User login
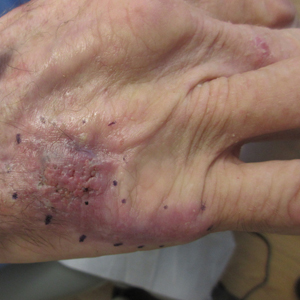
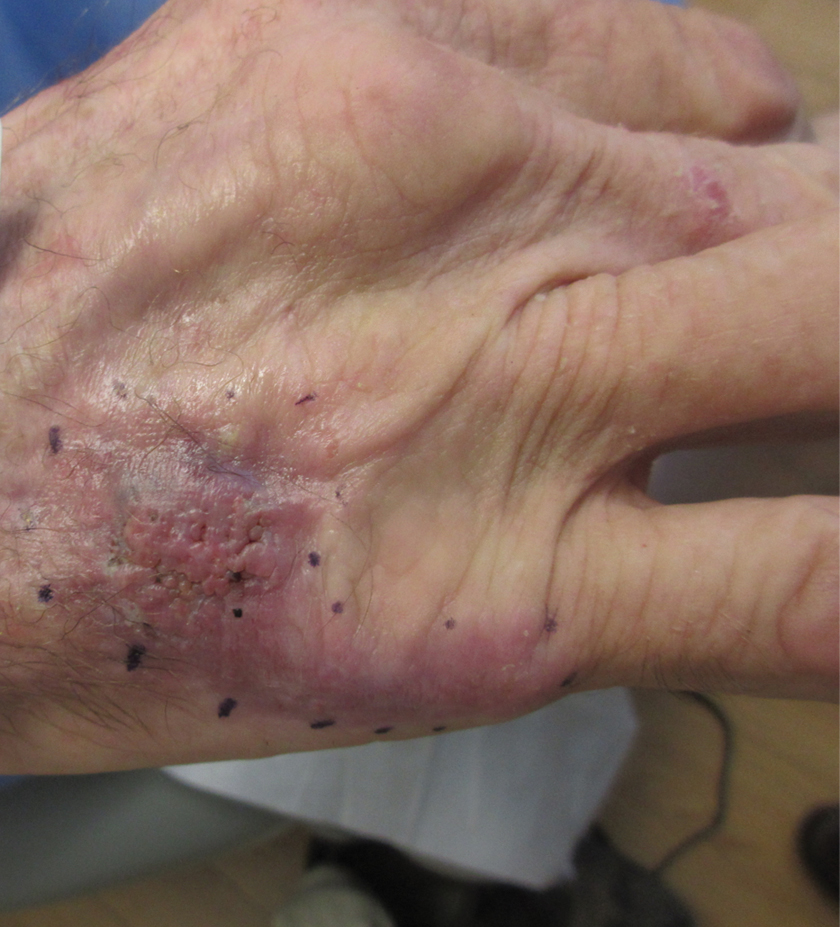
Nonhealing Violaceous Plaque of the Hand Following a Splinter Injury
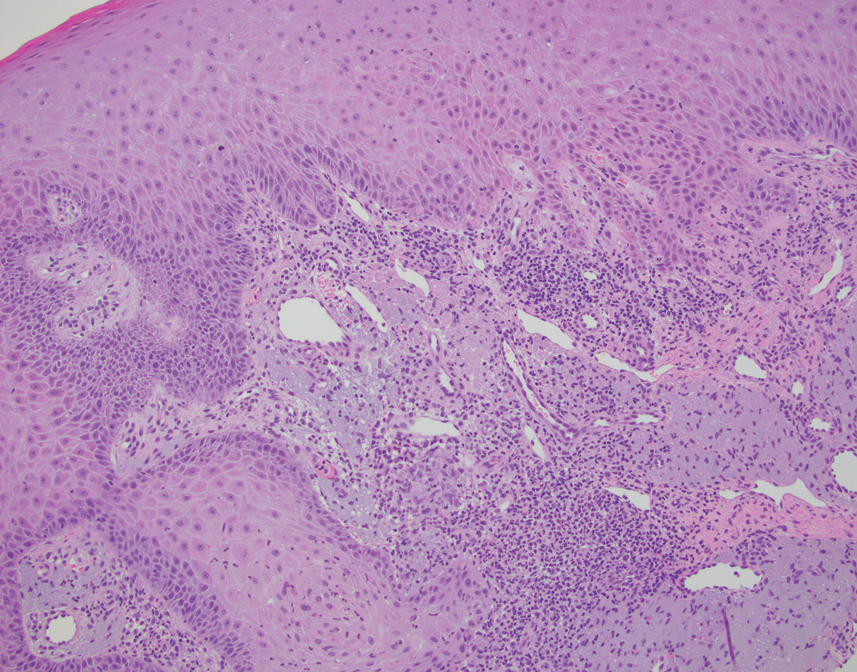
The Diagnosis: Chromoblastomycosis
This case highlights the importance of routine skin biopsy and tissue culture when clinical suspicion for mycotic infection is high. Despite nonspecific biopsy results (Figure), a diagnosis of chromoblastomycosis (CBM) was reached based on tissue culture. Surgical excision was not possible in our patient due to the size and location of the lesion. The patient was referred to infectious disease, with the plan to start long-term itraconazole for at least 6 to 12 months.
