User login
If you give a mouse a genetically engineered bitcoin wallet
The world’s most valuable mouse
You’ve heard of Mighty Mouse. Now say hello to the world’s newest mouse superhero, Crypto-Mouse! After being bitten by a radioactive cryptocurrency investor, Crypto-Mouse can tap directly into the power of the blockchain itself, allowing it to perform incredible, death-defying feats of strength!
We’re going to stop right there before Crypto-Mouse gains entry into the Marvel cinematic universe. Let’s rewind to the beginning, because that’s precisely where this crazy scheme is at. In late January, a new decentralized autonomous organization, BitMouseDAO, launched to enormous … -ly little fanfare, according to Vice. Two investors as of Jan. 31. But what they lack in money they make up for in sheer ambition.
BitMouseDAO’s $100 million dollar idea is to genetically engineer mice to carry bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency and one of the most valuable. This isn’t as crazy an idea as it sounds since DNA can be modified to store information, potentially even bitcoin information. Their plan is to create a private bitcoin wallet, which will be stored in the mouse DNA, and purchase online bitcoin to store in this wallet.
BitMouseDAO, being a “collection of artists,” plans to partner with a lab to translate its private key into a specific DNA sequence to be encoded into the mice during fertilization; or, if that doesn’t work, inject them with a harmless virus that carries the key.
Since these are artists, their ultimate plan is to use their bitcoin mice to make NFTs (scratch that off your cryptocurrency bingo card) and auction them off to people. Or, as Vice put it, BitMouseDAO essentially plans to send preserved dead mice to people. Artistic dead mice! Artistic dead mice worth millions! Maybe. Even BitMouseDAO admits bitcoin could be worthless by the time the project gets off the ground.
If this all sounds completely insane, that’s because it is. But it also sounds crazy enough to work. Now, if you’ll excuse us, we’re off to write a screenplay about a scrappy group of high-tech thieves who steal a group of genetically altered bitcoin mice to sell for millions, only to keep them as their adorable pets. Trust us Hollywood, it’ll make millions!
Alcoholic monkeys vs. the future of feces
Which is more important, the journey or the destination? Science is all about the destination, yes? Solving the problem, saving a life, expanding horizons. That’s science. Or is it? The scientific method is a process, so does that make it a journey?
For us, today’s journey begins at the University of Iowa, where investigators are trying to reduce alcohol consumption. A worthy goal, and they seem to have made some progress by targeting a liver hormone called fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21). But we’re more interested in the process right now, so bring on the alcoholic monkeys. And no, that’s not a death metal/reggae fusion band. Should be, though.
“The vervet monkey population is [composed] of alcohol avoiders, moderate alcohol drinkers, and a group of heavy drinkers,” Matthew Potthoff, PhD, and associates wrote in Cell Metabolism. When this particular bunch of heavy-drinking vervets were given FGF21, they consumed 50% less alcohol than did vehicle-treated controls, so mission accomplished.
Maybe it could be a breakfast cereal. Who wouldn’t enjoy a bowl of alcoholic monkeys in the morning?
And after breakfast, you might be ready for a digitized bowel movement, courtesy of researchers at University of California, San Diego. They’re studying ulcerative colitis (UC) by examining the gut microbiome, and their “most useful biological sample is patient stool,” according to a written statement from the university.
“Once we had all the technology to digitize the stool, the question was, is this going to tell us what’s happening in these patients? The answer turned out to be yes,” co-senior author Rob Knight, PhD, said in the statement. “Digitizing fecal material is the future.” The road to UC treatment, in other words, is paved with digital stool.
About 40% of the UC patients had elevated protease levels, and their high-protease feces were then transplanted into germ-free mice, which subsequently developed colitis and were successfully treated with protease inhibitors. And that is our final destination.
As our revered founder and mentor, Josephine Lotmevich, used to say, an alcoholic monkey in the hand is worth a number 2 in the bush.
Raise a glass to delinquency
You wouldn’t think that a glass of water could lead to a life of crime, but a recent study suggests just that.
Children exposed to lead in their drinking water during their early years had a 21% higher risk of delinquency after the age of 14 years and a 38% higher risk of having a record for a serious complaint, Jackie MacDonald Gibson and associates said in a statement on Eurekalert.
Data for the study came from Wake County, N.C., which includes rural areas, wealthy exurban developments, and predominantly Black communities. The investigators compared the blood lead levels for children tested between 1998 and 2011 with juvenile delinquency reports of the same children from the N.C. Department of Public Safety.
The main culprit, they found, was well water. Blood lead levels were 11% higher in the children whose water came from private wells, compared with children using community water. About 13% of U.S. households rely on private wells, which are not regulated under the Safe Drinking Water Act, for their water supply.
The researchers said there is an urgent need for better drinking-water solutions in communities that rely on well water, whether it be through subsidized home filtration or infrastructure redevelopment.
An earlier study had estimated that preventing just one child from entering the adult criminal justice system would save $1.3 to $1.5 million in 1997 dollars. That’s about $2.2 to $2.5 million dollars today!
If you do the math, it’s not hard to see what’s cheaper (and healthier) in the long run.
A ‘dirty’ scam
Another one? This is just getting sad. You’ve probably heard of muds and clays being good for the skin and maybe you’ve gone to a spa and sat in a mud bath, but would you believe it if someone told you that mud can cure all your ailments? No? Neither would we. Senatorial candidate Beto O’Rourke was definitely someone who brought this strange treatment to light, but it seems like this is something that has been going on for years, even before the pandemic.
A company called Black Oxygen Organics (BOO) was selling “magic dirt” for $110 per 4-ounce package. It claimed the dirt was high in fulvic acid and humic acid, which are good for many things. They were, however, literally getting this mud from bogs with landfills nearby, Mel magazine reported.
That doesn’t sound appealing at all, but wait, there’s more. People were eating, drinking, bathing, and feeding their families this sludge in hopes that they would be cured of their ailments. A lot of people jumped aboard the magic dirt train when the pandemic arose, but it quickly became clear that this mud was not as helpful as BOO claimed it to be.
“We began to receive inquiries and calls on our website with people having problems and issues. Ultimately, we sent the products out for independent testing, and then when that came back and showed that there were toxic heavy metals [lead, arsenic, and cadmium among them] at an unsafe level, that’s when we knew we had to act,” Atlanta-based attorney Matt Wetherington, who filed a federal lawsuit against BOO, told Mel.
After a very complicated series of events involving an expose by NBC, product recalls, extortion claims, and grassroots activism, BOO was shut down by both the Canadian and U.S. governments.
As always, please listen only to health care professionals when you wish to use natural remedies for illnesses and ailments.
The world’s most valuable mouse
You’ve heard of Mighty Mouse. Now say hello to the world’s newest mouse superhero, Crypto-Mouse! After being bitten by a radioactive cryptocurrency investor, Crypto-Mouse can tap directly into the power of the blockchain itself, allowing it to perform incredible, death-defying feats of strength!
We’re going to stop right there before Crypto-Mouse gains entry into the Marvel cinematic universe. Let’s rewind to the beginning, because that’s precisely where this crazy scheme is at. In late January, a new decentralized autonomous organization, BitMouseDAO, launched to enormous … -ly little fanfare, according to Vice. Two investors as of Jan. 31. But what they lack in money they make up for in sheer ambition.
BitMouseDAO’s $100 million dollar idea is to genetically engineer mice to carry bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency and one of the most valuable. This isn’t as crazy an idea as it sounds since DNA can be modified to store information, potentially even bitcoin information. Their plan is to create a private bitcoin wallet, which will be stored in the mouse DNA, and purchase online bitcoin to store in this wallet.
BitMouseDAO, being a “collection of artists,” plans to partner with a lab to translate its private key into a specific DNA sequence to be encoded into the mice during fertilization; or, if that doesn’t work, inject them with a harmless virus that carries the key.
Since these are artists, their ultimate plan is to use their bitcoin mice to make NFTs (scratch that off your cryptocurrency bingo card) and auction them off to people. Or, as Vice put it, BitMouseDAO essentially plans to send preserved dead mice to people. Artistic dead mice! Artistic dead mice worth millions! Maybe. Even BitMouseDAO admits bitcoin could be worthless by the time the project gets off the ground.
If this all sounds completely insane, that’s because it is. But it also sounds crazy enough to work. Now, if you’ll excuse us, we’re off to write a screenplay about a scrappy group of high-tech thieves who steal a group of genetically altered bitcoin mice to sell for millions, only to keep them as their adorable pets. Trust us Hollywood, it’ll make millions!
Alcoholic monkeys vs. the future of feces
Which is more important, the journey or the destination? Science is all about the destination, yes? Solving the problem, saving a life, expanding horizons. That’s science. Or is it? The scientific method is a process, so does that make it a journey?
For us, today’s journey begins at the University of Iowa, where investigators are trying to reduce alcohol consumption. A worthy goal, and they seem to have made some progress by targeting a liver hormone called fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21). But we’re more interested in the process right now, so bring on the alcoholic monkeys. And no, that’s not a death metal/reggae fusion band. Should be, though.
“The vervet monkey population is [composed] of alcohol avoiders, moderate alcohol drinkers, and a group of heavy drinkers,” Matthew Potthoff, PhD, and associates wrote in Cell Metabolism. When this particular bunch of heavy-drinking vervets were given FGF21, they consumed 50% less alcohol than did vehicle-treated controls, so mission accomplished.
Maybe it could be a breakfast cereal. Who wouldn’t enjoy a bowl of alcoholic monkeys in the morning?
And after breakfast, you might be ready for a digitized bowel movement, courtesy of researchers at University of California, San Diego. They’re studying ulcerative colitis (UC) by examining the gut microbiome, and their “most useful biological sample is patient stool,” according to a written statement from the university.
“Once we had all the technology to digitize the stool, the question was, is this going to tell us what’s happening in these patients? The answer turned out to be yes,” co-senior author Rob Knight, PhD, said in the statement. “Digitizing fecal material is the future.” The road to UC treatment, in other words, is paved with digital stool.
About 40% of the UC patients had elevated protease levels, and their high-protease feces were then transplanted into germ-free mice, which subsequently developed colitis and were successfully treated with protease inhibitors. And that is our final destination.
As our revered founder and mentor, Josephine Lotmevich, used to say, an alcoholic monkey in the hand is worth a number 2 in the bush.
Raise a glass to delinquency
You wouldn’t think that a glass of water could lead to a life of crime, but a recent study suggests just that.
Children exposed to lead in their drinking water during their early years had a 21% higher risk of delinquency after the age of 14 years and a 38% higher risk of having a record for a serious complaint, Jackie MacDonald Gibson and associates said in a statement on Eurekalert.
Data for the study came from Wake County, N.C., which includes rural areas, wealthy exurban developments, and predominantly Black communities. The investigators compared the blood lead levels for children tested between 1998 and 2011 with juvenile delinquency reports of the same children from the N.C. Department of Public Safety.
The main culprit, they found, was well water. Blood lead levels were 11% higher in the children whose water came from private wells, compared with children using community water. About 13% of U.S. households rely on private wells, which are not regulated under the Safe Drinking Water Act, for their water supply.
The researchers said there is an urgent need for better drinking-water solutions in communities that rely on well water, whether it be through subsidized home filtration or infrastructure redevelopment.
An earlier study had estimated that preventing just one child from entering the adult criminal justice system would save $1.3 to $1.5 million in 1997 dollars. That’s about $2.2 to $2.5 million dollars today!
If you do the math, it’s not hard to see what’s cheaper (and healthier) in the long run.
A ‘dirty’ scam
Another one? This is just getting sad. You’ve probably heard of muds and clays being good for the skin and maybe you’ve gone to a spa and sat in a mud bath, but would you believe it if someone told you that mud can cure all your ailments? No? Neither would we. Senatorial candidate Beto O’Rourke was definitely someone who brought this strange treatment to light, but it seems like this is something that has been going on for years, even before the pandemic.
A company called Black Oxygen Organics (BOO) was selling “magic dirt” for $110 per 4-ounce package. It claimed the dirt was high in fulvic acid and humic acid, which are good for many things. They were, however, literally getting this mud from bogs with landfills nearby, Mel magazine reported.
That doesn’t sound appealing at all, but wait, there’s more. People were eating, drinking, bathing, and feeding their families this sludge in hopes that they would be cured of their ailments. A lot of people jumped aboard the magic dirt train when the pandemic arose, but it quickly became clear that this mud was not as helpful as BOO claimed it to be.
“We began to receive inquiries and calls on our website with people having problems and issues. Ultimately, we sent the products out for independent testing, and then when that came back and showed that there were toxic heavy metals [lead, arsenic, and cadmium among them] at an unsafe level, that’s when we knew we had to act,” Atlanta-based attorney Matt Wetherington, who filed a federal lawsuit against BOO, told Mel.
After a very complicated series of events involving an expose by NBC, product recalls, extortion claims, and grassroots activism, BOO was shut down by both the Canadian and U.S. governments.
As always, please listen only to health care professionals when you wish to use natural remedies for illnesses and ailments.
The world’s most valuable mouse
You’ve heard of Mighty Mouse. Now say hello to the world’s newest mouse superhero, Crypto-Mouse! After being bitten by a radioactive cryptocurrency investor, Crypto-Mouse can tap directly into the power of the blockchain itself, allowing it to perform incredible, death-defying feats of strength!
We’re going to stop right there before Crypto-Mouse gains entry into the Marvel cinematic universe. Let’s rewind to the beginning, because that’s precisely where this crazy scheme is at. In late January, a new decentralized autonomous organization, BitMouseDAO, launched to enormous … -ly little fanfare, according to Vice. Two investors as of Jan. 31. But what they lack in money they make up for in sheer ambition.
BitMouseDAO’s $100 million dollar idea is to genetically engineer mice to carry bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency and one of the most valuable. This isn’t as crazy an idea as it sounds since DNA can be modified to store information, potentially even bitcoin information. Their plan is to create a private bitcoin wallet, which will be stored in the mouse DNA, and purchase online bitcoin to store in this wallet.
BitMouseDAO, being a “collection of artists,” plans to partner with a lab to translate its private key into a specific DNA sequence to be encoded into the mice during fertilization; or, if that doesn’t work, inject them with a harmless virus that carries the key.
Since these are artists, their ultimate plan is to use their bitcoin mice to make NFTs (scratch that off your cryptocurrency bingo card) and auction them off to people. Or, as Vice put it, BitMouseDAO essentially plans to send preserved dead mice to people. Artistic dead mice! Artistic dead mice worth millions! Maybe. Even BitMouseDAO admits bitcoin could be worthless by the time the project gets off the ground.
If this all sounds completely insane, that’s because it is. But it also sounds crazy enough to work. Now, if you’ll excuse us, we’re off to write a screenplay about a scrappy group of high-tech thieves who steal a group of genetically altered bitcoin mice to sell for millions, only to keep them as their adorable pets. Trust us Hollywood, it’ll make millions!
Alcoholic monkeys vs. the future of feces
Which is more important, the journey or the destination? Science is all about the destination, yes? Solving the problem, saving a life, expanding horizons. That’s science. Or is it? The scientific method is a process, so does that make it a journey?
For us, today’s journey begins at the University of Iowa, where investigators are trying to reduce alcohol consumption. A worthy goal, and they seem to have made some progress by targeting a liver hormone called fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21). But we’re more interested in the process right now, so bring on the alcoholic monkeys. And no, that’s not a death metal/reggae fusion band. Should be, though.
“The vervet monkey population is [composed] of alcohol avoiders, moderate alcohol drinkers, and a group of heavy drinkers,” Matthew Potthoff, PhD, and associates wrote in Cell Metabolism. When this particular bunch of heavy-drinking vervets were given FGF21, they consumed 50% less alcohol than did vehicle-treated controls, so mission accomplished.
Maybe it could be a breakfast cereal. Who wouldn’t enjoy a bowl of alcoholic monkeys in the morning?
And after breakfast, you might be ready for a digitized bowel movement, courtesy of researchers at University of California, San Diego. They’re studying ulcerative colitis (UC) by examining the gut microbiome, and their “most useful biological sample is patient stool,” according to a written statement from the university.
“Once we had all the technology to digitize the stool, the question was, is this going to tell us what’s happening in these patients? The answer turned out to be yes,” co-senior author Rob Knight, PhD, said in the statement. “Digitizing fecal material is the future.” The road to UC treatment, in other words, is paved with digital stool.
About 40% of the UC patients had elevated protease levels, and their high-protease feces were then transplanted into germ-free mice, which subsequently developed colitis and were successfully treated with protease inhibitors. And that is our final destination.
As our revered founder and mentor, Josephine Lotmevich, used to say, an alcoholic monkey in the hand is worth a number 2 in the bush.
Raise a glass to delinquency
You wouldn’t think that a glass of water could lead to a life of crime, but a recent study suggests just that.
Children exposed to lead in their drinking water during their early years had a 21% higher risk of delinquency after the age of 14 years and a 38% higher risk of having a record for a serious complaint, Jackie MacDonald Gibson and associates said in a statement on Eurekalert.
Data for the study came from Wake County, N.C., which includes rural areas, wealthy exurban developments, and predominantly Black communities. The investigators compared the blood lead levels for children tested between 1998 and 2011 with juvenile delinquency reports of the same children from the N.C. Department of Public Safety.
The main culprit, they found, was well water. Blood lead levels were 11% higher in the children whose water came from private wells, compared with children using community water. About 13% of U.S. households rely on private wells, which are not regulated under the Safe Drinking Water Act, for their water supply.
The researchers said there is an urgent need for better drinking-water solutions in communities that rely on well water, whether it be through subsidized home filtration or infrastructure redevelopment.
An earlier study had estimated that preventing just one child from entering the adult criminal justice system would save $1.3 to $1.5 million in 1997 dollars. That’s about $2.2 to $2.5 million dollars today!
If you do the math, it’s not hard to see what’s cheaper (and healthier) in the long run.
A ‘dirty’ scam
Another one? This is just getting sad. You’ve probably heard of muds and clays being good for the skin and maybe you’ve gone to a spa and sat in a mud bath, but would you believe it if someone told you that mud can cure all your ailments? No? Neither would we. Senatorial candidate Beto O’Rourke was definitely someone who brought this strange treatment to light, but it seems like this is something that has been going on for years, even before the pandemic.
A company called Black Oxygen Organics (BOO) was selling “magic dirt” for $110 per 4-ounce package. It claimed the dirt was high in fulvic acid and humic acid, which are good for many things. They were, however, literally getting this mud from bogs with landfills nearby, Mel magazine reported.
That doesn’t sound appealing at all, but wait, there’s more. People were eating, drinking, bathing, and feeding their families this sludge in hopes that they would be cured of their ailments. A lot of people jumped aboard the magic dirt train when the pandemic arose, but it quickly became clear that this mud was not as helpful as BOO claimed it to be.
“We began to receive inquiries and calls on our website with people having problems and issues. Ultimately, we sent the products out for independent testing, and then when that came back and showed that there were toxic heavy metals [lead, arsenic, and cadmium among them] at an unsafe level, that’s when we knew we had to act,” Atlanta-based attorney Matt Wetherington, who filed a federal lawsuit against BOO, told Mel.
After a very complicated series of events involving an expose by NBC, product recalls, extortion claims, and grassroots activism, BOO was shut down by both the Canadian and U.S. governments.
As always, please listen only to health care professionals when you wish to use natural remedies for illnesses and ailments.
We’re dying to tell you about fatigability
Are you tired? Or are you death tired?
When we’re feeling that burnout monster creep in we sometimes say that we’re being worked to death or that we’re dead tired, but what if that feeling could predict when it’s your actual time to go?
In a recent study published in the Journals of Gerontology: Series A, epidemiologists from the University of Pittsburgh were able to associate a level of “physical fatigability” with mortality.
The researchers administered the Pittsburgh Fatigability Scale to almost 3,000 participants aged ≥ 60 years, who ranked from 0 to 5 on how tired they thought they would be after doing activities like light housework or a leisurely 30-minute walk. After accounting for factors such as preexisting conditions and mental health, the researchers found that people who scored 25 or more points were 2.3 times more likely to die in the next 2.7 years, compared with those who scored under 25.
So what does that tell us about the importance of being continuously active? It’s pretty important.
“Previous research indicates that getting more physical activity can reduce a person’s fatigability. Our study is the first to link more severe physical fatigability to an earlier death,” lead author Nancy W. Glynn, PhD, said in a separate statement. The best way to keep physically active, she suggested, is to set manageable goals and a routine.
