User login
Measles Resurgence: A Dermatologist’s Guide
Measles Resurgence: A Dermatologist’s Guide
Measles, also known as rubeola, is a highly contagious paramyxovirus that has neared elimination in the United States since 2000 due to widespread adoption of the measles vaccine; however, measles recently has made a comeback, with outbreaks reported in more than 60 countries. In the United States, vaccine hesitancy coupled with decreasing vaccination rates, international travel to endemic areas, and decreased funding and resources for monitoring and immunization programs likely led to a re-emergence of measles cases.1,2 The resurgence of measles is troubling given its infectiousness and potential severity in at-risk populations. Since measles has a basic reproduction number of 12 to 18 (ie, 1 infected individual will on average infect 12 to 18 others3), it has the capacity to spread quickly. This is why, prior to the development of the measles vaccine in the 1960s, it was responsible for millions of deaths across the globe.
Prior to the introduction of the measles vaccine, both physicians and the public generally were aware of the signs and symptoms of measles due to its prevalence; however, since there have been so few cases in recent decades, images and descriptions of patients presenting with measles can be found only in textbooks, and many physicians are ill-prepared to diagnose the disease.4 In response to the recent surge in measles cases, dermatologists—who often are among the first medical professionals to encounter febrile patients with rashes—must be prepared to bridge this divide. Herein, we review the clinical signs, diagnostic approach, operational precautions, and public health responsibilities that dermatologists must relearn amid the current measles outbreak.
Background
Measles is primarily transmitted via respiratory droplets and may remain airborne for up to 2 hours.5 It also can be transmitted through direct contact with secretions such as mucus. Indirect transmission via fomites, while certainly plausible, is thought to be the least effective mechanism of transmission.6 Following exposure, the incubation period ranges from 7 to 21 days, during which the virus replicates asymptomatically before causing clinical disease.7 Herd immunity for measles requires 93% immunity in the population; public health agencies typically target greater than 95% immunity.8 Humans are the only reservoir for the measles virus, making eradication possible.
The road to eradication began with the introduction of the measles vaccine in 1963 and subsequent development of the combined measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine in 1971. As MMR is a live vaccine, 2 doses confer approximately 97% protection.9 The first dose is given at 12 to 15 months of age, and the second dose is given at 4 to 6 years of age. Immunity is considered lifelong, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Health Organization do not recommend routine measles boosters for individuals who have completed the primary 2-dose series.10,11
Widespread vaccination led to a dramatic reduction in incidence, with many countries eliminating measles infections.7 The United States declared measles eliminated in 2000, with confirmed cases between 2000 and 2020 ranging from 37 to 1282.12 Vaccination progress stalled in the late 1990s due to vaccine hesitancy resulting from (subsequently debunked) reports of an association between the MMR vaccine and autism.13 Despite efforts to correct this misinformation, many patients continue to espouse these concerns.
Recognizing Measles: Clinical Presentation
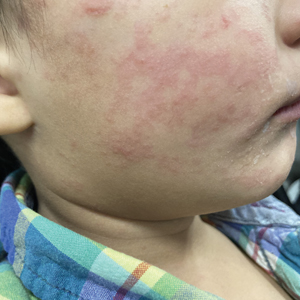
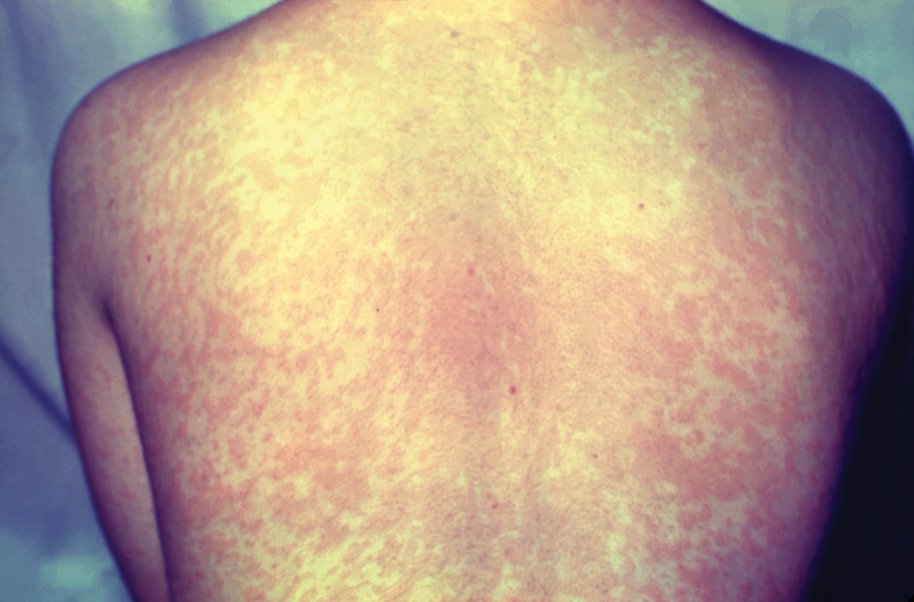
Measles, which most often manifests in childhood but also can occur in adults, follows a distinctive clinical course. The prodromal phase is characterized by high fever, cough, coryza (nasal congestion), and conjunctivitis— conjunctivitis—the 3 “Cs” that serve as early warning signs of the disease. Patients may develop small white macules on the buccal mucosa known as Koplik spots (phonetically the fourth “C”), which appear just before the rash. Three to 5 days after the onset of systemic symptoms, patients will develop a classic morbilliform exanthem. In some cases, the exanthem manifests on the head and neck (Figure 1)—first behind the ears and along the hairline, then spreading caudally to the trunk and extremities. The lesions may become confluent, with patients presenting with diffuse erythema. The exanthem fades over several days to weeks, often accompanied by superficial desquamation.14
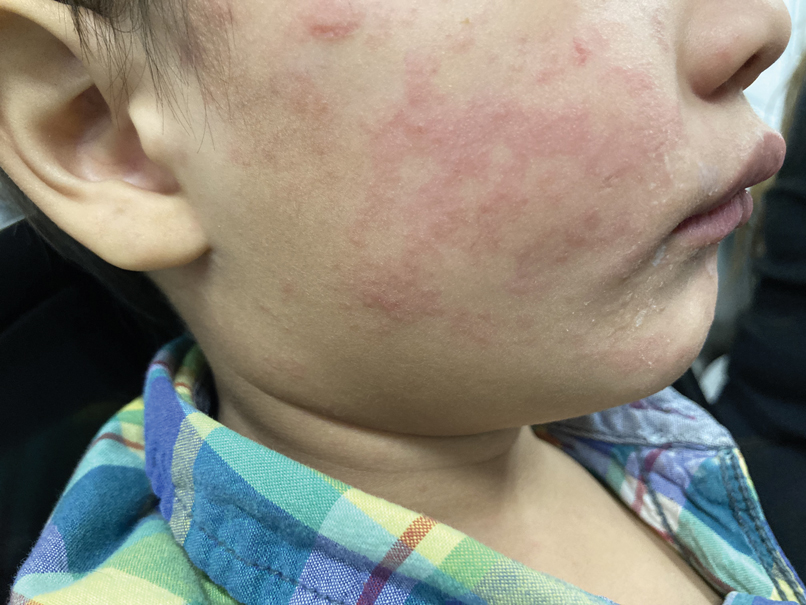
Given the nonspecificity of the early symptoms of measles, a high index of suspicion is needed for patients presenting with a febrile illness and a morbilliform eruption (Figure 2). Consideration of MMR vaccination status, exposure history, and local outbreak patterns can help guide risk stratification and the need for testing. Immunocompromised individuals, including those receiving immunosuppressive therapies for dermatologic conditions, may present atypically, lacking the prototypical exanthem or displaying milder signs and further complicating the diagnosis.15 The differential diagnosis for measles includes a drug reaction or other viral exanthem, and a detailed history may help elucidate the culprit.
Evaluation and Diagnosis
Definitive diagnosis of measles relies on both molecular and serologic testing. Nasopharyngeal swabs for measles polymerase chain reaction testing are obtained using synthetic (noncotton) swabs placed in a viral transport medium. Serum samples also should be collected for measles IgM and IgG antibody testing. Importantly, measles is a reportable illness, and testing may be coordinated with local departments of health.
Determining a patient’s immune status may be important for certain populations. Patients with documented 2-dose MMR vaccination, positive measles IgG serology, or a prior confirmed measles infection are considered immune. While a positive measles IgG indicates immunity, a negative result in an exposed patient should prompt consideration of postexposure prophylaxis with intravenous immunoglobulin.
Many patients, specifically those presenting to dermatology, are taking immunomodulatory or immunosuppressive medications—a contraindication for vaccination with the live MMR vaccine. At the time of publication, there was a single reported case of a patient taking a tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor for rheumatoid arthritis who had acquired measles.16 While the benefits of titer assessment in patients who are starting or continuing immunomodulatory therapy are not known and currently it is not recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, dermatologists might consider checking MMR titers and vaccinating (or referring for vaccination) nonimmune patients.17
Infection Control
Early identification of a suspected measles case is paramount. Patients in whom measles is a possibility should be isolated as quickly as possible, and the patient and accompanying caregivers should be masked. Clinical staff should don appropriate personal protective equipment, including an N95 mask. Coordination with the local department of health must occur as soon as measles is suspected.
If testing is an option in the outpatient setting, a nasopharyngeal viral swab and serologic titers can be obtained. If testing is not available on site, patients should be sent to appropriate care facilities; prenotification is critical to prevent nosocomial outbreaks. Patients should be encouraged to isolate and avoid public spaces and/or public transport for 4 days following development of an exanthem.18 Offices should develop clinical protocols for suspected measles cases with training for clinical and office staff.
Final Thoughts
As measles outbreaks become more prevalent, it is incumbent upon physicians to remind ourselves of the signs and symptoms of this largely eliminated disease so that we may pursue early detection and intervention strategies. The primary cutaneous manifestations of measles make dermatologists critical to early recognition and containment efforts. Dermatologists should prepare for the arrival of patients with measles by maintaining vigilance for the classic signs of the disease, implementing stringent isolation protocols, verifying patient immunity when appropriate, and partnering closely with public health authorities.
More broadly, efforts to contain and re-establish a paradigm for eliminating measles outbreaks must be pursued. Encouraging vaccination and developing programs to help combat misinformation surrounding vaccines are critical to this effort. In an era of vaccine hesitancy, measles is a multidisciplinary public health emergency. Dermatologists must remain ready.
- Bedford H, Elliman D. Measles rates are rising again. BMJ. 2024;384.
- Harris E. Measles outbreaks grow amid declining vaccination rates. JAMA. 2023;330:2242.
- Guerra FM, Bolotin S, Lim G, et al. The basic reproduction number (R0) of measles: a systematic review. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017;17:E420-E428.
- Swartz MK. Measles: public and professional education. J Pediatr Health Care. 2019;33:367-368.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim infection prevention and control recommendations for measles in healthcare settings. Accessed April 27, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/infection-control/hcp/measles/
- Moss WJ, Griffin DE, Feinstone WH. Measles. In: Vaccines for Biodefense and Emerging and Neglected Diseases. Elsevier; 2009: 551-565.
- Moss WJ. Measles. Lancet. 2017;390:2490-2502.
