User login
Extended virus shedding after COVID-19 in some patients with cancer
Live-virus shedding was detected in 18 patients who had undergone hematopoietic stem cell transplants or chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy and in 2 patients with lymphoma.
The finding was reported Dec. 1 in a research letter in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Individuals who are otherwise healthy when they get COVID-19 are “no longer infectious after the first week of illness,” said lead author Mini Kamboj, MD, chief medical epidemiologist, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
“We need to keep an open mind about how [much] longer immunocompromised patients could pose an infection risk to others,” she added.
Dr. Kamboj said in an interview that her team’s previous experience with stem cell transplant recipients had suggested that severely immunocompromised patients shed other viruses (such as respiratory syncytial virus, parainfluenza, and influenza) for longer periods of time than do healthy controls.
Based on their latest findings, the investigators suggest that current guidelines for COVID-19 isolation precautions may need to be revised for immunocompromised patients. Even if only a small proportion of patients with cancer who have COVID-19 remain contagious for prolonged periods of time, “it’s a residual risk that we need to address,” Dr. Kamboj said.
Dr. Kamboj also suggested that physicians follow test-based criteria to determine when a patient undergoing transplant can be released from isolation.
Shedding of viable virus
For this study, the investigators used cell cultures to detect viable virus in serially collected nasopharyngeal and sputum samples from 20 immunocompromised patients who had COVID-19 (diagnosed with COVID-19 between March 10 and April 20).
Patients had lymphoma (n = 8), multiple myeloma (n= 7), acute leukemia/myelodysplastic syndrome (n = 4), and chronic leukemia (n = 1). There were 16 patients who had undergone transplant, 2 who had received CAR T-cell therapy, and 2 who had received other therapy.
There were 15 patients receiving active treatment or chemotherapy, and 11 developed severe COVID-19 infection.
In total, 78 respiratory samples were collected.
“Viral RNA was detected for up to 78 days after the onset of symptoms,” the researchers reported, “[and] viable virus was detected in 10 of 14 nasopharyngeal samples (71%) that were available from the first day of laboratory testing.”
Five patients were followed up, and from these patients, the team grew virus in culture for up to 61 days after symptom onset. Two among this small group of five patients had received allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and one patient had been treated with CAR T-cell therapy within the previous 6 months. This patient remained seronegative for antibodies to the coronavirus.
For 11 patients, the team obtained serial sample genomes and found that “each patient was infected by a distinct virus and there were no major changes in the consensus sequences of the original serial specimens or cultured isolates.” These findings were consistent with persistent infection, they noted.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Live-virus shedding was detected in 18 patients who had undergone hematopoietic stem cell transplants or chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy and in 2 patients with lymphoma.
The finding was reported Dec. 1 in a research letter in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Individuals who are otherwise healthy when they get COVID-19 are “no longer infectious after the first week of illness,” said lead author Mini Kamboj, MD, chief medical epidemiologist, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
“We need to keep an open mind about how [much] longer immunocompromised patients could pose an infection risk to others,” she added.
Dr. Kamboj said in an interview that her team’s previous experience with stem cell transplant recipients had suggested that severely immunocompromised patients shed other viruses (such as respiratory syncytial virus, parainfluenza, and influenza) for longer periods of time than do healthy controls.
Based on their latest findings, the investigators suggest that current guidelines for COVID-19 isolation precautions may need to be revised for immunocompromised patients. Even if only a small proportion of patients with cancer who have COVID-19 remain contagious for prolonged periods of time, “it’s a residual risk that we need to address,” Dr. Kamboj said.
Dr. Kamboj also suggested that physicians follow test-based criteria to determine when a patient undergoing transplant can be released from isolation.
Shedding of viable virus
For this study, the investigators used cell cultures to detect viable virus in serially collected nasopharyngeal and sputum samples from 20 immunocompromised patients who had COVID-19 (diagnosed with COVID-19 between March 10 and April 20).
Patients had lymphoma (n = 8), multiple myeloma (n= 7), acute leukemia/myelodysplastic syndrome (n = 4), and chronic leukemia (n = 1). There were 16 patients who had undergone transplant, 2 who had received CAR T-cell therapy, and 2 who had received other therapy.
There were 15 patients receiving active treatment or chemotherapy, and 11 developed severe COVID-19 infection.
In total, 78 respiratory samples were collected.
“Viral RNA was detected for up to 78 days after the onset of symptoms,” the researchers reported, “[and] viable virus was detected in 10 of 14 nasopharyngeal samples (71%) that were available from the first day of laboratory testing.”
Five patients were followed up, and from these patients, the team grew virus in culture for up to 61 days after symptom onset. Two among this small group of five patients had received allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and one patient had been treated with CAR T-cell therapy within the previous 6 months. This patient remained seronegative for antibodies to the coronavirus.
For 11 patients, the team obtained serial sample genomes and found that “each patient was infected by a distinct virus and there were no major changes in the consensus sequences of the original serial specimens or cultured isolates.” These findings were consistent with persistent infection, they noted.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Live-virus shedding was detected in 18 patients who had undergone hematopoietic stem cell transplants or chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy and in 2 patients with lymphoma.
The finding was reported Dec. 1 in a research letter in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Individuals who are otherwise healthy when they get COVID-19 are “no longer infectious after the first week of illness,” said lead author Mini Kamboj, MD, chief medical epidemiologist, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
“We need to keep an open mind about how [much] longer immunocompromised patients could pose an infection risk to others,” she added.
Dr. Kamboj said in an interview that her team’s previous experience with stem cell transplant recipients had suggested that severely immunocompromised patients shed other viruses (such as respiratory syncytial virus, parainfluenza, and influenza) for longer periods of time than do healthy controls.
Based on their latest findings, the investigators suggest that current guidelines for COVID-19 isolation precautions may need to be revised for immunocompromised patients. Even if only a small proportion of patients with cancer who have COVID-19 remain contagious for prolonged periods of time, “it’s a residual risk that we need to address,” Dr. Kamboj said.
Dr. Kamboj also suggested that physicians follow test-based criteria to determine when a patient undergoing transplant can be released from isolation.
Shedding of viable virus
For this study, the investigators used cell cultures to detect viable virus in serially collected nasopharyngeal and sputum samples from 20 immunocompromised patients who had COVID-19 (diagnosed with COVID-19 between March 10 and April 20).
Patients had lymphoma (n = 8), multiple myeloma (n= 7), acute leukemia/myelodysplastic syndrome (n = 4), and chronic leukemia (n = 1). There were 16 patients who had undergone transplant, 2 who had received CAR T-cell therapy, and 2 who had received other therapy.
There were 15 patients receiving active treatment or chemotherapy, and 11 developed severe COVID-19 infection.
In total, 78 respiratory samples were collected.
“Viral RNA was detected for up to 78 days after the onset of symptoms,” the researchers reported, “[and] viable virus was detected in 10 of 14 nasopharyngeal samples (71%) that were available from the first day of laboratory testing.”
Five patients were followed up, and from these patients, the team grew virus in culture for up to 61 days after symptom onset. Two among this small group of five patients had received allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and one patient had been treated with CAR T-cell therapy within the previous 6 months. This patient remained seronegative for antibodies to the coronavirus.
For 11 patients, the team obtained serial sample genomes and found that “each patient was infected by a distinct virus and there were no major changes in the consensus sequences of the original serial specimens or cultured isolates.” These findings were consistent with persistent infection, they noted.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rapid relief of opioid-induced constipation with MNTX
Subcutaneously administered methylnaltrexone (MNTX) (Relistor), a peripherally acting mu-opioid receptor antagonist, relieves opioid-induced constipation (OID) in both chronic, noncancer-related illness and cancer-related illness, a new analysis concludes.
“While these are two very different patient groups, the ability to have something to treat OIC in noncancer patients who stay on opioids for whatever reason helps, because [otherwise] these patients are not doing well,” said lead author Eric Shah, MD, motility director for the Dartmouth program at Dartmouth Hitchcock Health, Lebanon, N.H.
Importantly, peripherally acting mu-opioid receptor antagonists such as MNTX do not affect overall pain control to any significant extent, which is “reassuring,” he said in an interview.
These drugs decrease the constipating effects of opioids without reversing CNS-mediated opioid effects, he explained.
“Methylnaltrexone has already been approved for the treatment of OIC in adults with chronic noncancer pain as well as for OIC in adults with advanced illness who are receiving palliative care, which is often the case in patients with cancer-related pain,” he noted.
Dr. Shah discussed the new analysis during PAINWeek 2020, the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine 19th Annual Pain Medicine Meeting.
The analysis was based on a review of data collected in two previously reported randomized, placebo-controlled studies (study 302 and 4000), which were used to gain approval.
The new analysis shows that “the drug works up front, and the effect is able to be maintained. I think the studies are clinically relevant in that patients are able to have a bowel movement quickly after you give them an injectable formulation when they are vomiting or otherwise can’t tolerate a pill and they are feeling miserable,” Dr. Shah commented. Many patients with OIC are constipated for reasons other than from opioid use. They often have other side effects from opioids, including bloating, nausea, and vomiting.
“When patients go to the emergency room, it’s not just that they are not able to have a bowel movement; they are often also vomiting, so it’s important to have agents that can be given in a manner that avoids the need for oral medication,” Dr. Shah said. MNTX is the only peripherally acting opioid antagonist available in a subcutaneous formulation.
Moreover, if patients are able to control these symptoms at home with an injectable formulation, they may not need to go to the ED for treatment of their gastrointestinal distress, he added.
Viable product
In a comment, Darren Brenner, MD, associate professor of medicine and surgery, Northwestern University, Chicago, who has worked with this subcutaneous formulation, said it is “definitely a viable product.
“The data presented here were in patients with advanced illness receiving palliative care when other laxatives have failed, and the difference and the potential benefit for MNTX is that it is the only peripherally acting mu-opioid receptor antagonist that is approved for advanced cancer,” he added. The other products that are currently approved, naloxegol (Movantik) and naldemedine (Symproic), are both indicated for chronic, noncancer pain.
The other potential benefit of subcutaneous MNTX is that it can work very rapidly for the patients who respond to it. “One of the things investigators did not mention in these two trials but which has been shown in previous studies is that almost half of patients who respond to this drug respond within the first 30 minutes of receiving the injection,” Dr. Brenner said in an interview.
This can be very beneficial in an emergency setting, because it may avoid having patients admitted to hospital. They can be discharged and sent home with enough drug to use on demand, Dr. Brenner suggested.
New analysis of data from studies 302 and 4000
Both studies were carried out in adults with advanced illness and OIC whose conditions were refractory to laxative use. Both of the studies were placebo controlled.
Study 302 involved 78 patients with cancer and 56 patients with noncancer-related OIC. MNTX was given at a dose of 0.15 mg/kg subcutaneously every other day for 2 weeks.
Study 4000 included 152 patients with cancer and OIC and 78 patients with noncancer-related OIC. In this study, the dose of MNTX was based on body weight. Seven or fewer doses of either 8 mg or 12 mg were given subcutaneously for 2 weeks.
The main endpoints of both studies was the proportion of patients who achieved a rescue-free laxation (RFL) response within 4 hours after the first dose and the proportion of patients with an RFL response within 4 hours for two or more of the first four doses within 24 hours.
Dr. Shah explained that RFL is a meaningful clinical endpoint. Patients could achieve a bowel movement with the two prespecified time endpoints in both studies.
Not all patients were hospitalized for OIC, Dr. Shah noted. Entry criteria were strict and included having fewer than three bowel movements during the previous week and no clinically significant laxation (defecation) within 48 hours of receiving the first dose of study drug.
“In both studies, a significantly greater proportion of patients treated with MNTX versus placebo achieved an RFL within 4 hours after the first dose among both cancer and noncancer patients,” the investigators reported.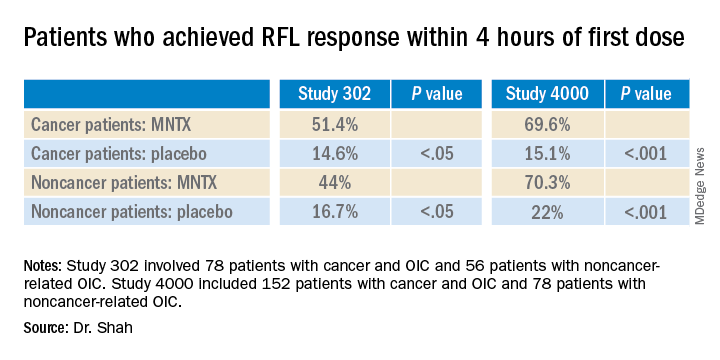
Results were relatively comparable between cancer and noncancer patients who were treated for OIC in study 4000, the investigators noted.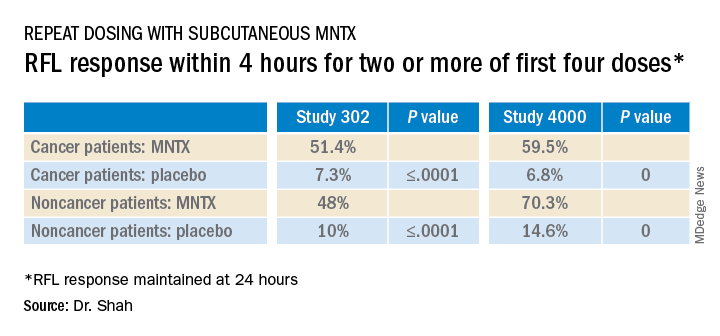
Both studies were sponsored by Salix Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Shah has received travel fees from Salix Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Brenner has served as a consultant for Salix Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, and Purdue Pharma. AstraZeneca developed naloxegol.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Subcutaneously administered methylnaltrexone (MNTX) (Relistor), a peripherally acting mu-opioid receptor antagonist, relieves opioid-induced constipation (OID) in both chronic, noncancer-related illness and cancer-related illness, a new analysis concludes.
“While these are two very different patient groups, the ability to have something to treat OIC in noncancer patients who stay on opioids for whatever reason helps, because [otherwise] these patients are not doing well,” said lead author Eric Shah, MD, motility director for the Dartmouth program at Dartmouth Hitchcock Health, Lebanon, N.H.
Importantly, peripherally acting mu-opioid receptor antagonists such as MNTX do not affect overall pain control to any significant extent, which is “reassuring,” he said in an interview.
These drugs decrease the constipating effects of opioids without reversing CNS-mediated opioid effects, he explained.
“Methylnaltrexone has already been approved for the treatment of OIC in adults with chronic noncancer pain as well as for OIC in adults with advanced illness who are receiving palliative care, which is often the case in patients with cancer-related pain,” he noted.
Dr. Shah discussed the new analysis during PAINWeek 2020, the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine 19th Annual Pain Medicine Meeting.
The analysis was based on a review of data collected in two previously reported randomized, placebo-controlled studies (study 302 and 4000), which were used to gain approval.
The new analysis shows that “the drug works up front, and the effect is able to be maintained. I think the studies are clinically relevant in that patients are able to have a bowel movement quickly after you give them an injectable formulation when they are vomiting or otherwise can’t tolerate a pill and they are feeling miserable,” Dr. Shah commented. Many patients with OIC are constipated for reasons other than from opioid use. They often have other side effects from opioids, including bloating, nausea, and vomiting.
“When patients go to the emergency room, it’s not just that they are not able to have a bowel movement; they are often also vomiting, so it’s important to have agents that can be given in a manner that avoids the need for oral medication,” Dr. Shah said. MNTX is the only peripherally acting opioid antagonist available in a subcutaneous formulation.
Moreover, if patients are able to control these symptoms at home with an injectable formulation, they may not need to go to the ED for treatment of their gastrointestinal distress, he added.
Viable product
In a comment, Darren Brenner, MD, associate professor of medicine and surgery, Northwestern University, Chicago, who has worked with this subcutaneous formulation, said it is “definitely a viable product.
“The data presented here were in patients with advanced illness receiving palliative care when other laxatives have failed, and the difference and the potential benefit for MNTX is that it is the only peripherally acting mu-opioid receptor antagonist that is approved for advanced cancer,” he added. The other products that are currently approved, naloxegol (Movantik) and naldemedine (Symproic), are both indicated for chronic, noncancer pain.
The other potential benefit of subcutaneous MNTX is that it can work very rapidly for the patients who respond to it. “One of the things investigators did not mention in these two trials but which has been shown in previous studies is that almost half of patients who respond to this drug respond within the first 30 minutes of receiving the injection,” Dr. Brenner said in an interview.
This can be very beneficial in an emergency setting, because it may avoid having patients admitted to hospital. They can be discharged and sent home with enough drug to use on demand, Dr. Brenner suggested.
New analysis of data from studies 302 and 4000
Both studies were carried out in adults with advanced illness and OIC whose conditions were refractory to laxative use. Both of the studies were placebo controlled.
Study 302 involved 78 patients with cancer and 56 patients with noncancer-related OIC. MNTX was given at a dose of 0.15 mg/kg subcutaneously every other day for 2 weeks.
Study 4000 included 152 patients with cancer and OIC and 78 patients with noncancer-related OIC. In this study, the dose of MNTX was based on body weight. Seven or fewer doses of either 8 mg or 12 mg were given subcutaneously for 2 weeks.
The main endpoints of both studies was the proportion of patients who achieved a rescue-free laxation (RFL) response within 4 hours after the first dose and the proportion of patients with an RFL response within 4 hours for two or more of the first four doses within 24 hours.