Cases of CBM were first documented in 1914 and distinguished by the appearance of spherical, brown, muriform cells on skin biopsy—features that now serve as the hallmark of CBM diagnoses.1,2 The implantation mycosis commonly is caused by agents such as Fonsecaea pedrosoi and Fonsecaea monophora of the bantiana-clade, as classified according to molecular phylogeny2; these agents have been isolated from soil, plants, and wood sources in tropical and subtropical regions and are strongly associated with agricultural activities.3
Chromoblastomycosis lesions tend to be asymptomatic with a variable amount of time between inoculation and lesion presentation, delaying medical care by months to years.3 The fungus causes a granulomatous reaction after skin damage, with noticeable pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia of the epidermis and granulomas formed by epithelioid and Langerhans cells in the dermis.4 Typically, CBM initially presents as an erythematous macular skin lesion, which then progresses to become more pink, papular, and sometimes pruritic.2 Muriform (sclerotic) bodies, which reflect fungal components, extrude transepidermally and appear as black dots on the lesion’s surface.4 Chromoblastomycosis is limited to the subcutaneous tissue and has been classified into 5 types of lesions: nodular, tumoral, verrucous, scarring, and plaque.2 Diagnosis is established using fungal tests such as potassium hydroxide direct microscopy, which exposes muriform bodies often in combination with dematiaceous hyphae, while fungal culture of F pedrosoi in Sabouraud agar produces velvety dark colonies.3 Although an immune response to CBM infection remains unclear, it has been demonstrated that the response differs based on the severity of the infection. The severe form of CBM produces high levels of IL-10, low levels of IFN-γ, and inefficient T-cell proliferation, while milder forms of CBM display low levels of IL-10, high levels of IFN-γ, and efficient T-cell proliferation.5 Complications of CBM include chronic lymphedema, ankylosis, and secondary bacterial infections, which largely are observed in advanced cases; malignant transformation to squamous cell carcinoma, though rare, also has been observed.6
Several therapeutic methods have been implemented in the treatment of CBM, but lesions often remain refractory, especially in advanced cases.6 Approaches to treatment can be divided into antifungal and physical methods. Commonly employed antifungal agents include itraconazole and terbinafine, which must be taken daily for a period ranging from 6 months to 1 year or longer; flucytosine with or without amphotericin also has been employed.4 Among the physical methods, surgical excision is not suggested due to possible dissemination of disease; other options include cryotherapy, thermotherapy, and laser vaporization.6 The prognosis has improved since the use of extended-spectrum triazoles, but high rates of refractory disease remain unchanged.2
The differential diagnosis includes other infections. Nocardiosis is a bacterial infection in which cutaneous disease can result in actinomycetoma, which presents with grains that are small, round, and stain blue on hematoxylin and eosin with eosinophilic rays at the periphery.7 Although the clinical features and pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia seen in CBM can mimic squamous cell carcinoma, the latter would show variable degrees of differentiation, keratinization, nuclear atypia, and architectural atypia with a negative tissue culture.8 Eumycetoma is a fungal infection that typically is not caused by F pedrosoi but rather most commonly Madurella mycetomatis.9 Leishmaniasis is a parasitic infection in which a biopsy of cutaneous lesions often displays parasite-filled histiocytes.10
- Rudolph M. Über die brasilianische “figueira” (vorläufige mitteilung). Arch Schiffs Trop Hyg. 1914;18:498-499.
- Queiroz-Telles F, de Hoog S, Santos DW, et al. Chromoblastomycosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2017;30:233-276. doi:10.1128/CMR.00032-16
- Brito AC, Bittencourt MJS. Chromoblastomycosis: an etiological, epidemiological, clinical, diagnostic, and treatment update. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93:495-506. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20187321
- Kurien G, Sugumar K, Chandran V. Chromoblastomycosis. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. Accessed June 4, 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470253/
- Mazo Fávero Gimenes V, Da Glória de Souza M, Ferreira KS, et al. Cytokines and lymphocyte proliferation in patients with different clinical forms of chromoblastomycosis. Microbes Infect. 2005;7:708-713. doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2005.01.006
- Krzys´ciak PM, Pindycka-Piaszczyn´ska M, Piaszczyn´ski M. Chromoblastomycosis. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2014;31:310-321. doi:10.5114/pdia.2014.40949
- Siddig EE, van de Sande WWJ, Fahal AH. Actinomycetoma laboratory-based diagnosis: a mini-review. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2021;115:355-363.