- Maintain the vaccination coverage level of 2 doses of the MMR vaccine for children in kindergarten— IID04. Healthy People 2030 website. Accessed May 6, 2025. https://odphp.health.gov/healthypeople/objectives-and-data/browse-objectives/vaccination/maintain-vaccination-coverage-level-2-doses-mmr-vaccine-children-kindergarten-iid-04
- Franconeri L, Antona D, Cauchemez S, et al. Two-dose measles vaccine effectiveness remains high over time: a French observational study, 2017–2019. Vaccine. 2023;41:5797-5804.
- World Health Organization. Measles. Accessed May 8, 2025. https:// www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/measles
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles vaccine recommendations. Accessed May 8, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/hcp/vaccine-considerations/index.html
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles cases and outbreaks. Accessed May 6, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/cases-outbreaks.html
- Dyer C. Lancet retracts Wakefield’s MMR paper. BMJ. 2010;340.
- Alves Graber EM, Andrade FJ, Bost W, et al. An update and review of measles for emergency physicians. J Emerg Med. 2020;58:610-615.
- Kaplan LJ, Daum RS, Smaron M, et al. Severe measles in immunocompromised patients. JAMA. 1992;267:1237-1241.
- Takahashi E, Kurosaka D, Yoshida K, et al. Onset of modified measles after etanercept treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. Japanese J Clin Immunol. 2010;33:37-41.
- Worth A, Waldman RA, Dieckhaus K, et al. Art of prevention: our approach to the measles-mumps-rubella vaccine in adult patients vaccinated against measles before 1968 on biologic therapy for the treatment of psoriasis. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019;6:94.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinical overview of measles (rubeola). Accessed May 8, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/hcp/clinical-overview/index.html
Measles, also known as rubeola, is a highly contagious paramyxovirus that has neared elimination in the United States since 2000 due to widespread adoption of the measles vaccine; however, measles recently has made a comeback, with outbreaks reported in more than 60 countries. In the United States, vaccine hesitancy coupled with decreasing vaccination rates, international travel to endemic areas, and decreased funding and resources for monitoring and immunization programs likely led to a re-emergence of measles cases.1,2 The resurgence of measles is troubling given its infectiousness and potential severity in at-risk populations. Since measles has a basic reproduction number of 12 to 18 (ie, 1 infected individual will on average infect 12 to 18 others3), it has the capacity to spread quickly. This is why, prior to the development of the measles vaccine in the 1960s, it was responsible for millions of deaths across the globe.
Prior to the introduction of the measles vaccine, both physicians and the public generally were aware of the signs and symptoms of measles due to its prevalence; however, since there have been so few cases in recent decades, images and descriptions of patients presenting with measles can be found only in textbooks, and many physicians are ill-prepared to diagnose the disease.4 In response to the recent surge in measles cases, dermatologists—who often are among the first medical professionals to encounter febrile patients with rashes—must be prepared to bridge this divide. Herein, we review the clinical signs, diagnostic approach, operational precautions, and public health responsibilities that dermatologists must relearn amid the current measles outbreak.
Background
Measles is primarily transmitted via respiratory droplets and may remain airborne for up to 2 hours.5 It also can be transmitted through direct contact with secretions such as mucus. Indirect transmission via fomites, while certainly plausible, is thought to be the least effective mechanism of transmission.6 Following exposure, the incubation period ranges from 7 to 21 days, during which the virus replicates asymptomatically before causing clinical disease.7 Herd immunity for measles requires 93% immunity in the population; public health agencies typically target greater than 95% immunity.8 Humans are the only reservoir for the measles virus, making eradication possible.
The road to eradication began with the introduction of the measles vaccine in 1963 and subsequent development of the combined measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine in 1971. As MMR is a live vaccine, 2 doses confer approximately 97% protection.9 The first dose is given at 12 to 15 months of age, and the second dose is given at 4 to 6 years of age. Immunity is considered lifelong, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Health Organization do not recommend routine measles boosters for individuals who have completed the primary 2-dose series.10,11
Widespread vaccination led to a dramatic reduction in incidence, with many countries eliminating measles infections.7 The United States declared measles eliminated in 2000, with confirmed cases between 2000 and 2020 ranging from 37 to 1282.12 Vaccination progress stalled in the late 1990s due to vaccine hesitancy resulting from (subsequently debunked) reports of an association between the MMR vaccine and autism.13 Despite efforts to correct this misinformation, many patients continue to espouse these concerns.
Recognizing Measles: Clinical Presentation
Measles, which most often manifests in childhood but also can occur in adults, follows a distinctive clinical course. The prodromal phase is characterized by high fever, cough, coryza (nasal congestion), and conjunctivitis— conjunctivitis—the 3 “Cs” that serve as early warning signs of the disease. Patients may develop small white macules on the buccal mucosa known as Koplik spots (phonetically the fourth “C”), which appear just before the rash. Three to 5 days after the onset of systemic symptoms, patients will develop a classic morbilliform exanthem. In some cases, the exanthem manifests on the head and neck (Figure 1)—first behind the ears and along the hairline, then spreading caudally to the trunk and extremities. The lesions may become confluent, with patients presenting with diffuse erythema. The exanthem fades over several days to weeks, often accompanied by superficial desquamation.14

Given the nonspecificity of the early symptoms of measles, a high index of suspicion is needed for patients presenting with a febrile illness and a morbilliform eruption (Figure 2). Consideration of MMR vaccination status, exposure history, and local outbreak patterns can help guide risk stratification and the need for testing. Immunocompromised individuals, including those receiving immunosuppressive therapies for dermatologic conditions, may present atypically, lacking the prototypical exanthem or displaying milder signs and further complicating the diagnosis.15 The differential diagnosis for measles includes a drug reaction or other viral exanthem, and a detailed history may help elucidate the culprit.

Evaluation and Diagnosis
Definitive diagnosis of measles relies on both molecular and serologic testing. Nasopharyngeal swabs for measles polymerase chain reaction testing are obtained using synthetic (noncotton) swabs placed in a viral transport medium. Serum samples also should be collected for measles IgM and IgG antibody testing. Importantly, measles is a reportable illness, and testing may be coordinated with local departments of health.
Determining a patient’s immune status may be important for certain populations. Patients with documented 2-dose MMR vaccination, positive measles IgG serology, or a prior confirmed measles infection are considered immune. While a positive measles IgG indicates immunity, a negative result in an exposed patient should prompt consideration of postexposure prophylaxis with intravenous immunoglobulin.
Many patients, specifically those presenting to dermatology, are taking immunomodulatory or immunosuppressive medications—a contraindication for vaccination with the live MMR vaccine. At the time of publication, there was a single reported case of a patient taking a tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor for rheumatoid arthritis who had acquired measles.16 While the benefits of titer assessment in patients who are starting or continuing immunomodulatory therapy are not known and currently it is not recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, dermatologists might consider checking MMR titers and vaccinating (or referring for vaccination) nonimmune patients.17
Infection Control
Early identification of a suspected measles case is paramount. Patients in whom measles is a possibility should be isolated as quickly as possible, and the patient and accompanying caregivers should be masked. Clinical staff should don appropriate personal protective equipment, including an N95 mask. Coordination with the local department of health must occur as soon as measles is suspected.
If testing is an option in the outpatient setting, a nasopharyngeal viral swab and serologic titers can be obtained. If testing is not available on site, patients should be sent to appropriate care facilities; prenotification is critical to prevent nosocomial outbreaks. Patients should be encouraged to isolate and avoid public spaces and/or public transport for 4 days following development of an exanthem.18 Offices should develop clinical protocols for suspected measles cases with training for clinical and office staff.
Final Thoughts
As measles outbreaks become more prevalent, it is incumbent upon physicians to remind ourselves of the signs and symptoms of this largely eliminated disease so that we may pursue early detection and intervention strategies. The primary cutaneous manifestations of measles make dermatologists critical to early recognition and containment efforts. Dermatologists should prepare for the arrival of patients with measles by maintaining vigilance for the classic signs of the disease, implementing stringent isolation protocols, verifying patient immunity when appropriate, and partnering closely with public health authorities.
More broadly, efforts to contain and re-establish a paradigm for eliminating measles outbreaks must be pursued. Encouraging vaccination and developing programs to help combat misinformation surrounding vaccines are critical to this effort. In an era of vaccine hesitancy, measles is a multidisciplinary public health emergency. Dermatologists must remain ready.
Measles, also known as rubeola, is a highly contagious paramyxovirus that has neared elimination in the United States since 2000 due to widespread adoption of the measles vaccine; however, measles recently has made a comeback, with outbreaks reported in more than 60 countries. In the United States, vaccine hesitancy coupled with decreasing vaccination rates, international travel to endemic areas, and decreased funding and resources for monitoring and immunization programs likely led to a re-emergence of measles cases.1,2 The resurgence of measles is troubling given its infectiousness and potential severity in at-risk populations. Since measles has a basic reproduction number of 12 to 18 (ie, 1 infected individual will on average infect 12 to 18 others3), it has the capacity to spread quickly. This is why, prior to the development of the measles vaccine in the 1960s, it was responsible for millions of deaths across the globe.
Prior to the introduction of the measles vaccine, both physicians and the public generally were aware of the signs and symptoms of measles due to its prevalence; however, since there have been so few cases in recent decades, images and descriptions of patients presenting with measles can be found only in textbooks, and many physicians are ill-prepared to diagnose the disease.4 In response to the recent surge in measles cases, dermatologists—who often are among the first medical professionals to encounter febrile patients with rashes—must be prepared to bridge this divide. Herein, we review the clinical signs, diagnostic approach, operational precautions, and public health responsibilities that dermatologists must relearn amid the current measles outbreak.
Background
Measles is primarily transmitted via respiratory droplets and may remain airborne for up to 2 hours.5 It also can be transmitted through direct contact with secretions such as mucus. Indirect transmission via fomites, while certainly plausible, is thought to be the least effective mechanism of transmission.6 Following exposure, the incubation period ranges from 7 to 21 days, during which the virus replicates asymptomatically before causing clinical disease.7 Herd immunity for measles requires 93% immunity in the population; public health agencies typically target greater than 95% immunity.8 Humans are the only reservoir for the measles virus, making eradication possible.
The road to eradication began with the introduction of the measles vaccine in 1963 and subsequent development of the combined measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine in 1971. As MMR is a live vaccine, 2 doses confer approximately 97% protection.9 The first dose is given at 12 to 15 months of age, and the second dose is given at 4 to 6 years of age. Immunity is considered lifelong, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Health Organization do not recommend routine measles boosters for individuals who have completed the primary 2-dose series.10,11
Widespread vaccination led to a dramatic reduction in incidence, with many countries eliminating measles infections.7 The United States declared measles eliminated in 2000, with confirmed cases between 2000 and 2020 ranging from 37 to 1282.12 Vaccination progress stalled in the late 1990s due to vaccine hesitancy resulting from (subsequently debunked) reports of an association between the MMR vaccine and autism.13 Despite efforts to correct this misinformation, many patients continue to espouse these concerns.
