User login
Lymphocyte, monocyte data can predict treatment response in follicular lymphoma
Absolute lymphocyte cell (ALC) and absolute monocyte cell (AMC) counts, as well as their ratio (LMR) proved to be prognostic factors for treatment results, as shown by a database analysis of follicular lymphoma (FL) patients.
Progressive disease and stable disease after first-line therapy, as well as the mortality rate, were significantly associated with lower ALC, higher AMC, and higher LMR, according to the report published online.
Researchers analyzed the data of 100 FL variant patients admitted and treated between January 2009 and June 2018 at a single center.
Area under the curve analysis for discriminating between survival times showed 0.57 x 109 cells/L was the most discriminative ALC cutoff value, 1.24 x 109/L was the most discriminative AMC cutoff value, and 1.63 x 109/L was the most discriminative LMR cutoff value.
Shorter overall survival (OS) was significantly associated with lower ALC, compared with those having higher ALC. Shorter OS and progression-free survival (PFS) were significantly associated with higher AMC, compared with those having lower AMC. Shorter OS and PFS were also significantly associated with lower LMR, compared with those having higher LMR.
Overall, a high-risk score in the Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index (FLIPI) and having a low LMR were considered risk factors for prediction of OS in all the studied FL patients in univariate analysis and multivariate analysis, according to the researchers.
“Our results prove the effect of lymphocyte and monocyte in the tumor immune response, which gives opportunity to several therapeutic strategies that target myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), including monocytes and their progeny and improves the T-cell function in eradication strategies,” the researchers concluded.
No study funding or disclosure details were provided.
SOURCE: Mohsen A et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020 Mar 20. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2020.03.007.
Absolute lymphocyte cell (ALC) and absolute monocyte cell (AMC) counts, as well as their ratio (LMR) proved to be prognostic factors for treatment results, as shown by a database analysis of follicular lymphoma (FL) patients.
Progressive disease and stable disease after first-line therapy, as well as the mortality rate, were significantly associated with lower ALC, higher AMC, and higher LMR, according to the report published online.
Researchers analyzed the data of 100 FL variant patients admitted and treated between January 2009 and June 2018 at a single center.
Area under the curve analysis for discriminating between survival times showed 0.57 x 109 cells/L was the most discriminative ALC cutoff value, 1.24 x 109/L was the most discriminative AMC cutoff value, and 1.63 x 109/L was the most discriminative LMR cutoff value.
Shorter overall survival (OS) was significantly associated with lower ALC, compared with those having higher ALC. Shorter OS and progression-free survival (PFS) were significantly associated with higher AMC, compared with those having lower AMC. Shorter OS and PFS were also significantly associated with lower LMR, compared with those having higher LMR.
Overall, a high-risk score in the Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index (FLIPI) and having a low LMR were considered risk factors for prediction of OS in all the studied FL patients in univariate analysis and multivariate analysis, according to the researchers.
“Our results prove the effect of lymphocyte and monocyte in the tumor immune response, which gives opportunity to several therapeutic strategies that target myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), including monocytes and their progeny and improves the T-cell function in eradication strategies,” the researchers concluded.
No study funding or disclosure details were provided.
SOURCE: Mohsen A et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020 Mar 20. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2020.03.007.
Absolute lymphocyte cell (ALC) and absolute monocyte cell (AMC) counts, as well as their ratio (LMR) proved to be prognostic factors for treatment results, as shown by a database analysis of follicular lymphoma (FL) patients.
Progressive disease and stable disease after first-line therapy, as well as the mortality rate, were significantly associated with lower ALC, higher AMC, and higher LMR, according to the report published online.
Researchers analyzed the data of 100 FL variant patients admitted and treated between January 2009 and June 2018 at a single center.
Area under the curve analysis for discriminating between survival times showed 0.57 x 109 cells/L was the most discriminative ALC cutoff value, 1.24 x 109/L was the most discriminative AMC cutoff value, and 1.63 x 109/L was the most discriminative LMR cutoff value.
Shorter overall survival (OS) was significantly associated with lower ALC, compared with those having higher ALC. Shorter OS and progression-free survival (PFS) were significantly associated with higher AMC, compared with those having lower AMC. Shorter OS and PFS were also significantly associated with lower LMR, compared with those having higher LMR.
Overall, a high-risk score in the Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index (FLIPI) and having a low LMR were considered risk factors for prediction of OS in all the studied FL patients in univariate analysis and multivariate analysis, according to the researchers.
“Our results prove the effect of lymphocyte and monocyte in the tumor immune response, which gives opportunity to several therapeutic strategies that target myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), including monocytes and their progeny and improves the T-cell function in eradication strategies,” the researchers concluded.
No study funding or disclosure details were provided.
SOURCE: Mohsen A et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020 Mar 20. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2020.03.007.
FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA AND LEUKEMIA
Cardiovascular problems already apparent in children with hemophilia A
Negative cardiovascular health indicators were found to be higher in children with hemophilia A, compared with healthy children, according to a small research study.
Biochemical, imaging, and metabolic analyses were performed to compare 17 boys with severe hemophilia A to 23 healthy boys designated as controls.
The myocardial performance index (MPI) was evaluated using tissue Doppler echocardiography. In addition, peripheral and central blood pressure and arterial stiffness were assessed, as were carotid intima–media thicknesses (CIMTs), serum glucose, insulin, insulin resistance, and lipoprotein levels.
Increased MPI is considered an indicator of global deterioration in myocardial functions.
There were no differences between the two groups in terms of age and biochemical parameters, according to the researchers. There were also no significant differences found between the groups in terms of CIMT, peripheral blood pressure, and central systolic blood pressure.
However, the HDL cholesterol levels in the hemophilia group were significantly lower than those in the control group (P < .05). Five of the hemophilia patients had insulin resistance (29.4%), whereas four had low HDL cholesterol levels (23.5%).
The researchers found that the MPI values in the hemophilia group were higher than those in the control group (0.41 vs. 0.34; P = .004). In addition, left ventricle ejection time (ET), which is a predictor of mortality in heart failure and ischemic heart disease, was shorter in the hemophilia group than it was in the control group (266.6 vs. 284.4; P = .014).
As arterial stiffness increases, ejection time decreases owing to the deteriorating myocardial systolic functions, and it has also been reported in the literature that arterial stiffness affects left ventricular systolic functions, according to the authors.
“Arterial stiffness and high [central diastolic blood pressure] developing in patients with severe hemophilia A since their childhood are important risk factors for coronary artery diseases. Predisposition to dyslipidemia and [insulin resistance] noted in the hemophilia group also negatively contributes to this process. Adolescent patients with hemophilia should be monitored for hypertension, obesity, dyslipidemia, and [insulin resistance],” the authors concluded.
The study received no external funding. The authors did not report disclosures.
SOURCE: Özdemir ZC et al. Thrombosis Res. 2020;189:102-7.
Negative cardiovascular health indicators were found to be higher in children with hemophilia A, compared with healthy children, according to a small research study.
Biochemical, imaging, and metabolic analyses were performed to compare 17 boys with severe hemophilia A to 23 healthy boys designated as controls.
The myocardial performance index (MPI) was evaluated using tissue Doppler echocardiography. In addition, peripheral and central blood pressure and arterial stiffness were assessed, as were carotid intima–media thicknesses (CIMTs), serum glucose, insulin, insulin resistance, and lipoprotein levels.
Increased MPI is considered an indicator of global deterioration in myocardial functions.
There were no differences between the two groups in terms of age and biochemical parameters, according to the researchers. There were also no significant differences found between the groups in terms of CIMT, peripheral blood pressure, and central systolic blood pressure.