A nice walk around the neighborhood during golden hour or a little bit of yoga before breakfast could be a great way to keep the body moving, because you know what they say: Use it or lose it.
This work is NFT protected: Do not screenshot
If you’ve been following the nonmedical news, you’ve likely heard the term “NFT” explode in the past few months. Standing for nonfungible token, NFTs are, at least theoretically, a proof of ownership for digital creations that prevents anyone other than the buyer from reselling the artwork. Sounds like a great idea: It protects artists and buyers alike.
Much like its cousin cryptocurrency, however, the NFT world is rife with speculation, scams, misunderstanding, and drawings of bored monkeys. It’s the Wild West out there in the digital art universe: One poor unfortunate accidentally sold a $300k NFT image for $3,000, a group of investors spent $3 million buying an NFT for a rare version of Dune believing it gave them the copyright (it did not), and an Indonesian engineering student’s 5-year series of expressionless selfies is now worth a million dollars.
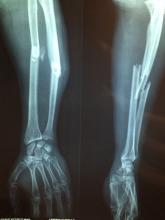
This is a column detailing weird medical news, however, so with our setup complete (though our understanding of NFTs is very much not), we move to France and meet our hero (?), Emmanuel Masmejean, an orthopedic surgeon who apparently wasn’t making enough money in his lucrative medical career.
In a move of apocalyptic madness, he threw ethics out the window, delved into his archive, and found an x-ray of a young woman with a bullet lodged in her arm. The woman was a survivor of the Bataclan mass shooting and bombing in 2015, and don’t you worry, our intrepid entrepreneur made sure to identify her as such when he tried selling the x-ray as an NFT on an online art website for $2,776. Yes, this is very much a violation of doctor-patient confidentiality, and no, that’s not a lot of money to risk your medical career on.
Naturally, the woman was horrified and shocked to learn that the image was being sold, her lawyer told the Guardian. When the doctor called her, he merely attempted to justify his action, rather than apologizing or showing any remorse. Dr. Masmejean is now facing legal action and a disciplinary charge for his attempted entry into the NFT world for publishing the image without permission, and the NFT has been removed from the website. Should have stuck with the bored monkeys.
Avatars could be the future
Zoom, FaceTime, and Skype are great when people can’t be together in the same room, state, or country. Not the same as being somewhere in person, but a pretty good replacement during a global pandemic. But what if you had a robot that could be present for you?
Seven-year-old Joshua Martinangeli of Berlin has a severe lung disease and needs to wear a tube in his neck, so he cannot attend school. A robot avatar, donated to Joshua through a private initiative, sits in his seat in the classroom and is able to interact with the students and teacher, according to Reuters. A light on the avatar blinks when Joshua wants to speak and the children can talk with him too. Joshua and his classmates agree that it’s not the same as him really being there to talk and learn, but it’s a great way to keep him included.
“We are the only district in Berlin that has bought four avatars for its schools. The impetus was COVID-19, but I think this will be the future well beyond the pandemic,” Torsten Kuehne, district education councilor, told Reuters.
So where do we get an avatar to go out and run errands? Can we send it to the office instead of Zooming the next meeting? Or maybe our avatar could go to the gym for us. But how do we get the results to show up on our bodies? C’mon science, figure this out.
Futility, thy name is Kiribati
Before we get to the rest of our regularly scheduled hilarity, a brief geography lesson is in order: Kiribati is an island nation – actually 32 atolls and one coral island – in the central Pacific Ocean. Those atolls are spread out across 1.4 million square miles around the intersection of the equator and the International Date Line, so Kiribati is the only country in the world located in all four hemispheres.
Now, back to the news.
Kiribati closed its borders early in the COVID-19 pandemic and recorded only two cases in almost 2 years. Things were going so well that the authorities recently decided to reopen the country to international travelers. Silly authorities.
The first plane was set to arrive on Jan. 14 from Fiji. This being the age of COVID, plans were made and precautions were taken. All 54 passengers quarantined for 2 weeks before the flight and underwent regular testing, the Guardian noted, and “they were only allowed on the flight after returning negative tests.”
You guessed it. Two-thirds of those 54 people tested positive for COVID-19 after landing in Kiribati.
All of the passengers were quarantined, but since then a security guard at the quarantine center has tested positive, as has someone who was not involved in the quarantine. According to NPR, the government said that “there is now an assumption that COVID-19 is now spreading in the community on South Tarawa and Betio.”
Moral of the story? You can’t beat COVID, so never try.
[EDITOR: Is that really the message we want to send to our readers?]
If you can’t beat them, join them.
[EDITOR: Nope. Try again.]
Resistance is futile?
[EDITOR: Sigh. Close enough.]
Are you tired? Or are you death tired?
When we’re feeling that burnout monster creep in we sometimes say that we’re being worked to death or that we’re dead tired, but what if that feeling could predict when it’s your actual time to go?
In a recent study published in the Journals of Gerontology: Series A, epidemiologists from the University of Pittsburgh were able to associate a level of “physical fatigability” with mortality.
The researchers administered the Pittsburgh Fatigability Scale to almost 3,000 participants aged ≥ 60 years, who ranked from 0 to 5 on how tired they thought they would be after doing activities like light housework or a leisurely 30-minute walk. After accounting for factors such as preexisting conditions and mental health, the researchers found that people who scored 25 or more points were 2.3 times more likely to die in the next 2.7 years, compared with those who scored under 25.
So what does that tell us about the importance of being continuously active? It’s pretty important.
“Previous research indicates that getting more physical activity can reduce a person’s fatigability. Our study is the first to link more severe physical fatigability to an earlier death,” lead author Nancy W. Glynn, PhD, said in a separate statement. The best way to keep physically active, she suggested, is to set manageable goals and a routine.
A nice walk around the neighborhood during golden hour or a little bit of yoga before breakfast could be a great way to keep the body moving, because you know what they say: Use it or lose it.
This work is NFT protected: Do not screenshot
If you’ve been following the nonmedical news, you’ve likely heard the term “NFT” explode in the past few months. Standing for nonfungible token, NFTs are, at least theoretically, a proof of ownership for digital creations that prevents anyone other than the buyer from reselling the artwork. Sounds like a great idea: It protects artists and buyers alike.
Much like its cousin cryptocurrency, however, the NFT world is rife with speculation, scams, misunderstanding, and drawings of bored monkeys. It’s the Wild West out there in the digital art universe: One poor unfortunate accidentally sold a $300k NFT image for $3,000, a group of investors spent $3 million buying an NFT for a rare version of Dune believing it gave them the copyright (it did not), and an Indonesian engineering student’s 5-year series of expressionless selfies is now worth a million dollars.
This is a column detailing weird medical news, however, so with our setup complete (though our understanding of NFTs is very much not), we move to France and meet our hero (?), Emmanuel Masmejean, an orthopedic surgeon who apparently wasn’t making enough money in his lucrative medical career.
In a move of apocalyptic madness, he threw ethics out the window, delved into his archive, and found an x-ray of a young woman with a bullet lodged in her arm. The woman was a survivor of the Bataclan mass shooting and bombing in 2015, and don’t you worry, our intrepid entrepreneur made sure to identify her as such when he tried selling the x-ray as an NFT on an online art website for $2,776. Yes, this is very much a violation of doctor-patient confidentiality, and no, that’s not a lot of money to risk your medical career on.
Naturally, the woman was horrified and shocked to learn that the image was being sold, her lawyer told the Guardian. When the doctor called her, he merely attempted to justify his action, rather than apologizing or showing any remorse. Dr. Masmejean is now facing legal action and a disciplinary charge for his attempted entry into the NFT world for publishing the image without permission, and the NFT has been removed from the website. Should have stuck with the bored monkeys.
Avatars could be the future
Zoom, FaceTime, and Skype are great when people can’t be together in the same room, state, or country. Not the same as being somewhere in person, but a pretty good replacement during a global pandemic. But what if you had a robot that could be present for you?
Seven-year-old Joshua Martinangeli of Berlin has a severe lung disease and needs to wear a tube in his neck, so he cannot attend school. A robot avatar, donated to Joshua through a private initiative, sits in his seat in the classroom and is able to interact with the students and teacher, according to Reuters. A light on the avatar blinks when Joshua wants to speak and the children can talk with him too. Joshua and his classmates agree that it’s not the same as him really being there to talk and learn, but it’s a great way to keep him included.
“We are the only district in Berlin that has bought four avatars for its schools. The impetus was COVID-19, but I think this will be the future well beyond the pandemic,” Torsten Kuehne, district education councilor, told Reuters.
So where do we get an avatar to go out and run errands? Can we send it to the office instead of Zooming the next meeting? Or maybe our avatar could go to the gym for us. But how do we get the results to show up on our bodies? C’mon science, figure this out.
Futility, thy name is Kiribati
Before we get to the rest of our regularly scheduled hilarity, a brief geography lesson is in order: Kiribati is an island nation – actually 32 atolls and one coral island – in the central Pacific Ocean. Those atolls are spread out across 1.4 million square miles around the intersection of the equator and the International Date Line, so Kiribati is the only country in the world located in all four hemispheres.
Now, back to the news.
Kiribati closed its borders early in the COVID-19 pandemic and recorded only two cases in almost 2 years. Things were going so well that the authorities recently decided to reopen the country to international travelers. Silly authorities.
The first plane was set to arrive on Jan. 14 from Fiji. This being the age of COVID, plans were made and precautions were taken. All 54 passengers quarantined for 2 weeks before the flight and underwent regular testing, the Guardian noted, and “they were only allowed on the flight after returning negative tests.”
You guessed it. Two-thirds of those 54 people tested positive for COVID-19 after landing in Kiribati.
All of the passengers were quarantined, but since then a security guard at the quarantine center has tested positive, as has someone who was not involved in the quarantine. According to NPR, the government said that “there is now an assumption that COVID-19 is now spreading in the community on South Tarawa and Betio.”
Moral of the story? You can’t beat COVID, so never try.
[EDITOR: Is that really the message we want to send to our readers?]
If you can’t beat them, join them.
[EDITOR: Nope. Try again.]
Resistance is futile?
[EDITOR: Sigh. Close enough.]
Are you tired? Or are you death tired?
When we’re feeling that burnout monster creep in we sometimes say that we’re being worked to death or that we’re dead tired, but what if that feeling could predict when it’s your actual time to go?
In a recent study published in the Journals of Gerontology: Series A, epidemiologists from the University of Pittsburgh were able to associate a level of “physical fatigability” with mortality.
The researchers administered the Pittsburgh Fatigability Scale to almost 3,000 participants aged ≥ 60 years, who ranked from 0 to 5 on how tired they thought they would be after doing activities like light housework or a leisurely 30-minute walk. After accounting for factors such as preexisting conditions and mental health, the researchers found that people who scored 25 or more points were 2.3 times more likely to die in the next 2.7 years, compared with those who scored under 25.
So what does that tell us about the importance of being continuously active? It’s pretty important.
“Previous research indicates that getting more physical activity can reduce a person’s fatigability. Our study is the first to link more severe physical fatigability to an earlier death,” lead author Nancy W. Glynn, PhD, said in a separate statement. The best way to keep physically active, she suggested, is to set manageable goals and a routine.
A nice walk around the neighborhood during golden hour or a little bit of yoga before breakfast could be a great way to keep the body moving, because you know what they say: Use it or lose it.
This work is NFT protected: Do not screenshot
If you’ve been following the nonmedical news, you’ve likely heard the term “NFT” explode in the past few months. Standing for nonfungible token, NFTs are, at least theoretically, a proof of ownership for digital creations that prevents anyone other than the buyer from reselling the artwork. Sounds like a great idea: It protects artists and buyers alike.
Much like its cousin cryptocurrency, however, the NFT world is rife with speculation, scams, misunderstanding, and drawings of bored monkeys. It’s the Wild West out there in the digital art universe: One poor unfortunate accidentally sold a $300k NFT image for $3,000, a group of investors spent $3 million buying an NFT for a rare version of Dune believing it gave them the copyright (it did not), and an Indonesian engineering student’s 5-year series of expressionless selfies is now worth a million dollars.
This is a column detailing weird medical news, however, so with our setup complete (though our understanding of NFTs is very much not), we move to France and meet our hero (?), Emmanuel Masmejean, an orthopedic surgeon who apparently wasn’t making enough money in his lucrative medical career.
In a move of apocalyptic madness, he threw ethics out the window, delved into his archive, and found an x-ray of a young woman with a bullet lodged in her arm. The woman was a survivor of the Bataclan mass shooting and bombing in 2015, and don’t you worry, our intrepid entrepreneur made sure to identify her as such when he tried selling the x-ray as an NFT on an online art website for $2,776. Yes, this is very much a violation of doctor-patient confidentiality, and no, that’s not a lot of money to risk your medical career on.
Naturally, the woman was horrified and shocked to learn that the image was being sold, her lawyer told the Guardian. When the doctor called her, he merely attempted to justify his action, rather than apologizing or showing any remorse. Dr. Masmejean is now facing legal action and a disciplinary charge for his attempted entry into the NFT world for publishing the image without permission, and the NFT has been removed from the website. Should have stuck with the bored monkeys.
Avatars could be the future
Zoom, FaceTime, and Skype are great when people can’t be together in the same room, state, or country. Not the same as being somewhere in person, but a pretty good replacement during a global pandemic. But what if you had a robot that could be present for you?
Seven-year-old Joshua Martinangeli of Berlin has a severe lung disease and needs to wear a tube in his neck, so he cannot attend school. A robot avatar, donated to Joshua through a private initiative, sits in his seat in the classroom and is able to interact with the students and teacher, according to Reuters. A light on the avatar blinks when Joshua wants to speak and the children can talk with him too. Joshua and his classmates agree that it’s not the same as him really being there to talk and learn, but it’s a great way to keep him included.
“We are the only district in Berlin that has bought four avatars for its schools. The impetus was COVID-19, but I think this will be the future well beyond the pandemic,” Torsten Kuehne, district education councilor, told Reuters.
So where do we get an avatar to go out and run errands? Can we send it to the office instead of Zooming the next meeting? Or maybe our avatar could go to the gym for us. But how do we get the results to show up on our bodies? C’mon science, figure this out.
Futility, thy name is Kiribati
Before we get to the rest of our regularly scheduled hilarity, a brief geography lesson is in order: Kiribati is an island nation – actually 32 atolls and one coral island – in the central Pacific Ocean. Those atolls are spread out across 1.4 million square miles around the intersection of the equator and the International Date Line, so Kiribati is the only country in the world located in all four hemispheres.
Now, back to the news.
Kiribati closed its borders early in the COVID-19 pandemic and recorded only two cases in almost 2 years. Things were going so well that the authorities recently decided to reopen the country to international travelers. Silly authorities.
The first plane was set to arrive on Jan. 14 from Fiji. This being the age of COVID, plans were made and precautions were taken. All 54 passengers quarantined for 2 weeks before the flight and underwent regular testing, the Guardian noted, and “they were only allowed on the flight after returning negative tests.”
You guessed it. Two-thirds of those 54 people tested positive for COVID-19 after landing in Kiribati.
All of the passengers were quarantined, but since then a security guard at the quarantine center has tested positive, as has someone who was not involved in the quarantine. According to NPR, the government said that “there is now an assumption that COVID-19 is now spreading in the community on South Tarawa and Betio.”
Moral of the story? You can’t beat COVID, so never try.
[EDITOR: Is that really the message we want to send to our readers?]
If you can’t beat them, join them.
[EDITOR: Nope. Try again.]
Resistance is futile?
[EDITOR: Sigh. Close enough.]
Make America beautiful: Support mask mandates
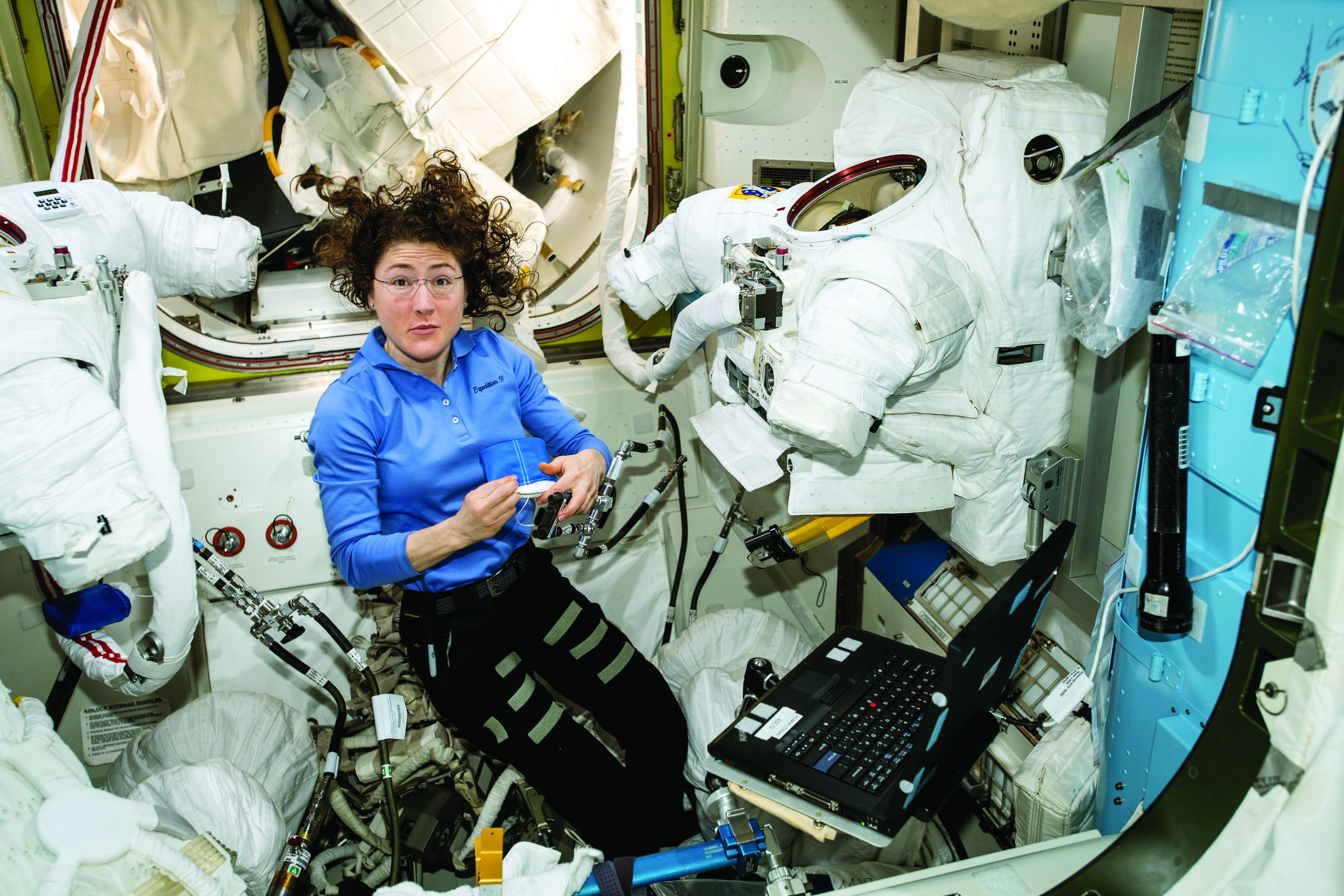
In space, no one can hear your red blood cells scream
There are many reasons why space is the final frontier, not least of which are the major health issues space travel places on the human body. So until a shady billionaire finds an alien protomolecule on a Saturnian moon and starts splicing it with human DNA so we can hang out in space all day without a spacesuit, we’re stuck with things like space anemia, a condition many astronauts develop after extended time in space.
Space anemia has been known for many years, but it was assumed that it developed as a reaction to microgravity and was a short-term phenomenon only – a temporary compensation as fluids and blood volume adjusted themselves. But as new research shows, that assumption seems to be wrong.
For the study, published in Nature Medicine, 13 astronauts who were in space for at least 120 days – long enough for all their red blood cells to have been produced in space – had their blood tested consistently. Before their flights, the astronauts created and destroyed 2 million red blood cells per second, but while they were in space, they destroyed 3 million cells per second. Notably, this process continued for the entire duration of the space flight. So, not a temporary reaction.
