User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Roflumilast foam effectively eases seborrheic dermatitis
.
More than half experienced clearance of their symptoms, and three out of five achieved a significant improvement in pruritus, it was revealed during a late-breaking session at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Common condition led to rapid recruitment
“Seborrheic dermatitis is a disease that’s very common, yet in my opinion, undertreated in dermatology,” said Andrew Blauvelt, MD, MBA, who presented the findings.
“It’s so common that when we did this trial, I was very surprised to see how easy it was to recruit,” said Dr. Blauvelt, a dermatologist who is president of the Oregon Medical Research Center, Portland. “Patients came in rapidly, out of the woodwork – they were desperate.”
While there are several tried and tested treatments for the condition, such as topical steroids and antifungal agents, he noted that they have their limitations: “Sometimes efficacy, sometimes the ability to be used on hair-bearing areas.”
Roflumilast is a phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor that is available for topical use in a 0.3% cream formulation (Zoryve). This formulation gained FDA approval for plaque psoriasis for patients ages 12 and older this summer and is also under investigation as a treatment for atopic dermatitis.
It’s the same product in both preparations, Dr. Blauvelt said during the discussion period. “The only major difference between the cream and the foam is the propellant used to make it into a foam. Otherwise, they have the exact same list of ingredients.”
Dr. Blauvelt reported that just over 450 patients had been recruited at 53 U.S. centers into the 8-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
For inclusion, patients had to have moderate seborrheic dermatitis, defined as an Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) score of three or more. Dr. Blauvelt noted that patients as young as 9 years old could be recruited, and there was no upper age limit. The average age of participating patients, however, was around 42 years.
Multiple improvements seen in ‘happy trial’
The primary endpoint was an IGA score of 0 or 1 with at least a 2-grade improvement (IGA success) after 8 weeks of treatment. This was achieved by 80% of patients who were treated with roflumilast 0.3% foam, compared with 60% of those who were treated with the vehicle (P less than .0001).
Dr. Blauvelt pointed out that significant improvements had also been seen after 2 weeks (about 42% vs. about 26%; P = .0003) and 4 weeks (about 72% vs. about 49%; P less than .0001) of treatment.
“Now if we raise the bar a little higher” and ask how many patients were completely clear of their seborrheic dermatitis, Dr. Blauvelt said, it was 50% at 8 weeks, more than a third at 4 weeks, over 15% at 2 weeks with the foam, and significantly lower at just under 30%, 15%, and 7% in the vehicle group.
A 4-point or more improvement in the Worst Itch Numeric Rating Scale (WI-NRS) – accepted as the minimally clinically important difference – was achieved by more than 60% of patients treated with the foam at week 8, just under 50% at week 4, and just over 30% at week 2. Corresponding rates in the vehicle group were around 40%, 30%, and 15%.
“Many patients responded in this trial. So much so that when I was doing it, I called it the ‘happy trial.’ Every time I saw patients in this trial, they seemed to be happy,” Dr. Blauvelt said anecdotally.
“In terms of adverse events, the drug turned out to be very safe, and there didn’t seem to be any issues with any things that we see with, for example, oral phosphodiesterase inhibitors,” he added.
The tolerability findings suggest that the foam vehicle “was an excellent vehicle to be used for this particular drug,” with no signs of skin irritation, as rated by patients or investigators.
Lesson for practice: Advise patients to moisturize?
“It seems like the vehicle would be a good skincare product for patients,” observed the session’s cochair, Jo Lambert, MD, PhD, professor and academic head of the department of dermatology at Ghent University Hospital, Belgium.
It was “a pretty dramatic vehicle response, right?” Dr. Blauvelt responded. “We normally don’t think of telling seborrheic dermatitis patients to moisturize,” he added.
“I think one of the interesting findings is perhaps we should be telling them to moisturize their scalp or moisturize their face, or it could be something unique to this particular foam.”
The study was funded by Arcutis Biotherapeutics. Dr. Blauvelt disclosed that he was an investigator for the trial and acted as consultant to the company, receiving grants/research funding and/or honoraria. Several of the study’s co-investigators are employees of Arcutis. Dr. Lambert was not involved in the study and cochaired the late-breaking session during which the STRATUM trial findings were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
.
More than half experienced clearance of their symptoms, and three out of five achieved a significant improvement in pruritus, it was revealed during a late-breaking session at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Common condition led to rapid recruitment
“Seborrheic dermatitis is a disease that’s very common, yet in my opinion, undertreated in dermatology,” said Andrew Blauvelt, MD, MBA, who presented the findings.
“It’s so common that when we did this trial, I was very surprised to see how easy it was to recruit,” said Dr. Blauvelt, a dermatologist who is president of the Oregon Medical Research Center, Portland. “Patients came in rapidly, out of the woodwork – they were desperate.”
While there are several tried and tested treatments for the condition, such as topical steroids and antifungal agents, he noted that they have their limitations: “Sometimes efficacy, sometimes the ability to be used on hair-bearing areas.”
Roflumilast is a phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor that is available for topical use in a 0.3% cream formulation (Zoryve). This formulation gained FDA approval for plaque psoriasis for patients ages 12 and older this summer and is also under investigation as a treatment for atopic dermatitis.
It’s the same product in both preparations, Dr. Blauvelt said during the discussion period. “The only major difference between the cream and the foam is the propellant used to make it into a foam. Otherwise, they have the exact same list of ingredients.”
Dr. Blauvelt reported that just over 450 patients had been recruited at 53 U.S. centers into the 8-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
For inclusion, patients had to have moderate seborrheic dermatitis, defined as an Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) score of three or more. Dr. Blauvelt noted that patients as young as 9 years old could be recruited, and there was no upper age limit. The average age of participating patients, however, was around 42 years.
Multiple improvements seen in ‘happy trial’
The primary endpoint was an IGA score of 0 or 1 with at least a 2-grade improvement (IGA success) after 8 weeks of treatment. This was achieved by 80% of patients who were treated with roflumilast 0.3% foam, compared with 60% of those who were treated with the vehicle (P less than .0001).
Dr. Blauvelt pointed out that significant improvements had also been seen after 2 weeks (about 42% vs. about 26%; P = .0003) and 4 weeks (about 72% vs. about 49%; P less than .0001) of treatment.
“Now if we raise the bar a little higher” and ask how many patients were completely clear of their seborrheic dermatitis, Dr. Blauvelt said, it was 50% at 8 weeks, more than a third at 4 weeks, over 15% at 2 weeks with the foam, and significantly lower at just under 30%, 15%, and 7% in the vehicle group.
A 4-point or more improvement in the Worst Itch Numeric Rating Scale (WI-NRS) – accepted as the minimally clinically important difference – was achieved by more than 60% of patients treated with the foam at week 8, just under 50% at week 4, and just over 30% at week 2. Corresponding rates in the vehicle group were around 40%, 30%, and 15%.
“Many patients responded in this trial. So much so that when I was doing it, I called it the ‘happy trial.’ Every time I saw patients in this trial, they seemed to be happy,” Dr. Blauvelt said anecdotally.
“In terms of adverse events, the drug turned out to be very safe, and there didn’t seem to be any issues with any things that we see with, for example, oral phosphodiesterase inhibitors,” he added.
The tolerability findings suggest that the foam vehicle “was an excellent vehicle to be used for this particular drug,” with no signs of skin irritation, as rated by patients or investigators.
Lesson for practice: Advise patients to moisturize?
“It seems like the vehicle would be a good skincare product for patients,” observed the session’s cochair, Jo Lambert, MD, PhD, professor and academic head of the department of dermatology at Ghent University Hospital, Belgium.
It was “a pretty dramatic vehicle response, right?” Dr. Blauvelt responded. “We normally don’t think of telling seborrheic dermatitis patients to moisturize,” he added.
“I think one of the interesting findings is perhaps we should be telling them to moisturize their scalp or moisturize their face, or it could be something unique to this particular foam.”
The study was funded by Arcutis Biotherapeutics. Dr. Blauvelt disclosed that he was an investigator for the trial and acted as consultant to the company, receiving grants/research funding and/or honoraria. Several of the study’s co-investigators are employees of Arcutis. Dr. Lambert was not involved in the study and cochaired the late-breaking session during which the STRATUM trial findings were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
.
More than half experienced clearance of their symptoms, and three out of five achieved a significant improvement in pruritus, it was revealed during a late-breaking session at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Common condition led to rapid recruitment
“Seborrheic dermatitis is a disease that’s very common, yet in my opinion, undertreated in dermatology,” said Andrew Blauvelt, MD, MBA, who presented the findings.
“It’s so common that when we did this trial, I was very surprised to see how easy it was to recruit,” said Dr. Blauvelt, a dermatologist who is president of the Oregon Medical Research Center, Portland. “Patients came in rapidly, out of the woodwork – they were desperate.”
While there are several tried and tested treatments for the condition, such as topical steroids and antifungal agents, he noted that they have their limitations: “Sometimes efficacy, sometimes the ability to be used on hair-bearing areas.”
Roflumilast is a phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor that is available for topical use in a 0.3% cream formulation (Zoryve). This formulation gained FDA approval for plaque psoriasis for patients ages 12 and older this summer and is also under investigation as a treatment for atopic dermatitis.
It’s the same product in both preparations, Dr. Blauvelt said during the discussion period. “The only major difference between the cream and the foam is the propellant used to make it into a foam. Otherwise, they have the exact same list of ingredients.”
Dr. Blauvelt reported that just over 450 patients had been recruited at 53 U.S. centers into the 8-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
For inclusion, patients had to have moderate seborrheic dermatitis, defined as an Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) score of three or more. Dr. Blauvelt noted that patients as young as 9 years old could be recruited, and there was no upper age limit. The average age of participating patients, however, was around 42 years.
Multiple improvements seen in ‘happy trial’
The primary endpoint was an IGA score of 0 or 1 with at least a 2-grade improvement (IGA success) after 8 weeks of treatment. This was achieved by 80% of patients who were treated with roflumilast 0.3% foam, compared with 60% of those who were treated with the vehicle (P less than .0001).
Dr. Blauvelt pointed out that significant improvements had also been seen after 2 weeks (about 42% vs. about 26%; P = .0003) and 4 weeks (about 72% vs. about 49%; P less than .0001) of treatment.
“Now if we raise the bar a little higher” and ask how many patients were completely clear of their seborrheic dermatitis, Dr. Blauvelt said, it was 50% at 8 weeks, more than a third at 4 weeks, over 15% at 2 weeks with the foam, and significantly lower at just under 30%, 15%, and 7% in the vehicle group.
A 4-point or more improvement in the Worst Itch Numeric Rating Scale (WI-NRS) – accepted as the minimally clinically important difference – was achieved by more than 60% of patients treated with the foam at week 8, just under 50% at week 4, and just over 30% at week 2. Corresponding rates in the vehicle group were around 40%, 30%, and 15%.
“Many patients responded in this trial. So much so that when I was doing it, I called it the ‘happy trial.’ Every time I saw patients in this trial, they seemed to be happy,” Dr. Blauvelt said anecdotally.
“In terms of adverse events, the drug turned out to be very safe, and there didn’t seem to be any issues with any things that we see with, for example, oral phosphodiesterase inhibitors,” he added.
The tolerability findings suggest that the foam vehicle “was an excellent vehicle to be used for this particular drug,” with no signs of skin irritation, as rated by patients or investigators.
Lesson for practice: Advise patients to moisturize?
“It seems like the vehicle would be a good skincare product for patients,” observed the session’s cochair, Jo Lambert, MD, PhD, professor and academic head of the department of dermatology at Ghent University Hospital, Belgium.
It was “a pretty dramatic vehicle response, right?” Dr. Blauvelt responded. “We normally don’t think of telling seborrheic dermatitis patients to moisturize,” he added.
“I think one of the interesting findings is perhaps we should be telling them to moisturize their scalp or moisturize their face, or it could be something unique to this particular foam.”
The study was funded by Arcutis Biotherapeutics. Dr. Blauvelt disclosed that he was an investigator for the trial and acted as consultant to the company, receiving grants/research funding and/or honoraria. Several of the study’s co-investigators are employees of Arcutis. Dr. Lambert was not involved in the study and cochaired the late-breaking session during which the STRATUM trial findings were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE EADV CONGRESS
Dupilumab offers ‘clinically meaningful’ improvements in prurigo nodularis
(Dupixent), indicate results from the phase 2 LIBERTY-PN PRIME trial.
The research was presented at the annual Congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
More than 150 patients with severe PN whose quality of life was impaired were randomly assigned to receive dupilumab (Dupixent) or placebo for 24 weeks. Use of the monoclonal antibody was associated with significant improvements in itch scores.
The researchers also found that the percentage of patients who had no or few PN lesions increased substantially with use of dupilumab, and there were no new safety signals, confirming results from previous studies. Dupilumab, an interleukin-4 receptor alpha antagonist administered by injection, was initially approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for treating atopic dermatitis in 2022.
Study presenter Gil Yosipovitch, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of Miami, emphasized that the improvements in itch and skin lesions seen in these patients were “clinically meaningful.”
In the discussion after the presentation, Dr. Yosipovitch was asked whether the presence or absence of atopy had any bearing on the results.
He replied that although there were too few patients with atopy in the current study to answer that question, other data indicate that there is no overall difference between patients with atopy and those without atopy.
Asked whether dupilumab should be used for only 24 weeks, Dr. Yosipovitch said his that “impression” is that there can be a “honeymoon period” during which the medication is stopped and the treating clinician sees “what happens.”
“It would be interesting in the future” to find out, he added, but he noted that whatever the result, patients would need treatment “for the rest of their life.”
Dr. Yosipovitch, director of the Miami Itch Center and the study’s principal investigator, began his presentation by noting that currently, no systemic therapies have been approved by the FDA or the European Medicines Agency for PN.
Although treatments such as topical medications, ultraviolet light therapy, immunosuppressive agents, and systemic neuromodulators are used off label, for many patients with moderate to severe PN, disease control is inadequate, and the patients are “miserable.”
Recently, the phase 3 LIBERTY-PN PRIME2 trial showed that dupilumab significantly reduced itch and skin lesions for patients with PN, and the safety profile was consistent with that seen in approved indications for the drug.
Dr. Yosipovitch explained that LIBERTY-PN PRIME was a phase 2 study in which, after a screening period, patients with PN were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive dupilumab as a 600-mg loading dose followed by 300 mg twice weekly or a matched placebo. Treatment was given for 24 weeks, after which there was a post treatment 12-week follow-up period.
Participants were aged 18-80 years and had been diagnosed with PN for a period of at least 3 months. To be included in the trial, patients had to have an average Worst Itch Numerical Rating Scale (WI-NRS) score of at least 7 and at least 20 lesions, among other criteria. (Patients were allowed to continue treatment with mid- to low-potency topical steroids or topical calcineurin inhibitors if they had been taking them at baseline.)
Among 151 patients in the study, the mean age was 50.1 years, and 66.2% were women. The majority (53.0%) were White; 7.3% were Black; and 35.8% were Asian; 40.4% of patients had a history of atopy. The mean WI-NRS was 8.5, and the mean skin pain score on a 10-point scale was 7.2.
The Investigator’s Global Assessment for PN stage of disease (IGA PN-S) was also employed in the trial. That measure uses a 5-point scale to assess disease severity, with 0 indicating no lesions and 4 indicating more than 100 lesions. At baseline, 28.7% of patients had a score of 4, and the remainder had a score of 3, indicating the presence of 20-100 PN lesions.
Dr. Yosipovitch said that quality of life for these patients was “low” and that scores on the Hospital Anxiety and Depression scale indicated that the participants, many of whom had previously received topical and systemic medications for their PN, indicated they were depressed.
He showed that at week 24, the proportion of patients who had experienced an improvement in the WI-NRS score of greater than or equal to 4 (the study’s primary endpoint) was significantly greater with dupilumab, at 60.0% versus 18.4% among patients given placebo (P < .0001).
Moreover, the proportion of patients at week 24 with an IGA PN-S score of 0 or 1 (the secondary endpoint) was 48.0% in the active treatment group, versus 18.4% with placebo (P =.0004).
With regard to safety, rates of any treatment-emergent adverse events were similar between the groups, at 70.7% for dupilumab and 62.7% for placebo, as were rates for severe treatment-emergent adverse events, at 6.7% and 10.7%, respectively.
Rates of treatment-emergent adverse events of interest, such as skin infections, conjunctivitis, herpes viral infections, and injection site reactions, also suggested that there was no increased risk with active treatment.
Dupilumab is currently under review at the FDA and in Europe for the treatment of PN, according to dupilumab manufacturers Regeneron and Sanofi.
The study was sponsored by Sanofi in collaboration with Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Yosipovitch has relationships with Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Bellus Health, Eli Lilly, Galderma, GSK, Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals, LEO Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, and Trevi Therapeutics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
(Dupixent), indicate results from the phase 2 LIBERTY-PN PRIME trial.
The research was presented at the annual Congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
More than 150 patients with severe PN whose quality of life was impaired were randomly assigned to receive dupilumab (Dupixent) or placebo for 24 weeks. Use of the monoclonal antibody was associated with significant improvements in itch scores.
The researchers also found that the percentage of patients who had no or few PN lesions increased substantially with use of dupilumab, and there were no new safety signals, confirming results from previous studies. Dupilumab, an interleukin-4 receptor alpha antagonist administered by injection, was initially approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for treating atopic dermatitis in 2022.
Study presenter Gil Yosipovitch, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of Miami, emphasized that the improvements in itch and skin lesions seen in these patients were “clinically meaningful.”
In the discussion after the presentation, Dr. Yosipovitch was asked whether the presence or absence of atopy had any bearing on the results.
He replied that although there were too few patients with atopy in the current study to answer that question, other data indicate that there is no overall difference between patients with atopy and those without atopy.
Asked whether dupilumab should be used for only 24 weeks, Dr. Yosipovitch said his that “impression” is that there can be a “honeymoon period” during which the medication is stopped and the treating clinician sees “what happens.”
“It would be interesting in the future” to find out, he added, but he noted that whatever the result, patients would need treatment “for the rest of their life.”
Dr. Yosipovitch, director of the Miami Itch Center and the study’s principal investigator, began his presentation by noting that currently, no systemic therapies have been approved by the FDA or the European Medicines Agency for PN.
Although treatments such as topical medications, ultraviolet light therapy, immunosuppressive agents, and systemic neuromodulators are used off label, for many patients with moderate to severe PN, disease control is inadequate, and the patients are “miserable.”
Recently, the phase 3 LIBERTY-PN PRIME2 trial showed that dupilumab significantly reduced itch and skin lesions for patients with PN, and the safety profile was consistent with that seen in approved indications for the drug.
Dr. Yosipovitch explained that LIBERTY-PN PRIME was a phase 2 study in which, after a screening period, patients with PN were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive dupilumab as a 600-mg loading dose followed by 300 mg twice weekly or a matched placebo. Treatment was given for 24 weeks, after which there was a post treatment 12-week follow-up period.
Participants were aged 18-80 years and had been diagnosed with PN for a period of at least 3 months. To be included in the trial, patients had to have an average Worst Itch Numerical Rating Scale (WI-NRS) score of at least 7 and at least 20 lesions, among other criteria. (Patients were allowed to continue treatment with mid- to low-potency topical steroids or topical calcineurin inhibitors if they had been taking them at baseline.)
Among 151 patients in the study, the mean age was 50.1 years, and 66.2% were women. The majority (53.0%) were White; 7.3% were Black; and 35.8% were Asian; 40.4% of patients had a history of atopy. The mean WI-NRS was 8.5, and the mean skin pain score on a 10-point scale was 7.2.
The Investigator’s Global Assessment for PN stage of disease (IGA PN-S) was also employed in the trial. That measure uses a 5-point scale to assess disease severity, with 0 indicating no lesions and 4 indicating more than 100 lesions. At baseline, 28.7% of patients had a score of 4, and the remainder had a score of 3, indicating the presence of 20-100 PN lesions.
Dr. Yosipovitch said that quality of life for these patients was “low” and that scores on the Hospital Anxiety and Depression scale indicated that the participants, many of whom had previously received topical and systemic medications for their PN, indicated they were depressed.
He showed that at week 24, the proportion of patients who had experienced an improvement in the WI-NRS score of greater than or equal to 4 (the study’s primary endpoint) was significantly greater with dupilumab, at 60.0% versus 18.4% among patients given placebo (P < .0001).
Moreover, the proportion of patients at week 24 with an IGA PN-S score of 0 or 1 (the secondary endpoint) was 48.0% in the active treatment group, versus 18.4% with placebo (P =.0004).
With regard to safety, rates of any treatment-emergent adverse events were similar between the groups, at 70.7% for dupilumab and 62.7% for placebo, as were rates for severe treatment-emergent adverse events, at 6.7% and 10.7%, respectively.
Rates of treatment-emergent adverse events of interest, such as skin infections, conjunctivitis, herpes viral infections, and injection site reactions, also suggested that there was no increased risk with active treatment.
Dupilumab is currently under review at the FDA and in Europe for the treatment of PN, according to dupilumab manufacturers Regeneron and Sanofi.
The study was sponsored by Sanofi in collaboration with Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Yosipovitch has relationships with Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Bellus Health, Eli Lilly, Galderma, GSK, Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals, LEO Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, and Trevi Therapeutics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
(Dupixent), indicate results from the phase 2 LIBERTY-PN PRIME trial.
The research was presented at the annual Congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
More than 150 patients with severe PN whose quality of life was impaired were randomly assigned to receive dupilumab (Dupixent) or placebo for 24 weeks. Use of the monoclonal antibody was associated with significant improvements in itch scores.
The researchers also found that the percentage of patients who had no or few PN lesions increased substantially with use of dupilumab, and there were no new safety signals, confirming results from previous studies. Dupilumab, an interleukin-4 receptor alpha antagonist administered by injection, was initially approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for treating atopic dermatitis in 2022.
Study presenter Gil Yosipovitch, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of Miami, emphasized that the improvements in itch and skin lesions seen in these patients were “clinically meaningful.”
In the discussion after the presentation, Dr. Yosipovitch was asked whether the presence or absence of atopy had any bearing on the results.
He replied that although there were too few patients with atopy in the current study to answer that question, other data indicate that there is no overall difference between patients with atopy and those without atopy.
Asked whether dupilumab should be used for only 24 weeks, Dr. Yosipovitch said his that “impression” is that there can be a “honeymoon period” during which the medication is stopped and the treating clinician sees “what happens.”
“It would be interesting in the future” to find out, he added, but he noted that whatever the result, patients would need treatment “for the rest of their life.”
Dr. Yosipovitch, director of the Miami Itch Center and the study’s principal investigator, began his presentation by noting that currently, no systemic therapies have been approved by the FDA or the European Medicines Agency for PN.
Although treatments such as topical medications, ultraviolet light therapy, immunosuppressive agents, and systemic neuromodulators are used off label, for many patients with moderate to severe PN, disease control is inadequate, and the patients are “miserable.”
Recently, the phase 3 LIBERTY-PN PRIME2 trial showed that dupilumab significantly reduced itch and skin lesions for patients with PN, and the safety profile was consistent with that seen in approved indications for the drug.