However, the HDL cholesterol levels in the hemophilia group were significantly lower than those in the control group (P < .05). Five of the hemophilia patients had insulin resistance (29.4%), whereas four had low HDL cholesterol levels (23.5%).
The researchers found that the MPI values in the hemophilia group were higher than those in the control group (0.41 vs. 0.34; P = .004). In addition, left ventricle ejection time (ET), which is a predictor of mortality in heart failure and ischemic heart disease, was shorter in the hemophilia group than it was in the control group (266.6 vs. 284.4; P = .014).
As arterial stiffness increases, ejection time decreases owing to the deteriorating myocardial systolic functions, and it has also been reported in the literature that arterial stiffness affects left ventricular systolic functions, according to the authors.
“Arterial stiffness and high [central diastolic blood pressure] developing in patients with severe hemophilia A since their childhood are important risk factors for coronary artery diseases. Predisposition to dyslipidemia and [insulin resistance] noted in the hemophilia group also negatively contributes to this process. Adolescent patients with hemophilia should be monitored for hypertension, obesity, dyslipidemia, and [insulin resistance],” the authors concluded.
The study received no external funding. The authors did not report disclosures.
SOURCE: Özdemir ZC et al. Thrombosis Res. 2020;189:102-7.
Negative cardiovascular health indicators were found to be higher in children with hemophilia A, compared with healthy children, according to a small research study.
Biochemical, imaging, and metabolic analyses were performed to compare 17 boys with severe hemophilia A to 23 healthy boys designated as controls.
The myocardial performance index (MPI) was evaluated using tissue Doppler echocardiography. In addition, peripheral and central blood pressure and arterial stiffness were assessed, as were carotid intima–media thicknesses (CIMTs), serum glucose, insulin, insulin resistance, and lipoprotein levels.
Increased MPI is considered an indicator of global deterioration in myocardial functions.
There were no differences between the two groups in terms of age and biochemical parameters, according to the researchers. There were also no significant differences found between the groups in terms of CIMT, peripheral blood pressure, and central systolic blood pressure.
However, the HDL cholesterol levels in the hemophilia group were significantly lower than those in the control group (P < .05). Five of the hemophilia patients had insulin resistance (29.4%), whereas four had low HDL cholesterol levels (23.5%).
The researchers found that the MPI values in the hemophilia group were higher than those in the control group (0.41 vs. 0.34; P = .004). In addition, left ventricle ejection time (ET), which is a predictor of mortality in heart failure and ischemic heart disease, was shorter in the hemophilia group than it was in the control group (266.6 vs. 284.4; P = .014).
As arterial stiffness increases, ejection time decreases owing to the deteriorating myocardial systolic functions, and it has also been reported in the literature that arterial stiffness affects left ventricular systolic functions, according to the authors.
“Arterial stiffness and high [central diastolic blood pressure] developing in patients with severe hemophilia A since their childhood are important risk factors for coronary artery diseases. Predisposition to dyslipidemia and [insulin resistance] noted in the hemophilia group also negatively contributes to this process. Adolescent patients with hemophilia should be monitored for hypertension, obesity, dyslipidemia, and [insulin resistance],” the authors concluded.
The study received no external funding. The authors did not report disclosures.
SOURCE: Özdemir ZC et al. Thrombosis Res. 2020;189:102-7.
FROM THROMBOSIS RESEARCH
Frailty indexes fail in sorting elderly MM patients
Despite the perceived benefits of their use in guiding treatment, frailty indexes were not reliable in differentiating elderly multiple myeloma (MM) patients, according to an analysis of a prospective cohort of 40 patients studied at a single institution.
The researchers examined three different models of frailty using data available in the Cancer and Aging Research Group tool to define frailty in their cohort: the international myeloma working group (IMWG) frailty model, the revised myeloma comorbidity index (R-MCI), and the Carolina Frailty Index (CFI).
The researchers found that, for their same population, applying the IMWG frailty index yielded 3 (7.5%) patients categorized as fit, 15 (37.5%) categorized as intermediate fit, and 22 (55%) categorized as frail. The R-MCI yielded 4 (10%) patients categorized as fit, 29 (72.5%) as intermediate, and 7 (17.5%) as frail. When using the CFI, 17 (42.5%) patients were categorized as fit, 8 (20%) were intermediate, and 15 (37.5%) were frail. Of particular note, among 28 patients categorized as frail by at least one of the three indexes, only 3 (11%) patients were categorized as frail by all three models.
The reasons for the differences were discussed by the authors, who pointed out that patients categorized as frail by the IMWG or R-MCI tended to be older than those categorized as frail by CFI, reflecting the fact that the IMWG and R-MCI both include age as a component of frailty, while the CFI does not. In addition, each index incorporates comorbidities into its assessment of frailty in a different way.
For example, falls and depression are incorporated as components of the CFI, reflected in the higher proportion of patients reporting a prior fall and more symptoms of depression in the group categorized as frail by the CFI model than in the IMWG or R-MCI. In the CFI as well, each of the individual instrumental activities of daily living is a component of the model, rather than the summary score, as in the IMWG and R-MCI.
“Our findings highlight the differences in currently available approaches to applying the concept of frailty to older adults with cancer. This problem is not unique to oncology, as there is a continued lack of consensus on defining the concept of frailty in the general geriatric population,” the researchers stated. “Further studies are needed to establish the role of frailty indexes in predicting toxicity of therapy and other outcomes of importance in older adults with multiple myeloma,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute and other U.S. government agencies. The authors reported having no conflicts.
SOURCE: Isaacs A et al. J Geriat Onc. 2020;11(2):311-15.
Despite the perceived benefits of their use in guiding treatment, frailty indexes were not reliable in differentiating elderly multiple myeloma (MM) patients, according to an analysis of a prospective cohort of 40 patients studied at a single institution.
The researchers examined three different models of frailty using data available in the Cancer and Aging Research Group tool to define frailty in their cohort: the international myeloma working group (IMWG) frailty model, the revised myeloma comorbidity index (R-MCI), and the Carolina Frailty Index (CFI).
The researchers found that, for their same population, applying the IMWG frailty index yielded 3 (7.5%) patients categorized as fit, 15 (37.5%) categorized as intermediate fit, and 22 (55%) categorized as frail. The R-MCI yielded 4 (10%) patients categorized as fit, 29 (72.5%) as intermediate, and 7 (17.5%) as frail. When using the CFI, 17 (42.5%) patients were categorized as fit, 8 (20%) were intermediate, and 15 (37.5%) were frail. Of particular note, among 28 patients categorized as frail by at least one of the three indexes, only 3 (11%) patients were categorized as frail by all three models.
The reasons for the differences were discussed by the authors, who pointed out that patients categorized as frail by the IMWG or R-MCI tended to be older than those categorized as frail by CFI, reflecting the fact that the IMWG and R-MCI both include age as a component of frailty, while the CFI does not. In addition, each index incorporates comorbidities into its assessment of frailty in a different way.
For example, falls and depression are incorporated as components of the CFI, reflected in the higher proportion of patients reporting a prior fall and more symptoms of depression in the group categorized as frail by the CFI model than in the IMWG or R-MCI. In the CFI as well, each of the individual instrumental activities of daily living is a component of the model, rather than the summary score, as in the IMWG and R-MCI.
“Our findings highlight the differences in currently available approaches to applying the concept of frailty to older adults with cancer. This problem is not unique to oncology, as there is a continued lack of consensus on defining the concept of frailty in the general geriatric population,” the researchers stated. “Further studies are needed to establish the role of frailty indexes in predicting toxicity of therapy and other outcomes of importance in older adults with multiple myeloma,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute and other U.S. government agencies. The authors reported having no conflicts.
SOURCE: Isaacs A et al. J Geriat Onc. 2020;11(2):311-15.
