User login
Ichthyosiform Sarcoidosis and Systemic Involvement
Sarcoidosis is a multiorgan, systemic, granulomatous disease that most commonly affects the cutaneous, pulmonary, ocular, and cardiac organ systems. Cutaneous involvement occurs in approximately 20% to 35% of patients, with approximately 25% of patients demonstrating only dermatologic findings.1 Cutaneous sarcoidosis can have a highly variable presentation. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis (IS) is a rare form of this disease that has been described as presenting as polygonal adherent scales.2 It often is associated with internal organ involvement. We present a case of IS without any organ system involvement at the time of diagnosis. A review of the English-language literature was performed to ascertain the internal organ associations most commonly reported with IS.
Case Report
A 66-year-old black woman presented to dermatology with dark scaly patches noted by her primary care physician to be present on both of the lower extremities. The patient believed they were present for at least 4 years. She described dark spots confined to the lower legs that had gradually increased in size. Review of systems was negative for fever, chills, night sweats, weight loss, vision changes, cough, dyspnea, and joint pains, and there was no history of either personal or familial cutaneous diseases.
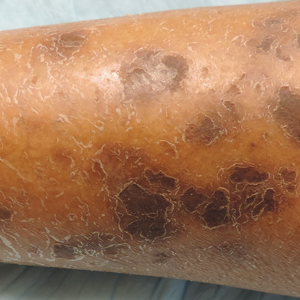
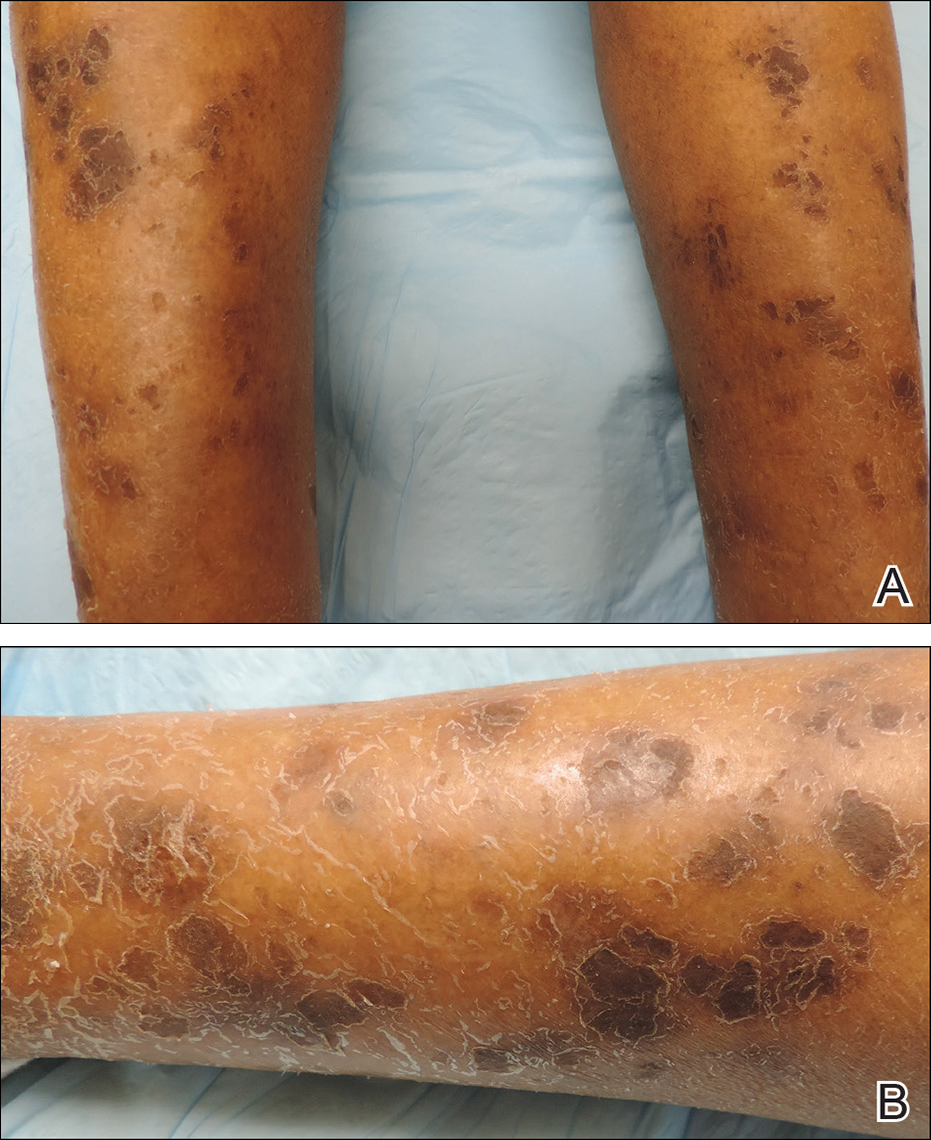
Physical examination revealed cutaneous patches of thin white scale with a sharp edge in arciform patterns on the lower extremities. Several of these patches were hyperpigmented and xerotic in appearance (Figure 1). The patches were limited to the lower legs, with no other lesions noted.
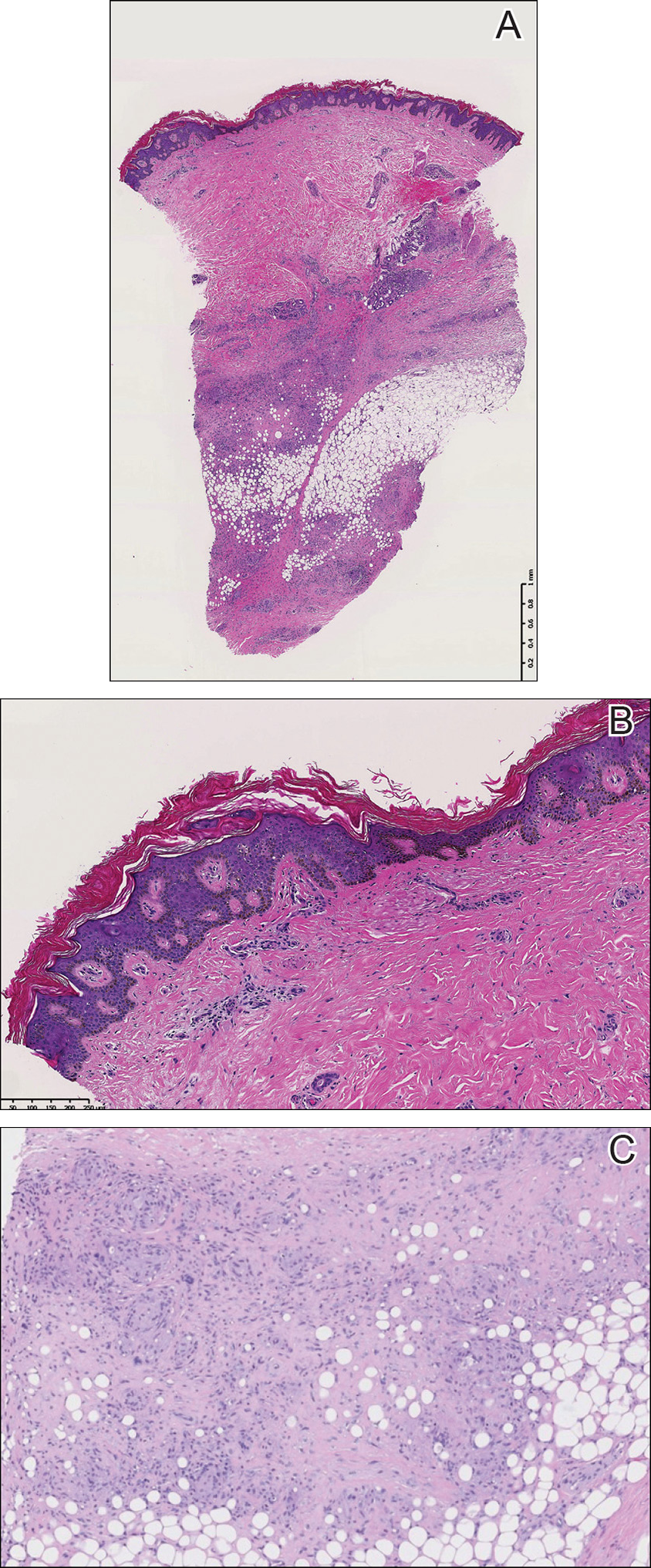
A punch biopsy of the skin on the right lower leg was performed. Histopathologic analysis showed epidermal compact hyperkeratosis with deep granulomatous infiltration into the subcutaneous tissue (Figures 2A and 2B). At high power, these granulomas were noted to be noncaseating naked granulomas composed of epithelioid histiocytes surrounded by sparse lymphocytic inflammation (Figure 2C). Special stains including acid-fast bacilli, Fite, and periodic acid–Schiff were negative. The diagnosis of IS was made based on clinical presentation and primarily by histopathologic analysis.
The patient’s cutaneous lesions were treated with fluocinonide ointment 0.05% twice daily. Although she did not notice a dramatic improvement in the plaques, they stabilized in size. Her primary care physician was notified and advised to begin a workup for involvement of other organ systems by sarcoidosis. Her initial evaluation, which included a chest radiograph and electrocardiogram, were unremarkable. Despite multiple attempts to persuade the patient to return for further follow-up, neither dermatology nor her primary care physician were able to complete a full workup.
Comment
Etiology
Although there are several theories regarding the etiology of sarcoidosis, the exact cause remains unknown. The body’s immune response, infectious agents, genetics, and the environment have all been thought to play a role. It has been well established that helper T cell (TH1) production of interferon and increased levels of tumor necrosis factor propagate the inflammatory response seen in sarcoidosis.3 More recently, TH17 cells have been found in cutaneous lesions, bronchoalveolar lavage samples, and the blood of patients with sarcoidosis, especially in those with active disease progression.3 Infectious agents such as mycobacteria and propionibacteria DNA or RNA also have been found in sarcoid samples.4 Several HLA-DRB1 variants have been associated with an increased incidence of sarcoidosis.5
Presentation
Characteristic dermatologic findings of sarcoidosis include macules, papules, nodules, and plaques located on the face, especially the nose, cheeks, and ears, and on the shins or ankles, as well as similar lesions around tattoos or scars. Sarcoid lesions also have been described as angiolupoid, lichenoid, annular, verrucous, ulcerative, and psoriasiform. Here we present an example of the uncommon type, ichthyosiform. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis is a rare variant described primarily in dark-skinned individuals, a finding supported by both our case and prior reports. Most reported cases have described IS lesions as having a pasted-on appearance, with adherent centers on the extensor surfaces of the lower extremities, head, and/or neck.6 Our case follows this descriptive pattern previously reported with adherent patches limited to the lower extremities.