Dr. Yosipovitch explained that LIBERTY-PN PRIME was a phase 2 study in which, after a screening period, patients with PN were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive dupilumab as a 600-mg loading dose followed by 300 mg twice weekly or a matched placebo. Treatment was given for 24 weeks, after which there was a post treatment 12-week follow-up period.
Participants were aged 18-80 years and had been diagnosed with PN for a period of at least 3 months. To be included in the trial, patients had to have an average Worst Itch Numerical Rating Scale (WI-NRS) score of at least 7 and at least 20 lesions, among other criteria. (Patients were allowed to continue treatment with mid- to low-potency topical steroids or topical calcineurin inhibitors if they had been taking them at baseline.)
Among 151 patients in the study, the mean age was 50.1 years, and 66.2% were women. The majority (53.0%) were White; 7.3% were Black; and 35.8% were Asian; 40.4% of patients had a history of atopy. The mean WI-NRS was 8.5, and the mean skin pain score on a 10-point scale was 7.2.
The Investigator’s Global Assessment for PN stage of disease (IGA PN-S) was also employed in the trial. That measure uses a 5-point scale to assess disease severity, with 0 indicating no lesions and 4 indicating more than 100 lesions. At baseline, 28.7% of patients had a score of 4, and the remainder had a score of 3, indicating the presence of 20-100 PN lesions.
Dr. Yosipovitch said that quality of life for these patients was “low” and that scores on the Hospital Anxiety and Depression scale indicated that the participants, many of whom had previously received topical and systemic medications for their PN, indicated they were depressed.
He showed that at week 24, the proportion of patients who had experienced an improvement in the WI-NRS score of greater than or equal to 4 (the study’s primary endpoint) was significantly greater with dupilumab, at 60.0% versus 18.4% among patients given placebo (P < .0001).
Moreover, the proportion of patients at week 24 with an IGA PN-S score of 0 or 1 (the secondary endpoint) was 48.0% in the active treatment group, versus 18.4% with placebo (P =.0004).
With regard to safety, rates of any treatment-emergent adverse events were similar between the groups, at 70.7% for dupilumab and 62.7% for placebo, as were rates for severe treatment-emergent adverse events, at 6.7% and 10.7%, respectively.
Rates of treatment-emergent adverse events of interest, such as skin infections, conjunctivitis, herpes viral infections, and injection site reactions, also suggested that there was no increased risk with active treatment.
Dupilumab is currently under review at the FDA and in Europe for the treatment of PN, according to dupilumab manufacturers Regeneron and Sanofi.
The study was sponsored by Sanofi in collaboration with Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Yosipovitch has relationships with Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Bellus Health, Eli Lilly, Galderma, GSK, Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals, LEO Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, and Trevi Therapeutics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE EADV CONGRESS
Dermatoses often occur in people who wear face masks
according to a recently published systematic review and meta-analysis.
“This report finds the most statistically significant risk factor for developing a facial dermatosis under a face mask is how long one wears the mask. Specifically, wearing a mask for more than 4 to 6 hours correlated most strongly with the development of a facial skin problem,” Jami L. Miller, MD, associate professor of dermatology, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., told this news organization. Dr. Miller was not involved in the study.
“The type of mask and the environment were of less significance,” she added.
Mask wearing for infection control has been common during the COVID-19 pandemic and will likely continue for some time, study coauthors Lim Yi Shen Justin, MBBS, and Yik Weng Yew*, MBBS, MPH, PhD, Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, write in Contact Dermatitis. And cross-sectional studies have suggested a link between mask wearing and various facial dermatoses.
To evaluate this link, as well as potential risk factors for facial dermatoses, the researchers reviewed 37 studies published between 2004 and 2022 involving 29,557 adult participants self-reporting regular use of any face mask type across 17 countries in Europe and Asia. The mask types commonly studied in the papers they analyzed included surgical masks and respirators.
Facial dermatoses were self-reported in 30 studies (81.1%) and were diagnosed by trained dermatologists in seven studies (18.9%).
Dr. Justin and Dr. Yew found that:
- The overall prevalence of facial dermatoses was 55%
- Individually, facial dermatitis, itch, acne, and pressure injuries were consistently reported as facial dermatoses, with pooled prevalence rates of 24%, 30%, 31%, and 31%, respectively
- The duration of mask wearing was the most significant risk factor for facial dermatoses (P < .001)
- Respirators, including N95 masks, were not more likely than surgical masks to be linked with facial dermatoses
“Understanding risk factors of mask wearing, including situation, duration, and type of mask, may allow for targeted interventions to mitigate problems,” Dr. Yew told this news organization.
He advised taking a break from mask wearing after 4 to 6 hours to improve outcomes.
Dr. Yew acknowledged limitations, including that most of the reviewed studies relied on self-reported symptoms.
“Patient factors were not investigated in most studies; therefore, we were not able to ascertain their contributory role in the development of facial dermatoses from mask wearing,” he said. “We were also unable to prove causation between risk factors and outcome.”
Four dermatologists welcome the findings
Dr. Miller called this an “interesting, and certainly relevant” study, now that mask wearing is common and facial skin problems are fairly common complaints in medical visits.
“As the authors say, irritants or contact allergens with longer exposures can be expected to cause a more severe dermatitis than short contact,” she said. “Longer duration also can cause occlusion of pores and hair follicles, which can be expected to worsen acne and folliculitis.”
“I was surprised that the type of mask did not seem to matter significantly,” she added. “Patients wearing N95 masks may be relieved to know N95s do not cause more skin problems than lighter masks.”
Still, Dr. Miller had several questions, including if the materials and chemical finishes that vary by manufacturer may affect skin conditions.
Olga Bunimovich, MD, assistant professor, department of dermatology, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pennsylvania, called this study “an excellent step towards characterizing the role masks play in facial dermatoses.”
“The study provides a window into the prevalence of these conditions, as well as some understanding of the factors that may be contributing to it,” Dr. Bunimovich, who was not part of the study, added. But “we can also utilize this information to alter behavior in the work environment, allowing ‘mask-free’ breaks to decrease the risk of facial dermatoses.”
Elma Baron, MD, professor and director, Skin Study Center, department of dermatology, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Cleveland, expected skin problems to be linked with mask wearing but didn’t expect the prevalence to be as high as 55%, which she called “very significant.”
“Mask wearing is an important means to prevent transmission of communicable infections, and the practice will most likely continue,” she said.
“Given the data, it is reasonable to advise patients who are already prone to these specific dermatoses to be proactive,” she added. “Early intervention with proper topical medications, preferably prescribed by a dermatologist or other health care provider, and changing masks frequently before they get soaked with moisture, will hopefully lessen the severity of skin rashes and minimize the negative impact on quality of life.”
Also commenting on the study, Susan Massick, MD, dermatologist and clinical associate professor of internal medicine, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Westerville, said in an interview that she urges people to wear masks, despite these risks.
“The majority of concerns are straightforward, manageable, and overall benign,” she said. “We have a multitude of treatments that can help control, address, or improve symptoms.”
“Masks are an effective and easy way to protect yourself from infection, and they remain one of the most reliable preventions we have,” Dr. Massick noted. “The findings in this article should not preclude anyone from wearing a mask, nor should facial dermatoses be a cause for people to stop wearing their masks.”
The study received no funding. The authors, as well as Dr. Baron, Dr. Miller, Dr. Bunimovich, and Dr. Massick, who were not involved in the study, reported no relevant financial relationships. All experts commented by email.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Correction, 9/22/22: An earlier version of this article misstated the name of Dr. Yik Weng Yew.
according to a recently published systematic review and meta-analysis.
“This report finds the most statistically significant risk factor for developing a facial dermatosis under a face mask is how long one wears the mask. Specifically, wearing a mask for more than 4 to 6 hours correlated most strongly with the development of a facial skin problem,” Jami L. Miller, MD, associate professor of dermatology, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., told this news organization. Dr. Miller was not involved in the study.
“The type of mask and the environment were of less significance,” she added.
Mask wearing for infection control has been common during the COVID-19 pandemic and will likely continue for some time, study coauthors Lim Yi Shen Justin, MBBS, and Yik Weng Yew*, MBBS, MPH, PhD, Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, write in Contact Dermatitis. And cross-sectional studies have suggested a link between mask wearing and various facial dermatoses.
To evaluate this link, as well as potential risk factors for facial dermatoses, the researchers reviewed 37 studies published between 2004 and 2022 involving 29,557 adult participants self-reporting regular use of any face mask type across 17 countries in Europe and Asia. The mask types commonly studied in the papers they analyzed included surgical masks and respirators.
Facial dermatoses were self-reported in 30 studies (81.1%) and were diagnosed by trained dermatologists in seven studies (18.9%).
Dr. Justin and Dr. Yew found that:
- The overall prevalence of facial dermatoses was 55%
- Individually, facial dermatitis, itch, acne, and pressure injuries were consistently reported as facial dermatoses, with pooled prevalence rates of 24%, 30%, 31%, and 31%, respectively
- The duration of mask wearing was the most significant risk factor for facial dermatoses (P < .001)
- Respirators, including N95 masks, were not more likely than surgical masks to be linked with facial dermatoses
“Understanding risk factors of mask wearing, including situation, duration, and type of mask, may allow for targeted interventions to mitigate problems,” Dr. Yew told this news organization.
He advised taking a break from mask wearing after 4 to 6 hours to improve outcomes.
Dr. Yew acknowledged limitations, including that most of the reviewed studies relied on self-reported symptoms.
“Patient factors were not investigated in most studies; therefore, we were not able to ascertain their contributory role in the development of facial dermatoses from mask wearing,” he said. “We were also unable to prove causation between risk factors and outcome.”
Four dermatologists welcome the findings
Dr. Miller called this an “interesting, and certainly relevant” study, now that mask wearing is common and facial skin problems are fairly common complaints in medical visits.
“As the authors say, irritants or contact allergens with longer exposures can be expected to cause a more severe dermatitis than short contact,” she said. “Longer duration also can cause occlusion of pores and hair follicles, which can be expected to worsen acne and folliculitis.”
“I was surprised that the type of mask did not seem to matter significantly,” she added. “Patients wearing N95 masks may be relieved to know N95s do not cause more skin problems than lighter masks.”
Still, Dr. Miller had several questions, including if the materials and chemical finishes that vary by manufacturer may affect skin conditions.
Olga Bunimovich, MD, assistant professor, department of dermatology, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pennsylvania, called this study “an excellent step towards characterizing the role masks play in facial dermatoses.”
“The study provides a window into the prevalence of these conditions, as well as some understanding of the factors that may be contributing to it,” Dr. Bunimovich, who was not part of the study, added. But “we can also utilize this information to alter behavior in the work environment, allowing ‘mask-free’ breaks to decrease the risk of facial dermatoses.”
Elma Baron, MD, professor and director, Skin Study Center, department of dermatology, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Cleveland, expected skin problems to be linked with mask wearing but didn’t expect the prevalence to be as high as 55%, which she called “very significant.”
“Mask wearing is an important means to prevent transmission of communicable infections, and the practice will most likely continue,” she said.
“Given the data, it is reasonable to advise patients who are already prone to these specific dermatoses to be proactive,” she added. “Early intervention with proper topical medications, preferably prescribed by a dermatologist or other health care provider, and changing masks frequently before they get soaked with moisture, will hopefully lessen the severity of skin rashes and minimize the negative impact on quality of life.”
Also commenting on the study, Susan Massick, MD, dermatologist and clinical associate professor of internal medicine, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Westerville, said in an interview that she urges people to wear masks, despite these risks.
“The majority of concerns are straightforward, manageable, and overall benign,” she said. “We have a multitude of treatments that can help control, address, or improve symptoms.”
“Masks are an effective and easy way to protect yourself from infection, and they remain one of the most reliable preventions we have,” Dr. Massick noted. “The findings in this article should not preclude anyone from wearing a mask, nor should facial dermatoses be a cause for people to stop wearing their masks.”
The study received no funding. The authors, as well as Dr. Baron, Dr. Miller, Dr. Bunimovich, and Dr. Massick, who were not involved in the study, reported no relevant financial relationships. All experts commented by email.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Correction, 9/22/22: An earlier version of this article misstated the name of Dr. Yik Weng Yew.
according to a recently published systematic review and meta-analysis.
“This report finds the most statistically significant risk factor for developing a facial dermatosis under a face mask is how long one wears the mask. Specifically, wearing a mask for more than 4 to 6 hours correlated most strongly with the development of a facial skin problem,” Jami L. Miller, MD, associate professor of dermatology, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., told this news organization. Dr. Miller was not involved in the study.
“The type of mask and the environment were of less significance,” she added.
Mask wearing for infection control has been common during the COVID-19 pandemic and will likely continue for some time, study coauthors Lim Yi Shen Justin, MBBS, and Yik Weng Yew*, MBBS, MPH, PhD, Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, write in Contact Dermatitis. And cross-sectional studies have suggested a link between mask wearing and various facial dermatoses.
To evaluate this link, as well as potential risk factors for facial dermatoses, the researchers reviewed 37 studies published between 2004 and 2022 involving 29,557 adult participants self-reporting regular use of any face mask type across 17 countries in Europe and Asia. The mask types commonly studied in the papers they analyzed included surgical masks and respirators.
Facial dermatoses were self-reported in 30 studies (81.1%) and were diagnosed by trained dermatologists in seven studies (18.9%).
Dr. Justin and Dr. Yew found that:
- The overall prevalence of facial dermatoses was 55%
- Individually, facial dermatitis, itch, acne, and pressure injuries were consistently reported as facial dermatoses, with pooled prevalence rates of 24%, 30%, 31%, and 31%, respectively
- The duration of mask wearing was the most significant risk factor for facial dermatoses (P < .001)
- Respirators, including N95 masks, were not more likely than surgical masks to be linked with facial dermatoses
“Understanding risk factors of mask wearing, including situation, duration, and type of mask, may allow for targeted interventions to mitigate problems,” Dr. Yew told this news organization.
He advised taking a break from mask wearing after 4 to 6 hours to improve outcomes.
Dr. Yew acknowledged limitations, including that most of the reviewed studies relied on self-reported symptoms.
“Patient factors were not investigated in most studies; therefore, we were not able to ascertain their contributory role in the development of facial dermatoses from mask wearing,” he said. “We were also unable to prove causation between risk factors and outcome.”
Four dermatologists welcome the findings
Dr. Miller called this an “interesting, and certainly relevant” study, now that mask wearing is common and facial skin problems are fairly common complaints in medical visits.
“As the authors say, irritants or contact allergens with longer exposures can be expected to cause a more severe dermatitis than short contact,” she said. “Longer duration also can cause occlusion of pores and hair follicles, which can be expected to worsen acne and folliculitis.”
“I was surprised that the type of mask did not seem to matter significantly,” she added. “Patients wearing N95 masks may be relieved to know N95s do not cause more skin problems than lighter masks.”
Still, Dr. Miller had several questions, including if the materials and chemical finishes that vary by manufacturer may affect skin conditions.
Olga Bunimovich, MD, assistant professor, department of dermatology, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pennsylvania, called this study “an excellent step towards characterizing the role masks play in facial dermatoses.”
“The study provides a window into the prevalence of these conditions, as well as some understanding of the factors that may be contributing to it,” Dr. Bunimovich, who was not part of the study, added. But “we can also utilize this information to alter behavior in the work environment, allowing ‘mask-free’ breaks to decrease the risk of facial dermatoses.”
Elma Baron, MD, professor and director, Skin Study Center, department of dermatology, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Cleveland, expected skin problems to be linked with mask wearing but didn’t expect the prevalence to be as high as 55%, which she called “very significant.”
“Mask wearing is an important means to prevent transmission of communicable infections, and the practice will most likely continue,” she said.
“Given the data, it is reasonable to advise patients who are already prone to these specific dermatoses to be proactive,” she added. “Early intervention with proper topical medications, preferably prescribed by a dermatologist or other health care provider, and changing masks frequently before they get soaked with moisture, will hopefully lessen the severity of skin rashes and minimize the negative impact on quality of life.”
Also commenting on the study, Susan Massick, MD, dermatologist and clinical associate professor of internal medicine, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Westerville, said in an interview that she urges people to wear masks, despite these risks.
“The majority of concerns are straightforward, manageable, and overall benign,” she said. “We have a multitude of treatments that can help control, address, or improve symptoms.”
“Masks are an effective and easy way to protect yourself from infection, and they remain one of the most reliable preventions we have,” Dr. Massick noted. “The findings in this article should not preclude anyone from wearing a mask, nor should facial dermatoses be a cause for people to stop wearing their masks.”
The study received no funding. The authors, as well as Dr. Baron, Dr. Miller, Dr. Bunimovich, and Dr. Massick, who were not involved in the study, reported no relevant financial relationships. All experts commented by email.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Correction, 9/22/22: An earlier version of this article misstated the name of Dr. Yik Weng Yew.
FDA approves oral TYK2 inhibitor deucravacitinib for treating psoriasis
the manufacturer announced on Sept. 9.
Deucravacitinib targets TYK2, which inhibits signaling of interleukin-23, interleukin-12, and type 1 interferons, key cytokines involved in the pathogenesis of multiple immune-mediated diseases, according to Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS). This is the first approval for deucravacitinib, which will be marketed as Sotyktu, and the first drug in this class to be approved.
It is also currently under review for the same indication in Europe and Japan, and elsewhere, and for treating pustular psoriasis and erythrodermic psoriasis in Japan.
FDA approval was based on the results of POETYK PSO-1 and POETYK PSO-2, phase 3 trials of almost 1,700 adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. In these studies, treatment with once-daily deucravacitinib showed significant and clinically meaningful improvements in skin clearance and symptoms, compared with placebo and with apremilast (Otezla), according to the company.
In the two studies, patients were randomly assigned to receive 6 mg daily of deucravacitinib, placebo, or a 30-mg twice-daily dose of apremilast, the oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor approved for psoriasis. The primary endpoints were the percentage of patients who achieved a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 75 response and a static Physician’s Global Assessment (sPGA) score of 0 or 1 (clear or almost clear) at 16 weeks.
At 16 weeks, 58% and 53% of patients receiving deucravacitinib in the POETYK PSO-1 and POETYK PSO-2 studies, respectively, achieved PASI 75 response, compared with 13% and 9% of those receiving placebo (P < .0001 for both) and 35% and 40% receiving apremilast (P < .0001, P = .0004, respectively), according to the company’s announcement of the approval. PASI 75 responses were maintained through 52 weeks among the patients who remained on treatment, in both studies, according to BMS.
In the POETYK PSO-1 and PSO-2 studies, respectively, 54% and 50% of those on deucravacitinib achieved an sPGA of 0/1 at 16 weeks, compared with 7% and 9% of those receiving placebo (P < .0001 for both) and 32% and 34% of those receiving apremilast (P < .0001 for both).
Across the two studies, at 16 weeks, the most common adverse events that affected at least 1% of patients on deucravacitinib and that occurred at higher rates than in the placebo group were upper respiratory infections (19.2%), increases in serum creatine phosphokinase (2.7%), herpes simplex (2%), mouth ulcers (1.9%), folliculitis (1.7%), and acne (1.4%). Adverse events resulting in discontinuation of treatment were reported in 2.4% of persons receiving deucravacitinib and 5.2% of those receiving apremilast, compared with 3.8% of those receiving placebo.
Up to 16 weeks, according to the BMS statement, 28% of persons receiving deucravacitinib had infections, most of which were mild to moderate and not serious and did not result in stopping treatment, compared with 22% of those receiving placebo. In addition, five patients treated with deucravacitinib and five patients receiving placebo had serious infections, and three patients receiving deucravacitinib had cancer (not including nonmelanoma skin cancer).
Deucravacitinib is also being evaluated in clinical trials for psoriatic arthritis, lupus, and inflammatory bowel disease. It is not recommended for use in combination with other potent immunosuppressants, according to BMS.
The prescribing information and patient medication guide are available online.
The POETYK PSO-1 and POETYK PSO-2 studies were funded by Bristol Myers Squibb.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
the manufacturer announced on Sept. 9.
Deucravacitinib targets TYK2, which inhibits signaling of interleukin-23, interleukin-12, and type 1 interferons, key cytokines involved in the pathogenesis of multiple immune-mediated diseases, according to Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS). This is the first approval for deucravacitinib, which will be marketed as Sotyktu, and the first drug in this class to be approved.
It is also currently under review for the same indication in Europe and Japan, and elsewhere, and for treating pustular psoriasis and erythrodermic psoriasis in Japan.
FDA approval was based on the results of POETYK PSO-1 and POETYK PSO-2, phase 3 trials of almost 1,700 adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. In these studies, treatment with once-daily deucravacitinib showed significant and clinically meaningful improvements in skin clearance and symptoms, compared with placebo and with apremilast (Otezla), according to the company.
In the two studies, patients were randomly assigned to receive 6 mg daily of deucravacitinib, placebo, or a 30-mg twice-daily dose of apremilast, the oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor approved for psoriasis. The primary endpoints were the percentage of patients who achieved a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 75 response and a static Physician’s Global Assessment (sPGA) score of 0 or 1 (clear or almost clear) at 16 weeks.
At 16 weeks, 58% and 53% of patients receiving deucravacitinib in the POETYK PSO-1 and POETYK PSO-2 studies, respectively, achieved PASI 75 response, compared with 13% and 9% of those receiving placebo (P < .0001 for both) and 35% and 40% receiving apremilast (P < .0001, P = .0004, respectively), according to the company’s announcement of the approval. PASI 75 responses were maintained through 52 weeks among the patients who remained on treatment, in both studies, according to BMS.
In the POETYK PSO-1 and PSO-2 studies, respectively, 54% and 50% of those on deucravacitinib achieved an sPGA of 0/1 at 16 weeks, compared with 7% and 9% of those receiving placebo (P < .0001 for both) and 32% and 34% of those receiving apremilast (P < .0001 for both).
Across the two studies, at 16 weeks, the most common adverse events that affected at least 1% of patients on deucravacitinib and that occurred at higher rates than in the placebo group were upper respiratory infections (19.2%), increases in serum creatine phosphokinase (2.7%), herpes simplex (2%), mouth ulcers (1.9%), folliculitis (1.7%), and acne (1.4%). Adverse events resulting in discontinuation of treatment were reported in 2.4% of persons receiving deucravacitinib and 5.2% of those receiving apremilast, compared with 3.8% of those receiving placebo.
Up to 16 weeks, according to the BMS statement, 28% of persons receiving deucravacitinib had infections, most of which were mild to moderate and not serious and did not result in stopping treatment, compared with 22% of those receiving placebo. In addition, five patients treated with deucravacitinib and five patients receiving placebo had serious infections, and three patients receiving deucravacitinib had cancer (not including nonmelanoma skin cancer).
Deucravacitinib is also being evaluated in clinical trials for psoriatic arthritis, lupus, and inflammatory bowel disease. It is not recommended for use in combination with other potent immunosuppressants, according to BMS.
The prescribing information and patient medication guide are available online.
The POETYK PSO-1 and POETYK PSO-2 studies were funded by Bristol Myers Squibb.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
the manufacturer announced on Sept. 9.
