfortable about seeking help with emotional issues resulting from their military service.
However, ≤ 8% veterans in the TVMI study used any health programs, even when they screened positive for mental health problems. Veterans who did use counseling services, however, improved their depression symptoms. Engaging veterans at various time points could help keep mental health problems from worsening during—and beyond—the transition.
'Energy Insecurity' Tied to Anxiety, Depression Risk
'Energy Insecurity' Tied to Anxiety, Depression Risk
TOPLINE:
Energy insecurity, the inability to meet household energy needs, was associated with more than twice the odds of having depression and anxiety symptoms than energy security in US adults, a new cross-sectional study showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Using data from the US Census Bureau's online Household Pulse Survey, administered between 2022 and 2024, researchers conducted a cross-sectional study with a weighted population of > 187 million US adults (51% women; 64% White, 16% Hispanic, 10% Black, and 5% Asian). About a quarter of the population was in each of 4 age groups: 18-34 years, 35-49 years, 50-64 years, and ≥ 65 years.
- Three indicators of energy insecurity—inability to pay energy bills, maintaining unsafe/unhealthy home temperatures, and forgoing expenses on basic necessities to pay energy bills—were assessed individually and as a composite measure.
- Mental health was assessed using modified versions of the 2-item Patient Health Questionnaire for depression and the 2-item Generalized Anxiety Disorder scale for anxiety.
- The analysis was adjusted for other social determinants of health, including unemployment, housing instability, and food insecurity. Covariates included a wide range of factors, such as age, educational level, sex, and annual household income.
TAKEAWAY:
- In all, > 43% of the population reported having ≥ 1 form of energy security; around 22% reported being unable to pay energy bills, 22% maintained unsafe home temperatures, and nearly 34% forewent spending on basic necessities to pay energy bills.
- Individuals who gave up spending on basic necessities to pay energy bills had higher odds of anxiety (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.79) and depression (aOR, 1.74) than those who did not.
- Adults with energy insecurity on the composite measure had higher odds for anxiety (aOR, 2.29) and depression (aOR, 2.31) than those with energy security.
- Food insecurity was also associated with poorer mental health, with higher odds for symptoms of depression (aOR, 2.05) and anxiety (aOR, 2.07).
IN PRACTICE:
"Despite its high prevalence, energy insecurity remains underrecognized in public health and policy intervention strategies," the investigators wrote.
"These findings suggest that energy insecurity is a widespread and important factor associated with mental health symptoms and may warrant consideration in efforts to reduce adverse mental health outcomes," they added.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Michelle Graf, PhD, Carter School of Public Policy, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta. It was published online on October 27 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional nature of the data limited causal interference and increased the possibility of reverse causality. The questionnaire captured subjective interpretations of unsafe and unhealthy indoor temperatures, which may have varied among respondents. Additionally, the recall periods for energy insecurity and mental health outcomes were different.
DISCLOSURES:
The investigators reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Energy insecurity, the inability to meet household energy needs, was associated with more than twice the odds of having depression and anxiety symptoms than energy security in US adults, a new cross-sectional study showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Using data from the US Census Bureau's online Household Pulse Survey, administered between 2022 and 2024, researchers conducted a cross-sectional study with a weighted population of > 187 million US adults (51% women; 64% White, 16% Hispanic, 10% Black, and 5% Asian). About a quarter of the population was in each of 4 age groups: 18-34 years, 35-49 years, 50-64 years, and ≥ 65 years.
- Three indicators of energy insecurity—inability to pay energy bills, maintaining unsafe/unhealthy home temperatures, and forgoing expenses on basic necessities to pay energy bills—were assessed individually and as a composite measure.
- Mental health was assessed using modified versions of the 2-item Patient Health Questionnaire for depression and the 2-item Generalized Anxiety Disorder scale for anxiety.
- The analysis was adjusted for other social determinants of health, including unemployment, housing instability, and food insecurity. Covariates included a wide range of factors, such as age, educational level, sex, and annual household income.
TAKEAWAY:
- In all, > 43% of the population reported having ≥ 1 form of energy security; around 22% reported being unable to pay energy bills, 22% maintained unsafe home temperatures, and nearly 34% forewent spending on basic necessities to pay energy bills.
- Individuals who gave up spending on basic necessities to pay energy bills had higher odds of anxiety (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.79) and depression (aOR, 1.74) than those who did not.
- Adults with energy insecurity on the composite measure had higher odds for anxiety (aOR, 2.29) and depression (aOR, 2.31) than those with energy security.
- Food insecurity was also associated with poorer mental health, with higher odds for symptoms of depression (aOR, 2.05) and anxiety (aOR, 2.07).
IN PRACTICE:
"Despite its high prevalence, energy insecurity remains underrecognized in public health and policy intervention strategies," the investigators wrote.
"These findings suggest that energy insecurity is a widespread and important factor associated with mental health symptoms and may warrant consideration in efforts to reduce adverse mental health outcomes," they added.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Michelle Graf, PhD, Carter School of Public Policy, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta. It was published online on October 27 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional nature of the data limited causal interference and increased the possibility of reverse causality. The questionnaire captured subjective interpretations of unsafe and unhealthy indoor temperatures, which may have varied among respondents. Additionally, the recall periods for energy insecurity and mental health outcomes were different.
DISCLOSURES:
The investigators reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Energy insecurity, the inability to meet household energy needs, was associated with more than twice the odds of having depression and anxiety symptoms than energy security in US adults, a new cross-sectional study showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Using data from the US Census Bureau's online Household Pulse Survey, administered between 2022 and 2024, researchers conducted a cross-sectional study with a weighted population of > 187 million US adults (51% women; 64% White, 16% Hispanic, 10% Black, and 5% Asian). About a quarter of the population was in each of 4 age groups: 18-34 years, 35-49 years, 50-64 years, and ≥ 65 years.
- Three indicators of energy insecurity—inability to pay energy bills, maintaining unsafe/unhealthy home temperatures, and forgoing expenses on basic necessities to pay energy bills—were assessed individually and as a composite measure.
- Mental health was assessed using modified versions of the 2-item Patient Health Questionnaire for depression and the 2-item Generalized Anxiety Disorder scale for anxiety.
- The analysis was adjusted for other social determinants of health, including unemployment, housing instability, and food insecurity. Covariates included a wide range of factors, such as age, educational level, sex, and annual household income.
TAKEAWAY:
- In all, > 43% of the population reported having ≥ 1 form of energy security; around 22% reported being unable to pay energy bills, 22% maintained unsafe home temperatures, and nearly 34% forewent spending on basic necessities to pay energy bills.
- Individuals who gave up spending on basic necessities to pay energy bills had higher odds of anxiety (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.79) and depression (aOR, 1.74) than those who did not.
- Adults with energy insecurity on the composite measure had higher odds for anxiety (aOR, 2.29) and depression (aOR, 2.31) than those with energy security.
- Food insecurity was also associated with poorer mental health, with higher odds for symptoms of depression (aOR, 2.05) and anxiety (aOR, 2.07).
IN PRACTICE:
"Despite its high prevalence, energy insecurity remains underrecognized in public health and policy intervention strategies," the investigators wrote.
"These findings suggest that energy insecurity is a widespread and important factor associated with mental health symptoms and may warrant consideration in efforts to reduce adverse mental health outcomes," they added.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Michelle Graf, PhD, Carter School of Public Policy, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta. It was published online on October 27 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional nature of the data limited causal interference and increased the possibility of reverse causality. The questionnaire captured subjective interpretations of unsafe and unhealthy indoor temperatures, which may have varied among respondents. Additionally, the recall periods for energy insecurity and mental health outcomes were different.
DISCLOSURES:
The investigators reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
'Energy Insecurity' Tied to Anxiety, Depression Risk
'Energy Insecurity' Tied to Anxiety, Depression Risk
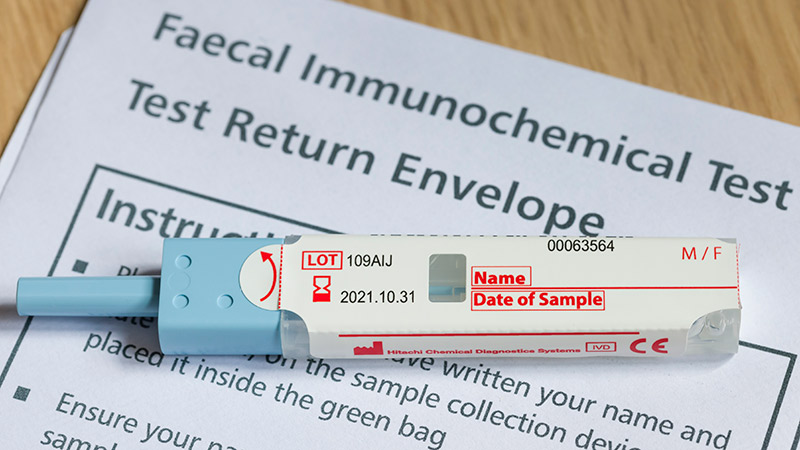
Patients With a Positive FIT Fail to Get Follow-Up Colonoscopies
Patients With a Positive FIT Fail to Get Follow-Up Colonoscopies
PHOENIX -- Patients with or without polyp removal in an index colonoscopy commonly receive follow-up surveillance with a fecal immunochemical test (FIT), yet many of these patients do not receive a recommended colonoscopy after a positive FIT.
"In this large US study, we found interval FITs are frequently performed in patients with and without prior polypectomy," said first author Natalie J. Wilson, MD, of the University of Minnesota in Minneapolis, while presenting the findings this week at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting.
"These findings reinforce the importance of colonoscopy following positive interval FIT, given the high risk of advanced neoplasia and colorectal cancer, regardless of polypectomy history," Wilson said.
Guideline recommendations stress the need for follow-up surveillance with a colonoscopy, particularly in patients who have had a prior polypectomy, due to the higher risk.
Reasons patients may instead turn to FIT include cost or other factors.
To determine just how often that happens, how having a previous polypectomy affects FIT results, and how adherent patients are to follow up if a FIT result is positive, Wilson and her colleagues evaluated data from nearly 4.8 million individuals in the Veterans Health Administration Corporate Data Warehouse who underwent colonoscopy between 2000 and 2004.
Of the patients, 10.9% were found to have subsequently received interval FIT within 10 years of the index colonoscopy, and of those patients, nearly half (49.9%) had received a polypectomy at the index colonoscopy.
The average time from the colonoscopy/polypectomy to the interval FIT was 5.9 years (5.6 years in the polypectomy group vs 6.2 years in the nonpolypectomy group).
Among the FIT screenings, results were positive in 17.2% of postpolypectomy patients and 14.1% of patients who no prior polypectomy, indicating a history of polypectomy to be predictive of positive interval FIT (odds ratio [OR], 1.12; P < .0001).
Notably, while a follow-up colonoscopy is considered essential following a positive FIT result -- and having a previous polypectomy should add further emergency to the matter -- the study showed only 50.4% of those who had an earlier polypectomy went on to receive the recommended follow-up colonoscopy after a positive follow-up FIT, and the rate was 49.3% among those who had not received a polypectomy (P = .001).
For those who did receive a follow-up colonoscopy after a positive FIT, the duration of time to receiving the colonoscopy was longer among those who had a prior polypectomy, at 2.9 months compared with 2.5 months in the nonpolypectomy group (P < .001).
Colonoscopy results following a positive FIT showed higher rates of detections among patients who had prior polypectomies than among those with no prior polypectomy, including tubular adenomas (54.7% vs 45.8%), tubulovillous adenomas (5.6% vs 4.7%), adenomas with high-grade dysplasia (0.8% vs 0.7%), sessile serrated lesions (3.52% vs 2.4%), advanced colorectal neoplasia (9.2% vs 7.9%), and colorectal cancer (3.3% vs 3.0%).
However, a prior polypectomy was not independently predictive of colorectal cancer (OR, 0.96; P = .65) or advanced colorectal neoplasia (OR, 0.97; P = .57) in the postcolonoscopy interval FIT.
The findings underscore that "positive results carried a high risk of advanced neoplasia or cancer, irrespective or prior polypectomy history," Wilson said.
Commenting on the study, William D. Chey, MD, chief of the Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, Michigan, noted that the study "addresses one of the biggest challenges we face as a profession, which is making sure that patients who have a positive stool test get a colonoscopy."
He noted that the low rate of just 50% of recipients of positive FITs going on to receive a colonoscopy is consistent with what is observed in other trials.
"Other data suggest that the rate might even be significantly higher -- at 70% to 80%, depending upon the population and the test," Chey told Medscape Medical News.
Reasons for the failure to receive the follow-up testing range from income restrictions (due to the high cost of a colonoscopy, especially if not covered by insurance), education, speaking a foreign language, and other factors, he said.
