User login
A Nationwide Survey of Dermatology Faculty and Mentors on Their Advice for the Dermatology Match Process
A Nationwide Survey of Dermatology Faculty and Mentors on Their Advice for the Dermatology Match Process
While strong relationships with mentors and advisers are critical to navigating the competitive dermatology match process, the advice medical students receive from different individuals can be contradictory. Unaccredited information online—particularly on social media—as well as data reported by applicants can add to potential confusion.1 Published research has elicited comments and observations from successfully matched medical students about highly discussed topics such as presentations and publications, letters of recommendation, away rotations, and interviews.2,3 However, there currently are no published data about advice that dermatology mentors actually offer medical students. In this study, we aimed to investigate this gap in the current literature and examine the advice dermatology faculty, program directors, and other mentors at institutions accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education across the United States give to medical students applying to dermatology residency.
Methods
A 14-question Johns Hopkins Qualtrics survey was sent via the Association of Professors of Dermatology (APD) listserve in June 2024 soliciting responses from members who consider themselves to be mentors to dermatology applicants across the United States. The survey included multiple-choice questions with the option to select multiple answers and a space for open-ended responses. The questions first gathered information on the respondents, including the capacity in which the mentors advised medical students (eg, program director, department chair, clinical faculty). Mentors were asked for the number of years they had been advising mentees and if they were advising students with a home dermatology program. In addition, mentors were asked what advice they give their mentees about aspects of the application process, including gap years, dual applications, research involvement, couples matching, program signaling, away rotations, internship year, letters of recommendation, geographic signaling, interviewing advice, and volunteering during medical school.
On August 18, 2024, survey results from 115 respondents were aggregated. The responses for each question were quantitatively assessed to determine whether there was consensus on specific advice offered. The open-ended responses also were qualitatively assessed to determine the most common responses.
Results
The respondents included program directors (30% [35/115]), clinical faculty (22% [25/115]), department chairs (18% [21/115]), assistant program directors (15% [17/115]), medical school clerkship directors (8% [9/115]), primary mentors (ie, faculty who did not fall into any of the aforementioned categories but still advised medical students interested in dermatology)(5% [6/115]), division chiefs (1% [1/115]), and deans (1% [1/115]). Respondents had been advising students for a median of 10 years (range, 1-40 years [25th percentile, 5.00 years; 75th percentile, 13.75 years]). The majority (90% [103/115]) of mentors surveyed were advising students with a home dermatology program.
Areas of Consensus
In some areas, there was broad consensus among the advice offered by the mentors that were surveyed (eTable).
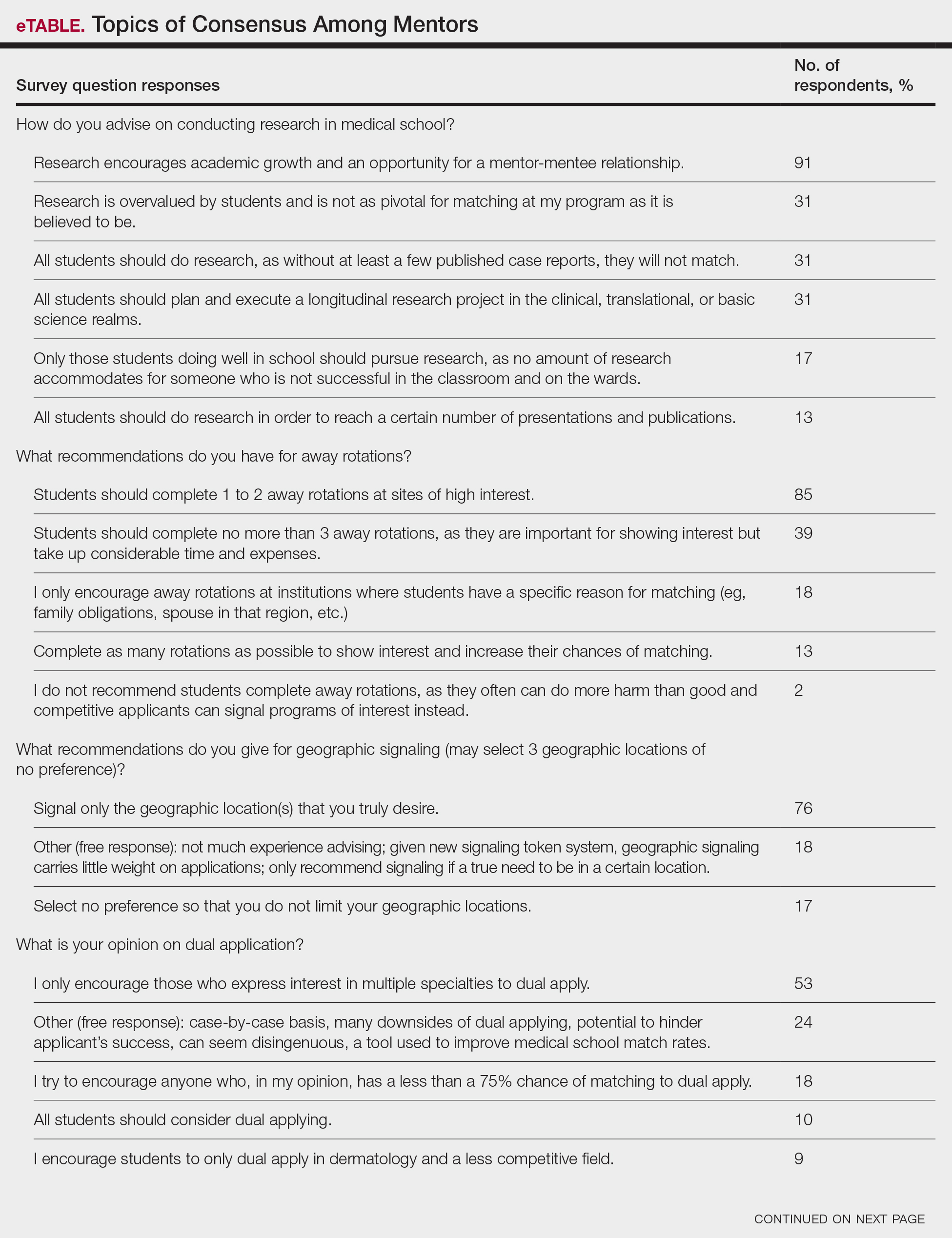

Research During Medical School—More than 91% (105/115) of the respondents recommended research to encourage academic growth and indicated that the most important reason for conducting research during medical school is to foster mentor-mentee relationships; however, more than one-third of respondents believed research is overvalued by students and research productivity is not as critical for matching as they perceive it to be. When these responses were categorized by respondent positions, 29% (15/52) of program or assistant directors indicated agreement with the statement that research is overvalued.
Away Rotations—There also was a consensus about the importance of away rotations, with 85% (98/115) of respondents advising students to complete 1 to 2 away rotations at sites of high interest, and 13% (15/115) suggesting that students complete as many away rotations as possible. It is worth noting, however, that the official APD Residency Program Directors Section’s statement on away rotations recommends no more than 2 away rotations (or no more than 3 for students with no home program).4
Reapplication Advice—Additionally, in a situation where students do not match into a dermatology residency program, the vast majority (71% [82/115]) of respondents advised students to rank competitive intern years to foster connections and improve the chance of matching on the second attempt.
Volunteering During Medical School—Seventy-seven percent (89/115) of mentors encouraged students to engage in volunteerism and advocacy during medical school to create a well-rounded application, and 69% (79/115) of mentors encouraged students to display leadership in their volunteer efforts.
Areas Without Consensus
Letters of Recommendation—Most respondents recommended submitting letters of recommendation only from dermatology professionals (55% [63/115]), with the remainder recommending students request a letter from anyone who could provide a strong recommendation regardless of specialty mix (42% [48/115]).
Dermatologic Subspecialties—For students interested in dermatologic subspecialties, 73% (84/115) of mentors advised that students be honest during interviews but keep an open mind that interests during residencies may change. Forty-three percent (49/115) of respondents encouraged students to promote a subspecialty interest during their interview only if they can demonstrate effort within that subspecialty on their application.
Couples Matching—Most respondents approach couples matching on a case-by-case basis and assess individual priorities when they do advise on this topic. Respondents often advise applicants to identify a few cities/regions and focus strongly on the programs within those regions to avoid spreading themselves too thin; however, one-third (38/115) of respondents indicated that they do not personally offer advice regarding the couples match.
Areas With Diverse Opinions
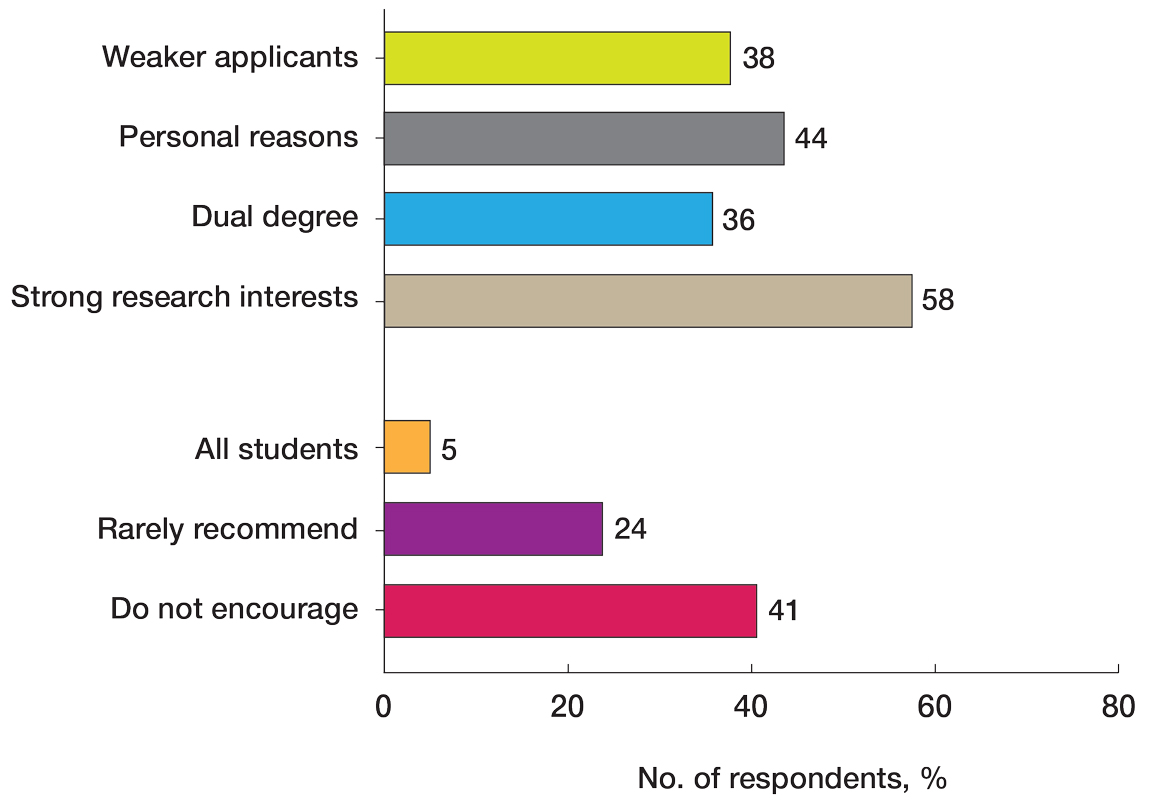
Gap Years—Nearly one-quarter (24% [28/115]) of mentors reported that they rarely recommend students take a year off and only support those who are adamant about doing so, or that they never support taking a gap year at all. A slight majority (58% [67/115]) recommend a gap year for students strongly interested in dermatologic research, and 38% (44/115) recommend a gap year for students with weaker applications (Figure 1). We received many open-ended responses to this question, with mentors frequently indicating that they advise students to take a gap year on a case-by-case basis, with 44% (51/115) of commenters recommending that students only take paid gap-year research positions.
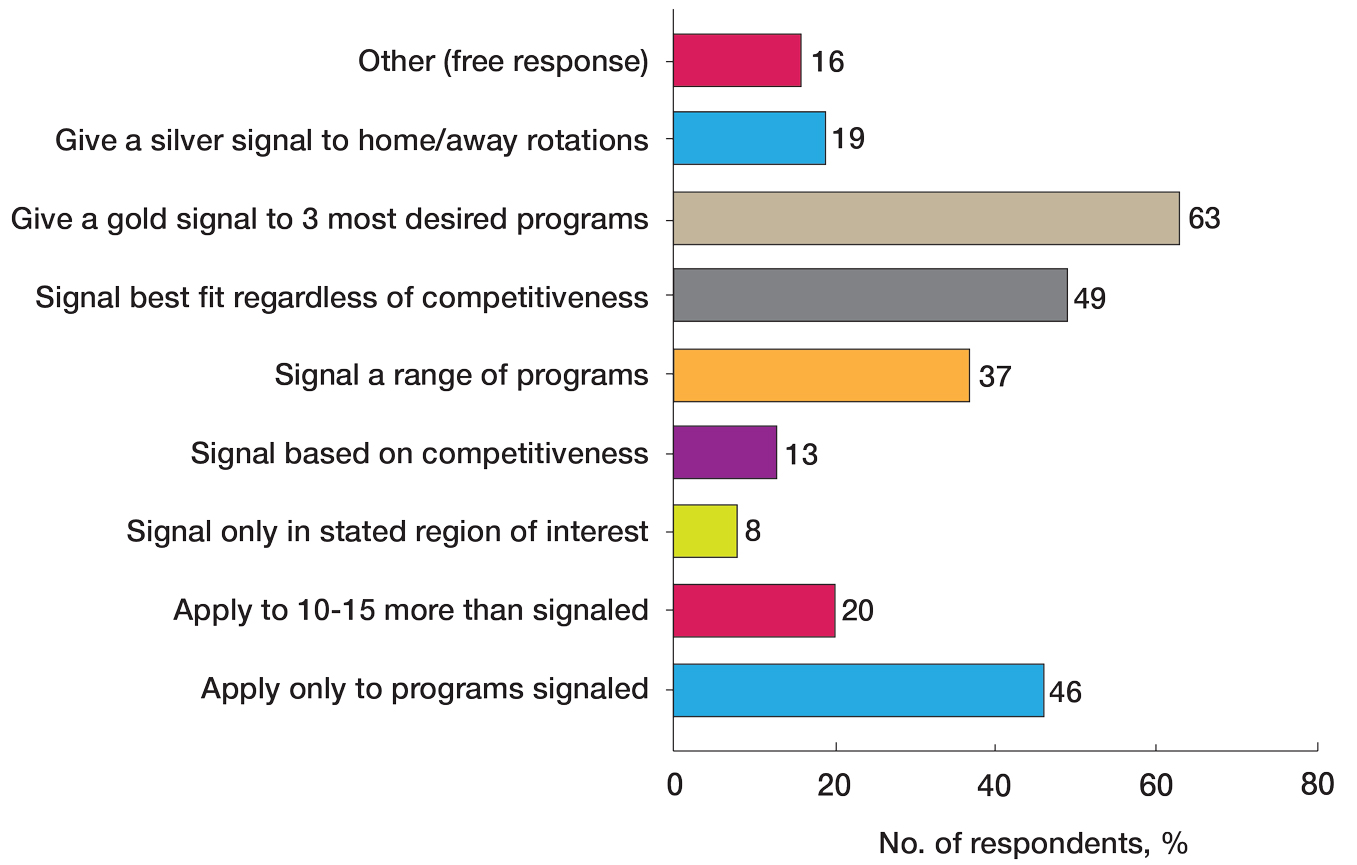
Program Signaling—The dermatology residency application process implemented a system of preference signaling tokens (PSTs) starting with the 2021-2022 cycle. Not quite half (46% [53/115]) of respondents recommend students apply only to places that they signaled, while 20% (23/115) advise responding to 10 to 15 additional programs. Very few (8% [9/115]) advise students to signal only in their stated region of interest. Approximately half (49% [56/115]) of mentors recommend students only signal based on the programs they feel would be the best fit for them without regard for perceived competitiveness—which aligns with the APD Residency Program Directors Section’s recommendation4—while 37% (43/115) recommend students distribute their signals to a wide range of programs. Sixty-three percent (72/115) of respondents recommend gold signaling to the student’s 3 most desired programs regardless of home and away rotation considerations, while 19% (22/115) recommend students give silver signals to their home and away rotation programs, as a rotation is already a signal of a strong desire to be there (Figure 2).
Dual Application—Fifty-three percent (61/115) of mentors recommended dual applying only for those truly interested in multiple specialties. Eighteen percent (21/115) of respondents advised dual applying for those with less than a 75% chance of matching. Twenty-five percent (29/115) of respondents free-wrote comments about approaching dual applying on a case-by-case basis, with many discussing the downsides of dual application and raising concerns that dual applications can hinder applicants’ success, can seem disingenuous, and seem to be a tool used to improve medical school match rates without benefit for the student.
We also stratified the data to compare overall responses from the total cohort with those from only program and assistant program directors. Across the 14 questions, responses from program and assistant program directors alone were similar to the overall cohort results
Comment
This study evaluated nationwide data on mentorship advising in dermatology, detailing mentors’ advice regarding research, gap years, dual applications, away rotations, intern year, couples matching, program signaling, and volunteering during medical school. Based on our results, most respondents agree on the importance of research during medical school, the utility of away rotations, and the value of volunteering during medical school. Similarly, respondents agreed on the importance of having strong letters of recommendation; while some advised asking only dermatology faculty to write letters, others did not have a specialty preference for the letter writers. Respondents also had varying views about sharing interest in subspecialties during residency interviews. Many of the respondents do not provide recommendations regarding geographic signaling and couples matching, expressing that these are parts of an application that are important to approach on a case-by-case basis. Lastly, respondents had diverse opinions regarding the utility of gap years, whether to encourage or discourage dual applications, and how to advise regarding program signaling.
Our results also showed that one-third of respondents believed that research is not as important as it is perceived to be by dermatology applicants. While engaging in research during medical school was almost unanimously encouraged to foster mentor-mentee relationships, respondents expressed that the number of research experiences and publications was not critical. This is an important topic of discussion, as taking a dedicated year away from medical school to complete a research fellowship is becoming a trend among dermatology applicants.5 There has been discussion both on unofficial online platforms as well as in the published literature regarding the pressure for medical students interested in dermatology to publish, which may result in a gap year for research.6 The literature on the utility of a gap year in match rates is sparse, with one study showing no difference in match rates among Mayo Clinic dermatology residents who took research years vs those who did not.7 However, this contrasts with match rates at top dermatology residency programs where 41% of applicants who took a gap year matched vs 19% who did not.7,8 These conflicting data are reflected in our study results, with respondents expressing different opinions on the utility of gap years.
There also are important equity concerns regarding the role of research years in the dermatology residency match process. Dermatology is one of the least racially diverse specialties, although there have been efforts to increase representation among residents and attending physicians.9-11 Research years can be important contributors to this lack of representation, as these often are unpaid and can discourage economically disadvantaged students from applying.9-11 Additionally, applicants may not have the flexibility to defer future salary for a year to match into dermatology; therefore, mentors should offer multiple options to individual applicants instead of solely encouraging gap years, given the conflicting feelings regarding their productivity.
Another topic of disagreement was dual application. Approximately one-third of respondents said they encourage either all students or those with less than a 75% chance of matching to dual apply, while about half only encourage students who are truly interested in multiple specialties to do so. Additionally, a large subset of respondents said they do not encourage dual applications due to concerns that they make applicants a worse candidate for each specialty and overall have negative effects on matching. Twenty-five percent of respondents opted to leave an open-ended response to this question: some offered the perspective that, if applicants feel a need to dual apply due to a weaker application, they do not advise the applicant to apply to dermatology. Many open ended responses underscored that the respondent does not encourage dual applications because they are inherently more time consuming, could hinder the applicant’s success, can seem disingenuous, and are a tool used to improve medical school match rates without being beneficial for the student. Some respondents also favored reapplying to dermatology the following year instead of dual applying. Finally, a subset of mentors indicated that they approach dual applications on a case-by-case basis, and others reported they do not have much experience advising on this topic. Currently, there are no known data in the literature on the efficacy and utility of dual applications in the dermatology match process; therefore, our study provides valuable insight for applicants interested in the impacts of the dual application. Overall, students should approach this option with mentors on an individual basis but ultimately should be aware of the concerns and mixed perceptions of the dual application process.
With regard to program signaling, previous research has shown that PSTs have a large impact on the chance of being granted an interview.12 In our study, we provide a comprehensive overview of advising regarding these signals. While mentors often responded that they did not have much experience advising in this domain—and it is too soon to tell the impact of this program signaling—many offered differing opinions. Many said they recommend that students give a gold signal to their 3 most desired programs regardless of home and away rotations and perceived competitiveness, which follows the guidelines issued by the APD; however, 19% recommend only giving silver signals to home and away rotation programs, as participation in those programs is considered a sufficient signal of interest. Additionally, about half of mentors recommended that students only apply where they signal, whereas 20% recommended applying to 10 to 15 programs beyond those signaled. Future studies should investigate the impact of PSTs on interview invitations once sufficient application cycles have occurred.
Study Limitations
This study was conducted via email to the APD listserve. The total number of faculty on this listserve is unknown; therefore, we do not know the total response rate of the survey. Additionally, we surveyed mentors in this listserve, who therefore receive more emails and overall correspondence about the dermatology match and may be more involved in these conversations. The mentors who responded to our survey may have a different approach and response to our various survey questions than a given mentor across the United States who did not respond to this survey. A final limitation of our study is that the survey responses a mentor gives may not fully match the advice that they give their students privately.
Conclusion
Our survey of dermatology mentors across the United States provides valuable insight into how mentors advise for a strong dermatology residency application. Mentors agreed on the importance of research during medical school, away rotations, strong letters of recommendation, and volunteerism and advocacy to promote a strong residency application. Important topics of disagreement include the decision for dermatology applicants to take a dedicated gap year in medical school, how to use tokens/signals effectively, and the dual application process. Our findings also underscore important application components that applicants and mentors should approach on an individual basis. Future studies should investigate the impact of signals/tokens on the match process as well as the utility of gap years and dual applications, working to standardize the advice applicants receive.
- Ramachandran V, Nguyen HY, Dao H Jr. Does it match? analyzing self-reported online dermatology match data to charting outcomes in the match. Dermatol Online J. 2020;26:13030 /qt4604h1w4.
- Kolli SS, Feldman SR, Huang WW. The dermatology residency application process. Dermatol Online J. 2021;26:13030/qt4k1570vj.
- Stratman EJ, Ness RM. Factors associated with successful matching to dermatology residency programs by reapplicants and other applicants who previously graduated from medical school. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:196-202. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2010.303
- Association of Professors of Dermatology Residency Program Directors Section Information Regarding the 2023-2024 Application Cycle. Published 2023. Accessed June 1, 2024. https://students-residents.aamc.org/media/12386/download
- Alikhan A, Sivamani RK, Mutizwa MM, et al. Advice for medical students interested in dermatology: perspectives from fourth year students who matched. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:4.
- Wang JV, Keller M. Pressure to publish for residency applicants in dermatology. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt56x1t7ww.
- Costello CM, Harvey JA, Besch-Stokes JG, et al. The role research gap years play in a successful dermatology match. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:226-230. doi:10.1111/ijd.15964
- Yeh C, Desai AD, Wassef C, et al. The importance of mentorship during research gap years for the dermatology residency match. Int J Dermatol. 2023;62:E209-E210. doi:10.1111/ijd.16084
- Zheng DX, Gallo Marin B, Mulligan KM, et al. Inequity concerns surrounding research years and the dermatology residency match. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:E247-E248. doi:10.1111/ijd.16179
- Vasquez R, Jeong H, Florez-Pollack S, et al. What are the barriers faced by under-represented minorities applying to dermatology? a qualitative cross-sectional study of applicants applying to a large dermatology residency program. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1770-1773. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.067
- Jones VA, Clark KA, Cordova A, et al. Challenging the status quo: increasing diversity in dermatology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:E421. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.185
- Dirr MA, Brownstone N, Zakria D, et al. Dermatology match preference signaling tokens: impact and implications. Dermatol Surg. 2022;48:1367-1368. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003645
While strong relationships with mentors and advisers are critical to navigating the competitive dermatology match process, the advice medical students receive from different individuals can be contradictory. Unaccredited information online—particularly on social media—as well as data reported by applicants can add to potential confusion.1 Published research has elicited comments and observations from successfully matched medical students about highly discussed topics such as presentations and publications, letters of recommendation, away rotations, and interviews.2,3 However, there currently are no published data about advice that dermatology mentors actually offer medical students. In this study, we aimed to investigate this gap in the current literature and examine the advice dermatology faculty, program directors, and other mentors at institutions accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education across the United States give to medical students applying to dermatology residency.
Methods
A 14-question Johns Hopkins Qualtrics survey was sent via the Association of Professors of Dermatology (APD) listserve in June 2024 soliciting responses from members who consider themselves to be mentors to dermatology applicants across the United States. The survey included multiple-choice questions with the option to select multiple answers and a space for open-ended responses. The questions first gathered information on the respondents, including the capacity in which the mentors advised medical students (eg, program director, department chair, clinical faculty). Mentors were asked for the number of years they had been advising mentees and if they were advising students with a home dermatology program. In addition, mentors were asked what advice they give their mentees about aspects of the application process, including gap years, dual applications, research involvement, couples matching, program signaling, away rotations, internship year, letters of recommendation, geographic signaling, interviewing advice, and volunteering during medical school.
On August 18, 2024, survey results from 115 respondents were aggregated. The responses for each question were quantitatively assessed to determine whether there was consensus on specific advice offered. The open-ended responses also were qualitatively assessed to determine the most common responses.
Results
The respondents included program directors (30% [35/115]), clinical faculty (22% [25/115]), department chairs (18% [21/115]), assistant program directors (15% [17/115]), medical school clerkship directors (8% [9/115]), primary mentors (ie, faculty who did not fall into any of the aforementioned categories but still advised medical students interested in dermatology)(5% [6/115]), division chiefs (1% [1/115]), and deans (1% [1/115]). Respondents had been advising students for a median of 10 years (range, 1-40 years [25th percentile, 5.00 years; 75th percentile, 13.75 years]). The majority (90% [103/115]) of mentors surveyed were advising students with a home dermatology program.
Areas of Consensus
In some areas, there was broad consensus among the advice offered by the mentors that were surveyed (eTable).