Deucravacitinib targets TYK2, which inhibits signaling of interleukin-23, interleukin-12, and type 1 interferons, key cytokines involved in the pathogenesis of multiple immune-mediated diseases, according to Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS). This is the first approval for deucravacitinib, which will be marketed as Sotyktu, and the first drug in this class to be approved.
It is also currently under review for the same indication in Europe and Japan, and elsewhere, and for treating pustular psoriasis and erythrodermic psoriasis in Japan.
FDA approval was based on the results of POETYK PSO-1 and POETYK PSO-2, phase 3 trials of almost 1,700 adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. In these studies, treatment with once-daily deucravacitinib showed significant and clinically meaningful improvements in skin clearance and symptoms, compared with placebo and with apremilast (Otezla), according to the company.
In the two studies, patients were randomly assigned to receive 6 mg daily of deucravacitinib, placebo, or a 30-mg twice-daily dose of apremilast, the oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor approved for psoriasis. The primary endpoints were the percentage of patients who achieved a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 75 response and a static Physician’s Global Assessment (sPGA) score of 0 or 1 (clear or almost clear) at 16 weeks.
At 16 weeks, 58% and 53% of patients receiving deucravacitinib in the POETYK PSO-1 and POETYK PSO-2 studies, respectively, achieved PASI 75 response, compared with 13% and 9% of those receiving placebo (P < .0001 for both) and 35% and 40% receiving apremilast (P < .0001, P = .0004, respectively), according to the company’s announcement of the approval. PASI 75 responses were maintained through 52 weeks among the patients who remained on treatment, in both studies, according to BMS.
In the POETYK PSO-1 and PSO-2 studies, respectively, 54% and 50% of those on deucravacitinib achieved an sPGA of 0/1 at 16 weeks, compared with 7% and 9% of those receiving placebo (P < .0001 for both) and 32% and 34% of those receiving apremilast (P < .0001 for both).
Across the two studies, at 16 weeks, the most common adverse events that affected at least 1% of patients on deucravacitinib and that occurred at higher rates than in the placebo group were upper respiratory infections (19.2%), increases in serum creatine phosphokinase (2.7%), herpes simplex (2%), mouth ulcers (1.9%), folliculitis (1.7%), and acne (1.4%). Adverse events resulting in discontinuation of treatment were reported in 2.4% of persons receiving deucravacitinib and 5.2% of those receiving apremilast, compared with 3.8% of those receiving placebo.
Up to 16 weeks, according to the BMS statement, 28% of persons receiving deucravacitinib had infections, most of which were mild to moderate and not serious and did not result in stopping treatment, compared with 22% of those receiving placebo. In addition, five patients treated with deucravacitinib and five patients receiving placebo had serious infections, and three patients receiving deucravacitinib had cancer (not including nonmelanoma skin cancer).
Deucravacitinib is also being evaluated in clinical trials for psoriatic arthritis, lupus, and inflammatory bowel disease. It is not recommended for use in combination with other potent immunosuppressants, according to BMS.
The prescribing information and patient medication guide are available online.
The POETYK PSO-1 and POETYK PSO-2 studies were funded by Bristol Myers Squibb.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Flashy, blingy doc sabotages his own malpractice trial in rural farm town
During a medical malpractice trial in New Jersey, jurors waited nearly 4 hours for the physician defendant to show up. When he did arrive, the body-building surgeon was sporting two thick gold chains and a diamond pinky ring, and had the top buttons of his shirt open enough to reveal his chest hair.
“This trial was in a very rural, farming community,” recalls medical liability defense attorney Catherine Flynn, of Flynn Watts LLC, based in Parsippany, N.J. “Many of the jurors were wearing flannel shirts and jeans. The doctor’s wife walked in wearing a five-carat diamond ring and other jewelry.”
Ms. Flynn took the couple aside and asked them to remove the jewelry. She explained that the opulent accessories could damage the jury’s view of the physician. The surgeon and his wife, however, refused to remove their jewelry, she said. They didn’t think it was a big deal.
The case against the surgeon involved intraoperative damage to a patient when the physician inadvertently removed a portion of nerve in the area of the procedure. After repair of the nerve, the patient had a positive result. However, the patient alleged the surgeon’s negligence resulted in permanent damage despite the successful repair.
Jurors ultimately found the physician negligent in the case and awarded the plaintiff $1.2 million. Ms. Flynn believes that physician’s flamboyant attire and arrogant nature tainted the jury’s decision.
“In certain counties in New Jersey, his attire would not have been a problem,” she said. “In this rural, farming county, it was a huge problem. You have to know your audience. There are a lot of other things that come into play in a medical malpractice case, but when it comes to damages in a case, you don’t want to be sending the message that supports what somebody’s bias may already be telling them about a doctor.”
The surgeon appealed the verdict, and the case ultimately settled for a lesser amount, according to Ms. Flynn.
An over-the-top wardrobe is just one way that physicians can negatively influence jurors during legal trials. From subtle facial expressions to sudden outbursts to downright rudeness, attorneys have witnessed countless examples of physicians sabotaging their own trials.
“The minute you enter the courthouse, jurors or potential jurors are sizing you up,” says health law attorney Michael Clark, of Womble Bond Dickinson (US) LLP, based in Houston. “The same phenomenon occurs in a deposition. Awareness of how you are being assessed at all times, and the image that is needed, is important since a negative impression by jurors can have a detrimental effect on a physician’s case.”
Juror: We didn’t like the doctor’s shoes
In another case, attorneys warned a physician defendant against dressing in his signature wardrobe during his trial. Against their advice, the doctor showed up daily to his trial in bright pastel, monochromatic suits with matching Gucci-brand shoes, said medical liability defense attorney Meredith C. Lander, of Kaufman Borgeest & Ryan LLP, based in Connecticut. On the witness stand, the doctor was long-winded and wasn’t “terribly likable,” Ms. Lander said.
However, the evidence weighed in the physician’s favor, and there was strong testimony by defense experts. The physician won the case, Ms. Lander said, but after the verdict, the jury foreperson approached the trial attorney and made some disparaging remarks about the defendant.
“The foreperson said the jury didn’t like the doctor or his ‘Gucci suits and shoes,’ but they believed the experts,” Ms. Lander said.
Disruptive behavior can also harm jurors’ perception of physicians, Ms. Flynn adds. During one instance, a surgeon insisted on sitting next to Ms. Flynn, although she generally requests clients sit in the first row so that jurors are not so focused on their reactions during testimony. The surgeon loudly peppered Ms. Flynn with questions as witnesses testified, prompting a reprimand from the judge.
“The judge admonished the doctor several times and said, ‘Doctor, you’re raising your voice. You’ll get a chance to speak with your attorney during the break,’ ” Ms. Flynn recalled. “The doctor refused to stop talking, and the judge told him in front of the jury to go sit in the back of the courtroom. His reaction was, ‘Why do I have to move?! I need to sit here!’ ”
The surgeon eventually moved to the back of the courtroom and a sheriff’s deputy stood next to him. Testimony continued until a note in the form of a paper airplane landed on the table in front of Ms. Flynn. She carefully crumpled the note and tossed it in the wastebasket. Luckily, this drew a laugh from jurors, she said.
But things got worse when the surgeon testified. Rather than answer the questions, he interrupted and started telling jurors his own version of events.
“The judge finally said, ‘Doctor, if you don’t listen to your attorney and answer her questions, I’m going to make you get off the stand,’ ” Ms. Flynn said. “That was the most unbelievable, egregious self-sabotage trial moment I’ve ever experienced.”
Fortunately, the physician’s legal case was strong, and the experts who testified drove the defense’s side home, Ms. Flynn said. The surgeon won the case.
Attorney: Watch what you say in the elevator
Other, more subtle behaviors – while often unintentional – can also be damaging.
Physicians often let their guard down while outside the courtroom and can unknowingly wind up next to a juror in an elevator or standing in a hallway, said Laura Postilion, a partner at Quintairos, Prieto, Wood & Boyer, P.A., based in Chicago.
“For instance, a doctor is in an elevator and feels that some witness on the stand was lying,” Ms. Postilion said. “They might be very upset about it and start ranting about a witness lying, not realizing there is a juror is in the elevator with you.”
Physicians should also be cautious when speaking on the phone to their family or friends during a trial break.
“At the Daley Center in downtown Chicago, there are these long corridors and long line of windows; a lot of people will stand there during breaks. A doctor may be talking to his or her spouse and saying, ‘Yeah, this juror is sleeping!’ Jurors are [often] looking for drama. They’re looking for somebody letting their guard down. Hearing a doctor speak badly about them would certainly give them a reason to dislike the physician.”
Ms. Postilion warns against talking about jurors in or outside of the courtroom. This includes parking structures, she said.
Physicians can take additional steps to save themselves from negative judgment from jurors, attorneys say. Even before the trial starts, Ms. Postilion advises clients to make their social media accounts private. Some curious jurors may look up a physician’s social media accounts to learn more about their personal life, political leanings, or social beliefs, which could prejudice them against the doctor, she said.
Once on the stand, the words and tone used are key. The last thing a physician defendant wants is to come across as arrogant or condescending to jurors, said medical liability defense attorney Michael Moroney, of Flynn Watts LLC.
“For instance, a defendant might say, ‘Well, let me make this simple for you,’ as if they’re talking to a bunch of schoolchildren,” he said. “You don’t know who’s on the jury. That type of language can be offensive.”
Ms. Lander counsels her clients to refrain from using the common phrase, “honestly,” before answering questions on the stand.
“Everything you’re saying on the stand is presumed to be honest,” she said. “When you start an answer with, ‘Honestly…’ out of habit, it really does undercut everything that follows and everything else that’s already been said. It suggests that you were not being honest in your other answers.”
Attitude, body language speak volumes
Keep in mind that plaintiffs’ attorneys will try their best to rattle physicians on the stand and get them to appear unlikeable, says Mr. Clark, the Houston-based health law attorney. Physicians who lose their cool and begin arguing with attorneys play into their strategy.
“Plaintiffs’ attorneys have been trained in ways to get under their skin,” he said. “Righteous indignation and annoyance are best left for a rare occasion. Think about how you feel in a social setting when people are bickering in front of you. It’s uncomfortable at best. That’s how a jury feels too.”
Body language is also important, Mr. Clark notes. Physicians should avoid crossed arms, leaning back and rocking, or putting a hand on their mouth while testifying, he said. Many attorneys have practice sessions with their clients and record the interaction so that doctors can watch it and see how they look.
“Know your strengths and weaknesses,” he said. “Get help from your lawyer and perhaps consultants about how to improve these skills. Practice and preparation are important.”
Ms. Postilion goes over courtroom clothing with physician clients before trial. Anything “too flashy, too high-end, or too dumpy” should be avoided, she said. Getting accustomed to the courtroom and practicing in an empty courtroom are good ways to ensure that a physician’s voice is loud enough and projecting far enough in the courtroom, she adds.
“The doctor should try to be the best version of him- or herself to jurors,” she said. “A jury can pick up someone who’s trying to be something they’re not. A good attorney can help the doctor find the best version of themselves and capitalize on it. What is it that you want the jury to know about your care of the patient? Take that overall feeling and make sure it’s clearly expressed to the jury.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
During a medical malpractice trial in New Jersey, jurors waited nearly 4 hours for the physician defendant to show up. When he did arrive, the body-building surgeon was sporting two thick gold chains and a diamond pinky ring, and had the top buttons of his shirt open enough to reveal his chest hair.
“This trial was in a very rural, farming community,” recalls medical liability defense attorney Catherine Flynn, of Flynn Watts LLC, based in Parsippany, N.J. “Many of the jurors were wearing flannel shirts and jeans. The doctor’s wife walked in wearing a five-carat diamond ring and other jewelry.”
Ms. Flynn took the couple aside and asked them to remove the jewelry. She explained that the opulent accessories could damage the jury’s view of the physician. The surgeon and his wife, however, refused to remove their jewelry, she said. They didn’t think it was a big deal.
The case against the surgeon involved intraoperative damage to a patient when the physician inadvertently removed a portion of nerve in the area of the procedure. After repair of the nerve, the patient had a positive result. However, the patient alleged the surgeon’s negligence resulted in permanent damage despite the successful repair.
Jurors ultimately found the physician negligent in the case and awarded the plaintiff $1.2 million. Ms. Flynn believes that physician’s flamboyant attire and arrogant nature tainted the jury’s decision.
“In certain counties in New Jersey, his attire would not have been a problem,” she said. “In this rural, farming county, it was a huge problem. You have to know your audience. There are a lot of other things that come into play in a medical malpractice case, but when it comes to damages in a case, you don’t want to be sending the message that supports what somebody’s bias may already be telling them about a doctor.”
The surgeon appealed the verdict, and the case ultimately settled for a lesser amount, according to Ms. Flynn.
An over-the-top wardrobe is just one way that physicians can negatively influence jurors during legal trials. From subtle facial expressions to sudden outbursts to downright rudeness, attorneys have witnessed countless examples of physicians sabotaging their own trials.
“The minute you enter the courthouse, jurors or potential jurors are sizing you up,” says health law attorney Michael Clark, of Womble Bond Dickinson (US) LLP, based in Houston. “The same phenomenon occurs in a deposition. Awareness of how you are being assessed at all times, and the image that is needed, is important since a negative impression by jurors can have a detrimental effect on a physician’s case.”
Juror: We didn’t like the doctor’s shoes
In another case, attorneys warned a physician defendant against dressing in his signature wardrobe during his trial. Against their advice, the doctor showed up daily to his trial in bright pastel, monochromatic suits with matching Gucci-brand shoes, said medical liability defense attorney Meredith C. Lander, of Kaufman Borgeest & Ryan LLP, based in Connecticut. On the witness stand, the doctor was long-winded and wasn’t “terribly likable,” Ms. Lander said.
However, the evidence weighed in the physician’s favor, and there was strong testimony by defense experts. The physician won the case, Ms. Lander said, but after the verdict, the jury foreperson approached the trial attorney and made some disparaging remarks about the defendant.
“The foreperson said the jury didn’t like the doctor or his ‘Gucci suits and shoes,’ but they believed the experts,” Ms. Lander said.
Disruptive behavior can also harm jurors’ perception of physicians, Ms. Flynn adds. During one instance, a surgeon insisted on sitting next to Ms. Flynn, although she generally requests clients sit in the first row so that jurors are not so focused on their reactions during testimony. The surgeon loudly peppered Ms. Flynn with questions as witnesses testified, prompting a reprimand from the judge.
“The judge admonished the doctor several times and said, ‘Doctor, you’re raising your voice. You’ll get a chance to speak with your attorney during the break,’ ” Ms. Flynn recalled. “The doctor refused to stop talking, and the judge told him in front of the jury to go sit in the back of the courtroom. His reaction was, ‘Why do I have to move?! I need to sit here!’ ”
The surgeon eventually moved to the back of the courtroom and a sheriff’s deputy stood next to him. Testimony continued until a note in the form of a paper airplane landed on the table in front of Ms. Flynn. She carefully crumpled the note and tossed it in the wastebasket. Luckily, this drew a laugh from jurors, she said.
But things got worse when the surgeon testified. Rather than answer the questions, he interrupted and started telling jurors his own version of events.
“The judge finally said, ‘Doctor, if you don’t listen to your attorney and answer her questions, I’m going to make you get off the stand,’ ” Ms. Flynn said. “That was the most unbelievable, egregious self-sabotage trial moment I’ve ever experienced.”
Fortunately, the physician’s legal case was strong, and the experts who testified drove the defense’s side home, Ms. Flynn said. The surgeon won the case.
Attorney: Watch what you say in the elevator
Other, more subtle behaviors – while often unintentional – can also be damaging.
Physicians often let their guard down while outside the courtroom and can unknowingly wind up next to a juror in an elevator or standing in a hallway, said Laura Postilion, a partner at Quintairos, Prieto, Wood & Boyer, P.A., based in Chicago.
“For instance, a doctor is in an elevator and feels that some witness on the stand was lying,” Ms. Postilion said. “They might be very upset about it and start ranting about a witness lying, not realizing there is a juror is in the elevator with you.”
Physicians should also be cautious when speaking on the phone to their family or friends during a trial break.
“At the Daley Center in downtown Chicago, there are these long corridors and long line of windows; a lot of people will stand there during breaks. A doctor may be talking to his or her spouse and saying, ‘Yeah, this juror is sleeping!’ Jurors are [often] looking for drama. They’re looking for somebody letting their guard down. Hearing a doctor speak badly about them would certainly give them a reason to dislike the physician.”
Ms. Postilion warns against talking about jurors in or outside of the courtroom. This includes parking structures, she said.
Physicians can take additional steps to save themselves from negative judgment from jurors, attorneys say. Even before the trial starts, Ms. Postilion advises clients to make their social media accounts private. Some curious jurors may look up a physician’s social media accounts to learn more about their personal life, political leanings, or social beliefs, which could prejudice them against the doctor, she said.
Once on the stand, the words and tone used are key. The last thing a physician defendant wants is to come across as arrogant or condescending to jurors, said medical liability defense attorney Michael Moroney, of Flynn Watts LLC.
“For instance, a defendant might say, ‘Well, let me make this simple for you,’ as if they’re talking to a bunch of schoolchildren,” he said. “You don’t know who’s on the jury. That type of language can be offensive.”
Ms. Lander counsels her clients to refrain from using the common phrase, “honestly,” before answering questions on the stand.
“Everything you’re saying on the stand is presumed to be honest,” she said. “When you start an answer with, ‘Honestly…’ out of habit, it really does undercut everything that follows and everything else that’s already been said. It suggests that you were not being honest in your other answers.”
Attitude, body language speak volumes
Keep in mind that plaintiffs’ attorneys will try their best to rattle physicians on the stand and get them to appear unlikeable, says Mr. Clark, the Houston-based health law attorney. Physicians who lose their cool and begin arguing with attorneys play into their strategy.
“Plaintiffs’ attorneys have been trained in ways to get under their skin,” he said. “Righteous indignation and annoyance are best left for a rare occasion. Think about how you feel in a social setting when people are bickering in front of you. It’s uncomfortable at best. That’s how a jury feels too.”
Body language is also important, Mr. Clark notes. Physicians should avoid crossed arms, leaning back and rocking, or putting a hand on their mouth while testifying, he said. Many attorneys have practice sessions with their clients and record the interaction so that doctors can watch it and see how they look.
“Know your strengths and weaknesses,” he said. “Get help from your lawyer and perhaps consultants about how to improve these skills. Practice and preparation are important.”
Ms. Postilion goes over courtroom clothing with physician clients before trial. Anything “too flashy, too high-end, or too dumpy” should be avoided, she said. Getting accustomed to the courtroom and practicing in an empty courtroom are good ways to ensure that a physician’s voice is loud enough and projecting far enough in the courtroom, she adds.
“The doctor should try to be the best version of him- or herself to jurors,” she said. “A jury can pick up someone who’s trying to be something they’re not. A good attorney can help the doctor find the best version of themselves and capitalize on it. What is it that you want the jury to know about your care of the patient? Take that overall feeling and make sure it’s clearly expressed to the jury.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
During a medical malpractice trial in New Jersey, jurors waited nearly 4 hours for the physician defendant to show up. When he did arrive, the body-building surgeon was sporting two thick gold chains and a diamond pinky ring, and had the top buttons of his shirt open enough to reveal his chest hair.
“This trial was in a very rural, farming community,” recalls medical liability defense attorney Catherine Flynn, of Flynn Watts LLC, based in Parsippany, N.J. “Many of the jurors were wearing flannel shirts and jeans. The doctor’s wife walked in wearing a five-carat diamond ring and other jewelry.”
Ms. Flynn took the couple aside and asked them to remove the jewelry. She explained that the opulent accessories could damage the jury’s view of the physician. The surgeon and his wife, however, refused to remove their jewelry, she said. They didn’t think it was a big deal.
The case against the surgeon involved intraoperative damage to a patient when the physician inadvertently removed a portion of nerve in the area of the procedure. After repair of the nerve, the patient had a positive result. However, the patient alleged the surgeon’s negligence resulted in permanent damage despite the successful repair.
Jurors ultimately found the physician negligent in the case and awarded the plaintiff $1.2 million. Ms. Flynn believes that physician’s flamboyant attire and arrogant nature tainted the jury’s decision.
“In certain counties in New Jersey, his attire would not have been a problem,” she said. “In this rural, farming county, it was a huge problem. You have to know your audience. There are a lot of other things that come into play in a medical malpractice case, but when it comes to damages in a case, you don’t want to be sending the message that supports what somebody’s bias may already be telling them about a doctor.”
The surgeon appealed the verdict, and the case ultimately settled for a lesser amount, according to Ms. Flynn.
An over-the-top wardrobe is just one way that physicians can negatively influence jurors during legal trials. From subtle facial expressions to sudden outbursts to downright rudeness, attorneys have witnessed countless examples of physicians sabotaging their own trials.
“The minute you enter the courthouse, jurors or potential jurors are sizing you up,” says health law attorney Michael Clark, of Womble Bond Dickinson (US) LLP, based in Houston. “The same phenomenon occurs in a deposition. Awareness of how you are being assessed at all times, and the image that is needed, is important since a negative impression by jurors can have a detrimental effect on a physician’s case.”
Juror: We didn’t like the doctor’s shoes
In another case, attorneys warned a physician defendant against dressing in his signature wardrobe during his trial. Against their advice, the doctor showed up daily to his trial in bright pastel, monochromatic suits with matching Gucci-brand shoes, said medical liability defense attorney Meredith C. Lander, of Kaufman Borgeest & Ryan LLP, based in Connecticut. On the witness stand, the doctor was long-winded and wasn’t “terribly likable,” Ms. Lander said.
However, the evidence weighed in the physician’s favor, and there was strong testimony by defense experts. The physician won the case, Ms. Lander said, but after the verdict, the jury foreperson approached the trial attorney and made some disparaging remarks about the defendant.
“The foreperson said the jury didn’t like the doctor or his ‘Gucci suits and shoes,’ but they believed the experts,” Ms. Lander said.
Disruptive behavior can also harm jurors’ perception of physicians, Ms. Flynn adds. During one instance, a surgeon insisted on sitting next to Ms. Flynn, although she generally requests clients sit in the first row so that jurors are not so focused on their reactions during testimony. The surgeon loudly peppered Ms. Flynn with questions as witnesses testified, prompting a reprimand from the judge.
“The judge admonished the doctor several times and said, ‘Doctor, you’re raising your voice. You’ll get a chance to speak with your attorney during the break,’ ” Ms. Flynn recalled. “The doctor refused to stop talking, and the judge told him in front of the jury to go sit in the back of the courtroom. His reaction was, ‘Why do I have to move?! I need to sit here!’ ”
The surgeon eventually moved to the back of the courtroom and a sheriff’s deputy stood next to him. Testimony continued until a note in the form of a paper airplane landed on the table in front of Ms. Flynn. She carefully crumpled the note and tossed it in the wastebasket. Luckily, this drew a laugh from jurors, she said.
But things got worse when the surgeon testified. Rather than answer the questions, he interrupted and started telling jurors his own version of events.
“The judge finally said, ‘Doctor, if you don’t listen to your attorney and answer her questions, I’m going to make you get off the stand,’ ” Ms. Flynn said. “That was the most unbelievable, egregious self-sabotage trial moment I’ve ever experienced.”