The relatively high rates of colon cancers detected by FIT in the study, in those with and without a prior polypectomy, along with findings from other studies "should raise questions about whether there might be a role for FIT testing in addition to colonoscopy." However, much stronger evidence would be needed, Chey noted.
In the meantime, a key issue is "how do we do a better job of making sure that individuals who have a positive FIT test get a colonoscopy," he said.
"I think a lot of this is going to come down to how it's down at the primary care level."
Chey added that in that, and any other setting, "the main message that needs to get out to people who are undergoing stool-based screening is that the stool test is only the first part of the screening process, and if it's positive, a follow-up colonoscopy must be performed.
"Otherwise, the stool-based test is of no value."
Wilson had no disclosures to report. Chey's disclosures include consulting and/or other relationships with Ardelyx, Atmo, Biomerica, Commonwealth Diagnostics International, Corprata, Dieta, Evinature, Food Marble, Gemelli, Kiwi BioScience, Modify Health, Nestle, Phathom, Redhill, Salix/Valean, Takeda, and Vibrant.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHOENIX -- Patients with or without polyp removal in an index colonoscopy commonly receive follow-up surveillance with a fecal immunochemical test (FIT), yet many of these patients do not receive a recommended colonoscopy after a positive FIT.
"In this large US study, we found interval FITs are frequently performed in patients with and without prior polypectomy," said first author Natalie J. Wilson, MD, of the University of Minnesota in Minneapolis, while presenting the findings this week at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting.
"These findings reinforce the importance of colonoscopy following positive interval FIT, given the high risk of advanced neoplasia and colorectal cancer, regardless of polypectomy history," Wilson said.
Guideline recommendations stress the need for follow-up surveillance with a colonoscopy, particularly in patients who have had a prior polypectomy, due to the higher risk.
Reasons patients may instead turn to FIT include cost or other factors.
To determine just how often that happens, how having a previous polypectomy affects FIT results, and how adherent patients are to follow up if a FIT result is positive, Wilson and her colleagues evaluated data from nearly 4.8 million individuals in the Veterans Health Administration Corporate Data Warehouse who underwent colonoscopy between 2000 and 2004.
Of the patients, 10.9% were found to have subsequently received interval FIT within 10 years of the index colonoscopy, and of those patients, nearly half (49.9%) had received a polypectomy at the index colonoscopy.
The average time from the colonoscopy/polypectomy to the interval FIT was 5.9 years (5.6 years in the polypectomy group vs 6.2 years in the nonpolypectomy group).
Among the FIT screenings, results were positive in 17.2% of postpolypectomy patients and 14.1% of patients who no prior polypectomy, indicating a history of polypectomy to be predictive of positive interval FIT (odds ratio [OR], 1.12; P < .0001).
Notably, while a follow-up colonoscopy is considered essential following a positive FIT result -- and having a previous polypectomy should add further emergency to the matter -- the study showed only 50.4% of those who had an earlier polypectomy went on to receive the recommended follow-up colonoscopy after a positive follow-up FIT, and the rate was 49.3% among those who had not received a polypectomy (P = .001).
For those who did receive a follow-up colonoscopy after a positive FIT, the duration of time to receiving the colonoscopy was longer among those who had a prior polypectomy, at 2.9 months compared with 2.5 months in the nonpolypectomy group (P < .001).
Colonoscopy results following a positive FIT showed higher rates of detections among patients who had prior polypectomies than among those with no prior polypectomy, including tubular adenomas (54.7% vs 45.8%), tubulovillous adenomas (5.6% vs 4.7%), adenomas with high-grade dysplasia (0.8% vs 0.7%), sessile serrated lesions (3.52% vs 2.4%), advanced colorectal neoplasia (9.2% vs 7.9%), and colorectal cancer (3.3% vs 3.0%).
However, a prior polypectomy was not independently predictive of colorectal cancer (OR, 0.96; P = .65) or advanced colorectal neoplasia (OR, 0.97; P = .57) in the postcolonoscopy interval FIT.
The findings underscore that "positive results carried a high risk of advanced neoplasia or cancer, irrespective or prior polypectomy history," Wilson said.
Commenting on the study, William D. Chey, MD, chief of the Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, Michigan, noted that the study "addresses one of the biggest challenges we face as a profession, which is making sure that patients who have a positive stool test get a colonoscopy."
He noted that the low rate of just 50% of recipients of positive FITs going on to receive a colonoscopy is consistent with what is observed in other trials.
"Other data suggest that the rate might even be significantly higher -- at 70% to 80%, depending upon the population and the test," Chey told Medscape Medical News.
Reasons for the failure to receive the follow-up testing range from income restrictions (due to the high cost of a colonoscopy, especially if not covered by insurance), education, speaking a foreign language, and other factors, he said.
The relatively high rates of colon cancers detected by FIT in the study, in those with and without a prior polypectomy, along with findings from other studies "should raise questions about whether there might be a role for FIT testing in addition to colonoscopy." However, much stronger evidence would be needed, Chey noted.
In the meantime, a key issue is "how do we do a better job of making sure that individuals who have a positive FIT test get a colonoscopy," he said.
"I think a lot of this is going to come down to how it's down at the primary care level."
Chey added that in that, and any other setting, "the main message that needs to get out to people who are undergoing stool-based screening is that the stool test is only the first part of the screening process, and if it's positive, a follow-up colonoscopy must be performed.
"Otherwise, the stool-based test is of no value."
Wilson had no disclosures to report. Chey's disclosures include consulting and/or other relationships with Ardelyx, Atmo, Biomerica, Commonwealth Diagnostics International, Corprata, Dieta, Evinature, Food Marble, Gemelli, Kiwi BioScience, Modify Health, Nestle, Phathom, Redhill, Salix/Valean, Takeda, and Vibrant.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHOENIX -- Patients with or without polyp removal in an index colonoscopy commonly receive follow-up surveillance with a fecal immunochemical test (FIT), yet many of these patients do not receive a recommended colonoscopy after a positive FIT.
"In this large US study, we found interval FITs are frequently performed in patients with and without prior polypectomy," said first author Natalie J. Wilson, MD, of the University of Minnesota in Minneapolis, while presenting the findings this week at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting.
"These findings reinforce the importance of colonoscopy following positive interval FIT, given the high risk of advanced neoplasia and colorectal cancer, regardless of polypectomy history," Wilson said.
Guideline recommendations stress the need for follow-up surveillance with a colonoscopy, particularly in patients who have had a prior polypectomy, due to the higher risk.
Reasons patients may instead turn to FIT include cost or other factors.
To determine just how often that happens, how having a previous polypectomy affects FIT results, and how adherent patients are to follow up if a FIT result is positive, Wilson and her colleagues evaluated data from nearly 4.8 million individuals in the Veterans Health Administration Corporate Data Warehouse who underwent colonoscopy between 2000 and 2004.
Of the patients, 10.9% were found to have subsequently received interval FIT within 10 years of the index colonoscopy, and of those patients, nearly half (49.9%) had received a polypectomy at the index colonoscopy.
The average time from the colonoscopy/polypectomy to the interval FIT was 5.9 years (5.6 years in the polypectomy group vs 6.2 years in the nonpolypectomy group).
Among the FIT screenings, results were positive in 17.2% of postpolypectomy patients and 14.1% of patients who no prior polypectomy, indicating a history of polypectomy to be predictive of positive interval FIT (odds ratio [OR], 1.12; P < .0001).
Notably, while a follow-up colonoscopy is considered essential following a positive FIT result -- and having a previous polypectomy should add further emergency to the matter -- the study showed only 50.4% of those who had an earlier polypectomy went on to receive the recommended follow-up colonoscopy after a positive follow-up FIT, and the rate was 49.3% among those who had not received a polypectomy (P = .001).
For those who did receive a follow-up colonoscopy after a positive FIT, the duration of time to receiving the colonoscopy was longer among those who had a prior polypectomy, at 2.9 months compared with 2.5 months in the nonpolypectomy group (P < .001).
Colonoscopy results following a positive FIT showed higher rates of detections among patients who had prior polypectomies than among those with no prior polypectomy, including tubular adenomas (54.7% vs 45.8%), tubulovillous adenomas (5.6% vs 4.7%), adenomas with high-grade dysplasia (0.8% vs 0.7%), sessile serrated lesions (3.52% vs 2.4%), advanced colorectal neoplasia (9.2% vs 7.9%), and colorectal cancer (3.3% vs 3.0%).
However, a prior polypectomy was not independently predictive of colorectal cancer (OR, 0.96; P = .65) or advanced colorectal neoplasia (OR, 0.97; P = .57) in the postcolonoscopy interval FIT.
The findings underscore that "positive results carried a high risk of advanced neoplasia or cancer, irrespective or prior polypectomy history," Wilson said.
Commenting on the study, William D. Chey, MD, chief of the Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, Michigan, noted that the study "addresses one of the biggest challenges we face as a profession, which is making sure that patients who have a positive stool test get a colonoscopy."
He noted that the low rate of just 50% of recipients of positive FITs going on to receive a colonoscopy is consistent with what is observed in other trials.
"Other data suggest that the rate might even be significantly higher -- at 70% to 80%, depending upon the population and the test," Chey told Medscape Medical News.
Reasons for the failure to receive the follow-up testing range from income restrictions (due to the high cost of a colonoscopy, especially if not covered by insurance), education, speaking a foreign language, and other factors, he said.
The relatively high rates of colon cancers detected by FIT in the study, in those with and without a prior polypectomy, along with findings from other studies "should raise questions about whether there might be a role for FIT testing in addition to colonoscopy." However, much stronger evidence would be needed, Chey noted.
In the meantime, a key issue is "how do we do a better job of making sure that individuals who have a positive FIT test get a colonoscopy," he said.
"I think a lot of this is going to come down to how it's down at the primary care level."
Chey added that in that, and any other setting, "the main message that needs to get out to people who are undergoing stool-based screening is that the stool test is only the first part of the screening process, and if it's positive, a follow-up colonoscopy must be performed.
"Otherwise, the stool-based test is of no value."
Wilson had no disclosures to report. Chey's disclosures include consulting and/or other relationships with Ardelyx, Atmo, Biomerica, Commonwealth Diagnostics International, Corprata, Dieta, Evinature, Food Marble, Gemelli, Kiwi BioScience, Modify Health, Nestle, Phathom, Redhill, Salix/Valean, Takeda, and Vibrant.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients With a Positive FIT Fail to Get Follow-Up Colonoscopies
Patients With a Positive FIT Fail to Get Follow-Up Colonoscopies
What Drives Lung Cancer in Nonsmokers?
TOPLINE:
A comprehensive review of 92 studies found that 15% to 20% of lung cancers occurred among nonsmokers and were associated with environmental and germline risk factors. These cancers frequently harbored actionable genomic drivers, and targeted EGFR and ALK therapies produced significant diseasefree survival (DFS) and overall survival benefits.
METHODOLOGY:
- Lung cancer continues to be the leading cause of cancer death worldwide, causing about 1.8 million deaths in 2022, with smoking remaining the predominant risk factor. However, the incidence of lung cancer among nonsmokers (those who have smoked less than 100 cigarettes in their lifetime) is rising, varies by sex and geography, and is linked to environmental exposures and family history. The misperception that lung cancer is almost invariably caused by smoking may delay assessment and diagnosis.
- Researchers conducted a review of 92 studies on lung cancer in nonsmokers: 6 meta-analyses or systematic reviews, 16 randomized clinical trials, eight prospective cohort studies, seven retrospective cohort studies, three cross-sectional studies, four observational or case-control studies, 13 genomic studies, and 35 other studies.
- Overall, lung cancer among nonsmokers accounted for 15% to 20% of all lung cancer cases. Most lung cancers in nonsmokers were adenocarcinomas (60% to 80%), with a median age at diagnosis of 67 years in this group compared with 70 years in people with a history of smoking.
- Data analysis from three US hospital networks showed that the proportion of lung cancer among nonsmokers increased from 8.0% to 14.9% between 1990 and 2013. A pooled analysis of seven Finnish cohorts reported an absolute increase in lung cancer among nonsmokers from 6.9 per 100,000 person-years in 1972 to 12.9 per 100,000 person-years in 2015.
- The age-adjusted incidence rate of lung cancer in the US between 2000 and 2013 was 17.5 per 100,000 individuals among Asian female nonsmokers compared with 10.1 per 100,000 among non-Hispanic White female nonsmokers.
TAKEAWAY:
- Environmental and occupational risk factors were secondhand smoke, residential radon, outdoor and household air pollution (PM2.5), asbestos and silica exposure, and prior thoracic radiotherapy. Having a first-degree relative with lung cancer increased the risk of developing lung cancer, and genome-wide association studies identified susceptibility loci associated with lung cancer risk in nonsmokers.