- Parekh V, Seykora JT. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Lab Med. 2017;37:503-525. doi:10.1016/j.cll .2017.06.003
- Nenoff P, van de Sande WWJ, Fahal AH, et al. Eumycetoma and actinomycetoma—an update on causative agents, epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnostics and therapy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1873-1883. doi:10.1111/jdv.13008
- Saliba M, Shalhoub A, Taraif S, et al. Cutaneous leishmaniasis: an evolving disease with ancient roots. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:834-843. doi:10.1111/ijd.14451
The Diagnosis: Chromoblastomycosis
This case highlights the importance of routine skin biopsy and tissue culture when clinical suspicion for mycotic infection is high. Despite nonspecific biopsy results (Figure), a diagnosis of chromoblastomycosis (CBM) was reached based on tissue culture. Surgical excision was not possible in our patient due to the size and location of the lesion. The patient was referred to infectious disease, with the plan to start long-term itraconazole for at least 6 to 12 months.

Cases of CBM were first documented in 1914 and distinguished by the appearance of spherical, brown, muriform cells on skin biopsy—features that now serve as the hallmark of CBM diagnoses.1,2 The implantation mycosis commonly is caused by agents such as Fonsecaea pedrosoi and Fonsecaea monophora of the bantiana-clade, as classified according to molecular phylogeny2; these agents have been isolated from soil, plants, and wood sources in tropical and subtropical regions and are strongly associated with agricultural activities.3
Chromoblastomycosis lesions tend to be asymptomatic with a variable amount of time between inoculation and lesion presentation, delaying medical care by months to years.3 The fungus causes a granulomatous reaction after skin damage, with noticeable pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia of the epidermis and granulomas formed by epithelioid and Langerhans cells in the dermis.4 Typically, CBM initially presents as an erythematous macular skin lesion, which then progresses to become more pink, papular, and sometimes pruritic.2 Muriform (sclerotic) bodies, which reflect fungal components, extrude transepidermally and appear as black dots on the lesion’s surface.4 Chromoblastomycosis is limited to the subcutaneous tissue and has been classified into 5 types of lesions: nodular, tumoral, verrucous, scarring, and plaque.2 Diagnosis is established using fungal tests such as potassium hydroxide direct microscopy, which exposes muriform bodies often in combination with dematiaceous hyphae, while fungal culture of F pedrosoi in Sabouraud agar produces velvety dark colonies.3 Although an immune response to CBM infection remains unclear, it has been demonstrated that the response differs based on the severity of the infection. The severe form of CBM produces high levels of IL-10, low levels of IFN-γ, and inefficient T-cell proliferation, while milder forms of CBM display low levels of IL-10, high levels of IFN-γ, and efficient T-cell proliferation.5 Complications of CBM include chronic lymphedema, ankylosis, and secondary bacterial infections, which largely are observed in advanced cases; malignant transformation to squamous cell carcinoma, though rare, also has been observed.6
Several therapeutic methods have been implemented in the treatment of CBM, but lesions often remain refractory, especially in advanced cases.6 Approaches to treatment can be divided into antifungal and physical methods. Commonly employed antifungal agents include itraconazole and terbinafine, which must be taken daily for a period ranging from 6 months to 1 year or longer; flucytosine with or without amphotericin also has been employed.4 Among the physical methods, surgical excision is not suggested due to possible dissemination of disease; other options include cryotherapy, thermotherapy, and laser vaporization.6 The prognosis has improved since the use of extended-spectrum triazoles, but high rates of refractory disease remain unchanged.2
The differential diagnosis includes other infections. Nocardiosis is a bacterial infection in which cutaneous disease can result in actinomycetoma, which presents with grains that are small, round, and stain blue on hematoxylin and eosin with eosinophilic rays at the periphery.7 Although the clinical features and pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia seen in CBM can mimic squamous cell carcinoma, the latter would show variable degrees of differentiation, keratinization, nuclear atypia, and architectural atypia with a negative tissue culture.8 Eumycetoma is a fungal infection that typically is not caused by F pedrosoi but rather most commonly Madurella mycetomatis.9 Leishmaniasis is a parasitic infection in which a biopsy of cutaneous lesions often displays parasite-filled histiocytes.10
The Diagnosis: Chromoblastomycosis
This case highlights the importance of routine skin biopsy and tissue culture when clinical suspicion for mycotic infection is high. Despite nonspecific biopsy results (Figure), a diagnosis of chromoblastomycosis (CBM) was reached based on tissue culture. Surgical excision was not possible in our patient due to the size and location of the lesion. The patient was referred to infectious disease, with the plan to start long-term itraconazole for at least 6 to 12 months.