Fortunately, the physician’s legal case was strong, and the experts who testified drove the defense’s side home, Ms. Flynn said. The surgeon won the case.
Attorney: Watch what you say in the elevator
Other, more subtle behaviors – while often unintentional – can also be damaging.
Physicians often let their guard down while outside the courtroom and can unknowingly wind up next to a juror in an elevator or standing in a hallway, said Laura Postilion, a partner at Quintairos, Prieto, Wood & Boyer, P.A., based in Chicago.
“For instance, a doctor is in an elevator and feels that some witness on the stand was lying,” Ms. Postilion said. “They might be very upset about it and start ranting about a witness lying, not realizing there is a juror is in the elevator with you.”
Physicians should also be cautious when speaking on the phone to their family or friends during a trial break.
“At the Daley Center in downtown Chicago, there are these long corridors and long line of windows; a lot of people will stand there during breaks. A doctor may be talking to his or her spouse and saying, ‘Yeah, this juror is sleeping!’ Jurors are [often] looking for drama. They’re looking for somebody letting their guard down. Hearing a doctor speak badly about them would certainly give them a reason to dislike the physician.”
Ms. Postilion warns against talking about jurors in or outside of the courtroom. This includes parking structures, she said.
Physicians can take additional steps to save themselves from negative judgment from jurors, attorneys say. Even before the trial starts, Ms. Postilion advises clients to make their social media accounts private. Some curious jurors may look up a physician’s social media accounts to learn more about their personal life, political leanings, or social beliefs, which could prejudice them against the doctor, she said.
Once on the stand, the words and tone used are key. The last thing a physician defendant wants is to come across as arrogant or condescending to jurors, said medical liability defense attorney Michael Moroney, of Flynn Watts LLC.
“For instance, a defendant might say, ‘Well, let me make this simple for you,’ as if they’re talking to a bunch of schoolchildren,” he said. “You don’t know who’s on the jury. That type of language can be offensive.”
Ms. Lander counsels her clients to refrain from using the common phrase, “honestly,” before answering questions on the stand.
“Everything you’re saying on the stand is presumed to be honest,” she said. “When you start an answer with, ‘Honestly…’ out of habit, it really does undercut everything that follows and everything else that’s already been said. It suggests that you were not being honest in your other answers.”
Attitude, body language speak volumes
Keep in mind that plaintiffs’ attorneys will try their best to rattle physicians on the stand and get them to appear unlikeable, says Mr. Clark, the Houston-based health law attorney. Physicians who lose their cool and begin arguing with attorneys play into their strategy.
“Plaintiffs’ attorneys have been trained in ways to get under their skin,” he said. “Righteous indignation and annoyance are best left for a rare occasion. Think about how you feel in a social setting when people are bickering in front of you. It’s uncomfortable at best. That’s how a jury feels too.”
Body language is also important, Mr. Clark notes. Physicians should avoid crossed arms, leaning back and rocking, or putting a hand on their mouth while testifying, he said. Many attorneys have practice sessions with their clients and record the interaction so that doctors can watch it and see how they look.
“Know your strengths and weaknesses,” he said. “Get help from your lawyer and perhaps consultants about how to improve these skills. Practice and preparation are important.”
Ms. Postilion goes over courtroom clothing with physician clients before trial. Anything “too flashy, too high-end, or too dumpy” should be avoided, she said. Getting accustomed to the courtroom and practicing in an empty courtroom are good ways to ensure that a physician’s voice is loud enough and projecting far enough in the courtroom, she adds.
“The doctor should try to be the best version of him- or herself to jurors,” she said. “A jury can pick up someone who’s trying to be something they’re not. A good attorney can help the doctor find the best version of themselves and capitalize on it. What is it that you want the jury to know about your care of the patient? Take that overall feeling and make sure it’s clearly expressed to the jury.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Overall survival dips with vitamin D deficiency in melanoma
, according to research presented at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Whereas the 5-year overall survival was 90% when vitamin D serum levels were above a 10 ng/mL threshold, it was 84% when levels fell below it. Notably, the gap in overall survival between those above and below the threshold appeared to widen as time went on.
The research adds to existing evidence that “vitamin D levels can play an important and independent role in patients’ survival outcomes,” study investigator Inés Gracia-Darder, MD, told this news organization. “The important application in clinical practice would be to know if vitamin D supplementation influences the survival of melanoma patients,” said Dr. Gracia-Darder, a clinical specialist in dermatology at the Hospital Universitari Son Espases, Mallorca, Spain.
Known association, but not much data
“It is not a new finding,” but there are limited data, especially in melanoma, said Julie De Smedt, MD, of KU Leuven, Belgium, who was asked to comment on the results. Other groups have shown, certainly for cancer in general, that vitamin D can have an effect on overall survival.
“Low levels of vitamin D are associated with the pathological parameters of the melanoma, such as the thickness of the tumor,” Dr. De Smedt said in an interview, indicating that it’s not just overall survival that might be affected.
“So we assume that also has an effect on melanoma-specific survival,” she added.
That assumption, however, is not supported by the data Dr. Gracia-Darder presented, as there was no difference in melanoma-specific survival among the two groups of patients that had been studied.
Retrospective cohort analysis
Vitamin D levels had been studied in 264 patients who were included in the retrospective cohort analysis. All had invasive melanomas, and all had been seen at the Hospital Clinic of Barcelona between January 1998 and June 2021. Their mean age was 57 years, and the median follow-up was 6.7 years.
For inclusion, all patients had to have had their vitamin D levels measured after being diagnosed with melanoma; those with a 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 serum level of less than 10 ng/mL were deemed to be vitamin D deficient, whereas those with levels of 10 ng/mL and above were deemed normal or insufficient.
A measurement less than 10 ng/mL is considered vitamin D deficiency, Dr. De Smedt said. “But there is a difference between countries, and there’s also a difference between societies,” noting the cut-off used in the lab where she works is 20 ng/mL. This makes it difficult to compare studies, she said.
Independent association with overall survival
Seasonal variation in vitamin D levels were considered as a possible confounding factor, but Dr. Gracia-Darder noted that there was a similar distribution of measurements taken between October to March and April to September.
Univariate and multivariate analyses established vitamin D deficiency as being independently associated with overall survival with hazard ratios of 2.34 and 2.45, respectively.
Other predictive factors were having a higher Breslow index, as well as older age and gender.
Time to recommend vitamin D supplementation?
So should patients with melanoma have their vitamin D levels routinely checked? And what about advising them to take vitamin D supplements?
“In our practice, we analyze the vitamin D levels of our patients,” Dr. Gracia-Darder said. Patients are told to limit their exposure to the sun because of their skin cancer, so they are very likely to become vitamin D deficient.
While dietary changes or supplements might be suggested, there’s no real evidence to support upping vitamin D levels to date, so “future prospective studies are needed,” Dr. Gracia-Darder added.
Such studies have already started, including one in Italy, one in Australia, and another study that Dr. De Smedt has been involved with for the past few years.
Called the ViDMe study, it’s a multicenter, randomized, double-blind trial in which patients are being given a high-dose oral vitamin D supplement or placebo once a month for at least 1 year. About 430 patients with a first cutaneous malignant melanoma have been included in the trial, which started in December 2012.
It is hoped that the results will show that the supplementation will have had a protective effect on the risk of relapse and that there will be a correlation between vitamin D levels in the blood and vitamin D receptor immunoreactivity in the tumor.
“The study is still blinded,” Dr. De Smedt said. “We will unblind in the coming months and then at the end of the year, maybe next year, we will have the results.”
The study reported by Dr. Gracia-Darder did not receive any specific funding. Dr. Gracia-Darder disclosed that the melanoma unit where the study was performed receives many grants and funds to carry out research. She reported no other relevant financial relationships. Dr. De Smedt had no relevant financial relationships. The ViDMe study is sponsored by the Universitaire Ziekenhuizen Leuven.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to research presented at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Whereas the 5-year overall survival was 90% when vitamin D serum levels were above a 10 ng/mL threshold, it was 84% when levels fell below it. Notably, the gap in overall survival between those above and below the threshold appeared to widen as time went on.
The research adds to existing evidence that “vitamin D levels can play an important and independent role in patients’ survival outcomes,” study investigator Inés Gracia-Darder, MD, told this news organization. “The important application in clinical practice would be to know if vitamin D supplementation influences the survival of melanoma patients,” said Dr. Gracia-Darder, a clinical specialist in dermatology at the Hospital Universitari Son Espases, Mallorca, Spain.
Known association, but not much data
“It is not a new finding,” but there are limited data, especially in melanoma, said Julie De Smedt, MD, of KU Leuven, Belgium, who was asked to comment on the results. Other groups have shown, certainly for cancer in general, that vitamin D can have an effect on overall survival.
“Low levels of vitamin D are associated with the pathological parameters of the melanoma, such as the thickness of the tumor,” Dr. De Smedt said in an interview, indicating that it’s not just overall survival that might be affected.
“So we assume that also has an effect on melanoma-specific survival,” she added.
That assumption, however, is not supported by the data Dr. Gracia-Darder presented, as there was no difference in melanoma-specific survival among the two groups of patients that had been studied.
Retrospective cohort analysis
Vitamin D levels had been studied in 264 patients who were included in the retrospective cohort analysis. All had invasive melanomas, and all had been seen at the Hospital Clinic of Barcelona between January 1998 and June 2021. Their mean age was 57 years, and the median follow-up was 6.7 years.
For inclusion, all patients had to have had their vitamin D levels measured after being diagnosed with melanoma; those with a 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 serum level of less than 10 ng/mL were deemed to be vitamin D deficient, whereas those with levels of 10 ng/mL and above were deemed normal or insufficient.
A measurement less than 10 ng/mL is considered vitamin D deficiency, Dr. De Smedt said. “But there is a difference between countries, and there’s also a difference between societies,” noting the cut-off used in the lab where she works is 20 ng/mL. This makes it difficult to compare studies, she said.
Independent association with overall survival
Seasonal variation in vitamin D levels were considered as a possible confounding factor, but Dr. Gracia-Darder noted that there was a similar distribution of measurements taken between October to March and April to September.
Univariate and multivariate analyses established vitamin D deficiency as being independently associated with overall survival with hazard ratios of 2.34 and 2.45, respectively.
Other predictive factors were having a higher Breslow index, as well as older age and gender.
Time to recommend vitamin D supplementation?
So should patients with melanoma have their vitamin D levels routinely checked? And what about advising them to take vitamin D supplements?
“In our practice, we analyze the vitamin D levels of our patients,” Dr. Gracia-Darder said. Patients are told to limit their exposure to the sun because of their skin cancer, so they are very likely to become vitamin D deficient.
While dietary changes or supplements might be suggested, there’s no real evidence to support upping vitamin D levels to date, so “future prospective studies are needed,” Dr. Gracia-Darder added.
Such studies have already started, including one in Italy, one in Australia, and another study that Dr. De Smedt has been involved with for the past few years.
Called the ViDMe study, it’s a multicenter, randomized, double-blind trial in which patients are being given a high-dose oral vitamin D supplement or placebo once a month for at least 1 year. About 430 patients with a first cutaneous malignant melanoma have been included in the trial, which started in December 2012.
It is hoped that the results will show that the supplementation will have had a protective effect on the risk of relapse and that there will be a correlation between vitamin D levels in the blood and vitamin D receptor immunoreactivity in the tumor.
“The study is still blinded,” Dr. De Smedt said. “We will unblind in the coming months and then at the end of the year, maybe next year, we will have the results.”
The study reported by Dr. Gracia-Darder did not receive any specific funding. Dr. Gracia-Darder disclosed that the melanoma unit where the study was performed receives many grants and funds to carry out research. She reported no other relevant financial relationships. Dr. De Smedt had no relevant financial relationships. The ViDMe study is sponsored by the Universitaire Ziekenhuizen Leuven.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to research presented at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Whereas the 5-year overall survival was 90% when vitamin D serum levels were above a 10 ng/mL threshold, it was 84% when levels fell below it. Notably, the gap in overall survival between those above and below the threshold appeared to widen as time went on.
The research adds to existing evidence that “vitamin D levels can play an important and independent role in patients’ survival outcomes,” study investigator Inés Gracia-Darder, MD, told this news organization. “The important application in clinical practice would be to know if vitamin D supplementation influences the survival of melanoma patients,” said Dr. Gracia-Darder, a clinical specialist in dermatology at the Hospital Universitari Son Espases, Mallorca, Spain.
Known association, but not much data
“It is not a new finding,” but there are limited data, especially in melanoma, said Julie De Smedt, MD, of KU Leuven, Belgium, who was asked to comment on the results. Other groups have shown, certainly for cancer in general, that vitamin D can have an effect on overall survival.
“Low levels of vitamin D are associated with the pathological parameters of the melanoma, such as the thickness of the tumor,” Dr. De Smedt said in an interview, indicating that it’s not just overall survival that might be affected.
“So we assume that also has an effect on melanoma-specific survival,” she added.
That assumption, however, is not supported by the data Dr. Gracia-Darder presented, as there was no difference in melanoma-specific survival among the two groups of patients that had been studied.
Retrospective cohort analysis
Vitamin D levels had been studied in 264 patients who were included in the retrospective cohort analysis. All had invasive melanomas, and all had been seen at the Hospital Clinic of Barcelona between January 1998 and June 2021. Their mean age was 57 years, and the median follow-up was 6.7 years.
For inclusion, all patients had to have had their vitamin D levels measured after being diagnosed with melanoma; those with a 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 serum level of less than 10 ng/mL were deemed to be vitamin D deficient, whereas those with levels of 10 ng/mL and above were deemed normal or insufficient.
A measurement less than 10 ng/mL is considered vitamin D deficiency, Dr. De Smedt said. “But there is a difference between countries, and there’s also a difference between societies,” noting the cut-off used in the lab where she works is 20 ng/mL. This makes it difficult to compare studies, she said.
Independent association with overall survival
Seasonal variation in vitamin D levels were considered as a possible confounding factor, but Dr. Gracia-Darder noted that there was a similar distribution of measurements taken between October to March and April to September.
Univariate and multivariate analyses established vitamin D deficiency as being independently associated with overall survival with hazard ratios of 2.34 and 2.45, respectively.
Other predictive factors were having a higher Breslow index, as well as older age and gender.
Time to recommend vitamin D supplementation?
So should patients with melanoma have their vitamin D levels routinely checked? And what about advising them to take vitamin D supplements?
“In our practice, we analyze the vitamin D levels of our patients,” Dr. Gracia-Darder said. Patients are told to limit their exposure to the sun because of their skin cancer, so they are very likely to become vitamin D deficient.
While dietary changes or supplements might be suggested, there’s no real evidence to support upping vitamin D levels to date, so “future prospective studies are needed,” Dr. Gracia-Darder added.
Such studies have already started, including one in Italy, one in Australia, and another study that Dr. De Smedt has been involved with for the past few years.
Called the ViDMe study, it’s a multicenter, randomized, double-blind trial in which patients are being given a high-dose oral vitamin D supplement or placebo once a month for at least 1 year. About 430 patients with a first cutaneous malignant melanoma have been included in the trial, which started in December 2012.
It is hoped that the results will show that the supplementation will have had a protective effect on the risk of relapse and that there will be a correlation between vitamin D levels in the blood and vitamin D receptor immunoreactivity in the tumor.
“The study is still blinded,” Dr. De Smedt said. “We will unblind in the coming months and then at the end of the year, maybe next year, we will have the results.”
The study reported by Dr. Gracia-Darder did not receive any specific funding. Dr. Gracia-Darder disclosed that the melanoma unit where the study was performed receives many grants and funds to carry out research. She reported no other relevant financial relationships. Dr. De Smedt had no relevant financial relationships. The ViDMe study is sponsored by the Universitaire Ziekenhuizen Leuven.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE EADV CONGRESS
Hidradenitis Suppurativa
THE PRESENTATION
Severe long-standing hidradenitis suppurativa (Hurley stage III) with architectural changes, ropy scarring, granulation tissue, and purulent discharge in the axilla of a 35-year-old Black man (A) and a 42-year-old Hispanic woman with a light skin tone (B).
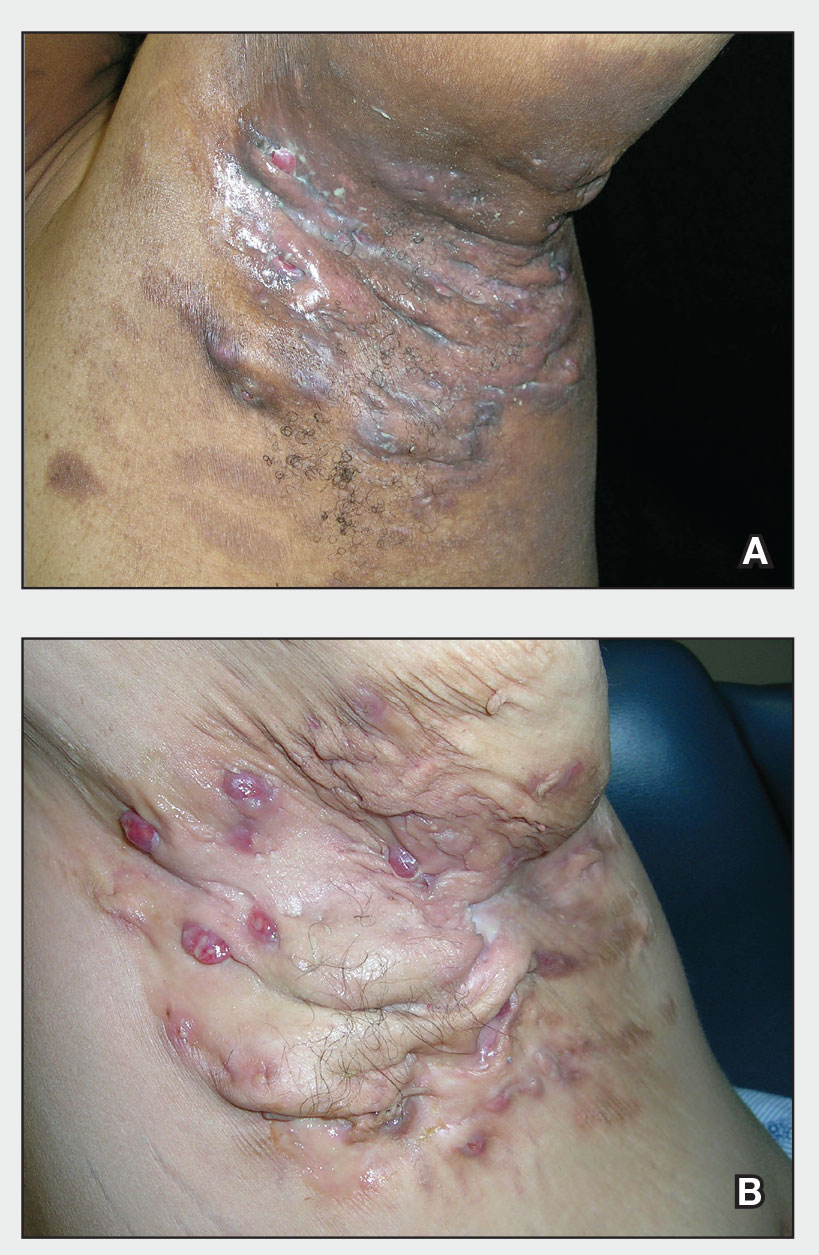
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory condition of the follicular epithelium that most commonly is found in the axillae and buttocks, as well as the inguinal, perianal, and submammary areas. It is characterized by firm and tender chronic nodules, abscesses complicated by sinus tracts, fistulae, and scarring thought to be related to follicular occlusion. Double-open comedones also may be seen.
The Hurley staging system is widely used to characterize the extent of disease in HS patients:
- Stage I (mild): nodule(s) and abscess(es) without sinus tracts (tunnels) or scarring;
- Stage II (moderate): recurrent nodule(s) and abscess(es) with a limited number of sinus tracts (tunnels) and/or scarring; and
- Stage III (severe): multiple or extensive sinus tracts (tunnels), abscesses, and/or scarring across the entire area.
Epidemiology
Hidradenitis suppurativa is most common in adults and African American patients. It has a prevalence of 1.3% in African Americans.1 When it occurs in children, it generally develops after the onset of puberty. The incidence is higher in females as well as individuals with a history of smoking and obesity (a higher body mass index).2-5
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
The erythema associated with HS may be difficult to see in darker skin tones, but violaceous, dark brown, and gray lesions may be present. When active HS lesions subside, intense hyperpigmentation may be left behind, and in some skin tones a pink or violaceous lesion may be apparent.
Worth noting
Hidradenitis suppurativa is disfiguring and has a negative impact on quality of life, including social relationships. Mental health support and screening tools are useful. Pain also is a common concern and may warrant referral to a pain specialist.6 In early disease, HS lesions can be misdiagnosed as an infection that recurs in the same location.
Treatments for HS include oral antibiotics (ie, tetracyclines, rifampin, clindamycin), topical antibiotics, immunosuppressing biologics, metformin, and spironolactone.7 Surgical interventions may be considered earlier in HS management and vary based on the location and severity of the lesions.8
Patients with HS are at risk for developing squamous cell carcinoma in scars even many years later9; therefore, patients should perform skin checks and be referred to a dermatologist. Squamous cell carcinoma is most commonly found on the buttocks of men with HS and has a poor prognosis.
Health disparity highlight
Although those of African American and African descent have the highest rates of HS,1 the clinical trials for adalimumab (the only biologic approved for HS) enrolled a low number of Black patients.
Thirty HS comorbidities have been identified. Garg et al10 recommended that dermatologists perform examinations for comorbid conditions involving the skin and conduct a simple review of systems for extracutaneous comorbidities. Access to medical care is essential, and health care system barriers affect the ability of some patients to receive adequate continuity of care.
The diagnosis of HS often is delayed due to lack of HS knowledge about the condition in the medical community at large and delayed presentation to a dermatologist.
- Sachdeva M, Shah M, Alavi A. Race-specific prevalence of hidradenitis suppurativa [published online November 11, 2020]. J Cutan Med Surg. 2021;25:177-187. doi:10.1177/1203475420972348
- Zouboulis CC, Goyal M, Byrd AS. Hidradenitis suppurativa in skin of colour. Exp Dermatol. 2021;30(suppl 1):27-30. doi:10.1111 /exd.14341
- Shalom G, Cohen AD. The epidemiology of hidradenitis suppurativa: what do we know? Br J Dermatol. 2019;180:712-713.
- Theut Riis P, Pedersen OB, Sigsgaard V, et al. Prevalence of patients with self-reported hidradenitis suppurativa in a cohort of Danish blood donors: a cross-sectional study. Br J Dermatol. 2019;180:774-781.
- Jemec GB, Kimball AB. Hidradenitis suppurativa: epidemiology and scope of the problem. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73 (5 suppl 1):S4-S7.
- Savage KT, Singh V, Patel ZS, et al. Pain management in hidradenitis suppurativa and a proposed treatment algorithm [published online September 17, 2020]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:187-199. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.09.039
- Alikhan A, Sayed C, Alavi A, et al. North American clinical management guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa: a publication from the United States and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations: part II: topical, intralesional, and systemic medical management [published online March 11, 2019]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:91-101.