Despite the perceived benefits of their use in guiding treatment, frailty indexes were not reliable in differentiating elderly multiple myeloma (MM) patients, according to an analysis of a prospective cohort of 40 patients studied at a single institution.
The researchers examined three different models of frailty using data available in the Cancer and Aging Research Group tool to define frailty in their cohort: the international myeloma working group (IMWG) frailty model, the revised myeloma comorbidity index (R-MCI), and the Carolina Frailty Index (CFI).
The researchers found that, for their same population, applying the IMWG frailty index yielded 3 (7.5%) patients categorized as fit, 15 (37.5%) categorized as intermediate fit, and 22 (55%) categorized as frail. The R-MCI yielded 4 (10%) patients categorized as fit, 29 (72.5%) as intermediate, and 7 (17.5%) as frail. When using the CFI, 17 (42.5%) patients were categorized as fit, 8 (20%) were intermediate, and 15 (37.5%) were frail. Of particular note, among 28 patients categorized as frail by at least one of the three indexes, only 3 (11%) patients were categorized as frail by all three models.
The reasons for the differences were discussed by the authors, who pointed out that patients categorized as frail by the IMWG or R-MCI tended to be older than those categorized as frail by CFI, reflecting the fact that the IMWG and R-MCI both include age as a component of frailty, while the CFI does not. In addition, each index incorporates comorbidities into its assessment of frailty in a different way.
For example, falls and depression are incorporated as components of the CFI, reflected in the higher proportion of patients reporting a prior fall and more symptoms of depression in the group categorized as frail by the CFI model than in the IMWG or R-MCI. In the CFI as well, each of the individual instrumental activities of daily living is a component of the model, rather than the summary score, as in the IMWG and R-MCI.
“Our findings highlight the differences in currently available approaches to applying the concept of frailty to older adults with cancer. This problem is not unique to oncology, as there is a continued lack of consensus on defining the concept of frailty in the general geriatric population,” the researchers stated. “Further studies are needed to establish the role of frailty indexes in predicting toxicity of therapy and other outcomes of importance in older adults with multiple myeloma,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute and other U.S. government agencies. The authors reported having no conflicts.
SOURCE: Isaacs A et al. J Geriat Onc. 2020;11(2):311-15.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF GERIATRIC ONCOLOGY
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Although 28 multiple myeloma patients were deemed frail by at least one model, only 3 patients were deemed frail by all three models.
Study details: A total of 40 adults aged 65 years and over with MM were assessed by three frailty indexes.
Disclosures: The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute and other U.S. government agencies. The authors reported having no conflicts.
Source: Isaacs A et al. J Geriat Onc. 2020;11(2):311-5.
One-third of high-risk CLL patients received treatment counter to recommendations
Approximately , according to a study based upon data from the informCLL registry. In addition, low levels of prognostic marker testing in these patients was a concern.
Researchers assessed data from 840 enrolled CLL patients, of whom 459 (55%) were previously untreated, and 381 (45%) had relapsed/refractory disease. In terms of therapy, chemoimmunotherapy was more common in previously untreated patients, compared with relapsed/refractory patients (42% vs. 23%), whereas ibrutinib was more frequently used in relapsed/refractory vs. previously untreated patients (51% vs. 39%), according to the researchers.
Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) testing, TP53 mutation, and immunoglobulin heavy chain somatic hypermutation biomarker testing were performed infrequently across all patients at registry enrollment, according to the authors.
Among patients who were tested, the rate of mutated TP53 was the same for previously untreated (14/54; 26%) and relapsed/refractory patients (9/35; 26%). In those patients who were tested, 34% with del(17p), a chromosomal deletion, and 26% of mutated TP53 patients received chemoimmunotherapy combinations. The authors stated that this was concerning in that it contradicts consensus guidelines based on data from several clinical studies. Chemoimmunotherapy is not recommended for these high-risk patients because of poor disease and survival outcomes with this treatment strategy, according to the authors.
“Current clinical practice is not keeping pace with recommendations and guidelines for prognostic
marker testing and subsequent selection of appropriate therapy,” the authors stated.
“Even with the approval of novel agents and updated guidelines, low rates of prognostic biomarker testing may lead to suboptimal therapy choices for patients with unknown risk status. In addition, we note that the presence of high-risk features (del(17p) and TP53) is unfortunately not translating to choosing the optimal therapy for these patients,” the researchers concluded.
The study was sponsored by an AbbVie Company and Janssen. The authors reported consulting and grants from these and other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Mato AR et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020;20(3):174-83.
Approximately , according to a study based upon data from the informCLL registry. In addition, low levels of prognostic marker testing in these patients was a concern.
Researchers assessed data from 840 enrolled CLL patients, of whom 459 (55%) were previously untreated, and 381 (45%) had relapsed/refractory disease. In terms of therapy, chemoimmunotherapy was more common in previously untreated patients, compared with relapsed/refractory patients (42% vs. 23%), whereas ibrutinib was more frequently used in relapsed/refractory vs. previously untreated patients (51% vs. 39%), according to the researchers.
Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) testing, TP53 mutation, and immunoglobulin heavy chain somatic hypermutation biomarker testing were performed infrequently across all patients at registry enrollment, according to the authors.
Among patients who were tested, the rate of mutated TP53 was the same for previously untreated (14/54; 26%) and relapsed/refractory patients (9/35; 26%). In those patients who were tested, 34% with del(17p), a chromosomal deletion, and 26% of mutated TP53 patients received chemoimmunotherapy combinations. The authors stated that this was concerning in that it contradicts consensus guidelines based on data from several clinical studies. Chemoimmunotherapy is not recommended for these high-risk patients because of poor disease and survival outcomes with this treatment strategy, according to the authors.
“Current clinical practice is not keeping pace with recommendations and guidelines for prognostic
marker testing and subsequent selection of appropriate therapy,” the authors stated.
“Even with the approval of novel agents and updated guidelines, low rates of prognostic biomarker testing may lead to suboptimal therapy choices for patients with unknown risk status. In addition, we note that the presence of high-risk features (del(17p) and TP53) is unfortunately not translating to choosing the optimal therapy for these patients,” the researchers concluded.
The study was sponsored by an AbbVie Company and Janssen. The authors reported consulting and grants from these and other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Mato AR et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020;20(3):174-83.
Approximately , according to a study based upon data from the informCLL registry. In addition, low levels of prognostic marker testing in these patients was a concern.
Researchers assessed data from 840 enrolled CLL patients, of whom 459 (55%) were previously untreated, and 381 (45%) had relapsed/refractory disease. In terms of therapy, chemoimmunotherapy was more common in previously untreated patients, compared with relapsed/refractory patients (42% vs. 23%), whereas ibrutinib was more frequently used in relapsed/refractory vs. previously untreated patients (51% vs. 39%), according to the researchers.
Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) testing, TP53 mutation, and immunoglobulin heavy chain somatic hypermutation biomarker testing were performed infrequently across all patients at registry enrollment, according to the authors.
Among patients who were tested, the rate of mutated TP53 was the same for previously untreated (14/54; 26%) and relapsed/refractory patients (9/35; 26%). In those patients who were tested, 34% with del(17p), a chromosomal deletion, and 26% of mutated TP53 patients received chemoimmunotherapy combinations. The authors stated that this was concerning in that it contradicts consensus guidelines based on data from several clinical studies. Chemoimmunotherapy is not recommended for these high-risk patients because of poor disease and survival outcomes with this treatment strategy, according to the authors.
“Current clinical practice is not keeping pace with recommendations and guidelines for prognostic
marker testing and subsequent selection of appropriate therapy,” the authors stated.