Cases of CBM were first documented in 1914 and distinguished by the appearance of spherical, brown, muriform cells on skin biopsy—features that now serve as the hallmark of CBM diagnoses.1,2 The implantation mycosis commonly is caused by agents such as Fonsecaea pedrosoi and Fonsecaea monophora of the bantiana-clade, as classified according to molecular phylogeny2; these agents have been isolated from soil, plants, and wood sources in tropical and subtropical regions and are strongly associated with agricultural activities.3
Chromoblastomycosis lesions tend to be asymptomatic with a variable amount of time between inoculation and lesion presentation, delaying medical care by months to years.3 The fungus causes a granulomatous reaction after skin damage, with noticeable pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia of the epidermis and granulomas formed by epithelioid and Langerhans cells in the dermis.4 Typically, CBM initially presents as an erythematous macular skin lesion, which then progresses to become more pink, papular, and sometimes pruritic.2 Muriform (sclerotic) bodies, which reflect fungal components, extrude transepidermally and appear as black dots on the lesion’s surface.4 Chromoblastomycosis is limited to the subcutaneous tissue and has been classified into 5 types of lesions: nodular, tumoral, verrucous, scarring, and plaque.2 Diagnosis is established using fungal tests such as potassium hydroxide direct microscopy, which exposes muriform bodies often in combination with dematiaceous hyphae, while fungal culture of F pedrosoi in Sabouraud agar produces velvety dark colonies.3 Although an immune response to CBM infection remains unclear, it has been demonstrated that the response differs based on the severity of the infection. The severe form of CBM produces high levels of IL-10, low levels of IFN-γ, and inefficient T-cell proliferation, while milder forms of CBM display low levels of IL-10, high levels of IFN-γ, and efficient T-cell proliferation.5 Complications of CBM include chronic lymphedema, ankylosis, and secondary bacterial infections, which largely are observed in advanced cases; malignant transformation to squamous cell carcinoma, though rare, also has been observed.6
Several therapeutic methods have been implemented in the treatment of CBM, but lesions often remain refractory, especially in advanced cases.6 Approaches to treatment can be divided into antifungal and physical methods. Commonly employed antifungal agents include itraconazole and terbinafine, which must be taken daily for a period ranging from 6 months to 1 year or longer; flucytosine with or without amphotericin also has been employed.4 Among the physical methods, surgical excision is not suggested due to possible dissemination of disease; other options include cryotherapy, thermotherapy, and laser vaporization.6 The prognosis has improved since the use of extended-spectrum triazoles, but high rates of refractory disease remain unchanged.2
The differential diagnosis includes other infections. Nocardiosis is a bacterial infection in which cutaneous disease can result in actinomycetoma, which presents with grains that are small, round, and stain blue on hematoxylin and eosin with eosinophilic rays at the periphery.7 Although the clinical features and pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia seen in CBM can mimic squamous cell carcinoma, the latter would show variable degrees of differentiation, keratinization, nuclear atypia, and architectural atypia with a negative tissue culture.8 Eumycetoma is a fungal infection that typically is not caused by F pedrosoi but rather most commonly Madurella mycetomatis.9 Leishmaniasis is a parasitic infection in which a biopsy of cutaneous lesions often displays parasite-filled histiocytes.10
- Rudolph M. Über die brasilianische “figueira” (vorläufige mitteilung). Arch Schiffs Trop Hyg. 1914;18:498-499.
- Queiroz-Telles F, de Hoog S, Santos DW, et al. Chromoblastomycosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2017;30:233-276. doi:10.1128/CMR.00032-16
- Brito AC, Bittencourt MJS. Chromoblastomycosis: an etiological, epidemiological, clinical, diagnostic, and treatment update. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93:495-506. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20187321
- Kurien G, Sugumar K, Chandran V. Chromoblastomycosis. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. Accessed June 4, 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470253/
- Mazo Fávero Gimenes V, Da Glória de Souza M, Ferreira KS, et al. Cytokines and lymphocyte proliferation in patients with different clinical forms of chromoblastomycosis. Microbes Infect. 2005;7:708-713. doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2005.01.006
- Krzys´ciak PM, Pindycka-Piaszczyn´ska M, Piaszczyn´ski M. Chromoblastomycosis. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2014;31:310-321. doi:10.5114/pdia.2014.40949
- Siddig EE, van de Sande WWJ, Fahal AH. Actinomycetoma laboratory-based diagnosis: a mini-review. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2021;115:355-363.
- Parekh V, Seykora JT. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Lab Med. 2017;37:503-525. doi:10.1016/j.cll .2017.06.003
- Nenoff P, van de Sande WWJ, Fahal AH, et al. Eumycetoma and actinomycetoma—an update on causative agents, epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnostics and therapy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1873-1883. doi:10.1111/jdv.13008
- Saliba M, Shalhoub A, Taraif S, et al. Cutaneous leishmaniasis: an evolving disease with ancient roots. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:834-843. doi:10.1111/ijd.14451
- Rudolph M. Über die brasilianische “figueira” (vorläufige mitteilung). Arch Schiffs Trop Hyg. 1914;18:498-499.