Dr. Shah explained that RFL is a meaningful clinical endpoint. Patients could achieve a bowel movement with the two prespecified time endpoints in both studies.
Not all patients were hospitalized for OIC, Dr. Shah noted. Entry criteria were strict and included having fewer than three bowel movements during the previous week and no clinically significant laxation (defecation) within 48 hours of receiving the first dose of study drug.
“In both studies, a significantly greater proportion of patients treated with MNTX versus placebo achieved an RFL within 4 hours after the first dose among both cancer and noncancer patients,” the investigators reported.
Results were relatively comparable between cancer and noncancer patients who were treated for OIC in study 4000, the investigators noted.
Both studies were sponsored by Salix Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Shah has received travel fees from Salix Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Brenner has served as a consultant for Salix Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, and Purdue Pharma. AstraZeneca developed naloxegol.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Subcutaneously administered methylnaltrexone (MNTX) (Relistor), a peripherally acting mu-opioid receptor antagonist, relieves opioid-induced constipation (OID) in both chronic, noncancer-related illness and cancer-related illness, a new analysis concludes.
“While these are two very different patient groups, the ability to have something to treat OIC in noncancer patients who stay on opioids for whatever reason helps, because [otherwise] these patients are not doing well,” said lead author Eric Shah, MD, motility director for the Dartmouth program at Dartmouth Hitchcock Health, Lebanon, N.H.
Importantly, peripherally acting mu-opioid receptor antagonists such as MNTX do not affect overall pain control to any significant extent, which is “reassuring,” he said in an interview.
These drugs decrease the constipating effects of opioids without reversing CNS-mediated opioid effects, he explained.
“Methylnaltrexone has already been approved for the treatment of OIC in adults with chronic noncancer pain as well as for OIC in adults with advanced illness who are receiving palliative care, which is often the case in patients with cancer-related pain,” he noted.
Dr. Shah discussed the new analysis during PAINWeek 2020, the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine 19th Annual Pain Medicine Meeting.
The analysis was based on a review of data collected in two previously reported randomized, placebo-controlled studies (study 302 and 4000), which were used to gain approval.
The new analysis shows that “the drug works up front, and the effect is able to be maintained. I think the studies are clinically relevant in that patients are able to have a bowel movement quickly after you give them an injectable formulation when they are vomiting or otherwise can’t tolerate a pill and they are feeling miserable,” Dr. Shah commented. Many patients with OIC are constipated for reasons other than from opioid use. They often have other side effects from opioids, including bloating, nausea, and vomiting.
“When patients go to the emergency room, it’s not just that they are not able to have a bowel movement; they are often also vomiting, so it’s important to have agents that can be given in a manner that avoids the need for oral medication,” Dr. Shah said. MNTX is the only peripherally acting opioid antagonist available in a subcutaneous formulation.
Moreover, if patients are able to control these symptoms at home with an injectable formulation, they may not need to go to the ED for treatment of their gastrointestinal distress, he added.
Viable product
In a comment, Darren Brenner, MD, associate professor of medicine and surgery, Northwestern University, Chicago, who has worked with this subcutaneous formulation, said it is “definitely a viable product.
“The data presented here were in patients with advanced illness receiving palliative care when other laxatives have failed, and the difference and the potential benefit for MNTX is that it is the only peripherally acting mu-opioid receptor antagonist that is approved for advanced cancer,” he added. The other products that are currently approved, naloxegol (Movantik) and naldemedine (Symproic), are both indicated for chronic, noncancer pain.
The other potential benefit of subcutaneous MNTX is that it can work very rapidly for the patients who respond to it. “One of the things investigators did not mention in these two trials but which has been shown in previous studies is that almost half of patients who respond to this drug respond within the first 30 minutes of receiving the injection,” Dr. Brenner said in an interview.
This can be very beneficial in an emergency setting, because it may avoid having patients admitted to hospital. They can be discharged and sent home with enough drug to use on demand, Dr. Brenner suggested.
New analysis of data from studies 302 and 4000
Both studies were carried out in adults with advanced illness and OIC whose conditions were refractory to laxative use. Both of the studies were placebo controlled.
Study 302 involved 78 patients with cancer and 56 patients with noncancer-related OIC. MNTX was given at a dose of 0.15 mg/kg subcutaneously every other day for 2 weeks.
Study 4000 included 152 patients with cancer and OIC and 78 patients with noncancer-related OIC. In this study, the dose of MNTX was based on body weight. Seven or fewer doses of either 8 mg or 12 mg were given subcutaneously for 2 weeks.
The main endpoints of both studies was the proportion of patients who achieved a rescue-free laxation (RFL) response within 4 hours after the first dose and the proportion of patients with an RFL response within 4 hours for two or more of the first four doses within 24 hours.
Dr. Shah explained that RFL is a meaningful clinical endpoint. Patients could achieve a bowel movement with the two prespecified time endpoints in both studies.
Not all patients were hospitalized for OIC, Dr. Shah noted. Entry criteria were strict and included having fewer than three bowel movements during the previous week and no clinically significant laxation (defecation) within 48 hours of receiving the first dose of study drug.
“In both studies, a significantly greater proportion of patients treated with MNTX versus placebo achieved an RFL within 4 hours after the first dose among both cancer and noncancer patients,” the investigators reported.
Results were relatively comparable between cancer and noncancer patients who were treated for OIC in study 4000, the investigators noted.
Both studies were sponsored by Salix Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Shah has received travel fees from Salix Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Brenner has served as a consultant for Salix Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, and Purdue Pharma. AstraZeneca developed naloxegol.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Low-dose radiotherapy for lung inflammation in severe COVID-19
The first study to suggest benefit from low-dose radiotherapy for severe COVID-19–induced pneumonia involved only 20 patients, but the results were so promising that two larger randomized trials are now underway.
“RESCUE-119 was a trial based on the hypothesis that low-dose radiation therapy may help eliminate the stormy cytokine release and unchecked edema in hospitalized COVID-19 patients,” said Mohammed Khan, MD, PhD, Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University, Atlanta.
“We found patients had a quicker improvement in their time to clinical recovery with low-dose radiation therapy, compared to controls, and this was significant even in this small cohort of patients,” he said.
Dr. Khan was speaking at a special press briefing held during the virtual American Society for Radiation Oncology Annual Meeting 2020.
A total of 20 patients were involved in the trial. Ten patients were treated with low-dose radiotherapy; 10 others, who served as control patients, were treated with the best supportive care and COVID-directed therapies. The control patients were matched for age and comorbidities. All these patients were hospitalized and were oxygen dependent, Dr. Khan noted. In addition, for all patients, serial x-rays demonstrated consolidation and damage in the lung.
The intervention consisted of whole-lung low-dose radiotherapy delivered at a dose of 1.5 Gy.
The first five patients were assessed at an interim endpoint of 7 days to confirm the safety of the procedure. Subsequently, a total of 10 patients were treated with radiotherapy and were followed to day 28.
The main study endpoints were time to clinical recovery, determined on the basis of the patient’s being taken off oxygen, and improvement, evidenced on either serial x-rays or by inflammatory biomarkers.
The median time to clinical recovery was almost three times faster for the patients who received low-dose radiotherapy, at a median of 3 days; for control patients, the median was 12 days (P = .048).
“We also saw a trend toward getting patients out of hospital sooner,” Dr. Khan added. The mean time to hospital discharge was 12 days for the patients who received low-dose radiotherapy, compared with 20 days for control patients (P = .19).
Only one patient required intubation after receiving low-dose radiotherapy, whereas 4 of 10 control patients required some sort of intubation (P = .12), he noted.
Investigators also saw improvements on serial x-rays in 9 of 10 patients treated with low-dose radiotherapy, compared with only 4 patients in the control group. There was also a significant improvement in delirium among the low-dose radiotherapy group compared with control patients (P < .01). Before receiving low-dose radiotherapy, C-reactive protein levels increased by 22% per day. After receiving the 1.5-Gy radiation treatment, there was a sharp reduction in C-reactive protein levels (P < .01) as well as in lactate dehydrogenase levels (P = .03).
Overall survival, however, did not differ between the two treatment groups; 90% of both groups were alive at day 28.
“By focally dampening cytokine hyperactivation, [low-dose radiotherapy] may improve COVID-19 outcomes through immunomodulation,” Dr. Khan explained.
VENTED and PRE-VENT trials
These results from the small RESCUE-119 trial led to the launch of two larger phase 2 trials, the VENTED and the PRE-VENT trials, noted Arnab Chakravarti, MD, professor and chair of radiation oncology, the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus.
To be enrolled in the VENTED trial, patients must have received mechanical ventilation. They will receive at least one dose of ultra-low-dose bilateral whole-lung radiotherapy, with the option of receiving a second dose. The primary objective is 30-day mortality rate.
“The hypothesis is that low-dose thoracic radiation will decrease inflammation and improve outcomes for these intubated COVID-19 patients,” Dr. Chakravarti explained.
The PRE-VENT trial will explore low-dose thoracic radiotherapy for hospitalized patients with severe respiratory compromise who have not yet been intubated. Two doses of low-dose radiotherapy will be tested and compared. The primary study objective is to determine which of the two doses appears to be the most efficacious, Dr. Chakravarti noted.
“The ultimate question to which we remain agnostic is whether the potential benefits of low-dose radiation therapy outweigh the risks,” he said.
Low-dose radiotherapy is readily available in most countries, unlike the newly developed COVID-19 drugs, which are only available in the developed world, he noted. “This creates a bit more economic equity in terms of COVID-19 treatment.”
In addition, it may offer a therapeutic option that could be useful in the future, “as low-dose radiation therapy does not discriminate against various viruses that may cause another pandemic,” he commented. It could offer “a stopgap measure where we don’t have to shut down society completely, which, as we have all witnessed, can cause tremendous financial and social unrest.”
Reasonable question
Whether or not radiotherapy has value for the short-term management of severe pulmonary inflammation caused by COVID-19 is a reasonable question to evaluate in clinical trials, commented discussant Ramesh Rengan, MD, PhD, professor and chair, department of radiation oncology, University of Washington, Seattle.
He noted that inflammatory cells are highly sensitive to radiation, and low-dose radiotherapy has been used effectively in other inflammatory conditions, such as arthritis. Indeed, before the discovery of antibiotics, low-dose radiation was used with reasonable efficacy to treat pneumonia.
“The pneumonia associated with this viral infection is a bit unique in that what happens is the infection triggers an inflammatory cascade – the so-called cytokine storm – that essentially overwhelms the lungs, thereby leading, unfortunately, to mortality,” Dr. Rengan noted. “So a big focus of our energy is how to stop this inflammatory cascade from occurring.”
Corticosteroids are currently the only therapeutic intervention that has shown any mortality benefit in COVID-19, he pointed out.
The question now being asked is: “Can we suppress inflammation specifically within the lung?” Dr. Rengan continued. The main problem with radiotherapy is that it has different effects on various tissues, both immediately and over the long term.
“The immediate benefit that we will likely see from these studies is the immediate sterilization of inflammatory cells,” he said. However, injury to normal lung tissue from low-dose radiotherapy could lead to inflammation weeks or months later, and this could contribute to the disease burden and increase the risk of dying.
Dr. Rengan also noted that there are some very real practical concerns about offering radiotherapy to COVID-19 patients, including potential COVID-19 transmission to vulnerable cancer patients.
Nevertheless, Dr. Rengan said the results to date are very important and that ongoing trials will provide important new information about the long-term impact of this particular treatment in high-risk patients.
“This is a race to the bottom – we are trying to find the lowest possible dose of radiation therapy that we can deliver to sterilize these inflammatory cells without creating any harm to the surrounding tissue,” he said.
“It also brings radiation oncologists into the fight against this deadly disease,” he added.
Dr. Rengan has received honoraria from Novocur and has served as a consultant to AstraZeneca.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The first study to suggest benefit from low-dose radiotherapy for severe COVID-19–induced pneumonia involved only 20 patients, but the results were so promising that two larger randomized trials are now underway.
“RESCUE-119 was a trial based on the hypothesis that low-dose radiation therapy may help eliminate the stormy cytokine release and unchecked edema in hospitalized COVID-19 patients,” said Mohammed Khan, MD, PhD, Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University, Atlanta.
“We found patients had a quicker improvement in their time to clinical recovery with low-dose radiation therapy, compared to controls, and this was significant even in this small cohort of patients,” he said.
Dr. Khan was speaking at a special press briefing held during the virtual American Society for Radiation Oncology Annual Meeting 2020.
A total of 20 patients were involved in the trial. Ten patients were treated with low-dose radiotherapy; 10 others, who served as control patients, were treated with the best supportive care and COVID-directed therapies. The control patients were matched for age and comorbidities. All these patients were hospitalized and were oxygen dependent, Dr. Khan noted. In addition, for all patients, serial x-rays demonstrated consolidation and damage in the lung.
The intervention consisted of whole-lung low-dose radiotherapy delivered at a dose of 1.5 Gy.
The first five patients were assessed at an interim endpoint of 7 days to confirm the safety of the procedure. Subsequently, a total of 10 patients were treated with radiotherapy and were followed to day 28.
The main study endpoints were time to clinical recovery, determined on the basis of the patient’s being taken off oxygen, and improvement, evidenced on either serial x-rays or by inflammatory biomarkers.
The median time to clinical recovery was almost three times faster for the patients who received low-dose radiotherapy, at a median of 3 days; for control patients, the median was 12 days (P = .048).
“We also saw a trend toward getting patients out of hospital sooner,” Dr. Khan added. The mean time to hospital discharge was 12 days for the patients who received low-dose radiotherapy, compared with 20 days for control patients (P = .19).
Only one patient required intubation after receiving low-dose radiotherapy, whereas 4 of 10 control patients required some sort of intubation (P = .12), he noted.
Investigators also saw improvements on serial x-rays in 9 of 10 patients treated with low-dose radiotherapy, compared with only 4 patients in the control group. There was also a significant improvement in delirium among the low-dose radiotherapy group compared with control patients (P < .01). Before receiving low-dose radiotherapy, C-reactive protein levels increased by 22% per day. After receiving the 1.5-Gy radiation treatment, there was a sharp reduction in C-reactive protein levels (P < .01) as well as in lactate dehydrogenase levels (P = .03).
Overall survival, however, did not differ between the two treatment groups; 90% of both groups were alive at day 28.
“By focally dampening cytokine hyperactivation, [low-dose radiotherapy] may improve COVID-19 outcomes through immunomodulation,” Dr. Khan explained.
VENTED and PRE-VENT trials
These results from the small RESCUE-119 trial led to the launch of two larger phase 2 trials, the VENTED and the PRE-VENT trials, noted Arnab Chakravarti, MD, professor and chair of radiation oncology, the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus.
To be enrolled in the VENTED trial, patients must have received mechanical ventilation. They will receive at least one dose of ultra-low-dose bilateral whole-lung radiotherapy, with the option of receiving a second dose. The primary objective is 30-day mortality rate.
“The hypothesis is that low-dose thoracic radiation will decrease inflammation and improve outcomes for these intubated COVID-19 patients,” Dr. Chakravarti explained.
The PRE-VENT trial will explore low-dose thoracic radiotherapy for hospitalized patients with severe respiratory compromise who have not yet been intubated. Two doses of low-dose radiotherapy will be tested and compared. The primary study objective is to determine which of the two doses appears to be the most efficacious, Dr. Chakravarti noted.
“The ultimate question to which we remain agnostic is whether the potential benefits of low-dose radiation therapy outweigh the risks,” he said.
Low-dose radiotherapy is readily available in most countries, unlike the newly developed COVID-19 drugs, which are only available in the developed world, he noted. “This creates a bit more economic equity in terms of COVID-19 treatment.”
In addition, it may offer a therapeutic option that could be useful in the future, “as low-dose radiation therapy does not discriminate against various viruses that may cause another pandemic,” he commented. It could offer “a stopgap measure where we don’t have to shut down society completely, which, as we have all witnessed, can cause tremendous financial and social unrest.”
Reasonable question
Whether or not radiotherapy has value for the short-term management of severe pulmonary inflammation caused by COVID-19 is a reasonable question to evaluate in clinical trials, commented discussant Ramesh Rengan, MD, PhD, professor and chair, department of radiation oncology, University of Washington, Seattle.
He noted that inflammatory cells are highly sensitive to radiation, and low-dose radiotherapy has been used effectively in other inflammatory conditions, such as arthritis. Indeed, before the discovery of antibiotics, low-dose radiation was used with reasonable efficacy to treat pneumonia.
“The pneumonia associated with this viral infection is a bit unique in that what happens is the infection triggers an inflammatory cascade – the so-called cytokine storm – that essentially overwhelms the lungs, thereby leading, unfortunately, to mortality,” Dr. Rengan noted. “So a big focus of our energy is how to stop this inflammatory cascade from occurring.”
Corticosteroids are currently the only therapeutic intervention that has shown any mortality benefit in COVID-19, he pointed out.
The question now being asked is: “Can we suppress inflammation specifically within the lung?” Dr. Rengan continued. The main problem with radiotherapy is that it has different effects on various tissues, both immediately and over the long term.
“The immediate benefit that we will likely see from these studies is the immediate sterilization of inflammatory cells,” he said. However, injury to normal lung tissue from low-dose radiotherapy could lead to inflammation weeks or months later, and this could contribute to the disease burden and increase the risk of dying.
Dr. Rengan also noted that there are some very real practical concerns about offering radiotherapy to COVID-19 patients, including potential COVID-19 transmission to vulnerable cancer patients.