“Even with the approval of novel agents and updated guidelines, low rates of prognostic biomarker testing may lead to suboptimal therapy choices for patients with unknown risk status. In addition, we note that the presence of high-risk features (del(17p) and TP53) is unfortunately not translating to choosing the optimal therapy for these patients,” the researchers concluded.
The study was sponsored by an AbbVie Company and Janssen. The authors reported consulting and grants from these and other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Mato AR et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020;20(3):174-83.
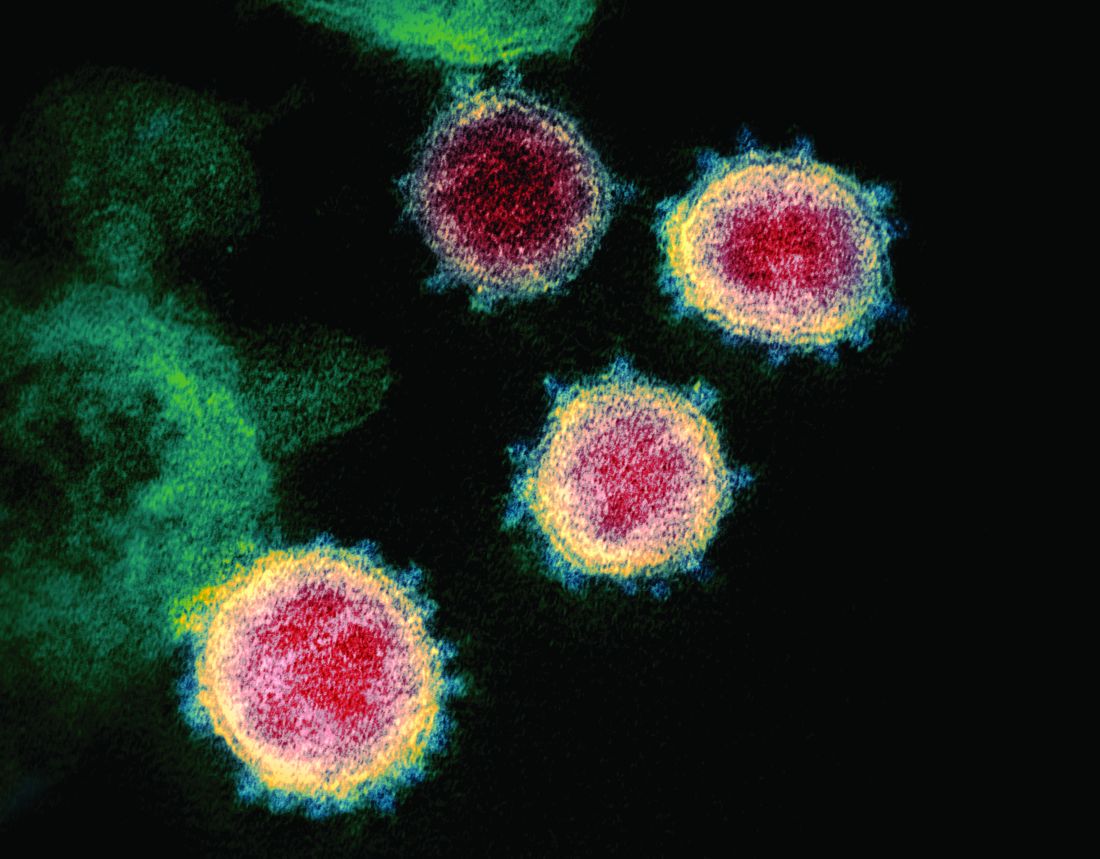
Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19: Is tocilizumab effective?
A large amount of data suggest that mild or severe cytokine storms, accompanied by high expression of interleukin-6 (IL-6), occur in patients with severe coronavirus disease and can be an important cause of death. Blocking the signal transduction pathway of IL-6 is expected to become a new method for the treatment of patients with severe COVID-19, with the IL-6 inhibitor, tocilizumab (Actemra), poised to become an effective drug for these patients, according to the authors of a review published online in the International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents.
The reviewers from China detailed the metabolic pathways and regulation of cytokine release syndrome, especially with respect to what is known about severe COVID-19, and discussed the results of recent trials with tocilizumab, which is currently used for treatment of CRS in a variety of cancers and other metabolic disorders.
Tocilizumab is a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody against human IL-6 receptor of immunoglobulin IgG1 subtype and has been approved for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. The antibody specifically binds soluble- and membrane-bound IL-6 receptors (sIL-6R and mIL-6R) and inhibits sIL-6R– and mIL-6R–mediated signal transduction. It has been shown to be effective in the treatment of severe CRS patients. In 2017, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved tocilizumab for the treatment of CRS caused by CAR-T (chimeric antigen receptor T-cell immunotherapy) therapy.
A small clinical trial in China examined the effectiveness of tocilizumab in 21 patients who met the criteria for severe or critical COVID-19, including respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation, shock, or admission to the ICU with other organ failure. After a few days of tocilizumab treatment, the body temperatures returned to normal (initially, all 21 patients had fevers), and all other symptoms were significantly improved, according to the authors. A total of 75% (15/20) of the patients reduced their oxygen intake, and 1 patient did not need oxygen. CT scanning showed that 90.5% (19/21) of the patients had absorption of pulmonary lesions, and lab tests showed that the proportion of peripheral blood lymphocytes and C-reactive protein in the patients returned to normal.
The main deficiency of the study was that only the level of IL-6 in peripheral blood before treatment with tocilizumab was reported (mean value, 132.38 ± 278.54 pg/mL), but the level of IL-6 following treatment was not given, according to the reviewers. Serum levels of IL-6 in normal patients are undetectable or very low.
Based upon their analysis of COVID-19’s possible mechanism and the small samples of clinical data available, tocilizumab appeared effective, and “we suggest that it should be used in critically ill COVID-19 patients with significantly elevated IL-6,” the authors stated.
“CRS occurs in a large number of patients with severe COVID-19, which is also an important cause of death. IL-6 is the key molecule of CRS, so IL-6R antagonist tocilizumab may be an important drug to save patients’ lives,” the researchers concluded.
This study was supported by China Mega-Project for Infectious Diseases and the China Mega-Project for Innovative Drugs. The authors reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Zhang C et al. Int J Antimicrobial Agents. 2020. doi. org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105954.
A large amount of data suggest that mild or severe cytokine storms, accompanied by high expression of interleukin-6 (IL-6), occur in patients with severe coronavirus disease and can be an important cause of death. Blocking the signal transduction pathway of IL-6 is expected to become a new method for the treatment of patients with severe COVID-19, with the IL-6 inhibitor, tocilizumab (Actemra), poised to become an effective drug for these patients, according to the authors of a review published online in the International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents.
The reviewers from China detailed the metabolic pathways and regulation of cytokine release syndrome, especially with respect to what is known about severe COVID-19, and discussed the results of recent trials with tocilizumab, which is currently used for treatment of CRS in a variety of cancers and other metabolic disorders.
Tocilizumab is a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody against human IL-6 receptor of immunoglobulin IgG1 subtype and has been approved for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. The antibody specifically binds soluble- and membrane-bound IL-6 receptors (sIL-6R and mIL-6R) and inhibits sIL-6R– and mIL-6R–mediated signal transduction. It has been shown to be effective in the treatment of severe CRS patients. In 2017, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved tocilizumab for the treatment of CRS caused by CAR-T (chimeric antigen receptor T-cell immunotherapy) therapy.
A small clinical trial in China examined the effectiveness of tocilizumab in 21 patients who met the criteria for severe or critical COVID-19, including respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation, shock, or admission to the ICU with other organ failure. After a few days of tocilizumab treatment, the body temperatures returned to normal (initially, all 21 patients had fevers), and all other symptoms were significantly improved, according to the authors. A total of 75% (15/20) of the patients reduced their oxygen intake, and 1 patient did not need oxygen. CT scanning showed that 90.5% (19/21) of the patients had absorption of pulmonary lesions, and lab tests showed that the proportion of peripheral blood lymphocytes and C-reactive protein in the patients returned to normal.