Consequently, 5 of the 13 astronauts developed anemia when they returned to Earth. (Interesting space fact: Having fewer blood cells isn’t a problem while you’re in space; the effects of anemia only manifest when the body returns to full gravity.) The anemia disappeared after a few months, but the astronauts were still destroying 30% more red blood cells a year after their spaceflight than they were before leaving Earth.
You may be thinking: Well, if they were destroying 50% more red blood cells while in space, how come they didn’t all develop severe anemia? The researchers theorized that production was boosted as well, which sounds like a good thing. The body is compensating, as it should. Unfortunately, that increased production stresses bone marrow function and the demand for energy spikes. That’s not such a good thing. And of course, many of the astronauts got anemia anyway.
To tackle the issue, the researchers emphasized the importance of feeding astronauts a proper diet, plus potential supplements before spaceflight. So don’t worry, Captain Kirk will be able to arm wrestle Klingons and romance suspiciously human-looking aliens without fear of keeling over from anemia-induced fatigue. Earth will stay safe.
Tell me with your eyes
Communication can be hard, even under the best of circumstances, but for many nonverbal patients in the intensive care unit who can’t move, getting a point across to the health care team can be a huge struggle in itself.
Health care professionals have been making do with eye-blinking or head-nodding, but what if that’s just not enough? New research shows that it’s not, and there’s a more effective way for patients to say what they mean just by looking.
In a study published in the Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, researchers looked into using eye-tracking systems for nonverbal ICU patients to communicate. Eye-tracking isn’t anything new, but using it as a form of communication among nonverbal patients with critical illness hasn’t been looked at before.
How does it work? The eye-tracking system is set up in the patient’s line of sight and its various algorithms and software collect data to calculate where exactly the patient is looking. Established scores and scales assess the patient’s mood, quality of life, pain, and self-esteem.
The researchers found that participating patients were actually experiencing more negative moods, pain, and feelings of frustration than was once believed. Making this tool even more valuable for treatment adjustment and meeting patients’ needs.
In this case, it means that health care providers are getting an eyeful … of communication.
Make America grave again
Here we go again. Somebody just found something else that the United States is not the best at. To go along with math and science education, infrastructure investment, quality of life …
That’s going to go on for a while, so let’s get to the new stuff. An international group of researchers surveyed end-of-life care in 81 countries and ranked them based on the assessment of 181 experts in those countries. They looked at 13 different factors, including proper management of pain and comfort, having a clean and safe space, being treated kindly, lack of cost barriers to appropriate care, and treatments that address quality of life and don’t just extend life.
… press freedom, industrial production, racial equality, Internet connectivity …
Their report card, published in the Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, gave six countries an A, with Great Britain at the top. The other five were Ireland, Taiwan, Australia, South Korea, and Costa Rica. The lowest grade went to Paraguay in 81st place, with Lebanon, Brazil, Senegal, and Haiti just ahead.
… environmental stewardship, body-mass index, social mobility, COVID safeness …
The United States, getting a firm grasp on mediocrity, ranked 43rd. Here are some countries that did better: North Macedonia (7th), Sri Lanka (16th), Uganda (31st), and Uruguay 33rd). In the United States, “we spend so much money trying to get people to live longer, but we don’t spend enough money in helping people die better,” lead author Eric A. Finkelstein, PhD, said in a written statement.
… economic stability, and soccer; we’re also not the best at dying. Wait, did we already say that?
The face mask that launched a thousand ships
Face masks, clearly, have been a source of social strife during the pandemic. People may not agree on mandates, but a mask can be a pretty-low-maintenance face shield if you don’t feel like putting on make-up or want to cover up some blemishes.
Before the pandemic, people thought that those wearing face masks were less attractive because the masks represented illness or disease, according to Dr. Michael Lewis of Cardiff (Wales) University. Back then, no one really wore masks besides doctors and nurses, so if you saw someone wearing one on the street, you probably wondered what they were trying to hide.
Now, though, the subject of face mask attractiveness has been revisited by Dr. Lewis and his associate, Oliver Hies, who found that face masks now make people more attractive.
“Our study suggests faces are considered most attractive when covered by medical face masks. … At a time when we feel vulnerable, we may find the wearing of medical masks reassuring and so feel more positive towards the wearer,” Dr. Lewis told the Guardian.
He suggested that we’re no longer looking at people wearing a mask as disease riddled, but rather doing their part to protect society. Or maybe we focus more on someone’s eyes when that’s all there is to look at. Or, maybe we wind up making up what the rest of someone’s face looks like to meet our attractiveness criteria.
However you feel about masks, they’re cheaper than plastic surgery. And you can go out wearing a new face every day.
In space, no one can hear your red blood cells scream
There are many reasons why space is the final frontier, not least of which are the major health issues space travel places on the human body. So until a shady billionaire finds an alien protomolecule on a Saturnian moon and starts splicing it with human DNA so we can hang out in space all day without a spacesuit, we’re stuck with things like space anemia, a condition many astronauts develop after extended time in space.
Space anemia has been known for many years, but it was assumed that it developed as a reaction to microgravity and was a short-term phenomenon only – a temporary compensation as fluids and blood volume adjusted themselves. But as new research shows, that assumption seems to be wrong.
For the study, published in Nature Medicine, 13 astronauts who were in space for at least 120 days – long enough for all their red blood cells to have been produced in space – had their blood tested consistently. Before their flights, the astronauts created and destroyed 2 million red blood cells per second, but while they were in space, they destroyed 3 million cells per second. Notably, this process continued for the entire duration of the space flight. So, not a temporary reaction.
Consequently, 5 of the 13 astronauts developed anemia when they returned to Earth. (Interesting space fact: Having fewer blood cells isn’t a problem while you’re in space; the effects of anemia only manifest when the body returns to full gravity.) The anemia disappeared after a few months, but the astronauts were still destroying 30% more red blood cells a year after their spaceflight than they were before leaving Earth.
You may be thinking: Well, if they were destroying 50% more red blood cells while in space, how come they didn’t all develop severe anemia? The researchers theorized that production was boosted as well, which sounds like a good thing. The body is compensating, as it should. Unfortunately, that increased production stresses bone marrow function and the demand for energy spikes. That’s not such a good thing. And of course, many of the astronauts got anemia anyway.
To tackle the issue, the researchers emphasized the importance of feeding astronauts a proper diet, plus potential supplements before spaceflight. So don’t worry, Captain Kirk will be able to arm wrestle Klingons and romance suspiciously human-looking aliens without fear of keeling over from anemia-induced fatigue. Earth will stay safe.
Tell me with your eyes
Communication can be hard, even under the best of circumstances, but for many nonverbal patients in the intensive care unit who can’t move, getting a point across to the health care team can be a huge struggle in itself.
Health care professionals have been making do with eye-blinking or head-nodding, but what if that’s just not enough? New research shows that it’s not, and there’s a more effective way for patients to say what they mean just by looking.
In a study published in the Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, researchers looked into using eye-tracking systems for nonverbal ICU patients to communicate. Eye-tracking isn’t anything new, but using it as a form of communication among nonverbal patients with critical illness hasn’t been looked at before.
How does it work? The eye-tracking system is set up in the patient’s line of sight and its various algorithms and software collect data to calculate where exactly the patient is looking. Established scores and scales assess the patient’s mood, quality of life, pain, and self-esteem.
The researchers found that participating patients were actually experiencing more negative moods, pain, and feelings of frustration than was once believed. Making this tool even more valuable for treatment adjustment and meeting patients’ needs.
In this case, it means that health care providers are getting an eyeful … of communication.
Make America grave again
Here we go again. Somebody just found something else that the United States is not the best at. To go along with math and science education, infrastructure investment, quality of life …
That’s going to go on for a while, so let’s get to the new stuff. An international group of researchers surveyed end-of-life care in 81 countries and ranked them based on the assessment of 181 experts in those countries. They looked at 13 different factors, including proper management of pain and comfort, having a clean and safe space, being treated kindly, lack of cost barriers to appropriate care, and treatments that address quality of life and don’t just extend life.
… press freedom, industrial production, racial equality, Internet connectivity …
Their report card, published in the Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, gave six countries an A, with Great Britain at the top. The other five were Ireland, Taiwan, Australia, South Korea, and Costa Rica. The lowest grade went to Paraguay in 81st place, with Lebanon, Brazil, Senegal, and Haiti just ahead.
… environmental stewardship, body-mass index, social mobility, COVID safeness …
The United States, getting a firm grasp on mediocrity, ranked 43rd. Here are some countries that did better: North Macedonia (7th), Sri Lanka (16th), Uganda (31st), and Uruguay 33rd). In the United States, “we spend so much money trying to get people to live longer, but we don’t spend enough money in helping people die better,” lead author Eric A. Finkelstein, PhD, said in a written statement.
… economic stability, and soccer; we’re also not the best at dying. Wait, did we already say that?
The face mask that launched a thousand ships
Face masks, clearly, have been a source of social strife during the pandemic. People may not agree on mandates, but a mask can be a pretty-low-maintenance face shield if you don’t feel like putting on make-up or want to cover up some blemishes.
Before the pandemic, people thought that those wearing face masks were less attractive because the masks represented illness or disease, according to Dr. Michael Lewis of Cardiff (Wales) University. Back then, no one really wore masks besides doctors and nurses, so if you saw someone wearing one on the street, you probably wondered what they were trying to hide.
Now, though, the subject of face mask attractiveness has been revisited by Dr. Lewis and his associate, Oliver Hies, who found that face masks now make people more attractive.
“Our study suggests faces are considered most attractive when covered by medical face masks. … At a time when we feel vulnerable, we may find the wearing of medical masks reassuring and so feel more positive towards the wearer,” Dr. Lewis told the Guardian.
He suggested that we’re no longer looking at people wearing a mask as disease riddled, but rather doing their part to protect society. Or maybe we focus more on someone’s eyes when that’s all there is to look at. Or, maybe we wind up making up what the rest of someone’s face looks like to meet our attractiveness criteria.
However you feel about masks, they’re cheaper than plastic surgery. And you can go out wearing a new face every day.
In space, no one can hear your red blood cells scream
There are many reasons why space is the final frontier, not least of which are the major health issues space travel places on the human body. So until a shady billionaire finds an alien protomolecule on a Saturnian moon and starts splicing it with human DNA so we can hang out in space all day without a spacesuit, we’re stuck with things like space anemia, a condition many astronauts develop after extended time in space.
Space anemia has been known for many years, but it was assumed that it developed as a reaction to microgravity and was a short-term phenomenon only – a temporary compensation as fluids and blood volume adjusted themselves. But as new research shows, that assumption seems to be wrong.
For the study, published in Nature Medicine, 13 astronauts who were in space for at least 120 days – long enough for all their red blood cells to have been produced in space – had their blood tested consistently. Before their flights, the astronauts created and destroyed 2 million red blood cells per second, but while they were in space, they destroyed 3 million cells per second. Notably, this process continued for the entire duration of the space flight. So, not a temporary reaction.
Consequently, 5 of the 13 astronauts developed anemia when they returned to Earth. (Interesting space fact: Having fewer blood cells isn’t a problem while you’re in space; the effects of anemia only manifest when the body returns to full gravity.) The anemia disappeared after a few months, but the astronauts were still destroying 30% more red blood cells a year after their spaceflight than they were before leaving Earth.
You may be thinking: Well, if they were destroying 50% more red blood cells while in space, how come they didn’t all develop severe anemia? The researchers theorized that production was boosted as well, which sounds like a good thing. The body is compensating, as it should. Unfortunately, that increased production stresses bone marrow function and the demand for energy spikes. That’s not such a good thing. And of course, many of the astronauts got anemia anyway.
To tackle the issue, the researchers emphasized the importance of feeding astronauts a proper diet, plus potential supplements before spaceflight. So don’t worry, Captain Kirk will be able to arm wrestle Klingons and romance suspiciously human-looking aliens without fear of keeling over from anemia-induced fatigue. Earth will stay safe.
Tell me with your eyes
Communication can be hard, even under the best of circumstances, but for many nonverbal patients in the intensive care unit who can’t move, getting a point across to the health care team can be a huge struggle in itself.
Health care professionals have been making do with eye-blinking or head-nodding, but what if that’s just not enough? New research shows that it’s not, and there’s a more effective way for patients to say what they mean just by looking.
In a study published in the Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, researchers looked into using eye-tracking systems for nonverbal ICU patients to communicate. Eye-tracking isn’t anything new, but using it as a form of communication among nonverbal patients with critical illness hasn’t been looked at before.
How does it work? The eye-tracking system is set up in the patient’s line of sight and its various algorithms and software collect data to calculate where exactly the patient is looking. Established scores and scales assess the patient’s mood, quality of life, pain, and self-esteem.
The researchers found that participating patients were actually experiencing more negative moods, pain, and feelings of frustration than was once believed. Making this tool even more valuable for treatment adjustment and meeting patients’ needs.
In this case, it means that health care providers are getting an eyeful … of communication.
Make America grave again
Here we go again. Somebody just found something else that the United States is not the best at. To go along with math and science education, infrastructure investment, quality of life …
That’s going to go on for a while, so let’s get to the new stuff. An international group of researchers surveyed end-of-life care in 81 countries and ranked them based on the assessment of 181 experts in those countries. They looked at 13 different factors, including proper management of pain and comfort, having a clean and safe space, being treated kindly, lack of cost barriers to appropriate care, and treatments that address quality of life and don’t just extend life.
… press freedom, industrial production, racial equality, Internet connectivity …
Their report card, published in the Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, gave six countries an A, with Great Britain at the top. The other five were Ireland, Taiwan, Australia, South Korea, and Costa Rica. The lowest grade went to Paraguay in 81st place, with Lebanon, Brazil, Senegal, and Haiti just ahead.
… environmental stewardship, body-mass index, social mobility, COVID safeness …
The United States, getting a firm grasp on mediocrity, ranked 43rd. Here are some countries that did better: North Macedonia (7th), Sri Lanka (16th), Uganda (31st), and Uruguay 33rd). In the United States, “we spend so much money trying to get people to live longer, but we don’t spend enough money in helping people die better,” lead author Eric A. Finkelstein, PhD, said in a written statement.
… economic stability, and soccer; we’re also not the best at dying. Wait, did we already say that?
The face mask that launched a thousand ships
Face masks, clearly, have been a source of social strife during the pandemic. People may not agree on mandates, but a mask can be a pretty-low-maintenance face shield if you don’t feel like putting on make-up or want to cover up some blemishes.
Before the pandemic, people thought that those wearing face masks were less attractive because the masks represented illness or disease, according to Dr. Michael Lewis of Cardiff (Wales) University. Back then, no one really wore masks besides doctors and nurses, so if you saw someone wearing one on the street, you probably wondered what they were trying to hide.
Now, though, the subject of face mask attractiveness has been revisited by Dr. Lewis and his associate, Oliver Hies, who found that face masks now make people more attractive.
“Our study suggests faces are considered most attractive when covered by medical face masks. … At a time when we feel vulnerable, we may find the wearing of medical masks reassuring and so feel more positive towards the wearer,” Dr. Lewis told the Guardian.
He suggested that we’re no longer looking at people wearing a mask as disease riddled, but rather doing their part to protect society. Or maybe we focus more on someone’s eyes when that’s all there is to look at. Or, maybe we wind up making up what the rest of someone’s face looks like to meet our attractiveness criteria.
However you feel about masks, they’re cheaper than plastic surgery. And you can go out wearing a new face every day.
Urine for a new vaccine alternative
Urine for a new vaccine alternative
Yep, you read that right: Another vaccine alternative. Urine sounds disgusting, but you’ve got to admit, it’s resourceful at least.
Christopher Key, the leader of a group of antivaxxers known as the “Vaccine Police,” is now claiming that you should do “urine therapy,” when means drinking your own pee to ward off COVID-19. According to My. Key, “tons and tons of research” shows the benefits of drinking urine to fight COVID-19, the Guardian reported.
He doesn’t seem like the best source of information, especially since he’s been arrested in the past for refusing to wear a mask in a store. Not wanting to wear a mask in a store doesn’t seem like much, but he also believes that those who administer the COVID-19 vaccine should be “executed” and he tried to impersonate a law official toattempt to arrest a Democratic governor for vaccine mandates.
The overwhelming amount of COVID-19 misinformation has been stressful, yet sometimes laugh-worthy. Urine is not the first “cure” and probably won’t be the last. If you heard something works in a sketchy group on Facebook, it’s probably safe to assume that it absolutely does not. Please don’t recycle your urine.
Vaccine or beer? You must now choose
As the COVID-19 pandemic drags on toward its third year, the large subset of the population who refuse to get vaccinated has proved nearly intractable. Governments have tried numerous incentives to boost vaccination rates, ranging from free beer to million dollar lotteries. Needless to say, beyond their ability to generate LOTME stories, these incentives have been less than effective.
As the frankly unfairly contagious Omicron variant makes it way through the world, our friends in the Great White North have decided enough is enough. If the carrot doesn’t work, the people of Quebec are going to get the stick. Starting on Jan. 18, vaccination cards will be required to enter stores that sell alcohol or cannabis, better known as the things that have gotten us all through this pandemic.
And you know what? Cutting off the booze supply seems to be working. Christian Dubé, Quebec’s health minister, said that the number of vaccination appointments had quadrupled in the new year, rising from 1,500 per day to 6,000 per day, according to the CTV News report. Now, those aren’t massive numbers, but this is big empty Canada we’re talking about, and the unvaccinated make up about 10% of Quebec’s population, so 6,000 a day is quite impressive.
Mr. Dubé added that additional nonessential businesses could be added to the restriction list in the coming weeks, but we’re not sure it’ll be necessary. Those middle-aged soccer moms will do anything to secure their daily merlot. Also, alcohol and cannabis nonessential? The LOTME staff is appalled and offended at this insinuation.
All I need is the polyester that I breathe
When you do laundry, you’re probably thinking more of how to get that ketchup stain out of your white shirt than the effect it has on the environment. Well, research shows it actually has some significance.
That significance comes in the form of microfibers, which are released from natural fabrics such as cotton and from synthetic fabrics such as polyester, which are also considered to be microplastics.
The microfibers that get released in the water when we wash clothes are filtered out eventually, but the dryer is the real culprit, according to a study in Environmental Science & Technology Letters. We’re talking a discharge of up to 120 million microfiber fragments directly into the air annually from just one dryer!
Dryers, they found, emitted between 1.4-40 times more microfibers than did washing machines in previous studies. And polyester fabrics produced more fragments when load sizes increased, while fragment production from cotton fabrics remained constant.
Recent findings suggest that inhaling these microfibers can cause lung inflammation, increase cancer risk, and induce asthma attacks. The authors of the current study suggested additional filtration should be done on dryer vents to reduce the amount of pollutants emitted into the air.
Who would have thought just drying your sheets could be such a dangerous act?
It’s always in the last place you look
At least a million times every morning in this country, a million children yell something like this as they get ready for school: “Mom, have you seen my ...?”
Well, thanks to Defector.com, now we know what Mom should yell back: “Look in your weird cousin Mortimer!”
We will explain ... again.
When they’re not dealing with COVID-19, the folks who work in emergency departments spend a lot of their time removing things that are stuck in people’s bodily orifices. The U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission even keeps track of them.
So if you’re looking for the number 8 button from the TV remote, or maybe a bullet, check Mortimer’s nose. Maybe you’re missing a lollipop, a hairpin, or some espresso beans. Mortimer’s friend Beulah might have put them in her ear.
Has an earbud gone missing? Another friend of Mortimer’s went to the ED with something stuck in his throat and said that he had a “pill in one hand and his earbud in the other hand, got distracted and took the earbud instead.” Yes, that is an actual quote (via Defector) from the CPSC database.
What about that old saying that someone’s lost his marbles? Well, the ED found one of Mortimer’s marbles ... in his penis. Also a spork, and a bread twist tie, and a chopstick. No, not all at the same time. As for Beulah, a barbell and a Spider-Man action figure somehow found their way – not at the same time, thank goodness – into her vagina.
And have you ever heard someone say that they’re “not going to stand for this”? Mortimer has, so he sat down ... on a light bulb, and a rolling pin, and a billiard ball. Yup, the ED had to remove these items from his rectum.
But not all at the same time, thank goodness.
Urine for a new vaccine alternative
Yep, you read that right: Another vaccine alternative. Urine sounds disgusting, but you’ve got to admit, it’s resourceful at least.
