User login
EMERGENCY MEDICINE is a practical, peer-reviewed monthly publication and Web site that meets the educational needs of emergency clinicians and urgent care clinicians for their practice.
Consensus document reviews determination of brain death
The document, a result of the World Brain Death Project, surveys the clinical aspects of this determination, such as clinical testing, apnea testing, and the number of examinations required, as well as its social and legal aspects, including documentation, qualifications for making the determination, and religious attitudes toward BD/DNC.
The recommendations are the minimum criteria for BD/DNC, and countries and professional societies may choose to adopt stricter criteria, the authors noted. Seventeen supplements to the consensus statement contain detailed reports on topics the statement examines, including focuses on both adults and children.
“Perhaps the most important points of this project are, first, to show the worldwide acceptance of the concept of BD/DNC and what the minimum requirements are for BD/DNC,” said corresponding author Gene Sung, MD, MPH, director of the neurocritical care and stroke division at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. Second, “this standard is centered around a clinical determination without the need for other testing.”
The consensus document and supplements were published online Aug. 3 in JAMA.
Comprehensive review
A lack of rigor has led to many differences in the determination of BD/DNC, said Dr. Sung. “Some of the variance that is common are the numbers of exams and examiners that are required and whether ancillary tests are required for determination of BD/DNC. In addition, a lot of guidelines and protocols that are in use are not thorough in detailing how to do the examinations and what to do in different circumstances.”
Professional societies such as the World Federation of Intensive and Critical Care recruited experts in BD/DNC to develop recommendations, which were based on relevant articles that they identified during a literature search. “We wanted to develop a fairly comprehensive document that, along with the 17 supplements, builds a foundation to show how to determine BD/DNC – what the minimum clinical criteria needed are and what to do in special circumstances,” Dr. Sung said.
Major sections of the statement include recommendations for the minimum clinical standards for the determination of BD/DNC in adults and children.
Determination must begin by establishing that the patient has sustained an irreversible brain injury that resulted in the loss of all brain function, according to the authors. Confounders such as pharmacologic paralysis and the effect of CNS depressant medications should be ruled out.
In addition, clinical evaluation must include an assessment for coma and an evaluation for brain stem areflexia. Among other criteria, the pupils should be fixed and nonresponsive to light, the face should not move in response to noxious cranial stimulation, and the gag and cough reflexes should be absent. Apnea testing is recommended to evaluate the responsiveness of respiratory centers in the medulla.
Although the definition of BD/DNC is the same in children as in adults, less evidence is available for the determination of BD/DNC in the very young. The authors thus advised a cautious approach to the evaluation of infants and younger children.
Recommendations vary by age and often require serial examinations, including apnea testing, they noted.
Ancillary testing
The consensus statement also reviews ancillary testing, which the authors recommend be required when the minimum clinical examination, including the apnea test, cannot be completed and when it is in the presence of confounding conditions that cannot be resolved.
The authors recommended digital subtraction angiography, radionuclide studies, and transcranial Doppler ultrasonography as ancillary tests based on blood flow in the brain. However, CT angiography and magnetic resonance angiography not be used.
A lack of guidance makes performing an apnea test in patients receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) challenging, according to the authors. Nevertheless, they recommended that the same principles of BD/DNC be applied to adults and children receiving ECMO.
They further recommended a period of preoxygenation before the apnea test, and the document describes in detail the method for administering this test to people receiving ECMO.
Another potentially challenging situation pointed out in the consensus document is the determination of BD/DNC in patients who have been treated with targeted temperature management. Therapeutic hypothermia, particularly if it is preceded or accompanied by sedation, can temporarily impair brain stem reflexes, thus mimicking BD/DNC.
The new document includes a flowchart and step-by-step recommendations as well as suggestions for determining BD/DNC under these circumstances.
Among document limitations acknowledged by the authors is the lack of high-quality data from randomized, controlled trials on which to base their recommendations.
In addition, economic, technological, or personnel limitations may reduce the available options for ancillary testing, they added. Also, the recommendations do not incorporate contributions from patients or social or religious groups, although the authors were mindful of their concerns.
To promote the national and international harmonization of BD/DNC criteria, “medical societies and countries can evaluate their own policies in relation to this document and fix any deficiencies,” Dr. Sung said.
“Many countries do not have any BD/DNC policies and can use the documents from this project to create their own. There may need to be discussions with legal, governmental, religious, and societal leaders to help understand and accept BD/DNC and to help enact policies in different communities,” he added.
Divergent definitions
The determination of death is not simply a scientific question, but also a philosophical, religious, and cultural question, wrote Robert D. Truog, MD, director of the Harvard Center for Bioethics, Boston, and colleagues in an accompanying editorial. Future research should consider cultural differences over these questions.
“Most important is that there be a clear and logical consistency between the definition of death and the tests that are used to diagnose it,” Dr. Truog said.
The concept of whole brain death was advanced as an equivalent to biological death, “such that, when the brain dies, the body literally disintegrates, just as it does after cardiac arrest,” but evidence indicates that this claim is untrue, Dr. Truog said. Current tests also do not diagnose the death of the whole brain.
Another hypothesis is that brain stem death represents the irreversible loss of consciousness and the capacity for spontaneous respiration.
“Instead of focusing on biology, [this definition] focuses on values and is based on the claim that when a person is in a state of irreversible apneic unconsciousness, we may consider them to be dead,” said Dr. Truog. He and his coeditorialists argued that the concept of whole brain death should be replaced with that of brain stem death.
“This report should be a call for our profession, as well as for federal and state lawmakers, to reform our laws so that they are consistent with our diagnostic criteria,” Dr. Truog said.
“The most straightforward way of doing this would be to change U.S. law and adopt the British standard of brain stem death, and then refine our testing to make the diagnosis of irreversible apneic unconsciousness as reliable and safe as possible,” he concluded.
The drafting of the consensus statement was not supported by outside funding. Dr. Sung reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Truog reported receiving compensation from Sanofi and Covance for participating in data and safety monitoring boards unrelated to the consensus document.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The document, a result of the World Brain Death Project, surveys the clinical aspects of this determination, such as clinical testing, apnea testing, and the number of examinations required, as well as its social and legal aspects, including documentation, qualifications for making the determination, and religious attitudes toward BD/DNC.
The recommendations are the minimum criteria for BD/DNC, and countries and professional societies may choose to adopt stricter criteria, the authors noted. Seventeen supplements to the consensus statement contain detailed reports on topics the statement examines, including focuses on both adults and children.
“Perhaps the most important points of this project are, first, to show the worldwide acceptance of the concept of BD/DNC and what the minimum requirements are for BD/DNC,” said corresponding author Gene Sung, MD, MPH, director of the neurocritical care and stroke division at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. Second, “this standard is centered around a clinical determination without the need for other testing.”
The consensus document and supplements were published online Aug. 3 in JAMA.
Comprehensive review
A lack of rigor has led to many differences in the determination of BD/DNC, said Dr. Sung. “Some of the variance that is common are the numbers of exams and examiners that are required and whether ancillary tests are required for determination of BD/DNC. In addition, a lot of guidelines and protocols that are in use are not thorough in detailing how to do the examinations and what to do in different circumstances.”
Professional societies such as the World Federation of Intensive and Critical Care recruited experts in BD/DNC to develop recommendations, which were based on relevant articles that they identified during a literature search. “We wanted to develop a fairly comprehensive document that, along with the 17 supplements, builds a foundation to show how to determine BD/DNC – what the minimum clinical criteria needed are and what to do in special circumstances,” Dr. Sung said.
Major sections of the statement include recommendations for the minimum clinical standards for the determination of BD/DNC in adults and children.
Determination must begin by establishing that the patient has sustained an irreversible brain injury that resulted in the loss of all brain function, according to the authors. Confounders such as pharmacologic paralysis and the effect of CNS depressant medications should be ruled out.
In addition, clinical evaluation must include an assessment for coma and an evaluation for brain stem areflexia. Among other criteria, the pupils should be fixed and nonresponsive to light, the face should not move in response to noxious cranial stimulation, and the gag and cough reflexes should be absent. Apnea testing is recommended to evaluate the responsiveness of respiratory centers in the medulla.
Although the definition of BD/DNC is the same in children as in adults, less evidence is available for the determination of BD/DNC in the very young. The authors thus advised a cautious approach to the evaluation of infants and younger children.
Recommendations vary by age and often require serial examinations, including apnea testing, they noted.
Ancillary testing
The consensus statement also reviews ancillary testing, which the authors recommend be required when the minimum clinical examination, including the apnea test, cannot be completed and when it is in the presence of confounding conditions that cannot be resolved.
The authors recommended digital subtraction angiography, radionuclide studies, and transcranial Doppler ultrasonography as ancillary tests based on blood flow in the brain. However, CT angiography and magnetic resonance angiography not be used.
A lack of guidance makes performing an apnea test in patients receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) challenging, according to the authors. Nevertheless, they recommended that the same principles of BD/DNC be applied to adults and children receiving ECMO.
They further recommended a period of preoxygenation before the apnea test, and the document describes in detail the method for administering this test to people receiving ECMO.
Another potentially challenging situation pointed out in the consensus document is the determination of BD/DNC in patients who have been treated with targeted temperature management. Therapeutic hypothermia, particularly if it is preceded or accompanied by sedation, can temporarily impair brain stem reflexes, thus mimicking BD/DNC.
The new document includes a flowchart and step-by-step recommendations as well as suggestions for determining BD/DNC under these circumstances.
Among document limitations acknowledged by the authors is the lack of high-quality data from randomized, controlled trials on which to base their recommendations.
In addition, economic, technological, or personnel limitations may reduce the available options for ancillary testing, they added. Also, the recommendations do not incorporate contributions from patients or social or religious groups, although the authors were mindful of their concerns.
To promote the national and international harmonization of BD/DNC criteria, “medical societies and countries can evaluate their own policies in relation to this document and fix any deficiencies,” Dr. Sung said.
“Many countries do not have any BD/DNC policies and can use the documents from this project to create their own. There may need to be discussions with legal, governmental, religious, and societal leaders to help understand and accept BD/DNC and to help enact policies in different communities,” he added.
Divergent definitions
The determination of death is not simply a scientific question, but also a philosophical, religious, and cultural question, wrote Robert D. Truog, MD, director of the Harvard Center for Bioethics, Boston, and colleagues in an accompanying editorial. Future research should consider cultural differences over these questions.
“Most important is that there be a clear and logical consistency between the definition of death and the tests that are used to diagnose it,” Dr. Truog said.
The concept of whole brain death was advanced as an equivalent to biological death, “such that, when the brain dies, the body literally disintegrates, just as it does after cardiac arrest,” but evidence indicates that this claim is untrue, Dr. Truog said. Current tests also do not diagnose the death of the whole brain.
Another hypothesis is that brain stem death represents the irreversible loss of consciousness and the capacity for spontaneous respiration.
“Instead of focusing on biology, [this definition] focuses on values and is based on the claim that when a person is in a state of irreversible apneic unconsciousness, we may consider them to be dead,” said Dr. Truog. He and his coeditorialists argued that the concept of whole brain death should be replaced with that of brain stem death.
“This report should be a call for our profession, as well as for federal and state lawmakers, to reform our laws so that they are consistent with our diagnostic criteria,” Dr. Truog said.
“The most straightforward way of doing this would be to change U.S. law and adopt the British standard of brain stem death, and then refine our testing to make the diagnosis of irreversible apneic unconsciousness as reliable and safe as possible,” he concluded.
The drafting of the consensus statement was not supported by outside funding. Dr. Sung reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Truog reported receiving compensation from Sanofi and Covance for participating in data and safety monitoring boards unrelated to the consensus document.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The document, a result of the World Brain Death Project, surveys the clinical aspects of this determination, such as clinical testing, apnea testing, and the number of examinations required, as well as its social and legal aspects, including documentation, qualifications for making the determination, and religious attitudes toward BD/DNC.
The recommendations are the minimum criteria for BD/DNC, and countries and professional societies may choose to adopt stricter criteria, the authors noted. Seventeen supplements to the consensus statement contain detailed reports on topics the statement examines, including focuses on both adults and children.
“Perhaps the most important points of this project are, first, to show the worldwide acceptance of the concept of BD/DNC and what the minimum requirements are for BD/DNC,” said corresponding author Gene Sung, MD, MPH, director of the neurocritical care and stroke division at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. Second, “this standard is centered around a clinical determination without the need for other testing.”
The consensus document and supplements were published online Aug. 3 in JAMA.
Comprehensive review
A lack of rigor has led to many differences in the determination of BD/DNC, said Dr. Sung. “Some of the variance that is common are the numbers of exams and examiners that are required and whether ancillary tests are required for determination of BD/DNC. In addition, a lot of guidelines and protocols that are in use are not thorough in detailing how to do the examinations and what to do in different circumstances.”
Professional societies such as the World Federation of Intensive and Critical Care recruited experts in BD/DNC to develop recommendations, which were based on relevant articles that they identified during a literature search. “We wanted to develop a fairly comprehensive document that, along with the 17 supplements, builds a foundation to show how to determine BD/DNC – what the minimum clinical criteria needed are and what to do in special circumstances,” Dr. Sung said.
Major sections of the statement include recommendations for the minimum clinical standards for the determination of BD/DNC in adults and children.
Determination must begin by establishing that the patient has sustained an irreversible brain injury that resulted in the loss of all brain function, according to the authors. Confounders such as pharmacologic paralysis and the effect of CNS depressant medications should be ruled out.
In addition, clinical evaluation must include an assessment for coma and an evaluation for brain stem areflexia. Among other criteria, the pupils should be fixed and nonresponsive to light, the face should not move in response to noxious cranial stimulation, and the gag and cough reflexes should be absent. Apnea testing is recommended to evaluate the responsiveness of respiratory centers in the medulla.
Although the definition of BD/DNC is the same in children as in adults, less evidence is available for the determination of BD/DNC in the very young. The authors thus advised a cautious approach to the evaluation of infants and younger children.
Recommendations vary by age and often require serial examinations, including apnea testing, they noted.
Ancillary testing
The consensus statement also reviews ancillary testing, which the authors recommend be required when the minimum clinical examination, including the apnea test, cannot be completed and when it is in the presence of confounding conditions that cannot be resolved.
The authors recommended digital subtraction angiography, radionuclide studies, and transcranial Doppler ultrasonography as ancillary tests based on blood flow in the brain. However, CT angiography and magnetic resonance angiography not be used.
A lack of guidance makes performing an apnea test in patients receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) challenging, according to the authors. Nevertheless, they recommended that the same principles of BD/DNC be applied to adults and children receiving ECMO.
They further recommended a period of preoxygenation before the apnea test, and the document describes in detail the method for administering this test to people receiving ECMO.
Another potentially challenging situation pointed out in the consensus document is the determination of BD/DNC in patients who have been treated with targeted temperature management. Therapeutic hypothermia, particularly if it is preceded or accompanied by sedation, can temporarily impair brain stem reflexes, thus mimicking BD/DNC.
The new document includes a flowchart and step-by-step recommendations as well as suggestions for determining BD/DNC under these circumstances.
Among document limitations acknowledged by the authors is the lack of high-quality data from randomized, controlled trials on which to base their recommendations.
In addition, economic, technological, or personnel limitations may reduce the available options for ancillary testing, they added. Also, the recommendations do not incorporate contributions from patients or social or religious groups, although the authors were mindful of their concerns.
To promote the national and international harmonization of BD/DNC criteria, “medical societies and countries can evaluate their own policies in relation to this document and fix any deficiencies,” Dr. Sung said.
“Many countries do not have any BD/DNC policies and can use the documents from this project to create their own. There may need to be discussions with legal, governmental, religious, and societal leaders to help understand and accept BD/DNC and to help enact policies in different communities,” he added.
Divergent definitions
The determination of death is not simply a scientific question, but also a philosophical, religious, and cultural question, wrote Robert D. Truog, MD, director of the Harvard Center for Bioethics, Boston, and colleagues in an accompanying editorial. Future research should consider cultural differences over these questions.
“Most important is that there be a clear and logical consistency between the definition of death and the tests that are used to diagnose it,” Dr. Truog said.
The concept of whole brain death was advanced as an equivalent to biological death, “such that, when the brain dies, the body literally disintegrates, just as it does after cardiac arrest,” but evidence indicates that this claim is untrue, Dr. Truog said. Current tests also do not diagnose the death of the whole brain.
Another hypothesis is that brain stem death represents the irreversible loss of consciousness and the capacity for spontaneous respiration.
“Instead of focusing on biology, [this definition] focuses on values and is based on the claim that when a person is in a state of irreversible apneic unconsciousness, we may consider them to be dead,” said Dr. Truog. He and his coeditorialists argued that the concept of whole brain death should be replaced with that of brain stem death.
“This report should be a call for our profession, as well as for federal and state lawmakers, to reform our laws so that they are consistent with our diagnostic criteria,” Dr. Truog said.
“The most straightforward way of doing this would be to change U.S. law and adopt the British standard of brain stem death, and then refine our testing to make the diagnosis of irreversible apneic unconsciousness as reliable and safe as possible,” he concluded.
The drafting of the consensus statement was not supported by outside funding. Dr. Sung reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Truog reported receiving compensation from Sanofi and Covance for participating in data and safety monitoring boards unrelated to the consensus document.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Guidance covers glycemia in dexamethasone-treated COVID-19 patients
New guidance from the U.K. National Diabetes COVID-19 Response Group addresses glucose management in patients with COVID-19 who are receiving dexamethasone therapy.
Although there are already guidelines that address inpatient management of steroid-induced hyperglycemia, the authors of the new document wrote that this new expert opinion paper was needed “given the ‘triple insult’ of dexamethasone-induced–impaired glucose metabolism, COVID-19–induced insulin resistance, and COVID-19–impaired insulin production.”
RECOVERY trial spurs response
The document, which is the latest in a series from the Association of British Clinical Diabetologists, was published online Aug. 2 in Diabetic Medicine. The group is chaired by Gerry Rayman, MD, consultant physician at the diabetes centre and diabetes research unit, East Suffolk (England) and North East NHS Foundation Trust.
The guidance was developed in response to the recent “breakthrough” Randomised Evaluation of COVID-19 Therapy (RECOVERY) trial, which showed that dexamethasone reduced deaths in patients with COVID-19 on ventilators or receiving oxygen therapy. The advice is not intended for critical care units but can be adapted for that use.
The dose used in RECOVERY – 6 mg daily for 10 days – is 400%-500% greater than the therapeutic glucocorticoid replacement dose. High glucocorticoid doses can exacerbate hyperglycemia in people with established diabetes, unmask undiagnosed diabetes, precipitate hyperglycemia or new-onset diabetes, and can also cause hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state (HHS), the authors explained.
They recommended a target glucose of 6.0-10.0 mmol/L (108-180 mg/dL), although they say up to 12 mmol/L (216 mg/dL) is “acceptable.” They then gave advice on frequency of monitoring for people with and without known diabetes, exclusion of diabetic ketoacidosis and HHS, correction of initial hyperglycemia and maintenance of glycemic control using subcutaneous insulin, and prevention of hypoglycemia at the end of dexamethasone therapy (day 10) with insulin down-titration, discharge, and follow-up.
The detailed insulin guidance covers dose escalation for both insulin-treated and insulin-naive patients. A table suggests increasing correction doses of rapid-acting insulin based on prior total daily dose or weight.
Use of once- or twice-daily NPH insulin is recommended for patients whose glucose has risen above 12 mmol/L, in some cases with the addition of a long-acting analog. A second chart gives dose adjustments for those insulins. Additional guidance addresses patients on insulin pumps.
Guidance useful for U.S. physicians
Francisco Pasquel, MD, assistant professor of medicine in the division of endocrinology at Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview that he believes the guidance is “acceptable” for worldwide use, and that “it’s coherent and consistent with what we typically do.”
However, Dr. Pasquel, who founded COVID-in-Diabetes, an online repository of published guidance and shared experience – to which this new document has now been added – did take issue with one piece of advice. The guidance says that patients already taking premixed insulin formulations can continue using them while increasing the dose by 20%-40%. Given the risk of hypoglycemia associated with those formulations, Dr. Pasquel said he would switch those patients to NPH during the time that they’re on dexamethasone.
He also noted that the rapid-acting insulin dose range of 2-10 units provided in the first table, for correction of initial hyperglycemia, are more conservative than those used at his hospital, where correction doses of up to 14-16 units are sometimes necessary.
But Dr. Pasquel praised the group’s overall efforts since the pandemic began, noting that “they’re very organized and constantly updating their recommendations. They have a unified system in the [National Health Service], so it’s easier to standardize. They have a unique [electronic health record] which is far superior to what we do from a public health perspective.”
Dr. Rayman reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Pasquel reported receiving research funding from Dexcom, Merck, and the National Institutes of Health, and consulting for AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Merck, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
New guidance from the U.K. National Diabetes COVID-19 Response Group addresses glucose management in patients with COVID-19 who are receiving dexamethasone therapy.