- Queiroz-Telles F, de Hoog S, Santos DW, et al. Chromoblastomycosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2017;30:233-276. doi:10.1128/CMR.00032-16
- Brito AC, Bittencourt MJS. Chromoblastomycosis: an etiological, epidemiological, clinical, diagnostic, and treatment update. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93:495-506. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20187321
- Kurien G, Sugumar K, Chandran V. Chromoblastomycosis. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. Accessed June 4, 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470253/
- Mazo Fávero Gimenes V, Da Glória de Souza M, Ferreira KS, et al. Cytokines and lymphocyte proliferation in patients with different clinical forms of chromoblastomycosis. Microbes Infect. 2005;7:708-713. doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2005.01.006
- Krzys´ciak PM, Pindycka-Piaszczyn´ska M, Piaszczyn´ski M. Chromoblastomycosis. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2014;31:310-321. doi:10.5114/pdia.2014.40949
- Siddig EE, van de Sande WWJ, Fahal AH. Actinomycetoma laboratory-based diagnosis: a mini-review. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2021;115:355-363.
- Parekh V, Seykora JT. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Lab Med. 2017;37:503-525. doi:10.1016/j.cll .2017.06.003
- Nenoff P, van de Sande WWJ, Fahal AH, et al. Eumycetoma and actinomycetoma—an update on causative agents, epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnostics and therapy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1873-1883. doi:10.1111/jdv.13008
- Saliba M, Shalhoub A, Taraif S, et al. Cutaneous leishmaniasis: an evolving disease with ancient roots. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:834-843. doi:10.1111/ijd.14451
A 70-year-old immunocompetent man presented to the dermatology department with a progressive asymptomatic hand wound of 2 years’ duration following a splinter injury in Belize. Prior treatment included oral antibiotics without improvement. Physical examination revealed a 5.1×3.0 cm, pink to violaceous, nonpurulent plaque with a cobblestonelike appearance on the dorsal aspect of the right hand. Both the initial and a repeat skin biopsy revealed nonspecific changes, including hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, acute and chronic inflammation, and vascular ectasia. Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver staining was negative for fungal organisms. One month after the repeat biopsy, a tissue culture returned positive for the rare Fonsecaea pedrosoi.
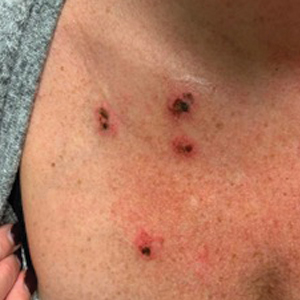
Necrotic Ulcerations After the Use of an Over-the-counter Mole and Skin Tag Removal Product
To the Editor:
Several mole and skin tag removal products are available online and over the counter (OTC).1 Patients concerned with the cosmetic appearance of nevi may use these products as a do-it-yourself alternative to surgical removal. However, these products have the potential to cause harm.2 Beyond the cosmetic adverse effects of skin necrosis and scar formation, these products can mask premalignant and malignant skin lesions.2 Herein, we describe a patient with a family history of melanoma who developed facial and chest ulcerations with necrosis after applying an OTC mole and skin tag removal product.
A 45-year-old woman with fair skin presented to a clinic with multiple superficial ulcerations measuring approximately 1 cm in diameter with necrotic black bases and erythematous rims on the face, right side of the upper chest, and left earlobe after using the Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set, an OTC mole and skin tag removal product. The patient reported using the product 24 hours prior for the cosmetic removal of multiple nevi. After applying the product, she observed that it “immediately melted [her] skin” and the areas where the product was applied “turned black.” She reported that the product was applied to the skin for no longer than 30 seconds, after which she developed the necrotic lesions (Figure). After removing the product, she applied an OTC ointment containing bacitracin, neomycin, and polymyxin B to the lesions.
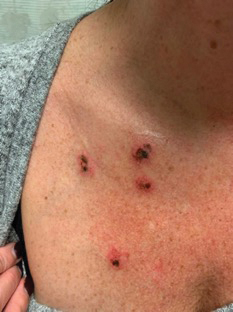
The patient had no history of nonmelanoma skin cancers or atypical nevi. She had a family history of melanoma in her mother and maternal uncle. The treatment plan was aimed primarily at reducing scar formation. We advised frequent application of petroleum-based ointments for moisture and overlying silicone scar tape to protect the area from photodamage and promote wound healing. We further advocated for sun protection and the use of a physical sunscreen on the lesions as they healed. We discussed potential laser-based scar revision options in the future.
With more than 180 reviews on Amazon and almost 70% of these reviews made within the month prior to compiling this manuscript, the Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set appeared to be popular; however, the product currently is unavailable on Amazon. Testimonials and before-and-after pictures advertising the product show an all-natural, safe, and effective method as an alternative to surgical removal of skin tags and nevi. The product website claims that skin tags and moles will “fall off naturally within 7 to 10 days” and the product can be used for “almost all skin types.” Users are instructed to apply the removal product and wipe it off when the skin surrounding the mole becomes swollen. The product kit also includes a repair lotion, which claims to help heal the skin after scab formation and scar development.