Recognizing Measles: Clinical Presentation
Measles, which most often manifests in childhood but also can occur in adults, follows a distinctive clinical course. The prodromal phase is characterized by high fever, cough, coryza (nasal congestion), and conjunctivitis— conjunctivitis—the 3 “Cs” that serve as early warning signs of the disease. Patients may develop small white macules on the buccal mucosa known as Koplik spots (phonetically the fourth “C”), which appear just before the rash. Three to 5 days after the onset of systemic symptoms, patients will develop a classic morbilliform exanthem. In some cases, the exanthem manifests on the head and neck (Figure 1)—first behind the ears and along the hairline, then spreading caudally to the trunk and extremities. The lesions may become confluent, with patients presenting with diffuse erythema. The exanthem fades over several days to weeks, often accompanied by superficial desquamation.14

Given the nonspecificity of the early symptoms of measles, a high index of suspicion is needed for patients presenting with a febrile illness and a morbilliform eruption (Figure 2). Consideration of MMR vaccination status, exposure history, and local outbreak patterns can help guide risk stratification and the need for testing. Immunocompromised individuals, including those receiving immunosuppressive therapies for dermatologic conditions, may present atypically, lacking the prototypical exanthem or displaying milder signs and further complicating the diagnosis.15 The differential diagnosis for measles includes a drug reaction or other viral exanthem, and a detailed history may help elucidate the culprit.

Evaluation and Diagnosis
Definitive diagnosis of measles relies on both molecular and serologic testing. Nasopharyngeal swabs for measles polymerase chain reaction testing are obtained using synthetic (noncotton) swabs placed in a viral transport medium. Serum samples also should be collected for measles IgM and IgG antibody testing. Importantly, measles is a reportable illness, and testing may be coordinated with local departments of health.
Determining a patient’s immune status may be important for certain populations. Patients with documented 2-dose MMR vaccination, positive measles IgG serology, or a prior confirmed measles infection are considered immune. While a positive measles IgG indicates immunity, a negative result in an exposed patient should prompt consideration of postexposure prophylaxis with intravenous immunoglobulin.
Many patients, specifically those presenting to dermatology, are taking immunomodulatory or immunosuppressive medications—a contraindication for vaccination with the live MMR vaccine. At the time of publication, there was a single reported case of a patient taking a tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor for rheumatoid arthritis who had acquired measles.16 While the benefits of titer assessment in patients who are starting or continuing immunomodulatory therapy are not known and currently it is not recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, dermatologists might consider checking MMR titers and vaccinating (or referring for vaccination) nonimmune patients.17
Infection Control
Early identification of a suspected measles case is paramount. Patients in whom measles is a possibility should be isolated as quickly as possible, and the patient and accompanying caregivers should be masked. Clinical staff should don appropriate personal protective equipment, including an N95 mask. Coordination with the local department of health must occur as soon as measles is suspected.
If testing is an option in the outpatient setting, a nasopharyngeal viral swab and serologic titers can be obtained. If testing is not available on site, patients should be sent to appropriate care facilities; prenotification is critical to prevent nosocomial outbreaks. Patients should be encouraged to isolate and avoid public spaces and/or public transport for 4 days following development of an exanthem.18 Offices should develop clinical protocols for suspected measles cases with training for clinical and office staff.
Final Thoughts
As measles outbreaks become more prevalent, it is incumbent upon physicians to remind ourselves of the signs and symptoms of this largely eliminated disease so that we may pursue early detection and intervention strategies. The primary cutaneous manifestations of measles make dermatologists critical to early recognition and containment efforts. Dermatologists should prepare for the arrival of patients with measles by maintaining vigilance for the classic signs of the disease, implementing stringent isolation protocols, verifying patient immunity when appropriate, and partnering closely with public health authorities.
More broadly, efforts to contain and re-establish a paradigm for eliminating measles outbreaks must be pursued. Encouraging vaccination and developing programs to help combat misinformation surrounding vaccines are critical to this effort. In an era of vaccine hesitancy, measles is a multidisciplinary public health emergency. Dermatologists must remain ready.
- Bedford H, Elliman D. Measles rates are rising again. BMJ. 2024;384.
- Harris E. Measles outbreaks grow amid declining vaccination rates. JAMA. 2023;330:2242.
- Guerra FM, Bolotin S, Lim G, et al. The basic reproduction number (R0) of measles: a systematic review. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017;17:E420-E428.
- Swartz MK. Measles: public and professional education. J Pediatr Health Care. 2019;33:367-368.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim infection prevention and control recommendations for measles in healthcare settings. Accessed April 27, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/infection-control/hcp/measles/
- Moss WJ, Griffin DE, Feinstone WH. Measles. In: Vaccines for Biodefense and Emerging and Neglected Diseases. Elsevier; 2009: 551-565.
- Moss WJ. Measles. Lancet. 2017;390:2490-2502.
- Maintain the vaccination coverage level of 2 doses of the MMR vaccine for children in kindergarten— IID04. Healthy People 2030 website. Accessed May 6, 2025. https://odphp.health.gov/healthypeople/objectives-and-data/browse-objectives/vaccination/maintain-vaccination-coverage-level-2-doses-mmr-vaccine-children-kindergarten-iid-04
- Franconeri L, Antona D, Cauchemez S, et al. Two-dose measles vaccine effectiveness remains high over time: a French observational study, 2017–2019. Vaccine. 2023;41:5797-5804.
- World Health Organization. Measles. Accessed May 8, 2025. https:// www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/measles
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles vaccine recommendations. Accessed May 8, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/hcp/vaccine-considerations/index.html
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles cases and outbreaks. Accessed May 6, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/cases-outbreaks.html
- Dyer C. Lancet retracts Wakefield’s MMR paper. BMJ. 2010;340.
- Alves Graber EM, Andrade FJ, Bost W, et al. An update and review of measles for emergency physicians. J Emerg Med. 2020;58:610-615.
- Kaplan LJ, Daum RS, Smaron M, et al. Severe measles in immunocompromised patients. JAMA. 1992;267:1237-1241.
- Takahashi E, Kurosaka D, Yoshida K, et al. Onset of modified measles after etanercept treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. Japanese J Clin Immunol. 2010;33:37-41.
- Worth A, Waldman RA, Dieckhaus K, et al. Art of prevention: our approach to the measles-mumps-rubella vaccine in adult patients vaccinated against measles before 1968 on biologic therapy for the treatment of psoriasis. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019;6:94.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinical overview of measles (rubeola). Accessed May 8, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/hcp/clinical-overview/index.html
- Bedford H, Elliman D. Measles rates are rising again. BMJ. 2024;384.
- Harris E. Measles outbreaks grow amid declining vaccination rates. JAMA. 2023;330:2242.
- Guerra FM, Bolotin S, Lim G, et al. The basic reproduction number (R0) of measles: a systematic review. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017;17:E420-E428.
- Swartz MK. Measles: public and professional education. J Pediatr Health Care. 2019;33:367-368.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim infection prevention and control recommendations for measles in healthcare settings. Accessed April 27, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/infection-control/hcp/measles/
- Moss WJ, Griffin DE, Feinstone WH. Measles. In: Vaccines for Biodefense and Emerging and Neglected Diseases. Elsevier; 2009: 551-565.
- Moss WJ. Measles. Lancet. 2017;390:2490-2502.
- Maintain the vaccination coverage level of 2 doses of the MMR vaccine for children in kindergarten— IID04. Healthy People 2030 website. Accessed May 6, 2025. https://odphp.health.gov/healthypeople/objectives-and-data/browse-objectives/vaccination/maintain-vaccination-coverage-level-2-doses-mmr-vaccine-children-kindergarten-iid-04
- Franconeri L, Antona D, Cauchemez S, et al. Two-dose measles vaccine effectiveness remains high over time: a French observational study, 2017–2019. Vaccine. 2023;41:5797-5804.
- World Health Organization. Measles. Accessed May 8, 2025. https:// www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/measles
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles vaccine recommendations. Accessed May 8, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/hcp/vaccine-considerations/index.html
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles cases and outbreaks. Accessed May 6, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/cases-outbreaks.html
- Dyer C. Lancet retracts Wakefield’s MMR paper. BMJ. 2010;340.
- Alves Graber EM, Andrade FJ, Bost W, et al. An update and review of measles for emergency physicians. J Emerg Med. 2020;58:610-615.
- Kaplan LJ, Daum RS, Smaron M, et al. Severe measles in immunocompromised patients. JAMA. 1992;267:1237-1241.
- Takahashi E, Kurosaka D, Yoshida K, et al. Onset of modified measles after etanercept treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. Japanese J Clin Immunol. 2010;33:37-41.
- Worth A, Waldman RA, Dieckhaus K, et al. Art of prevention: our approach to the measles-mumps-rubella vaccine in adult patients vaccinated against measles before 1968 on biologic therapy for the treatment of psoriasis. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019;6:94.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinical overview of measles (rubeola). Accessed May 8, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/hcp/clinical-overview/index.html
Measles Resurgence: A Dermatologist’s Guide
Measles Resurgence: A Dermatologist’s Guide
HIV Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP): A Survey of Dermatologists’ Knowledge and Practice Patterns
To the Editor:
In a 2010 landmark paper, researchers reported that the Preexposure Prophylaxis Initiative (iPrEx) trial demonstrated that once-daily pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) with emtricitabine plus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, which was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and packaged together as Truvada (Gilead Sciences, Inc), achieved a 44% reduction in the incidence of HIV infection compared to the placebo arm of the study (64/1248 HIV infections in the placebo group vs 36/1251 in the intervention group).1 Subsequently, the US Department of Health and Human Services proposed an initiative to reduce new HIV infections by 90% by 2030.2 The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that 1.1 million Americans have an indication for PrEP, yet only approximately 400,000 individuals currently take PrEP.3,4
Increasing awareness of PrEP and its indications is essential because PrEP exerts its greatest benefit when used broadly. Awareness among primary care and infectious disease physicians was reported at 76%5; awareness among other medical specialists remains unknown. Awareness of PrEP among dermatologists is important because dermatologists play an important role in the diagnosis and treatment of many sexually transmitted infections (STIs), which are a risk factor for transmission of HIV. As providers who treat STIs, dermatologists are in a prime position to educate patients about PrEP, refer them for treatment, and prescribe the regimen. We conducted a survey to assess dermatologists’ knowledge about and attitudes toward PrEP. We also provide a brief summary of prescribing information about common PrEP regimens to fill in the knowledge gap among dermatologists as a way to promote its utilization.
An electronic survey was distributed to 486 members of the Association of Professors of Dermatology based in the United States using the web-based survey application REDCap. The study was approved by the New York University Grossman School of Medicine (New York, New York) institutional review board. Eighty-one anonymous survey responses were completed and returned (response rate, 16.6%). Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics.
The mean age (SD) of respondents was 39.1 (9.7) years; 49.4% (40/81) were male; and 74.1% (60/81) were attending physicians, with a mean (SD) of 9.4 (8.6) years of practice. Clinical practices were predominantly from the northeast (46.9% [38/81]) and mostly in an academic setting (74.1% [60/81]). As shown in Table 1, most surveyed dermatologists reported being aware of PrEP (93.8% [76/81]), but a minority (42.0% [34/81]) were familiar with indications for its use; even fewer (4.9% [4/81]) were current prescribers. Referral to other physicians for PrEP was reported by 58.0% (47/81) of respondents.