The main deficiency of the study was that only the level of IL-6 in peripheral blood before treatment with tocilizumab was reported (mean value, 132.38 ± 278.54 pg/mL), but the level of IL-6 following treatment was not given, according to the reviewers. Serum levels of IL-6 in normal patients are undetectable or very low.
Based upon their analysis of COVID-19’s possible mechanism and the small samples of clinical data available, tocilizumab appeared effective, and “we suggest that it should be used in critically ill COVID-19 patients with significantly elevated IL-6,” the authors stated.
“CRS occurs in a large number of patients with severe COVID-19, which is also an important cause of death. IL-6 is the key molecule of CRS, so IL-6R antagonist tocilizumab may be an important drug to save patients’ lives,” the researchers concluded.
This study was supported by China Mega-Project for Infectious Diseases and the China Mega-Project for Innovative Drugs. The authors reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Zhang C et al. Int J Antimicrobial Agents. 2020. doi. org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105954.
A large amount of data suggest that mild or severe cytokine storms, accompanied by high expression of interleukin-6 (IL-6), occur in patients with severe coronavirus disease and can be an important cause of death. Blocking the signal transduction pathway of IL-6 is expected to become a new method for the treatment of patients with severe COVID-19, with the IL-6 inhibitor, tocilizumab (Actemra), poised to become an effective drug for these patients, according to the authors of a review published online in the International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents.
The reviewers from China detailed the metabolic pathways and regulation of cytokine release syndrome, especially with respect to what is known about severe COVID-19, and discussed the results of recent trials with tocilizumab, which is currently used for treatment of CRS in a variety of cancers and other metabolic disorders.
Tocilizumab is a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody against human IL-6 receptor of immunoglobulin IgG1 subtype and has been approved for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. The antibody specifically binds soluble- and membrane-bound IL-6 receptors (sIL-6R and mIL-6R) and inhibits sIL-6R– and mIL-6R–mediated signal transduction. It has been shown to be effective in the treatment of severe CRS patients. In 2017, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved tocilizumab for the treatment of CRS caused by CAR-T (chimeric antigen receptor T-cell immunotherapy) therapy.
A small clinical trial in China examined the effectiveness of tocilizumab in 21 patients who met the criteria for severe or critical COVID-19, including respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation, shock, or admission to the ICU with other organ failure. After a few days of tocilizumab treatment, the body temperatures returned to normal (initially, all 21 patients had fevers), and all other symptoms were significantly improved, according to the authors. A total of 75% (15/20) of the patients reduced their oxygen intake, and 1 patient did not need oxygen. CT scanning showed that 90.5% (19/21) of the patients had absorption of pulmonary lesions, and lab tests showed that the proportion of peripheral blood lymphocytes and C-reactive protein in the patients returned to normal.
The main deficiency of the study was that only the level of IL-6 in peripheral blood before treatment with tocilizumab was reported (mean value, 132.38 ± 278.54 pg/mL), but the level of IL-6 following treatment was not given, according to the reviewers. Serum levels of IL-6 in normal patients are undetectable or very low.
Based upon their analysis of COVID-19’s possible mechanism and the small samples of clinical data available, tocilizumab appeared effective, and “we suggest that it should be used in critically ill COVID-19 patients with significantly elevated IL-6,” the authors stated.
“CRS occurs in a large number of patients with severe COVID-19, which is also an important cause of death. IL-6 is the key molecule of CRS, so IL-6R antagonist tocilizumab may be an important drug to save patients’ lives,” the researchers concluded.
This study was supported by China Mega-Project for Infectious Diseases and the China Mega-Project for Innovative Drugs. The authors reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Zhang C et al. Int J Antimicrobial Agents. 2020. doi. org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105954.
FROM THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS
First report of MM patient successfully treated for COVID-19 with tocilizumab
Recent research has shown that severe cases of COVID-19 show an excessive immune response and a strong cytokine storm, which may include high levels of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GSF) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Following up on that research, investigators from China reported the first case of COVID-19 in a patient with multiple myeloma (MM) who was successfully treated with the humanized anti–IL-6 receptor antibody tocilizumab (an off-label use in the United States). The exceptional case report was published online in Blood Advances, an American Society of Hematology journal.
A 60-year-old man working in Wuhan, China, developed chest tightness without fever and cough on Feb. 1, 2020, and was admitted immediately after computed tomography (CT) imaging of his chest showed multiple ground-glass opacities and pneumatocele located in both subpleural spaces. He received 400 mg of moxifloxacin IV daily for 3 days while swab specimens were collected and tested by real-time reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction. A positive result for SARS-CoV-2 infection was received 3 days later. The patient was subsequently given 200-mg umifenovir (Arbidol) tablets orally, three times daily, for antiviral treatment.
The patient had a history of symptomatic MM, which was diagnosed in 2015. The patient received two cycles of induction chemotherapy consisting of bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone, and his symptoms completely disappeared. After that, he received thalidomide for maintenance.
Chest CT imaging on hospital day 8 showed that the bilateral, multiple ground-glass opacities from the first scan remained, and laboratory investigations revealed a high level of serum IL-6. On hospital day 9, the patient was given a single, one-time dose of 8 mg/kg tocilizumab, administered by IV. On hospital day 12, his chest tightness disappeared. “After tocilizumab administration, the IL-6 level decreased gradually over the following 10 days (from 121.59 to 20.81 pg/mL), then increased rapidly to the peak (317.38 pg/mL), and then decreased to a low level (117.10 pg/mL). The transient rebounding of the IL-6 level to the peak does not mean COVID-19 relapse: Instead, this might be attributed to the recovery of the normal T cells,” the authors wrote.
On hospital day 19, the patient’s chest CT scan showed that the range of ground-glass opacities had obviously decreased, and he was declared cured and discharged from the hospital. The patient had no symptoms of MM, and related laboratory findings were all in normal ranges, according to the researchers.
“This case is the first to prove that tocilizumab is effective in the treatment of COVID-19 in MM with obvious clinical recovery; however, randomized controlled trials are needed to determine the safety and efficacy of tocilizumab,” the researchers concluded.
The authors declared that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Zhang X et al. Blood Adv. 2020;4(7):1307-10.
Recent research has shown that severe cases of COVID-19 show an excessive immune response and a strong cytokine storm, which may include high levels of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GSF) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Following up on that research, investigators from China reported the first case of COVID-19 in a patient with multiple myeloma (MM) who was successfully treated with the humanized anti–IL-6 receptor antibody tocilizumab (an off-label use in the United States). The exceptional case report was published online in Blood Advances, an American Society of Hematology journal.
A 60-year-old man working in Wuhan, China, developed chest tightness without fever and cough on Feb. 1, 2020, and was admitted immediately after computed tomography (CT) imaging of his chest showed multiple ground-glass opacities and pneumatocele located in both subpleural spaces. He received 400 mg of moxifloxacin IV daily for 3 days while swab specimens were collected and tested by real-time reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction. A positive result for SARS-CoV-2 infection was received 3 days later. The patient was subsequently given 200-mg umifenovir (Arbidol) tablets orally, three times daily, for antiviral treatment.
The patient had a history of symptomatic MM, which was diagnosed in 2015. The patient received two cycles of induction chemotherapy consisting of bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone, and his symptoms completely disappeared. After that, he received thalidomide for maintenance.