- Vellaichamy G, Braunberger TL, Nahhas AF, et al. Surgical procedures for hidradenitis suppurativa. Cutis. 2018;102:13-16.
- Jung JM, Lee KH, Kim Y-J, et al. Assessment of overall and specific cancer risks in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:844-853.
- Garg A, Malviya N, Strunk A, et al. Comorbidity screening in hidradenitis suppurativa: evidence-based recommendations from the US and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations [published online January 23, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1092-1101. doi:10.1016/j. jaad.2021.01.059
THE PRESENTATION
Severe long-standing hidradenitis suppurativa (Hurley stage III) with architectural changes, ropy scarring, granulation tissue, and purulent discharge in the axilla of a 35-year-old Black man (A) and a 42-year-old Hispanic woman with a light skin tone (B).

Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory condition of the follicular epithelium that most commonly is found in the axillae and buttocks, as well as the inguinal, perianal, and submammary areas. It is characterized by firm and tender chronic nodules, abscesses complicated by sinus tracts, fistulae, and scarring thought to be related to follicular occlusion. Double-open comedones also may be seen.
The Hurley staging system is widely used to characterize the extent of disease in HS patients:
- Stage I (mild): nodule(s) and abscess(es) without sinus tracts (tunnels) or scarring;
- Stage II (moderate): recurrent nodule(s) and abscess(es) with a limited number of sinus tracts (tunnels) and/or scarring; and
- Stage III (severe): multiple or extensive sinus tracts (tunnels), abscesses, and/or scarring across the entire area.
Epidemiology
Hidradenitis suppurativa is most common in adults and African American patients. It has a prevalence of 1.3% in African Americans.1 When it occurs in children, it generally develops after the onset of puberty. The incidence is higher in females as well as individuals with a history of smoking and obesity (a higher body mass index).2-5
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
The erythema associated with HS may be difficult to see in darker skin tones, but violaceous, dark brown, and gray lesions may be present. When active HS lesions subside, intense hyperpigmentation may be left behind, and in some skin tones a pink or violaceous lesion may be apparent.
Worth noting
Hidradenitis suppurativa is disfiguring and has a negative impact on quality of life, including social relationships. Mental health support and screening tools are useful. Pain also is a common concern and may warrant referral to a pain specialist.6 In early disease, HS lesions can be misdiagnosed as an infection that recurs in the same location.
Treatments for HS include oral antibiotics (ie, tetracyclines, rifampin, clindamycin), topical antibiotics, immunosuppressing biologics, metformin, and spironolactone.7 Surgical interventions may be considered earlier in HS management and vary based on the location and severity of the lesions.8
Patients with HS are at risk for developing squamous cell carcinoma in scars even many years later9; therefore, patients should perform skin checks and be referred to a dermatologist. Squamous cell carcinoma is most commonly found on the buttocks of men with HS and has a poor prognosis.
Health disparity highlight
Although those of African American and African descent have the highest rates of HS,1 the clinical trials for adalimumab (the only biologic approved for HS) enrolled a low number of Black patients.
Thirty HS comorbidities have been identified. Garg et al10 recommended that dermatologists perform examinations for comorbid conditions involving the skin and conduct a simple review of systems for extracutaneous comorbidities. Access to medical care is essential, and health care system barriers affect the ability of some patients to receive adequate continuity of care.
The diagnosis of HS often is delayed due to lack of HS knowledge about the condition in the medical community at large and delayed presentation to a dermatologist.
THE PRESENTATION
Severe long-standing hidradenitis suppurativa (Hurley stage III) with architectural changes, ropy scarring, granulation tissue, and purulent discharge in the axilla of a 35-year-old Black man (A) and a 42-year-old Hispanic woman with a light skin tone (B).

Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory condition of the follicular epithelium that most commonly is found in the axillae and buttocks, as well as the inguinal, perianal, and submammary areas. It is characterized by firm and tender chronic nodules, abscesses complicated by sinus tracts, fistulae, and scarring thought to be related to follicular occlusion. Double-open comedones also may be seen.
The Hurley staging system is widely used to characterize the extent of disease in HS patients:
- Stage I (mild): nodule(s) and abscess(es) without sinus tracts (tunnels) or scarring;
- Stage II (moderate): recurrent nodule(s) and abscess(es) with a limited number of sinus tracts (tunnels) and/or scarring; and
- Stage III (severe): multiple or extensive sinus tracts (tunnels), abscesses, and/or scarring across the entire area.
Epidemiology
Hidradenitis suppurativa is most common in adults and African American patients. It has a prevalence of 1.3% in African Americans.1 When it occurs in children, it generally develops after the onset of puberty. The incidence is higher in females as well as individuals with a history of smoking and obesity (a higher body mass index).2-5
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
The erythema associated with HS may be difficult to see in darker skin tones, but violaceous, dark brown, and gray lesions may be present. When active HS lesions subside, intense hyperpigmentation may be left behind, and in some skin tones a pink or violaceous lesion may be apparent.
Worth noting
Hidradenitis suppurativa is disfiguring and has a negative impact on quality of life, including social relationships. Mental health support and screening tools are useful. Pain also is a common concern and may warrant referral to a pain specialist.6 In early disease, HS lesions can be misdiagnosed as an infection that recurs in the same location.
Treatments for HS include oral antibiotics (ie, tetracyclines, rifampin, clindamycin), topical antibiotics, immunosuppressing biologics, metformin, and spironolactone.7 Surgical interventions may be considered earlier in HS management and vary based on the location and severity of the lesions.8
Patients with HS are at risk for developing squamous cell carcinoma in scars even many years later9; therefore, patients should perform skin checks and be referred to a dermatologist. Squamous cell carcinoma is most commonly found on the buttocks of men with HS and has a poor prognosis.
Health disparity highlight
Although those of African American and African descent have the highest rates of HS,1 the clinical trials for adalimumab (the only biologic approved for HS) enrolled a low number of Black patients.
Thirty HS comorbidities have been identified. Garg et al10 recommended that dermatologists perform examinations for comorbid conditions involving the skin and conduct a simple review of systems for extracutaneous comorbidities. Access to medical care is essential, and health care system barriers affect the ability of some patients to receive adequate continuity of care.
The diagnosis of HS often is delayed due to lack of HS knowledge about the condition in the medical community at large and delayed presentation to a dermatologist.
- Sachdeva M, Shah M, Alavi A. Race-specific prevalence of hidradenitis suppurativa [published online November 11, 2020]. J Cutan Med Surg. 2021;25:177-187. doi:10.1177/1203475420972348
- Zouboulis CC, Goyal M, Byrd AS. Hidradenitis suppurativa in skin of colour. Exp Dermatol. 2021;30(suppl 1):27-30. doi:10.1111 /exd.14341
- Shalom G, Cohen AD. The epidemiology of hidradenitis suppurativa: what do we know? Br J Dermatol. 2019;180:712-713.
- Theut Riis P, Pedersen OB, Sigsgaard V, et al. Prevalence of patients with self-reported hidradenitis suppurativa in a cohort of Danish blood donors: a cross-sectional study. Br J Dermatol. 2019;180:774-781.
- Jemec GB, Kimball AB. Hidradenitis suppurativa: epidemiology and scope of the problem. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73 (5 suppl 1):S4-S7.
- Savage KT, Singh V, Patel ZS, et al. Pain management in hidradenitis suppurativa and a proposed treatment algorithm [published online September 17, 2020]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:187-199. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.09.039
- Alikhan A, Sayed C, Alavi A, et al. North American clinical management guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa: a publication from the United States and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations: part II: topical, intralesional, and systemic medical management [published online March 11, 2019]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:91-101.
- Vellaichamy G, Braunberger TL, Nahhas AF, et al. Surgical procedures for hidradenitis suppurativa. Cutis. 2018;102:13-16.
- Jung JM, Lee KH, Kim Y-J, et al. Assessment of overall and specific cancer risks in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:844-853.
- Garg A, Malviya N, Strunk A, et al. Comorbidity screening in hidradenitis suppurativa: evidence-based recommendations from the US and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations [published online January 23, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1092-1101. doi:10.1016/j. jaad.2021.01.059
- Sachdeva M, Shah M, Alavi A. Race-specific prevalence of hidradenitis suppurativa [published online November 11, 2020]. J Cutan Med Surg. 2021;25:177-187. doi:10.1177/1203475420972348
- Zouboulis CC, Goyal M, Byrd AS. Hidradenitis suppurativa in skin of colour. Exp Dermatol. 2021;30(suppl 1):27-30. doi:10.1111 /exd.14341
- Shalom G, Cohen AD. The epidemiology of hidradenitis suppurativa: what do we know? Br J Dermatol. 2019;180:712-713.
- Theut Riis P, Pedersen OB, Sigsgaard V, et al. Prevalence of patients with self-reported hidradenitis suppurativa in a cohort of Danish blood donors: a cross-sectional study. Br J Dermatol. 2019;180:774-781.
- Jemec GB, Kimball AB. Hidradenitis suppurativa: epidemiology and scope of the problem. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73 (5 suppl 1):S4-S7.
- Savage KT, Singh V, Patel ZS, et al. Pain management in hidradenitis suppurativa and a proposed treatment algorithm [published online September 17, 2020]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:187-199. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.09.039
- Alikhan A, Sayed C, Alavi A, et al. North American clinical management guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa: a publication from the United States and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations: part II: topical, intralesional, and systemic medical management [published online March 11, 2019]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:91-101.
- Vellaichamy G, Braunberger TL, Nahhas AF, et al. Surgical procedures for hidradenitis suppurativa. Cutis. 2018;102:13-16.
- Jung JM, Lee KH, Kim Y-J, et al. Assessment of overall and specific cancer risks in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:844-853.
- Garg A, Malviya N, Strunk A, et al. Comorbidity screening in hidradenitis suppurativa: evidence-based recommendations from the US and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations [published online January 23, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1092-1101. doi:10.1016/j. jaad.2021.01.059
Erythematous Papule on the Nasal Ala
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Lymphoid Hyperplasia
Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia (CLH)(also known as pseudolymphoma or lymphocytoma cutis) is a benign inflammatory condition that typically presents as a flesh-colored to erythematous or violaceous papule or nodule on the head or neck. Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia may arise in response to an antigenic stimulus, such as an insect bite, infectious agent (eg, Borrelia species), medication, or foreign body (eg, tattoos and piercings).1,2 Given the benign nature and potential for spontaneous resolution, treatment is conservative; however, high-potency topical steroids, cryosurgery, surgical excision, or local radiotherapy may lead to improvement.3 Our patient was started on clobetasol ointment 0.05% and topical tacrolimus 0.1%. After 3 months of use, she reported lesion improvement, but a new lesion appeared on the nose superior to the original. She was offered a steroid injection and liquid nitrogen freezing but was lost to follow-up.
The histopathologic features of CLH are variable and can resemble a cutaneous B- or T-cell lymphoma (quiz images). If there is B-cell predominance, histopathology typically shows a dense dermal infiltrate of lymphocytes admixed with sparse histiocytes, eosinophils, and plasma cells. Multiple germinal-center phenotype lymphoid follicles also may be seen.4 Histopathology of T-cell–predominant CLH commonly shows CD4+ T helper lymphocytes admixed with CD8+ T cells within the dermis with possible papillary dermal edema and red cell extravasation.5 Immunohistochemical stains for CD3, CD4, CD8, and CD20 usually are positive. Most lymphocytes are CD3+ T cells. Admixed clusters of CD20+ B cells may be present.
Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia is a vascular tumor of the skin composed of endothelial cells and inflammatory cells.6,7 The condition presents as single or multiple flesh-colored to purple papules most commonly on the face, scalp, and ears.8 Histologically, lesions appear as well-circumscribed collections of blood vessels composed of plump endothelial cells and an inflammatory infiltrate with lymphocytes and eosinophils (Figure 1A). Endothelial cells also may have an epithelioid appearance.7 Apparent fenestrations—holes within endothelial cells—may be present (Figure 1B). Surgical excision is the preferred treatment of angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia. Success with laser and cryosurgery also has been reported.
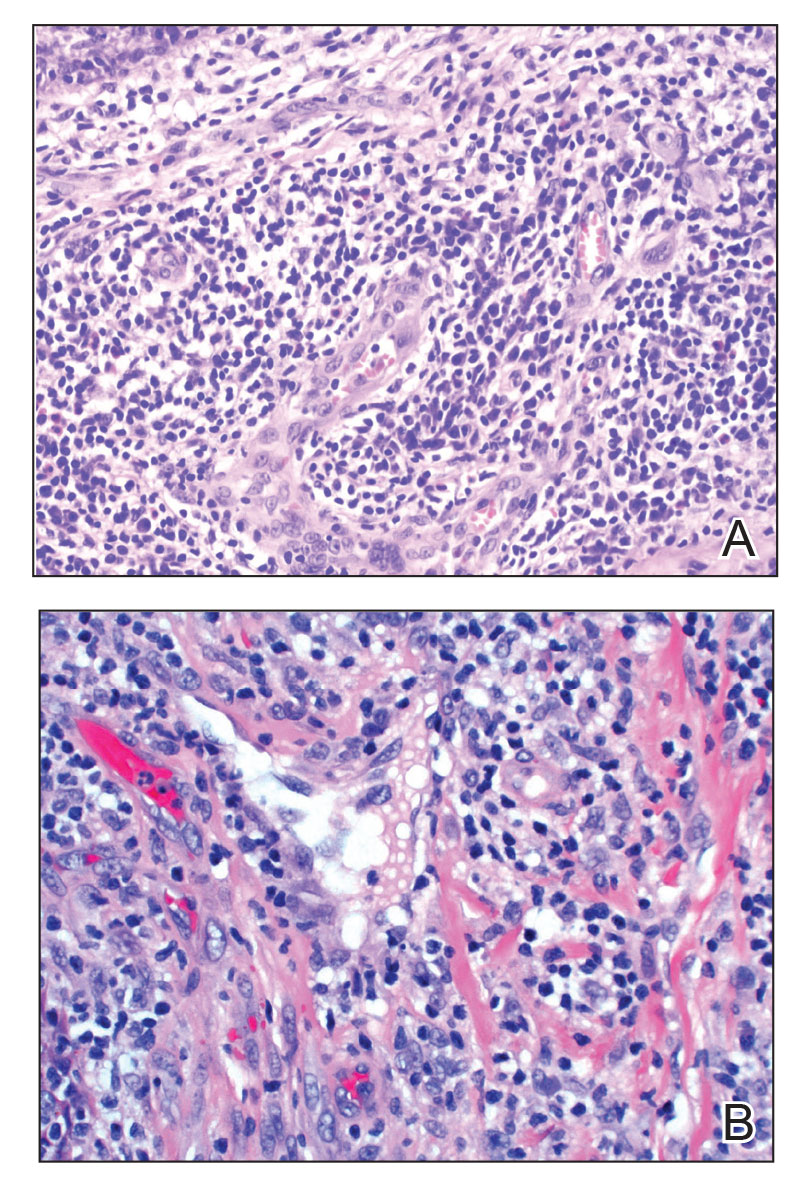
Granuloma faciale typically presents as a solitary redbrown papule or plaque on the face. Linear arborizing vessels and dilated follicular openings with brown globules frequently are seen on dermoscopy.9 Although it may resemble CLH clinically, the histopathology of granuloma faciale is characterized by a perivascular and interstitial dermal infiltrate of numerous eosinophils admixed with lymphocytes, plasma cells, and neutrophils underneath a grenz zone (Figure 2).10 Leukocytoclastic vasculitis may be seen in early lesions, and lesions can show variable angiocentric fibrosis.11 Treatment options include intralesional triamcinolone, topical steroids or calcineurin inhibitors, topical psoralen plus UVA, surgical excision, and laser therapy, but outcomes are variable.12
Leukemia cutis is a malignant hematopoietic skin infiltration that presents as multiple pink to red-brown, firm, hemorrhagic papules most frequently involving the head, neck, and trunk.13 Rarely, lesions of leukemia cutis may present as ulcers or bullae. Most lesions occur at presentation of systemic leukemia or in the setting of established leukemia. The cutaneous involvement portends a poor prognosis, strongly correlating with additional extramedullary leukemic involvement.14 Histologic features vary based on the specific type of leukemia (eg, acute myelogenous leukemia). Generally, neoplastic infiltration of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue in a nodular, diffuse, perivascular, or interstitial pattern is seen (Figure 3).15 Leukemia cutis typically resolves after successful treatment of the underlying leukemia.
Mycosis fungoides (MF) is the most common type of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. In its early stages, MF presents as erythematous, brown, scaly patches and plaques. With progression to the tumor stage of disease, clonal expansion of CD4+ T cells leads to the development of purple papules and nodules.16 Microscopic findings of MF are dependent on the stage of disease. Early patch lesions show superficial or lichenoid lymphocytic infiltration of the epidermal basal layer.17 In the plaque stage, dermal infiltrates and epidermotropism become more pronounced, with increased atypical lymphocytes with cerebriform nuclei and interspersed inflammatory cells (Figure 4). In the tumor stage, lymphocytic infiltrates may involve the entirety of the dermis or extend into the subcutaneous tissue, and malignant cells become larger in size.17 Mycosis fungoides lesions typically stain positive for helper T-cell markers with a minority staining positive for CD8.
- Zhou LL, Mistry N. Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia (pseudolymphoma). CMAJ. 2018;190:E398.
- Lackey JN, Xia Y, Cho S, et al. Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia: a case report and brief review of the literature. Cutis. 2007;79:445-448.
- Albrecht J, Fine LA, Piette W. Drug-associated lymphoma and pseudolymphoma: recognition and management. Dermatol Clin. 2007;25:233-244, vii.
- Arai E, Shimizu M, Hirose T. A review of 55 cases of cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia: reassessment of the histopathologic findings leading to reclassification of 4 lesions as cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma and 19 as pseudolymphomatous folliculitis. Hum Pathol. 2005;36:505-511.
- Bergman R, Khamaysi Z, Sahar D, et al. Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia presenting as a solitary facial nodule: clinical, histopathological, immunophenotypical, and molecular studies. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:1561-1566.
- Wells GC, Whimster IW. Subcutaneous angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia. Br J Dermatol. 1969;81:1-14.
- Guo R, Gavino AC. Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2015;139:683-686.
- Olsen TG, Helwig EB. Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia. a clinicopathologic study of 116 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985;12:781-796.
- Lallas A, Sidiropoulos T, Lefaki I, et al. Photo letter to the editor: dermoscopy of granuloma faciale. J Dermatol Case Rep. 2012;6:59-60.
- Oliveira CC, Ianhez PE, Marques SA, et al. Granuloma faciale: clinical, morphological and immunohistochemical aspects in a series of 10 patients. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:803-807.
- Marcoval J, Moreno A, Peyr J. Granuloma faciale: a clinicopathological study of 11 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:269-273.
- Lindhaus C, Elsner P. Granuloma faciale treatment: a systematic review. Acta Derm Venereol. 2018;98:14-18.
- Haidari W, Strowd LC. Clinical characterization of leukemia cutis presentation. Cutis. 2019;104:326-330; E3.
- Rao AG, Danturty I. Leukemia cutis. Indian J Dermatol. 2012;57:504.
- Desch JK, Smoller BR. The spectrum of cutaneous disease in leukemias. J Cutan Pathol. 1993;20:407-410.
- Yamashita T, Abbade LP, Marques ME, et al. Mycosis fungoides and Sezary syndrome: clinical, histopathological and immunohistochemical review and update. An Bras Dermatol. 2012;87:817-828; quiz 829-830.
- Smoller BR, Bishop K, Glusac E, et al. Reassessment of histologic parameters in the diagnosis of mycosis fungoides. Am J Surg Pathol. 1995;19:1423-1430.
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Lymphoid Hyperplasia
Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia (CLH)(also known as pseudolymphoma or lymphocytoma cutis) is a benign inflammatory condition that typically presents as a flesh-colored to erythematous or violaceous papule or nodule on the head or neck. Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia may arise in response to an antigenic stimulus, such as an insect bite, infectious agent (eg, Borrelia species), medication, or foreign body (eg, tattoos and piercings).1,2 Given the benign nature and potential for spontaneous resolution, treatment is conservative; however, high-potency topical steroids, cryosurgery, surgical excision, or local radiotherapy may lead to improvement.3 Our patient was started on clobetasol ointment 0.05% and topical tacrolimus 0.1%. After 3 months of use, she reported lesion improvement, but a new lesion appeared on the nose superior to the original. She was offered a steroid injection and liquid nitrogen freezing but was lost to follow-up.
The histopathologic features of CLH are variable and can resemble a cutaneous B- or T-cell lymphoma (quiz images). If there is B-cell predominance, histopathology typically shows a dense dermal infiltrate of lymphocytes admixed with sparse histiocytes, eosinophils, and plasma cells. Multiple germinal-center phenotype lymphoid follicles also may be seen.4 Histopathology of T-cell–predominant CLH commonly shows CD4+ T helper lymphocytes admixed with CD8+ T cells within the dermis with possible papillary dermal edema and red cell extravasation.5 Immunohistochemical stains for CD3, CD4, CD8, and CD20 usually are positive. Most lymphocytes are CD3+ T cells. Admixed clusters of CD20+ B cells may be present.
Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia is a vascular tumor of the skin composed of endothelial cells and inflammatory cells.6,7 The condition presents as single or multiple flesh-colored to purple papules most commonly on the face, scalp, and ears.8 Histologically, lesions appear as well-circumscribed collections of blood vessels composed of plump endothelial cells and an inflammatory infiltrate with lymphocytes and eosinophils (Figure 1A). Endothelial cells also may have an epithelioid appearance.7 Apparent fenestrations—holes within endothelial cells—may be present (Figure 1B). Surgical excision is the preferred treatment of angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia. Success with laser and cryosurgery also has been reported.

Granuloma faciale typically presents as a solitary redbrown papule or plaque on the face. Linear arborizing vessels and dilated follicular openings with brown globules frequently are seen on dermoscopy.9 Although it may resemble CLH clinically, the histopathology of granuloma faciale is characterized by a perivascular and interstitial dermal infiltrate of numerous eosinophils admixed with lymphocytes, plasma cells, and neutrophils underneath a grenz zone (Figure 2).10 Leukocytoclastic vasculitis may be seen in early lesions, and lesions can show variable angiocentric fibrosis.11 Treatment options include intralesional triamcinolone, topical steroids or calcineurin inhibitors, topical psoralen plus UVA, surgical excision, and laser therapy, but outcomes are variable.12

Leukemia cutis is a malignant hematopoietic skin infiltration that presents as multiple pink to red-brown, firm, hemorrhagic papules most frequently involving the head, neck, and trunk.13 Rarely, lesions of leukemia cutis may present as ulcers or bullae. Most lesions occur at presentation of systemic leukemia or in the setting of established leukemia. The cutaneous involvement portends a poor prognosis, strongly correlating with additional extramedullary leukemic involvement.14 Histologic features vary based on the specific type of leukemia (eg, acute myelogenous leukemia). Generally, neoplastic infiltration of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue in a nodular, diffuse, perivascular, or interstitial pattern is seen (Figure 3).15 Leukemia cutis typically resolves after successful treatment of the underlying leukemia.