Research During Medical School—More than 91% (105/115) of the respondents recommended research to encourage academic growth and indicated that the most important reason for conducting research during medical school is to foster mentor-mentee relationships; however, more than one-third of respondents believed research is overvalued by students and research productivity is not as critical for matching as they perceive it to be. When these responses were categorized by respondent positions, 29% (15/52) of program or assistant directors indicated agreement with the statement that research is overvalued.
Away Rotations—There also was a consensus about the importance of away rotations, with 85% (98/115) of respondents advising students to complete 1 to 2 away rotations at sites of high interest, and 13% (15/115) suggesting that students complete as many away rotations as possible. It is worth noting, however, that the official APD Residency Program Directors Section’s statement on away rotations recommends no more than 2 away rotations (or no more than 3 for students with no home program).4
Reapplication Advice—Additionally, in a situation where students do not match into a dermatology residency program, the vast majority (71% [82/115]) of respondents advised students to rank competitive intern years to foster connections and improve the chance of matching on the second attempt.
Volunteering During Medical School—Seventy-seven percent (89/115) of mentors encouraged students to engage in volunteerism and advocacy during medical school to create a well-rounded application, and 69% (79/115) of mentors encouraged students to display leadership in their volunteer efforts.
Areas Without Consensus
Letters of Recommendation—Most respondents recommended submitting letters of recommendation only from dermatology professionals (55% [63/115]), with the remainder recommending students request a letter from anyone who could provide a strong recommendation regardless of specialty mix (42% [48/115]).
Dermatologic Subspecialties—For students interested in dermatologic subspecialties, 73% (84/115) of mentors advised that students be honest during interviews but keep an open mind that interests during residencies may change. Forty-three percent (49/115) of respondents encouraged students to promote a subspecialty interest during their interview only if they can demonstrate effort within that subspecialty on their application.
Couples Matching—Most respondents approach couples matching on a case-by-case basis and assess individual priorities when they do advise on this topic. Respondents often advise applicants to identify a few cities/regions and focus strongly on the programs within those regions to avoid spreading themselves too thin; however, one-third (38/115) of respondents indicated that they do not personally offer advice regarding the couples match.
Areas With Diverse Opinions
Gap Years—Nearly one-quarter (24% [28/115]) of mentors reported that they rarely recommend students take a year off and only support those who are adamant about doing so, or that they never support taking a gap year at all. A slight majority (58% [67/115]) recommend a gap year for students strongly interested in dermatologic research, and 38% (44/115) recommend a gap year for students with weaker applications (Figure 1). We received many open-ended responses to this question, with mentors frequently indicating that they advise students to take a gap year on a case-by-case basis, with 44% (51/115) of commenters recommending that students only take paid gap-year research positions.

Program Signaling—The dermatology residency application process implemented a system of preference signaling tokens (PSTs) starting with the 2021-2022 cycle. Not quite half (46% [53/115]) of respondents recommend students apply only to places that they signaled, while 20% (23/115) advise responding to 10 to 15 additional programs. Very few (8% [9/115]) advise students to signal only in their stated region of interest. Approximately half (49% [56/115]) of mentors recommend students only signal based on the programs they feel would be the best fit for them without regard for perceived competitiveness—which aligns with the APD Residency Program Directors Section’s recommendation4—while 37% (43/115) recommend students distribute their signals to a wide range of programs. Sixty-three percent (72/115) of respondents recommend gold signaling to the student’s 3 most desired programs regardless of home and away rotation considerations, while 19% (22/115) recommend students give silver signals to their home and away rotation programs, as a rotation is already a signal of a strong desire to be there (Figure 2).

Dual Application—Fifty-three percent (61/115) of mentors recommended dual applying only for those truly interested in multiple specialties. Eighteen percent (21/115) of respondents advised dual applying for those with less than a 75% chance of matching. Twenty-five percent (29/115) of respondents free-wrote comments about approaching dual applying on a case-by-case basis, with many discussing the downsides of dual application and raising concerns that dual applications can hinder applicants’ success, can seem disingenuous, and seem to be a tool used to improve medical school match rates without benefit for the student.
We also stratified the data to compare overall responses from the total cohort with those from only program and assistant program directors. Across the 14 questions, responses from program and assistant program directors alone were similar to the overall cohort results
Comment
This study evaluated nationwide data on mentorship advising in dermatology, detailing mentors’ advice regarding research, gap years, dual applications, away rotations, intern year, couples matching, program signaling, and volunteering during medical school. Based on our results, most respondents agree on the importance of research during medical school, the utility of away rotations, and the value of volunteering during medical school. Similarly, respondents agreed on the importance of having strong letters of recommendation; while some advised asking only dermatology faculty to write letters, others did not have a specialty preference for the letter writers. Respondents also had varying views about sharing interest in subspecialties during residency interviews. Many of the respondents do not provide recommendations regarding geographic signaling and couples matching, expressing that these are parts of an application that are important to approach on a case-by-case basis. Lastly, respondents had diverse opinions regarding the utility of gap years, whether to encourage or discourage dual applications, and how to advise regarding program signaling.
Our results also showed that one-third of respondents believed that research is not as important as it is perceived to be by dermatology applicants. While engaging in research during medical school was almost unanimously encouraged to foster mentor-mentee relationships, respondents expressed that the number of research experiences and publications was not critical. This is an important topic of discussion, as taking a dedicated year away from medical school to complete a research fellowship is becoming a trend among dermatology applicants.5 There has been discussion both on unofficial online platforms as well as in the published literature regarding the pressure for medical students interested in dermatology to publish, which may result in a gap year for research.6 The literature on the utility of a gap year in match rates is sparse, with one study showing no difference in match rates among Mayo Clinic dermatology residents who took research years vs those who did not.7 However, this contrasts with match rates at top dermatology residency programs where 41% of applicants who took a gap year matched vs 19% who did not.7,8 These conflicting data are reflected in our study results, with respondents expressing different opinions on the utility of gap years.
There also are important equity concerns regarding the role of research years in the dermatology residency match process. Dermatology is one of the least racially diverse specialties, although there have been efforts to increase representation among residents and attending physicians.9-11 Research years can be important contributors to this lack of representation, as these often are unpaid and can discourage economically disadvantaged students from applying.9-11 Additionally, applicants may not have the flexibility to defer future salary for a year to match into dermatology; therefore, mentors should offer multiple options to individual applicants instead of solely encouraging gap years, given the conflicting feelings regarding their productivity.
Another topic of disagreement was dual application. Approximately one-third of respondents said they encourage either all students or those with less than a 75% chance of matching to dual apply, while about half only encourage students who are truly interested in multiple specialties to do so. Additionally, a large subset of respondents said they do not encourage dual applications due to concerns that they make applicants a worse candidate for each specialty and overall have negative effects on matching. Twenty-five percent of respondents opted to leave an open-ended response to this question: some offered the perspective that, if applicants feel a need to dual apply due to a weaker application, they do not advise the applicant to apply to dermatology. Many open ended responses underscored that the respondent does not encourage dual applications because they are inherently more time consuming, could hinder the applicant’s success, can seem disingenuous, and are a tool used to improve medical school match rates without being beneficial for the student. Some respondents also favored reapplying to dermatology the following year instead of dual applying. Finally, a subset of mentors indicated that they approach dual applications on a case-by-case basis, and others reported they do not have much experience advising on this topic. Currently, there are no known data in the literature on the efficacy and utility of dual applications in the dermatology match process; therefore, our study provides valuable insight for applicants interested in the impacts of the dual application. Overall, students should approach this option with mentors on an individual basis but ultimately should be aware of the concerns and mixed perceptions of the dual application process.
With regard to program signaling, previous research has shown that PSTs have a large impact on the chance of being granted an interview.12 In our study, we provide a comprehensive overview of advising regarding these signals. While mentors often responded that they did not have much experience advising in this domain—and it is too soon to tell the impact of this program signaling—many offered differing opinions. Many said they recommend that students give a gold signal to their 3 most desired programs regardless of home and away rotations and perceived competitiveness, which follows the guidelines issued by the APD; however, 19% recommend only giving silver signals to home and away rotation programs, as participation in those programs is considered a sufficient signal of interest. Additionally, about half of mentors recommended that students only apply where they signal, whereas 20% recommended applying to 10 to 15 programs beyond those signaled. Future studies should investigate the impact of PSTs on interview invitations once sufficient application cycles have occurred.
Study Limitations
This study was conducted via email to the APD listserve. The total number of faculty on this listserve is unknown; therefore, we do not know the total response rate of the survey. Additionally, we surveyed mentors in this listserve, who therefore receive more emails and overall correspondence about the dermatology match and may be more involved in these conversations. The mentors who responded to our survey may have a different approach and response to our various survey questions than a given mentor across the United States who did not respond to this survey. A final limitation of our study is that the survey responses a mentor gives may not fully match the advice that they give their students privately.
Conclusion
Our survey of dermatology mentors across the United States provides valuable insight into how mentors advise for a strong dermatology residency application. Mentors agreed on the importance of research during medical school, away rotations, strong letters of recommendation, and volunteerism and advocacy to promote a strong residency application. Important topics of disagreement include the decision for dermatology applicants to take a dedicated gap year in medical school, how to use tokens/signals effectively, and the dual application process. Our findings also underscore important application components that applicants and mentors should approach on an individual basis. Future studies should investigate the impact of signals/tokens on the match process as well as the utility of gap years and dual applications, working to standardize the advice applicants receive.
While strong relationships with mentors and advisers are critical to navigating the competitive dermatology match process, the advice medical students receive from different individuals can be contradictory. Unaccredited information online—particularly on social media—as well as data reported by applicants can add to potential confusion.1 Published research has elicited comments and observations from successfully matched medical students about highly discussed topics such as presentations and publications, letters of recommendation, away rotations, and interviews.2,3 However, there currently are no published data about advice that dermatology mentors actually offer medical students. In this study, we aimed to investigate this gap in the current literature and examine the advice dermatology faculty, program directors, and other mentors at institutions accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education across the United States give to medical students applying to dermatology residency.
Methods
A 14-question Johns Hopkins Qualtrics survey was sent via the Association of Professors of Dermatology (APD) listserve in June 2024 soliciting responses from members who consider themselves to be mentors to dermatology applicants across the United States. The survey included multiple-choice questions with the option to select multiple answers and a space for open-ended responses. The questions first gathered information on the respondents, including the capacity in which the mentors advised medical students (eg, program director, department chair, clinical faculty). Mentors were asked for the number of years they had been advising mentees and if they were advising students with a home dermatology program. In addition, mentors were asked what advice they give their mentees about aspects of the application process, including gap years, dual applications, research involvement, couples matching, program signaling, away rotations, internship year, letters of recommendation, geographic signaling, interviewing advice, and volunteering during medical school.
On August 18, 2024, survey results from 115 respondents were aggregated. The responses for each question were quantitatively assessed to determine whether there was consensus on specific advice offered. The open-ended responses also were qualitatively assessed to determine the most common responses.
Results
The respondents included program directors (30% [35/115]), clinical faculty (22% [25/115]), department chairs (18% [21/115]), assistant program directors (15% [17/115]), medical school clerkship directors (8% [9/115]), primary mentors (ie, faculty who did not fall into any of the aforementioned categories but still advised medical students interested in dermatology)(5% [6/115]), division chiefs (1% [1/115]), and deans (1% [1/115]). Respondents had been advising students for a median of 10 years (range, 1-40 years [25th percentile, 5.00 years; 75th percentile, 13.75 years]). The majority (90% [103/115]) of mentors surveyed were advising students with a home dermatology program.
Areas of Consensus
In some areas, there was broad consensus among the advice offered by the mentors that were surveyed (eTable).