Histopathology
The key histopathologic finding is the presence of noncaseating granulomas on biopsy. Sarcoid “specific” lesions rest on the identification of the noncaseating granulomas, while “nonspecific” lesions such as erythema nodosum fail to demonstrate this finding.1
Systemic Involvement
The IS type is believed to be an excellent marker for systemic disease, with approximately 95% of reported cases having some form of systemic illness.6 Acquired ichthyosis should warrant further investigation for systemic disease. Early recognition could be beneficial for the patient because the ichthyosiform type is believed to precede the diagnosis of systemic disease in most cases by a median of 3 months.6
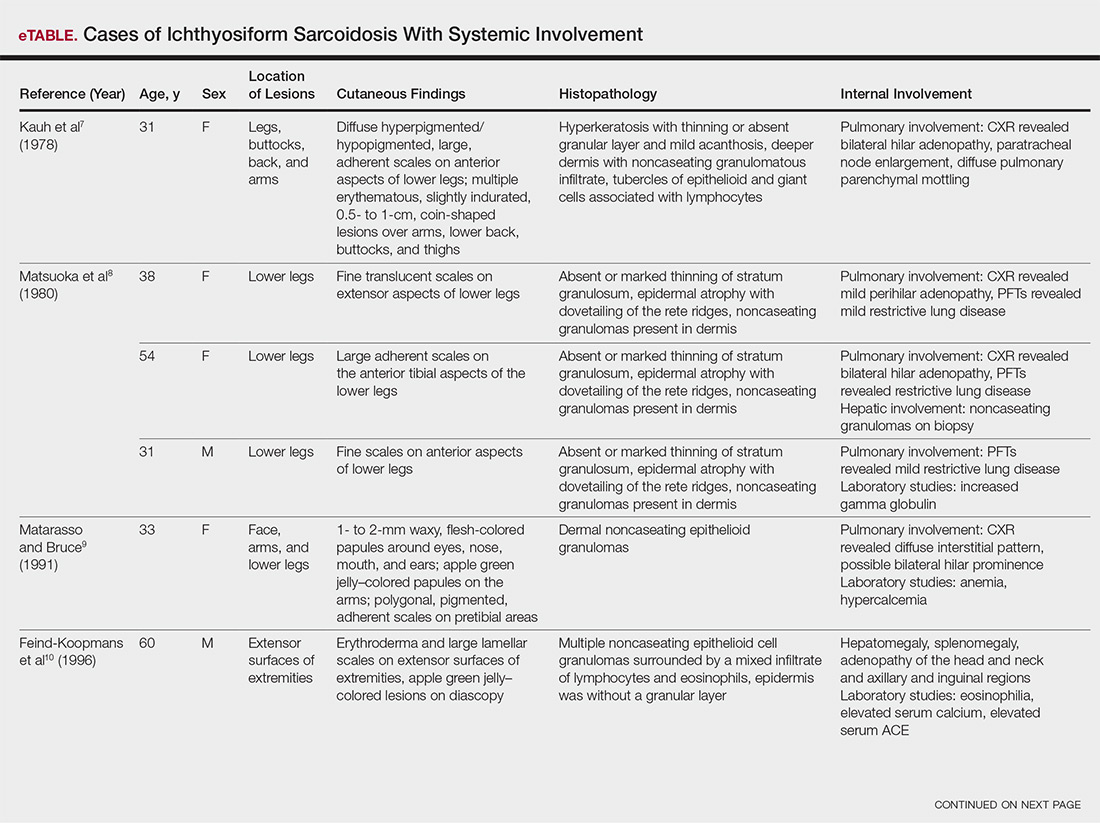
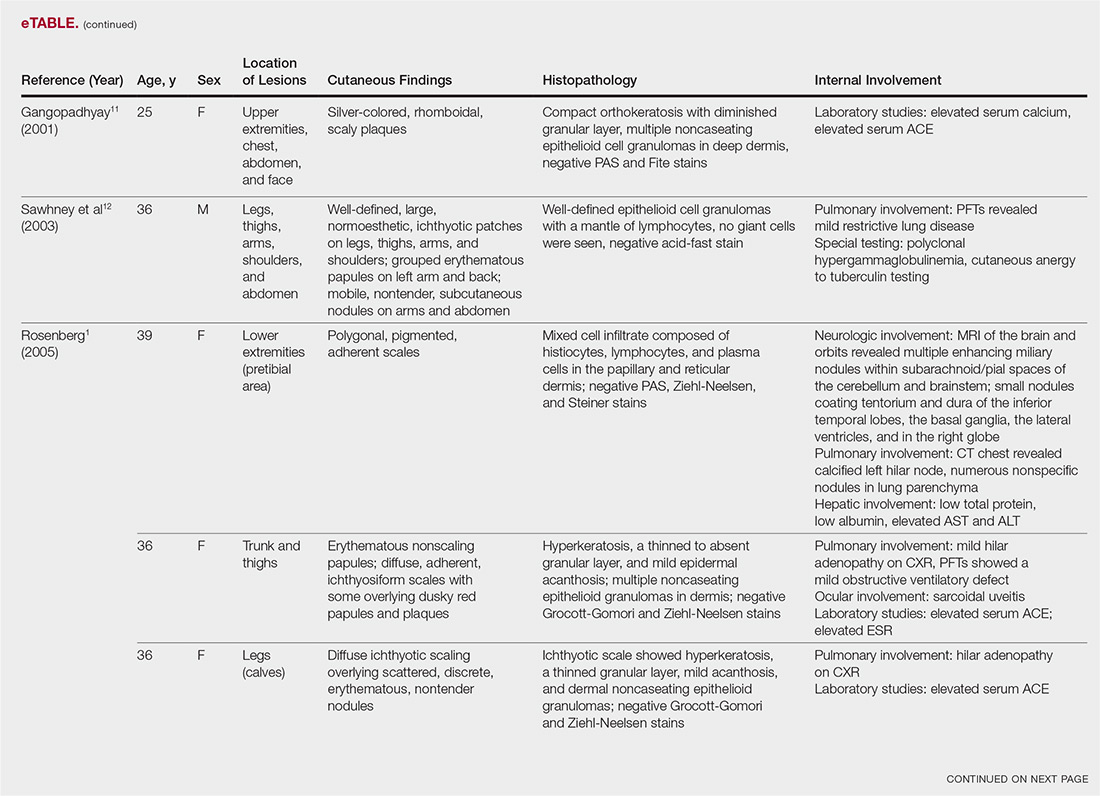
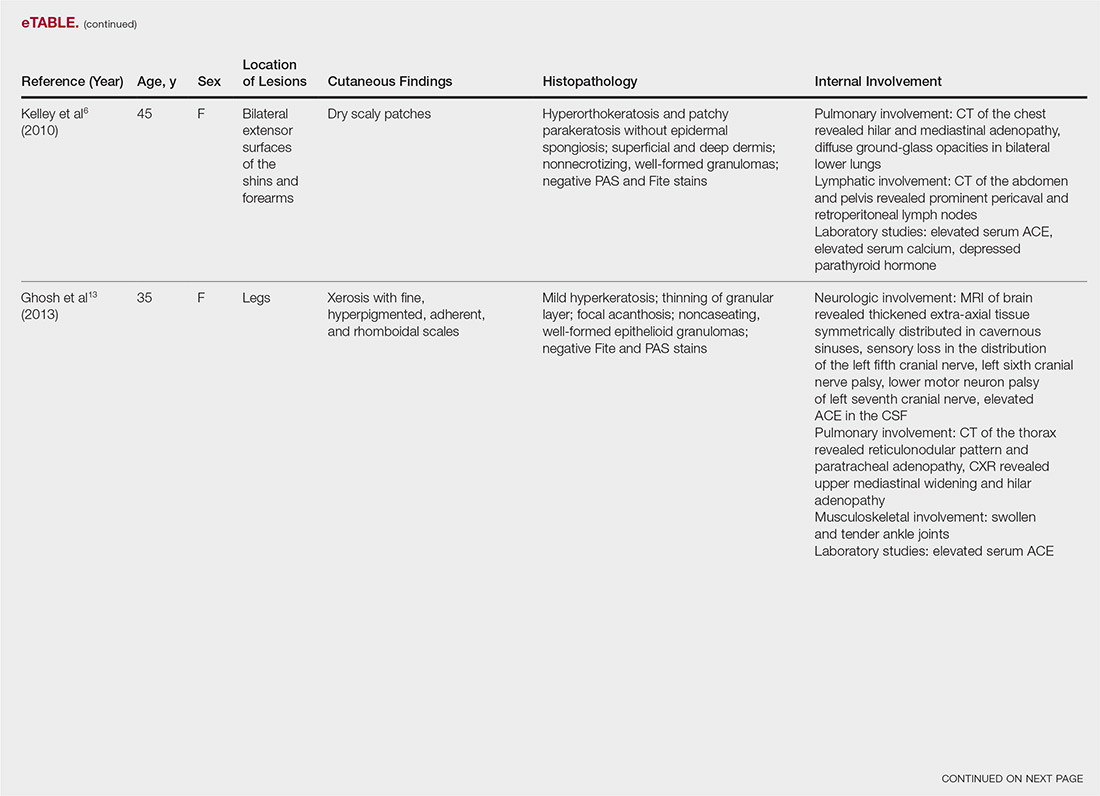
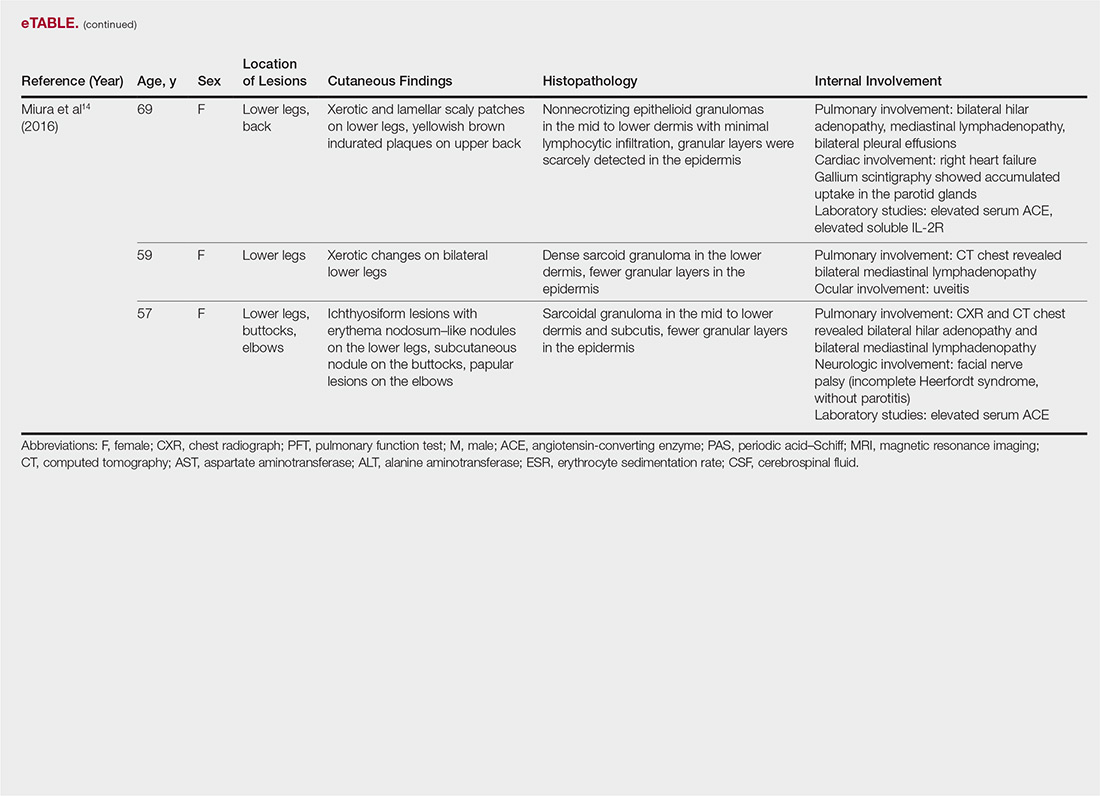
The most common site of internal sarcoid involvement is the lungs, but the lymph nodes, eyes, liver, spleen, heart, and central nervous system also can be involved. Patients can present with nonspecific symptoms such as erythema nodosum in the skin, dyspnea, cough, chest pain, vision changes, enlarged lymph nodes, headaches, joint pain, fever, fatigue, weight loss, and malaise. According to a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the term ichthyosiform sarcoidosis, 16 cases have been reported in the English-language literature (eTable).1,6-14 Of these 16 cases, 3 involved men and 13 involved women. The median age of a patient diagnosed with IS was 37 years. The respiratory system was found to be the most common organ system involved (14 of 16 patients), with hilar adenopathy and restrictive lung disease being the most common findings. Neurologic findings and hepatic involvement also were seen in 3 and 3 patients, respectively. Eight of 16 cases had an elevated serum angiotensin-converting enzyme level. Details of systemic involvement in other cases of IS are listed in the eTable.
Management
Most patients are given topical corticosteroids for their cutaneous lesions, but patients with systemic involvement will likely need some type of systemic immunosuppressive therapy to control their disease. Systemic therapy often is warranted in IS because of reports of rapid progression. Our case differs from these prior reports in the relative stability of the disease at the last patient encounter. Systemic treatment commonly includes oral corticosteroids such as prednisone. Other options, such as hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate, azathioprine, pentoxifylline, thalidomide, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, and infliximab, can be considered if other treatments fail.13 Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis patients should continue to have regular follow-up to monitor for disease progression.
Differential
When evaluating an acquired ichthyosis, dermatologists can consider other associations such as Hodgkin disease, hypothyroidism, multiple myeloma, carcinomatosis, and chronic malnutrition.1 Skin biopsy demonstrating granuloma formation also is not specific for sarcoidosis. Other etiologies, such as autoimmune diseases, immunodeficiency disorders, infections, foreign body granulomas, neoplasms, and drug reactions, should be considered.15 All patients with acquired ichthyosis should undergo a thorough evaluation for internal involvement.
Conclusion
We presented a case of IS, a rare type of sarcoidosis commonly associated with further internal involvement of the respiratory, nervous, or hepatic organ systems. Recognition of an acquired form of ichthyosis and its potential disease associations, including sarcoidosis, is important to improve early detection of any internal disease, allowing prompt initiation of treatment.
- Rosenberg B. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis. Dermatol Online J. 2005;11:15.
- Banse-Kupin L, Pelachyk JM. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis: report of two cases and review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987;17:616-620.
- Sanchez M, Haimovic A, Prystowsky S. Sarcoidosis. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:389-416.
- Celada LJ, Hawkins C, Drake WP. The etiologic role of infectious antigens in sarcoidosis pathogenesis. Clin Chest Med. 2015;36:561-568.
- Fingerlin TE, Hamzeh N, Maier LA. Genetics of sarcoidosis. Clin Chest Med. 2015;36:569-584.
- Kelley BP, George DE, LeLeux TM, et al. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis: a case report and review of the literature. Dermatol Online J. 2010;16:5.
- Kauh YC, Goody HE, Luscombe HA. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis. Arch Dermatol. 1978;114:100-101.
- Matsuoka LY, LeVine M, Glasser S, et al. Ichthyosiform sarcoid. Cutis. 1980;25:188-189.
- Matarasso SL, Bruce S. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis: report of a case. Cutis. 1991;47:405-408.
- Feind-Koopmans AG, Lucker GP, van de Kerkhof PC. Acquired ichthyosiform erythroderma and sarcoidosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:826-828.
- Gangopadhyay AK. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2001;67:91-92.
