User login
Taking the heat out of coffee’s esophageal cancer risk
Whether coffee is good or bad for health is a frequent debate in the media, fueled by apparently conflicting studies suggesting the plethora of bioactive chemicals in the popular brew could either raise or lower cancer risk.
Now, an analysis by Cambridge scientists has suggested that while coffee is not associated with enhanced overall risk of non–digestive system cancers among people genetically predicted to drink more of it,
, although this might be explained by a tendency for drinking it warm or hot, the study in the journal Clinical Nutrition suggested.
Regular coffee drinking has been linked to a slightly lower risk of all-cause mortality. However, it remains unclear whether coffee consumption is associated with a lower risk of dying from cancer.
Hotly debated
In 2016, a working group of international scientists convened by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) found no conclusive evidence for a carcinogenic effect of drinking coffee. However, the experts did find that drinking very hot beverages was a probable cause of esophageal cancer, making “the temperature, rather than the drinks themselves” the most likely cause, according to the organization’s director.
This latest study concurred. “We provide strong evidence for a causal relationship which is large in magnitude (threefold) and consistent across sensitivity analyses and in a replication study,” it stated.
The Cambridge researchers, assisted by colleagues at the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm and Bristol Medical School, conducted a Mendelian randomization study to investigate causal associations between coffee consumption and 22 site-specific cancers using data of individuals of European descent in the UK Biobank.
They reported “no strong evidence supporting a causal relationship between genetically-predicted coffee consumption and the majority of cancers studied” (odds ratio [OR], in the main analysis 1.05, 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.98-1.14, P = .183), and remained without association after adjustments for predicted BMI, smoking, or alcohol consumption.
However, genetically predicted coffee consumption was linked to an increased risk of digestive system cancer (OR, 1.28, 95% CI, 1.09-1.51, P = .003), and the risk was largely attributed to “a strong association with esophageal cancer” (OR, 2.79, 95% CI, 1.73-4.50, P = 2.5x10-5). This risk association remained persistent after adjustment for confounders, the researchers said.
Coffee or tea?
Further analysis of the data found that increased risk of esophageal cancer was consistently associated with genetically predicted coffee consumption by individuals with a preference for warm and hot drinks. Among this group, a similar esophageal cancer risk profile among those who reported drinking one to three cups of coffee a day and those who said they did not drink coffee was most likely due to a high prevalence of tea drinking, the study authors said.
“It is, therefore, plausible that a carcinogenic effect of coffee relates to thermal injury broadly, rather than being specific to coffee or its constituents,” said the scientists, who highlighted that this was also pointed out by the IARC in its statement 6 years ago.
Genetically predicted coffee consumption was also found to be associated with increased risk of multiple myeloma (OR, 2.25, 95% CI, 1.30-3.89, P = .004) and reduced ovarian cancer risk (OR, 0.63, 95% CI, 0.43-0.93, P = .020).
The authors concluded there was “evidence for coffee consumption being causally associated with risk of esophageal cancer, with some evidence this is related to a temperature effect.” Otherwise, “our results do not support a linear causal association with the majority of cancer types studied, other than limited evidence for harmful and protective associations with multiple myeloma and ovarian cancers respectively.”
Further studies were needed to investigate “the possible mechanisms of coffee consumption in esophageal carcinogenesis,” they said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
Whether coffee is good or bad for health is a frequent debate in the media, fueled by apparently conflicting studies suggesting the plethora of bioactive chemicals in the popular brew could either raise or lower cancer risk.
Now, an analysis by Cambridge scientists has suggested that while coffee is not associated with enhanced overall risk of non–digestive system cancers among people genetically predicted to drink more of it,
, although this might be explained by a tendency for drinking it warm or hot, the study in the journal Clinical Nutrition suggested.
Regular coffee drinking has been linked to a slightly lower risk of all-cause mortality. However, it remains unclear whether coffee consumption is associated with a lower risk of dying from cancer.
Hotly debated
In 2016, a working group of international scientists convened by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) found no conclusive evidence for a carcinogenic effect of drinking coffee. However, the experts did find that drinking very hot beverages was a probable cause of esophageal cancer, making “the temperature, rather than the drinks themselves” the most likely cause, according to the organization’s director.