Research During Medical School—More than 91% (105/115) of the respondents recommended research to encourage academic growth and indicated that the most important reason for conducting research during medical school is to foster mentor-mentee relationships; however, more than one-third of respondents believed research is overvalued by students and research productivity is not as critical for matching as they perceive it to be. When these responses were categorized by respondent positions, 29% (15/52) of program or assistant directors indicated agreement with the statement that research is overvalued.
Away Rotations—There also was a consensus about the importance of away rotations, with 85% (98/115) of respondents advising students to complete 1 to 2 away rotations at sites of high interest, and 13% (15/115) suggesting that students complete as many away rotations as possible. It is worth noting, however, that the official APD Residency Program Directors Section’s statement on away rotations recommends no more than 2 away rotations (or no more than 3 for students with no home program).4
Reapplication Advice—Additionally, in a situation where students do not match into a dermatology residency program, the vast majority (71% [82/115]) of respondents advised students to rank competitive intern years to foster connections and improve the chance of matching on the second attempt.
Volunteering During Medical School—Seventy-seven percent (89/115) of mentors encouraged students to engage in volunteerism and advocacy during medical school to create a well-rounded application, and 69% (79/115) of mentors encouraged students to display leadership in their volunteer efforts.
Areas Without Consensus
Letters of Recommendation—Most respondents recommended submitting letters of recommendation only from dermatology professionals (55% [63/115]), with the remainder recommending students request a letter from anyone who could provide a strong recommendation regardless of specialty mix (42% [48/115]).
Dermatologic Subspecialties—For students interested in dermatologic subspecialties, 73% (84/115) of mentors advised that students be honest during interviews but keep an open mind that interests during residencies may change. Forty-three percent (49/115) of respondents encouraged students to promote a subspecialty interest during their interview only if they can demonstrate effort within that subspecialty on their application.
Couples Matching—Most respondents approach couples matching on a case-by-case basis and assess individual priorities when they do advise on this topic. Respondents often advise applicants to identify a few cities/regions and focus strongly on the programs within those regions to avoid spreading themselves too thin; however, one-third (38/115) of respondents indicated that they do not personally offer advice regarding the couples match.
Areas With Diverse Opinions
Gap Years—Nearly one-quarter (24% [28/115]) of mentors reported that they rarely recommend students take a year off and only support those who are adamant about doing so, or that they never support taking a gap year at all. A slight majority (58% [67/115]) recommend a gap year for students strongly interested in dermatologic research, and 38% (44/115) recommend a gap year for students with weaker applications (Figure 1). We received many open-ended responses to this question, with mentors frequently indicating that they advise students to take a gap year on a case-by-case basis, with 44% (51/115) of commenters recommending that students only take paid gap-year research positions.

Program Signaling—The dermatology residency application process implemented a system of preference signaling tokens (PSTs) starting with the 2021-2022 cycle. Not quite half (46% [53/115]) of respondents recommend students apply only to places that they signaled, while 20% (23/115) advise responding to 10 to 15 additional programs. Very few (8% [9/115]) advise students to signal only in their stated region of interest. Approximately half (49% [56/115]) of mentors recommend students only signal based on the programs they feel would be the best fit for them without regard for perceived competitiveness—which aligns with the APD Residency Program Directors Section’s recommendation4—while 37% (43/115) recommend students distribute their signals to a wide range of programs. Sixty-three percent (72/115) of respondents recommend gold signaling to the student’s 3 most desired programs regardless of home and away rotation considerations, while 19% (22/115) recommend students give silver signals to their home and away rotation programs, as a rotation is already a signal of a strong desire to be there (Figure 2).