Although there are already guidelines that address inpatient management of steroid-induced hyperglycemia, the authors of the new document wrote that this new expert opinion paper was needed “given the ‘triple insult’ of dexamethasone-induced–impaired glucose metabolism, COVID-19–induced insulin resistance, and COVID-19–impaired insulin production.”
RECOVERY trial spurs response
The document, which is the latest in a series from the Association of British Clinical Diabetologists, was published online Aug. 2 in Diabetic Medicine. The group is chaired by Gerry Rayman, MD, consultant physician at the diabetes centre and diabetes research unit, East Suffolk (England) and North East NHS Foundation Trust.
The guidance was developed in response to the recent “breakthrough” Randomised Evaluation of COVID-19 Therapy (RECOVERY) trial, which showed that dexamethasone reduced deaths in patients with COVID-19 on ventilators or receiving oxygen therapy. The advice is not intended for critical care units but can be adapted for that use.
The dose used in RECOVERY – 6 mg daily for 10 days – is 400%-500% greater than the therapeutic glucocorticoid replacement dose. High glucocorticoid doses can exacerbate hyperglycemia in people with established diabetes, unmask undiagnosed diabetes, precipitate hyperglycemia or new-onset diabetes, and can also cause hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state (HHS), the authors explained.
They recommended a target glucose of 6.0-10.0 mmol/L (108-180 mg/dL), although they say up to 12 mmol/L (216 mg/dL) is “acceptable.” They then gave advice on frequency of monitoring for people with and without known diabetes, exclusion of diabetic ketoacidosis and HHS, correction of initial hyperglycemia and maintenance of glycemic control using subcutaneous insulin, and prevention of hypoglycemia at the end of dexamethasone therapy (day 10) with insulin down-titration, discharge, and follow-up.
The detailed insulin guidance covers dose escalation for both insulin-treated and insulin-naive patients. A table suggests increasing correction doses of rapid-acting insulin based on prior total daily dose or weight.
Use of once- or twice-daily NPH insulin is recommended for patients whose glucose has risen above 12 mmol/L, in some cases with the addition of a long-acting analog. A second chart gives dose adjustments for those insulins. Additional guidance addresses patients on insulin pumps.
Guidance useful for U.S. physicians
Francisco Pasquel, MD, assistant professor of medicine in the division of endocrinology at Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview that he believes the guidance is “acceptable” for worldwide use, and that “it’s coherent and consistent with what we typically do.”
However, Dr. Pasquel, who founded COVID-in-Diabetes, an online repository of published guidance and shared experience – to which this new document has now been added – did take issue with one piece of advice. The guidance says that patients already taking premixed insulin formulations can continue using them while increasing the dose by 20%-40%. Given the risk of hypoglycemia associated with those formulations, Dr. Pasquel said he would switch those patients to NPH during the time that they’re on dexamethasone.
He also noted that the rapid-acting insulin dose range of 2-10 units provided in the first table, for correction of initial hyperglycemia, are more conservative than those used at his hospital, where correction doses of up to 14-16 units are sometimes necessary.
But Dr. Pasquel praised the group’s overall efforts since the pandemic began, noting that “they’re very organized and constantly updating their recommendations. They have a unified system in the [National Health Service], so it’s easier to standardize. They have a unique [electronic health record] which is far superior to what we do from a public health perspective.”
Dr. Rayman reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Pasquel reported receiving research funding from Dexcom, Merck, and the National Institutes of Health, and consulting for AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Merck, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
New guidance from the U.K. National Diabetes COVID-19 Response Group addresses glucose management in patients with COVID-19 who are receiving dexamethasone therapy.
Although there are already guidelines that address inpatient management of steroid-induced hyperglycemia, the authors of the new document wrote that this new expert opinion paper was needed “given the ‘triple insult’ of dexamethasone-induced–impaired glucose metabolism, COVID-19–induced insulin resistance, and COVID-19–impaired insulin production.”
RECOVERY trial spurs response
The document, which is the latest in a series from the Association of British Clinical Diabetologists, was published online Aug. 2 in Diabetic Medicine. The group is chaired by Gerry Rayman, MD, consultant physician at the diabetes centre and diabetes research unit, East Suffolk (England) and North East NHS Foundation Trust.
The guidance was developed in response to the recent “breakthrough” Randomised Evaluation of COVID-19 Therapy (RECOVERY) trial, which showed that dexamethasone reduced deaths in patients with COVID-19 on ventilators or receiving oxygen therapy. The advice is not intended for critical care units but can be adapted for that use.
The dose used in RECOVERY – 6 mg daily for 10 days – is 400%-500% greater than the therapeutic glucocorticoid replacement dose. High glucocorticoid doses can exacerbate hyperglycemia in people with established diabetes, unmask undiagnosed diabetes, precipitate hyperglycemia or new-onset diabetes, and can also cause hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state (HHS), the authors explained.
They recommended a target glucose of 6.0-10.0 mmol/L (108-180 mg/dL), although they say up to 12 mmol/L (216 mg/dL) is “acceptable.” They then gave advice on frequency of monitoring for people with and without known diabetes, exclusion of diabetic ketoacidosis and HHS, correction of initial hyperglycemia and maintenance of glycemic control using subcutaneous insulin, and prevention of hypoglycemia at the end of dexamethasone therapy (day 10) with insulin down-titration, discharge, and follow-up.
The detailed insulin guidance covers dose escalation for both insulin-treated and insulin-naive patients. A table suggests increasing correction doses of rapid-acting insulin based on prior total daily dose or weight.
Use of once- or twice-daily NPH insulin is recommended for patients whose glucose has risen above 12 mmol/L, in some cases with the addition of a long-acting analog. A second chart gives dose adjustments for those insulins. Additional guidance addresses patients on insulin pumps.
Guidance useful for U.S. physicians
Francisco Pasquel, MD, assistant professor of medicine in the division of endocrinology at Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview that he believes the guidance is “acceptable” for worldwide use, and that “it’s coherent and consistent with what we typically do.”
However, Dr. Pasquel, who founded COVID-in-Diabetes, an online repository of published guidance and shared experience – to which this new document has now been added – did take issue with one piece of advice. The guidance says that patients already taking premixed insulin formulations can continue using them while increasing the dose by 20%-40%. Given the risk of hypoglycemia associated with those formulations, Dr. Pasquel said he would switch those patients to NPH during the time that they’re on dexamethasone.
He also noted that the rapid-acting insulin dose range of 2-10 units provided in the first table, for correction of initial hyperglycemia, are more conservative than those used at his hospital, where correction doses of up to 14-16 units are sometimes necessary.
But Dr. Pasquel praised the group’s overall efforts since the pandemic began, noting that “they’re very organized and constantly updating their recommendations. They have a unified system in the [National Health Service], so it’s easier to standardize. They have a unique [electronic health record] which is far superior to what we do from a public health perspective.”
Dr. Rayman reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Pasquel reported receiving research funding from Dexcom, Merck, and the National Institutes of Health, and consulting for AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Merck, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
ED visits for mental health, substance use doubled in 1 decade
ED visits related to mental health conditions increased nearly twofold from 2007-2008 to 2015-2016, new research suggests.
Data from the National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey (NHAMCS) showed that, over the 10-year study period, the proportion of ED visits for mental health diagnoses increased from 6.6% to 10.9%, with substance use accounting for much of the increase.
Although there have been policy efforts, such as expanding access to mental health care as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) of 2011, the senior author Taeho Greg Rhee, PhD, MSW, said in an interview.
“Treating mental health conditions in EDs is often considered suboptimal” because of limited time for full psychiatric assessment, lack of trained providers, and limited privacy in EDs, said Dr. Rhee of Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
The findings were published online July 28 in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
“Outdated” research
Roughly one-fifth of U.S. adults experience some type of mental, behavioral, or emotional disorder annually. Moreover, the suicide rate has been steadily increasing, and there continues to be a “raging opioid epidemic,” the researchers wrote.
Despite these alarming figures, 57.4% of adults with mental illness reported in 2017 that they had not received any mental health treatment in the past year, reported the investigators.
Previous research has suggested that many adults have difficulty seeking outpatient mental health treatment and may turn to EDs instead. However, most studies of mental health ED use “are by now outdated, as they used data from years prior to the full implementation of the ACA,” the researchers noted.
“More Americans are suffering from mental illness, and given the recent policy efforts of expanding access to mental health care, we were questioning if ED visits due to mental health has changed or not,” Dr. Rhee said.
To investigate the question, the researchers conducted a cross-sectional analysis of data from the NHAMCS, a publicly available dataset provided by the National Center for Health Statistics of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
They grouped psychiatric diagnoses into five categories: mood disorders, anxiety disorders, psychosis or schizophrenia, suicide attempt or ideation, or other/unspecified. Substance use diagnoses were grouped into six categories: alcohol, amphetamine, cannabis, cocaine, opioid, or other/unspecified.
These categories were used to determine the type of disorder a patient had, whether the patient had both psychiatric and substance-related diagnoses, and whether the patient received multiple mental health diagnoses at the time of the ED visit.
Sociodemographic covariates included age, sex, race/ethnicity, and insurance coverage.
Twofold and fourfold increases
Of 100.9 million outpatient ED visits that took place between 2007 and 2016, approximately 8.4 million (8.3%) were for psychiatric or substance use–related diagnoses. Also, the visits were more likely from adults who were younger than 45 years, male, non-Hispanic White, and covered by Medicaid or other public insurance types (58.5%, 52.5%, 65.2%, and 58.6%, respectively).
The overall rate of ED visits for any mental health diagnosis nearly doubled between 2007-2008 and 2015-2016. The rate of visits in which both psychiatric and substance use–related diagnoses increased fourfold during that time span. ED visits involving at least two mental health diagnoses increased twofold.
Additional changes in the number of visits are listed below (for each, P < .001).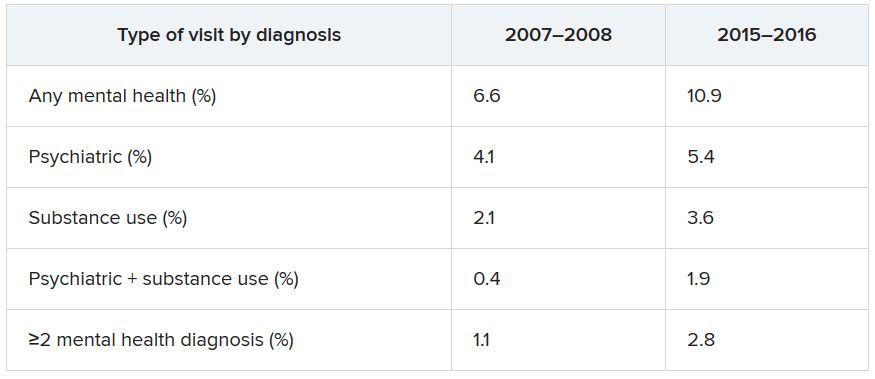
When these comparisons were adjusted for age, sex, and race/ethnicity, “linearly increasing trends of mental health–related ED visits were consistently found in all categories,” the authors reported. No trends were found regarding age, sex, or race/ethnicity. By contrast, mental health–related ED visits in which Medicaid was identified as the primary source of insurance nearly doubled between 2007–2008 and 2015–2016 (from 27.2% to 42.8%).
Other/unspecified psychiatric diagnoses, such as adjustment disorder and personality disorders, almost tripled between 2007-2008 and 2015-2016 (from 1,040 to 2,961 per 100,000 ED visits). ED visits for mood disorders and anxiety disorders also increased over time.
Alcohol-related ED visits were the most common substance use visits, increasing from 1,669 in 2007-2008 to 3,007 per 100,000 visits in 2015-2016. Amphetamine- and opioid-related ED visits more than doubled, and other/unspecified–related ED visits more than tripled during that time.
“One explanation why ED visits for mental health conditions have increased is that substance-related problems, which include overdose/self-injury issues, have increased over time,” Dr. Rhee noted, which “makes sense,” inasmuch as opioid, cannabis, and amphetamine use has increased across the country.
Another explanation is that, although mental health care access has been expanded through the ACA, “people, especially those with lower socioeconomic backgrounds, do not know how to get access to care and are still underserved,” he said.
“If mental health–related ED visits continue to increase in the future, there are several steps to be made. ED providers need to be better equipped with mental health care, and behavioral health should be better integrated as part of the care coordination,” said Dr. Rhee.
He added that reimbursement models across different insurance types, such as Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurance, “should consider expanding their coverage of mental health treatment in ED settings.”
“Canary in the coal mine”
Commenting on the study in an interview, Benjamin Druss, MD, MPH, professor and Rosalynn Carter Chair in Mental Health, Rollins School of Public Health, Emory University, Atlanta, called EDs the “canaries in the coal mine” for the broader health system.
The growing number of ED visits for behavioral problems “could represent both a rise in acute conditions such as substance use and lack of access to outpatient treatment,” said Dr. Druss, who was not involved with the research.
The findings “suggest the importance of strategies to effectively manage patients with behavioral conditions in ED settings and to effectively link them with high-quality outpatient care,” he noted.
Dr. Rhee has received funding from the National Institute on Aging and the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention. The other study authors and Dr. Druss report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
ED visits related to mental health conditions increased nearly twofold from 2007-2008 to 2015-2016, new research suggests.
Data from the National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey (NHAMCS) showed that, over the 10-year study period, the proportion of ED visits for mental health diagnoses increased from 6.6% to 10.9%, with substance use accounting for much of the increase.
Although there have been policy efforts, such as expanding access to mental health care as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) of 2011, the senior author Taeho Greg Rhee, PhD, MSW, said in an interview.
“Treating mental health conditions in EDs is often considered suboptimal” because of limited time for full psychiatric assessment, lack of trained providers, and limited privacy in EDs, said Dr. Rhee of Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
The findings were published online July 28 in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
“Outdated” research
Roughly one-fifth of U.S. adults experience some type of mental, behavioral, or emotional disorder annually. Moreover, the suicide rate has been steadily increasing, and there continues to be a “raging opioid epidemic,” the researchers wrote.
Despite these alarming figures, 57.4% of adults with mental illness reported in 2017 that they had not received any mental health treatment in the past year, reported the investigators.
Previous research has suggested that many adults have difficulty seeking outpatient mental health treatment and may turn to EDs instead. However, most studies of mental health ED use “are by now outdated, as they used data from years prior to the full implementation of the ACA,” the researchers noted.
“More Americans are suffering from mental illness, and given the recent policy efforts of expanding access to mental health care, we were questioning if ED visits due to mental health has changed or not,” Dr. Rhee said.
To investigate the question, the researchers conducted a cross-sectional analysis of data from the NHAMCS, a publicly available dataset provided by the National Center for Health Statistics of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
They grouped psychiatric diagnoses into five categories: mood disorders, anxiety disorders, psychosis or schizophrenia, suicide attempt or ideation, or other/unspecified. Substance use diagnoses were grouped into six categories: alcohol, amphetamine, cannabis, cocaine, opioid, or other/unspecified.
These categories were used to determine the type of disorder a patient had, whether the patient had both psychiatric and substance-related diagnoses, and whether the patient received multiple mental health diagnoses at the time of the ED visit.
Sociodemographic covariates included age, sex, race/ethnicity, and insurance coverage.
Twofold and fourfold increases
Of 100.9 million outpatient ED visits that took place between 2007 and 2016, approximately 8.4 million (8.3%) were for psychiatric or substance use–related diagnoses. Also, the visits were more likely from adults who were younger than 45 years, male, non-Hispanic White, and covered by Medicaid or other public insurance types (58.5%, 52.5%, 65.2%, and 58.6%, respectively).
The overall rate of ED visits for any mental health diagnosis nearly doubled between 2007-2008 and 2015-2016. The rate of visits in which both psychiatric and substance use–related diagnoses increased fourfold during that time span. ED visits involving at least two mental health diagnoses increased twofold.
Additional changes in the number of visits are listed below (for each, P < .001).
When these comparisons were adjusted for age, sex, and race/ethnicity, “linearly increasing trends of mental health–related ED visits were consistently found in all categories,” the authors reported. No trends were found regarding age, sex, or race/ethnicity. By contrast, mental health–related ED visits in which Medicaid was identified as the primary source of insurance nearly doubled between 2007–2008 and 2015–2016 (from 27.2% to 42.8%).
Other/unspecified psychiatric diagnoses, such as adjustment disorder and personality disorders, almost tripled between 2007-2008 and 2015-2016 (from 1,040 to 2,961 per 100,000 ED visits). ED visits for mood disorders and anxiety disorders also increased over time.
Alcohol-related ED visits were the most common substance use visits, increasing from 1,669 in 2007-2008 to 3,007 per 100,000 visits in 2015-2016. Amphetamine- and opioid-related ED visits more than doubled, and other/unspecified–related ED visits more than tripled during that time.
“One explanation why ED visits for mental health conditions have increased is that substance-related problems, which include overdose/self-injury issues, have increased over time,” Dr. Rhee noted, which “makes sense,” inasmuch as opioid, cannabis, and amphetamine use has increased across the country.
Another explanation is that, although mental health care access has been expanded through the ACA, “people, especially those with lower socioeconomic backgrounds, do not know how to get access to care and are still underserved,” he said.
“If mental health–related ED visits continue to increase in the future, there are several steps to be made. ED providers need to be better equipped with mental health care, and behavioral health should be better integrated as part of the care coordination,” said Dr. Rhee.
He added that reimbursement models across different insurance types, such as Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurance, “should consider expanding their coverage of mental health treatment in ED settings.”
“Canary in the coal mine”
Commenting on the study in an interview, Benjamin Druss, MD, MPH, professor and Rosalynn Carter Chair in Mental Health, Rollins School of Public Health, Emory University, Atlanta, called EDs the “canaries in the coal mine” for the broader health system.
The growing number of ED visits for behavioral problems “could represent both a rise in acute conditions such as substance use and lack of access to outpatient treatment,” said Dr. Druss, who was not involved with the research.
The findings “suggest the importance of strategies to effectively manage patients with behavioral conditions in ED settings and to effectively link them with high-quality outpatient care,” he noted.
Dr. Rhee has received funding from the National Institute on Aging and the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention. The other study authors and Dr. Druss report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
ED visits related to mental health conditions increased nearly twofold from 2007-2008 to 2015-2016, new research suggests.
Data from the National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey (NHAMCS) showed that, over the 10-year study period, the proportion of ED visits for mental health diagnoses increased from 6.6% to 10.9%, with substance use accounting for much of the increase.
Although there have been policy efforts, such as expanding access to mental health care as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) of 2011, the senior author Taeho Greg Rhee, PhD, MSW, said in an interview.
“Treating mental health conditions in EDs is often considered suboptimal” because of limited time for full psychiatric assessment, lack of trained providers, and limited privacy in EDs, said Dr. Rhee of Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
The findings were published online July 28 in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
“Outdated” research
Roughly one-fifth of U.S. adults experience some type of mental, behavioral, or emotional disorder annually. Moreover, the suicide rate has been steadily increasing, and there continues to be a “raging opioid epidemic,” the researchers wrote.
Despite these alarming figures, 57.4% of adults with mental illness reported in 2017 that they had not received any mental health treatment in the past year, reported the investigators.
Previous research has suggested that many adults have difficulty seeking outpatient mental health treatment and may turn to EDs instead. However, most studies of mental health ED use “are by now outdated, as they used data from years prior to the full implementation of the ACA,” the researchers noted.
“More Americans are suffering from mental illness, and given the recent policy efforts of expanding access to mental health care, we were questioning if ED visits due to mental health has changed or not,” Dr. Rhee said.
To investigate the question, the researchers conducted a cross-sectional analysis of data from the NHAMCS, a publicly available dataset provided by the National Center for Health Statistics of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
They grouped psychiatric diagnoses into five categories: mood disorders, anxiety disorders, psychosis or schizophrenia, suicide attempt or ideation, or other/unspecified. Substance use diagnoses were grouped into six categories: alcohol, amphetamine, cannabis, cocaine, opioid, or other/unspecified.
These categories were used to determine the type of disorder a patient had, whether the patient had both psychiatric and substance-related diagnoses, and whether the patient received multiple mental health diagnoses at the time of the ED visit.
Sociodemographic covariates included age, sex, race/ethnicity, and insurance coverage.
Twofold and fourfold increases
Of 100.9 million outpatient ED visits that took place between 2007 and 2016, approximately 8.4 million (8.3%) were for psychiatric or substance use–related diagnoses. Also, the visits were more likely from adults who were younger than 45 years, male, non-Hispanic White, and covered by Medicaid or other public insurance types (58.5%, 52.5%, 65.2%, and 58.6%, respectively).
The overall rate of ED visits for any mental health diagnosis nearly doubled between 2007-2008 and 2015-2016. The rate of visits in which both psychiatric and substance use–related diagnoses increased fourfold during that time span. ED visits involving at least two mental health diagnoses increased twofold.