Mycosis fungoides (MF) is the most common type of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. In its early stages, MF presents as erythematous, brown, scaly patches and plaques. With progression to the tumor stage of disease, clonal expansion of CD4+ T cells leads to the development of purple papules and nodules.16 Microscopic findings of MF are dependent on the stage of disease. Early patch lesions show superficial or lichenoid lymphocytic infiltration of the epidermal basal layer.17 In the plaque stage, dermal infiltrates and epidermotropism become more pronounced, with increased atypical lymphocytes with cerebriform nuclei and interspersed inflammatory cells (Figure 4). In the tumor stage, lymphocytic infiltrates may involve the entirety of the dermis or extend into the subcutaneous tissue, and malignant cells become larger in size.17 Mycosis fungoides lesions typically stain positive for helper T-cell markers with a minority staining positive for CD8.

The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Lymphoid Hyperplasia
Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia (CLH)(also known as pseudolymphoma or lymphocytoma cutis) is a benign inflammatory condition that typically presents as a flesh-colored to erythematous or violaceous papule or nodule on the head or neck. Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia may arise in response to an antigenic stimulus, such as an insect bite, infectious agent (eg, Borrelia species), medication, or foreign body (eg, tattoos and piercings).1,2 Given the benign nature and potential for spontaneous resolution, treatment is conservative; however, high-potency topical steroids, cryosurgery, surgical excision, or local radiotherapy may lead to improvement.3 Our patient was started on clobetasol ointment 0.05% and topical tacrolimus 0.1%. After 3 months of use, she reported lesion improvement, but a new lesion appeared on the nose superior to the original. She was offered a steroid injection and liquid nitrogen freezing but was lost to follow-up.
The histopathologic features of CLH are variable and can resemble a cutaneous B- or T-cell lymphoma (quiz images). If there is B-cell predominance, histopathology typically shows a dense dermal infiltrate of lymphocytes admixed with sparse histiocytes, eosinophils, and plasma cells. Multiple germinal-center phenotype lymphoid follicles also may be seen.4 Histopathology of T-cell–predominant CLH commonly shows CD4+ T helper lymphocytes admixed with CD8+ T cells within the dermis with possible papillary dermal edema and red cell extravasation.5 Immunohistochemical stains for CD3, CD4, CD8, and CD20 usually are positive. Most lymphocytes are CD3+ T cells. Admixed clusters of CD20+ B cells may be present.
Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia is a vascular tumor of the skin composed of endothelial cells and inflammatory cells.6,7 The condition presents as single or multiple flesh-colored to purple papules most commonly on the face, scalp, and ears.8 Histologically, lesions appear as well-circumscribed collections of blood vessels composed of plump endothelial cells and an inflammatory infiltrate with lymphocytes and eosinophils (Figure 1A). Endothelial cells also may have an epithelioid appearance.7 Apparent fenestrations—holes within endothelial cells—may be present (Figure 1B). Surgical excision is the preferred treatment of angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia. Success with laser and cryosurgery also has been reported.

Granuloma faciale typically presents as a solitary redbrown papule or plaque on the face. Linear arborizing vessels and dilated follicular openings with brown globules frequently are seen on dermoscopy.9 Although it may resemble CLH clinically, the histopathology of granuloma faciale is characterized by a perivascular and interstitial dermal infiltrate of numerous eosinophils admixed with lymphocytes, plasma cells, and neutrophils underneath a grenz zone (Figure 2).10 Leukocytoclastic vasculitis may be seen in early lesions, and lesions can show variable angiocentric fibrosis.11 Treatment options include intralesional triamcinolone, topical steroids or calcineurin inhibitors, topical psoralen plus UVA, surgical excision, and laser therapy, but outcomes are variable.12

Leukemia cutis is a malignant hematopoietic skin infiltration that presents as multiple pink to red-brown, firm, hemorrhagic papules most frequently involving the head, neck, and trunk.13 Rarely, lesions of leukemia cutis may present as ulcers or bullae. Most lesions occur at presentation of systemic leukemia or in the setting of established leukemia. The cutaneous involvement portends a poor prognosis, strongly correlating with additional extramedullary leukemic involvement.14 Histologic features vary based on the specific type of leukemia (eg, acute myelogenous leukemia). Generally, neoplastic infiltration of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue in a nodular, diffuse, perivascular, or interstitial pattern is seen (Figure 3).15 Leukemia cutis typically resolves after successful treatment of the underlying leukemia.

Mycosis fungoides (MF) is the most common type of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. In its early stages, MF presents as erythematous, brown, scaly patches and plaques. With progression to the tumor stage of disease, clonal expansion of CD4+ T cells leads to the development of purple papules and nodules.16 Microscopic findings of MF are dependent on the stage of disease. Early patch lesions show superficial or lichenoid lymphocytic infiltration of the epidermal basal layer.17 In the plaque stage, dermal infiltrates and epidermotropism become more pronounced, with increased atypical lymphocytes with cerebriform nuclei and interspersed inflammatory cells (Figure 4). In the tumor stage, lymphocytic infiltrates may involve the entirety of the dermis or extend into the subcutaneous tissue, and malignant cells become larger in size.17 Mycosis fungoides lesions typically stain positive for helper T-cell markers with a minority staining positive for CD8.

- Zhou LL, Mistry N. Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia (pseudolymphoma). CMAJ. 2018;190:E398.
- Lackey JN, Xia Y, Cho S, et al. Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia: a case report and brief review of the literature. Cutis. 2007;79:445-448.
- Albrecht J, Fine LA, Piette W. Drug-associated lymphoma and pseudolymphoma: recognition and management. Dermatol Clin. 2007;25:233-244, vii.
- Arai E, Shimizu M, Hirose T. A review of 55 cases of cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia: reassessment of the histopathologic findings leading to reclassification of 4 lesions as cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma and 19 as pseudolymphomatous folliculitis. Hum Pathol. 2005;36:505-511.
- Bergman R, Khamaysi Z, Sahar D, et al. Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia presenting as a solitary facial nodule: clinical, histopathological, immunophenotypical, and molecular studies. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:1561-1566.
- Wells GC, Whimster IW. Subcutaneous angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia. Br J Dermatol. 1969;81:1-14.
- Guo R, Gavino AC. Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2015;139:683-686.
- Olsen TG, Helwig EB. Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia. a clinicopathologic study of 116 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985;12:781-796.
- Lallas A, Sidiropoulos T, Lefaki I, et al. Photo letter to the editor: dermoscopy of granuloma faciale. J Dermatol Case Rep. 2012;6:59-60.
- Oliveira CC, Ianhez PE, Marques SA, et al. Granuloma faciale: clinical, morphological and immunohistochemical aspects in a series of 10 patients. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:803-807.
- Marcoval J, Moreno A, Peyr J. Granuloma faciale: a clinicopathological study of 11 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:269-273.
- Lindhaus C, Elsner P. Granuloma faciale treatment: a systematic review. Acta Derm Venereol. 2018;98:14-18.
- Haidari W, Strowd LC. Clinical characterization of leukemia cutis presentation. Cutis. 2019;104:326-330; E3.
- Rao AG, Danturty I. Leukemia cutis. Indian J Dermatol. 2012;57:504.
- Desch JK, Smoller BR. The spectrum of cutaneous disease in leukemias. J Cutan Pathol. 1993;20:407-410.
- Yamashita T, Abbade LP, Marques ME, et al. Mycosis fungoides and Sezary syndrome: clinical, histopathological and immunohistochemical review and update. An Bras Dermatol. 2012;87:817-828; quiz 829-830.
- Smoller BR, Bishop K, Glusac E, et al. Reassessment of histologic parameters in the diagnosis of mycosis fungoides. Am J Surg Pathol. 1995;19:1423-1430.
- Zhou LL, Mistry N. Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia (pseudolymphoma). CMAJ. 2018;190:E398.
- Lackey JN, Xia Y, Cho S, et al. Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia: a case report and brief review of the literature. Cutis. 2007;79:445-448.
- Albrecht J, Fine LA, Piette W. Drug-associated lymphoma and pseudolymphoma: recognition and management. Dermatol Clin. 2007;25:233-244, vii.
- Arai E, Shimizu M, Hirose T. A review of 55 cases of cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia: reassessment of the histopathologic findings leading to reclassification of 4 lesions as cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma and 19 as pseudolymphomatous folliculitis. Hum Pathol. 2005;36:505-511.
- Bergman R, Khamaysi Z, Sahar D, et al. Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia presenting as a solitary facial nodule: clinical, histopathological, immunophenotypical, and molecular studies. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:1561-1566.
- Wells GC, Whimster IW. Subcutaneous angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia. Br J Dermatol. 1969;81:1-14.
- Guo R, Gavino AC. Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2015;139:683-686.
- Olsen TG, Helwig EB. Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia. a clinicopathologic study of 116 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985;12:781-796.
- Lallas A, Sidiropoulos T, Lefaki I, et al. Photo letter to the editor: dermoscopy of granuloma faciale. J Dermatol Case Rep. 2012;6:59-60.
- Oliveira CC, Ianhez PE, Marques SA, et al. Granuloma faciale: clinical, morphological and immunohistochemical aspects in a series of 10 patients. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:803-807.
- Marcoval J, Moreno A, Peyr J. Granuloma faciale: a clinicopathological study of 11 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:269-273.
- Lindhaus C, Elsner P. Granuloma faciale treatment: a systematic review. Acta Derm Venereol. 2018;98:14-18.
- Haidari W, Strowd LC. Clinical characterization of leukemia cutis presentation. Cutis. 2019;104:326-330; E3.
- Rao AG, Danturty I. Leukemia cutis. Indian J Dermatol. 2012;57:504.
- Desch JK, Smoller BR. The spectrum of cutaneous disease in leukemias. J Cutan Pathol. 1993;20:407-410.
- Yamashita T, Abbade LP, Marques ME, et al. Mycosis fungoides and Sezary syndrome: clinical, histopathological and immunohistochemical review and update. An Bras Dermatol. 2012;87:817-828; quiz 829-830.
- Smoller BR, Bishop K, Glusac E, et al. Reassessment of histologic parameters in the diagnosis of mycosis fungoides. Am J Surg Pathol. 1995;19:1423-1430.
A 35-year-old woman presented with a slowly growing, smooth, erythematous papule of 2 months’ duration on the left nasal ala surrounding a piercing (top, inset) that had been performed 4 years prior. A tangential biopsy was obtained for histopathologic evaluation.
Novel study offers clues to sex bias in lupus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), or lupus, shows a marked sex bias, affecting about nine females for every one male, according to Susan Kovats, PhD, who studies sex differences in immunity at the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation in Oklahoma City. This characteristic of lupus suggests that hormones are involved in the pathogenesis of the disease. It also suggests, Dr. Kovats said, that the X chromosome might play a role.
Though studies since the 1970s have indicated a significant role for hormones, the issue is still complex and not well understood, and relatively little research has been done on the molecular mechanisms that might be responsible. This may be because of difficulties with influencing the immune system in vitro, said George A. Robinson, PhD, of University College London’s Centre for Rheumatology.
But Dr. Robinson and his team found a unique way of investigating the role of sex chromosomes and hormones in the inflammatory profiles across subjects of different sex, gender, age, and disease status. In research published online in The Lancet Rheumatology, Dr. Robinson and his team looked at immune cells taken from both cisgender men and women and transgender men and women, and thus were able to “get a more physiological view of what sex hormones are doing to the immune system,” he said.
Dr. Kovats agreed that it was a useful approach. “The transgender people provided an opportunity to effectively separate sex hormone levels from chromosome content,” she said in an interview.
Methods and findings
Peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) samples were taken from cisgender individuals with and without juvenile-onset lupus and assessed for 28 immune-cell subsets, including different T-cell, B-cell, and monotype subsets. Subjects included 39 postpubertal cisgender men and women (17 men and 22 women) who did not have juvenile-onset lupus, and 35 postpubertal cisgender men and women (12 men and 23 women) who did have juvenile onset lupus. All were aged 16-25 years. The transgender group included five transgender men and five transgender women (aged 18-19) who were undergoing gender-affirming sex hormone treatment.
The analysis found that one of the key differences between young postpubertal cisgender men and age-matched cisgender women was that the men had significantly elevated frequencies of regulatory T cells (T-reg cells), and the T-reg cells from young cisgender men had greater suppressive capacity in vitro than did those from cisgender women. In addition, RNA sequencing data from isolated T-reg cells showed the transcriptomic signature of the cisgender men’s T-regs were significantly enriched for genes in the P13K-AKT signaling pathway. The frequency of T-reg cells was not influenced by sex hormones, but their transcriptomic profile was affected.
“These results are beginning to give us an indication of which genes might be differentially regulated by sex hormones and how these are associated with autoimmunity,” Dr. Robinson said. “We’ve also found that, depending on whether you’re a cisgender man or woman, you may have a different pathogenic process to developing lupus. It’s not necessarily that one mechanism drives the disease across both sexes.”
New approaches, better insights
Dr. Kovats was particularly impressed by the methods of this study. “It was a natural study, the kind of thing we can usually do only in mice,” she said.
“One problem with studies on the effects of hormones in disease is that historically researchers have not paid that much attention to the actual hormone levels in the humans they studied. They might look at 100 women and 100 men, roughly between the ages of 20 and 50. We’re starting to see more, but there aren’t a lot of studies correlating numbers of cells in blood with actual hormone levels in the person. And as we know, just because someone’s a certain age doesn’t mean that they have a textbook hormone level. Early menopause, birth-control pills, many things can affect those levels.”
The researchers hope that these findings will shed light on the mechanisms that create sexual bias in autoimmune diseases, particularly lupus, as well as help researchers to better understand the innate and adaptive immunological differences between men and women. It could also be useful in the clinical setting, Dr. Robinson said. Because of the extreme sex bias in lupus, doctors see far more women with the illness than men. When they do see men with lupus, they need to be able to consider how the patient’s sex affects the development and course of the disease. “I think that people need to start looking at patients as clinically different, depending on their sex and gender,” he said. Information like that analyzed in this study could help with that. This could be especially important because as Dr. Kovats pointed out, although men get lupus far less often than women, when they do have it, they tend to have more severe disease.
Help from machines
This study was groundbreaking in another area as well. The researchers used machine learning to analyze the data. “We’ve started working a lot more with these analysis methods to try to answer as much as we can with these smaller data sets,” Dr. Robinson said. “Rather than the conventional analysis that we would typically perform, we’re able to use machine learning and artificial intelligence to try and learn from the data and increase the numbers that we’re working with by using a training data set. This allows us to interrogate the data with a lot more precision.”
The authors declared no competing interests.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), or lupus, shows a marked sex bias, affecting about nine females for every one male, according to Susan Kovats, PhD, who studies sex differences in immunity at the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation in Oklahoma City. This characteristic of lupus suggests that hormones are involved in the pathogenesis of the disease. It also suggests, Dr. Kovats said, that the X chromosome might play a role.
Though studies since the 1970s have indicated a significant role for hormones, the issue is still complex and not well understood, and relatively little research has been done on the molecular mechanisms that might be responsible. This may be because of difficulties with influencing the immune system in vitro, said George A. Robinson, PhD, of University College London’s Centre for Rheumatology.
But Dr. Robinson and his team found a unique way of investigating the role of sex chromosomes and hormones in the inflammatory profiles across subjects of different sex, gender, age, and disease status. In research published online in The Lancet Rheumatology, Dr. Robinson and his team looked at immune cells taken from both cisgender men and women and transgender men and women, and thus were able to “get a more physiological view of what sex hormones are doing to the immune system,” he said.
Dr. Kovats agreed that it was a useful approach. “The transgender people provided an opportunity to effectively separate sex hormone levels from chromosome content,” she said in an interview.
Methods and findings
Peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) samples were taken from cisgender individuals with and without juvenile-onset lupus and assessed for 28 immune-cell subsets, including different T-cell, B-cell, and monotype subsets. Subjects included 39 postpubertal cisgender men and women (17 men and 22 women) who did not have juvenile-onset lupus, and 35 postpubertal cisgender men and women (12 men and 23 women) who did have juvenile onset lupus. All were aged 16-25 years. The transgender group included five transgender men and five transgender women (aged 18-19) who were undergoing gender-affirming sex hormone treatment.
The analysis found that one of the key differences between young postpubertal cisgender men and age-matched cisgender women was that the men had significantly elevated frequencies of regulatory T cells (T-reg cells), and the T-reg cells from young cisgender men had greater suppressive capacity in vitro than did those from cisgender women. In addition, RNA sequencing data from isolated T-reg cells showed the transcriptomic signature of the cisgender men’s T-regs were significantly enriched for genes in the P13K-AKT signaling pathway. The frequency of T-reg cells was not influenced by sex hormones, but their transcriptomic profile was affected.
“These results are beginning to give us an indication of which genes might be differentially regulated by sex hormones and how these are associated with autoimmunity,” Dr. Robinson said. “We’ve also found that, depending on whether you’re a cisgender man or woman, you may have a different pathogenic process to developing lupus. It’s not necessarily that one mechanism drives the disease across both sexes.”
New approaches, better insights
Dr. Kovats was particularly impressed by the methods of this study. “It was a natural study, the kind of thing we can usually do only in mice,” she said.
“One problem with studies on the effects of hormones in disease is that historically researchers have not paid that much attention to the actual hormone levels in the humans they studied. They might look at 100 women and 100 men, roughly between the ages of 20 and 50. We’re starting to see more, but there aren’t a lot of studies correlating numbers of cells in blood with actual hormone levels in the person. And as we know, just because someone’s a certain age doesn’t mean that they have a textbook hormone level. Early menopause, birth-control pills, many things can affect those levels.”
The researchers hope that these findings will shed light on the mechanisms that create sexual bias in autoimmune diseases, particularly lupus, as well as help researchers to better understand the innate and adaptive immunological differences between men and women. It could also be useful in the clinical setting, Dr. Robinson said. Because of the extreme sex bias in lupus, doctors see far more women with the illness than men. When they do see men with lupus, they need to be able to consider how the patient’s sex affects the development and course of the disease. “I think that people need to start looking at patients as clinically different, depending on their sex and gender,” he said. Information like that analyzed in this study could help with that. This could be especially important because as Dr. Kovats pointed out, although men get lupus far less often than women, when they do have it, they tend to have more severe disease.
Help from machines
This study was groundbreaking in another area as well. The researchers used machine learning to analyze the data. “We’ve started working a lot more with these analysis methods to try to answer as much as we can with these smaller data sets,” Dr. Robinson said. “Rather than the conventional analysis that we would typically perform, we’re able to use machine learning and artificial intelligence to try and learn from the data and increase the numbers that we’re working with by using a training data set. This allows us to interrogate the data with a lot more precision.”
The authors declared no competing interests.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), or lupus, shows a marked sex bias, affecting about nine females for every one male, according to Susan Kovats, PhD, who studies sex differences in immunity at the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation in Oklahoma City. This characteristic of lupus suggests that hormones are involved in the pathogenesis of the disease. It also suggests, Dr. Kovats said, that the X chromosome might play a role.
Though studies since the 1970s have indicated a significant role for hormones, the issue is still complex and not well understood, and relatively little research has been done on the molecular mechanisms that might be responsible. This may be because of difficulties with influencing the immune system in vitro, said George A. Robinson, PhD, of University College London’s Centre for Rheumatology.
But Dr. Robinson and his team found a unique way of investigating the role of sex chromosomes and hormones in the inflammatory profiles across subjects of different sex, gender, age, and disease status. In research published online in The Lancet Rheumatology, Dr. Robinson and his team looked at immune cells taken from both cisgender men and women and transgender men and women, and thus were able to “get a more physiological view of what sex hormones are doing to the immune system,” he said.
Dr. Kovats agreed that it was a useful approach. “The transgender people provided an opportunity to effectively separate sex hormone levels from chromosome content,” she said in an interview.
Methods and findings
Peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) samples were taken from cisgender individuals with and without juvenile-onset lupus and assessed for 28 immune-cell subsets, including different T-cell, B-cell, and monotype subsets. Subjects included 39 postpubertal cisgender men and women (17 men and 22 women) who did not have juvenile-onset lupus, and 35 postpubertal cisgender men and women (12 men and 23 women) who did have juvenile onset lupus. All were aged 16-25 years. The transgender group included five transgender men and five transgender women (aged 18-19) who were undergoing gender-affirming sex hormone treatment.
The analysis found that one of the key differences between young postpubertal cisgender men and age-matched cisgender women was that the men had significantly elevated frequencies of regulatory T cells (T-reg cells), and the T-reg cells from young cisgender men had greater suppressive capacity in vitro than did those from cisgender women. In addition, RNA sequencing data from isolated T-reg cells showed the transcriptomic signature of the cisgender men’s T-regs were significantly enriched for genes in the P13K-AKT signaling pathway. The frequency of T-reg cells was not influenced by sex hormones, but their transcriptomic profile was affected.
“These results are beginning to give us an indication of which genes might be differentially regulated by sex hormones and how these are associated with autoimmunity,” Dr. Robinson said. “We’ve also found that, depending on whether you’re a cisgender man or woman, you may have a different pathogenic process to developing lupus. It’s not necessarily that one mechanism drives the disease across both sexes.”
New approaches, better insights
Dr. Kovats was particularly impressed by the methods of this study. “It was a natural study, the kind of thing we can usually do only in mice,” she said.
“One problem with studies on the effects of hormones in disease is that historically researchers have not paid that much attention to the actual hormone levels in the humans they studied. They might look at 100 women and 100 men, roughly between the ages of 20 and 50. We’re starting to see more, but there aren’t a lot of studies correlating numbers of cells in blood with actual hormone levels in the person. And as we know, just because someone’s a certain age doesn’t mean that they have a textbook hormone level. Early menopause, birth-control pills, many things can affect those levels.”
The researchers hope that these findings will shed light on the mechanisms that create sexual bias in autoimmune diseases, particularly lupus, as well as help researchers to better understand the innate and adaptive immunological differences between men and women. It could also be useful in the clinical setting, Dr. Robinson said. Because of the extreme sex bias in lupus, doctors see far more women with the illness than men. When they do see men with lupus, they need to be able to consider how the patient’s sex affects the development and course of the disease. “I think that people need to start looking at patients as clinically different, depending on their sex and gender,” he said. Information like that analyzed in this study could help with that. This could be especially important because as Dr. Kovats pointed out, although men get lupus far less often than women, when they do have it, they tend to have more severe disease.
Help from machines
This study was groundbreaking in another area as well. The researchers used machine learning to analyze the data. “We’ve started working a lot more with these analysis methods to try to answer as much as we can with these smaller data sets,” Dr. Robinson said. “Rather than the conventional analysis that we would typically perform, we’re able to use machine learning and artificial intelligence to try and learn from the data and increase the numbers that we’re working with by using a training data set. This allows us to interrogate the data with a lot more precision.”
The authors declared no competing interests.
FROM THE LANCET RHEUMATOLOGY
Can Atopic Dermatitis and Allergic Contact Dermatitis Coexist?