Dual Application—Fifty-three percent (61/115) of mentors recommended dual applying only for those truly interested in multiple specialties. Eighteen percent (21/115) of respondents advised dual applying for those with less than a 75% chance of matching. Twenty-five percent (29/115) of respondents free-wrote comments about approaching dual applying on a case-by-case basis, with many discussing the downsides of dual application and raising concerns that dual applications can hinder applicants’ success, can seem disingenuous, and seem to be a tool used to improve medical school match rates without benefit for the student.
We also stratified the data to compare overall responses from the total cohort with those from only program and assistant program directors. Across the 14 questions, responses from program and assistant program directors alone were similar to the overall cohort results
Comment
This study evaluated nationwide data on mentorship advising in dermatology, detailing mentors’ advice regarding research, gap years, dual applications, away rotations, intern year, couples matching, program signaling, and volunteering during medical school. Based on our results, most respondents agree on the importance of research during medical school, the utility of away rotations, and the value of volunteering during medical school. Similarly, respondents agreed on the importance of having strong letters of recommendation; while some advised asking only dermatology faculty to write letters, others did not have a specialty preference for the letter writers. Respondents also had varying views about sharing interest in subspecialties during residency interviews. Many of the respondents do not provide recommendations regarding geographic signaling and couples matching, expressing that these are parts of an application that are important to approach on a case-by-case basis. Lastly, respondents had diverse opinions regarding the utility of gap years, whether to encourage or discourage dual applications, and how to advise regarding program signaling.
Our results also showed that one-third of respondents believed that research is not as important as it is perceived to be by dermatology applicants. While engaging in research during medical school was almost unanimously encouraged to foster mentor-mentee relationships, respondents expressed that the number of research experiences and publications was not critical. This is an important topic of discussion, as taking a dedicated year away from medical school to complete a research fellowship is becoming a trend among dermatology applicants.5 There has been discussion both on unofficial online platforms as well as in the published literature regarding the pressure for medical students interested in dermatology to publish, which may result in a gap year for research.6 The literature on the utility of a gap year in match rates is sparse, with one study showing no difference in match rates among Mayo Clinic dermatology residents who took research years vs those who did not.7 However, this contrasts with match rates at top dermatology residency programs where 41% of applicants who took a gap year matched vs 19% who did not.7,8 These conflicting data are reflected in our study results, with respondents expressing different opinions on the utility of gap years.
There also are important equity concerns regarding the role of research years in the dermatology residency match process. Dermatology is one of the least racially diverse specialties, although there have been efforts to increase representation among residents and attending physicians.9-11 Research years can be important contributors to this lack of representation, as these often are unpaid and can discourage economically disadvantaged students from applying.9-11 Additionally, applicants may not have the flexibility to defer future salary for a year to match into dermatology; therefore, mentors should offer multiple options to individual applicants instead of solely encouraging gap years, given the conflicting feelings regarding their productivity.
Another topic of disagreement was dual application. Approximately one-third of respondents said they encourage either all students or those with less than a 75% chance of matching to dual apply, while about half only encourage students who are truly interested in multiple specialties to do so. Additionally, a large subset of respondents said they do not encourage dual applications due to concerns that they make applicants a worse candidate for each specialty and overall have negative effects on matching. Twenty-five percent of respondents opted to leave an open-ended response to this question: some offered the perspective that, if applicants feel a need to dual apply due to a weaker application, they do not advise the applicant to apply to dermatology. Many open ended responses underscored that the respondent does not encourage dual applications because they are inherently more time consuming, could hinder the applicant’s success, can seem disingenuous, and are a tool used to improve medical school match rates without being beneficial for the student. Some respondents also favored reapplying to dermatology the following year instead of dual applying. Finally, a subset of mentors indicated that they approach dual applications on a case-by-case basis, and others reported they do not have much experience advising on this topic. Currently, there are no known data in the literature on the efficacy and utility of dual applications in the dermatology match process; therefore, our study provides valuable insight for applicants interested in the impacts of the dual application. Overall, students should approach this option with mentors on an individual basis but ultimately should be aware of the concerns and mixed perceptions of the dual application process.
With regard to program signaling, previous research has shown that PSTs have a large impact on the chance of being granted an interview.12 In our study, we provide a comprehensive overview of advising regarding these signals. While mentors often responded that they did not have much experience advising in this domain—and it is too soon to tell the impact of this program signaling—many offered differing opinions. Many said they recommend that students give a gold signal to their 3 most desired programs regardless of home and away rotations and perceived competitiveness, which follows the guidelines issued by the APD; however, 19% recommend only giving silver signals to home and away rotation programs, as participation in those programs is considered a sufficient signal of interest. Additionally, about half of mentors recommended that students only apply where they signal, whereas 20% recommended applying to 10 to 15 programs beyond those signaled. Future studies should investigate the impact of PSTs on interview invitations once sufficient application cycles have occurred.
Study Limitations
This study was conducted via email to the APD listserve. The total number of faculty on this listserve is unknown; therefore, we do not know the total response rate of the survey. Additionally, we surveyed mentors in this listserve, who therefore receive more emails and overall correspondence about the dermatology match and may be more involved in these conversations. The mentors who responded to our survey may have a different approach and response to our various survey questions than a given mentor across the United States who did not respond to this survey. A final limitation of our study is that the survey responses a mentor gives may not fully match the advice that they give their students privately.
Conclusion
Our survey of dermatology mentors across the United States provides valuable insight into how mentors advise for a strong dermatology residency application. Mentors agreed on the importance of research during medical school, away rotations, strong letters of recommendation, and volunteerism and advocacy to promote a strong residency application. Important topics of disagreement include the decision for dermatology applicants to take a dedicated gap year in medical school, how to use tokens/signals effectively, and the dual application process. Our findings also underscore important application components that applicants and mentors should approach on an individual basis. Future studies should investigate the impact of signals/tokens on the match process as well as the utility of gap years and dual applications, working to standardize the advice applicants receive.
- Ramachandran V, Nguyen HY, Dao H Jr. Does it match? analyzing self-reported online dermatology match data to charting outcomes in the match. Dermatol Online J. 2020;26:13030 /qt4604h1w4.
- Kolli SS, Feldman SR, Huang WW. The dermatology residency application process. Dermatol Online J. 2021;26:13030/qt4k1570vj.
- Stratman EJ, Ness RM. Factors associated with successful matching to dermatology residency programs by reapplicants and other applicants who previously graduated from medical school. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:196-202. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2010.303
- Association of Professors of Dermatology Residency Program Directors Section Information Regarding the 2023-2024 Application Cycle. Published 2023. Accessed June 1, 2024. https://students-residents.aamc.org/media/12386/download
- Alikhan A, Sivamani RK, Mutizwa MM, et al. Advice for medical students interested in dermatology: perspectives from fourth year students who matched. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:4.
- Wang JV, Keller M. Pressure to publish for residency applicants in dermatology. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt56x1t7ww.
- Costello CM, Harvey JA, Besch-Stokes JG, et al. The role research gap years play in a successful dermatology match. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:226-230. doi:10.1111/ijd.15964
- Yeh C, Desai AD, Wassef C, et al. The importance of mentorship during research gap years for the dermatology residency match. Int J Dermatol. 2023;62:E209-E210. doi:10.1111/ijd.16084
- Zheng DX, Gallo Marin B, Mulligan KM, et al. Inequity concerns surrounding research years and the dermatology residency match. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:E247-E248. doi:10.1111/ijd.16179
- Vasquez R, Jeong H, Florez-Pollack S, et al. What are the barriers faced by under-represented minorities applying to dermatology? a qualitative cross-sectional study of applicants applying to a large dermatology residency program. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1770-1773. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.067
- Jones VA, Clark KA, Cordova A, et al. Challenging the status quo: increasing diversity in dermatology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:E421. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.185
- Dirr MA, Brownstone N, Zakria D, et al. Dermatology match preference signaling tokens: impact and implications. Dermatol Surg. 2022;48:1367-1368. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003645
- Ramachandran V, Nguyen HY, Dao H Jr. Does it match? analyzing self-reported online dermatology match data to charting outcomes in the match. Dermatol Online J. 2020;26:13030 /qt4604h1w4.
- Kolli SS, Feldman SR, Huang WW. The dermatology residency application process. Dermatol Online J. 2021;26:13030/qt4k1570vj.
- Stratman EJ, Ness RM. Factors associated with successful matching to dermatology residency programs by reapplicants and other applicants who previously graduated from medical school. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:196-202. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2010.303
- Association of Professors of Dermatology Residency Program Directors Section Information Regarding the 2023-2024 Application Cycle. Published 2023. Accessed June 1, 2024. https://students-residents.aamc.org/media/12386/download
- Alikhan A, Sivamani RK, Mutizwa MM, et al. Advice for medical students interested in dermatology: perspectives from fourth year students who matched. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:4.
- Wang JV, Keller M. Pressure to publish for residency applicants in dermatology. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt56x1t7ww.
- Costello CM, Harvey JA, Besch-Stokes JG, et al. The role research gap years play in a successful dermatology match. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:226-230. doi:10.1111/ijd.15964
- Yeh C, Desai AD, Wassef C, et al. The importance of mentorship during research gap years for the dermatology residency match. Int J Dermatol. 2023;62:E209-E210. doi:10.1111/ijd.16084
- Zheng DX, Gallo Marin B, Mulligan KM, et al. Inequity concerns surrounding research years and the dermatology residency match. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:E247-E248. doi:10.1111/ijd.16179
- Vasquez R, Jeong H, Florez-Pollack S, et al. What are the barriers faced by under-represented minorities applying to dermatology? a qualitative cross-sectional study of applicants applying to a large dermatology residency program. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1770-1773. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.067
- Jones VA, Clark KA, Cordova A, et al. Challenging the status quo: increasing diversity in dermatology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:E421. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.185
- Dirr MA, Brownstone N, Zakria D, et al. Dermatology match preference signaling tokens: impact and implications. Dermatol Surg. 2022;48:1367-1368. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003645
A Nationwide Survey of Dermatology Faculty and Mentors on Their Advice for the Dermatology Match Process
A Nationwide Survey of Dermatology Faculty and Mentors on Their Advice for the Dermatology Match Process
PRACTICE POINTS
- Dermatology mentors should abide by Association of Professors of Dermatology guidelines when advising regarding signals and away rotations.
- Mentors agree with the utility of research during medical school, completing away rotations, and volunteering during medical school.
- There are differing opinions regarding the utility of a research year, program signaling, couples matching, and dual applying.
The Role of Inpatient Dermatology Consultations
Dermatology is an often-underutilized resource in the hospital setting. As the health care landscape has evolved, so has the role of the inpatient dermatologist.1-3 Structural changes in the health system and advances in therapies have shifted dermatology from an admitting service to an almost exclusively outpatient practice. Improved treatment modalities led to decreases in the number of patients requiring admission for chronic dermatoses, and outpatient clinics began offering therapies once limited to hospitals.1,4 Inpatient dermatology consultations emerged and continue to have profound effects on hospitalized patients regardless of their reason for admission.1-11
Inpatient dermatologists supply knowledge in areas primary medical teams lack, and there is evidence that dermatology consultations improve the quality of care while decreasing cost.2,5-7 Establishing correct diagnoses, preventing exposure to unnecessary medications, and reducing hospitalization duration and readmission rates are a few ways dermatology consultations positively impact hospitalized patients.2,5-7,9,10 This study highlights the role of the dermatologist in the care of hospitalized patients at a large academic medical center in an urban setting and reveals how consultation supports the efficiency and efficacy of other services.
Materials and Methods
Study Design—This single-institution, cross-sectional retrospective study included all hospitalized patients at the Thomas Jefferson University Hospital (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania), who received an inpatient dermatology consultation completed by physicians of Jefferson Dermatology Associates between January 1, 2019, and December 31, 2019. The institutional review board at Thomas Jefferson University approved this study.
Data Collection—A list of all inpatient dermatology consultations in 2019 was provided by Jefferson Dermatology Associates. Through a retrospective chart review, data regarding the consultations were collected from the electronic medical record (Epic Systems) and recorded into the Research Electronic Data Capture system. Data on patient demographics, the primary medical team, the dermatology evaluation, and the hospital course of the patient were collected.
Results
Patient Characteristics—Dermatology received 253 inpatient consultation requests during this time period; 53% of patients were female and 47% were male, with a mean age of 55 years. Most patients were White (57%), while 34% were Black. Five percent and 4% of patients were Asian and Hispanic or Latino, respectively (Table 1). The mean duration of hospitalization for all patients was 15 days, and the average number of days to discharge following the first encounter with dermatology was 10 days.
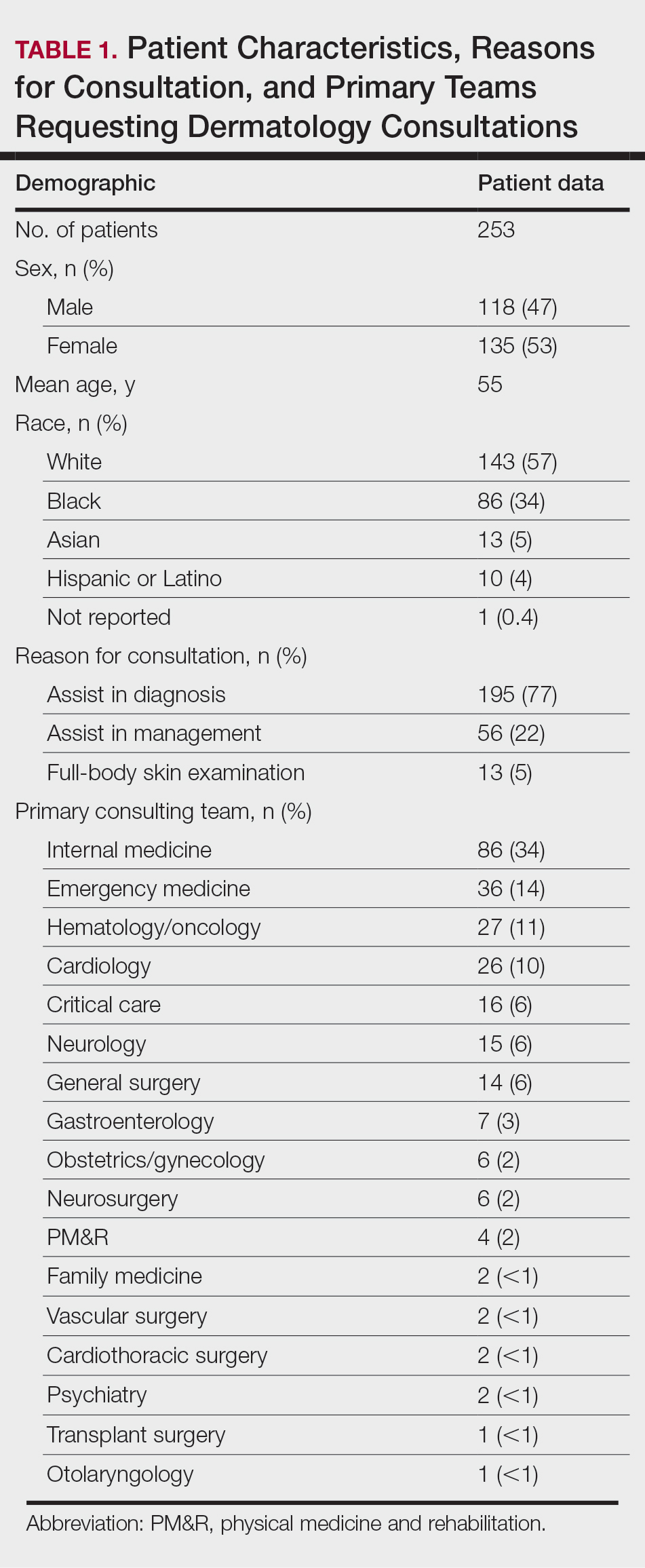
Requesting Team and Reason for Consultation—Internal medicine consulted dermatology most frequently (34% of all consultations), followed by emergency medicine (14%) and a variety of other services (Table 1). Most dermatology consultations were placed to assist in achieving a diagnosis of a cutaneous condition (77%), while a minority were to assist in the management of a previously diagnosed disease (22%). A small fraction of consultations (5%) were to complete full-body skin examinations (FBSEs) to rule out infection or malignancy in candidates for organ transplantation, left ventricular assist devices, or certain chemotherapies. One FBSE was conducted to search for a primary tumor in a patient diagnosed with metastatic melanoma.
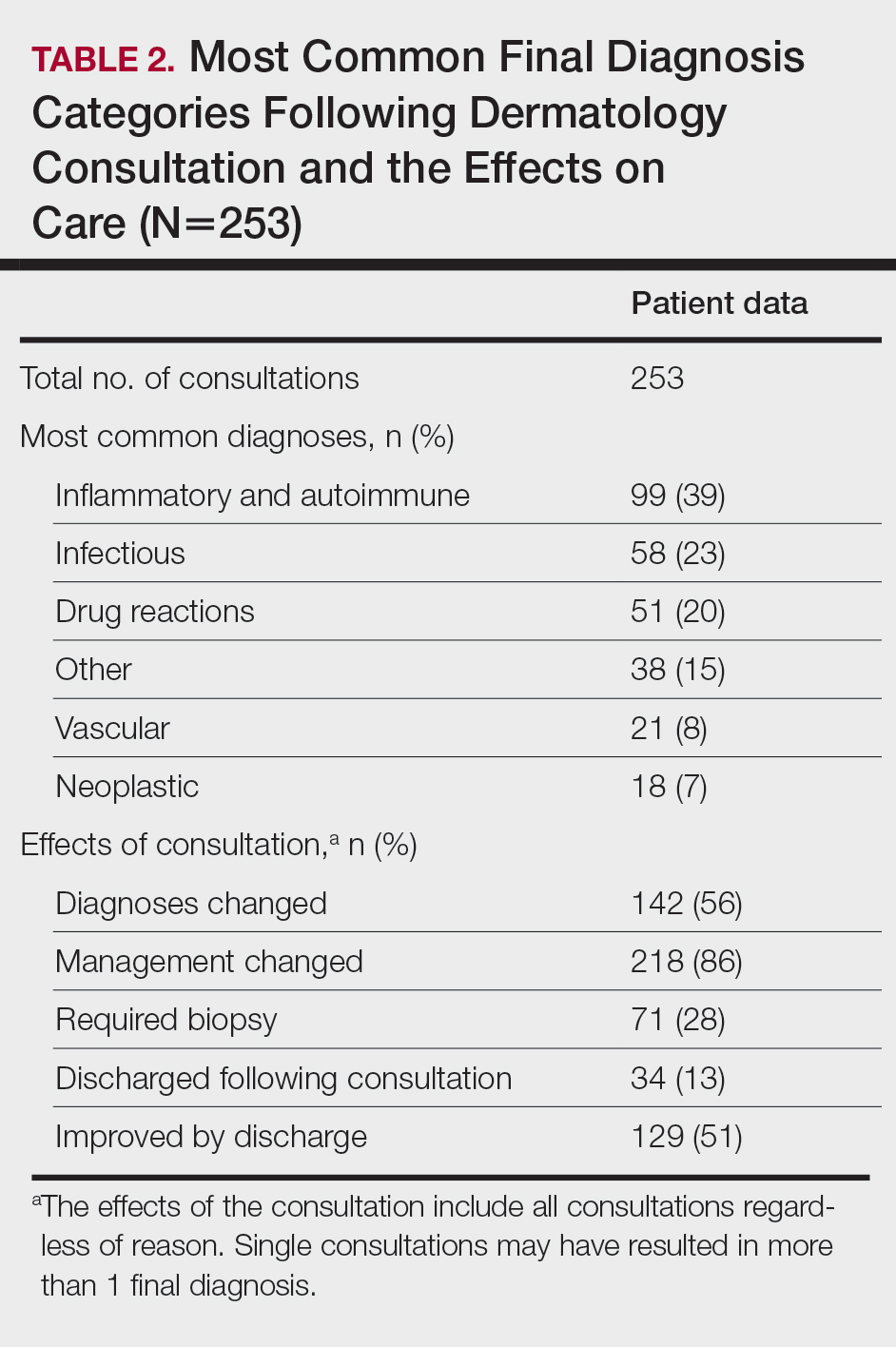
Most Common Final Diagnoses and Consultation Impact—Table 2 lists the most common final diagnosis categories, as well as the effects of the consultation on diagnosis, management, biopsies, hospitalization, and clinical improvement as documented by the primary medical provider. The most common final diagnoses were inflammatory and autoimmune (39%), such as contact dermatitis and seborrheic dermatitis; infectious (23%), such as varicella (primary or zoster) and bacterial furunculosis; drug reactions (20%), such as morbilliform drug eruptions; vascular (8%), such as vasculitis and calciphylaxis; neoplastic (7%), such as keratinocyte carcinomas and leukemia cutis; and other (15%), such as xerosis, keratosis pilaris, and miliaria rubra.
Impact on Diagnosis—Fifty-six percent of all consultations resulted in a change in diagnosis. When dermatology was consulted specifically to assist in the diagnosis of a patient (195 consultations), the working diagnosis of the primary team was changed 69% of the time. Thirty-five of these consultation requests had no preliminary diagnosis, and the primary team listed the working diagnosis as either rash or a morphologic description of the lesion(s). Sixty-three percent of suspected drug eruptions ended with a diagnosis of a form of drug eruption, while 20% of consultations for suspected cellulitis or bacterial infections were confirmed to be cellulitis or soft tissue infections.
Impact on Management—Regardless of the reason for the consultation, most consultations (86%) resulted in a change in management. The remaining 14% consisted of FBSEs with benign findings; cases of cutaneous metastases and leukemia cutis managed by oncology; as well as select cases of purpura fulminans, postfebrile desquamation, and postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Changes in management included alterations in medications, requests for additional laboratory work or imaging, additional consultation requests, biopsies, or specific wound care instructions. Seventy-five percent of all consultations were given specific medication recommendations by dermatology. Most (61%) were recommended to be given a topical steroid, antibiotic, or both. However, 45% of all consultations were recommended to initiate a systemic medication, most commonly antihistamines, antibiotics, steroids, antivirals, or immunomodulators. Dermatology recommended discontinuing specific medications in 16% of all consultations, with antibiotics being the most frequent culprit (17 antibiotics discontinued), owing to drug eruptions or misdiagnosed infections. Vancomycin, piperacillin-tazobactam, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole were the most frequently discontinued antibiotics.
Dermatology was consulted for assistance in management of previously diagnosed cutaneous conditions 56 times (22% of all consultations), often regarding complicated cases of hidradenitis suppurativa (9 cases), pyoderma gangrenosum (5 cases), bullous pemphigoid (4 cases), or erythroderma (4 cases). Most of these cases required a single dermatology encounter to provide recommendations (71%), and 21% required 1 additional follow-up. Sixty-three percent of patients consulted for management assistance were noted to have improvement in their cutaneous condition by time of discharge, as documented by the primary provider in the medical record.
Twenty-eight percent of all consultations required at least 1 biopsy. Seventy-two percent of all biopsies were consistent with the dermatologist’s working diagnosis or highest-ranked differential diagnosis, and 16% of biopsy results were consistent with the second- or third-ranked diagnosis. The primary teams requested a biopsy 38 times to assist in diagnosis, as documented in the progress note or consultation request. Only 21 of these consultations (55% of requests) received at least 1 biopsy, as the remaining consultations did not require a biopsy to establish a diagnosis. The most common final diagnoses of consultations receiving biopsies included drug eruptions (5), leukemia cutis (4), vasculopathies (4), vasculitis (4), and calciphylaxis (3).
Impact on Hospitalization and Efficacy—Dermatology performed 217 consultations regarding patients already admitted to the hospital, and 92% remained hospitalized either due to comorbidities or complicated cutaneous conditions following the consultation. The remaining 8% were cleared for discharge. Dermatology received 36 consultation requests from emergency medicine physicians. Fifty-three percent of these patients were admitted, while the remaining 47% were discharged from the emergency department or its observation unit following evaluation.
Fifty-one percent of all consultations were noted to have improvement in their cutaneous condition by the time of discharge, as noted in the physical examination, progress note, or discharge summary of the primary team. Thirty percent of cases remained stable, where improvement was not noted in in the medical record. Most of these cases involved keratinocyte carcinomas scheduled for outpatient excision, benign melanocytic nevi found on FBSE, and benign etiologies that led to immediate discharge following consultation. Three percent of all consultations were noted to have worsened following consultation, including cases of calciphylaxis, vasculopathies, and purpura fulminans, as well as patients who elected for palliative care and hospice. The cutaneous condition by the time of discharge could not be determined from the medical record in 16% of all consultations.
Eighty-five percent of all consultations required a single encounter with dermatology. An additional 10% required a single follow-up with dermatology, while only 5% of patients required 3 or more encounters. Notably, these cases included patients with 1 or more severe cutaneous diseases, such as Sweet syndrome, calciphylaxis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis, and hidradenitis suppurativa.
Comment
Although dermatology often is viewed as an outpatient specialty, this study provides a glimpse into the ways inpatient dermatology consultations optimize the care of hospitalized patients. Most consultations involved assistance in diagnosing an unknown condition, but several regarded pre-existing skin disorders requiring management aid. As a variety of medical specialties requested consultations, dermatology was able to provide care to a diverse group of patients with conditions varying in complexity and severity. Several specialties benefited from niche dermatologic expertise: hematology and oncology frequently requested dermatology to assist in diagnosis and management of the toxic effects of chemotherapy, cutaneous metastasis, or suspected cutaneous infections in immunocompromised patients. Cardiology patients were frequently evaluated for potential malignancy or infection prior to heart transplantation and initiation of antirejection immunosuppressants. Dermatology was consulted to differentiate cutaneous manifestations of critical illness from underlying systemic disease in the intensive care unit, and patients presenting to the emergency department often were examined to determine if hospital admission was necessary, with 47% of these consultations resulting in a discharge following evaluation by a dermatologist.
Our results were consistent with prior studies1,5,6 that have reported frequent changes in final diagnosis following dermatology consultation, with 69% of working diagnoses changed in this study when consultation was requested for diagnostic assistance. When dermatology was consulted for diagnostic assistance, several of these cases lacked a preliminary differential diagnosis. Although the absence of a documented differential diagnosis may not necessarily reflect a lack of suspicion for a particular etiology, 86% of all consultations included a ranked differential or working diagnosis either in the consultation request or progress note prior to consultation. The final diagnoses of consultations without a preliminary diagnosis varied from the mild and localized to systemic and severe, further suggesting these cases reflected knowledge gaps of the primary medical team.
Integration of dermatology into the care of hospitalized patients could provide an opportunity for education of primary medical teams. With frequent consultation, primary medical teams may become more comfortable diagnosing and managing common cutaneous conditions specific to their specialty or extended hospitalizations.
Several consultations were requested to aid in management of cases of hidradenitis suppurativa, pyoderma gangrenosum, or bullous pemphigoid that either failed outpatient therapy or were complicated by superinfections. Despite the ranges in complexity, the majority of all consultations required a single encounter and led to improvement by the time of discharge, demonstrating the efficacy and efficiency of inpatient dermatologists.
Dermatology consultations often led to changes in management involving medications and additional workup. Changes in management also extended to specific wound care instructions provided by dermatology, as expected for cases of Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis, Sweet syndrome, hidradenitis suppurativa, and pyoderma gangrenosum. However, patients with the sequelae of extended hospitalizations, such as chronic wounds, pressure ulcers, and edema bullae, also benefited from this expertise.
When patients required a biopsy, the final diagnoses were consistent with the dermatologist’s number one differential diagnosis or top 3 differential diagnoses 72% and 88% of the time, respectively. Only 55% of cases where the primary team requested a biopsy ultimately required a biopsy, as many involved clinical diagnoses such as urticaria. Not only was dermatology accurate in their preliminary diagnoses, but they decreased cost and morbidity by avoiding unnecessary procedures.
This study provided additional evidence to support the integration of dermatology into the hospital setting for the benefit of patients, primary medical teams, and hospital systems. Dermatology offers high-value care through the efficient diagnosis and management of hospitalized patients, which contributes to decreased cost and improved outcomes.2,5-7,9,10 This study highlighted lesser-known areas of impact, such as the various specialty-specific services dermatology provides as well as the high rates of reported improvement following consultation. Future studies should continue to explore the field’s unique impact on hospitalized medicine as well as other avenues of care delivery, such as telemedicine, that may encourage dermatologists to participate in consultations and increase the volume of patients who may benefit from their care.
- Madigan LM, Fox LP. Where are we now with inpatient consultative dermatology?: assessing the value and evolution of this subspecialty over the past decade. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1804-1808. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.01.031
- Noe MH, Rosenbach M. Inpatient dermatologists—crucial for the management of skin diseases in hospitalized patients [editorial]. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:524-525. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.6195
- Strowd LC. Inpatient dermatology: a paradigm shift in the management of skin disease in the hospital. Br J Dermatol. 2019;180:966-967. doi:10.1111/bjd.17778
- Kirsner RS, Yang DG, Kerdel FA. The changing status of inpatient dermatology at American academic dermatology programs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40:755-757. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(99)70158-1
- Kroshinsky D, Cotliar J, Hughey LC, et al. Association of dermatology consultation with accuracy of cutaneous disorder diagnoses in hospitalized patients: a multicenter analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:477-480. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2015.5098
- Ko LN, Garza-Mayers AC, St John J, et al. Effect of dermatology consultation on outcomes for patients with presumed cellulitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:529-533. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.6196
- Li DG, Xia FD, Khosravi H, et al. Outcomes of early dermatology consultation for inpatients diagnosed with cellulitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:537-543. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.6197
- Milani-Nejad N, Zhang M, Kaffenberger BH. Association of dermatology consultations with patient care outcomes in hospitalized patients with inflammatory skin diseases. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:523-528. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.6130
- Imadojemu S, Rosenbach M. Dermatologists must take an active role in the diagnosis of cellulitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:134-135. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.4230
- Hughey LC. The impact dermatologists can have on misdiagnosis of cellulitis and overuse of antibiotics: closing the gap. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:1061-1062. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.1164
- Ko LN, Kroshinsky D. Dermatology hospitalists: a multicenter survey study characterizing the infrastructure of consultative dermatology in select American hospitals. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:553-558. doi:10.1111/ijd.13939
Dermatology is an often-underutilized resource in the hospital setting. As the health care landscape has evolved, so has the role of the inpatient dermatologist.1-3 Structural changes in the health system and advances in therapies have shifted dermatology from an admitting service to an almost exclusively outpatient practice. Improved treatment modalities led to decreases in the number of patients requiring admission for chronic dermatoses, and outpatient clinics began offering therapies once limited to hospitals.1,4 Inpatient dermatology consultations emerged and continue to have profound effects on hospitalized patients regardless of their reason for admission.1-11
Inpatient dermatologists supply knowledge in areas primary medical teams lack, and there is evidence that dermatology consultations improve the quality of care while decreasing cost.2,5-7 Establishing correct diagnoses, preventing exposure to unnecessary medications, and reducing hospitalization duration and readmission rates are a few ways dermatology consultations positively impact hospitalized patients.2,5-7,9,10 This study highlights the role of the dermatologist in the care of hospitalized patients at a large academic medical center in an urban setting and reveals how consultation supports the efficiency and efficacy of other services.
Materials and Methods
Study Design—This single-institution, cross-sectional retrospective study included all hospitalized patients at the Thomas Jefferson University Hospital (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania), who received an inpatient dermatology consultation completed by physicians of Jefferson Dermatology Associates between January 1, 2019, and December 31, 2019. The institutional review board at Thomas Jefferson University approved this study.
Data Collection—A list of all inpatient dermatology consultations in 2019 was provided by Jefferson Dermatology Associates. Through a retrospective chart review, data regarding the consultations were collected from the electronic medical record (Epic Systems) and recorded into the Research Electronic Data Capture system. Data on patient demographics, the primary medical team, the dermatology evaluation, and the hospital course of the patient were collected.
Results
Patient Characteristics—Dermatology received 253 inpatient consultation requests during this time period; 53% of patients were female and 47% were male, with a mean age of 55 years. Most patients were White (57%), while 34% were Black. Five percent and 4% of patients were Asian and Hispanic or Latino, respectively (Table 1). The mean duration of hospitalization for all patients was 15 days, and the average number of days to discharge following the first encounter with dermatology was 10 days.