- Sawhney M, Sharma YK, Gera V, et al. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis following chemotherapy of Hodgkin’s disease. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2003;69:220-222.
- Ghosh UC, Ghosh SK, Hazra K, et al. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis revisited. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013;79:795-798.
- Miura T, Kato Y, Yamamoto T. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis: report of three cases from Japan and literature review. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2016;33:392-397.
- Fernandez-Faith E, McDonnell J. Cutaneous sarcoidosis: differential diagnosis. Clin Dermatol. 2007;25:276-287.
Sarcoidosis is a multiorgan, systemic, granulomatous disease that most commonly affects the cutaneous, pulmonary, ocular, and cardiac organ systems. Cutaneous involvement occurs in approximately 20% to 35% of patients, with approximately 25% of patients demonstrating only dermatologic findings.1 Cutaneous sarcoidosis can have a highly variable presentation. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis (IS) is a rare form of this disease that has been described as presenting as polygonal adherent scales.2 It often is associated with internal organ involvement. We present a case of IS without any organ system involvement at the time of diagnosis. A review of the English-language literature was performed to ascertain the internal organ associations most commonly reported with IS.
Case Report
A 66-year-old black woman presented to dermatology with dark scaly patches noted by her primary care physician to be present on both of the lower extremities. The patient believed they were present for at least 4 years. She described dark spots confined to the lower legs that had gradually increased in size. Review of systems was negative for fever, chills, night sweats, weight loss, vision changes, cough, dyspnea, and joint pains, and there was no history of either personal or familial cutaneous diseases.
Physical examination revealed cutaneous patches of thin white scale with a sharp edge in arciform patterns on the lower extremities. Several of these patches were hyperpigmented and xerotic in appearance (Figure 1). The patches were limited to the lower legs, with no other lesions noted.

A punch biopsy of the skin on the right lower leg was performed. Histopathologic analysis showed epidermal compact hyperkeratosis with deep granulomatous infiltration into the subcutaneous tissue (Figures 2A and 2B). At high power, these granulomas were noted to be noncaseating naked granulomas composed of epithelioid histiocytes surrounded by sparse lymphocytic inflammation (Figure 2C). Special stains including acid-fast bacilli, Fite, and periodic acid–Schiff were negative. The diagnosis of IS was made based on clinical presentation and primarily by histopathologic analysis.

The patient’s cutaneous lesions were treated with fluocinonide ointment 0.05% twice daily. Although she did not notice a dramatic improvement in the plaques, they stabilized in size. Her primary care physician was notified and advised to begin a workup for involvement of other organ systems by sarcoidosis. Her initial evaluation, which included a chest radiograph and electrocardiogram, were unremarkable. Despite multiple attempts to persuade the patient to return for further follow-up, neither dermatology nor her primary care physician were able to complete a full workup.
Comment
Etiology
Although there are several theories regarding the etiology of sarcoidosis, the exact cause remains unknown. The body’s immune response, infectious agents, genetics, and the environment have all been thought to play a role. It has been well established that helper T cell (TH1) production of interferon and increased levels of tumor necrosis factor propagate the inflammatory response seen in sarcoidosis.3 More recently, TH17 cells have been found in cutaneous lesions, bronchoalveolar lavage samples, and the blood of patients with sarcoidosis, especially in those with active disease progression.3 Infectious agents such as mycobacteria and propionibacteria DNA or RNA also have been found in sarcoid samples.4 Several HLA-DRB1 variants have been associated with an increased incidence of sarcoidosis.5
Presentation
Characteristic dermatologic findings of sarcoidosis include macules, papules, nodules, and plaques located on the face, especially the nose, cheeks, and ears, and on the shins or ankles, as well as similar lesions around tattoos or scars. Sarcoid lesions also have been described as angiolupoid, lichenoid, annular, verrucous, ulcerative, and psoriasiform. Here we present an example of the uncommon type, ichthyosiform. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis is a rare variant described primarily in dark-skinned individuals, a finding supported by both our case and prior reports. Most reported cases have described IS lesions as having a pasted-on appearance, with adherent centers on the extensor surfaces of the lower extremities, head, and/or neck.6 Our case follows this descriptive pattern previously reported with adherent patches limited to the lower extremities.
