User login
In older patients with immune-mediated TTP, atypical features may delay diagnosis
Older patients with immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (iTTP) more often have an atypical neurological presentation, which could result in a delayed diagnosis, according to authors of a recent retrospective analysis.
“Practitioners should be aware of this in order to shorten the time to treatment, which could improve the prognosis in older iTTP patients,” Paul Coppo, MD, PhD, of Hôpital Saint-Antoine, Paris, and coauthors wrote in Blood.
The older patients also had increased 1-month and 1-year mortality compared with younger patients, and had more than a threefold risk of long-term mortality compared with elderly patients without iTTP, according to the study report.
The analysis included 411 patients with iTTP entered into a national registry in France between 2000 and 2016. Seventy-one patients were 60 years of age or older.
Time from hospital admission to diagnosis was 3 days for those older patients, versus just 1 day for patients under 60 years of age (P = .0001), Dr. Coppo and colleagues reported.
Clinical records were available for 67 of the older iTTP patients, of whom 17 had no evidence of delayed diagnosis. The remainder had a “possible diagnostic delay,” according to the report; among those, the iTTP diagnosis was preceded by neurological manifestations in 26 cases, and transient ischemic stroke that usually led to focal deficiency or aphasia in 14 cases. Other features preceding the diagnosis included malaise, behavioral abnormalities, seizure, and dizziness.
Many of these findings are “not specific to a disease, and they are less alarming than in young patients,” the researchers wrote. “In this context, the presence of a thrombocytopenia with anemia should alert physicians to this possible rare diagnosis.”
Older patients also presented with less pronounced cytopenias compared with younger patients, which could have contributed to a late diagnosis, they added.
Older age is a known risk factor for mortality related to iTTP. In the present study, rates of 1-month mortality were 37% for patients aged 60 years and older, and 9% for those younger than age 60 (P less than .0001). The 1-year mortality rates were 49% and 11% for older and younger patients, respectively (P less than .0001).
Compared with older individuals without iTTP from a different study, older iTTP patients had a lower long-term survival rate. iTTP remained an independent risk factor for death even after adjustment for age, sex, and some comorbidities (hazard ratio, 3.44; 95% confidence interval, 2.02-5.87).
The study was partly funded by a grant from the French Ministry of Health. Dr. Coppo reported that he is a clinical advisory board member for Alexion, Ablynx (now part of Sanofi), Shire, and Octapharma. Two other co-authors reported participating in advisory boards for Ablynx.
SOURCE: Prevel R et al. Blood. 2019 Sep 17. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000748.
Older patients with immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (iTTP) more often have an atypical neurological presentation, which could result in a delayed diagnosis, according to authors of a recent retrospective analysis.
“Practitioners should be aware of this in order to shorten the time to treatment, which could improve the prognosis in older iTTP patients,” Paul Coppo, MD, PhD, of Hôpital Saint-Antoine, Paris, and coauthors wrote in Blood.
The older patients also had increased 1-month and 1-year mortality compared with younger patients, and had more than a threefold risk of long-term mortality compared with elderly patients without iTTP, according to the study report.
The analysis included 411 patients with iTTP entered into a national registry in France between 2000 and 2016. Seventy-one patients were 60 years of age or older.
Time from hospital admission to diagnosis was 3 days for those older patients, versus just 1 day for patients under 60 years of age (P = .0001), Dr. Coppo and colleagues reported.
Clinical records were available for 67 of the older iTTP patients, of whom 17 had no evidence of delayed diagnosis. The remainder had a “possible diagnostic delay,” according to the report; among those, the iTTP diagnosis was preceded by neurological manifestations in 26 cases, and transient ischemic stroke that usually led to focal deficiency or aphasia in 14 cases. Other features preceding the diagnosis included malaise, behavioral abnormalities, seizure, and dizziness.
Many of these findings are “not specific to a disease, and they are less alarming than in young patients,” the researchers wrote. “In this context, the presence of a thrombocytopenia with anemia should alert physicians to this possible rare diagnosis.”
Older patients also presented with less pronounced cytopenias compared with younger patients, which could have contributed to a late diagnosis, they added.
Older age is a known risk factor for mortality related to iTTP. In the present study, rates of 1-month mortality were 37% for patients aged 60 years and older, and 9% for those younger than age 60 (P less than .0001). The 1-year mortality rates were 49% and 11% for older and younger patients, respectively (P less than .0001).
Compared with older individuals without iTTP from a different study, older iTTP patients had a lower long-term survival rate. iTTP remained an independent risk factor for death even after adjustment for age, sex, and some comorbidities (hazard ratio, 3.44; 95% confidence interval, 2.02-5.87).
The study was partly funded by a grant from the French Ministry of Health. Dr. Coppo reported that he is a clinical advisory board member for Alexion, Ablynx (now part of Sanofi), Shire, and Octapharma. Two other co-authors reported participating in advisory boards for Ablynx.
SOURCE: Prevel R et al. Blood. 2019 Sep 17. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000748.
Older patients with immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (iTTP) more often have an atypical neurological presentation, which could result in a delayed diagnosis, according to authors of a recent retrospective analysis.
“Practitioners should be aware of this in order to shorten the time to treatment, which could improve the prognosis in older iTTP patients,” Paul Coppo, MD, PhD, of Hôpital Saint-Antoine, Paris, and coauthors wrote in Blood.
The older patients also had increased 1-month and 1-year mortality compared with younger patients, and had more than a threefold risk of long-term mortality compared with elderly patients without iTTP, according to the study report.
The analysis included 411 patients with iTTP entered into a national registry in France between 2000 and 2016. Seventy-one patients were 60 years of age or older.
Time from hospital admission to diagnosis was 3 days for those older patients, versus just 1 day for patients under 60 years of age (P = .0001), Dr. Coppo and colleagues reported.
Clinical records were available for 67 of the older iTTP patients, of whom 17 had no evidence of delayed diagnosis. The remainder had a “possible diagnostic delay,” according to the report; among those, the iTTP diagnosis was preceded by neurological manifestations in 26 cases, and transient ischemic stroke that usually led to focal deficiency or aphasia in 14 cases. Other features preceding the diagnosis included malaise, behavioral abnormalities, seizure, and dizziness.
Many of these findings are “not specific to a disease, and they are less alarming than in young patients,” the researchers wrote. “In this context, the presence of a thrombocytopenia with anemia should alert physicians to this possible rare diagnosis.”
Older patients also presented with less pronounced cytopenias compared with younger patients, which could have contributed to a late diagnosis, they added.
Older age is a known risk factor for mortality related to iTTP. In the present study, rates of 1-month mortality were 37% for patients aged 60 years and older, and 9% for those younger than age 60 (P less than .0001). The 1-year mortality rates were 49% and 11% for older and younger patients, respectively (P less than .0001).
Compared with older individuals without iTTP from a different study, older iTTP patients had a lower long-term survival rate. iTTP remained an independent risk factor for death even after adjustment for age, sex, and some comorbidities (hazard ratio, 3.44; 95% confidence interval, 2.02-5.87).
The study was partly funded by a grant from the French Ministry of Health. Dr. Coppo reported that he is a clinical advisory board member for Alexion, Ablynx (now part of Sanofi), Shire, and Octapharma. Two other co-authors reported participating in advisory boards for Ablynx.
SOURCE: Prevel R et al. Blood. 2019 Sep 17. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000748.
FROM BLOOD
Follow-up shows favorable results with acalabrutinib in MCL
Acalabrutinib monotherapy can produce durable responses in relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), according to updated results from a phase 2 trial.
The drug produced an overall response rate (ORR) of 81%, and the median duration of response was 26 months.
These are the highest such figures reported “among all approved single-agent therapies for the treatment of relapsed/refractory MCL,” Michael Wang, MD, of the MD Anderson Cancer Center at the University of Texas in Houston and colleagues wrote in a letter in Leukemia.
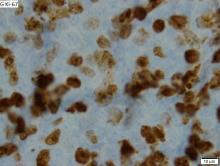
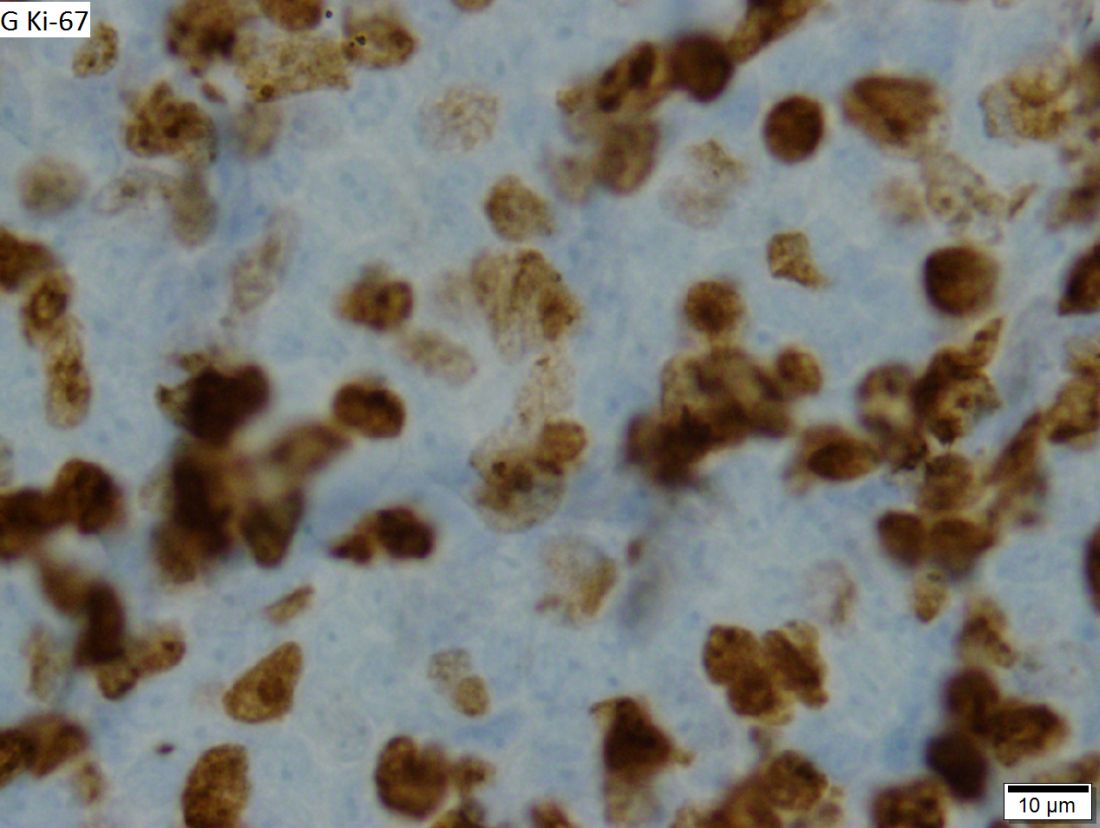
Dr. Wang and colleagues reported updated results in 124 patients treated on the ACE-LY-004 trial. At baseline, the patients had a median age of 68 years (range, 42-90 years), and 80% were men. Three-quarters of patients had stage IV disease, 72% had extranodal disease, 21% had blastoid/pleomorphic MCL, and 26% had a Ki-67 proliferation index of 50% or greater.
At a median follow-up of 26 months, 40% (n = 49) of patients were still on acalabrutinib, and 61% (n = 76) were still in follow-up for survival. Six patients went on to allogeneic transplant at a median of 19 days after stopping acalabrutinib.
The ORR was 81% (100/124), and the complete response (CR) rate was 43% (n = 53). Four patients who initially had a partial response converted to a CR with longer follow-up. The estimated 24-month duration of response was 52.4%.
“ORR was consistent across patients with refractory disease and those with blastoid/pleomorphic MCL, despite those patients having a higher mean Ki-67 index [of 50% or greater], suggesting that some patients with poorer prognosis may also benefit from acalabrutinib,” Dr. Wang and colleagues wrote.
There were 29 patients evaluable for minimal residual disease (MRD) assessment. Seven patients (24%) had MRD-negative disease in the peripheral blood after they achieved a CR. An additional patient with a CR became MRD negative when a second blood sample was taken about 6 months after the first.
“Despite limited samples, these results demonstrate that continued use of acalabrutinib can lead to undetectable MRD in patients with CR,” Dr. Wang and his colleagues wrote. “Since most patients with MRD data are still on treatment (27/29), relationships between MRD negativity and durability of response cannot be made at this time.”
The median progression-free survival was 20 months, and the median overall survival was not reached. The estimated 24-month progression-free survival rate was 49.0%, and the estimated 24-month overall survival rate was 72.4%. Patients with low/intermediate Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores, classical MCL, and a Ki-67 index less than 50% had a longer duration of response and survival.
The adverse event profile was “largely consistent with earlier reporting,” Dr. Wang and colleagues wrote. The most frequent adverse events were headache (38%), diarrhea (36%), fatigue (28%), cough (22%), and myalgia (21%). The most common grade 3/4 adverse events were anemia (10%), neutropenia (10%), and pneumonia (6%).
Ten patients developed second primary cancers. There were no new atrial fibrillation events and no new hypertension events. The frequency of infections decreased over time, as did the number of bleeding events. However, two of three major hemorrhage events occurred after the previous report was published.
There were 43 deaths (35%), 29 of them because of disease progression. Six patients died of adverse events, two died of unknown causes, and two died of secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Other causes of death included multiorgan failure, intestinal obstruction, lung cancer, and graft-versus-host disease.
This study was sponsored by Acerta Pharma, a member of the AstraZeneca Group. The researchers reported relationships with AstraZeneca/Acerta Pharma and many other companies.
SOURCE: Wang M et al. Leukemia. 2019 Sep 26. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0575-9.
Acalabrutinib monotherapy can produce durable responses in relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), according to updated results from a phase 2 trial.
The drug produced an overall response rate (ORR) of 81%, and the median duration of response was 26 months.
These are the highest such figures reported “among all approved single-agent therapies for the treatment of relapsed/refractory MCL,” Michael Wang, MD, of the MD Anderson Cancer Center at the University of Texas in Houston and colleagues wrote in a letter in Leukemia.
Dr. Wang and colleagues reported updated results in 124 patients treated on the ACE-LY-004 trial. At baseline, the patients had a median age of 68 years (range, 42-90 years), and 80% were men. Three-quarters of patients had stage IV disease, 72% had extranodal disease, 21% had blastoid/pleomorphic MCL, and 26% had a Ki-67 proliferation index of 50% or greater.
At a median follow-up of 26 months, 40% (n = 49) of patients were still on acalabrutinib, and 61% (n = 76) were still in follow-up for survival. Six patients went on to allogeneic transplant at a median of 19 days after stopping acalabrutinib.