This latest study concurred. “We provide strong evidence for a causal relationship which is large in magnitude (threefold) and consistent across sensitivity analyses and in a replication study,” it stated.
The Cambridge researchers, assisted by colleagues at the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm and Bristol Medical School, conducted a Mendelian randomization study to investigate causal associations between coffee consumption and 22 site-specific cancers using data of individuals of European descent in the UK Biobank.
They reported “no strong evidence supporting a causal relationship between genetically-predicted coffee consumption and the majority of cancers studied” (odds ratio [OR], in the main analysis 1.05, 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.98-1.14, P = .183), and remained without association after adjustments for predicted BMI, smoking, or alcohol consumption.
However, genetically predicted coffee consumption was linked to an increased risk of digestive system cancer (OR, 1.28, 95% CI, 1.09-1.51, P = .003), and the risk was largely attributed to “a strong association with esophageal cancer” (OR, 2.79, 95% CI, 1.73-4.50, P = 2.5x10-5). This risk association remained persistent after adjustment for confounders, the researchers said.
Coffee or tea?
Further analysis of the data found that increased risk of esophageal cancer was consistently associated with genetically predicted coffee consumption by individuals with a preference for warm and hot drinks. Among this group, a similar esophageal cancer risk profile among those who reported drinking one to three cups of coffee a day and those who said they did not drink coffee was most likely due to a high prevalence of tea drinking, the study authors said.
“It is, therefore, plausible that a carcinogenic effect of coffee relates to thermal injury broadly, rather than being specific to coffee or its constituents,” said the scientists, who highlighted that this was also pointed out by the IARC in its statement 6 years ago.
Genetically predicted coffee consumption was also found to be associated with increased risk of multiple myeloma (OR, 2.25, 95% CI, 1.30-3.89, P = .004) and reduced ovarian cancer risk (OR, 0.63, 95% CI, 0.43-0.93, P = .020).
The authors concluded there was “evidence for coffee consumption being causally associated with risk of esophageal cancer, with some evidence this is related to a temperature effect.” Otherwise, “our results do not support a linear causal association with the majority of cancer types studied, other than limited evidence for harmful and protective associations with multiple myeloma and ovarian cancers respectively.”
Further studies were needed to investigate “the possible mechanisms of coffee consumption in esophageal carcinogenesis,” they said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
Whether coffee is good or bad for health is a frequent debate in the media, fueled by apparently conflicting studies suggesting the plethora of bioactive chemicals in the popular brew could either raise or lower cancer risk.
Now, an analysis by Cambridge scientists has suggested that while coffee is not associated with enhanced overall risk of non–digestive system cancers among people genetically predicted to drink more of it,
, although this might be explained by a tendency for drinking it warm or hot, the study in the journal Clinical Nutrition suggested.
Regular coffee drinking has been linked to a slightly lower risk of all-cause mortality. However, it remains unclear whether coffee consumption is associated with a lower risk of dying from cancer.
Hotly debated
In 2016, a working group of international scientists convened by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) found no conclusive evidence for a carcinogenic effect of drinking coffee. However, the experts did find that drinking very hot beverages was a probable cause of esophageal cancer, making “the temperature, rather than the drinks themselves” the most likely cause, according to the organization’s director.
This latest study concurred. “We provide strong evidence for a causal relationship which is large in magnitude (threefold) and consistent across sensitivity analyses and in a replication study,” it stated.
The Cambridge researchers, assisted by colleagues at the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm and Bristol Medical School, conducted a Mendelian randomization study to investigate causal associations between coffee consumption and 22 site-specific cancers using data of individuals of European descent in the UK Biobank.
They reported “no strong evidence supporting a causal relationship between genetically-predicted coffee consumption and the majority of cancers studied” (odds ratio [OR], in the main analysis 1.05, 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.98-1.14, P = .183), and remained without association after adjustments for predicted BMI, smoking, or alcohol consumption.