Additional changes in the number of visits are listed below (for each, P < .001).
When these comparisons were adjusted for age, sex, and race/ethnicity, “linearly increasing trends of mental health–related ED visits were consistently found in all categories,” the authors reported. No trends were found regarding age, sex, or race/ethnicity. By contrast, mental health–related ED visits in which Medicaid was identified as the primary source of insurance nearly doubled between 2007–2008 and 2015–2016 (from 27.2% to 42.8%).
Other/unspecified psychiatric diagnoses, such as adjustment disorder and personality disorders, almost tripled between 2007-2008 and 2015-2016 (from 1,040 to 2,961 per 100,000 ED visits). ED visits for mood disorders and anxiety disorders also increased over time.
Alcohol-related ED visits were the most common substance use visits, increasing from 1,669 in 2007-2008 to 3,007 per 100,000 visits in 2015-2016. Amphetamine- and opioid-related ED visits more than doubled, and other/unspecified–related ED visits more than tripled during that time.
“One explanation why ED visits for mental health conditions have increased is that substance-related problems, which include overdose/self-injury issues, have increased over time,” Dr. Rhee noted, which “makes sense,” inasmuch as opioid, cannabis, and amphetamine use has increased across the country.
Another explanation is that, although mental health care access has been expanded through the ACA, “people, especially those with lower socioeconomic backgrounds, do not know how to get access to care and are still underserved,” he said.
“If mental health–related ED visits continue to increase in the future, there are several steps to be made. ED providers need to be better equipped with mental health care, and behavioral health should be better integrated as part of the care coordination,” said Dr. Rhee.
He added that reimbursement models across different insurance types, such as Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurance, “should consider expanding their coverage of mental health treatment in ED settings.”
“Canary in the coal mine”
Commenting on the study in an interview, Benjamin Druss, MD, MPH, professor and Rosalynn Carter Chair in Mental Health, Rollins School of Public Health, Emory University, Atlanta, called EDs the “canaries in the coal mine” for the broader health system.
The growing number of ED visits for behavioral problems “could represent both a rise in acute conditions such as substance use and lack of access to outpatient treatment,” said Dr. Druss, who was not involved with the research.
The findings “suggest the importance of strategies to effectively manage patients with behavioral conditions in ED settings and to effectively link them with high-quality outpatient care,” he noted.
Dr. Rhee has received funding from the National Institute on Aging and the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention. The other study authors and Dr. Druss report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
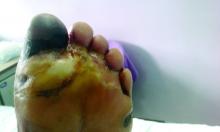
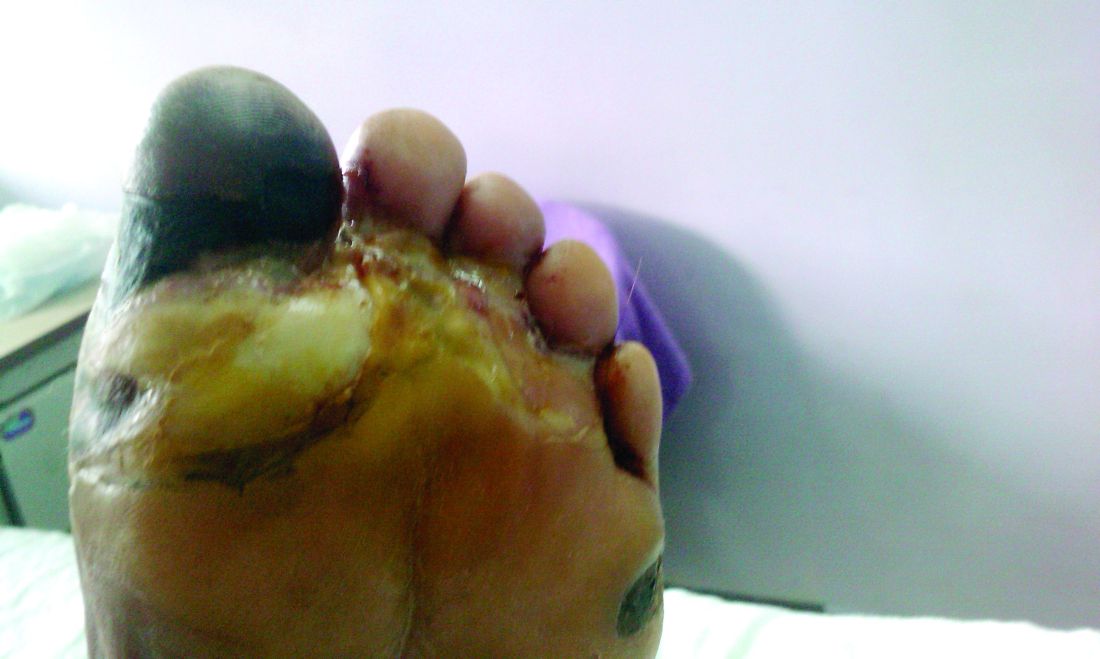
Diabetic amputations soared amid Italian pandemic lockdown
Amid a mandatory national lockdown, the rates of amputations skyrocketed at a hospital far from the hardest-hit region as many patients developed gangrene.
The findings offer critical lessons for the United States, said wound care specialist William H. Tettelbach, MD, of Western Peaks Specialty Hospital near Salt Lake City. “It’s become more obvious that outpatient wound care is a critical care need for the community because of the risk of ignoring these chronic wounds and letting them remain open. We cannot let these services be closed down like some were when the pandemic started.”
The study, led by Paola Caruso, MD, of the University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli in Naples, appeared in Diabetes Care.
The researchers launched the study to understand how patients with diabetes and DFU fared during the height of the pandemic in Italy, where tens of thousands of people died, mainly in the northern region of the country. They focused on patients in the southern region who were admitted to the division of endocrinology and metabolic diseases at the Teaching Hospital at the University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli.
The study compared 25 patients who were admitted from March 9 to May 18, 2020, with 38 patients who were admitted from a longer period between January and May 2019. The demographics of the groups are similar, with average ages in the early 60s and more men than women (21:4, respectively, in 2020 and 23:15, respectively, in 2019.)
The results reveal high numbers of emergent and serious cases in 2020. Compared with 2019, fewer were outpatients (16% vs. 45%, P = .028) and more were emergency patients (76% vs. 26%, P < .001).
Clinically, gangrene was much more common in the 2020 group, compared with the 2019 group (64% vs. 29%, P = .009), as was amputation (60% vs. 18%, P = .001).
The researchers determined that amputation was more than three times more likely in the 2020 versus the 2019 group (relative risk, 3.26; 95% confidence interval, 1.55-6.84) even though the 2019 period was longer. After adjustment for gender, the heightened risk in 2020 was 2.50 (95% CI, 1.18-5.29).
There was no statistically significant increase in the risk of revascularization.
“The COVID-19 lockdown may have had a detrimental impact on amputation risk because of the sudden interruption of DFU care and lower-limb preservation pathways, resulting in delayed diagnosis and treatment,” the researchers wrote. “DFU is often characterized by progressive clinical course, which can rapidly lead patients to critical worsening of their ulcers.”
They added that “the higher risk of amputation observed during COVID-19 lockdown confirms the need for proper and timely management of DFU patients to prevent dramatic outcomes responsible for a reduction of quality of life and increased morbidity and mortality.”
The study authors didn’t discuss why more patients seemed to have stayed home and not gotten proper care. It’s not clear if they were scared to get treatment or couldn’t obtain it because of the national shutdown.
Both have been factors affecting diabetic foot care in the United States during the pandemic, said Dr. Tettelbach. He called the study “timely and pertinent,” and said it highlights how wound care is “a critical need” that must remain available even when other medical services such as elective surgeries are shut down.
Infection-control protocols such as allowing patients to wait for appointments in their cars instead of waiting rooms will alleviate the fears of certain patients about seeking in-person care during the pandemic, he said. But some patients will be afraid to come in no matter what, he said, and home health may be the best solution for their care.
Several of the study authors reported various disclosures. Dr. Tettelbach reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Caruso P et al. Diabetes Care. 2020 Jul 23. doi:10.2337/dc20-1347.
Amid a mandatory national lockdown, the rates of amputations skyrocketed at a hospital far from the hardest-hit region as many patients developed gangrene.
The findings offer critical lessons for the United States, said wound care specialist William H. Tettelbach, MD, of Western Peaks Specialty Hospital near Salt Lake City. “It’s become more obvious that outpatient wound care is a critical care need for the community because of the risk of ignoring these chronic wounds and letting them remain open. We cannot let these services be closed down like some were when the pandemic started.”
The study, led by Paola Caruso, MD, of the University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli in Naples, appeared in Diabetes Care.
The researchers launched the study to understand how patients with diabetes and DFU fared during the height of the pandemic in Italy, where tens of thousands of people died, mainly in the northern region of the country. They focused on patients in the southern region who were admitted to the division of endocrinology and metabolic diseases at the Teaching Hospital at the University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli.
The study compared 25 patients who were admitted from March 9 to May 18, 2020, with 38 patients who were admitted from a longer period between January and May 2019. The demographics of the groups are similar, with average ages in the early 60s and more men than women (21:4, respectively, in 2020 and 23:15, respectively, in 2019.)
The results reveal high numbers of emergent and serious cases in 2020. Compared with 2019, fewer were outpatients (16% vs. 45%, P = .028) and more were emergency patients (76% vs. 26%, P < .001).
Clinically, gangrene was much more common in the 2020 group, compared with the 2019 group (64% vs. 29%, P = .009), as was amputation (60% vs. 18%, P = .001).
The researchers determined that amputation was more than three times more likely in the 2020 versus the 2019 group (relative risk, 3.26; 95% confidence interval, 1.55-6.84) even though the 2019 period was longer. After adjustment for gender, the heightened risk in 2020 was 2.50 (95% CI, 1.18-5.29).
There was no statistically significant increase in the risk of revascularization.
“The COVID-19 lockdown may have had a detrimental impact on amputation risk because of the sudden interruption of DFU care and lower-limb preservation pathways, resulting in delayed diagnosis and treatment,” the researchers wrote. “DFU is often characterized by progressive clinical course, which can rapidly lead patients to critical worsening of their ulcers.”
They added that “the higher risk of amputation observed during COVID-19 lockdown confirms the need for proper and timely management of DFU patients to prevent dramatic outcomes responsible for a reduction of quality of life and increased morbidity and mortality.”
The study authors didn’t discuss why more patients seemed to have stayed home and not gotten proper care. It’s not clear if they were scared to get treatment or couldn’t obtain it because of the national shutdown.
Both have been factors affecting diabetic foot care in the United States during the pandemic, said Dr. Tettelbach. He called the study “timely and pertinent,” and said it highlights how wound care is “a critical need” that must remain available even when other medical services such as elective surgeries are shut down.
Infection-control protocols such as allowing patients to wait for appointments in their cars instead of waiting rooms will alleviate the fears of certain patients about seeking in-person care during the pandemic, he said. But some patients will be afraid to come in no matter what, he said, and home health may be the best solution for their care.
Several of the study authors reported various disclosures. Dr. Tettelbach reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Caruso P et al. Diabetes Care. 2020 Jul 23. doi:10.2337/dc20-1347.
Amid a mandatory national lockdown, the rates of amputations skyrocketed at a hospital far from the hardest-hit region as many patients developed gangrene.
The findings offer critical lessons for the United States, said wound care specialist William H. Tettelbach, MD, of Western Peaks Specialty Hospital near Salt Lake City. “It’s become more obvious that outpatient wound care is a critical care need for the community because of the risk of ignoring these chronic wounds and letting them remain open. We cannot let these services be closed down like some were when the pandemic started.”
The study, led by Paola Caruso, MD, of the University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli in Naples, appeared in Diabetes Care.
The researchers launched the study to understand how patients with diabetes and DFU fared during the height of the pandemic in Italy, where tens of thousands of people died, mainly in the northern region of the country. They focused on patients in the southern region who were admitted to the division of endocrinology and metabolic diseases at the Teaching Hospital at the University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli.
The study compared 25 patients who were admitted from March 9 to May 18, 2020, with 38 patients who were admitted from a longer period between January and May 2019. The demographics of the groups are similar, with average ages in the early 60s and more men than women (21:4, respectively, in 2020 and 23:15, respectively, in 2019.)
The results reveal high numbers of emergent and serious cases in 2020. Compared with 2019, fewer were outpatients (16% vs. 45%, P = .028) and more were emergency patients (76% vs. 26%, P < .001).
Clinically, gangrene was much more common in the 2020 group, compared with the 2019 group (64% vs. 29%, P = .009), as was amputation (60% vs. 18%, P = .001).
The researchers determined that amputation was more than three times more likely in the 2020 versus the 2019 group (relative risk, 3.26; 95% confidence interval, 1.55-6.84) even though the 2019 period was longer. After adjustment for gender, the heightened risk in 2020 was 2.50 (95% CI, 1.18-5.29).
There was no statistically significant increase in the risk of revascularization.
“The COVID-19 lockdown may have had a detrimental impact on amputation risk because of the sudden interruption of DFU care and lower-limb preservation pathways, resulting in delayed diagnosis and treatment,” the researchers wrote. “DFU is often characterized by progressive clinical course, which can rapidly lead patients to critical worsening of their ulcers.”
They added that “the higher risk of amputation observed during COVID-19 lockdown confirms the need for proper and timely management of DFU patients to prevent dramatic outcomes responsible for a reduction of quality of life and increased morbidity and mortality.”
The study authors didn’t discuss why more patients seemed to have stayed home and not gotten proper care. It’s not clear if they were scared to get treatment or couldn’t obtain it because of the national shutdown.
Both have been factors affecting diabetic foot care in the United States during the pandemic, said Dr. Tettelbach. He called the study “timely and pertinent,” and said it highlights how wound care is “a critical need” that must remain available even when other medical services such as elective surgeries are shut down.
Infection-control protocols such as allowing patients to wait for appointments in their cars instead of waiting rooms will alleviate the fears of certain patients about seeking in-person care during the pandemic, he said. But some patients will be afraid to come in no matter what, he said, and home health may be the best solution for their care.
Several of the study authors reported various disclosures. Dr. Tettelbach reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Caruso P et al. Diabetes Care. 2020 Jul 23. doi:10.2337/dc20-1347.
FROM DIABETES CARE
Cardiorespiratory fitness may alter AFib ablation outcomes
Higher baseline cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) is associated with better outcomes after atrial fibrillation (AFib) ablation, according to new research.
In a single-center, retrospective cohort study, patients with the highest level of baseline CRF had significantly lower rates of arrhythmia recurrence and death than did patients with lower levels of CRF.
“It is stunning how just a simple measure, in this case walking on a treadmill, can predict whether atrial fibrillation ablation will be a successful endeavor or if it will fail,” senior author Wael A. Jaber, MD, professor of medicine, Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
“We found that ablation was not successful in most patients who had poor functional class and, conversely, that it was successful in most patients who were in tip-top shape when they walked on the treadmill. Our results can help clinicians inform patients about what they can expect after the procedure, depending on the baseline fitness level,” Dr. Jaber said.
The study was published online Aug. 2 in Heart Rhythm.
Several studies have shown a reduction in AFib incidence among individuals who report a physically active lifestyle, but the extent to which baseline CRF influences arrhythmia rates after AFib ablation is unknown, the authors note.
For the study, Dr. Jaber and colleagues analyzed results in 591 consecutive patients (mean age, 66.5 years; 75% male) with symptomatic paroxysmal or persistent AFib who underwent de novo AFib ablation at their institution. Only patients who had undergone an exercise stress test in the 12 months before AFib ablation (average, 4.5 months) were included.
Age- and sex-specific predicted metabolic equivalents (METs) were calculated using the St. James model for women and the Veterans Affairs referral model for men. The number of METs achieved was then divided by the predicted METs, and the patients were categorized into low (<85% predicted; n = 152), adequate (85%-100% predicted; n = 115), and high (>100% predicted; n = 324) CRF groups. Functional capacity was characterized as poor in 56 patients (9.5%), fair in 94 (16.0%), average in 225 (38.1%), good in 169 (28.6%), and high in 47 (8.0%).
During a mean follow-up of 32 months, arrhythmia recurrence was observed in 79% of patients in the low-CRF group, 54% of patients in the adequate-CRF group, and 27.5% of patients in the high-CRF group (P < .0001). Rates of repeat arrhythmia-related hospitalization, repeat rhythm-control procedures, and the need for ongoing antiarrhythmic therapy (ATT) were significantly lower in the high-CRF group. Specifically, ATT was stopped in 56% of patients in the high-CRF group, compared with 24% in the adequate-CRF group and 11% in the low-CRF group (P < .0001). Rehospitalization for arrhythmia was required in 18.5%, 38.0%, and 60.5% of cases, respectively, and repeat direct-current cardioversion or ablation was performed in 26.0%, 49.0%, and 65.0%, respectively (P < .0001 for both).
Death occurred in 11% of the low-CRF group, compared with 4% in the adequate-CRF group and 2.5% in the high-CRF group. Most (70%) of the deaths were caused by cardiovascular events, including heart failure, cardiac arrest, and coronary artery disease. The most common cause of noncardiac death was respiratory failure (13%), followed by sepsis (10%), malignancy (3%), and complications of Parkinson’s disease (3%).
“Although there was a statistically significant association between higher CRF and lower mortality in this cohort, the findings are to be viewed through the prism of a small sample size and relatively low death rate,” the authors wrote.
Don’t “overpromise” results
“The important message for clinicians is that when, you are discussing what to expect after atrial fibrillation ablation with your patients, do not overpromise the results. You can inform them that the success of the procedure depends more on how they perform on the baseline exercise test, and less on the ablation itself,” Dr. Jaber said.
Clinicians might want to consider advising their patients to become more active and increase their fitness level before undergoing the procedure, but whether doing so will improve outcomes is still unknown.
“This is what we don’t know. It makes sense. Hopefully, our results will encourage people to be more active before they arrive here for the procedure,” he said. “Our study is retrospective and is hypothesis generating, but we are planning a prospective study where patients will be referred to cardiac rehab prior to having ablation to try to improve their functional class to see if this will improve outcomes.”
Survival of the fittest
In an accompanying editorial commentary, Eric Black-Maier, MD, and Jonathan P. Piccini Sr, MD, from Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., wrote that the findings have “important implications for clinical practice and raise important additional questions.”
They note that catheter ablation as a first-line rhythm-control strategy, per current recommendations, “seems reasonable” in individuals with high baseline cardiorespiratory fitness, but that the benefit is less clear for patients with poor baseline CRF and uncontrolled risk factors.
“Significant limitations in functional status may be at least partially attributable to uncontrolled [AFib], and patients with limited exercise capacity may stand to gain most from successful catheter ablation,” the editorialists wrote.
“Furthermore, because shorter time from [AFib] diagnosis to catheter ablation has been associated with improved outcomes, the decision to postpone ablation in favor of lifestyle modification is not without potential adverse consequences,” they added.
Dr. Black-Maier and Dr. Piccini agree with the need for additional prospective randomized clinical trials to confirm that exercise training to improve cardiorespiratory fitness before AFib ablation is practical and effective for reducing arrhythmia recurrence.
“Over the past 50-plus years, our understanding of cardiorespiratory fitness, exercise capacity, and arrhythmia occurrence in patients with [AFib] continues to evolve,” the editorialists concluded. Data from the study “clearly demonstrate that arrhythmia-free survival is indeed survival of the fittest. Time will tell if exercise training and improvements in cardiorespiratory fitness can change outcomes after ablation.”
The study was sponsored by the Cleveland Clinic. Dr. Jaber and Dr. Black-Maier report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Piccini receives grants for clinical research from Abbott, the American Heart Association, the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation, Bayer, Boston Scientific, and Philips and serves as a consultant to Abbott, Allergan, ARCA Biopharma, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, LivaNova, Medtronic, Milestone, MyoKardia, Sanofi, Philips, and UpToDate.
A version of this story originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Higher baseline cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) is associated with better outcomes after atrial fibrillation (AFib) ablation, according to new research.
In a single-center, retrospective cohort study, patients with the highest level of baseline CRF had significantly lower rates of arrhythmia recurrence and death than did patients with lower levels of CRF.
“It is stunning how just a simple measure, in this case walking on a treadmill, can predict whether atrial fibrillation ablation will be a successful endeavor or if it will fail,” senior author Wael A. Jaber, MD, professor of medicine, Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
“We found that ablation was not successful in most patients who had poor functional class and, conversely, that it was successful in most patients who were in tip-top shape when they walked on the treadmill. Our results can help clinicians inform patients about what they can expect after the procedure, depending on the baseline fitness level,” Dr. Jaber said.
The study was published online Aug. 2 in Heart Rhythm.
Several studies have shown a reduction in AFib incidence among individuals who report a physically active lifestyle, but the extent to which baseline CRF influences arrhythmia rates after AFib ablation is unknown, the authors note.