Chest CT imaging on hospital day 8 showed that the bilateral, multiple ground-glass opacities from the first scan remained, and laboratory investigations revealed a high level of serum IL-6. On hospital day 9, the patient was given a single, one-time dose of 8 mg/kg tocilizumab, administered by IV. On hospital day 12, his chest tightness disappeared. “After tocilizumab administration, the IL-6 level decreased gradually over the following 10 days (from 121.59 to 20.81 pg/mL), then increased rapidly to the peak (317.38 pg/mL), and then decreased to a low level (117.10 pg/mL). The transient rebounding of the IL-6 level to the peak does not mean COVID-19 relapse: Instead, this might be attributed to the recovery of the normal T cells,” the authors wrote.
On hospital day 19, the patient’s chest CT scan showed that the range of ground-glass opacities had obviously decreased, and he was declared cured and discharged from the hospital. The patient had no symptoms of MM, and related laboratory findings were all in normal ranges, according to the researchers.
“This case is the first to prove that tocilizumab is effective in the treatment of COVID-19 in MM with obvious clinical recovery; however, randomized controlled trials are needed to determine the safety and efficacy of tocilizumab,” the researchers concluded.
The authors declared that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Zhang X et al. Blood Adv. 2020;4(7):1307-10.
Recent research has shown that severe cases of COVID-19 show an excessive immune response and a strong cytokine storm, which may include high levels of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GSF) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Following up on that research, investigators from China reported the first case of COVID-19 in a patient with multiple myeloma (MM) who was successfully treated with the humanized anti–IL-6 receptor antibody tocilizumab (an off-label use in the United States). The exceptional case report was published online in Blood Advances, an American Society of Hematology journal.
A 60-year-old man working in Wuhan, China, developed chest tightness without fever and cough on Feb. 1, 2020, and was admitted immediately after computed tomography (CT) imaging of his chest showed multiple ground-glass opacities and pneumatocele located in both subpleural spaces. He received 400 mg of moxifloxacin IV daily for 3 days while swab specimens were collected and tested by real-time reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction. A positive result for SARS-CoV-2 infection was received 3 days later. The patient was subsequently given 200-mg umifenovir (Arbidol) tablets orally, three times daily, for antiviral treatment.
The patient had a history of symptomatic MM, which was diagnosed in 2015. The patient received two cycles of induction chemotherapy consisting of bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone, and his symptoms completely disappeared. After that, he received thalidomide for maintenance.
Chest CT imaging on hospital day 8 showed that the bilateral, multiple ground-glass opacities from the first scan remained, and laboratory investigations revealed a high level of serum IL-6. On hospital day 9, the patient was given a single, one-time dose of 8 mg/kg tocilizumab, administered by IV. On hospital day 12, his chest tightness disappeared. “After tocilizumab administration, the IL-6 level decreased gradually over the following 10 days (from 121.59 to 20.81 pg/mL), then increased rapidly to the peak (317.38 pg/mL), and then decreased to a low level (117.10 pg/mL). The transient rebounding of the IL-6 level to the peak does not mean COVID-19 relapse: Instead, this might be attributed to the recovery of the normal T cells,” the authors wrote.
On hospital day 19, the patient’s chest CT scan showed that the range of ground-glass opacities had obviously decreased, and he was declared cured and discharged from the hospital. The patient had no symptoms of MM, and related laboratory findings were all in normal ranges, according to the researchers.
“This case is the first to prove that tocilizumab is effective in the treatment of COVID-19 in MM with obvious clinical recovery; however, randomized controlled trials are needed to determine the safety and efficacy of tocilizumab,” the researchers concluded.
The authors declared that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Zhang X et al. Blood Adv. 2020;4(7):1307-10.
FROM BLOOD ADVANCES
Case study shows CLL may mask COVID-19 infection
Characteristics of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia can mask COVID-19 infection, creating a risk for patients, practitioners, and the community, according to a case study published in the Lancet Haematology.
A 39-year-old man with a history of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) presented at a clinic in Wenzhou, China, with symptoms of fever, sore throat, productive cough, and dyspnea, according to the authors. COVID-19 infection was not initially suspected, as his whole blood cell and lymphocyte counts were high, the CLL masked a potential infection, and the patient claimed he had no suspect recent travel history.
However, a CT chest scan showed bilateral ground-glass opacities and a small amount of fluid in the patient’s left pleural cavity, leading the attending physician to suspect COVID-19. Testing was ordered and the real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction assay result was positive. The patient was immediately transferred to the isolation ward for management and confirmed COVID-19 infection.
Subsequently, the patient admitted travel to the COVID-19 epicenter in Wuhan province, although it was 25 days prior, indicating a longer period of incubation than generally believed, according to the authors. The patient survived treatment and was eventually discharged.
“Clinical and biochemical data of COVID-19 might be partly masked by coexisting chronic lymphocytic leukemia; better diagnostic strategies (i.e., superior CT differential techniques such as radiomics) could be used for diagnosis,” the researchers concluded, speculating that the apparently longer-than-normal COVID-19 incubation period might be the result of the patient’s compromised immune system.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jin X-H et al. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7(4):E351-2.
Characteristics of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia can mask COVID-19 infection, creating a risk for patients, practitioners, and the community, according to a case study published in the Lancet Haematology.
A 39-year-old man with a history of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) presented at a clinic in Wenzhou, China, with symptoms of fever, sore throat, productive cough, and dyspnea, according to the authors. COVID-19 infection was not initially suspected, as his whole blood cell and lymphocyte counts were high, the CLL masked a potential infection, and the patient claimed he had no suspect recent travel history.
However, a CT chest scan showed bilateral ground-glass opacities and a small amount of fluid in the patient’s left pleural cavity, leading the attending physician to suspect COVID-19. Testing was ordered and the real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction assay result was positive. The patient was immediately transferred to the isolation ward for management and confirmed COVID-19 infection.
Subsequently, the patient admitted travel to the COVID-19 epicenter in Wuhan province, although it was 25 days prior, indicating a longer period of incubation than generally believed, according to the authors. The patient survived treatment and was eventually discharged.
“Clinical and biochemical data of COVID-19 might be partly masked by coexisting chronic lymphocytic leukemia; better diagnostic strategies (i.e., superior CT differential techniques such as radiomics) could be used for diagnosis,” the researchers concluded, speculating that the apparently longer-than-normal COVID-19 incubation period might be the result of the patient’s compromised immune system.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jin X-H et al. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7(4):E351-2.
Characteristics of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia can mask COVID-19 infection, creating a risk for patients, practitioners, and the community, according to a case study published in the Lancet Haematology.
A 39-year-old man with a history of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) presented at a clinic in Wenzhou, China, with symptoms of fever, sore throat, productive cough, and dyspnea, according to the authors. COVID-19 infection was not initially suspected, as his whole blood cell and lymphocyte counts were high, the CLL masked a potential infection, and the patient claimed he had no suspect recent travel history.
However, a CT chest scan showed bilateral ground-glass opacities and a small amount of fluid in the patient’s left pleural cavity, leading the attending physician to suspect COVID-19. Testing was ordered and the real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction assay result was positive. The patient was immediately transferred to the isolation ward for management and confirmed COVID-19 infection.
Subsequently, the patient admitted travel to the COVID-19 epicenter in Wuhan province, although it was 25 days prior, indicating a longer period of incubation than generally believed, according to the authors. The patient survived treatment and was eventually discharged.
“Clinical and biochemical data of COVID-19 might be partly masked by coexisting chronic lymphocytic leukemia; better diagnostic strategies (i.e., superior CT differential techniques such as radiomics) could be used for diagnosis,” the researchers concluded, speculating that the apparently longer-than-normal COVID-19 incubation period might be the result of the patient’s compromised immune system.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jin X-H et al. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7(4):E351-2.