- Family history and inherited susceptibility increased lung cancer risk in never smokers (odds ratio [OR] for lung cancer in those with a first–degree relative, 1.51), and clonal hematopoiesis was also associated with higher risk (OR, 1.43). Importantly, tumors in nonsmokers were frequently driven by actionable somatic alterations (EGFR mutations, 40% to 60% in nonsmokers compared with 10% in smokers) and enrichment of ALK/ROS1/RET/ERBB2/NTRK/NRG1 fusions; 78% to 92% of adenocarcinomas in nonsmokers harbored actionable drivers (compared with 49.5% in ever smokers), and nonsmokers had a substantially lower tumor mutational burden (10–fold lower).
- Similar to individuals with a history of smoking, nonsmokers with lung cancer presented with cough, pain, dyspnea, or weight loss or had disease detected incidentally. Surgical resection remained the preferred treatment for anatomically resectable lung cancer (stages I-III) in medically eligible patients, with follow-up CT screening recommended every 6 months for 2 to 3 years and then annually.
- Targeted adjuvant therapy substantially improved outcomes for resected EGFR–mutant or ALK–rearranged non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Four-year DFS was increased to 70% with osimertinib compared with 29% with placebo (hazard ratio [HR], 0.23) and 5–year overall survival was increased to 85% compared with 73% (HR, 0.49). Two–year DFS was 93.8% with alectinib compared with 63% with placebo (HR, 0.24). In unresectable EGFR-mutated stage III NSCLC, median progression-free survival was 39.1 months with adjuvant osimertinib compared with 5.6 months with placebo. For resected ALKpositive disease, 2–year DFS was 93.8% with adjuvant alectinib compared with 63.0% with chemotherapy (HR, 0.24).
- However, singleagent single agent programmed cell death protein 1 inhibitors or programmed death-ligand 1 inhibitors demonstrated limited efficacy in EGFR or ALK–driven tumors, and benefit was attenuated in never smokers. Regarding screening and early detection, the US Preventive Services Task Force did not recommend lowdose CT screening for nonsmokers, whereas Taiwan implemented a biennial screening program for selected nonsmoking high–risk groups.
IN PRACTICE:
“Among patients with lung cancer, nonsmoking individuals are more likely to have genomic alterations, such as EGFR mutations or ALK gene rearrangements, and these patients have improved survival when treated with TKIs compared with chemotherapy,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Cian Murphy, PhD, Cancer Evolution and Genome Instability Laboratory, Francis Crick Institute, London, England, was published online in JAMA.
LIMITATIONS:
Becausesmoking history was often not included in many databases, cancer registries, and trials, the incidence and prevalence of lung cancer in nonsmokers could not be accurately determined. Additionally, accurate quantification of environmental exposures, such as air pollution, presented significant challenges. The quality of the evidence was not formally evaluated, and some relevant articles may have been missed in the literature review.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received support from multiple organizations, including the Rosetrees Trust, Ruth Strauss Foundation, Cancer Research UK, and the National Health and Medical Research Council. Several authors reported receiving grants or personal fees from and having other ties with various sources. Full disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A comprehensive review of 92 studies found that 15% to 20% of lung cancers occurred among nonsmokers and were associated with environmental and germline risk factors. These cancers frequently harbored actionable genomic drivers, and targeted EGFR and ALK therapies produced significant diseasefree survival (DFS) and overall survival benefits.
METHODOLOGY:
- Lung cancer continues to be the leading cause of cancer death worldwide, causing about 1.8 million deaths in 2022, with smoking remaining the predominant risk factor. However, the incidence of lung cancer among nonsmokers (those who have smoked less than 100 cigarettes in their lifetime) is rising, varies by sex and geography, and is linked to environmental exposures and family history. The misperception that lung cancer is almost invariably caused by smoking may delay assessment and diagnosis.
- Researchers conducted a review of 92 studies on lung cancer in nonsmokers: 6 meta-analyses or systematic reviews, 16 randomized clinical trials, eight prospective cohort studies, seven retrospective cohort studies, three cross-sectional studies, four observational or case-control studies, 13 genomic studies, and 35 other studies.
- Overall, lung cancer among nonsmokers accounted for 15% to 20% of all lung cancer cases. Most lung cancers in nonsmokers were adenocarcinomas (60% to 80%), with a median age at diagnosis of 67 years in this group compared with 70 years in people with a history of smoking.
- Data analysis from three US hospital networks showed that the proportion of lung cancer among nonsmokers increased from 8.0% to 14.9% between 1990 and 2013. A pooled analysis of seven Finnish cohorts reported an absolute increase in lung cancer among nonsmokers from 6.9 per 100,000 person-years in 1972 to 12.9 per 100,000 person-years in 2015.
- The age-adjusted incidence rate of lung cancer in the US between 2000 and 2013 was 17.5 per 100,000 individuals among Asian female nonsmokers compared with 10.1 per 100,000 among non-Hispanic White female nonsmokers.
TAKEAWAY:
- Environmental and occupational risk factors were secondhand smoke, residential radon, outdoor and household air pollution (PM2.5), asbestos and silica exposure, and prior thoracic radiotherapy. Having a first-degree relative with lung cancer increased the risk of developing lung cancer, and genome-wide association studies identified susceptibility loci associated with lung cancer risk in nonsmokers.
- Family history and inherited susceptibility increased lung cancer risk in never smokers (odds ratio [OR] for lung cancer in those with a first–degree relative, 1.51), and clonal hematopoiesis was also associated with higher risk (OR, 1.43). Importantly, tumors in nonsmokers were frequently driven by actionable somatic alterations (EGFR mutations, 40% to 60% in nonsmokers compared with 10% in smokers) and enrichment of ALK/ROS1/RET/ERBB2/NTRK/NRG1 fusions; 78% to 92% of adenocarcinomas in nonsmokers harbored actionable drivers (compared with 49.5% in ever smokers), and nonsmokers had a substantially lower tumor mutational burden (10–fold lower).
- Similar to individuals with a history of smoking, nonsmokers with lung cancer presented with cough, pain, dyspnea, or weight loss or had disease detected incidentally. Surgical resection remained the preferred treatment for anatomically resectable lung cancer (stages I-III) in medically eligible patients, with follow-up CT screening recommended every 6 months for 2 to 3 years and then annually.
- Targeted adjuvant therapy substantially improved outcomes for resected EGFR–mutant or ALK–rearranged non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Four-year DFS was increased to 70% with osimertinib compared with 29% with placebo (hazard ratio [HR], 0.23) and 5–year overall survival was increased to 85% compared with 73% (HR, 0.49). Two–year DFS was 93.8% with alectinib compared with 63% with placebo (HR, 0.24). In unresectable EGFR-mutated stage III NSCLC, median progression-free survival was 39.1 months with adjuvant osimertinib compared with 5.6 months with placebo. For resected ALKpositive disease, 2–year DFS was 93.8% with adjuvant alectinib compared with 63.0% with chemotherapy (HR, 0.24).
- However, singleagent single agent programmed cell death protein 1 inhibitors or programmed death-ligand 1 inhibitors demonstrated limited efficacy in EGFR or ALK–driven tumors, and benefit was attenuated in never smokers. Regarding screening and early detection, the US Preventive Services Task Force did not recommend lowdose CT screening for nonsmokers, whereas Taiwan implemented a biennial screening program for selected nonsmoking high–risk groups.
IN PRACTICE:
“Among patients with lung cancer, nonsmoking individuals are more likely to have genomic alterations, such as EGFR mutations or ALK gene rearrangements, and these patients have improved survival when treated with TKIs compared with chemotherapy,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Cian Murphy, PhD, Cancer Evolution and Genome Instability Laboratory, Francis Crick Institute, London, England, was published online in JAMA.
LIMITATIONS:
Becausesmoking history was often not included in many databases, cancer registries, and trials, the incidence and prevalence of lung cancer in nonsmokers could not be accurately determined. Additionally, accurate quantification of environmental exposures, such as air pollution, presented significant challenges. The quality of the evidence was not formally evaluated, and some relevant articles may have been missed in the literature review.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received support from multiple organizations, including the Rosetrees Trust, Ruth Strauss Foundation, Cancer Research UK, and the National Health and Medical Research Council. Several authors reported receiving grants or personal fees from and having other ties with various sources. Full disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A comprehensive review of 92 studies found that 15% to 20% of lung cancers occurred among nonsmokers and were associated with environmental and germline risk factors. These cancers frequently harbored actionable genomic drivers, and targeted EGFR and ALK therapies produced significant diseasefree survival (DFS) and overall survival benefits.
METHODOLOGY:
- Lung cancer continues to be the leading cause of cancer death worldwide, causing about 1.8 million deaths in 2022, with smoking remaining the predominant risk factor. However, the incidence of lung cancer among nonsmokers (those who have smoked less than 100 cigarettes in their lifetime) is rising, varies by sex and geography, and is linked to environmental exposures and family history. The misperception that lung cancer is almost invariably caused by smoking may delay assessment and diagnosis.
- Researchers conducted a review of 92 studies on lung cancer in nonsmokers: 6 meta-analyses or systematic reviews, 16 randomized clinical trials, eight prospective cohort studies, seven retrospective cohort studies, three cross-sectional studies, four observational or case-control studies, 13 genomic studies, and 35 other studies.
- Overall, lung cancer among nonsmokers accounted for 15% to 20% of all lung cancer cases. Most lung cancers in nonsmokers were adenocarcinomas (60% to 80%), with a median age at diagnosis of 67 years in this group compared with 70 years in people with a history of smoking.
- Data analysis from three US hospital networks showed that the proportion of lung cancer among nonsmokers increased from 8.0% to 14.9% between 1990 and 2013. A pooled analysis of seven Finnish cohorts reported an absolute increase in lung cancer among nonsmokers from 6.9 per 100,000 person-years in 1972 to 12.9 per 100,000 person-years in 2015.
- The age-adjusted incidence rate of lung cancer in the US between 2000 and 2013 was 17.5 per 100,000 individuals among Asian female nonsmokers compared with 10.1 per 100,000 among non-Hispanic White female nonsmokers.
TAKEAWAY:
- Environmental and occupational risk factors were secondhand smoke, residential radon, outdoor and household air pollution (PM2.5), asbestos and silica exposure, and prior thoracic radiotherapy. Having a first-degree relative with lung cancer increased the risk of developing lung cancer, and genome-wide association studies identified susceptibility loci associated with lung cancer risk in nonsmokers.
- Family history and inherited susceptibility increased lung cancer risk in never smokers (odds ratio [OR] for lung cancer in those with a first–degree relative, 1.51), and clonal hematopoiesis was also associated with higher risk (OR, 1.43). Importantly, tumors in nonsmokers were frequently driven by actionable somatic alterations (EGFR mutations, 40% to 60% in nonsmokers compared with 10% in smokers) and enrichment of ALK/ROS1/RET/ERBB2/NTRK/NRG1 fusions; 78% to 92% of adenocarcinomas in nonsmokers harbored actionable drivers (compared with 49.5% in ever smokers), and nonsmokers had a substantially lower tumor mutational burden (10–fold lower).
- Similar to individuals with a history of smoking, nonsmokers with lung cancer presented with cough, pain, dyspnea, or weight loss or had disease detected incidentally. Surgical resection remained the preferred treatment for anatomically resectable lung cancer (stages I-III) in medically eligible patients, with follow-up CT screening recommended every 6 months for 2 to 3 years and then annually.
- Targeted adjuvant therapy substantially improved outcomes for resected EGFR–mutant or ALK–rearranged non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Four-year DFS was increased to 70% with osimertinib compared with 29% with placebo (hazard ratio [HR], 0.23) and 5–year overall survival was increased to 85% compared with 73% (HR, 0.49). Two–year DFS was 93.8% with alectinib compared with 63% with placebo (HR, 0.24). In unresectable EGFR-mutated stage III NSCLC, median progression-free survival was 39.1 months with adjuvant osimertinib compared with 5.6 months with placebo. For resected ALKpositive disease, 2–year DFS was 93.8% with adjuvant alectinib compared with 63.0% with chemotherapy (HR, 0.24).
- However, singleagent single agent programmed cell death protein 1 inhibitors or programmed death-ligand 1 inhibitors demonstrated limited efficacy in EGFR or ALK–driven tumors, and benefit was attenuated in never smokers. Regarding screening and early detection, the US Preventive Services Task Force did not recommend lowdose CT screening for nonsmokers, whereas Taiwan implemented a biennial screening program for selected nonsmoking high–risk groups.
IN PRACTICE:
“Among patients with lung cancer, nonsmoking individuals are more likely to have genomic alterations, such as EGFR mutations or ALK gene rearrangements, and these patients have improved survival when treated with TKIs compared with chemotherapy,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Cian Murphy, PhD, Cancer Evolution and Genome Instability Laboratory, Francis Crick Institute, London, England, was published online in JAMA.