The ORR was 81% (100/124), and the complete response (CR) rate was 43% (n = 53). Four patients who initially had a partial response converted to a CR with longer follow-up. The estimated 24-month duration of response was 52.4%.
“ORR was consistent across patients with refractory disease and those with blastoid/pleomorphic MCL, despite those patients having a higher mean Ki-67 index [of 50% or greater], suggesting that some patients with poorer prognosis may also benefit from acalabrutinib,” Dr. Wang and colleagues wrote.
There were 29 patients evaluable for minimal residual disease (MRD) assessment. Seven patients (24%) had MRD-negative disease in the peripheral blood after they achieved a CR. An additional patient with a CR became MRD negative when a second blood sample was taken about 6 months after the first.
“Despite limited samples, these results demonstrate that continued use of acalabrutinib can lead to undetectable MRD in patients with CR,” Dr. Wang and his colleagues wrote. “Since most patients with MRD data are still on treatment (27/29), relationships between MRD negativity and durability of response cannot be made at this time.”
The median progression-free survival was 20 months, and the median overall survival was not reached. The estimated 24-month progression-free survival rate was 49.0%, and the estimated 24-month overall survival rate was 72.4%. Patients with low/intermediate Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores, classical MCL, and a Ki-67 index less than 50% had a longer duration of response and survival.
The adverse event profile was “largely consistent with earlier reporting,” Dr. Wang and colleagues wrote. The most frequent adverse events were headache (38%), diarrhea (36%), fatigue (28%), cough (22%), and myalgia (21%). The most common grade 3/4 adverse events were anemia (10%), neutropenia (10%), and pneumonia (6%).
Ten patients developed second primary cancers. There were no new atrial fibrillation events and no new hypertension events. The frequency of infections decreased over time, as did the number of bleeding events. However, two of three major hemorrhage events occurred after the previous report was published.
There were 43 deaths (35%), 29 of them because of disease progression. Six patients died of adverse events, two died of unknown causes, and two died of secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Other causes of death included multiorgan failure, intestinal obstruction, lung cancer, and graft-versus-host disease.
This study was sponsored by Acerta Pharma, a member of the AstraZeneca Group. The researchers reported relationships with AstraZeneca/Acerta Pharma and many other companies.
SOURCE: Wang M et al. Leukemia. 2019 Sep 26. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0575-9.
Acalabrutinib monotherapy can produce durable responses in relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), according to updated results from a phase 2 trial.
The drug produced an overall response rate (ORR) of 81%, and the median duration of response was 26 months.
These are the highest such figures reported “among all approved single-agent therapies for the treatment of relapsed/refractory MCL,” Michael Wang, MD, of the MD Anderson Cancer Center at the University of Texas in Houston and colleagues wrote in a letter in Leukemia.
Dr. Wang and colleagues reported updated results in 124 patients treated on the ACE-LY-004 trial. At baseline, the patients had a median age of 68 years (range, 42-90 years), and 80% were men. Three-quarters of patients had stage IV disease, 72% had extranodal disease, 21% had blastoid/pleomorphic MCL, and 26% had a Ki-67 proliferation index of 50% or greater.
At a median follow-up of 26 months, 40% (n = 49) of patients were still on acalabrutinib, and 61% (n = 76) were still in follow-up for survival. Six patients went on to allogeneic transplant at a median of 19 days after stopping acalabrutinib.
The ORR was 81% (100/124), and the complete response (CR) rate was 43% (n = 53). Four patients who initially had a partial response converted to a CR with longer follow-up. The estimated 24-month duration of response was 52.4%.
“ORR was consistent across patients with refractory disease and those with blastoid/pleomorphic MCL, despite those patients having a higher mean Ki-67 index [of 50% or greater], suggesting that some patients with poorer prognosis may also benefit from acalabrutinib,” Dr. Wang and colleagues wrote.
There were 29 patients evaluable for minimal residual disease (MRD) assessment. Seven patients (24%) had MRD-negative disease in the peripheral blood after they achieved a CR. An additional patient with a CR became MRD negative when a second blood sample was taken about 6 months after the first.
“Despite limited samples, these results demonstrate that continued use of acalabrutinib can lead to undetectable MRD in patients with CR,” Dr. Wang and his colleagues wrote. “Since most patients with MRD data are still on treatment (27/29), relationships between MRD negativity and durability of response cannot be made at this time.”
The median progression-free survival was 20 months, and the median overall survival was not reached. The estimated 24-month progression-free survival rate was 49.0%, and the estimated 24-month overall survival rate was 72.4%. Patients with low/intermediate Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores, classical MCL, and a Ki-67 index less than 50% had a longer duration of response and survival.
The adverse event profile was “largely consistent with earlier reporting,” Dr. Wang and colleagues wrote. The most frequent adverse events were headache (38%), diarrhea (36%), fatigue (28%), cough (22%), and myalgia (21%). The most common grade 3/4 adverse events were anemia (10%), neutropenia (10%), and pneumonia (6%).
Ten patients developed second primary cancers. There were no new atrial fibrillation events and no new hypertension events. The frequency of infections decreased over time, as did the number of bleeding events. However, two of three major hemorrhage events occurred after the previous report was published.
There were 43 deaths (35%), 29 of them because of disease progression. Six patients died of adverse events, two died of unknown causes, and two died of secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Other causes of death included multiorgan failure, intestinal obstruction, lung cancer, and graft-versus-host disease.
This study was sponsored by Acerta Pharma, a member of the AstraZeneca Group. The researchers reported relationships with AstraZeneca/Acerta Pharma and many other companies.
SOURCE: Wang M et al. Leukemia. 2019 Sep 26. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0575-9.
FROM LEUKEMIA
What is the optimal duration of maintenance in myeloma?
SAN FRANCISCO – Should patients with multiple myeloma receive maintenance therapy until progression?
Yvonne A. Efebera, MD, of The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital in Columbus, and Nina Shah, MD, of the University of California San Francisco Health, faced off on this question at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Dr. Shah said maintenance therapy improves survival in myeloma patients, so it follows that treating them until progression would confer a survival advantage. While Dr. Efebera agreed that maintenance can improve survival, she said the optimal duration of that treatment is unknown.
Treat until progression
Dr. Shah cited studies suggesting that maintenance improves progression-free survival (PFS) and may prolong overall survival (OS) in multiple myeloma.
A meta-analysis of data from the IFM 2005-02, CALGB 100104, and GIMEMA RV-MM-PI-209 trials showed that lenalidomide maintenance prolonged PFS and OS. The median PFS was 52.8 months in patients who received maintenance and 23.5 months in those who received placebo or observation (hazard ratio [HR], 0.48). At a median follow-up of 79.5 months, the median OS was not reached for the maintenance group and was 86.0 months for the no-maintenance group (HR, 0.75; P = .001; J Clin Oncol. 2017 Oct 10;35[29]:3279-89).
In the Myeloma XI trial, maintenance improved PFS, but not OS, in both transplant-eligible and ineligible patients. Overall, the median PFS was 39 months in the lenalidomide maintenance arm and 20 months in the observation arm (P less than .0001). Among transplant-eligible patients, the median PFS was 57 months and 30 months, respectively (P less than .0001). Among transplant-ineligible patients, the median PFS was 26 months and 11 months, respectively (P less than .0001; Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:57-73).
These data suggest maintenance can improve survival, “but the question is, how long should we have therapy,” Dr. Shah said. “No one has looked at this in a prospective manner, so we really have to look at our retrospective data.”
One study suggested a longer duration of lenalidomide maintenance improves PFS. The HR for progression or death was 0.39 for patients who received maintenance for 12-24 months, compared with those who received maintenance for less than 12 months. The HR was 0.13 for patients who received maintenance for more than 24 months, compared with less than 12 months (Leuk Lymphoma. 2019 Feb;60[2]:511-4).
Dr. Shah also cited a pooled analysis of three phase 3 trials suggesting that continuous therapy is superior to fixed-duration therapy in patients with newly diagnosed myeloma. The median PFS was 32 months with continuous therapy and 16 months with fixed-duration therapy (P less than .001). The 4-year OS was 69% and 60%, respectively (P = .003; J Clin Oncol. 2015 Oct 20;33[30]:3459-66).
These data suggest that “continuous therapy, more therapy, has a survival advantage,” Dr. Shah said.
Don’t treat until progression
Dr. Efebera also discussed data from studies showing that lenalidomide maintenance can prolong survival in multiple myeloma. However, she said, it’s unclear how long maintenance should last.
Different durations of maintenance have proved effective in different trials. In the CALGB 100104 trial, the median duration of maintenance was 31 months (Lancet Haematol. 2017 Sep;4[9]:e431-e442). In the meta-analysis of the CALGB, IFM, and GIMEMA trials, the median duration was 22 months. And in Myeloma XI, the median duration was 18 months.
As there is no randomized trial comparing different durations of maintenance, Dr. Efebera proposed that researchers conduct one. She said this “perfect study” would involve induction with an immunomodulatory agent, a proteasome inhibitor, dexamethasone, and perhaps an anti-CD38 therapy. Transplant-eligible patients would receive four cycles of induction before transplant. Transplant-ineligible patients would receive eight cycles of induction. Then, all patients would be randomized to lenalidomide maintenance for 3 years, 5 years, or 7-10 years.
Until a trial like this reveals the optimal duration of maintenance, we cannot conclude that treating patients until progression is better, Dr. Efebera said.
She added that maintenance has been shown to have detrimental effects, and these should be taken into consideration. For instance, neutropenia, other hematologic adverse events, and second primary malignancies have been shown to be more common among patients who receive lenalidomide maintenance (N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:1782-91).
The cost of maintenance is another factor to consider. Researchers analyzed data from the CALGB 100104 and IFM 2005-02 trials to compare the cost of lenalidomide maintenance with no maintenance. In the CALGB 100104 trial, patients who received lenalidomide maintenance had 5.72 quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), and those who received no maintenance had 4.61 QALYs. The incremental cost-utility ratio (ICUR) was more than 277,000 euros per QALY.
In the IFM2005-02 trial, patients in the lenalidomide group had 5.13 QALYs, and those who didn’t receive maintenance had 4.98 QALYs. The ICUR was more than 1.5 million euros per QALY. The researchers said the high ICURs and budgetary impact add “uncertainty about the maximum prudent duration of the treatment” (Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019 May 31. doi: 10.1038/s41409-019-0574-5).
Dr. Efebera reported relationships with Akcea Therapeutics, Janssen, and Takeda. Dr. Shah reported having no relevant financial relationships.
SAN FRANCISCO – Should patients with multiple myeloma receive maintenance therapy until progression?
Yvonne A. Efebera, MD, of The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital in Columbus, and Nina Shah, MD, of the University of California San Francisco Health, faced off on this question at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Dr. Shah said maintenance therapy improves survival in myeloma patients, so it follows that treating them until progression would confer a survival advantage. While Dr. Efebera agreed that maintenance can improve survival, she said the optimal duration of that treatment is unknown.
Treat until progression
Dr. Shah cited studies suggesting that maintenance improves progression-free survival (PFS) and may prolong overall survival (OS) in multiple myeloma.
A meta-analysis of data from the IFM 2005-02, CALGB 100104, and GIMEMA RV-MM-PI-209 trials showed that lenalidomide maintenance prolonged PFS and OS. The median PFS was 52.8 months in patients who received maintenance and 23.5 months in those who received placebo or observation (hazard ratio [HR], 0.48). At a median follow-up of 79.5 months, the median OS was not reached for the maintenance group and was 86.0 months for the no-maintenance group (HR, 0.75; P = .001; J Clin Oncol. 2017 Oct 10;35[29]:3279-89).
In the Myeloma XI trial, maintenance improved PFS, but not OS, in both transplant-eligible and ineligible patients. Overall, the median PFS was 39 months in the lenalidomide maintenance arm and 20 months in the observation arm (P less than .0001). Among transplant-eligible patients, the median PFS was 57 months and 30 months, respectively (P less than .0001). Among transplant-ineligible patients, the median PFS was 26 months and 11 months, respectively (P less than .0001; Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:57-73).
These data suggest maintenance can improve survival, “but the question is, how long should we have therapy,” Dr. Shah said. “No one has looked at this in a prospective manner, so we really have to look at our retrospective data.”
One study suggested a longer duration of lenalidomide maintenance improves PFS. The HR for progression or death was 0.39 for patients who received maintenance for 12-24 months, compared with those who received maintenance for less than 12 months. The HR was 0.13 for patients who received maintenance for more than 24 months, compared with less than 12 months (Leuk Lymphoma. 2019 Feb;60[2]:511-4).
Dr. Shah also cited a pooled analysis of three phase 3 trials suggesting that continuous therapy is superior to fixed-duration therapy in patients with newly diagnosed myeloma. The median PFS was 32 months with continuous therapy and 16 months with fixed-duration therapy (P less than .001). The 4-year OS was 69% and 60%, respectively (P = .003; J Clin Oncol. 2015 Oct 20;33[30]:3459-66).
These data suggest that “continuous therapy, more therapy, has a survival advantage,” Dr. Shah said.
Don’t treat until progression
Dr. Efebera also discussed data from studies showing that lenalidomide maintenance can prolong survival in multiple myeloma. However, she said, it’s unclear how long maintenance should last.
Different durations of maintenance have proved effective in different trials. In the CALGB 100104 trial, the median duration of maintenance was 31 months (Lancet Haematol. 2017 Sep;4[9]:e431-e442). In the meta-analysis of the CALGB, IFM, and GIMEMA trials, the median duration was 22 months. And in Myeloma XI, the median duration was 18 months.
As there is no randomized trial comparing different durations of maintenance, Dr. Efebera proposed that researchers conduct one. She said this “perfect study” would involve induction with an immunomodulatory agent, a proteasome inhibitor, dexamethasone, and perhaps an anti-CD38 therapy. Transplant-eligible patients would receive four cycles of induction before transplant. Transplant-ineligible patients would receive eight cycles of induction. Then, all patients would be randomized to lenalidomide maintenance for 3 years, 5 years, or 7-10 years.
Until a trial like this reveals the optimal duration of maintenance, we cannot conclude that treating patients until progression is better, Dr. Efebera said.
She added that maintenance has been shown to have detrimental effects, and these should be taken into consideration. For instance, neutropenia, other hematologic adverse events, and second primary malignancies have been shown to be more common among patients who receive lenalidomide maintenance (N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:1782-91).
The cost of maintenance is another factor to consider. Researchers analyzed data from the CALGB 100104 and IFM 2005-02 trials to compare the cost of lenalidomide maintenance with no maintenance. In the CALGB 100104 trial, patients who received lenalidomide maintenance had 5.72 quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), and those who received no maintenance had 4.61 QALYs. The incremental cost-utility ratio (ICUR) was more than 277,000 euros per QALY.