Atopic dermatitis (AD) and allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) are 2 common inflammatory skin conditions that may have similar clinical presentations. Historically, it was thought that these conditions could not be diagnosed simultaneously due to their differing immune mechanisms; however, this belief has been challenged by recent evidence suggesting a more nuanced relationship between the 2 disease processes. In this review, we examine the complex interplay between AD and ACD and explain how shifts in conventional understanding of the 2 conditions shaped our evolving recognition of their ability to coexist.
Epidemiology of AD and ACD
Atopic dermatitis is the most common inflammatory skin disease in children and adolescents, with an estimated prevalence reaching 21%.1 In 60% of cases, onset of AD will occur within the first year of life, and 90% of cases begin within the first 5 years.2 Resolution may occur by adulthood; however, AD may continue to impact up to 8% to 9% of adults, with an increased prevalence in those older than 75 years.1 This may represent an underestimation of the burden of adult AD; one systematic review of 17 studies found that the pooled proportion of adult-onset AD was greater than 25%.3
In contrast, ACD previously was assumed to be a disease that more commonly impacted adults and only rarely children, primarily due to an early misconception that children were not frequently exposed to contact allergens and their immune systems were too immature to react to them even if exposed.4,5 However, it is now known that children do have risk factors for development of ACD, including a thinner stratum corneum and potentially a more absorbent skin surface.4 In addition, a 2022 study by the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) found similar rates of ACD in children (n=1871) and adults (n=41,699) referred for patch testing (55.2% and 57.3%, respectively) as well as similar rates of having at least 1 relevant positive patch test (49.2% and 52.2%).6
In opposition to traditional beliefs, these findings highlight that AD and ACD can occur across age groups.
Immune Mechanism
The pathogenesis of AD represents a multifactorial process involving the immune system, cutaneous flora, genetic predisposition, and surrounding environment. Immunologically, acute AD is driven by a predominantly TH2 helper T-cell response with high levels of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-137; TH22, TH17, and TH1 also have been implicated.8 Notably, TH17 is found in high levels during the acute eczema phase, while TH1 and TH22are associated with the chronic phase.7
The pathophysiology of ACD is not completely understood. The classic paradigm involves 2 phases: sensitization and elicitation. Sensitization involves antigen-presenting cells that take up allergens absorbed by the skin to present them in regional lymph nodes where antigen-specific T lymphocytes are generated. Elicitation occurs upon re-exposure to the allergen, at which time the primed T lymphocytes are recruited to the skin, causing inflammation.9 Allergic contact dermatitis initially was thought to be driven by TH1 cytokines and IL-17 but now is understood to be more complex.10 Studies have revealed immune polarization of contact allergens, demonstrating that nickel primarily induces a TH1/TH17 response, whereas fragrance and rubber accelerators skew to TH2; TH9 and TH22 also may be involved depending on the causative allergen.11,12
Of note, the immunologic differences between AD and ACD led early investigators to believe that patients with AD were relatively protected from ACD.13 However, as previously described, there are several overlapping cytokines between AD and ACD. Furthermore, research has revealed that risk of contact sensitization might be increased in the chronic eczema phase due to the shared TH1 pathway.14 Barrier-disrupted skin (such as that in AD) also may increase the cytokine response and the density of antigen-presenting cells, leading to a proallergic state.15 This suggests that the immunologic pathways of AD and ACD are more intertwined than was previously understood.
Underlying Risk Factors
Skin barrier dysfunction is a key step in the pathogenesis of AD. Patients with AD commonly have loss-of-function mutations in the filaggrin gene, a protein that is key to the function of the stratum corneum. Loss of this protein may not only impact the immune response as previously noted but also may lead to increased transepidermal water loss and bacterial colonization.16 Interestingly, a 2014 review examined how this mutation could lead to an increased risk of sensitization to bivalent metal ions via an impaired chelating ability of the skin.17 Furthermore, a 2016 study conducted in Dutch construction workers revealed an increased risk for contact dermatitis (irritant and allergic) for those with a loss-of-function filaggrin mutation.18
Importantly, this same mutation may explain why patients with AD tend to have increased skin colonization by Staphylococcus aureus. The abundance of S aureus and the relative decrease in the diversity of other microorganisms on the skin may be associated with increased AD severity.19 Likewise, S aureus may play a role in the pathogenesis of ACD via production of its exotoxin directed at the T-cell receptor V beta 17 region. In particular, this receptor has been associated with nickel sensitization.17
Another risk factor to consider is increased exposure to contact sensitizers when treating AD. For instance, management often includes use of over-the-counter emollients, natural or botanical remedies with purported benefits for AD, cleansers, and detergents. However, these products can contain some of the most prevalent contact allergens seen in those with AD, including methyl-isothiazolinone, formaldehyde releasers, and fragrance.20 Topical corticosteroids also are frequently used, and ACD to steroid molecules can occur, particularly to tixocortol-21-pivalate (a marker for class A corticosteroids) and budesonide (a marker for class B corticosteroids).21 Other allergens (eg, benzyl alcohol, propylene glycol) also may be found as inactive ingredients of topical corticosteroids.22 These exposures may place AD patients at risk for ACD.
The Coexistence of AD and ACD
Given the overlapping epidemiology, immunology, and potentially increased risk for the development of ACD in patients with AD, it would be reasonable to assume that the 2 diagnoses could coexist; however, is there clinical data to support this idea? Based on recent database reviews, the answer appears to be yes.20,23-26 An analysis from the Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry revealed that 30% of 1142 pediatric patch test cases analyzed were diagnosed as AD and ACD simultaneously.24 The NACDG found similar results in its 2021 review, as 29.5% of children (n=1648) and 20.7% of adults (n=36,834) had a concurrent diagnosis of AD and ACD.20 Notably, older results from these databases also demonstrated an association between the 2 conditions.23,25,26
It remains unclear whether the prevalence of ACD is higher in those with or without AD. A comprehensive systematic review conducted in 2017 examined this topic through analysis of 74 studies. The results demonstrated a similar prevalence of contact sensitization in individuals with and without AD.27 Another systematic review of 31 studies conducted in 2017 found a higher prevalence for ACD in children without AD; however, the authors noted that the included studies were too variable (eg, size, design, allergens tested) to draw definitive conclusions.28
Even though there is no clear overall increased risk for ACD in patients with AD, research has suggested that certain allergens may be more prevalent in the setting of AD. An NACDG study found that adults with AD had increased odds of reacting to 10 of the top 25 NACDG screening allergens compared to those without AD.20 Other studies have found that AD patients may be more likely to become sensitized to certain allergens, such as fragrance and lanolin.14
Considerations for Management
Diagnosis of ACD in patients with AD can be challenging because these conditions may present similarly with chronic, pruritic, inflammatory patches and plaques. Chronic ACD may be misdiagnosed as AD if patch testing is not performed.29 Given the prevalence of ACD in the setting of AD, there should be a low threshold to pursue patch testing, especially when dermatitis is recalcitrant to standard therapies or presents in an atypical distribution (ie, perioral, predominantly head/neck, hand and foot, isolated eyelid involvement, buttocks).4,30 Various allergen series are available for patch testing adults and children including the NACDG Standard Series, American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series, or the Pediatric Baseline Series.31-33
If potentially relevant allergens are uncovered by patch testing, patients should be counseled on avoidance strategies. However, allergen avoidance may not always lead to complete symptom resolution, especially if AD is present concomitantly with ACD. Therefore, use of topical or systemic therapies still may be required. Topical corticosteroids can be used when dermatitis is acute and localized. Systemic corticosteroids are utilized for both diagnoses when cases are more severe or extensive, but their adverse-effect profile limits long-term use. Other systemic treatments, including conventional agents (ie, azathioprine, cyclosporine, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil), biologics, and small molecule inhibitors also may be considered for severe cases.34,35 Dupilumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-4/IL-13, is approved for use in moderate to severe AD in patients 6 months and older. Recent evidence has suggested that dupilumab also may be an effective off-label treatment choice for ACD when allergen avoidance alone is insufficient.36 Studies have been conducted on secukinumab, a monoclonal antibody against IL-17; however, it has not been shown to be effective in either AD or ACD.37,38 This indicates that targeted biologics may not always be successful in treating these diagnoses, likely due to their complex immune pathways. Finally, there is an emerging role for JAK inhibitors. Three are approved for AD: topical ruxolitinib, oral abrocitinib, and oral upadacitinib.39 Further investigation is needed to determine the efficacy of JAK inhibitors in ACD.
Final Interpretation
Evolving evidence shows that AD and ACD can occur at the same time despite the historical perspective that their immune pathways were too polarized for this to happen. Atopic dermatitis may be an important risk factor for subsequent development of ACD. Management should include a low threshold to perform patch testing, while pharmacotherapies utilized in the treatment of both conditions should be considered.
- Chan LN, Magyari A, Ye M, et al. The epidemiology of atopic dermatitis in older adults: a population-based study in the United Kingdom. PLoS One. 2021;16:E0258219. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0258219
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Chamlin SL, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 1. diagnosis and assessment of atopic dermatitis [published online November 27, 2013]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:338-351. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.10.010
- Lee HH, Patel KR, Singam V, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence and phenotype of adult-onset atopic dermatitis [published online June 2, 2018]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1526-1532.e7. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.05.1241
- Borok J, Matiz C, Goldenberg A, et al. Contact dermatitis in atopic dermatitis children—past, present, and future. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019;56:86-98. doi:10.1007/s12016-018-8711-2
- Goldenberg A, Silverberg N, Silverberg JI, et al. Pediatric allergic contact dermatitis: lessons for better care. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2015;3:661-667; quiz 668. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2015.02.007
- Silverberg JI, Hou A, Warshaw EM, et al. Age-related differences in patch testing results among children: analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2018 [published online July 24, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:818-826. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.07.030
- Tokura Y, Phadungsaksawasdi P, Ito T. Atopic dermatitis as Th2 disease revisited. J Cutan Immunol Allergy. 2018;1:158-164. doi:10.1002/cia2.12033
- Brunner PM, Guttman-Yassky E, Leung DY. The immunology of atopic dermatitis and its reversibility with broad-spectrum and targeted therapies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139(suppl 4):S65-S76. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2017.01.011
- Murphy PB, Atwater AR, Mueller M. Allergic Contact Dermatitis. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532866/
- He D, Wu L, Kim HK, et al. IL-17 and IFN-gamma mediate the elicitation of contact hypersensitivity responses by different mechanisms and both are required for optimal responses [published online June 24, 2009]. J Immunol. 2009;183:1463-1470. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0804108.
- Dhingra N, Shemer A, Correa da Rosa J, et al. Molecular profiling of contact dermatitis skin identifies allergen-dependent differences in immune response [published April 25, 2014]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:362-372. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2014.03.009
- Owen JL, Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. The role and diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:293-302. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0340-7
- Uehara M, Sawai T. A longitudinal study of contact sensitivity in patients with atopic dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 1989;125:366-368.
- Yüksel YT, Nørreslet LB, Thyssen JP. Allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Curr Derm Rep. 2021;10:67-76.
- Gittler JK, Krueger JG, Guttman-Yassky E. Atopic dermatitis results in intrinsic barrier and immune abnormalities: implications for contact dermatitis [published online August 28, 2012]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;131:300-313. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2012.06.048
- Drislane C, Irvine AD. The role of filaggrin in atopic dermatitis and allergic disease [published online October 14, 2019]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020;124:36-43. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2019.10.008
- Thyssen JP, McFadden JP, Kimber I. The multiple factors affectingthe association between atopic dermatitis and contact sensitization [published online December 26, 2013]. Allergy. 2014;69:28-36. doi:10.1111/all.12358
- Timmerman JG, Heederik D, Spee T, et al. Contact dermatitis in the construction industry: the role of filaggrin loss-of-function mutations [published online December 12, 2015]. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:348-355. doi:10.1111/bjd.14215
- Edslev SM, Agner T, Andersen PS. Skin microbiome in atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100:adv00164. doi:
10.2340/00015555-3514 - Silverberg JI, Hou A, Warshaw EM, et al. Prevalence and trend of allergen sensitization in adults and children with atopic dermatitis referred for patch testing, North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2016 [published online March 27, 2021]. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9:2853-2866.e14. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2021.03.028
- Pratt MD, Mufti A, Lipson J, et al. Patch test reactions to corticosteroids: retrospective analysis from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group 2007-2014. Dermatitis. 2017;28:58-63. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000251
- Xiong M, Peterson MY, Hylwa S. Allergic contact dermatitis from benzyl alcohol in hydrocortisone cream [published online January 14, 2022]. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;86:424-425. doi:10.1111/cod.14042
- Goldenberg A, Mousdicas N, Silverberg N, et al. Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry inaugural case data. Dermatitis. 2016;27:293-302. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000214
- Jacob SE, McGowan M, Silverberg NB, et al. Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry data on contact allergy in children with atopic dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:765-770. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.6136
- Zug KA, McGinley-Smith D, Warshaw EM, et al. Contact allergy in children referred for patch testing: North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2004. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:1329-1336. doi:10.1001/archderm.144.10.1329
- Zug KA, Pham AK, Belsito DV, et al. Patch testing in children from 2005 to 2012: results from the North American contact dermatitis group. Dermatitis. 2014;25:345-355. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000083
- Hamann CR, Hamann D, Egeberg A, et al. Association between atopic dermatitis and contact sensitization: a systematic review and meta-analysis [published online April 6, 2017]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:70-78. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.02.001
- Simonsen AB, Johansen JD, Deleuran M, et al. Contact allergy in children with atopic dermatitis: a systematic review [published online June 12, 2017]. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:395-405. doi:10.1111/bjd.15628
- Chen R, Raffi J, Murase JE. Tocopherol allergic dermatitis masquerading as lifelong atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2020;31:E3-E4. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000543
- Tam I, Yu J. Pediatric contact dermatitis: what’s new. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020;32:524-530. doi:10.1097/MOP.0000000000000919
- Cohen DE, Rao S, Brancaccio RR. Use of the North American Contact Dermatitis Group Standard 65-allergen series alone in the evaluation of allergic contact dermatitis: a series of 794 patients. Dermatitis. 2008;19:137-141.
- Schalock PC, Dunnick CA, Nedorost S, et al. American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series: 2020 update. Dermatitis. 2020;31:279-282. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000621
- Yu J, Atwater AR, Brod B, et al. Pediatric baseline patch test series: Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Workgroup. Dermatitis. 2018;29:206-212. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000385
- Bußmann C, Novak N. Systemic therapy of atopic dermatitis. Allergol Select. 2017;1:1-8. doi:10.5414/ALX01285E
- Sung CT, McGowan MA, Machler BC, et al. Systemic treatments for allergic contact dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2019;30:46-53. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000435
- Johnson H, Adler BL, Yu J. Dupilumab for allergic contact dermatitis: an overview of its use and impact on patch testing. Cutis. 2022;109:265-267, E4-E5. doi:10.12788/cutis.0519
- Todberg T, Zachariae C, Krustrup D, et al. The effect of treatment with anti-interleukin-17 in patients with allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:431-432. doi:10.1111/cod.12988
- Ungar B, Pavel AB, Li R, et al. Phase 2 randomized, double-blind study of IL-17 targeting with secukinumab in atopic dermatitis [published online May 16, 2020]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;147:394-397. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.055
- Perche PO, Cook MK, Feldman SR. Abrocitinib: a new FDA-approved drug for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis [published online May 19, 2022]. Ann Pharmacother. doi:10.1177/10600280221096713
Atopic dermatitis (AD) and allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) are 2 common inflammatory skin conditions that may have similar clinical presentations. Historically, it was thought that these conditions could not be diagnosed simultaneously due to their differing immune mechanisms; however, this belief has been challenged by recent evidence suggesting a more nuanced relationship between the 2 disease processes. In this review, we examine the complex interplay between AD and ACD and explain how shifts in conventional understanding of the 2 conditions shaped our evolving recognition of their ability to coexist.
Epidemiology of AD and ACD
Atopic dermatitis is the most common inflammatory skin disease in children and adolescents, with an estimated prevalence reaching 21%.1 In 60% of cases, onset of AD will occur within the first year of life, and 90% of cases begin within the first 5 years.2 Resolution may occur by adulthood; however, AD may continue to impact up to 8% to 9% of adults, with an increased prevalence in those older than 75 years.1 This may represent an underestimation of the burden of adult AD; one systematic review of 17 studies found that the pooled proportion of adult-onset AD was greater than 25%.3
In contrast, ACD previously was assumed to be a disease that more commonly impacted adults and only rarely children, primarily due to an early misconception that children were not frequently exposed to contact allergens and their immune systems were too immature to react to them even if exposed.4,5 However, it is now known that children do have risk factors for development of ACD, including a thinner stratum corneum and potentially a more absorbent skin surface.4 In addition, a 2022 study by the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) found similar rates of ACD in children (n=1871) and adults (n=41,699) referred for patch testing (55.2% and 57.3%, respectively) as well as similar rates of having at least 1 relevant positive patch test (49.2% and 52.2%).6
In opposition to traditional beliefs, these findings highlight that AD and ACD can occur across age groups.
Immune Mechanism
The pathogenesis of AD represents a multifactorial process involving the immune system, cutaneous flora, genetic predisposition, and surrounding environment. Immunologically, acute AD is driven by a predominantly TH2 helper T-cell response with high levels of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-137; TH22, TH17, and TH1 also have been implicated.8 Notably, TH17 is found in high levels during the acute eczema phase, while TH1 and TH22are associated with the chronic phase.7
The pathophysiology of ACD is not completely understood. The classic paradigm involves 2 phases: sensitization and elicitation. Sensitization involves antigen-presenting cells that take up allergens absorbed by the skin to present them in regional lymph nodes where antigen-specific T lymphocytes are generated. Elicitation occurs upon re-exposure to the allergen, at which time the primed T lymphocytes are recruited to the skin, causing inflammation.9 Allergic contact dermatitis initially was thought to be driven by TH1 cytokines and IL-17 but now is understood to be more complex.10 Studies have revealed immune polarization of contact allergens, demonstrating that nickel primarily induces a TH1/TH17 response, whereas fragrance and rubber accelerators skew to TH2; TH9 and TH22 also may be involved depending on the causative allergen.11,12
Of note, the immunologic differences between AD and ACD led early investigators to believe that patients with AD were relatively protected from ACD.13 However, as previously described, there are several overlapping cytokines between AD and ACD. Furthermore, research has revealed that risk of contact sensitization might be increased in the chronic eczema phase due to the shared TH1 pathway.14 Barrier-disrupted skin (such as that in AD) also may increase the cytokine response and the density of antigen-presenting cells, leading to a proallergic state.15 This suggests that the immunologic pathways of AD and ACD are more intertwined than was previously understood.
Underlying Risk Factors
Skin barrier dysfunction is a key step in the pathogenesis of AD. Patients with AD commonly have loss-of-function mutations in the filaggrin gene, a protein that is key to the function of the stratum corneum. Loss of this protein may not only impact the immune response as previously noted but also may lead to increased transepidermal water loss and bacterial colonization.16 Interestingly, a 2014 review examined how this mutation could lead to an increased risk of sensitization to bivalent metal ions via an impaired chelating ability of the skin.17 Furthermore, a 2016 study conducted in Dutch construction workers revealed an increased risk for contact dermatitis (irritant and allergic) for those with a loss-of-function filaggrin mutation.18
Importantly, this same mutation may explain why patients with AD tend to have increased skin colonization by Staphylococcus aureus. The abundance of S aureus and the relative decrease in the diversity of other microorganisms on the skin may be associated with increased AD severity.19 Likewise, S aureus may play a role in the pathogenesis of ACD via production of its exotoxin directed at the T-cell receptor V beta 17 region. In particular, this receptor has been associated with nickel sensitization.17
Another risk factor to consider is increased exposure to contact sensitizers when treating AD. For instance, management often includes use of over-the-counter emollients, natural or botanical remedies with purported benefits for AD, cleansers, and detergents. However, these products can contain some of the most prevalent contact allergens seen in those with AD, including methyl-isothiazolinone, formaldehyde releasers, and fragrance.20 Topical corticosteroids also are frequently used, and ACD to steroid molecules can occur, particularly to tixocortol-21-pivalate (a marker for class A corticosteroids) and budesonide (a marker for class B corticosteroids).21 Other allergens (eg, benzyl alcohol, propylene glycol) also may be found as inactive ingredients of topical corticosteroids.22 These exposures may place AD patients at risk for ACD.
The Coexistence of AD and ACD
Given the overlapping epidemiology, immunology, and potentially increased risk for the development of ACD in patients with AD, it would be reasonable to assume that the 2 diagnoses could coexist; however, is there clinical data to support this idea? Based on recent database reviews, the answer appears to be yes.20,23-26 An analysis from the Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry revealed that 30% of 1142 pediatric patch test cases analyzed were diagnosed as AD and ACD simultaneously.24 The NACDG found similar results in its 2021 review, as 29.5% of children (n=1648) and 20.7% of adults (n=36,834) had a concurrent diagnosis of AD and ACD.20 Notably, older results from these databases also demonstrated an association between the 2 conditions.23,25,26
It remains unclear whether the prevalence of ACD is higher in those with or without AD. A comprehensive systematic review conducted in 2017 examined this topic through analysis of 74 studies. The results demonstrated a similar prevalence of contact sensitization in individuals with and without AD.27 Another systematic review of 31 studies conducted in 2017 found a higher prevalence for ACD in children without AD; however, the authors noted that the included studies were too variable (eg, size, design, allergens tested) to draw definitive conclusions.28
Even though there is no clear overall increased risk for ACD in patients with AD, research has suggested that certain allergens may be more prevalent in the setting of AD. An NACDG study found that adults with AD had increased odds of reacting to 10 of the top 25 NACDG screening allergens compared to those without AD.20 Other studies have found that AD patients may be more likely to become sensitized to certain allergens, such as fragrance and lanolin.14
Considerations for Management
Diagnosis of ACD in patients with AD can be challenging because these conditions may present similarly with chronic, pruritic, inflammatory patches and plaques. Chronic ACD may be misdiagnosed as AD if patch testing is not performed.29 Given the prevalence of ACD in the setting of AD, there should be a low threshold to pursue patch testing, especially when dermatitis is recalcitrant to standard therapies or presents in an atypical distribution (ie, perioral, predominantly head/neck, hand and foot, isolated eyelid involvement, buttocks).4,30 Various allergen series are available for patch testing adults and children including the NACDG Standard Series, American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series, or the Pediatric Baseline Series.31-33
If potentially relevant allergens are uncovered by patch testing, patients should be counseled on avoidance strategies. However, allergen avoidance may not always lead to complete symptom resolution, especially if AD is present concomitantly with ACD. Therefore, use of topical or systemic therapies still may be required. Topical corticosteroids can be used when dermatitis is acute and localized. Systemic corticosteroids are utilized for both diagnoses when cases are more severe or extensive, but their adverse-effect profile limits long-term use. Other systemic treatments, including conventional agents (ie, azathioprine, cyclosporine, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil), biologics, and small molecule inhibitors also may be considered for severe cases.34,35 Dupilumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-4/IL-13, is approved for use in moderate to severe AD in patients 6 months and older. Recent evidence has suggested that dupilumab also may be an effective off-label treatment choice for ACD when allergen avoidance alone is insufficient.36 Studies have been conducted on secukinumab, a monoclonal antibody against IL-17; however, it has not been shown to be effective in either AD or ACD.37,38 This indicates that targeted biologics may not always be successful in treating these diagnoses, likely due to their complex immune pathways. Finally, there is an emerging role for JAK inhibitors. Three are approved for AD: topical ruxolitinib, oral abrocitinib, and oral upadacitinib.39 Further investigation is needed to determine the efficacy of JAK inhibitors in ACD.