LIMITATIONS:
Becausesmoking history was often not included in many databases, cancer registries, and trials, the incidence and prevalence of lung cancer in nonsmokers could not be accurately determined. Additionally, accurate quantification of environmental exposures, such as air pollution, presented significant challenges. The quality of the evidence was not formally evaluated, and some relevant articles may have been missed in the literature review.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received support from multiple organizations, including the Rosetrees Trust, Ruth Strauss Foundation, Cancer Research UK, and the National Health and Medical Research Council. Several authors reported receiving grants or personal fees from and having other ties with various sources. Full disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When in the Treatment Sequence Should Metastatic CRC Be Retreated With an Anti-EGFR?
BERLIN — Re-treatment with an antiepidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) agent is effective in patients with chemorefractory metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) with RAS and BRAF wild-type tumors confirmed on circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), although the sequencing of therapy does not seem to matter, suggest overall survival results from the crossover trial PARERE.
The findings nevertheless indicate that anti-EGFR rechallenge with panitumumab may prolong progression-free survival (PFS) over the multiple kinase inhibitor regorafenib. This suggests that “the most pragmatic choice” would be to give the anti-EGFR before regorafenib, said study presenter Marco Maria Germani, MD, Department of Translational Research and New Technologies in Medicine and Surgery, University of Pisa, Pisa, Italy.
The caveat, however, is in patients who have an anti-EGFR interval since previously receiving the drugs of < 6 months. Those patients appeared to do better if they had regorafenib first and then anti-EGFR rechallenge.
Overall, Germani said that “since [trifluridine/tipiracil] plus bevacizumab is today the third-line standard of care” in this patient population, “anti-EGFR re-treatment might be considered after progression” on that combination.
Germani presented the research on October 18 at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Meeting 2025, which was simultaneously published in the Annals of Oncology.
Michel P. Ducreux, MD, PhD, head of the Digestive Cancer Committee at Gustave Roussy, Villejuif, France, and invited discussant for the results, said, despite the study being negative, it is “very important to continue to perform this kind of trial to evaluate the [ideal] sequence in the treatment of our patients.”
He continued that the secondary endpoints in the trial of PFS and objective response and disease control rates were “fairly in favor of the use of rechallenge before regorafenib, and in my opinion, this is really quite convincing.”
Ducreux, who was not involved in PARERE trail, also pointed to the sex difference seen in the study, which suggested that women responded much better to having anti-EGFR retreatment before regorafenib than did men.
Similar findings have been reported in a number of other trials, and previous work has suggested that there are sex differences in the pharmacokinetics of several anticancer drugs. However, while this is “very important,” he said that “we never consider it, because we are not able to really explain [it].”
Overall, he concluded that, on the basis of these results, he would agree with the notion that it is better to propose a rechallenge with anti-EGFR treatment as the fourth-line therapy in this patient population, before administering regorafenib.
Ducreux explained that, after a partial response, tumors acquire resistance to EGFR inhibitors through alterations and mutations that occur during treatment, via nongenetic mechanisms, and through treatment-induced selection for preexisting mutations.
Previous work has shown that mutations, such as in the RAS gene, are detectable early during EGFR inhibitor therapy, but that they then decay exponentially once the drugs are stopped, with the potential that tumors regain their sensitivity to them.
Germani said that this means that ctDNA-guided retreatment with anti-EGFR therapies is a “promising approach” in pretreated patients with RAS and BRAF wild-type mCRC, and that the sequencing of the drugs may be important. Indeed, the REVERCE trial showed that giving regorafenib followed by the anti-EGFR drug cetuzximab was associated with longer overall survival than the other way around in anti-EGFR medication-naive patients.
Methods and Results
For PARERE, the researchers enrolled patients aged at least 18 years with RAS and BRAF wild-type mCRC who were previously treated with a first-line anti-EGFR-containing regimen and had at least a partial response or stable disease for at least 6 months.
The patients were also required to have had at least one intervening anti-EGFR-free line of therapy, and to have previously received treatment with fluoropyrimidine, oxaliplatin, irinotecan, and anti-angiogenics. At least 4 months were required to have passed between the end of anti-EGFR administration and screening for the study.
In all, 428 patients were screened between December 2020 and December 2024, with 213 patients with RAS and BRAF wild-type mCRC, as detected on ctDNA, enrolled. They were randomized to panitumumab or regorafenib until first progression, followed by regorafenib, if they started on panitumumab, or panitumumab, if they started on regorafenib, until second progression.
The median age of the patients was 61 years among those who started on panitumumab and 64 years among those initially given regorafenib in the trial, and 63% and 57%, respectively, were male. The median number of prior lines of therapy was two in both groups, and 65% and 69%, respectively, had received pantitumumab as their first-line anti-EGFR.
Initial findings from the study presented at the 2025 ASCO Annual Meeting indicated that, after a median follow-up of 23.5 months, there was no significant difference in the median first PFS between the two treatment arms.
However, patients who started with panitumumab had a significant improvement in both the objective response and disease control rates (P < .001), as well as a signal for a potentially longer median second PFS, than those who started with regorafenib, particularly on the per-protocol analysis.
Presenting the overall survival results, Germani said that there was no significant difference between the groups on the intention-to-treat analysis, at a stratified hazard ratio of 1.13 (P = .440), or on the per-protocol analysis, at a hazard ratio of 1.07 (P = .730).
“We then ran a subgroup analysis,” he continued, “and we found out that an anti-EGFR-free interval before liquid biopsy shorter than 6 months was associated with less benefit from a panitumumab [first] sequence, which is biologically sound.”
It was also observed that women did significantly better when having panitumumab first, whereas men did not, for which “we do not have a clear biological explanation,” Germani added.
Confining the analysis to so-called “hyperselected” patients, who not only were RAS and BRAF wild type but also had no pathogenic mutations associated with anti-EGFR resistance, did not reveal any significant overall survival differences between the treatment groups.
However, Ducreux took issue with the way in which hyperselection, which is turning up more and more regularly in trials, is defined, as the choice of which mutations to include varies widely. He suggested that a consensus group be assembled to resolve this issue.
Looking more broadly, the researchers were able to show that, in this updated analysis, anti-EGFR re-treatment was superior to regorafenib regardless of the treatment sequence in terms of PFS, at 4.2 months vs 2.4 months (P = .103) when given first in the trial, and 3.9 months vs 2.7 months (P = .019) when given second in the trial, as well as in terms of objective response and disease control rates.
Adverse Events
In terms of safety, the results showed that, as expected, acneiform rash, fatigue, and hypomagnesemia were the most common adverse events associated with panitumumb, while those with regorafenib were fatigue, hand-foot skin reactions, and hypertension.
There were no notable differences in the number of patients receiving a post-study treatment nor in the post-study therapeutic choices, between the study arms.
The study was sponsored by GONO Foundation and partially supported by Amgen and Bayer. Germani declared having relationships with MSD and Amgen. Ducreux declared having relationships with Amgen, Bayer, BeiGene, Incyte, Jazz, Merck KGaA, Merck Serono, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pierre Fabre, Roche, Servier, Keocyt, AbbVie, Abcely, Arcus, Bayer, BMS, Boehringer, GlaxoSmithKline, Sanofi, Scandion, and Zymeworks.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BERLIN — Re-treatment with an antiepidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) agent is effective in patients with chemorefractory metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) with RAS and BRAF wild-type tumors confirmed on circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), although the sequencing of therapy does not seem to matter, suggest overall survival results from the crossover trial PARERE.
The findings nevertheless indicate that anti-EGFR rechallenge with panitumumab may prolong progression-free survival (PFS) over the multiple kinase inhibitor regorafenib. This suggests that “the most pragmatic choice” would be to give the anti-EGFR before regorafenib, said study presenter Marco Maria Germani, MD, Department of Translational Research and New Technologies in Medicine and Surgery, University of Pisa, Pisa, Italy.
The caveat, however, is in patients who have an anti-EGFR interval since previously receiving the drugs of < 6 months. Those patients appeared to do better if they had regorafenib first and then anti-EGFR rechallenge.
Overall, Germani said that “since [trifluridine/tipiracil] plus bevacizumab is today the third-line standard of care” in this patient population, “anti-EGFR re-treatment might be considered after progression” on that combination.
Germani presented the research on October 18 at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Meeting 2025, which was simultaneously published in the Annals of Oncology.
Michel P. Ducreux, MD, PhD, head of the Digestive Cancer Committee at Gustave Roussy, Villejuif, France, and invited discussant for the results, said, despite the study being negative, it is “very important to continue to perform this kind of trial to evaluate the [ideal] sequence in the treatment of our patients.”
He continued that the secondary endpoints in the trial of PFS and objective response and disease control rates were “fairly in favor of the use of rechallenge before regorafenib, and in my opinion, this is really quite convincing.”
Ducreux, who was not involved in PARERE trail, also pointed to the sex difference seen in the study, which suggested that women responded much better to having anti-EGFR retreatment before regorafenib than did men.
Similar findings have been reported in a number of other trials, and previous work has suggested that there are sex differences in the pharmacokinetics of several anticancer drugs. However, while this is “very important,” he said that “we never consider it, because we are not able to really explain [it].”
Overall, he concluded that, on the basis of these results, he would agree with the notion that it is better to propose a rechallenge with anti-EGFR treatment as the fourth-line therapy in this patient population, before administering regorafenib.
Ducreux explained that, after a partial response, tumors acquire resistance to EGFR inhibitors through alterations and mutations that occur during treatment, via nongenetic mechanisms, and through treatment-induced selection for preexisting mutations.
Previous work has shown that mutations, such as in the RAS gene, are detectable early during EGFR inhibitor therapy, but that they then decay exponentially once the drugs are stopped, with the potential that tumors regain their sensitivity to them.
Germani said that this means that ctDNA-guided retreatment with anti-EGFR therapies is a “promising approach” in pretreated patients with RAS and BRAF wild-type mCRC, and that the sequencing of the drugs may be important. Indeed, the REVERCE trial showed that giving regorafenib followed by the anti-EGFR drug cetuzximab was associated with longer overall survival than the other way around in anti-EGFR medication-naive patients.
Methods and Results
For PARERE, the researchers enrolled patients aged at least 18 years with RAS and BRAF wild-type mCRC who were previously treated with a first-line anti-EGFR-containing regimen and had at least a partial response or stable disease for at least 6 months.
The patients were also required to have had at least one intervening anti-EGFR-free line of therapy, and to have previously received treatment with fluoropyrimidine, oxaliplatin, irinotecan, and anti-angiogenics. At least 4 months were required to have passed between the end of anti-EGFR administration and screening for the study.
In all, 428 patients were screened between December 2020 and December 2024, with 213 patients with RAS and BRAF wild-type mCRC, as detected on ctDNA, enrolled. They were randomized to panitumumab or regorafenib until first progression, followed by regorafenib, if they started on panitumumab, or panitumumab, if they started on regorafenib, until second progression.
The median age of the patients was 61 years among those who started on panitumumab and 64 years among those initially given regorafenib in the trial, and 63% and 57%, respectively, were male. The median number of prior lines of therapy was two in both groups, and 65% and 69%, respectively, had received pantitumumab as their first-line anti-EGFR.
Initial findings from the study presented at the 2025 ASCO Annual Meeting indicated that, after a median follow-up of 23.5 months, there was no significant difference in the median first PFS between the two treatment arms.
However, patients who started with panitumumab had a significant improvement in both the objective response and disease control rates (P < .001), as well as a signal for a potentially longer median second PFS, than those who started with regorafenib, particularly on the per-protocol analysis.
Presenting the overall survival results, Germani said that there was no significant difference between the groups on the intention-to-treat analysis, at a stratified hazard ratio of 1.13 (P = .440), or on the per-protocol analysis, at a hazard ratio of 1.07 (P = .730).
“We then ran a subgroup analysis,” he continued, “and we found out that an anti-EGFR-free interval before liquid biopsy shorter than 6 months was associated with less benefit from a panitumumab [first] sequence, which is biologically sound.”
It was also observed that women did significantly better when having panitumumab first, whereas men did not, for which “we do not have a clear biological explanation,” Germani added.
Confining the analysis to so-called “hyperselected” patients, who not only were RAS and BRAF wild type but also had no pathogenic mutations associated with anti-EGFR resistance, did not reveal any significant overall survival differences between the treatment groups.
However, Ducreux took issue with the way in which hyperselection, which is turning up more and more regularly in trials, is defined, as the choice of which mutations to include varies widely. He suggested that a consensus group be assembled to resolve this issue.