In the IFM2005-02 trial, patients in the lenalidomide group had 5.13 QALYs, and those who didn’t receive maintenance had 4.98 QALYs. The ICUR was more than 1.5 million euros per QALY. The researchers said the high ICURs and budgetary impact add “uncertainty about the maximum prudent duration of the treatment” (Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019 May 31. doi: 10.1038/s41409-019-0574-5).
Dr. Efebera reported relationships with Akcea Therapeutics, Janssen, and Takeda. Dr. Shah reported having no relevant financial relationships.
SAN FRANCISCO – Should patients with multiple myeloma receive maintenance therapy until progression?
Yvonne A. Efebera, MD, of The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital in Columbus, and Nina Shah, MD, of the University of California San Francisco Health, faced off on this question at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Dr. Shah said maintenance therapy improves survival in myeloma patients, so it follows that treating them until progression would confer a survival advantage. While Dr. Efebera agreed that maintenance can improve survival, she said the optimal duration of that treatment is unknown.
Treat until progression
Dr. Shah cited studies suggesting that maintenance improves progression-free survival (PFS) and may prolong overall survival (OS) in multiple myeloma.
A meta-analysis of data from the IFM 2005-02, CALGB 100104, and GIMEMA RV-MM-PI-209 trials showed that lenalidomide maintenance prolonged PFS and OS. The median PFS was 52.8 months in patients who received maintenance and 23.5 months in those who received placebo or observation (hazard ratio [HR], 0.48). At a median follow-up of 79.5 months, the median OS was not reached for the maintenance group and was 86.0 months for the no-maintenance group (HR, 0.75; P = .001; J Clin Oncol. 2017 Oct 10;35[29]:3279-89).
In the Myeloma XI trial, maintenance improved PFS, but not OS, in both transplant-eligible and ineligible patients. Overall, the median PFS was 39 months in the lenalidomide maintenance arm and 20 months in the observation arm (P less than .0001). Among transplant-eligible patients, the median PFS was 57 months and 30 months, respectively (P less than .0001). Among transplant-ineligible patients, the median PFS was 26 months and 11 months, respectively (P less than .0001; Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:57-73).
These data suggest maintenance can improve survival, “but the question is, how long should we have therapy,” Dr. Shah said. “No one has looked at this in a prospective manner, so we really have to look at our retrospective data.”
One study suggested a longer duration of lenalidomide maintenance improves PFS. The HR for progression or death was 0.39 for patients who received maintenance for 12-24 months, compared with those who received maintenance for less than 12 months. The HR was 0.13 for patients who received maintenance for more than 24 months, compared with less than 12 months (Leuk Lymphoma. 2019 Feb;60[2]:511-4).
Dr. Shah also cited a pooled analysis of three phase 3 trials suggesting that continuous therapy is superior to fixed-duration therapy in patients with newly diagnosed myeloma. The median PFS was 32 months with continuous therapy and 16 months with fixed-duration therapy (P less than .001). The 4-year OS was 69% and 60%, respectively (P = .003; J Clin Oncol. 2015 Oct 20;33[30]:3459-66).
These data suggest that “continuous therapy, more therapy, has a survival advantage,” Dr. Shah said.
Don’t treat until progression
Dr. Efebera also discussed data from studies showing that lenalidomide maintenance can prolong survival in multiple myeloma. However, she said, it’s unclear how long maintenance should last.
Different durations of maintenance have proved effective in different trials. In the CALGB 100104 trial, the median duration of maintenance was 31 months (Lancet Haematol. 2017 Sep;4[9]:e431-e442). In the meta-analysis of the CALGB, IFM, and GIMEMA trials, the median duration was 22 months. And in Myeloma XI, the median duration was 18 months.
As there is no randomized trial comparing different durations of maintenance, Dr. Efebera proposed that researchers conduct one. She said this “perfect study” would involve induction with an immunomodulatory agent, a proteasome inhibitor, dexamethasone, and perhaps an anti-CD38 therapy. Transplant-eligible patients would receive four cycles of induction before transplant. Transplant-ineligible patients would receive eight cycles of induction. Then, all patients would be randomized to lenalidomide maintenance for 3 years, 5 years, or 7-10 years.
Until a trial like this reveals the optimal duration of maintenance, we cannot conclude that treating patients until progression is better, Dr. Efebera said.
She added that maintenance has been shown to have detrimental effects, and these should be taken into consideration. For instance, neutropenia, other hematologic adverse events, and second primary malignancies have been shown to be more common among patients who receive lenalidomide maintenance (N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:1782-91).
The cost of maintenance is another factor to consider. Researchers analyzed data from the CALGB 100104 and IFM 2005-02 trials to compare the cost of lenalidomide maintenance with no maintenance. In the CALGB 100104 trial, patients who received lenalidomide maintenance had 5.72 quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), and those who received no maintenance had 4.61 QALYs. The incremental cost-utility ratio (ICUR) was more than 277,000 euros per QALY.
In the IFM2005-02 trial, patients in the lenalidomide group had 5.13 QALYs, and those who didn’t receive maintenance had 4.98 QALYs. The ICUR was more than 1.5 million euros per QALY. The researchers said the high ICURs and budgetary impact add “uncertainty about the maximum prudent duration of the treatment” (Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019 May 31. doi: 10.1038/s41409-019-0574-5).
Dr. Efebera reported relationships with Akcea Therapeutics, Janssen, and Takeda. Dr. Shah reported having no relevant financial relationships.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM NCCN HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES
Hypoxia-related discoveries net Nobel Prize
Three researchers have won the 2019 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine “for their discoveries of how cells sense and adapt to oxygen availability.”
William G. Kaelin Jr., MD; Sir Peter J. Ratcliffe, MB ChB, MD; and Gregg L. Semenza, MD, PhD, described the molecular machinery that regulates gene activity in response to oxygen levels.
Their work “established the basis for our understanding of how oxygen levels affect cellular metabolism and physiological function” and “paved the way for promising new strategies to fight anemia, cancer, and many other diseases,” according to a statement by The Nobel Assembly at Karolinska Institutet.
Dr. Semenza, of Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore, studied how the erythropoietin (EPO) gene is regulated by oxygen levels. Via experiments in mice, he identified DNA segments next to the EPO gene that mediate the response to hypoxia.
Dr. Ratcliffe, of the University of Oxford (England) and the Francis Crick Institute in London, also studied oxygen-dependent regulation of the EPO gene. Both his and Dr. Semenza’s groups found the oxygen-sensing mechanism was present in nearly all tissues.
Dr. Semenza also discovered a protein complex, hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF), that binds to the identified DNA segments in an oxygen-dependent manner. Additional investigation revealed that HIF consists of two transcription factors, HIF-1a and ARNT.
Several research groups found that HIF-1a is protected from degradation in hypoxia. In low-oxygen conditions, the amount of HIF-1a increases so it can bind to and regulate EPO and other genes with HIF-binding DNA segments. However, at normal oxygen levels, ubiquitin is added to HIF-1a, tagging it for degradation in the proteasome. It wasn’t clear how ubiquitin binds to HIF-1a in an oxygen-dependent manner, but Dr. Kaelin’s work provided some insight.
Dr. Kaelin, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, was researching von Hippel-Lindau’s (VHL) syndrome, an inherited disorder in which mutations can lead to tumors in multiple organs. He found the VHL gene encodes a protein that prevents cancer onset, and cancer cells without a functional VHL gene express high levels of hypoxia-regulated genes.
Research by other groups showed that VHL is part of a complex that labels proteins with ubiquitin, tagging them for degradation. Dr. Ratcliffe and his group found that VHL is required for the degradation of HIF-1a at normal oxygen levels.
Dr. Kaelin’s and Dr. Ratcliffe’s groups also showed that, under normal oxygen conditions, hydroxyl groups are added at two locations in HIF-1a. This modification – prolyl hydroxylation – allows VHL to bind to HIF-1a. So the researchers found that normal oxygen levels control HIF-1a degradation with the help of prolyl hydroxylases.
Additional research by Dr. Ratcliffe’s group and others revealed the specific prolyl hydroxylases involved in HIF-1a degradation. The researchers also found that HIF-1a’s gene-activating function was regulated by oxygen-dependent hydroxylation.
This work has improved the understanding of how different oxygen levels regulate physiological processes. In particular, oxygen sensing is essential for erythropoiesis, so these findings have implications for the treatment of anemia.
“There are several drugs that are now in clinical trials that serve to increase HIF activity and, as a result, will increase the production of erythropoietin and stimulate red blood cell production,” Dr. Semenza said in an interview after the announcement of his Nobel win. “These are all small molecules that can be given by mouth, and that may be a great convenience for patients who, at the present time, may require injections of recombinant human erythropoietin.”
Three researchers have won the 2019 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine “for their discoveries of how cells sense and adapt to oxygen availability.”
William G. Kaelin Jr., MD; Sir Peter J. Ratcliffe, MB ChB, MD; and Gregg L. Semenza, MD, PhD, described the molecular machinery that regulates gene activity in response to oxygen levels.
Their work “established the basis for our understanding of how oxygen levels affect cellular metabolism and physiological function” and “paved the way for promising new strategies to fight anemia, cancer, and many other diseases,” according to a statement by The Nobel Assembly at Karolinska Institutet.
Dr. Semenza, of Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore, studied how the erythropoietin (EPO) gene is regulated by oxygen levels. Via experiments in mice, he identified DNA segments next to the EPO gene that mediate the response to hypoxia.
Dr. Ratcliffe, of the University of Oxford (England) and the Francis Crick Institute in London, also studied oxygen-dependent regulation of the EPO gene. Both his and Dr. Semenza’s groups found the oxygen-sensing mechanism was present in nearly all tissues.
Dr. Semenza also discovered a protein complex, hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF), that binds to the identified DNA segments in an oxygen-dependent manner. Additional investigation revealed that HIF consists of two transcription factors, HIF-1a and ARNT.
Several research groups found that HIF-1a is protected from degradation in hypoxia. In low-oxygen conditions, the amount of HIF-1a increases so it can bind to and regulate EPO and other genes with HIF-binding DNA segments. However, at normal oxygen levels, ubiquitin is added to HIF-1a, tagging it for degradation in the proteasome. It wasn’t clear how ubiquitin binds to HIF-1a in an oxygen-dependent manner, but Dr. Kaelin’s work provided some insight.
Dr. Kaelin, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, was researching von Hippel-Lindau’s (VHL) syndrome, an inherited disorder in which mutations can lead to tumors in multiple organs. He found the VHL gene encodes a protein that prevents cancer onset, and cancer cells without a functional VHL gene express high levels of hypoxia-regulated genes.
Research by other groups showed that VHL is part of a complex that labels proteins with ubiquitin, tagging them for degradation. Dr. Ratcliffe and his group found that VHL is required for the degradation of HIF-1a at normal oxygen levels.
Dr. Kaelin’s and Dr. Ratcliffe’s groups also showed that, under normal oxygen conditions, hydroxyl groups are added at two locations in HIF-1a. This modification – prolyl hydroxylation – allows VHL to bind to HIF-1a. So the researchers found that normal oxygen levels control HIF-1a degradation with the help of prolyl hydroxylases.
Additional research by Dr. Ratcliffe’s group and others revealed the specific prolyl hydroxylases involved in HIF-1a degradation. The researchers also found that HIF-1a’s gene-activating function was regulated by oxygen-dependent hydroxylation.
This work has improved the understanding of how different oxygen levels regulate physiological processes. In particular, oxygen sensing is essential for erythropoiesis, so these findings have implications for the treatment of anemia.
“There are several drugs that are now in clinical trials that serve to increase HIF activity and, as a result, will increase the production of erythropoietin and stimulate red blood cell production,” Dr. Semenza said in an interview after the announcement of his Nobel win. “These are all small molecules that can be given by mouth, and that may be a great convenience for patients who, at the present time, may require injections of recombinant human erythropoietin.”
Three researchers have won the 2019 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine “for their discoveries of how cells sense and adapt to oxygen availability.”
William G. Kaelin Jr., MD; Sir Peter J. Ratcliffe, MB ChB, MD; and Gregg L. Semenza, MD, PhD, described the molecular machinery that regulates gene activity in response to oxygen levels.
Their work “established the basis for our understanding of how oxygen levels affect cellular metabolism and physiological function” and “paved the way for promising new strategies to fight anemia, cancer, and many other diseases,” according to a statement by The Nobel Assembly at Karolinska Institutet.
Dr. Semenza, of Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore, studied how the erythropoietin (EPO) gene is regulated by oxygen levels. Via experiments in mice, he identified DNA segments next to the EPO gene that mediate the response to hypoxia.
Dr. Ratcliffe, of the University of Oxford (England) and the Francis Crick Institute in London, also studied oxygen-dependent regulation of the EPO gene. Both his and Dr. Semenza’s groups found the oxygen-sensing mechanism was present in nearly all tissues.
Dr. Semenza also discovered a protein complex, hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF), that binds to the identified DNA segments in an oxygen-dependent manner. Additional investigation revealed that HIF consists of two transcription factors, HIF-1a and ARNT.
Several research groups found that HIF-1a is protected from degradation in hypoxia. In low-oxygen conditions, the amount of HIF-1a increases so it can bind to and regulate EPO and other genes with HIF-binding DNA segments. However, at normal oxygen levels, ubiquitin is added to HIF-1a, tagging it for degradation in the proteasome. It wasn’t clear how ubiquitin binds to HIF-1a in an oxygen-dependent manner, but Dr. Kaelin’s work provided some insight.
Dr. Kaelin, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, was researching von Hippel-Lindau’s (VHL) syndrome, an inherited disorder in which mutations can lead to tumors in multiple organs. He found the VHL gene encodes a protein that prevents cancer onset, and cancer cells without a functional VHL gene express high levels of hypoxia-regulated genes.
Research by other groups showed that VHL is part of a complex that labels proteins with ubiquitin, tagging them for degradation. Dr. Ratcliffe and his group found that VHL is required for the degradation of HIF-1a at normal oxygen levels.
Dr. Kaelin’s and Dr. Ratcliffe’s groups also showed that, under normal oxygen conditions, hydroxyl groups are added at two locations in HIF-1a. This modification – prolyl hydroxylation – allows VHL to bind to HIF-1a. So the researchers found that normal oxygen levels control HIF-1a degradation with the help of prolyl hydroxylases.
Additional research by Dr. Ratcliffe’s group and others revealed the specific prolyl hydroxylases involved in HIF-1a degradation. The researchers also found that HIF-1a’s gene-activating function was regulated by oxygen-dependent hydroxylation.
This work has improved the understanding of how different oxygen levels regulate physiological processes. In particular, oxygen sensing is essential for erythropoiesis, so these findings have implications for the treatment of anemia.