Requesting Team and Reason for Consultation—Internal medicine consulted dermatology most frequently (34% of all consultations), followed by emergency medicine (14%) and a variety of other services (Table 1). Most dermatology consultations were placed to assist in achieving a diagnosis of a cutaneous condition (77%), while a minority were to assist in the management of a previously diagnosed disease (22%). A small fraction of consultations (5%) were to complete full-body skin examinations (FBSEs) to rule out infection or malignancy in candidates for organ transplantation, left ventricular assist devices, or certain chemotherapies. One FBSE was conducted to search for a primary tumor in a patient diagnosed with metastatic melanoma.
Most Common Final Diagnoses and Consultation Impact—Table 2 lists the most common final diagnosis categories, as well as the effects of the consultation on diagnosis, management, biopsies, hospitalization, and clinical improvement as documented by the primary medical provider. The most common final diagnoses were inflammatory and autoimmune (39%), such as contact dermatitis and seborrheic dermatitis; infectious (23%), such as varicella (primary or zoster) and bacterial furunculosis; drug reactions (20%), such as morbilliform drug eruptions; vascular (8%), such as vasculitis and calciphylaxis; neoplastic (7%), such as keratinocyte carcinomas and leukemia cutis; and other (15%), such as xerosis, keratosis pilaris, and miliaria rubra.

Impact on Diagnosis—Fifty-six percent of all consultations resulted in a change in diagnosis. When dermatology was consulted specifically to assist in the diagnosis of a patient (195 consultations), the working diagnosis of the primary team was changed 69% of the time. Thirty-five of these consultation requests had no preliminary diagnosis, and the primary team listed the working diagnosis as either rash or a morphologic description of the lesion(s). Sixty-three percent of suspected drug eruptions ended with a diagnosis of a form of drug eruption, while 20% of consultations for suspected cellulitis or bacterial infections were confirmed to be cellulitis or soft tissue infections.
Impact on Management—Regardless of the reason for the consultation, most consultations (86%) resulted in a change in management. The remaining 14% consisted of FBSEs with benign findings; cases of cutaneous metastases and leukemia cutis managed by oncology; as well as select cases of purpura fulminans, postfebrile desquamation, and postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Changes in management included alterations in medications, requests for additional laboratory work or imaging, additional consultation requests, biopsies, or specific wound care instructions. Seventy-five percent of all consultations were given specific medication recommendations by dermatology. Most (61%) were recommended to be given a topical steroid, antibiotic, or both. However, 45% of all consultations were recommended to initiate a systemic medication, most commonly antihistamines, antibiotics, steroids, antivirals, or immunomodulators. Dermatology recommended discontinuing specific medications in 16% of all consultations, with antibiotics being the most frequent culprit (17 antibiotics discontinued), owing to drug eruptions or misdiagnosed infections. Vancomycin, piperacillin-tazobactam, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole were the most frequently discontinued antibiotics.
Dermatology was consulted for assistance in management of previously diagnosed cutaneous conditions 56 times (22% of all consultations), often regarding complicated cases of hidradenitis suppurativa (9 cases), pyoderma gangrenosum (5 cases), bullous pemphigoid (4 cases), or erythroderma (4 cases). Most of these cases required a single dermatology encounter to provide recommendations (71%), and 21% required 1 additional follow-up. Sixty-three percent of patients consulted for management assistance were noted to have improvement in their cutaneous condition by time of discharge, as documented by the primary provider in the medical record.
Twenty-eight percent of all consultations required at least 1 biopsy. Seventy-two percent of all biopsies were consistent with the dermatologist’s working diagnosis or highest-ranked differential diagnosis, and 16% of biopsy results were consistent with the second- or third-ranked diagnosis. The primary teams requested a biopsy 38 times to assist in diagnosis, as documented in the progress note or consultation request. Only 21 of these consultations (55% of requests) received at least 1 biopsy, as the remaining consultations did not require a biopsy to establish a diagnosis. The most common final diagnoses of consultations receiving biopsies included drug eruptions (5), leukemia cutis (4), vasculopathies (4), vasculitis (4), and calciphylaxis (3).
Impact on Hospitalization and Efficacy—Dermatology performed 217 consultations regarding patients already admitted to the hospital, and 92% remained hospitalized either due to comorbidities or complicated cutaneous conditions following the consultation. The remaining 8% were cleared for discharge. Dermatology received 36 consultation requests from emergency medicine physicians. Fifty-three percent of these patients were admitted, while the remaining 47% were discharged from the emergency department or its observation unit following evaluation.
Fifty-one percent of all consultations were noted to have improvement in their cutaneous condition by the time of discharge, as noted in the physical examination, progress note, or discharge summary of the primary team. Thirty percent of cases remained stable, where improvement was not noted in in the medical record. Most of these cases involved keratinocyte carcinomas scheduled for outpatient excision, benign melanocytic nevi found on FBSE, and benign etiologies that led to immediate discharge following consultation. Three percent of all consultations were noted to have worsened following consultation, including cases of calciphylaxis, vasculopathies, and purpura fulminans, as well as patients who elected for palliative care and hospice. The cutaneous condition by the time of discharge could not be determined from the medical record in 16% of all consultations.
Eighty-five percent of all consultations required a single encounter with dermatology. An additional 10% required a single follow-up with dermatology, while only 5% of patients required 3 or more encounters. Notably, these cases included patients with 1 or more severe cutaneous diseases, such as Sweet syndrome, calciphylaxis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis, and hidradenitis suppurativa.
Comment
Although dermatology often is viewed as an outpatient specialty, this study provides a glimpse into the ways inpatient dermatology consultations optimize the care of hospitalized patients. Most consultations involved assistance in diagnosing an unknown condition, but several regarded pre-existing skin disorders requiring management aid. As a variety of medical specialties requested consultations, dermatology was able to provide care to a diverse group of patients with conditions varying in complexity and severity. Several specialties benefited from niche dermatologic expertise: hematology and oncology frequently requested dermatology to assist in diagnosis and management of the toxic effects of chemotherapy, cutaneous metastasis, or suspected cutaneous infections in immunocompromised patients. Cardiology patients were frequently evaluated for potential malignancy or infection prior to heart transplantation and initiation of antirejection immunosuppressants. Dermatology was consulted to differentiate cutaneous manifestations of critical illness from underlying systemic disease in the intensive care unit, and patients presenting to the emergency department often were examined to determine if hospital admission was necessary, with 47% of these consultations resulting in a discharge following evaluation by a dermatologist.
Our results were consistent with prior studies1,5,6 that have reported frequent changes in final diagnosis following dermatology consultation, with 69% of working diagnoses changed in this study when consultation was requested for diagnostic assistance. When dermatology was consulted for diagnostic assistance, several of these cases lacked a preliminary differential diagnosis. Although the absence of a documented differential diagnosis may not necessarily reflect a lack of suspicion for a particular etiology, 86% of all consultations included a ranked differential or working diagnosis either in the consultation request or progress note prior to consultation. The final diagnoses of consultations without a preliminary diagnosis varied from the mild and localized to systemic and severe, further suggesting these cases reflected knowledge gaps of the primary medical team.
Integration of dermatology into the care of hospitalized patients could provide an opportunity for education of primary medical teams. With frequent consultation, primary medical teams may become more comfortable diagnosing and managing common cutaneous conditions specific to their specialty or extended hospitalizations.
Several consultations were requested to aid in management of cases of hidradenitis suppurativa, pyoderma gangrenosum, or bullous pemphigoid that either failed outpatient therapy or were complicated by superinfections. Despite the ranges in complexity, the majority of all consultations required a single encounter and led to improvement by the time of discharge, demonstrating the efficacy and efficiency of inpatient dermatologists.
Dermatology consultations often led to changes in management involving medications and additional workup. Changes in management also extended to specific wound care instructions provided by dermatology, as expected for cases of Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis, Sweet syndrome, hidradenitis suppurativa, and pyoderma gangrenosum. However, patients with the sequelae of extended hospitalizations, such as chronic wounds, pressure ulcers, and edema bullae, also benefited from this expertise.
When patients required a biopsy, the final diagnoses were consistent with the dermatologist’s number one differential diagnosis or top 3 differential diagnoses 72% and 88% of the time, respectively. Only 55% of cases where the primary team requested a biopsy ultimately required a biopsy, as many involved clinical diagnoses such as urticaria. Not only was dermatology accurate in their preliminary diagnoses, but they decreased cost and morbidity by avoiding unnecessary procedures.
This study provided additional evidence to support the integration of dermatology into the hospital setting for the benefit of patients, primary medical teams, and hospital systems. Dermatology offers high-value care through the efficient diagnosis and management of hospitalized patients, which contributes to decreased cost and improved outcomes.2,5-7,9,10 This study highlighted lesser-known areas of impact, such as the various specialty-specific services dermatology provides as well as the high rates of reported improvement following consultation. Future studies should continue to explore the field’s unique impact on hospitalized medicine as well as other avenues of care delivery, such as telemedicine, that may encourage dermatologists to participate in consultations and increase the volume of patients who may benefit from their care.
Dermatology is an often-underutilized resource in the hospital setting. As the health care landscape has evolved, so has the role of the inpatient dermatologist.1-3 Structural changes in the health system and advances in therapies have shifted dermatology from an admitting service to an almost exclusively outpatient practice. Improved treatment modalities led to decreases in the number of patients requiring admission for chronic dermatoses, and outpatient clinics began offering therapies once limited to hospitals.1,4 Inpatient dermatology consultations emerged and continue to have profound effects on hospitalized patients regardless of their reason for admission.1-11
Inpatient dermatologists supply knowledge in areas primary medical teams lack, and there is evidence that dermatology consultations improve the quality of care while decreasing cost.2,5-7 Establishing correct diagnoses, preventing exposure to unnecessary medications, and reducing hospitalization duration and readmission rates are a few ways dermatology consultations positively impact hospitalized patients.2,5-7,9,10 This study highlights the role of the dermatologist in the care of hospitalized patients at a large academic medical center in an urban setting and reveals how consultation supports the efficiency and efficacy of other services.
Materials and Methods
Study Design—This single-institution, cross-sectional retrospective study included all hospitalized patients at the Thomas Jefferson University Hospital (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania), who received an inpatient dermatology consultation completed by physicians of Jefferson Dermatology Associates between January 1, 2019, and December 31, 2019. The institutional review board at Thomas Jefferson University approved this study.
Data Collection—A list of all inpatient dermatology consultations in 2019 was provided by Jefferson Dermatology Associates. Through a retrospective chart review, data regarding the consultations were collected from the electronic medical record (Epic Systems) and recorded into the Research Electronic Data Capture system. Data on patient demographics, the primary medical team, the dermatology evaluation, and the hospital course of the patient were collected.
Results
Patient Characteristics—Dermatology received 253 inpatient consultation requests during this time period; 53% of patients were female and 47% were male, with a mean age of 55 years. Most patients were White (57%), while 34% were Black. Five percent and 4% of patients were Asian and Hispanic or Latino, respectively (Table 1). The mean duration of hospitalization for all patients was 15 days, and the average number of days to discharge following the first encounter with dermatology was 10 days.

Requesting Team and Reason for Consultation—Internal medicine consulted dermatology most frequently (34% of all consultations), followed by emergency medicine (14%) and a variety of other services (Table 1). Most dermatology consultations were placed to assist in achieving a diagnosis of a cutaneous condition (77%), while a minority were to assist in the management of a previously diagnosed disease (22%). A small fraction of consultations (5%) were to complete full-body skin examinations (FBSEs) to rule out infection or malignancy in candidates for organ transplantation, left ventricular assist devices, or certain chemotherapies. One FBSE was conducted to search for a primary tumor in a patient diagnosed with metastatic melanoma.
Most Common Final Diagnoses and Consultation Impact—Table 2 lists the most common final diagnosis categories, as well as the effects of the consultation on diagnosis, management, biopsies, hospitalization, and clinical improvement as documented by the primary medical provider. The most common final diagnoses were inflammatory and autoimmune (39%), such as contact dermatitis and seborrheic dermatitis; infectious (23%), such as varicella (primary or zoster) and bacterial furunculosis; drug reactions (20%), such as morbilliform drug eruptions; vascular (8%), such as vasculitis and calciphylaxis; neoplastic (7%), such as keratinocyte carcinomas and leukemia cutis; and other (15%), such as xerosis, keratosis pilaris, and miliaria rubra.