Looking more broadly, the researchers were able to show that, in this updated analysis, anti-EGFR re-treatment was superior to regorafenib regardless of the treatment sequence in terms of PFS, at 4.2 months vs 2.4 months (P = .103) when given first in the trial, and 3.9 months vs 2.7 months (P = .019) when given second in the trial, as well as in terms of objective response and disease control rates.
Adverse Events
In terms of safety, the results showed that, as expected, acneiform rash, fatigue, and hypomagnesemia were the most common adverse events associated with panitumumb, while those with regorafenib were fatigue, hand-foot skin reactions, and hypertension.
There were no notable differences in the number of patients receiving a post-study treatment nor in the post-study therapeutic choices, between the study arms.
The study was sponsored by GONO Foundation and partially supported by Amgen and Bayer. Germani declared having relationships with MSD and Amgen. Ducreux declared having relationships with Amgen, Bayer, BeiGene, Incyte, Jazz, Merck KGaA, Merck Serono, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pierre Fabre, Roche, Servier, Keocyt, AbbVie, Abcely, Arcus, Bayer, BMS, Boehringer, GlaxoSmithKline, Sanofi, Scandion, and Zymeworks.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BERLIN — Re-treatment with an antiepidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) agent is effective in patients with chemorefractory metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) with RAS and BRAF wild-type tumors confirmed on circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), although the sequencing of therapy does not seem to matter, suggest overall survival results from the crossover trial PARERE.
The findings nevertheless indicate that anti-EGFR rechallenge with panitumumab may prolong progression-free survival (PFS) over the multiple kinase inhibitor regorafenib. This suggests that “the most pragmatic choice” would be to give the anti-EGFR before regorafenib, said study presenter Marco Maria Germani, MD, Department of Translational Research and New Technologies in Medicine and Surgery, University of Pisa, Pisa, Italy.
The caveat, however, is in patients who have an anti-EGFR interval since previously receiving the drugs of < 6 months. Those patients appeared to do better if they had regorafenib first and then anti-EGFR rechallenge.
Overall, Germani said that “since [trifluridine/tipiracil] plus bevacizumab is today the third-line standard of care” in this patient population, “anti-EGFR re-treatment might be considered after progression” on that combination.
Germani presented the research on October 18 at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Meeting 2025, which was simultaneously published in the Annals of Oncology.
Michel P. Ducreux, MD, PhD, head of the Digestive Cancer Committee at Gustave Roussy, Villejuif, France, and invited discussant for the results, said, despite the study being negative, it is “very important to continue to perform this kind of trial to evaluate the [ideal] sequence in the treatment of our patients.”
He continued that the secondary endpoints in the trial of PFS and objective response and disease control rates were “fairly in favor of the use of rechallenge before regorafenib, and in my opinion, this is really quite convincing.”
Ducreux, who was not involved in PARERE trail, also pointed to the sex difference seen in the study, which suggested that women responded much better to having anti-EGFR retreatment before regorafenib than did men.
Similar findings have been reported in a number of other trials, and previous work has suggested that there are sex differences in the pharmacokinetics of several anticancer drugs. However, while this is “very important,” he said that “we never consider it, because we are not able to really explain [it].”
Overall, he concluded that, on the basis of these results, he would agree with the notion that it is better to propose a rechallenge with anti-EGFR treatment as the fourth-line therapy in this patient population, before administering regorafenib.
Ducreux explained that, after a partial response, tumors acquire resistance to EGFR inhibitors through alterations and mutations that occur during treatment, via nongenetic mechanisms, and through treatment-induced selection for preexisting mutations.
Previous work has shown that mutations, such as in the RAS gene, are detectable early during EGFR inhibitor therapy, but that they then decay exponentially once the drugs are stopped, with the potential that tumors regain their sensitivity to them.
Germani said that this means that ctDNA-guided retreatment with anti-EGFR therapies is a “promising approach” in pretreated patients with RAS and BRAF wild-type mCRC, and that the sequencing of the drugs may be important. Indeed, the REVERCE trial showed that giving regorafenib followed by the anti-EGFR drug cetuzximab was associated with longer overall survival than the other way around in anti-EGFR medication-naive patients.
Methods and Results
For PARERE, the researchers enrolled patients aged at least 18 years with RAS and BRAF wild-type mCRC who were previously treated with a first-line anti-EGFR-containing regimen and had at least a partial response or stable disease for at least 6 months.
The patients were also required to have had at least one intervening anti-EGFR-free line of therapy, and to have previously received treatment with fluoropyrimidine, oxaliplatin, irinotecan, and anti-angiogenics. At least 4 months were required to have passed between the end of anti-EGFR administration and screening for the study.
In all, 428 patients were screened between December 2020 and December 2024, with 213 patients with RAS and BRAF wild-type mCRC, as detected on ctDNA, enrolled. They were randomized to panitumumab or regorafenib until first progression, followed by regorafenib, if they started on panitumumab, or panitumumab, if they started on regorafenib, until second progression.
The median age of the patients was 61 years among those who started on panitumumab and 64 years among those initially given regorafenib in the trial, and 63% and 57%, respectively, were male. The median number of prior lines of therapy was two in both groups, and 65% and 69%, respectively, had received pantitumumab as their first-line anti-EGFR.
Initial findings from the study presented at the 2025 ASCO Annual Meeting indicated that, after a median follow-up of 23.5 months, there was no significant difference in the median first PFS between the two treatment arms.
However, patients who started with panitumumab had a significant improvement in both the objective response and disease control rates (P < .001), as well as a signal for a potentially longer median second PFS, than those who started with regorafenib, particularly on the per-protocol analysis.
Presenting the overall survival results, Germani said that there was no significant difference between the groups on the intention-to-treat analysis, at a stratified hazard ratio of 1.13 (P = .440), or on the per-protocol analysis, at a hazard ratio of 1.07 (P = .730).
“We then ran a subgroup analysis,” he continued, “and we found out that an anti-EGFR-free interval before liquid biopsy shorter than 6 months was associated with less benefit from a panitumumab [first] sequence, which is biologically sound.”
It was also observed that women did significantly better when having panitumumab first, whereas men did not, for which “we do not have a clear biological explanation,” Germani added.
Confining the analysis to so-called “hyperselected” patients, who not only were RAS and BRAF wild type but also had no pathogenic mutations associated with anti-EGFR resistance, did not reveal any significant overall survival differences between the treatment groups.
However, Ducreux took issue with the way in which hyperselection, which is turning up more and more regularly in trials, is defined, as the choice of which mutations to include varies widely. He suggested that a consensus group be assembled to resolve this issue.
Looking more broadly, the researchers were able to show that, in this updated analysis, anti-EGFR re-treatment was superior to regorafenib regardless of the treatment sequence in terms of PFS, at 4.2 months vs 2.4 months (P = .103) when given first in the trial, and 3.9 months vs 2.7 months (P = .019) when given second in the trial, as well as in terms of objective response and disease control rates.
Adverse Events
In terms of safety, the results showed that, as expected, acneiform rash, fatigue, and hypomagnesemia were the most common adverse events associated with panitumumb, while those with regorafenib were fatigue, hand-foot skin reactions, and hypertension.
There were no notable differences in the number of patients receiving a post-study treatment nor in the post-study therapeutic choices, between the study arms.
The study was sponsored by GONO Foundation and partially supported by Amgen and Bayer. Germani declared having relationships with MSD and Amgen. Ducreux declared having relationships with Amgen, Bayer, BeiGene, Incyte, Jazz, Merck KGaA, Merck Serono, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pierre Fabre, Roche, Servier, Keocyt, AbbVie, Abcely, Arcus, Bayer, BMS, Boehringer, GlaxoSmithKline, Sanofi, Scandion, and Zymeworks.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ENDO 2025
NICE Endorses Oral Alternative to Chemo in Prostate Cancer
A faster, oral alternative to docetaxel is set to reach NHS clinics after the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommended darolutamide (Nubeqa, Bayer) in combination with androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) for men with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer who are unable to receive or tolerate chemotherapy.
Detailed in NICE’s final draft guidance, the decision will make darolutamide available through the NHS in England and Wales to approximately 6000 patients, offering a new oral therapy for those who with limited alternatives to docetaxel or other androgen-receptor inhibitors.
New Option for Chemo-Ineligible Patients
Darolutamide functions by blocking hormones that fuel cancer growth, specifically depriving prostate cancer cells of testosterone required for multiplication and spread. Patients take two tablets twice daily alongside standard ADT.
Peter Johnson, national clinical director for cancer at NHS England, welcomed the decision and expects this approval to give clinicians and their patients “more flexibility to choose the approach best suited to individual circumstances and clinical needs.”
The guidance was finalised 5 weeks ahead of the standard review timeline, underscoring NICE’s commitment to accelerating access to effective prostate cancer treatments.
Clinical Trial Evidence
The NICE’s decision was supported by evidence from the phase 3 ARASENS trial (N = 1306).
The results showed that adding darolutamide to ADT and docetaxel significantly improved overall survival in metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer, reducing the risk for death by 32% compared with ADT and docetaxel alone. Progression-free outcomes, measured by time to castration-resistant disease or death, also favoured darolutamide.
A NICE network meta-analysis of the TITAN, ARCHES, LATITUDE, and STAMPEDE trials suggested that combining ADT with androgen-receptor pathway inhibitors such as apalutamide, enzalutamide, and abiraterone provides comparable survival benefits in this disease setting.
Cost and Implementation
NICE determined that darolutamide plus ADT delivers similar or lower overall costs to the NHS compared with apalutamide plus ADT. The list price is £4040.00 for a 28-day supply (112 × 300-mg tablets), though Bayer has agreed to a confidential commercial discount.
The guidance requires healthcare providers to use the least expensive suitable treatment option, considering administration costs, dosages, price per dose, and commercial arrangements when choosing between darolutamide plus ADT and apalutamide plus ADT.
NHS England and integrated care boards must provide funding within 30 days of final publication, with routine commissioning beginning after this interim period.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A faster, oral alternative to docetaxel is set to reach NHS clinics after the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommended darolutamide (Nubeqa, Bayer) in combination with androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) for men with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer who are unable to receive or tolerate chemotherapy.
Detailed in NICE’s final draft guidance, the decision will make darolutamide available through the NHS in England and Wales to approximately 6000 patients, offering a new oral therapy for those who with limited alternatives to docetaxel or other androgen-receptor inhibitors.
New Option for Chemo-Ineligible Patients
Darolutamide functions by blocking hormones that fuel cancer growth, specifically depriving prostate cancer cells of testosterone required for multiplication and spread. Patients take two tablets twice daily alongside standard ADT.
Peter Johnson, national clinical director for cancer at NHS England, welcomed the decision and expects this approval to give clinicians and their patients “more flexibility to choose the approach best suited to individual circumstances and clinical needs.”
The guidance was finalised 5 weeks ahead of the standard review timeline, underscoring NICE’s commitment to accelerating access to effective prostate cancer treatments.
Clinical Trial Evidence
The NICE’s decision was supported by evidence from the phase 3 ARASENS trial (N = 1306).
The results showed that adding darolutamide to ADT and docetaxel significantly improved overall survival in metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer, reducing the risk for death by 32% compared with ADT and docetaxel alone. Progression-free outcomes, measured by time to castration-resistant disease or death, also favoured darolutamide.
A NICE network meta-analysis of the TITAN, ARCHES, LATITUDE, and STAMPEDE trials suggested that combining ADT with androgen-receptor pathway inhibitors such as apalutamide, enzalutamide, and abiraterone provides comparable survival benefits in this disease setting.
Cost and Implementation
NICE determined that darolutamide plus ADT delivers similar or lower overall costs to the NHS compared with apalutamide plus ADT. The list price is £4040.00 for a 28-day supply (112 × 300-mg tablets), though Bayer has agreed to a confidential commercial discount.
The guidance requires healthcare providers to use the least expensive suitable treatment option, considering administration costs, dosages, price per dose, and commercial arrangements when choosing between darolutamide plus ADT and apalutamide plus ADT.
NHS England and integrated care boards must provide funding within 30 days of final publication, with routine commissioning beginning after this interim period.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A faster, oral alternative to docetaxel is set to reach NHS clinics after the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommended darolutamide (Nubeqa, Bayer) in combination with androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) for men with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer who are unable to receive or tolerate chemotherapy.
Detailed in NICE’s final draft guidance, the decision will make darolutamide available through the NHS in England and Wales to approximately 6000 patients, offering a new oral therapy for those who with limited alternatives to docetaxel or other androgen-receptor inhibitors.
New Option for Chemo-Ineligible Patients
Darolutamide functions by blocking hormones that fuel cancer growth, specifically depriving prostate cancer cells of testosterone required for multiplication and spread. Patients take two tablets twice daily alongside standard ADT.
Peter Johnson, national clinical director for cancer at NHS England, welcomed the decision and expects this approval to give clinicians and their patients “more flexibility to choose the approach best suited to individual circumstances and clinical needs.”