For the study, Dr. Jaber and colleagues analyzed results in 591 consecutive patients (mean age, 66.5 years; 75% male) with symptomatic paroxysmal or persistent AFib who underwent de novo AFib ablation at their institution. Only patients who had undergone an exercise stress test in the 12 months before AFib ablation (average, 4.5 months) were included.
Age- and sex-specific predicted metabolic equivalents (METs) were calculated using the St. James model for women and the Veterans Affairs referral model for men. The number of METs achieved was then divided by the predicted METs, and the patients were categorized into low (<85% predicted; n = 152), adequate (85%-100% predicted; n = 115), and high (>100% predicted; n = 324) CRF groups. Functional capacity was characterized as poor in 56 patients (9.5%), fair in 94 (16.0%), average in 225 (38.1%), good in 169 (28.6%), and high in 47 (8.0%).
During a mean follow-up of 32 months, arrhythmia recurrence was observed in 79% of patients in the low-CRF group, 54% of patients in the adequate-CRF group, and 27.5% of patients in the high-CRF group (P < .0001). Rates of repeat arrhythmia-related hospitalization, repeat rhythm-control procedures, and the need for ongoing antiarrhythmic therapy (ATT) were significantly lower in the high-CRF group. Specifically, ATT was stopped in 56% of patients in the high-CRF group, compared with 24% in the adequate-CRF group and 11% in the low-CRF group (P < .0001). Rehospitalization for arrhythmia was required in 18.5%, 38.0%, and 60.5% of cases, respectively, and repeat direct-current cardioversion or ablation was performed in 26.0%, 49.0%, and 65.0%, respectively (P < .0001 for both).
Death occurred in 11% of the low-CRF group, compared with 4% in the adequate-CRF group and 2.5% in the high-CRF group. Most (70%) of the deaths were caused by cardiovascular events, including heart failure, cardiac arrest, and coronary artery disease. The most common cause of noncardiac death was respiratory failure (13%), followed by sepsis (10%), malignancy (3%), and complications of Parkinson’s disease (3%).
“Although there was a statistically significant association between higher CRF and lower mortality in this cohort, the findings are to be viewed through the prism of a small sample size and relatively low death rate,” the authors wrote.
Don’t “overpromise” results
“The important message for clinicians is that when, you are discussing what to expect after atrial fibrillation ablation with your patients, do not overpromise the results. You can inform them that the success of the procedure depends more on how they perform on the baseline exercise test, and less on the ablation itself,” Dr. Jaber said.
Clinicians might want to consider advising their patients to become more active and increase their fitness level before undergoing the procedure, but whether doing so will improve outcomes is still unknown.
“This is what we don’t know. It makes sense. Hopefully, our results will encourage people to be more active before they arrive here for the procedure,” he said. “Our study is retrospective and is hypothesis generating, but we are planning a prospective study where patients will be referred to cardiac rehab prior to having ablation to try to improve their functional class to see if this will improve outcomes.”
Survival of the fittest
In an accompanying editorial commentary, Eric Black-Maier, MD, and Jonathan P. Piccini Sr, MD, from Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., wrote that the findings have “important implications for clinical practice and raise important additional questions.”
They note that catheter ablation as a first-line rhythm-control strategy, per current recommendations, “seems reasonable” in individuals with high baseline cardiorespiratory fitness, but that the benefit is less clear for patients with poor baseline CRF and uncontrolled risk factors.
“Significant limitations in functional status may be at least partially attributable to uncontrolled [AFib], and patients with limited exercise capacity may stand to gain most from successful catheter ablation,” the editorialists wrote.
“Furthermore, because shorter time from [AFib] diagnosis to catheter ablation has been associated with improved outcomes, the decision to postpone ablation in favor of lifestyle modification is not without potential adverse consequences,” they added.
Dr. Black-Maier and Dr. Piccini agree with the need for additional prospective randomized clinical trials to confirm that exercise training to improve cardiorespiratory fitness before AFib ablation is practical and effective for reducing arrhythmia recurrence.
“Over the past 50-plus years, our understanding of cardiorespiratory fitness, exercise capacity, and arrhythmia occurrence in patients with [AFib] continues to evolve,” the editorialists concluded. Data from the study “clearly demonstrate that arrhythmia-free survival is indeed survival of the fittest. Time will tell if exercise training and improvements in cardiorespiratory fitness can change outcomes after ablation.”
The study was sponsored by the Cleveland Clinic. Dr. Jaber and Dr. Black-Maier report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Piccini receives grants for clinical research from Abbott, the American Heart Association, the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation, Bayer, Boston Scientific, and Philips and serves as a consultant to Abbott, Allergan, ARCA Biopharma, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, LivaNova, Medtronic, Milestone, MyoKardia, Sanofi, Philips, and UpToDate.
A version of this story originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Higher baseline cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) is associated with better outcomes after atrial fibrillation (AFib) ablation, according to new research.
In a single-center, retrospective cohort study, patients with the highest level of baseline CRF had significantly lower rates of arrhythmia recurrence and death than did patients with lower levels of CRF.
“It is stunning how just a simple measure, in this case walking on a treadmill, can predict whether atrial fibrillation ablation will be a successful endeavor or if it will fail,” senior author Wael A. Jaber, MD, professor of medicine, Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
“We found that ablation was not successful in most patients who had poor functional class and, conversely, that it was successful in most patients who were in tip-top shape when they walked on the treadmill. Our results can help clinicians inform patients about what they can expect after the procedure, depending on the baseline fitness level,” Dr. Jaber said.
The study was published online Aug. 2 in Heart Rhythm.
Several studies have shown a reduction in AFib incidence among individuals who report a physically active lifestyle, but the extent to which baseline CRF influences arrhythmia rates after AFib ablation is unknown, the authors note.
For the study, Dr. Jaber and colleagues analyzed results in 591 consecutive patients (mean age, 66.5 years; 75% male) with symptomatic paroxysmal or persistent AFib who underwent de novo AFib ablation at their institution. Only patients who had undergone an exercise stress test in the 12 months before AFib ablation (average, 4.5 months) were included.
Age- and sex-specific predicted metabolic equivalents (METs) were calculated using the St. James model for women and the Veterans Affairs referral model for men. The number of METs achieved was then divided by the predicted METs, and the patients were categorized into low (<85% predicted; n = 152), adequate (85%-100% predicted; n = 115), and high (>100% predicted; n = 324) CRF groups. Functional capacity was characterized as poor in 56 patients (9.5%), fair in 94 (16.0%), average in 225 (38.1%), good in 169 (28.6%), and high in 47 (8.0%).
During a mean follow-up of 32 months, arrhythmia recurrence was observed in 79% of patients in the low-CRF group, 54% of patients in the adequate-CRF group, and 27.5% of patients in the high-CRF group (P < .0001). Rates of repeat arrhythmia-related hospitalization, repeat rhythm-control procedures, and the need for ongoing antiarrhythmic therapy (ATT) were significantly lower in the high-CRF group. Specifically, ATT was stopped in 56% of patients in the high-CRF group, compared with 24% in the adequate-CRF group and 11% in the low-CRF group (P < .0001). Rehospitalization for arrhythmia was required in 18.5%, 38.0%, and 60.5% of cases, respectively, and repeat direct-current cardioversion or ablation was performed in 26.0%, 49.0%, and 65.0%, respectively (P < .0001 for both).
Death occurred in 11% of the low-CRF group, compared with 4% in the adequate-CRF group and 2.5% in the high-CRF group. Most (70%) of the deaths were caused by cardiovascular events, including heart failure, cardiac arrest, and coronary artery disease. The most common cause of noncardiac death was respiratory failure (13%), followed by sepsis (10%), malignancy (3%), and complications of Parkinson’s disease (3%).
“Although there was a statistically significant association between higher CRF and lower mortality in this cohort, the findings are to be viewed through the prism of a small sample size and relatively low death rate,” the authors wrote.
Don’t “overpromise” results
“The important message for clinicians is that when, you are discussing what to expect after atrial fibrillation ablation with your patients, do not overpromise the results. You can inform them that the success of the procedure depends more on how they perform on the baseline exercise test, and less on the ablation itself,” Dr. Jaber said.
Clinicians might want to consider advising their patients to become more active and increase their fitness level before undergoing the procedure, but whether doing so will improve outcomes is still unknown.
“This is what we don’t know. It makes sense. Hopefully, our results will encourage people to be more active before they arrive here for the procedure,” he said. “Our study is retrospective and is hypothesis generating, but we are planning a prospective study where patients will be referred to cardiac rehab prior to having ablation to try to improve their functional class to see if this will improve outcomes.”
Survival of the fittest
In an accompanying editorial commentary, Eric Black-Maier, MD, and Jonathan P. Piccini Sr, MD, from Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., wrote that the findings have “important implications for clinical practice and raise important additional questions.”
They note that catheter ablation as a first-line rhythm-control strategy, per current recommendations, “seems reasonable” in individuals with high baseline cardiorespiratory fitness, but that the benefit is less clear for patients with poor baseline CRF and uncontrolled risk factors.
“Significant limitations in functional status may be at least partially attributable to uncontrolled [AFib], and patients with limited exercise capacity may stand to gain most from successful catheter ablation,” the editorialists wrote.
“Furthermore, because shorter time from [AFib] diagnosis to catheter ablation has been associated with improved outcomes, the decision to postpone ablation in favor of lifestyle modification is not without potential adverse consequences,” they added.
Dr. Black-Maier and Dr. Piccini agree with the need for additional prospective randomized clinical trials to confirm that exercise training to improve cardiorespiratory fitness before AFib ablation is practical and effective for reducing arrhythmia recurrence.
“Over the past 50-plus years, our understanding of cardiorespiratory fitness, exercise capacity, and arrhythmia occurrence in patients with [AFib] continues to evolve,” the editorialists concluded. Data from the study “clearly demonstrate that arrhythmia-free survival is indeed survival of the fittest. Time will tell if exercise training and improvements in cardiorespiratory fitness can change outcomes after ablation.”
The study was sponsored by the Cleveland Clinic. Dr. Jaber and Dr. Black-Maier report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Piccini receives grants for clinical research from Abbott, the American Heart Association, the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation, Bayer, Boston Scientific, and Philips and serves as a consultant to Abbott, Allergan, ARCA Biopharma, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, LivaNova, Medtronic, Milestone, MyoKardia, Sanofi, Philips, and UpToDate.
A version of this story originally appeared on Medscape.com.
SGLT2 inhibitors have a breakout year
The benefits from sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor drugs proven during the past year for cutting heart failure hospitalization rates substantially in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and slowing progression of chronic kidney disease, all regardless of diabetes status, have thrust this drug class into the top tier of agents for potentially treating millions of patients with cardiac or renal disease.
The sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, first licensed for U.S. marketing in 2013 purely for glycemic control, have, during the 5 years since the first cardiovascular outcome trial results for the class came out, shown benefits in a range of patients reminiscent of what’s been established for ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs).
The wide-reaching benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors have recently become even more relevant by showing clinically meaningful effects in patients without type 2 diabetes (T2D). And in an uncanny coincidence, the SGLT2 inhibitors appear to act in complementary harmony with the ACE inhibitors and ARBs for preserving heart and renal function. These properties have made the SGLT2 inhibitors especially attractive as a new weapon for controlling the ascendant disorder of cardiorenal syndrome.
“SGLT2 inhibitors have a relatively greater impact on cardiovascular outcomes, compared with ACE inhibitors and ARBs, but the effects [of the two classes] are synergistic and ideally patients receive both,” said Peter McCullough, MD, a specialist in treating cardiorenal syndrome and other cardiovascular and renal disorders at Baylor, Scott, and White Heart and Vascular Hospital in Dallas. The SGLT2 inhibitors are among the drugs best suited to both treating and preventing cardiorenal syndrome by targeting both ends of the disorder, said Dr. McCullough, who chaired an American Heart Association panel that last year issued a scientific statement on cardiorenal syndrome (Circulation. 2019 Apr 16;139[16]:e840-78).
Although data on the SGLT2 inhibitors “are evolving,” the drug class is “going in the direction” of being “reasonably compared” with the ACE inhibitors and ARBs, said Javed Butler, MD, professor and chair of medicine at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson. “There are certainly complementary benefits that we see for both cardiovascular and renal outcomes.”
“We’ll think more and more about the SGLT2 inhibitors like renin-angiotensin system [RAS] inhibitors,” said David Z. Cherney, MD, referring to the drug class that includes ACE inhibitors and ARBs. “We should start to approach SGLT2 inhibitors like RAS inhibitors, with pleiotropic effects that go beyond glucose,” said Dr. Cherney, a nephrologist and professor of medicine at the University of Toronto, during the virtual annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association in June 2020.
Working together in the nephron
One of the clearest complementary interactions between the SGLT2 inhibitors and the RAS inhibitors is their ability to reduce intraglomerular pressure, a key mechanism that slows nephron loss and progression of chronic kidney disease. SGLT2 inhibitors reduce sodium absorption in the proximal tubule that causes, through tubuloglomerular feedback, afferent arteriole constriction that lowers intraglomerular pressure, while the RAS inhibitors inhibit efferent arteriole constriction mediated by angiotensin II, also cutting intraglomerular pressure. Together, “they almost work in tandem,” explained Janani Rangaswami, MD, a nephrologist at Einstein Medical Center in Philadelphia, vice chair of the Kidney Council of the AHA, and first author of the 2019 cardiorenal syndrome AHA statement.
“Many had worried that if we target both the afferent and efferent arterioles simultaneously, it might increase the risk for acute kidney injury. What has been reassuring in both the recent data from the DAPA-HF trial and in recent meta-analysis was no evidence of increased risk for acute kidney injury with use of the SGLT2 inhibitor,” Dr. Rangaswami said in an interview. For example, a recent report on more than 39,000 Canadian patients with T2D who were at least 66 years old and newly begun on either an SGLT2 inhibitor or a different oral diabetes drug (a dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitor), found a statistically significant 21% lower rate of acute kidney injury during the first 90 days on treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor in a propensity score–matched analysis (CMAJ. 2020 Apr 6;192: e351-60).
Much of the concern about possible acute kidney injury stemmed from a property that the SGLT2 inhibitors share with RAS inhibitors: They cause an initial, reversible decline in glomerular filtration rate (GFR), followed by longer-term nephron preservation, a pattern attributable to reduced intraglomerular pressure. The question early on was: “ ‘Does this harm the kidney?’ But what we’ve seen is that patients do better over time, even with this initial hit. Whenever you offload the glomerulus you cut barotrauma and protect renal function,” explained Silvio E. Inzucchi, MD, professor of medicine at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and director of the Yale Medicine Diabetes Center.
Dr. Inzucchi cautioned, however, that a small number of patients starting treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor may have their GFR drop too sharply, especially if their GFR was low to start with. “You need to be careful, especially at the lower end of the GFR range. I recheck renal function after 1 month” after a patient starts an SGLT2. Patients whose level falls too low may need to discontinue. He added that it’s hard to set a uniform threshold for alarm, and instead assess patients on a case-by-case basis, but “you need some threshold in mind, where you will stop” treatment.
A smarter diuretic
One of the most intriguing renal effects of SGLT2 inhibitors is their diuretic action. During a talk at the virtual ADA scientific sessions, cardiologist Jeffrey Testani, MD, called them “smart” diuretics, because their effect on diuresis is relatively modest but comes without the neurohormonal price paid when patients take conventional loop diuretics.
”Loop diuretics are particularly bad,” causing neurohormonal activation that includes norepinephrine, renin, and vasopressin, said Dr. Testani, director of heart failure research at Yale. They also fail to produce a meaningful drop in blood volume despite causing substantial natriuresis.
In contrast, SGLT2 inhibitors cause “moderate” natriuresis while producing a significant cut in blood volume. “The body seems content with this lower plasma volume without activating catecholamines or renin, and that’s how the SGLT2 inhibitors differ from other diuretics,” said Dr. Inzucchi.
The class also maintains serum levels of potassium and magnesium, produces significant improvements in serum uric acid levels, and avoids the electrolyte abnormalities, volume depletion, and acute kidney injury that can occur with conventional distal diuretics, Dr. Testani said.
In short, the SGLT2 inhibitors “are safe and easy-to-use diuretics,” which allows them to fill a “huge unmet need for patients with heart failure.” As evidence accumulates for the benefits of the drug class in patients with heart failure and renal disease, “uptake will be extensive,” Dr. Testani predicted, driven in part by how easy it is to add the class to existing cardiorenal drug regimens.
Other standard therapies for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) risk electrolyte abnormalities, renal dysfunction, significantly lower blood pressure, often make patients feel worse, and involve a slow and laborious titration process, Dr. Testani noted. The SGLT2 inhibitor agents avoid these issues, a property that has played out in quality of life assessments of patients with HFrEF who received a drug from this class.
Outcomes met in trial after trial
In the DAPA-HF trial, with 4,443 patients with HFrEF and divided roughly equally between those with or without T2D, treatment with dapagliflozin (Farxiga) linked with significant improvements in health status and quality of life measured by the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (Circulation. 2020 Jan 14;141[2]:90-9). “Not all treatments for HFrEF improve symptoms,” but in this study the SGTL2 inhibitor dapagliflozin did, boosting the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire score by about the same magnitude as treatment with a cardiac resynchronization device in patients with HFrEF, said Mikhail N. Kosiborod, MD, director of Cardiometabolic Research at Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute in Kansas City, Mo., speaking at the virtual ADA scientific sessions.
Two more recent renal observations have further solidified the growing role of these drugs for kidney protection. Results from the CREDENCE trial that looked at canagliflozin (Invokana) treatment in 4,401 patients with T2D and albuminuria and chronic kidney disease showed canagliflozin treatment cut the primary, composite renal endpoint by a statistically significant 30%, compared with placebo (N Engl J Med. 2019 Jun 13;380[24]:2295-306). The study stopped earlier than planned because of how effective canagliflozin appeared.
“Never before has a renal protection clinical trial stopped for overwhelming efficacy,” noted nephrologist Katherine R. Tuttle, MD, executive director for research at Providence Health Care in Spokane, Wash. “It’s very exciting to have a treatment that works on both the heart and kidney, given their interrelationship,” she said during the ADA sessions. Dr. Tuttle called the cardiorenal effects from the SGLT2 inhibitors “amazing.”
Just as the DAPA-HF trial’s primary outcome showed the ability of at least one drug from the class, dapagliflozin, to improve outcomes in HFrEF patients without T2D, topline results recently reported from the DAPA-CDK trial showed for the first time renal protection by an SGLT2 inhibitor in patients with chronic kidney disease but no T2D, in a study with about 4,300 patients.
Although detailed results from DAPA-CKD are not yet available, so far the outcomes seem consistent with the CREDENCE findings, and the cumulative renal findings for the class show the SGLT2 inhibitors have “potential for a profound impact on the patients we see in every nephrology clinic, and with dual cardiorenal disease,” said Dr. Rangaswami. The class is now established as “standard of care for patients with chronic kidney disease. The CREDENCE results made that clear.”
The DAPA-CKD findings in patients with chronic kidney disease regardless of their diabetes status “are very important. We really have not had any advances in this space for some time, and chronic kidney disease patients have very poor outcomes, both cardiovascular and renal,” commented Dr. Butler. The advantage from using this drug class in these patients “is huge.”
The DAPA-CKD findings are a “major advance,” agreed Dr. McCullough.
SGLT2 inhibitor use needs to grow
Experts lament that although the evidence favoring the class has been very bullish, prescribing uptake has been slow, perhaps partly explained by the retail U.S. cost for most of these agents, generally about $17/day.
Cost is, unfortunately, an issue right now for these drugs, said Dr. Butler. Generic formulations are imminent, “but we cannot accept waiting. Providing this therapy when insurance coverage is available,” is essential.
The FDA has already granted tentative approval to some generic formulations, although resolution of patent issues can delay generics actually reaching the market. “Generic dapagliflozin will have a major impact; the marketplace for these drugs will shift very quickly,” predicted Dr. McCullough.
But price may not be the sole barrier, cautioned Dr. Rangaswami. “I don’t think it’s just a cost issue. Several factors explain the slow uptake,” of the SGLT2 inhibitors. “The biggest barrier is that this is a new drug class, and understanding how to use the class is not yet where it needs to be in the physician community.” One of the biggest problems is that the SGLT2 inhibitors are still primarily regarded as drugs to treat hyperglycemia.
Physicians who treat patients with heart or renal disease “need to wrap their head around the idea that a drug with antihyperglycemic effects is now in their practice territory, and something they need to prescribe,” she noted. Currently “there is a reluctance to prescribe these drugs given the perception that they are antihyperglycemic agents, and usually get deferred to primary care physicians or endocrinologists. This results in huge missed opportunities by cardiologists and nephrologists in initiating these agents that have major cardiorenal risk reduction effects.”