Impact on Diagnosis—Fifty-six percent of all consultations resulted in a change in diagnosis. When dermatology was consulted specifically to assist in the diagnosis of a patient (195 consultations), the working diagnosis of the primary team was changed 69% of the time. Thirty-five of these consultation requests had no preliminary diagnosis, and the primary team listed the working diagnosis as either rash or a morphologic description of the lesion(s). Sixty-three percent of suspected drug eruptions ended with a diagnosis of a form of drug eruption, while 20% of consultations for suspected cellulitis or bacterial infections were confirmed to be cellulitis or soft tissue infections.
Impact on Management—Regardless of the reason for the consultation, most consultations (86%) resulted in a change in management. The remaining 14% consisted of FBSEs with benign findings; cases of cutaneous metastases and leukemia cutis managed by oncology; as well as select cases of purpura fulminans, postfebrile desquamation, and postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Changes in management included alterations in medications, requests for additional laboratory work or imaging, additional consultation requests, biopsies, or specific wound care instructions. Seventy-five percent of all consultations were given specific medication recommendations by dermatology. Most (61%) were recommended to be given a topical steroid, antibiotic, or both. However, 45% of all consultations were recommended to initiate a systemic medication, most commonly antihistamines, antibiotics, steroids, antivirals, or immunomodulators. Dermatology recommended discontinuing specific medications in 16% of all consultations, with antibiotics being the most frequent culprit (17 antibiotics discontinued), owing to drug eruptions or misdiagnosed infections. Vancomycin, piperacillin-tazobactam, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole were the most frequently discontinued antibiotics.
Dermatology was consulted for assistance in management of previously diagnosed cutaneous conditions 56 times (22% of all consultations), often regarding complicated cases of hidradenitis suppurativa (9 cases), pyoderma gangrenosum (5 cases), bullous pemphigoid (4 cases), or erythroderma (4 cases). Most of these cases required a single dermatology encounter to provide recommendations (71%), and 21% required 1 additional follow-up. Sixty-three percent of patients consulted for management assistance were noted to have improvement in their cutaneous condition by time of discharge, as documented by the primary provider in the medical record.
Twenty-eight percent of all consultations required at least 1 biopsy. Seventy-two percent of all biopsies were consistent with the dermatologist’s working diagnosis or highest-ranked differential diagnosis, and 16% of biopsy results were consistent with the second- or third-ranked diagnosis. The primary teams requested a biopsy 38 times to assist in diagnosis, as documented in the progress note or consultation request. Only 21 of these consultations (55% of requests) received at least 1 biopsy, as the remaining consultations did not require a biopsy to establish a diagnosis. The most common final diagnoses of consultations receiving biopsies included drug eruptions (5), leukemia cutis (4), vasculopathies (4), vasculitis (4), and calciphylaxis (3).
Impact on Hospitalization and Efficacy—Dermatology performed 217 consultations regarding patients already admitted to the hospital, and 92% remained hospitalized either due to comorbidities or complicated cutaneous conditions following the consultation. The remaining 8% were cleared for discharge. Dermatology received 36 consultation requests from emergency medicine physicians. Fifty-three percent of these patients were admitted, while the remaining 47% were discharged from the emergency department or its observation unit following evaluation.
Fifty-one percent of all consultations were noted to have improvement in their cutaneous condition by the time of discharge, as noted in the physical examination, progress note, or discharge summary of the primary team. Thirty percent of cases remained stable, where improvement was not noted in in the medical record. Most of these cases involved keratinocyte carcinomas scheduled for outpatient excision, benign melanocytic nevi found on FBSE, and benign etiologies that led to immediate discharge following consultation. Three percent of all consultations were noted to have worsened following consultation, including cases of calciphylaxis, vasculopathies, and purpura fulminans, as well as patients who elected for palliative care and hospice. The cutaneous condition by the time of discharge could not be determined from the medical record in 16% of all consultations.
Eighty-five percent of all consultations required a single encounter with dermatology. An additional 10% required a single follow-up with dermatology, while only 5% of patients required 3 or more encounters. Notably, these cases included patients with 1 or more severe cutaneous diseases, such as Sweet syndrome, calciphylaxis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis, and hidradenitis suppurativa.
Comment
Although dermatology often is viewed as an outpatient specialty, this study provides a glimpse into the ways inpatient dermatology consultations optimize the care of hospitalized patients. Most consultations involved assistance in diagnosing an unknown condition, but several regarded pre-existing skin disorders requiring management aid. As a variety of medical specialties requested consultations, dermatology was able to provide care to a diverse group of patients with conditions varying in complexity and severity. Several specialties benefited from niche dermatologic expertise: hematology and oncology frequently requested dermatology to assist in diagnosis and management of the toxic effects of chemotherapy, cutaneous metastasis, or suspected cutaneous infections in immunocompromised patients. Cardiology patients were frequently evaluated for potential malignancy or infection prior to heart transplantation and initiation of antirejection immunosuppressants. Dermatology was consulted to differentiate cutaneous manifestations of critical illness from underlying systemic disease in the intensive care unit, and patients presenting to the emergency department often were examined to determine if hospital admission was necessary, with 47% of these consultations resulting in a discharge following evaluation by a dermatologist.
Our results were consistent with prior studies1,5,6 that have reported frequent changes in final diagnosis following dermatology consultation, with 69% of working diagnoses changed in this study when consultation was requested for diagnostic assistance. When dermatology was consulted for diagnostic assistance, several of these cases lacked a preliminary differential diagnosis. Although the absence of a documented differential diagnosis may not necessarily reflect a lack of suspicion for a particular etiology, 86% of all consultations included a ranked differential or working diagnosis either in the consultation request or progress note prior to consultation. The final diagnoses of consultations without a preliminary diagnosis varied from the mild and localized to systemic and severe, further suggesting these cases reflected knowledge gaps of the primary medical team.
Integration of dermatology into the care of hospitalized patients could provide an opportunity for education of primary medical teams. With frequent consultation, primary medical teams may become more comfortable diagnosing and managing common cutaneous conditions specific to their specialty or extended hospitalizations.
Several consultations were requested to aid in management of cases of hidradenitis suppurativa, pyoderma gangrenosum, or bullous pemphigoid that either failed outpatient therapy or were complicated by superinfections. Despite the ranges in complexity, the majority of all consultations required a single encounter and led to improvement by the time of discharge, demonstrating the efficacy and efficiency of inpatient dermatologists.
Dermatology consultations often led to changes in management involving medications and additional workup. Changes in management also extended to specific wound care instructions provided by dermatology, as expected for cases of Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis, Sweet syndrome, hidradenitis suppurativa, and pyoderma gangrenosum. However, patients with the sequelae of extended hospitalizations, such as chronic wounds, pressure ulcers, and edema bullae, also benefited from this expertise.
When patients required a biopsy, the final diagnoses were consistent with the dermatologist’s number one differential diagnosis or top 3 differential diagnoses 72% and 88% of the time, respectively. Only 55% of cases where the primary team requested a biopsy ultimately required a biopsy, as many involved clinical diagnoses such as urticaria. Not only was dermatology accurate in their preliminary diagnoses, but they decreased cost and morbidity by avoiding unnecessary procedures.
This study provided additional evidence to support the integration of dermatology into the hospital setting for the benefit of patients, primary medical teams, and hospital systems. Dermatology offers high-value care through the efficient diagnosis and management of hospitalized patients, which contributes to decreased cost and improved outcomes.2,5-7,9,10 This study highlighted lesser-known areas of impact, such as the various specialty-specific services dermatology provides as well as the high rates of reported improvement following consultation. Future studies should continue to explore the field’s unique impact on hospitalized medicine as well as other avenues of care delivery, such as telemedicine, that may encourage dermatologists to participate in consultations and increase the volume of patients who may benefit from their care.
- Madigan LM, Fox LP. Where are we now with inpatient consultative dermatology?: assessing the value and evolution of this subspecialty over the past decade. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1804-1808. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.01.031
- Noe MH, Rosenbach M. Inpatient dermatologists—crucial for the management of skin diseases in hospitalized patients [editorial]. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:524-525. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.6195
- Strowd LC. Inpatient dermatology: a paradigm shift in the management of skin disease in the hospital. Br J Dermatol. 2019;180:966-967. doi:10.1111/bjd.17778
- Kirsner RS, Yang DG, Kerdel FA. The changing status of inpatient dermatology at American academic dermatology programs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40:755-757. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(99)70158-1
- Kroshinsky D, Cotliar J, Hughey LC, et al. Association of dermatology consultation with accuracy of cutaneous disorder diagnoses in hospitalized patients: a multicenter analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:477-480. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2015.5098
- Ko LN, Garza-Mayers AC, St John J, et al. Effect of dermatology consultation on outcomes for patients with presumed cellulitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:529-533. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.6196
- Li DG, Xia FD, Khosravi H, et al. Outcomes of early dermatology consultation for inpatients diagnosed with cellulitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:537-543. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.6197
- Milani-Nejad N, Zhang M, Kaffenberger BH. Association of dermatology consultations with patient care outcomes in hospitalized patients with inflammatory skin diseases. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:523-528. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.6130
- Imadojemu S, Rosenbach M. Dermatologists must take an active role in the diagnosis of cellulitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:134-135. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.4230
- Hughey LC. The impact dermatologists can have on misdiagnosis of cellulitis and overuse of antibiotics: closing the gap. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:1061-1062. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.1164
- Ko LN, Kroshinsky D. Dermatology hospitalists: a multicenter survey study characterizing the infrastructure of consultative dermatology in select American hospitals. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:553-558. doi:10.1111/ijd.13939
- Madigan LM, Fox LP. Where are we now with inpatient consultative dermatology?: assessing the value and evolution of this subspecialty over the past decade. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1804-1808. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.01.031
- Noe MH, Rosenbach M. Inpatient dermatologists—crucial for the management of skin diseases in hospitalized patients [editorial]. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:524-525. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.6195
- Strowd LC. Inpatient dermatology: a paradigm shift in the management of skin disease in the hospital. Br J Dermatol. 2019;180:966-967. doi:10.1111/bjd.17778
- Kirsner RS, Yang DG, Kerdel FA. The changing status of inpatient dermatology at American academic dermatology programs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40:755-757. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(99)70158-1
- Kroshinsky D, Cotliar J, Hughey LC, et al. Association of dermatology consultation with accuracy of cutaneous disorder diagnoses in hospitalized patients: a multicenter analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:477-480. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2015.5098
- Ko LN, Garza-Mayers AC, St John J, et al. Effect of dermatology consultation on outcomes for patients with presumed cellulitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:529-533. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.6196
- Li DG, Xia FD, Khosravi H, et al. Outcomes of early dermatology consultation for inpatients diagnosed with cellulitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:537-543. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.6197
- Milani-Nejad N, Zhang M, Kaffenberger BH. Association of dermatology consultations with patient care outcomes in hospitalized patients with inflammatory skin diseases. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:523-528. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.6130
- Imadojemu S, Rosenbach M. Dermatologists must take an active role in the diagnosis of cellulitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:134-135. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.4230
- Hughey LC. The impact dermatologists can have on misdiagnosis of cellulitis and overuse of antibiotics: closing the gap. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:1061-1062. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.1164
- Ko LN, Kroshinsky D. Dermatology hospitalists: a multicenter survey study characterizing the infrastructure of consultative dermatology in select American hospitals. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:553-558. doi:10.1111/ijd.13939
Practice Points
- Inpatient dermatologists fill knowledge gaps that often alter the diagnosis, management, and hospital course of hospitalized patients.
- Several medical specialties benefit from niche expertise of inpatient dermatologists specific to their patient population.
- Integration of inpatient dermatology consultations can prevent unnecessary hospital admissions and medication administration.
Imatinib Mesylate–Induced Lichenoid Drug Eruption
Imatinib mesylate is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor initially approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2001 for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). The indications for imatinib have expanded since its initial approval. It is increasingly important that dermatologists recognize adverse cutaneous manifestations associated with imatinib and are aware of their management and outcomes to avoid unnecessarily discontinuing a potentially lifesaving medication.
Adverse cutaneous manifestations in response to imatinib are not infrequent, accounting for 7% to 21% of all side effects.1 The most frequent cutaneous manifestations of imatinib are dry skin, alopecia, facial edema, and photosensitivity rash, respectively.1 Other less common manifestations include exfoliative dermatitis, nail disorders, psoriasis, folliculitis, hypotrichosis, urticaria, petechiae, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, Sweet syndrome, and leukocytoclastic vasculitis.
We report a case of imatinib-induced lichenoid drug eruption (LDE), a rare cutaneous side effect of imatinib use, along with a review of the literature.
Case Report
An 86-year-old man with a history of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) and myelodysplastic syndrome presented with diffuse hyperpigmented skin lesions on the trunk, arms, legs, and lower lip of 2 weeks’ duration. He had been taking imatinib 400 mg once daily for 5 months for GIST. Although the oncologist stopped the medication 2 weeks prior, the lesions were persistent and gradually expanded to involve the trunk, arms, legs, and lower lip. He denied any pain or pruritus. Physical examination revealed multiple ill-defined, brown to violaceous, slightly scaly macules and patches on the trunk (Figures 1A and 1B), arms, and legs (Figure 1C), as well as violaceous to erythematous patches on the mucosal aspect of the lower lip (Figure 2). Two 4-mm punch biopsies were performed from the chest and back, which revealed an atrophic epidermis, lichenoid infiltration, and multiple melanophages in the upper dermis consistent with LDE (Figure 3). Direct immunofluorescence was negative. Therefore, based on the clinicopathologic correlation, the diagnosis of imatinib-induced LDE was made. He was treated with clobetasol ointment twice daily for 3 weeks with some improvement. His GIST was stable on follow-up computed tomography 3 months after presentation, and imatinib was resumed 1 month later with continued rash that was stable with topical corticosteroid treatment.
Comment
In addition to CML, imatinib has been approved for acute lymphoblastic leukemia, myelodysplastic syndromes, aggressive systemic mastocytosis, hypereosinophilic syndrome, chronic eosinophilic leukemia, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, and GIST. Moreover, off-label use of imatinib for various other tyrosine kinase–positive cancers and rheumatologic conditions have been documented.2,3 With the expanding use of imatinib, there will be more occasions for dermatologists to encounter cutaneous manifestations associated with its use.
According to a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms imatinib mesylate lichenoid drug, there have been few case reports of LDE associated with imatinib in the literature (eTable).4-24 Compared to classic LDE, imatinib-induced LDE has a few characteristic findings. Classic LDE frequently spares the oral mucosa and genitalia, but imatinib-induced LDE with manifestations on the oral mucosa and genitalia as well as cutaneous eruptions have been reported.4-9 In fact, the first known case of imatinib-induced LDE was an oral eruption in a patient with CML.4 In patients with oral involvement, lesions have been described as lacy reticular macules and violaceous papules, erosions, and ulcers.4,5,12 Interestingly, of those cases manifesting as concomitant oral and cutaneous LDE, the oral eruptions recurred more frequently, with 3 of 12 patients having recurrence of oral lesions after the cutaneous manifestations resolved.8,16 Genital manifestations of imatinib-induced LDE were much less common.9,11
To date, subsequent reports of imatinib-induced LDE have documented skin manifestations consistent with classic LDE occurring in a diffuse, bilateral, photodistributed pattern.10,15,16 One case presented with diffuse hyperpigmentation associated with LDE in a Japanese patient.20 The authors suggested this finding may be more prominent in patients with skin of color,20 which is consistent with the current case. Nail findings such as subungual hyperkeratosis and longitudinal ridging also have been reported.9,11
The latency period between initiation of imat-inib and onset of LDE generally ranges from 1 to 12 months, with onset most commonly occurring between 2 to 5 months or with dosage increase (eTable). Imatinib-induced LDE primarily has been documented with a 400-mg dose, with 1 case of a 600-mg dose and 1 case of an 800-mg dose, which suggests dose dependency. Furthermore, reports exist of several patients responding well to dose reduction with subsequent recurrence on dose reescalation.13,15
Historically, LDE resolves with discontinuation of the drug after a few weeks to months. When discontinuation of imatinib is unfavorable or patients report symptoms including severe pruritus or pain, treatment should be considered. Topical or oral corticosteroids can be used to treat imatinib-induced LDE, similar to lichen planus. When oral corticosteroids are contraindicated (eg, due to poor patient tolerance), oral acitretin at 25 to 35 mg once daily for 6 to 12 weeks has been reported as an alternative treatment.25
In the majority of cases of imatinib-induced LDE, it was undesirable to stop imatinib (eTable). Notably, in half the reported cases, imatinib was able to be continued and patients were treated symptomatically with either oral and/or topical steroids and/or acitretin with complete remission or tolerable recurrences. Dalmau et al9 reported 3 patients who responded poorly to topical and oral steroids and were subsequently treated with acitretin 25 mg once daily; 2 of 3 patients responded favorably to treatment and imatinib was able to be continued. In the current case imatinib initially helped, but because his rash was relatively asymptomatic, imatinib was restarted with control of rash with topical steroids. He developed some pancytopenia, which required intermittent stoppage of the imatinib.
Conclusion
We present a case of imatinib-induced cutaneous and oral LDE in a patient with GIST. Topical corticosteroids, oral acitretin, and oral steroids all may be reasonable treatment options if discontinuing imatinib is not possible in a symptomatic patient. If these therapies fail and the eruption is extensive or intolerable, dosage adjustment is another option to consider before discontinuation of imatinib.
- Scheinfeld N. Imatinib mesylate and dermatology part 2: a review of the cutaneous side effects of imatinib mesylate. J Drugs Dermatol. 2006;5:228-231.
- Kim H, Kim NH, Kang HJ, et al. Successful long-term use of imatinib mesylate in pediatric patients with sclerodermatous chronic GVHD. Pediatr Transplant. 2012;16:910-912.
- Prey S, Ezzedine K, Doussau A, et al. Imatinib mesylate in scleroderma-associated diffuse skin fibrosis: a phase II multicentre randomized double-blinded controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:1138-1144.
- Lim DS, Muir J. Oral lichenoid reaction to imatinib (STI 571, gleevec). Dermatology. 2002;205:169-171.
- Ena P, Chiarolini F, Siddi GM, et al. Oral lichenoid eruption secondary to imatinib (glivec). J Dermatolog Treat. 2004;15:253-255.
- Roux C, Boisseau-Garsaud AM, Saint-Cyr I, et al. Lichenoid cutaneous reaction to imatinib. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2004;131:571-573.
- Prabhash K, Doval DC. Lichenoid eruption due to imat-inib. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2005;71:287-288.
- Pascual JC, Matarredona J, Miralles J, et al. Oral and cutaneous lichenoid reaction secondary to imatinib: report of two cases. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:1471-1473.
- Dalmau J, Peramiquel L, Puig L, et al. Imatinib-associated lichenoid eruption: acitretin treatment allows maintained antineoplastic effect. Br J Dermatol. 2006;154:1213-1216.
- Chan CY, Browning J, Smith-Zagone MJ, et al. Cutaneous lichenoid dermatitis associated with imatinib mesylate. Dermatol Online J. 2007;13:29.
- Wahiduzzaman M, Pubalan M. Oral and cutaneous lichenoid reaction with nail changes secondary to imatinib: report of a case and literature review. Dermatol Online J. 2008;14:14.
- Basso FG, Boer CC, Correa ME, et al. Skin and oral lesions associated to imatinib mesylate therapy. Support Care Cancer. 2009;17:465-468.
- Kawakami T, Kawanabe T, Soma Y. Cutaneous lichenoid eruption caused by imatinib mesylate in a Japanese patient with chronic myeloid leukaemia. Acta Derm Venereol. 2009;89:325-326.
- Sendagorta E, Herranz P, Feito M, et al. Lichenoid drug eruption related to imatinib: report of a new case and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:E315-E316.
- Kuraishi N, Nagai Y, Hasegawa M, et al. Lichenoid drug eruption with palmoplantar hyperkeratosis due to imatinib mesylate: a case report and a review of the literature. Acta Derm Venereol. 2010;90:73-76.
- Brazzelli V, Muzio F, Manna G, et al. Photo-induced dermatitis and oral lichenoid reaction in a chronic myeloid leukemia patient treated with imatinib mesylate. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2012;28:2-5.
- Ghosh SK. Generalized lichenoid drug eruption associated with imatinib mesylate therapy. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:388-392.
- Lee J, Chung J, Jung M, et al. Lichenoid drug eruption after low-dose imatinib mesylate therapy. Ann Dermatol. 2013;25:500-502.
- Machaczka M, Gossart M. Multiple skin lesions caused by imatinib mesylate treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2013;123:251-252.
- Kagimoto Y, Mizuashi M, Kikuchi K, et al. Lichenoid drug eruption with hyperpigmentation caused by imatinib mesylate [published online June 20, 2013]. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:E161-E162.
- Arshdeep, De D, Malhotra P, et al. Imatinib mesylate-induced severe lichenoid rash. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2014;80:93-95.
- Lau YM, Lam YK, Leung KH, et al. Trachyonychia in a patient with chronic myeloid leukaemia after imatinib mesylate. Hong Kong Med J. 2014;20:464.e2.
- Bhatia A, Kanish B, Chaudhary P. Lichenoid drug eruption due to imatinib mesylate. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2015;5:68-69.
- Luo JR, Xiang XJ, Xiong JP. Lichenoid drug eruption caused by imatinib mesylate in a Chinese patient with gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2016;54:719-722.
- Laurberg G, Geiger JM, Hjorth N, et al. Treatment of lichen planus with acitretin. a double-blind, placebo-controlled study in 65 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991;24:434-437.
Imatinib mesylate is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor initially approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2001 for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). The indications for imatinib have expanded since its initial approval. It is increasingly important that dermatologists recognize adverse cutaneous manifestations associated with imatinib and are aware of their management and outcomes to avoid unnecessarily discontinuing a potentially lifesaving medication.
Adverse cutaneous manifestations in response to imatinib are not infrequent, accounting for 7% to 21% of all side effects.1 The most frequent cutaneous manifestations of imatinib are dry skin, alopecia, facial edema, and photosensitivity rash, respectively.1 Other less common manifestations include exfoliative dermatitis, nail disorders, psoriasis, folliculitis, hypotrichosis, urticaria, petechiae, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, Sweet syndrome, and leukocytoclastic vasculitis.
We report a case of imatinib-induced lichenoid drug eruption (LDE), a rare cutaneous side effect of imatinib use, along with a review of the literature.
Case Report
An 86-year-old man with a history of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) and myelodysplastic syndrome presented with diffuse hyperpigmented skin lesions on the trunk, arms, legs, and lower lip of 2 weeks’ duration. He had been taking imatinib 400 mg once daily for 5 months for GIST. Although the oncologist stopped the medication 2 weeks prior, the lesions were persistent and gradually expanded to involve the trunk, arms, legs, and lower lip. He denied any pain or pruritus. Physical examination revealed multiple ill-defined, brown to violaceous, slightly scaly macules and patches on the trunk (Figures 1A and 1B), arms, and legs (Figure 1C), as well as violaceous to erythematous patches on the mucosal aspect of the lower lip (Figure 2). Two 4-mm punch biopsies were performed from the chest and back, which revealed an atrophic epidermis, lichenoid infiltration, and multiple melanophages in the upper dermis consistent with LDE (Figure 3). Direct immunofluorescence was negative. Therefore, based on the clinicopathologic correlation, the diagnosis of imatinib-induced LDE was made. He was treated with clobetasol ointment twice daily for 3 weeks with some improvement. His GIST was stable on follow-up computed tomography 3 months after presentation, and imatinib was resumed 1 month later with continued rash that was stable with topical corticosteroid treatment.