“There are several drugs that are now in clinical trials that serve to increase HIF activity and, as a result, will increase the production of erythropoietin and stimulate red blood cell production,” Dr. Semenza said in an interview after the announcement of his Nobel win. “These are all small molecules that can be given by mouth, and that may be a great convenience for patients who, at the present time, may require injections of recombinant human erythropoietin.”
Targeted agents vs. chemoimmunotherapy as first-line treatment of CLL
SAN FRANCISCO – Should targeted agents replace chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) as first-line treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)? A recent debate suggests there’s no consensus.
William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and Jennifer R. Brown, MD, PhD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, debated the topic at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Dr. Wierda argued that CLL patients should receive a BTK inhibitor or BCL2 inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab, as first-line therapy because these targeted agents have been shown to provide better progression-free survival (PFS) than CIT, and the targeted therapies may prolong overall survival (OS) as well.
Dr. Brown countered that targeted agents don’t improve PFS for all CLL patients, improved PFS doesn’t always translate to improved OS, and targeted agents cost more than CIT.
No role for CIT as first-line treatment
“We have two approaches right now, with nonchemoimmunotherapy-based treatment,” Dr. Wierda said. “One approach, with small-molecule inhibitors, is to have a sustained and durable period of disease control, particularly with BTK inhibitors. The other strategy that has emerged is deep remissions with fixed-duration treatment with BCL2 small-molecule inhibitor-based therapy, which, I would argue, is better than being exposed to genotoxic chemoimmunotherapy.”
Dr. Wierda went on to explain that the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib has been shown to improve PFS, compared with CIT, in phase 3 trials.
In the iLLUMINATE trial, researchers compared ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab as first-line treatment in CLL. At a median follow-up of 31.3 months, the median PFS was not reached in the ibrutinib arm and was 19 months in the chlorambucil arm (P less than .0001; Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56).
In the A041202 study, researchers compared ibrutinib alone (Ib) or in combination with rituximab (Ib-R) to bendamustine plus rituximab (BR) in untreated, older patients with CLL. The 2-year PFS estimates were 74% in the BR arm, 87% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (P less than .001 for BR vs. Ib or Ib-R; N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the E1912 trial, researchers compared Ib-R to fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) in younger, untreated CLL patients. The 3-year PFS was 89.4% with Ib-R and 72.9% with FCR (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43).
Dr. Wierda noted that the E1912 trial also showed superior OS with Ib-R. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% with Ib-R and 91.5% with FCR (P less than .001). However, there was no significant difference in OS between the treatment arms in the A041202 trial or the iLLUMINATE trial.
“But I would argue that is, in part, because of short follow-up,” Dr. Wierda said. “The trials were all designed to look at progression-free survival, not overall survival. With longer follow-up, we may see differences in overall survival emerging.”
Dr. Wierda went on to say that fixed‐duration treatment with the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax can improve PFS over CIT.
In the phase 3 CLL14 trial, researchers compared fixed-duration treatment with venetoclax plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated CLL patients with comorbidities. The estimated PFS at 2 years was 88.2% in the venetoclax group and 64.1% in the chlorambucil group (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
“[There was] no difference in overall survival,” Dr. Wierda noted. “But, again, I would argue ... that follow-up is relatively limited. We may ultimately see a difference in overall survival.”
Based on these findings, Dr. Wierda made the following treatment recommendations:
- Any CLL patient with del(17p) or TP53 mutation, and older, unfit patients with unmutated IGHV should receive a BTK inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab.
- All young, fit patients, and older, unfit patients with mutated IGHV should receive a BCL2 inhibitor plus obinutuzumab.
Dr. Wierda also noted that ibrutinib and venetoclax in combination have shown early promise for patients with previously untreated CLL (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2095-2103).
CIT still has a role as first-line treatment
Dr. Brown suggested that a PFS benefit may not be enough to recommend targeted agents over CIT. For one thing, the PFS benefit doesn’t apply to all patients, as the IGHV-mutated subgroup does equally well with CIT and targeted agents.
In the IGHV-mutated group from the E1912 trial, the 3-year PFS was 88% for patients who received Ib-R and those who received FCR (N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). In the A041202 study, the 2-year PFS among IGHV-mutated patients was 87% in the BR arm, 86% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the CLL14 trial, PFS rates were similar among IGHV-mutated patients who received chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab and IGHV-mutated or unmutated patients who received venetoclax and obinutuzumab (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
Dr. Brown also noted that the overall improvement in PFS observed with ibrutinib and venetoclax doesn’t always translate to improved OS.
In the A041202 study, there was no significant difference in OS between the Ib, Ib-R, and BR arms (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28). There was no significant difference in OS between the ibrutinib and chlorambucil arms in the iLLUMINATE trial (Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56). And there was no significant difference in OS between the venetoclax and chlorambucil arms in the CLL14 trial (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
However, in the RESONATE-2 trial, ibrutinib provided an OS benefit over chlorambucil. The 2-year OS was 95% and 84%, respectively (P = .0145; Haematologica. Sept 2018;103:1502-10). Dr. Brown said the OS advantage in this study was due to the “very poor comparator of chlorambucil and very limited crossover.”
As Dr. Wierda mentioned, the OS rate was higher with Ib-R than with FCR in the E1912 trial. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% and 91.5%, respectively (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). Dr. Brown noted, however, that there were few deaths in this study, and many of them “were not clearly related to the disease or its treatment.”
Dr. Brown also pointed out that FCR has been shown to have curative potential in IGHV-mutated CLL in both the FCR300 trial (Blood. 2016 127:303-9) and the CLL8 trial (Blood. 2016 127:208-15).
Another factor to consider is the greater cost of targeted agents. One analysis suggested the per-patient lifetime cost of CLL treatment in the United States will increase from $147,000 to $604,000 as targeted therapies overtake CIT as first-line treatment (J Clin Oncol. 2017 Jan 10;35[2]:166-174).
“Given all of the above, chemoimmunotherapy is going to remain part of the treatment repertoire for CLL,” Dr. Brown said. “It’s our only known potential cure for the fit, mutated patients ... and can also result in prolonged treatment-free intervals for patients who are older. As we manage CLL as a chronic disease over a lifetime, we need to continue to have this in our armamentarium.”
Specifically, Dr. Brown said CIT is appropriate for patients who don’t have del(17p) or mutated TP53. FCR should be given to young, fit patients with IGHV-mutated CLL, and FCR or BR should be given to older patients and young, fit patients with IGHV-unmutated CLL.
Dr. Brown and Dr. Wierda reported financial ties to multiple pharmaceutical companies, including makers of CLL treatments.
SAN FRANCISCO – Should targeted agents replace chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) as first-line treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)? A recent debate suggests there’s no consensus.
William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and Jennifer R. Brown, MD, PhD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, debated the topic at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Dr. Wierda argued that CLL patients should receive a BTK inhibitor or BCL2 inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab, as first-line therapy because these targeted agents have been shown to provide better progression-free survival (PFS) than CIT, and the targeted therapies may prolong overall survival (OS) as well.
Dr. Brown countered that targeted agents don’t improve PFS for all CLL patients, improved PFS doesn’t always translate to improved OS, and targeted agents cost more than CIT.
No role for CIT as first-line treatment
“We have two approaches right now, with nonchemoimmunotherapy-based treatment,” Dr. Wierda said. “One approach, with small-molecule inhibitors, is to have a sustained and durable period of disease control, particularly with BTK inhibitors. The other strategy that has emerged is deep remissions with fixed-duration treatment with BCL2 small-molecule inhibitor-based therapy, which, I would argue, is better than being exposed to genotoxic chemoimmunotherapy.”
Dr. Wierda went on to explain that the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib has been shown to improve PFS, compared with CIT, in phase 3 trials.
In the iLLUMINATE trial, researchers compared ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab as first-line treatment in CLL. At a median follow-up of 31.3 months, the median PFS was not reached in the ibrutinib arm and was 19 months in the chlorambucil arm (P less than .0001; Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56).
In the A041202 study, researchers compared ibrutinib alone (Ib) or in combination with rituximab (Ib-R) to bendamustine plus rituximab (BR) in untreated, older patients with CLL. The 2-year PFS estimates were 74% in the BR arm, 87% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (P less than .001 for BR vs. Ib or Ib-R; N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the E1912 trial, researchers compared Ib-R to fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) in younger, untreated CLL patients. The 3-year PFS was 89.4% with Ib-R and 72.9% with FCR (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43).
Dr. Wierda noted that the E1912 trial also showed superior OS with Ib-R. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% with Ib-R and 91.5% with FCR (P less than .001). However, there was no significant difference in OS between the treatment arms in the A041202 trial or the iLLUMINATE trial.
“But I would argue that is, in part, because of short follow-up,” Dr. Wierda said. “The trials were all designed to look at progression-free survival, not overall survival. With longer follow-up, we may see differences in overall survival emerging.”
Dr. Wierda went on to say that fixed‐duration treatment with the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax can improve PFS over CIT.
In the phase 3 CLL14 trial, researchers compared fixed-duration treatment with venetoclax plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated CLL patients with comorbidities. The estimated PFS at 2 years was 88.2% in the venetoclax group and 64.1% in the chlorambucil group (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
“[There was] no difference in overall survival,” Dr. Wierda noted. “But, again, I would argue ... that follow-up is relatively limited. We may ultimately see a difference in overall survival.”
Based on these findings, Dr. Wierda made the following treatment recommendations:
- Any CLL patient with del(17p) or TP53 mutation, and older, unfit patients with unmutated IGHV should receive a BTK inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab.
- All young, fit patients, and older, unfit patients with mutated IGHV should receive a BCL2 inhibitor plus obinutuzumab.
Dr. Wierda also noted that ibrutinib and venetoclax in combination have shown early promise for patients with previously untreated CLL (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2095-2103).
CIT still has a role as first-line treatment
Dr. Brown suggested that a PFS benefit may not be enough to recommend targeted agents over CIT. For one thing, the PFS benefit doesn’t apply to all patients, as the IGHV-mutated subgroup does equally well with CIT and targeted agents.
In the IGHV-mutated group from the E1912 trial, the 3-year PFS was 88% for patients who received Ib-R and those who received FCR (N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). In the A041202 study, the 2-year PFS among IGHV-mutated patients was 87% in the BR arm, 86% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the CLL14 trial, PFS rates were similar among IGHV-mutated patients who received chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab and IGHV-mutated or unmutated patients who received venetoclax and obinutuzumab (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
Dr. Brown also noted that the overall improvement in PFS observed with ibrutinib and venetoclax doesn’t always translate to improved OS.
In the A041202 study, there was no significant difference in OS between the Ib, Ib-R, and BR arms (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28). There was no significant difference in OS between the ibrutinib and chlorambucil arms in the iLLUMINATE trial (Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56). And there was no significant difference in OS between the venetoclax and chlorambucil arms in the CLL14 trial (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
However, in the RESONATE-2 trial, ibrutinib provided an OS benefit over chlorambucil. The 2-year OS was 95% and 84%, respectively (P = .0145; Haematologica. Sept 2018;103:1502-10). Dr. Brown said the OS advantage in this study was due to the “very poor comparator of chlorambucil and very limited crossover.”
As Dr. Wierda mentioned, the OS rate was higher with Ib-R than with FCR in the E1912 trial. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% and 91.5%, respectively (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). Dr. Brown noted, however, that there were few deaths in this study, and many of them “were not clearly related to the disease or its treatment.”
Dr. Brown also pointed out that FCR has been shown to have curative potential in IGHV-mutated CLL in both the FCR300 trial (Blood. 2016 127:303-9) and the CLL8 trial (Blood. 2016 127:208-15).
Another factor to consider is the greater cost of targeted agents. One analysis suggested the per-patient lifetime cost of CLL treatment in the United States will increase from $147,000 to $604,000 as targeted therapies overtake CIT as first-line treatment (J Clin Oncol. 2017 Jan 10;35[2]:166-174).
“Given all of the above, chemoimmunotherapy is going to remain part of the treatment repertoire for CLL,” Dr. Brown said. “It’s our only known potential cure for the fit, mutated patients ... and can also result in prolonged treatment-free intervals for patients who are older. As we manage CLL as a chronic disease over a lifetime, we need to continue to have this in our armamentarium.”
Specifically, Dr. Brown said CIT is appropriate for patients who don’t have del(17p) or mutated TP53. FCR should be given to young, fit patients with IGHV-mutated CLL, and FCR or BR should be given to older patients and young, fit patients with IGHV-unmutated CLL.
Dr. Brown and Dr. Wierda reported financial ties to multiple pharmaceutical companies, including makers of CLL treatments.
SAN FRANCISCO – Should targeted agents replace chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) as first-line treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)? A recent debate suggests there’s no consensus.
William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and Jennifer R. Brown, MD, PhD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, debated the topic at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Dr. Wierda argued that CLL patients should receive a BTK inhibitor or BCL2 inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab, as first-line therapy because these targeted agents have been shown to provide better progression-free survival (PFS) than CIT, and the targeted therapies may prolong overall survival (OS) as well.
Dr. Brown countered that targeted agents don’t improve PFS for all CLL patients, improved PFS doesn’t always translate to improved OS, and targeted agents cost more than CIT.
No role for CIT as first-line treatment
“We have two approaches right now, with nonchemoimmunotherapy-based treatment,” Dr. Wierda said. “One approach, with small-molecule inhibitors, is to have a sustained and durable period of disease control, particularly with BTK inhibitors. The other strategy that has emerged is deep remissions with fixed-duration treatment with BCL2 small-molecule inhibitor-based therapy, which, I would argue, is better than being exposed to genotoxic chemoimmunotherapy.”
Dr. Wierda went on to explain that the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib has been shown to improve PFS, compared with CIT, in phase 3 trials.
In the iLLUMINATE trial, researchers compared ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab as first-line treatment in CLL. At a median follow-up of 31.3 months, the median PFS was not reached in the ibrutinib arm and was 19 months in the chlorambucil arm (P less than .0001; Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56).
In the A041202 study, researchers compared ibrutinib alone (Ib) or in combination with rituximab (Ib-R) to bendamustine plus rituximab (BR) in untreated, older patients with CLL. The 2-year PFS estimates were 74% in the BR arm, 87% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (P less than .001 for BR vs. Ib or Ib-R; N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the E1912 trial, researchers compared Ib-R to fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) in younger, untreated CLL patients. The 3-year PFS was 89.4% with Ib-R and 72.9% with FCR (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43).
Dr. Wierda noted that the E1912 trial also showed superior OS with Ib-R. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% with Ib-R and 91.5% with FCR (P less than .001). However, there was no significant difference in OS between the treatment arms in the A041202 trial or the iLLUMINATE trial.
“But I would argue that is, in part, because of short follow-up,” Dr. Wierda said. “The trials were all designed to look at progression-free survival, not overall survival. With longer follow-up, we may see differences in overall survival emerging.”