The key role that cardiologists need to play in prescribing the SGLT2 inhibitors was brought home in a recent study of two representative U.S. health systems that showed patients with T2D were far more likely to see a cardiologist than an endocrinologist (Cardiovasc Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Jun;9[2]:56-9).
“The SGLT2 inhibitors are definitely a game-changing drug class,” summed up Dr. Rangaswami. “We’re going to see a lot of use in patients with heart and kidney disease.”
Dr. Cherney has been a consultant to or has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, and Sanofi. Dr. Butler has had financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. McCullough and Dr. Rangaswami had no disclosures. Dr. Inzucchi has been a consultant to or helped run trials for Abbott, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi/Lexicon, and vTv Therapeutics. Dr. Testani has been a consultant to AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, cardionomic, FIRE1 Magenta Med, Novartis, Reprieve, Sanofi, and W.L. Gore. Dr. Kosiborod has been a consultant to or led trials for Amarin, Amgen, Applied Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Glytec, Janssen, Eli Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Vifor. Dr. Tuttle has been a consultant to AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead, Goldfinch Bio, Eli Lilly, and Novo Nordisk.
The benefits from sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor drugs proven during the past year for cutting heart failure hospitalization rates substantially in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and slowing progression of chronic kidney disease, all regardless of diabetes status, have thrust this drug class into the top tier of agents for potentially treating millions of patients with cardiac or renal disease.
The sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, first licensed for U.S. marketing in 2013 purely for glycemic control, have, during the 5 years since the first cardiovascular outcome trial results for the class came out, shown benefits in a range of patients reminiscent of what’s been established for ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs).
The wide-reaching benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors have recently become even more relevant by showing clinically meaningful effects in patients without type 2 diabetes (T2D). And in an uncanny coincidence, the SGLT2 inhibitors appear to act in complementary harmony with the ACE inhibitors and ARBs for preserving heart and renal function. These properties have made the SGLT2 inhibitors especially attractive as a new weapon for controlling the ascendant disorder of cardiorenal syndrome.
“SGLT2 inhibitors have a relatively greater impact on cardiovascular outcomes, compared with ACE inhibitors and ARBs, but the effects [of the two classes] are synergistic and ideally patients receive both,” said Peter McCullough, MD, a specialist in treating cardiorenal syndrome and other cardiovascular and renal disorders at Baylor, Scott, and White Heart and Vascular Hospital in Dallas. The SGLT2 inhibitors are among the drugs best suited to both treating and preventing cardiorenal syndrome by targeting both ends of the disorder, said Dr. McCullough, who chaired an American Heart Association panel that last year issued a scientific statement on cardiorenal syndrome (Circulation. 2019 Apr 16;139[16]:e840-78).
Although data on the SGLT2 inhibitors “are evolving,” the drug class is “going in the direction” of being “reasonably compared” with the ACE inhibitors and ARBs, said Javed Butler, MD, professor and chair of medicine at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson. “There are certainly complementary benefits that we see for both cardiovascular and renal outcomes.”
“We’ll think more and more about the SGLT2 inhibitors like renin-angiotensin system [RAS] inhibitors,” said David Z. Cherney, MD, referring to the drug class that includes ACE inhibitors and ARBs. “We should start to approach SGLT2 inhibitors like RAS inhibitors, with pleiotropic effects that go beyond glucose,” said Dr. Cherney, a nephrologist and professor of medicine at the University of Toronto, during the virtual annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association in June 2020.
Working together in the nephron
One of the clearest complementary interactions between the SGLT2 inhibitors and the RAS inhibitors is their ability to reduce intraglomerular pressure, a key mechanism that slows nephron loss and progression of chronic kidney disease. SGLT2 inhibitors reduce sodium absorption in the proximal tubule that causes, through tubuloglomerular feedback, afferent arteriole constriction that lowers intraglomerular pressure, while the RAS inhibitors inhibit efferent arteriole constriction mediated by angiotensin II, also cutting intraglomerular pressure. Together, “they almost work in tandem,” explained Janani Rangaswami, MD, a nephrologist at Einstein Medical Center in Philadelphia, vice chair of the Kidney Council of the AHA, and first author of the 2019 cardiorenal syndrome AHA statement.
“Many had worried that if we target both the afferent and efferent arterioles simultaneously, it might increase the risk for acute kidney injury. What has been reassuring in both the recent data from the DAPA-HF trial and in recent meta-analysis was no evidence of increased risk for acute kidney injury with use of the SGLT2 inhibitor,” Dr. Rangaswami said in an interview. For example, a recent report on more than 39,000 Canadian patients with T2D who were at least 66 years old and newly begun on either an SGLT2 inhibitor or a different oral diabetes drug (a dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitor), found a statistically significant 21% lower rate of acute kidney injury during the first 90 days on treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor in a propensity score–matched analysis (CMAJ. 2020 Apr 6;192: e351-60).
Much of the concern about possible acute kidney injury stemmed from a property that the SGLT2 inhibitors share with RAS inhibitors: They cause an initial, reversible decline in glomerular filtration rate (GFR), followed by longer-term nephron preservation, a pattern attributable to reduced intraglomerular pressure. The question early on was: “ ‘Does this harm the kidney?’ But what we’ve seen is that patients do better over time, even with this initial hit. Whenever you offload the glomerulus you cut barotrauma and protect renal function,” explained Silvio E. Inzucchi, MD, professor of medicine at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and director of the Yale Medicine Diabetes Center.
Dr. Inzucchi cautioned, however, that a small number of patients starting treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor may have their GFR drop too sharply, especially if their GFR was low to start with. “You need to be careful, especially at the lower end of the GFR range. I recheck renal function after 1 month” after a patient starts an SGLT2. Patients whose level falls too low may need to discontinue. He added that it’s hard to set a uniform threshold for alarm, and instead assess patients on a case-by-case basis, but “you need some threshold in mind, where you will stop” treatment.
A smarter diuretic
One of the most intriguing renal effects of SGLT2 inhibitors is their diuretic action. During a talk at the virtual ADA scientific sessions, cardiologist Jeffrey Testani, MD, called them “smart” diuretics, because their effect on diuresis is relatively modest but comes without the neurohormonal price paid when patients take conventional loop diuretics.
”Loop diuretics are particularly bad,” causing neurohormonal activation that includes norepinephrine, renin, and vasopressin, said Dr. Testani, director of heart failure research at Yale. They also fail to produce a meaningful drop in blood volume despite causing substantial natriuresis.
In contrast, SGLT2 inhibitors cause “moderate” natriuresis while producing a significant cut in blood volume. “The body seems content with this lower plasma volume without activating catecholamines or renin, and that’s how the SGLT2 inhibitors differ from other diuretics,” said Dr. Inzucchi.
The class also maintains serum levels of potassium and magnesium, produces significant improvements in serum uric acid levels, and avoids the electrolyte abnormalities, volume depletion, and acute kidney injury that can occur with conventional distal diuretics, Dr. Testani said.
In short, the SGLT2 inhibitors “are safe and easy-to-use diuretics,” which allows them to fill a “huge unmet need for patients with heart failure.” As evidence accumulates for the benefits of the drug class in patients with heart failure and renal disease, “uptake will be extensive,” Dr. Testani predicted, driven in part by how easy it is to add the class to existing cardiorenal drug regimens.
Other standard therapies for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) risk electrolyte abnormalities, renal dysfunction, significantly lower blood pressure, often make patients feel worse, and involve a slow and laborious titration process, Dr. Testani noted. The SGLT2 inhibitor agents avoid these issues, a property that has played out in quality of life assessments of patients with HFrEF who received a drug from this class.
Outcomes met in trial after trial
In the DAPA-HF trial, with 4,443 patients with HFrEF and divided roughly equally between those with or without T2D, treatment with dapagliflozin (Farxiga) linked with significant improvements in health status and quality of life measured by the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (Circulation. 2020 Jan 14;141[2]:90-9). “Not all treatments for HFrEF improve symptoms,” but in this study the SGTL2 inhibitor dapagliflozin did, boosting the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire score by about the same magnitude as treatment with a cardiac resynchronization device in patients with HFrEF, said Mikhail N. Kosiborod, MD, director of Cardiometabolic Research at Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute in Kansas City, Mo., speaking at the virtual ADA scientific sessions.
Two more recent renal observations have further solidified the growing role of these drugs for kidney protection. Results from the CREDENCE trial that looked at canagliflozin (Invokana) treatment in 4,401 patients with T2D and albuminuria and chronic kidney disease showed canagliflozin treatment cut the primary, composite renal endpoint by a statistically significant 30%, compared with placebo (N Engl J Med. 2019 Jun 13;380[24]:2295-306). The study stopped earlier than planned because of how effective canagliflozin appeared.
“Never before has a renal protection clinical trial stopped for overwhelming efficacy,” noted nephrologist Katherine R. Tuttle, MD, executive director for research at Providence Health Care in Spokane, Wash. “It’s very exciting to have a treatment that works on both the heart and kidney, given their interrelationship,” she said during the ADA sessions. Dr. Tuttle called the cardiorenal effects from the SGLT2 inhibitors “amazing.”
Just as the DAPA-HF trial’s primary outcome showed the ability of at least one drug from the class, dapagliflozin, to improve outcomes in HFrEF patients without T2D, topline results recently reported from the DAPA-CDK trial showed for the first time renal protection by an SGLT2 inhibitor in patients with chronic kidney disease but no T2D, in a study with about 4,300 patients.
Although detailed results from DAPA-CKD are not yet available, so far the outcomes seem consistent with the CREDENCE findings, and the cumulative renal findings for the class show the SGLT2 inhibitors have “potential for a profound impact on the patients we see in every nephrology clinic, and with dual cardiorenal disease,” said Dr. Rangaswami. The class is now established as “standard of care for patients with chronic kidney disease. The CREDENCE results made that clear.”
The DAPA-CKD findings in patients with chronic kidney disease regardless of their diabetes status “are very important. We really have not had any advances in this space for some time, and chronic kidney disease patients have very poor outcomes, both cardiovascular and renal,” commented Dr. Butler. The advantage from using this drug class in these patients “is huge.”
The DAPA-CKD findings are a “major advance,” agreed Dr. McCullough.
SGLT2 inhibitor use needs to grow
Experts lament that although the evidence favoring the class has been very bullish, prescribing uptake has been slow, perhaps partly explained by the retail U.S. cost for most of these agents, generally about $17/day.
Cost is, unfortunately, an issue right now for these drugs, said Dr. Butler. Generic formulations are imminent, “but we cannot accept waiting. Providing this therapy when insurance coverage is available,” is essential.
The FDA has already granted tentative approval to some generic formulations, although resolution of patent issues can delay generics actually reaching the market. “Generic dapagliflozin will have a major impact; the marketplace for these drugs will shift very quickly,” predicted Dr. McCullough.
But price may not be the sole barrier, cautioned Dr. Rangaswami. “I don’t think it’s just a cost issue. Several factors explain the slow uptake,” of the SGLT2 inhibitors. “The biggest barrier is that this is a new drug class, and understanding how to use the class is not yet where it needs to be in the physician community.” One of the biggest problems is that the SGLT2 inhibitors are still primarily regarded as drugs to treat hyperglycemia.
Physicians who treat patients with heart or renal disease “need to wrap their head around the idea that a drug with antihyperglycemic effects is now in their practice territory, and something they need to prescribe,” she noted. Currently “there is a reluctance to prescribe these drugs given the perception that they are antihyperglycemic agents, and usually get deferred to primary care physicians or endocrinologists. This results in huge missed opportunities by cardiologists and nephrologists in initiating these agents that have major cardiorenal risk reduction effects.”
The key role that cardiologists need to play in prescribing the SGLT2 inhibitors was brought home in a recent study of two representative U.S. health systems that showed patients with T2D were far more likely to see a cardiologist than an endocrinologist (Cardiovasc Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Jun;9[2]:56-9).
“The SGLT2 inhibitors are definitely a game-changing drug class,” summed up Dr. Rangaswami. “We’re going to see a lot of use in patients with heart and kidney disease.”
Dr. Cherney has been a consultant to or has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, and Sanofi. Dr. Butler has had financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. McCullough and Dr. Rangaswami had no disclosures. Dr. Inzucchi has been a consultant to or helped run trials for Abbott, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi/Lexicon, and vTv Therapeutics. Dr. Testani has been a consultant to AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, cardionomic, FIRE1 Magenta Med, Novartis, Reprieve, Sanofi, and W.L. Gore. Dr. Kosiborod has been a consultant to or led trials for Amarin, Amgen, Applied Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Glytec, Janssen, Eli Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Vifor. Dr. Tuttle has been a consultant to AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead, Goldfinch Bio, Eli Lilly, and Novo Nordisk.
The benefits from sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor drugs proven during the past year for cutting heart failure hospitalization rates substantially in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and slowing progression of chronic kidney disease, all regardless of diabetes status, have thrust this drug class into the top tier of agents for potentially treating millions of patients with cardiac or renal disease.
The sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, first licensed for U.S. marketing in 2013 purely for glycemic control, have, during the 5 years since the first cardiovascular outcome trial results for the class came out, shown benefits in a range of patients reminiscent of what’s been established for ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs).
The wide-reaching benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors have recently become even more relevant by showing clinically meaningful effects in patients without type 2 diabetes (T2D). And in an uncanny coincidence, the SGLT2 inhibitors appear to act in complementary harmony with the ACE inhibitors and ARBs for preserving heart and renal function. These properties have made the SGLT2 inhibitors especially attractive as a new weapon for controlling the ascendant disorder of cardiorenal syndrome.
“SGLT2 inhibitors have a relatively greater impact on cardiovascular outcomes, compared with ACE inhibitors and ARBs, but the effects [of the two classes] are synergistic and ideally patients receive both,” said Peter McCullough, MD, a specialist in treating cardiorenal syndrome and other cardiovascular and renal disorders at Baylor, Scott, and White Heart and Vascular Hospital in Dallas. The SGLT2 inhibitors are among the drugs best suited to both treating and preventing cardiorenal syndrome by targeting both ends of the disorder, said Dr. McCullough, who chaired an American Heart Association panel that last year issued a scientific statement on cardiorenal syndrome (Circulation. 2019 Apr 16;139[16]:e840-78).
Although data on the SGLT2 inhibitors “are evolving,” the drug class is “going in the direction” of being “reasonably compared” with the ACE inhibitors and ARBs, said Javed Butler, MD, professor and chair of medicine at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson. “There are certainly complementary benefits that we see for both cardiovascular and renal outcomes.”
“We’ll think more and more about the SGLT2 inhibitors like renin-angiotensin system [RAS] inhibitors,” said David Z. Cherney, MD, referring to the drug class that includes ACE inhibitors and ARBs. “We should start to approach SGLT2 inhibitors like RAS inhibitors, with pleiotropic effects that go beyond glucose,” said Dr. Cherney, a nephrologist and professor of medicine at the University of Toronto, during the virtual annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association in June 2020.
Working together in the nephron
One of the clearest complementary interactions between the SGLT2 inhibitors and the RAS inhibitors is their ability to reduce intraglomerular pressure, a key mechanism that slows nephron loss and progression of chronic kidney disease. SGLT2 inhibitors reduce sodium absorption in the proximal tubule that causes, through tubuloglomerular feedback, afferent arteriole constriction that lowers intraglomerular pressure, while the RAS inhibitors inhibit efferent arteriole constriction mediated by angiotensin II, also cutting intraglomerular pressure. Together, “they almost work in tandem,” explained Janani Rangaswami, MD, a nephrologist at Einstein Medical Center in Philadelphia, vice chair of the Kidney Council of the AHA, and first author of the 2019 cardiorenal syndrome AHA statement.
“Many had worried that if we target both the afferent and efferent arterioles simultaneously, it might increase the risk for acute kidney injury. What has been reassuring in both the recent data from the DAPA-HF trial and in recent meta-analysis was no evidence of increased risk for acute kidney injury with use of the SGLT2 inhibitor,” Dr. Rangaswami said in an interview. For example, a recent report on more than 39,000 Canadian patients with T2D who were at least 66 years old and newly begun on either an SGLT2 inhibitor or a different oral diabetes drug (a dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitor), found a statistically significant 21% lower rate of acute kidney injury during the first 90 days on treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor in a propensity score–matched analysis (CMAJ. 2020 Apr 6;192: e351-60).
Much of the concern about possible acute kidney injury stemmed from a property that the SGLT2 inhibitors share with RAS inhibitors: They cause an initial, reversible decline in glomerular filtration rate (GFR), followed by longer-term nephron preservation, a pattern attributable to reduced intraglomerular pressure. The question early on was: “ ‘Does this harm the kidney?’ But what we’ve seen is that patients do better over time, even with this initial hit. Whenever you offload the glomerulus you cut barotrauma and protect renal function,” explained Silvio E. Inzucchi, MD, professor of medicine at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and director of the Yale Medicine Diabetes Center.
Dr. Inzucchi cautioned, however, that a small number of patients starting treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor may have their GFR drop too sharply, especially if their GFR was low to start with. “You need to be careful, especially at the lower end of the GFR range. I recheck renal function after 1 month” after a patient starts an SGLT2. Patients whose level falls too low may need to discontinue. He added that it’s hard to set a uniform threshold for alarm, and instead assess patients on a case-by-case basis, but “you need some threshold in mind, where you will stop” treatment.
A smarter diuretic
One of the most intriguing renal effects of SGLT2 inhibitors is their diuretic action. During a talk at the virtual ADA scientific sessions, cardiologist Jeffrey Testani, MD, called them “smart” diuretics, because their effect on diuresis is relatively modest but comes without the neurohormonal price paid when patients take conventional loop diuretics.
”Loop diuretics are particularly bad,” causing neurohormonal activation that includes norepinephrine, renin, and vasopressin, said Dr. Testani, director of heart failure research at Yale. They also fail to produce a meaningful drop in blood volume despite causing substantial natriuresis.
In contrast, SGLT2 inhibitors cause “moderate” natriuresis while producing a significant cut in blood volume. “The body seems content with this lower plasma volume without activating catecholamines or renin, and that’s how the SGLT2 inhibitors differ from other diuretics,” said Dr. Inzucchi.
The class also maintains serum levels of potassium and magnesium, produces significant improvements in serum uric acid levels, and avoids the electrolyte abnormalities, volume depletion, and acute kidney injury that can occur with conventional distal diuretics, Dr. Testani said.
In short, the SGLT2 inhibitors “are safe and easy-to-use diuretics,” which allows them to fill a “huge unmet need for patients with heart failure.” As evidence accumulates for the benefits of the drug class in patients with heart failure and renal disease, “uptake will be extensive,” Dr. Testani predicted, driven in part by how easy it is to add the class to existing cardiorenal drug regimens.
Other standard therapies for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) risk electrolyte abnormalities, renal dysfunction, significantly lower blood pressure, often make patients feel worse, and involve a slow and laborious titration process, Dr. Testani noted. The SGLT2 inhibitor agents avoid these issues, a property that has played out in quality of life assessments of patients with HFrEF who received a drug from this class.
Outcomes met in trial after trial
In the DAPA-HF trial, with 4,443 patients with HFrEF and divided roughly equally between those with or without T2D, treatment with dapagliflozin (Farxiga) linked with significant improvements in health status and quality of life measured by the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (Circulation. 2020 Jan 14;141[2]:90-9). “Not all treatments for HFrEF improve symptoms,” but in this study the SGTL2 inhibitor dapagliflozin did, boosting the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire score by about the same magnitude as treatment with a cardiac resynchronization device in patients with HFrEF, said Mikhail N. Kosiborod, MD, director of Cardiometabolic Research at Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute in Kansas City, Mo., speaking at the virtual ADA scientific sessions.
Two more recent renal observations have further solidified the growing role of these drugs for kidney protection. Results from the CREDENCE trial that looked at canagliflozin (Invokana) treatment in 4,401 patients with T2D and albuminuria and chronic kidney disease showed canagliflozin treatment cut the primary, composite renal endpoint by a statistically significant 30%, compared with placebo (N Engl J Med. 2019 Jun 13;380[24]:2295-306). The study stopped earlier than planned because of how effective canagliflozin appeared.
“Never before has a renal protection clinical trial stopped for overwhelming efficacy,” noted nephrologist Katherine R. Tuttle, MD, executive director for research at Providence Health Care in Spokane, Wash. “It’s very exciting to have a treatment that works on both the heart and kidney, given their interrelationship,” she said during the ADA sessions. Dr. Tuttle called the cardiorenal effects from the SGLT2 inhibitors “amazing.”
Just as the DAPA-HF trial’s primary outcome showed the ability of at least one drug from the class, dapagliflozin, to improve outcomes in HFrEF patients without T2D, topline results recently reported from the DAPA-CDK trial showed for the first time renal protection by an SGLT2 inhibitor in patients with chronic kidney disease but no T2D, in a study with about 4,300 patients.