The ingredients listed on the product packaging are salicylic acid 25%, Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) leaf oil, propylene glycol, hydroxyethylcellulose, and alcohol. Salicylic acid 25% is a superficial peeling agent that penetrates the epidermis to the dermoepidermal junction. The potential side effects are mild and include superficial desquamation and epidermolysis.3 The Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set is not regulated by the US Food and Drug Administration and may contain variable concentrations of salicylic acid and other unknown compounds. Higher concentrations of salicylic acid can penetrate the full thickness of the epidermis into the papillary dermis, which can result in postinflammatory pigmentation, superficial infection, scarring, and deeper desquamation and epidermolysis.3 The product website advertises the use of only natural ingredients and an “advanced blend of concentrated natural ingredients contributing a broad spectrum of healing properties” in the formula. Although these claims are attractive to patients seeking alternatives to surgical approaches to nevi removal, the unfounded claims and unregulated ingredients may pose a threat to unsuspecting consumers.
Other OTC and “all-natural” mole removal products previously have been reported to cause harm.2Sanguinaria canadensis, also known as bloodroot, contains an alkaloid compound (sanguinarine) that has been shown to induce mitochondrial apoptosis and activation of Bcl-2 proteins in keratinocytes.4 Some products, such as Wart & Mole Vanish cream, may claim not to contain bloodroot specifically. However, sanguinarine can be extracted from other plants and may be listed as Argemone mexicana, Chelidonium majus, or Macleaya cordata in the ingredients list.5 The use of alternative medicine products such as black or yellow salve for the removal of suspected skin cancers also is not recommended because these escharotic treatments have not been proven safe or effective, and the manufacturing process for these compounds is unregulated.6,7 Self-treatment with alternative remedies for nevi or suspected skin cancers has been associated with progression of disease and even death due to metastatic spread.2
Self-removal of moles is concerning because the nevi are masked by necrotic lesions and can no longer be assessed by dermoscopy or histopathology. Furthermore, the compounds in the Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set may have unknown effects on the transformation of premalignant cells. They also may mask an underlying process for which clinically proven and effective treatments such as cryotherapy, prescription topical agents, and surgical excision are warranted. Awareness of this product and similar products is important to educate patients on the harmful effects they may cause.
- Clayton R, Turner R. Cosmetic surgery: who needs surgeons when you’ve got creams? Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:1383-1384.
- McAllister JC, Petzold CR, Lio PA. Adverse effects of a mole removal cream. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:628-629.
- Soleymani T, Lanoue J, Rahman Z. A practical approach to chemical peels: a review of fundamentals and step-by-step algorithmic protocol for treatment. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2018;11:21-28.
- Adhami VM, Aziz MH, Mukhatar M, et al. Activation of prodeath Bcl-2 family proteins and mitochondrial apoptosis pathway by sanguinarine in immortalized human HaCaT keratinocytes. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:3176-3182.
- Santos AC, Adkilen P. The alkaloids of Argemone mexicana. J Am Chem Soc. 1932;54:2923-2924.
- Osswald SS, Elston DM, Farley MF, et al. Self-treatment of a basal cell carcinoma with “black and yellow salve.” J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:509-511.
- McDaniel S, Goldman GD. Consequences of using escharotic agents as primary treatment for nonmelanoma skin cancer. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1593-1596.
To the Editor:
Several mole and skin tag removal products are available online and over the counter (OTC).1 Patients concerned with the cosmetic appearance of nevi may use these products as a do-it-yourself alternative to surgical removal. However, these products have the potential to cause harm.2 Beyond the cosmetic adverse effects of skin necrosis and scar formation, these products can mask premalignant and malignant skin lesions.2 Herein, we describe a patient with a family history of melanoma who developed facial and chest ulcerations with necrosis after applying an OTC mole and skin tag removal product.
A 45-year-old woman with fair skin presented to a clinic with multiple superficial ulcerations measuring approximately 1 cm in diameter with necrotic black bases and erythematous rims on the face, right side of the upper chest, and left earlobe after using the Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set, an OTC mole and skin tag removal product. The patient reported using the product 24 hours prior for the cosmetic removal of multiple nevi. After applying the product, she observed that it “immediately melted [her] skin” and the areas where the product was applied “turned black.” She reported that the product was applied to the skin for no longer than 30 seconds, after which she developed the necrotic lesions (Figure). After removing the product, she applied an OTC ointment containing bacitracin, neomycin, and polymyxin B to the lesions.

The patient had no history of nonmelanoma skin cancers or atypical nevi. She had a family history of melanoma in her mother and maternal uncle. The treatment plan was aimed primarily at reducing scar formation. We advised frequent application of petroleum-based ointments for moisture and overlying silicone scar tape to protect the area from photodamage and promote wound healing. We further advocated for sun protection and the use of a physical sunscreen on the lesions as they healed. We discussed potential laser-based scar revision options in the future.