The guidance was finalised 5 weeks ahead of the standard review timeline, underscoring NICE’s commitment to accelerating access to effective prostate cancer treatments.
Clinical Trial Evidence
The NICE’s decision was supported by evidence from the phase 3 ARASENS trial (N = 1306).
The results showed that adding darolutamide to ADT and docetaxel significantly improved overall survival in metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer, reducing the risk for death by 32% compared with ADT and docetaxel alone. Progression-free outcomes, measured by time to castration-resistant disease or death, also favoured darolutamide.
A NICE network meta-analysis of the TITAN, ARCHES, LATITUDE, and STAMPEDE trials suggested that combining ADT with androgen-receptor pathway inhibitors such as apalutamide, enzalutamide, and abiraterone provides comparable survival benefits in this disease setting.
Cost and Implementation
NICE determined that darolutamide plus ADT delivers similar or lower overall costs to the NHS compared with apalutamide plus ADT. The list price is £4040.00 for a 28-day supply (112 × 300-mg tablets), though Bayer has agreed to a confidential commercial discount.
The guidance requires healthcare providers to use the least expensive suitable treatment option, considering administration costs, dosages, price per dose, and commercial arrangements when choosing between darolutamide plus ADT and apalutamide plus ADT.
NHS England and integrated care boards must provide funding within 30 days of final publication, with routine commissioning beginning after this interim period.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two ADCs Offer More Hope for Patients With Advanced TNBC
BERLIN — Patients with previously untreated locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) who are not candidates for immunotherapy may experience improved survival outcomes with TROP2-directed antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), suggested two trials presented at European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Meeting 2025 on October 19.
ASCENT-03 compared sacituzumab govitecan with standard of care chemotherapy, finding that the drug was associated with a 38% improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) in this patient population that has, traditionally, a poor prognosis. Overall survival data remain immature.
TROPION-Breast02 studied datopotamab deruxtecan (Dato-DXd) against investigator’s choice of chemotherapy. The PFS improvement with the ADC was 43%, while patients also experienced a 21% improvement in overall survival. In both cases, the safety profile of the experimental drugs was deemed to be manageable.
Discussant Ana C. Garrido-Castro, MD, director, Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Research, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, who was not involved in either study, said that both sacituzumab govitecan and Dato-DXd showed a PFS benefit. The choice between them, leaving aside overall survival until the data are mature, will be largely based on factors such as the safety profile and the patient preference, she continued.
Sacituzumab govitecan is associated with an increase in neutropenia, nausea, and diarrhea, she pointed out, while Dato-DXd has increased rates of ocular surface toxicity, oral mucositis/stomatitis, and requires monitoring for interstitial lung disease.
Dato-DXd has a higher objective response rate than chemotherapy, unlike sacituzumab govitecan, but, crucially, requires one infusion vs 2 for sacituzumab govitecan per 21-day cycle, and has a shorter total infusion time.
There are nevertheless a number of unanswered questions about the drugs, including how the ADCs affect quality of life, and how common patient adherence to the recommended prophylaxis is. Patients with early relapse of < 12 months remain an “urgent unmet need,” Garrido-Castro said, and the role of immunotherapy rechallenge remains to be explored.
ADCs are also being tested in the neo-adjuvant TNBC setting, and the potential impact of that on the use of the drugs in the metastatic setting is currently unclear. In addition, there are questions around access to therapy.
“Ultimately, it will be very important to have a better understanding of the biomarkers of response and resistance and toxicity to these agents, and whether we should be sequencing antibody drug conjugates,” Garrido-Castro said. “All of this will help shape the next wave of treatment strategies for this patient population.”
She concluded: “Today, marks a paradigm shift of metastatic TNBC, in my opinion. ASCENT-03 and TROPION-Breast02 support TROP2 ADC therapy as the new preferred first-line regimen for this patient population.”
Method and Results of ASCENT-03
ASCENT-03 study presenter Javier C. Cortés, MD, PhD, International Breast Cancer Center, Pangaea Oncology, Quiron Group, Barcelona, Spain, said there is currently an unmet clinical need in the approximately 60% of patients with previously untreated metastatic TNBC who are not candidates for immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Median PFS in previous first-line studies was < 6 months with chemotherapy — the current standard of care — and Cortés said that around half of the patients who receive that in the first-line do not receive second-line therapy because of clinical deterioration or death.
“The sobering truth is that across studies in the US and Europe, approximately 25% to 30% of patients diagnosed with metastatic TNBC are no longer alive at 6 months from their metastatic diagnosis,” said Garrido-Castro. “So if there is a new drug that is able to significantly improve PFS with an acceptable toxicity profile, this should be sufficient to change the current standard of care in the first-line setting.”
As sacituzumab govitecan is already approved for second-line metastatic TNBC and for pretreated hormone receptor positive/HER2- metastatic breast cancer, the ASCENT-03 researchers studied the drug in patients with previously untreated locally advanced inoperable, or metastatic TNBC.
The patients were deemed not to be candidates for PD-L1 inhibitors through having PD-L1-negative tumors, by having PD-L1-positive tumors that had previously been treated with PD-L1 inhibitors in the curative setting, or by having a comorbidity that precluded PD-L1 inhibitor use.
The patients were required to have finished any prior treatment in the curative setting at least 6 months previously. Previously treated, stable central nervous system metastases were allowed.
They were randomized to sacituzumab govitecan or chemotherapy, comprising paclitaxel or nab-paclitaxel, or gemcitabine plus carboplatin, until progression, as verified by blinded independent central review (BICR), or unacceptable toxicity. Patients who progressed on chemotherapy were offered crossover to second-line sacituzumab govitecan.
In all, 558 patients were randomized. The median age was 56 years in the sacituzumab govitecan group vs 54 years in the chemotherapy group. The majority (64% in both groups) of patients were White individuals. The most common metastatic site was the lung (59% vs 61%), and 58% of patients in both groups had previously received a taxane.
Cortés reported that sacituzumab govitecan was associated with a “statistically significant and clinically meaningful” improvement in PFS by BICR, at a median of 9.7 months vs 6.9 months, or a hazard ratio (HR) of 0.62 (P < .0001). This benefit was seen across prespecified subgroups.
The objective response rate was almost identical between the two treatment groups, at 48% with sacituzumab govitecan vs 46% with chemotherapy, although the median duration of response was longer with the ADC, at 12.2 months vs 7.2 months.
Cortés showed the latest results on overall survival. This showed no significant difference between the two treatments, although he underlined that the data are not yet mature.
He also reported that the rates of grade ≥ 3 treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were similar in the two groups, at 66% with sacituzumab govitecan vs 62% with chemotherapy. However, the rates of TEAEs leading to treatment discontinuation (4% vs 12%) or dose reduction (37% vs 45%) were lower with the ADC.
Cortés concluded that the results suggest that sacituzumab govitecan “is a good option for patients with triple negative breast cancer when they develop metastasis and are unable to receive immune checkpoint inhibitors.”
TROPION-Breast02 Methods and Results
Presenting TROPION-Breast02, Rebecca A. Dent, MD, MSc, National Cancer Center Singapore and Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore, explained that the trial looked at a patient population similar to that of ASCENT-03, here focusing instead on Dato-DXd.
Patients were included if they had histologically or cytologically documented locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic TNBC, no prior chemotherapy or targeted systemic therapy in this setting, and in whom immunotherapy was not an option.
They were randomized to Dato-DXd or the investigator’s choice of chemotherapy, with treatment continued until investigator-assessed progressive disease on RECIST v1.1, unacceptable toxicity, or another criterion for discontinuation was met.
In total, 642 patients were enrolled. The median age was 56 years for those in the Dato-DXd group and 57 years for those in chemotherapy group, and less than half (41% in the Dato-DXd group and 48% in the chemotherapy group) were White individuals. The number of metastatic sites was less than three in 64% and 67% of patients, respectively.
Dent showed that Dato-DXd was associated with a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in BICR-assessed PFS, at a median of 10.8 months vs 5.6 months with chemotherapy, at a HR of 0.57 (P < .0001). The findings were replicated across the prespecified subgroups.
There was a marked overall survival benefit with Dato-DXd, at a median of 23.7 months vs 18.7 months, at a HR of 0.79 (P = .0291). Dent reported that, at 18 months, 61.2% of patients in the Dato-DXd group were still alive vs 51.3% in the chemotherapy group. Again, the benefit was seen across subgroups.
The confirmed objective response rate with Dato-DXd was far higher than that with chemotherapy, at 62.5% vs 29.3%, or an odds ratio of 4.24. The duration of response was also longer, at 12.3 months vs 7.1 months.
Rates of grade ≥ 3 adverse events were comparable, at 33% with Dato-DXd vs 29% with chemotherapy, although there were more events associated with dose reduction (27% vs 18%) and dose interruption (24% vs 19%) with the ADC.
“These results support Dato-DXd as the first new first-line standard of care for patients with locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic TNBC for whom immunotherapy is not an option,” Dent said.
“What’s important is the patients enrolled into this trial are clearly representative of real world patients that we are treating in our clinics every day. These patients are often excluded from our current clinical trials,” she said.
ASCENT-03 was funded by Gilead Sciences.
TROPION-Breast02 was funded by AstraZeneca.Cortés declared relationships with Roche, AstraZeneca, Seattle Genetics, Daiichi Sankyo, Lilly, Merck Sharpe & Dohme, Leuko, Bioasis, Clovis oncology, Boehringer Ingelheim, Ellipses, HiberCell, BioInvent, GEMoaB, Gilead, Menarini, Zymeworks, Reveal Genomics, Expres2ion Biotechnologies, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie, Scorpion Therapeutics, Bridgebio, Biocon, Biontech, Circle Pharma, Delcath Systems, Hexagon Bio, Novartis, Eisai, Pfizer, Stemline Therapeutics, MAJ3 Capital, Leuko, Ariad Pharmaceuticals, Baxalta GmbH/Servier Affaires, Bayer healthcare, Guardant Health, and PIQUR Therapeutics.
Dent declared relationships with AstraZeneca, MSD, Pfizer, Eisai, Novartis, Daiichi Sankyo/AstraZeneca, Roche, and Gilead Sciences.
Garrido-Castro declared relationships with AstraZeneca, MSD, Pfizer, Eisai, Novartis, Daiichi Sankyo/AstraZeneca, Roche, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer, TD Cowen, and Roche/Genentech.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BERLIN — Patients with previously untreated locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) who are not candidates for immunotherapy may experience improved survival outcomes with TROP2-directed antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), suggested two trials presented at European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Meeting 2025 on October 19.
ASCENT-03 compared sacituzumab govitecan with standard of care chemotherapy, finding that the drug was associated with a 38% improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) in this patient population that has, traditionally, a poor prognosis. Overall survival data remain immature.
TROPION-Breast02 studied datopotamab deruxtecan (Dato-DXd) against investigator’s choice of chemotherapy. The PFS improvement with the ADC was 43%, while patients also experienced a 21% improvement in overall survival. In both cases, the safety profile of the experimental drugs was deemed to be manageable.
Discussant Ana C. Garrido-Castro, MD, director, Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Research, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, who was not involved in either study, said that both sacituzumab govitecan and Dato-DXd showed a PFS benefit. The choice between them, leaving aside overall survival until the data are mature, will be largely based on factors such as the safety profile and the patient preference, she continued.
Sacituzumab govitecan is associated with an increase in neutropenia, nausea, and diarrhea, she pointed out, while Dato-DXd has increased rates of ocular surface toxicity, oral mucositis/stomatitis, and requires monitoring for interstitial lung disease.
Dato-DXd has a higher objective response rate than chemotherapy, unlike sacituzumab govitecan, but, crucially, requires one infusion vs 2 for sacituzumab govitecan per 21-day cycle, and has a shorter total infusion time.
There are nevertheless a number of unanswered questions about the drugs, including how the ADCs affect quality of life, and how common patient adherence to the recommended prophylaxis is. Patients with early relapse of < 12 months remain an “urgent unmet need,” Garrido-Castro said, and the role of immunotherapy rechallenge remains to be explored.
ADCs are also being tested in the neo-adjuvant TNBC setting, and the potential impact of that on the use of the drugs in the metastatic setting is currently unclear. In addition, there are questions around access to therapy.
“Ultimately, it will be very important to have a better understanding of the biomarkers of response and resistance and toxicity to these agents, and whether we should be sequencing antibody drug conjugates,” Garrido-Castro said. “All of this will help shape the next wave of treatment strategies for this patient population.”
She concluded: “Today, marks a paradigm shift of metastatic TNBC, in my opinion. ASCENT-03 and TROPION-Breast02 support TROP2 ADC therapy as the new preferred first-line regimen for this patient population.”