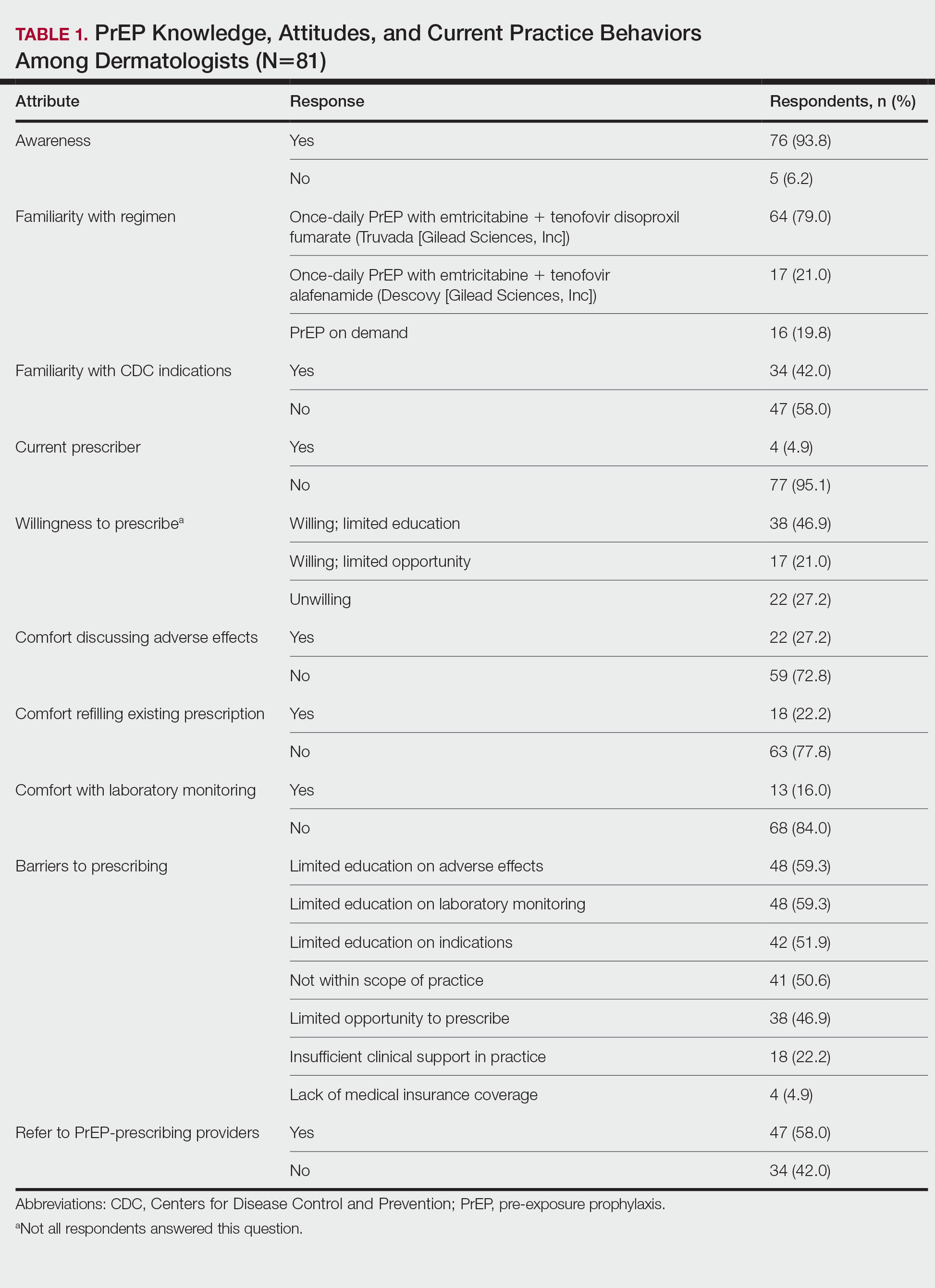
Despite respondents’ awareness of PrEP as a preventive measure (93.8% [76/81]) and their willingness to prescribe it (67.9% [55/81]), many reported being largely unfamiliar with its indications (58.0% [47/81]) and uncomfortable discussing its adverse effects (72.8% [59/81]), conducting appropriate laboratory monitoring (84.0% [68/81]), and refilling existing prescriptions (77.8% [63/81]). Respondents’ lack of education about PrEP was a barrier to prescribing (51.9% [42/81] to 59.3% [48/81]) and explains why a small minority (4.9% [4/81]) currently prescribe the regimen.
Our study sought to characterize current clinical knowledge about and practice patterns of PrEP among dermatologists. Dermatologists often encounter patients who present with an STI, which is a risk factor for HIV infection, but our survey respondents reported several barriers to utilizing PrEP. The difference in the degree of respondents’ willingness to prescribe PrEP (67.9%) and those who self-identified as prescribers (4.9%) suggests a role for dermatologists in prescribing or discussing PrEP with their patients—albeit a currently undefined role.
The results of our study suggested that half (41/81) of dermatologists believe that PrEP prescription is out of their scope of practice, likely due to a combination of scheduling, laboratory monitoring, and medicolegal concerns. For dermatologists who are interested in being PrEP prescribers, our results suggested that closing the knowledge gap around PrEP among dermatologists through training and education could improve comfort with this medication and lead to changes in practice to prevent the spread of HIV infection.
PrEP is indicated for HIV-negative patients who have HIV-positive sexual partners, utilize barrier protection methods inconsistently, or had a diagnosis of an STI in the last 6 months.6 In 2012, the FDA approved once-daily use of emtricitabine plus tenofovir for primary prevention of HIV infection. Post hoc analysis of iPrEx trial data revealed that once-daily PrEP taken regularly had a 92% to 100% protective effect against HIV.7
Regrettably, real-world uptake of PrEP has been slower than desired. The most recent data (2021) show that nearly 1 million individuals worldwide take PrEP; however, this represents only approximately one-third of those eligible.8 Utilization is notably lower among Black and Latino populations who stand to gain the most from PrEP given their higher risk of contracting HIV compared to their White counterparts.9 As such, improving access to PrEP through expanded provider awareness is essential to decrease the risk for HIV infection and transmission.
Emtricitabine plus tenofovir is safe and well tolerated; more common adverse effects are headache, nausea, vomiting, rash, and loss of appetite. Tenofovir likely decreases bone mineral density, even in HIV-negative patients10; mineralization seems to recover after the medication is discontinued.11 Rarely, tenofovir can increase the level of creatinine and hepatic transaminases; a recent report on its long-term side effects has shown small nonprogressive decreases in glomerular filtration rate.12 Monitoring kidney function is a component of prescribing PrEP (Table 2).

In 2019, emtricitabine plus tenofovir was reformulated with tenofovir alafenamide; the new combination regimen received FDA approval for once-daily PrEP under the brand name Descovy (Gilead Sciences, Inc). The new formulation results in a lower blood concentration of tenofovir and has been reported to present less of a risk for bone and kidney toxicity.13,14
Notably, emtricitabine plus tenofovir alafenamide might accumulate faster in peripheral lymphatic tissue than emtricitabine plus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. This property has led to a new regimen known as “on-demand PrEP,” which follows a 2-1-1 dosing regimen: Patients take a double dose 2 to 24 hours before sexual activity, 1 dose on the day of sexual activity, and 1 dose the day after sexual activity.15 Because some patients at risk for HIV infection might not be consistently sexually active, on-demand PrEP allows them to cycle on and off the medication. Barriers to implementing on-demand PrEP include requiring that sexual activity be planned and an adverse effect profile similar to daily-use PrEP.16
The FDA recently approved a long-acting, once-monthly combination injectable PrEP of cabotegravir and rilpivirine.17 The long duration of action of this PrEP will benefit patients who report problems with medication adherence.
Our study demonstrates low frequency in prescribing patterns of PrEP among dermatologists and suggests that an addressable barrier to such prescribing is the lack of knowledge on how to prescribe it safely, which warrants further clinical investigation. We summarize an approach to prescribing PrEP in Table 2. Our study was limited by a small sample of mostly academic dermatologists and selection bias, which may diminish the generalizability of findings. A study of a larger, more representative group of dermatologists likely would show different prescribing patterns and degrees of knowledge about PrEP. Research is needed to study the impact of educational interventions that aim to increase both knowledge and prescribing of PrEP among dermatologists.
- Grant RM, Lama JR, Anderson PL, et al; iPrEx Study Team. Preexposure chemoprophylaxis for HIV prevention in men who have sex with men. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:2587-2599. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1011205
- Fauci AS, Redfield RR, Sigounas G, et al. Ending the HIV epidemic: a plan for the United States. JAMA. 2019;321:844-845. doi:10.1001/jama.2019.1343
- Smith DK, Van Handel M, Grey J. Estimates of adults with indications for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis by jurisdiction, transmission risk group, and race/ethnicity, United States, 2015. Ann Epidemiol. 2018;28:850-857.e9. doi:10.1016/j.annepidem.2018.05.003
- Song HJ, Squires P, Wilson D, et al. Trends in HIV preexposure prophylaxis prescribing in the United States, 2012-2018. JAMA. 2020;324:395-397. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.7312
- Petroll AE, Walsh JL, Owczarzak JL, et al. PrEP awareness, familiarity, comfort, and prescribing experience among US primary care providers and HIV specialists. AIDS Behav. 2017;21:1256-1267. doi:10.1007/s10461-016-1625-1
- US Public Health Service. Preexposure prophylaxis for the prevention of HIV infection in the United States—2021 update. a clinical practice guideline. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed September 15, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/risk/prep/cdc-hiv-prep-guidelines-2021.pdf
- Riddell J 4th, Amico KR, Mayer KH. HIV preexposure prophylaxis: a review. JAMA. 2018;319:1261-1268. doi:10.1001/JAMA.2018.1917
- Segal K, Fitch L, Riaz F, et al. The evolution of oral PrEP access: tracking trends in global oral PrEP use over time. J Int AIDS Soc. 2021;24:27-28.