Christopher Key, the leader of a group of antivaxxers known as the “Vaccine Police,” is now claiming that you should do “urine therapy,” when means drinking your own pee to ward off COVID-19. According to My. Key, “tons and tons of research” shows the benefits of drinking urine to fight COVID-19, the Guardian reported.
He doesn’t seem like the best source of information, especially since he’s been arrested in the past for refusing to wear a mask in a store. Not wanting to wear a mask in a store doesn’t seem like much, but he also believes that those who administer the COVID-19 vaccine should be “executed” and he tried to impersonate a law official toattempt to arrest a Democratic governor for vaccine mandates.
The overwhelming amount of COVID-19 misinformation has been stressful, yet sometimes laugh-worthy. Urine is not the first “cure” and probably won’t be the last. If you heard something works in a sketchy group on Facebook, it’s probably safe to assume that it absolutely does not. Please don’t recycle your urine.
Vaccine or beer? You must now choose
As the COVID-19 pandemic drags on toward its third year, the large subset of the population who refuse to get vaccinated has proved nearly intractable. Governments have tried numerous incentives to boost vaccination rates, ranging from free beer to million dollar lotteries. Needless to say, beyond their ability to generate LOTME stories, these incentives have been less than effective.
As the frankly unfairly contagious Omicron variant makes it way through the world, our friends in the Great White North have decided enough is enough. If the carrot doesn’t work, the people of Quebec are going to get the stick. Starting on Jan. 18, vaccination cards will be required to enter stores that sell alcohol or cannabis, better known as the things that have gotten us all through this pandemic.
And you know what? Cutting off the booze supply seems to be working. Christian Dubé, Quebec’s health minister, said that the number of vaccination appointments had quadrupled in the new year, rising from 1,500 per day to 6,000 per day, according to the CTV News report. Now, those aren’t massive numbers, but this is big empty Canada we’re talking about, and the unvaccinated make up about 10% of Quebec’s population, so 6,000 a day is quite impressive.
Mr. Dubé added that additional nonessential businesses could be added to the restriction list in the coming weeks, but we’re not sure it’ll be necessary. Those middle-aged soccer moms will do anything to secure their daily merlot. Also, alcohol and cannabis nonessential? The LOTME staff is appalled and offended at this insinuation.
All I need is the polyester that I breathe
When you do laundry, you’re probably thinking more of how to get that ketchup stain out of your white shirt than the effect it has on the environment. Well, research shows it actually has some significance.
That significance comes in the form of microfibers, which are released from natural fabrics such as cotton and from synthetic fabrics such as polyester, which are also considered to be microplastics.
The microfibers that get released in the water when we wash clothes are filtered out eventually, but the dryer is the real culprit, according to a study in Environmental Science & Technology Letters. We’re talking a discharge of up to 120 million microfiber fragments directly into the air annually from just one dryer!
Dryers, they found, emitted between 1.4-40 times more microfibers than did washing machines in previous studies. And polyester fabrics produced more fragments when load sizes increased, while fragment production from cotton fabrics remained constant.
Recent findings suggest that inhaling these microfibers can cause lung inflammation, increase cancer risk, and induce asthma attacks. The authors of the current study suggested additional filtration should be done on dryer vents to reduce the amount of pollutants emitted into the air.
Who would have thought just drying your sheets could be such a dangerous act?
It’s always in the last place you look
At least a million times every morning in this country, a million children yell something like this as they get ready for school: “Mom, have you seen my ...?”
Well, thanks to Defector.com, now we know what Mom should yell back: “Look in your weird cousin Mortimer!”
We will explain ... again.
When they’re not dealing with COVID-19, the folks who work in emergency departments spend a lot of their time removing things that are stuck in people’s bodily orifices. The U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission even keeps track of them.
So if you’re looking for the number 8 button from the TV remote, or maybe a bullet, check Mortimer’s nose. Maybe you’re missing a lollipop, a hairpin, or some espresso beans. Mortimer’s friend Beulah might have put them in her ear.
Has an earbud gone missing? Another friend of Mortimer’s went to the ED with something stuck in his throat and said that he had a “pill in one hand and his earbud in the other hand, got distracted and took the earbud instead.” Yes, that is an actual quote (via Defector) from the CPSC database.
What about that old saying that someone’s lost his marbles? Well, the ED found one of Mortimer’s marbles ... in his penis. Also a spork, and a bread twist tie, and a chopstick. No, not all at the same time. As for Beulah, a barbell and a Spider-Man action figure somehow found their way – not at the same time, thank goodness – into her vagina.
And have you ever heard someone say that they’re “not going to stand for this”? Mortimer has, so he sat down ... on a light bulb, and a rolling pin, and a billiard ball. Yup, the ED had to remove these items from his rectum.
But not all at the same time, thank goodness.
Urine for a new vaccine alternative
Yep, you read that right: Another vaccine alternative. Urine sounds disgusting, but you’ve got to admit, it’s resourceful at least.
Christopher Key, the leader of a group of antivaxxers known as the “Vaccine Police,” is now claiming that you should do “urine therapy,” when means drinking your own pee to ward off COVID-19. According to My. Key, “tons and tons of research” shows the benefits of drinking urine to fight COVID-19, the Guardian reported.
He doesn’t seem like the best source of information, especially since he’s been arrested in the past for refusing to wear a mask in a store. Not wanting to wear a mask in a store doesn’t seem like much, but he also believes that those who administer the COVID-19 vaccine should be “executed” and he tried to impersonate a law official toattempt to arrest a Democratic governor for vaccine mandates.
The overwhelming amount of COVID-19 misinformation has been stressful, yet sometimes laugh-worthy. Urine is not the first “cure” and probably won’t be the last. If you heard something works in a sketchy group on Facebook, it’s probably safe to assume that it absolutely does not. Please don’t recycle your urine.
Vaccine or beer? You must now choose
As the COVID-19 pandemic drags on toward its third year, the large subset of the population who refuse to get vaccinated has proved nearly intractable. Governments have tried numerous incentives to boost vaccination rates, ranging from free beer to million dollar lotteries. Needless to say, beyond their ability to generate LOTME stories, these incentives have been less than effective.
As the frankly unfairly contagious Omicron variant makes it way through the world, our friends in the Great White North have decided enough is enough. If the carrot doesn’t work, the people of Quebec are going to get the stick. Starting on Jan. 18, vaccination cards will be required to enter stores that sell alcohol or cannabis, better known as the things that have gotten us all through this pandemic.
And you know what? Cutting off the booze supply seems to be working. Christian Dubé, Quebec’s health minister, said that the number of vaccination appointments had quadrupled in the new year, rising from 1,500 per day to 6,000 per day, according to the CTV News report. Now, those aren’t massive numbers, but this is big empty Canada we’re talking about, and the unvaccinated make up about 10% of Quebec’s population, so 6,000 a day is quite impressive.
Mr. Dubé added that additional nonessential businesses could be added to the restriction list in the coming weeks, but we’re not sure it’ll be necessary. Those middle-aged soccer moms will do anything to secure their daily merlot. Also, alcohol and cannabis nonessential? The LOTME staff is appalled and offended at this insinuation.
All I need is the polyester that I breathe
When you do laundry, you’re probably thinking more of how to get that ketchup stain out of your white shirt than the effect it has on the environment. Well, research shows it actually has some significance.
That significance comes in the form of microfibers, which are released from natural fabrics such as cotton and from synthetic fabrics such as polyester, which are also considered to be microplastics.
The microfibers that get released in the water when we wash clothes are filtered out eventually, but the dryer is the real culprit, according to a study in Environmental Science & Technology Letters. We’re talking a discharge of up to 120 million microfiber fragments directly into the air annually from just one dryer!
Dryers, they found, emitted between 1.4-40 times more microfibers than did washing machines in previous studies. And polyester fabrics produced more fragments when load sizes increased, while fragment production from cotton fabrics remained constant.
Recent findings suggest that inhaling these microfibers can cause lung inflammation, increase cancer risk, and induce asthma attacks. The authors of the current study suggested additional filtration should be done on dryer vents to reduce the amount of pollutants emitted into the air.
Who would have thought just drying your sheets could be such a dangerous act?
It’s always in the last place you look
At least a million times every morning in this country, a million children yell something like this as they get ready for school: “Mom, have you seen my ...?”
Well, thanks to Defector.com, now we know what Mom should yell back: “Look in your weird cousin Mortimer!”
We will explain ... again.
When they’re not dealing with COVID-19, the folks who work in emergency departments spend a lot of their time removing things that are stuck in people’s bodily orifices. The U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission even keeps track of them.
So if you’re looking for the number 8 button from the TV remote, or maybe a bullet, check Mortimer’s nose. Maybe you’re missing a lollipop, a hairpin, or some espresso beans. Mortimer’s friend Beulah might have put them in her ear.
Has an earbud gone missing? Another friend of Mortimer’s went to the ED with something stuck in his throat and said that he had a “pill in one hand and his earbud in the other hand, got distracted and took the earbud instead.” Yes, that is an actual quote (via Defector) from the CPSC database.
What about that old saying that someone’s lost his marbles? Well, the ED found one of Mortimer’s marbles ... in his penis. Also a spork, and a bread twist tie, and a chopstick. No, not all at the same time. As for Beulah, a barbell and a Spider-Man action figure somehow found their way – not at the same time, thank goodness – into her vagina.
And have you ever heard someone say that they’re “not going to stand for this”? Mortimer has, so he sat down ... on a light bulb, and a rolling pin, and a billiard ball. Yup, the ED had to remove these items from his rectum.
But not all at the same time, thank goodness.
Who needs self-driving cars when we’ve got goldfish?
If a fish can drive …
Have you ever seen a sparrow swim? Have you ever seen an elephant fly? How about a goldfish driving a car? Well, one of these is not just something out of a children’s book.
In a recent study, investigators from Ben-Gurion University did the impossible and got a fish to drive a robotic car on land. How?
No, there wasn’t a tiny steering wheel inside the tank. The researchers created a tank with video recognition ability to sync with the fish. This video shows that the car, on which the tank sat, would navigate in the direction that the fish swam. The goal was to get the fish to “drive” toward a visual target, and with a little training the fish was successful regardless of start point, the researchers explained.
So what does that tell us about the brain and behavior? Shachar Givon, who was part of the research team, said the “study hints that navigational ability is universal rather than specific to the environment.”
The study’s domain transfer methodology (putting one species in the environment of another and have them cope with an unfamiliar task) shows that other animals also have the cognitive ability to transfer skills from one terrestrial environment to another.
That leads us to lesson two. Goldfish are much smarter than we think. So please don’t tap on the glass.
We prefer ‘It’s not writing a funny LOTME article’!
So many medical journals spend all their time grappling with such silly dilemmas as curing cancer or beating COVID-19. Boring! Fortunately, the BMJ dares to stand above the rest by dedicating its Christmas issue to answering the real issues in medicine. And what was the biggest question? Which is the more accurate idiom: “It’s not rocket science,” or “It’s not brain surgery”?
English researchers collected data from 329 aerospace engineers and 72 neurosurgeons who took the Great British Intelligence Test and compared the results against 18,000 people in the general public.
The engineers and neurosurgeons were basically identical in four of the six domains, but neurosurgeons had the advantage when it came to semantic problem solving and engineers had an edge at mental manipulation and attention. The aerospace engineers were identical to the public in all domains, but neurosurgeons held an advantage in problem-solving speed and a disadvantage in memory recall speed.
The researchers noted that exposure to Latin and Greek etymologies during their education gave neurosurgeons the advantage in semantic problem solving, while the aerospace engineers’ advantage in mental manipulation stems from skills taught during engineering training.
But is there a definitive answer to the question? If you’ve got an easy task in front of you, which is more accurate to say: “It’s not rocket science” or “It’s not brain surgery”? Can we get a drum roll?
It’s not brain surgery! At least, as long as the task doesn’t involve rapid problem solving. The investigators hedged further by saying that “It’s a walk in the park” is probably more accurate. Plus, “other specialties might deserve to be on that pedestal, and future work should aim to determine the most deserving profession,” they wrote. Well, at least we’ve got something to look forward to in BMJ’s next Christmas issue.
For COVID-19, a syringe is the sheep of things to come
The logical approach to fighting COVID-19 hasn’t really worked with a lot of people, so how about something more emotional?
People love animals, so they might be a good way to promote the use of vaccines and masks. Puppies are awfully cute, and so are koalas and pandas. And who can say no to a sea otter?
Well, forget it. Instead, we’ve got elephants … and sheep … and goats. Oh my.
First, elephant Santas. The Jirasartwitthaya school in Ayutthaya, Thailand, was recently visited by five elephants in Santa Claus costumes who handed out hand sanitizer and face masks to the students, Reuters said.
“I’m so glad that I got a balloon from the elephant. My heart is pounding very fast,” student Biuon Greham said. And balloons. The elephants handed out sanitizer and masks and balloons. There’s a sentence we never thought we’d write.
And those sheep and goats we mentioned? That was a different party.
Hanspeter Etzold, who “works with shepherds, companies, and animals to run team-building events in the northern German town of Schneverdingen,” according to Reuters, had an idea to promote the use of the COVID-19 vaccine. And yes, it involved sheep and goats.
Mr. Etzold worked with shepherd Wiebke Schmidt-Kochan, who arranged her 700 goats and sheep into the shape of a 100-meter-long syringe using bits of bread laying on the ground. “Sheep are such likable animals – maybe they can get the message over better,” Mr. Etzold told AP.
If those are the carrots in an animals-as-carrots-and-sticks approach, then maybe this golf-club-chomping crab could be the stick. We’re certainly not going to argue with it.
To be or not to be … seen
Increased Zoom meetings have been another side effect of the COVID-19 pandemic as more and more people have been working and learning from home.
A recent study from Washington State University looked at two groups of people who Zoomed on a regular basis: employees and students. Individuals who made the change to remote work/learning were surveyed in the summer and fall of 2020. They completed assessments with questions on their work/classes and their level of self-consciousness.
Those with low self-esteem did not enjoy having to see themselves on camera, and those with higher self-esteem actually enjoyed it more. “Most people believe that seeing yourself during virtual meetings contributes to making the overall experience worse, but that’s not what showed up in my data,” said Kristine Kuhn, PhD, the study’s author.
Dr. Kuhn found that having the choice of whether to have the camera on made a big difference in how the participants felt. Having that control made it a more positive experience. Most professors/bosses would probably like to see the faces of those in the Zoom meetings, but it might be better to let people choose for themselves. The unbrushed-hair club would certainly agree.
If a fish can drive …
Have you ever seen a sparrow swim? Have you ever seen an elephant fly? How about a goldfish driving a car? Well, one of these is not just something out of a children’s book.
In a recent study, investigators from Ben-Gurion University did the impossible and got a fish to drive a robotic car on land. How?
No, there wasn’t a tiny steering wheel inside the tank. The researchers created a tank with video recognition ability to sync with the fish. This video shows that the car, on which the tank sat, would navigate in the direction that the fish swam. The goal was to get the fish to “drive” toward a visual target, and with a little training the fish was successful regardless of start point, the researchers explained.
So what does that tell us about the brain and behavior? Shachar Givon, who was part of the research team, said the “study hints that navigational ability is universal rather than specific to the environment.”
The study’s domain transfer methodology (putting one species in the environment of another and have them cope with an unfamiliar task) shows that other animals also have the cognitive ability to transfer skills from one terrestrial environment to another.
That leads us to lesson two. Goldfish are much smarter than we think. So please don’t tap on the glass.
We prefer ‘It’s not writing a funny LOTME article’!
So many medical journals spend all their time grappling with such silly dilemmas as curing cancer or beating COVID-19. Boring! Fortunately, the BMJ dares to stand above the rest by dedicating its Christmas issue to answering the real issues in medicine. And what was the biggest question? Which is the more accurate idiom: “It’s not rocket science,” or “It’s not brain surgery”?
English researchers collected data from 329 aerospace engineers and 72 neurosurgeons who took the Great British Intelligence Test and compared the results against 18,000 people in the general public.
The engineers and neurosurgeons were basically identical in four of the six domains, but neurosurgeons had the advantage when it came to semantic problem solving and engineers had an edge at mental manipulation and attention. The aerospace engineers were identical to the public in all domains, but neurosurgeons held an advantage in problem-solving speed and a disadvantage in memory recall speed.
The researchers noted that exposure to Latin and Greek etymologies during their education gave neurosurgeons the advantage in semantic problem solving, while the aerospace engineers’ advantage in mental manipulation stems from skills taught during engineering training.
But is there a definitive answer to the question? If you’ve got an easy task in front of you, which is more accurate to say: “It’s not rocket science” or “It’s not brain surgery”? Can we get a drum roll?
It’s not brain surgery! At least, as long as the task doesn’t involve rapid problem solving. The investigators hedged further by saying that “It’s a walk in the park” is probably more accurate. Plus, “other specialties might deserve to be on that pedestal, and future work should aim to determine the most deserving profession,” they wrote. Well, at least we’ve got something to look forward to in BMJ’s next Christmas issue.
For COVID-19, a syringe is the sheep of things to come
The logical approach to fighting COVID-19 hasn’t really worked with a lot of people, so how about something more emotional?
People love animals, so they might be a good way to promote the use of vaccines and masks. Puppies are awfully cute, and so are koalas and pandas. And who can say no to a sea otter?
Well, forget it. Instead, we’ve got elephants … and sheep … and goats. Oh my.
First, elephant Santas. The Jirasartwitthaya school in Ayutthaya, Thailand, was recently visited by five elephants in Santa Claus costumes who handed out hand sanitizer and face masks to the students, Reuters said.
“I’m so glad that I got a balloon from the elephant. My heart is pounding very fast,” student Biuon Greham said. And balloons. The elephants handed out sanitizer and masks and balloons. There’s a sentence we never thought we’d write.
And those sheep and goats we mentioned? That was a different party.
Hanspeter Etzold, who “works with shepherds, companies, and animals to run team-building events in the northern German town of Schneverdingen,” according to Reuters, had an idea to promote the use of the COVID-19 vaccine. And yes, it involved sheep and goats.
Mr. Etzold worked with shepherd Wiebke Schmidt-Kochan, who arranged her 700 goats and sheep into the shape of a 100-meter-long syringe using bits of bread laying on the ground. “Sheep are such likable animals – maybe they can get the message over better,” Mr. Etzold told AP.
If those are the carrots in an animals-as-carrots-and-sticks approach, then maybe this golf-club-chomping crab could be the stick. We’re certainly not going to argue with it.
To be or not to be … seen
Increased Zoom meetings have been another side effect of the COVID-19 pandemic as more and more people have been working and learning from home.
A recent study from Washington State University looked at two groups of people who Zoomed on a regular basis: employees and students. Individuals who made the change to remote work/learning were surveyed in the summer and fall of 2020. They completed assessments with questions on their work/classes and their level of self-consciousness.
Those with low self-esteem did not enjoy having to see themselves on camera, and those with higher self-esteem actually enjoyed it more. “Most people believe that seeing yourself during virtual meetings contributes to making the overall experience worse, but that’s not what showed up in my data,” said Kristine Kuhn, PhD, the study’s author.
Dr. Kuhn found that having the choice of whether to have the camera on made a big difference in how the participants felt. Having that control made it a more positive experience. Most professors/bosses would probably like to see the faces of those in the Zoom meetings, but it might be better to let people choose for themselves. The unbrushed-hair club would certainly agree.
If a fish can drive …
Have you ever seen a sparrow swim? Have you ever seen an elephant fly? How about a goldfish driving a car? Well, one of these is not just something out of a children’s book.
In a recent study, investigators from Ben-Gurion University did the impossible and got a fish to drive a robotic car on land. How?
No, there wasn’t a tiny steering wheel inside the tank. The researchers created a tank with video recognition ability to sync with the fish. This video shows that the car, on which the tank sat, would navigate in the direction that the fish swam. The goal was to get the fish to “drive” toward a visual target, and with a little training the fish was successful regardless of start point, the researchers explained.
So what does that tell us about the brain and behavior? Shachar Givon, who was part of the research team, said the “study hints that navigational ability is universal rather than specific to the environment.”
The study’s domain transfer methodology (putting one species in the environment of another and have them cope with an unfamiliar task) shows that other animals also have the cognitive ability to transfer skills from one terrestrial environment to another.
That leads us to lesson two. Goldfish are much smarter than we think. So please don’t tap on the glass.
We prefer ‘It’s not writing a funny LOTME article’!