Nevertheless, Dr. Rengan said the results to date are very important and that ongoing trials will provide important new information about the long-term impact of this particular treatment in high-risk patients.
“This is a race to the bottom – we are trying to find the lowest possible dose of radiation therapy that we can deliver to sterilize these inflammatory cells without creating any harm to the surrounding tissue,” he said.
“It also brings radiation oncologists into the fight against this deadly disease,” he added.
Dr. Rengan has received honoraria from Novocur and has served as a consultant to AstraZeneca.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The first study to suggest benefit from low-dose radiotherapy for severe COVID-19–induced pneumonia involved only 20 patients, but the results were so promising that two larger randomized trials are now underway.
“RESCUE-119 was a trial based on the hypothesis that low-dose radiation therapy may help eliminate the stormy cytokine release and unchecked edema in hospitalized COVID-19 patients,” said Mohammed Khan, MD, PhD, Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University, Atlanta.
“We found patients had a quicker improvement in their time to clinical recovery with low-dose radiation therapy, compared to controls, and this was significant even in this small cohort of patients,” he said.
Dr. Khan was speaking at a special press briefing held during the virtual American Society for Radiation Oncology Annual Meeting 2020.
A total of 20 patients were involved in the trial. Ten patients were treated with low-dose radiotherapy; 10 others, who served as control patients, were treated with the best supportive care and COVID-directed therapies. The control patients were matched for age and comorbidities. All these patients were hospitalized and were oxygen dependent, Dr. Khan noted. In addition, for all patients, serial x-rays demonstrated consolidation and damage in the lung.
The intervention consisted of whole-lung low-dose radiotherapy delivered at a dose of 1.5 Gy.
The first five patients were assessed at an interim endpoint of 7 days to confirm the safety of the procedure. Subsequently, a total of 10 patients were treated with radiotherapy and were followed to day 28.
The main study endpoints were time to clinical recovery, determined on the basis of the patient’s being taken off oxygen, and improvement, evidenced on either serial x-rays or by inflammatory biomarkers.
The median time to clinical recovery was almost three times faster for the patients who received low-dose radiotherapy, at a median of 3 days; for control patients, the median was 12 days (P = .048).
“We also saw a trend toward getting patients out of hospital sooner,” Dr. Khan added. The mean time to hospital discharge was 12 days for the patients who received low-dose radiotherapy, compared with 20 days for control patients (P = .19).
Only one patient required intubation after receiving low-dose radiotherapy, whereas 4 of 10 control patients required some sort of intubation (P = .12), he noted.
Investigators also saw improvements on serial x-rays in 9 of 10 patients treated with low-dose radiotherapy, compared with only 4 patients in the control group. There was also a significant improvement in delirium among the low-dose radiotherapy group compared with control patients (P < .01). Before receiving low-dose radiotherapy, C-reactive protein levels increased by 22% per day. After receiving the 1.5-Gy radiation treatment, there was a sharp reduction in C-reactive protein levels (P < .01) as well as in lactate dehydrogenase levels (P = .03).
Overall survival, however, did not differ between the two treatment groups; 90% of both groups were alive at day 28.
“By focally dampening cytokine hyperactivation, [low-dose radiotherapy] may improve COVID-19 outcomes through immunomodulation,” Dr. Khan explained.
VENTED and PRE-VENT trials
These results from the small RESCUE-119 trial led to the launch of two larger phase 2 trials, the VENTED and the PRE-VENT trials, noted Arnab Chakravarti, MD, professor and chair of radiation oncology, the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus.
To be enrolled in the VENTED trial, patients must have received mechanical ventilation. They will receive at least one dose of ultra-low-dose bilateral whole-lung radiotherapy, with the option of receiving a second dose. The primary objective is 30-day mortality rate.
“The hypothesis is that low-dose thoracic radiation will decrease inflammation and improve outcomes for these intubated COVID-19 patients,” Dr. Chakravarti explained.
The PRE-VENT trial will explore low-dose thoracic radiotherapy for hospitalized patients with severe respiratory compromise who have not yet been intubated. Two doses of low-dose radiotherapy will be tested and compared. The primary study objective is to determine which of the two doses appears to be the most efficacious, Dr. Chakravarti noted.
“The ultimate question to which we remain agnostic is whether the potential benefits of low-dose radiation therapy outweigh the risks,” he said.
Low-dose radiotherapy is readily available in most countries, unlike the newly developed COVID-19 drugs, which are only available in the developed world, he noted. “This creates a bit more economic equity in terms of COVID-19 treatment.”
In addition, it may offer a therapeutic option that could be useful in the future, “as low-dose radiation therapy does not discriminate against various viruses that may cause another pandemic,” he commented. It could offer “a stopgap measure where we don’t have to shut down society completely, which, as we have all witnessed, can cause tremendous financial and social unrest.”
Reasonable question
Whether or not radiotherapy has value for the short-term management of severe pulmonary inflammation caused by COVID-19 is a reasonable question to evaluate in clinical trials, commented discussant Ramesh Rengan, MD, PhD, professor and chair, department of radiation oncology, University of Washington, Seattle.
He noted that inflammatory cells are highly sensitive to radiation, and low-dose radiotherapy has been used effectively in other inflammatory conditions, such as arthritis. Indeed, before the discovery of antibiotics, low-dose radiation was used with reasonable efficacy to treat pneumonia.
“The pneumonia associated with this viral infection is a bit unique in that what happens is the infection triggers an inflammatory cascade – the so-called cytokine storm – that essentially overwhelms the lungs, thereby leading, unfortunately, to mortality,” Dr. Rengan noted. “So a big focus of our energy is how to stop this inflammatory cascade from occurring.”
Corticosteroids are currently the only therapeutic intervention that has shown any mortality benefit in COVID-19, he pointed out.
The question now being asked is: “Can we suppress inflammation specifically within the lung?” Dr. Rengan continued. The main problem with radiotherapy is that it has different effects on various tissues, both immediately and over the long term.
“The immediate benefit that we will likely see from these studies is the immediate sterilization of inflammatory cells,” he said. However, injury to normal lung tissue from low-dose radiotherapy could lead to inflammation weeks or months later, and this could contribute to the disease burden and increase the risk of dying.
Dr. Rengan also noted that there are some very real practical concerns about offering radiotherapy to COVID-19 patients, including potential COVID-19 transmission to vulnerable cancer patients.
Nevertheless, Dr. Rengan said the results to date are very important and that ongoing trials will provide important new information about the long-term impact of this particular treatment in high-risk patients.
“This is a race to the bottom – we are trying to find the lowest possible dose of radiation therapy that we can deliver to sterilize these inflammatory cells without creating any harm to the surrounding tissue,” he said.
“It also brings radiation oncologists into the fight against this deadly disease,” he added.
Dr. Rengan has received honoraria from Novocur and has served as a consultant to AstraZeneca.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Surgery may not be needed with locally advanced rectal cancer
A short course of radiation therapy followed by neoadjuvant chemotherapy resulted in a clinical complete response (CR) in almost half of 90 patients with locally advanced rectal cancer, allowing the majority of responders to skip surgical resection, a retrospective study indicates.
Specifically, at a median follow-up of 16.6 months for living patients, the initial clinical CR rate was 48% overall.
“While we do not have enough follow-up yet to know the late side-effect profile of this regimen, our preliminary results are promising,” Re-I Chin, MD, of Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri, told Medscape Medical News in an email.
The study was presented at the virtual 2020 meeting of the American Society of Radiation Oncology (ASTRO).
“Certainly, longer follow-up will be needed in this study, but none of the observed patients to date has experienced an unsalvageable failure,” said meeting discussant Amol Narang, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland.
He reminded conference attendees that, despite good evidence supporting equivalency in oncologic outcomes between short-course radiation and long-course chemoradiation, the former is “highly underutilized in the US” with a mere 1% usage rate between 2004 and 2014.
The current study’s short-course treatment approach was compared in this setting to long-course chemoradiation and adjuvant chemotherapy in the RAPIDO trial reported at the 2020 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), Narang pointed out.
Short-course patients had a higher rate of pathological complete response (pCR) and a lower rate of treatment failure compared with patients who received long-course chemoradiation and adjuvant chemotherapy; both patient groups underwent total mesorectal excision — which is different from the current analysis. The RAPIDO investigators concluded that the approach featuring the short course “can be considered as a new standard of care.”
Narang said the data collectively “begs the question as to whether the superiority of long-course chemoradiation should really have to be demonstrated to justify its use.”
But Chin highlighted toxicity issues. “Historically, there have been concerns regarding toxicity with short-course radiation therapy since it requires larger doses of radiation given over a shorter period of time,” Chin explained. “But [the short course] is particularly convenient for patients since it saves them more than a month of daily trips to the radiation oncology department.”
Seven local failures
The single-center study involved patients with newly diagnosed, nonmetastatic rectal adenocarcinoma treated with short-course radiation therapy followed by chemotherapy in 2018 and 2019. Nearly all (96%) had locally advanced disease, with either a T3/T4 tumor or node-positive disease. Median tumor size was 4.6 cm.
“Many of the patients in the study had low lying tumors,” Chin reported, with a median distance from the anal verge of 7 cm.
Radiation therapy was delivered in 25 Gy given in five fractions over 5 consecutive days, with the option to boost the dose to 30 Gy or 35 Gy in five fractions if extra-mesorectal lymph nodes were involved. Conventional 3D or intensity-modulated radiation was used and all patients completed treatment.
The median interval between diagnosis of rectal cancer and initiation of radiation therapy was 1.4 months, while the median interval between completion of radiation to initiation of chemotherapy was 2.7 weeks.
The most common chemotherapy regimen was FOLFOX – consisting of leucovorin, fluorouracil (5-FU), and oxaliplatin – or modified FOLFOX. For patients who received six or more cycles of chemotherapy, the median time spent on treatment was 3.9 months.
For those who completed at least six cycles of chemotherapy, the overall clinical CR was 51%, and, for patients with locally advanced disease, the clinical CR rate was 49%. Five of the 43 patients who achieved an initial clinical CR still underwent surgical resection because of patient or physician preference. Among this small group of patients, 4 of the 5 achieved a pCR, and the remaining patient achieved a pathological partial response (pPR).
A total of 42 patients (47% of the group) achieved a partial response following the radiation plus chemotherapy paradigm, and one patient had progressive disease. All underwent surgical resection. One patient did not complete chemotherapy and did not get surgery and subsequently died.
This left 38 patients to be managed nonoperatively. In this nonoperative cohort, 79% of patients continued to have a clinical CR at the end of follow-up. Of the 7 patients with local failure, 6 were salvaged by surgery, one was salvaged by chemotherapy, and all 7 treatment failures had no evidence of disease at last follow-up.
Of the small group of 5 patients who achieved an initial clinical CR following short-course radiation therapy and neoadjuvant chemotherapy, there were no further events in this group, whereas, for patients who achieved only an initial partial response or who had progressive disease, 72% remained event-free.
Approximately half of those who achieved a clinical CR to the treatment regimen had no late gastrointestinal toxicities, and no grade 3 or 4 toxicities were observed. “Surgical resection of tumors — even without a permanent stoma — can result in significantly decreased bowel function, so our goal is to treat patients without surgery and maintain good bowel function,” Chin noted.
“For rectal cancer, both short-course radiation therapy and nonoperative management are emerging treatment paradigms that may be more cost-effective and convenient compared to long-course chemoradiation followed by surgery, [especially since] the COVID-19 pandemic...has spurred changes in clinical practices in radiation oncology,” she said.
Chin has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Narang reports receiving research support from Boston Scientific.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A short course of radiation therapy followed by neoadjuvant chemotherapy resulted in a clinical complete response (CR) in almost half of 90 patients with locally advanced rectal cancer, allowing the majority of responders to skip surgical resection, a retrospective study indicates.
Specifically, at a median follow-up of 16.6 months for living patients, the initial clinical CR rate was 48% overall.
“While we do not have enough follow-up yet to know the late side-effect profile of this regimen, our preliminary results are promising,” Re-I Chin, MD, of Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri, told Medscape Medical News in an email.
The study was presented at the virtual 2020 meeting of the American Society of Radiation Oncology (ASTRO).
“Certainly, longer follow-up will be needed in this study, but none of the observed patients to date has experienced an unsalvageable failure,” said meeting discussant Amol Narang, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland.
He reminded conference attendees that, despite good evidence supporting equivalency in oncologic outcomes between short-course radiation and long-course chemoradiation, the former is “highly underutilized in the US” with a mere 1% usage rate between 2004 and 2014.
The current study’s short-course treatment approach was compared in this setting to long-course chemoradiation and adjuvant chemotherapy in the RAPIDO trial reported at the 2020 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), Narang pointed out.
Short-course patients had a higher rate of pathological complete response (pCR) and a lower rate of treatment failure compared with patients who received long-course chemoradiation and adjuvant chemotherapy; both patient groups underwent total mesorectal excision — which is different from the current analysis. The RAPIDO investigators concluded that the approach featuring the short course “can be considered as a new standard of care.”
Narang said the data collectively “begs the question as to whether the superiority of long-course chemoradiation should really have to be demonstrated to justify its use.”
But Chin highlighted toxicity issues. “Historically, there have been concerns regarding toxicity with short-course radiation therapy since it requires larger doses of radiation given over a shorter period of time,” Chin explained. “But [the short course] is particularly convenient for patients since it saves them more than a month of daily trips to the radiation oncology department.”
Seven local failures
The single-center study involved patients with newly diagnosed, nonmetastatic rectal adenocarcinoma treated with short-course radiation therapy followed by chemotherapy in 2018 and 2019. Nearly all (96%) had locally advanced disease, with either a T3/T4 tumor or node-positive disease. Median tumor size was 4.6 cm.
“Many of the patients in the study had low lying tumors,” Chin reported, with a median distance from the anal verge of 7 cm.
Radiation therapy was delivered in 25 Gy given in five fractions over 5 consecutive days, with the option to boost the dose to 30 Gy or 35 Gy in five fractions if extra-mesorectal lymph nodes were involved. Conventional 3D or intensity-modulated radiation was used and all patients completed treatment.
The median interval between diagnosis of rectal cancer and initiation of radiation therapy was 1.4 months, while the median interval between completion of radiation to initiation of chemotherapy was 2.7 weeks.
The most common chemotherapy regimen was FOLFOX – consisting of leucovorin, fluorouracil (5-FU), and oxaliplatin – or modified FOLFOX. For patients who received six or more cycles of chemotherapy, the median time spent on treatment was 3.9 months.
For those who completed at least six cycles of chemotherapy, the overall clinical CR was 51%, and, for patients with locally advanced disease, the clinical CR rate was 49%. Five of the 43 patients who achieved an initial clinical CR still underwent surgical resection because of patient or physician preference. Among this small group of patients, 4 of the 5 achieved a pCR, and the remaining patient achieved a pathological partial response (pPR).
A total of 42 patients (47% of the group) achieved a partial response following the radiation plus chemotherapy paradigm, and one patient had progressive disease. All underwent surgical resection. One patient did not complete chemotherapy and did not get surgery and subsequently died.
This left 38 patients to be managed nonoperatively. In this nonoperative cohort, 79% of patients continued to have a clinical CR at the end of follow-up. Of the 7 patients with local failure, 6 were salvaged by surgery, one was salvaged by chemotherapy, and all 7 treatment failures had no evidence of disease at last follow-up.
Of the small group of 5 patients who achieved an initial clinical CR following short-course radiation therapy and neoadjuvant chemotherapy, there were no further events in this group, whereas, for patients who achieved only an initial partial response or who had progressive disease, 72% remained event-free.
Approximately half of those who achieved a clinical CR to the treatment regimen had no late gastrointestinal toxicities, and no grade 3 or 4 toxicities were observed. “Surgical resection of tumors — even without a permanent stoma — can result in significantly decreased bowel function, so our goal is to treat patients without surgery and maintain good bowel function,” Chin noted.
“For rectal cancer, both short-course radiation therapy and nonoperative management are emerging treatment paradigms that may be more cost-effective and convenient compared to long-course chemoradiation followed by surgery, [especially since] the COVID-19 pandemic...has spurred changes in clinical practices in radiation oncology,” she said.
Chin has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Narang reports receiving research support from Boston Scientific.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A short course of radiation therapy followed by neoadjuvant chemotherapy resulted in a clinical complete response (CR) in almost half of 90 patients with locally advanced rectal cancer, allowing the majority of responders to skip surgical resection, a retrospective study indicates.
Specifically, at a median follow-up of 16.6 months for living patients, the initial clinical CR rate was 48% overall.
“While we do not have enough follow-up yet to know the late side-effect profile of this regimen, our preliminary results are promising,” Re-I Chin, MD, of Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri, told Medscape Medical News in an email.
The study was presented at the virtual 2020 meeting of the American Society of Radiation Oncology (ASTRO).
“Certainly, longer follow-up will be needed in this study, but none of the observed patients to date has experienced an unsalvageable failure,” said meeting discussant Amol Narang, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland.
He reminded conference attendees that, despite good evidence supporting equivalency in oncologic outcomes between short-course radiation and long-course chemoradiation, the former is “highly underutilized in the US” with a mere 1% usage rate between 2004 and 2014.
The current study’s short-course treatment approach was compared in this setting to long-course chemoradiation and adjuvant chemotherapy in the RAPIDO trial reported at the 2020 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), Narang pointed out.
Short-course patients had a higher rate of pathological complete response (pCR) and a lower rate of treatment failure compared with patients who received long-course chemoradiation and adjuvant chemotherapy; both patient groups underwent total mesorectal excision — which is different from the current analysis. The RAPIDO investigators concluded that the approach featuring the short course “can be considered as a new standard of care.”
Narang said the data collectively “begs the question as to whether the superiority of long-course chemoradiation should really have to be demonstrated to justify its use.”
But Chin highlighted toxicity issues. “Historically, there have been concerns regarding toxicity with short-course radiation therapy since it requires larger doses of radiation given over a shorter period of time,” Chin explained. “But [the short course] is particularly convenient for patients since it saves them more than a month of daily trips to the radiation oncology department.”
Seven local failures
The single-center study involved patients with newly diagnosed, nonmetastatic rectal adenocarcinoma treated with short-course radiation therapy followed by chemotherapy in 2018 and 2019. Nearly all (96%) had locally advanced disease, with either a T3/T4 tumor or node-positive disease. Median tumor size was 4.6 cm.
“Many of the patients in the study had low lying tumors,” Chin reported, with a median distance from the anal verge of 7 cm.
Radiation therapy was delivered in 25 Gy given in five fractions over 5 consecutive days, with the option to boost the dose to 30 Gy or 35 Gy in five fractions if extra-mesorectal lymph nodes were involved. Conventional 3D or intensity-modulated radiation was used and all patients completed treatment.
The median interval between diagnosis of rectal cancer and initiation of radiation therapy was 1.4 months, while the median interval between completion of radiation to initiation of chemotherapy was 2.7 weeks.
The most common chemotherapy regimen was FOLFOX – consisting of leucovorin, fluorouracil (5-FU), and oxaliplatin – or modified FOLFOX. For patients who received six or more cycles of chemotherapy, the median time spent on treatment was 3.9 months.
For those who completed at least six cycles of chemotherapy, the overall clinical CR was 51%, and, for patients with locally advanced disease, the clinical CR rate was 49%. Five of the 43 patients who achieved an initial clinical CR still underwent surgical resection because of patient or physician preference. Among this small group of patients, 4 of the 5 achieved a pCR, and the remaining patient achieved a pathological partial response (pPR).
A total of 42 patients (47% of the group) achieved a partial response following the radiation plus chemotherapy paradigm, and one patient had progressive disease. All underwent surgical resection. One patient did not complete chemotherapy and did not get surgery and subsequently died.
This left 38 patients to be managed nonoperatively. In this nonoperative cohort, 79% of patients continued to have a clinical CR at the end of follow-up. Of the 7 patients with local failure, 6 were salvaged by surgery, one was salvaged by chemotherapy, and all 7 treatment failures had no evidence of disease at last follow-up.
Of the small group of 5 patients who achieved an initial clinical CR following short-course radiation therapy and neoadjuvant chemotherapy, there were no further events in this group, whereas, for patients who achieved only an initial partial response or who had progressive disease, 72% remained event-free.
Approximately half of those who achieved a clinical CR to the treatment regimen had no late gastrointestinal toxicities, and no grade 3 or 4 toxicities were observed. “Surgical resection of tumors — even without a permanent stoma — can result in significantly decreased bowel function, so our goal is to treat patients without surgery and maintain good bowel function,” Chin noted.
“For rectal cancer, both short-course radiation therapy and nonoperative management are emerging treatment paradigms that may be more cost-effective and convenient compared to long-course chemoradiation followed by surgery, [especially since] the COVID-19 pandemic...has spurred changes in clinical practices in radiation oncology,” she said.
Chin has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Narang reports receiving research support from Boston Scientific.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HIV drugs prevent type 2 diabetes, may be path to new therapy
A class of drugs long used to treat HIV and hepatitis B viral infections appears to prevent the development of diabetes in a substantial proportion of patients who take these agents, an analysis of multiple databases has shown.
“Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors [NRTIs], drugs approved to treat HIV-1 and hepatitis B infections, also block inflammasome activation,” Jayakrishna Ambati, MD, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, and colleagues wrote in Nature Communications.
“[We showed that] the adjusted risk of incident diabetes is 33% lower in patients with NRTI exposure. ... These data suggest the possibility of repurposing an approved class of drugs for prevention of diabetes,” they wrote.
The researchers made a small chemical modification to NRTIs that led to their developing a new class of drugs, which they have termed “kamuvudines.” Kamuvudines are nontoxic derivatives of NRTIs, Dr. Ambati said in an interview.
“People take NRTIs because they need to live with HIV, but giving them to the general population is not a great idea because of the toxicities associated with long-term NRTI use. So our focus is not to go forward specifically with NRTIs but rather with these new molecules that are far less toxic, and that is how we envision a clinical trial going forward,” Dr. Ambati noted.
Researchers screened five databases of >100,000 patients
Dr. Ambati and colleagues analyzed information from five databases in which patients who had been exposed to an NRTI but who had not previously been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes were assessed for the subsequent development of diabetes over varying time intervals. In one, the Veterans Health Administration database – from the largest integrated health care system in the United States – the analysis spanned a period of 17 years.
Of 79,744 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of HIV or hepatitis B in the Veterans Health Administration database, the risk for type 2 diabetes was reduced by 34% among NRTI users, compared with nonusers after adjusting for potential confounders (P < .0001).
The reduction in diabetes risk was similar among HIV-positive and hepatitis B–positive patients.
These results were reaffirmed by further analyses of four other databases, the investigators reported. One of these, the employer-based health insurance Truven database, had data on 23,634 patients who had been diagnosed with HIV or hepatitis B. After adjusting for potential confounders, NRTI users had a 39% lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes, compared with nonusers (P < .0001).
The risk of developing type 2 diabetes was somewhat lower among NRTI users in the Pearl Diver database, which includes predominantly private health insurance claims. Of 16,045 patients diagnosed with HIV or hepatitis B included in this database, the risk for type 2 diabetes was 26% lower among NRTI users, compared with nonusers (P = .004).
A similar magnitude of risk reduction was seen in the analysis of the Clinformatics dataset. Among 6,341 users of NRTIs, the risk for type 2 diabetes was 27% lower than it was for nonusers (P = .009).
The least reduction in diabetes risk was in the Medicare database, in which only 3,097 patients had been diagnosed with either HIV or hepatitis B. Among these patients, the risk for diabetes was 17% lower among NRTI users than it was for nonusers (P = .137).
One-third reduction across multiple databases enhances confidence
“Collectively, among 128,861 patients with HIV-1 or hepatitis B, users of NRTIs had a 33% reduced hazard of developing type 2 diabetes,” Dr. Ambati and colleagues emphasize.
“The fact that the protective effect against the development of diabetes was replicated in multiple databases in studies from multiple institutions enhances confidence in the results,” Dr. Ambati noted in a statement from the University of Virginia.
Dr. Ambati and colleagues also showed that the NRTI lamivudine restores insulin sensitivity in human cells from type 2 diabetes patients.
That drug prevented induction of insulin resistance in human cells from people who did not have diabetes. It also prevented inflammasome activation in mice fed a high-fat diet.
“These investigations of human cell, mouse and population database systems collectively suggest a potential beneficial effect of NRTIs in forestalling diabetes onset,” they stressed.
Trial assessing kamuvudines slated to begin next year
In the interview, Dr. Ambati explained that inflammasomes are protein complexes that form a large superstructure within the cell. “When activated, they lead to the production of some very powerful inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-1 beta and IL-18.”
Although there are many different types of inflammasomes, the one implicated in type 2 diabetes, as well as many other chronic diseases, including macular degeneration, is the NLRP3 inflammasome.
Activation of this molecule promotes insulin resistance, a key driver of type 2 diabetes, he explained.
Importantly, previous research showed that the way the NRTIs block this inflammasome has nothing to do with their anti-HIV activity.
After making a small chemical modification in the NRTIs, Dr. Ambati and colleagues were able to show that the resulting agents, which they have dubbed “kamuvudines,” are able to block inflammasome activation independently of their antiviral effects.
They hope that this modification will reduce the toxicities associated with the agents. This would be necessary if kamuvudines were to be more widely used in a noninfected, healthier population, Ambati stressed.
Dr. Ambati and his colleague, Paul Ashton, PhD, cofounder of Inflammasone Therapeutics, plan a clinical trial with one of these kamuvudines in macular degeneration, which they hope will begin early next year.
“We are trying to pick a disease where we can show efficacy fairly quickly in a small number of people,” Dr. Ashton explained in an interview. “We’re very enthusiastic about this as it looks really, really promising.”
Dr. Ambati and Dr. Ashton cofounded Inflammasone Therapeutics, located in Boston. Dr. Ashton is the CEO of the company.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A class of drugs long used to treat HIV and hepatitis B viral infections appears to prevent the development of diabetes in a substantial proportion of patients who take these agents, an analysis of multiple databases has shown.
“Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors [NRTIs], drugs approved to treat HIV-1 and hepatitis B infections, also block inflammasome activation,” Jayakrishna Ambati, MD, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, and colleagues wrote in Nature Communications.
“[We showed that] the adjusted risk of incident diabetes is 33% lower in patients with NRTI exposure. ... These data suggest the possibility of repurposing an approved class of drugs for prevention of diabetes,” they wrote.
The researchers made a small chemical modification to NRTIs that led to their developing a new class of drugs, which they have termed “kamuvudines.” Kamuvudines are nontoxic derivatives of NRTIs, Dr. Ambati said in an interview.
“People take NRTIs because they need to live with HIV, but giving them to the general population is not a great idea because of the toxicities associated with long-term NRTI use. So our focus is not to go forward specifically with NRTIs but rather with these new molecules that are far less toxic, and that is how we envision a clinical trial going forward,” Dr. Ambati noted.
Researchers screened five databases of >100,000 patients
Dr. Ambati and colleagues analyzed information from five databases in which patients who had been exposed to an NRTI but who had not previously been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes were assessed for the subsequent development of diabetes over varying time intervals. In one, the Veterans Health Administration database – from the largest integrated health care system in the United States – the analysis spanned a period of 17 years.
Of 79,744 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of HIV or hepatitis B in the Veterans Health Administration database, the risk for type 2 diabetes was reduced by 34% among NRTI users, compared with nonusers after adjusting for potential confounders (P < .0001).
The reduction in diabetes risk was similar among HIV-positive and hepatitis B–positive patients.
These results were reaffirmed by further analyses of four other databases, the investigators reported. One of these, the employer-based health insurance Truven database, had data on 23,634 patients who had been diagnosed with HIV or hepatitis B. After adjusting for potential confounders, NRTI users had a 39% lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes, compared with nonusers (P < .0001).
The risk of developing type 2 diabetes was somewhat lower among NRTI users in the Pearl Diver database, which includes predominantly private health insurance claims. Of 16,045 patients diagnosed with HIV or hepatitis B included in this database, the risk for type 2 diabetes was 26% lower among NRTI users, compared with nonusers (P = .004).
A similar magnitude of risk reduction was seen in the analysis of the Clinformatics dataset. Among 6,341 users of NRTIs, the risk for type 2 diabetes was 27% lower than it was for nonusers (P = .009).
The least reduction in diabetes risk was in the Medicare database, in which only 3,097 patients had been diagnosed with either HIV or hepatitis B. Among these patients, the risk for diabetes was 17% lower among NRTI users than it was for nonusers (P = .137).
One-third reduction across multiple databases enhances confidence
“Collectively, among 128,861 patients with HIV-1 or hepatitis B, users of NRTIs had a 33% reduced hazard of developing type 2 diabetes,” Dr. Ambati and colleagues emphasize.
“The fact that the protective effect against the development of diabetes was replicated in multiple databases in studies from multiple institutions enhances confidence in the results,” Dr. Ambati noted in a statement from the University of Virginia.
Dr. Ambati and colleagues also showed that the NRTI lamivudine restores insulin sensitivity in human cells from type 2 diabetes patients.
That drug prevented induction of insulin resistance in human cells from people who did not have diabetes. It also prevented inflammasome activation in mice fed a high-fat diet.
“These investigations of human cell, mouse and population database systems collectively suggest a potential beneficial effect of NRTIs in forestalling diabetes onset,” they stressed.
Trial assessing kamuvudines slated to begin next year
In the interview, Dr. Ambati explained that inflammasomes are protein complexes that form a large superstructure within the cell. “When activated, they lead to the production of some very powerful inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-1 beta and IL-18.”
Although there are many different types of inflammasomes, the one implicated in type 2 diabetes, as well as many other chronic diseases, including macular degeneration, is the NLRP3 inflammasome.
Activation of this molecule promotes insulin resistance, a key driver of type 2 diabetes, he explained.
Importantly, previous research showed that the way the NRTIs block this inflammasome has nothing to do with their anti-HIV activity.
After making a small chemical modification in the NRTIs, Dr. Ambati and colleagues were able to show that the resulting agents, which they have dubbed “kamuvudines,” are able to block inflammasome activation independently of their antiviral effects.
They hope that this modification will reduce the toxicities associated with the agents. This would be necessary if kamuvudines were to be more widely used in a noninfected, healthier population, Ambati stressed.
Dr. Ambati and his colleague, Paul Ashton, PhD, cofounder of Inflammasone Therapeutics, plan a clinical trial with one of these kamuvudines in macular degeneration, which they hope will begin early next year.
“We are trying to pick a disease where we can show efficacy fairly quickly in a small number of people,” Dr. Ashton explained in an interview. “We’re very enthusiastic about this as it looks really, really promising.”
Dr. Ambati and Dr. Ashton cofounded Inflammasone Therapeutics, located in Boston. Dr. Ashton is the CEO of the company.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A class of drugs long used to treat HIV and hepatitis B viral infections appears to prevent the development of diabetes in a substantial proportion of patients who take these agents, an analysis of multiple databases has shown.
“Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors [NRTIs], drugs approved to treat HIV-1 and hepatitis B infections, also block inflammasome activation,” Jayakrishna Ambati, MD, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, and colleagues wrote in Nature Communications.
“[We showed that] the adjusted risk of incident diabetes is 33% lower in patients with NRTI exposure. ... These data suggest the possibility of repurposing an approved class of drugs for prevention of diabetes,” they wrote.
The researchers made a small chemical modification to NRTIs that led to their developing a new class of drugs, which they have termed “kamuvudines.” Kamuvudines are nontoxic derivatives of NRTIs, Dr. Ambati said in an interview.
“People take NRTIs because they need to live with HIV, but giving them to the general population is not a great idea because of the toxicities associated with long-term NRTI use. So our focus is not to go forward specifically with NRTIs but rather with these new molecules that are far less toxic, and that is how we envision a clinical trial going forward,” Dr. Ambati noted.
Researchers screened five databases of >100,000 patients
Dr. Ambati and colleagues analyzed information from five databases in which patients who had been exposed to an NRTI but who had not previously been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes were assessed for the subsequent development of diabetes over varying time intervals. In one, the Veterans Health Administration database – from the largest integrated health care system in the United States – the analysis spanned a period of 17 years.
Of 79,744 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of HIV or hepatitis B in the Veterans Health Administration database, the risk for type 2 diabetes was reduced by 34% among NRTI users, compared with nonusers after adjusting for potential confounders (P < .0001).
The reduction in diabetes risk was similar among HIV-positive and hepatitis B–positive patients.
These results were reaffirmed by further analyses of four other databases, the investigators reported. One of these, the employer-based health insurance Truven database, had data on 23,634 patients who had been diagnosed with HIV or hepatitis B. After adjusting for potential confounders, NRTI users had a 39% lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes, compared with nonusers (P < .0001).
The risk of developing type 2 diabetes was somewhat lower among NRTI users in the Pearl Diver database, which includes predominantly private health insurance claims. Of 16,045 patients diagnosed with HIV or hepatitis B included in this database, the risk for type 2 diabetes was 26% lower among NRTI users, compared with nonusers (P = .004).
A similar magnitude of risk reduction was seen in the analysis of the Clinformatics dataset. Among 6,341 users of NRTIs, the risk for type 2 diabetes was 27% lower than it was for nonusers (P = .009).
The least reduction in diabetes risk was in the Medicare database, in which only 3,097 patients had been diagnosed with either HIV or hepatitis B. Among these patients, the risk for diabetes was 17% lower among NRTI users than it was for nonusers (P = .137).
One-third reduction across multiple databases enhances confidence
“Collectively, among 128,861 patients with HIV-1 or hepatitis B, users of NRTIs had a 33% reduced hazard of developing type 2 diabetes,” Dr. Ambati and colleagues emphasize.
“The fact that the protective effect against the development of diabetes was replicated in multiple databases in studies from multiple institutions enhances confidence in the results,” Dr. Ambati noted in a statement from the University of Virginia.
Dr. Ambati and colleagues also showed that the NRTI lamivudine restores insulin sensitivity in human cells from type 2 diabetes patients.
That drug prevented induction of insulin resistance in human cells from people who did not have diabetes. It also prevented inflammasome activation in mice fed a high-fat diet.
“These investigations of human cell, mouse and population database systems collectively suggest a potential beneficial effect of NRTIs in forestalling diabetes onset,” they stressed.
Trial assessing kamuvudines slated to begin next year
In the interview, Dr. Ambati explained that inflammasomes are protein complexes that form a large superstructure within the cell. “When activated, they lead to the production of some very powerful inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-1 beta and IL-18.”
Although there are many different types of inflammasomes, the one implicated in type 2 diabetes, as well as many other chronic diseases, including macular degeneration, is the NLRP3 inflammasome.
Activation of this molecule promotes insulin resistance, a key driver of type 2 diabetes, he explained.
Importantly, previous research showed that the way the NRTIs block this inflammasome has nothing to do with their anti-HIV activity.
After making a small chemical modification in the NRTIs, Dr. Ambati and colleagues were able to show that the resulting agents, which they have dubbed “kamuvudines,” are able to block inflammasome activation independently of their antiviral effects.
They hope that this modification will reduce the toxicities associated with the agents. This would be necessary if kamuvudines were to be more widely used in a noninfected, healthier population, Ambati stressed.
Dr. Ambati and his colleague, Paul Ashton, PhD, cofounder of Inflammasone Therapeutics, plan a clinical trial with one of these kamuvudines in macular degeneration, which they hope will begin early next year.
“We are trying to pick a disease where we can show efficacy fairly quickly in a small number of people,” Dr. Ashton explained in an interview. “We’re very enthusiastic about this as it looks really, really promising.”
Dr. Ambati and Dr. Ashton cofounded Inflammasone Therapeutics, located in Boston. Dr. Ashton is the CEO of the company.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Thermography plus software shows efficacy for breast cancer screening
Sensitivity and area under the curve (AUC) analyses of thermography that is combined with diagnostic software demonstrate “the efficacy of the tool for breast cancer screening,” concludes an observational, comparative study from India published online Oct. 1 in JCO Global Oncology, a publication of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Siva Teja Kakileti of Niramai Health Analytix, Koramangala, Bangalore, India, and colleagues said that the product, Thermalytix, is potentially a good fit for low- and middle-income countries because it is portable and provides automated quantitative analysis of thermal images – and thus can be conducted by technicians with “minimal training.”
Conventional thermography involves manual interpretation of complex thermal images, which “often results in erroneous results owing to subjectivity,” said the study authors.
That manual interpretation of thermal images might involve looking at 200 color shades, which is “high cognitive overload for the thermographer,” explained Mr. Kakileti in an interview.
However, an American mammography expert who was approached for comment dismissed thermography – even with the new twist of software-aided diagnostic scoring by Thermalytix – as wholly inappropriate for the detection of early breast cancer, owing to inherent limitations.
“Thermal imaging of any type has no value in finding early breast cancer,” Daniel Kopans, MD, of Harvard University and Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview. He said that thermal imaging only detects heat on the skin and perhaps a few millimeters beneath the skin and thus misses deeper cancers, the heat from which is carried away by the vascular system.
The new study included 470 women who presented for breast screening at two centers in Bangalore, India. A total of 238 women had symptoms such as breast lump, nipple discharge, skin changes, or breast pain; the remaining 232 women were asymptomatic.
All participants underwent a Thermalytix test and one or more standard-of-care tests for breast cancer screening (such as mammography, ultrasonography, biopsy, fine-needle aspiration, or elastography). A total of 78 women, or 16.6% of the group overall, were diagnosed with a malignancy. For the overall group of 470 women, Thermalytix had a sensitivity of 91.02% (symptomatic, 89.85%; asymptomatic,100%) and a specificity of 82.39% (symptomatic, 69.04%; asymptomatic, 92.41%) in detection of breast malignancy. Thermalytix showed an overall AUC of 0.90, with an AUC of 0.82 for symptomatic and 0.98 for asymptomatic women.
The study authors characterized both the sensitivity and AUC as “high.”
The results from the study, which the authors characterized as preliminary, encouraged the study sponsor, Niramai, to start planning a large-scale, multicountry trial.
But Dr. Kopans, who serves as a consultant to DART, which produces digital breast tomosynthesis units in China, suggested that this research will be fruitless. “Thermal imaging seems to raise its head every few years since it is passive, but it does not work and is a waste of money,” Dr. Kopans reiterated.
“Its use can be dangerous by dissuading women from being screened with mammography, which has been proven to save lives,” he stressed.
Thermalytix compared with mammography
Investigators also compared screening results in the subset of 242 women who underwent both Thermalytix and mammography. Results showed that Thermalytix had a higher sensitivity than did mammography (91.23% vs. 85.96%), but mammography had a higher specificity than Thermalytix did (94.05% vs. 68.65%).
In the asymptomatic group who underwent both tests (n = 95), four cancers were detected, and Thermalytix demonstrated superior sensitivity than mammography (100% vs. 50%), Mr. Kakileti and colleagues state.
Thermalytix evaluates vascularity variations too
In the subset of 228 women who did not undergo mammography (owing to dense breasts, younger age, or other reasons), Thermalytix detected tumors in all but 3 of 21 patients who went on to be diagnosed with breast cancer. The authors state that, because their artificial intelligence–based analysis uses vascularity, as well as temperature variations on the skin, to complement hot-spot detection, it is able to detect small lesions.
In the current study, 24 malignant tumors were less than 2 cm in diameter, and Thermalytix was able to identify 17 of the tumors as positive, for a 71% sensitivity rate for T1 tumors. This compared with a 68% sensitivity rate for mammography for detecting the same T1 tumors. Thermalytix also showed promising results in women younger than 40 years, for whom screening mammography is not usually recommended. The automated test picked up all 11 tumors eventually diagnosed in this younger cohort.
“Thermalytix is a portable, noninvasive, radiation-free test that has shown promising results in this preliminary study,” the investigators wrote, “[and] it can be an affordable and scalable method of screening in remote areas,” they added.
“We believe that Thermalytix ... is poised to be a promising modality for breast cancer screening,” Mr. Kakileti and colleagues summarized.
The FDA warns about thermography in place of mammography
The US Food and Drug Administration fairly recently warned against the use of thermography as an alternative to mammography for breast cancer screening or diagnosis, noting that it has received reports that facilities where thermography is offered often provide false information about the technology that can mislead patients into believing that it is either an alternative to or a better option than mammography.
Dr. Kopans says that other groups have invested in thermography research. “The Israelis spent millions working on a similar approach that didn’t work,” he commented.
The new software from Thermalytix, which is derived from artificial intelligence, is a “gimmick,” says the Boston radiologist. “If the basic information is not there, a computer cannot find it,” he stated, referring to what he believes are deeper-tissue tumors that are inaccessible to heat-detecting technology.
Mr. Kakileti is an employee of Nirami Health Analytix and owns stock and has filed patents with the company. Other investigators are also employed by the same company or receive research and other funding or have patents filed by the company as well. Dr. Kopans serves as a consultant to DART, which produces digital breast tomosynthesis units in China.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Sensitivity and area under the curve (AUC) analyses of thermography that is combined with diagnostic software demonstrate “the efficacy of the tool for breast cancer screening,” concludes an observational, comparative study from India published online Oct. 1 in JCO Global Oncology, a publication of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Siva Teja Kakileti of Niramai Health Analytix, Koramangala, Bangalore, India, and colleagues said that the product, Thermalytix, is potentially a good fit for low- and middle-income countries because it is portable and provides automated quantitative analysis of thermal images – and thus can be conducted by technicians with “minimal training.”
Conventional thermography involves manual interpretation of complex thermal images, which “often results in erroneous results owing to subjectivity,” said the study authors.
That manual interpretation of thermal images might involve looking at 200 color shades, which is “high cognitive overload for the thermographer,” explained Mr. Kakileti in an interview.
However, an American mammography expert who was approached for comment dismissed thermography – even with the new twist of software-aided diagnostic scoring by Thermalytix – as wholly inappropriate for the detection of early breast cancer, owing to inherent limitations.
“Thermal imaging of any type has no value in finding early breast cancer,” Daniel Kopans, MD, of Harvard University and Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview. He said that thermal imaging only detects heat on the skin and perhaps a few millimeters beneath the skin and thus misses deeper cancers, the heat from which is carried away by the vascular system.
The new study included 470 women who presented for breast screening at two centers in Bangalore, India. A total of 238 women had symptoms such as breast lump, nipple discharge, skin changes, or breast pain; the remaining 232 women were asymptomatic.
All participants underwent a Thermalytix test and one or more standard-of-care tests for breast cancer screening (such as mammography, ultrasonography, biopsy, fine-needle aspiration, or elastography). A total of 78 women, or 16.6% of the group overall, were diagnosed with a malignancy. For the overall group of 470 women, Thermalytix had a sensitivity of 91.02% (symptomatic, 89.85%; asymptomatic,100%) and a specificity of 82.39% (symptomatic, 69.04%; asymptomatic, 92.41%) in detection of breast malignancy. Thermalytix showed an overall AUC of 0.90, with an AUC of 0.82 for symptomatic and 0.98 for asymptomatic women.
The study authors characterized both the sensitivity and AUC as “high.”
The results from the study, which the authors characterized as preliminary, encouraged the study sponsor, Niramai, to start planning a large-scale, multicountry trial.
But Dr. Kopans, who serves as a consultant to DART, which produces digital breast tomosynthesis units in China, suggested that this research will be fruitless. “Thermal imaging seems to raise its head every few years since it is passive, but it does not work and is a waste of money,” Dr. Kopans reiterated.
“Its use can be dangerous by dissuading women from being screened with mammography, which has been proven to save lives,” he stressed.
Thermalytix compared with mammography
Investigators also compared screening results in the subset of 242 women who underwent both Thermalytix and mammography. Results showed that Thermalytix had a higher sensitivity than did mammography (91.23% vs. 85.96%), but mammography had a higher specificity than Thermalytix did (94.05% vs. 68.65%).
In the asymptomatic group who underwent both tests (n = 95), four cancers were detected, and Thermalytix demonstrated superior sensitivity than mammography (100% vs. 50%), Mr. Kakileti and colleagues state.
Thermalytix evaluates vascularity variations too
In the subset of 228 women who did not undergo mammography (owing to dense breasts, younger age, or other reasons), Thermalytix detected tumors in all but 3 of 21 patients who went on to be diagnosed with breast cancer. The authors state that, because their artificial intelligence–based analysis uses vascularity, as well as temperature variations on the skin, to complement hot-spot detection, it is able to detect small lesions.
In the current study, 24 malignant tumors were less than 2 cm in diameter, and Thermalytix was able to identify 17 of the tumors as positive, for a 71% sensitivity rate for T1 tumors. This compared with a 68% sensitivity rate for mammography for detecting the same T1 tumors. Thermalytix also showed promising results in women younger than 40 years, for whom screening mammography is not usually recommended. The automated test picked up all 11 tumors eventually diagnosed in this younger cohort.
“Thermalytix is a portable, noninvasive, radiation-free test that has shown promising results in this preliminary study,” the investigators wrote, “[and] it can be an affordable and scalable method of screening in remote areas,” they added.
“We believe that Thermalytix ... is poised to be a promising modality for breast cancer screening,” Mr. Kakileti and colleagues summarized.
The FDA warns about thermography in place of mammography
The US Food and Drug Administration fairly recently warned against the use of thermography as an alternative to mammography for breast cancer screening or diagnosis, noting that it has received reports that facilities where thermography is offered often provide false information about the technology that can mislead patients into believing that it is either an alternative to or a better option than mammography.
Dr. Kopans says that other groups have invested in thermography research. “The Israelis spent millions working on a similar approach that didn’t work,” he commented.
The new software from Thermalytix, which is derived from artificial intelligence, is a “gimmick,” says the Boston radiologist. “If the basic information is not there, a computer cannot find it,” he stated, referring to what he believes are deeper-tissue tumors that are inaccessible to heat-detecting technology.
Mr. Kakileti is an employee of Nirami Health Analytix and owns stock and has filed patents with the company. Other investigators are also employed by the same company or receive research and other funding or have patents filed by the company as well. Dr. Kopans serves as a consultant to DART, which produces digital breast tomosynthesis units in China.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Sensitivity and area under the curve (AUC) analyses of thermography that is combined with diagnostic software demonstrate “the efficacy of the tool for breast cancer screening,” concludes an observational, comparative study from India published online Oct. 1 in JCO Global Oncology, a publication of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Siva Teja Kakileti of Niramai Health Analytix, Koramangala, Bangalore, India, and colleagues said that the product, Thermalytix, is potentially a good fit for low- and middle-income countries because it is portable and provides automated quantitative analysis of thermal images – and thus can be conducted by technicians with “minimal training.”
Conventional thermography involves manual interpretation of complex thermal images, which “often results in erroneous results owing to subjectivity,” said the study authors.
That manual interpretation of thermal images might involve looking at 200 color shades, which is “high cognitive overload for the thermographer,” explained Mr. Kakileti in an interview.
However, an American mammography expert who was approached for comment dismissed thermography – even with the new twist of software-aided diagnostic scoring by Thermalytix – as wholly inappropriate for the detection of early breast cancer, owing to inherent limitations.
“Thermal imaging of any type has no value in finding early breast cancer,” Daniel Kopans, MD, of Harvard University and Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview. He said that thermal imaging only detects heat on the skin and perhaps a few millimeters beneath the skin and thus misses deeper cancers, the heat from which is carried away by the vascular system.
The new study included 470 women who presented for breast screening at two centers in Bangalore, India. A total of 238 women had symptoms such as breast lump, nipple discharge, skin changes, or breast pain; the remaining 232 women were asymptomatic.
All participants underwent a Thermalytix test and one or more standard-of-care tests for breast cancer screening (such as mammography, ultrasonography, biopsy, fine-needle aspiration, or elastography). A total of 78 women, or 16.6% of the group overall, were diagnosed with a malignancy. For the overall group of 470 women, Thermalytix had a sensitivity of 91.02% (symptomatic, 89.85%; asymptomatic,100%) and a specificity of 82.39% (symptomatic, 69.04%; asymptomatic, 92.41%) in detection of breast malignancy. Thermalytix showed an overall AUC of 0.90, with an AUC of 0.82 for symptomatic and 0.98 for asymptomatic women.
The study authors characterized both the sensitivity and AUC as “high.”
The results from the study, which the authors characterized as preliminary, encouraged the study sponsor, Niramai, to start planning a large-scale, multicountry trial.
But Dr. Kopans, who serves as a consultant to DART, which produces digital breast tomosynthesis units in China, suggested that this research will be fruitless. “Thermal imaging seems to raise its head every few years since it is passive, but it does not work and is a waste of money,” Dr. Kopans reiterated.
“Its use can be dangerous by dissuading women from being screened with mammography, which has been proven to save lives,” he stressed.
Thermalytix compared with mammography
Investigators also compared screening results in the subset of 242 women who underwent both Thermalytix and mammography. Results showed that Thermalytix had a higher sensitivity than did mammography (91.23% vs. 85.96%), but mammography had a higher specificity than Thermalytix did (94.05% vs. 68.65%).
In the asymptomatic group who underwent both tests (n = 95), four cancers were detected, and Thermalytix demonstrated superior sensitivity than mammography (100% vs. 50%), Mr. Kakileti and colleagues state.
Thermalytix evaluates vascularity variations too
In the subset of 228 women who did not undergo mammography (owing to dense breasts, younger age, or other reasons), Thermalytix detected tumors in all but 3 of 21 patients who went on to be diagnosed with breast cancer. The authors state that, because their artificial intelligence–based analysis uses vascularity, as well as temperature variations on the skin, to complement hot-spot detection, it is able to detect small lesions.
In the current study, 24 malignant tumors were less than 2 cm in diameter, and Thermalytix was able to identify 17 of the tumors as positive, for a 71% sensitivity rate for T1 tumors. This compared with a 68% sensitivity rate for mammography for detecting the same T1 tumors. Thermalytix also showed promising results in women younger than 40 years, for whom screening mammography is not usually recommended. The automated test picked up all 11 tumors eventually diagnosed in this younger cohort.
“Thermalytix is a portable, noninvasive, radiation-free test that has shown promising results in this preliminary study,” the investigators wrote, “[and] it can be an affordable and scalable method of screening in remote areas,” they added.
“We believe that Thermalytix ... is poised to be a promising modality for breast cancer screening,” Mr. Kakileti and colleagues summarized.
The FDA warns about thermography in place of mammography
The US Food and Drug Administration fairly recently warned against the use of thermography as an alternative to mammography for breast cancer screening or diagnosis, noting that it has received reports that facilities where thermography is offered often provide false information about the technology that can mislead patients into believing that it is either an alternative to or a better option than mammography.
Dr. Kopans says that other groups have invested in thermography research. “The Israelis spent millions working on a similar approach that didn’t work,” he commented.
The new software from Thermalytix, which is derived from artificial intelligence, is a “gimmick,” says the Boston radiologist. “If the basic information is not there, a computer cannot find it,” he stated, referring to what he believes are deeper-tissue tumors that are inaccessible to heat-detecting technology.
Mr. Kakileti is an employee of Nirami Health Analytix and owns stock and has filed patents with the company. Other investigators are also employed by the same company or receive research and other funding or have patents filed by the company as well. Dr. Kopans serves as a consultant to DART, which produces digital breast tomosynthesis units in China.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Deaths sky high in hospitalized COVID patients with kidney injury
More evidence indicates that the development of acute kidney injury
“This ... is the first study in the United States to report the persistence of kidney dysfunction (lack of recovery) in survivors of COVID-19–associated AKI [and] this is in marked contrast to other forms of AKI where over 80% of patients recover their renal function by 10 days,” Lili Chan, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues observed.
The research is a retrospective, observational cohort study published online Sept. 3 in the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology
“We may be facing an epidemic of post–COVID-19 kidney disease and that, in turn, could mean much greater numbers of patients who require kidney dialysis and even transplants,” said senior author Girish Nadkarni, MD, a nephrologist, in a statement from Mount Sinai.
Nephrologists will need to prepare for a significant uptick in patients with chronic kidney disease as a result of exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19, the researchers warned.
“These findings may help centers with resource planning and preparing for the increased load resulting from survivors of COVID-19–associated AKI who do not experience recovery of kidney function,” they added.
Analysis of patients from February to end of May 2020
“AKI among hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in the United States is not well described,” they noted in their article.
And so they analyzed data from five major hospitals in the Mount Sinai Health System between Feb. 27 and May 30 of this year, during which 3,993 patients were hospitalized within the system for COVID-19. The MSHS has a patient population of racially and ethnically diverse citizens from New York.
AKI was defined using Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) criteria. AKI occurred in 46% of the overall cohort of patients, 19% of whom required dialysis.
However, among those patients who required admission to the ICU, over three-quarters (76%) developed AKI and almost one-third of ICU patients required dialysis, the investigators said.
“The median time from hospital admission until AKI diagnoses was 1 day and the median time from AKI diagnosis to dialysis was 3 days,” they explain.
The proportion of patients with stages 1, 2, or 3 AKI among those admitted to hospital were 39%, 19%, and 42%, respectively. In patients requiring admission to ICU, 28% had stage 1 AKI, 17% had stage 2, and 56% had stage 3.
And among those who required dialysis for AKI, the median peak serum creatinine was 8.2 mg/dL, compared with 2.2 mg/dL for those who did not require dialysis.
Predictors of AKI: male sex, potassium levels, and preexisting CKD
Almost two thirds of patients (65%) had recovered from their kidney injury by the time they left hospital but 35% had acute kidney disease. Of this latter group, on follow-up, 36% had recovered from it, the investigators noted.
Conversely, of those patients who had recovered from AKI by hospital discharge, 14% went on to develop acute kidney disease at the time of follow-up.
And 30% of patients who had required dialysis at some point during their hospital care required dialysis again within 72 hours of being discharged, the investigators noted.
Predictors of severe AKI included male sex (adjusted odds ratio, 1.46), potassium levels on admission (aOR, 1.7), and preexisting chronic kidney disease (CKD) (aOR, 2.8).
Most compellingly, “in-hospital mortality in patients who experienced AKI was 50% [versus] 8% in patients without AKI (P < .001),” Dr. Nadkarni and colleagues reported.
Among those who required ICU care, 42% of patients with AKI died, compared with 7% of those in ICU who did not develop AKI, while in patients cared for outside of ICU, 62% with AKI died compared with only 13% of those who did not develop AKI.
And after adjusting for demographics, comorbidities, and laboratory values, the aOR for death was 11.4 times higher for ICU patients with AKI, compared with ICU patients without AKI, the authors emphasize.
In all patients who developed AKI, the aOR for mortality was 9.2, compared with patients who did not develop AKI, they added.
Perhaps predictably, the risk of death rose with increasing stage of AKI, and patients with stage 3 AKI who required dialysis were at highest risk of death, the authors observe.
Sheer number of AKI cases, need for dialysis unprecedented
“The sheer number of AKI cases and the overwhelming need for dialysis that we are seeing in the context of COVID-19 is unprecedented,” Dr. Nadkarni said.
“These findings bring clinical evidence to the hypothesis of lingering organ dysfunction among patients recovering from COVID-19 and serve as a reminder to hospitals around the country to be very strategic in the allocation of resources to care for patients who experience AKI,” he cautioned.
“We are grappling with a great deal of uncertainty as to how the virus will impact the kidneys in the long haul,” Dr. Nadkarni added. “We may be facing an epidemic of post–COVID-19 kidney disease, and that, in turn, could mean much greater numbers of patients who require kidney dialysis and even transplants.”
Dr. Nadkarni reported serving as a consultant and advisory board member for RenalytixAI and owns equity in the company.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More evidence indicates that the development of acute kidney injury
“This ... is the first study in the United States to report the persistence of kidney dysfunction (lack of recovery) in survivors of COVID-19–associated AKI [and] this is in marked contrast to other forms of AKI where over 80% of patients recover their renal function by 10 days,” Lili Chan, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues observed.
The research is a retrospective, observational cohort study published online Sept. 3 in the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology
“We may be facing an epidemic of post–COVID-19 kidney disease and that, in turn, could mean much greater numbers of patients who require kidney dialysis and even transplants,” said senior author Girish Nadkarni, MD, a nephrologist, in a statement from Mount Sinai.
Nephrologists will need to prepare for a significant uptick in patients with chronic kidney disease as a result of exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19, the researchers warned.
“These findings may help centers with resource planning and preparing for the increased load resulting from survivors of COVID-19–associated AKI who do not experience recovery of kidney function,” they added.
Analysis of patients from February to end of May 2020
“AKI among hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in the United States is not well described,” they noted in their article.
And so they analyzed data from five major hospitals in the Mount Sinai Health System between Feb. 27 and May 30 of this year, during which 3,993 patients were hospitalized within the system for COVID-19. The MSHS has a patient population of racially and ethnically diverse citizens from New York.
AKI was defined using Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) criteria. AKI occurred in 46% of the overall cohort of patients, 19% of whom required dialysis.
However, among those patients who required admission to the ICU, over three-quarters (76%) developed AKI and almost one-third of ICU patients required dialysis, the investigators said.
“The median time from hospital admission until AKI diagnoses was 1 day and the median time from AKI diagnosis to dialysis was 3 days,” they explain.
The proportion of patients with stages 1, 2, or 3 AKI among those admitted to hospital were 39%, 19%, and 42%, respectively. In patients requiring admission to ICU, 28% had stage 1 AKI, 17% had stage 2, and 56% had stage 3.
And among those who required dialysis for AKI, the median peak serum creatinine was 8.2 mg/dL, compared with 2.2 mg/dL for those who did not require dialysis.
Predictors of AKI: male sex, potassium levels, and preexisting CKD
Almost two thirds of patients (65%) had recovered from their kidney injury by the time they left hospital but 35% had acute kidney disease. Of this latter group, on follow-up, 36% had recovered from it, the investigators noted.
Conversely, of those patients who had recovered from AKI by hospital discharge, 14% went on to develop acute kidney disease at the time of follow-up.
And 30% of patients who had required dialysis at some point during their hospital care required dialysis again within 72 hours of being discharged, the investigators noted.
Predictors of severe AKI included male sex (adjusted odds ratio, 1.46), potassium levels on admission (aOR, 1.7), and preexisting chronic kidney disease (CKD) (aOR, 2.8).
Most compellingly, “in-hospital mortality in patients who experienced AKI was 50% [versus] 8% in patients without AKI (P < .001),” Dr. Nadkarni and colleagues reported.
Among those who required ICU care, 42% of patients with AKI died, compared with 7% of those in ICU who did not develop AKI, while in patients cared for outside of ICU, 62% with AKI died compared with only 13% of those who did not develop AKI.
And after adjusting for demographics, comorbidities, and laboratory values, the aOR for death was 11.4 times higher for ICU patients with AKI, compared with ICU patients without AKI, the authors emphasize.
In all patients who developed AKI, the aOR for mortality was 9.2, compared with patients who did not develop AKI, they added.
Perhaps predictably, the risk of death rose with increasing stage of AKI, and patients with stage 3 AKI who required dialysis were at highest risk of death, the authors observe.
Sheer number of AKI cases, need for dialysis unprecedented
“The sheer number of AKI cases and the overwhelming need for dialysis that we are seeing in the context of COVID-19 is unprecedented,” Dr. Nadkarni said.
“These findings bring clinical evidence to the hypothesis of lingering organ dysfunction among patients recovering from COVID-19 and serve as a reminder to hospitals around the country to be very strategic in the allocation of resources to care for patients who experience AKI,” he cautioned.
“We are grappling with a great deal of uncertainty as to how the virus will impact the kidneys in the long haul,” Dr. Nadkarni added. “We may be facing an epidemic of post–COVID-19 kidney disease, and that, in turn, could mean much greater numbers of patients who require kidney dialysis and even transplants.”
Dr. Nadkarni reported serving as a consultant and advisory board member for RenalytixAI and owns equity in the company.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More evidence indicates that the development of acute kidney injury
“This ... is the first study in the United States to report the persistence of kidney dysfunction (lack of recovery) in survivors of COVID-19–associated AKI [and] this is in marked contrast to other forms of AKI where over 80% of patients recover their renal function by 10 days,” Lili Chan, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues observed.
The research is a retrospective, observational cohort study published online Sept. 3 in the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology
“We may be facing an epidemic of post–COVID-19 kidney disease and that, in turn, could mean much greater numbers of patients who require kidney dialysis and even transplants,” said senior author Girish Nadkarni, MD, a nephrologist, in a statement from Mount Sinai.
Nephrologists will need to prepare for a significant uptick in patients with chronic kidney disease as a result of exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19, the researchers warned.
“These findings may help centers with resource planning and preparing for the increased load resulting from survivors of COVID-19–associated AKI who do not experience recovery of kidney function,” they added.
Analysis of patients from February to end of May 2020
“AKI among hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in the United States is not well described,” they noted in their article.
And so they analyzed data from five major hospitals in the Mount Sinai Health System between Feb. 27 and May 30 of this year, during which 3,993 patients were hospitalized within the system for COVID-19. The MSHS has a patient population of racially and ethnically diverse citizens from New York.
AKI was defined using Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) criteria. AKI occurred in 46% of the overall cohort of patients, 19% of whom required dialysis.
However, among those patients who required admission to the ICU, over three-quarters (76%) developed AKI and almost one-third of ICU patients required dialysis, the investigators said.
“The median time from hospital admission until AKI diagnoses was 1 day and the median time from AKI diagnosis to dialysis was 3 days,” they explain.
The proportion of patients with stages 1, 2, or 3 AKI among those admitted to hospital were 39%, 19%, and 42%, respectively. In patients requiring admission to ICU, 28% had stage 1 AKI, 17% had stage 2, and 56% had stage 3.
And among those who required dialysis for AKI, the median peak serum creatinine was 8.2 mg/dL, compared with 2.2 mg/dL for those who did not require dialysis.
Predictors of AKI: male sex, potassium levels, and preexisting CKD
Almost two thirds of patients (65%) had recovered from their kidney injury by the time they left hospital but 35% had acute kidney disease. Of this latter group, on follow-up, 36% had recovered from it, the investigators noted.
Conversely, of those patients who had recovered from AKI by hospital discharge, 14% went on to develop acute kidney disease at the time of follow-up.
And 30% of patients who had required dialysis at some point during their hospital care required dialysis again within 72 hours of being discharged, the investigators noted.
Predictors of severe AKI included male sex (adjusted odds ratio, 1.46), potassium levels on admission (aOR, 1.7), and preexisting chronic kidney disease (CKD) (aOR, 2.8).
Most compellingly, “in-hospital mortality in patients who experienced AKI was 50% [versus] 8% in patients without AKI (P < .001),” Dr. Nadkarni and colleagues reported.
Among those who required ICU care, 42% of patients with AKI died, compared with 7% of those in ICU who did not develop AKI, while in patients cared for outside of ICU, 62% with AKI died compared with only 13% of those who did not develop AKI.
And after adjusting for demographics, comorbidities, and laboratory values, the aOR for death was 11.4 times higher for ICU patients with AKI, compared with ICU patients without AKI, the authors emphasize.
In all patients who developed AKI, the aOR for mortality was 9.2, compared with patients who did not develop AKI, they added.
Perhaps predictably, the risk of death rose with increasing stage of AKI, and patients with stage 3 AKI who required dialysis were at highest risk of death, the authors observe.
Sheer number of AKI cases, need for dialysis unprecedented
“The sheer number of AKI cases and the overwhelming need for dialysis that we are seeing in the context of COVID-19 is unprecedented,” Dr. Nadkarni said.
“These findings bring clinical evidence to the hypothesis of lingering organ dysfunction among patients recovering from COVID-19 and serve as a reminder to hospitals around the country to be very strategic in the allocation of resources to care for patients who experience AKI,” he cautioned.
“We are grappling with a great deal of uncertainty as to how the virus will impact the kidneys in the long haul,” Dr. Nadkarni added. “We may be facing an epidemic of post–COVID-19 kidney disease, and that, in turn, could mean much greater numbers of patients who require kidney dialysis and even transplants.”
Dr. Nadkarni reported serving as a consultant and advisory board member for RenalytixAI and owns equity in the company.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
First guideline on NGS testing in cancer, from ESMO
Recommendations on the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) tests for patients with metastatic cancer have been issued by the European Society for Medical Oncology, the first recommendations of their kind to be published by any medical society.
“Until now, there were no recommendations from scientific societies on how to use this technique in daily clinical practice to profile metastatic cancers,” Fernanda Mosele, MD, medical oncologist, Gustave Roussy, Villejuif, France, said in a statement.
NGS testing is already used extensively in oncology, particularly in metastatic cancer, she noted. The technology is used to assess the sequence of DNA in genes from a tumor tissue sample. Numerous genes can be quickly sequenced at the same time at relatively low cost. The results provide information on mutations that are present, which, in turn, helps with deciding which treatments to use, including drugs targeting the identified mutations.
“Our intent is that they [the guidelines] will unify decision-making about how NGS should be used for patients with metastatic cancer,” Dr. Mosele said.
The recommendations were published online August 25 in Annals of Oncology.
Overall, ESMO recommends the use of tumor multigene NGS for non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), prostate cancer, ovarian cancer, and cholangiocarcinoma.
For other cancers, the authors said that NGS is not recommended in clinical practice but could be used for research purposes.
However, patients should be informed that it is unlikely that test results would benefit them much personally.
Physicians and patients may decide together to subject the tumor to mutational testing using a large panel of genes, provided testing doesn’t burden the health care system with additional costs.
“This recommendation acknowledges that a small number of patients could benefit from a drug because they have a rare mutation,” Joaquin Mateo, MD, chair of the ESMO working group, said in a statement.
“So beyond the cancers in which everyone should receive NGS, there is room for physicians and patients to discuss the pros and cons of ordering these tests,” he added.
ESMO also does not recommend the use of off-label drugs matched to any genomic alteration detected by NGS unless an access program and a decisional procedure have been developed, either regionally or nationally.
No need for NGS testing of other cancers
In contrast to NSCLC, “there is currently no need to perform tumor multigene NGS for patients with mBC [metastatic breast cancer] in the context of daily practice,” ESMO stated.
This is largely because somatic sequencing cannot fully substitute for germline testing for BRCA status, and other mutations, such as HER2, can be detected using immunohistochemistry (IHC).
The same can be said for patients with metastatic gastric cancer, inasmuch as detection of alterations can and should be done using cheaper testing methods, ESMO pointed out.
However, ESMO members still emphasized that it’s important to include patients with metastatic breast cancer in molecular screening programs as well as in clinical trials testing targeted agents.
Similarly, there is no need to test metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) using multigene NGS in daily practice, inasmuch as most level 1 alterations in mCRC can be determined by IHC or PCR.
However, NGS can be considered as an alternative to PCR-based tests in mCRC, provided NGS is not associated with additional cost.
ESMO again recommended that research centers include mCRC patients in molecular screening programs in order for them to have access to innovative clinical trial agents.
As for advanced prostate cancer, ESMO does recommend that clinicians perform NGS on tissue samples to assess the tumor’s mutational status, at least for the presence of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations, when patients have access to the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors for treatment.
The authors cautioned, however, that this strategy is unlikely to be cost-effective, so larger panels should be used only when there are specific agreements with payers.
Multigene NGS is also not recommended for patients with advanced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), although ESMO points out that it is the role of research centers to propose multigene sequencing for these patients in the context of molecular screening programs.
This is again to facilitate access to innovative drugs for these patients.
Similar to recommendations for patients with advanced PDAC, patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) do not need to have tumor multigene NGS either.
Considering the high unmet needs of HCC patients, ESMO feels that research centers should propose multigene sequencing to patients with advanced HCC in the context of molecular screening programs.
In contrast, ESMO recommended that tumor multigene NGS be used to detect actionable alterations in patients with advanced cholangiocarcinoma.
Again, they predict that this strategy is unlikely to be cost-effective, so larger panels should only be used if a specific agreement is in place with payers.
ESMO also assessed the frequency of level 1 alterations in less frequent tumor types, including ovarian cancers. Because BRCA1 and BRCA2 somatic mutations in ovarian tumors have been associated with increased response to the PARP inhibitors, the use of multigene NGS is justified with this malignancy, ESMO states.
The authors also recommend that tumor mutational burden be determined in cervical cancer, moderately differentiated neuroendocrine tumors, salivary cancers, vulvar cancer, and thyroid cancers.
Dr. Mosele has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Many coauthors have relationships with the pharmaceutical industry, as listed in the article.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Recommendations on the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) tests for patients with metastatic cancer have been issued by the European Society for Medical Oncology, the first recommendations of their kind to be published by any medical society.
“Until now, there were no recommendations from scientific societies on how to use this technique in daily clinical practice to profile metastatic cancers,” Fernanda Mosele, MD, medical oncologist, Gustave Roussy, Villejuif, France, said in a statement.
NGS testing is already used extensively in oncology, particularly in metastatic cancer, she noted. The technology is used to assess the sequence of DNA in genes from a tumor tissue sample. Numerous genes can be quickly sequenced at the same time at relatively low cost. The results provide information on mutations that are present, which, in turn, helps with deciding which treatments to use, including drugs targeting the identified mutations.
“Our intent is that they [the guidelines] will unify decision-making about how NGS should be used for patients with metastatic cancer,” Dr. Mosele said.
The recommendations were published online August 25 in Annals of Oncology.
Overall, ESMO recommends the use of tumor multigene NGS for non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), prostate cancer, ovarian cancer, and cholangiocarcinoma.
For other cancers, the authors said that NGS is not recommended in clinical practice but could be used for research purposes.
However, patients should be informed that it is unlikely that test results would benefit them much personally.
Physicians and patients may decide together to subject the tumor to mutational testing using a large panel of genes, provided testing doesn’t burden the health care system with additional costs.
“This recommendation acknowledges that a small number of patients could benefit from a drug because they have a rare mutation,” Joaquin Mateo, MD, chair of the ESMO working group, said in a statement.
“So beyond the cancers in which everyone should receive NGS, there is room for physicians and patients to discuss the pros and cons of ordering these tests,” he added.
ESMO also does not recommend the use of off-label drugs matched to any genomic alteration detected by NGS unless an access program and a decisional procedure have been developed, either regionally or nationally.
No need for NGS testing of other cancers
In contrast to NSCLC, “there is currently no need to perform tumor multigene NGS for patients with mBC [metastatic breast cancer] in the context of daily practice,” ESMO stated.
This is largely because somatic sequencing cannot fully substitute for germline testing for BRCA status, and other mutations, such as HER2, can be detected using immunohistochemistry (IHC).
The same can be said for patients with metastatic gastric cancer, inasmuch as detection of alterations can and should be done using cheaper testing methods, ESMO pointed out.
However, ESMO members still emphasized that it’s important to include patients with metastatic breast cancer in molecular screening programs as well as in clinical trials testing targeted agents.
Similarly, there is no need to test metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) using multigene NGS in daily practice, inasmuch as most level 1 alterations in mCRC can be determined by IHC or PCR.
However, NGS can be considered as an alternative to PCR-based tests in mCRC, provided NGS is not associated with additional cost.
ESMO again recommended that research centers include mCRC patients in molecular screening programs in order for them to have access to innovative clinical trial agents.
As for advanced prostate cancer, ESMO does recommend that clinicians perform NGS on tissue samples to assess the tumor’s mutational status, at least for the presence of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations, when patients have access to the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors for treatment.
The authors cautioned, however, that this strategy is unlikely to be cost-effective, so larger panels should be used only when there are specific agreements with payers.
Multigene NGS is also not recommended for patients with advanced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), although ESMO points out that it is the role of research centers to propose multigene sequencing for these patients in the context of molecular screening programs.
This is again to facilitate access to innovative drugs for these patients.
Similar to recommendations for patients with advanced PDAC, patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) do not need to have tumor multigene NGS either.
Considering the high unmet needs of HCC patients, ESMO feels that research centers should propose multigene sequencing to patients with advanced HCC in the context of molecular screening programs.
In contrast, ESMO recommended that tumor multigene NGS be used to detect actionable alterations in patients with advanced cholangiocarcinoma.
Again, they predict that this strategy is unlikely to be cost-effective, so larger panels should only be used if a specific agreement is in place with payers.
ESMO also assessed the frequency of level 1 alterations in less frequent tumor types, including ovarian cancers. Because BRCA1 and BRCA2 somatic mutations in ovarian tumors have been associated with increased response to the PARP inhibitors, the use of multigene NGS is justified with this malignancy, ESMO states.
The authors also recommend that tumor mutational burden be determined in cervical cancer, moderately differentiated neuroendocrine tumors, salivary cancers, vulvar cancer, and thyroid cancers.
Dr. Mosele has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Many coauthors have relationships with the pharmaceutical industry, as listed in the article.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Recommendations on the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) tests for patients with metastatic cancer have been issued by the European Society for Medical Oncology, the first recommendations of their kind to be published by any medical society.
“Until now, there were no recommendations from scientific societies on how to use this technique in daily clinical practice to profile metastatic cancers,” Fernanda Mosele, MD, medical oncologist, Gustave Roussy, Villejuif, France, said in a statement.
NGS testing is already used extensively in oncology, particularly in metastatic cancer, she noted. The technology is used to assess the sequence of DNA in genes from a tumor tissue sample. Numerous genes can be quickly sequenced at the same time at relatively low cost. The results provide information on mutations that are present, which, in turn, helps with deciding which treatments to use, including drugs targeting the identified mutations.
“Our intent is that they [the guidelines] will unify decision-making about how NGS should be used for patients with metastatic cancer,” Dr. Mosele said.
The recommendations were published online August 25 in Annals of Oncology.
Overall, ESMO recommends the use of tumor multigene NGS for non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), prostate cancer, ovarian cancer, and cholangiocarcinoma.
For other cancers, the authors said that NGS is not recommended in clinical practice but could be used for research purposes.
However, patients should be informed that it is unlikely that test results would benefit them much personally.
Physicians and patients may decide together to subject the tumor to mutational testing using a large panel of genes, provided testing doesn’t burden the health care system with additional costs.
“This recommendation acknowledges that a small number of patients could benefit from a drug because they have a rare mutation,” Joaquin Mateo, MD, chair of the ESMO working group, said in a statement.
“So beyond the cancers in which everyone should receive NGS, there is room for physicians and patients to discuss the pros and cons of ordering these tests,” he added.
ESMO also does not recommend the use of off-label drugs matched to any genomic alteration detected by NGS unless an access program and a decisional procedure have been developed, either regionally or nationally.
No need for NGS testing of other cancers
In contrast to NSCLC, “there is currently no need to perform tumor multigene NGS for patients with mBC [metastatic breast cancer] in the context of daily practice,” ESMO stated.
This is largely because somatic sequencing cannot fully substitute for germline testing for BRCA status, and other mutations, such as HER2, can be detected using immunohistochemistry (IHC).
The same can be said for patients with metastatic gastric cancer, inasmuch as detection of alterations can and should be done using cheaper testing methods, ESMO pointed out.
However, ESMO members still emphasized that it’s important to include patients with metastatic breast cancer in molecular screening programs as well as in clinical trials testing targeted agents.
Similarly, there is no need to test metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) using multigene NGS in daily practice, inasmuch as most level 1 alterations in mCRC can be determined by IHC or PCR.
However, NGS can be considered as an alternative to PCR-based tests in mCRC, provided NGS is not associated with additional cost.
ESMO again recommended that research centers include mCRC patients in molecular screening programs in order for them to have access to innovative clinical trial agents.
As for advanced prostate cancer, ESMO does recommend that clinicians perform NGS on tissue samples to assess the tumor’s mutational status, at least for the presence of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations, when patients have access to the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors for treatment.
The authors cautioned, however, that this strategy is unlikely to be cost-effective, so larger panels should be used only when there are specific agreements with payers.
Multigene NGS is also not recommended for patients with advanced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), although ESMO points out that it is the role of research centers to propose multigene sequencing for these patients in the context of molecular screening programs.
This is again to facilitate access to innovative drugs for these patients.
Similar to recommendations for patients with advanced PDAC, patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) do not need to have tumor multigene NGS either.
Considering the high unmet needs of HCC patients, ESMO feels that research centers should propose multigene sequencing to patients with advanced HCC in the context of molecular screening programs.
In contrast, ESMO recommended that tumor multigene NGS be used to detect actionable alterations in patients with advanced cholangiocarcinoma.
Again, they predict that this strategy is unlikely to be cost-effective, so larger panels should only be used if a specific agreement is in place with payers.
ESMO also assessed the frequency of level 1 alterations in less frequent tumor types, including ovarian cancers. Because BRCA1 and BRCA2 somatic mutations in ovarian tumors have been associated with increased response to the PARP inhibitors, the use of multigene NGS is justified with this malignancy, ESMO states.
The authors also recommend that tumor mutational burden be determined in cervical cancer, moderately differentiated neuroendocrine tumors, salivary cancers, vulvar cancer, and thyroid cancers.
Dr. Mosele has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Many coauthors have relationships with the pharmaceutical industry, as listed in the article.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Immunotherapy should not be withheld because of sex, age, or PS
The improvement in survival in many cancer types that is seen with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), when compared to control therapies, is not affected by the patient’s sex, age, or Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (PS), according to a new meta-analysis.
Therefore, treatment with these immunotherapies should not be withheld on the basis of these factors, the authors concluded.
Asked whether there have been such instances of withholding ICIs, lead author Yucai Wang, MD, PhD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, told Medscape Medical News: “We did this study solely based on scientific questions we had and not because we were seeing any bias at the moment in the use of ICIs.
“And we saw that the survival benefits were very similar across all of the categories [we analyzed], with a survival benefit of about 20% from immunotherapy across the board, which is clinically meaningful,” he added.
The study was published online August 7 in JAMA Network Open.
“The comparable survival advantage between patients of different sex, age, and ECOG PS may encourage more patients to receive ICI treatment regardless of cancer types, lines of therapy, agents of immunotherapy, and intervention therapies,” the authors commented.
Wang noted that there have been conflicting reports in the literature suggesting that male patients may benefit more from immunotherapy than female patients and that older patients may benefit more from the same treatment than younger patients.
However, there are also suggestions in the literature that women experience a stronger immune response than men and that, with aging, the immune system generally undergoes immunosenescence.
In addition, the PS of oncology patients has been implicated in how well patients respond to immunotherapy.
Wang noted that the findings of past studies have contradicted each other.
Findings of the Meta-Analysis
The meta-analysis included 37 randomized clinical trials that involved a total of 23,760 patients with a variety of advanced cancers. “Most of the trials were phase 3 (n = 34) and conduced for subsequent lines of therapy (n = 22),” the authors explained.
The most common cancers treated with an ICI were non–small cell lung cancer and melanoma.
Pooled overall survival (OS) hazard ratios (HRs) were calculated on the basis of sex, age (younger than 65 years and 65 years and older), and an ECOG PS of 0 and 1 or higher.
Responses were stratified on the basis of cancer type, line of therapy, the ICI used, and the immunotherapy strategy used in the ICI arm.
Most of the drugs evaluated were PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors. The specific drugs assessed included ipilimumab, tremelimumab, nivolumab, pembrolizumab, atezolizumab, durvalumab, and avelumab.
A total of 32 trials that involved more than 20,000 patients reported HRs for death according to the patients’ sex. Thirty-four trials that involved more than 21,000 patients reported HRs for death according to patients’ age, and 30 trials that involved more than 19,000 patients reported HRs for death according to patients’ ECOG PS.
No significant differences in OS benefit were seen by cancer type, line of therapy, agent of immunotherapy, or intervention strategy, the investigators pointed out.
There were also no differences in survival benefit associated with immunotherapy vs control therapies for patients with an ECOG PS of 0 and an ECOG PS of 1 or greater. The OS benefit was 0.81 for those with an ECOG PS of 0 and 0.79 for those with an ECOG PS of 1 or greater.
Wang has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com .
The improvement in survival in many cancer types that is seen with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), when compared to control therapies, is not affected by the patient’s sex, age, or Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (PS), according to a new meta-analysis.
Therefore, treatment with these immunotherapies should not be withheld on the basis of these factors, the authors concluded.
Asked whether there have been such instances of withholding ICIs, lead author Yucai Wang, MD, PhD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, told Medscape Medical News: “We did this study solely based on scientific questions we had and not because we were seeing any bias at the moment in the use of ICIs.
“And we saw that the survival benefits were very similar across all of the categories [we analyzed], with a survival benefit of about 20% from immunotherapy across the board, which is clinically meaningful,” he added.
The study was published online August 7 in JAMA Network Open.
“The comparable survival advantage between patients of different sex, age, and ECOG PS may encourage more patients to receive ICI treatment regardless of cancer types, lines of therapy, agents of immunotherapy, and intervention therapies,” the authors commented.
Wang noted that there have been conflicting reports in the literature suggesting that male patients may benefit more from immunotherapy than female patients and that older patients may benefit more from the same treatment than younger patients.
However, there are also suggestions in the literature that women experience a stronger immune response than men and that, with aging, the immune system generally undergoes immunosenescence.
In addition, the PS of oncology patients has been implicated in how well patients respond to immunotherapy.
Wang noted that the findings of past studies have contradicted each other.
Findings of the Meta-Analysis
The meta-analysis included 37 randomized clinical trials that involved a total of 23,760 patients with a variety of advanced cancers. “Most of the trials were phase 3 (n = 34) and conduced for subsequent lines of therapy (n = 22),” the authors explained.
The most common cancers treated with an ICI were non–small cell lung cancer and melanoma.
Pooled overall survival (OS) hazard ratios (HRs) were calculated on the basis of sex, age (younger than 65 years and 65 years and older), and an ECOG PS of 0 and 1 or higher.
Responses were stratified on the basis of cancer type, line of therapy, the ICI used, and the immunotherapy strategy used in the ICI arm.
Most of the drugs evaluated were PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors. The specific drugs assessed included ipilimumab, tremelimumab, nivolumab, pembrolizumab, atezolizumab, durvalumab, and avelumab.
A total of 32 trials that involved more than 20,000 patients reported HRs for death according to the patients’ sex. Thirty-four trials that involved more than 21,000 patients reported HRs for death according to patients’ age, and 30 trials that involved more than 19,000 patients reported HRs for death according to patients’ ECOG PS.
No significant differences in OS benefit were seen by cancer type, line of therapy, agent of immunotherapy, or intervention strategy, the investigators pointed out.
There were also no differences in survival benefit associated with immunotherapy vs control therapies for patients with an ECOG PS of 0 and an ECOG PS of 1 or greater. The OS benefit was 0.81 for those with an ECOG PS of 0 and 0.79 for those with an ECOG PS of 1 or greater.
Wang has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com .
The improvement in survival in many cancer types that is seen with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), when compared to control therapies, is not affected by the patient’s sex, age, or Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (PS), according to a new meta-analysis.
Therefore, treatment with these immunotherapies should not be withheld on the basis of these factors, the authors concluded.
Asked whether there have been such instances of withholding ICIs, lead author Yucai Wang, MD, PhD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, told Medscape Medical News: “We did this study solely based on scientific questions we had and not because we were seeing any bias at the moment in the use of ICIs.
“And we saw that the survival benefits were very similar across all of the categories [we analyzed], with a survival benefit of about 20% from immunotherapy across the board, which is clinically meaningful,” he added.
The study was published online August 7 in JAMA Network Open.
“The comparable survival advantage between patients of different sex, age, and ECOG PS may encourage more patients to receive ICI treatment regardless of cancer types, lines of therapy, agents of immunotherapy, and intervention therapies,” the authors commented.
Wang noted that there have been conflicting reports in the literature suggesting that male patients may benefit more from immunotherapy than female patients and that older patients may benefit more from the same treatment than younger patients.
However, there are also suggestions in the literature that women experience a stronger immune response than men and that, with aging, the immune system generally undergoes immunosenescence.
In addition, the PS of oncology patients has been implicated in how well patients respond to immunotherapy.
Wang noted that the findings of past studies have contradicted each other.
Findings of the Meta-Analysis
The meta-analysis included 37 randomized clinical trials that involved a total of 23,760 patients with a variety of advanced cancers. “Most of the trials were phase 3 (n = 34) and conduced for subsequent lines of therapy (n = 22),” the authors explained.
The most common cancers treated with an ICI were non–small cell lung cancer and melanoma.
Pooled overall survival (OS) hazard ratios (HRs) were calculated on the basis of sex, age (younger than 65 years and 65 years and older), and an ECOG PS of 0 and 1 or higher.
Responses were stratified on the basis of cancer type, line of therapy, the ICI used, and the immunotherapy strategy used in the ICI arm.
Most of the drugs evaluated were PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors. The specific drugs assessed included ipilimumab, tremelimumab, nivolumab, pembrolizumab, atezolizumab, durvalumab, and avelumab.
A total of 32 trials that involved more than 20,000 patients reported HRs for death according to the patients’ sex. Thirty-four trials that involved more than 21,000 patients reported HRs for death according to patients’ age, and 30 trials that involved more than 19,000 patients reported HRs for death according to patients’ ECOG PS.
No significant differences in OS benefit were seen by cancer type, line of therapy, agent of immunotherapy, or intervention strategy, the investigators pointed out.
There were also no differences in survival benefit associated with immunotherapy vs control therapies for patients with an ECOG PS of 0 and an ECOG PS of 1 or greater. The OS benefit was 0.81 for those with an ECOG PS of 0 and 0.79 for those with an ECOG PS of 1 or greater.
Wang has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com .
Black/White gap gone: ‘The only cancer where this has happened’
The historically higher incidence rates of lung cancer among Black men, compared with White men, in the United States have all but been eliminated, at least among most men in the younger age groups, a new analysis from the American Cancer Society (ACS) indicates.
Among women, the trend is even more impressive, as the Black/White gap in lung cancer incidence rates has actually reversed in younger women. Black women in certain age groups are now less likely to develop lung cancer than White women, the same study indicates.
These trends reflect the steeper declines in smoking rates among Blacks in the US, compared with comparably-aged Whites, say the authors.
“This is the only cancer where this has happened,” lead author Ahmedin Jemal, DVM, PhD, senior vice president for Data Science at the American Cancer Society, told Medscape Medical News.
“If you look at cancers that are affected by access to screening and treatment, the disparity between the Blacks and the Whites has been increasing over the years because tests and treatment require access to insurance, so the Whites are getting more of them than the Blacks,” Jemal explained.
“But for smoking, all you have to do for prevention is just don’t smoke, so this is a success story that really should be highlighted,” he emphasized.
The study was published online Aug. 20 in JNCI Cancer: Spectrum.
Nationwide Incidence Data
For this study, Jemal and colleagues collected nationwide incidence data on individuals between ages 30 and 54 who had been diagnosed with lung cancer between 1997 and 2016.
“We categorized age at diagnosis by 5-year age intervals (from 30-34 to 50-54 years) and year of diagnosis by 5-year calendar period (from 1997-2001 to 2012-2016),” the investigators explain.
Analyses showed that lung cancer incidence rates generally decreased among both Black and White men during the study interval but the decline in incidence rates was steeper in Black men than in White men. As a consequence, the Black-to-White incidence rate ratios (IRRs) became similar in men born between 1967 and 1972 and reversed in women born since about 1967. For example, the Black-to-White IRRs in men between the ages of 40 and 44 who were born between 1957 and 1972 declined from 1.92 to 1.03.
Similarly, lung cancer incidence rates during the study interval declined among both Black and White women between the ages of 30 and 49 but, again, the decline was “considerably larger” among Black women. As a consequence, the Black-to-White IRR in women age 45 to 49 dropped from 1.25 during the period 1997-2001 down to 0.83 during the period 2012-2016.
This is in stark contrast to historical trends in lung cancer incidence rates, which were over 30% higher among similarly aged Black women born in the late 1950s. Now, lung cancer incidence rates are about 30% lower for similarly aged Black women born in 1972, compared with White women.
For Black and White women between age 50 and 54, lung cancer incidence rates either declined only slightly or remained stable during the study interval, the investigators reported.
The one exception to the diminishing gap in lung cancer incidence rates between Black and White men was an observed increase in IRRs in men born around the period 1977-1982
Among this group of men, who were between age 30 and 39 in the years 2012-2016, lung cancer incidence rates were higher in Black men than in White men.
As the authors point out, this increase in lung cancer rates among young Black men likely reflects a rapid rise in smoking seen among Black youth in the 1990s.
This trend coincided with an R.J. Reynolds tobacco ad campaign in which African Americans were targeted; between 1991 and 1997, the prevalence of smoking among Black high school students doubled from 14.1% to 28.2%, the investigators point out, citing a 2008 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report on cigarette use among US high school students.
Smoking Prevalence Rates
Smoking prevalence rates were derived from National Health Interview Survey data from 1970 to 2016.
Mirroring findings in the racial patterns of lung cancer incidence rates, smoking prevalence rates declined in successive birth cohorts in both Black and White males and females, but the decline was again steeper in Black men and women than it was in White men and women.
As a result, the historically higher sex-specific smoking prevalence rates seen historically in Blacks disappeared in men born around 1960, and reversed in women born at the same time, Jemal and colleagues point out.
As the authors explain, the more rapid decline in smoking prevalence after 1960 is likely a reflection of the “precipitous” drop in smoking initiation rates among Black teenagers starting about the late 1970s through to the early 1990s.
For example, among 12th graders, smoking prevalence rates between 1977 and 1992 dropped from 36.7% to 8.1% among Black teens. In stark contrast, they hardly changed at all among White teens, dropping only from 38.3% in 1977 to 31.8% in 1992.
Jemal suggested that steeper decline in smoking initiation rates seen between the late 1970s and early 90s reflects the fact that Black teenagers were deterred from smoking because the cost of cigarettes kept going up.
He also suggested that smoking is less acceptable in the Black community than it is in the White community, especially among churchgoers, where smoking is severely frowned upon and nonsmoking is the community “norm.”
Additionally, Black youth may simply be heeding government antismoking messages to a greater extent than White youth, Jemal suggested.
He wondered if there are parallels now in the current pandemic. “When I go to a store here in Georgia, I would say almost all Blacks are wearing a mask [even though masks are not mandatory in Georgia] whereas it’s amazing the number of Whites who don’t wear a mask,” he recounts.
“So it would seem that Whites feel that government is simply interfering with their lives, while Blacks have a better perspective of the harms of smoking, so they are listening to the government’s antismoking campaigns,” he speculated.
Some Isolated Areas
Asked to comment on the study’s findings, Otis Brawley, MD, Bloomberg, distinguished professor of oncology and epidemiology at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, said that, while overall Black smoking rates are declining, there are some isolated areas where they are still very high.
For example, in his hometown of Baltimore, recent prevalence rates indicate that over 30% of Blacks are still smoking, “so these areas with high usage are still areas to focus on,” he told Medscape Medical News.
On the other hand, the study also supports the benefits of local, state, and federal government efforts to promote antismoking messages and tobacco-control activities over the past number of years.
“It proves that tactics used to control tobacco use have had some effect [even though] the study also shows that the tobacco industry’s advertising tactics such as the R.J. Reynolds targeted ads in the 90s can have deleterious effects,” Brawley noted.
Lung cancer has traditionally been one of the biggest drivers in the Black/White cancer mortality gap, Brawley said, adding that steeper declines in smoking initiation rates among Blacks compared with Whites are the main reason why this disparity is decreasing.
The study was supported by the Intramural Research Department of the American Cancer Society. The study authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Brawley declares he does some consulting work for pharmaceutical company Genentech.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The historically higher incidence rates of lung cancer among Black men, compared with White men, in the United States have all but been eliminated, at least among most men in the younger age groups, a new analysis from the American Cancer Society (ACS) indicates.
Among women, the trend is even more impressive, as the Black/White gap in lung cancer incidence rates has actually reversed in younger women. Black women in certain age groups are now less likely to develop lung cancer than White women, the same study indicates.
These trends reflect the steeper declines in smoking rates among Blacks in the US, compared with comparably-aged Whites, say the authors.
“This is the only cancer where this has happened,” lead author Ahmedin Jemal, DVM, PhD, senior vice president for Data Science at the American Cancer Society, told Medscape Medical News.
“If you look at cancers that are affected by access to screening and treatment, the disparity between the Blacks and the Whites has been increasing over the years because tests and treatment require access to insurance, so the Whites are getting more of them than the Blacks,” Jemal explained.
“But for smoking, all you have to do for prevention is just don’t smoke, so this is a success story that really should be highlighted,” he emphasized.
The study was published online Aug. 20 in JNCI Cancer: Spectrum.
Nationwide Incidence Data
For this study, Jemal and colleagues collected nationwide incidence data on individuals between ages 30 and 54 who had been diagnosed with lung cancer between 1997 and 2016.
“We categorized age at diagnosis by 5-year age intervals (from 30-34 to 50-54 years) and year of diagnosis by 5-year calendar period (from 1997-2001 to 2012-2016),” the investigators explain.
Analyses showed that lung cancer incidence rates generally decreased among both Black and White men during the study interval but the decline in incidence rates was steeper in Black men than in White men. As a consequence, the Black-to-White incidence rate ratios (IRRs) became similar in men born between 1967 and 1972 and reversed in women born since about 1967. For example, the Black-to-White IRRs in men between the ages of 40 and 44 who were born between 1957 and 1972 declined from 1.92 to 1.03.
Similarly, lung cancer incidence rates during the study interval declined among both Black and White women between the ages of 30 and 49 but, again, the decline was “considerably larger” among Black women. As a consequence, the Black-to-White IRR in women age 45 to 49 dropped from 1.25 during the period 1997-2001 down to 0.83 during the period 2012-2016.
This is in stark contrast to historical trends in lung cancer incidence rates, which were over 30% higher among similarly aged Black women born in the late 1950s. Now, lung cancer incidence rates are about 30% lower for similarly aged Black women born in 1972, compared with White women.
For Black and White women between age 50 and 54, lung cancer incidence rates either declined only slightly or remained stable during the study interval, the investigators reported.
The one exception to the diminishing gap in lung cancer incidence rates between Black and White men was an observed increase in IRRs in men born around the period 1977-1982
Among this group of men, who were between age 30 and 39 in the years 2012-2016, lung cancer incidence rates were higher in Black men than in White men.
As the authors point out, this increase in lung cancer rates among young Black men likely reflects a rapid rise in smoking seen among Black youth in the 1990s.
This trend coincided with an R.J. Reynolds tobacco ad campaign in which African Americans were targeted; between 1991 and 1997, the prevalence of smoking among Black high school students doubled from 14.1% to 28.2%, the investigators point out, citing a 2008 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report on cigarette use among US high school students.
Smoking Prevalence Rates
Smoking prevalence rates were derived from National Health Interview Survey data from 1970 to 2016.
Mirroring findings in the racial patterns of lung cancer incidence rates, smoking prevalence rates declined in successive birth cohorts in both Black and White males and females, but the decline was again steeper in Black men and women than it was in White men and women.
As a result, the historically higher sex-specific smoking prevalence rates seen historically in Blacks disappeared in men born around 1960, and reversed in women born at the same time, Jemal and colleagues point out.
As the authors explain, the more rapid decline in smoking prevalence after 1960 is likely a reflection of the “precipitous” drop in smoking initiation rates among Black teenagers starting about the late 1970s through to the early 1990s.
For example, among 12th graders, smoking prevalence rates between 1977 and 1992 dropped from 36.7% to 8.1% among Black teens. In stark contrast, they hardly changed at all among White teens, dropping only from 38.3% in 1977 to 31.8% in 1992.
Jemal suggested that steeper decline in smoking initiation rates seen between the late 1970s and early 90s reflects the fact that Black teenagers were deterred from smoking because the cost of cigarettes kept going up.
He also suggested that smoking is less acceptable in the Black community than it is in the White community, especially among churchgoers, where smoking is severely frowned upon and nonsmoking is the community “norm.”
Additionally, Black youth may simply be heeding government antismoking messages to a greater extent than White youth, Jemal suggested.
He wondered if there are parallels now in the current pandemic. “When I go to a store here in Georgia, I would say almost all Blacks are wearing a mask [even though masks are not mandatory in Georgia] whereas it’s amazing the number of Whites who don’t wear a mask,” he recounts.
“So it would seem that Whites feel that government is simply interfering with their lives, while Blacks have a better perspective of the harms of smoking, so they are listening to the government’s antismoking campaigns,” he speculated.
Some Isolated Areas
Asked to comment on the study’s findings, Otis Brawley, MD, Bloomberg, distinguished professor of oncology and epidemiology at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, said that, while overall Black smoking rates are declining, there are some isolated areas where they are still very high.
For example, in his hometown of Baltimore, recent prevalence rates indicate that over 30% of Blacks are still smoking, “so these areas with high usage are still areas to focus on,” he told Medscape Medical News.
On the other hand, the study also supports the benefits of local, state, and federal government efforts to promote antismoking messages and tobacco-control activities over the past number of years.
“It proves that tactics used to control tobacco use have had some effect [even though] the study also shows that the tobacco industry’s advertising tactics such as the R.J. Reynolds targeted ads in the 90s can have deleterious effects,” Brawley noted.
Lung cancer has traditionally been one of the biggest drivers in the Black/White cancer mortality gap, Brawley said, adding that steeper declines in smoking initiation rates among Blacks compared with Whites are the main reason why this disparity is decreasing.
The study was supported by the Intramural Research Department of the American Cancer Society. The study authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Brawley declares he does some consulting work for pharmaceutical company Genentech.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The historically higher incidence rates of lung cancer among Black men, compared with White men, in the United States have all but been eliminated, at least among most men in the younger age groups, a new analysis from the American Cancer Society (ACS) indicates.
Among women, the trend is even more impressive, as the Black/White gap in lung cancer incidence rates has actually reversed in younger women. Black women in certain age groups are now less likely to develop lung cancer than White women, the same study indicates.
These trends reflect the steeper declines in smoking rates among Blacks in the US, compared with comparably-aged Whites, say the authors.
“This is the only cancer where this has happened,” lead author Ahmedin Jemal, DVM, PhD, senior vice president for Data Science at the American Cancer Society, told Medscape Medical News.
“If you look at cancers that are affected by access to screening and treatment, the disparity between the Blacks and the Whites has been increasing over the years because tests and treatment require access to insurance, so the Whites are getting more of them than the Blacks,” Jemal explained.
“But for smoking, all you have to do for prevention is just don’t smoke, so this is a success story that really should be highlighted,” he emphasized.
The study was published online Aug. 20 in JNCI Cancer: Spectrum.
Nationwide Incidence Data
For this study, Jemal and colleagues collected nationwide incidence data on individuals between ages 30 and 54 who had been diagnosed with lung cancer between 1997 and 2016.
“We categorized age at diagnosis by 5-year age intervals (from 30-34 to 50-54 years) and year of diagnosis by 5-year calendar period (from 1997-2001 to 2012-2016),” the investigators explain.
Analyses showed that lung cancer incidence rates generally decreased among both Black and White men during the study interval but the decline in incidence rates was steeper in Black men than in White men. As a consequence, the Black-to-White incidence rate ratios (IRRs) became similar in men born between 1967 and 1972 and reversed in women born since about 1967. For example, the Black-to-White IRRs in men between the ages of 40 and 44 who were born between 1957 and 1972 declined from 1.92 to 1.03.
Similarly, lung cancer incidence rates during the study interval declined among both Black and White women between the ages of 30 and 49 but, again, the decline was “considerably larger” among Black women. As a consequence, the Black-to-White IRR in women age 45 to 49 dropped from 1.25 during the period 1997-2001 down to 0.83 during the period 2012-2016.
This is in stark contrast to historical trends in lung cancer incidence rates, which were over 30% higher among similarly aged Black women born in the late 1950s. Now, lung cancer incidence rates are about 30% lower for similarly aged Black women born in 1972, compared with White women.
For Black and White women between age 50 and 54, lung cancer incidence rates either declined only slightly or remained stable during the study interval, the investigators reported.
The one exception to the diminishing gap in lung cancer incidence rates between Black and White men was an observed increase in IRRs in men born around the period 1977-1982
Among this group of men, who were between age 30 and 39 in the years 2012-2016, lung cancer incidence rates were higher in Black men than in White men.
As the authors point out, this increase in lung cancer rates among young Black men likely reflects a rapid rise in smoking seen among Black youth in the 1990s.
This trend coincided with an R.J. Reynolds tobacco ad campaign in which African Americans were targeted; between 1991 and 1997, the prevalence of smoking among Black high school students doubled from 14.1% to 28.2%, the investigators point out, citing a 2008 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report on cigarette use among US high school students.
Smoking Prevalence Rates
Smoking prevalence rates were derived from National Health Interview Survey data from 1970 to 2016.
Mirroring findings in the racial patterns of lung cancer incidence rates, smoking prevalence rates declined in successive birth cohorts in both Black and White males and females, but the decline was again steeper in Black men and women than it was in White men and women.
As a result, the historically higher sex-specific smoking prevalence rates seen historically in Blacks disappeared in men born around 1960, and reversed in women born at the same time, Jemal and colleagues point out.
As the authors explain, the more rapid decline in smoking prevalence after 1960 is likely a reflection of the “precipitous” drop in smoking initiation rates among Black teenagers starting about the late 1970s through to the early 1990s.
For example, among 12th graders, smoking prevalence rates between 1977 and 1992 dropped from 36.7% to 8.1% among Black teens. In stark contrast, they hardly changed at all among White teens, dropping only from 38.3% in 1977 to 31.8% in 1992.
Jemal suggested that steeper decline in smoking initiation rates seen between the late 1970s and early 90s reflects the fact that Black teenagers were deterred from smoking because the cost of cigarettes kept going up.
He also suggested that smoking is less acceptable in the Black community than it is in the White community, especially among churchgoers, where smoking is severely frowned upon and nonsmoking is the community “norm.”
Additionally, Black youth may simply be heeding government antismoking messages to a greater extent than White youth, Jemal suggested.
He wondered if there are parallels now in the current pandemic. “When I go to a store here in Georgia, I would say almost all Blacks are wearing a mask [even though masks are not mandatory in Georgia] whereas it’s amazing the number of Whites who don’t wear a mask,” he recounts.
“So it would seem that Whites feel that government is simply interfering with their lives, while Blacks have a better perspective of the harms of smoking, so they are listening to the government’s antismoking campaigns,” he speculated.
Some Isolated Areas
Asked to comment on the study’s findings, Otis Brawley, MD, Bloomberg, distinguished professor of oncology and epidemiology at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, said that, while overall Black smoking rates are declining, there are some isolated areas where they are still very high.
For example, in his hometown of Baltimore, recent prevalence rates indicate that over 30% of Blacks are still smoking, “so these areas with high usage are still areas to focus on,” he told Medscape Medical News.
On the other hand, the study also supports the benefits of local, state, and federal government efforts to promote antismoking messages and tobacco-control activities over the past number of years.
“It proves that tactics used to control tobacco use have had some effect [even though] the study also shows that the tobacco industry’s advertising tactics such as the R.J. Reynolds targeted ads in the 90s can have deleterious effects,” Brawley noted.
Lung cancer has traditionally been one of the biggest drivers in the Black/White cancer mortality gap, Brawley said, adding that steeper declines in smoking initiation rates among Blacks compared with Whites are the main reason why this disparity is decreasing.
The study was supported by the Intramural Research Department of the American Cancer Society. The study authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Brawley declares he does some consulting work for pharmaceutical company Genentech.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.