However, genetically predicted coffee consumption was linked to an increased risk of digestive system cancer (OR, 1.28, 95% CI, 1.09-1.51, P = .003), and the risk was largely attributed to “a strong association with esophageal cancer” (OR, 2.79, 95% CI, 1.73-4.50, P = 2.5x10-5). This risk association remained persistent after adjustment for confounders, the researchers said.
Coffee or tea?
Further analysis of the data found that increased risk of esophageal cancer was consistently associated with genetically predicted coffee consumption by individuals with a preference for warm and hot drinks. Among this group, a similar esophageal cancer risk profile among those who reported drinking one to three cups of coffee a day and those who said they did not drink coffee was most likely due to a high prevalence of tea drinking, the study authors said.
“It is, therefore, plausible that a carcinogenic effect of coffee relates to thermal injury broadly, rather than being specific to coffee or its constituents,” said the scientists, who highlighted that this was also pointed out by the IARC in its statement 6 years ago.
Genetically predicted coffee consumption was also found to be associated with increased risk of multiple myeloma (OR, 2.25, 95% CI, 1.30-3.89, P = .004) and reduced ovarian cancer risk (OR, 0.63, 95% CI, 0.43-0.93, P = .020).
The authors concluded there was “evidence for coffee consumption being causally associated with risk of esophageal cancer, with some evidence this is related to a temperature effect.” Otherwise, “our results do not support a linear causal association with the majority of cancer types studied, other than limited evidence for harmful and protective associations with multiple myeloma and ovarian cancers respectively.”
Further studies were needed to investigate “the possible mechanisms of coffee consumption in esophageal carcinogenesis,” they said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
FROM CLINICAL NUTRITION
How strength training can help you live longer
People who lift weights understand they’re playing a long game.
Once they get past the “newbie gains” – the quick and exciting increases in muscle strength and size – it takes time, effort, and patience to keep making progress.
Whether they know it or not, they’re also playing the longevity game.
A growing body of research shows that resistance training adds years to both lifespan and “healthspan” – the period of life when we’re in good health.
A 2022 study review from Japanese researchers linked “muscle-strengthening activities” to a 15% lower risk of all-cause mortality.
Resistance exercise was also linked to a lower risk of cardiovascular disease (17%), cancer (12%), and diabetes (17%).
We’ve known for a long time that strength is an excellent predictor of future health. Lots of research has shown that, if all else is equal, stronger men and women have a much lower risk of dying during a given period than people with less strength.
This new research shows that strength training offers similar protection, regardless of the results of that training. So even if you don’t think you’re getting as strong or as lean as you’d like to be, you should keep it up – because chances are, you’re still helping your health in a big way.
How strength training helps as you age
For longevity, strength training seems to be especially effective for older adults, says Roger Fielding, PhD, of Tufts University Medford, Mass., who’s been studying the role of exercise in the aging process since the early 1990s.
“With aging, we see clear deficits in muscle function and bone health,” he says. “That all can be slowed, attenuated, or reversed with appropriate exercise.”
His concept of “appropriate” has changed a lot in the past 3 decades. “When I first started studying this stuff, we would try to give people a very formalized prescription” for strength training, he says.
That strength-training prescription typically included a lot of sets (three per exercise), moderate reps (8-12 per set), and relatively heavy weights. It also required professional supervision in a well-equipped gym, which was both unappealing and impractical for most of the target population.
“What I’ve learned is that even lower-intensity strength training, at home, without a lot of specialized equipment, has some benefits,” he says.
Which benefits? That’s harder to say.
The research linking resistance exercise to lower mortality comes from large, population-wide surveys, looking at tens or even hundreds of thousands of people. The broad category of “muscle-strengthening exercises” can include anything from calisthenics in the living room to a serious bodybuilding or power-lifting program.
They’re also based on self-reporting by the people studied. Because of that, “we should be careful how we interpret some of these studies,” Dr. Fielding says.
How much strength training should you do?
That warning seems especially appropriate for the study’s most surprising conclusion: The maximum longevity benefit comes from one or two resistance exercise sessions a week totaling 30-60 minutes.
The study adds that it’s unclear why more strength training would have diminishing or even negative returns.
Robert Linkul, owner of Training the Older Adult in Shingle Springs, Calif., thinks the answer is perfectly clear.