Comment
In addition to CML, imatinib has been approved for acute lymphoblastic leukemia, myelodysplastic syndromes, aggressive systemic mastocytosis, hypereosinophilic syndrome, chronic eosinophilic leukemia, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, and GIST. Moreover, off-label use of imatinib for various other tyrosine kinase–positive cancers and rheumatologic conditions have been documented.2,3 With the expanding use of imatinib, there will be more occasions for dermatologists to encounter cutaneous manifestations associated with its use.
According to a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms imatinib mesylate lichenoid drug, there have been few case reports of LDE associated with imatinib in the literature (eTable).4-24 Compared to classic LDE, imatinib-induced LDE has a few characteristic findings. Classic LDE frequently spares the oral mucosa and genitalia, but imatinib-induced LDE with manifestations on the oral mucosa and genitalia as well as cutaneous eruptions have been reported.4-9 In fact, the first known case of imatinib-induced LDE was an oral eruption in a patient with CML.4 In patients with oral involvement, lesions have been described as lacy reticular macules and violaceous papules, erosions, and ulcers.4,5,12 Interestingly, of those cases manifesting as concomitant oral and cutaneous LDE, the oral eruptions recurred more frequently, with 3 of 12 patients having recurrence of oral lesions after the cutaneous manifestations resolved.8,16 Genital manifestations of imatinib-induced LDE were much less common.9,11
To date, subsequent reports of imatinib-induced LDE have documented skin manifestations consistent with classic LDE occurring in a diffuse, bilateral, photodistributed pattern.10,15,16 One case presented with diffuse hyperpigmentation associated with LDE in a Japanese patient.20 The authors suggested this finding may be more prominent in patients with skin of color,20 which is consistent with the current case. Nail findings such as subungual hyperkeratosis and longitudinal ridging also have been reported.9,11
The latency period between initiation of imat-inib and onset of LDE generally ranges from 1 to 12 months, with onset most commonly occurring between 2 to 5 months or with dosage increase (eTable). Imatinib-induced LDE primarily has been documented with a 400-mg dose, with 1 case of a 600-mg dose and 1 case of an 800-mg dose, which suggests dose dependency. Furthermore, reports exist of several patients responding well to dose reduction with subsequent recurrence on dose reescalation.13,15
Historically, LDE resolves with discontinuation of the drug after a few weeks to months. When discontinuation of imatinib is unfavorable or patients report symptoms including severe pruritus or pain, treatment should be considered. Topical or oral corticosteroids can be used to treat imatinib-induced LDE, similar to lichen planus. When oral corticosteroids are contraindicated (eg, due to poor patient tolerance), oral acitretin at 25 to 35 mg once daily for 6 to 12 weeks has been reported as an alternative treatment.25
In the majority of cases of imatinib-induced LDE, it was undesirable to stop imatinib (eTable). Notably, in half the reported cases, imatinib was able to be continued and patients were treated symptomatically with either oral and/or topical steroids and/or acitretin with complete remission or tolerable recurrences. Dalmau et al9 reported 3 patients who responded poorly to topical and oral steroids and were subsequently treated with acitretin 25 mg once daily; 2 of 3 patients responded favorably to treatment and imatinib was able to be continued. In the current case imatinib initially helped, but because his rash was relatively asymptomatic, imatinib was restarted with control of rash with topical steroids. He developed some pancytopenia, which required intermittent stoppage of the imatinib.
Conclusion
We present a case of imatinib-induced cutaneous and oral LDE in a patient with GIST. Topical corticosteroids, oral acitretin, and oral steroids all may be reasonable treatment options if discontinuing imatinib is not possible in a symptomatic patient. If these therapies fail and the eruption is extensive or intolerable, dosage adjustment is another option to consider before discontinuation of imatinib.
Imatinib mesylate is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor initially approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2001 for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). The indications for imatinib have expanded since its initial approval. It is increasingly important that dermatologists recognize adverse cutaneous manifestations associated with imatinib and are aware of their management and outcomes to avoid unnecessarily discontinuing a potentially lifesaving medication.
Adverse cutaneous manifestations in response to imatinib are not infrequent, accounting for 7% to 21% of all side effects.1 The most frequent cutaneous manifestations of imatinib are dry skin, alopecia, facial edema, and photosensitivity rash, respectively.1 Other less common manifestations include exfoliative dermatitis, nail disorders, psoriasis, folliculitis, hypotrichosis, urticaria, petechiae, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, Sweet syndrome, and leukocytoclastic vasculitis.
We report a case of imatinib-induced lichenoid drug eruption (LDE), a rare cutaneous side effect of imatinib use, along with a review of the literature.
Case Report
An 86-year-old man with a history of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) and myelodysplastic syndrome presented with diffuse hyperpigmented skin lesions on the trunk, arms, legs, and lower lip of 2 weeks’ duration. He had been taking imatinib 400 mg once daily for 5 months for GIST. Although the oncologist stopped the medication 2 weeks prior, the lesions were persistent and gradually expanded to involve the trunk, arms, legs, and lower lip. He denied any pain or pruritus. Physical examination revealed multiple ill-defined, brown to violaceous, slightly scaly macules and patches on the trunk (Figures 1A and 1B), arms, and legs (Figure 1C), as well as violaceous to erythematous patches on the mucosal aspect of the lower lip (Figure 2). Two 4-mm punch biopsies were performed from the chest and back, which revealed an atrophic epidermis, lichenoid infiltration, and multiple melanophages in the upper dermis consistent with LDE (Figure 3). Direct immunofluorescence was negative. Therefore, based on the clinicopathologic correlation, the diagnosis of imatinib-induced LDE was made. He was treated with clobetasol ointment twice daily for 3 weeks with some improvement. His GIST was stable on follow-up computed tomography 3 months after presentation, and imatinib was resumed 1 month later with continued rash that was stable with topical corticosteroid treatment.



Comment
In addition to CML, imatinib has been approved for acute lymphoblastic leukemia, myelodysplastic syndromes, aggressive systemic mastocytosis, hypereosinophilic syndrome, chronic eosinophilic leukemia, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, and GIST. Moreover, off-label use of imatinib for various other tyrosine kinase–positive cancers and rheumatologic conditions have been documented.2,3 With the expanding use of imatinib, there will be more occasions for dermatologists to encounter cutaneous manifestations associated with its use.
According to a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms imatinib mesylate lichenoid drug, there have been few case reports of LDE associated with imatinib in the literature (eTable).4-24 Compared to classic LDE, imatinib-induced LDE has a few characteristic findings. Classic LDE frequently spares the oral mucosa and genitalia, but imatinib-induced LDE with manifestations on the oral mucosa and genitalia as well as cutaneous eruptions have been reported.4-9 In fact, the first known case of imatinib-induced LDE was an oral eruption in a patient with CML.4 In patients with oral involvement, lesions have been described as lacy reticular macules and violaceous papules, erosions, and ulcers.4,5,12 Interestingly, of those cases manifesting as concomitant oral and cutaneous LDE, the oral eruptions recurred more frequently, with 3 of 12 patients having recurrence of oral lesions after the cutaneous manifestations resolved.8,16 Genital manifestations of imatinib-induced LDE were much less common.9,11
To date, subsequent reports of imatinib-induced LDE have documented skin manifestations consistent with classic LDE occurring in a diffuse, bilateral, photodistributed pattern.10,15,16 One case presented with diffuse hyperpigmentation associated with LDE in a Japanese patient.20 The authors suggested this finding may be more prominent in patients with skin of color,20 which is consistent with the current case. Nail findings such as subungual hyperkeratosis and longitudinal ridging also have been reported.9,11
The latency period between initiation of imat-inib and onset of LDE generally ranges from 1 to 12 months, with onset most commonly occurring between 2 to 5 months or with dosage increase (eTable). Imatinib-induced LDE primarily has been documented with a 400-mg dose, with 1 case of a 600-mg dose and 1 case of an 800-mg dose, which suggests dose dependency. Furthermore, reports exist of several patients responding well to dose reduction with subsequent recurrence on dose reescalation.13,15
Historically, LDE resolves with discontinuation of the drug after a few weeks to months. When discontinuation of imatinib is unfavorable or patients report symptoms including severe pruritus or pain, treatment should be considered. Topical or oral corticosteroids can be used to treat imatinib-induced LDE, similar to lichen planus. When oral corticosteroids are contraindicated (eg, due to poor patient tolerance), oral acitretin at 25 to 35 mg once daily for 6 to 12 weeks has been reported as an alternative treatment.25
In the majority of cases of imatinib-induced LDE, it was undesirable to stop imatinib (eTable). Notably, in half the reported cases, imatinib was able to be continued and patients were treated symptomatically with either oral and/or topical steroids and/or acitretin with complete remission or tolerable recurrences. Dalmau et al9 reported 3 patients who responded poorly to topical and oral steroids and were subsequently treated with acitretin 25 mg once daily; 2 of 3 patients responded favorably to treatment and imatinib was able to be continued. In the current case imatinib initially helped, but because his rash was relatively asymptomatic, imatinib was restarted with control of rash with topical steroids. He developed some pancytopenia, which required intermittent stoppage of the imatinib.
Conclusion
We present a case of imatinib-induced cutaneous and oral LDE in a patient with GIST. Topical corticosteroids, oral acitretin, and oral steroids all may be reasonable treatment options if discontinuing imatinib is not possible in a symptomatic patient. If these therapies fail and the eruption is extensive or intolerable, dosage adjustment is another option to consider before discontinuation of imatinib.
- Scheinfeld N. Imatinib mesylate and dermatology part 2: a review of the cutaneous side effects of imatinib mesylate. J Drugs Dermatol. 2006;5:228-231.
- Kim H, Kim NH, Kang HJ, et al. Successful long-term use of imatinib mesylate in pediatric patients with sclerodermatous chronic GVHD. Pediatr Transplant. 2012;16:910-912.
- Prey S, Ezzedine K, Doussau A, et al. Imatinib mesylate in scleroderma-associated diffuse skin fibrosis: a phase II multicentre randomized double-blinded controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:1138-1144.
- Lim DS, Muir J. Oral lichenoid reaction to imatinib (STI 571, gleevec). Dermatology. 2002;205:169-171.
- Ena P, Chiarolini F, Siddi GM, et al. Oral lichenoid eruption secondary to imatinib (glivec). J Dermatolog Treat. 2004;15:253-255.
- Roux C, Boisseau-Garsaud AM, Saint-Cyr I, et al. Lichenoid cutaneous reaction to imatinib. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2004;131:571-573.
- Prabhash K, Doval DC. Lichenoid eruption due to imat-inib. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2005;71:287-288.
- Pascual JC, Matarredona J, Miralles J, et al. Oral and cutaneous lichenoid reaction secondary to imatinib: report of two cases. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:1471-1473.
- Dalmau J, Peramiquel L, Puig L, et al. Imatinib-associated lichenoid eruption: acitretin treatment allows maintained antineoplastic effect. Br J Dermatol. 2006;154:1213-1216.
- Chan CY, Browning J, Smith-Zagone MJ, et al. Cutaneous lichenoid dermatitis associated with imatinib mesylate. Dermatol Online J. 2007;13:29.
- Wahiduzzaman M, Pubalan M. Oral and cutaneous lichenoid reaction with nail changes secondary to imatinib: report of a case and literature review. Dermatol Online J. 2008;14:14.
- Basso FG, Boer CC, Correa ME, et al. Skin and oral lesions associated to imatinib mesylate therapy. Support Care Cancer. 2009;17:465-468.
- Kawakami T, Kawanabe T, Soma Y. Cutaneous lichenoid eruption caused by imatinib mesylate in a Japanese patient with chronic myeloid leukaemia. Acta Derm Venereol. 2009;89:325-326.
- Sendagorta E, Herranz P, Feito M, et al. Lichenoid drug eruption related to imatinib: report of a new case and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:E315-E316.
- Kuraishi N, Nagai Y, Hasegawa M, et al. Lichenoid drug eruption with palmoplantar hyperkeratosis due to imatinib mesylate: a case report and a review of the literature. Acta Derm Venereol. 2010;90:73-76.
- Brazzelli V, Muzio F, Manna G, et al. Photo-induced dermatitis and oral lichenoid reaction in a chronic myeloid leukemia patient treated with imatinib mesylate. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2012;28:2-5.
- Ghosh SK. Generalized lichenoid drug eruption associated with imatinib mesylate therapy. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:388-392.
- Lee J, Chung J, Jung M, et al. Lichenoid drug eruption after low-dose imatinib mesylate therapy. Ann Dermatol. 2013;25:500-502.
- Machaczka M, Gossart M. Multiple skin lesions caused by imatinib mesylate treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2013;123:251-252.
- Kagimoto Y, Mizuashi M, Kikuchi K, et al. Lichenoid drug eruption with hyperpigmentation caused by imatinib mesylate [published online June 20, 2013]. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:E161-E162.
- Arshdeep, De D, Malhotra P, et al. Imatinib mesylate-induced severe lichenoid rash. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2014;80:93-95.
- Lau YM, Lam YK, Leung KH, et al. Trachyonychia in a patient with chronic myeloid leukaemia after imatinib mesylate. Hong Kong Med J. 2014;20:464.e2.
- Bhatia A, Kanish B, Chaudhary P. Lichenoid drug eruption due to imatinib mesylate. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2015;5:68-69.
- Luo JR, Xiang XJ, Xiong JP. Lichenoid drug eruption caused by imatinib mesylate in a Chinese patient with gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2016;54:719-722.
- Laurberg G, Geiger JM, Hjorth N, et al. Treatment of lichen planus with acitretin. a double-blind, placebo-controlled study in 65 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991;24:434-437.
- Scheinfeld N. Imatinib mesylate and dermatology part 2: a review of the cutaneous side effects of imatinib mesylate. J Drugs Dermatol. 2006;5:228-231.
- Kim H, Kim NH, Kang HJ, et al. Successful long-term use of imatinib mesylate in pediatric patients with sclerodermatous chronic GVHD. Pediatr Transplant. 2012;16:910-912.
- Prey S, Ezzedine K, Doussau A, et al. Imatinib mesylate in scleroderma-associated diffuse skin fibrosis: a phase II multicentre randomized double-blinded controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:1138-1144.
- Lim DS, Muir J. Oral lichenoid reaction to imatinib (STI 571, gleevec). Dermatology. 2002;205:169-171.
- Ena P, Chiarolini F, Siddi GM, et al. Oral lichenoid eruption secondary to imatinib (glivec). J Dermatolog Treat. 2004;15:253-255.
- Roux C, Boisseau-Garsaud AM, Saint-Cyr I, et al. Lichenoid cutaneous reaction to imatinib. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2004;131:571-573.
- Prabhash K, Doval DC. Lichenoid eruption due to imat-inib. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2005;71:287-288.
- Pascual JC, Matarredona J, Miralles J, et al. Oral and cutaneous lichenoid reaction secondary to imatinib: report of two cases. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:1471-1473.
- Dalmau J, Peramiquel L, Puig L, et al. Imatinib-associated lichenoid eruption: acitretin treatment allows maintained antineoplastic effect. Br J Dermatol. 2006;154:1213-1216.
- Chan CY, Browning J, Smith-Zagone MJ, et al. Cutaneous lichenoid dermatitis associated with imatinib mesylate. Dermatol Online J. 2007;13:29.
- Wahiduzzaman M, Pubalan M. Oral and cutaneous lichenoid reaction with nail changes secondary to imatinib: report of a case and literature review. Dermatol Online J. 2008;14:14.
- Basso FG, Boer CC, Correa ME, et al. Skin and oral lesions associated to imatinib mesylate therapy. Support Care Cancer. 2009;17:465-468.
- Kawakami T, Kawanabe T, Soma Y. Cutaneous lichenoid eruption caused by imatinib mesylate in a Japanese patient with chronic myeloid leukaemia. Acta Derm Venereol. 2009;89:325-326.
- Sendagorta E, Herranz P, Feito M, et al. Lichenoid drug eruption related to imatinib: report of a new case and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:E315-E316.
- Kuraishi N, Nagai Y, Hasegawa M, et al. Lichenoid drug eruption with palmoplantar hyperkeratosis due to imatinib mesylate: a case report and a review of the literature. Acta Derm Venereol. 2010;90:73-76.
- Brazzelli V, Muzio F, Manna G, et al. Photo-induced dermatitis and oral lichenoid reaction in a chronic myeloid leukemia patient treated with imatinib mesylate. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2012;28:2-5.
- Ghosh SK. Generalized lichenoid drug eruption associated with imatinib mesylate therapy. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:388-392.
- Lee J, Chung J, Jung M, et al. Lichenoid drug eruption after low-dose imatinib mesylate therapy. Ann Dermatol. 2013;25:500-502.
- Machaczka M, Gossart M. Multiple skin lesions caused by imatinib mesylate treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2013;123:251-252.
- Kagimoto Y, Mizuashi M, Kikuchi K, et al. Lichenoid drug eruption with hyperpigmentation caused by imatinib mesylate [published online June 20, 2013]. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:E161-E162.
- Arshdeep, De D, Malhotra P, et al. Imatinib mesylate-induced severe lichenoid rash. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2014;80:93-95.
- Lau YM, Lam YK, Leung KH, et al. Trachyonychia in a patient with chronic myeloid leukaemia after imatinib mesylate. Hong Kong Med J. 2014;20:464.e2.
- Bhatia A, Kanish B, Chaudhary P. Lichenoid drug eruption due to imatinib mesylate. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2015;5:68-69.
- Luo JR, Xiang XJ, Xiong JP. Lichenoid drug eruption caused by imatinib mesylate in a Chinese patient with gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2016;54:719-722.
- Laurberg G, Geiger JM, Hjorth N, et al. Treatment of lichen planus with acitretin. a double-blind, placebo-controlled study in 65 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991;24:434-437.
Practice Points
- Imatinib mesylate can cause cutaneous adverse reactions including dry skin, alopecia, facial edema, photosensitivity rash, and lichenoid drug eruption (LDE).
- Topical corticosteroids, oral acitretin, and oral steroids may be reasonable treatment options for imatinib-induced LDE if discontinuing imatinib is not possible in a symptomatic patient.
Rupioid Psoriasis and Other Skin Diseases With Rupioid Manifestations
Case Report
A 28-year-old man presented to the dermatology department with cone-shaped, oyster shell–like skin lesions on the scalp, trunk, arms, and legs of 1 month’s duration. He denied any fever, pruritus, pain, joint stiffness, or arthralgia. His family history was remarkable for psoriasis in his paternal grandfather and uncle.
A few years prior to the eruption, the patient developed a rash in the bilateral inguinal area but did not seek medical attention. One month prior to presentation, the rash began to spread to the scalp, trunk, arms, and legs. He was treated in the emergency department with a 5-day course of oral prednisone without any noticeable improvement. At the time of presentation to the dermatology clinic, he was found to have multiple well-demarcated erythematous plaques with conical, oyster shell–like, dirty-appearing, hyperkeratotic crusts (Figure 1). Rapid plasma reagin testing was negative. A 4-mm punch biopsy specimen from the right upper arm demonstrated thick parakeratosis with a remarkable Munro microabscess, regular psoriasiform acanthosis with thin suprapapillary epidermal plates, absent granular layer, and prominent papillary dermal edema (Figure 2). In the stratum corneum, there was seroexudate with numerous red blood cells between the parakeratosis.