So many medical journals spend all their time grappling with such silly dilemmas as curing cancer or beating COVID-19. Boring! Fortunately, the BMJ dares to stand above the rest by dedicating its Christmas issue to answering the real issues in medicine. And what was the biggest question? Which is the more accurate idiom: “It’s not rocket science,” or “It’s not brain surgery”?
English researchers collected data from 329 aerospace engineers and 72 neurosurgeons who took the Great British Intelligence Test and compared the results against 18,000 people in the general public.
The engineers and neurosurgeons were basically identical in four of the six domains, but neurosurgeons had the advantage when it came to semantic problem solving and engineers had an edge at mental manipulation and attention. The aerospace engineers were identical to the public in all domains, but neurosurgeons held an advantage in problem-solving speed and a disadvantage in memory recall speed.
The researchers noted that exposure to Latin and Greek etymologies during their education gave neurosurgeons the advantage in semantic problem solving, while the aerospace engineers’ advantage in mental manipulation stems from skills taught during engineering training.
But is there a definitive answer to the question? If you’ve got an easy task in front of you, which is more accurate to say: “It’s not rocket science” or “It’s not brain surgery”? Can we get a drum roll?
It’s not brain surgery! At least, as long as the task doesn’t involve rapid problem solving. The investigators hedged further by saying that “It’s a walk in the park” is probably more accurate. Plus, “other specialties might deserve to be on that pedestal, and future work should aim to determine the most deserving profession,” they wrote. Well, at least we’ve got something to look forward to in BMJ’s next Christmas issue.
For COVID-19, a syringe is the sheep of things to come
The logical approach to fighting COVID-19 hasn’t really worked with a lot of people, so how about something more emotional?
People love animals, so they might be a good way to promote the use of vaccines and masks. Puppies are awfully cute, and so are koalas and pandas. And who can say no to a sea otter?
Well, forget it. Instead, we’ve got elephants … and sheep … and goats. Oh my.
First, elephant Santas. The Jirasartwitthaya school in Ayutthaya, Thailand, was recently visited by five elephants in Santa Claus costumes who handed out hand sanitizer and face masks to the students, Reuters said.
“I’m so glad that I got a balloon from the elephant. My heart is pounding very fast,” student Biuon Greham said. And balloons. The elephants handed out sanitizer and masks and balloons. There’s a sentence we never thought we’d write.
And those sheep and goats we mentioned? That was a different party.
Hanspeter Etzold, who “works with shepherds, companies, and animals to run team-building events in the northern German town of Schneverdingen,” according to Reuters, had an idea to promote the use of the COVID-19 vaccine. And yes, it involved sheep and goats.
Mr. Etzold worked with shepherd Wiebke Schmidt-Kochan, who arranged her 700 goats and sheep into the shape of a 100-meter-long syringe using bits of bread laying on the ground. “Sheep are such likable animals – maybe they can get the message over better,” Mr. Etzold told AP.
If those are the carrots in an animals-as-carrots-and-sticks approach, then maybe this golf-club-chomping crab could be the stick. We’re certainly not going to argue with it.
To be or not to be … seen
Increased Zoom meetings have been another side effect of the COVID-19 pandemic as more and more people have been working and learning from home.
A recent study from Washington State University looked at two groups of people who Zoomed on a regular basis: employees and students. Individuals who made the change to remote work/learning were surveyed in the summer and fall of 2020. They completed assessments with questions on their work/classes and their level of self-consciousness.
Those with low self-esteem did not enjoy having to see themselves on camera, and those with higher self-esteem actually enjoyed it more. “Most people believe that seeing yourself during virtual meetings contributes to making the overall experience worse, but that’s not what showed up in my data,” said Kristine Kuhn, PhD, the study’s author.
Dr. Kuhn found that having the choice of whether to have the camera on made a big difference in how the participants felt. Having that control made it a more positive experience. Most professors/bosses would probably like to see the faces of those in the Zoom meetings, but it might be better to let people choose for themselves. The unbrushed-hair club would certainly agree.
A very strange place to find a tooth
A nose for the tooth
Have you ever had a stuffy nose that just wouldn’t go away? Those irritating head colds have nothing on the stuffy nose a man in New York recently had to go through. A stuffy nose to top all stuffy noses. One stuffy nose to rule them all, as it were.
This man went to a Mount Sinai clinic with difficulty breathing through his right nostril, a problem that had been going on for years. Let us repeat that: A stuffy nose that lasted for years. The exam revealed a white mass jutting through the back of the septum and a CT scan confirmed the diagnosis. Perhaps you’ve already guessed, since the headline does give things away. Yes, this man had a tooth growing into his nose.
The problem was a half-inch-long ectopic tooth. Ectopic teeth are rare, occurring in less than 1% of people, but an ectopic tooth growing backward into the nasal cavity? Well, that’s so uncommon that this man got a case report in the New England Journal of Medicine.
This story does have a happy ending. Not all ectopic teeth need to be treated, but this one really did have to go. The offending tooth was surgically removed and, at a 3-month follow-up, the stuffy nose issue was completely resolved. So our friend gets the best of both worlds: His issue gets cured and he gets a case report in a major medical publication. If that’s not living the dream, we don’t know what is, and that’s the tooth.
Lettuce recommend you a sleep aid
Lettuce is great for many things. The star in a salad? Of course. The fresh element in a BLT? Yep. A sleep aid? According to a TikTok hack with almost 5 million views, the pinch hitter in a sandwich is switching leagues to be used like a tea for faster sleep. But, does it really work? Researchers say yes and no, according to a recent report at Tyla.com.
Studies conducted in 2013 and 2017 pointed toward a compound called lactucin, which is found in the plant’s n-butanol fraction. In the 2013 study, mice that received n-butanol fraction fell asleep faster and stayed asleep longer. In 2017, researchers found that lettuce made mice sleep longer and helped protect against cell inflammation and damage.
OK, so it works on mice. But what about humans? In the TikTok video, user Shapla Hoque pours hot water on a few lettuce leaves in a mug with a peppermint tea bag (for flavor). After 10 minutes, when the leaves are soaked and soggy, she removes them and drinks the lettuce tea. By the end of the video she’s visibly drowsy and ready to crash. Does this hold water?
Here’s the no. Dr. Charlotte Norton of the Slimming Clinic told Tyla.com that yeah, there are some properties in lettuce that will help you fall asleep, such as lactucarium, which is prominent in romaine. But you would need a massive amount of lettuce to get any effect. The TikTok video, she said, is an example of the placebo effect.
Brains get a rise out of Viagra
A lot of medications are used off label. Antidepressants for COVID have taken the cake recently, but here’s a new one: Viagra for Alzheimer’s disease.
Although there’s no definite link yet between the two, neuron models derived from induced pluripotent stem cells from patients with Alzheimer’s suggest that sildenafil increases neurite growth and decreases phospho-tau expression, Jiansong Fang, PhD, of the Cleveland Clinic, and associates said in Nature Aging.
Their research is an attempt to find untapped sources of new treatments among existing drugs. They began the search with 1,600 approved drugs and focused on those that target the buildup of beta amyloid and tau proteins in the brain, according to the Daily Beast.
Since sildenafil is obviously for men, more research will need to be done on how this drug affects women. Don’t start stocking up just yet.
Omicron is not a social-distancing robot
COVID, safe to say, has not been your typical, run-of-the-mill pandemic. People have protested social distancing. People have protested lockdowns. People have protested mask mandates. People have protested vaccine mandates. People have protested people protesting vaccine mandates.
Someone used a fake arm to get a COVID vaccine card. People have tried to reverse their COVID vaccinations. People had COVID contamination parties.
The common denominator? People. Humans. Maybe what we need is a nonhuman intervention. To fight COVID, we need a hero. A robotic hero.
And where can we find such a hero? The University of Maryland, of course, where computer scientists and engineers are working on an autonomous mobile robot to enforce indoor social-distancing rules.
Their robot can detect lapses in social distancing using cameras, both thermal and visual, along with a LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) sensor. It then sorts the offenders into various groups depending on whether they are standing still or moving and predicts their future movement using a state-of-the-art hybrid collision avoidance method known as Frozone, Adarsh Jagan Sathyamoorthy and associates explained in PLOS One.
“Once it reaches the breach, the robot encourages people to move apart via text that appears on a mounted display,” ScienceDaily said.
Maybe you were expecting a Terminator-type robot coming to enforce social distancing requirements rather than a simple text message. Let’s just hope that all COVID guidelines are followed, including social distancing, so the pandemic will finally end and won’t “be back.”
A nose for the tooth
Have you ever had a stuffy nose that just wouldn’t go away? Those irritating head colds have nothing on the stuffy nose a man in New York recently had to go through. A stuffy nose to top all stuffy noses. One stuffy nose to rule them all, as it were.
This man went to a Mount Sinai clinic with difficulty breathing through his right nostril, a problem that had been going on for years. Let us repeat that: A stuffy nose that lasted for years. The exam revealed a white mass jutting through the back of the septum and a CT scan confirmed the diagnosis. Perhaps you’ve already guessed, since the headline does give things away. Yes, this man had a tooth growing into his nose.
The problem was a half-inch-long ectopic tooth. Ectopic teeth are rare, occurring in less than 1% of people, but an ectopic tooth growing backward into the nasal cavity? Well, that’s so uncommon that this man got a case report in the New England Journal of Medicine.
This story does have a happy ending. Not all ectopic teeth need to be treated, but this one really did have to go. The offending tooth was surgically removed and, at a 3-month follow-up, the stuffy nose issue was completely resolved. So our friend gets the best of both worlds: His issue gets cured and he gets a case report in a major medical publication. If that’s not living the dream, we don’t know what is, and that’s the tooth.
Lettuce recommend you a sleep aid
Lettuce is great for many things. The star in a salad? Of course. The fresh element in a BLT? Yep. A sleep aid? According to a TikTok hack with almost 5 million views, the pinch hitter in a sandwich is switching leagues to be used like a tea for faster sleep. But, does it really work? Researchers say yes and no, according to a recent report at Tyla.com.
Studies conducted in 2013 and 2017 pointed toward a compound called lactucin, which is found in the plant’s n-butanol fraction. In the 2013 study, mice that received n-butanol fraction fell asleep faster and stayed asleep longer. In 2017, researchers found that lettuce made mice sleep longer and helped protect against cell inflammation and damage.
OK, so it works on mice. But what about humans? In the TikTok video, user Shapla Hoque pours hot water on a few lettuce leaves in a mug with a peppermint tea bag (for flavor). After 10 minutes, when the leaves are soaked and soggy, she removes them and drinks the lettuce tea. By the end of the video she’s visibly drowsy and ready to crash. Does this hold water?
Here’s the no. Dr. Charlotte Norton of the Slimming Clinic told Tyla.com that yeah, there are some properties in lettuce that will help you fall asleep, such as lactucarium, which is prominent in romaine. But you would need a massive amount of lettuce to get any effect. The TikTok video, she said, is an example of the placebo effect.
Brains get a rise out of Viagra
A lot of medications are used off label. Antidepressants for COVID have taken the cake recently, but here’s a new one: Viagra for Alzheimer’s disease.
Although there’s no definite link yet between the two, neuron models derived from induced pluripotent stem cells from patients with Alzheimer’s suggest that sildenafil increases neurite growth and decreases phospho-tau expression, Jiansong Fang, PhD, of the Cleveland Clinic, and associates said in Nature Aging.
Their research is an attempt to find untapped sources of new treatments among existing drugs. They began the search with 1,600 approved drugs and focused on those that target the buildup of beta amyloid and tau proteins in the brain, according to the Daily Beast.
Since sildenafil is obviously for men, more research will need to be done on how this drug affects women. Don’t start stocking up just yet.
Omicron is not a social-distancing robot
COVID, safe to say, has not been your typical, run-of-the-mill pandemic. People have protested social distancing. People have protested lockdowns. People have protested mask mandates. People have protested vaccine mandates. People have protested people protesting vaccine mandates.
Someone used a fake arm to get a COVID vaccine card. People have tried to reverse their COVID vaccinations. People had COVID contamination parties.
The common denominator? People. Humans. Maybe what we need is a nonhuman intervention. To fight COVID, we need a hero. A robotic hero.
And where can we find such a hero? The University of Maryland, of course, where computer scientists and engineers are working on an autonomous mobile robot to enforce indoor social-distancing rules.
Their robot can detect lapses in social distancing using cameras, both thermal and visual, along with a LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) sensor. It then sorts the offenders into various groups depending on whether they are standing still or moving and predicts their future movement using a state-of-the-art hybrid collision avoidance method known as Frozone, Adarsh Jagan Sathyamoorthy and associates explained in PLOS One.
“Once it reaches the breach, the robot encourages people to move apart via text that appears on a mounted display,” ScienceDaily said.
Maybe you were expecting a Terminator-type robot coming to enforce social distancing requirements rather than a simple text message. Let’s just hope that all COVID guidelines are followed, including social distancing, so the pandemic will finally end and won’t “be back.”
A nose for the tooth
Have you ever had a stuffy nose that just wouldn’t go away? Those irritating head colds have nothing on the stuffy nose a man in New York recently had to go through. A stuffy nose to top all stuffy noses. One stuffy nose to rule them all, as it were.
This man went to a Mount Sinai clinic with difficulty breathing through his right nostril, a problem that had been going on for years. Let us repeat that: A stuffy nose that lasted for years. The exam revealed a white mass jutting through the back of the septum and a CT scan confirmed the diagnosis. Perhaps you’ve already guessed, since the headline does give things away. Yes, this man had a tooth growing into his nose.
The problem was a half-inch-long ectopic tooth. Ectopic teeth are rare, occurring in less than 1% of people, but an ectopic tooth growing backward into the nasal cavity? Well, that’s so uncommon that this man got a case report in the New England Journal of Medicine.
This story does have a happy ending. Not all ectopic teeth need to be treated, but this one really did have to go. The offending tooth was surgically removed and, at a 3-month follow-up, the stuffy nose issue was completely resolved. So our friend gets the best of both worlds: His issue gets cured and he gets a case report in a major medical publication. If that’s not living the dream, we don’t know what is, and that’s the tooth.
Lettuce recommend you a sleep aid
Lettuce is great for many things. The star in a salad? Of course. The fresh element in a BLT? Yep. A sleep aid? According to a TikTok hack with almost 5 million views, the pinch hitter in a sandwich is switching leagues to be used like a tea for faster sleep. But, does it really work? Researchers say yes and no, according to a recent report at Tyla.com.
Studies conducted in 2013 and 2017 pointed toward a compound called lactucin, which is found in the plant’s n-butanol fraction. In the 2013 study, mice that received n-butanol fraction fell asleep faster and stayed asleep longer. In 2017, researchers found that lettuce made mice sleep longer and helped protect against cell inflammation and damage.
OK, so it works on mice. But what about humans? In the TikTok video, user Shapla Hoque pours hot water on a few lettuce leaves in a mug with a peppermint tea bag (for flavor). After 10 minutes, when the leaves are soaked and soggy, she removes them and drinks the lettuce tea. By the end of the video she’s visibly drowsy and ready to crash. Does this hold water?
Here’s the no. Dr. Charlotte Norton of the Slimming Clinic told Tyla.com that yeah, there are some properties in lettuce that will help you fall asleep, such as lactucarium, which is prominent in romaine. But you would need a massive amount of lettuce to get any effect. The TikTok video, she said, is an example of the placebo effect.
Brains get a rise out of Viagra
A lot of medications are used off label. Antidepressants for COVID have taken the cake recently, but here’s a new one: Viagra for Alzheimer’s disease.
Although there’s no definite link yet between the two, neuron models derived from induced pluripotent stem cells from patients with Alzheimer’s suggest that sildenafil increases neurite growth and decreases phospho-tau expression, Jiansong Fang, PhD, of the Cleveland Clinic, and associates said in Nature Aging.
Their research is an attempt to find untapped sources of new treatments among existing drugs. They began the search with 1,600 approved drugs and focused on those that target the buildup of beta amyloid and tau proteins in the brain, according to the Daily Beast.
Since sildenafil is obviously for men, more research will need to be done on how this drug affects women. Don’t start stocking up just yet.
Omicron is not a social-distancing robot
COVID, safe to say, has not been your typical, run-of-the-mill pandemic. People have protested social distancing. People have protested lockdowns. People have protested mask mandates. People have protested vaccine mandates. People have protested people protesting vaccine mandates.
Someone used a fake arm to get a COVID vaccine card. People have tried to reverse their COVID vaccinations. People had COVID contamination parties.
The common denominator? People. Humans. Maybe what we need is a nonhuman intervention. To fight COVID, we need a hero. A robotic hero.
And where can we find such a hero? The University of Maryland, of course, where computer scientists and engineers are working on an autonomous mobile robot to enforce indoor social-distancing rules.
Their robot can detect lapses in social distancing using cameras, both thermal and visual, along with a LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) sensor. It then sorts the offenders into various groups depending on whether they are standing still or moving and predicts their future movement using a state-of-the-art hybrid collision avoidance method known as Frozone, Adarsh Jagan Sathyamoorthy and associates explained in PLOS One.
“Once it reaches the breach, the robot encourages people to move apart via text that appears on a mounted display,” ScienceDaily said.
Maybe you were expecting a Terminator-type robot coming to enforce social distancing requirements rather than a simple text message. Let’s just hope that all COVID guidelines are followed, including social distancing, so the pandemic will finally end and won’t “be back.”
Misinterpretation is a science, not an art
It isn’t autocorrect’s fault this time, we swear
We’ve come a long way with communication technology. Back in the day, when Gondor needed to call for aid, they had to pull off the greatest signal fire montage of all time. Now we can send each other texts back and forth in an instant. (“Hey Theoden, send army, need help pls” doesn’t quite have the same gravitas though.) The question is, how do our brains keep up with such rapidly advancing technology?
Er, they don’t. Not really. Instead, our brains create shortcuts called “good-enough language processing,” which is exactly what it sounds like.
Psychologists and psycholinguists have been studying misinterpretations such as good-enough language processing since the 1970s. Recently, however, psycholinguists from the Centre for Language and Brain at Higher School of Economics in Moscow have found that, when it comes to reading comprehension over text, older adults are using their knowledge of the world over how it’s grammatically formed in the sentence.
In the study, 349 people were asked to read and interpret four sentences, the third of which (translated from Russian) was: “Misha met the firefighter’s dentist, who had put out a fire in the warehouse.” When asked who put the fire out, 79% of older adults (aged 55 years and older), utilizing good-enough language processing, said the firefighter put out the fire. You probably glossed over that sentence and assumed the same thing. But this time, the dentist was the real hero.
That said, adolescents (aged 13-17) and young adults (aged 20-30) weren’t much better, and got that particular sentence wrong 63%-68% of the time. According to the researchers, good-enough language processing forms in adolescence and intensifies throughout adulthood.
Moral of the story? We should utilize signal fires more often. Less room for misinterpretation. When the beacons of Minas Tirith were lit, Rohan answered.
Singing … your … lungs … out
There’s nothing quite like a karaoke bar to unleash your inner rock star. Hey, why not just go for it, everyone is just as bad at singing as you. That’s part of the fun.
A 25-year-old man named Wang Zhe may have taken the karaoke concept a bit too far, however. While out with friends at a birthday party, Mr. Zhe let loose on a song with a particularly large number of high notes. He tried his best, gamely attacking the song until he felt a pain in his chest. He didn’t think much of it, although he did cut his performance short, but then he awoke the next morning unable to breathe properly.
After a trip to the hospital, he explained the sequence of events to the doctors, and an x-ray found that the culprit of the pain and difficulty breathing was a life-threatening condition in which air bubbles are created between the chest and lung. All the force Mr. Zhe had used trying to sing made air sacks in his lung burst, causing the air bubbles and his lung to be compressed to 15% of what it should be. Mr. Zhe needed surgery to remove the air bubbles, but fortunately turned out just fine.
So, if you’re ever at a karaoke bar, looking for a song to sing, maybe avoid the ones with super high notes and stick with something a little lower. We’re picturing something like Paul Robeson singing Ol’ Man River. That oughta do the trick.
And the word of the year is …
Flibbertigibbet. Bamboozle. Gobbledygook. If the LOTME staff had any say, those would be the words of the year every year, but sadly, we’re not in charge of such things. Instead, we’ll just have to defer to Oxford and Merriam-Webster, both of whom have recently chosen their words of the year. No word yet on whether or not they made their announcement at a red carpet gala dinner attended by all the most fashionable and powerful words out there, but we’re hoping that’s what happened.