“Less might be more for the beginning lifter,” he says. That’s why his new clients typically begin with two 50-minute workouts a week. But after 3 months, they need to train three times a week to continue seeing gains.
He currently has 14 clients who have been with him at least 16 years. Most of them started in their 50s and are now in their 60s or 70s. If there were any downside to working out more than two times a week, he’s pretty sure he would’ve seen it by now.
Live longer and move longer, too
Mr. Linkul says that his training program includes a lot more than lifting. Clients start each workout with 10-15 minutes of mobility and warm-up exercises. That’s followed by 15 minutes of strength training and 15 minutes of high-intensity resistance training (HIRT).
HIRT uses functional exercises – lifting and carrying dumbbells or kettlebells; pushing or pulling a weighted sled – to improve strength and endurance at the same time.
“Most of the clients I get are training for real-life function,” Mr. Linkul says.
Falling is one of their biggest concerns, and for good reason: According to the World Health Organization, it’s the second-leading cause of unintentional injury–related deaths worldwide, behind only traffic accidents.
Their other major concern is losing their independence, which often follows a fall. “They want to feel they’re not near using a cane or a walker or being stuck in a wheelchair,” he says. “The more we train, the further we get from that.”
That’s where strength training offers its most unique advantages, according to a 2019 study from researchers at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont. Resistance exercise is “particularly potent for maintaining mobility in older adults,” the study says.
Training for life
Traditional aerobic exercise also offers many of the same benefits, including longer life and a lower risk of cardiovascular disease, cancer, and diabetes.
But there’s no need to choose one or the other. As a recent study) noted, combining aerobic and strength exercises leads to a lower risk of early death than either of them separately.
Which makes perfect sense to Dr. Fielding.
“Usually, people who’re physically active aren’t just doing strength training alone,” he says. “Some exercise is better than no exercise,” and more is usually better than less. “People have to find things they like to do and want to do and are able to do consistently.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
People who lift weights understand they’re playing a long game.
Once they get past the “newbie gains” – the quick and exciting increases in muscle strength and size – it takes time, effort, and patience to keep making progress.
Whether they know it or not, they’re also playing the longevity game.
A growing body of research shows that resistance training adds years to both lifespan and “healthspan” – the period of life when we’re in good health.
A 2022 study review from Japanese researchers linked “muscle-strengthening activities” to a 15% lower risk of all-cause mortality.
Resistance exercise was also linked to a lower risk of cardiovascular disease (17%), cancer (12%), and diabetes (17%).
We’ve known for a long time that strength is an excellent predictor of future health. Lots of research has shown that, if all else is equal, stronger men and women have a much lower risk of dying during a given period than people with less strength.
This new research shows that strength training offers similar protection, regardless of the results of that training. So even if you don’t think you’re getting as strong or as lean as you’d like to be, you should keep it up – because chances are, you’re still helping your health in a big way.
How strength training helps as you age
For longevity, strength training seems to be especially effective for older adults, says Roger Fielding, PhD, of Tufts University Medford, Mass., who’s been studying the role of exercise in the aging process since the early 1990s.
“With aging, we see clear deficits in muscle function and bone health,” he says. “That all can be slowed, attenuated, or reversed with appropriate exercise.”
His concept of “appropriate” has changed a lot in the past 3 decades. “When I first started studying this stuff, we would try to give people a very formalized prescription” for strength training, he says.
That strength-training prescription typically included a lot of sets (three per exercise), moderate reps (8-12 per set), and relatively heavy weights. It also required professional supervision in a well-equipped gym, which was both unappealing and impractical for most of the target population.
“What I’ve learned is that even lower-intensity strength training, at home, without a lot of specialized equipment, has some benefits,” he says.
Which benefits? That’s harder to say.
The research linking resistance exercise to lower mortality comes from large, population-wide surveys, looking at tens or even hundreds of thousands of people. The broad category of “muscle-strengthening exercises” can include anything from calisthenics in the living room to a serious bodybuilding or power-lifting program.
They’re also based on self-reporting by the people studied. Because of that, “we should be careful how we interpret some of these studies,” Dr. Fielding says.
How much strength training should you do?