Histopathology
The key histopathologic finding is the presence of noncaseating granulomas on biopsy. Sarcoid “specific” lesions rest on the identification of the noncaseating granulomas, while “nonspecific” lesions such as erythema nodosum fail to demonstrate this finding.1
Systemic Involvement
The IS type is believed to be an excellent marker for systemic disease, with approximately 95% of reported cases having some form of systemic illness.6 Acquired ichthyosis should warrant further investigation for systemic disease. Early recognition could be beneficial for the patient because the ichthyosiform type is believed to precede the diagnosis of systemic disease in most cases by a median of 3 months.6
The most common site of internal sarcoid involvement is the lungs, but the lymph nodes, eyes, liver, spleen, heart, and central nervous system also can be involved. Patients can present with nonspecific symptoms such as erythema nodosum in the skin, dyspnea, cough, chest pain, vision changes, enlarged lymph nodes, headaches, joint pain, fever, fatigue, weight loss, and malaise. According to a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the term ichthyosiform sarcoidosis, 16 cases have been reported in the English-language literature (eTable).1,6-14 Of these 16 cases, 3 involved men and 13 involved women. The median age of a patient diagnosed with IS was 37 years. The respiratory system was found to be the most common organ system involved (14 of 16 patients), with hilar adenopathy and restrictive lung disease being the most common findings. Neurologic findings and hepatic involvement also were seen in 3 and 3 patients, respectively. Eight of 16 cases had an elevated serum angiotensin-converting enzyme level. Details of systemic involvement in other cases of IS are listed in the eTable.




Management
Most patients are given topical corticosteroids for their cutaneous lesions, but patients with systemic involvement will likely need some type of systemic immunosuppressive therapy to control their disease. Systemic therapy often is warranted in IS because of reports of rapid progression. Our case differs from these prior reports in the relative stability of the disease at the last patient encounter. Systemic treatment commonly includes oral corticosteroids such as prednisone. Other options, such as hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate, azathioprine, pentoxifylline, thalidomide, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, and infliximab, can be considered if other treatments fail.13 Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis patients should continue to have regular follow-up to monitor for disease progression.
Differential
When evaluating an acquired ichthyosis, dermatologists can consider other associations such as Hodgkin disease, hypothyroidism, multiple myeloma, carcinomatosis, and chronic malnutrition.1 Skin biopsy demonstrating granuloma formation also is not specific for sarcoidosis. Other etiologies, such as autoimmune diseases, immunodeficiency disorders, infections, foreign body granulomas, neoplasms, and drug reactions, should be considered.15 All patients with acquired ichthyosis should undergo a thorough evaluation for internal involvement.
Conclusion
We presented a case of IS, a rare type of sarcoidosis commonly associated with further internal involvement of the respiratory, nervous, or hepatic organ systems. Recognition of an acquired form of ichthyosis and its potential disease associations, including sarcoidosis, is important to improve early detection of any internal disease, allowing prompt initiation of treatment.
Sarcoidosis is a multiorgan, systemic, granulomatous disease that most commonly affects the cutaneous, pulmonary, ocular, and cardiac organ systems. Cutaneous involvement occurs in approximately 20% to 35% of patients, with approximately 25% of patients demonstrating only dermatologic findings.1 Cutaneous sarcoidosis can have a highly variable presentation. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis (IS) is a rare form of this disease that has been described as presenting as polygonal adherent scales.2 It often is associated with internal organ involvement. We present a case of IS without any organ system involvement at the time of diagnosis. A review of the English-language literature was performed to ascertain the internal organ associations most commonly reported with IS.
Case Report
A 66-year-old black woman presented to dermatology with dark scaly patches noted by her primary care physician to be present on both of the lower extremities. The patient believed they were present for at least 4 years. She described dark spots confined to the lower legs that had gradually increased in size. Review of systems was negative for fever, chills, night sweats, weight loss, vision changes, cough, dyspnea, and joint pains, and there was no history of either personal or familial cutaneous diseases.
Physical examination revealed cutaneous patches of thin white scale with a sharp edge in arciform patterns on the lower extremities. Several of these patches were hyperpigmented and xerotic in appearance (Figure 1). The patches were limited to the lower legs, with no other lesions noted.

A punch biopsy of the skin on the right lower leg was performed. Histopathologic analysis showed epidermal compact hyperkeratosis with deep granulomatous infiltration into the subcutaneous tissue (Figures 2A and 2B). At high power, these granulomas were noted to be noncaseating naked granulomas composed of epithelioid histiocytes surrounded by sparse lymphocytic inflammation (Figure 2C). Special stains including acid-fast bacilli, Fite, and periodic acid–Schiff were negative. The diagnosis of IS was made based on clinical presentation and primarily by histopathologic analysis.

The patient’s cutaneous lesions were treated with fluocinonide ointment 0.05% twice daily. Although she did not notice a dramatic improvement in the plaques, they stabilized in size. Her primary care physician was notified and advised to begin a workup for involvement of other organ systems by sarcoidosis. Her initial evaluation, which included a chest radiograph and electrocardiogram, were unremarkable. Despite multiple attempts to persuade the patient to return for further follow-up, neither dermatology nor her primary care physician were able to complete a full workup.
Comment
Etiology
Although there are several theories regarding the etiology of sarcoidosis, the exact cause remains unknown. The body’s immune response, infectious agents, genetics, and the environment have all been thought to play a role. It has been well established that helper T cell (TH1) production of interferon and increased levels of tumor necrosis factor propagate the inflammatory response seen in sarcoidosis.3 More recently, TH17 cells have been found in cutaneous lesions, bronchoalveolar lavage samples, and the blood of patients with sarcoidosis, especially in those with active disease progression.3 Infectious agents such as mycobacteria and propionibacteria DNA or RNA also have been found in sarcoid samples.4 Several HLA-DRB1 variants have been associated with an increased incidence of sarcoidosis.5
Presentation
Characteristic dermatologic findings of sarcoidosis include macules, papules, nodules, and plaques located on the face, especially the nose, cheeks, and ears, and on the shins or ankles, as well as similar lesions around tattoos or scars. Sarcoid lesions also have been described as angiolupoid, lichenoid, annular, verrucous, ulcerative, and psoriasiform. Here we present an example of the uncommon type, ichthyosiform. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis is a rare variant described primarily in dark-skinned individuals, a finding supported by both our case and prior reports. Most reported cases have described IS lesions as having a pasted-on appearance, with adherent centers on the extensor surfaces of the lower extremities, head, and/or neck.6 Our case follows this descriptive pattern previously reported with adherent patches limited to the lower extremities.
Histopathology
The key histopathologic finding is the presence of noncaseating granulomas on biopsy. Sarcoid “specific” lesions rest on the identification of the noncaseating granulomas, while “nonspecific” lesions such as erythema nodosum fail to demonstrate this finding.1
Systemic Involvement
The IS type is believed to be an excellent marker for systemic disease, with approximately 95% of reported cases having some form of systemic illness.6 Acquired ichthyosis should warrant further investigation for systemic disease. Early recognition could be beneficial for the patient because the ichthyosiform type is believed to precede the diagnosis of systemic disease in most cases by a median of 3 months.6
The most common site of internal sarcoid involvement is the lungs, but the lymph nodes, eyes, liver, spleen, heart, and central nervous system also can be involved. Patients can present with nonspecific symptoms such as erythema nodosum in the skin, dyspnea, cough, chest pain, vision changes, enlarged lymph nodes, headaches, joint pain, fever, fatigue, weight loss, and malaise. According to a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the term ichthyosiform sarcoidosis, 16 cases have been reported in the English-language literature (eTable).1,6-14 Of these 16 cases, 3 involved men and 13 involved women. The median age of a patient diagnosed with IS was 37 years. The respiratory system was found to be the most common organ system involved (14 of 16 patients), with hilar adenopathy and restrictive lung disease being the most common findings. Neurologic findings and hepatic involvement also were seen in 3 and 3 patients, respectively. Eight of 16 cases had an elevated serum angiotensin-converting enzyme level. Details of systemic involvement in other cases of IS are listed in the eTable.




Management
Most patients are given topical corticosteroids for their cutaneous lesions, but patients with systemic involvement will likely need some type of systemic immunosuppressive therapy to control their disease. Systemic therapy often is warranted in IS because of reports of rapid progression. Our case differs from these prior reports in the relative stability of the disease at the last patient encounter. Systemic treatment commonly includes oral corticosteroids such as prednisone. Other options, such as hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate, azathioprine, pentoxifylline, thalidomide, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, and infliximab, can be considered if other treatments fail.13 Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis patients should continue to have regular follow-up to monitor for disease progression.
Differential
When evaluating an acquired ichthyosis, dermatologists can consider other associations such as Hodgkin disease, hypothyroidism, multiple myeloma, carcinomatosis, and chronic malnutrition.1 Skin biopsy demonstrating granuloma formation also is not specific for sarcoidosis. Other etiologies, such as autoimmune diseases, immunodeficiency disorders, infections, foreign body granulomas, neoplasms, and drug reactions, should be considered.15 All patients with acquired ichthyosis should undergo a thorough evaluation for internal involvement.
Conclusion
We presented a case of IS, a rare type of sarcoidosis commonly associated with further internal involvement of the respiratory, nervous, or hepatic organ systems. Recognition of an acquired form of ichthyosis and its potential disease associations, including sarcoidosis, is important to improve early detection of any internal disease, allowing prompt initiation of treatment.
- Rosenberg B. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis. Dermatol Online J. 2005;11:15.
- Banse-Kupin L, Pelachyk JM. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis: report of two cases and review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987;17:616-620.
- Sanchez M, Haimovic A, Prystowsky S. Sarcoidosis. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:389-416.
- Celada LJ, Hawkins C, Drake WP. The etiologic role of infectious antigens in sarcoidosis pathogenesis. Clin Chest Med. 2015;36:561-568.
- Fingerlin TE, Hamzeh N, Maier LA. Genetics of sarcoidosis. Clin Chest Med. 2015;36:569-584.
- Kelley BP, George DE, LeLeux TM, et al. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis: a case report and review of the literature. Dermatol Online J. 2010;16:5.
- Kauh YC, Goody HE, Luscombe HA. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis. Arch Dermatol. 1978;114:100-101.
- Matsuoka LY, LeVine M, Glasser S, et al. Ichthyosiform sarcoid. Cutis. 1980;25:188-189.
- Matarasso SL, Bruce S. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis: report of a case. Cutis. 1991;47:405-408.
- Feind-Koopmans AG, Lucker GP, van de Kerkhof PC. Acquired ichthyosiform erythroderma and sarcoidosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:826-828.
- Gangopadhyay AK. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2001;67:91-92.
- Sawhney M, Sharma YK, Gera V, et al. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis following chemotherapy of Hodgkin’s disease. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2003;69:220-222.