With more than 180 reviews on Amazon and almost 70% of these reviews made within the month prior to compiling this manuscript, the Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set appeared to be popular; however, the product currently is unavailable on Amazon. Testimonials and before-and-after pictures advertising the product show an all-natural, safe, and effective method as an alternative to surgical removal of skin tags and nevi. The product website claims that skin tags and moles will “fall off naturally within 7 to 10 days” and the product can be used for “almost all skin types.” Users are instructed to apply the removal product and wipe it off when the skin surrounding the mole becomes swollen. The product kit also includes a repair lotion, which claims to help heal the skin after scab formation and scar development.
The ingredients listed on the product packaging are salicylic acid 25%, Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) leaf oil, propylene glycol, hydroxyethylcellulose, and alcohol. Salicylic acid 25% is a superficial peeling agent that penetrates the epidermis to the dermoepidermal junction. The potential side effects are mild and include superficial desquamation and epidermolysis.3 The Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set is not regulated by the US Food and Drug Administration and may contain variable concentrations of salicylic acid and other unknown compounds. Higher concentrations of salicylic acid can penetrate the full thickness of the epidermis into the papillary dermis, which can result in postinflammatory pigmentation, superficial infection, scarring, and deeper desquamation and epidermolysis.3 The product website advertises the use of only natural ingredients and an “advanced blend of concentrated natural ingredients contributing a broad spectrum of healing properties” in the formula. Although these claims are attractive to patients seeking alternatives to surgical approaches to nevi removal, the unfounded claims and unregulated ingredients may pose a threat to unsuspecting consumers.
Other OTC and “all-natural” mole removal products previously have been reported to cause harm.2Sanguinaria canadensis, also known as bloodroot, contains an alkaloid compound (sanguinarine) that has been shown to induce mitochondrial apoptosis and activation of Bcl-2 proteins in keratinocytes.4 Some products, such as Wart & Mole Vanish cream, may claim not to contain bloodroot specifically. However, sanguinarine can be extracted from other plants and may be listed as Argemone mexicana, Chelidonium majus, or Macleaya cordata in the ingredients list.5 The use of alternative medicine products such as black or yellow salve for the removal of suspected skin cancers also is not recommended because these escharotic treatments have not been proven safe or effective, and the manufacturing process for these compounds is unregulated.6,7 Self-treatment with alternative remedies for nevi or suspected skin cancers has been associated with progression of disease and even death due to metastatic spread.2
Self-removal of moles is concerning because the nevi are masked by necrotic lesions and can no longer be assessed by dermoscopy or histopathology. Furthermore, the compounds in the Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set may have unknown effects on the transformation of premalignant cells. They also may mask an underlying process for which clinically proven and effective treatments such as cryotherapy, prescription topical agents, and surgical excision are warranted. Awareness of this product and similar products is important to educate patients on the harmful effects they may cause.
To the Editor:
Several mole and skin tag removal products are available online and over the counter (OTC).1 Patients concerned with the cosmetic appearance of nevi may use these products as a do-it-yourself alternative to surgical removal. However, these products have the potential to cause harm.2 Beyond the cosmetic adverse effects of skin necrosis and scar formation, these products can mask premalignant and malignant skin lesions.2 Herein, we describe a patient with a family history of melanoma who developed facial and chest ulcerations with necrosis after applying an OTC mole and skin tag removal product.
A 45-year-old woman with fair skin presented to a clinic with multiple superficial ulcerations measuring approximately 1 cm in diameter with necrotic black bases and erythematous rims on the face, right side of the upper chest, and left earlobe after using the Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set, an OTC mole and skin tag removal product. The patient reported using the product 24 hours prior for the cosmetic removal of multiple nevi. After applying the product, she observed that it “immediately melted [her] skin” and the areas where the product was applied “turned black.” She reported that the product was applied to the skin for no longer than 30 seconds, after which she developed the necrotic lesions (Figure). After removing the product, she applied an OTC ointment containing bacitracin, neomycin, and polymyxin B to the lesions.

The patient had no history of nonmelanoma skin cancers or atypical nevi. She had a family history of melanoma in her mother and maternal uncle. The treatment plan was aimed primarily at reducing scar formation. We advised frequent application of petroleum-based ointments for moisture and overlying silicone scar tape to protect the area from photodamage and promote wound healing. We further advocated for sun protection and the use of a physical sunscreen on the lesions as they healed. We discussed potential laser-based scar revision options in the future.