Dr. Wierda went on to say that fixed‐duration treatment with the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax can improve PFS over CIT.
In the phase 3 CLL14 trial, researchers compared fixed-duration treatment with venetoclax plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated CLL patients with comorbidities. The estimated PFS at 2 years was 88.2% in the venetoclax group and 64.1% in the chlorambucil group (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
“[There was] no difference in overall survival,” Dr. Wierda noted. “But, again, I would argue ... that follow-up is relatively limited. We may ultimately see a difference in overall survival.”
Based on these findings, Dr. Wierda made the following treatment recommendations:
- Any CLL patient with del(17p) or TP53 mutation, and older, unfit patients with unmutated IGHV should receive a BTK inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab.
- All young, fit patients, and older, unfit patients with mutated IGHV should receive a BCL2 inhibitor plus obinutuzumab.
Dr. Wierda also noted that ibrutinib and venetoclax in combination have shown early promise for patients with previously untreated CLL (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2095-2103).
CIT still has a role as first-line treatment
Dr. Brown suggested that a PFS benefit may not be enough to recommend targeted agents over CIT. For one thing, the PFS benefit doesn’t apply to all patients, as the IGHV-mutated subgroup does equally well with CIT and targeted agents.
In the IGHV-mutated group from the E1912 trial, the 3-year PFS was 88% for patients who received Ib-R and those who received FCR (N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). In the A041202 study, the 2-year PFS among IGHV-mutated patients was 87% in the BR arm, 86% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the CLL14 trial, PFS rates were similar among IGHV-mutated patients who received chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab and IGHV-mutated or unmutated patients who received venetoclax and obinutuzumab (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
Dr. Brown also noted that the overall improvement in PFS observed with ibrutinib and venetoclax doesn’t always translate to improved OS.
In the A041202 study, there was no significant difference in OS between the Ib, Ib-R, and BR arms (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28). There was no significant difference in OS between the ibrutinib and chlorambucil arms in the iLLUMINATE trial (Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56). And there was no significant difference in OS between the venetoclax and chlorambucil arms in the CLL14 trial (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
However, in the RESONATE-2 trial, ibrutinib provided an OS benefit over chlorambucil. The 2-year OS was 95% and 84%, respectively (P = .0145; Haematologica. Sept 2018;103:1502-10). Dr. Brown said the OS advantage in this study was due to the “very poor comparator of chlorambucil and very limited crossover.”
As Dr. Wierda mentioned, the OS rate was higher with Ib-R than with FCR in the E1912 trial. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% and 91.5%, respectively (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). Dr. Brown noted, however, that there were few deaths in this study, and many of them “were not clearly related to the disease or its treatment.”
Dr. Brown also pointed out that FCR has been shown to have curative potential in IGHV-mutated CLL in both the FCR300 trial (Blood. 2016 127:303-9) and the CLL8 trial (Blood. 2016 127:208-15).
Another factor to consider is the greater cost of targeted agents. One analysis suggested the per-patient lifetime cost of CLL treatment in the United States will increase from $147,000 to $604,000 as targeted therapies overtake CIT as first-line treatment (J Clin Oncol. 2017 Jan 10;35[2]:166-174).
“Given all of the above, chemoimmunotherapy is going to remain part of the treatment repertoire for CLL,” Dr. Brown said. “It’s our only known potential cure for the fit, mutated patients ... and can also result in prolonged treatment-free intervals for patients who are older. As we manage CLL as a chronic disease over a lifetime, we need to continue to have this in our armamentarium.”
Specifically, Dr. Brown said CIT is appropriate for patients who don’t have del(17p) or mutated TP53. FCR should be given to young, fit patients with IGHV-mutated CLL, and FCR or BR should be given to older patients and young, fit patients with IGHV-unmutated CLL.
Dr. Brown and Dr. Wierda reported financial ties to multiple pharmaceutical companies, including makers of CLL treatments.
REPORTING FROM NCCN HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES
Decoding biosimilar approvals
SAN FRANCISCO – Several factors must be considered when extrapolating biosimilar results, according to a speaker at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
In this context, “extrapolation” means expanding the use of an approved biosimilar from one indication to another, based on efficacy and safety data from the first indication, Andrew D. Zelenetz, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, explained at the meeting.
To determine if extrapolation is appropriate, regulatory agencies consider the biosimilar’s mechanism of action in each indication; pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity in the different patient populations; differences in expected toxicities for each condition and population; and any other factor that may affect safety or efficacy.
To illustrate the process, Dr. Zelenetz explained how results with a rituximab biosimilar in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) cannot be extrapolated to B‐cell non‐Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), but results with that same biosimilar in follicular lymphoma can be extrapolated to other types of B-cell NHL.
The biosimilar is rituximab-abbs (CT‐P10, Truxima). In a phase 1 trial of patients with RA, rituximab-abbs demonstrated biosimilarity to the reference product (Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76[3]:566‐70).
The RA results cannot be extrapolated to B-cell NHL for a few reasons, according to Dr. Zelenetz. He noted that rituximab’s mechanism of action is antibody-dependent cell‐mediated cytotoxicity in both RA and NHL. However, the target in RA is the normal B cell, and the target in NHL is the malignant B cell.
In addition, the pharmacokinetics of rituximab are “drastically different” in RA and NHL, Dr. Zelenetz said. Differences in pharmacokinetics support different dosing approaches in the two diseases.
Another big difference is immunogenicity. Anti‐CD20 antibodies develop in 15%-17% of RA patients, Dr. Zelenetz said, but the risk of antibody development is less than 1% in lymphoma.
Though extrapolation from RA to B‐cell NHL was not possible, it was possible to extrapolate results with rituximab-abbs in follicular lymphoma to other B-cell NHLs.
The study used was a phase 3 trial comparing rituximab-abbs to rituximab – both in combination with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone – in patients with newly diagnosed, advanced stage follicular lymphoma.
This study showed no difference in pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics between rituximab-abbs and rituximab. The two agents also had comparable safety profiles and produced similar response rates (Lancet Haematol. 2017 Jul 13;4:e362‐73).
Rituximab‐abbs was approved in the United States based on these data, and results from this trial were extrapolated to other types of B-cell NHL. The results were extrapolated because the mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity of rituximab are the same across B-cell NHLs, Dr. Zelenetz noted.
“Extrapolation is a critical part of biosimilarity development,” he said. “As long as scientific justification for extrapolation exists, I believe that extrapolation makes good sense.”
Dr. Zelenetz reported relationships with AbbVie, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Celgene, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, MEI Pharma, MorphoSys AG, Novartis, Pharmacyclics, and Roche.
SAN FRANCISCO – Several factors must be considered when extrapolating biosimilar results, according to a speaker at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
In this context, “extrapolation” means expanding the use of an approved biosimilar from one indication to another, based on efficacy and safety data from the first indication, Andrew D. Zelenetz, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, explained at the meeting.
To determine if extrapolation is appropriate, regulatory agencies consider the biosimilar’s mechanism of action in each indication; pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity in the different patient populations; differences in expected toxicities for each condition and population; and any other factor that may affect safety or efficacy.
To illustrate the process, Dr. Zelenetz explained how results with a rituximab biosimilar in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) cannot be extrapolated to B‐cell non‐Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), but results with that same biosimilar in follicular lymphoma can be extrapolated to other types of B-cell NHL.
The biosimilar is rituximab-abbs (CT‐P10, Truxima). In a phase 1 trial of patients with RA, rituximab-abbs demonstrated biosimilarity to the reference product (Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76[3]:566‐70).
The RA results cannot be extrapolated to B-cell NHL for a few reasons, according to Dr. Zelenetz. He noted that rituximab’s mechanism of action is antibody-dependent cell‐mediated cytotoxicity in both RA and NHL. However, the target in RA is the normal B cell, and the target in NHL is the malignant B cell.
In addition, the pharmacokinetics of rituximab are “drastically different” in RA and NHL, Dr. Zelenetz said. Differences in pharmacokinetics support different dosing approaches in the two diseases.
Another big difference is immunogenicity. Anti‐CD20 antibodies develop in 15%-17% of RA patients, Dr. Zelenetz said, but the risk of antibody development is less than 1% in lymphoma.
Though extrapolation from RA to B‐cell NHL was not possible, it was possible to extrapolate results with rituximab-abbs in follicular lymphoma to other B-cell NHLs.
The study used was a phase 3 trial comparing rituximab-abbs to rituximab – both in combination with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone – in patients with newly diagnosed, advanced stage follicular lymphoma.
This study showed no difference in pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics between rituximab-abbs and rituximab. The two agents also had comparable safety profiles and produced similar response rates (Lancet Haematol. 2017 Jul 13;4:e362‐73).
Rituximab‐abbs was approved in the United States based on these data, and results from this trial were extrapolated to other types of B-cell NHL. The results were extrapolated because the mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity of rituximab are the same across B-cell NHLs, Dr. Zelenetz noted.
“Extrapolation is a critical part of biosimilarity development,” he said. “As long as scientific justification for extrapolation exists, I believe that extrapolation makes good sense.”
Dr. Zelenetz reported relationships with AbbVie, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Celgene, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, MEI Pharma, MorphoSys AG, Novartis, Pharmacyclics, and Roche.
SAN FRANCISCO – Several factors must be considered when extrapolating biosimilar results, according to a speaker at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
In this context, “extrapolation” means expanding the use of an approved biosimilar from one indication to another, based on efficacy and safety data from the first indication, Andrew D. Zelenetz, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, explained at the meeting.
To determine if extrapolation is appropriate, regulatory agencies consider the biosimilar’s mechanism of action in each indication; pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity in the different patient populations; differences in expected toxicities for each condition and population; and any other factor that may affect safety or efficacy.
To illustrate the process, Dr. Zelenetz explained how results with a rituximab biosimilar in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) cannot be extrapolated to B‐cell non‐Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), but results with that same biosimilar in follicular lymphoma can be extrapolated to other types of B-cell NHL.
The biosimilar is rituximab-abbs (CT‐P10, Truxima). In a phase 1 trial of patients with RA, rituximab-abbs demonstrated biosimilarity to the reference product (Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76[3]:566‐70).
The RA results cannot be extrapolated to B-cell NHL for a few reasons, according to Dr. Zelenetz. He noted that rituximab’s mechanism of action is antibody-dependent cell‐mediated cytotoxicity in both RA and NHL. However, the target in RA is the normal B cell, and the target in NHL is the malignant B cell.
In addition, the pharmacokinetics of rituximab are “drastically different” in RA and NHL, Dr. Zelenetz said. Differences in pharmacokinetics support different dosing approaches in the two diseases.
Another big difference is immunogenicity. Anti‐CD20 antibodies develop in 15%-17% of RA patients, Dr. Zelenetz said, but the risk of antibody development is less than 1% in lymphoma.
Though extrapolation from RA to B‐cell NHL was not possible, it was possible to extrapolate results with rituximab-abbs in follicular lymphoma to other B-cell NHLs.
The study used was a phase 3 trial comparing rituximab-abbs to rituximab – both in combination with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone – in patients with newly diagnosed, advanced stage follicular lymphoma.
This study showed no difference in pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics between rituximab-abbs and rituximab. The two agents also had comparable safety profiles and produced similar response rates (Lancet Haematol. 2017 Jul 13;4:e362‐73).
Rituximab‐abbs was approved in the United States based on these data, and results from this trial were extrapolated to other types of B-cell NHL. The results were extrapolated because the mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity of rituximab are the same across B-cell NHLs, Dr. Zelenetz noted.
“Extrapolation is a critical part of biosimilarity development,” he said. “As long as scientific justification for extrapolation exists, I believe that extrapolation makes good sense.”
Dr. Zelenetz reported relationships with AbbVie, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Celgene, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, MEI Pharma, MorphoSys AG, Novartis, Pharmacyclics, and Roche.
REPORTING FROM NCCN HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES
Study finds no standard for treatment discontinuation in myeloma
BOSTON — There is “no standard of care and no clear pattern” for discontinuing treatment in multiple myeloma, according to a speaker at the International Myeloma Workshop.
Data from a large, observational study revealed that a wide range of treatment regimens are used for first-, second-, and third-line therapy in multiple myeloma. The duration of therapy and time to next treatment were shorter in this real-world study than in prior clinical trials, and reasons for treatment discontinuation varied by regimen and line of therapy.
Katja Weisel, MD, of University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf in Germany, presented these findings at the workshop, held by the International Myeloma Society.
The study, INSIGHT MM, is the largest global, prospective, observational study of multiple myeloma to date, according to Dr. Weisel. The study, which began July 1, 2016, has enrolled patients in the United States (n = 1,004), Europe (n = 1,612), Latin America (n = 367), and Asia (n = 218).
Dr. Weisel and her colleagues evaluated duration of therapy, reasons for treatment discontinuation, and subsequent therapies in a subset of patients on INSIGHT MM. The researchers’ analysis revealed “broad heterogeneity” across lines of therapy, Dr. Weisel said, adding that patients are receiving multiple regimens in addition to the most commonly prescribed regimens in myeloma.
First-line therapy
“In first-line treatment, we see predominantly bortezomib-based triplets ... regardless of transplant-eligible or transplant-ineligible patients,” Dr. Weisel said. “This is followed by doublets and other more rarely [applied] regimens.”
First-line therapies in 1,175 patients included:
- Bortezomib, cyclophosphamide, and dexamethasone (VCd) – 323 patients.
- Bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (VRd) – 321 patients.
- Bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone (VTd) – 200 patients.
- Bortezomib and dexamethasone (Vd) – 102 patients.
- Lenalidomide and dexamethasone (Rd) – 90 patients.
- Bortezomib, melphalan, and prednisone (VMP) – 53 patients.
- Carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (KRd) – 47 patients.
- Daratumumab-based regimens (Dara) – 32 patients.
- Carfilzomib and dexamethasone (Kd) – 5 patients.
- Ixazomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (IRd) – 2 patients.
Of the 1,175 newly diagnosed patients, 894 did not proceed to transplant after first-line therapy, but 281 did. Most of the patients who went on to transplant had received VRd (n = 82), VTd (n = 76), or VCd (n = 75).
Second- and third-line therapies
“In second-line treatment, we have still a dominance of the len-dex regimen all over the world,” Dr. Weisel said. “There is an emerging use of daratumumab in various combinations, and then you see the whole spectrum of approved triplet and doublet regimens.”
In the third line, the most commonly used regimens are daratumumab-based combinations and Rd.
There were 548 patients who received second-line treatment and 332 who received third-line therapy. The regimens used were:
- Rd – 130 patients second line, 71 third line.
- Dara – 121 patients second line, 105 third line.
- KRd – 61 patients second line, 17 third line.
- VCd – 57 patients second line, 19 third line.