- Ghosh UC, Ghosh SK, Hazra K, et al. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis revisited. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013;79:795-798.
- Miura T, Kato Y, Yamamoto T. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis: report of three cases from Japan and literature review. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2016;33:392-397.
- Fernandez-Faith E, McDonnell J. Cutaneous sarcoidosis: differential diagnosis. Clin Dermatol. 2007;25:276-287.
- Rosenberg B. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis. Dermatol Online J. 2005;11:15.
- Banse-Kupin L, Pelachyk JM. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis: report of two cases and review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987;17:616-620.
- Sanchez M, Haimovic A, Prystowsky S. Sarcoidosis. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:389-416.
- Celada LJ, Hawkins C, Drake WP. The etiologic role of infectious antigens in sarcoidosis pathogenesis. Clin Chest Med. 2015;36:561-568.
- Fingerlin TE, Hamzeh N, Maier LA. Genetics of sarcoidosis. Clin Chest Med. 2015;36:569-584.
- Kelley BP, George DE, LeLeux TM, et al. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis: a case report and review of the literature. Dermatol Online J. 2010;16:5.
- Kauh YC, Goody HE, Luscombe HA. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis. Arch Dermatol. 1978;114:100-101.
- Matsuoka LY, LeVine M, Glasser S, et al. Ichthyosiform sarcoid. Cutis. 1980;25:188-189.
- Matarasso SL, Bruce S. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis: report of a case. Cutis. 1991;47:405-408.
- Feind-Koopmans AG, Lucker GP, van de Kerkhof PC. Acquired ichthyosiform erythroderma and sarcoidosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:826-828.
- Gangopadhyay AK. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2001;67:91-92.
- Sawhney M, Sharma YK, Gera V, et al. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis following chemotherapy of Hodgkin’s disease. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2003;69:220-222.
- Ghosh UC, Ghosh SK, Hazra K, et al. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis revisited. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013;79:795-798.
- Miura T, Kato Y, Yamamoto T. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis: report of three cases from Japan and literature review. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2016;33:392-397.
- Fernandez-Faith E, McDonnell J. Cutaneous sarcoidosis: differential diagnosis. Clin Dermatol. 2007;25:276-287.
Practice Points
- Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis is a rare form of sarcoidosis that presents as polygonal adherent scales.
- Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis is commonly associated with pulmonary, neurologic, and hepatic involvement.
- Acquired ichthyosis should warrant further investigation for systemic disease.
Pigmented Squamous Cell Carcinoma Presenting as Longitudinal Melanonychia in a Transplant Recipient
Case Report
A 62-year-old black man presented for examination of a dark longitudinal streak located adjacent to the lateral nail fold on the third finger of the left hand. The lesion had been present for several months, during which time it had slowly expanded in size. The fingertip had recently become tender, which interfered with the patient’s ability to work. His past medical history was remarkable for end-stage renal disease secondary to glomerulonephritis with nephrotic syndrome of unclear etiology. He initially was treated by an outside physician using peritoneal dialysis for 3 years until he underwent renal transplantation in 2004 with a cadaveric organ. Other remarkable medical conditions included posttransplantation diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and gout. His multidrug regimen included 2 immunosuppressive medications: oral cyclosporine 125 mg twice daily and oral mycophenolate mofetil 250 mg twice daily.
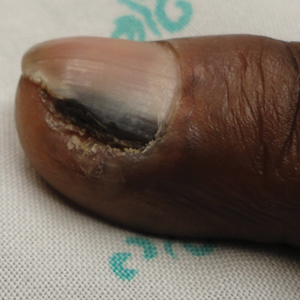
A broad, irregular, black, pigmented, subungual band was noted on the left third finger. The lesion appeared to emanate from below the nail cuticle and traveled along the nail longitudinally toward the distal tip. The band appeared darker at the edge adjacent to the lateral nail fold and grew lighter near the middle of the nail where its free edge was noted to be irregular. A slightly thickened lateral nail fold with an irregular, small, sawtoothlike hyperkeratosis and hyperpigmentation also was noted (Figure 1).
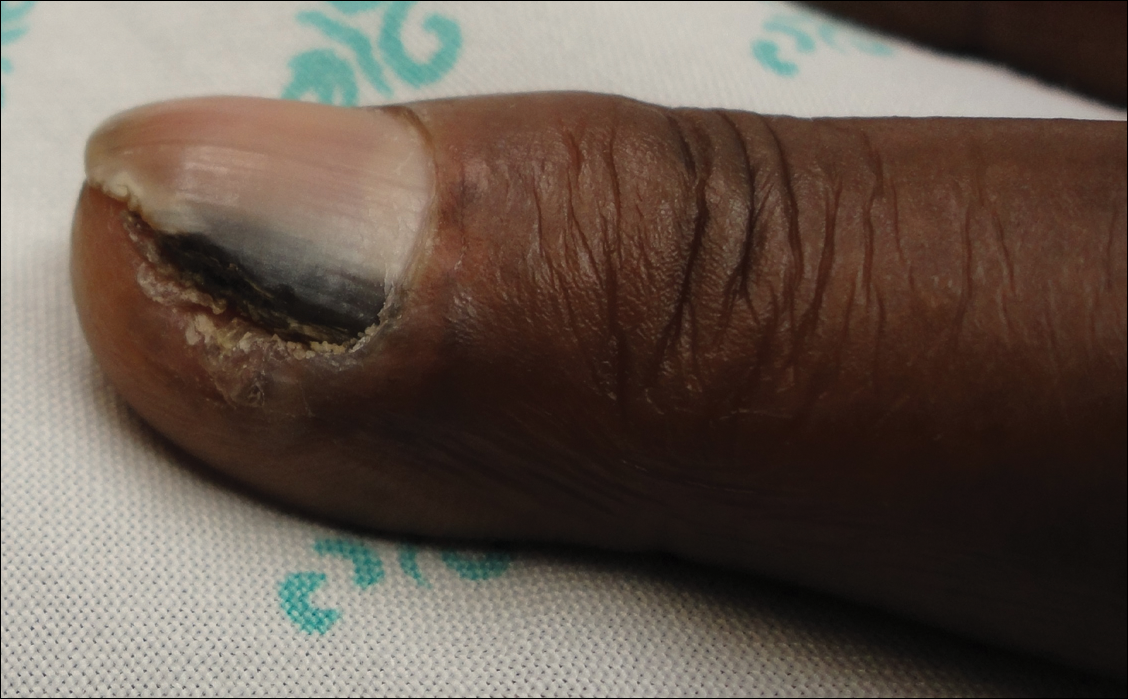
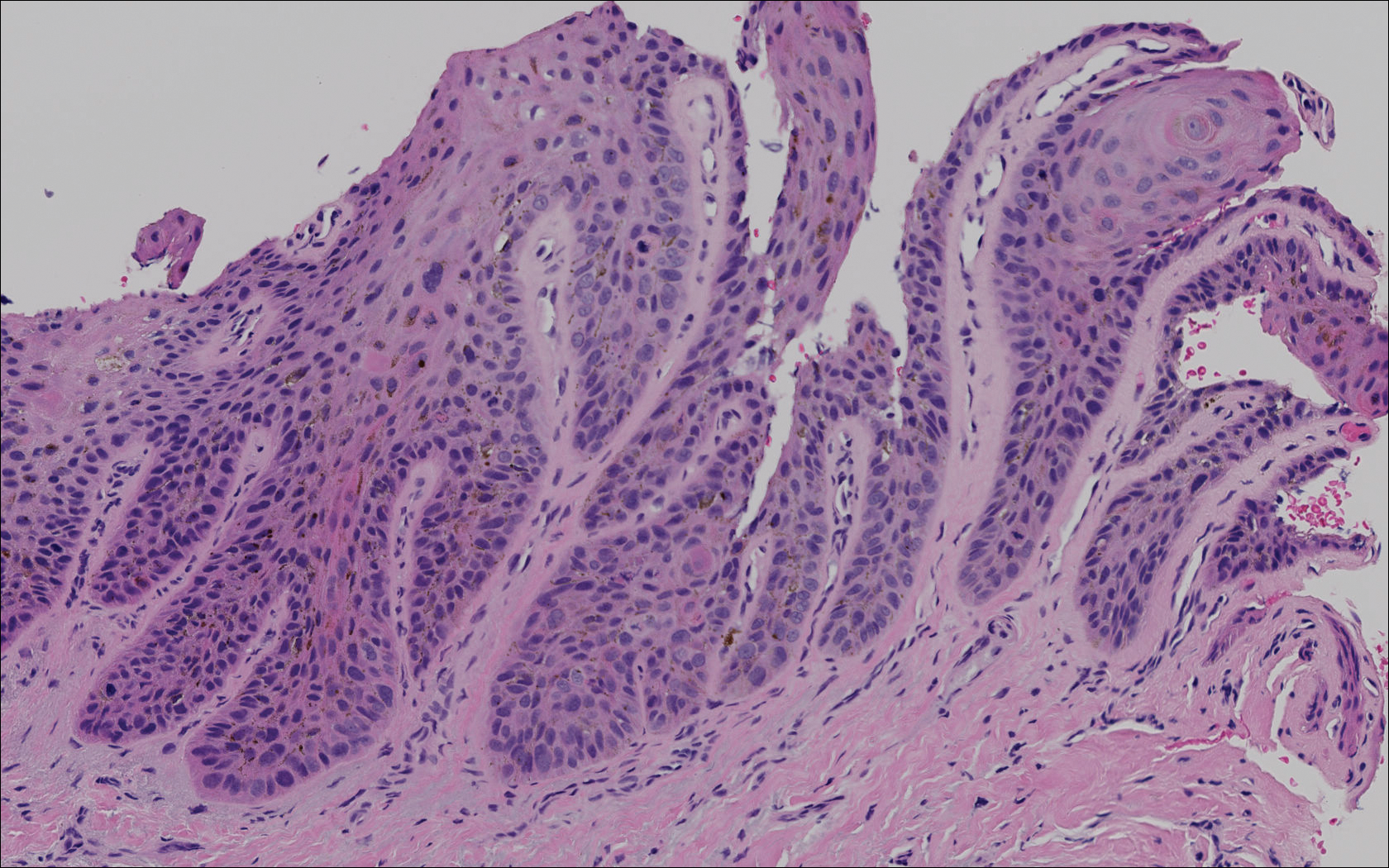
Subungual melanoma, onychomycosis, squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), and a verruca copresenting with onychomycosis were considered in the differential diagnosis. The patient underwent nail avulsion and biopsy of the nail bed as well as the nail matrix. Histopathology was notable for malignant dyskeratosis with a lack of nuclear maturation, occasional mitoses, multinucleation, and individual cell keratinization (Figure 2). Immunostaining for S100 was negative, while staining for cytokeratins AE1/AE3 was positive. Deposition of melanin pigment in the malignant dyskeratotic cells was noted. Periodic acid–Schiff staining identified pseudohyphae without invasion of the nail plate. A diagnosis of pigmented SCC (pSCC) was made. The patient’s nail also was sent for fungal cultures that later grew Candida glabrata and Candida parapsilosis.
