User login
at a large academic medical center, a cross-sectional observational study has determined.
Prescription or illegal opioid use can have profound implications for surgical outcomes and continued postoperative medication abuse. “Preoperative opioid use was associated with a greater burden of comorbid disease and multiple risk factors for poor recovery. ... Opioid-tolerant patients are at risk for opioid-associated adverse events and are less likely to discontinue opioid-based therapy after their surgery,” wrote Paul E. Hilliard, MD, and a team of researchers at the University of Michigan Health System. Although the question of preoperative opioid use has been examined and the Michigan findings are consistent with earlier estimates of prevalence (Ann Surg. 2017;265[4]:695-701), this study sought a more detailed profile of both the characteristics of these patients and the types of procedures correlated with opioid use.
Patient data were derived primarily from two ongoing institutional registries, the Michigan Genomics Initiative and the Analgesic Outcomes Study. Each of these projects involved recruiting nonemergency surgery patients to participate and self-report on pain and affect issues. Opioid use data were extracted from the preop anesthesia history and from physical examination. A total of 34,186 patients were recruited for this study; 54.2% were women, 89.1% were white, and the mean age was 53.1 years. Overall, 23.1% of these patients were taking opioids of various kinds, mostly by prescription along with nonprescription opioids and illegal drugs of other kinds.
The most common opioids found in this patient sample were hydrocodone bitartrate (59.4%), tramadol hydrochloride (21.2%) and oxycodone hydrochloride (18.5%), although the duration or frequency of use was not determined.
“In our experience, in surveys like this patients are pretty honest. [The data do not] track to their medical record, but was done privately for research. That having been said, I am sure there is significant underreporting,” study coauthor Michael J. Englesbe, MD, FACS, said in an interview. In addition to some nondisclosure by study participants, the exclusion of patients admitted to surgery from the ED could mean that 23.1% is a conservative estimate, he noted.
Patient characteristics included in the study (tobacco use, alcohol use, sleep apnea, pain, life satisfaction, depression, anxiety) were self-reported and validated using tools such as the Brief Pain Inventory, the Fibromyalgia Survey, and the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. Procedural data were derived from patient records and ICD-10 data and rated via the ASA score and Charlson Comorbidity Index.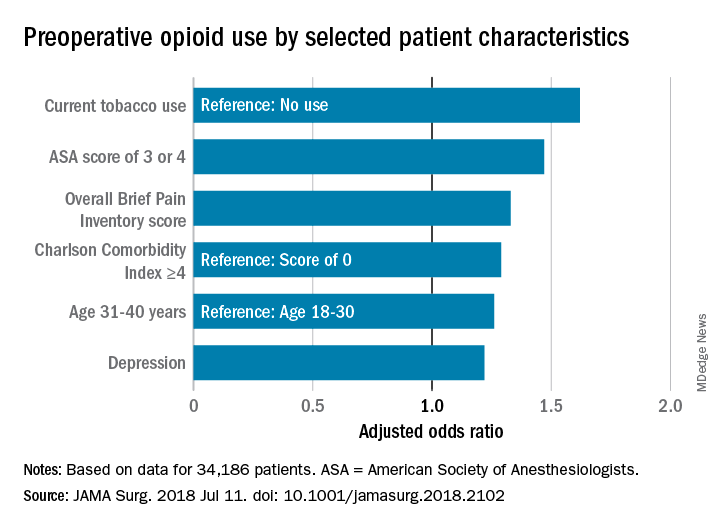
A multivariate analysis of patient characteristics found that age between 31 and 40, tobacco use, heavy alcohol use, pain score, depression, comorbidities reflected in a higher ASA score, and Charlson Comorbidity Score were all significant risk factors for presurgical opiate use.
Patients who were scheduled for surgical procedures involving lower extremities (adjusted odds ratio 3.61, 95% confidence interval, 2.81-4.64) were at the highest risk for opioid use, followed by pelvis surgery, excluding hip (aOR, 3.09, 95% CI, 1.88-5.08), upper arm or elbow (aOR, 3.07, 95% CI, 2.12-4.45), and spine surgery (aOR, 2.68, 95% CI, 2.15-3.32).