- Elion RA, Kabiri M, Mayer KH, et al. Estimated impact of targeted pre-exposure prophylaxis: strategies for men who have sex with men in the United States. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16:1592. doi:10.3390/ijerph16091592
- Kasonde M, Niska RW, Rose C, et al. Bone mineral density changes among HIV-uninfected young adults in a randomised trial of pre-exposure prophylaxis with tenofovir-emtricitabine or placebo in Botswana. PLoS One. 2014;9:e90111. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0090111
- Glidden DV, Mulligan K, McMahan V, et al. Brief report: recovery of bone mineral density after discontinuation of tenofovir-based HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2017;76:177-182. doi:10.1097/QAI.0000000000001475
- Tang EC, Vittinghoff E, Anderson PL, et al. Changes in kidney function associated with daily tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine for HIV preexposure prophylaxis use in the United States Demonstration Project. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2018;77:193-198. doi:10.1097/QAI.0000000000001566
- Gupta SK, Post FA, Arribas JR, et al. Renal safety of tenofovir alafenamide vs. tenofovir disoproxil fumarate: a pooled analysis of 26 clinical trials. AIDS. 2019;33:1455-1465. doi:10.1097/QAD.0000000000002223
- Agarwal K, Brunetto M, Seto WK, et al; GS-US-320-0110; GS-US-320-0108 Investigators. 96 weeks treatment of tenofovir alafenamide vs. tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for hepatitis B virus infection [published online January 17, 2018]. J Hepatol. 2018;68:672-681. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2017.11.039
- Molina JM, Capitant C, Spire B, et al; ANRS IPERGAY Study Group. On-demand preexposure prophylaxis in men at high risk for HIV-1 infection [published online December 1, 2015]. N Engl J Med. 2015;3;2237-2246. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1506273
- Saberi P, Scott HM. On-demand oral pre-exposure prophylaxis with tenofovir/emtricitabine: what every clinician needs to know. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35:1285-1288. doi:10.1007/s11606-020-05651-2
- Landovitz RJ, Li S, Grinsztejn B, et al. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of long-acting injectable cabotegravir in low-risk HIV-uninfected individuals: HPTN 077, a phase 2a randomized controlled trial. PLoS Med. 2018;15:e1002690. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1002690
To the Editor:
In a 2010 landmark paper, researchers reported that the Preexposure Prophylaxis Initiative (iPrEx) trial demonstrated that once-daily pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) with emtricitabine plus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, which was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and packaged together as Truvada (Gilead Sciences, Inc), achieved a 44% reduction in the incidence of HIV infection compared to the placebo arm of the study (64/1248 HIV infections in the placebo group vs 36/1251 in the intervention group).1 Subsequently, the US Department of Health and Human Services proposed an initiative to reduce new HIV infections by 90% by 2030.2 The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that 1.1 million Americans have an indication for PrEP, yet only approximately 400,000 individuals currently take PrEP.3,4
Increasing awareness of PrEP and its indications is essential because PrEP exerts its greatest benefit when used broadly. Awareness among primary care and infectious disease physicians was reported at 76%5; awareness among other medical specialists remains unknown. Awareness of PrEP among dermatologists is important because dermatologists play an important role in the diagnosis and treatment of many sexually transmitted infections (STIs), which are a risk factor for transmission of HIV. As providers who treat STIs, dermatologists are in a prime position to educate patients about PrEP, refer them for treatment, and prescribe the regimen. We conducted a survey to assess dermatologists’ knowledge about and attitudes toward PrEP. We also provide a brief summary of prescribing information about common PrEP regimens to fill in the knowledge gap among dermatologists as a way to promote its utilization.
An electronic survey was distributed to 486 members of the Association of Professors of Dermatology based in the United States using the web-based survey application REDCap. The study was approved by the New York University Grossman School of Medicine (New York, New York) institutional review board. Eighty-one anonymous survey responses were completed and returned (response rate, 16.6%). Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics.
The mean age (SD) of respondents was 39.1 (9.7) years; 49.4% (40/81) were male; and 74.1% (60/81) were attending physicians, with a mean (SD) of 9.4 (8.6) years of practice. Clinical practices were predominantly from the northeast (46.9% [38/81]) and mostly in an academic setting (74.1% [60/81]). As shown in Table 1, most surveyed dermatologists reported being aware of PrEP (93.8% [76/81]), but a minority (42.0% [34/81]) were familiar with indications for its use; even fewer (4.9% [4/81]) were current prescribers. Referral to other physicians for PrEP was reported by 58.0% (47/81) of respondents.

Despite respondents’ awareness of PrEP as a preventive measure (93.8% [76/81]) and their willingness to prescribe it (67.9% [55/81]), many reported being largely unfamiliar with its indications (58.0% [47/81]) and uncomfortable discussing its adverse effects (72.8% [59/81]), conducting appropriate laboratory monitoring (84.0% [68/81]), and refilling existing prescriptions (77.8% [63/81]). Respondents’ lack of education about PrEP was a barrier to prescribing (51.9% [42/81] to 59.3% [48/81]) and explains why a small minority (4.9% [4/81]) currently prescribe the regimen.
Our study sought to characterize current clinical knowledge about and practice patterns of PrEP among dermatologists. Dermatologists often encounter patients who present with an STI, which is a risk factor for HIV infection, but our survey respondents reported several barriers to utilizing PrEP. The difference in the degree of respondents’ willingness to prescribe PrEP (67.9%) and those who self-identified as prescribers (4.9%) suggests a role for dermatologists in prescribing or discussing PrEP with their patients—albeit a currently undefined role.
The results of our study suggested that half (41/81) of dermatologists believe that PrEP prescription is out of their scope of practice, likely due to a combination of scheduling, laboratory monitoring, and medicolegal concerns. For dermatologists who are interested in being PrEP prescribers, our results suggested that closing the knowledge gap around PrEP among dermatologists through training and education could improve comfort with this medication and lead to changes in practice to prevent the spread of HIV infection.
PrEP is indicated for HIV-negative patients who have HIV-positive sexual partners, utilize barrier protection methods inconsistently, or had a diagnosis of an STI in the last 6 months.6 In 2012, the FDA approved once-daily use of emtricitabine plus tenofovir for primary prevention of HIV infection. Post hoc analysis of iPrEx trial data revealed that once-daily PrEP taken regularly had a 92% to 100% protective effect against HIV.7
Regrettably, real-world uptake of PrEP has been slower than desired. The most recent data (2021) show that nearly 1 million individuals worldwide take PrEP; however, this represents only approximately one-third of those eligible.8 Utilization is notably lower among Black and Latino populations who stand to gain the most from PrEP given their higher risk of contracting HIV compared to their White counterparts.9 As such, improving access to PrEP through expanded provider awareness is essential to decrease the risk for HIV infection and transmission.
Emtricitabine plus tenofovir is safe and well tolerated; more common adverse effects are headache, nausea, vomiting, rash, and loss of appetite. Tenofovir likely decreases bone mineral density, even in HIV-negative patients10; mineralization seems to recover after the medication is discontinued.11 Rarely, tenofovir can increase the level of creatinine and hepatic transaminases; a recent report on its long-term side effects has shown small nonprogressive decreases in glomerular filtration rate.12 Monitoring kidney function is a component of prescribing PrEP (Table 2).

In 2019, emtricitabine plus tenofovir was reformulated with tenofovir alafenamide; the new combination regimen received FDA approval for once-daily PrEP under the brand name Descovy (Gilead Sciences, Inc). The new formulation results in a lower blood concentration of tenofovir and has been reported to present less of a risk for bone and kidney toxicity.13,14
Notably, emtricitabine plus tenofovir alafenamide might accumulate faster in peripheral lymphatic tissue than emtricitabine plus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. This property has led to a new regimen known as “on-demand PrEP,” which follows a 2-1-1 dosing regimen: Patients take a double dose 2 to 24 hours before sexual activity, 1 dose on the day of sexual activity, and 1 dose the day after sexual activity.15 Because some patients at risk for HIV infection might not be consistently sexually active, on-demand PrEP allows them to cycle on and off the medication. Barriers to implementing on-demand PrEP include requiring that sexual activity be planned and an adverse effect profile similar to daily-use PrEP.16
The FDA recently approved a long-acting, once-monthly combination injectable PrEP of cabotegravir and rilpivirine.17 The long duration of action of this PrEP will benefit patients who report problems with medication adherence.
Our study demonstrates low frequency in prescribing patterns of PrEP among dermatologists and suggests that an addressable barrier to such prescribing is the lack of knowledge on how to prescribe it safely, which warrants further clinical investigation. We summarize an approach to prescribing PrEP in Table 2. Our study was limited by a small sample of mostly academic dermatologists and selection bias, which may diminish the generalizability of findings. A study of a larger, more representative group of dermatologists likely would show different prescribing patterns and degrees of knowledge about PrEP. Research is needed to study the impact of educational interventions that aim to increase both knowledge and prescribing of PrEP among dermatologists.
To the Editor:
In a 2010 landmark paper, researchers reported that the Preexposure Prophylaxis Initiative (iPrEx) trial demonstrated that once-daily pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) with emtricitabine plus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, which was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and packaged together as Truvada (Gilead Sciences, Inc), achieved a 44% reduction in the incidence of HIV infection compared to the placebo arm of the study (64/1248 HIV infections in the placebo group vs 36/1251 in the intervention group).1 Subsequently, the US Department of Health and Human Services proposed an initiative to reduce new HIV infections by 90% by 2030.2 The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that 1.1 million Americans have an indication for PrEP, yet only approximately 400,000 individuals currently take PrEP.3,4
Increasing awareness of PrEP and its indications is essential because PrEP exerts its greatest benefit when used broadly. Awareness among primary care and infectious disease physicians was reported at 76%5; awareness among other medical specialists remains unknown. Awareness of PrEP among dermatologists is important because dermatologists play an important role in the diagnosis and treatment of many sexually transmitted infections (STIs), which are a risk factor for transmission of HIV. As providers who treat STIs, dermatologists are in a prime position to educate patients about PrEP, refer them for treatment, and prescribe the regimen. We conducted a survey to assess dermatologists’ knowledge about and attitudes toward PrEP. We also provide a brief summary of prescribing information about common PrEP regimens to fill in the knowledge gap among dermatologists as a way to promote its utilization.
An electronic survey was distributed to 486 members of the Association of Professors of Dermatology based in the United States using the web-based survey application REDCap. The study was approved by the New York University Grossman School of Medicine (New York, New York) institutional review board. Eighty-one anonymous survey responses were completed and returned (response rate, 16.6%). Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics.
The mean age (SD) of respondents was 39.1 (9.7) years; 49.4% (40/81) were male; and 74.1% (60/81) were attending physicians, with a mean (SD) of 9.4 (8.6) years of practice. Clinical practices were predominantly from the northeast (46.9% [38/81]) and mostly in an academic setting (74.1% [60/81]). As shown in Table 1, most surveyed dermatologists reported being aware of PrEP (93.8% [76/81]), but a minority (42.0% [34/81]) were familiar with indications for its use; even fewer (4.9% [4/81]) were current prescribers. Referral to other physicians for PrEP was reported by 58.0% (47/81) of respondents.

Despite respondents’ awareness of PrEP as a preventive measure (93.8% [76/81]) and their willingness to prescribe it (67.9% [55/81]), many reported being largely unfamiliar with its indications (58.0% [47/81]) and uncomfortable discussing its adverse effects (72.8% [59/81]), conducting appropriate laboratory monitoring (84.0% [68/81]), and refilling existing prescriptions (77.8% [63/81]). Respondents’ lack of education about PrEP was a barrier to prescribing (51.9% [42/81] to 59.3% [48/81]) and explains why a small minority (4.9% [4/81]) currently prescribe the regimen.
Our study sought to characterize current clinical knowledge about and practice patterns of PrEP among dermatologists. Dermatologists often encounter patients who present with an STI, which is a risk factor for HIV infection, but our survey respondents reported several barriers to utilizing PrEP. The difference in the degree of respondents’ willingness to prescribe PrEP (67.9%) and those who self-identified as prescribers (4.9%) suggests a role for dermatologists in prescribing or discussing PrEP with their patients—albeit a currently undefined role.
The results of our study suggested that half (41/81) of dermatologists believe that PrEP prescription is out of their scope of practice, likely due to a combination of scheduling, laboratory monitoring, and medicolegal concerns. For dermatologists who are interested in being PrEP prescribers, our results suggested that closing the knowledge gap around PrEP among dermatologists through training and education could improve comfort with this medication and lead to changes in practice to prevent the spread of HIV infection.