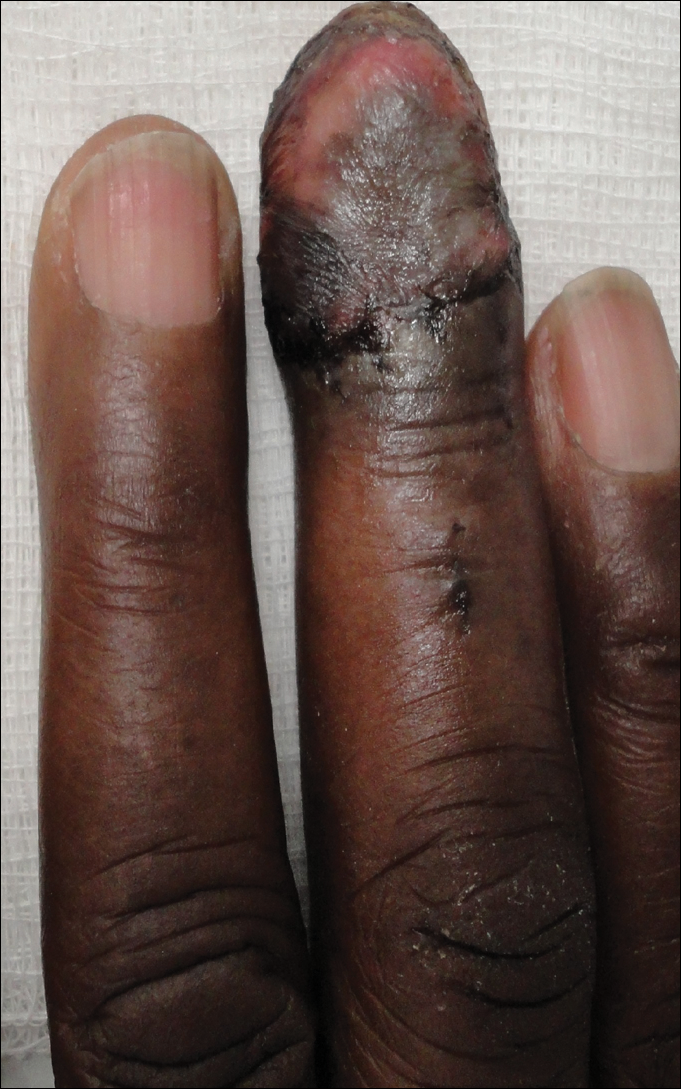
The patient underwent Mohs micrographic surgery for removal of the pSCC, which was found to be more extensive than originally suspected and required en bloc excision of the nail repaired with a full-thickness skin graft from the left forearm. The area healed well with some hyperpigmentation (Figure 3).
Comment
Among the various types of skin cancer, an estimated 700,000 patients are diagnosed with SCC annually, making it the second most common form of skin cancer in the United States.1 Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common skin cancer among whites in the United States, while in contrast SCC is the most common skin cancer in patients with skin of color.2 Only an estimated 2% to 5% of all SCCs are pigmented, and this variant is more commonly seen in patients with skin of color.3-5 One analysis of 52 cases of pSCC showed that common features included a flat or slightly raised appearance and hyperpigmentation with varying levels of scaling.6 Studies have shown an altered presentation of pSCC in black skin with increased melanin production and thickness of the stratum corneum in contrast with cases seen in white patients.7 Other potential features include scaling, erosive changes, and sharply demarcated borders. Squamous cell carcinoma typically occurs in sun-exposed areas, reflecting its association with UV light damage; however, SCC in skin of color patients has been noted to occur in sun-protected areas and in areas of chronic scarring.8 Pigmented SCC also appears to follow this distribution, as affected areas are not necessarily in direct exposure to the sun. Pigmented SCCs have been associated with pruritus and/or burning pain, which also was seen in our case when our patient complained of tenderness at the site.
We describe the case of a subungual pSCC clinically presenting as longitudinal melanonychia. Pigmented SCC presenting as longitudinal melanonychia was first described by Baran and Simon in 1988.9 Since that time, it has been reported that approximately 10% of subungual pSCCs clinically present as longitudinal melanonychia.10,11 A retrospective study reviewing 35 cases of SCC of the nail apparatus found that 5 (14.3%) cases presented as longitudinal melanonychia.10 Another retrospective study found that 6 of 51 (11.8%) cases of SCCs affecting the nail unit presented as the warty type of SCC in association with longitudinal melanonychia.12 Cases of pSCC in situ appearing as longitudinal melanonychia also have been reported.13,14
Risk factors for the development of pSCC include advanced age, male sex, presence of human papilloma virus, and use of immunosuppressants.15 Male predominance and advanced age at the time of diagnosis (mean age, 67 years) have been observed in pSCC cases.16 It is now well established that renal transplant recipients have an increased risk of SCC, with a reported incidence rate of 5% to 6%.16 When these patients develop an SCC, they typically follow a more aggressive course. Renal transplantation has a higher ratio than cardiac transplantation for SCC development (2.37:1), whereas cardiac transplantation is associated with a higher risk of BCC development.17 A study of 384 transplant recipients found that 96 (25.0%) had a postsurgical nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC), with a ratio of SCC to BCC of 1.2:1.16 The calculated incidence of NMSC at 10 and 20 years posttransplantation was 24.2% and 54.4%, respectively. Another study also determined that SCC rates (50.0%) in postrenal transplant recipients were approximately twice that of BCC (27.0%).18
A daily regimen of immunosuppressive medications such as cyclosporine and mycophenolate mofetil showed an increased risk for development of NMSC.15 Immunosuppressive medications play an important role in the pathogenesis of SCC due to a direct oncogenic effect as well as impairment of the immune system’s ability to fight precancerous developments.15 A 4-year study of 100 renal transplant recipients using mycophenolate mofetil as part of an immunosuppressive regimen reported 22% NMSC findings among 9 patients.19 On average, patients developed an NMSC approximately 61 months posttransplantation, with a wide range from 2 to 120 months.
Advanced age was another important risk factor, with each decade of life producing a 60% increase in instantaneous risk of SCC development for transplant recipients.15 A steady increase in risk was related to the length of time adhering to an immunosuppressive regimen, especially from 2 to 6 years, and then remaining constant in subsequent years. For older patients on immunosuppressant regimens for more than 8 years, the calculated relative risk was noted to be over 200 times greater than the normal population’s development of skin cancers.18
Conclusion
Although cases of pSCC presenting as longitudinal melanonychia have previously been reported,9-14,20 our case is unique in that it describes pSCC in a renal transplant recipient. Our patient had many of the known risk factors for the development of pSCC including male sex, advanced age, skin of color, history of renal transplantation, and immunosuppressive therapy. Although regular full-body skin examinations are an accepted part of renal transplantation follow-up due to SCC risk, our case emphasizes the need to remain vigilant due to possible atypical presentations among the immunosuppressed. The nail unit should not be overlooked during the clinical examination of renal transplant recipients as demonstrated by our patient’s rare presentation of pSCC in the nail.
- Karia PS, Han J, Schmults CD. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: estimated incidence of disease, nodal metastasis, and deaths from disease in the United States, 2012 [published online February 1, 2013]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:957-966.
- Tan KB, Tan SH, Aw DC, et al. Simulators of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: diagnostic challenges on small biopsies and clinicopathological correlation [published online June 25, 2013]. J Skin Cancer. 2013;2013:752864.
- McCall CO, Chen SC. Squamous cell carcinoma of the legs in African Americans. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:524-529.
- Krishna R, Lewis A, Orengo IF, et al. Pigmented Bowen’s disease (squamous cell carcinoma in situ): a mimic of malignant melanoma. Dermatol Surg. 2001;27:673-674.
- Brinca A, Teixeira V, Goncalo M, et al. A large pigmented lesion mimicking malignant melanoma. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2012;37:817-818.
- Cameron A, Rosendahl C, Tschandl P, et al. Dermatoscopy of pigmented Bowen’s disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:597-604.
- Singh B, Bhaya M, Shaha A, et al. Presentation, course, and outcome of head and neck cancers in African Americans: a case-control study. Laryngoscope. 1998;108(8 pt 1):1159-1163.
- Cancer Facts and Figures 2006. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society; 2006.
- Baran R, Simon C. Longitudinal melanonychia: a symptom of Bowen’s disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1988;18:1359-1360.
- Dalle S, Depape L, Phan A, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma of the nail apparatus: clinicopathological study of 35 cases. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:871-874.
- Ishida M, Iwai M, Yoshida K, et al. Subungual pigmented squamous cell carcinoma presenting as longitudinal melanonychia: a case report with review of the literature. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7:844-847.
- Lecerf P, Richert B, Theunis A, et al. A retrospective study of squamous cell carcinoma of the nail unit diagnosed in a Belgian general hospital over a 15-year period. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:253-261.
- Saito T, Uchi H, Moroi Y, et al. Subungual Bowen disease revealed by longitudinal melanonychia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:E240-E241.
- Saxena A, Kasper DA, Campanelli CD, et al. Pigmented Bowen’s disease clinically mimicking melanoma on the nail. Dermatol Surg. 2006;32:1522-1525.
- Mackenzie KA, Wells JE, Lynn KL, et al. First and subsequent nonmelanoma skin cancers: incidence and predictors in a population of New Zealand renal transplant recipients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25:300-306.
- Gutiérrez-Mendoza D, Narro-Llorente R, Karam-Orantes M, et al. Dermoscopy clues in pigmented Bowen’s disease [published online ahead of print September 16, 2010]. Dermatol Res Pract. 2010;2010.
- Euvards S, Kanitakis J, Pouteil-Noble C, et al. Comparative epidemiologic study of premalignant and malignant epithelial cutaneous lesions developing after kidney and heart transplantation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;33(2 pt 1):222-229.