Although detailed results from DAPA-CKD are not yet available, so far the outcomes seem consistent with the CREDENCE findings, and the cumulative renal findings for the class show the SGLT2 inhibitors have “potential for a profound impact on the patients we see in every nephrology clinic, and with dual cardiorenal disease,” said Dr. Rangaswami. The class is now established as “standard of care for patients with chronic kidney disease. The CREDENCE results made that clear.”
The DAPA-CKD findings in patients with chronic kidney disease regardless of their diabetes status “are very important. We really have not had any advances in this space for some time, and chronic kidney disease patients have very poor outcomes, both cardiovascular and renal,” commented Dr. Butler. The advantage from using this drug class in these patients “is huge.”
The DAPA-CKD findings are a “major advance,” agreed Dr. McCullough.
SGLT2 inhibitor use needs to grow
Experts lament that although the evidence favoring the class has been very bullish, prescribing uptake has been slow, perhaps partly explained by the retail U.S. cost for most of these agents, generally about $17/day.
Cost is, unfortunately, an issue right now for these drugs, said Dr. Butler. Generic formulations are imminent, “but we cannot accept waiting. Providing this therapy when insurance coverage is available,” is essential.
The FDA has already granted tentative approval to some generic formulations, although resolution of patent issues can delay generics actually reaching the market. “Generic dapagliflozin will have a major impact; the marketplace for these drugs will shift very quickly,” predicted Dr. McCullough.
But price may not be the sole barrier, cautioned Dr. Rangaswami. “I don’t think it’s just a cost issue. Several factors explain the slow uptake,” of the SGLT2 inhibitors. “The biggest barrier is that this is a new drug class, and understanding how to use the class is not yet where it needs to be in the physician community.” One of the biggest problems is that the SGLT2 inhibitors are still primarily regarded as drugs to treat hyperglycemia.
Physicians who treat patients with heart or renal disease “need to wrap their head around the idea that a drug with antihyperglycemic effects is now in their practice territory, and something they need to prescribe,” she noted. Currently “there is a reluctance to prescribe these drugs given the perception that they are antihyperglycemic agents, and usually get deferred to primary care physicians or endocrinologists. This results in huge missed opportunities by cardiologists and nephrologists in initiating these agents that have major cardiorenal risk reduction effects.”
The key role that cardiologists need to play in prescribing the SGLT2 inhibitors was brought home in a recent study of two representative U.S. health systems that showed patients with T2D were far more likely to see a cardiologist than an endocrinologist (Cardiovasc Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Jun;9[2]:56-9).
“The SGLT2 inhibitors are definitely a game-changing drug class,” summed up Dr. Rangaswami. “We’re going to see a lot of use in patients with heart and kidney disease.”
Dr. Cherney has been a consultant to or has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, and Sanofi. Dr. Butler has had financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. McCullough and Dr. Rangaswami had no disclosures. Dr. Inzucchi has been a consultant to or helped run trials for Abbott, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi/Lexicon, and vTv Therapeutics. Dr. Testani has been a consultant to AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, cardionomic, FIRE1 Magenta Med, Novartis, Reprieve, Sanofi, and W.L. Gore. Dr. Kosiborod has been a consultant to or led trials for Amarin, Amgen, Applied Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Glytec, Janssen, Eli Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Vifor. Dr. Tuttle has been a consultant to AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead, Goldfinch Bio, Eli Lilly, and Novo Nordisk.
AHA on cannabis: No evidence of heart benefits, but potential harms
Evidence for a link between cannabis use and cardiovascular health remains unsupported, and the potential risks outweigh any potential benefits, according to a scientific statement from the American Heart Association.
The increased legalization of cannabis and cannabis products in the United States has driven medical professionals to evaluate the safety and efficacy of cannabis in relation to health conditions, wrote Robert L. Page II, PharmD, of the University of Colorado, Aurora, and colleagues.
In a statement published in Circulation, the researchers noted that although cannabis has been shown to relieve pain and other symptoms in certain conditions, clinicians in the United States have been limited from studying its health effects because of federal law restrictions. “Cannabis remains a schedule I controlled substance, deeming no accepted medical use, a high potential for abuse, and an unacceptable safety profile,” the researchers wrote.
The statement addresses issues with the use of cannabis by individuals with cardiovascular disease or those at increased risk. Observational studies have shown no cardiovascular benefits associated with cannabis, the writers noted. The most common chemicals in cannabis include THC (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) and CBD (cannabidiol).
Some research has shown associations between CBD cardiovascular features including lower blood pressure and reduced inflammation, the writers noted. However, THC, the component of cannabis associated with a “high” or intoxication, has been associated with heart rhythm abnormalities. The writers cited data suggesting an increased risk of heart attacks, atrial fibrillation and heart failure, although more research is needed.
The statement outlines common cannabis formulations including plant-based, extracts, crystalline forms, edible products, and tinctures. In addition, the statement notes that synthetic cannabis products are marketed and used in the United States without subject to regulation.
“Over the past 5 years, we have seen a surge in cannabis use, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic here in Colorado, especially among adolescents and young adults,” Dr. Page said in an interview. Because of the surge, health care practitioners need to familiarize themselves with not only the benefits, but risks associated with cannabis use regardless of the formulation,” he said. As heart disease remains a leading cause of death in the United States, understanding the cardiovascular risks associated with cannabis is crucial at this time.
Dr. Page noted that popular attitudes about cannabis could pose risks to users’ cardiovascular health. “One leading misconception about cannabis is because it is ‘natural’ it must be safe,” Dr. Page said. “As with all medications, cannabis has side effects, some of which can be cardiovascular in nature,” he said. “Significant drug-drug interactions can occur as CBD and THC, both found in cannabis, inhibit CYP3A4, which metabolizes a large number of medications used to treat many cardiovascular conditions,” he noted.
“Unfortunately, much of the published data is observational in nature due to the federal restrictions on cannabis as a schedule I drug,” said Dr. Page. “Nonetheless, safety signals have emerged regarding cannabis use and adverse cardiovascular outcomes, including myocardial infarction, heart failure, and atrial fibrillation. Carefully designed prospective short- and long-term studies regarding cannabis use and cardiovascular safety are needed,” he emphasized.
Areas in particular need of additional research include the cardiovascular effects of cannabis in several vulnerable populations such as adolescents, older adults, pregnant women, transplant recipients, and those with underlying cardiovascular disease, said Dr. Page.
“Nonetheless, based on the safety signals described within this Clinical Science Statement, an open discussion regarding the risks of using cannabis needs to occur between patient and health care providers,” he said. “Furthermore, patients must be transparent regarding their cannabis use with their cardiologist and primary care provider. The cannabis story will continue to evolve and is a rapidly moving/changing target,” he said.
“Whether cannabis use is a definitive risk factor for cardiovascular disease as with tobacco use is still unknown, and both acute and long-term studies are desperately needed to address this issue,” he said.
Dr. Page had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Page et al. Circulation. 2020 Aug 5. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000883.
Evidence for a link between cannabis use and cardiovascular health remains unsupported, and the potential risks outweigh any potential benefits, according to a scientific statement from the American Heart Association.
The increased legalization of cannabis and cannabis products in the United States has driven medical professionals to evaluate the safety and efficacy of cannabis in relation to health conditions, wrote Robert L. Page II, PharmD, of the University of Colorado, Aurora, and colleagues.
In a statement published in Circulation, the researchers noted that although cannabis has been shown to relieve pain and other symptoms in certain conditions, clinicians in the United States have been limited from studying its health effects because of federal law restrictions. “Cannabis remains a schedule I controlled substance, deeming no accepted medical use, a high potential for abuse, and an unacceptable safety profile,” the researchers wrote.
The statement addresses issues with the use of cannabis by individuals with cardiovascular disease or those at increased risk. Observational studies have shown no cardiovascular benefits associated with cannabis, the writers noted. The most common chemicals in cannabis include THC (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) and CBD (cannabidiol).
Some research has shown associations between CBD cardiovascular features including lower blood pressure and reduced inflammation, the writers noted. However, THC, the component of cannabis associated with a “high” or intoxication, has been associated with heart rhythm abnormalities. The writers cited data suggesting an increased risk of heart attacks, atrial fibrillation and heart failure, although more research is needed.
The statement outlines common cannabis formulations including plant-based, extracts, crystalline forms, edible products, and tinctures. In addition, the statement notes that synthetic cannabis products are marketed and used in the United States without subject to regulation.
“Over the past 5 years, we have seen a surge in cannabis use, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic here in Colorado, especially among adolescents and young adults,” Dr. Page said in an interview. Because of the surge, health care practitioners need to familiarize themselves with not only the benefits, but risks associated with cannabis use regardless of the formulation,” he said. As heart disease remains a leading cause of death in the United States, understanding the cardiovascular risks associated with cannabis is crucial at this time.
Dr. Page noted that popular attitudes about cannabis could pose risks to users’ cardiovascular health. “One leading misconception about cannabis is because it is ‘natural’ it must be safe,” Dr. Page said. “As with all medications, cannabis has side effects, some of which can be cardiovascular in nature,” he said. “Significant drug-drug interactions can occur as CBD and THC, both found in cannabis, inhibit CYP3A4, which metabolizes a large number of medications used to treat many cardiovascular conditions,” he noted.
“Unfortunately, much of the published data is observational in nature due to the federal restrictions on cannabis as a schedule I drug,” said Dr. Page. “Nonetheless, safety signals have emerged regarding cannabis use and adverse cardiovascular outcomes, including myocardial infarction, heart failure, and atrial fibrillation. Carefully designed prospective short- and long-term studies regarding cannabis use and cardiovascular safety are needed,” he emphasized.
Areas in particular need of additional research include the cardiovascular effects of cannabis in several vulnerable populations such as adolescents, older adults, pregnant women, transplant recipients, and those with underlying cardiovascular disease, said Dr. Page.
“Nonetheless, based on the safety signals described within this Clinical Science Statement, an open discussion regarding the risks of using cannabis needs to occur between patient and health care providers,” he said. “Furthermore, patients must be transparent regarding their cannabis use with their cardiologist and primary care provider. The cannabis story will continue to evolve and is a rapidly moving/changing target,” he said.
“Whether cannabis use is a definitive risk factor for cardiovascular disease as with tobacco use is still unknown, and both acute and long-term studies are desperately needed to address this issue,” he said.
Dr. Page had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Page et al. Circulation. 2020 Aug 5. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000883.
Evidence for a link between cannabis use and cardiovascular health remains unsupported, and the potential risks outweigh any potential benefits, according to a scientific statement from the American Heart Association.
The increased legalization of cannabis and cannabis products in the United States has driven medical professionals to evaluate the safety and efficacy of cannabis in relation to health conditions, wrote Robert L. Page II, PharmD, of the University of Colorado, Aurora, and colleagues.
In a statement published in Circulation, the researchers noted that although cannabis has been shown to relieve pain and other symptoms in certain conditions, clinicians in the United States have been limited from studying its health effects because of federal law restrictions. “Cannabis remains a schedule I controlled substance, deeming no accepted medical use, a high potential for abuse, and an unacceptable safety profile,” the researchers wrote.
The statement addresses issues with the use of cannabis by individuals with cardiovascular disease or those at increased risk. Observational studies have shown no cardiovascular benefits associated with cannabis, the writers noted. The most common chemicals in cannabis include THC (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) and CBD (cannabidiol).
Some research has shown associations between CBD cardiovascular features including lower blood pressure and reduced inflammation, the writers noted. However, THC, the component of cannabis associated with a “high” or intoxication, has been associated with heart rhythm abnormalities. The writers cited data suggesting an increased risk of heart attacks, atrial fibrillation and heart failure, although more research is needed.
The statement outlines common cannabis formulations including plant-based, extracts, crystalline forms, edible products, and tinctures. In addition, the statement notes that synthetic cannabis products are marketed and used in the United States without subject to regulation.
“Over the past 5 years, we have seen a surge in cannabis use, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic here in Colorado, especially among adolescents and young adults,” Dr. Page said in an interview. Because of the surge, health care practitioners need to familiarize themselves with not only the benefits, but risks associated with cannabis use regardless of the formulation,” he said. As heart disease remains a leading cause of death in the United States, understanding the cardiovascular risks associated with cannabis is crucial at this time.
Dr. Page noted that popular attitudes about cannabis could pose risks to users’ cardiovascular health. “One leading misconception about cannabis is because it is ‘natural’ it must be safe,” Dr. Page said. “As with all medications, cannabis has side effects, some of which can be cardiovascular in nature,” he said. “Significant drug-drug interactions can occur as CBD and THC, both found in cannabis, inhibit CYP3A4, which metabolizes a large number of medications used to treat many cardiovascular conditions,” he noted.
“Unfortunately, much of the published data is observational in nature due to the federal restrictions on cannabis as a schedule I drug,” said Dr. Page. “Nonetheless, safety signals have emerged regarding cannabis use and adverse cardiovascular outcomes, including myocardial infarction, heart failure, and atrial fibrillation. Carefully designed prospective short- and long-term studies regarding cannabis use and cardiovascular safety are needed,” he emphasized.
Areas in particular need of additional research include the cardiovascular effects of cannabis in several vulnerable populations such as adolescents, older adults, pregnant women, transplant recipients, and those with underlying cardiovascular disease, said Dr. Page.
“Nonetheless, based on the safety signals described within this Clinical Science Statement, an open discussion regarding the risks of using cannabis needs to occur between patient and health care providers,” he said. “Furthermore, patients must be transparent regarding their cannabis use with their cardiologist and primary care provider. The cannabis story will continue to evolve and is a rapidly moving/changing target,” he said.
“Whether cannabis use is a definitive risk factor for cardiovascular disease as with tobacco use is still unknown, and both acute and long-term studies are desperately needed to address this issue,” he said.
Dr. Page had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Page et al. Circulation. 2020 Aug 5. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000883.
FROM CIRCULATION
All NSAIDs raise post-MI risk but some are safer than others: Next chapter
Patients on antithrombotics after an acute MI will face a greater risk for bleeding and secondary cardiovascular (CV) events if they start taking any nonaspirin NSAID, confirms a large observational study.
Like other research before it, the new study suggests those risks will be much lower for some nonaspirin NSAIDs than others. But it may also challenge at least some conventional thinking about the safety of these drugs, and is based solely on a large cohort in South Korea, a group for which such NSAID data has been in short supply.
“It was intriguing that our study presented better safety profiles with celecoxib and meloxicam versus other subtypes of NSAIDs,” noted the report, published online July 27 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Most of the NSAIDs included in the analysis, “including naproxen, conferred a significantly higher risk for cardiovascular and bleeding events, compared with celecoxib and meloxicam,” wrote the authors, led by Dong Oh Kang, MD, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, South Korea.
A main contribution of the study “is the thorough and comprehensive evaluation of the Korean population by use of the nationwide prescription claims database that reflects real-world clinical practice,” senior author Cheol Ung Choi, MD, PhD, of the same institution, said in an interview.
“Because we included the largest number of patients of any comparable clinical studies on NSAID treatment after MI thus far, our study may allow the generalizability of the adverse events of NSAIDs to all patients by constituting global evidence encompassing different population groups,” Dr. Choi said.
The analysis has limitations along with its strengths, the authors acknowledged, including its observational design and potential for confounding not addressed in statistical adjustments.
Observers of the study concurred, but some cited evidence pointing to such confounding that is serious enough to question the entire study’s validity.
Among the cohort of more than 100,000 patients followed for an average of about 2.3 years after their MI, the adjusted risk of thromboembolic CV events went up almost 7 times for those who took any NSAID for at least 4 consecutive weeks, compared with those who didn’t take NSAIDs, based on prescription records.
Their adjusted risk of bleeding events – which included gastrointestinal, intracranial, respiratory, or urinary tract bleeding or posthemorrhagic anemia, the group writes – was increased 300%.
There was wide variance in the adjusted hazard ratios for outcomes by type of NSAID. The risk of CV events climbed from a low of about 3 with meloxicam and almost 5 for celecoxib to more than 10 and 12 for naproxen and dexibuprofen, respectively.
The hazard ratios for bleeding ranged from about 3 for both meloxicam and celecoxib to more than 6 for naproxen.
Of note, celecoxib and meloxicam both preferentially target the cyclooxygenase type 2 (COX-2) pathway, and naproxen among NSAIDs once had a reputation for relative cardiac safety, although subsequent studies have challenged that notion.
“On the basis of the contemporary guidelines, NSAID treatment should be limited as much as possible after MI; however, our data suggest that celecoxib and meloxicam could be considered possible alternative choices in patients with MI when NSAID prescription is unavoidable,” the group wrote.
They acknowledged some limitations of the analysis, including an observational design and the possibility of unidentified confounders; that mortality outcomes were not available from the National Health Insurance Service database used in the study; and that the 2009-2013 span for the data didn’t allow consideration of more contemporary antiplatelet agents and direct oral anticoagulants.
Also, NSAID use was based on prescriptions without regard to over-the-counter usage. Although use of over-the-counter NSAIDs is common in Korea, “most MI patients in Korea are prescribed most medications, including NSAIDs, in the hospital. So I think that usage of over-the-counter NSAIDs did not change the results,” Dr. Choi said.
“This study breaks new ground by demonstrating cardiovascular safety of meloxicam (and not only of celecoxib), probably because of its higher COX-2 selectivity,” wrote the authors of an accompanying editorial, Juan J. Badimon, PhD, and Carlos G. Santos-Gallego, MD, both of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Notably, “this paper rejects the cardiovascular safety of naproxen, which had been suggested classically and in the previous Danish data, but that was not evident in this study.” The finding is consistent with the PRECISION trial, in which both bleeding and CV risk were increased with naproxen versus other NSAIDs, observed Dr. Badimon and Dr. Santos-Gallego.
They agreed with the authors in recommending that, “although NSAID treatment should be avoided in patients with MI, if the use of NSAIDs is inevitable due to comorbidities, the prescription of celecoxib and meloxicam could be considered as alternative options.”
But, “as no study is perfect, this article also presents some limitations,” the editorial agreed, citing some of the same issues noted by Dr. Kang and associates, along with potential confounding by indication and the lack of “clinical information to adjust (e.g., angiographic features, left ventricular function).”
“There’s undoubtedly residual confounding,” James M. Brophy, MD, PhD, a pharmacoepidemiologist at McGill University, Montreal, said in an interview.
The 400%-900% relative risks for CV events “are just too far in left field, compared to everything else we know,” he said. “There has never been a class of drugs that have shown this sort of magnitude of effect for adverse events.”
Even in PRECISION with its more than 24,000 high-coronary-risk patients randomized and followed for 5 years, Dr. Brophy observed, relative risks for the different NSAIDs varied by an order of magnitude of only 1-2.
“You should be interpreting things in the context of what is already known,” Dr. Brophy said. “The only conclusion I would draw is the paper is fatally flawed.”
The registry included 108,232 primarily male patients followed from their first diagnosed MI for CV and bleeding events. About 1.9% were prescribed at least one NSAID for 4 or more consecutive weeks during the follow-up period averaging 2.3 years, the group reported.
The most frequently prescribed NSAID was diclofenac, at about 72% of prescribed NSAIDs in the analysis for CV events and about 69% in the bleeding-event analysis.
Adding any NSAID to post-MI antithrombotic therapy led to an adjusted HR of 6.96 (P < .001) for CV events and 4.08 (P < .001) for bleeding events, compared with no NSAID treatment.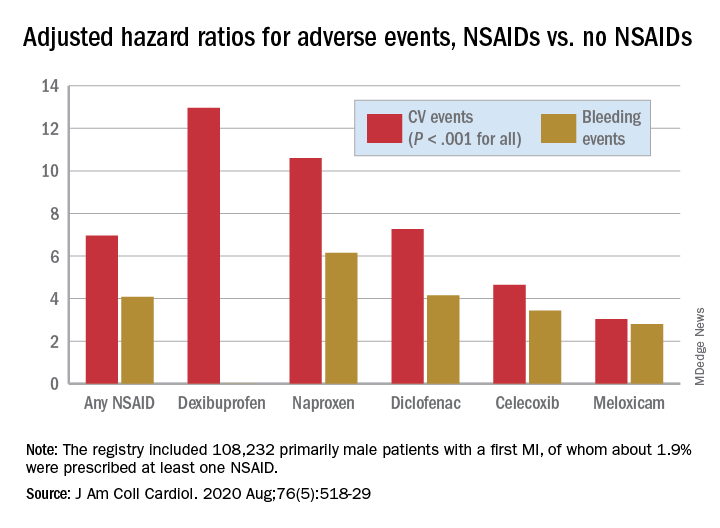
The 88% of the cohort who were on dual-antiplatelet therapy with aspirin and clopidogrel showed very nearly the same risk increases for both endpoints.