FROM THE LANCET HAEMATOLOGY
SARS serum neutralizing antibodies may inform the treatment of COVID-19
The immune responses of specific antibodies were maintained in more than 90% of recovered SARS-CoV patients for 2 years, raising the likelihood that the similarly behaving SARS-CoV-2 might provoke the same response, according to an online communication published in the Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection.
The authors cited a cohort study of convalescent SARS-CoV patients (56 cases, from the Beijing hospital of the Armed Forces Police, China) that showed that specific IgG antibodies and neutralizing antibodies were highly correlated, peaking at month 4 after the onset of disease and decreasing gradually thereafter.
This and other studies suggest that the immune responses of specific antibodies were maintained in more than 90% of recovered SARS-CoV patients for 2 years, according to the authors.
However, of particular concern is the fact that only 11.8% of patients acquire specific SARS-CoV Abs in the early period after recovery at day 7, not reaching 100% until day 90, which highlights the importance of the detection of antibody titers for convalescent COVID-19 patients, according to the authors. “Otherwise, these patients with low titers of antibodies may not be efficient for the clearance of SARS-CoV-2.”
The authors also cited a recent study that showed how neutralizing antibody from a convalescent SARS patient could block the SARS-CoV-2 from entering into target cells in vitro, and suggested that previous experimental SARS-CoV vaccines and neutralizing antibodies could provide novel preventive and therapeutic options for COVID-19.
“These experiences from SARS-CoV are expected to have some implications for the treatment, management and surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 patients,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE: Lin Q et al. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2020 Mar 25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmii.2020.03.015.
The immune responses of specific antibodies were maintained in more than 90% of recovered SARS-CoV patients for 2 years, raising the likelihood that the similarly behaving SARS-CoV-2 might provoke the same response, according to an online communication published in the Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection.
The authors cited a cohort study of convalescent SARS-CoV patients (56 cases, from the Beijing hospital of the Armed Forces Police, China) that showed that specific IgG antibodies and neutralizing antibodies were highly correlated, peaking at month 4 after the onset of disease and decreasing gradually thereafter.
This and other studies suggest that the immune responses of specific antibodies were maintained in more than 90% of recovered SARS-CoV patients for 2 years, according to the authors.
However, of particular concern is the fact that only 11.8% of patients acquire specific SARS-CoV Abs in the early period after recovery at day 7, not reaching 100% until day 90, which highlights the importance of the detection of antibody titers for convalescent COVID-19 patients, according to the authors. “Otherwise, these patients with low titers of antibodies may not be efficient for the clearance of SARS-CoV-2.”
The authors also cited a recent study that showed how neutralizing antibody from a convalescent SARS patient could block the SARS-CoV-2 from entering into target cells in vitro, and suggested that previous experimental SARS-CoV vaccines and neutralizing antibodies could provide novel preventive and therapeutic options for COVID-19.
“These experiences from SARS-CoV are expected to have some implications for the treatment, management and surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 patients,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE: Lin Q et al. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2020 Mar 25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmii.2020.03.015.
The immune responses of specific antibodies were maintained in more than 90% of recovered SARS-CoV patients for 2 years, raising the likelihood that the similarly behaving SARS-CoV-2 might provoke the same response, according to an online communication published in the Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection.
The authors cited a cohort study of convalescent SARS-CoV patients (56 cases, from the Beijing hospital of the Armed Forces Police, China) that showed that specific IgG antibodies and neutralizing antibodies were highly correlated, peaking at month 4 after the onset of disease and decreasing gradually thereafter.
This and other studies suggest that the immune responses of specific antibodies were maintained in more than 90% of recovered SARS-CoV patients for 2 years, according to the authors.
However, of particular concern is the fact that only 11.8% of patients acquire specific SARS-CoV Abs in the early period after recovery at day 7, not reaching 100% until day 90, which highlights the importance of the detection of antibody titers for convalescent COVID-19 patients, according to the authors. “Otherwise, these patients with low titers of antibodies may not be efficient for the clearance of SARS-CoV-2.”
The authors also cited a recent study that showed how neutralizing antibody from a convalescent SARS patient could block the SARS-CoV-2 from entering into target cells in vitro, and suggested that previous experimental SARS-CoV vaccines and neutralizing antibodies could provide novel preventive and therapeutic options for COVID-19.
“These experiences from SARS-CoV are expected to have some implications for the treatment, management and surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 patients,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE: Lin Q et al. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2020 Mar 25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmii.2020.03.015.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF MICROBIOLOGY, IMMUNOLOGY AND INFECTION
COVID-19: Adjusting practice in acute leukemia care
The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic poses significant risks to leukemia patients and their providers, impacting every aspect of care from diagnosis through therapy, according to an editorial letter published online in Leukemia Research.
One key concern to be considered is the risk of missed or delayed diagnosis due to the pandemic conditions. An estimated 50%-75% of patients with acute leukemia are febrile at diagnosis and this puts them at high risk of a misdiagnosis of COVID-19 upon initial evaluation. As with other oncological conditions (primary mediastinal lymphoma or lung cancer, for example), which often present with a cough with or without fever, their symptoms “are likely to be considered trivial after a negative SARS-CoV-2 test,” with patients then being sent home without further assessment. In a rapidly progressing disease such as acute leukemia, this could lead to critical delays in therapeutic intervention.
The authors, from the Service and Central Laboratory of Hematology, Lausanne (Switzerland) University Hospital, also discussed the problems that might occur with regard to most standard forms of therapy. In particular, they addressed potential impacts of the pandemic on chemotherapy, bone marrow transplantation, maintenance treatments, supportive measures, and targeted therapies.
Of particular concern, “most patients may suffer from postponed chemotherapy, due to a shortage of isolation beds and blood products or the wish to avoid immunosuppressive treatments,” the authors noted, warning that “delay in chemotherapy initiation may negatively affect prognosis, [particularly in patients under age 60] with favorable- or intermediate-risk disease.”
With regard to stem cell transplantation, the authors detail the many potential difficulties with regard to procedures involving both donors and recipients, and warn that in some cases, delay in transplant could result in the reappearance of a significant minimal residual disease, which has a well-established negative impact on survival.
The authors also noted that blood product shortages have already begun in most affected countries, and how, in response, transfusion societies have called for conservative transfusion policies in strict adherence to evidence-based guidelines for patient’s blood management.
“COVID-19 will result in numerous casualties. Acute leukemia patients are at a higher risk of severe complications,” the authors stated. In particular, physicians should especially be aware of how treatment for acute leukemia may have “interactions with other drugs used to treat SARS-CoV-2–related infections/complications such as antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and various other drugs that prolong QTc or impact targeted-therapy pharmacokinetics,” they concluded.
The authors reported that they received no government or private funding for this research, and that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Gavillet M et al. Leuk. Res. 2020. doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2020.106353.
The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic poses significant risks to leukemia patients and their providers, impacting every aspect of care from diagnosis through therapy, according to an editorial letter published online in Leukemia Research.
One key concern to be considered is the risk of missed or delayed diagnosis due to the pandemic conditions. An estimated 50%-75% of patients with acute leukemia are febrile at diagnosis and this puts them at high risk of a misdiagnosis of COVID-19 upon initial evaluation. As with other oncological conditions (primary mediastinal lymphoma or lung cancer, for example), which often present with a cough with or without fever, their symptoms “are likely to be considered trivial after a negative SARS-CoV-2 test,” with patients then being sent home without further assessment. In a rapidly progressing disease such as acute leukemia, this could lead to critical delays in therapeutic intervention.
The authors, from the Service and Central Laboratory of Hematology, Lausanne (Switzerland) University Hospital, also discussed the problems that might occur with regard to most standard forms of therapy. In particular, they addressed potential impacts of the pandemic on chemotherapy, bone marrow transplantation, maintenance treatments, supportive measures, and targeted therapies.