- Moloney FJ, Comber H, O’Lorcain P, et al. A population-based study of skin cancer incidence and prevalence in renal transplant patients. Br J Dermatol. 2006;154:498-504.
- Formicone F, Fargnoli MC, Pisani F, et al. Cutaneous manifestations in Italian kidney transplant recipients. Transplant Proc. 2005;37:2527-2528.
- Fernandes Massa A, Debarbieux S, Depaepe L, et al. Pigmented squamous cell carcinoma of the nail bed presenting as a melanonychia striata: diagnosis by perioperative reflectance confocal microscopy. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:198-199.
Case Report
A 62-year-old black man presented for examination of a dark longitudinal streak located adjacent to the lateral nail fold on the third finger of the left hand. The lesion had been present for several months, during which time it had slowly expanded in size. The fingertip had recently become tender, which interfered with the patient’s ability to work. His past medical history was remarkable for end-stage renal disease secondary to glomerulonephritis with nephrotic syndrome of unclear etiology. He initially was treated by an outside physician using peritoneal dialysis for 3 years until he underwent renal transplantation in 2004 with a cadaveric organ. Other remarkable medical conditions included posttransplantation diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and gout. His multidrug regimen included 2 immunosuppressive medications: oral cyclosporine 125 mg twice daily and oral mycophenolate mofetil 250 mg twice daily.
A broad, irregular, black, pigmented, subungual band was noted on the left third finger. The lesion appeared to emanate from below the nail cuticle and traveled along the nail longitudinally toward the distal tip. The band appeared darker at the edge adjacent to the lateral nail fold and grew lighter near the middle of the nail where its free edge was noted to be irregular. A slightly thickened lateral nail fold with an irregular, small, sawtoothlike hyperkeratosis and hyperpigmentation also was noted (Figure 1).

Subungual melanoma, onychomycosis, squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), and a verruca copresenting with onychomycosis were considered in the differential diagnosis. The patient underwent nail avulsion and biopsy of the nail bed as well as the nail matrix. Histopathology was notable for malignant dyskeratosis with a lack of nuclear maturation, occasional mitoses, multinucleation, and individual cell keratinization (Figure 2). Immunostaining for S100 was negative, while staining for cytokeratins AE1/AE3 was positive. Deposition of melanin pigment in the malignant dyskeratotic cells was noted. Periodic acid–Schiff staining identified pseudohyphae without invasion of the nail plate. A diagnosis of pigmented SCC (pSCC) was made. The patient’s nail also was sent for fungal cultures that later grew Candida glabrata and Candida parapsilosis.
The patient underwent Mohs micrographic surgery for removal of the pSCC, which was found to be more extensive than originally suspected and required en bloc excision of the nail repaired with a full-thickness skin graft from the left forearm. The area healed well with some hyperpigmentation (Figure 3).


Comment
Among the various types of skin cancer, an estimated 700,000 patients are diagnosed with SCC annually, making it the second most common form of skin cancer in the United States.1 Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common skin cancer among whites in the United States, while in contrast SCC is the most common skin cancer in patients with skin of color.2 Only an estimated 2% to 5% of all SCCs are pigmented, and this variant is more commonly seen in patients with skin of color.3-5 One analysis of 52 cases of pSCC showed that common features included a flat or slightly raised appearance and hyperpigmentation with varying levels of scaling.6 Studies have shown an altered presentation of pSCC in black skin with increased melanin production and thickness of the stratum corneum in contrast with cases seen in white patients.7 Other potential features include scaling, erosive changes, and sharply demarcated borders. Squamous cell carcinoma typically occurs in sun-exposed areas, reflecting its association with UV light damage; however, SCC in skin of color patients has been noted to occur in sun-protected areas and in areas of chronic scarring.8 Pigmented SCC also appears to follow this distribution, as affected areas are not necessarily in direct exposure to the sun. Pigmented SCCs have been associated with pruritus and/or burning pain, which also was seen in our case when our patient complained of tenderness at the site.
We describe the case of a subungual pSCC clinically presenting as longitudinal melanonychia. Pigmented SCC presenting as longitudinal melanonychia was first described by Baran and Simon in 1988.9 Since that time, it has been reported that approximately 10% of subungual pSCCs clinically present as longitudinal melanonychia.10,11 A retrospective study reviewing 35 cases of SCC of the nail apparatus found that 5 (14.3%) cases presented as longitudinal melanonychia.10 Another retrospective study found that 6 of 51 (11.8%) cases of SCCs affecting the nail unit presented as the warty type of SCC in association with longitudinal melanonychia.12 Cases of pSCC in situ appearing as longitudinal melanonychia also have been reported.13,14
Risk factors for the development of pSCC include advanced age, male sex, presence of human papilloma virus, and use of immunosuppressants.15 Male predominance and advanced age at the time of diagnosis (mean age, 67 years) have been observed in pSCC cases.16 It is now well established that renal transplant recipients have an increased risk of SCC, with a reported incidence rate of 5% to 6%.16 When these patients develop an SCC, they typically follow a more aggressive course. Renal transplantation has a higher ratio than cardiac transplantation for SCC development (2.37:1), whereas cardiac transplantation is associated with a higher risk of BCC development.17 A study of 384 transplant recipients found that 96 (25.0%) had a postsurgical nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC), with a ratio of SCC to BCC of 1.2:1.16 The calculated incidence of NMSC at 10 and 20 years posttransplantation was 24.2% and 54.4%, respectively. Another study also determined that SCC rates (50.0%) in postrenal transplant recipients were approximately twice that of BCC (27.0%).18
A daily regimen of immunosuppressive medications such as cyclosporine and mycophenolate mofetil showed an increased risk for development of NMSC.15 Immunosuppressive medications play an important role in the pathogenesis of SCC due to a direct oncogenic effect as well as impairment of the immune system’s ability to fight precancerous developments.15 A 4-year study of 100 renal transplant recipients using mycophenolate mofetil as part of an immunosuppressive regimen reported 22% NMSC findings among 9 patients.19 On average, patients developed an NMSC approximately 61 months posttransplantation, with a wide range from 2 to 120 months.
Advanced age was another important risk factor, with each decade of life producing a 60% increase in instantaneous risk of SCC development for transplant recipients.15 A steady increase in risk was related to the length of time adhering to an immunosuppressive regimen, especially from 2 to 6 years, and then remaining constant in subsequent years. For older patients on immunosuppressant regimens for more than 8 years, the calculated relative risk was noted to be over 200 times greater than the normal population’s development of skin cancers.18
Conclusion
Although cases of pSCC presenting as longitudinal melanonychia have previously been reported,9-14,20 our case is unique in that it describes pSCC in a renal transplant recipient. Our patient had many of the known risk factors for the development of pSCC including male sex, advanced age, skin of color, history of renal transplantation, and immunosuppressive therapy. Although regular full-body skin examinations are an accepted part of renal transplantation follow-up due to SCC risk, our case emphasizes the need to remain vigilant due to possible atypical presentations among the immunosuppressed. The nail unit should not be overlooked during the clinical examination of renal transplant recipients as demonstrated by our patient’s rare presentation of pSCC in the nail.
Case Report
A 62-year-old black man presented for examination of a dark longitudinal streak located adjacent to the lateral nail fold on the third finger of the left hand. The lesion had been present for several months, during which time it had slowly expanded in size. The fingertip had recently become tender, which interfered with the patient’s ability to work. His past medical history was remarkable for end-stage renal disease secondary to glomerulonephritis with nephrotic syndrome of unclear etiology. He initially was treated by an outside physician using peritoneal dialysis for 3 years until he underwent renal transplantation in 2004 with a cadaveric organ. Other remarkable medical conditions included posttransplantation diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and gout. His multidrug regimen included 2 immunosuppressive medications: oral cyclosporine 125 mg twice daily and oral mycophenolate mofetil 250 mg twice daily.
A broad, irregular, black, pigmented, subungual band was noted on the left third finger. The lesion appeared to emanate from below the nail cuticle and traveled along the nail longitudinally toward the distal tip. The band appeared darker at the edge adjacent to the lateral nail fold and grew lighter near the middle of the nail where its free edge was noted to be irregular. A slightly thickened lateral nail fold with an irregular, small, sawtoothlike hyperkeratosis and hyperpigmentation also was noted (Figure 1).

Subungual melanoma, onychomycosis, squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), and a verruca copresenting with onychomycosis were considered in the differential diagnosis. The patient underwent nail avulsion and biopsy of the nail bed as well as the nail matrix. Histopathology was notable for malignant dyskeratosis with a lack of nuclear maturation, occasional mitoses, multinucleation, and individual cell keratinization (Figure 2). Immunostaining for S100 was negative, while staining for cytokeratins AE1/AE3 was positive. Deposition of melanin pigment in the malignant dyskeratotic cells was noted. Periodic acid–Schiff staining identified pseudohyphae without invasion of the nail plate. A diagnosis of pigmented SCC (pSCC) was made. The patient’s nail also was sent for fungal cultures that later grew Candida glabrata and Candida parapsilosis.
The patient underwent Mohs micrographic surgery for removal of the pSCC, which was found to be more extensive than originally suspected and required en bloc excision of the nail repaired with a full-thickness skin graft from the left forearm. The area healed well with some hyperpigmentation (Figure 3).


Comment
Among the various types of skin cancer, an estimated 700,000 patients are diagnosed with SCC annually, making it the second most common form of skin cancer in the United States.1 Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common skin cancer among whites in the United States, while in contrast SCC is the most common skin cancer in patients with skin of color.2 Only an estimated 2% to 5% of all SCCs are pigmented, and this variant is more commonly seen in patients with skin of color.3-5 One analysis of 52 cases of pSCC showed that common features included a flat or slightly raised appearance and hyperpigmentation with varying levels of scaling.6 Studies have shown an altered presentation of pSCC in black skin with increased melanin production and thickness of the stratum corneum in contrast with cases seen in white patients.7 Other potential features include scaling, erosive changes, and sharply demarcated borders. Squamous cell carcinoma typically occurs in sun-exposed areas, reflecting its association with UV light damage; however, SCC in skin of color patients has been noted to occur in sun-protected areas and in areas of chronic scarring.8 Pigmented SCC also appears to follow this distribution, as affected areas are not necessarily in direct exposure to the sun. Pigmented SCCs have been associated with pruritus and/or burning pain, which also was seen in our case when our patient complained of tenderness at the site.