Method and Results of ASCENT-03
ASCENT-03 study presenter Javier C. Cortés, MD, PhD, International Breast Cancer Center, Pangaea Oncology, Quiron Group, Barcelona, Spain, said there is currently an unmet clinical need in the approximately 60% of patients with previously untreated metastatic TNBC who are not candidates for immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Median PFS in previous first-line studies was < 6 months with chemotherapy — the current standard of care — and Cortés said that around half of the patients who receive that in the first-line do not receive second-line therapy because of clinical deterioration or death.
“The sobering truth is that across studies in the US and Europe, approximately 25% to 30% of patients diagnosed with metastatic TNBC are no longer alive at 6 months from their metastatic diagnosis,” said Garrido-Castro. “So if there is a new drug that is able to significantly improve PFS with an acceptable toxicity profile, this should be sufficient to change the current standard of care in the first-line setting.”
As sacituzumab govitecan is already approved for second-line metastatic TNBC and for pretreated hormone receptor positive/HER2- metastatic breast cancer, the ASCENT-03 researchers studied the drug in patients with previously untreated locally advanced inoperable, or metastatic TNBC.
The patients were deemed not to be candidates for PD-L1 inhibitors through having PD-L1-negative tumors, by having PD-L1-positive tumors that had previously been treated with PD-L1 inhibitors in the curative setting, or by having a comorbidity that precluded PD-L1 inhibitor use.
The patients were required to have finished any prior treatment in the curative setting at least 6 months previously. Previously treated, stable central nervous system metastases were allowed.
They were randomized to sacituzumab govitecan or chemotherapy, comprising paclitaxel or nab-paclitaxel, or gemcitabine plus carboplatin, until progression, as verified by blinded independent central review (BICR), or unacceptable toxicity. Patients who progressed on chemotherapy were offered crossover to second-line sacituzumab govitecan.
In all, 558 patients were randomized. The median age was 56 years in the sacituzumab govitecan group vs 54 years in the chemotherapy group. The majority (64% in both groups) of patients were White individuals. The most common metastatic site was the lung (59% vs 61%), and 58% of patients in both groups had previously received a taxane.
Cortés reported that sacituzumab govitecan was associated with a “statistically significant and clinically meaningful” improvement in PFS by BICR, at a median of 9.7 months vs 6.9 months, or a hazard ratio (HR) of 0.62 (P < .0001). This benefit was seen across prespecified subgroups.
The objective response rate was almost identical between the two treatment groups, at 48% with sacituzumab govitecan vs 46% with chemotherapy, although the median duration of response was longer with the ADC, at 12.2 months vs 7.2 months.
Cortés showed the latest results on overall survival. This showed no significant difference between the two treatments, although he underlined that the data are not yet mature.
He also reported that the rates of grade ≥ 3 treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were similar in the two groups, at 66% with sacituzumab govitecan vs 62% with chemotherapy. However, the rates of TEAEs leading to treatment discontinuation (4% vs 12%) or dose reduction (37% vs 45%) were lower with the ADC.
Cortés concluded that the results suggest that sacituzumab govitecan “is a good option for patients with triple negative breast cancer when they develop metastasis and are unable to receive immune checkpoint inhibitors.”
TROPION-Breast02 Methods and Results
Presenting TROPION-Breast02, Rebecca A. Dent, MD, MSc, National Cancer Center Singapore and Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore, explained that the trial looked at a patient population similar to that of ASCENT-03, here focusing instead on Dato-DXd.
Patients were included if they had histologically or cytologically documented locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic TNBC, no prior chemotherapy or targeted systemic therapy in this setting, and in whom immunotherapy was not an option.
They were randomized to Dato-DXd or the investigator’s choice of chemotherapy, with treatment continued until investigator-assessed progressive disease on RECIST v1.1, unacceptable toxicity, or another criterion for discontinuation was met.
In total, 642 patients were enrolled. The median age was 56 years for those in the Dato-DXd group and 57 years for those in chemotherapy group, and less than half (41% in the Dato-DXd group and 48% in the chemotherapy group) were White individuals. The number of metastatic sites was less than three in 64% and 67% of patients, respectively.
Dent showed that Dato-DXd was associated with a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in BICR-assessed PFS, at a median of 10.8 months vs 5.6 months with chemotherapy, at a HR of 0.57 (P < .0001). The findings were replicated across the prespecified subgroups.
There was a marked overall survival benefit with Dato-DXd, at a median of 23.7 months vs 18.7 months, at a HR of 0.79 (P = .0291). Dent reported that, at 18 months, 61.2% of patients in the Dato-DXd group were still alive vs 51.3% in the chemotherapy group. Again, the benefit was seen across subgroups.
The confirmed objective response rate with Dato-DXd was far higher than that with chemotherapy, at 62.5% vs 29.3%, or an odds ratio of 4.24. The duration of response was also longer, at 12.3 months vs 7.1 months.
Rates of grade ≥ 3 adverse events were comparable, at 33% with Dato-DXd vs 29% with chemotherapy, although there were more events associated with dose reduction (27% vs 18%) and dose interruption (24% vs 19%) with the ADC.
“These results support Dato-DXd as the first new first-line standard of care for patients with locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic TNBC for whom immunotherapy is not an option,” Dent said.
“What’s important is the patients enrolled into this trial are clearly representative of real world patients that we are treating in our clinics every day. These patients are often excluded from our current clinical trials,” she said.
ASCENT-03 was funded by Gilead Sciences.
TROPION-Breast02 was funded by AstraZeneca.Cortés declared relationships with Roche, AstraZeneca, Seattle Genetics, Daiichi Sankyo, Lilly, Merck Sharpe & Dohme, Leuko, Bioasis, Clovis oncology, Boehringer Ingelheim, Ellipses, HiberCell, BioInvent, GEMoaB, Gilead, Menarini, Zymeworks, Reveal Genomics, Expres2ion Biotechnologies, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie, Scorpion Therapeutics, Bridgebio, Biocon, Biontech, Circle Pharma, Delcath Systems, Hexagon Bio, Novartis, Eisai, Pfizer, Stemline Therapeutics, MAJ3 Capital, Leuko, Ariad Pharmaceuticals, Baxalta GmbH/Servier Affaires, Bayer healthcare, Guardant Health, and PIQUR Therapeutics.
Dent declared relationships with AstraZeneca, MSD, Pfizer, Eisai, Novartis, Daiichi Sankyo/AstraZeneca, Roche, and Gilead Sciences.
Garrido-Castro declared relationships with AstraZeneca, MSD, Pfizer, Eisai, Novartis, Daiichi Sankyo/AstraZeneca, Roche, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer, TD Cowen, and Roche/Genentech.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BERLIN — Patients with previously untreated locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) who are not candidates for immunotherapy may experience improved survival outcomes with TROP2-directed antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), suggested two trials presented at European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Meeting 2025 on October 19.
ASCENT-03 compared sacituzumab govitecan with standard of care chemotherapy, finding that the drug was associated with a 38% improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) in this patient population that has, traditionally, a poor prognosis. Overall survival data remain immature.
TROPION-Breast02 studied datopotamab deruxtecan (Dato-DXd) against investigator’s choice of chemotherapy. The PFS improvement with the ADC was 43%, while patients also experienced a 21% improvement in overall survival. In both cases, the safety profile of the experimental drugs was deemed to be manageable.
Discussant Ana C. Garrido-Castro, MD, director, Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Research, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, who was not involved in either study, said that both sacituzumab govitecan and Dato-DXd showed a PFS benefit. The choice between them, leaving aside overall survival until the data are mature, will be largely based on factors such as the safety profile and the patient preference, she continued.
Sacituzumab govitecan is associated with an increase in neutropenia, nausea, and diarrhea, she pointed out, while Dato-DXd has increased rates of ocular surface toxicity, oral mucositis/stomatitis, and requires monitoring for interstitial lung disease.
Dato-DXd has a higher objective response rate than chemotherapy, unlike sacituzumab govitecan, but, crucially, requires one infusion vs 2 for sacituzumab govitecan per 21-day cycle, and has a shorter total infusion time.
There are nevertheless a number of unanswered questions about the drugs, including how the ADCs affect quality of life, and how common patient adherence to the recommended prophylaxis is. Patients with early relapse of < 12 months remain an “urgent unmet need,” Garrido-Castro said, and the role of immunotherapy rechallenge remains to be explored.
ADCs are also being tested in the neo-adjuvant TNBC setting, and the potential impact of that on the use of the drugs in the metastatic setting is currently unclear. In addition, there are questions around access to therapy.
“Ultimately, it will be very important to have a better understanding of the biomarkers of response and resistance and toxicity to these agents, and whether we should be sequencing antibody drug conjugates,” Garrido-Castro said. “All of this will help shape the next wave of treatment strategies for this patient population.”
She concluded: “Today, marks a paradigm shift of metastatic TNBC, in my opinion. ASCENT-03 and TROPION-Breast02 support TROP2 ADC therapy as the new preferred first-line regimen for this patient population.”
Method and Results of ASCENT-03
ASCENT-03 study presenter Javier C. Cortés, MD, PhD, International Breast Cancer Center, Pangaea Oncology, Quiron Group, Barcelona, Spain, said there is currently an unmet clinical need in the approximately 60% of patients with previously untreated metastatic TNBC who are not candidates for immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Median PFS in previous first-line studies was < 6 months with chemotherapy — the current standard of care — and Cortés said that around half of the patients who receive that in the first-line do not receive second-line therapy because of clinical deterioration or death.
“The sobering truth is that across studies in the US and Europe, approximately 25% to 30% of patients diagnosed with metastatic TNBC are no longer alive at 6 months from their metastatic diagnosis,” said Garrido-Castro. “So if there is a new drug that is able to significantly improve PFS with an acceptable toxicity profile, this should be sufficient to change the current standard of care in the first-line setting.”
As sacituzumab govitecan is already approved for second-line metastatic TNBC and for pretreated hormone receptor positive/HER2- metastatic breast cancer, the ASCENT-03 researchers studied the drug in patients with previously untreated locally advanced inoperable, or metastatic TNBC.
The patients were deemed not to be candidates for PD-L1 inhibitors through having PD-L1-negative tumors, by having PD-L1-positive tumors that had previously been treated with PD-L1 inhibitors in the curative setting, or by having a comorbidity that precluded PD-L1 inhibitor use.
The patients were required to have finished any prior treatment in the curative setting at least 6 months previously. Previously treated, stable central nervous system metastases were allowed.
They were randomized to sacituzumab govitecan or chemotherapy, comprising paclitaxel or nab-paclitaxel, or gemcitabine plus carboplatin, until progression, as verified by blinded independent central review (BICR), or unacceptable toxicity. Patients who progressed on chemotherapy were offered crossover to second-line sacituzumab govitecan.
In all, 558 patients were randomized. The median age was 56 years in the sacituzumab govitecan group vs 54 years in the chemotherapy group. The majority (64% in both groups) of patients were White individuals. The most common metastatic site was the lung (59% vs 61%), and 58% of patients in both groups had previously received a taxane.
Cortés reported that sacituzumab govitecan was associated with a “statistically significant and clinically meaningful” improvement in PFS by BICR, at a median of 9.7 months vs 6.9 months, or a hazard ratio (HR) of 0.62 (P < .0001). This benefit was seen across prespecified subgroups.
The objective response rate was almost identical between the two treatment groups, at 48% with sacituzumab govitecan vs 46% with chemotherapy, although the median duration of response was longer with the ADC, at 12.2 months vs 7.2 months.
Cortés showed the latest results on overall survival. This showed no significant difference between the two treatments, although he underlined that the data are not yet mature.
He also reported that the rates of grade ≥ 3 treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were similar in the two groups, at 66% with sacituzumab govitecan vs 62% with chemotherapy. However, the rates of TEAEs leading to treatment discontinuation (4% vs 12%) or dose reduction (37% vs 45%) were lower with the ADC.
Cortés concluded that the results suggest that sacituzumab govitecan “is a good option for patients with triple negative breast cancer when they develop metastasis and are unable to receive immune checkpoint inhibitors.”
TROPION-Breast02 Methods and Results
Presenting TROPION-Breast02, Rebecca A. Dent, MD, MSc, National Cancer Center Singapore and Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore, explained that the trial looked at a patient population similar to that of ASCENT-03, here focusing instead on Dato-DXd.
Patients were included if they had histologically or cytologically documented locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic TNBC, no prior chemotherapy or targeted systemic therapy in this setting, and in whom immunotherapy was not an option.
They were randomized to Dato-DXd or the investigator’s choice of chemotherapy, with treatment continued until investigator-assessed progressive disease on RECIST v1.1, unacceptable toxicity, or another criterion for discontinuation was met.