- Vd – 48 patients second line, 29 third line.
- VRd – 36 patients second line, 8 third line.
- Kd – 33 patients for both second and third line.
- IRd – 29 patients second line, 43 third line.
- VTd – 25 patients second line, 4 third line.
- VMP – 8 patients second line, 3 third line.
Duration of therapy
Most transplant-eligible patients received any first-line therapy (VRd, VTd, or VCd) for longer than 12 months. Among transplant-ineligible patients, Rd was the first-line therapy most likely to be given for 12 months or more.
None of the second-line regimens lasted longer than 12 months in a majority of patients, but daratumumab-based regimens and IRd were the therapies most likely to exceed 12 months’ duration in both second- and third-line treatment.
Time to next treatment
“The vast majority of [transplant-eligible] patients, close to 90% ... do not need a second-line treatment during the first year of treatment,” Dr. Weisel said. “However, for transplant-ineligible patients, this accounts only for the most effective regimens, VMP and Rd.”
For second- and third-line therapies, a 12-month or longer time to next treatment was most likely among patients who received IRd or daratumumab-based regimens.
Reasons for discontinuation
“Planned end of therapy only accounts for a small proportion of treatment discontinuations, especially in the relapsed setting,” Dr. Weisel said. “Patients are discontinuing treatment due to reasons other than relapse, ultimately receiving fixed-duration therapy.”
The most common reasons for discontinuation of first-line therapy were:
- Relapse for VCd.
- Planned end of therapy for VRd.
- Adverse events (AEs) for VD and VTd.
- AEs and “other reasons” for Rd.
The most common reasons for discontinuation of second-line therapy were:
- Planned end of therapy for VCd.
- AEs, relapse, and other reasons for VRd.
- Relapse for VD, KRd, and Dara.
- AEs for Rd and IRd.
- AEs and other reasons for Kd.
The most common reasons for discontinuation of third-line therapy were:
- AEs for VCd, Vd, and KRd.
- Relapse for Kd, IRd, and Dara.
- Relapse and other reasons for VRd.
- AEs and other reasons for Rd.
The most common AE leading to discontinuation, across all treatment regimens, was peripheral neuropathy. This suggests peripheral neuropathy is still the “biggest impediment for continuous treatment,” Dr. Weisel said.
INSIGHT MM is sponsored by Takeda. Dr. Weisel reported relationships with Takeda and several other companies.
SOURCE: Weisel K et al. IMW 2019, Abstract OAB-005.
BOSTON — There is “no standard of care and no clear pattern” for discontinuing treatment in multiple myeloma, according to a speaker at the International Myeloma Workshop.
Data from a large, observational study revealed that a wide range of treatment regimens are used for first-, second-, and third-line therapy in multiple myeloma. The duration of therapy and time to next treatment were shorter in this real-world study than in prior clinical trials, and reasons for treatment discontinuation varied by regimen and line of therapy.
Katja Weisel, MD, of University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf in Germany, presented these findings at the workshop, held by the International Myeloma Society.
The study, INSIGHT MM, is the largest global, prospective, observational study of multiple myeloma to date, according to Dr. Weisel. The study, which began July 1, 2016, has enrolled patients in the United States (n = 1,004), Europe (n = 1,612), Latin America (n = 367), and Asia (n = 218).
Dr. Weisel and her colleagues evaluated duration of therapy, reasons for treatment discontinuation, and subsequent therapies in a subset of patients on INSIGHT MM. The researchers’ analysis revealed “broad heterogeneity” across lines of therapy, Dr. Weisel said, adding that patients are receiving multiple regimens in addition to the most commonly prescribed regimens in myeloma.
First-line therapy
“In first-line treatment, we see predominantly bortezomib-based triplets ... regardless of transplant-eligible or transplant-ineligible patients,” Dr. Weisel said. “This is followed by doublets and other more rarely [applied] regimens.”
First-line therapies in 1,175 patients included:
- Bortezomib, cyclophosphamide, and dexamethasone (VCd) – 323 patients.
- Bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (VRd) – 321 patients.
- Bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone (VTd) – 200 patients.
- Bortezomib and dexamethasone (Vd) – 102 patients.
- Lenalidomide and dexamethasone (Rd) – 90 patients.
- Bortezomib, melphalan, and prednisone (VMP) – 53 patients.
- Carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (KRd) – 47 patients.
- Daratumumab-based regimens (Dara) – 32 patients.
- Carfilzomib and dexamethasone (Kd) – 5 patients.
- Ixazomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (IRd) – 2 patients.
Of the 1,175 newly diagnosed patients, 894 did not proceed to transplant after first-line therapy, but 281 did. Most of the patients who went on to transplant had received VRd (n = 82), VTd (n = 76), or VCd (n = 75).
Second- and third-line therapies
“In second-line treatment, we have still a dominance of the len-dex regimen all over the world,” Dr. Weisel said. “There is an emerging use of daratumumab in various combinations, and then you see the whole spectrum of approved triplet and doublet regimens.”
In the third line, the most commonly used regimens are daratumumab-based combinations and Rd.
There were 548 patients who received second-line treatment and 332 who received third-line therapy. The regimens used were:
- Rd – 130 patients second line, 71 third line.
- Dara – 121 patients second line, 105 third line.
- KRd – 61 patients second line, 17 third line.
- VCd – 57 patients second line, 19 third line.
- Vd – 48 patients second line, 29 third line.
- VRd – 36 patients second line, 8 third line.
- Kd – 33 patients for both second and third line.
- IRd – 29 patients second line, 43 third line.
- VTd – 25 patients second line, 4 third line.
- VMP – 8 patients second line, 3 third line.
Duration of therapy
Most transplant-eligible patients received any first-line therapy (VRd, VTd, or VCd) for longer than 12 months. Among transplant-ineligible patients, Rd was the first-line therapy most likely to be given for 12 months or more.
None of the second-line regimens lasted longer than 12 months in a majority of patients, but daratumumab-based regimens and IRd were the therapies most likely to exceed 12 months’ duration in both second- and third-line treatment.
Time to next treatment
“The vast majority of [transplant-eligible] patients, close to 90% ... do not need a second-line treatment during the first year of treatment,” Dr. Weisel said. “However, for transplant-ineligible patients, this accounts only for the most effective regimens, VMP and Rd.”
For second- and third-line therapies, a 12-month or longer time to next treatment was most likely among patients who received IRd or daratumumab-based regimens.
Reasons for discontinuation
“Planned end of therapy only accounts for a small proportion of treatment discontinuations, especially in the relapsed setting,” Dr. Weisel said. “Patients are discontinuing treatment due to reasons other than relapse, ultimately receiving fixed-duration therapy.”
The most common reasons for discontinuation of first-line therapy were:
- Relapse for VCd.
- Planned end of therapy for VRd.
- Adverse events (AEs) for VD and VTd.
- AEs and “other reasons” for Rd.
The most common reasons for discontinuation of second-line therapy were:
- Planned end of therapy for VCd.
- AEs, relapse, and other reasons for VRd.
- Relapse for VD, KRd, and Dara.
- AEs for Rd and IRd.
- AEs and other reasons for Kd.
The most common reasons for discontinuation of third-line therapy were:
- AEs for VCd, Vd, and KRd.
- Relapse for Kd, IRd, and Dara.
- Relapse and other reasons for VRd.
- AEs and other reasons for Rd.
The most common AE leading to discontinuation, across all treatment regimens, was peripheral neuropathy. This suggests peripheral neuropathy is still the “biggest impediment for continuous treatment,” Dr. Weisel said.
INSIGHT MM is sponsored by Takeda. Dr. Weisel reported relationships with Takeda and several other companies.
SOURCE: Weisel K et al. IMW 2019, Abstract OAB-005.
BOSTON — There is “no standard of care and no clear pattern” for discontinuing treatment in multiple myeloma, according to a speaker at the International Myeloma Workshop.
Data from a large, observational study revealed that a wide range of treatment regimens are used for first-, second-, and third-line therapy in multiple myeloma. The duration of therapy and time to next treatment were shorter in this real-world study than in prior clinical trials, and reasons for treatment discontinuation varied by regimen and line of therapy.
Katja Weisel, MD, of University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf in Germany, presented these findings at the workshop, held by the International Myeloma Society.
The study, INSIGHT MM, is the largest global, prospective, observational study of multiple myeloma to date, according to Dr. Weisel. The study, which began July 1, 2016, has enrolled patients in the United States (n = 1,004), Europe (n = 1,612), Latin America (n = 367), and Asia (n = 218).
Dr. Weisel and her colleagues evaluated duration of therapy, reasons for treatment discontinuation, and subsequent therapies in a subset of patients on INSIGHT MM. The researchers’ analysis revealed “broad heterogeneity” across lines of therapy, Dr. Weisel said, adding that patients are receiving multiple regimens in addition to the most commonly prescribed regimens in myeloma.
First-line therapy
“In first-line treatment, we see predominantly bortezomib-based triplets ... regardless of transplant-eligible or transplant-ineligible patients,” Dr. Weisel said. “This is followed by doublets and other more rarely [applied] regimens.”
First-line therapies in 1,175 patients included:
- Bortezomib, cyclophosphamide, and dexamethasone (VCd) – 323 patients.
- Bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (VRd) – 321 patients.
- Bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone (VTd) – 200 patients.
- Bortezomib and dexamethasone (Vd) – 102 patients.
- Lenalidomide and dexamethasone (Rd) – 90 patients.
- Bortezomib, melphalan, and prednisone (VMP) – 53 patients.
- Carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (KRd) – 47 patients.
- Daratumumab-based regimens (Dara) – 32 patients.
- Carfilzomib and dexamethasone (Kd) – 5 patients.
- Ixazomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (IRd) – 2 patients.
Of the 1,175 newly diagnosed patients, 894 did not proceed to transplant after first-line therapy, but 281 did. Most of the patients who went on to transplant had received VRd (n = 82), VTd (n = 76), or VCd (n = 75).
Second- and third-line therapies
“In second-line treatment, we have still a dominance of the len-dex regimen all over the world,” Dr. Weisel said. “There is an emerging use of daratumumab in various combinations, and then you see the whole spectrum of approved triplet and doublet regimens.”
In the third line, the most commonly used regimens are daratumumab-based combinations and Rd.
There were 548 patients who received second-line treatment and 332 who received third-line therapy. The regimens used were:
- Rd – 130 patients second line, 71 third line.
- Dara – 121 patients second line, 105 third line.
- KRd – 61 patients second line, 17 third line.
- VCd – 57 patients second line, 19 third line.
- Vd – 48 patients second line, 29 third line.
- VRd – 36 patients second line, 8 third line.
- Kd – 33 patients for both second and third line.
- IRd – 29 patients second line, 43 third line.
- VTd – 25 patients second line, 4 third line.
- VMP – 8 patients second line, 3 third line.
Duration of therapy
Most transplant-eligible patients received any first-line therapy (VRd, VTd, or VCd) for longer than 12 months. Among transplant-ineligible patients, Rd was the first-line therapy most likely to be given for 12 months or more.
None of the second-line regimens lasted longer than 12 months in a majority of patients, but daratumumab-based regimens and IRd were the therapies most likely to exceed 12 months’ duration in both second- and third-line treatment.
Time to next treatment
“The vast majority of [transplant-eligible] patients, close to 90% ... do not need a second-line treatment during the first year of treatment,” Dr. Weisel said. “However, for transplant-ineligible patients, this accounts only for the most effective regimens, VMP and Rd.”
For second- and third-line therapies, a 12-month or longer time to next treatment was most likely among patients who received IRd or daratumumab-based regimens.
Reasons for discontinuation
“Planned end of therapy only accounts for a small proportion of treatment discontinuations, especially in the relapsed setting,” Dr. Weisel said. “Patients are discontinuing treatment due to reasons other than relapse, ultimately receiving fixed-duration therapy.”
The most common reasons for discontinuation of first-line therapy were:
- Relapse for VCd.
- Planned end of therapy for VRd.
- Adverse events (AEs) for VD and VTd.
- AEs and “other reasons” for Rd.
The most common reasons for discontinuation of second-line therapy were:
- Planned end of therapy for VCd.
- AEs, relapse, and other reasons for VRd.
- Relapse for VD, KRd, and Dara.
- AEs for Rd and IRd.
- AEs and other reasons for Kd.
The most common reasons for discontinuation of third-line therapy were:
- AEs for VCd, Vd, and KRd.
- Relapse for Kd, IRd, and Dara.
- Relapse and other reasons for VRd.
- AEs and other reasons for Rd.
The most common AE leading to discontinuation, across all treatment regimens, was peripheral neuropathy. This suggests peripheral neuropathy is still the “biggest impediment for continuous treatment,” Dr. Weisel said.
INSIGHT MM is sponsored by Takeda. Dr. Weisel reported relationships with Takeda and several other companies.
SOURCE: Weisel K et al. IMW 2019, Abstract OAB-005.
REPORTING FROM IMW 2019
Immunotherapies under investigation in newly diagnosed B-ALL
SAN FRANCISCO – Positive results with blinatumomab and inotuzumab ozogamicin in the relapsed/refractory setting have prompted trials of these immunotherapies in newly diagnosed B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL).
Blinatumomab and inotuzumab have been shown to improve overall survival, compared with chemotherapy, in patients with relapsed/refractory B-ALL. However, most adults with relapsed/refractory B-ALL still die, so the initial therapy patients receive is “critical,” according to Jae Park, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
“Ideally, we do not want to deal with the relapse,” Dr. Park said. “It’s better to cure the disease the first time ... which is the reason clinical trials are incorporating these agents earlier.”
Dr. Park discussed these points at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Blinatumomab
Dr. Park cited the phase 3 TOWER trial, which showed that blinatumomab produced better response rates and overall survival compared with standard chemotherapy. The trial enrolled 405 patients with Ph-negative relapsed/refractory B-ALL who were randomized to blinatumomab (n = 271) or chemotherapy (n = 134).
The rate of complete response (CR) with full, partial, or incomplete hematologic recovery was 44% with blinatumomab and 25% with chemotherapy (P less than .001). The median overall survival was 7.7 months and 4.0 months, respectively (P = .01; N Engl J Med 2017; 376:836-47).
Based on these data, researchers decided to test blinatumomab in newly diagnosed, elderly patients (65 years and older) with Ph-negative B-ALL in the phase 2 SWOG 1318 study. The study enrolled 31 patients, and 29 were eligible. Their median age at baseline was 75 years (range 66‐84 years).
The patients received blinatumomab for two to five cycles, followed by 18 months of maintenance with prednisone, vincristine, 6-mercaptopurine, and methotrexate. One patient went on to transplant.
In all, 66% of patients achieved a CR or CR with incomplete count recovery. The estimated overall survival was 79% at 6 months and 65% at 1 year. These results were presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (Blood. 2018;132:33).