Further studies are needed to confirm the results “and ensure their generalizability to other populations,” Dr. Choi said. They should be validated especially using the claims data bases of countries near Korea, “such as Japan and Taiwan, to examine the reproducibility of the results in similar ethnic populations.”
That the study focused on a cohort in Korea is a strength, contended the authors as well as Dr. Badimon and Dr. Santos-Gallego, given “that most data about NSAIDs were extracted from Western populations, but the risk of thrombosis/bleeding post-MI varies according to ethnicity,” according to the editorial
Dr. Brophy agreed, but doubted that ethnic differences are responsible for variation in relative risks between the current results and other studies. “There are pharmacogenomic differences between different ethnicities as to how they activate these drugs. But I suspect that sort of difference is really minor. Maybe it leads to a 2% or a 5% difference in risks.”
Dr. Kang and associates, Dr. Badimon, Dr. Santos-Gallego, and Dr. Brophy disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients on antithrombotics after an acute MI will face a greater risk for bleeding and secondary cardiovascular (CV) events if they start taking any nonaspirin NSAID, confirms a large observational study.
Like other research before it, the new study suggests those risks will be much lower for some nonaspirin NSAIDs than others. But it may also challenge at least some conventional thinking about the safety of these drugs, and is based solely on a large cohort in South Korea, a group for which such NSAID data has been in short supply.
“It was intriguing that our study presented better safety profiles with celecoxib and meloxicam versus other subtypes of NSAIDs,” noted the report, published online July 27 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Most of the NSAIDs included in the analysis, “including naproxen, conferred a significantly higher risk for cardiovascular and bleeding events, compared with celecoxib and meloxicam,” wrote the authors, led by Dong Oh Kang, MD, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, South Korea.
A main contribution of the study “is the thorough and comprehensive evaluation of the Korean population by use of the nationwide prescription claims database that reflects real-world clinical practice,” senior author Cheol Ung Choi, MD, PhD, of the same institution, said in an interview.
“Because we included the largest number of patients of any comparable clinical studies on NSAID treatment after MI thus far, our study may allow the generalizability of the adverse events of NSAIDs to all patients by constituting global evidence encompassing different population groups,” Dr. Choi said.
The analysis has limitations along with its strengths, the authors acknowledged, including its observational design and potential for confounding not addressed in statistical adjustments.
Observers of the study concurred, but some cited evidence pointing to such confounding that is serious enough to question the entire study’s validity.
Among the cohort of more than 100,000 patients followed for an average of about 2.3 years after their MI, the adjusted risk of thromboembolic CV events went up almost 7 times for those who took any NSAID for at least 4 consecutive weeks, compared with those who didn’t take NSAIDs, based on prescription records.
Their adjusted risk of bleeding events – which included gastrointestinal, intracranial, respiratory, or urinary tract bleeding or posthemorrhagic anemia, the group writes – was increased 300%.
There was wide variance in the adjusted hazard ratios for outcomes by type of NSAID. The risk of CV events climbed from a low of about 3 with meloxicam and almost 5 for celecoxib to more than 10 and 12 for naproxen and dexibuprofen, respectively.
The hazard ratios for bleeding ranged from about 3 for both meloxicam and celecoxib to more than 6 for naproxen.
Of note, celecoxib and meloxicam both preferentially target the cyclooxygenase type 2 (COX-2) pathway, and naproxen among NSAIDs once had a reputation for relative cardiac safety, although subsequent studies have challenged that notion.
“On the basis of the contemporary guidelines, NSAID treatment should be limited as much as possible after MI; however, our data suggest that celecoxib and meloxicam could be considered possible alternative choices in patients with MI when NSAID prescription is unavoidable,” the group wrote.
They acknowledged some limitations of the analysis, including an observational design and the possibility of unidentified confounders; that mortality outcomes were not available from the National Health Insurance Service database used in the study; and that the 2009-2013 span for the data didn’t allow consideration of more contemporary antiplatelet agents and direct oral anticoagulants.
Also, NSAID use was based on prescriptions without regard to over-the-counter usage. Although use of over-the-counter NSAIDs is common in Korea, “most MI patients in Korea are prescribed most medications, including NSAIDs, in the hospital. So I think that usage of over-the-counter NSAIDs did not change the results,” Dr. Choi said.
“This study breaks new ground by demonstrating cardiovascular safety of meloxicam (and not only of celecoxib), probably because of its higher COX-2 selectivity,” wrote the authors of an accompanying editorial, Juan J. Badimon, PhD, and Carlos G. Santos-Gallego, MD, both of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Notably, “this paper rejects the cardiovascular safety of naproxen, which had been suggested classically and in the previous Danish data, but that was not evident in this study.” The finding is consistent with the PRECISION trial, in which both bleeding and CV risk were increased with naproxen versus other NSAIDs, observed Dr. Badimon and Dr. Santos-Gallego.
They agreed with the authors in recommending that, “although NSAID treatment should be avoided in patients with MI, if the use of NSAIDs is inevitable due to comorbidities, the prescription of celecoxib and meloxicam could be considered as alternative options.”
But, “as no study is perfect, this article also presents some limitations,” the editorial agreed, citing some of the same issues noted by Dr. Kang and associates, along with potential confounding by indication and the lack of “clinical information to adjust (e.g., angiographic features, left ventricular function).”
“There’s undoubtedly residual confounding,” James M. Brophy, MD, PhD, a pharmacoepidemiologist at McGill University, Montreal, said in an interview.
The 400%-900% relative risks for CV events “are just too far in left field, compared to everything else we know,” he said. “There has never been a class of drugs that have shown this sort of magnitude of effect for adverse events.”
Even in PRECISION with its more than 24,000 high-coronary-risk patients randomized and followed for 5 years, Dr. Brophy observed, relative risks for the different NSAIDs varied by an order of magnitude of only 1-2.
“You should be interpreting things in the context of what is already known,” Dr. Brophy said. “The only conclusion I would draw is the paper is fatally flawed.”
The registry included 108,232 primarily male patients followed from their first diagnosed MI for CV and bleeding events. About 1.9% were prescribed at least one NSAID for 4 or more consecutive weeks during the follow-up period averaging 2.3 years, the group reported.
The most frequently prescribed NSAID was diclofenac, at about 72% of prescribed NSAIDs in the analysis for CV events and about 69% in the bleeding-event analysis.
Adding any NSAID to post-MI antithrombotic therapy led to an adjusted HR of 6.96 (P < .001) for CV events and 4.08 (P < .001) for bleeding events, compared with no NSAID treatment.
The 88% of the cohort who were on dual-antiplatelet therapy with aspirin and clopidogrel showed very nearly the same risk increases for both endpoints.
Further studies are needed to confirm the results “and ensure their generalizability to other populations,” Dr. Choi said. They should be validated especially using the claims data bases of countries near Korea, “such as Japan and Taiwan, to examine the reproducibility of the results in similar ethnic populations.”
That the study focused on a cohort in Korea is a strength, contended the authors as well as Dr. Badimon and Dr. Santos-Gallego, given “that most data about NSAIDs were extracted from Western populations, but the risk of thrombosis/bleeding post-MI varies according to ethnicity,” according to the editorial
Dr. Brophy agreed, but doubted that ethnic differences are responsible for variation in relative risks between the current results and other studies. “There are pharmacogenomic differences between different ethnicities as to how they activate these drugs. But I suspect that sort of difference is really minor. Maybe it leads to a 2% or a 5% difference in risks.”
Dr. Kang and associates, Dr. Badimon, Dr. Santos-Gallego, and Dr. Brophy disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients on antithrombotics after an acute MI will face a greater risk for bleeding and secondary cardiovascular (CV) events if they start taking any nonaspirin NSAID, confirms a large observational study.
Like other research before it, the new study suggests those risks will be much lower for some nonaspirin NSAIDs than others. But it may also challenge at least some conventional thinking about the safety of these drugs, and is based solely on a large cohort in South Korea, a group for which such NSAID data has been in short supply.
“It was intriguing that our study presented better safety profiles with celecoxib and meloxicam versus other subtypes of NSAIDs,” noted the report, published online July 27 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Most of the NSAIDs included in the analysis, “including naproxen, conferred a significantly higher risk for cardiovascular and bleeding events, compared with celecoxib and meloxicam,” wrote the authors, led by Dong Oh Kang, MD, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, South Korea.
A main contribution of the study “is the thorough and comprehensive evaluation of the Korean population by use of the nationwide prescription claims database that reflects real-world clinical practice,” senior author Cheol Ung Choi, MD, PhD, of the same institution, said in an interview.
“Because we included the largest number of patients of any comparable clinical studies on NSAID treatment after MI thus far, our study may allow the generalizability of the adverse events of NSAIDs to all patients by constituting global evidence encompassing different population groups,” Dr. Choi said.
The analysis has limitations along with its strengths, the authors acknowledged, including its observational design and potential for confounding not addressed in statistical adjustments.
Observers of the study concurred, but some cited evidence pointing to such confounding that is serious enough to question the entire study’s validity.
Among the cohort of more than 100,000 patients followed for an average of about 2.3 years after their MI, the adjusted risk of thromboembolic CV events went up almost 7 times for those who took any NSAID for at least 4 consecutive weeks, compared with those who didn’t take NSAIDs, based on prescription records.
Their adjusted risk of bleeding events – which included gastrointestinal, intracranial, respiratory, or urinary tract bleeding or posthemorrhagic anemia, the group writes – was increased 300%.
There was wide variance in the adjusted hazard ratios for outcomes by type of NSAID. The risk of CV events climbed from a low of about 3 with meloxicam and almost 5 for celecoxib to more than 10 and 12 for naproxen and dexibuprofen, respectively.
The hazard ratios for bleeding ranged from about 3 for both meloxicam and celecoxib to more than 6 for naproxen.
Of note, celecoxib and meloxicam both preferentially target the cyclooxygenase type 2 (COX-2) pathway, and naproxen among NSAIDs once had a reputation for relative cardiac safety, although subsequent studies have challenged that notion.
“On the basis of the contemporary guidelines, NSAID treatment should be limited as much as possible after MI; however, our data suggest that celecoxib and meloxicam could be considered possible alternative choices in patients with MI when NSAID prescription is unavoidable,” the group wrote.
They acknowledged some limitations of the analysis, including an observational design and the possibility of unidentified confounders; that mortality outcomes were not available from the National Health Insurance Service database used in the study; and that the 2009-2013 span for the data didn’t allow consideration of more contemporary antiplatelet agents and direct oral anticoagulants.
Also, NSAID use was based on prescriptions without regard to over-the-counter usage. Although use of over-the-counter NSAIDs is common in Korea, “most MI patients in Korea are prescribed most medications, including NSAIDs, in the hospital. So I think that usage of over-the-counter NSAIDs did not change the results,” Dr. Choi said.
“This study breaks new ground by demonstrating cardiovascular safety of meloxicam (and not only of celecoxib), probably because of its higher COX-2 selectivity,” wrote the authors of an accompanying editorial, Juan J. Badimon, PhD, and Carlos G. Santos-Gallego, MD, both of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Notably, “this paper rejects the cardiovascular safety of naproxen, which had been suggested classically and in the previous Danish data, but that was not evident in this study.” The finding is consistent with the PRECISION trial, in which both bleeding and CV risk were increased with naproxen versus other NSAIDs, observed Dr. Badimon and Dr. Santos-Gallego.
They agreed with the authors in recommending that, “although NSAID treatment should be avoided in patients with MI, if the use of NSAIDs is inevitable due to comorbidities, the prescription of celecoxib and meloxicam could be considered as alternative options.”
But, “as no study is perfect, this article also presents some limitations,” the editorial agreed, citing some of the same issues noted by Dr. Kang and associates, along with potential confounding by indication and the lack of “clinical information to adjust (e.g., angiographic features, left ventricular function).”
“There’s undoubtedly residual confounding,” James M. Brophy, MD, PhD, a pharmacoepidemiologist at McGill University, Montreal, said in an interview.
The 400%-900% relative risks for CV events “are just too far in left field, compared to everything else we know,” he said. “There has never been a class of drugs that have shown this sort of magnitude of effect for adverse events.”
Even in PRECISION with its more than 24,000 high-coronary-risk patients randomized and followed for 5 years, Dr. Brophy observed, relative risks for the different NSAIDs varied by an order of magnitude of only 1-2.
“You should be interpreting things in the context of what is already known,” Dr. Brophy said. “The only conclusion I would draw is the paper is fatally flawed.”
The registry included 108,232 primarily male patients followed from their first diagnosed MI for CV and bleeding events. About 1.9% were prescribed at least one NSAID for 4 or more consecutive weeks during the follow-up period averaging 2.3 years, the group reported.
The most frequently prescribed NSAID was diclofenac, at about 72% of prescribed NSAIDs in the analysis for CV events and about 69% in the bleeding-event analysis.
Adding any NSAID to post-MI antithrombotic therapy led to an adjusted HR of 6.96 (P < .001) for CV events and 4.08 (P < .001) for bleeding events, compared with no NSAID treatment.
The 88% of the cohort who were on dual-antiplatelet therapy with aspirin and clopidogrel showed very nearly the same risk increases for both endpoints.
Further studies are needed to confirm the results “and ensure their generalizability to other populations,” Dr. Choi said. They should be validated especially using the claims data bases of countries near Korea, “such as Japan and Taiwan, to examine the reproducibility of the results in similar ethnic populations.”
That the study focused on a cohort in Korea is a strength, contended the authors as well as Dr. Badimon and Dr. Santos-Gallego, given “that most data about NSAIDs were extracted from Western populations, but the risk of thrombosis/bleeding post-MI varies according to ethnicity,” according to the editorial
Dr. Brophy agreed, but doubted that ethnic differences are responsible for variation in relative risks between the current results and other studies. “There are pharmacogenomic differences between different ethnicities as to how they activate these drugs. But I suspect that sort of difference is really minor. Maybe it leads to a 2% or a 5% difference in risks.”
Dr. Kang and associates, Dr. Badimon, Dr. Santos-Gallego, and Dr. Brophy disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Oculostenotic reflex still holds sway, survey shows
Most interventional cardiologists still rely solely upon angiography in making revascularization decisions about intermediate stenoses in the setting of stable coronary artery disease – and in doing so they end up making the wrong call nearly 40% of the time, according to the results of an international survey presented at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
“We saw a strong tendency to visually overestimate the percent diameter stenosis,” reported Gabor G. Toth, MD, an interventional cardiologist at the Medical University of Graz (Austria).
The same tendency has been highlighted in numerous randomized trials and observational studies. That’s why both European and U.S. guidelines now strongly recommend invasive functional assessment, such as fractional-flow reserve (FFR) testing, in evaluating the significance of intermediate stenoses in the absence of noninvasive evidence of ischemia. The new survey findings point to an important disconnect between these guideline recommendations and current clinical practice, he noted.
Dr. Toth presented the results of the second web-based, international survey on interventional decision-making strategy sponsored by the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions. He contrasted the findings with those of the previously reported first international online survey, conducted 6 years earlier, for which he was first author (Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2014 Dec;7[6]:751-9).
The two surveys were identically designed. In both, participants answered questions that enabled investigators to place them into one of four categories based upon the extent of their experience in interventional cardiology. The participants were also presented with 5 angiograms of focal intermediate stenoses and asked to determine the stenosis significance of each lesion. No information on the functional significance of the stenoses was included; however, the respondents could request additional diagnostic information by “ordering” adjunctive invasive functional assessment tests, including FFR, quantitative coronary angiography, intravascular ultrasound, or optical coherence tomography. Importantly, participating cardiologists were asked to make their decisions based upon best possible clinical practice in a hypothetical scenario where financial constraints had no role.
The second international survey was conducted during the latter half of 2019. The 334 interventional cardiologists who responded performed a total of 978 case evaluations including 2,054 coronary lesion assessments.
About 59% of all decisions were made solely on the basis of angiographic appearance without any information as to the functional significance of a given stenosis: Indeed, 13% of all stenoses were thereby declared to be “certainly” nonsignificant, and 46% were deemed “certainly” significant. In total, that figure was down significantly from the 71% rate in the first survey. In the first survey, 47% of decisions based upon angiographic appearance alone were discordant with FFR results known to the investigators, compared with a 39% discordance rate in the second survey.
Of the physician decisions made in the second survey, 10% involved a request for intravascular imaging, essentially unchanged from the 9% rate in the first survey. However, there was a significant increase over time in requests for invasive functional assessment tests: 25% in the first survey, rising to 31% in the second. This increase was entirely driven by additional requests for data on nonhyperemic pressure ratios; there was no difference in requests for FFR testing between the 2013 and 2019 surveys.
Clinician experience played an interesting role in decision-making: “Experience does not have an impact on the accuracy of angiographically based decisions, but experience does have an impact on understanding the need for adjunctive functional diagnostic testing,” Dr. Toth explained.
Indeed, 21% of decisions made by the least-experienced interventional cardiologists involved a request for adjunctive invasive functional assessment, compared with 24% of decisions by physicians in the third quartile of experience, 32% in the second, and 37% of decisions made by the most experienced clinicians.
Discussant Michael Haude, MD, PhD, said that “these results clearly show that eyeball angioguidance is still the dominant tool used in decision-making, and that this eyeball angioguidance continuously overestimates the stenosis when you compare the results to quantitative coronary angiography.
“These results, surprisingly for me, show a quite low uptake of the invasive functional assessments despite overwhelming scientific data leading to clear guideline-based recommendations. Why is this the case, even after financial constraints are ruled out? Probably because FFR is still a complex invasive procedure. Maybe, in the future, quantitative flow-ratio angiography [which requires no pressure wire] or CT-based FFR will be more popular,” said Dr. Haude, an interventional cardiologist at the Rheinland Clinic in Neuss, Germany.
He reported receiving research grants from Biotronik and serving as a paid consultant to that company as well as Cardiac Dimensions, Orbus Neich, and Philips. Dr. Toth reported having no financial conflicts regarding the international survey.
Most interventional cardiologists still rely solely upon angiography in making revascularization decisions about intermediate stenoses in the setting of stable coronary artery disease – and in doing so they end up making the wrong call nearly 40% of the time, according to the results of an international survey presented at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
“We saw a strong tendency to visually overestimate the percent diameter stenosis,” reported Gabor G. Toth, MD, an interventional cardiologist at the Medical University of Graz (Austria).
The same tendency has been highlighted in numerous randomized trials and observational studies. That’s why both European and U.S. guidelines now strongly recommend invasive functional assessment, such as fractional-flow reserve (FFR) testing, in evaluating the significance of intermediate stenoses in the absence of noninvasive evidence of ischemia. The new survey findings point to an important disconnect between these guideline recommendations and current clinical practice, he noted.
Dr. Toth presented the results of the second web-based, international survey on interventional decision-making strategy sponsored by the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions. He contrasted the findings with those of the previously reported first international online survey, conducted 6 years earlier, for which he was first author (Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2014 Dec;7[6]:751-9).
The two surveys were identically designed. In both, participants answered questions that enabled investigators to place them into one of four categories based upon the extent of their experience in interventional cardiology. The participants were also presented with 5 angiograms of focal intermediate stenoses and asked to determine the stenosis significance of each lesion. No information on the functional significance of the stenoses was included; however, the respondents could request additional diagnostic information by “ordering” adjunctive invasive functional assessment tests, including FFR, quantitative coronary angiography, intravascular ultrasound, or optical coherence tomography. Importantly, participating cardiologists were asked to make their decisions based upon best possible clinical practice in a hypothetical scenario where financial constraints had no role.
The second international survey was conducted during the latter half of 2019. The 334 interventional cardiologists who responded performed a total of 978 case evaluations including 2,054 coronary lesion assessments.
About 59% of all decisions were made solely on the basis of angiographic appearance without any information as to the functional significance of a given stenosis: Indeed, 13% of all stenoses were thereby declared to be “certainly” nonsignificant, and 46% were deemed “certainly” significant. In total, that figure was down significantly from the 71% rate in the first survey. In the first survey, 47% of decisions based upon angiographic appearance alone were discordant with FFR results known to the investigators, compared with a 39% discordance rate in the second survey.
Of the physician decisions made in the second survey, 10% involved a request for intravascular imaging, essentially unchanged from the 9% rate in the first survey. However, there was a significant increase over time in requests for invasive functional assessment tests: 25% in the first survey, rising to 31% in the second. This increase was entirely driven by additional requests for data on nonhyperemic pressure ratios; there was no difference in requests for FFR testing between the 2013 and 2019 surveys.
Clinician experience played an interesting role in decision-making: “Experience does not have an impact on the accuracy of angiographically based decisions, but experience does have an impact on understanding the need for adjunctive functional diagnostic testing,” Dr. Toth explained.
Indeed, 21% of decisions made by the least-experienced interventional cardiologists involved a request for adjunctive invasive functional assessment, compared with 24% of decisions by physicians in the third quartile of experience, 32% in the second, and 37% of decisions made by the most experienced clinicians.