PrEP is indicated for HIV-negative patients who have HIV-positive sexual partners, utilize barrier protection methods inconsistently, or had a diagnosis of an STI in the last 6 months.6 In 2012, the FDA approved once-daily use of emtricitabine plus tenofovir for primary prevention of HIV infection. Post hoc analysis of iPrEx trial data revealed that once-daily PrEP taken regularly had a 92% to 100% protective effect against HIV.7
Regrettably, real-world uptake of PrEP has been slower than desired. The most recent data (2021) show that nearly 1 million individuals worldwide take PrEP; however, this represents only approximately one-third of those eligible.8 Utilization is notably lower among Black and Latino populations who stand to gain the most from PrEP given their higher risk of contracting HIV compared to their White counterparts.9 As such, improving access to PrEP through expanded provider awareness is essential to decrease the risk for HIV infection and transmission.
Emtricitabine plus tenofovir is safe and well tolerated; more common adverse effects are headache, nausea, vomiting, rash, and loss of appetite. Tenofovir likely decreases bone mineral density, even in HIV-negative patients10; mineralization seems to recover after the medication is discontinued.11 Rarely, tenofovir can increase the level of creatinine and hepatic transaminases; a recent report on its long-term side effects has shown small nonprogressive decreases in glomerular filtration rate.12 Monitoring kidney function is a component of prescribing PrEP (Table 2).

In 2019, emtricitabine plus tenofovir was reformulated with tenofovir alafenamide; the new combination regimen received FDA approval for once-daily PrEP under the brand name Descovy (Gilead Sciences, Inc). The new formulation results in a lower blood concentration of tenofovir and has been reported to present less of a risk for bone and kidney toxicity.13,14
Notably, emtricitabine plus tenofovir alafenamide might accumulate faster in peripheral lymphatic tissue than emtricitabine plus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. This property has led to a new regimen known as “on-demand PrEP,” which follows a 2-1-1 dosing regimen: Patients take a double dose 2 to 24 hours before sexual activity, 1 dose on the day of sexual activity, and 1 dose the day after sexual activity.15 Because some patients at risk for HIV infection might not be consistently sexually active, on-demand PrEP allows them to cycle on and off the medication. Barriers to implementing on-demand PrEP include requiring that sexual activity be planned and an adverse effect profile similar to daily-use PrEP.16
The FDA recently approved a long-acting, once-monthly combination injectable PrEP of cabotegravir and rilpivirine.17 The long duration of action of this PrEP will benefit patients who report problems with medication adherence.
Our study demonstrates low frequency in prescribing patterns of PrEP among dermatologists and suggests that an addressable barrier to such prescribing is the lack of knowledge on how to prescribe it safely, which warrants further clinical investigation. We summarize an approach to prescribing PrEP in Table 2. Our study was limited by a small sample of mostly academic dermatologists and selection bias, which may diminish the generalizability of findings. A study of a larger, more representative group of dermatologists likely would show different prescribing patterns and degrees of knowledge about PrEP. Research is needed to study the impact of educational interventions that aim to increase both knowledge and prescribing of PrEP among dermatologists.
- Grant RM, Lama JR, Anderson PL, et al; iPrEx Study Team. Preexposure chemoprophylaxis for HIV prevention in men who have sex with men. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:2587-2599. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1011205
- Fauci AS, Redfield RR, Sigounas G, et al. Ending the HIV epidemic: a plan for the United States. JAMA. 2019;321:844-845. doi:10.1001/jama.2019.1343
- Smith DK, Van Handel M, Grey J. Estimates of adults with indications for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis by jurisdiction, transmission risk group, and race/ethnicity, United States, 2015. Ann Epidemiol. 2018;28:850-857.e9. doi:10.1016/j.annepidem.2018.05.003
- Song HJ, Squires P, Wilson D, et al. Trends in HIV preexposure prophylaxis prescribing in the United States, 2012-2018. JAMA. 2020;324:395-397. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.7312
- Petroll AE, Walsh JL, Owczarzak JL, et al. PrEP awareness, familiarity, comfort, and prescribing experience among US primary care providers and HIV specialists. AIDS Behav. 2017;21:1256-1267. doi:10.1007/s10461-016-1625-1
- US Public Health Service. Preexposure prophylaxis for the prevention of HIV infection in the United States—2021 update. a clinical practice guideline. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed September 15, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/risk/prep/cdc-hiv-prep-guidelines-2021.pdf
- Riddell J 4th, Amico KR, Mayer KH. HIV preexposure prophylaxis: a review. JAMA. 2018;319:1261-1268. doi:10.1001/JAMA.2018.1917
- Segal K, Fitch L, Riaz F, et al. The evolution of oral PrEP access: tracking trends in global oral PrEP use over time. J Int AIDS Soc. 2021;24:27-28.
- Elion RA, Kabiri M, Mayer KH, et al. Estimated impact of targeted pre-exposure prophylaxis: strategies for men who have sex with men in the United States. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16:1592. doi:10.3390/ijerph16091592
- Kasonde M, Niska RW, Rose C, et al. Bone mineral density changes among HIV-uninfected young adults in a randomised trial of pre-exposure prophylaxis with tenofovir-emtricitabine or placebo in Botswana. PLoS One. 2014;9:e90111. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0090111
- Glidden DV, Mulligan K, McMahan V, et al. Brief report: recovery of bone mineral density after discontinuation of tenofovir-based HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2017;76:177-182. doi:10.1097/QAI.0000000000001475
- Tang EC, Vittinghoff E, Anderson PL, et al. Changes in kidney function associated with daily tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine for HIV preexposure prophylaxis use in the United States Demonstration Project. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2018;77:193-198. doi:10.1097/QAI.0000000000001566
- Gupta SK, Post FA, Arribas JR, et al. Renal safety of tenofovir alafenamide vs. tenofovir disoproxil fumarate: a pooled analysis of 26 clinical trials. AIDS. 2019;33:1455-1465. doi:10.1097/QAD.0000000000002223
- Agarwal K, Brunetto M, Seto WK, et al; GS-US-320-0110; GS-US-320-0108 Investigators. 96 weeks treatment of tenofovir alafenamide vs. tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for hepatitis B virus infection [published online January 17, 2018]. J Hepatol. 2018;68:672-681. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2017.11.039
- Molina JM, Capitant C, Spire B, et al; ANRS IPERGAY Study Group. On-demand preexposure prophylaxis in men at high risk for HIV-1 infection [published online December 1, 2015]. N Engl J Med. 2015;3;2237-2246. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1506273
- Saberi P, Scott HM. On-demand oral pre-exposure prophylaxis with tenofovir/emtricitabine: what every clinician needs to know. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35:1285-1288. doi:10.1007/s11606-020-05651-2
- Landovitz RJ, Li S, Grinsztejn B, et al. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of long-acting injectable cabotegravir in low-risk HIV-uninfected individuals: HPTN 077, a phase 2a randomized controlled trial. PLoS Med. 2018;15:e1002690. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1002690
- Grant RM, Lama JR, Anderson PL, et al; iPrEx Study Team. Preexposure chemoprophylaxis for HIV prevention in men who have sex with men. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:2587-2599. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1011205
- Fauci AS, Redfield RR, Sigounas G, et al. Ending the HIV epidemic: a plan for the United States. JAMA. 2019;321:844-845. doi:10.1001/jama.2019.1343
- Smith DK, Van Handel M, Grey J. Estimates of adults with indications for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis by jurisdiction, transmission risk group, and race/ethnicity, United States, 2015. Ann Epidemiol. 2018;28:850-857.e9. doi:10.1016/j.annepidem.2018.05.003
- Song HJ, Squires P, Wilson D, et al. Trends in HIV preexposure prophylaxis prescribing in the United States, 2012-2018. JAMA. 2020;324:395-397. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.7312
- Petroll AE, Walsh JL, Owczarzak JL, et al. PrEP awareness, familiarity, comfort, and prescribing experience among US primary care providers and HIV specialists. AIDS Behav. 2017;21:1256-1267. doi:10.1007/s10461-016-1625-1
- US Public Health Service. Preexposure prophylaxis for the prevention of HIV infection in the United States—2021 update. a clinical practice guideline. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed September 15, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/risk/prep/cdc-hiv-prep-guidelines-2021.pdf
- Riddell J 4th, Amico KR, Mayer KH. HIV preexposure prophylaxis: a review. JAMA. 2018;319:1261-1268. doi:10.1001/JAMA.2018.1917
- Segal K, Fitch L, Riaz F, et al. The evolution of oral PrEP access: tracking trends in global oral PrEP use over time. J Int AIDS Soc. 2021;24:27-28.
- Elion RA, Kabiri M, Mayer KH, et al. Estimated impact of targeted pre-exposure prophylaxis: strategies for men who have sex with men in the United States. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16:1592. doi:10.3390/ijerph16091592
- Kasonde M, Niska RW, Rose C, et al. Bone mineral density changes among HIV-uninfected young adults in a randomised trial of pre-exposure prophylaxis with tenofovir-emtricitabine or placebo in Botswana. PLoS One. 2014;9:e90111. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0090111
- Glidden DV, Mulligan K, McMahan V, et al. Brief report: recovery of bone mineral density after discontinuation of tenofovir-based HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2017;76:177-182. doi:10.1097/QAI.0000000000001475
- Tang EC, Vittinghoff E, Anderson PL, et al. Changes in kidney function associated with daily tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine for HIV preexposure prophylaxis use in the United States Demonstration Project. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2018;77:193-198. doi:10.1097/QAI.0000000000001566
- Gupta SK, Post FA, Arribas JR, et al. Renal safety of tenofovir alafenamide vs. tenofovir disoproxil fumarate: a pooled analysis of 26 clinical trials. AIDS. 2019;33:1455-1465. doi:10.1097/QAD.0000000000002223
- Agarwal K, Brunetto M, Seto WK, et al; GS-US-320-0110; GS-US-320-0108 Investigators. 96 weeks treatment of tenofovir alafenamide vs. tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for hepatitis B virus infection [published online January 17, 2018]. J Hepatol. 2018;68:672-681. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2017.11.039
- Molina JM, Capitant C, Spire B, et al; ANRS IPERGAY Study Group. On-demand preexposure prophylaxis in men at high risk for HIV-1 infection [published online December 1, 2015]. N Engl J Med. 2015;3;2237-2246. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1506273
- Saberi P, Scott HM. On-demand oral pre-exposure prophylaxis with tenofovir/emtricitabine: what every clinician needs to know. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35:1285-1288. doi:10.1007/s11606-020-05651-2
- Landovitz RJ, Li S, Grinsztejn B, et al. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of long-acting injectable cabotegravir in low-risk HIV-uninfected individuals: HPTN 077, a phase 2a randomized controlled trial. PLoS Med. 2018;15:e1002690. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1002690
Practice Points
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) often have skin manifestations, with patients presenting to dermatologists.
- Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) uses antiretrovirals taken prophylactically to prevent transmission of and infection with HIV. Dermatologists are aware of PrEP, but several barriers prevent them from being prescribers.
- Patients with a history of an STI should be considered for PrEP.