That warning seems especially appropriate for the study’s most surprising conclusion: The maximum longevity benefit comes from one or two resistance exercise sessions a week totaling 30-60 minutes.
The study adds that it’s unclear why more strength training would have diminishing or even negative returns.
Robert Linkul, owner of Training the Older Adult in Shingle Springs, Calif., thinks the answer is perfectly clear.
“Less might be more for the beginning lifter,” he says. That’s why his new clients typically begin with two 50-minute workouts a week. But after 3 months, they need to train three times a week to continue seeing gains.
He currently has 14 clients who have been with him at least 16 years. Most of them started in their 50s and are now in their 60s or 70s. If there were any downside to working out more than two times a week, he’s pretty sure he would’ve seen it by now.
Live longer and move longer, too
Mr. Linkul says that his training program includes a lot more than lifting. Clients start each workout with 10-15 minutes of mobility and warm-up exercises. That’s followed by 15 minutes of strength training and 15 minutes of high-intensity resistance training (HIRT).
HIRT uses functional exercises – lifting and carrying dumbbells or kettlebells; pushing or pulling a weighted sled – to improve strength and endurance at the same time.
“Most of the clients I get are training for real-life function,” Mr. Linkul says.
Falling is one of their biggest concerns, and for good reason: According to the World Health Organization, it’s the second-leading cause of unintentional injury–related deaths worldwide, behind only traffic accidents.
Their other major concern is losing their independence, which often follows a fall. “They want to feel they’re not near using a cane or a walker or being stuck in a wheelchair,” he says. “The more we train, the further we get from that.”
That’s where strength training offers its most unique advantages, according to a 2019 study from researchers at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont. Resistance exercise is “particularly potent for maintaining mobility in older adults,” the study says.
Training for life
Traditional aerobic exercise also offers many of the same benefits, including longer life and a lower risk of cardiovascular disease, cancer, and diabetes.
But there’s no need to choose one or the other. As a recent study) noted, combining aerobic and strength exercises leads to a lower risk of early death than either of them separately.
Which makes perfect sense to Dr. Fielding.
“Usually, people who’re physically active aren’t just doing strength training alone,” he says. “Some exercise is better than no exercise,” and more is usually better than less. “People have to find things they like to do and want to do and are able to do consistently.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
People who lift weights understand they’re playing a long game.
Once they get past the “newbie gains” – the quick and exciting increases in muscle strength and size – it takes time, effort, and patience to keep making progress.
Whether they know it or not, they’re also playing the longevity game.
A growing body of research shows that resistance training adds years to both lifespan and “healthspan” – the period of life when we’re in good health.
A 2022 study review from Japanese researchers linked “muscle-strengthening activities” to a 15% lower risk of all-cause mortality.
Resistance exercise was also linked to a lower risk of cardiovascular disease (17%), cancer (12%), and diabetes (17%).
We’ve known for a long time that strength is an excellent predictor of future health. Lots of research has shown that, if all else is equal, stronger men and women have a much lower risk of dying during a given period than people with less strength.
This new research shows that strength training offers similar protection, regardless of the results of that training. So even if you don’t think you’re getting as strong or as lean as you’d like to be, you should keep it up – because chances are, you’re still helping your health in a big way.
How strength training helps as you age
For longevity, strength training seems to be especially effective for older adults, says Roger Fielding, PhD, of Tufts University Medford, Mass., who’s been studying the role of exercise in the aging process since the early 1990s.
“With aging, we see clear deficits in muscle function and bone health,” he says. “That all can be slowed, attenuated, or reversed with appropriate exercise.”
His concept of “appropriate” has changed a lot in the past 3 decades. “When I first started studying this stuff, we would try to give people a very formalized prescription” for strength training, he says.
That strength-training prescription typically included a lot of sets (three per exercise), moderate reps (8-12 per set), and relatively heavy weights. It also required professional supervision in a well-equipped gym, which was both unappealing and impractical for most of the target population.
“What I’ve learned is that even lower-intensity strength training, at home, without a lot of specialized equipment, has some benefits,” he says.
Which benefits? That’s harder to say.