With more than 180 reviews on Amazon and almost 70% of these reviews made within the month prior to compiling this manuscript, the Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set appeared to be popular; however, the product currently is unavailable on Amazon. Testimonials and before-and-after pictures advertising the product show an all-natural, safe, and effective method as an alternative to surgical removal of skin tags and nevi. The product website claims that skin tags and moles will “fall off naturally within 7 to 10 days” and the product can be used for “almost all skin types.” Users are instructed to apply the removal product and wipe it off when the skin surrounding the mole becomes swollen. The product kit also includes a repair lotion, which claims to help heal the skin after scab formation and scar development.
The ingredients listed on the product packaging are salicylic acid 25%, Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) leaf oil, propylene glycol, hydroxyethylcellulose, and alcohol. Salicylic acid 25% is a superficial peeling agent that penetrates the epidermis to the dermoepidermal junction. The potential side effects are mild and include superficial desquamation and epidermolysis.3 The Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set is not regulated by the US Food and Drug Administration and may contain variable concentrations of salicylic acid and other unknown compounds. Higher concentrations of salicylic acid can penetrate the full thickness of the epidermis into the papillary dermis, which can result in postinflammatory pigmentation, superficial infection, scarring, and deeper desquamation and epidermolysis.3 The product website advertises the use of only natural ingredients and an “advanced blend of concentrated natural ingredients contributing a broad spectrum of healing properties” in the formula. Although these claims are attractive to patients seeking alternatives to surgical approaches to nevi removal, the unfounded claims and unregulated ingredients may pose a threat to unsuspecting consumers.
Other OTC and “all-natural” mole removal products previously have been reported to cause harm.2Sanguinaria canadensis, also known as bloodroot, contains an alkaloid compound (sanguinarine) that has been shown to induce mitochondrial apoptosis and activation of Bcl-2 proteins in keratinocytes.4 Some products, such as Wart & Mole Vanish cream, may claim not to contain bloodroot specifically. However, sanguinarine can be extracted from other plants and may be listed as Argemone mexicana, Chelidonium majus, or Macleaya cordata in the ingredients list.5 The use of alternative medicine products such as black or yellow salve for the removal of suspected skin cancers also is not recommended because these escharotic treatments have not been proven safe or effective, and the manufacturing process for these compounds is unregulated.6,7 Self-treatment with alternative remedies for nevi or suspected skin cancers has been associated with progression of disease and even death due to metastatic spread.2
Self-removal of moles is concerning because the nevi are masked by necrotic lesions and can no longer be assessed by dermoscopy or histopathology. Furthermore, the compounds in the Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set may have unknown effects on the transformation of premalignant cells. They also may mask an underlying process for which clinically proven and effective treatments such as cryotherapy, prescription topical agents, and surgical excision are warranted. Awareness of this product and similar products is important to educate patients on the harmful effects they may cause.
- Clayton R, Turner R. Cosmetic surgery: who needs surgeons when you’ve got creams? Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:1383-1384.
- McAllister JC, Petzold CR, Lio PA. Adverse effects of a mole removal cream. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:628-629.
- Soleymani T, Lanoue J, Rahman Z. A practical approach to chemical peels: a review of fundamentals and step-by-step algorithmic protocol for treatment. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2018;11:21-28.
- Adhami VM, Aziz MH, Mukhatar M, et al. Activation of prodeath Bcl-2 family proteins and mitochondrial apoptosis pathway by sanguinarine in immortalized human HaCaT keratinocytes. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:3176-3182.
- Santos AC, Adkilen P. The alkaloids of Argemone mexicana. J Am Chem Soc. 1932;54:2923-2924.
- Osswald SS, Elston DM, Farley MF, et al. Self-treatment of a basal cell carcinoma with “black and yellow salve.” J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:509-511.
- McDaniel S, Goldman GD. Consequences of using escharotic agents as primary treatment for nonmelanoma skin cancer. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1593-1596.
- Clayton R, Turner R. Cosmetic surgery: who needs surgeons when you’ve got creams? Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:1383-1384.
- McAllister JC, Petzold CR, Lio PA. Adverse effects of a mole removal cream. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:628-629.
- Soleymani T, Lanoue J, Rahman Z. A practical approach to chemical peels: a review of fundamentals and step-by-step algorithmic protocol for treatment. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2018;11:21-28.
- Adhami VM, Aziz MH, Mukhatar M, et al. Activation of prodeath Bcl-2 family proteins and mitochondrial apoptosis pathway by sanguinarine in immortalized human HaCaT keratinocytes. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:3176-3182.
- Santos AC, Adkilen P. The alkaloids of Argemone mexicana. J Am Chem Soc. 1932;54:2923-2924.
- Osswald SS, Elston DM, Farley MF, et al. Self-treatment of a basal cell carcinoma with “black and yellow salve.” J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:509-511.
- McDaniel S, Goldman GD. Consequences of using escharotic agents as primary treatment for nonmelanoma skin cancer. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1593-1596.
Practice Point
- Self-administered mole and skin tag removal products are rising in popularity, but unregulated ingredients in over-the-counter products that are not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration may mask underlying transformation of atypical nevi.