Another study of blinatumomab as frontline treatment is the ECOG-E1910 trial. In this phase 3 study, researchers are testing chemotherapy, with or without blinatumomab, in adults (aged 30-70 years) with newly diagnosed, BCR-ABL-negative B-ALL. Results from this study are not yet available.
Inotuzumab ozogamicin
Dr. Park also discussed the INOVATE trial, in which inotuzumab ozogamicin bested standard chemotherapy. The trial enrolled patients with Ph-positive or negative, relapsed/refractory B-ALL.
The patients were randomized to inotuzumab (n = 141) or investigator’s choice of chemotherapy (n = 138). Some patients, 41% in the inotuzumab arm and 11% in the chemotherapy arm, went on to transplant.
The CR rate was 80.7% in the inotuzumab arm and 29.4% in the chemotherapy arm (P less than .001). The median progression-free survival was 5 months and 1.8 months, respectively (P less than .001). The median overall survival was 7.7 months and 6.7 months, respectively (P = .04; N Engl J Med 2016; 375:740-53).
Based on these results, researchers are testing inotuzumab as frontline therapy in young adults (aged 18-39 years) with CD22-positive, Ph-negative B-ALL. In the phase 3 A041501 trial, patients are receiving inotuzumab after the first and second courses of treatment with the CALGB 10403 chemotherapy regimen. Results from this trial are not yet available.
Dr. Park reported relationships with Allogene Therapeutics, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Incyte, Kite Pharma, Novartis, and Takeda.
SAN FRANCISCO – Positive results with blinatumomab and inotuzumab ozogamicin in the relapsed/refractory setting have prompted trials of these immunotherapies in newly diagnosed B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL).
Blinatumomab and inotuzumab have been shown to improve overall survival, compared with chemotherapy, in patients with relapsed/refractory B-ALL. However, most adults with relapsed/refractory B-ALL still die, so the initial therapy patients receive is “critical,” according to Jae Park, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
“Ideally, we do not want to deal with the relapse,” Dr. Park said. “It’s better to cure the disease the first time ... which is the reason clinical trials are incorporating these agents earlier.”
Dr. Park discussed these points at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Blinatumomab
Dr. Park cited the phase 3 TOWER trial, which showed that blinatumomab produced better response rates and overall survival compared with standard chemotherapy. The trial enrolled 405 patients with Ph-negative relapsed/refractory B-ALL who were randomized to blinatumomab (n = 271) or chemotherapy (n = 134).
The rate of complete response (CR) with full, partial, or incomplete hematologic recovery was 44% with blinatumomab and 25% with chemotherapy (P less than .001). The median overall survival was 7.7 months and 4.0 months, respectively (P = .01; N Engl J Med 2017; 376:836-47).
Based on these data, researchers decided to test blinatumomab in newly diagnosed, elderly patients (65 years and older) with Ph-negative B-ALL in the phase 2 SWOG 1318 study. The study enrolled 31 patients, and 29 were eligible. Their median age at baseline was 75 years (range 66‐84 years).
The patients received blinatumomab for two to five cycles, followed by 18 months of maintenance with prednisone, vincristine, 6-mercaptopurine, and methotrexate. One patient went on to transplant.
In all, 66% of patients achieved a CR or CR with incomplete count recovery. The estimated overall survival was 79% at 6 months and 65% at 1 year. These results were presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (Blood. 2018;132:33).
Another study of blinatumomab as frontline treatment is the ECOG-E1910 trial. In this phase 3 study, researchers are testing chemotherapy, with or without blinatumomab, in adults (aged 30-70 years) with newly diagnosed, BCR-ABL-negative B-ALL. Results from this study are not yet available.
Inotuzumab ozogamicin
Dr. Park also discussed the INOVATE trial, in which inotuzumab ozogamicin bested standard chemotherapy. The trial enrolled patients with Ph-positive or negative, relapsed/refractory B-ALL.
The patients were randomized to inotuzumab (n = 141) or investigator’s choice of chemotherapy (n = 138). Some patients, 41% in the inotuzumab arm and 11% in the chemotherapy arm, went on to transplant.
The CR rate was 80.7% in the inotuzumab arm and 29.4% in the chemotherapy arm (P less than .001). The median progression-free survival was 5 months and 1.8 months, respectively (P less than .001). The median overall survival was 7.7 months and 6.7 months, respectively (P = .04; N Engl J Med 2016; 375:740-53).
Based on these results, researchers are testing inotuzumab as frontline therapy in young adults (aged 18-39 years) with CD22-positive, Ph-negative B-ALL. In the phase 3 A041501 trial, patients are receiving inotuzumab after the first and second courses of treatment with the CALGB 10403 chemotherapy regimen. Results from this trial are not yet available.
Dr. Park reported relationships with Allogene Therapeutics, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Incyte, Kite Pharma, Novartis, and Takeda.
SAN FRANCISCO – Positive results with blinatumomab and inotuzumab ozogamicin in the relapsed/refractory setting have prompted trials of these immunotherapies in newly diagnosed B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL).
Blinatumomab and inotuzumab have been shown to improve overall survival, compared with chemotherapy, in patients with relapsed/refractory B-ALL. However, most adults with relapsed/refractory B-ALL still die, so the initial therapy patients receive is “critical,” according to Jae Park, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
“Ideally, we do not want to deal with the relapse,” Dr. Park said. “It’s better to cure the disease the first time ... which is the reason clinical trials are incorporating these agents earlier.”
Dr. Park discussed these points at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Blinatumomab
Dr. Park cited the phase 3 TOWER trial, which showed that blinatumomab produced better response rates and overall survival compared with standard chemotherapy. The trial enrolled 405 patients with Ph-negative relapsed/refractory B-ALL who were randomized to blinatumomab (n = 271) or chemotherapy (n = 134).
The rate of complete response (CR) with full, partial, or incomplete hematologic recovery was 44% with blinatumomab and 25% with chemotherapy (P less than .001). The median overall survival was 7.7 months and 4.0 months, respectively (P = .01; N Engl J Med 2017; 376:836-47).
Based on these data, researchers decided to test blinatumomab in newly diagnosed, elderly patients (65 years and older) with Ph-negative B-ALL in the phase 2 SWOG 1318 study. The study enrolled 31 patients, and 29 were eligible. Their median age at baseline was 75 years (range 66‐84 years).
The patients received blinatumomab for two to five cycles, followed by 18 months of maintenance with prednisone, vincristine, 6-mercaptopurine, and methotrexate. One patient went on to transplant.
In all, 66% of patients achieved a CR or CR with incomplete count recovery. The estimated overall survival was 79% at 6 months and 65% at 1 year. These results were presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (Blood. 2018;132:33).
Another study of blinatumomab as frontline treatment is the ECOG-E1910 trial. In this phase 3 study, researchers are testing chemotherapy, with or without blinatumomab, in adults (aged 30-70 years) with newly diagnosed, BCR-ABL-negative B-ALL. Results from this study are not yet available.
Inotuzumab ozogamicin
Dr. Park also discussed the INOVATE trial, in which inotuzumab ozogamicin bested standard chemotherapy. The trial enrolled patients with Ph-positive or negative, relapsed/refractory B-ALL.
The patients were randomized to inotuzumab (n = 141) or investigator’s choice of chemotherapy (n = 138). Some patients, 41% in the inotuzumab arm and 11% in the chemotherapy arm, went on to transplant.
The CR rate was 80.7% in the inotuzumab arm and 29.4% in the chemotherapy arm (P less than .001). The median progression-free survival was 5 months and 1.8 months, respectively (P less than .001). The median overall survival was 7.7 months and 6.7 months, respectively (P = .04; N Engl J Med 2016; 375:740-53).
Based on these results, researchers are testing inotuzumab as frontline therapy in young adults (aged 18-39 years) with CD22-positive, Ph-negative B-ALL. In the phase 3 A041501 trial, patients are receiving inotuzumab after the first and second courses of treatment with the CALGB 10403 chemotherapy regimen. Results from this trial are not yet available.
Dr. Park reported relationships with Allogene Therapeutics, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Incyte, Kite Pharma, Novartis, and Takeda.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM NCCN HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES
Novel research aims to improve ED care in sickle cell disease
Several initiatives are in the works to improve the management of patients with sickle cell disease in the ED, experts said at a recent webinar held by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
In 2014, the NHLBI released evidence-based guidelines for the management of patients with sickle cell disease. The expert panel provided recommendations on the treatment of acute complications of sickle cell disease, many of which are common reasons for ED visits.
Optimizing the treatment of acute complications, namely vasoocclusive crisis, is essential to ensure improved long-term outcomes, explained Paula Tanabe, PhD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Pain management
While the majority of pain-related ED visits in sickle cell are the result of vasoocclusive crisis, other causes, such as acute chest syndrome, abdominal catastrophes, and splenic sequestration, are also important.
The hallmark of pain management in this population is rapid and aggressive treatment with intravenous opioids. The use of individualized doses is also important, but if not available, an sickle cell disease–specific pain protocol can be used, she explained.
Recent evidence has confirmed the benefit of using an individualized (patient-specific) dosing protocol. Dr. Tanabe reported the results of a randomized pilot study that compared two pain protocols for patients undergoing a vasoocclusive episode in the ED.
“The reason we pursued this project is to generate additional evidence beyond the expert panel,” she said.
The primary outcome of the study was the difference in pain scores from arrival to discharge between patients receiving an individualized or weight-based dosing protocol. Secondary outcomes included safety, pain experience, and side effects, among others.
The researchers found that patients who received an individualized protocol had significantly lower pain scores, compared with a standard weight-based protocol (between-protocol pain score difference, 15.6 plus or minus 5.0; P = .002).
Additionally, patients in the individualized dosing arm were admitted less often than those in the weight-based arm (P = .03), Dr. Tanabe reported.
The findings from the previous study formed the basis for an ongoing study that is further examining the impact of patient-specific dosing in patients who present with a vasoocclusive episode. The COMPARE VOE study is currently enrolling patients and is being funded by NHLBI.
The NHLBI also provides funding to eight Sickle Cell Disease Implementation Consortium sites throughout the United States. The objective of this grant funding is to help implement NHLBI recommendations in the emergency setting.
Quality improvement
“One area [that] we want to improve is how quickly we administer [analgesic therapy] to patients when they are experiencing a vasoocclusive episode,” said Caroline Freiermuth, MD, of the University of Cincinnati.
Some common barriers to delivering rapid analgesia in this setting include difficulties in obtaining intravenous access, high patient volumes, lack of education, and provider biases, she explained.
With respect to high patient volumes, one strategy that may help overcome this barrier is to triage patients as Emergency Severity Index level 2, allowing for accelerated room placement.
Sickle cell patients undergoing vasoocclusive crisis meet the criteria for level 2 based on morbidity, degree of pain, and the level of resources often required.
Another important strategy is improving education related to sickle cell disease, particularly the high morbidity and mortality seen in these patients, Dr. Freiermuth said.
“The median lifespan for patients with HbSS disease is in the 40s, basically half of the lifespan of a typical American,” she said.
At present, acute chest syndrome is the principal cause of death in patients with sickle cell disease, and most frequently occurs during a vasoocclusive episode. As a result, screening for this complication is essential to reduce mortality in the emergency setting.
Dr. Freiermuth explained that one of the best ways to prevent acute chest syndrome is to encourage the use of incentive spirometry in patients undergoing a vasoocclusive episode.
In order to increase the likelihood of obtaining intravenous access, the use of ultrasound may help guide placement. Educating nurses on the proper use of ultrasound-guided placement of intravenous catheters is one practical approach, she said.
Alternatively, opioid analgesia can be administered subcutaneously. Benefits of subcutaneous delivery include comparable pharmacokinetics, less pain, and a reduced likelihood of sterile abscesses that are often seen with intramuscular administration.
Dr. Freiermuth outlined the quality-improvement initiative being tested at her institution, which involves the administration of parenteral opioid therapy during triage for sickle cell patients undergoing a suspected vasoocclusive crisis. The initiative was developed with input from both the emergency and hematology departments at the site.
Early results have shown no significant changes using this approach, but the data is still preliminary. Initial feedback has revealed that time to room placement has been the greatest barrier, she reported.
Dr. Tanabe reported grant/research support from the National Institutes of Health and the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Dr. Freiermuth reported research support from Pfizer.
Several initiatives are in the works to improve the management of patients with sickle cell disease in the ED, experts said at a recent webinar held by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
In 2014, the NHLBI released evidence-based guidelines for the management of patients with sickle cell disease. The expert panel provided recommendations on the treatment of acute complications of sickle cell disease, many of which are common reasons for ED visits.
Optimizing the treatment of acute complications, namely vasoocclusive crisis, is essential to ensure improved long-term outcomes, explained Paula Tanabe, PhD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Pain management
While the majority of pain-related ED visits in sickle cell are the result of vasoocclusive crisis, other causes, such as acute chest syndrome, abdominal catastrophes, and splenic sequestration, are also important.
The hallmark of pain management in this population is rapid and aggressive treatment with intravenous opioids. The use of individualized doses is also important, but if not available, an sickle cell disease–specific pain protocol can be used, she explained.
Recent evidence has confirmed the benefit of using an individualized (patient-specific) dosing protocol. Dr. Tanabe reported the results of a randomized pilot study that compared two pain protocols for patients undergoing a vasoocclusive episode in the ED.
“The reason we pursued this project is to generate additional evidence beyond the expert panel,” she said.
The primary outcome of the study was the difference in pain scores from arrival to discharge between patients receiving an individualized or weight-based dosing protocol. Secondary outcomes included safety, pain experience, and side effects, among others.
The researchers found that patients who received an individualized protocol had significantly lower pain scores, compared with a standard weight-based protocol (between-protocol pain score difference, 15.6 plus or minus 5.0; P = .002).
Additionally, patients in the individualized dosing arm were admitted less often than those in the weight-based arm (P = .03), Dr. Tanabe reported.
The findings from the previous study formed the basis for an ongoing study that is further examining the impact of patient-specific dosing in patients who present with a vasoocclusive episode. The COMPARE VOE study is currently enrolling patients and is being funded by NHLBI.
The NHLBI also provides funding to eight Sickle Cell Disease Implementation Consortium sites throughout the United States. The objective of this grant funding is to help implement NHLBI recommendations in the emergency setting.
Quality improvement
“One area [that] we want to improve is how quickly we administer [analgesic therapy] to patients when they are experiencing a vasoocclusive episode,” said Caroline Freiermuth, MD, of the University of Cincinnati.
Some common barriers to delivering rapid analgesia in this setting include difficulties in obtaining intravenous access, high patient volumes, lack of education, and provider biases, she explained.
With respect to high patient volumes, one strategy that may help overcome this barrier is to triage patients as Emergency Severity Index level 2, allowing for accelerated room placement.