Male Genital Examinations: Special Considerations and Pearls for Dermatologists
Men have unique dermatologic needs yet are significantly less likely than women to visit a dermatologist’s office.1 Male patients might have preconceived notions about the nature of dermatology visits and necessary areas of the body to be examined: For example, male patients might associate the genital examination with a urologist and not expect a dermatologist to complete such a seemingly private examination.2
Genital examinations are currently underperformed: Only one-quarter of dermatologists report examining a male patient’s genitals at most or all visits.3 In this commentary, we discuss the importance of genital examinations in men’s dermatology, specific issues that can arise, and strategies to enhance the quality and frequency of genital examinations in male patients.
Invaluable Aspect of Care
Thorough inspection of a male patient’s genital region is an important part of conducting a total-body skin examination (TBSE) for routine surveillance and evaluation of genital dermatoses. Sexually transmitted infections, warts, and other common lesions can be missed in diagnosis without careful inspection of the genital region. Additionally, scrotal malignancies, such as primary and metastatic melanoma and basal cell carcinoma, though rare, might be overlooked until symptoms become severe.4,5
There is no substitute for a physical examination but, in certain circumstances, it might be appropriate for a dermatologist to ask a patient if he has concerning lesions on his genitals. However, patients often are unsure of worrisome signs, and areas of the perineum might not be easily visible to a patient. Genital inspection during the physical examination allows for a teachable moment, during which the dermatologist can educate the patient about benign lesions and variants, such as pearly penile papules, seborrheic keratoses, and sebaceous cysts.6 These lesions might not require intervention but should be monitored for atypical features or infection.6
Also, the dermatologist might incidentally discover transmissible lesions, such as condylomata caused by human papillomavirus, which has been shown to be present in approximately 50% of men in the United States7—many of whom are unaware. Inflammatory dermatoses, such as psoriasis, often affect the genitals and go unnoticed; prompt intervention can decrease the likelihood of complications.6
Protocol for Genital Examinations
To examine the genitals, all surfaces of the penis, scrotum, and perineum should be evaluated, with anatomic and pathologic variants noted. The patient or physician should stretch the penis, maneuvering it in multiple directions so that all aspects can be examined. In uncircumcised men, the foreskin should be retracted so that the head of the penis can be examined, followed by replacement of the foreskin by the patient.8 The scrotum also should be examined and lifted to fully view the perineum.
Providers should not grasp the penis with the whole hand but use the thumb and first finger to hold the head of the penis to maneuver it.8 Similarly, using the back of the hand and fingers to manipulate the genitals establishes boundaries and sets a clinical tone for the examination.
Unintentional Erection
Unique to the male dermatologic examination is the unintentional patient erection; a physician might be unsure of how to approach such a potentially awkward situation. An erection is not always an indication of sexual arousal; rather, it can reflect an autonomic reflex in response to physical stimulation. Erections occur commonly in health care settings, especially if the genitals are being manipulated.9
Generally, the course of action here depends on the patient’s response.10 For patients who appear unbothered, it might be appropriate to ignore the erection and proceed with the examination, especially if the physician is not actively examining the genital region. If the patient appears embarrassed, the physician can say “This is completely normal” or “Random erections are common” to normalize the situation. Joking or laughing should be avoided. For a patient who appears upset, the physician can step outside the room for a brief period to give the patient privacy, then re-enter and ask him if he is comfortable continuing with the examination.
When a patient develops an erection, the physician might become uncomfortable and, consciously or subconsciously, increase the pace of the examination, which is a natural tendency, but expediency at the expense of comprehensive care is inappropriate.
Examiner’s Body Language and Tone
Throughout the genital examination, the physician should be mindful of their comments and body language to avoid exacerbating patient vulnerability. Using anatomic terms, rather than colloquial ones, to describe the genitalia is advised to prevent misunderstanding and maintain a professional clinical environment. Providers should be prepared to explain anatomic terms because some patients are not familiar with medical terminology.
Presence of a Chaperone
Involving a chaperone, as recommended by the American Medical Association, might make a patient more comfortable and alleviate potential misunderstanding. Still, physicians should be aware that some patients might feel uncomfortable with a chaperone, interpreting their presence as an expectation of impropriety.11 Universal offering of a chaperone to all patients, regardless of the gender of the physician, as well as appropriate signage in the clinical environment, normalizes chaperone invitation and use.
Other Helpful Considerations
Various strategies in the male genital examination can increase patient and physician comfort and improve care:
- The patient should be offered a gown before a TBSE or any skin examination during which the genitals will be examined.
- The patient should be allowed to keep his shorts or underwear on to avoid the feeling of being naked, which can provoke anxiety. Prior to beginning the examination, disclose that it will include “under the covered areas.”
- Ask the patient for permission to conduct the examination, enumerate the steps, and provide a rationale for a genital examination. These steps help gain cooperation, alleviate anticipation, and prevent surprise.
- To increase the patient’s comfort level, he can be asked whether he prefers to be examined supine or standing.
- Consider allowing the patient, himself, to expose and manipulate his genitals during the examination to increase his involvement and sense of autonomy.
- For genital examinations, patients often prefer that the examiner be a physician of the same gender. Accommodating a patient’s request regarding the examiner’s gender might not always be possible, but the medical practice should make an honest attempt to oblige.
Lastly, providers should be cognizant of the needs of male sexual and gender minority populations (ie, gay, bisexual, transgender/gender diverse, queer or questioning, intersex, and asexual persons). For example, transgender women might retain male anatomy or have surgical alteration of the genital region that also requires evaluation. In such patient populations, the genital examination is equally important to evaluate for dermatologic conditions that require treatment.
Final Thoughts
The male genital examination is an important component of the TBSE, as dermatologists can recognize lesions before symptoms present. Robust educational methods for trainees and practitioners in dermatology are lacking, and development of curricula might be beneficial to increase comfort in performing the genital examination. Still, use of the procedures described in this commentary can normalize the men’s genital examination, optimize the physical examination, and improve men’s overall dermatologic health.
- Tripathi R, Knusel KD, Ezaldein HH, et al. Association of demographic and socioeconomic characteristics with differences in use of outpatient dermatology services in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1286-1291.
- Brezinski EA, Harskamp CT, Ledo L, et al. Public perception of dermatologists and comparison with other medical specialties: results from a national survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:875-881.
- Rieder EA, Mu EW, Wang J, et al. Dermatologist practices during total body skin examinations: a survey study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:516-520.
- Gonzalez CD, Hawkes JE, Bowles TL. Malignant melanoma scrotal metastasis: the importance of the genital examination. JAAD Case Rep. 2017;3:10-12.
- Solimani F, Juratli H, Hoch M, et al. Basal cell carcinoma of the scrotum: an important but easily overlooked entity. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:E254-E255.
- Gabrielson AT, Le TV, Fontenot C, et al. Male genital dermatology: a primer for the sexual medicine physician. Sex Med Rev. 2019;7:71-83.
- Han JJ, Beltran TH, Song JW, et al. Prevalence of genital human papillomavirus infection and human papillomavirus vaccination rates among US adult men: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2013-2014. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:810-816.
- Albaugh JA, Kellogg-Spadt S. Genital and dermatologic examination. part II: the male patient. Urol Nurs. 2003;23:366-367.
- Dean RC, Lue TF. Physiology of penile erection and pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. Urol Clin North Am. 2005;32:379-395.
- Norwick P, Weston GK, Grant-Kels JM. Erection ethics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:1225.
- Vogel L. Chaperones: friend or foe, and to whom? CMAJ. 2012;184:642-643.
Men have unique dermatologic needs yet are significantly less likely than women to visit a dermatologist’s office.1 Male patients might have preconceived notions about the nature of dermatology visits and necessary areas of the body to be examined: For example, male patients might associate the genital examination with a urologist and not expect a dermatologist to complete such a seemingly private examination.2
Genital examinations are currently underperformed: Only one-quarter of dermatologists report examining a male patient’s genitals at most or all visits.3 In this commentary, we discuss the importance of genital examinations in men’s dermatology, specific issues that can arise, and strategies to enhance the quality and frequency of genital examinations in male patients.
Invaluable Aspect of Care
Thorough inspection of a male patient’s genital region is an important part of conducting a total-body skin examination (TBSE) for routine surveillance and evaluation of genital dermatoses. Sexually transmitted infections, warts, and other common lesions can be missed in diagnosis without careful inspection of the genital region. Additionally, scrotal malignancies, such as primary and metastatic melanoma and basal cell carcinoma, though rare, might be overlooked until symptoms become severe.4,5
There is no substitute for a physical examination but, in certain circumstances, it might be appropriate for a dermatologist to ask a patient if he has concerning lesions on his genitals. However, patients often are unsure of worrisome signs, and areas of the perineum might not be easily visible to a patient. Genital inspection during the physical examination allows for a teachable moment, during which the dermatologist can educate the patient about benign lesions and variants, such as pearly penile papules, seborrheic keratoses, and sebaceous cysts.6 These lesions might not require intervention but should be monitored for atypical features or infection.6
Also, the dermatologist might incidentally discover transmissible lesions, such as condylomata caused by human papillomavirus, which has been shown to be present in approximately 50% of men in the United States7—many of whom are unaware. Inflammatory dermatoses, such as psoriasis, often affect the genitals and go unnoticed; prompt intervention can decrease the likelihood of complications.6
Protocol for Genital Examinations
To examine the genitals, all surfaces of the penis, scrotum, and perineum should be evaluated, with anatomic and pathologic variants noted. The patient or physician should stretch the penis, maneuvering it in multiple directions so that all aspects can be examined. In uncircumcised men, the foreskin should be retracted so that the head of the penis can be examined, followed by replacement of the foreskin by the patient.8 The scrotum also should be examined and lifted to fully view the perineum.
Providers should not grasp the penis with the whole hand but use the thumb and first finger to hold the head of the penis to maneuver it.8 Similarly, using the back of the hand and fingers to manipulate the genitals establishes boundaries and sets a clinical tone for the examination.
Unintentional Erection
Unique to the male dermatologic examination is the unintentional patient erection; a physician might be unsure of how to approach such a potentially awkward situation. An erection is not always an indication of sexual arousal; rather, it can reflect an autonomic reflex in response to physical stimulation. Erections occur commonly in health care settings, especially if the genitals are being manipulated.9
Generally, the course of action here depends on the patient’s response.10 For patients who appear unbothered, it might be appropriate to ignore the erection and proceed with the examination, especially if the physician is not actively examining the genital region. If the patient appears embarrassed, the physician can say “This is completely normal” or “Random erections are common” to normalize the situation. Joking or laughing should be avoided. For a patient who appears upset, the physician can step outside the room for a brief period to give the patient privacy, then re-enter and ask him if he is comfortable continuing with the examination.
When a patient develops an erection, the physician might become uncomfortable and, consciously or subconsciously, increase the pace of the examination, which is a natural tendency, but expediency at the expense of comprehensive care is inappropriate.
Examiner’s Body Language and Tone
Throughout the genital examination, the physician should be mindful of their comments and body language to avoid exacerbating patient vulnerability. Using anatomic terms, rather than colloquial ones, to describe the genitalia is advised to prevent misunderstanding and maintain a professional clinical environment. Providers should be prepared to explain anatomic terms because some patients are not familiar with medical terminology.