|
|
| Figure 1. Multiple well-demarcated erythematous plaques with hyperkeratotic crust on the back (A). Closer view of erythematous plaques with conical, oyster shell–like, dirty-appearing, hyperkeratotic crust (B). |
|
| Figure 2. Thick parakeratosis with a remarkable Munro microabscess, regular psoriasiform acanthosis with thin suprapapillary epidermal plates, absent granular layer, and prominent papillary dermal edema (H&E, original magnification ×100). |
The patient was diagnosed with rupioid psoriasis. The lesions dramatically improved with methotrexate 10 mg weekly and topical steroids. Two months following diagnosis the patient presented with persistent hyperkeratotic lesions on the back, as he had difficulty reaching the lesions to apply topical medications; intralesional steroid injections were added. This regimen resulted in near-complete resolution maintained at his most recent follow-up 2 years following diagnosis in our clinic.
Comment
Rupia is based on the Greek word rhupos, which means dirt or filth. The term rupioid has been used to describe well-demarcated, cone-shaped plaques with thick, dark, lamellate, and adherent crusts on the skin somewhat resembling oyster or limpet shells. Histologically, a serosanguineous exudate along with thick skin helps to impart a “dirty” appearance to rupioid lesions. Rupioid manifestations have been clinically observed in a variety of diseases, including rupioid psoriasis,1-3 reactive arthritis,4 disseminated histoplasmosis,5 keratotic scabies,6 secondary syphilis,7 and photosensitive skin lesions in association with aminoaciduria.8 To diagnose the underlying infectious or inflammatory diseases beneath the thick crusts, skin biopsy and a blood test for syphilis may be necessary.
Rupioid psoriasis is a morphologic subtype of plaque psoriasis with hyperkeratotic lesions that resemble an oyster or limpet shell. Patients with thick plaque psoriasis are more likely to be male with a higher incidence of nail disease and psoriatic arthritis as well as a greater body surface area affected than patients with thin plaque psoriasis.1 Although most cases of rupioid psoriasis were associated with psoriatic arthritis,3 our patient showed no evidence of psoriatic arthritis or nail changes.
Reactive arthritis may have a similar appearance to rupioid psoriasis but may be distinguished by a geographic relief map configuration with coalescing, keratotic and desquamating lesions, as well as associated urethritis, arthritis, and conjunctivitis.4 A rupioid eruption was reported as a manifestation of disseminated histoplasmosis with dirty-appearing, heaped-up, crusted lesions present on the cheeks, nose, and forehead on clinical examination and several intracellular and extracellular oval structures on histologic examination with periodic acid–Schiff and Gomori methenamine-silver stain.5 Malignant or rupioid syphilis refers to the stage in which papulopustules of pustular syphilis undergo central necrosis due to endarteritis obliterans and intravascular thrombosis.7
In our case, the patient’s psoriasis could have flared after discontinuation of the prednisone that was administered by the emergency department physician. Most cases have been treated with combined systemic and topical therapy.9 For systemic treatment, cyclosporine, intramuscular or oral methotrexate, adalimumab, and ustekinumab3 have been used with remarkable improvement. Hyperkeratotic types of psoriasis are generally thought to be resistant to topical therapy because of poor penetration of applied agents; however, a case of rupioid psoriasis without arthritis was successfully treated with topical steroids without concomitant systemic medications.2
Conclusion
Rupioid psoriasis is a morphological subtype of plaque psoriasis with hyperkeratotic lesions that resemble a limpet shell. Rupioid skin manifestations may be seen in a variety of diseases including rupioid psoriasis, reactive arthritis, disseminated histoplasmosis, keratotic scabies, secondary syphilis, and photosensitive skin lesions associated with aminoaciduria. Diagnosis of rupioid psoriasis often requires additional testing such as skin biopsy, skin scraping, and blood tests, and it typically requires systemic therapy for treatment.
1. Christensen TE, Callis KP, Papenfuss J, et al. Observations of psoriasis in the absence of therapeutic intervention identifies two unappreciated morphologic variants, thin-plaque and thick-plaque psoriasis, and their associated phenotypes. J Invest Dermatol. 2006;126:2397-2403.
2. Feldman SR, Brown KL, Heald P. ‘Coral reef’ psoriasis: a marker of resistance to topical treatment. J Dermatolog Treat. 2008;19:257-258.
3. Necas M, Vasku V. Ustekinumab in the treatment of severe rupioid psoriasis: a case report. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Panonica Adriat. 2010;19:23-27.
4. Sehgal VN, Koranne RV, Shyam Prasad AL. Unusual manifestations of Reiter’s disease in a child. Dermatologica. 1985;170:77-79.
5. Corti M, Villafañe MF, Palmieri O, et al. Rupioid histoplasmosis: first case reported in an AIDS patient in Argentina. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2010;52:279-280.
6. Costa JB, Rocha de Sousa VL, da Trindade Neto PB, et al. Norwegian scabies mimicking rupioid psoriasis. An Bras Dermatol. 2012;87:910-913.
7. Bhagwat PV, Tophakhane RS, Rathod RM, et al. Rupioid syphilis in an HIV patient. Indian J Dermatol Venereol. 2009;75:201-202.
8. Haim S, Gilhar A, Cohen A. Cutaneous manifestations associated with aminoaciduria. report of two cases. Dermatologica. 1978;156:244-250.
9. Murakami T, Ohtsuki M, Nakagawa H. Rupioid psoriasis with arthropathy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2000;25:409-412.
Case Report
A 28-year-old man presented to the dermatology department with cone-shaped, oyster shell–like skin lesions on the scalp, trunk, arms, and legs of 1 month’s duration. He denied any fever, pruritus, pain, joint stiffness, or arthralgia. His family history was remarkable for psoriasis in his paternal grandfather and uncle.
A few years prior to the eruption, the patient developed a rash in the bilateral inguinal area but did not seek medical attention. One month prior to presentation, the rash began to spread to the scalp, trunk, arms, and legs. He was treated in the emergency department with a 5-day course of oral prednisone without any noticeable improvement. At the time of presentation to the dermatology clinic, he was found to have multiple well-demarcated erythematous plaques with conical, oyster shell–like, dirty-appearing, hyperkeratotic crusts (Figure 1). Rapid plasma reagin testing was negative. A 4-mm punch biopsy specimen from the right upper arm demonstrated thick parakeratosis with a remarkable Munro microabscess, regular psoriasiform acanthosis with thin suprapapillary epidermal plates, absent granular layer, and prominent papillary dermal edema (Figure 2). In the stratum corneum, there was seroexudate with numerous red blood cells between the parakeratosis.

|

|
| Figure 1. Multiple well-demarcated erythematous plaques with hyperkeratotic crust on the back (A). Closer view of erythematous plaques with conical, oyster shell–like, dirty-appearing, hyperkeratotic crust (B). |

|
| Figure 2. Thick parakeratosis with a remarkable Munro microabscess, regular psoriasiform acanthosis with thin suprapapillary epidermal plates, absent granular layer, and prominent papillary dermal edema (H&E, original magnification ×100). |
The patient was diagnosed with rupioid psoriasis. The lesions dramatically improved with methotrexate 10 mg weekly and topical steroids. Two months following diagnosis the patient presented with persistent hyperkeratotic lesions on the back, as he had difficulty reaching the lesions to apply topical medications; intralesional steroid injections were added. This regimen resulted in near-complete resolution maintained at his most recent follow-up 2 years following diagnosis in our clinic.
Comment
Rupia is based on the Greek word rhupos, which means dirt or filth. The term rupioid has been used to describe well-demarcated, cone-shaped plaques with thick, dark, lamellate, and adherent crusts on the skin somewhat resembling oyster or limpet shells. Histologically, a serosanguineous exudate along with thick skin helps to impart a “dirty” appearance to rupioid lesions. Rupioid manifestations have been clinically observed in a variety of diseases, including rupioid psoriasis,1-3 reactive arthritis,4 disseminated histoplasmosis,5 keratotic scabies,6 secondary syphilis,7 and photosensitive skin lesions in association with aminoaciduria.8 To diagnose the underlying infectious or inflammatory diseases beneath the thick crusts, skin biopsy and a blood test for syphilis may be necessary.
Rupioid psoriasis is a morphologic subtype of plaque psoriasis with hyperkeratotic lesions that resemble an oyster or limpet shell. Patients with thick plaque psoriasis are more likely to be male with a higher incidence of nail disease and psoriatic arthritis as well as a greater body surface area affected than patients with thin plaque psoriasis.1 Although most cases of rupioid psoriasis were associated with psoriatic arthritis,3 our patient showed no evidence of psoriatic arthritis or nail changes.
Reactive arthritis may have a similar appearance to rupioid psoriasis but may be distinguished by a geographic relief map configuration with coalescing, keratotic and desquamating lesions, as well as associated urethritis, arthritis, and conjunctivitis.4 A rupioid eruption was reported as a manifestation of disseminated histoplasmosis with dirty-appearing, heaped-up, crusted lesions present on the cheeks, nose, and forehead on clinical examination and several intracellular and extracellular oval structures on histologic examination with periodic acid–Schiff and Gomori methenamine-silver stain.5 Malignant or rupioid syphilis refers to the stage in which papulopustules of pustular syphilis undergo central necrosis due to endarteritis obliterans and intravascular thrombosis.7
In our case, the patient’s psoriasis could have flared after discontinuation of the prednisone that was administered by the emergency department physician. Most cases have been treated with combined systemic and topical therapy.9 For systemic treatment, cyclosporine, intramuscular or oral methotrexate, adalimumab, and ustekinumab3 have been used with remarkable improvement. Hyperkeratotic types of psoriasis are generally thought to be resistant to topical therapy because of poor penetration of applied agents; however, a case of rupioid psoriasis without arthritis was successfully treated with topical steroids without concomitant systemic medications.2
Conclusion
Rupioid psoriasis is a morphological subtype of plaque psoriasis with hyperkeratotic lesions that resemble a limpet shell. Rupioid skin manifestations may be seen in a variety of diseases including rupioid psoriasis, reactive arthritis, disseminated histoplasmosis, keratotic scabies, secondary syphilis, and photosensitive skin lesions associated with aminoaciduria. Diagnosis of rupioid psoriasis often requires additional testing such as skin biopsy, skin scraping, and blood tests, and it typically requires systemic therapy for treatment.
Case Report
A 28-year-old man presented to the dermatology department with cone-shaped, oyster shell–like skin lesions on the scalp, trunk, arms, and legs of 1 month’s duration. He denied any fever, pruritus, pain, joint stiffness, or arthralgia. His family history was remarkable for psoriasis in his paternal grandfather and uncle.
A few years prior to the eruption, the patient developed a rash in the bilateral inguinal area but did not seek medical attention. One month prior to presentation, the rash began to spread to the scalp, trunk, arms, and legs. He was treated in the emergency department with a 5-day course of oral prednisone without any noticeable improvement. At the time of presentation to the dermatology clinic, he was found to have multiple well-demarcated erythematous plaques with conical, oyster shell–like, dirty-appearing, hyperkeratotic crusts (Figure 1). Rapid plasma reagin testing was negative. A 4-mm punch biopsy specimen from the right upper arm demonstrated thick parakeratosis with a remarkable Munro microabscess, regular psoriasiform acanthosis with thin suprapapillary epidermal plates, absent granular layer, and prominent papillary dermal edema (Figure 2). In the stratum corneum, there was seroexudate with numerous red blood cells between the parakeratosis.

|

|
| Figure 1. Multiple well-demarcated erythematous plaques with hyperkeratotic crust on the back (A). Closer view of erythematous plaques with conical, oyster shell–like, dirty-appearing, hyperkeratotic crust (B). |

|
| Figure 2. Thick parakeratosis with a remarkable Munro microabscess, regular psoriasiform acanthosis with thin suprapapillary epidermal plates, absent granular layer, and prominent papillary dermal edema (H&E, original magnification ×100). |
The patient was diagnosed with rupioid psoriasis. The lesions dramatically improved with methotrexate 10 mg weekly and topical steroids. Two months following diagnosis the patient presented with persistent hyperkeratotic lesions on the back, as he had difficulty reaching the lesions to apply topical medications; intralesional steroid injections were added. This regimen resulted in near-complete resolution maintained at his most recent follow-up 2 years following diagnosis in our clinic.
Comment
Rupia is based on the Greek word rhupos, which means dirt or filth. The term rupioid has been used to describe well-demarcated, cone-shaped plaques with thick, dark, lamellate, and adherent crusts on the skin somewhat resembling oyster or limpet shells. Histologically, a serosanguineous exudate along with thick skin helps to impart a “dirty” appearance to rupioid lesions. Rupioid manifestations have been clinically observed in a variety of diseases, including rupioid psoriasis,1-3 reactive arthritis,4 disseminated histoplasmosis,5 keratotic scabies,6 secondary syphilis,7 and photosensitive skin lesions in association with aminoaciduria.8 To diagnose the underlying infectious or inflammatory diseases beneath the thick crusts, skin biopsy and a blood test for syphilis may be necessary.
Rupioid psoriasis is a morphologic subtype of plaque psoriasis with hyperkeratotic lesions that resemble an oyster or limpet shell. Patients with thick plaque psoriasis are more likely to be male with a higher incidence of nail disease and psoriatic arthritis as well as a greater body surface area affected than patients with thin plaque psoriasis.1 Although most cases of rupioid psoriasis were associated with psoriatic arthritis,3 our patient showed no evidence of psoriatic arthritis or nail changes.
Reactive arthritis may have a similar appearance to rupioid psoriasis but may be distinguished by a geographic relief map configuration with coalescing, keratotic and desquamating lesions, as well as associated urethritis, arthritis, and conjunctivitis.4 A rupioid eruption was reported as a manifestation of disseminated histoplasmosis with dirty-appearing, heaped-up, crusted lesions present on the cheeks, nose, and forehead on clinical examination and several intracellular and extracellular oval structures on histologic examination with periodic acid–Schiff and Gomori methenamine-silver stain.5 Malignant or rupioid syphilis refers to the stage in which papulopustules of pustular syphilis undergo central necrosis due to endarteritis obliterans and intravascular thrombosis.7
In our case, the patient’s psoriasis could have flared after discontinuation of the prednisone that was administered by the emergency department physician. Most cases have been treated with combined systemic and topical therapy.9 For systemic treatment, cyclosporine, intramuscular or oral methotrexate, adalimumab, and ustekinumab3 have been used with remarkable improvement. Hyperkeratotic types of psoriasis are generally thought to be resistant to topical therapy because of poor penetration of applied agents; however, a case of rupioid psoriasis without arthritis was successfully treated with topical steroids without concomitant systemic medications.2
Conclusion
Rupioid psoriasis is a morphological subtype of plaque psoriasis with hyperkeratotic lesions that resemble a limpet shell. Rupioid skin manifestations may be seen in a variety of diseases including rupioid psoriasis, reactive arthritis, disseminated histoplasmosis, keratotic scabies, secondary syphilis, and photosensitive skin lesions associated with aminoaciduria. Diagnosis of rupioid psoriasis often requires additional testing such as skin biopsy, skin scraping, and blood tests, and it typically requires systemic therapy for treatment.
1. Christensen TE, Callis KP, Papenfuss J, et al. Observations of psoriasis in the absence of therapeutic intervention identifies two unappreciated morphologic variants, thin-plaque and thick-plaque psoriasis, and their associated phenotypes. J Invest Dermatol. 2006;126:2397-2403.
2. Feldman SR, Brown KL, Heald P. ‘Coral reef’ psoriasis: a marker of resistance to topical treatment. J Dermatolog Treat. 2008;19:257-258.
3. Necas M, Vasku V. Ustekinumab in the treatment of severe rupioid psoriasis: a case report. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Panonica Adriat. 2010;19:23-27.
4. Sehgal VN, Koranne RV, Shyam Prasad AL. Unusual manifestations of Reiter’s disease in a child. Dermatologica. 1985;170:77-79.
5. Corti M, Villafañe MF, Palmieri O, et al. Rupioid histoplasmosis: first case reported in an AIDS patient in Argentina. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2010;52:279-280.
6. Costa JB, Rocha de Sousa VL, da Trindade Neto PB, et al. Norwegian scabies mimicking rupioid psoriasis. An Bras Dermatol. 2012;87:910-913.
7. Bhagwat PV, Tophakhane RS, Rathod RM, et al. Rupioid syphilis in an HIV patient. Indian J Dermatol Venereol. 2009;75:201-202.
8. Haim S, Gilhar A, Cohen A. Cutaneous manifestations associated with aminoaciduria. report of two cases. Dermatologica. 1978;156:244-250.
9. Murakami T, Ohtsuki M, Nakagawa H. Rupioid psoriasis with arthropathy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2000;25:409-412.
1. Christensen TE, Callis KP, Papenfuss J, et al. Observations of psoriasis in the absence of therapeutic intervention identifies two unappreciated morphologic variants, thin-plaque and thick-plaque psoriasis, and their associated phenotypes. J Invest Dermatol. 2006;126:2397-2403.
2. Feldman SR, Brown KL, Heald P. ‘Coral reef’ psoriasis: a marker of resistance to topical treatment. J Dermatolog Treat. 2008;19:257-258.
3. Necas M, Vasku V. Ustekinumab in the treatment of severe rupioid psoriasis: a case report. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Panonica Adriat. 2010;19:23-27.
4. Sehgal VN, Koranne RV, Shyam Prasad AL. Unusual manifestations of Reiter’s disease in a child. Dermatologica. 1985;170:77-79.
5. Corti M, Villafañe MF, Palmieri O, et al. Rupioid histoplasmosis: first case reported in an AIDS patient in Argentina. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2010;52:279-280.
6. Costa JB, Rocha de Sousa VL, da Trindade Neto PB, et al. Norwegian scabies mimicking rupioid psoriasis. An Bras Dermatol. 2012;87:910-913.
7. Bhagwat PV, Tophakhane RS, Rathod RM, et al. Rupioid syphilis in an HIV patient. Indian J Dermatol Venereol. 2009;75:201-202.
8. Haim S, Gilhar A, Cohen A. Cutaneous manifestations associated with aminoaciduria. report of two cases. Dermatologica. 1978;156:244-250.
9. Murakami T, Ohtsuki M, Nakagawa H. Rupioid psoriasis with arthropathy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2000;25:409-412.
- Diseases with rupioid manifestations include rupioid psoriasis, reactive arthritis, disseminated histoplasmosis, keratotic scabies, secondary syphilis, and photosensitive skin lesions associated with aminoaciduria.
- Skin biopsy, skin scraping, and blood tests may be necessary to diagnose the underlying diseases beneath the thick crusts and to rule out other diagnoses within the differential.
- Treatment of rupioid psoriasis is no different than typical plaque psoriasis, except for the need for systemic therapy in most cases due to the thick scale.