The research linking resistance exercise to lower mortality comes from large, population-wide surveys, looking at tens or even hundreds of thousands of people. The broad category of “muscle-strengthening exercises” can include anything from calisthenics in the living room to a serious bodybuilding or power-lifting program.
They’re also based on self-reporting by the people studied. Because of that, “we should be careful how we interpret some of these studies,” Dr. Fielding says.
How much strength training should you do?
That warning seems especially appropriate for the study’s most surprising conclusion: The maximum longevity benefit comes from one or two resistance exercise sessions a week totaling 30-60 minutes.
The study adds that it’s unclear why more strength training would have diminishing or even negative returns.
Robert Linkul, owner of Training the Older Adult in Shingle Springs, Calif., thinks the answer is perfectly clear.
“Less might be more for the beginning lifter,” he says. That’s why his new clients typically begin with two 50-minute workouts a week. But after 3 months, they need to train three times a week to continue seeing gains.
He currently has 14 clients who have been with him at least 16 years. Most of them started in their 50s and are now in their 60s or 70s. If there were any downside to working out more than two times a week, he’s pretty sure he would’ve seen it by now.
Live longer and move longer, too
Mr. Linkul says that his training program includes a lot more than lifting. Clients start each workout with 10-15 minutes of mobility and warm-up exercises. That’s followed by 15 minutes of strength training and 15 minutes of high-intensity resistance training (HIRT).
HIRT uses functional exercises – lifting and carrying dumbbells or kettlebells; pushing or pulling a weighted sled – to improve strength and endurance at the same time.
“Most of the clients I get are training for real-life function,” Mr. Linkul says.
Falling is one of their biggest concerns, and for good reason: According to the World Health Organization, it’s the second-leading cause of unintentional injury–related deaths worldwide, behind only traffic accidents.
Their other major concern is losing their independence, which often follows a fall. “They want to feel they’re not near using a cane or a walker or being stuck in a wheelchair,” he says. “The more we train, the further we get from that.”
That’s where strength training offers its most unique advantages, according to a 2019 study from researchers at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont. Resistance exercise is “particularly potent for maintaining mobility in older adults,” the study says.
Training for life
Traditional aerobic exercise also offers many of the same benefits, including longer life and a lower risk of cardiovascular disease, cancer, and diabetes.
But there’s no need to choose one or the other. As a recent study) noted, combining aerobic and strength exercises leads to a lower risk of early death than either of them separately.
Which makes perfect sense to Dr. Fielding.
“Usually, people who’re physically active aren’t just doing strength training alone,” he says. “Some exercise is better than no exercise,” and more is usually better than less. “People have to find things they like to do and want to do and are able to do consistently.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Early rhythm control improves cardiovascular outcomes in AFib patients regardless of stroke risk
These findings broaden support for early rhythm control, suggesting that physicians should be presenting the option to all patients diagnosed with AFib in routine clinical practice, lead author Daehoon Kim, MD, of Yonsei University, Seoul, South Korea, and colleagues reported.
In 2020, the EAST-AFNET 4 trial showed that early rhythm control was better than rate control for reducing adverse cardiovascular outcomes, but the trial only included patients at risk of stroke with a CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 2, leaving it unclear whether healthier patients might benefit from the same approach.
“Although the primary indication for rhythm control is to alleviate AF[ib]-related symptoms and improve quality of life, the current guidelines suggest younger age and no or few comorbid conditions as factors favoring rhythm control,” the investigators wrote in Annals of Internal Medicine. “Thus, the effect of rhythm control on cardiovascular outcomes in this population requires elucidation.”
Methods and results
The present study aimed to address this knowledge gap by reviewing data from 54,216 patients with AFib who had rhythm control (ablation or medication) or rate control within one year of diagnosis. Among these patients, 69.3% would have qualified for the EAST-AFNET 4 trial based on higher stroke risk, while the remaining 30.7% of patients would not have been eligible because of lower stroke risk. Median age, consequently, was higher in the former group, at 70 years, versus 54 years in the latter group.
Evaluating the same primary composite outcome as the EAST-AFNET 4 trial (cardiovascular death, ischemic stroke, hospitalization for heart failure, or MI) showed that patients benefited from rhythm control over rate control regardless of risk group.