Presence of a Chaperone
Involving a chaperone, as recommended by the American Medical Association, might make a patient more comfortable and alleviate potential misunderstanding. Still, physicians should be aware that some patients might feel uncomfortable with a chaperone, interpreting their presence as an expectation of impropriety.11 Universal offering of a chaperone to all patients, regardless of the gender of the physician, as well as appropriate signage in the clinical environment, normalizes chaperone invitation and use.
Other Helpful Considerations
Various strategies in the male genital examination can increase patient and physician comfort and improve care:
- The patient should be offered a gown before a TBSE or any skin examination during which the genitals will be examined.
- The patient should be allowed to keep his shorts or underwear on to avoid the feeling of being naked, which can provoke anxiety. Prior to beginning the examination, disclose that it will include “under the covered areas.”
- Ask the patient for permission to conduct the examination, enumerate the steps, and provide a rationale for a genital examination. These steps help gain cooperation, alleviate anticipation, and prevent surprise.
- To increase the patient’s comfort level, he can be asked whether he prefers to be examined supine or standing.
- Consider allowing the patient, himself, to expose and manipulate his genitals during the examination to increase his involvement and sense of autonomy.
- For genital examinations, patients often prefer that the examiner be a physician of the same gender. Accommodating a patient’s request regarding the examiner’s gender might not always be possible, but the medical practice should make an honest attempt to oblige.
Lastly, providers should be cognizant of the needs of male sexual and gender minority populations (ie, gay, bisexual, transgender/gender diverse, queer or questioning, intersex, and asexual persons). For example, transgender women might retain male anatomy or have surgical alteration of the genital region that also requires evaluation. In such patient populations, the genital examination is equally important to evaluate for dermatologic conditions that require treatment.
Final Thoughts
The male genital examination is an important component of the TBSE, as dermatologists can recognize lesions before symptoms present. Robust educational methods for trainees and practitioners in dermatology are lacking, and development of curricula might be beneficial to increase comfort in performing the genital examination. Still, use of the procedures described in this commentary can normalize the men’s genital examination, optimize the physical examination, and improve men’s overall dermatologic health.
Men have unique dermatologic needs yet are significantly less likely than women to visit a dermatologist’s office.1 Male patients might have preconceived notions about the nature of dermatology visits and necessary areas of the body to be examined: For example, male patients might associate the genital examination with a urologist and not expect a dermatologist to complete such a seemingly private examination.2
Genital examinations are currently underperformed: Only one-quarter of dermatologists report examining a male patient’s genitals at most or all visits.3 In this commentary, we discuss the importance of genital examinations in men’s dermatology, specific issues that can arise, and strategies to enhance the quality and frequency of genital examinations in male patients.
Invaluable Aspect of Care
Thorough inspection of a male patient’s genital region is an important part of conducting a total-body skin examination (TBSE) for routine surveillance and evaluation of genital dermatoses. Sexually transmitted infections, warts, and other common lesions can be missed in diagnosis without careful inspection of the genital region. Additionally, scrotal malignancies, such as primary and metastatic melanoma and basal cell carcinoma, though rare, might be overlooked until symptoms become severe.4,5
There is no substitute for a physical examination but, in certain circumstances, it might be appropriate for a dermatologist to ask a patient if he has concerning lesions on his genitals. However, patients often are unsure of worrisome signs, and areas of the perineum might not be easily visible to a patient. Genital inspection during the physical examination allows for a teachable moment, during which the dermatologist can educate the patient about benign lesions and variants, such as pearly penile papules, seborrheic keratoses, and sebaceous cysts.6 These lesions might not require intervention but should be monitored for atypical features or infection.6
Also, the dermatologist might incidentally discover transmissible lesions, such as condylomata caused by human papillomavirus, which has been shown to be present in approximately 50% of men in the United States7—many of whom are unaware. Inflammatory dermatoses, such as psoriasis, often affect the genitals and go unnoticed; prompt intervention can decrease the likelihood of complications.6
Protocol for Genital Examinations
To examine the genitals, all surfaces of the penis, scrotum, and perineum should be evaluated, with anatomic and pathologic variants noted. The patient or physician should stretch the penis, maneuvering it in multiple directions so that all aspects can be examined. In uncircumcised men, the foreskin should be retracted so that the head of the penis can be examined, followed by replacement of the foreskin by the patient.8 The scrotum also should be examined and lifted to fully view the perineum.
Providers should not grasp the penis with the whole hand but use the thumb and first finger to hold the head of the penis to maneuver it.8 Similarly, using the back of the hand and fingers to manipulate the genitals establishes boundaries and sets a clinical tone for the examination.
Unintentional Erection
Unique to the male dermatologic examination is the unintentional patient erection; a physician might be unsure of how to approach such a potentially awkward situation. An erection is not always an indication of sexual arousal; rather, it can reflect an autonomic reflex in response to physical stimulation. Erections occur commonly in health care settings, especially if the genitals are being manipulated.9
Generally, the course of action here depends on the patient’s response.10 For patients who appear unbothered, it might be appropriate to ignore the erection and proceed with the examination, especially if the physician is not actively examining the genital region. If the patient appears embarrassed, the physician can say “This is completely normal” or “Random erections are common” to normalize the situation. Joking or laughing should be avoided. For a patient who appears upset, the physician can step outside the room for a brief period to give the patient privacy, then re-enter and ask him if he is comfortable continuing with the examination.
When a patient develops an erection, the physician might become uncomfortable and, consciously or subconsciously, increase the pace of the examination, which is a natural tendency, but expediency at the expense of comprehensive care is inappropriate.
Examiner’s Body Language and Tone
Throughout the genital examination, the physician should be mindful of their comments and body language to avoid exacerbating patient vulnerability. Using anatomic terms, rather than colloquial ones, to describe the genitalia is advised to prevent misunderstanding and maintain a professional clinical environment. Providers should be prepared to explain anatomic terms because some patients are not familiar with medical terminology.
Presence of a Chaperone
Involving a chaperone, as recommended by the American Medical Association, might make a patient more comfortable and alleviate potential misunderstanding. Still, physicians should be aware that some patients might feel uncomfortable with a chaperone, interpreting their presence as an expectation of impropriety.11 Universal offering of a chaperone to all patients, regardless of the gender of the physician, as well as appropriate signage in the clinical environment, normalizes chaperone invitation and use.
Other Helpful Considerations
Various strategies in the male genital examination can increase patient and physician comfort and improve care:
- The patient should be offered a gown before a TBSE or any skin examination during which the genitals will be examined.
- The patient should be allowed to keep his shorts or underwear on to avoid the feeling of being naked, which can provoke anxiety. Prior to beginning the examination, disclose that it will include “under the covered areas.”
- Ask the patient for permission to conduct the examination, enumerate the steps, and provide a rationale for a genital examination. These steps help gain cooperation, alleviate anticipation, and prevent surprise.
- To increase the patient’s comfort level, he can be asked whether he prefers to be examined supine or standing.
- Consider allowing the patient, himself, to expose and manipulate his genitals during the examination to increase his involvement and sense of autonomy.
- For genital examinations, patients often prefer that the examiner be a physician of the same gender. Accommodating a patient’s request regarding the examiner’s gender might not always be possible, but the medical practice should make an honest attempt to oblige.
Lastly, providers should be cognizant of the needs of male sexual and gender minority populations (ie, gay, bisexual, transgender/gender diverse, queer or questioning, intersex, and asexual persons). For example, transgender women might retain male anatomy or have surgical alteration of the genital region that also requires evaluation. In such patient populations, the genital examination is equally important to evaluate for dermatologic conditions that require treatment.
Final Thoughts
The male genital examination is an important component of the TBSE, as dermatologists can recognize lesions before symptoms present. Robust educational methods for trainees and practitioners in dermatology are lacking, and development of curricula might be beneficial to increase comfort in performing the genital examination. Still, use of the procedures described in this commentary can normalize the men’s genital examination, optimize the physical examination, and improve men’s overall dermatologic health.
- Tripathi R, Knusel KD, Ezaldein HH, et al. Association of demographic and socioeconomic characteristics with differences in use of outpatient dermatology services in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1286-1291.
- Brezinski EA, Harskamp CT, Ledo L, et al. Public perception of dermatologists and comparison with other medical specialties: results from a national survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:875-881.
- Rieder EA, Mu EW, Wang J, et al. Dermatologist practices during total body skin examinations: a survey study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:516-520.
- Gonzalez CD, Hawkes JE, Bowles TL. Malignant melanoma scrotal metastasis: the importance of the genital examination. JAAD Case Rep. 2017;3:10-12.
- Solimani F, Juratli H, Hoch M, et al. Basal cell carcinoma of the scrotum: an important but easily overlooked entity. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:E254-E255.
- Gabrielson AT, Le TV, Fontenot C, et al. Male genital dermatology: a primer for the sexual medicine physician. Sex Med Rev. 2019;7:71-83.
- Han JJ, Beltran TH, Song JW, et al. Prevalence of genital human papillomavirus infection and human papillomavirus vaccination rates among US adult men: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2013-2014. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:810-816.
- Albaugh JA, Kellogg-Spadt S. Genital and dermatologic examination. part II: the male patient. Urol Nurs. 2003;23:366-367.
- Dean RC, Lue TF. Physiology of penile erection and pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. Urol Clin North Am. 2005;32:379-395.
- Norwick P, Weston GK, Grant-Kels JM. Erection ethics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:1225.
- Vogel L. Chaperones: friend or foe, and to whom? CMAJ. 2012;184:642-643.
- Tripathi R, Knusel KD, Ezaldein HH, et al. Association of demographic and socioeconomic characteristics with differences in use of outpatient dermatology services in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1286-1291.
- Brezinski EA, Harskamp CT, Ledo L, et al. Public perception of dermatologists and comparison with other medical specialties: results from a national survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:875-881.
- Rieder EA, Mu EW, Wang J, et al. Dermatologist practices during total body skin examinations: a survey study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:516-520.
- Gonzalez CD, Hawkes JE, Bowles TL. Malignant melanoma scrotal metastasis: the importance of the genital examination. JAAD Case Rep. 2017;3:10-12.
- Solimani F, Juratli H, Hoch M, et al. Basal cell carcinoma of the scrotum: an important but easily overlooked entity. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:E254-E255.
- Gabrielson AT, Le TV, Fontenot C, et al. Male genital dermatology: a primer for the sexual medicine physician. Sex Med Rev. 2019;7:71-83.
- Han JJ, Beltran TH, Song JW, et al. Prevalence of genital human papillomavirus infection and human papillomavirus vaccination rates among US adult men: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2013-2014. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:810-816.
- Albaugh JA, Kellogg-Spadt S. Genital and dermatologic examination. part II: the male patient. Urol Nurs. 2003;23:366-367.
- Dean RC, Lue TF. Physiology of penile erection and pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. Urol Clin North Am. 2005;32:379-395.
- Norwick P, Weston GK, Grant-Kels JM. Erection ethics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:1225.
- Vogel L. Chaperones: friend or foe, and to whom? CMAJ. 2012;184:642-643.
Practice Points
- Genital examinations are an important aspect of comprehensive dermatologic care for male patients.
- Unintentional patient erections are unique to male patients and should be addressed professionally, depending on the patient’s reaction.
- In addition to being mindful of body language and tone, dermatologists may consider involving a chaperone when performing genital examinations to optimize patient experience.