We’ll start with Oxford, since they did choose first. We all know Oxford is the bad boy of the dictionary world, so they’ve chosen a casual colloquialism related to the big COVID-sized elephant in the room (or should it be elephant-sized COVID in the room?): Vax. According to them, while vax has been hanging around since the 1980s, it’s only been in the past year that it’s exploded in popularity in a wide range of contexts (we can’t imagine what those would be). According to Oxford, “as a short pithy word, it appeals, perhaps especially to media commentators, when more formal alternatives are much more long-winded.”
Speaking of long-winded, that brings us to Merriam-Webster, the sheltered nerd of the dictionary world. Clearly they’re too good for vax, so they’ve gone with vaccine as their 2021 word of the year. Vaccine, according to Merriam-Webster, carries two big stories: The impressive and herculean feat of bringing a COVID-19 vaccine so quickly to so many people, and the complex political and social upheaval between vaccine supporters and deniers.
Vaccine also serves as a great bookend for Merriam-Webster’s 2020 word of the year: Pandemic. In 2020, the pandemic started, and in 2021, thanks to the vaccine, the pandemic ends. That’s how it works, right? We have a vaccine, it’s all over now. What’s that? Omicron? No! Bad COVID! You do that outside, not on the carpet!
It isn’t autocorrect’s fault this time, we swear
We’ve come a long way with communication technology. Back in the day, when Gondor needed to call for aid, they had to pull off the greatest signal fire montage of all time. Now we can send each other texts back and forth in an instant. (“Hey Theoden, send army, need help pls” doesn’t quite have the same gravitas though.) The question is, how do our brains keep up with such rapidly advancing technology?
Er, they don’t. Not really. Instead, our brains create shortcuts called “good-enough language processing,” which is exactly what it sounds like.
Psychologists and psycholinguists have been studying misinterpretations such as good-enough language processing since the 1970s. Recently, however, psycholinguists from the Centre for Language and Brain at Higher School of Economics in Moscow have found that, when it comes to reading comprehension over text, older adults are using their knowledge of the world over how it’s grammatically formed in the sentence.
In the study, 349 people were asked to read and interpret four sentences, the third of which (translated from Russian) was: “Misha met the firefighter’s dentist, who had put out a fire in the warehouse.” When asked who put the fire out, 79% of older adults (aged 55 years and older), utilizing good-enough language processing, said the firefighter put out the fire. You probably glossed over that sentence and assumed the same thing. But this time, the dentist was the real hero.
That said, adolescents (aged 13-17) and young adults (aged 20-30) weren’t much better, and got that particular sentence wrong 63%-68% of the time. According to the researchers, good-enough language processing forms in adolescence and intensifies throughout adulthood.
Moral of the story? We should utilize signal fires more often. Less room for misinterpretation. When the beacons of Minas Tirith were lit, Rohan answered.
Singing … your … lungs … out
There’s nothing quite like a karaoke bar to unleash your inner rock star. Hey, why not just go for it, everyone is just as bad at singing as you. That’s part of the fun.
A 25-year-old man named Wang Zhe may have taken the karaoke concept a bit too far, however. While out with friends at a birthday party, Mr. Zhe let loose on a song with a particularly large number of high notes. He tried his best, gamely attacking the song until he felt a pain in his chest. He didn’t think much of it, although he did cut his performance short, but then he awoke the next morning unable to breathe properly.
After a trip to the hospital, he explained the sequence of events to the doctors, and an x-ray found that the culprit of the pain and difficulty breathing was a life-threatening condition in which air bubbles are created between the chest and lung. All the force Mr. Zhe had used trying to sing made air sacks in his lung burst, causing the air bubbles and his lung to be compressed to 15% of what it should be. Mr. Zhe needed surgery to remove the air bubbles, but fortunately turned out just fine.
So, if you’re ever at a karaoke bar, looking for a song to sing, maybe avoid the ones with super high notes and stick with something a little lower. We’re picturing something like Paul Robeson singing Ol’ Man River. That oughta do the trick.
And the word of the year is …
Flibbertigibbet. Bamboozle. Gobbledygook. If the LOTME staff had any say, those would be the words of the year every year, but sadly, we’re not in charge of such things. Instead, we’ll just have to defer to Oxford and Merriam-Webster, both of whom have recently chosen their words of the year. No word yet on whether or not they made their announcement at a red carpet gala dinner attended by all the most fashionable and powerful words out there, but we’re hoping that’s what happened.
We’ll start with Oxford, since they did choose first. We all know Oxford is the bad boy of the dictionary world, so they’ve chosen a casual colloquialism related to the big COVID-sized elephant in the room (or should it be elephant-sized COVID in the room?): Vax. According to them, while vax has been hanging around since the 1980s, it’s only been in the past year that it’s exploded in popularity in a wide range of contexts (we can’t imagine what those would be). According to Oxford, “as a short pithy word, it appeals, perhaps especially to media commentators, when more formal alternatives are much more long-winded.”
Speaking of long-winded, that brings us to Merriam-Webster, the sheltered nerd of the dictionary world. Clearly they’re too good for vax, so they’ve gone with vaccine as their 2021 word of the year. Vaccine, according to Merriam-Webster, carries two big stories: The impressive and herculean feat of bringing a COVID-19 vaccine so quickly to so many people, and the complex political and social upheaval between vaccine supporters and deniers.
Vaccine also serves as a great bookend for Merriam-Webster’s 2020 word of the year: Pandemic. In 2020, the pandemic started, and in 2021, thanks to the vaccine, the pandemic ends. That’s how it works, right? We have a vaccine, it’s all over now. What’s that? Omicron? No! Bad COVID! You do that outside, not on the carpet!
It isn’t autocorrect’s fault this time, we swear
We’ve come a long way with communication technology. Back in the day, when Gondor needed to call for aid, they had to pull off the greatest signal fire montage of all time. Now we can send each other texts back and forth in an instant. (“Hey Theoden, send army, need help pls” doesn’t quite have the same gravitas though.) The question is, how do our brains keep up with such rapidly advancing technology?
Er, they don’t. Not really. Instead, our brains create shortcuts called “good-enough language processing,” which is exactly what it sounds like.
Psychologists and psycholinguists have been studying misinterpretations such as good-enough language processing since the 1970s. Recently, however, psycholinguists from the Centre for Language and Brain at Higher School of Economics in Moscow have found that, when it comes to reading comprehension over text, older adults are using their knowledge of the world over how it’s grammatically formed in the sentence.
In the study, 349 people were asked to read and interpret four sentences, the third of which (translated from Russian) was: “Misha met the firefighter’s dentist, who had put out a fire in the warehouse.” When asked who put the fire out, 79% of older adults (aged 55 years and older), utilizing good-enough language processing, said the firefighter put out the fire. You probably glossed over that sentence and assumed the same thing. But this time, the dentist was the real hero.
That said, adolescents (aged 13-17) and young adults (aged 20-30) weren’t much better, and got that particular sentence wrong 63%-68% of the time. According to the researchers, good-enough language processing forms in adolescence and intensifies throughout adulthood.
Moral of the story? We should utilize signal fires more often. Less room for misinterpretation. When the beacons of Minas Tirith were lit, Rohan answered.
Singing … your … lungs … out
There’s nothing quite like a karaoke bar to unleash your inner rock star. Hey, why not just go for it, everyone is just as bad at singing as you. That’s part of the fun.
A 25-year-old man named Wang Zhe may have taken the karaoke concept a bit too far, however. While out with friends at a birthday party, Mr. Zhe let loose on a song with a particularly large number of high notes. He tried his best, gamely attacking the song until he felt a pain in his chest. He didn’t think much of it, although he did cut his performance short, but then he awoke the next morning unable to breathe properly.
After a trip to the hospital, he explained the sequence of events to the doctors, and an x-ray found that the culprit of the pain and difficulty breathing was a life-threatening condition in which air bubbles are created between the chest and lung. All the force Mr. Zhe had used trying to sing made air sacks in his lung burst, causing the air bubbles and his lung to be compressed to 15% of what it should be. Mr. Zhe needed surgery to remove the air bubbles, but fortunately turned out just fine.
So, if you’re ever at a karaoke bar, looking for a song to sing, maybe avoid the ones with super high notes and stick with something a little lower. We’re picturing something like Paul Robeson singing Ol’ Man River. That oughta do the trick.
And the word of the year is …
Flibbertigibbet. Bamboozle. Gobbledygook. If the LOTME staff had any say, those would be the words of the year every year, but sadly, we’re not in charge of such things. Instead, we’ll just have to defer to Oxford and Merriam-Webster, both of whom have recently chosen their words of the year. No word yet on whether or not they made their announcement at a red carpet gala dinner attended by all the most fashionable and powerful words out there, but we’re hoping that’s what happened.
We’ll start with Oxford, since they did choose first. We all know Oxford is the bad boy of the dictionary world, so they’ve chosen a casual colloquialism related to the big COVID-sized elephant in the room (or should it be elephant-sized COVID in the room?): Vax. According to them, while vax has been hanging around since the 1980s, it’s only been in the past year that it’s exploded in popularity in a wide range of contexts (we can’t imagine what those would be). According to Oxford, “as a short pithy word, it appeals, perhaps especially to media commentators, when more formal alternatives are much more long-winded.”
Speaking of long-winded, that brings us to Merriam-Webster, the sheltered nerd of the dictionary world. Clearly they’re too good for vax, so they’ve gone with vaccine as their 2021 word of the year. Vaccine, according to Merriam-Webster, carries two big stories: The impressive and herculean feat of bringing a COVID-19 vaccine so quickly to so many people, and the complex political and social upheaval between vaccine supporters and deniers.
Vaccine also serves as a great bookend for Merriam-Webster’s 2020 word of the year: Pandemic. In 2020, the pandemic started, and in 2021, thanks to the vaccine, the pandemic ends. That’s how it works, right? We have a vaccine, it’s all over now. What’s that? Omicron? No! Bad COVID! You do that outside, not on the carpet!
The neurological super powers of grandma are real
Deer, COVID, how?
Usually humans cannot get close enough to a deer to really be face-to-face, so it’s easy to question how on Earth deer are contracting COVID-19. Well, stranger things have happened, and honestly, we’ve just stopped questioning most of them.
Exhibit A comes to us from a Penn State University study: Eighty percent of deer sampled in Iowa in December 2020 and January 2021 – as part of the state’s chronic wasting disease surveillance program – were found to be positive for COVID-19.
A statement from the university said that “white-tailed deer may be a reservoir for the virus to continually circulate and raise concerns about the emergence of new strains that may prove a threat to wildlife and, possibly, to humans.” The investigators also suggested that deer probably caught the virus from humans and then transmitted it to other deer.
If you or someone you know is a hunter or a white-tailed deer, it’s best to proceed with caution. There’s no evidence that COVID-19 has jumped from deer to humans, but hunters should wear masks and gloves while working with deer, worrying not just about the deer’s face, but also … you know, the gastrointestinal parts, Robert Salata, MD, of University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, told Syracuse.com. It also shouldn’t be too risky to eat venison, he said, just make sure the meat is cooked thoroughly.
The more you know!
The neurological super powers of grandma are real
What is it about grandmothers that makes them seem almost magical at times? They somehow always know how you feel. And they can almost always tell when something is wrong. They also seem to be the biggest ally a child will have against his or her parents.
So what makes these super matriarchs? The answer is in the brain.
Apparently there’s a function in the brains of grandmothers geared toward “emotional empathy.” James Rilling, PhD, of Emory University, lead author of a recent study focused on looking at the brain function of grandmothers, suggested that they’re neurologically tapped into feeling how their grandchildren feel: “If their grandchild is smiling, they’re feeling the child’s joy. And if their grandchild is crying, they’re feeling the child’s pain and distress.”
And then there’s the cute factor. Never underestimate a child’s ability to manipulate his or her grandmother’s brain.
So how do the researchers know this? Functional MRI showed more brain activity in the parts of the brain that deal with emotional empathy and movement in the participating grandmas when shown pictures of their grandchildren. Images of their own adult children lit up areas more associated with cognitive empathy. So less emotional and more mental/logical understanding.
Kids, don’t tell Mom about the secret midnight snacks with grandma. She wouldn’t get it.
Then there’s the grandmother hypothesis, which suggests that women tend to live longer to provide some kind of evolutionary benefit to their children and grandchildren. Evidence also exists that children with positive engagement from their grandmothers tend to have better social and academic outcomes, behavior, and physical health.
A lot of credit on how children turn out, of course, goes to parents, but more can be said about grandmas. Don’t let the age and freshly baked cookies fool you. They have neurologic superpowers within.
Brain cleanup on aisle 5
You’ve got your local grocery store down. You know the ins and outs; you know where everything is. Last week you did your trip in record time. This week, however, you have to stop at a different store. Same chain, but a different location. You stroll in, confidently walk toward the first aisle for your fruits and veggies, and ... it’s all ice cream. Oops.
There’s a lot we don’t understand about the brain, including how it remembers familiar environments to avoid confusion. Or why it fails to do so, as with our grocery store example. However, thanks to a study from the University of Arizona, we may have an answer.
For the experiment, a group of participants watched a video tour of three virtual cities. Those cities were very similar, being laid out in basically identical fashion. Stores could be found in the same places, but the identity of those stores varied. Some stores were in all three cities, some were in two, and some were unique. Participants were asked to memorize the layouts, and those who got things more than 80% correct ran through the test again, only this time their brain activity was monitored through MRI.
In general, brain activity was similar for the participants; after all, they were recalling similar environments. However, when asked about stores that appeared in multiple cities, brain activity varied dramatically. This indicated to the researchers that the brain was recalling shared stores as if they were more dissimilar than two completely disparate and unique stores, a concept often known to brain scientists as “repulsion.” It also indicates that the memories regarding shared environments are stored in the prefrontal cortex, not the hippocampus, which typically handles memory.
The researchers plan to apply this information to questions about diseases such as Alzheimer’s, so the next time you get turned around in a weirdly unfamiliar grocery store, just think: “It’s okay, I’m helping to solve a terrible brain disease.”
The real endgame: Friction is the winner
Spoiler alert! If you haven’t seen “Avengers: Infinity War” yet, we’re about to ruin it for you.
For those still with us, here’s the spoiler: Thanos would not have been able to snap his fingers while wearing the Infinity Gauntlet.
Saad Bhamla, PhD, of Georgia Tech University’s school of chemical and biomolecular engineering, had been studying powerful and ultrafast motions in living organisms along with several colleagues before the movie came out in 2018, and when they saw the finger-snapping scene it got them wondering.
Being scientists of course, they had no choice. They got out their high-speed imaging equipment, automated image processing software, and dynamic force sensors and analyzed finger snaps, paying close attention to friction by covering fingers with “different materials, including metallic thimbles to simulate the effects of trying to snap while wearing a metallic gauntlet, much like Thanos,” according to a statement on Eurekalert.
With finger snaps, it’s all about the rotational velocity. The angular acceleration involved is the fastest ever measured in a human, with a professional baseball pitcher’s throwing arm a distant second.
Dr. Bhamla’s reaction to their work explains why scientists are the ones doing science. “When I first saw the data, I jumped out of my chair,” he said in the written statement.
Rotational velocities dropped dramatically when the friction-reducing thimbles were used, so there was no snap. Which means that billions and billions of fictional lives could have been saved if the filmmakers had just talked to the right scientist.
That scientist, clearly, is Dr. Bhamla, who said that “this is the only scientific project in my lab in which we could snap our fingers and get data.”
Deer, COVID, how?
Usually humans cannot get close enough to a deer to really be face-to-face, so it’s easy to question how on Earth deer are contracting COVID-19. Well, stranger things have happened, and honestly, we’ve just stopped questioning most of them.
Exhibit A comes to us from a Penn State University study: Eighty percent of deer sampled in Iowa in December 2020 and January 2021 – as part of the state’s chronic wasting disease surveillance program – were found to be positive for COVID-19.
A statement from the university said that “white-tailed deer may be a reservoir for the virus to continually circulate and raise concerns about the emergence of new strains that may prove a threat to wildlife and, possibly, to humans.” The investigators also suggested that deer probably caught the virus from humans and then transmitted it to other deer.
If you or someone you know is a hunter or a white-tailed deer, it’s best to proceed with caution. There’s no evidence that COVID-19 has jumped from deer to humans, but hunters should wear masks and gloves while working with deer, worrying not just about the deer’s face, but also … you know, the gastrointestinal parts, Robert Salata, MD, of University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, told Syracuse.com. It also shouldn’t be too risky to eat venison, he said, just make sure the meat is cooked thoroughly.
The more you know!
The neurological super powers of grandma are real
What is it about grandmothers that makes them seem almost magical at times? They somehow always know how you feel. And they can almost always tell when something is wrong. They also seem to be the biggest ally a child will have against his or her parents.
So what makes these super matriarchs? The answer is in the brain.
Apparently there’s a function in the brains of grandmothers geared toward “emotional empathy.” James Rilling, PhD, of Emory University, lead author of a recent study focused on looking at the brain function of grandmothers, suggested that they’re neurologically tapped into feeling how their grandchildren feel: “If their grandchild is smiling, they’re feeling the child’s joy. And if their grandchild is crying, they’re feeling the child’s pain and distress.”
And then there’s the cute factor. Never underestimate a child’s ability to manipulate his or her grandmother’s brain.
So how do the researchers know this? Functional MRI showed more brain activity in the parts of the brain that deal with emotional empathy and movement in the participating grandmas when shown pictures of their grandchildren. Images of their own adult children lit up areas more associated with cognitive empathy. So less emotional and more mental/logical understanding.
Kids, don’t tell Mom about the secret midnight snacks with grandma. She wouldn’t get it.
Then there’s the grandmother hypothesis, which suggests that women tend to live longer to provide some kind of evolutionary benefit to their children and grandchildren. Evidence also exists that children with positive engagement from their grandmothers tend to have better social and academic outcomes, behavior, and physical health.
A lot of credit on how children turn out, of course, goes to parents, but more can be said about grandmas. Don’t let the age and freshly baked cookies fool you. They have neurologic superpowers within.
Brain cleanup on aisle 5
You’ve got your local grocery store down. You know the ins and outs; you know where everything is. Last week you did your trip in record time. This week, however, you have to stop at a different store. Same chain, but a different location. You stroll in, confidently walk toward the first aisle for your fruits and veggies, and ... it’s all ice cream. Oops.
There’s a lot we don’t understand about the brain, including how it remembers familiar environments to avoid confusion. Or why it fails to do so, as with our grocery store example. However, thanks to a study from the University of Arizona, we may have an answer.
For the experiment, a group of participants watched a video tour of three virtual cities. Those cities were very similar, being laid out in basically identical fashion. Stores could be found in the same places, but the identity of those stores varied. Some stores were in all three cities, some were in two, and some were unique. Participants were asked to memorize the layouts, and those who got things more than 80% correct ran through the test again, only this time their brain activity was monitored through MRI.
In general, brain activity was similar for the participants; after all, they were recalling similar environments. However, when asked about stores that appeared in multiple cities, brain activity varied dramatically. This indicated to the researchers that the brain was recalling shared stores as if they were more dissimilar than two completely disparate and unique stores, a concept often known to brain scientists as “repulsion.” It also indicates that the memories regarding shared environments are stored in the prefrontal cortex, not the hippocampus, which typically handles memory.
The researchers plan to apply this information to questions about diseases such as Alzheimer’s, so the next time you get turned around in a weirdly unfamiliar grocery store, just think: “It’s okay, I’m helping to solve a terrible brain disease.”
The real endgame: Friction is the winner
Spoiler alert! If you haven’t seen “Avengers: Infinity War” yet, we’re about to ruin it for you.
For those still with us, here’s the spoiler: Thanos would not have been able to snap his fingers while wearing the Infinity Gauntlet.
Saad Bhamla, PhD, of Georgia Tech University’s school of chemical and biomolecular engineering, had been studying powerful and ultrafast motions in living organisms along with several colleagues before the movie came out in 2018, and when they saw the finger-snapping scene it got them wondering.
Being scientists of course, they had no choice. They got out their high-speed imaging equipment, automated image processing software, and dynamic force sensors and analyzed finger snaps, paying close attention to friction by covering fingers with “different materials, including metallic thimbles to simulate the effects of trying to snap while wearing a metallic gauntlet, much like Thanos,” according to a statement on Eurekalert.