We describe the case of a subungual pSCC clinically presenting as longitudinal melanonychia. Pigmented SCC presenting as longitudinal melanonychia was first described by Baran and Simon in 1988.9 Since that time, it has been reported that approximately 10% of subungual pSCCs clinically present as longitudinal melanonychia.10,11 A retrospective study reviewing 35 cases of SCC of the nail apparatus found that 5 (14.3%) cases presented as longitudinal melanonychia.10 Another retrospective study found that 6 of 51 (11.8%) cases of SCCs affecting the nail unit presented as the warty type of SCC in association with longitudinal melanonychia.12 Cases of pSCC in situ appearing as longitudinal melanonychia also have been reported.13,14
Risk factors for the development of pSCC include advanced age, male sex, presence of human papilloma virus, and use of immunosuppressants.15 Male predominance and advanced age at the time of diagnosis (mean age, 67 years) have been observed in pSCC cases.16 It is now well established that renal transplant recipients have an increased risk of SCC, with a reported incidence rate of 5% to 6%.16 When these patients develop an SCC, they typically follow a more aggressive course. Renal transplantation has a higher ratio than cardiac transplantation for SCC development (2.37:1), whereas cardiac transplantation is associated with a higher risk of BCC development.17 A study of 384 transplant recipients found that 96 (25.0%) had a postsurgical nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC), with a ratio of SCC to BCC of 1.2:1.16 The calculated incidence of NMSC at 10 and 20 years posttransplantation was 24.2% and 54.4%, respectively. Another study also determined that SCC rates (50.0%) in postrenal transplant recipients were approximately twice that of BCC (27.0%).18
A daily regimen of immunosuppressive medications such as cyclosporine and mycophenolate mofetil showed an increased risk for development of NMSC.15 Immunosuppressive medications play an important role in the pathogenesis of SCC due to a direct oncogenic effect as well as impairment of the immune system’s ability to fight precancerous developments.15 A 4-year study of 100 renal transplant recipients using mycophenolate mofetil as part of an immunosuppressive regimen reported 22% NMSC findings among 9 patients.19 On average, patients developed an NMSC approximately 61 months posttransplantation, with a wide range from 2 to 120 months.
Advanced age was another important risk factor, with each decade of life producing a 60% increase in instantaneous risk of SCC development for transplant recipients.15 A steady increase in risk was related to the length of time adhering to an immunosuppressive regimen, especially from 2 to 6 years, and then remaining constant in subsequent years. For older patients on immunosuppressant regimens for more than 8 years, the calculated relative risk was noted to be over 200 times greater than the normal population’s development of skin cancers.18
Conclusion
Although cases of pSCC presenting as longitudinal melanonychia have previously been reported,9-14,20 our case is unique in that it describes pSCC in a renal transplant recipient. Our patient had many of the known risk factors for the development of pSCC including male sex, advanced age, skin of color, history of renal transplantation, and immunosuppressive therapy. Although regular full-body skin examinations are an accepted part of renal transplantation follow-up due to SCC risk, our case emphasizes the need to remain vigilant due to possible atypical presentations among the immunosuppressed. The nail unit should not be overlooked during the clinical examination of renal transplant recipients as demonstrated by our patient’s rare presentation of pSCC in the nail.
- Karia PS, Han J, Schmults CD. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: estimated incidence of disease, nodal metastasis, and deaths from disease in the United States, 2012 [published online February 1, 2013]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:957-966.
- Tan KB, Tan SH, Aw DC, et al. Simulators of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: diagnostic challenges on small biopsies and clinicopathological correlation [published online June 25, 2013]. J Skin Cancer. 2013;2013:752864.
- McCall CO, Chen SC. Squamous cell carcinoma of the legs in African Americans. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:524-529.
- Krishna R, Lewis A, Orengo IF, et al. Pigmented Bowen’s disease (squamous cell carcinoma in situ): a mimic of malignant melanoma. Dermatol Surg. 2001;27:673-674.
- Brinca A, Teixeira V, Goncalo M, et al. A large pigmented lesion mimicking malignant melanoma. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2012;37:817-818.
- Cameron A, Rosendahl C, Tschandl P, et al. Dermatoscopy of pigmented Bowen’s disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:597-604.
- Singh B, Bhaya M, Shaha A, et al. Presentation, course, and outcome of head and neck cancers in African Americans: a case-control study. Laryngoscope. 1998;108(8 pt 1):1159-1163.
- Cancer Facts and Figures 2006. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society; 2006.
- Baran R, Simon C. Longitudinal melanonychia: a symptom of Bowen’s disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1988;18:1359-1360.
- Dalle S, Depape L, Phan A, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma of the nail apparatus: clinicopathological study of 35 cases. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:871-874.
- Ishida M, Iwai M, Yoshida K, et al. Subungual pigmented squamous cell carcinoma presenting as longitudinal melanonychia: a case report with review of the literature. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7:844-847.
- Lecerf P, Richert B, Theunis A, et al. A retrospective study of squamous cell carcinoma of the nail unit diagnosed in a Belgian general hospital over a 15-year period. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:253-261.
- Saito T, Uchi H, Moroi Y, et al. Subungual Bowen disease revealed by longitudinal melanonychia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:E240-E241.
- Saxena A, Kasper DA, Campanelli CD, et al. Pigmented Bowen’s disease clinically mimicking melanoma on the nail. Dermatol Surg. 2006;32:1522-1525.
- Mackenzie KA, Wells JE, Lynn KL, et al. First and subsequent nonmelanoma skin cancers: incidence and predictors in a population of New Zealand renal transplant recipients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25:300-306.
- Gutiérrez-Mendoza D, Narro-Llorente R, Karam-Orantes M, et al. Dermoscopy clues in pigmented Bowen’s disease [published online ahead of print September 16, 2010]. Dermatol Res Pract. 2010;2010.
- Euvards S, Kanitakis J, Pouteil-Noble C, et al. Comparative epidemiologic study of premalignant and malignant epithelial cutaneous lesions developing after kidney and heart transplantation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;33(2 pt 1):222-229.
- Moloney FJ, Comber H, O’Lorcain P, et al. A population-based study of skin cancer incidence and prevalence in renal transplant patients. Br J Dermatol. 2006;154:498-504.
- Formicone F, Fargnoli MC, Pisani F, et al. Cutaneous manifestations in Italian kidney transplant recipients. Transplant Proc. 2005;37:2527-2528.
- Fernandes Massa A, Debarbieux S, Depaepe L, et al. Pigmented squamous cell carcinoma of the nail bed presenting as a melanonychia striata: diagnosis by perioperative reflectance confocal microscopy. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:198-199.
- Karia PS, Han J, Schmults CD. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: estimated incidence of disease, nodal metastasis, and deaths from disease in the United States, 2012 [published online February 1, 2013]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:957-966.
- Tan KB, Tan SH, Aw DC, et al. Simulators of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: diagnostic challenges on small biopsies and clinicopathological correlation [published online June 25, 2013]. J Skin Cancer. 2013;2013:752864.
- McCall CO, Chen SC. Squamous cell carcinoma of the legs in African Americans. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:524-529.
- Krishna R, Lewis A, Orengo IF, et al. Pigmented Bowen’s disease (squamous cell carcinoma in situ): a mimic of malignant melanoma. Dermatol Surg. 2001;27:673-674.
- Brinca A, Teixeira V, Goncalo M, et al. A large pigmented lesion mimicking malignant melanoma. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2012;37:817-818.
- Cameron A, Rosendahl C, Tschandl P, et al. Dermatoscopy of pigmented Bowen’s disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:597-604.
- Singh B, Bhaya M, Shaha A, et al. Presentation, course, and outcome of head and neck cancers in African Americans: a case-control study. Laryngoscope. 1998;108(8 pt 1):1159-1163.
- Cancer Facts and Figures 2006. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society; 2006.
- Baran R, Simon C. Longitudinal melanonychia: a symptom of Bowen’s disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1988;18:1359-1360.
- Dalle S, Depape L, Phan A, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma of the nail apparatus: clinicopathological study of 35 cases. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:871-874.
- Ishida M, Iwai M, Yoshida K, et al. Subungual pigmented squamous cell carcinoma presenting as longitudinal melanonychia: a case report with review of the literature. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7:844-847.
- Lecerf P, Richert B, Theunis A, et al. A retrospective study of squamous cell carcinoma of the nail unit diagnosed in a Belgian general hospital over a 15-year period. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:253-261.
- Saito T, Uchi H, Moroi Y, et al. Subungual Bowen disease revealed by longitudinal melanonychia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:E240-E241.
- Saxena A, Kasper DA, Campanelli CD, et al. Pigmented Bowen’s disease clinically mimicking melanoma on the nail. Dermatol Surg. 2006;32:1522-1525.
- Mackenzie KA, Wells JE, Lynn KL, et al. First and subsequent nonmelanoma skin cancers: incidence and predictors in a population of New Zealand renal transplant recipients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25:300-306.
- Gutiérrez-Mendoza D, Narro-Llorente R, Karam-Orantes M, et al. Dermoscopy clues in pigmented Bowen’s disease [published online ahead of print September 16, 2010]. Dermatol Res Pract. 2010;2010.
- Euvards S, Kanitakis J, Pouteil-Noble C, et al. Comparative epidemiologic study of premalignant and malignant epithelial cutaneous lesions developing after kidney and heart transplantation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;33(2 pt 1):222-229.
- Moloney FJ, Comber H, O’Lorcain P, et al. A population-based study of skin cancer incidence and prevalence in renal transplant patients. Br J Dermatol. 2006;154:498-504.
- Formicone F, Fargnoli MC, Pisani F, et al. Cutaneous manifestations in Italian kidney transplant recipients. Transplant Proc. 2005;37:2527-2528.
- Fernandes Massa A, Debarbieux S, Depaepe L, et al. Pigmented squamous cell carcinoma of the nail bed presenting as a melanonychia striata: diagnosis by perioperative reflectance confocal microscopy. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:198-199.
Practice Points
- Risk factors for the development of pigmented squamous cell carcinoma (pSCC) include older age, male sex, and use of immunosuppressant medications.
- Subungual pSCC can present as longitudinal melanonychia and should be considered in the differential diagnosis for melanonychia in patients with skin of color or those who are immunosuppressed.