Discussant Michael Haude, MD, PhD, said that “these results clearly show that eyeball angioguidance is still the dominant tool used in decision-making, and that this eyeball angioguidance continuously overestimates the stenosis when you compare the results to quantitative coronary angiography.
“These results, surprisingly for me, show a quite low uptake of the invasive functional assessments despite overwhelming scientific data leading to clear guideline-based recommendations. Why is this the case, even after financial constraints are ruled out? Probably because FFR is still a complex invasive procedure. Maybe, in the future, quantitative flow-ratio angiography [which requires no pressure wire] or CT-based FFR will be more popular,” said Dr. Haude, an interventional cardiologist at the Rheinland Clinic in Neuss, Germany.
He reported receiving research grants from Biotronik and serving as a paid consultant to that company as well as Cardiac Dimensions, Orbus Neich, and Philips. Dr. Toth reported having no financial conflicts regarding the international survey.
Most interventional cardiologists still rely solely upon angiography in making revascularization decisions about intermediate stenoses in the setting of stable coronary artery disease – and in doing so they end up making the wrong call nearly 40% of the time, according to the results of an international survey presented at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
“We saw a strong tendency to visually overestimate the percent diameter stenosis,” reported Gabor G. Toth, MD, an interventional cardiologist at the Medical University of Graz (Austria).
The same tendency has been highlighted in numerous randomized trials and observational studies. That’s why both European and U.S. guidelines now strongly recommend invasive functional assessment, such as fractional-flow reserve (FFR) testing, in evaluating the significance of intermediate stenoses in the absence of noninvasive evidence of ischemia. The new survey findings point to an important disconnect between these guideline recommendations and current clinical practice, he noted.
Dr. Toth presented the results of the second web-based, international survey on interventional decision-making strategy sponsored by the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions. He contrasted the findings with those of the previously reported first international online survey, conducted 6 years earlier, for which he was first author (Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2014 Dec;7[6]:751-9).
The two surveys were identically designed. In both, participants answered questions that enabled investigators to place them into one of four categories based upon the extent of their experience in interventional cardiology. The participants were also presented with 5 angiograms of focal intermediate stenoses and asked to determine the stenosis significance of each lesion. No information on the functional significance of the stenoses was included; however, the respondents could request additional diagnostic information by “ordering” adjunctive invasive functional assessment tests, including FFR, quantitative coronary angiography, intravascular ultrasound, or optical coherence tomography. Importantly, participating cardiologists were asked to make their decisions based upon best possible clinical practice in a hypothetical scenario where financial constraints had no role.
The second international survey was conducted during the latter half of 2019. The 334 interventional cardiologists who responded performed a total of 978 case evaluations including 2,054 coronary lesion assessments.
About 59% of all decisions were made solely on the basis of angiographic appearance without any information as to the functional significance of a given stenosis: Indeed, 13% of all stenoses were thereby declared to be “certainly” nonsignificant, and 46% were deemed “certainly” significant. In total, that figure was down significantly from the 71% rate in the first survey. In the first survey, 47% of decisions based upon angiographic appearance alone were discordant with FFR results known to the investigators, compared with a 39% discordance rate in the second survey.
Of the physician decisions made in the second survey, 10% involved a request for intravascular imaging, essentially unchanged from the 9% rate in the first survey. However, there was a significant increase over time in requests for invasive functional assessment tests: 25% in the first survey, rising to 31% in the second. This increase was entirely driven by additional requests for data on nonhyperemic pressure ratios; there was no difference in requests for FFR testing between the 2013 and 2019 surveys.
Clinician experience played an interesting role in decision-making: “Experience does not have an impact on the accuracy of angiographically based decisions, but experience does have an impact on understanding the need for adjunctive functional diagnostic testing,” Dr. Toth explained.
Indeed, 21% of decisions made by the least-experienced interventional cardiologists involved a request for adjunctive invasive functional assessment, compared with 24% of decisions by physicians in the third quartile of experience, 32% in the second, and 37% of decisions made by the most experienced clinicians.
Discussant Michael Haude, MD, PhD, said that “these results clearly show that eyeball angioguidance is still the dominant tool used in decision-making, and that this eyeball angioguidance continuously overestimates the stenosis when you compare the results to quantitative coronary angiography.
“These results, surprisingly for me, show a quite low uptake of the invasive functional assessments despite overwhelming scientific data leading to clear guideline-based recommendations. Why is this the case, even after financial constraints are ruled out? Probably because FFR is still a complex invasive procedure. Maybe, in the future, quantitative flow-ratio angiography [which requires no pressure wire] or CT-based FFR will be more popular,” said Dr. Haude, an interventional cardiologist at the Rheinland Clinic in Neuss, Germany.
He reported receiving research grants from Biotronik and serving as a paid consultant to that company as well as Cardiac Dimensions, Orbus Neich, and Philips. Dr. Toth reported having no financial conflicts regarding the international survey.
REPORTING FROM EUROPCR 2020
ACC panel defines, advises on heart failure with ‘recovered’ EF
Because heart failure patients with recovered ejection fraction are a complex and diverse group, little consensus has emerged on how to define, diagnose, and manage this growing population.
To provide some clarity for identifying and treating these patients, a Journal of the American College of Cardiology scientific expert panel has issued a consensus document. Published Aug. 3 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, it provides a working definition of heart failure with recovered ejection fraction (HFrecEF) and recommends approaches for treatment and follow-up.
Defining a new class of HF
“Part of the impetus of this was to bring attention to what we think is a new class of heart failure, and it requires different treatment modalities and different ways of thinking about it,” expert panel member Douglas L. Mann, MD, cardiologist-in-chief at Barnes Jewish Hospital in St. Louis, said in an interview. “It’s a newly discovered HF biology about which we know very little and it’s very confusing to just go on the ejection fraction alone.”
The panel, led by Jane E. Wilcox, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, recommends three components for a working definition of HFrecEF: 1) documentation of a decreased left ventricle ejection fraction (LVEF) of less than 40% at baseline; 2) a 10% or greater absolute improvement in LVEF; and 3) a second measurement of LVEF >40%.
“We try to give it a nomenclature that clearly indicates what it is,” Dr. Mann said. “There has been a lot of confusing terminology.” Among the terms the panel calls out in the lexicon of modestly recovered EF, in addition to HFrecEF, are HF improved EF, HF with preserved EF (HFpEF), borderline HFpEF and HF with mid-range EF (HFmrEF).
The panel also recommends that guideline-based medical and device therapies for HFrecEF should continue indefinitely until there’s a better understanding of the biology and clinical epidemiology of HFrecEF, and that these patients should have close clinical follow-up because of the high risk of HF relapse.
Determining EF’s ‘trajectory’
The findings presented in the statement should help cardiologists distinguish HFrecEF from HFpEF, Dr. Mann noted. “Because EF is moving, we also have to emphasize the importance of following the trajectory of EF,” he said. “It’s not enough to know where the EF is; you have to know where it came from – if it had been from a higher number or a lower number – because that will help inform you about the patient’s disease.”
In that regard, the panel states that the level of change in LVEF – the “trajectory” – will provide clues to the nature and extent of myocardial injury, degree and duration of LV remodeling, and the type of therapy that’s indicated. Clinicians should consider HFmrEF, a description the European Society of Cardiology has endorsed, as an entity different from HFrecEF without data on LVEF trajectory.
The statement delves into the biology of HFrecEF, defining reverse LV remodeling as the restoration of some normalization to cardiac myocyte size and LV chamber geometry that results in a leftward shift toward normalization of end-diastolic pressure volume. The panel also noted that cardiac remodeling in reverse LV remodeling and recovery of LV function is bidirectional and involves multiple molecular and cellular changes that contribute to changes in the heart’s size, shape and function, and explains the role gene expression has in HF-related LV changes.
The statement explores the recovery of LV function, noting that spontaneous recovery often occurs when the cause of the myocardial dysfunction resolves. Common causes are chronic tachycardia and thyroid disease.
That panel noted that “super responders” to cardiac resynchronization therapy can provide insight into HFrecEF. Favorable responders include women, patients with nonischemic HF, very wide ECG ventricular depolarization wavelength with left-bundle branch block morphology, and dyssynchrony on ECG.
The panel states that, “regardless of the definition of HFrecEF,” the evidence suggests that younger patients, women, and those with nonischemic disease, shorter disease duration, and relatively few comorbidities are more likely to recover LVEF – and their outcomes are typically better than those of patients with HF reduced EF (HFrEF) and HFpEF.
Clinicians should bear in mind, however, that patients on guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) who achieve complete normalization of LV structure and function are prone to recurrent LV dysfunction and HF. The panel explored the role of potential treatment for three different etiologies of HF. Little is known about Takotsubo cardiomyopathy, considered a transient form of LV dysfunction, in terms of how many of these patients will develop HFrEF or if they’ll benefit from GDMT. Alcohol-induced cardiomyopathy patients should continue on medical therapy even if they have HFrecEF, as should patients with fulminant and nonfulminant myocarditis.
Managing HFrecEF
Management should include assessment of jugular vein distention and signs of volume overload – “particularly concerning in HFrecEF” – the panel noted. ECG is cost effective, and signs of left-bundle branch block are predictors of low success with GDMT alone. The panel also recommended a family history going back three generations and consideration of genetic testing to determine the risk for sudden cardiac death. Two-dimensional ECG can help predict GDMT response and cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging can provide information about myocardial substrate at the time of diagnosis of HFrEF.
The panel suggested four areas for future research: 1) improved phenotyping of HFrEF; 2) use of inception cohorts to better understand the natural history of HFrecEF; 3) clinical trials to better define those clinical care components most effective at maintaining remission; and 4) basic studies to better define the biology of HFrecEF. “The goal,” wrote Dr. Wilcox and colleagues, “is to develop new therapeutic targets that will enable patients with HFrecEF to experience a durable remission from HF.”
Dr. Wilcox reported receiving funding from the National Institutes of Health and the American Heart Association, and financial relationships with Abbott, Medtronic, and Cytokinetics. Dr. Mann has received funding from NIH and reports financial relationships with MyoKardia and Novartis. Coauthors reported funding from NIH and AHA and financial relationships with Novartis, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Thoratec Corporation (Abbott), Sanofi, Pfizer, MyoKardia and American Regent.
SOURCE: Wilcox JE et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76:719-34.
Because heart failure patients with recovered ejection fraction are a complex and diverse group, little consensus has emerged on how to define, diagnose, and manage this growing population.
To provide some clarity for identifying and treating these patients, a Journal of the American College of Cardiology scientific expert panel has issued a consensus document. Published Aug. 3 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, it provides a working definition of heart failure with recovered ejection fraction (HFrecEF) and recommends approaches for treatment and follow-up.
Defining a new class of HF
“Part of the impetus of this was to bring attention to what we think is a new class of heart failure, and it requires different treatment modalities and different ways of thinking about it,” expert panel member Douglas L. Mann, MD, cardiologist-in-chief at Barnes Jewish Hospital in St. Louis, said in an interview. “It’s a newly discovered HF biology about which we know very little and it’s very confusing to just go on the ejection fraction alone.”
The panel, led by Jane E. Wilcox, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, recommends three components for a working definition of HFrecEF: 1) documentation of a decreased left ventricle ejection fraction (LVEF) of less than 40% at baseline; 2) a 10% or greater absolute improvement in LVEF; and 3) a second measurement of LVEF >40%.
“We try to give it a nomenclature that clearly indicates what it is,” Dr. Mann said. “There has been a lot of confusing terminology.” Among the terms the panel calls out in the lexicon of modestly recovered EF, in addition to HFrecEF, are HF improved EF, HF with preserved EF (HFpEF), borderline HFpEF and HF with mid-range EF (HFmrEF).
The panel also recommends that guideline-based medical and device therapies for HFrecEF should continue indefinitely until there’s a better understanding of the biology and clinical epidemiology of HFrecEF, and that these patients should have close clinical follow-up because of the high risk of HF relapse.
Determining EF’s ‘trajectory’
The findings presented in the statement should help cardiologists distinguish HFrecEF from HFpEF, Dr. Mann noted. “Because EF is moving, we also have to emphasize the importance of following the trajectory of EF,” he said. “It’s not enough to know where the EF is; you have to know where it came from – if it had been from a higher number or a lower number – because that will help inform you about the patient’s disease.”
In that regard, the panel states that the level of change in LVEF – the “trajectory” – will provide clues to the nature and extent of myocardial injury, degree and duration of LV remodeling, and the type of therapy that’s indicated. Clinicians should consider HFmrEF, a description the European Society of Cardiology has endorsed, as an entity different from HFrecEF without data on LVEF trajectory.
The statement delves into the biology of HFrecEF, defining reverse LV remodeling as the restoration of some normalization to cardiac myocyte size and LV chamber geometry that results in a leftward shift toward normalization of end-diastolic pressure volume. The panel also noted that cardiac remodeling in reverse LV remodeling and recovery of LV function is bidirectional and involves multiple molecular and cellular changes that contribute to changes in the heart’s size, shape and function, and explains the role gene expression has in HF-related LV changes.
The statement explores the recovery of LV function, noting that spontaneous recovery often occurs when the cause of the myocardial dysfunction resolves. Common causes are chronic tachycardia and thyroid disease.
That panel noted that “super responders” to cardiac resynchronization therapy can provide insight into HFrecEF. Favorable responders include women, patients with nonischemic HF, very wide ECG ventricular depolarization wavelength with left-bundle branch block morphology, and dyssynchrony on ECG.
The panel states that, “regardless of the definition of HFrecEF,” the evidence suggests that younger patients, women, and those with nonischemic disease, shorter disease duration, and relatively few comorbidities are more likely to recover LVEF – and their outcomes are typically better than those of patients with HF reduced EF (HFrEF) and HFpEF.
Clinicians should bear in mind, however, that patients on guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) who achieve complete normalization of LV structure and function are prone to recurrent LV dysfunction and HF. The panel explored the role of potential treatment for three different etiologies of HF. Little is known about Takotsubo cardiomyopathy, considered a transient form of LV dysfunction, in terms of how many of these patients will develop HFrEF or if they’ll benefit from GDMT. Alcohol-induced cardiomyopathy patients should continue on medical therapy even if they have HFrecEF, as should patients with fulminant and nonfulminant myocarditis.
Managing HFrecEF
Management should include assessment of jugular vein distention and signs of volume overload – “particularly concerning in HFrecEF” – the panel noted. ECG is cost effective, and signs of left-bundle branch block are predictors of low success with GDMT alone. The panel also recommended a family history going back three generations and consideration of genetic testing to determine the risk for sudden cardiac death. Two-dimensional ECG can help predict GDMT response and cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging can provide information about myocardial substrate at the time of diagnosis of HFrEF.
The panel suggested four areas for future research: 1) improved phenotyping of HFrEF; 2) use of inception cohorts to better understand the natural history of HFrecEF; 3) clinical trials to better define those clinical care components most effective at maintaining remission; and 4) basic studies to better define the biology of HFrecEF. “The goal,” wrote Dr. Wilcox and colleagues, “is to develop new therapeutic targets that will enable patients with HFrecEF to experience a durable remission from HF.”
Dr. Wilcox reported receiving funding from the National Institutes of Health and the American Heart Association, and financial relationships with Abbott, Medtronic, and Cytokinetics. Dr. Mann has received funding from NIH and reports financial relationships with MyoKardia and Novartis. Coauthors reported funding from NIH and AHA and financial relationships with Novartis, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Thoratec Corporation (Abbott), Sanofi, Pfizer, MyoKardia and American Regent.
SOURCE: Wilcox JE et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76:719-34.
Because heart failure patients with recovered ejection fraction are a complex and diverse group, little consensus has emerged on how to define, diagnose, and manage this growing population.
To provide some clarity for identifying and treating these patients, a Journal of the American College of Cardiology scientific expert panel has issued a consensus document. Published Aug. 3 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, it provides a working definition of heart failure with recovered ejection fraction (HFrecEF) and recommends approaches for treatment and follow-up.
Defining a new class of HF
“Part of the impetus of this was to bring attention to what we think is a new class of heart failure, and it requires different treatment modalities and different ways of thinking about it,” expert panel member Douglas L. Mann, MD, cardiologist-in-chief at Barnes Jewish Hospital in St. Louis, said in an interview. “It’s a newly discovered HF biology about which we know very little and it’s very confusing to just go on the ejection fraction alone.”
The panel, led by Jane E. Wilcox, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, recommends three components for a working definition of HFrecEF: 1) documentation of a decreased left ventricle ejection fraction (LVEF) of less than 40% at baseline; 2) a 10% or greater absolute improvement in LVEF; and 3) a second measurement of LVEF >40%.
“We try to give it a nomenclature that clearly indicates what it is,” Dr. Mann said. “There has been a lot of confusing terminology.” Among the terms the panel calls out in the lexicon of modestly recovered EF, in addition to HFrecEF, are HF improved EF, HF with preserved EF (HFpEF), borderline HFpEF and HF with mid-range EF (HFmrEF).
The panel also recommends that guideline-based medical and device therapies for HFrecEF should continue indefinitely until there’s a better understanding of the biology and clinical epidemiology of HFrecEF, and that these patients should have close clinical follow-up because of the high risk of HF relapse.
Determining EF’s ‘trajectory’
The findings presented in the statement should help cardiologists distinguish HFrecEF from HFpEF, Dr. Mann noted. “Because EF is moving, we also have to emphasize the importance of following the trajectory of EF,” he said. “It’s not enough to know where the EF is; you have to know where it came from – if it had been from a higher number or a lower number – because that will help inform you about the patient’s disease.”
In that regard, the panel states that the level of change in LVEF – the “trajectory” – will provide clues to the nature and extent of myocardial injury, degree and duration of LV remodeling, and the type of therapy that’s indicated. Clinicians should consider HFmrEF, a description the European Society of Cardiology has endorsed, as an entity different from HFrecEF without data on LVEF trajectory.
The statement delves into the biology of HFrecEF, defining reverse LV remodeling as the restoration of some normalization to cardiac myocyte size and LV chamber geometry that results in a leftward shift toward normalization of end-diastolic pressure volume. The panel also noted that cardiac remodeling in reverse LV remodeling and recovery of LV function is bidirectional and involves multiple molecular and cellular changes that contribute to changes in the heart’s size, shape and function, and explains the role gene expression has in HF-related LV changes.
The statement explores the recovery of LV function, noting that spontaneous recovery often occurs when the cause of the myocardial dysfunction resolves. Common causes are chronic tachycardia and thyroid disease.
That panel noted that “super responders” to cardiac resynchronization therapy can provide insight into HFrecEF. Favorable responders include women, patients with nonischemic HF, very wide ECG ventricular depolarization wavelength with left-bundle branch block morphology, and dyssynchrony on ECG.
The panel states that, “regardless of the definition of HFrecEF,” the evidence suggests that younger patients, women, and those with nonischemic disease, shorter disease duration, and relatively few comorbidities are more likely to recover LVEF – and their outcomes are typically better than those of patients with HF reduced EF (HFrEF) and HFpEF.
Clinicians should bear in mind, however, that patients on guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) who achieve complete normalization of LV structure and function are prone to recurrent LV dysfunction and HF. The panel explored the role of potential treatment for three different etiologies of HF. Little is known about Takotsubo cardiomyopathy, considered a transient form of LV dysfunction, in terms of how many of these patients will develop HFrEF or if they’ll benefit from GDMT. Alcohol-induced cardiomyopathy patients should continue on medical therapy even if they have HFrecEF, as should patients with fulminant and nonfulminant myocarditis.
Managing HFrecEF
Management should include assessment of jugular vein distention and signs of volume overload – “particularly concerning in HFrecEF” – the panel noted. ECG is cost effective, and signs of left-bundle branch block are predictors of low success with GDMT alone. The panel also recommended a family history going back three generations and consideration of genetic testing to determine the risk for sudden cardiac death. Two-dimensional ECG can help predict GDMT response and cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging can provide information about myocardial substrate at the time of diagnosis of HFrEF.
The panel suggested four areas for future research: 1) improved phenotyping of HFrEF; 2) use of inception cohorts to better understand the natural history of HFrecEF; 3) clinical trials to better define those clinical care components most effective at maintaining remission; and 4) basic studies to better define the biology of HFrecEF. “The goal,” wrote Dr. Wilcox and colleagues, “is to develop new therapeutic targets that will enable patients with HFrecEF to experience a durable remission from HF.”
Dr. Wilcox reported receiving funding from the National Institutes of Health and the American Heart Association, and financial relationships with Abbott, Medtronic, and Cytokinetics. Dr. Mann has received funding from NIH and reports financial relationships with MyoKardia and Novartis. Coauthors reported funding from NIH and AHA and financial relationships with Novartis, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Thoratec Corporation (Abbott), Sanofi, Pfizer, MyoKardia and American Regent.
SOURCE: Wilcox JE et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76:719-34.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY