User login
Telemedicine Alopecia Assessment: Highlighting Patients With Skin of Color
Practice Gap
In accordance with World Health Organization guidelines on social distancing to limit transmission of SARS-CoV-2, dermatologists have relied on teledermatology (TD) to develop novel adaptations of traditional workflows, optimize patient care, and limit in-person appointments during the COVID-19 pandemic. Pandemic-induced physical and emotional stress were anticipated to increase the incidence of dermatologic diseases with psychologic triggers.
The connection between hair loss and emotional stress is well documented for telogen effluvium and alopecia areata.1,2 As anticipated, dermatology visits increased during the COVID-19 pandemic for the diagnosis of alopecia1-4; a survey performed during the pandemic found that alopecia was one of the most common diagnoses dermatologists made through telehealth platforms.5
This article provides a practical guide for dermatology practitioners to efficiently and accurately assess alopecia by TD in all patients, with added considerations for skin of color patients.
Diagnostic Tools
The intersection of TD, as an effective mechanism for the diagnosis and treatment of dermatologic disorders, and the increase in alopecia observed during the COVID-19 pandemic prompted us to develop a workflow for conducting virtual scalp examinations. Seven dermatologists (A.M., A.A., O.A., N.E., V.C., C.M.B., S.C.T.) who are experts in hair disorders contributed to developing workflows to optimize the assessment of alopecia through a virtual scalp examination, with an emphasis on patients of color. These experts completed a 7-question survey (Table) detailing their approach to the virtual scalp examination. One author (B.N.W.) served as an independent reviewer and collated responses into the following workflows.

Telemedicine Previsit Workflow
Components of the previsit workflow include:
• Instruct patients to provide all laboratory values and biopsy reports before the appointment.
• Test for a stable Wi-Fi connection using a speed test (available at https://www.speedtest.net/). A speed of 10 megabits/second or more is required for high-quality video via TD.6
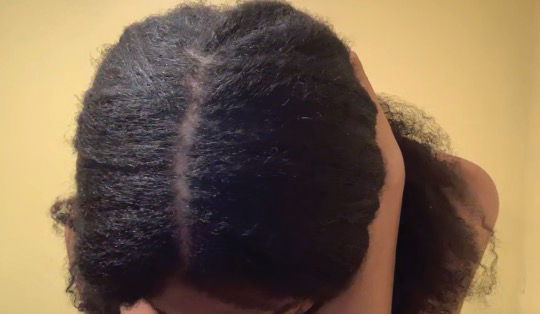
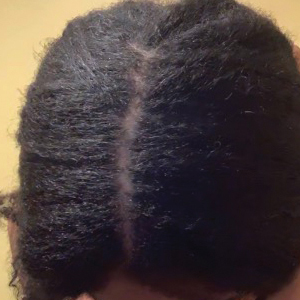
• Provide a handout illustrating the required photographs of the anterior hairline; the mid scalp, including vertex, bilateral parietal, and occipital scalp; and posterior hairline. Photographs should be uploaded 2 hours before the visit. Figures 1 and 2 are examples of photographs that should be requested.
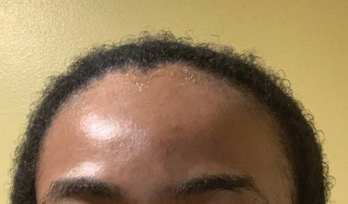
• Request images with 2 or 3 different angles of the area of the scalp with the greatest involvement to help appreciate primary and secondary characteristics.
• Encourage patients to present with clean, recently shampooed, dried, and detangled natural hair, unless they have an itchy or flaky scalp.
• For concerns of scalp, hairline, eyebrow, or facial flaking and scaling, instruct the patient to avoid applying a moisturizer before the visit.
• Instruct the patient to remove false eyelashes, eyelash extensions, eyebrow pencil, hair camouflage, hair accessories, braids, extensions, weaves, twists, and other hairstyles so that the hair can be maneuvered to expose the scalp surface.
• Instruct the patient to have a comb, pic, or brush, or more than one of these implements, available during the visit.
Telemedicine Visit Workflow
Components of the visit workflow include:
• If a stable Wi-Fi connection cannot be established, switch to an audio-only visit to collect a pertinent history. Advise the patient that in-person follow-up must be scheduled.
• Confirm that (1) the patient is in a private setting where the scalp can be viewed and (2) lighting is positioned in front of the patient.
• Ensure that the patient’s hairline, full face, eyebrows, and eyelashes and, upon request, the vertex and posterior scalp, are completely visible.
• Initiate the virtual scalp examination by instructing the patient how to perform a hair pull test. Then, examine the pattern and distribution of hair loss alongside supplemental photographs.
• Instruct the patient to apply pressure with the fingertips throughout the scalp to help localize tenderness, which, in combination with the pattern of hair loss observed, might inform the diagnosis.
• Instruct the patient to scan the scalp with the fingertips for “bumps” to locate papules, pustules, and keloidal scars.
Diagnostic Pearls
Distribution of Alopecia—The experts noted that the pattern, distribution, and location of hair loss determined from the telemedicine alopecia assessment provided important clues to distinguish the type of alopecia.
Diagnostic clues for diffuse or generalized alopecia include:
• Either of these findings might be indicative of telogen effluvium or acquired trichorrhexis nodosa. Results of the hair pull test can help distinguish between these diagnoses.
• Recent stressful life events along with the presence of telogen hairs extracted during a hair pull test support the diagnosis of telogen effluvium.
• A history of external stress on the hair—thermal, traction, or chemical—along with broken hair shafts following the hair pull test support the diagnosis of acquired trichorrhexis nodosa.
Diagnostic clues for focal or patchy alopecia include:
• Alopecia areata generally presents as focal hair loss in an annular distribution; pruritus, erythema, and scale are absent.
• Seborrheic dermatitis can present as pruritic erythematous patches with scale distributed on the scalp and, in some cases, in the eyebrows, nasolabial folds, or paranasal skin.7 Some skin of color patients present with petaloid seborrheic dermatitis—pink or hypopigmented polycyclic coalescing rings with minimal scale.7,8
• Discoid lupus erythematosus, similar to seborrheic dermatitis, might present as pruritic, scaly, hypopigmented patches. However, in the experience of the experts, a more common presentation is tender erythematous patches of hair loss with central hypopigmentation and surrounding hyperpigmentation.
Diagnostic clues for vertex and mid scalp alopecia include:
• Androgenetic alopecia typically presents as a reduction of terminal hair density in the vertex and mid scalp regions (with widening through the midline part) and fine hair along the anterior hairline.9 Signs of concomitant hyperandrogenism, including facial hirsutism, acne, and obesity, might be observed.10
• Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia typically affects the vertex and mid scalp with a shiny scalp appearance and follicular dropout.
Diagnostic clues for frontotemporal alopecia include:
• Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) often presents with spared single terminal hairs (lonely hair sign).
• Traction alopecia commonly presents with the fringe hair sign.
Scalp Symptoms—The experts noted that the presence of symptoms (eg, pain, tenderness, pruritus) in conjunction with the pattern of hair loss might support the diagnosis of an inflammatory scarring alopecia.
When do symptoms raise suspicion of central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia?
• Suspected in the setting of vertex alopecia associated with tenderness, pain, or itching.
When do symptoms raise suspicion of FFA?
• Suspected when patients experience frontotemporal tenderness, pain, or burning associated with alopecia.
• The skin hue of the affected area might be lighter in color than, and contrast with, the darker hue of the photoaged upper forehead.11
• The lonely hair sign can aid in diagnosing FFA and distinguish it from the fringe sign of traction alopecia.
• Concurrent madarosis, flesh-colored papules on the cheeks, or lichen planus pigmentosus identified by visual inspection of the face confirms the diagnosis.9,12 Madarosis of the eyebrow was frequently cited by the experts as an associated symptom of FFA.
When do symptoms raise suspicion of lichen planopilaris?
• Suspected in the presence of pruritus, burning, tenderness, or pain associated with perifollicular erythema and scale in the setting of vertex and parietal alopecia.13
• Anagen hair release is observed during the hair pull test.11,14• The experts cited flesh-colored papules and lichen planus pigmentosus as frequently associated symptoms of lichen planopilaris.
Practice Implications
There are limitations to a virtual scalp examination—the inability to perform a scalp biopsy or administer certain treatments—but the consensus of the expert panel is that an initial alopecia assessment can be completed successfully utilizing TD. Although TD is not a replacement for an in-person dermatology visit, this technology has allowed for the diagnosis, treatment, and continuing care of many common dermatologic conditions without the patient needing to travel to the office.5
With the increased frequency of hair loss concerns documented over the last year and more patients seeking TD, it is imperative that dermatologists feel confident performing a virtual hair and scalp examination on all patients.1,3,4
- Kutlu Ö, Aktas¸ H, I·mren IG, et al. Short-term stress-related increasing cases of alopecia areata during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Dermatolog Treat. 2020;1. doi:10.1080/09546634.2020.1782820
- Cline A, Kazemi A, Moy J, et al. A surge in the incidence of telogen effluvium in minority predominant communities heavily impacted by COVID-19. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:773-775. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.032
- Kutlu Ö, Metin A. Relative changes in the pattern of diseases presenting in dermatology outpatient clinic in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e14096. doi:10.1111/dth.14096
- Tanacan E, Aksoy Sarac G, Emeksiz MAC, et al. Changing trends in dermatology practice during COVID-19 pandemic: a single tertiary center experience. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e14136. doi:10.1111/dth.14136
- Sharma A, Jindal V, Singla P, et al. Will teledermatology be the silver lining during and after COVID-19? Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e13643. doi:10.1111/dth.13643
- Iscrupe L. How to receive virtual medical treatment while under quarantine. Allconnect website. Published March 26, 2020. Accessed December 9, 2021. https://www.allconnect.com/blog/online-doctor-visit-faq
- Elgash M, Dlova N, Ogunleye T, et al. Seborrheic dermatitis in skin of color: clinical considerations. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18:24-27.
- McLaurin CI. Annular facial dermatoses in blacks. Cutis. 1983;32:369-370, 384.
- Suchonwanit P, Hector CE, Bin Saif GA, McMichael AJ. Factors affecting the severity of central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:e338-343. doi:10.1111/ijd.13061
- Gabros S, Masood S. Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. Updated July 20, 2021. Accessed December 9, 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559187/
- Ross EK, Tan E, Shapiro J. Update on primary cicatricial alopecias. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:1-37. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2004.06.015
- Cobos G, Kim RH, Meehan S, et al. Lichen planus pigmentosus and lichen planopilaris. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt7hp8n6dn.
- Lyakhovitsky A, Amichai B, Sizopoulou C, et al. A case series of 46 patients with lichen planopilaris: demographics, clinical evaluation, and treatment experience. J Dermatolog Treat. 2015;26:275-279. doi:10.3109/09546634.2014.933165
- Tan E, Martinka M, Ball N, et al. Primary cicatricial alopecias: clinicopathology of 112 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:25-32. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2003.04.001
Practice Gap
In accordance with World Health Organization guidelines on social distancing to limit transmission of SARS-CoV-2, dermatologists have relied on teledermatology (TD) to develop novel adaptations of traditional workflows, optimize patient care, and limit in-person appointments during the COVID-19 pandemic. Pandemic-induced physical and emotional stress were anticipated to increase the incidence of dermatologic diseases with psychologic triggers.
The connection between hair loss and emotional stress is well documented for telogen effluvium and alopecia areata.1,2 As anticipated, dermatology visits increased during the COVID-19 pandemic for the diagnosis of alopecia1-4; a survey performed during the pandemic found that alopecia was one of the most common diagnoses dermatologists made through telehealth platforms.5
This article provides a practical guide for dermatology practitioners to efficiently and accurately assess alopecia by TD in all patients, with added considerations for skin of color patients.
Diagnostic Tools
The intersection of TD, as an effective mechanism for the diagnosis and treatment of dermatologic disorders, and the increase in alopecia observed during the COVID-19 pandemic prompted us to develop a workflow for conducting virtual scalp examinations. Seven dermatologists (A.M., A.A., O.A., N.E., V.C., C.M.B., S.C.T.) who are experts in hair disorders contributed to developing workflows to optimize the assessment of alopecia through a virtual scalp examination, with an emphasis on patients of color. These experts completed a 7-question survey (Table) detailing their approach to the virtual scalp examination. One author (B.N.W.) served as an independent reviewer and collated responses into the following workflows.

Telemedicine Previsit Workflow
Components of the previsit workflow include:
• Instruct patients to provide all laboratory values and biopsy reports before the appointment.
• Test for a stable Wi-Fi connection using a speed test (available at https://www.speedtest.net/). A speed of 10 megabits/second or more is required for high-quality video via TD.6

• Provide a handout illustrating the required photographs of the anterior hairline; the mid scalp, including vertex, bilateral parietal, and occipital scalp; and posterior hairline. Photographs should be uploaded 2 hours before the visit. Figures 1 and 2 are examples of photographs that should be requested.

• Request images with 2 or 3 different angles of the area of the scalp with the greatest involvement to help appreciate primary and secondary characteristics.
• Encourage patients to present with clean, recently shampooed, dried, and detangled natural hair, unless they have an itchy or flaky scalp.
• For concerns of scalp, hairline, eyebrow, or facial flaking and scaling, instruct the patient to avoid applying a moisturizer before the visit.
• Instruct the patient to remove false eyelashes, eyelash extensions, eyebrow pencil, hair camouflage, hair accessories, braids, extensions, weaves, twists, and other hairstyles so that the hair can be maneuvered to expose the scalp surface.
• Instruct the patient to have a comb, pic, or brush, or more than one of these implements, available during the visit.
Telemedicine Visit Workflow
Components of the visit workflow include:
• If a stable Wi-Fi connection cannot be established, switch to an audio-only visit to collect a pertinent history. Advise the patient that in-person follow-up must be scheduled.
• Confirm that (1) the patient is in a private setting where the scalp can be viewed and (2) lighting is positioned in front of the patient.
• Ensure that the patient’s hairline, full face, eyebrows, and eyelashes and, upon request, the vertex and posterior scalp, are completely visible.
• Initiate the virtual scalp examination by instructing the patient how to perform a hair pull test. Then, examine the pattern and distribution of hair loss alongside supplemental photographs.
• Instruct the patient to apply pressure with the fingertips throughout the scalp to help localize tenderness, which, in combination with the pattern of hair loss observed, might inform the diagnosis.
• Instruct the patient to scan the scalp with the fingertips for “bumps” to locate papules, pustules, and keloidal scars.
Diagnostic Pearls
Distribution of Alopecia—The experts noted that the pattern, distribution, and location of hair loss determined from the telemedicine alopecia assessment provided important clues to distinguish the type of alopecia.
Diagnostic clues for diffuse or generalized alopecia include:
• Either of these findings might be indicative of telogen effluvium or acquired trichorrhexis nodosa. Results of the hair pull test can help distinguish between these diagnoses.
• Recent stressful life events along with the presence of telogen hairs extracted during a hair pull test support the diagnosis of telogen effluvium.
• A history of external stress on the hair—thermal, traction, or chemical—along with broken hair shafts following the hair pull test support the diagnosis of acquired trichorrhexis nodosa.
Diagnostic clues for focal or patchy alopecia include:
• Alopecia areata generally presents as focal hair loss in an annular distribution; pruritus, erythema, and scale are absent.
• Seborrheic dermatitis can present as pruritic erythematous patches with scale distributed on the scalp and, in some cases, in the eyebrows, nasolabial folds, or paranasal skin.7 Some skin of color patients present with petaloid seborrheic dermatitis—pink or hypopigmented polycyclic coalescing rings with minimal scale.7,8
• Discoid lupus erythematosus, similar to seborrheic dermatitis, might present as pruritic, scaly, hypopigmented patches. However, in the experience of the experts, a more common presentation is tender erythematous patches of hair loss with central hypopigmentation and surrounding hyperpigmentation.
Diagnostic clues for vertex and mid scalp alopecia include:
• Androgenetic alopecia typically presents as a reduction of terminal hair density in the vertex and mid scalp regions (with widening through the midline part) and fine hair along the anterior hairline.9 Signs of concomitant hyperandrogenism, including facial hirsutism, acne, and obesity, might be observed.10
• Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia typically affects the vertex and mid scalp with a shiny scalp appearance and follicular dropout.
Diagnostic clues for frontotemporal alopecia include:
• Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) often presents with spared single terminal hairs (lonely hair sign).
• Traction alopecia commonly presents with the fringe hair sign.
Scalp Symptoms—The experts noted that the presence of symptoms (eg, pain, tenderness, pruritus) in conjunction with the pattern of hair loss might support the diagnosis of an inflammatory scarring alopecia.
When do symptoms raise suspicion of central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia?
• Suspected in the setting of vertex alopecia associated with tenderness, pain, or itching.
When do symptoms raise suspicion of FFA?
• Suspected when patients experience frontotemporal tenderness, pain, or burning associated with alopecia.
• The skin hue of the affected area might be lighter in color than, and contrast with, the darker hue of the photoaged upper forehead.11
• The lonely hair sign can aid in diagnosing FFA and distinguish it from the fringe sign of traction alopecia.
• Concurrent madarosis, flesh-colored papules on the cheeks, or lichen planus pigmentosus identified by visual inspection of the face confirms the diagnosis.9,12 Madarosis of the eyebrow was frequently cited by the experts as an associated symptom of FFA.
When do symptoms raise suspicion of lichen planopilaris?
• Suspected in the presence of pruritus, burning, tenderness, or pain associated with perifollicular erythema and scale in the setting of vertex and parietal alopecia.13
• Anagen hair release is observed during the hair pull test.11,14• The experts cited flesh-colored papules and lichen planus pigmentosus as frequently associated symptoms of lichen planopilaris.
Practice Implications
There are limitations to a virtual scalp examination—the inability to perform a scalp biopsy or administer certain treatments—but the consensus of the expert panel is that an initial alopecia assessment can be completed successfully utilizing TD. Although TD is not a replacement for an in-person dermatology visit, this technology has allowed for the diagnosis, treatment, and continuing care of many common dermatologic conditions without the patient needing to travel to the office.5
With the increased frequency of hair loss concerns documented over the last year and more patients seeking TD, it is imperative that dermatologists feel confident performing a virtual hair and scalp examination on all patients.1,3,4
Practice Gap
In accordance with World Health Organization guidelines on social distancing to limit transmission of SARS-CoV-2, dermatologists have relied on teledermatology (TD) to develop novel adaptations of traditional workflows, optimize patient care, and limit in-person appointments during the COVID-19 pandemic. Pandemic-induced physical and emotional stress were anticipated to increase the incidence of dermatologic diseases with psychologic triggers.
The connection between hair loss and emotional stress is well documented for telogen effluvium and alopecia areata.1,2 As anticipated, dermatology visits increased during the COVID-19 pandemic for the diagnosis of alopecia1-4; a survey performed during the pandemic found that alopecia was one of the most common diagnoses dermatologists made through telehealth platforms.5
This article provides a practical guide for dermatology practitioners to efficiently and accurately assess alopecia by TD in all patients, with added considerations for skin of color patients.
Diagnostic Tools
The intersection of TD, as an effective mechanism for the diagnosis and treatment of dermatologic disorders, and the increase in alopecia observed during the COVID-19 pandemic prompted us to develop a workflow for conducting virtual scalp examinations. Seven dermatologists (A.M., A.A., O.A., N.E., V.C., C.M.B., S.C.T.) who are experts in hair disorders contributed to developing workflows to optimize the assessment of alopecia through a virtual scalp examination, with an emphasis on patients of color. These experts completed a 7-question survey (Table) detailing their approach to the virtual scalp examination. One author (B.N.W.) served as an independent reviewer and collated responses into the following workflows.

Telemedicine Previsit Workflow
Components of the previsit workflow include:
• Instruct patients to provide all laboratory values and biopsy reports before the appointment.
• Test for a stable Wi-Fi connection using a speed test (available at https://www.speedtest.net/). A speed of 10 megabits/second or more is required for high-quality video via TD.6

• Provide a handout illustrating the required photographs of the anterior hairline; the mid scalp, including vertex, bilateral parietal, and occipital scalp; and posterior hairline. Photographs should be uploaded 2 hours before the visit. Figures 1 and 2 are examples of photographs that should be requested.

• Request images with 2 or 3 different angles of the area of the scalp with the greatest involvement to help appreciate primary and secondary characteristics.
• Encourage patients to present with clean, recently shampooed, dried, and detangled natural hair, unless they have an itchy or flaky scalp.
• For concerns of scalp, hairline, eyebrow, or facial flaking and scaling, instruct the patient to avoid applying a moisturizer before the visit.
• Instruct the patient to remove false eyelashes, eyelash extensions, eyebrow pencil, hair camouflage, hair accessories, braids, extensions, weaves, twists, and other hairstyles so that the hair can be maneuvered to expose the scalp surface.
• Instruct the patient to have a comb, pic, or brush, or more than one of these implements, available during the visit.
Telemedicine Visit Workflow
Components of the visit workflow include:
• If a stable Wi-Fi connection cannot be established, switch to an audio-only visit to collect a pertinent history. Advise the patient that in-person follow-up must be scheduled.
• Confirm that (1) the patient is in a private setting where the scalp can be viewed and (2) lighting is positioned in front of the patient.
• Ensure that the patient’s hairline, full face, eyebrows, and eyelashes and, upon request, the vertex and posterior scalp, are completely visible.
• Initiate the virtual scalp examination by instructing the patient how to perform a hair pull test. Then, examine the pattern and distribution of hair loss alongside supplemental photographs.
• Instruct the patient to apply pressure with the fingertips throughout the scalp to help localize tenderness, which, in combination with the pattern of hair loss observed, might inform the diagnosis.
• Instruct the patient to scan the scalp with the fingertips for “bumps” to locate papules, pustules, and keloidal scars.
Diagnostic Pearls
Distribution of Alopecia—The experts noted that the pattern, distribution, and location of hair loss determined from the telemedicine alopecia assessment provided important clues to distinguish the type of alopecia.
Diagnostic clues for diffuse or generalized alopecia include:
• Either of these findings might be indicative of telogen effluvium or acquired trichorrhexis nodosa. Results of the hair pull test can help distinguish between these diagnoses.
• Recent stressful life events along with the presence of telogen hairs extracted during a hair pull test support the diagnosis of telogen effluvium.
• A history of external stress on the hair—thermal, traction, or chemical—along with broken hair shafts following the hair pull test support the diagnosis of acquired trichorrhexis nodosa.
Diagnostic clues for focal or patchy alopecia include:
• Alopecia areata generally presents as focal hair loss in an annular distribution; pruritus, erythema, and scale are absent.
• Seborrheic dermatitis can present as pruritic erythematous patches with scale distributed on the scalp and, in some cases, in the eyebrows, nasolabial folds, or paranasal skin.7 Some skin of color patients present with petaloid seborrheic dermatitis—pink or hypopigmented polycyclic coalescing rings with minimal scale.7,8
• Discoid lupus erythematosus, similar to seborrheic dermatitis, might present as pruritic, scaly, hypopigmented patches. However, in the experience of the experts, a more common presentation is tender erythematous patches of hair loss with central hypopigmentation and surrounding hyperpigmentation.
Diagnostic clues for vertex and mid scalp alopecia include:
• Androgenetic alopecia typically presents as a reduction of terminal hair density in the vertex and mid scalp regions (with widening through the midline part) and fine hair along the anterior hairline.9 Signs of concomitant hyperandrogenism, including facial hirsutism, acne, and obesity, might be observed.10
• Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia typically affects the vertex and mid scalp with a shiny scalp appearance and follicular dropout.
Diagnostic clues for frontotemporal alopecia include:
• Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) often presents with spared single terminal hairs (lonely hair sign).
• Traction alopecia commonly presents with the fringe hair sign.
Scalp Symptoms—The experts noted that the presence of symptoms (eg, pain, tenderness, pruritus) in conjunction with the pattern of hair loss might support the diagnosis of an inflammatory scarring alopecia.
When do symptoms raise suspicion of central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia?
• Suspected in the setting of vertex alopecia associated with tenderness, pain, or itching.
When do symptoms raise suspicion of FFA?
• Suspected when patients experience frontotemporal tenderness, pain, or burning associated with alopecia.
• The skin hue of the affected area might be lighter in color than, and contrast with, the darker hue of the photoaged upper forehead.11
• The lonely hair sign can aid in diagnosing FFA and distinguish it from the fringe sign of traction alopecia.
• Concurrent madarosis, flesh-colored papules on the cheeks, or lichen planus pigmentosus identified by visual inspection of the face confirms the diagnosis.9,12 Madarosis of the eyebrow was frequently cited by the experts as an associated symptom of FFA.
When do symptoms raise suspicion of lichen planopilaris?
• Suspected in the presence of pruritus, burning, tenderness, or pain associated with perifollicular erythema and scale in the setting of vertex and parietal alopecia.13
• Anagen hair release is observed during the hair pull test.11,14• The experts cited flesh-colored papules and lichen planus pigmentosus as frequently associated symptoms of lichen planopilaris.
Practice Implications
There are limitations to a virtual scalp examination—the inability to perform a scalp biopsy or administer certain treatments—but the consensus of the expert panel is that an initial alopecia assessment can be completed successfully utilizing TD. Although TD is not a replacement for an in-person dermatology visit, this technology has allowed for the diagnosis, treatment, and continuing care of many common dermatologic conditions without the patient needing to travel to the office.5
With the increased frequency of hair loss concerns documented over the last year and more patients seeking TD, it is imperative that dermatologists feel confident performing a virtual hair and scalp examination on all patients.1,3,4
- Kutlu Ö, Aktas¸ H, I·mren IG, et al. Short-term stress-related increasing cases of alopecia areata during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Dermatolog Treat. 2020;1. doi:10.1080/09546634.2020.1782820
- Cline A, Kazemi A, Moy J, et al. A surge in the incidence of telogen effluvium in minority predominant communities heavily impacted by COVID-19. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:773-775. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.032
- Kutlu Ö, Metin A. Relative changes in the pattern of diseases presenting in dermatology outpatient clinic in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e14096. doi:10.1111/dth.14096
- Tanacan E, Aksoy Sarac G, Emeksiz MAC, et al. Changing trends in dermatology practice during COVID-19 pandemic: a single tertiary center experience. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e14136. doi:10.1111/dth.14136
- Sharma A, Jindal V, Singla P, et al. Will teledermatology be the silver lining during and after COVID-19? Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e13643. doi:10.1111/dth.13643
- Iscrupe L. How to receive virtual medical treatment while under quarantine. Allconnect website. Published March 26, 2020. Accessed December 9, 2021. https://www.allconnect.com/blog/online-doctor-visit-faq
- Elgash M, Dlova N, Ogunleye T, et al. Seborrheic dermatitis in skin of color: clinical considerations. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18:24-27.
- McLaurin CI. Annular facial dermatoses in blacks. Cutis. 1983;32:369-370, 384.
- Suchonwanit P, Hector CE, Bin Saif GA, McMichael AJ. Factors affecting the severity of central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:e338-343. doi:10.1111/ijd.13061
- Gabros S, Masood S. Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. Updated July 20, 2021. Accessed December 9, 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559187/
- Ross EK, Tan E, Shapiro J. Update on primary cicatricial alopecias. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:1-37. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2004.06.015
- Cobos G, Kim RH, Meehan S, et al. Lichen planus pigmentosus and lichen planopilaris. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt7hp8n6dn.
- Lyakhovitsky A, Amichai B, Sizopoulou C, et al. A case series of 46 patients with lichen planopilaris: demographics, clinical evaluation, and treatment experience. J Dermatolog Treat. 2015;26:275-279. doi:10.3109/09546634.2014.933165
- Tan E, Martinka M, Ball N, et al. Primary cicatricial alopecias: clinicopathology of 112 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:25-32. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2003.04.001
- Kutlu Ö, Aktas¸ H, I·mren IG, et al. Short-term stress-related increasing cases of alopecia areata during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Dermatolog Treat. 2020;1. doi:10.1080/09546634.2020.1782820
- Cline A, Kazemi A, Moy J, et al. A surge in the incidence of telogen effluvium in minority predominant communities heavily impacted by COVID-19. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:773-775. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.032
- Kutlu Ö, Metin A. Relative changes in the pattern of diseases presenting in dermatology outpatient clinic in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e14096. doi:10.1111/dth.14096
- Tanacan E, Aksoy Sarac G, Emeksiz MAC, et al. Changing trends in dermatology practice during COVID-19 pandemic: a single tertiary center experience. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e14136. doi:10.1111/dth.14136
- Sharma A, Jindal V, Singla P, et al. Will teledermatology be the silver lining during and after COVID-19? Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e13643. doi:10.1111/dth.13643
- Iscrupe L. How to receive virtual medical treatment while under quarantine. Allconnect website. Published March 26, 2020. Accessed December 9, 2021. https://www.allconnect.com/blog/online-doctor-visit-faq
- Elgash M, Dlova N, Ogunleye T, et al. Seborrheic dermatitis in skin of color: clinical considerations. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18:24-27.
- McLaurin CI. Annular facial dermatoses in blacks. Cutis. 1983;32:369-370, 384.
- Suchonwanit P, Hector CE, Bin Saif GA, McMichael AJ. Factors affecting the severity of central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:e338-343. doi:10.1111/ijd.13061
- Gabros S, Masood S. Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. Updated July 20, 2021. Accessed December 9, 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559187/
- Ross EK, Tan E, Shapiro J. Update on primary cicatricial alopecias. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:1-37. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2004.06.015
- Cobos G, Kim RH, Meehan S, et al. Lichen planus pigmentosus and lichen planopilaris. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt7hp8n6dn.
- Lyakhovitsky A, Amichai B, Sizopoulou C, et al. A case series of 46 patients with lichen planopilaris: demographics, clinical evaluation, and treatment experience. J Dermatolog Treat. 2015;26:275-279. doi:10.3109/09546634.2014.933165
- Tan E, Martinka M, Ball N, et al. Primary cicatricial alopecias: clinicopathology of 112 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:25-32. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2003.04.001
Multiethnic Training in Residency: A Survey of Dermatology Residents
Dermatologic treatment of patients with skin of color offers specific challenges. Studies have reported structural, morphologic, and physiologic distinctions among different ethnic groups,1 which may account for distinct clinical presentations of skin disease seen in patients with skin of color. Patients with skin of color are at increased risk for specific dermatologic conditions, such as postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, keloid development, and central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia.2,3 Furthermore, although skin cancer is less prevalent in patients with skin of color, it often presents at a more advanced stage and with a worse prognosis compared to white patients.4
Prior studies have demonstrated the need for increased exposure, education, and training in diseases pertaining to skin of color in US dermatology residency programs.6-8 The aim of this study was to assess if dermatologists in-training feel that their residency curriculum sufficiently educates them on the needs of patients with skin of color.
Methods
A 10-question anonymous survey was emailed to 109 dermatology residency programs to evaluate the attitudes of dermatology residents about their exposure to patients with skin of color and their skin-of-color curriculum. The study included individuals 18 years or older who were current residents in a dermatology program accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education.
Results
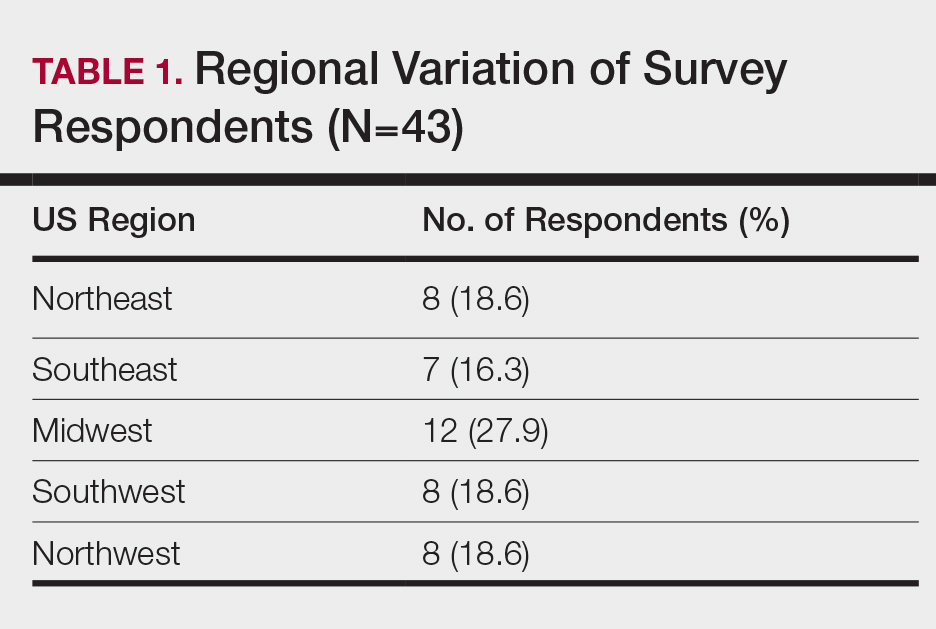
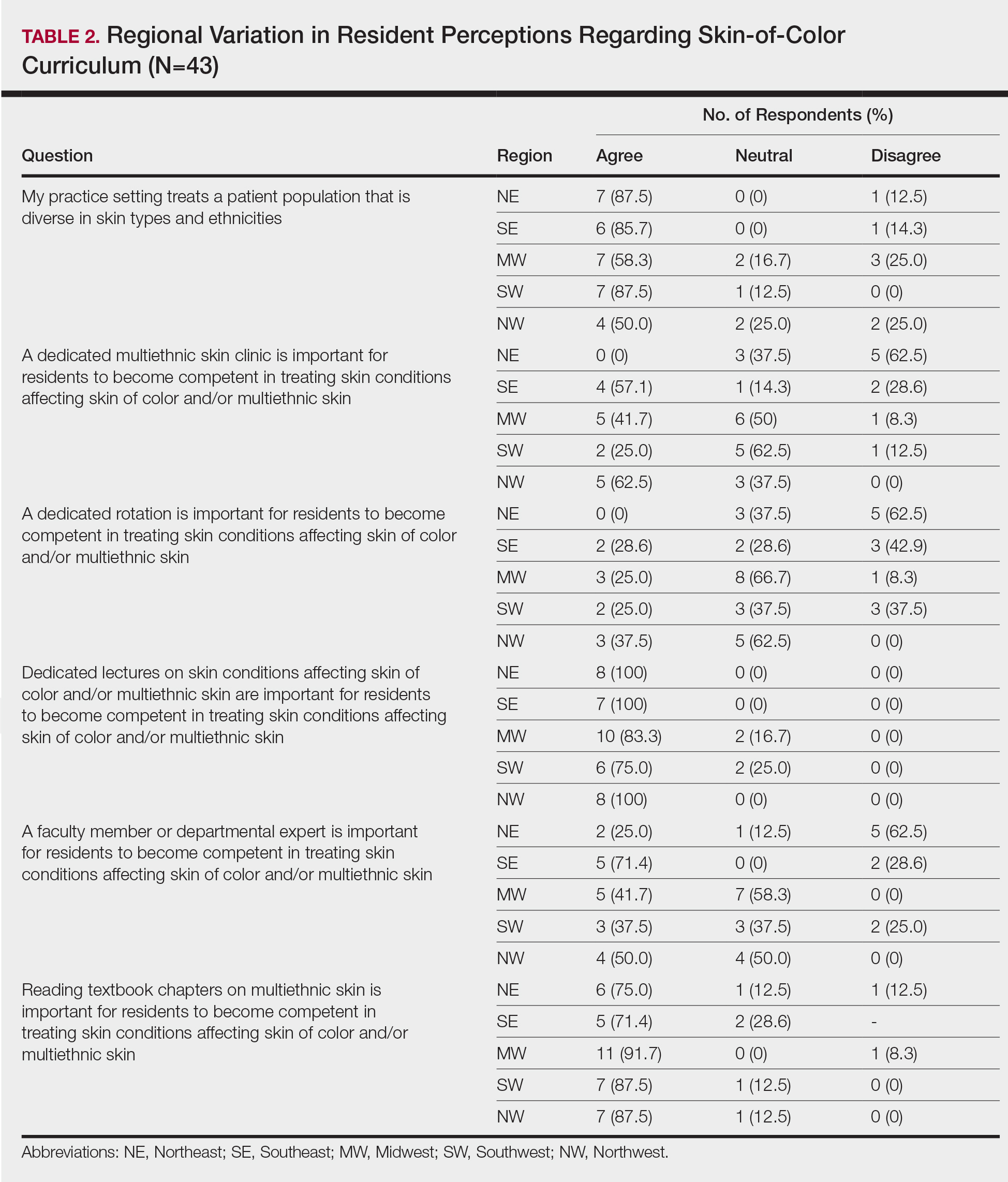
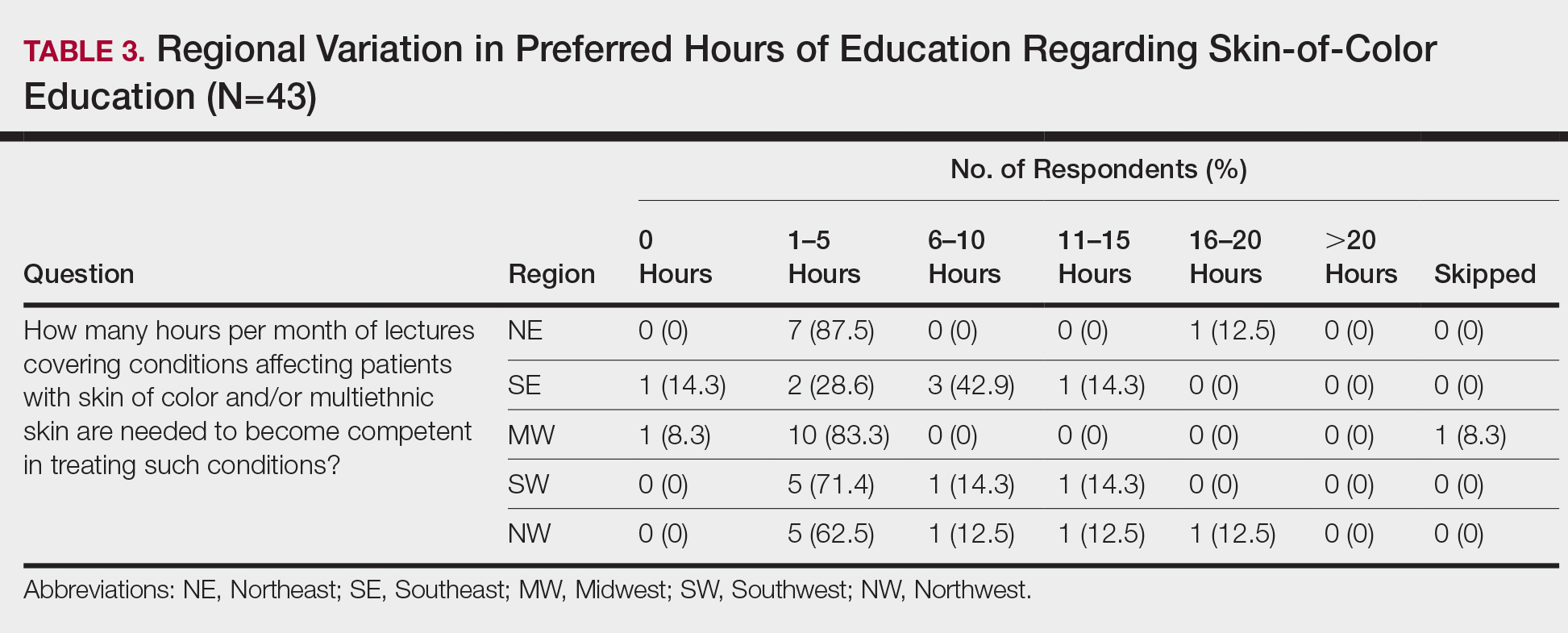
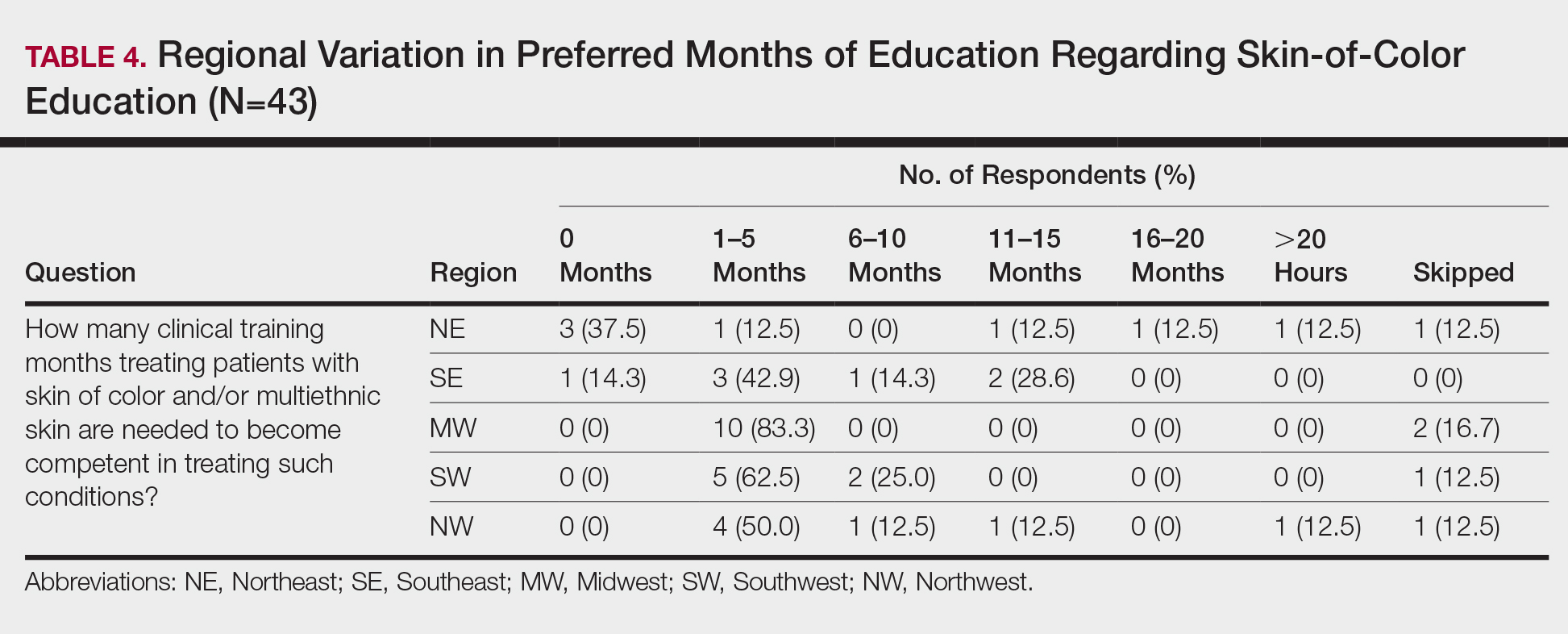
When asked the number of hours of lecture per month necessary to gain competence in conditions affecting patients with skin of color, 67% agreed that 1 to 5 hours was sufficient (Table 3). There were significant differences in the responses between the NE and SE (P=.024) and the SE and MW (P=.007). Of all respondents, 53% reported 1 to 5 months of clinical training are needed to gain competence in treating conditions affecting patients with skin of color, with significant differences in responses between the NE and MW (P<.001), the NE and SW (P=.019), and the SE and MW (P=.015)(Table 4).
Comment
Responses varied by practicing region
Although interactive lectures and textbook readings are important for obtaining a foundational understanding of dermatologic disease, they cannot substitute for clinical interactions and hands-on experience treating patients with skin of color.9 Not only do clinical interactions encourage independent reading and the study of encountered diagnoses, but intercommunication with patients may have a more profound and lasting impact on residents’ education.
Different regions of the United States have varying distributions of patients with skin of color, and dermatology residency program training reflects these disparities.6 In areas of less diversity, dermatology residents examine, diagnose, and treat substantially fewer patients with skin of color. The desire for more diverse training supports the prior findings of Nijhawan et al6 and is reflected in the responses we received in our study, whereby residents from the less ethnically diversified regions of the MW and NW were more likely to agree that clinics and rotations were necessary for training in preparation to sufficiently address the needs of patients with skin of color.
One way to compensate for the lack of ethnic diversity encountered in areas such as the MW and NW would be to develop educational programs featuring experts on skin of color.6 These specialists would not only train dermatology residents in areas of the country currently lacking ethnic diversity but also expand the expertise for treating patients with skin of color. Additionally, dedicated multiethnic skin clinics and externships devoted solely to treating patients with skin of color could be encouraged for residency training.6 Finally, community outreach through volunteer clinics may provide residents exposure to patients with skin of color seeking dermatologic care.10
This study was limited by the small number of respondents, but we were able to extract important trends and data from the collected responses. It is possible that respondents felt strongly about topics involving patients with skin of color, and the results were skewed to reflect individual bias. Additional limitations included not asking respondents for program names and population density (eg, urban, suburban, rural). Future studies should be directed toward analyzing how the diversity of the local population influences training in patients with skin of color, comparing program directors’ perceptions with residents’ perceptions on training in skin of color, and assessing patient perception of residents’ training in skin of color.
Conclusion
In the last decade it has become increasingly apparent that the US population is diversifying and that patients with skin of color will comprise a substantial proportion of the future population,8,11 which emphasizes the need for dermatology residency programs to ensure that residents receive adequate training and exposure to patients with skin of color as well as the distinct skin diseases seen more commonly in these populations.12
- Luther N, Darvin ME, Sterry W, et al. Ethnic differences in skin physiology, hair follicle morphology and follicular penetration. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2012;25:182-191.
- Shokeen D. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation in patients with skin of color. Cutis. 2016;97:E9-E11.
- Lawson CN, Hollinger J, Sethi S, et al. Updates in the understanding and treatments of skin & hair disorders in women of color. Int J Women’s Dermatol. 2017;3:S21-S37.
- Hu S, Parmet Y, Allen G, et al. Disparity in melanoma: a trend analysis of melanoma incidence and stage at diagnosis among whites, Hispanics, and blacks in Florida. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:1369-1374.
- Colby SL, Ortman JM; US Census Bureau. Projections of the Size and Composition of the U.S. Population: 2014 to 2060. Washington, DC: US Census Bureau; 2014. Current Population Reports, P25-1143. https://census.gov/content/dam/Census/library/publications/2015/demo/p25-1143.pdf. Published March 2015. Accessed May 13, 2020.
- Nijhawan RI, Jacob SE, Woolery-Lloyd H. Skin of color education in dermatology residency programs: does residency training reflect the changing demographics of the United States? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:615-618.
- Pritchett EN, Pandya AG, Ferguson NN, et al. Diversity in dermatology: roadmap for improvement. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:337-341.
- Pandya AG, Alexis AF, Berger TG, et al. Increasing racial and ethnic diversity in dermatology: a call to action. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:584-587.
- Ernst H, Colthorpe K. The efficacy of interactive lecturing for students with diverse science backgrounds. Adv Physiol Educ. 2007;31:41-44.
- Allday E. UCSF opens ‘skin of color’ dermatology clinic to address disparity in care. San Francisco Chronicle. March 20, 2019. https://www.sfchronicle.com/health/article/UCSF-opens-skin-of-color-dermatology-clinic-13704387.php. Accessed May 13, 2020.
- Van Voorhees AS, Enos CW. Diversity in dermatology residency programs. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2017;18:S46-S49.
- Enos CW, Harvey VM. From bench to bedside: the Hampton University Skin of Color Research Institute 2015 Skin of Color Symposium. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2017;18:S29-S30.
Dermatologic treatment of patients with skin of color offers specific challenges. Studies have reported structural, morphologic, and physiologic distinctions among different ethnic groups,1 which may account for distinct clinical presentations of skin disease seen in patients with skin of color. Patients with skin of color are at increased risk for specific dermatologic conditions, such as postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, keloid development, and central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia.2,3 Furthermore, although skin cancer is less prevalent in patients with skin of color, it often presents at a more advanced stage and with a worse prognosis compared to white patients.4
Prior studies have demonstrated the need for increased exposure, education, and training in diseases pertaining to skin of color in US dermatology residency programs.6-8 The aim of this study was to assess if dermatologists in-training feel that their residency curriculum sufficiently educates them on the needs of patients with skin of color.
Methods
A 10-question anonymous survey was emailed to 109 dermatology residency programs to evaluate the attitudes of dermatology residents about their exposure to patients with skin of color and their skin-of-color curriculum. The study included individuals 18 years or older who were current residents in a dermatology program accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education.
Results


When asked the number of hours of lecture per month necessary to gain competence in conditions affecting patients with skin of color, 67% agreed that 1 to 5 hours was sufficient (Table 3). There were significant differences in the responses between the NE and SE (P=.024) and the SE and MW (P=.007). Of all respondents, 53% reported 1 to 5 months of clinical training are needed to gain competence in treating conditions affecting patients with skin of color, with significant differences in responses between the NE and MW (P<.001), the NE and SW (P=.019), and the SE and MW (P=.015)(Table 4).


Comment
Responses varied by practicing region
Although interactive lectures and textbook readings are important for obtaining a foundational understanding of dermatologic disease, they cannot substitute for clinical interactions and hands-on experience treating patients with skin of color.9 Not only do clinical interactions encourage independent reading and the study of encountered diagnoses, but intercommunication with patients may have a more profound and lasting impact on residents’ education.
Different regions of the United States have varying distributions of patients with skin of color, and dermatology residency program training reflects these disparities.6 In areas of less diversity, dermatology residents examine, diagnose, and treat substantially fewer patients with skin of color. The desire for more diverse training supports the prior findings of Nijhawan et al6 and is reflected in the responses we received in our study, whereby residents from the less ethnically diversified regions of the MW and NW were more likely to agree that clinics and rotations were necessary for training in preparation to sufficiently address the needs of patients with skin of color.
One way to compensate for the lack of ethnic diversity encountered in areas such as the MW and NW would be to develop educational programs featuring experts on skin of color.6 These specialists would not only train dermatology residents in areas of the country currently lacking ethnic diversity but also expand the expertise for treating patients with skin of color. Additionally, dedicated multiethnic skin clinics and externships devoted solely to treating patients with skin of color could be encouraged for residency training.6 Finally, community outreach through volunteer clinics may provide residents exposure to patients with skin of color seeking dermatologic care.10
This study was limited by the small number of respondents, but we were able to extract important trends and data from the collected responses. It is possible that respondents felt strongly about topics involving patients with skin of color, and the results were skewed to reflect individual bias. Additional limitations included not asking respondents for program names and population density (eg, urban, suburban, rural). Future studies should be directed toward analyzing how the diversity of the local population influences training in patients with skin of color, comparing program directors’ perceptions with residents’ perceptions on training in skin of color, and assessing patient perception of residents’ training in skin of color.
Conclusion
In the last decade it has become increasingly apparent that the US population is diversifying and that patients with skin of color will comprise a substantial proportion of the future population,8,11 which emphasizes the need for dermatology residency programs to ensure that residents receive adequate training and exposure to patients with skin of color as well as the distinct skin diseases seen more commonly in these populations.12
Dermatologic treatment of patients with skin of color offers specific challenges. Studies have reported structural, morphologic, and physiologic distinctions among different ethnic groups,1 which may account for distinct clinical presentations of skin disease seen in patients with skin of color. Patients with skin of color are at increased risk for specific dermatologic conditions, such as postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, keloid development, and central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia.2,3 Furthermore, although skin cancer is less prevalent in patients with skin of color, it often presents at a more advanced stage and with a worse prognosis compared to white patients.4
Prior studies have demonstrated the need for increased exposure, education, and training in diseases pertaining to skin of color in US dermatology residency programs.6-8 The aim of this study was to assess if dermatologists in-training feel that their residency curriculum sufficiently educates them on the needs of patients with skin of color.
Methods
A 10-question anonymous survey was emailed to 109 dermatology residency programs to evaluate the attitudes of dermatology residents about their exposure to patients with skin of color and their skin-of-color curriculum. The study included individuals 18 years or older who were current residents in a dermatology program accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education.
Results


When asked the number of hours of lecture per month necessary to gain competence in conditions affecting patients with skin of color, 67% agreed that 1 to 5 hours was sufficient (Table 3). There were significant differences in the responses between the NE and SE (P=.024) and the SE and MW (P=.007). Of all respondents, 53% reported 1 to 5 months of clinical training are needed to gain competence in treating conditions affecting patients with skin of color, with significant differences in responses between the NE and MW (P<.001), the NE and SW (P=.019), and the SE and MW (P=.015)(Table 4).


Comment
Responses varied by practicing region
Although interactive lectures and textbook readings are important for obtaining a foundational understanding of dermatologic disease, they cannot substitute for clinical interactions and hands-on experience treating patients with skin of color.9 Not only do clinical interactions encourage independent reading and the study of encountered diagnoses, but intercommunication with patients may have a more profound and lasting impact on residents’ education.
Different regions of the United States have varying distributions of patients with skin of color, and dermatology residency program training reflects these disparities.6 In areas of less diversity, dermatology residents examine, diagnose, and treat substantially fewer patients with skin of color. The desire for more diverse training supports the prior findings of Nijhawan et al6 and is reflected in the responses we received in our study, whereby residents from the less ethnically diversified regions of the MW and NW were more likely to agree that clinics and rotations were necessary for training in preparation to sufficiently address the needs of patients with skin of color.
One way to compensate for the lack of ethnic diversity encountered in areas such as the MW and NW would be to develop educational programs featuring experts on skin of color.6 These specialists would not only train dermatology residents in areas of the country currently lacking ethnic diversity but also expand the expertise for treating patients with skin of color. Additionally, dedicated multiethnic skin clinics and externships devoted solely to treating patients with skin of color could be encouraged for residency training.6 Finally, community outreach through volunteer clinics may provide residents exposure to patients with skin of color seeking dermatologic care.10
This study was limited by the small number of respondents, but we were able to extract important trends and data from the collected responses. It is possible that respondents felt strongly about topics involving patients with skin of color, and the results were skewed to reflect individual bias. Additional limitations included not asking respondents for program names and population density (eg, urban, suburban, rural). Future studies should be directed toward analyzing how the diversity of the local population influences training in patients with skin of color, comparing program directors’ perceptions with residents’ perceptions on training in skin of color, and assessing patient perception of residents’ training in skin of color.
Conclusion
In the last decade it has become increasingly apparent that the US population is diversifying and that patients with skin of color will comprise a substantial proportion of the future population,8,11 which emphasizes the need for dermatology residency programs to ensure that residents receive adequate training and exposure to patients with skin of color as well as the distinct skin diseases seen more commonly in these populations.12
- Luther N, Darvin ME, Sterry W, et al. Ethnic differences in skin physiology, hair follicle morphology and follicular penetration. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2012;25:182-191.
- Shokeen D. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation in patients with skin of color. Cutis. 2016;97:E9-E11.
- Lawson CN, Hollinger J, Sethi S, et al. Updates in the understanding and treatments of skin & hair disorders in women of color. Int J Women’s Dermatol. 2017;3:S21-S37.
- Hu S, Parmet Y, Allen G, et al. Disparity in melanoma: a trend analysis of melanoma incidence and stage at diagnosis among whites, Hispanics, and blacks in Florida. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:1369-1374.
- Colby SL, Ortman JM; US Census Bureau. Projections of the Size and Composition of the U.S. Population: 2014 to 2060. Washington, DC: US Census Bureau; 2014. Current Population Reports, P25-1143. https://census.gov/content/dam/Census/library/publications/2015/demo/p25-1143.pdf. Published March 2015. Accessed May 13, 2020.
- Nijhawan RI, Jacob SE, Woolery-Lloyd H. Skin of color education in dermatology residency programs: does residency training reflect the changing demographics of the United States? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:615-618.
- Pritchett EN, Pandya AG, Ferguson NN, et al. Diversity in dermatology: roadmap for improvement. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:337-341.
- Pandya AG, Alexis AF, Berger TG, et al. Increasing racial and ethnic diversity in dermatology: a call to action. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:584-587.
- Ernst H, Colthorpe K. The efficacy of interactive lecturing for students with diverse science backgrounds. Adv Physiol Educ. 2007;31:41-44.
- Allday E. UCSF opens ‘skin of color’ dermatology clinic to address disparity in care. San Francisco Chronicle. March 20, 2019. https://www.sfchronicle.com/health/article/UCSF-opens-skin-of-color-dermatology-clinic-13704387.php. Accessed May 13, 2020.
- Van Voorhees AS, Enos CW. Diversity in dermatology residency programs. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2017;18:S46-S49.
- Enos CW, Harvey VM. From bench to bedside: the Hampton University Skin of Color Research Institute 2015 Skin of Color Symposium. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2017;18:S29-S30.
- Luther N, Darvin ME, Sterry W, et al. Ethnic differences in skin physiology, hair follicle morphology and follicular penetration. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2012;25:182-191.
- Shokeen D. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation in patients with skin of color. Cutis. 2016;97:E9-E11.
- Lawson CN, Hollinger J, Sethi S, et al. Updates in the understanding and treatments of skin & hair disorders in women of color. Int J Women’s Dermatol. 2017;3:S21-S37.
- Hu S, Parmet Y, Allen G, et al. Disparity in melanoma: a trend analysis of melanoma incidence and stage at diagnosis among whites, Hispanics, and blacks in Florida. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:1369-1374.
- Colby SL, Ortman JM; US Census Bureau. Projections of the Size and Composition of the U.S. Population: 2014 to 2060. Washington, DC: US Census Bureau; 2014. Current Population Reports, P25-1143. https://census.gov/content/dam/Census/library/publications/2015/demo/p25-1143.pdf. Published March 2015. Accessed May 13, 2020.
- Nijhawan RI, Jacob SE, Woolery-Lloyd H. Skin of color education in dermatology residency programs: does residency training reflect the changing demographics of the United States? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:615-618.
- Pritchett EN, Pandya AG, Ferguson NN, et al. Diversity in dermatology: roadmap for improvement. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:337-341.
- Pandya AG, Alexis AF, Berger TG, et al. Increasing racial and ethnic diversity in dermatology: a call to action. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:584-587.
- Ernst H, Colthorpe K. The efficacy of interactive lecturing for students with diverse science backgrounds. Adv Physiol Educ. 2007;31:41-44.
- Allday E. UCSF opens ‘skin of color’ dermatology clinic to address disparity in care. San Francisco Chronicle. March 20, 2019. https://www.sfchronicle.com/health/article/UCSF-opens-skin-of-color-dermatology-clinic-13704387.php. Accessed May 13, 2020.
- Van Voorhees AS, Enos CW. Diversity in dermatology residency programs. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2017;18:S46-S49.
- Enos CW, Harvey VM. From bench to bedside: the Hampton University Skin of Color Research Institute 2015 Skin of Color Symposium. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2017;18:S29-S30.
Practice Points
- To treat the ever-changing demographics of patients in the United States, dermatologists must receive adequate exposure and education regarding dermatologic conditions in patients from various ethnic backgrounds.
- Dermatology residents from less diverse regions are more likely to agree that dedicated clinics and rotations are important to gain competence compared to those from more diverse regions.
- In areas with less diversity, dedicated multiethnic skin clinics and faculty may be more important for assuring an adequate residency experience.
Hair and Scalp Disorders in Adult and Pediatric Patients With Skin of Color
One of the most common concerns among black patients is hair- and scalp-related disease. As increasing numbers of black patients opt to see dermatologists, it is imperative that all dermatologists be adequately trained to address the concerns of this patient population. When patients ask for help with common skin diseases of the hair and scalp, there are details that must be included in diagnosis, treatment, and hair care recommendations to reach goals for excellence in patient care. Herein, we provide must-know information to effectively approach this patient population.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
A study utilizing data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey from 1993 to 2009 revealed seborrheic dermatitis (SD) as the second most common diagnosis for black patients who visit a dermatologist.1 Prevalence data from a population of 1408 white, black, and Chinese patients from the United States and China revealed scalp flaking in 81% to 95% of black patients, 66% to 82% in white patients, and 30% to 42% in Chinese patients.2 Seborrheic dermatitis has a notable prevalence in black women and often is considered normal by patients. It can be exacerbated by infrequent shampooing (ranging from once per month or longer in between shampoos) and the inappropriate use of hair oils and pomades; it also has been associated with hair breakage, lichen simplex chronicus, and folliculitis. Seborrheic dermatitis must be distinguished from other disorders including sarcoidosis, psoriasis, discoid lupus erythematosus, tinea capitis, and lichen simplex chronicus.
Although there is a paucity of literature on the treatment of SD in black patients, components of treatment are similar to those recommended for other populations. Black women are advised to carefully utilize antidandruff shampoos containing zinc pyrithione, selenium sulfide, or tar to avoid hair shaft damage and dryness. Ketoconazole shampoo rarely is recommended and may be more appropriately used in men and boys, as hair fragility is less of a concern for them. The shampoo should be applied directly to the scalp rather than the hair shafts to minimize dryness, with no particular elongated contact time needed for these medicated shampoos to be effective. Because conditioners can wash off the active ingredients in therapeutic shampoos, antidandruff conditioners are recommended. Potent or ultrapotent topical corticosteroids applied to the scalp 3 to 4 times weekly initially will control the symptoms of itching as well as scaling, and mid-potency topical corticosteroid oil may be used at weekly intervals.
Hairline and facial involvement of SD often co-occurs, and low-potency topical steroids may be applied to the affected areas twice daily for 3 to 4 weeks, which may be repeated for flares. Topical calcineurin inhibitors or antifungal creams such as ketoconazole or econazole may then provide effective control. Encouraging patients to increase shampooing to once weekly or every 2 weeks and discontinue use of scalp pomades and oils also is recommended. Patients must know that an itchy scaly scalp represents a treatable disorder.
Acquired Trichorrhexis Nodosa
Hair fragility and breakage is common and multifactorial in black patients. Hair shaft breakage can occur on the vertex scalp in central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA), with random localized breakage due to scratching in SD. Heat, hair colorants, and chemical relaxers may result in diffuse damage and breakage.3 Sodium-, potassium-, and guanine hydroxide–containing chemical relaxers change the physical properties of the hair by rearranging disulfide bonds. They remove the monomolecular layer of fatty acids covalently bound to the cuticle that help prevent penetration of water into the hair shaft. Additionally, chemical relaxers weaken the hair shaft and decrease tensile strength.
Unlike hair relaxers, colorants are less likely to lead to catastrophic hair breakage after a single use and require frequent use, which leads to cumulative damage. Thermal straightening is another cause of hair-shaft weakening in black patients.4,5 Flat irons and curling irons can cause substantially more damage than blow-dryers due to the amount of heat generated. Flat irons may reach a high temperature of 230ºC (450ºF) as compared to 100°C (210°F) for a blow-dryer. Even the simple act of combing the hair can cause hair breakage, as demonstrated in African volunteers whose hair remained short in contrast to white and Asian volunteers, despite the fact that they had not cut their hair for 1 or more years.6,7 These volunteers had many hair strand knots that led to breakage during combing and hair grooming.6
There is no known prevalence data for acquired trichorrhexis nodosa, though a study of 30 white and black women demonstrated that broken hairs were significantly increased in black women (P=.0001).8 Another study by Hall et al9 of 103 black women showed that 55% of the women reported breakage of hair shafts with normal styling. Khumalo et al6 investigated hair shaft fragility and reported no trichothiodystrophy; the authors concluded that the cause of the hair fragility likely was physical trauma or an undiscovered structural abnormality. Franbourg et al10 examined the structure of hair fibers in white, Asian, and black patients and found no differences, but microfractures were only present in black patients and were determined to be the cause of hair breakage. These studies underscore the need for specific questioning of the patient on hair care including combing, washing, drying, and using products and chemicals.
The approach to the treatment of hair breakage involves correcting underlying abnormalities (eg, iron deficiency, hypothyroidism, nutritional deficiencies). Patients should “give their hair a rest” by discontinuing use of heat, colorants, and chemical relaxers. For patients who are unable to comply, advising them to stop these processes for 6 to 12 months will allow for repair of the hair shaft. To minimize damage from colorants, recommend semipermanent, demipermanent, or temporary dyes. Patients should be counseled to stop bleaching their hair or using permanent colorants. The use of heat protectant products on the hair before styling as well as layering moisturizing regimens starting with a moisturizing shampoo followed by a leave-in, dimethicone-containing conditioner marketed for dry damaged hair is suggested. Dimethicone thinly coats the hair shaft to restore hydrophobicity, smoothes cuticular scales, decreases frizz, and protects the hair from damage. Use of a 2-in-1 shampoo and conditioner containing anionic surfactants and wide-toothed, smooth (no jagged edges in the grooves) combs along with rare brushing are recommended. The hair may be worn in its natural state, but straightening with heat should be avoided. Air drying the hair can minimize breakage, but if thermal styling is necessary, patients should turn the temperature setting of the flat or curling iron down. Protective hair care practices may include placing a loosely sewn-in hair weave that will allow for good hair care, wearing loose braids, or using a wig. Serial trimming of the hair every 6 to 8 weeks is recommended. Improvement may take time, and patients should be advised of this timeline to prevent frustration.
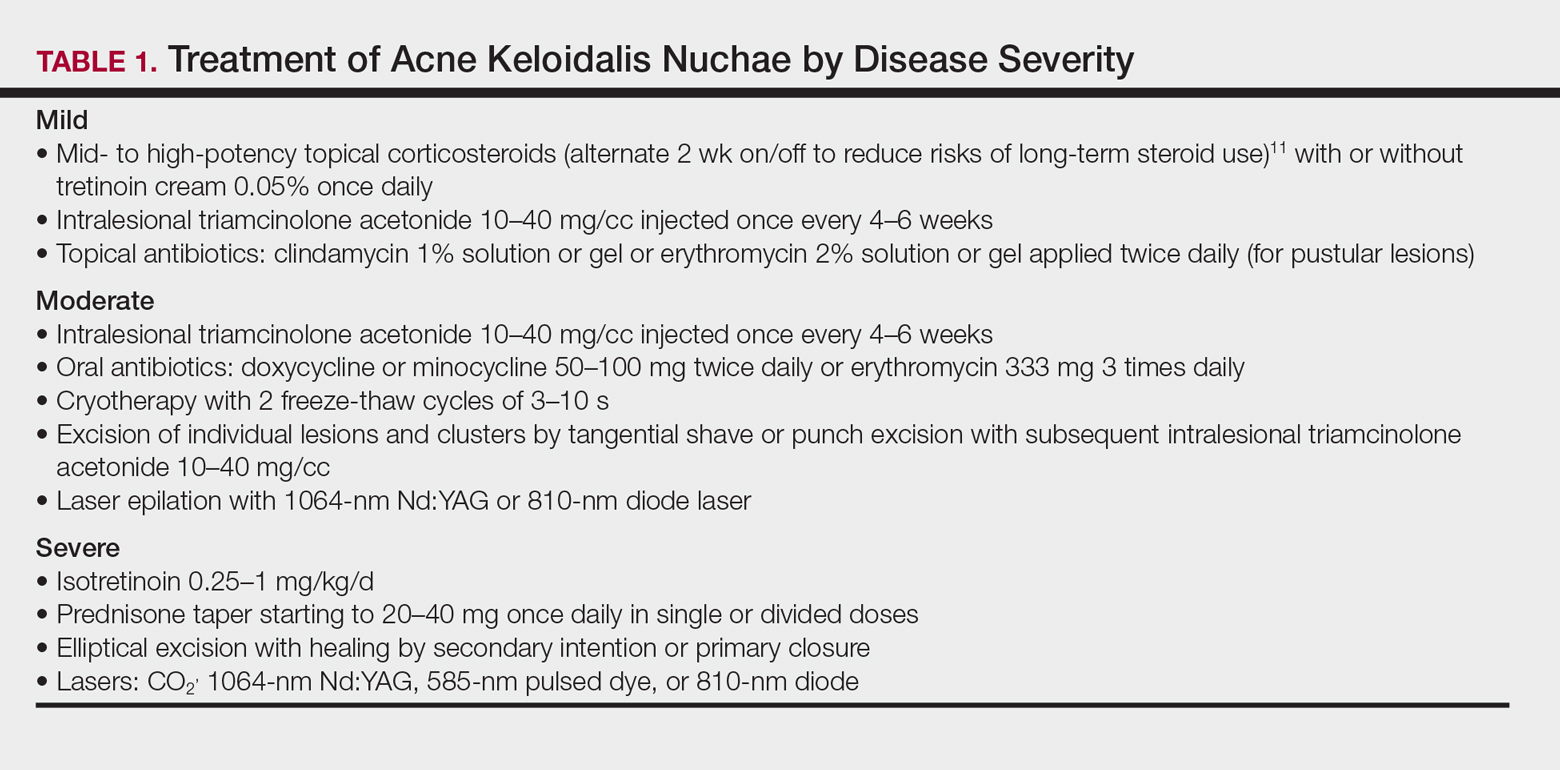
Acne Keloidalis Nuchae
Acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) is characterized by papules and pustules located on the occipital scalp and/or the nape of the neck, which may result in keloidal papules and plaques. The etiology is unknown, but ingrown hairs, genetics, trauma, infection, inflammation, and androgen hormones have been proposed to play a role.11 Although AKN may occur in black women, it is primarily a disorder in black men. The diagnosis is made based primarily on clinical findings, and a history of short haircuts may support the diagnosis. Treatment is tailored to the severity of the disease (Table 1). Avoidance of short haircuts and irritation from shirt collars may be helpful. Patients should be advised that the condition is controllable but not curable.
Pseudofolliculitis Barbae
Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB) is characterized by papules and pustules in the beard region that may result in postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, keloidal scar formation, and/or linear scarring. The coarse curled hairs characteristic of black men penetrate the follicle before exiting the skin and penetrate the skin after exiting the follicle, resulting in inflammation. Shaving methods and genetics also may contribute to the development of PFB. As with AKN, diagnosis is made clinically and does not require a skin biopsy. Important components of the patient’s history that should be obtained are hair removal practices and the use of over-the-counter products (eg, shave [pre and post] moisturizers, exfoliants, shaving creams or gels, keratin-softening agents containing α- or β-hydroxy acids). A bacterial culture may be appropriate if a notable pustular component is present. The patient should be advised to discontinue shaving if possible, which may require a physician’s letter explaining the necessity to the patient’s employer. Pseudofolliculitis barbae often can be prevented or lessened with the right hair removal strategy. Because there is not one optimal hair removal strategy that suits every patient, encourage the patient to experiment with different hair removal techniques, from depilatories to electric shavers, foil-guard razors, and multiple-blade razors. Preshave hydration and postshave moisturiza-tion also should be encouraged.12 Benzoyl peroxide–containing shave gels and cleansers, as well as moisturizers containing glycolic, salicylic, and phytic acids, may minimize ingrown hairs, papules, and inflammation.
Other useful topical agents include eflornithine hydrochloride to decrease hair growth, retinoids to soften hair fibers, mild topical steroids to reduce inflammation, and/or topical erythromycin or clindamycin if pustules are present.13 Oral antibiotics such as doxycycline, minocycline, or erythromycin can be added for more severe cases of inflammation or infection. Procedural interventions include laser hair removal to prevent PFB and intralesional triamcinolone 10 to 40 mg/cc every 4 to 6 weeks, with the total volume depending on the size and number of lesions.
Alopecia
Alopecia is the sixth most common diagnosis seen in black patients visiting a dermatologist.14 The physician’s response to the patient’s chief concern of hair loss is key to building a relationship of confidence and trust. Trivializing the concern or dismissing it will undermine the physician-patient relationship. A survey by Gathers and Mahan15 revealed that 68% of patients thought that physicians did not understand their hair.
Hair loss negatively impacts quality of life, and a study of 50 black South African women with alopecia demonstrated a notable disease burden. Factors with the highest impact were those related to self-image, relationships, and interactions with others.16
It is not unusual for black women to have multiple types of alopecia identified in one biopsy specimen. Wohltmann and Sperling17 demonstrated 2 or more different types of alopecia in more than 10% of biopsy specimens of alopecia, including CCCA, androgenetic alopecia, end-stage traction alopecia, telogen effluvium, and tinea capitis. A complete history, physical examination, and appropriate procedures (eg, hair pull test, dermatoscopic examination and scalp biopsy) likely will yield an accurate diagnosis. Table 2 highlights important questions that should be asked about the patient’s history.
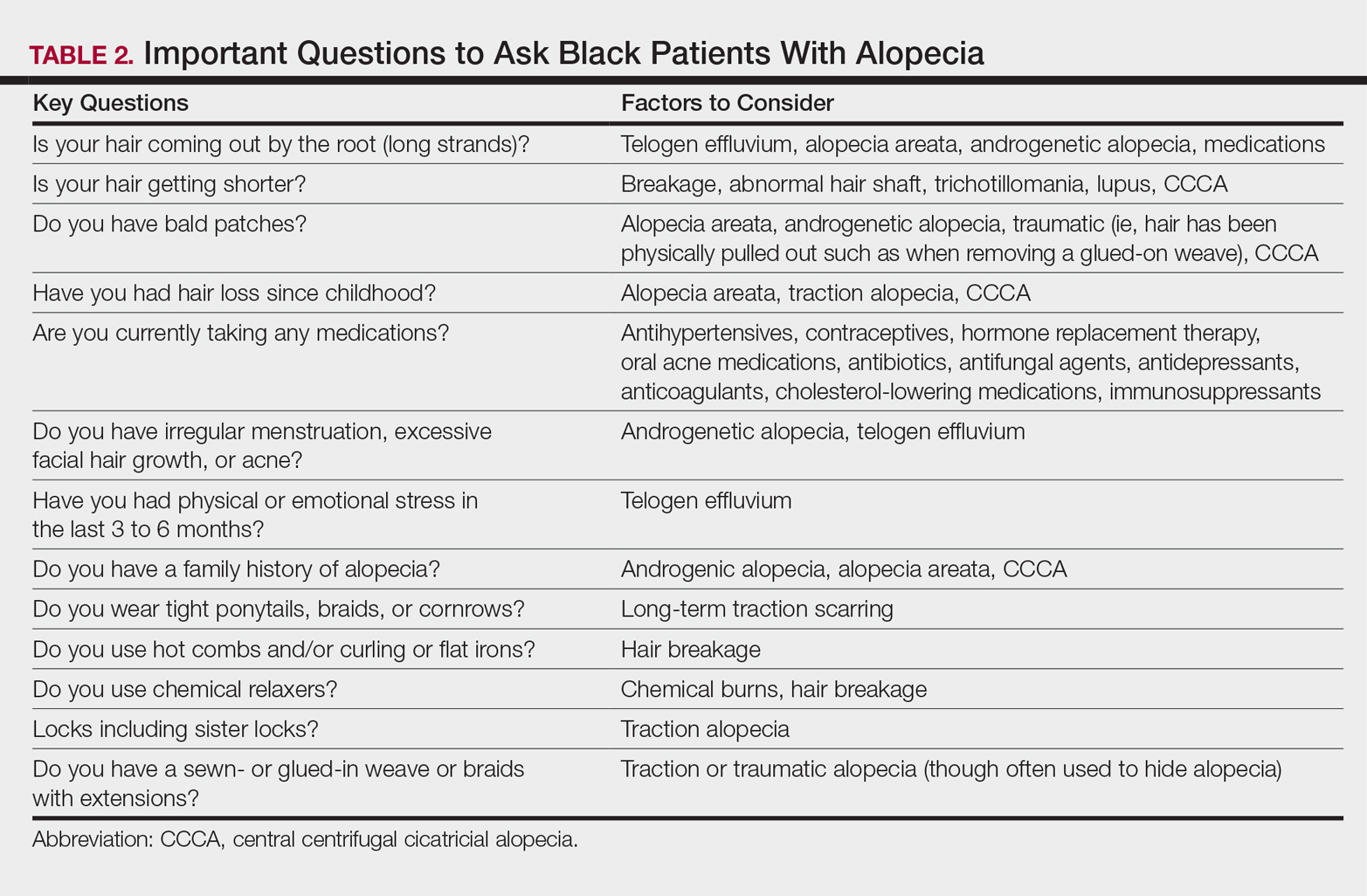
Physical examination of the scalp including dermatoscopic examination and a hair pull test as well as an evaluation of other hair-bearing areas may suggest a diagnosis that can be confirmed with a scalp biopsy.18,19 Selection of a biopsy site at the periphery of the alopecic area that includes hair and consultation with a dermatopathologist familiar with features of CCCA, traction, and traumatic alopecia are important for making an accurate diagnosis.
Tinea Capitis in Black Pediatric Patients
Tinea capitis, a fungal infection of the scalp and hair, is one of the most common issues in children with skin of color. Clinical presentation may include widely distributed scaling, annular scaly plaques, annular patches of alopecia studded with black dots (broken hairs), and/or annular inflammatory plaques. Although scalp hyperkeratosis often is a hallmark of pediatric tinea capitis, it is not diagnostic. The differential diagnosis of pediatric scalp hyperkeratosis/scaling includes tinea capitis, SD, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and sebopsoriasis.20,21 Clues to accurate diagnosis of tinea capitis may be found by examination of the adult who combs the child’s hair, as erythematous annular scaly plaques representing tinea corporis may be observed on the forearms or thighs. Although the thighs are a seemingly unusual location, the frequent practice of the child sitting on the floor between the legs of the adult during hairstyling provides a point of contact for the transmission of tinea from the child’s scalp to the thighs or forearms of the adult. Once tinea capitis is clinically suspected, the diagnosis is confirmed by a fungal culture. Adequate sampling is obtained by clipping hairs in an area of scaling for submission and vigorously rubbing the area of black dots or hyperkeratosis with a cotton swab.
Hubbard22 shed light on the decision to treat tinea capitis empirically or await the culture results. One hundred consecutive children (98 were black) presented with the constellation of scalp alopecia, scaling, pruritus, and occipital lymphadenopathy. Sixty-eight of those children had positive fungal cultures, and of them, 60 had both occipital lymphadenopathy and scaling and 55 had both occipital lymphadenopathy and alopecia.22 Thus, occipital lymphadenopathy in conjunction with alopecia and/or scaling is predictive of tinea capitis in this population and suggests that the initiation of treatment prior to confirmative culture results is appropriate.
The mainstay of treatment for tinea capitis is griseofulvin, but it is often underdosed and not continued for an adequate period of time to ensure clearance of the infection. Griseofulvin microsize (125 mg/5 mL) at the dosage of 20 to 25 mg/kg once daily for 8 to 12 weeks is recommended instead of a lower-dosed 4- to 6-week course.23,24
Options for treating a child with residual disease include increasing and/or extending the griseofulvin dosage, encouraging ingestion of fatty foods to enhance absorption, dividing the dosage of griseofulvin from once daily to twice daily, changing therapy to oral terbinafine due to resistance to griseofulvin, examining siblings as a source of reinfection, and reviewing the positive fungal culture report to distinguish Trichophyton tonsurans versus Microsporum canis as the causative agent and adjust treatment accordingly. Although griseofulvin is the first-line treatment for M canis, terbinafine, which is approved for children 4 years and older for tineacapitis, is most efficacious for T tonsurans.25 Treatment with terbinafine is weight based and should extend for 2 to 4 weeksfor T tonsurans and 8 to 12 weeks for M canis.
Antifungal shampoos may help reduce household spread of tinea and decrease transmissible fungal spores, but they may cause hair dryness and breakage.26,27 Antifungal shampoos can be applied directly onto the scalp for a 5- to 10-minute contact time and rinsed, and then the hair should be shampooed with a moisturizing shampoo followed by a moisturizing conditioner. Hair conditioners may decrease household spread of tinea capitis and should be used by the patient and other members of the household.28 Infection control may be enhanced by advising parents to dispose of hair pomades and washing hair accessories, combs, and brushes in hot soapy water, preferably in the dishwasher.
Hair Growth
The inability of the hair of black children to grow long is a common concern for parents of toddlers and preschool-aged children. Although the hair does grow, it grows more slowly than hair in white children (0.259 vs 0.330 mm per day), and it is likely to break faster than it is growing in black versus white children (146.6 vs 13.13 total broken hairs).8 Reassurance that the hair is indeed growing and that the length will increase as the child matures is important. Avoidance of hairstyles that promote traction and use of hair extensions, as well as use of moisturizing shampoos and conditioners, may minimize breakage and support the growth of healthy hair.
Conclusion
Hair- and scalp-related disease in black adults and children is commonly encountered in dermatology practice. It is important to understand the intrinsic characteristics of facial and scalp hair as well as hair care practices in this patient population that differ from those of white and Asian populations, such as frequency of shampooing, products, and styling. Familiarity with these differences may aid in effective diagnosis, treatment, and hair care recommendations in patients with these conditions.
- Davis SA, Naarahari S, Feldman SR, et al. Top dermatologic conditions in patients of color: an analysis of nationally representative data. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:466-473.
- Hickman JG, Cardin C, Dawson TL, et al. Dandruff, part I: scalp disease prevalence in Caucasians, African Americans, and Chinese and the effects of shampoo frequency on scalp health. Poster presented at: 60th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology; February 22-27, 2002; New Orleans, LA.
- Swee W, Klontz KC, Lambert LA. A nationwide outbreak of alopecia associated with the use of a hair-relaxing formulation. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:1104-1108.
- Nicholson AG, Harland CC, Bull RH, et al. Chemically induced cosmetic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1993;128:537-541.
- Detwiler SP, Carson JL, Woosley JT, et al. Bubble hair. case caused by an overheating hair dryer and reproducibility in normal hair with heat. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;30:54-60.
- Khumalo NP, Dawber RP, Ferguson DJ. Apparent fragility of African hair is unrelated to the cystine-rich protein distribution: a cytochemical electron microscopic study. Exp Dermatol. 2005;14:311-314.
- Robbins C. Hair breakage during combing. I. pathways of breakage. J Cosmet Sci. 2006;57:233-243.
- Lewallen R, Francis S, Fisher B, et al. Hair care practices and structural evaluation of scalp and hair shaft parameter in African American and Caucasian women. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2015;14:216-223.
- Hall RR, Francis S, Whitt-Glover M, et al. Hair care practices as a barrier to physical activity in African American women. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:310-314.
- Franbourg A, Hallegot P, Baltenneck F, et al. Current research on ethnic hair. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48(6 suppl):S115-S119.
- Ogunbiyi A. Acne keloidalis nuchae: prevalence, impact, and management challenges. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:483-489.
- Gray J, McMichael AJ. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: understanding the condition and the role of facial grooming. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38(suppl 1):24-27.
- Kundu RV, Patterson S. Dermatologic conditions in skin of color: part II. disorders occurring predominately in skin of color. Am Fam Physician. 2013;87:859-865.
- Davis SA, Naarahari S, Feldman SR, et al. Top dermatologic conditions in patients of color: an analysis of nationally representative data. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:466-473.
- Gathers RC, Mahan MG. African American women, hair care and health barriers. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:26-29.
- Dlova NC, Fabbrocini G, Lauro C, et al. Quality of life in South African black women with alopecia: a pilot study. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:875-881.
- Wohltmann WE, Sperling L. Histopathologic diagnosis of multifactorial alopecia. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:483-491.
- McDonald KA, Shelley AJ, Colantonio S, et al. Hair pull test: evidence-based update and revision of guidelines. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:472-477.
- Miteva M, Tosti A. Dermatoscopic features of central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:443-444.
- Coley MK, Bhanusali DG, Silverberg JI, et al. Scalp hyperkeratosis and alopecia in children of color. J Drugs Dermatol. 2011;10:511-516.
- Silverberg NB. Scalp hyperkeratosis in children with skin of color: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations. Cutis. 2015;95:199-204, 207.
- Hubbard TW. The predictive value of symptoms in diagnosing childhood tinea capitis. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1999;153:1150-1153.
- Kakourou T, Uksal U; European Society for Pediatric Dermatology. Guidelines for the management of tinea capitis in children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010;27:226-228.
- Sethi A, Antanya R. Systemic antifungal therapy for cutaneous infections in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2006;25:643-644.
- Gupta AK. Drummond-Main C. Meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials comparing particular doses of griseofulvin and terbinafine for the treatment of tinea capitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:1-6.
- Greer DL. Successful treatment of tinea capitis with 2% ketoconazole shampoo. Int J Dermatol 2000;39:302-304.
- Sharma V, Silverberg NB, Howard R, et al. Do hair care practices affect the acquisition of tinea capitis? a case-control study. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2001;155:818-821.
- Greer DL. Successful treatment of tinea capitis with 2% ketoconazole shampoo. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39:302-304.
One of the most common concerns among black patients is hair- and scalp-related disease. As increasing numbers of black patients opt to see dermatologists, it is imperative that all dermatologists be adequately trained to address the concerns of this patient population. When patients ask for help with common skin diseases of the hair and scalp, there are details that must be included in diagnosis, treatment, and hair care recommendations to reach goals for excellence in patient care. Herein, we provide must-know information to effectively approach this patient population.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
A study utilizing data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey from 1993 to 2009 revealed seborrheic dermatitis (SD) as the second most common diagnosis for black patients who visit a dermatologist.1 Prevalence data from a population of 1408 white, black, and Chinese patients from the United States and China revealed scalp flaking in 81% to 95% of black patients, 66% to 82% in white patients, and 30% to 42% in Chinese patients.2 Seborrheic dermatitis has a notable prevalence in black women and often is considered normal by patients. It can be exacerbated by infrequent shampooing (ranging from once per month or longer in between shampoos) and the inappropriate use of hair oils and pomades; it also has been associated with hair breakage, lichen simplex chronicus, and folliculitis. Seborrheic dermatitis must be distinguished from other disorders including sarcoidosis, psoriasis, discoid lupus erythematosus, tinea capitis, and lichen simplex chronicus.
Although there is a paucity of literature on the treatment of SD in black patients, components of treatment are similar to those recommended for other populations. Black women are advised to carefully utilize antidandruff shampoos containing zinc pyrithione, selenium sulfide, or tar to avoid hair shaft damage and dryness. Ketoconazole shampoo rarely is recommended and may be more appropriately used in men and boys, as hair fragility is less of a concern for them. The shampoo should be applied directly to the scalp rather than the hair shafts to minimize dryness, with no particular elongated contact time needed for these medicated shampoos to be effective. Because conditioners can wash off the active ingredients in therapeutic shampoos, antidandruff conditioners are recommended. Potent or ultrapotent topical corticosteroids applied to the scalp 3 to 4 times weekly initially will control the symptoms of itching as well as scaling, and mid-potency topical corticosteroid oil may be used at weekly intervals.
Hairline and facial involvement of SD often co-occurs, and low-potency topical steroids may be applied to the affected areas twice daily for 3 to 4 weeks, which may be repeated for flares. Topical calcineurin inhibitors or antifungal creams such as ketoconazole or econazole may then provide effective control. Encouraging patients to increase shampooing to once weekly or every 2 weeks and discontinue use of scalp pomades and oils also is recommended. Patients must know that an itchy scaly scalp represents a treatable disorder.
Acquired Trichorrhexis Nodosa
Hair fragility and breakage is common and multifactorial in black patients. Hair shaft breakage can occur on the vertex scalp in central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA), with random localized breakage due to scratching in SD. Heat, hair colorants, and chemical relaxers may result in diffuse damage and breakage.3 Sodium-, potassium-, and guanine hydroxide–containing chemical relaxers change the physical properties of the hair by rearranging disulfide bonds. They remove the monomolecular layer of fatty acids covalently bound to the cuticle that help prevent penetration of water into the hair shaft. Additionally, chemical relaxers weaken the hair shaft and decrease tensile strength.
Unlike hair relaxers, colorants are less likely to lead to catastrophic hair breakage after a single use and require frequent use, which leads to cumulative damage. Thermal straightening is another cause of hair-shaft weakening in black patients.4,5 Flat irons and curling irons can cause substantially more damage than blow-dryers due to the amount of heat generated. Flat irons may reach a high temperature of 230ºC (450ºF) as compared to 100°C (210°F) for a blow-dryer. Even the simple act of combing the hair can cause hair breakage, as demonstrated in African volunteers whose hair remained short in contrast to white and Asian volunteers, despite the fact that they had not cut their hair for 1 or more years.6,7 These volunteers had many hair strand knots that led to breakage during combing and hair grooming.6
There is no known prevalence data for acquired trichorrhexis nodosa, though a study of 30 white and black women demonstrated that broken hairs were significantly increased in black women (P=.0001).8 Another study by Hall et al9 of 103 black women showed that 55% of the women reported breakage of hair shafts with normal styling. Khumalo et al6 investigated hair shaft fragility and reported no trichothiodystrophy; the authors concluded that the cause of the hair fragility likely was physical trauma or an undiscovered structural abnormality. Franbourg et al10 examined the structure of hair fibers in white, Asian, and black patients and found no differences, but microfractures were only present in black patients and were determined to be the cause of hair breakage. These studies underscore the need for specific questioning of the patient on hair care including combing, washing, drying, and using products and chemicals.
The approach to the treatment of hair breakage involves correcting underlying abnormalities (eg, iron deficiency, hypothyroidism, nutritional deficiencies). Patients should “give their hair a rest” by discontinuing use of heat, colorants, and chemical relaxers. For patients who are unable to comply, advising them to stop these processes for 6 to 12 months will allow for repair of the hair shaft. To minimize damage from colorants, recommend semipermanent, demipermanent, or temporary dyes. Patients should be counseled to stop bleaching their hair or using permanent colorants. The use of heat protectant products on the hair before styling as well as layering moisturizing regimens starting with a moisturizing shampoo followed by a leave-in, dimethicone-containing conditioner marketed for dry damaged hair is suggested. Dimethicone thinly coats the hair shaft to restore hydrophobicity, smoothes cuticular scales, decreases frizz, and protects the hair from damage. Use of a 2-in-1 shampoo and conditioner containing anionic surfactants and wide-toothed, smooth (no jagged edges in the grooves) combs along with rare brushing are recommended. The hair may be worn in its natural state, but straightening with heat should be avoided. Air drying the hair can minimize breakage, but if thermal styling is necessary, patients should turn the temperature setting of the flat or curling iron down. Protective hair care practices may include placing a loosely sewn-in hair weave that will allow for good hair care, wearing loose braids, or using a wig. Serial trimming of the hair every 6 to 8 weeks is recommended. Improvement may take time, and patients should be advised of this timeline to prevent frustration.
Acne Keloidalis Nuchae
Acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) is characterized by papules and pustules located on the occipital scalp and/or the nape of the neck, which may result in keloidal papules and plaques. The etiology is unknown, but ingrown hairs, genetics, trauma, infection, inflammation, and androgen hormones have been proposed to play a role.11 Although AKN may occur in black women, it is primarily a disorder in black men. The diagnosis is made based primarily on clinical findings, and a history of short haircuts may support the diagnosis. Treatment is tailored to the severity of the disease (Table 1). Avoidance of short haircuts and irritation from shirt collars may be helpful. Patients should be advised that the condition is controllable but not curable.

Pseudofolliculitis Barbae
Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB) is characterized by papules and pustules in the beard region that may result in postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, keloidal scar formation, and/or linear scarring. The coarse curled hairs characteristic of black men penetrate the follicle before exiting the skin and penetrate the skin after exiting the follicle, resulting in inflammation. Shaving methods and genetics also may contribute to the development of PFB. As with AKN, diagnosis is made clinically and does not require a skin biopsy. Important components of the patient’s history that should be obtained are hair removal practices and the use of over-the-counter products (eg, shave [pre and post] moisturizers, exfoliants, shaving creams or gels, keratin-softening agents containing α- or β-hydroxy acids). A bacterial culture may be appropriate if a notable pustular component is present. The patient should be advised to discontinue shaving if possible, which may require a physician’s letter explaining the necessity to the patient’s employer. Pseudofolliculitis barbae often can be prevented or lessened with the right hair removal strategy. Because there is not one optimal hair removal strategy that suits every patient, encourage the patient to experiment with different hair removal techniques, from depilatories to electric shavers, foil-guard razors, and multiple-blade razors. Preshave hydration and postshave moisturiza-tion also should be encouraged.12 Benzoyl peroxide–containing shave gels and cleansers, as well as moisturizers containing glycolic, salicylic, and phytic acids, may minimize ingrown hairs, papules, and inflammation.
Other useful topical agents include eflornithine hydrochloride to decrease hair growth, retinoids to soften hair fibers, mild topical steroids to reduce inflammation, and/or topical erythromycin or clindamycin if pustules are present.13 Oral antibiotics such as doxycycline, minocycline, or erythromycin can be added for more severe cases of inflammation or infection. Procedural interventions include laser hair removal to prevent PFB and intralesional triamcinolone 10 to 40 mg/cc every 4 to 6 weeks, with the total volume depending on the size and number of lesions.
Alopecia
Alopecia is the sixth most common diagnosis seen in black patients visiting a dermatologist.14 The physician’s response to the patient’s chief concern of hair loss is key to building a relationship of confidence and trust. Trivializing the concern or dismissing it will undermine the physician-patient relationship. A survey by Gathers and Mahan15 revealed that 68% of patients thought that physicians did not understand their hair.
Hair loss negatively impacts quality of life, and a study of 50 black South African women with alopecia demonstrated a notable disease burden. Factors with the highest impact were those related to self-image, relationships, and interactions with others.16
It is not unusual for black women to have multiple types of alopecia identified in one biopsy specimen. Wohltmann and Sperling17 demonstrated 2 or more different types of alopecia in more than 10% of biopsy specimens of alopecia, including CCCA, androgenetic alopecia, end-stage traction alopecia, telogen effluvium, and tinea capitis. A complete history, physical examination, and appropriate procedures (eg, hair pull test, dermatoscopic examination and scalp biopsy) likely will yield an accurate diagnosis. Table 2 highlights important questions that should be asked about the patient’s history.

Physical examination of the scalp including dermatoscopic examination and a hair pull test as well as an evaluation of other hair-bearing areas may suggest a diagnosis that can be confirmed with a scalp biopsy.18,19 Selection of a biopsy site at the periphery of the alopecic area that includes hair and consultation with a dermatopathologist familiar with features of CCCA, traction, and traumatic alopecia are important for making an accurate diagnosis.
Tinea Capitis in Black Pediatric Patients
Tinea capitis, a fungal infection of the scalp and hair, is one of the most common issues in children with skin of color. Clinical presentation may include widely distributed scaling, annular scaly plaques, annular patches of alopecia studded with black dots (broken hairs), and/or annular inflammatory plaques. Although scalp hyperkeratosis often is a hallmark of pediatric tinea capitis, it is not diagnostic. The differential diagnosis of pediatric scalp hyperkeratosis/scaling includes tinea capitis, SD, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and sebopsoriasis.20,21 Clues to accurate diagnosis of tinea capitis may be found by examination of the adult who combs the child’s hair, as erythematous annular scaly plaques representing tinea corporis may be observed on the forearms or thighs. Although the thighs are a seemingly unusual location, the frequent practice of the child sitting on the floor between the legs of the adult during hairstyling provides a point of contact for the transmission of tinea from the child’s scalp to the thighs or forearms of the adult. Once tinea capitis is clinically suspected, the diagnosis is confirmed by a fungal culture. Adequate sampling is obtained by clipping hairs in an area of scaling for submission and vigorously rubbing the area of black dots or hyperkeratosis with a cotton swab.
Hubbard22 shed light on the decision to treat tinea capitis empirically or await the culture results. One hundred consecutive children (98 were black) presented with the constellation of scalp alopecia, scaling, pruritus, and occipital lymphadenopathy. Sixty-eight of those children had positive fungal cultures, and of them, 60 had both occipital lymphadenopathy and scaling and 55 had both occipital lymphadenopathy and alopecia.22 Thus, occipital lymphadenopathy in conjunction with alopecia and/or scaling is predictive of tinea capitis in this population and suggests that the initiation of treatment prior to confirmative culture results is appropriate.
The mainstay of treatment for tinea capitis is griseofulvin, but it is often underdosed and not continued for an adequate period of time to ensure clearance of the infection. Griseofulvin microsize (125 mg/5 mL) at the dosage of 20 to 25 mg/kg once daily for 8 to 12 weeks is recommended instead of a lower-dosed 4- to 6-week course.23,24
Options for treating a child with residual disease include increasing and/or extending the griseofulvin dosage, encouraging ingestion of fatty foods to enhance absorption, dividing the dosage of griseofulvin from once daily to twice daily, changing therapy to oral terbinafine due to resistance to griseofulvin, examining siblings as a source of reinfection, and reviewing the positive fungal culture report to distinguish Trichophyton tonsurans versus Microsporum canis as the causative agent and adjust treatment accordingly. Although griseofulvin is the first-line treatment for M canis, terbinafine, which is approved for children 4 years and older for tineacapitis, is most efficacious for T tonsurans.25 Treatment with terbinafine is weight based and should extend for 2 to 4 weeksfor T tonsurans and 8 to 12 weeks for M canis.
Antifungal shampoos may help reduce household spread of tinea and decrease transmissible fungal spores, but they may cause hair dryness and breakage.26,27 Antifungal shampoos can be applied directly onto the scalp for a 5- to 10-minute contact time and rinsed, and then the hair should be shampooed with a moisturizing shampoo followed by a moisturizing conditioner. Hair conditioners may decrease household spread of tinea capitis and should be used by the patient and other members of the household.28 Infection control may be enhanced by advising parents to dispose of hair pomades and washing hair accessories, combs, and brushes in hot soapy water, preferably in the dishwasher.
Hair Growth
The inability of the hair of black children to grow long is a common concern for parents of toddlers and preschool-aged children. Although the hair does grow, it grows more slowly than hair in white children (0.259 vs 0.330 mm per day), and it is likely to break faster than it is growing in black versus white children (146.6 vs 13.13 total broken hairs).8 Reassurance that the hair is indeed growing and that the length will increase as the child matures is important. Avoidance of hairstyles that promote traction and use of hair extensions, as well as use of moisturizing shampoos and conditioners, may minimize breakage and support the growth of healthy hair.
Conclusion
Hair- and scalp-related disease in black adults and children is commonly encountered in dermatology practice. It is important to understand the intrinsic characteristics of facial and scalp hair as well as hair care practices in this patient population that differ from those of white and Asian populations, such as frequency of shampooing, products, and styling. Familiarity with these differences may aid in effective diagnosis, treatment, and hair care recommendations in patients with these conditions.
One of the most common concerns among black patients is hair- and scalp-related disease. As increasing numbers of black patients opt to see dermatologists, it is imperative that all dermatologists be adequately trained to address the concerns of this patient population. When patients ask for help with common skin diseases of the hair and scalp, there are details that must be included in diagnosis, treatment, and hair care recommendations to reach goals for excellence in patient care. Herein, we provide must-know information to effectively approach this patient population.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
A study utilizing data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey from 1993 to 2009 revealed seborrheic dermatitis (SD) as the second most common diagnosis for black patients who visit a dermatologist.1 Prevalence data from a population of 1408 white, black, and Chinese patients from the United States and China revealed scalp flaking in 81% to 95% of black patients, 66% to 82% in white patients, and 30% to 42% in Chinese patients.2 Seborrheic dermatitis has a notable prevalence in black women and often is considered normal by patients. It can be exacerbated by infrequent shampooing (ranging from once per month or longer in between shampoos) and the inappropriate use of hair oils and pomades; it also has been associated with hair breakage, lichen simplex chronicus, and folliculitis. Seborrheic dermatitis must be distinguished from other disorders including sarcoidosis, psoriasis, discoid lupus erythematosus, tinea capitis, and lichen simplex chronicus.
Although there is a paucity of literature on the treatment of SD in black patients, components of treatment are similar to those recommended for other populations. Black women are advised to carefully utilize antidandruff shampoos containing zinc pyrithione, selenium sulfide, or tar to avoid hair shaft damage and dryness. Ketoconazole shampoo rarely is recommended and may be more appropriately used in men and boys, as hair fragility is less of a concern for them. The shampoo should be applied directly to the scalp rather than the hair shafts to minimize dryness, with no particular elongated contact time needed for these medicated shampoos to be effective. Because conditioners can wash off the active ingredients in therapeutic shampoos, antidandruff conditioners are recommended. Potent or ultrapotent topical corticosteroids applied to the scalp 3 to 4 times weekly initially will control the symptoms of itching as well as scaling, and mid-potency topical corticosteroid oil may be used at weekly intervals.
Hairline and facial involvement of SD often co-occurs, and low-potency topical steroids may be applied to the affected areas twice daily for 3 to 4 weeks, which may be repeated for flares. Topical calcineurin inhibitors or antifungal creams such as ketoconazole or econazole may then provide effective control. Encouraging patients to increase shampooing to once weekly or every 2 weeks and discontinue use of scalp pomades and oils also is recommended. Patients must know that an itchy scaly scalp represents a treatable disorder.
Acquired Trichorrhexis Nodosa
Hair fragility and breakage is common and multifactorial in black patients. Hair shaft breakage can occur on the vertex scalp in central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA), with random localized breakage due to scratching in SD. Heat, hair colorants, and chemical relaxers may result in diffuse damage and breakage.3 Sodium-, potassium-, and guanine hydroxide–containing chemical relaxers change the physical properties of the hair by rearranging disulfide bonds. They remove the monomolecular layer of fatty acids covalently bound to the cuticle that help prevent penetration of water into the hair shaft. Additionally, chemical relaxers weaken the hair shaft and decrease tensile strength.
Unlike hair relaxers, colorants are less likely to lead to catastrophic hair breakage after a single use and require frequent use, which leads to cumulative damage. Thermal straightening is another cause of hair-shaft weakening in black patients.4,5 Flat irons and curling irons can cause substantially more damage than blow-dryers due to the amount of heat generated. Flat irons may reach a high temperature of 230ºC (450ºF) as compared to 100°C (210°F) for a blow-dryer. Even the simple act of combing the hair can cause hair breakage, as demonstrated in African volunteers whose hair remained short in contrast to white and Asian volunteers, despite the fact that they had not cut their hair for 1 or more years.6,7 These volunteers had many hair strand knots that led to breakage during combing and hair grooming.6
There is no known prevalence data for acquired trichorrhexis nodosa, though a study of 30 white and black women demonstrated that broken hairs were significantly increased in black women (P=.0001).8 Another study by Hall et al9 of 103 black women showed that 55% of the women reported breakage of hair shafts with normal styling. Khumalo et al6 investigated hair shaft fragility and reported no trichothiodystrophy; the authors concluded that the cause of the hair fragility likely was physical trauma or an undiscovered structural abnormality. Franbourg et al10 examined the structure of hair fibers in white, Asian, and black patients and found no differences, but microfractures were only present in black patients and were determined to be the cause of hair breakage. These studies underscore the need for specific questioning of the patient on hair care including combing, washing, drying, and using products and chemicals.
The approach to the treatment of hair breakage involves correcting underlying abnormalities (eg, iron deficiency, hypothyroidism, nutritional deficiencies). Patients should “give their hair a rest” by discontinuing use of heat, colorants, and chemical relaxers. For patients who are unable to comply, advising them to stop these processes for 6 to 12 months will allow for repair of the hair shaft. To minimize damage from colorants, recommend semipermanent, demipermanent, or temporary dyes. Patients should be counseled to stop bleaching their hair or using permanent colorants. The use of heat protectant products on the hair before styling as well as layering moisturizing regimens starting with a moisturizing shampoo followed by a leave-in, dimethicone-containing conditioner marketed for dry damaged hair is suggested. Dimethicone thinly coats the hair shaft to restore hydrophobicity, smoothes cuticular scales, decreases frizz, and protects the hair from damage. Use of a 2-in-1 shampoo and conditioner containing anionic surfactants and wide-toothed, smooth (no jagged edges in the grooves) combs along with rare brushing are recommended. The hair may be worn in its natural state, but straightening with heat should be avoided. Air drying the hair can minimize breakage, but if thermal styling is necessary, patients should turn the temperature setting of the flat or curling iron down. Protective hair care practices may include placing a loosely sewn-in hair weave that will allow for good hair care, wearing loose braids, or using a wig. Serial trimming of the hair every 6 to 8 weeks is recommended. Improvement may take time, and patients should be advised of this timeline to prevent frustration.
Acne Keloidalis Nuchae
Acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) is characterized by papules and pustules located on the occipital scalp and/or the nape of the neck, which may result in keloidal papules and plaques. The etiology is unknown, but ingrown hairs, genetics, trauma, infection, inflammation, and androgen hormones have been proposed to play a role.11 Although AKN may occur in black women, it is primarily a disorder in black men. The diagnosis is made based primarily on clinical findings, and a history of short haircuts may support the diagnosis. Treatment is tailored to the severity of the disease (Table 1). Avoidance of short haircuts and irritation from shirt collars may be helpful. Patients should be advised that the condition is controllable but not curable.

Pseudofolliculitis Barbae
Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB) is characterized by papules and pustules in the beard region that may result in postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, keloidal scar formation, and/or linear scarring. The coarse curled hairs characteristic of black men penetrate the follicle before exiting the skin and penetrate the skin after exiting the follicle, resulting in inflammation. Shaving methods and genetics also may contribute to the development of PFB. As with AKN, diagnosis is made clinically and does not require a skin biopsy. Important components of the patient’s history that should be obtained are hair removal practices and the use of over-the-counter products (eg, shave [pre and post] moisturizers, exfoliants, shaving creams or gels, keratin-softening agents containing α- or β-hydroxy acids). A bacterial culture may be appropriate if a notable pustular component is present. The patient should be advised to discontinue shaving if possible, which may require a physician’s letter explaining the necessity to the patient’s employer. Pseudofolliculitis barbae often can be prevented or lessened with the right hair removal strategy. Because there is not one optimal hair removal strategy that suits every patient, encourage the patient to experiment with different hair removal techniques, from depilatories to electric shavers, foil-guard razors, and multiple-blade razors. Preshave hydration and postshave moisturiza-tion also should be encouraged.12 Benzoyl peroxide–containing shave gels and cleansers, as well as moisturizers containing glycolic, salicylic, and phytic acids, may minimize ingrown hairs, papules, and inflammation.
Other useful topical agents include eflornithine hydrochloride to decrease hair growth, retinoids to soften hair fibers, mild topical steroids to reduce inflammation, and/or topical erythromycin or clindamycin if pustules are present.13 Oral antibiotics such as doxycycline, minocycline, or erythromycin can be added for more severe cases of inflammation or infection. Procedural interventions include laser hair removal to prevent PFB and intralesional triamcinolone 10 to 40 mg/cc every 4 to 6 weeks, with the total volume depending on the size and number of lesions.
Alopecia
Alopecia is the sixth most common diagnosis seen in black patients visiting a dermatologist.14 The physician’s response to the patient’s chief concern of hair loss is key to building a relationship of confidence and trust. Trivializing the concern or dismissing it will undermine the physician-patient relationship. A survey by Gathers and Mahan15 revealed that 68% of patients thought that physicians did not understand their hair.
Hair loss negatively impacts quality of life, and a study of 50 black South African women with alopecia demonstrated a notable disease burden. Factors with the highest impact were those related to self-image, relationships, and interactions with others.16
It is not unusual for black women to have multiple types of alopecia identified in one biopsy specimen. Wohltmann and Sperling17 demonstrated 2 or more different types of alopecia in more than 10% of biopsy specimens of alopecia, including CCCA, androgenetic alopecia, end-stage traction alopecia, telogen effluvium, and tinea capitis. A complete history, physical examination, and appropriate procedures (eg, hair pull test, dermatoscopic examination and scalp biopsy) likely will yield an accurate diagnosis. Table 2 highlights important questions that should be asked about the patient’s history.

Physical examination of the scalp including dermatoscopic examination and a hair pull test as well as an evaluation of other hair-bearing areas may suggest a diagnosis that can be confirmed with a scalp biopsy.18,19 Selection of a biopsy site at the periphery of the alopecic area that includes hair and consultation with a dermatopathologist familiar with features of CCCA, traction, and traumatic alopecia are important for making an accurate diagnosis.
Tinea Capitis in Black Pediatric Patients
Tinea capitis, a fungal infection of the scalp and hair, is one of the most common issues in children with skin of color. Clinical presentation may include widely distributed scaling, annular scaly plaques, annular patches of alopecia studded with black dots (broken hairs), and/or annular inflammatory plaques. Although scalp hyperkeratosis often is a hallmark of pediatric tinea capitis, it is not diagnostic. The differential diagnosis of pediatric scalp hyperkeratosis/scaling includes tinea capitis, SD, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and sebopsoriasis.20,21 Clues to accurate diagnosis of tinea capitis may be found by examination of the adult who combs the child’s hair, as erythematous annular scaly plaques representing tinea corporis may be observed on the forearms or thighs. Although the thighs are a seemingly unusual location, the frequent practice of the child sitting on the floor between the legs of the adult during hairstyling provides a point of contact for the transmission of tinea from the child’s scalp to the thighs or forearms of the adult. Once tinea capitis is clinically suspected, the diagnosis is confirmed by a fungal culture. Adequate sampling is obtained by clipping hairs in an area of scaling for submission and vigorously rubbing the area of black dots or hyperkeratosis with a cotton swab.
Hubbard22 shed light on the decision to treat tinea capitis empirically or await the culture results. One hundred consecutive children (98 were black) presented with the constellation of scalp alopecia, scaling, pruritus, and occipital lymphadenopathy. Sixty-eight of those children had positive fungal cultures, and of them, 60 had both occipital lymphadenopathy and scaling and 55 had both occipital lymphadenopathy and alopecia.22 Thus, occipital lymphadenopathy in conjunction with alopecia and/or scaling is predictive of tinea capitis in this population and suggests that the initiation of treatment prior to confirmative culture results is appropriate.
The mainstay of treatment for tinea capitis is griseofulvin, but it is often underdosed and not continued for an adequate period of time to ensure clearance of the infection. Griseofulvin microsize (125 mg/5 mL) at the dosage of 20 to 25 mg/kg once daily for 8 to 12 weeks is recommended instead of a lower-dosed 4- to 6-week course.23,24
Options for treating a child with residual disease include increasing and/or extending the griseofulvin dosage, encouraging ingestion of fatty foods to enhance absorption, dividing the dosage of griseofulvin from once daily to twice daily, changing therapy to oral terbinafine due to resistance to griseofulvin, examining siblings as a source of reinfection, and reviewing the positive fungal culture report to distinguish Trichophyton tonsurans versus Microsporum canis as the causative agent and adjust treatment accordingly. Although griseofulvin is the first-line treatment for M canis, terbinafine, which is approved for children 4 years and older for tineacapitis, is most efficacious for T tonsurans.25 Treatment with terbinafine is weight based and should extend for 2 to 4 weeksfor T tonsurans and 8 to 12 weeks for M canis.
Antifungal shampoos may help reduce household spread of tinea and decrease transmissible fungal spores, but they may cause hair dryness and breakage.26,27 Antifungal shampoos can be applied directly onto the scalp for a 5- to 10-minute contact time and rinsed, and then the hair should be shampooed with a moisturizing shampoo followed by a moisturizing conditioner. Hair conditioners may decrease household spread of tinea capitis and should be used by the patient and other members of the household.28 Infection control may be enhanced by advising parents to dispose of hair pomades and washing hair accessories, combs, and brushes in hot soapy water, preferably in the dishwasher.
Hair Growth
The inability of the hair of black children to grow long is a common concern for parents of toddlers and preschool-aged children. Although the hair does grow, it grows more slowly than hair in white children (0.259 vs 0.330 mm per day), and it is likely to break faster than it is growing in black versus white children (146.6 vs 13.13 total broken hairs).8 Reassurance that the hair is indeed growing and that the length will increase as the child matures is important. Avoidance of hairstyles that promote traction and use of hair extensions, as well as use of moisturizing shampoos and conditioners, may minimize breakage and support the growth of healthy hair.
Conclusion
Hair- and scalp-related disease in black adults and children is commonly encountered in dermatology practice. It is important to understand the intrinsic characteristics of facial and scalp hair as well as hair care practices in this patient population that differ from those of white and Asian populations, such as frequency of shampooing, products, and styling. Familiarity with these differences may aid in effective diagnosis, treatment, and hair care recommendations in patients with these conditions.
- Davis SA, Naarahari S, Feldman SR, et al. Top dermatologic conditions in patients of color: an analysis of nationally representative data. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:466-473.
- Hickman JG, Cardin C, Dawson TL, et al. Dandruff, part I: scalp disease prevalence in Caucasians, African Americans, and Chinese and the effects of shampoo frequency on scalp health. Poster presented at: 60th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology; February 22-27, 2002; New Orleans, LA.
- Swee W, Klontz KC, Lambert LA. A nationwide outbreak of alopecia associated with the use of a hair-relaxing formulation. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:1104-1108.
- Nicholson AG, Harland CC, Bull RH, et al. Chemically induced cosmetic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1993;128:537-541.
- Detwiler SP, Carson JL, Woosley JT, et al. Bubble hair. case caused by an overheating hair dryer and reproducibility in normal hair with heat. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;30:54-60.
- Khumalo NP, Dawber RP, Ferguson DJ. Apparent fragility of African hair is unrelated to the cystine-rich protein distribution: a cytochemical electron microscopic study. Exp Dermatol. 2005;14:311-314.
- Robbins C. Hair breakage during combing. I. pathways of breakage. J Cosmet Sci. 2006;57:233-243.
- Lewallen R, Francis S, Fisher B, et al. Hair care practices and structural evaluation of scalp and hair shaft parameter in African American and Caucasian women. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2015;14:216-223.
- Hall RR, Francis S, Whitt-Glover M, et al. Hair care practices as a barrier to physical activity in African American women. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:310-314.
- Franbourg A, Hallegot P, Baltenneck F, et al. Current research on ethnic hair. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48(6 suppl):S115-S119.
- Ogunbiyi A. Acne keloidalis nuchae: prevalence, impact, and management challenges. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:483-489.
- Gray J, McMichael AJ. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: understanding the condition and the role of facial grooming. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38(suppl 1):24-27.
- Kundu RV, Patterson S. Dermatologic conditions in skin of color: part II. disorders occurring predominately in skin of color. Am Fam Physician. 2013;87:859-865.
- Davis SA, Naarahari S, Feldman SR, et al. Top dermatologic conditions in patients of color: an analysis of nationally representative data. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:466-473.
- Gathers RC, Mahan MG. African American women, hair care and health barriers. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:26-29.
- Dlova NC, Fabbrocini G, Lauro C, et al. Quality of life in South African black women with alopecia: a pilot study. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:875-881.
- Wohltmann WE, Sperling L. Histopathologic diagnosis of multifactorial alopecia. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:483-491.
- McDonald KA, Shelley AJ, Colantonio S, et al. Hair pull test: evidence-based update and revision of guidelines. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:472-477.
- Miteva M, Tosti A. Dermatoscopic features of central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:443-444.
- Coley MK, Bhanusali DG, Silverberg JI, et al. Scalp hyperkeratosis and alopecia in children of color. J Drugs Dermatol. 2011;10:511-516.
- Silverberg NB. Scalp hyperkeratosis in children with skin of color: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations. Cutis. 2015;95:199-204, 207.
- Hubbard TW. The predictive value of symptoms in diagnosing childhood tinea capitis. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1999;153:1150-1153.
- Kakourou T, Uksal U; European Society for Pediatric Dermatology. Guidelines for the management of tinea capitis in children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010;27:226-228.
- Sethi A, Antanya R. Systemic antifungal therapy for cutaneous infections in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2006;25:643-644.
- Gupta AK. Drummond-Main C. Meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials comparing particular doses of griseofulvin and terbinafine for the treatment of tinea capitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:1-6.
- Greer DL. Successful treatment of tinea capitis with 2% ketoconazole shampoo. Int J Dermatol 2000;39:302-304.
- Sharma V, Silverberg NB, Howard R, et al. Do hair care practices affect the acquisition of tinea capitis? a case-control study. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2001;155:818-821.
- Greer DL. Successful treatment of tinea capitis with 2% ketoconazole shampoo. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39:302-304.
- Davis SA, Naarahari S, Feldman SR, et al. Top dermatologic conditions in patients of color: an analysis of nationally representative data. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:466-473.
- Hickman JG, Cardin C, Dawson TL, et al. Dandruff, part I: scalp disease prevalence in Caucasians, African Americans, and Chinese and the effects of shampoo frequency on scalp health. Poster presented at: 60th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology; February 22-27, 2002; New Orleans, LA.
- Swee W, Klontz KC, Lambert LA. A nationwide outbreak of alopecia associated with the use of a hair-relaxing formulation. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:1104-1108.
- Nicholson AG, Harland CC, Bull RH, et al. Chemically induced cosmetic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1993;128:537-541.
- Detwiler SP, Carson JL, Woosley JT, et al. Bubble hair. case caused by an overheating hair dryer and reproducibility in normal hair with heat. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;30:54-60.
- Khumalo NP, Dawber RP, Ferguson DJ. Apparent fragility of African hair is unrelated to the cystine-rich protein distribution: a cytochemical electron microscopic study. Exp Dermatol. 2005;14:311-314.
- Robbins C. Hair breakage during combing. I. pathways of breakage. J Cosmet Sci. 2006;57:233-243.
- Lewallen R, Francis S, Fisher B, et al. Hair care practices and structural evaluation of scalp and hair shaft parameter in African American and Caucasian women. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2015;14:216-223.
- Hall RR, Francis S, Whitt-Glover M, et al. Hair care practices as a barrier to physical activity in African American women. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:310-314.
- Franbourg A, Hallegot P, Baltenneck F, et al. Current research on ethnic hair. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48(6 suppl):S115-S119.
- Ogunbiyi A. Acne keloidalis nuchae: prevalence, impact, and management challenges. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:483-489.
- Gray J, McMichael AJ. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: understanding the condition and the role of facial grooming. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38(suppl 1):24-27.
- Kundu RV, Patterson S. Dermatologic conditions in skin of color: part II. disorders occurring predominately in skin of color. Am Fam Physician. 2013;87:859-865.
- Davis SA, Naarahari S, Feldman SR, et al. Top dermatologic conditions in patients of color: an analysis of nationally representative data. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:466-473.
- Gathers RC, Mahan MG. African American women, hair care and health barriers. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:26-29.
- Dlova NC, Fabbrocini G, Lauro C, et al. Quality of life in South African black women with alopecia: a pilot study. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:875-881.
- Wohltmann WE, Sperling L. Histopathologic diagnosis of multifactorial alopecia. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:483-491.
- McDonald KA, Shelley AJ, Colantonio S, et al. Hair pull test: evidence-based update and revision of guidelines. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:472-477.
- Miteva M, Tosti A. Dermatoscopic features of central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:443-444.
- Coley MK, Bhanusali DG, Silverberg JI, et al. Scalp hyperkeratosis and alopecia in children of color. J Drugs Dermatol. 2011;10:511-516.
- Silverberg NB. Scalp hyperkeratosis in children with skin of color: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations. Cutis. 2015;95:199-204, 207.
- Hubbard TW. The predictive value of symptoms in diagnosing childhood tinea capitis. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1999;153:1150-1153.
- Kakourou T, Uksal U; European Society for Pediatric Dermatology. Guidelines for the management of tinea capitis in children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010;27:226-228.
- Sethi A, Antanya R. Systemic antifungal therapy for cutaneous infections in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2006;25:643-644.
- Gupta AK. Drummond-Main C. Meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials comparing particular doses of griseofulvin and terbinafine for the treatment of tinea capitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:1-6.
- Greer DL. Successful treatment of tinea capitis with 2% ketoconazole shampoo. Int J Dermatol 2000;39:302-304.
- Sharma V, Silverberg NB, Howard R, et al. Do hair care practices affect the acquisition of tinea capitis? a case-control study. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2001;155:818-821.
- Greer DL. Successful treatment of tinea capitis with 2% ketoconazole shampoo. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39:302-304.
Practice Points
- Instruct patients with acquired trichorrhexis nodosa to discontinue use of heat, colorants, and chemical relaxers on their hair.
- Create a contract with your seborrheic dermatitis patients to have them shampoo at least weekly or every 2 weeks.
- For children with treated tinea capitis that has not completely resolved, increase or extend the griseofulvin dosage, encourage ingestion of fatty foods to enhance absorption, and divide dosage of griseofulvin from once to twice daily.
- Selection of a biopsy site at the periphery of an alopecic area that includes hair and hair follicles and evaluation by a dermatopathologist familiar with the features of central centrifugal cicatricial, traction, and traumatic alopecias will ensure an accurate diagnosis of alopecia.