In total, 642 patients were enrolled. The median age was 56 years for those in the Dato-DXd group and 57 years for those in chemotherapy group, and less than half (41% in the Dato-DXd group and 48% in the chemotherapy group) were White individuals. The number of metastatic sites was less than three in 64% and 67% of patients, respectively.
Dent showed that Dato-DXd was associated with a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in BICR-assessed PFS, at a median of 10.8 months vs 5.6 months with chemotherapy, at a HR of 0.57 (P < .0001). The findings were replicated across the prespecified subgroups.
There was a marked overall survival benefit with Dato-DXd, at a median of 23.7 months vs 18.7 months, at a HR of 0.79 (P = .0291). Dent reported that, at 18 months, 61.2% of patients in the Dato-DXd group were still alive vs 51.3% in the chemotherapy group. Again, the benefit was seen across subgroups.
The confirmed objective response rate with Dato-DXd was far higher than that with chemotherapy, at 62.5% vs 29.3%, or an odds ratio of 4.24. The duration of response was also longer, at 12.3 months vs 7.1 months.
Rates of grade ≥ 3 adverse events were comparable, at 33% with Dato-DXd vs 29% with chemotherapy, although there were more events associated with dose reduction (27% vs 18%) and dose interruption (24% vs 19%) with the ADC.
“These results support Dato-DXd as the first new first-line standard of care for patients with locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic TNBC for whom immunotherapy is not an option,” Dent said.
“What’s important is the patients enrolled into this trial are clearly representative of real world patients that we are treating in our clinics every day. These patients are often excluded from our current clinical trials,” she said.
ASCENT-03 was funded by Gilead Sciences.
TROPION-Breast02 was funded by AstraZeneca.Cortés declared relationships with Roche, AstraZeneca, Seattle Genetics, Daiichi Sankyo, Lilly, Merck Sharpe & Dohme, Leuko, Bioasis, Clovis oncology, Boehringer Ingelheim, Ellipses, HiberCell, BioInvent, GEMoaB, Gilead, Menarini, Zymeworks, Reveal Genomics, Expres2ion Biotechnologies, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie, Scorpion Therapeutics, Bridgebio, Biocon, Biontech, Circle Pharma, Delcath Systems, Hexagon Bio, Novartis, Eisai, Pfizer, Stemline Therapeutics, MAJ3 Capital, Leuko, Ariad Pharmaceuticals, Baxalta GmbH/Servier Affaires, Bayer healthcare, Guardant Health, and PIQUR Therapeutics.
Dent declared relationships with AstraZeneca, MSD, Pfizer, Eisai, Novartis, Daiichi Sankyo/AstraZeneca, Roche, and Gilead Sciences.
Garrido-Castro declared relationships with AstraZeneca, MSD, Pfizer, Eisai, Novartis, Daiichi Sankyo/AstraZeneca, Roche, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer, TD Cowen, and Roche/Genentech.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ESMO 2025
Is High Quality VA Psychiatric Care Keeping Readmissions Rates Low?
Repeated and frequent hospitalizations—sometimes referred to as the revolving door phenomenon— are a particular risk for patients during the first month after discharge. Early psychiatric readmission is a standard indicator of adverse outcomes. However, the results
The quality of previous care has long been thought to be a driver of readmission. If that’s the case, a 2025 study suggests that on average veterans received high-quality inpatient psychiatric services at Veterans Health Administration (VHA) facilities across the nation and that may have been key to keeping readmissions down. Analyzing data from 88,954 veterans who received care at VHA Inpatient Mental Health (IMH) services, the researchers found a “relatively low” rate of readmission within 30 days: 7.1% compared with 8% to 31% of other psychiatric patients in the US. With 40,220 unique patients receiving IMH care per year on average between October 2019 and September 2022, a 7.1% readmission rate means > 2800 30-day readmissions annually.
Research has found that veterans who receive care at the VA have better outcomes than those treated in the private sector. Part of that has to do with practitioners who understand the unique needs of their patients. Veterans may have posttraumatic stress disorder or multiple diagnoses, such as depression, panic disorder, and a substance use disorder. Their mental health issues may also coexist with physical health problems, such as traumatic brain injuries due to explosions.
“If you’re trained at the VA, you learn something important about veteran mental health care that you’ll never get if you’re trained someplace else,” Rodney R. Baker, PhD, retired mental health director and chief of psychology for the South Texas VA Health Care System, said recently. Community clinicians may not know how to collect and incorporate information about a patient’s military history, including details about deployments, combat exposure, injuries, military sexual trauma, and unit culture. They may also lack expertise in navigating the transition between military and veteran life, now considered a critical adjustment period.
“This is a unique population,” said Conwell Smith, the American Psychological Association’s deputy chief of military and veteran policy. “Sending veterans out to the community without requiring that mental health care providers understand them is concerning.”
IMH services aim to stabilize mental health crises and improve veterans’ functioning through patient-centered, evidence-based, and recovery-oriented approaches shown to reduce readmission rates. Treatment generally involves a minimum of 4 hours of interdisciplinary, therapeutic programming each day. And upon discharge, the inpatient care team facilitates the patient’s transition to appropriate outpatient services.
Follow-up care, particularly during the first 30 days, has proved critical in reducing readmissions. In studies that have analyzed postdischarge interventions (psychoeducation, mentoring, community-based hospital treatment, use of continuous follow-up and compulsory community treatment), all found fewer hospitalizations when compared to a control group, or a smaller number of admissions after the intervention.
Mental health care for veterans should be provided by experienced practitioners—but those practitioners are leaving VA. According to the VA Office of Inspector General, 57% of medical centers report a shortage of psychologists. And according to the VA’s monthly Workforce Dashboard, the VHA lost 234 psychologists in the first 9 months of 2025. The VA has also announced plans to cut 30,000 jobs by the end of the year and impose caps on staff at every medical center.
“This approach locks in permanent VA understaffing just as demand for mental health services is projected to continue growing through 2030,” said Russell Lemle, PhD, a clinical psychologist and senior policy analyst for the Veterans Healthcare Policy Institute. “The private sector can’t fill this gap either—over a third of Americans live in areas already facing mental health professional shortages. That’s not taking care of our veterans.
“Unless actions are taken quickly to reverse the trend, its mental health services could easily diminish substantially within 10 to 20 years.”
Repeated and frequent hospitalizations—sometimes referred to as the revolving door phenomenon— are a particular risk for patients during the first month after discharge. Early psychiatric readmission is a standard indicator of adverse outcomes. However, the results
The quality of previous care has long been thought to be a driver of readmission. If that’s the case, a 2025 study suggests that on average veterans received high-quality inpatient psychiatric services at Veterans Health Administration (VHA) facilities across the nation and that may have been key to keeping readmissions down. Analyzing data from 88,954 veterans who received care at VHA Inpatient Mental Health (IMH) services, the researchers found a “relatively low” rate of readmission within 30 days: 7.1% compared with 8% to 31% of other psychiatric patients in the US. With 40,220 unique patients receiving IMH care per year on average between October 2019 and September 2022, a 7.1% readmission rate means > 2800 30-day readmissions annually.
Research has found that veterans who receive care at the VA have better outcomes than those treated in the private sector. Part of that has to do with practitioners who understand the unique needs of their patients. Veterans may have posttraumatic stress disorder or multiple diagnoses, such as depression, panic disorder, and a substance use disorder. Their mental health issues may also coexist with physical health problems, such as traumatic brain injuries due to explosions.
“If you’re trained at the VA, you learn something important about veteran mental health care that you’ll never get if you’re trained someplace else,” Rodney R. Baker, PhD, retired mental health director and chief of psychology for the South Texas VA Health Care System, said recently. Community clinicians may not know how to collect and incorporate information about a patient’s military history, including details about deployments, combat exposure, injuries, military sexual trauma, and unit culture. They may also lack expertise in navigating the transition between military and veteran life, now considered a critical adjustment period.
“This is a unique population,” said Conwell Smith, the American Psychological Association’s deputy chief of military and veteran policy. “Sending veterans out to the community without requiring that mental health care providers understand them is concerning.”
IMH services aim to stabilize mental health crises and improve veterans’ functioning through patient-centered, evidence-based, and recovery-oriented approaches shown to reduce readmission rates. Treatment generally involves a minimum of 4 hours of interdisciplinary, therapeutic programming each day. And upon discharge, the inpatient care team facilitates the patient’s transition to appropriate outpatient services.
Follow-up care, particularly during the first 30 days, has proved critical in reducing readmissions. In studies that have analyzed postdischarge interventions (psychoeducation, mentoring, community-based hospital treatment, use of continuous follow-up and compulsory community treatment), all found fewer hospitalizations when compared to a control group, or a smaller number of admissions after the intervention.
Mental health care for veterans should be provided by experienced practitioners—but those practitioners are leaving VA. According to the VA Office of Inspector General, 57% of medical centers report a shortage of psychologists. And according to the VA’s monthly Workforce Dashboard, the VHA lost 234 psychologists in the first 9 months of 2025. The VA has also announced plans to cut 30,000 jobs by the end of the year and impose caps on staff at every medical center.
“This approach locks in permanent VA understaffing just as demand for mental health services is projected to continue growing through 2030,” said Russell Lemle, PhD, a clinical psychologist and senior policy analyst for the Veterans Healthcare Policy Institute. “The private sector can’t fill this gap either—over a third of Americans live in areas already facing mental health professional shortages. That’s not taking care of our veterans.
“Unless actions are taken quickly to reverse the trend, its mental health services could easily diminish substantially within 10 to 20 years.”
Repeated and frequent hospitalizations—sometimes referred to as the revolving door phenomenon— are a particular risk for patients during the first month after discharge. Early psychiatric readmission is a standard indicator of adverse outcomes. However, the results
The quality of previous care has long been thought to be a driver of readmission. If that’s the case, a 2025 study suggests that on average veterans received high-quality inpatient psychiatric services at Veterans Health Administration (VHA) facilities across the nation and that may have been key to keeping readmissions down. Analyzing data from 88,954 veterans who received care at VHA Inpatient Mental Health (IMH) services, the researchers found a “relatively low” rate of readmission within 30 days: 7.1% compared with 8% to 31% of other psychiatric patients in the US. With 40,220 unique patients receiving IMH care per year on average between October 2019 and September 2022, a 7.1% readmission rate means > 2800 30-day readmissions annually.
Research has found that veterans who receive care at the VA have better outcomes than those treated in the private sector. Part of that has to do with practitioners who understand the unique needs of their patients. Veterans may have posttraumatic stress disorder or multiple diagnoses, such as depression, panic disorder, and a substance use disorder. Their mental health issues may also coexist with physical health problems, such as traumatic brain injuries due to explosions.
“If you’re trained at the VA, you learn something important about veteran mental health care that you’ll never get if you’re trained someplace else,” Rodney R. Baker, PhD, retired mental health director and chief of psychology for the South Texas VA Health Care System, said recently. Community clinicians may not know how to collect and incorporate information about a patient’s military history, including details about deployments, combat exposure, injuries, military sexual trauma, and unit culture. They may also lack expertise in navigating the transition between military and veteran life, now considered a critical adjustment period.
“This is a unique population,” said Conwell Smith, the American Psychological Association’s deputy chief of military and veteran policy. “Sending veterans out to the community without requiring that mental health care providers understand them is concerning.”
IMH services aim to stabilize mental health crises and improve veterans’ functioning through patient-centered, evidence-based, and recovery-oriented approaches shown to reduce readmission rates. Treatment generally involves a minimum of 4 hours of interdisciplinary, therapeutic programming each day. And upon discharge, the inpatient care team facilitates the patient’s transition to appropriate outpatient services.
Follow-up care, particularly during the first 30 days, has proved critical in reducing readmissions. In studies that have analyzed postdischarge interventions (psychoeducation, mentoring, community-based hospital treatment, use of continuous follow-up and compulsory community treatment), all found fewer hospitalizations when compared to a control group, or a smaller number of admissions after the intervention.
Mental health care for veterans should be provided by experienced practitioners—but those practitioners are leaving VA. According to the VA Office of Inspector General, 57% of medical centers report a shortage of psychologists. And according to the VA’s monthly Workforce Dashboard, the VHA lost 234 psychologists in the first 9 months of 2025. The VA has also announced plans to cut 30,000 jobs by the end of the year and impose caps on staff at every medical center.
“This approach locks in permanent VA understaffing just as demand for mental health services is projected to continue growing through 2030,” said Russell Lemle, PhD, a clinical psychologist and senior policy analyst for the Veterans Healthcare Policy Institute. “The private sector can’t fill this gap either—over a third of Americans live in areas already facing mental health professional shortages. That’s not taking care of our veterans.
“Unless actions are taken quickly to reverse the trend, its mental health services could easily diminish substantially within 10 to 20 years.”