With finger snaps, it’s all about the rotational velocity. The angular acceleration involved is the fastest ever measured in a human, with a professional baseball pitcher’s throwing arm a distant second.
Dr. Bhamla’s reaction to their work explains why scientists are the ones doing science. “When I first saw the data, I jumped out of my chair,” he said in the written statement.
Rotational velocities dropped dramatically when the friction-reducing thimbles were used, so there was no snap. Which means that billions and billions of fictional lives could have been saved if the filmmakers had just talked to the right scientist.
That scientist, clearly, is Dr. Bhamla, who said that “this is the only scientific project in my lab in which we could snap our fingers and get data.”
Deer, COVID, how?
Usually humans cannot get close enough to a deer to really be face-to-face, so it’s easy to question how on Earth deer are contracting COVID-19. Well, stranger things have happened, and honestly, we’ve just stopped questioning most of them.
Exhibit A comes to us from a Penn State University study: Eighty percent of deer sampled in Iowa in December 2020 and January 2021 – as part of the state’s chronic wasting disease surveillance program – were found to be positive for COVID-19.
A statement from the university said that “white-tailed deer may be a reservoir for the virus to continually circulate and raise concerns about the emergence of new strains that may prove a threat to wildlife and, possibly, to humans.” The investigators also suggested that deer probably caught the virus from humans and then transmitted it to other deer.
If you or someone you know is a hunter or a white-tailed deer, it’s best to proceed with caution. There’s no evidence that COVID-19 has jumped from deer to humans, but hunters should wear masks and gloves while working with deer, worrying not just about the deer’s face, but also … you know, the gastrointestinal parts, Robert Salata, MD, of University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, told Syracuse.com. It also shouldn’t be too risky to eat venison, he said, just make sure the meat is cooked thoroughly.
The more you know!
The neurological super powers of grandma are real
What is it about grandmothers that makes them seem almost magical at times? They somehow always know how you feel. And they can almost always tell when something is wrong. They also seem to be the biggest ally a child will have against his or her parents.
So what makes these super matriarchs? The answer is in the brain.
Apparently there’s a function in the brains of grandmothers geared toward “emotional empathy.” James Rilling, PhD, of Emory University, lead author of a recent study focused on looking at the brain function of grandmothers, suggested that they’re neurologically tapped into feeling how their grandchildren feel: “If their grandchild is smiling, they’re feeling the child’s joy. And if their grandchild is crying, they’re feeling the child’s pain and distress.”
And then there’s the cute factor. Never underestimate a child’s ability to manipulate his or her grandmother’s brain.
So how do the researchers know this? Functional MRI showed more brain activity in the parts of the brain that deal with emotional empathy and movement in the participating grandmas when shown pictures of their grandchildren. Images of their own adult children lit up areas more associated with cognitive empathy. So less emotional and more mental/logical understanding.
Kids, don’t tell Mom about the secret midnight snacks with grandma. She wouldn’t get it.
Then there’s the grandmother hypothesis, which suggests that women tend to live longer to provide some kind of evolutionary benefit to their children and grandchildren. Evidence also exists that children with positive engagement from their grandmothers tend to have better social and academic outcomes, behavior, and physical health.
A lot of credit on how children turn out, of course, goes to parents, but more can be said about grandmas. Don’t let the age and freshly baked cookies fool you. They have neurologic superpowers within.
Brain cleanup on aisle 5
You’ve got your local grocery store down. You know the ins and outs; you know where everything is. Last week you did your trip in record time. This week, however, you have to stop at a different store. Same chain, but a different location. You stroll in, confidently walk toward the first aisle for your fruits and veggies, and ... it’s all ice cream. Oops.
There’s a lot we don’t understand about the brain, including how it remembers familiar environments to avoid confusion. Or why it fails to do so, as with our grocery store example. However, thanks to a study from the University of Arizona, we may have an answer.
For the experiment, a group of participants watched a video tour of three virtual cities. Those cities were very similar, being laid out in basically identical fashion. Stores could be found in the same places, but the identity of those stores varied. Some stores were in all three cities, some were in two, and some were unique. Participants were asked to memorize the layouts, and those who got things more than 80% correct ran through the test again, only this time their brain activity was monitored through MRI.
In general, brain activity was similar for the participants; after all, they were recalling similar environments. However, when asked about stores that appeared in multiple cities, brain activity varied dramatically. This indicated to the researchers that the brain was recalling shared stores as if they were more dissimilar than two completely disparate and unique stores, a concept often known to brain scientists as “repulsion.” It also indicates that the memories regarding shared environments are stored in the prefrontal cortex, not the hippocampus, which typically handles memory.
The researchers plan to apply this information to questions about diseases such as Alzheimer’s, so the next time you get turned around in a weirdly unfamiliar grocery store, just think: “It’s okay, I’m helping to solve a terrible brain disease.”
The real endgame: Friction is the winner
Spoiler alert! If you haven’t seen “Avengers: Infinity War” yet, we’re about to ruin it for you.
For those still with us, here’s the spoiler: Thanos would not have been able to snap his fingers while wearing the Infinity Gauntlet.
Saad Bhamla, PhD, of Georgia Tech University’s school of chemical and biomolecular engineering, had been studying powerful and ultrafast motions in living organisms along with several colleagues before the movie came out in 2018, and when they saw the finger-snapping scene it got them wondering.
Being scientists of course, they had no choice. They got out their high-speed imaging equipment, automated image processing software, and dynamic force sensors and analyzed finger snaps, paying close attention to friction by covering fingers with “different materials, including metallic thimbles to simulate the effects of trying to snap while wearing a metallic gauntlet, much like Thanos,” according to a statement on Eurekalert.
With finger snaps, it’s all about the rotational velocity. The angular acceleration involved is the fastest ever measured in a human, with a professional baseball pitcher’s throwing arm a distant second.
Dr. Bhamla’s reaction to their work explains why scientists are the ones doing science. “When I first saw the data, I jumped out of my chair,” he said in the written statement.
Rotational velocities dropped dramatically when the friction-reducing thimbles were used, so there was no snap. Which means that billions and billions of fictional lives could have been saved if the filmmakers had just talked to the right scientist.
That scientist, clearly, is Dr. Bhamla, who said that “this is the only scientific project in my lab in which we could snap our fingers and get data.”
Step right up, folks, for a public dissection
The greatest autopsy on Earth?
The LOTME staff would like to apologize in advance. The following item contains historical facts.
P.T. Barnum is a rather controversial figure in American history. The greatest show on Earth was certainly popular in its day. However, Barnum got his start in 1835 by leasing a slave named Joyce Heth, an elderly Black woman who told vivid stories of caring for a young George Washington. He toured her around the country, advertising her as a 160-year-old woman who served as George Washington’s nanny. When Ms. Heth died the next year, Barnum sold tickets to the autopsy, charging the equivalent of $30 in today’s money.
When a doctor announced that Ms. Heth was actually 75-80 when she died, it caused great controversy in the press and ruined Barnum’s career. Wait, no, that’s not right. The opposite, actually. He weathered the storm, built his famous circus, and never again committed a hoax.
It’s difficult to quantify how wrong publicly dissecting a person and charging people to see said dissection is, but that was almost 200 years ago. At the very least, we can say that such terrible behavior is firmly in the distant past.
Oh wait.
David Saunders, a 98-year-old veteran of World War II and the Korean War, donated his body to science. His body, however, was purchased by DeathScience.org from a medical lab – with the buyer supposedly misleading the medical lab about its intentions, which was for use at the traveling Oddities and Curiosities Expo. Tickets went for up to $500 each to witness the public autopsy of Mr. Saunders’ body, which took place at a Marriott in Portland, Ore. It promised to be an exciting, all-day event from 9 a.m. to 4 p.m., with a break for lunch, of course. You can’t have an autopsy without a catered lunch.
Another public autopsy event was scheduled in Seattle but canceled after news of the first event broke. Oh, and for that extra little kick, Mr. Saunders died from COVID-19, meaning that all those paying customers were exposed.
P.T. Barnum is probably rolling over in his grave right now. His autopsy tickets were a bargain.
Go ahead, have that soda before math
We should all know by now that sugary drinks are bad, even artificially sweetened ones. It might not always stop us from drinking them, but we know the deal. But what if sugary drinks like soda could be helpful for girls in school?
You read that right. We said girls. A soda before class might have boys bouncing off the walls, but not girls. A recent study showed that not only was girls’ behavior unaffected by having a sugary drink, their math skills even improved.
Researchers analyzed the behavior of 4- to 6-year-old children before and after having a sugary drink. The sugar rush was actually calming for girls and helped them perform better with numerical skills, but the opposite was true for boys. “Our study is the first to provide large-scale experimental evidence on the impact of sugary drinks on preschool children. The results clearly indicate a causal impact of sugary drinks on children’s behavior and test scores,” Fritz Schiltz, PhD, said in a written statement.
This probably isn’t the green light to have as many sugary drinks as you want, but it might be interesting to see how your work is affected after a soda.
Chicken nuggets and the meat paradox
Two young children are fighting over the last chicken nugget when an adult comes in to see what’s going on.
Liam: Vegetable!
Olivia: Meat!
Liam: Chicken nuggets are vegetables!
Olivia: No, dorkface! They’re meat.
Caregiver: Good news, kids. You’re both right.
Olivia: How can we both be right?
At this point, a woman enters the room. She’s wearing a white lab coat, so she must be a scientist.
Dr. Scientist: You can’t both be right, Olivia. You are being fed a serving of the meat paradox. That’s why Liam here doesn’t know that chicken nuggets are made of chicken, which is a form of meat. Sadly, he’s not the only one.
In a recent study, scientists from Furman University in Greenville, S.C., found that 38% of 176 children aged 4-7 years thought that chicken nuggets were vegetables and more than 46% identified French fries as animal based.
Olivia: Did our caregiver lie to us, Dr. Scientist?
Dr. Scientist: Yes, Olivia. The researchers I mentioned explained that “many people experience unease while eating meat. Omnivores eat foods that entail animal suffering and death while at the same time endorsing the compassionate treatment of animals.” That’s the meat paradox.
Liam: What else did they say, Dr. Scientist?
Dr. Scientist: Over 70% of those children said that cows and pigs were not edible and 5% thought that cats and horses were. The investigators wrote “that children and youth should be viewed as agents of environmental change” in the future, but suggested that parents need to bring honesty to the table.
Caregiver: How did you get in here anyway? And how do you know their names?
Dr. Scientist: I’ve been rooting through your garbage for years. All in the name of science, of course.
Bedtimes aren’t just for children
There are multiple ways to prevent heart disease, but what if it could be as easy as switching your bedtime? A recent study in European Heart Journal–Digital Health suggests that there’s a sweet spot when it comes to sleep timing.
Through smartwatch-like devices, researchers measured the sleep-onset and wake-up times for 7 days in 88,026 participants aged 43-79 years. After 5.7 years of follow-up to see if anyone had a heart attack, stroke, or any other cardiovascular event, 3.6% developed some kind of cardiovascular disease.
Those who went to bed between 10 p.m. and 11 p.m. had a lower risk of developing heart disease. The risk was 25% higher for subjects who went to bed at midnight or later, 24% higher for bedtimes before 10 p.m., and 12% higher for bedtimes between 11 p.m. and midnight.
So, why can you go to bed before “The Tonight Show” and lower your cardiovascular risk but not before the nightly news? Well, it has something to do with your body’s natural clock.
“The optimum time to go to sleep is at a specific point in the body’s 24-hour cycle and deviations may be detrimental to health. The riskiest time was after midnight, potentially because it may reduce the likelihood of seeing morning light, which resets the body clock,” said study author Dr. David Plans of the University of Exeter, England.
Although a sleep schedule is preferred, it isn’t realistic all the time for those in certain occupations who might have to resort to other methods to keep their circadian clocks ticking optimally for their health. But if all it takes is prescribing a sleep time to reduce heart disease on a massive scale it would make a great “low-cost public health target.”
So bedtimes aren’t just for children.
The greatest autopsy on Earth?
The LOTME staff would like to apologize in advance. The following item contains historical facts.
P.T. Barnum is a rather controversial figure in American history. The greatest show on Earth was certainly popular in its day. However, Barnum got his start in 1835 by leasing a slave named Joyce Heth, an elderly Black woman who told vivid stories of caring for a young George Washington. He toured her around the country, advertising her as a 160-year-old woman who served as George Washington’s nanny. When Ms. Heth died the next year, Barnum sold tickets to the autopsy, charging the equivalent of $30 in today’s money.
When a doctor announced that Ms. Heth was actually 75-80 when she died, it caused great controversy in the press and ruined Barnum’s career. Wait, no, that’s not right. The opposite, actually. He weathered the storm, built his famous circus, and never again committed a hoax.
It’s difficult to quantify how wrong publicly dissecting a person and charging people to see said dissection is, but that was almost 200 years ago. At the very least, we can say that such terrible behavior is firmly in the distant past.
Oh wait.
David Saunders, a 98-year-old veteran of World War II and the Korean War, donated his body to science. His body, however, was purchased by DeathScience.org from a medical lab – with the buyer supposedly misleading the medical lab about its intentions, which was for use at the traveling Oddities and Curiosities Expo. Tickets went for up to $500 each to witness the public autopsy of Mr. Saunders’ body, which took place at a Marriott in Portland, Ore. It promised to be an exciting, all-day event from 9 a.m. to 4 p.m., with a break for lunch, of course. You can’t have an autopsy without a catered lunch.
Another public autopsy event was scheduled in Seattle but canceled after news of the first event broke. Oh, and for that extra little kick, Mr. Saunders died from COVID-19, meaning that all those paying customers were exposed.
P.T. Barnum is probably rolling over in his grave right now. His autopsy tickets were a bargain.
Go ahead, have that soda before math
We should all know by now that sugary drinks are bad, even artificially sweetened ones. It might not always stop us from drinking them, but we know the deal. But what if sugary drinks like soda could be helpful for girls in school?
You read that right. We said girls. A soda before class might have boys bouncing off the walls, but not girls. A recent study showed that not only was girls’ behavior unaffected by having a sugary drink, their math skills even improved.
Researchers analyzed the behavior of 4- to 6-year-old children before and after having a sugary drink. The sugar rush was actually calming for girls and helped them perform better with numerical skills, but the opposite was true for boys. “Our study is the first to provide large-scale experimental evidence on the impact of sugary drinks on preschool children. The results clearly indicate a causal impact of sugary drinks on children’s behavior and test scores,” Fritz Schiltz, PhD, said in a written statement.
This probably isn’t the green light to have as many sugary drinks as you want, but it might be interesting to see how your work is affected after a soda.
Chicken nuggets and the meat paradox
Two young children are fighting over the last chicken nugget when an adult comes in to see what’s going on.
Liam: Vegetable!
Olivia: Meat!
Liam: Chicken nuggets are vegetables!
Olivia: No, dorkface! They’re meat.
Caregiver: Good news, kids. You’re both right.
Olivia: How can we both be right?
At this point, a woman enters the room. She’s wearing a white lab coat, so she must be a scientist.
Dr. Scientist: You can’t both be right, Olivia. You are being fed a serving of the meat paradox. That’s why Liam here doesn’t know that chicken nuggets are made of chicken, which is a form of meat. Sadly, he’s not the only one.
In a recent study, scientists from Furman University in Greenville, S.C., found that 38% of 176 children aged 4-7 years thought that chicken nuggets were vegetables and more than 46% identified French fries as animal based.
Olivia: Did our caregiver lie to us, Dr. Scientist?
Dr. Scientist: Yes, Olivia. The researchers I mentioned explained that “many people experience unease while eating meat. Omnivores eat foods that entail animal suffering and death while at the same time endorsing the compassionate treatment of animals.” That’s the meat paradox.
Liam: What else did they say, Dr. Scientist?
Dr. Scientist: Over 70% of those children said that cows and pigs were not edible and 5% thought that cats and horses were. The investigators wrote “that children and youth should be viewed as agents of environmental change” in the future, but suggested that parents need to bring honesty to the table.
Caregiver: How did you get in here anyway? And how do you know their names?
Dr. Scientist: I’ve been rooting through your garbage for years. All in the name of science, of course.
Bedtimes aren’t just for children
There are multiple ways to prevent heart disease, but what if it could be as easy as switching your bedtime? A recent study in European Heart Journal–Digital Health suggests that there’s a sweet spot when it comes to sleep timing.
Through smartwatch-like devices, researchers measured the sleep-onset and wake-up times for 7 days in 88,026 participants aged 43-79 years. After 5.7 years of follow-up to see if anyone had a heart attack, stroke, or any other cardiovascular event, 3.6% developed some kind of cardiovascular disease.
Those who went to bed between 10 p.m. and 11 p.m. had a lower risk of developing heart disease. The risk was 25% higher for subjects who went to bed at midnight or later, 24% higher for bedtimes before 10 p.m., and 12% higher for bedtimes between 11 p.m. and midnight.
So, why can you go to bed before “The Tonight Show” and lower your cardiovascular risk but not before the nightly news? Well, it has something to do with your body’s natural clock.
“The optimum time to go to sleep is at a specific point in the body’s 24-hour cycle and deviations may be detrimental to health. The riskiest time was after midnight, potentially because it may reduce the likelihood of seeing morning light, which resets the body clock,” said study author Dr. David Plans of the University of Exeter, England.
Although a sleep schedule is preferred, it isn’t realistic all the time for those in certain occupations who might have to resort to other methods to keep their circadian clocks ticking optimally for their health. But if all it takes is prescribing a sleep time to reduce heart disease on a massive scale it would make a great “low-cost public health target.”
So bedtimes aren’t just for children.
The greatest autopsy on Earth?
The LOTME staff would like to apologize in advance. The following item contains historical facts.
P.T. Barnum is a rather controversial figure in American history. The greatest show on Earth was certainly popular in its day. However, Barnum got his start in 1835 by leasing a slave named Joyce Heth, an elderly Black woman who told vivid stories of caring for a young George Washington. He toured her around the country, advertising her as a 160-year-old woman who served as George Washington’s nanny. When Ms. Heth died the next year, Barnum sold tickets to the autopsy, charging the equivalent of $30 in today’s money.
When a doctor announced that Ms. Heth was actually 75-80 when she died, it caused great controversy in the press and ruined Barnum’s career. Wait, no, that’s not right. The opposite, actually. He weathered the storm, built his famous circus, and never again committed a hoax.
It’s difficult to quantify how wrong publicly dissecting a person and charging people to see said dissection is, but that was almost 200 years ago. At the very least, we can say that such terrible behavior is firmly in the distant past.
Oh wait.
David Saunders, a 98-year-old veteran of World War II and the Korean War, donated his body to science. His body, however, was purchased by DeathScience.org from a medical lab – with the buyer supposedly misleading the medical lab about its intentions, which was for use at the traveling Oddities and Curiosities Expo. Tickets went for up to $500 each to witness the public autopsy of Mr. Saunders’ body, which took place at a Marriott in Portland, Ore. It promised to be an exciting, all-day event from 9 a.m. to 4 p.m., with a break for lunch, of course. You can’t have an autopsy without a catered lunch.
Another public autopsy event was scheduled in Seattle but canceled after news of the first event broke. Oh, and for that extra little kick, Mr. Saunders died from COVID-19, meaning that all those paying customers were exposed.
P.T. Barnum is probably rolling over in his grave right now. His autopsy tickets were a bargain.
Go ahead, have that soda before math
We should all know by now that sugary drinks are bad, even artificially sweetened ones. It might not always stop us from drinking them, but we know the deal. But what if sugary drinks like soda could be helpful for girls in school?
You read that right. We said girls. A soda before class might have boys bouncing off the walls, but not girls. A recent study showed that not only was girls’ behavior unaffected by having a sugary drink, their math skills even improved.
Researchers analyzed the behavior of 4- to 6-year-old children before and after having a sugary drink. The sugar rush was actually calming for girls and helped them perform better with numerical skills, but the opposite was true for boys. “Our study is the first to provide large-scale experimental evidence on the impact of sugary drinks on preschool children. The results clearly indicate a causal impact of sugary drinks on children’s behavior and test scores,” Fritz Schiltz, PhD, said in a written statement.
This probably isn’t the green light to have as many sugary drinks as you want, but it might be interesting to see how your work is affected after a soda.
Chicken nuggets and the meat paradox
Two young children are fighting over the last chicken nugget when an adult comes in to see what’s going on.
Liam: Vegetable!
Olivia: Meat!
Liam: Chicken nuggets are vegetables!