Sickle cell patients undergoing vasoocclusive crisis meet the criteria for level 2 based on morbidity, degree of pain, and the level of resources often required.
Another important strategy is improving education related to sickle cell disease, particularly the high morbidity and mortality seen in these patients, Dr. Freiermuth said.
“The median lifespan for patients with HbSS disease is in the 40s, basically half of the lifespan of a typical American,” she said.
At present, acute chest syndrome is the principal cause of death in patients with sickle cell disease, and most frequently occurs during a vasoocclusive episode. As a result, screening for this complication is essential to reduce mortality in the emergency setting.
Dr. Freiermuth explained that one of the best ways to prevent acute chest syndrome is to encourage the use of incentive spirometry in patients undergoing a vasoocclusive episode.
In order to increase the likelihood of obtaining intravenous access, the use of ultrasound may help guide placement. Educating nurses on the proper use of ultrasound-guided placement of intravenous catheters is one practical approach, she said.
Alternatively, opioid analgesia can be administered subcutaneously. Benefits of subcutaneous delivery include comparable pharmacokinetics, less pain, and a reduced likelihood of sterile abscesses that are often seen with intramuscular administration.
Dr. Freiermuth outlined the quality-improvement initiative being tested at her institution, which involves the administration of parenteral opioid therapy during triage for sickle cell patients undergoing a suspected vasoocclusive crisis. The initiative was developed with input from both the emergency and hematology departments at the site.
Early results have shown no significant changes using this approach, but the data is still preliminary. Initial feedback has revealed that time to room placement has been the greatest barrier, she reported.
Dr. Tanabe reported grant/research support from the National Institutes of Health and the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Dr. Freiermuth reported research support from Pfizer.
Several initiatives are in the works to improve the management of patients with sickle cell disease in the ED, experts said at a recent webinar held by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
In 2014, the NHLBI released evidence-based guidelines for the management of patients with sickle cell disease. The expert panel provided recommendations on the treatment of acute complications of sickle cell disease, many of which are common reasons for ED visits.
Optimizing the treatment of acute complications, namely vasoocclusive crisis, is essential to ensure improved long-term outcomes, explained Paula Tanabe, PhD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Pain management
While the majority of pain-related ED visits in sickle cell are the result of vasoocclusive crisis, other causes, such as acute chest syndrome, abdominal catastrophes, and splenic sequestration, are also important.
The hallmark of pain management in this population is rapid and aggressive treatment with intravenous opioids. The use of individualized doses is also important, but if not available, an sickle cell disease–specific pain protocol can be used, she explained.
Recent evidence has confirmed the benefit of using an individualized (patient-specific) dosing protocol. Dr. Tanabe reported the results of a randomized pilot study that compared two pain protocols for patients undergoing a vasoocclusive episode in the ED.
“The reason we pursued this project is to generate additional evidence beyond the expert panel,” she said.
The primary outcome of the study was the difference in pain scores from arrival to discharge between patients receiving an individualized or weight-based dosing protocol. Secondary outcomes included safety, pain experience, and side effects, among others.
The researchers found that patients who received an individualized protocol had significantly lower pain scores, compared with a standard weight-based protocol (between-protocol pain score difference, 15.6 plus or minus 5.0; P = .002).
Additionally, patients in the individualized dosing arm were admitted less often than those in the weight-based arm (P = .03), Dr. Tanabe reported.
The findings from the previous study formed the basis for an ongoing study that is further examining the impact of patient-specific dosing in patients who present with a vasoocclusive episode. The COMPARE VOE study is currently enrolling patients and is being funded by NHLBI.
The NHLBI also provides funding to eight Sickle Cell Disease Implementation Consortium sites throughout the United States. The objective of this grant funding is to help implement NHLBI recommendations in the emergency setting.
Quality improvement
“One area [that] we want to improve is how quickly we administer [analgesic therapy] to patients when they are experiencing a vasoocclusive episode,” said Caroline Freiermuth, MD, of the University of Cincinnati.
Some common barriers to delivering rapid analgesia in this setting include difficulties in obtaining intravenous access, high patient volumes, lack of education, and provider biases, she explained.
With respect to high patient volumes, one strategy that may help overcome this barrier is to triage patients as Emergency Severity Index level 2, allowing for accelerated room placement.
Sickle cell patients undergoing vasoocclusive crisis meet the criteria for level 2 based on morbidity, degree of pain, and the level of resources often required.
Another important strategy is improving education related to sickle cell disease, particularly the high morbidity and mortality seen in these patients, Dr. Freiermuth said.
“The median lifespan for patients with HbSS disease is in the 40s, basically half of the lifespan of a typical American,” she said.
At present, acute chest syndrome is the principal cause of death in patients with sickle cell disease, and most frequently occurs during a vasoocclusive episode. As a result, screening for this complication is essential to reduce mortality in the emergency setting.
Dr. Freiermuth explained that one of the best ways to prevent acute chest syndrome is to encourage the use of incentive spirometry in patients undergoing a vasoocclusive episode.
In order to increase the likelihood of obtaining intravenous access, the use of ultrasound may help guide placement. Educating nurses on the proper use of ultrasound-guided placement of intravenous catheters is one practical approach, she said.
Alternatively, opioid analgesia can be administered subcutaneously. Benefits of subcutaneous delivery include comparable pharmacokinetics, less pain, and a reduced likelihood of sterile abscesses that are often seen with intramuscular administration.
Dr. Freiermuth outlined the quality-improvement initiative being tested at her institution, which involves the administration of parenteral opioid therapy during triage for sickle cell patients undergoing a suspected vasoocclusive crisis. The initiative was developed with input from both the emergency and hematology departments at the site.
Early results have shown no significant changes using this approach, but the data is still preliminary. Initial feedback has revealed that time to room placement has been the greatest barrier, she reported.
Dr. Tanabe reported grant/research support from the National Institutes of Health and the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Dr. Freiermuth reported research support from Pfizer.
REPORTING FROM AN NIH WEBINAR
Second-generation anti-BCMA CAR T-cell therapy shows promise in myeloma trial
BOSTON – CT053, a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, has demonstrated efficacy and tolerability in a phase 1 trial of patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.
CT053 produced an objective response rate of 87.5% and a complete response rate of 79.2%. All patients experienced grade 3 or higher adverse events (AEs), but none developed grade 3 or higher cytokine-release syndrome (CRS).
Siguo Hao, MD, of Xinhua Hospital, Shanghai (China) Jiaotong University, presented these results at the International Myeloma Workshop held by the International Myeloma Society.
Dr. Hao explained that CT053 consists of autologous T cells modified with a second-generation CAR that incorporates a fully human anti–B-cell maturation antigen single-chain fragment variant, a 4-1BB costimulatory domain, and a CD3-zeta–signaling domain.
In preclinical studies, CT053 induced dose-dependent cytotoxic effects on multiple myeloma cell lines and completely eradicated myeloma in mice.
Dr. Hao and his colleagues conducted the phase 1 study of CT053 at three sites (NCT03716856, NCT03302403, and NCT03380039). The study enrolled 30 patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, and 24 ultimately received CT053.
In the 24 patients, the median age was 60.2 years (range, 38.5-70.0 years), and the median time since diagnosis was 3.5 years (range, 0.3-10.8 years). Nine patients had progressive disease at baseline.
The patients had received a median of 5 prior therapies (range, 2-12). All patients had received a proteasome inhibitor, 22 had received an immunomodulatory agent, 10 had undergone a transplant, and 5 had received an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody.
For this study, patients received conditioning with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, followed by a single infusion of CT053. Most patients (n = 21) received 1.5 x 108 cells, but three received 0.5 x 108, 1 x 108, and 1.8 x 108 cells, respectively.
The median follow-up was 333 days. CAR T cells were detectable 1-7 days after infusion and peaked at 7-21 days. The cells persisted for a median of 172 days (range, 21-341 days).
A total of 21 patients responded to treatment (87.5%). There were 19 patients with a complete response or stringent complete response, 1 patient with a very good partial response, and 1 with a partial response.
Dr. Hao noted that CT053 was effective even at the lowest dose. The patient who received 0.5 x 108 cells initially achieved a very good partial response that deepened to a stringent complete response on day 502 after infusion.
Ten patients still had a stringent complete response at last follow-up, and two had a complete response. Nine patients progressed, and one patient relapsed after achieving a complete response. Three patients died, two from disease progression and one from a serious AE (neutropenic infection).
All 24 patients experienced a treatment-related AE, and all had grade 3 or higher hematologic AEs. Six patients had grade 3 or higher fever, six had grade 3 or higher infections and infestations, and one had grade 3 or higher neurotoxicity.
Three patients had grade 1 CRS, and 12 had grade 2 CRS. None of the patients had grade 3 or higher CRS.
This trial was sponsored by Xinhua Hospital/Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University, and First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University in collaboration with Carsgen Therapeutics. Dr. Hao did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Hao S et al. IMW 2019, Abstract OAB-082.
BOSTON – CT053, a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, has demonstrated efficacy and tolerability in a phase 1 trial of patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.
CT053 produced an objective response rate of 87.5% and a complete response rate of 79.2%. All patients experienced grade 3 or higher adverse events (AEs), but none developed grade 3 or higher cytokine-release syndrome (CRS).
Siguo Hao, MD, of Xinhua Hospital, Shanghai (China) Jiaotong University, presented these results at the International Myeloma Workshop held by the International Myeloma Society.
Dr. Hao explained that CT053 consists of autologous T cells modified with a second-generation CAR that incorporates a fully human anti–B-cell maturation antigen single-chain fragment variant, a 4-1BB costimulatory domain, and a CD3-zeta–signaling domain.
In preclinical studies, CT053 induced dose-dependent cytotoxic effects on multiple myeloma cell lines and completely eradicated myeloma in mice.
Dr. Hao and his colleagues conducted the phase 1 study of CT053 at three sites (NCT03716856, NCT03302403, and NCT03380039). The study enrolled 30 patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, and 24 ultimately received CT053.
In the 24 patients, the median age was 60.2 years (range, 38.5-70.0 years), and the median time since diagnosis was 3.5 years (range, 0.3-10.8 years). Nine patients had progressive disease at baseline.
The patients had received a median of 5 prior therapies (range, 2-12). All patients had received a proteasome inhibitor, 22 had received an immunomodulatory agent, 10 had undergone a transplant, and 5 had received an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody.
For this study, patients received conditioning with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, followed by a single infusion of CT053. Most patients (n = 21) received 1.5 x 108 cells, but three received 0.5 x 108, 1 x 108, and 1.8 x 108 cells, respectively.
The median follow-up was 333 days. CAR T cells were detectable 1-7 days after infusion and peaked at 7-21 days. The cells persisted for a median of 172 days (range, 21-341 days).
A total of 21 patients responded to treatment (87.5%). There were 19 patients with a complete response or stringent complete response, 1 patient with a very good partial response, and 1 with a partial response.
Dr. Hao noted that CT053 was effective even at the lowest dose. The patient who received 0.5 x 108 cells initially achieved a very good partial response that deepened to a stringent complete response on day 502 after infusion.
Ten patients still had a stringent complete response at last follow-up, and two had a complete response. Nine patients progressed, and one patient relapsed after achieving a complete response. Three patients died, two from disease progression and one from a serious AE (neutropenic infection).
All 24 patients experienced a treatment-related AE, and all had grade 3 or higher hematologic AEs. Six patients had grade 3 or higher fever, six had grade 3 or higher infections and infestations, and one had grade 3 or higher neurotoxicity.
Three patients had grade 1 CRS, and 12 had grade 2 CRS. None of the patients had grade 3 or higher CRS.
This trial was sponsored by Xinhua Hospital/Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University, and First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University in collaboration with Carsgen Therapeutics. Dr. Hao did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Hao S et al. IMW 2019, Abstract OAB-082.
BOSTON – CT053, a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, has demonstrated efficacy and tolerability in a phase 1 trial of patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.
CT053 produced an objective response rate of 87.5% and a complete response rate of 79.2%. All patients experienced grade 3 or higher adverse events (AEs), but none developed grade 3 or higher cytokine-release syndrome (CRS).
Siguo Hao, MD, of Xinhua Hospital, Shanghai (China) Jiaotong University, presented these results at the International Myeloma Workshop held by the International Myeloma Society.
Dr. Hao explained that CT053 consists of autologous T cells modified with a second-generation CAR that incorporates a fully human anti–B-cell maturation antigen single-chain fragment variant, a 4-1BB costimulatory domain, and a CD3-zeta–signaling domain.
In preclinical studies, CT053 induced dose-dependent cytotoxic effects on multiple myeloma cell lines and completely eradicated myeloma in mice.
Dr. Hao and his colleagues conducted the phase 1 study of CT053 at three sites (NCT03716856, NCT03302403, and NCT03380039). The study enrolled 30 patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, and 24 ultimately received CT053.
In the 24 patients, the median age was 60.2 years (range, 38.5-70.0 years), and the median time since diagnosis was 3.5 years (range, 0.3-10.8 years). Nine patients had progressive disease at baseline.
The patients had received a median of 5 prior therapies (range, 2-12). All patients had received a proteasome inhibitor, 22 had received an immunomodulatory agent, 10 had undergone a transplant, and 5 had received an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody.
For this study, patients received conditioning with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, followed by a single infusion of CT053. Most patients (n = 21) received 1.5 x 108 cells, but three received 0.5 x 108, 1 x 108, and 1.8 x 108 cells, respectively.
The median follow-up was 333 days. CAR T cells were detectable 1-7 days after infusion and peaked at 7-21 days. The cells persisted for a median of 172 days (range, 21-341 days).
A total of 21 patients responded to treatment (87.5%). There were 19 patients with a complete response or stringent complete response, 1 patient with a very good partial response, and 1 with a partial response.
Dr. Hao noted that CT053 was effective even at the lowest dose. The patient who received 0.5 x 108 cells initially achieved a very good partial response that deepened to a stringent complete response on day 502 after infusion.
Ten patients still had a stringent complete response at last follow-up, and two had a complete response. Nine patients progressed, and one patient relapsed after achieving a complete response. Three patients died, two from disease progression and one from a serious AE (neutropenic infection).
All 24 patients experienced a treatment-related AE, and all had grade 3 or higher hematologic AEs. Six patients had grade 3 or higher fever, six had grade 3 or higher infections and infestations, and one had grade 3 or higher neurotoxicity.
Three patients had grade 1 CRS, and 12 had grade 2 CRS. None of the patients had grade 3 or higher CRS.
This trial was sponsored by Xinhua Hospital/Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University, and First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University in collaboration with Carsgen Therapeutics. Dr. Hao did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Hao S et al. IMW 2019, Abstract OAB-082.
REPORTING FROM IMW 2019