The study also broke out the data by presurgery opioid usage and surgery service. Of patients having spine neurosurgery, 55.1% were already taking opioids, and among those having orthopedic spine surgery, 65.1% were taking opioids. General surgery patients were not among those mostly likely to be using opioids (gastrointestinal surgery, 19.3% and endocrine surgery 14.3%). “Certain surgical services may be more likely to encounter patients with high comorbidities for opioid use, and more targeted opioid education strategies aimed at those services may help to mitigate risk in the postoperative period,” the authors wrote.
“All surgeons should take a preop pain history. They should ask about current pain and previous pain experiences. They should also ask about a history of substance use disorder. This should lead into a discussion of the pain expectations from the procedure. Patients should expect to be in pain, that is normal. Pain-free surgery is rare. If a patient has a complex pain history or takes chronic opioids, the surgeon should consider referring them to anesthesia for formal preop pain management planning and potentially weaning of opioid dose prior to elective surgery,” noted Dr. Englesbe, the Cyrenus G. Darling Sr., MD and Cyrenus G Darling Jr., MD Professor of Surgery, and faculty at the Center for Healthcare Outcomes & Policy, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
Surgeons are likely to see patients with a past history of opioid dependence or who are recovering from substance abuse. “Every effort should be made to avoid opioids in these patients. We have developed a Pain Optimization Pathway which facilitates no postoperative opioids for these and other patients. These patients are at high risk to relapse and surgeons must know who these patients are so they can provide optimal care,” Dr. Englesbe added.The limitations of this study as reported by the authors include the single-center design, the nondiverse racial makeup of the sample, and the difficulty of ascertaining the dosing and duration of opioid use, both prescription and illegal.
The investigators reported no disclosures relevant to this study. This study was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health, the American College of Surgeons, and other noncommercial sources.
SOURCE: Hilliard PE et al. JAMA Surg. 2018 Jul 11. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2018.2102.
at a large academic medical center, a cross-sectional observational study has determined.
Prescription or illegal opioid use can have profound implications for surgical outcomes and continued postoperative medication abuse. “Preoperative opioid use was associated with a greater burden of comorbid disease and multiple risk factors for poor recovery. ... Opioid-tolerant patients are at risk for opioid-associated adverse events and are less likely to discontinue opioid-based therapy after their surgery,” wrote Paul E. Hilliard, MD, and a team of researchers at the University of Michigan Health System. Although the question of preoperative opioid use has been examined and the Michigan findings are consistent with earlier estimates of prevalence (Ann Surg. 2017;265[4]:695-701), this study sought a more detailed profile of both the characteristics of these patients and the types of procedures correlated with opioid use.
Patient data were derived primarily from two ongoing institutional registries, the Michigan Genomics Initiative and the Analgesic Outcomes Study. Each of these projects involved recruiting nonemergency surgery patients to participate and self-report on pain and affect issues. Opioid use data were extracted from the preop anesthesia history and from physical examination. A total of 34,186 patients were recruited for this study; 54.2% were women, 89.1% were white, and the mean age was 53.1 years. Overall, 23.1% of these patients were taking opioids of various kinds, mostly by prescription along with nonprescription opioids and illegal drugs of other kinds.
The most common opioids found in this patient sample were hydrocodone bitartrate (59.4%), tramadol hydrochloride (21.2%) and oxycodone hydrochloride (18.5%), although the duration or frequency of use was not determined.
“In our experience, in surveys like this patients are pretty honest. [The data do not] track to their medical record, but was done privately for research. That having been said, I am sure there is significant underreporting,” study coauthor Michael J. Englesbe, MD, FACS, said in an interview. In addition to some nondisclosure by study participants, the exclusion of patients admitted to surgery from the ED could mean that 23.1% is a conservative estimate, he noted.
Patient characteristics included in the study (tobacco use, alcohol use, sleep apnea, pain, life satisfaction, depression, anxiety) were self-reported and validated using tools such as the Brief Pain Inventory, the Fibromyalgia Survey, and the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. Procedural data were derived from patient records and ICD-10 data and rated via the ASA score and Charlson Comorbidity Index.
A multivariate analysis of patient characteristics found that age between 31 and 40, tobacco use, heavy alcohol use, pain score, depression, comorbidities reflected in a higher ASA score, and Charlson Comorbidity Score were all significant risk factors for presurgical opiate use.
Patients who were scheduled for surgical procedures involving lower extremities (adjusted odds ratio 3.61, 95% confidence interval, 2.81-4.64) were at the highest risk for opioid use, followed by pelvis surgery, excluding hip (aOR, 3.09, 95% CI, 1.88-5.08), upper arm or elbow (aOR, 3.07, 95% CI, 2.12-4.45), and spine surgery (aOR, 2.68, 95% CI, 2.15-3.32).
The study also broke out the data by presurgery opioid usage and surgery service. Of patients having spine neurosurgery, 55.1% were already taking opioids, and among those having orthopedic spine surgery, 65.1% were taking opioids. General surgery patients were not among those mostly likely to be using opioids (gastrointestinal surgery, 19.3% and endocrine surgery 14.3%). “Certain surgical services may be more likely to encounter patients with high comorbidities for opioid use, and more targeted opioid education strategies aimed at those services may help to mitigate risk in the postoperative period,” the authors wrote.
“All surgeons should take a preop pain history. They should ask about current pain and previous pain experiences. They should also ask about a history of substance use disorder. This should lead into a discussion of the pain expectations from the procedure. Patients should expect to be in pain, that is normal. Pain-free surgery is rare. If a patient has a complex pain history or takes chronic opioids, the surgeon should consider referring them to anesthesia for formal preop pain management planning and potentially weaning of opioid dose prior to elective surgery,” noted Dr. Englesbe, the Cyrenus G. Darling Sr., MD and Cyrenus G Darling Jr., MD Professor of Surgery, and faculty at the Center for Healthcare Outcomes & Policy, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
Surgeons are likely to see patients with a past history of opioid dependence or who are recovering from substance abuse. “Every effort should be made to avoid opioids in these patients. We have developed a Pain Optimization Pathway which facilitates no postoperative opioids for these and other patients. These patients are at high risk to relapse and surgeons must know who these patients are so they can provide optimal care,” Dr. Englesbe added.The limitations of this study as reported by the authors include the single-center design, the nondiverse racial makeup of the sample, and the difficulty of ascertaining the dosing and duration of opioid use, both prescription and illegal.
The investigators reported no disclosures relevant to this study. This study was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health, the American College of Surgeons, and other noncommercial sources.
SOURCE: Hilliard PE et al. JAMA Surg. 2018 Jul 11. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2018.2102.
at a large academic medical center, a cross-sectional observational study has determined.
Prescription or illegal opioid use can have profound implications for surgical outcomes and continued postoperative medication abuse. “Preoperative opioid use was associated with a greater burden of comorbid disease and multiple risk factors for poor recovery. ... Opioid-tolerant patients are at risk for opioid-associated adverse events and are less likely to discontinue opioid-based therapy after their surgery,” wrote Paul E. Hilliard, MD, and a team of researchers at the University of Michigan Health System. Although the question of preoperative opioid use has been examined and the Michigan findings are consistent with earlier estimates of prevalence (Ann Surg. 2017;265[4]:695-701), this study sought a more detailed profile of both the characteristics of these patients and the types of procedures correlated with opioid use.
Patient data were derived primarily from two ongoing institutional registries, the Michigan Genomics Initiative and the Analgesic Outcomes Study. Each of these projects involved recruiting nonemergency surgery patients to participate and self-report on pain and affect issues. Opioid use data were extracted from the preop anesthesia history and from physical examination. A total of 34,186 patients were recruited for this study; 54.2% were women, 89.1% were white, and the mean age was 53.1 years. Overall, 23.1% of these patients were taking opioids of various kinds, mostly by prescription along with nonprescription opioids and illegal drugs of other kinds.
The most common opioids found in this patient sample were hydrocodone bitartrate (59.4%), tramadol hydrochloride (21.2%) and oxycodone hydrochloride (18.5%), although the duration or frequency of use was not determined.
“In our experience, in surveys like this patients are pretty honest. [The data do not] track to their medical record, but was done privately for research. That having been said, I am sure there is significant underreporting,” study coauthor Michael J. Englesbe, MD, FACS, said in an interview. In addition to some nondisclosure by study participants, the exclusion of patients admitted to surgery from the ED could mean that 23.1% is a conservative estimate, he noted.
Patient characteristics included in the study (tobacco use, alcohol use, sleep apnea, pain, life satisfaction, depression, anxiety) were self-reported and validated using tools such as the Brief Pain Inventory, the Fibromyalgia Survey, and the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. Procedural data were derived from patient records and ICD-10 data and rated via the ASA score and Charlson Comorbidity Index.
A multivariate analysis of patient characteristics found that age between 31 and 40, tobacco use, heavy alcohol use, pain score, depression, comorbidities reflected in a higher ASA score, and Charlson Comorbidity Score were all significant risk factors for presurgical opiate use.
Patients who were scheduled for surgical procedures involving lower extremities (adjusted odds ratio 3.61, 95% confidence interval, 2.81-4.64) were at the highest risk for opioid use, followed by pelvis surgery, excluding hip (aOR, 3.09, 95% CI, 1.88-5.08), upper arm or elbow (aOR, 3.07, 95% CI, 2.12-4.45), and spine surgery (aOR, 2.68, 95% CI, 2.15-3.32).
The study also broke out the data by presurgery opioid usage and surgery service. Of patients having spine neurosurgery, 55.1% were already taking opioids, and among those having orthopedic spine surgery, 65.1% were taking opioids. General surgery patients were not among those mostly likely to be using opioids (gastrointestinal surgery, 19.3% and endocrine surgery 14.3%). “Certain surgical services may be more likely to encounter patients with high comorbidities for opioid use, and more targeted opioid education strategies aimed at those services may help to mitigate risk in the postoperative period,” the authors wrote.
“All surgeons should take a preop pain history. They should ask about current pain and previous pain experiences. They should also ask about a history of substance use disorder. This should lead into a discussion of the pain expectations from the procedure. Patients should expect to be in pain, that is normal. Pain-free surgery is rare. If a patient has a complex pain history or takes chronic opioids, the surgeon should consider referring them to anesthesia for formal preop pain management planning and potentially weaning of opioid dose prior to elective surgery,” noted Dr. Englesbe, the Cyrenus G. Darling Sr., MD and Cyrenus G Darling Jr., MD Professor of Surgery, and faculty at the Center for Healthcare Outcomes & Policy, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
Surgeons are likely to see patients with a past history of opioid dependence or who are recovering from substance abuse. “Every effort should be made to avoid opioids in these patients. We have developed a Pain Optimization Pathway which facilitates no postoperative opioids for these and other patients. These patients are at high risk to relapse and surgeons must know who these patients are so they can provide optimal care,” Dr. Englesbe added.The limitations of this study as reported by the authors include the single-center design, the nondiverse racial makeup of the sample, and the difficulty of ascertaining the dosing and duration of opioid use, both prescription and illegal.
The investigators reported no disclosures relevant to this study. This study was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health, the American College of Surgeons, and other noncommercial sources.
SOURCE: Hilliard PE et al. JAMA Surg. 2018 Jul 11. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2018.2102.
FROM JAMA SURGERY
Key clinical point: Preoperative opioid use is prevalent in patients who are having spinal surgery and have depression.
Major finding:
Study details: An observational study of 34,186 surgical patients in the University of Michigan Health system.
Disclosures: The investigators reported no disclosures relevant to this study. This study was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health, the American College of Surgeons, and other noncommercial sources.
Source: Hilliard P E et al. JAMA Surg. 2018 Jul 11;. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2018.2102.