Olivia: No, dorkface! They’re meat.
Caregiver: Good news, kids. You’re both right.
Olivia: How can we both be right?
At this point, a woman enters the room. She’s wearing a white lab coat, so she must be a scientist.
Dr. Scientist: You can’t both be right, Olivia. You are being fed a serving of the meat paradox. That’s why Liam here doesn’t know that chicken nuggets are made of chicken, which is a form of meat. Sadly, he’s not the only one.
In a recent study, scientists from Furman University in Greenville, S.C., found that 38% of 176 children aged 4-7 years thought that chicken nuggets were vegetables and more than 46% identified French fries as animal based.
Olivia: Did our caregiver lie to us, Dr. Scientist?
Dr. Scientist: Yes, Olivia. The researchers I mentioned explained that “many people experience unease while eating meat. Omnivores eat foods that entail animal suffering and death while at the same time endorsing the compassionate treatment of animals.” That’s the meat paradox.
Liam: What else did they say, Dr. Scientist?
Dr. Scientist: Over 70% of those children said that cows and pigs were not edible and 5% thought that cats and horses were. The investigators wrote “that children and youth should be viewed as agents of environmental change” in the future, but suggested that parents need to bring honesty to the table.
Caregiver: How did you get in here anyway? And how do you know their names?
Dr. Scientist: I’ve been rooting through your garbage for years. All in the name of science, of course.
Bedtimes aren’t just for children
There are multiple ways to prevent heart disease, but what if it could be as easy as switching your bedtime? A recent study in European Heart Journal–Digital Health suggests that there’s a sweet spot when it comes to sleep timing.
Through smartwatch-like devices, researchers measured the sleep-onset and wake-up times for 7 days in 88,026 participants aged 43-79 years. After 5.7 years of follow-up to see if anyone had a heart attack, stroke, or any other cardiovascular event, 3.6% developed some kind of cardiovascular disease.
Those who went to bed between 10 p.m. and 11 p.m. had a lower risk of developing heart disease. The risk was 25% higher for subjects who went to bed at midnight or later, 24% higher for bedtimes before 10 p.m., and 12% higher for bedtimes between 11 p.m. and midnight.
So, why can you go to bed before “The Tonight Show” and lower your cardiovascular risk but not before the nightly news? Well, it has something to do with your body’s natural clock.
“The optimum time to go to sleep is at a specific point in the body’s 24-hour cycle and deviations may be detrimental to health. The riskiest time was after midnight, potentially because it may reduce the likelihood of seeing morning light, which resets the body clock,” said study author Dr. David Plans of the University of Exeter, England.
Although a sleep schedule is preferred, it isn’t realistic all the time for those in certain occupations who might have to resort to other methods to keep their circadian clocks ticking optimally for their health. But if all it takes is prescribing a sleep time to reduce heart disease on a massive scale it would make a great “low-cost public health target.”
So bedtimes aren’t just for children.
James Bond taken down by an epidemiologist
No, Mr. Bond, I expect you to die
Movie watching usually requires a certain suspension of disbelief, and it’s safe to say James Bond movies require this more than most. Between the impossible gadgets and ludicrous doomsday plans, very few have ever stopped to consider the health risks of the James Bond universe.
Now, however, Bond, James Bond, has met his most formidable opponent: Wouter Graumans, a graduate student in epidemiology from the Netherlands. During a foray to Burkina Faso to study infectious diseases, Mr. Graumans came down with a case of food poisoning, which led him to wonder how 007 is able to trot across this big world of ours without contracting so much as a sinus infection.
Because Mr. Graumans is a man of science and conviction, mere speculation wasn’t enough. He and a group of coauthors wrote an entire paper on the health risks of the James Bond universe.
Doing so required watching over 3,000 minutes of numerous movies and analyzing Bond’s 86 total trips to 46 different countries based on current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advice for travel to those countries. Time which, the authors state in the abstract, “could easily have been spent on more pressing societal issues or forms of relaxation that are more acceptable in academic circles.”
Naturally, Mr. Bond’s line of work entails exposure to unpleasant things, such as poison, dehydration, heatstroke, and dangerous wildlife (everything from ticks to crocodiles), though oddly enough he never succumbs to any of it. He’s also curiously immune to hangovers, despite rarely drinking anything nonalcoholic. There are also less obvious risks: For one, 007 rarely washes his hands. During one movie, he handles raw chicken to lure away a pack of crocodiles but fails to wash his hands afterward, leaving him at risk for multiple food-borne illnesses.
Of course, we must address the elephant in the bedroom: Mr. Bond’s numerous, er, encounters with women. One would imagine the biggest risk to those women would be from the various STDs that likely course through Bond’s body, but of the 27% who died shortly after … encountering … him, all involved violence, with disease playing no obvious role. Who knows, maybe he’s clean? Stranger things have happened.
The timing of this article may seem a bit suspicious. Was it a PR stunt by the studio? Rest assured, the authors addressed this, noting that they received no funding for the study, and that, “given the futility of its academic value, this is deemed entirely appropriate by all authors.” We love when a punchline writes itself.
How to see Atlanta on $688.35 a day
The world is always changing, so we have to change with it. This week, LOTME becomes a travel guide, and our first stop is the Big A, the Big Peach, Dogwood City, Empire City of the South, Wakanda.
There’s lots to do in Atlanta: Celebrate a World Series win, visit the College Football Hall of Fame or the World of Coca Cola, or take the Stranger Things/Upside Down film locations tour. Serious adventurers, however, get out of the city and go to Emory Decatur Hospital in – you guessed it – Decatur (unofficial motto: “Everything is Greater in Decatur”).
Find the emergency room and ask for Taylor Davis, who will be your personal guide. She’ll show you how to check in at the desk, sit in the waiting room for 7 hours, and then leave without seeing any medical personnel or receiving any sort of attention whatsoever. All the things she did when she went there in July for a head injury.
Ms. Davis told Fox5 Atlanta: “I didn’t get my vitals taken, nobody called my name. I wasn’t seen at all.”
But wait! There’s more! By booking your trip through LOTMEgo* and using the code “Decatur,” you’ll get the Taylor Davis special, which includes a bill/cover charge for $688.35 from the hospital. An Emory Healthcare patient financial services employee told Ms. Davis that “you get charged before you are seen. Not for being seen.”
If all this has you ready to hop in your car (really?), then check out LOTMEgo* on Twittbook and InstaTok. You’ll also find trick-or-treating tips and discounts on haunted hospital tours.
*Does not actually exist
Breaking down the hot flash
Do you ever wonder why we scramble for cold things when we’re feeling nauseous? Whether it’s the cool air that needs to hit your face in the car or a cold, damp towel on the back of your neck, scientists think it could possibly be an evolutionary mechanism at the cellular level.
Motion sickness it’s actually a battle of body temperature, according to an article from LiveScience. Capillaries in the skin dilate, allowing for more blood flow near the skin’s surface and causing core temperature to fall. Once body temperature drops, the hypothalamus, which regulates temperature, tries to do its job by raising body temperature. Thus the hot flash!
The cold compress and cool air help fight the battle by counteracting the hypothalamus, but why the drop in body temperature to begin with?
There are a few theories. Dr. Robert Glatter, an emergency physician at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York, told LiveScience that the lack of oxygen needed in body tissue to survive at lower temperatures could be making it difficult to get oxygen to the body when a person is ill, and is “more likely an adaptive response influenced by poorly understood mechanisms at the cellular level.”
Another theory is that the nausea and body temperature shift is the body’s natural response to help people vomit.
Then there’s the theory of “defensive hypothermia,” which suggests that cold sweats are a possible mechanism to conserve energy so the body can fight off an intruder, which was supported by a 2014 study and a 2016 review.
It’s another one of the body’s many survival tricks.
Teachers were right: Pupils can do the math
Teachers liked to preach that we wouldn’t have calculators with us all the time, but that wound up not being true. Our phones have calculators at the press of a button. But maybe even calculators aren’t always needed because our pupils do more math than you think.
The pupil light reflex – constrict in light and dilate in darkness – is well known, but recent work shows that pupil size is also regulated by cognitive and perceptual factors. By presenting subjects with images of various numbers of dots and measuring pupil size, the investigators were able to show “that numerical information is intrinsically related to perception,” lead author Dr. Elisa Castaldi of Florence University noted in a written statement.
The researchers found that pupils are responsible for important survival techniques. Coauthor David Burr of the University of Sydney and the University of Florence gave an evolutionary perspective: “When we look around, we spontaneously perceive the form, size, movement and colour of a scene. Equally spontaneously, we perceive the number of items before us. This ability, shared with most other animals, is an evolutionary fundamental: It reveals immediately important quantities, such as how many apples there are on the tree, or how many enemies are attacking.”
Useful information, indeed, but our pupils seem to be more interested in the quantity of beers in the refrigerator.
No, Mr. Bond, I expect you to die
Movie watching usually requires a certain suspension of disbelief, and it’s safe to say James Bond movies require this more than most. Between the impossible gadgets and ludicrous doomsday plans, very few have ever stopped to consider the health risks of the James Bond universe.
Now, however, Bond, James Bond, has met his most formidable opponent: Wouter Graumans, a graduate student in epidemiology from the Netherlands. During a foray to Burkina Faso to study infectious diseases, Mr. Graumans came down with a case of food poisoning, which led him to wonder how 007 is able to trot across this big world of ours without contracting so much as a sinus infection.
Because Mr. Graumans is a man of science and conviction, mere speculation wasn’t enough. He and a group of coauthors wrote an entire paper on the health risks of the James Bond universe.
Doing so required watching over 3,000 minutes of numerous movies and analyzing Bond’s 86 total trips to 46 different countries based on current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advice for travel to those countries. Time which, the authors state in the abstract, “could easily have been spent on more pressing societal issues or forms of relaxation that are more acceptable in academic circles.”
Naturally, Mr. Bond’s line of work entails exposure to unpleasant things, such as poison, dehydration, heatstroke, and dangerous wildlife (everything from ticks to crocodiles), though oddly enough he never succumbs to any of it. He’s also curiously immune to hangovers, despite rarely drinking anything nonalcoholic. There are also less obvious risks: For one, 007 rarely washes his hands. During one movie, he handles raw chicken to lure away a pack of crocodiles but fails to wash his hands afterward, leaving him at risk for multiple food-borne illnesses.
Of course, we must address the elephant in the bedroom: Mr. Bond’s numerous, er, encounters with women. One would imagine the biggest risk to those women would be from the various STDs that likely course through Bond’s body, but of the 27% who died shortly after … encountering … him, all involved violence, with disease playing no obvious role. Who knows, maybe he’s clean? Stranger things have happened.
The timing of this article may seem a bit suspicious. Was it a PR stunt by the studio? Rest assured, the authors addressed this, noting that they received no funding for the study, and that, “given the futility of its academic value, this is deemed entirely appropriate by all authors.” We love when a punchline writes itself.
How to see Atlanta on $688.35 a day
The world is always changing, so we have to change with it. This week, LOTME becomes a travel guide, and our first stop is the Big A, the Big Peach, Dogwood City, Empire City of the South, Wakanda.
There’s lots to do in Atlanta: Celebrate a World Series win, visit the College Football Hall of Fame or the World of Coca Cola, or take the Stranger Things/Upside Down film locations tour. Serious adventurers, however, get out of the city and go to Emory Decatur Hospital in – you guessed it – Decatur (unofficial motto: “Everything is Greater in Decatur”).
Find the emergency room and ask for Taylor Davis, who will be your personal guide. She’ll show you how to check in at the desk, sit in the waiting room for 7 hours, and then leave without seeing any medical personnel or receiving any sort of attention whatsoever. All the things she did when she went there in July for a head injury.
Ms. Davis told Fox5 Atlanta: “I didn’t get my vitals taken, nobody called my name. I wasn’t seen at all.”
But wait! There’s more! By booking your trip through LOTMEgo* and using the code “Decatur,” you’ll get the Taylor Davis special, which includes a bill/cover charge for $688.35 from the hospital. An Emory Healthcare patient financial services employee told Ms. Davis that “you get charged before you are seen. Not for being seen.”
If all this has you ready to hop in your car (really?), then check out LOTMEgo* on Twittbook and InstaTok. You’ll also find trick-or-treating tips and discounts on haunted hospital tours.
*Does not actually exist
Breaking down the hot flash
Do you ever wonder why we scramble for cold things when we’re feeling nauseous? Whether it’s the cool air that needs to hit your face in the car or a cold, damp towel on the back of your neck, scientists think it could possibly be an evolutionary mechanism at the cellular level.
Motion sickness it’s actually a battle of body temperature, according to an article from LiveScience. Capillaries in the skin dilate, allowing for more blood flow near the skin’s surface and causing core temperature to fall. Once body temperature drops, the hypothalamus, which regulates temperature, tries to do its job by raising body temperature. Thus the hot flash!
The cold compress and cool air help fight the battle by counteracting the hypothalamus, but why the drop in body temperature to begin with?
There are a few theories. Dr. Robert Glatter, an emergency physician at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York, told LiveScience that the lack of oxygen needed in body tissue to survive at lower temperatures could be making it difficult to get oxygen to the body when a person is ill, and is “more likely an adaptive response influenced by poorly understood mechanisms at the cellular level.”
Another theory is that the nausea and body temperature shift is the body’s natural response to help people vomit.
Then there’s the theory of “defensive hypothermia,” which suggests that cold sweats are a possible mechanism to conserve energy so the body can fight off an intruder, which was supported by a 2014 study and a 2016 review.
It’s another one of the body’s many survival tricks.
Teachers were right: Pupils can do the math
Teachers liked to preach that we wouldn’t have calculators with us all the time, but that wound up not being true. Our phones have calculators at the press of a button. But maybe even calculators aren’t always needed because our pupils do more math than you think.
The pupil light reflex – constrict in light and dilate in darkness – is well known, but recent work shows that pupil size is also regulated by cognitive and perceptual factors. By presenting subjects with images of various numbers of dots and measuring pupil size, the investigators were able to show “that numerical information is intrinsically related to perception,” lead author Dr. Elisa Castaldi of Florence University noted in a written statement.
The researchers found that pupils are responsible for important survival techniques. Coauthor David Burr of the University of Sydney and the University of Florence gave an evolutionary perspective: “When we look around, we spontaneously perceive the form, size, movement and colour of a scene. Equally spontaneously, we perceive the number of items before us. This ability, shared with most other animals, is an evolutionary fundamental: It reveals immediately important quantities, such as how many apples there are on the tree, or how many enemies are attacking.”
Useful information, indeed, but our pupils seem to be more interested in the quantity of beers in the refrigerator.
No, Mr. Bond, I expect you to die
Movie watching usually requires a certain suspension of disbelief, and it’s safe to say James Bond movies require this more than most. Between the impossible gadgets and ludicrous doomsday plans, very few have ever stopped to consider the health risks of the James Bond universe.
Now, however, Bond, James Bond, has met his most formidable opponent: Wouter Graumans, a graduate student in epidemiology from the Netherlands. During a foray to Burkina Faso to study infectious diseases, Mr. Graumans came down with a case of food poisoning, which led him to wonder how 007 is able to trot across this big world of ours without contracting so much as a sinus infection.
Because Mr. Graumans is a man of science and conviction, mere speculation wasn’t enough. He and a group of coauthors wrote an entire paper on the health risks of the James Bond universe.
Doing so required watching over 3,000 minutes of numerous movies and analyzing Bond’s 86 total trips to 46 different countries based on current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advice for travel to those countries. Time which, the authors state in the abstract, “could easily have been spent on more pressing societal issues or forms of relaxation that are more acceptable in academic circles.”
Naturally, Mr. Bond’s line of work entails exposure to unpleasant things, such as poison, dehydration, heatstroke, and dangerous wildlife (everything from ticks to crocodiles), though oddly enough he never succumbs to any of it. He’s also curiously immune to hangovers, despite rarely drinking anything nonalcoholic. There are also less obvious risks: For one, 007 rarely washes his hands. During one movie, he handles raw chicken to lure away a pack of crocodiles but fails to wash his hands afterward, leaving him at risk for multiple food-borne illnesses.
Of course, we must address the elephant in the bedroom: Mr. Bond’s numerous, er, encounters with women. One would imagine the biggest risk to those women would be from the various STDs that likely course through Bond’s body, but of the 27% who died shortly after … encountering … him, all involved violence, with disease playing no obvious role. Who knows, maybe he’s clean? Stranger things have happened.
The timing of this article may seem a bit suspicious. Was it a PR stunt by the studio? Rest assured, the authors addressed this, noting that they received no funding for the study, and that, “given the futility of its academic value, this is deemed entirely appropriate by all authors.” We love when a punchline writes itself.
How to see Atlanta on $688.35 a day
The world is always changing, so we have to change with it. This week, LOTME becomes a travel guide, and our first stop is the Big A, the Big Peach, Dogwood City, Empire City of the South, Wakanda.
There’s lots to do in Atlanta: Celebrate a World Series win, visit the College Football Hall of Fame or the World of Coca Cola, or take the Stranger Things/Upside Down film locations tour. Serious adventurers, however, get out of the city and go to Emory Decatur Hospital in – you guessed it – Decatur (unofficial motto: “Everything is Greater in Decatur”).
Find the emergency room and ask for Taylor Davis, who will be your personal guide. She’ll show you how to check in at the desk, sit in the waiting room for 7 hours, and then leave without seeing any medical personnel or receiving any sort of attention whatsoever. All the things she did when she went there in July for a head injury.
Ms. Davis told Fox5 Atlanta: “I didn’t get my vitals taken, nobody called my name. I wasn’t seen at all.”
But wait! There’s more! By booking your trip through LOTMEgo* and using the code “Decatur,” you’ll get the Taylor Davis special, which includes a bill/cover charge for $688.35 from the hospital. An Emory Healthcare patient financial services employee told Ms. Davis that “you get charged before you are seen. Not for being seen.”
If all this has you ready to hop in your car (really?), then check out LOTMEgo* on Twittbook and InstaTok. You’ll also find trick-or-treating tips and discounts on haunted hospital tours.
*Does not actually exist
Breaking down the hot flash
Do you ever wonder why we scramble for cold things when we’re feeling nauseous? Whether it’s the cool air that needs to hit your face in the car or a cold, damp towel on the back of your neck, scientists think it could possibly be an evolutionary mechanism at the cellular level.
Motion sickness it’s actually a battle of body temperature, according to an article from LiveScience. Capillaries in the skin dilate, allowing for more blood flow near the skin’s surface and causing core temperature to fall. Once body temperature drops, the hypothalamus, which regulates temperature, tries to do its job by raising body temperature. Thus the hot flash!
The cold compress and cool air help fight the battle by counteracting the hypothalamus, but why the drop in body temperature to begin with?
There are a few theories. Dr. Robert Glatter, an emergency physician at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York, told LiveScience that the lack of oxygen needed in body tissue to survive at lower temperatures could be making it difficult to get oxygen to the body when a person is ill, and is “more likely an adaptive response influenced by poorly understood mechanisms at the cellular level.”
Another theory is that the nausea and body temperature shift is the body’s natural response to help people vomit.
Then there’s the theory of “defensive hypothermia,” which suggests that cold sweats are a possible mechanism to conserve energy so the body can fight off an intruder, which was supported by a 2014 study and a 2016 review.
It’s another one of the body’s many survival tricks.
Teachers were right: Pupils can do the math
Teachers liked to preach that we wouldn’t have calculators with us all the time, but that wound up not being true. Our phones have calculators at the press of a button. But maybe even calculators aren’t always needed because our pupils do more math than you think.
The pupil light reflex – constrict in light and dilate in darkness – is well known, but recent work shows that pupil size is also regulated by cognitive and perceptual factors. By presenting subjects with images of various numbers of dots and measuring pupil size, the investigators were able to show “that numerical information is intrinsically related to perception,” lead author Dr. Elisa Castaldi of Florence University noted in a written statement.
The researchers found that pupils are responsible for important survival techniques. Coauthor David Burr of the University of Sydney and the University of Florence gave an evolutionary perspective: “When we look around, we spontaneously perceive the form, size, movement and colour of a scene. Equally spontaneously, we perceive the number of items before us. This ability, shared with most other animals, is an evolutionary fundamental: It reveals immediately important quantities, such as how many apples there are on the tree, or how many enemies are attacking.”
Useful information, indeed, but our pupils seem to be more interested in the quantity of beers in the refrigerator.