Of particular concern, “most patients may suffer from postponed chemotherapy, due to a shortage of isolation beds and blood products or the wish to avoid immunosuppressive treatments,” the authors noted, warning that “delay in chemotherapy initiation may negatively affect prognosis, [particularly in patients under age 60] with favorable- or intermediate-risk disease.”
With regard to stem cell transplantation, the authors detail the many potential difficulties with regard to procedures involving both donors and recipients, and warn that in some cases, delay in transplant could result in the reappearance of a significant minimal residual disease, which has a well-established negative impact on survival.
The authors also noted that blood product shortages have already begun in most affected countries, and how, in response, transfusion societies have called for conservative transfusion policies in strict adherence to evidence-based guidelines for patient’s blood management.
“COVID-19 will result in numerous casualties. Acute leukemia patients are at a higher risk of severe complications,” the authors stated. In particular, physicians should especially be aware of how treatment for acute leukemia may have “interactions with other drugs used to treat SARS-CoV-2–related infections/complications such as antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and various other drugs that prolong QTc or impact targeted-therapy pharmacokinetics,” they concluded.
The authors reported that they received no government or private funding for this research, and that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Gavillet M et al. Leuk. Res. 2020. doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2020.106353.
The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic poses significant risks to leukemia patients and their providers, impacting every aspect of care from diagnosis through therapy, according to an editorial letter published online in Leukemia Research.
One key concern to be considered is the risk of missed or delayed diagnosis due to the pandemic conditions. An estimated 50%-75% of patients with acute leukemia are febrile at diagnosis and this puts them at high risk of a misdiagnosis of COVID-19 upon initial evaluation. As with other oncological conditions (primary mediastinal lymphoma or lung cancer, for example), which often present with a cough with or without fever, their symptoms “are likely to be considered trivial after a negative SARS-CoV-2 test,” with patients then being sent home without further assessment. In a rapidly progressing disease such as acute leukemia, this could lead to critical delays in therapeutic intervention.
The authors, from the Service and Central Laboratory of Hematology, Lausanne (Switzerland) University Hospital, also discussed the problems that might occur with regard to most standard forms of therapy. In particular, they addressed potential impacts of the pandemic on chemotherapy, bone marrow transplantation, maintenance treatments, supportive measures, and targeted therapies.
Of particular concern, “most patients may suffer from postponed chemotherapy, due to a shortage of isolation beds and blood products or the wish to avoid immunosuppressive treatments,” the authors noted, warning that “delay in chemotherapy initiation may negatively affect prognosis, [particularly in patients under age 60] with favorable- or intermediate-risk disease.”
With regard to stem cell transplantation, the authors detail the many potential difficulties with regard to procedures involving both donors and recipients, and warn that in some cases, delay in transplant could result in the reappearance of a significant minimal residual disease, which has a well-established negative impact on survival.
The authors also noted that blood product shortages have already begun in most affected countries, and how, in response, transfusion societies have called for conservative transfusion policies in strict adherence to evidence-based guidelines for patient’s blood management.
“COVID-19 will result in numerous casualties. Acute leukemia patients are at a higher risk of severe complications,” the authors stated. In particular, physicians should especially be aware of how treatment for acute leukemia may have “interactions with other drugs used to treat SARS-CoV-2–related infections/complications such as antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and various other drugs that prolong QTc or impact targeted-therapy pharmacokinetics,” they concluded.
The authors reported that they received no government or private funding for this research, and that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Gavillet M et al. Leuk. Res. 2020. doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2020.106353.
FROM LEUKEMIA RESEARCH
Low plasma sodium predicts complications in SCD acute pain episodes
Hyponatremia, defined as a plasma sodium concentration ≤ 135 mmol/L at admission, was associated with complications during episodes of acute pain from sickle cell disease, according to a large retrospective analysis.
The French study assessed 1,218 stays of 406 patients admitted for treatment of an acute painful episode of sickle cell disease between 2010-2015. The primary composite endpoint comprised acute chest syndrome, intensive care unit transfer, red blood cell transfusion or inpatient death. The analyses were adjusted for age, sex, hemoglobin genotype and concentration, LDH concentration, and white blood cell count, according to the researchers.
Hyponatremia at admission in the center was associated with the primary endpoint (adjusted odds ratio (OR) 1.95, P = .001). This association was independent from baseline demographic characteristics (age, sex, hemoglobin genotype) and from other prognostic factors examined in the study (lower hemoglobin concentration, higher white blood cell count and LDH concentration).
With regard to individual components of the primary endpoint, hyponatremia was associated with acute chest syndrome (OR 1.95, P = .008) and red blood cell transfusion (OR 2.71, P <.001), but not significantly with intensive care unit transfer (OR 1.83, P = .074). In addition, the adjusted mean length of stay was significantly longer by 1.1 days (P < .001) in patients with hyponatremia at admission.
The study received no funding and the researchers reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Rech JS et al. Amer J Med. 2020. doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.02.017.
Hyponatremia, defined as a plasma sodium concentration ≤ 135 mmol/L at admission, was associated with complications during episodes of acute pain from sickle cell disease, according to a large retrospective analysis.
The French study assessed 1,218 stays of 406 patients admitted for treatment of an acute painful episode of sickle cell disease between 2010-2015. The primary composite endpoint comprised acute chest syndrome, intensive care unit transfer, red blood cell transfusion or inpatient death. The analyses were adjusted for age, sex, hemoglobin genotype and concentration, LDH concentration, and white blood cell count, according to the researchers.
Hyponatremia at admission in the center was associated with the primary endpoint (adjusted odds ratio (OR) 1.95, P = .001). This association was independent from baseline demographic characteristics (age, sex, hemoglobin genotype) and from other prognostic factors examined in the study (lower hemoglobin concentration, higher white blood cell count and LDH concentration).
With regard to individual components of the primary endpoint, hyponatremia was associated with acute chest syndrome (OR 1.95, P = .008) and red blood cell transfusion (OR 2.71, P <.001), but not significantly with intensive care unit transfer (OR 1.83, P = .074). In addition, the adjusted mean length of stay was significantly longer by 1.1 days (P < .001) in patients with hyponatremia at admission.
The study received no funding and the researchers reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Rech JS et al. Amer J Med. 2020. doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.02.017.
Hyponatremia, defined as a plasma sodium concentration ≤ 135 mmol/L at admission, was associated with complications during episodes of acute pain from sickle cell disease, according to a large retrospective analysis.
The French study assessed 1,218 stays of 406 patients admitted for treatment of an acute painful episode of sickle cell disease between 2010-2015. The primary composite endpoint comprised acute chest syndrome, intensive care unit transfer, red blood cell transfusion or inpatient death. The analyses were adjusted for age, sex, hemoglobin genotype and concentration, LDH concentration, and white blood cell count, according to the researchers.
Hyponatremia at admission in the center was associated with the primary endpoint (adjusted odds ratio (OR) 1.95, P = .001). This association was independent from baseline demographic characteristics (age, sex, hemoglobin genotype) and from other prognostic factors examined in the study (lower hemoglobin concentration, higher white blood cell count and LDH concentration).
With regard to individual components of the primary endpoint, hyponatremia was associated with acute chest syndrome (OR 1.95, P = .008) and red blood cell transfusion (OR 2.71, P <.001), but not significantly with intensive care unit transfer (OR 1.83, P = .074). In addition, the adjusted mean length of stay was significantly longer by 1.1 days (P < .001) in patients with hyponatremia at admission.
The study received no funding and the researchers reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Rech JS et al. Amer J Med. 2020. doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.02.017.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MEDICINE