Final Interpretation
Evolving evidence shows that AD and ACD can occur at the same time despite the historical perspective that their immune pathways were too polarized for this to happen. Atopic dermatitis may be an important risk factor for subsequent development of ACD. Management should include a low threshold to perform patch testing, while pharmacotherapies utilized in the treatment of both conditions should be considered.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) and allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) are 2 common inflammatory skin conditions that may have similar clinical presentations. Historically, it was thought that these conditions could not be diagnosed simultaneously due to their differing immune mechanisms; however, this belief has been challenged by recent evidence suggesting a more nuanced relationship between the 2 disease processes. In this review, we examine the complex interplay between AD and ACD and explain how shifts in conventional understanding of the 2 conditions shaped our evolving recognition of their ability to coexist.
Epidemiology of AD and ACD
Atopic dermatitis is the most common inflammatory skin disease in children and adolescents, with an estimated prevalence reaching 21%.1 In 60% of cases, onset of AD will occur within the first year of life, and 90% of cases begin within the first 5 years.2 Resolution may occur by adulthood; however, AD may continue to impact up to 8% to 9% of adults, with an increased prevalence in those older than 75 years.1 This may represent an underestimation of the burden of adult AD; one systematic review of 17 studies found that the pooled proportion of adult-onset AD was greater than 25%.3
In contrast, ACD previously was assumed to be a disease that more commonly impacted adults and only rarely children, primarily due to an early misconception that children were not frequently exposed to contact allergens and their immune systems were too immature to react to them even if exposed.4,5 However, it is now known that children do have risk factors for development of ACD, including a thinner stratum corneum and potentially a more absorbent skin surface.4 In addition, a 2022 study by the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) found similar rates of ACD in children (n=1871) and adults (n=41,699) referred for patch testing (55.2% and 57.3%, respectively) as well as similar rates of having at least 1 relevant positive patch test (49.2% and 52.2%).6
In opposition to traditional beliefs, these findings highlight that AD and ACD can occur across age groups.
Immune Mechanism
The pathogenesis of AD represents a multifactorial process involving the immune system, cutaneous flora, genetic predisposition, and surrounding environment. Immunologically, acute AD is driven by a predominantly TH2 helper T-cell response with high levels of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-137; TH22, TH17, and TH1 also have been implicated.8 Notably, TH17 is found in high levels during the acute eczema phase, while TH1 and TH22are associated with the chronic phase.7
The pathophysiology of ACD is not completely understood. The classic paradigm involves 2 phases: sensitization and elicitation. Sensitization involves antigen-presenting cells that take up allergens absorbed by the skin to present them in regional lymph nodes where antigen-specific T lymphocytes are generated. Elicitation occurs upon re-exposure to the allergen, at which time the primed T lymphocytes are recruited to the skin, causing inflammation.9 Allergic contact dermatitis initially was thought to be driven by TH1 cytokines and IL-17 but now is understood to be more complex.10 Studies have revealed immune polarization of contact allergens, demonstrating that nickel primarily induces a TH1/TH17 response, whereas fragrance and rubber accelerators skew to TH2; TH9 and TH22 also may be involved depending on the causative allergen.11,12
Of note, the immunologic differences between AD and ACD led early investigators to believe that patients with AD were relatively protected from ACD.13 However, as previously described, there are several overlapping cytokines between AD and ACD. Furthermore, research has revealed that risk of contact sensitization might be increased in the chronic eczema phase due to the shared TH1 pathway.14 Barrier-disrupted skin (such as that in AD) also may increase the cytokine response and the density of antigen-presenting cells, leading to a proallergic state.15 This suggests that the immunologic pathways of AD and ACD are more intertwined than was previously understood.
Underlying Risk Factors
Skin barrier dysfunction is a key step in the pathogenesis of AD. Patients with AD commonly have loss-of-function mutations in the filaggrin gene, a protein that is key to the function of the stratum corneum. Loss of this protein may not only impact the immune response as previously noted but also may lead to increased transepidermal water loss and bacterial colonization.16 Interestingly, a 2014 review examined how this mutation could lead to an increased risk of sensitization to bivalent metal ions via an impaired chelating ability of the skin.17 Furthermore, a 2016 study conducted in Dutch construction workers revealed an increased risk for contact dermatitis (irritant and allergic) for those with a loss-of-function filaggrin mutation.18
Importantly, this same mutation may explain why patients with AD tend to have increased skin colonization by Staphylococcus aureus. The abundance of S aureus and the relative decrease in the diversity of other microorganisms on the skin may be associated with increased AD severity.19 Likewise, S aureus may play a role in the pathogenesis of ACD via production of its exotoxin directed at the T-cell receptor V beta 17 region. In particular, this receptor has been associated with nickel sensitization.17
Another risk factor to consider is increased exposure to contact sensitizers when treating AD. For instance, management often includes use of over-the-counter emollients, natural or botanical remedies with purported benefits for AD, cleansers, and detergents. However, these products can contain some of the most prevalent contact allergens seen in those with AD, including methyl-isothiazolinone, formaldehyde releasers, and fragrance.20 Topical corticosteroids also are frequently used, and ACD to steroid molecules can occur, particularly to tixocortol-21-pivalate (a marker for class A corticosteroids) and budesonide (a marker for class B corticosteroids).21 Other allergens (eg, benzyl alcohol, propylene glycol) also may be found as inactive ingredients of topical corticosteroids.22 These exposures may place AD patients at risk for ACD.
The Coexistence of AD and ACD
Given the overlapping epidemiology, immunology, and potentially increased risk for the development of ACD in patients with AD, it would be reasonable to assume that the 2 diagnoses could coexist; however, is there clinical data to support this idea? Based on recent database reviews, the answer appears to be yes.20,23-26 An analysis from the Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry revealed that 30% of 1142 pediatric patch test cases analyzed were diagnosed as AD and ACD simultaneously.24 The NACDG found similar results in its 2021 review, as 29.5% of children (n=1648) and 20.7% of adults (n=36,834) had a concurrent diagnosis of AD and ACD.20 Notably, older results from these databases also demonstrated an association between the 2 conditions.23,25,26
It remains unclear whether the prevalence of ACD is higher in those with or without AD. A comprehensive systematic review conducted in 2017 examined this topic through analysis of 74 studies. The results demonstrated a similar prevalence of contact sensitization in individuals with and without AD.27 Another systematic review of 31 studies conducted in 2017 found a higher prevalence for ACD in children without AD; however, the authors noted that the included studies were too variable (eg, size, design, allergens tested) to draw definitive conclusions.28
Even though there is no clear overall increased risk for ACD in patients with AD, research has suggested that certain allergens may be more prevalent in the setting of AD. An NACDG study found that adults with AD had increased odds of reacting to 10 of the top 25 NACDG screening allergens compared to those without AD.20 Other studies have found that AD patients may be more likely to become sensitized to certain allergens, such as fragrance and lanolin.14
Considerations for Management
Diagnosis of ACD in patients with AD can be challenging because these conditions may present similarly with chronic, pruritic, inflammatory patches and plaques. Chronic ACD may be misdiagnosed as AD if patch testing is not performed.29 Given the prevalence of ACD in the setting of AD, there should be a low threshold to pursue patch testing, especially when dermatitis is recalcitrant to standard therapies or presents in an atypical distribution (ie, perioral, predominantly head/neck, hand and foot, isolated eyelid involvement, buttocks).4,30 Various allergen series are available for patch testing adults and children including the NACDG Standard Series, American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series, or the Pediatric Baseline Series.31-33
If potentially relevant allergens are uncovered by patch testing, patients should be counseled on avoidance strategies. However, allergen avoidance may not always lead to complete symptom resolution, especially if AD is present concomitantly with ACD. Therefore, use of topical or systemic therapies still may be required. Topical corticosteroids can be used when dermatitis is acute and localized. Systemic corticosteroids are utilized for both diagnoses when cases are more severe or extensive, but their adverse-effect profile limits long-term use. Other systemic treatments, including conventional agents (ie, azathioprine, cyclosporine, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil), biologics, and small molecule inhibitors also may be considered for severe cases.34,35 Dupilumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-4/IL-13, is approved for use in moderate to severe AD in patients 6 months and older. Recent evidence has suggested that dupilumab also may be an effective off-label treatment choice for ACD when allergen avoidance alone is insufficient.36 Studies have been conducted on secukinumab, a monoclonal antibody against IL-17; however, it has not been shown to be effective in either AD or ACD.37,38 This indicates that targeted biologics may not always be successful in treating these diagnoses, likely due to their complex immune pathways. Finally, there is an emerging role for JAK inhibitors. Three are approved for AD: topical ruxolitinib, oral abrocitinib, and oral upadacitinib.39 Further investigation is needed to determine the efficacy of JAK inhibitors in ACD.
Final Interpretation
Evolving evidence shows that AD and ACD can occur at the same time despite the historical perspective that their immune pathways were too polarized for this to happen. Atopic dermatitis may be an important risk factor for subsequent development of ACD. Management should include a low threshold to perform patch testing, while pharmacotherapies utilized in the treatment of both conditions should be considered.
- Chan LN, Magyari A, Ye M, et al. The epidemiology of atopic dermatitis in older adults: a population-based study in the United Kingdom. PLoS One. 2021;16:E0258219. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0258219
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Chamlin SL, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 1. diagnosis and assessment of atopic dermatitis [published online November 27, 2013]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:338-351. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.10.010
- Lee HH, Patel KR, Singam V, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence and phenotype of adult-onset atopic dermatitis [published online June 2, 2018]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1526-1532.e7. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.05.1241
- Borok J, Matiz C, Goldenberg A, et al. Contact dermatitis in atopic dermatitis children—past, present, and future. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019;56:86-98. doi:10.1007/s12016-018-8711-2
- Goldenberg A, Silverberg N, Silverberg JI, et al. Pediatric allergic contact dermatitis: lessons for better care. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2015;3:661-667; quiz 668. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2015.02.007
- Silverberg JI, Hou A, Warshaw EM, et al. Age-related differences in patch testing results among children: analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2018 [published online July 24, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:818-826. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.07.030
- Tokura Y, Phadungsaksawasdi P, Ito T. Atopic dermatitis as Th2 disease revisited. J Cutan Immunol Allergy. 2018;1:158-164. doi:10.1002/cia2.12033
- Brunner PM, Guttman-Yassky E, Leung DY. The immunology of atopic dermatitis and its reversibility with broad-spectrum and targeted therapies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139(suppl 4):S65-S76. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2017.01.011
- Murphy PB, Atwater AR, Mueller M. Allergic Contact Dermatitis. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532866/
- He D, Wu L, Kim HK, et al. IL-17 and IFN-gamma mediate the elicitation of contact hypersensitivity responses by different mechanisms and both are required for optimal responses [published online June 24, 2009]. J Immunol. 2009;183:1463-1470. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0804108.
- Dhingra N, Shemer A, Correa da Rosa J, et al. Molecular profiling of contact dermatitis skin identifies allergen-dependent differences in immune response [published April 25, 2014]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:362-372. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2014.03.009
- Owen JL, Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. The role and diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:293-302. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0340-7
- Uehara M, Sawai T. A longitudinal study of contact sensitivity in patients with atopic dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 1989;125:366-368.
- Yüksel YT, Nørreslet LB, Thyssen JP. Allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Curr Derm Rep. 2021;10:67-76.
- Gittler JK, Krueger JG, Guttman-Yassky E. Atopic dermatitis results in intrinsic barrier and immune abnormalities: implications for contact dermatitis [published online August 28, 2012]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;131:300-313. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2012.06.048
- Drislane C, Irvine AD. The role of filaggrin in atopic dermatitis and allergic disease [published online October 14, 2019]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020;124:36-43. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2019.10.008
- Thyssen JP, McFadden JP, Kimber I. The multiple factors affectingthe association between atopic dermatitis and contact sensitization [published online December 26, 2013]. Allergy. 2014;69:28-36. doi:10.1111/all.12358
- Timmerman JG, Heederik D, Spee T, et al. Contact dermatitis in the construction industry: the role of filaggrin loss-of-function mutations [published online December 12, 2015]. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:348-355. doi:10.1111/bjd.14215
- Edslev SM, Agner T, Andersen PS. Skin microbiome in atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100:adv00164. doi:
10.2340/00015555-3514 - Silverberg JI, Hou A, Warshaw EM, et al. Prevalence and trend of allergen sensitization in adults and children with atopic dermatitis referred for patch testing, North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2016 [published online March 27, 2021]. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9:2853-2866.e14. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2021.03.028
- Pratt MD, Mufti A, Lipson J, et al. Patch test reactions to corticosteroids: retrospective analysis from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group 2007-2014. Dermatitis. 2017;28:58-63. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000251
- Xiong M, Peterson MY, Hylwa S. Allergic contact dermatitis from benzyl alcohol in hydrocortisone cream [published online January 14, 2022]. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;86:424-425. doi:10.1111/cod.14042
- Goldenberg A, Mousdicas N, Silverberg N, et al. Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry inaugural case data. Dermatitis. 2016;27:293-302. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000214
- Jacob SE, McGowan M, Silverberg NB, et al. Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry data on contact allergy in children with atopic dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:765-770. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.6136
- Zug KA, McGinley-Smith D, Warshaw EM, et al. Contact allergy in children referred for patch testing: North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2004. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:1329-1336. doi:10.1001/archderm.144.10.1329
- Zug KA, Pham AK, Belsito DV, et al. Patch testing in children from 2005 to 2012: results from the North American contact dermatitis group. Dermatitis. 2014;25:345-355. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000083
- Hamann CR, Hamann D, Egeberg A, et al. Association between atopic dermatitis and contact sensitization: a systematic review and meta-analysis [published online April 6, 2017]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:70-78. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.02.001
- Simonsen AB, Johansen JD, Deleuran M, et al. Contact allergy in children with atopic dermatitis: a systematic review [published online June 12, 2017]. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:395-405. doi:10.1111/bjd.15628
- Chen R, Raffi J, Murase JE. Tocopherol allergic dermatitis masquerading as lifelong atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2020;31:E3-E4. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000543
- Tam I, Yu J. Pediatric contact dermatitis: what’s new. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020;32:524-530. doi:10.1097/MOP.0000000000000919
- Cohen DE, Rao S, Brancaccio RR. Use of the North American Contact Dermatitis Group Standard 65-allergen series alone in the evaluation of allergic contact dermatitis: a series of 794 patients. Dermatitis. 2008;19:137-141.
- Schalock PC, Dunnick CA, Nedorost S, et al. American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series: 2020 update. Dermatitis. 2020;31:279-282. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000621
- Yu J, Atwater AR, Brod B, et al. Pediatric baseline patch test series: Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Workgroup. Dermatitis. 2018;29:206-212. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000385
- Bußmann C, Novak N. Systemic therapy of atopic dermatitis. Allergol Select. 2017;1:1-8. doi:10.5414/ALX01285E
- Sung CT, McGowan MA, Machler BC, et al. Systemic treatments for allergic contact dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2019;30:46-53. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000435
- Johnson H, Adler BL, Yu J. Dupilumab for allergic contact dermatitis: an overview of its use and impact on patch testing. Cutis. 2022;109:265-267, E4-E5. doi:10.12788/cutis.0519
- Todberg T, Zachariae C, Krustrup D, et al. The effect of treatment with anti-interleukin-17 in patients with allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:431-432. doi:10.1111/cod.12988
- Ungar B, Pavel AB, Li R, et al. Phase 2 randomized, double-blind study of IL-17 targeting with secukinumab in atopic dermatitis [published online May 16, 2020]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;147:394-397. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.055
- Perche PO, Cook MK, Feldman SR. Abrocitinib: a new FDA-approved drug for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis [published online May 19, 2022]. Ann Pharmacother. doi:10.1177/10600280221096713
- Chan LN, Magyari A, Ye M, et al. The epidemiology of atopic dermatitis in older adults: a population-based study in the United Kingdom. PLoS One. 2021;16:E0258219. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0258219
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Chamlin SL, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 1. diagnosis and assessment of atopic dermatitis [published online November 27, 2013]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:338-351. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.10.010
- Lee HH, Patel KR, Singam V, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence and phenotype of adult-onset atopic dermatitis [published online June 2, 2018]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1526-1532.e7. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.05.1241
- Borok J, Matiz C, Goldenberg A, et al. Contact dermatitis in atopic dermatitis children—past, present, and future. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019;56:86-98. doi:10.1007/s12016-018-8711-2
- Goldenberg A, Silverberg N, Silverberg JI, et al. Pediatric allergic contact dermatitis: lessons for better care. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2015;3:661-667; quiz 668. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2015.02.007
- Silverberg JI, Hou A, Warshaw EM, et al. Age-related differences in patch testing results among children: analysis of North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2018 [published online July 24, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:818-826. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.07.030
- Tokura Y, Phadungsaksawasdi P, Ito T. Atopic dermatitis as Th2 disease revisited. J Cutan Immunol Allergy. 2018;1:158-164. doi:10.1002/cia2.12033
- Brunner PM, Guttman-Yassky E, Leung DY. The immunology of atopic dermatitis and its reversibility with broad-spectrum and targeted therapies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139(suppl 4):S65-S76. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2017.01.011
- Murphy PB, Atwater AR, Mueller M. Allergic Contact Dermatitis. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532866/
- He D, Wu L, Kim HK, et al. IL-17 and IFN-gamma mediate the elicitation of contact hypersensitivity responses by different mechanisms and both are required for optimal responses [published online June 24, 2009]. J Immunol. 2009;183:1463-1470. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0804108.
- Dhingra N, Shemer A, Correa da Rosa J, et al. Molecular profiling of contact dermatitis skin identifies allergen-dependent differences in immune response [published April 25, 2014]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:362-372. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2014.03.009
- Owen JL, Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. The role and diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:293-302. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0340-7
- Uehara M, Sawai T. A longitudinal study of contact sensitivity in patients with atopic dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 1989;125:366-368.
- Yüksel YT, Nørreslet LB, Thyssen JP. Allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Curr Derm Rep. 2021;10:67-76.
- Gittler JK, Krueger JG, Guttman-Yassky E. Atopic dermatitis results in intrinsic barrier and immune abnormalities: implications for contact dermatitis [published online August 28, 2012]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;131:300-313. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2012.06.048
- Drislane C, Irvine AD. The role of filaggrin in atopic dermatitis and allergic disease [published online October 14, 2019]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020;124:36-43. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2019.10.008
- Thyssen JP, McFadden JP, Kimber I. The multiple factors affectingthe association between atopic dermatitis and contact sensitization [published online December 26, 2013]. Allergy. 2014;69:28-36. doi:10.1111/all.12358
- Timmerman JG, Heederik D, Spee T, et al. Contact dermatitis in the construction industry: the role of filaggrin loss-of-function mutations [published online December 12, 2015]. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:348-355. doi:10.1111/bjd.14215
- Edslev SM, Agner T, Andersen PS. Skin microbiome in atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100:adv00164. doi:
10.2340/00015555-3514 - Silverberg JI, Hou A, Warshaw EM, et al. Prevalence and trend of allergen sensitization in adults and children with atopic dermatitis referred for patch testing, North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2016 [published online March 27, 2021]. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9:2853-2866.e14. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2021.03.028
- Pratt MD, Mufti A, Lipson J, et al. Patch test reactions to corticosteroids: retrospective analysis from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group 2007-2014. Dermatitis. 2017;28:58-63. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000251
- Xiong M, Peterson MY, Hylwa S. Allergic contact dermatitis from benzyl alcohol in hydrocortisone cream [published online January 14, 2022]. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;86:424-425. doi:10.1111/cod.14042
- Goldenberg A, Mousdicas N, Silverberg N, et al. Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry inaugural case data. Dermatitis. 2016;27:293-302. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000214
- Jacob SE, McGowan M, Silverberg NB, et al. Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry data on contact allergy in children with atopic dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:765-770. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.6136
- Zug KA, McGinley-Smith D, Warshaw EM, et al. Contact allergy in children referred for patch testing: North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 2001-2004. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:1329-1336. doi:10.1001/archderm.144.10.1329
- Zug KA, Pham AK, Belsito DV, et al. Patch testing in children from 2005 to 2012: results from the North American contact dermatitis group. Dermatitis. 2014;25:345-355. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000083
- Hamann CR, Hamann D, Egeberg A, et al. Association between atopic dermatitis and contact sensitization: a systematic review and meta-analysis [published online April 6, 2017]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:70-78. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.02.001
- Simonsen AB, Johansen JD, Deleuran M, et al. Contact allergy in children with atopic dermatitis: a systematic review [published online June 12, 2017]. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:395-405. doi:10.1111/bjd.15628
- Chen R, Raffi J, Murase JE. Tocopherol allergic dermatitis masquerading as lifelong atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2020;31:E3-E4. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000543
- Tam I, Yu J. Pediatric contact dermatitis: what’s new. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020;32:524-530. doi:10.1097/MOP.0000000000000919
- Cohen DE, Rao S, Brancaccio RR. Use of the North American Contact Dermatitis Group Standard 65-allergen series alone in the evaluation of allergic contact dermatitis: a series of 794 patients. Dermatitis. 2008;19:137-141.
- Schalock PC, Dunnick CA, Nedorost S, et al. American Contact Dermatitis Society Core Allergen Series: 2020 update. Dermatitis. 2020;31:279-282. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000621
- Yu J, Atwater AR, Brod B, et al. Pediatric baseline patch test series: Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Workgroup. Dermatitis. 2018;29:206-212. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000385
- Bußmann C, Novak N. Systemic therapy of atopic dermatitis. Allergol Select. 2017;1:1-8. doi:10.5414/ALX01285E
- Sung CT, McGowan MA, Machler BC, et al. Systemic treatments for allergic contact dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2019;30:46-53. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000435
- Johnson H, Adler BL, Yu J. Dupilumab for allergic contact dermatitis: an overview of its use and impact on patch testing. Cutis. 2022;109:265-267, E4-E5. doi:10.12788/cutis.0519
- Todberg T, Zachariae C, Krustrup D, et al. The effect of treatment with anti-interleukin-17 in patients with allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:431-432. doi:10.1111/cod.12988
- Ungar B, Pavel AB, Li R, et al. Phase 2 randomized, double-blind study of IL-17 targeting with secukinumab in atopic dermatitis [published online May 16, 2020]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;147:394-397. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.055
- Perche PO, Cook MK, Feldman SR. Abrocitinib: a new FDA-approved drug for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis [published online May 19, 2022]. Ann Pharmacother. doi:10.1177/10600280221096713
Practice Points
- Although it previously was thought that atopic dermatitis (AD) and allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) could not coexist due to their polarized immune pathways, current evidence suggests otherwise.
- When both diagnoses are suspected, patch testing should be considered as well as therapeutic strategies that can treat both AD and ACD simultaneously.