Those in the higher risk group had a 14% reduced risk of negative cardiovascular outcomes (weighted hazard ratio, 0.86; 95% confidence interval, 0.81-0.92), while those in the lower risk group had a 19% reduced risk of adverse cardiovascular outcomes (weighted HR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.66-0.98). Safety profiles were similar across groups and management strategies.
Rhythm control well supported from statistical perspective
“We think that physicians should pursue early rhythm control in all patients diagnosed with AF[ib],” principal author Boyoung Joung, MD, PhD, of Yonsei University said in an interview. “Like catheter ablation, we support the idea that early rhythm control can be more effective and safely performed in younger and less frail populations.”
Xiaoxi Yao, PhD, MPH, associate professor of health services research at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., agreed that rhythm control is now well supported from a statistical perspective, but patients and physicians need to look beyond relative risk improvements, and remain pragmatic.
“There is a benefit, but the benefit is consistent in terms of hazard ratio, or relative risk,” Dr. Yao said in an interview. “You still find a smaller absolute risk difference.”
Patients in the United States – versus Korea where the investigators are based – also need to consider the out-of-pocket costs involved in rhythm control, Dr. Yao said, noting that unclear cost effectiveness may also prevent changes to American guidelines. Medication side effects and procedural risks should also be considered, she added, as well as time off from work needed for ablation.
Dr. Yao, who published a similar paper in June and previously evaluated the role of catheter ablation in routine practice, suggested that the youngest patients may have the most to gain from rhythm control. This is because even a small absolute benefit is magnified with time, she said.
“Since [younger patients] have another several decades to live ... then yes, there might be very significant long-term effects in terms of both symptom control and cardiovascular death and stroke,” Dr. Yao said.
For optimal patient selection, however, more advanced tools are needed, which is why Dr. Yao and her colleagues are exploring new technologies to improve risk-benefit analysis.
“We are not only interested in [a patient’s] baseline high or low risk, but also the extent of risk reduction [that rhythm control provides],” Dr. Yao said. “We are trying to see if there is an [artificial intelligence] or machine-learning approach that can help us provide each patient with a more accurate, individualized estimate to help them make their decision.”
Until then, Dr. Yao encouraged physicians to engage in shared decision-making with patients, making sure to discuss both statistical and practical considerations.
The study was funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare and the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety of the Republic of Korea. The investigators and Dr. Yao reported no conflicts.
These findings broaden support for early rhythm control, suggesting that physicians should be presenting the option to all patients diagnosed with AFib in routine clinical practice, lead author Daehoon Kim, MD, of Yonsei University, Seoul, South Korea, and colleagues reported.
In 2020, the EAST-AFNET 4 trial showed that early rhythm control was better than rate control for reducing adverse cardiovascular outcomes, but the trial only included patients at risk of stroke with a CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 2, leaving it unclear whether healthier patients might benefit from the same approach.
“Although the primary indication for rhythm control is to alleviate AF[ib]-related symptoms and improve quality of life, the current guidelines suggest younger age and no or few comorbid conditions as factors favoring rhythm control,” the investigators wrote in Annals of Internal Medicine. “Thus, the effect of rhythm control on cardiovascular outcomes in this population requires elucidation.”
Methods and results
The present study aimed to address this knowledge gap by reviewing data from 54,216 patients with AFib who had rhythm control (ablation or medication) or rate control within one year of diagnosis. Among these patients, 69.3% would have qualified for the EAST-AFNET 4 trial based on higher stroke risk, while the remaining 30.7% of patients would not have been eligible because of lower stroke risk. Median age, consequently, was higher in the former group, at 70 years, versus 54 years in the latter group.
Evaluating the same primary composite outcome as the EAST-AFNET 4 trial (cardiovascular death, ischemic stroke, hospitalization for heart failure, or MI) showed that patients benefited from rhythm control over rate control regardless of risk group.
Those in the higher risk group had a 14% reduced risk of negative cardiovascular outcomes (weighted hazard ratio, 0.86; 95% confidence interval, 0.81-0.92), while those in the lower risk group had a 19% reduced risk of adverse cardiovascular outcomes (weighted HR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.66-0.98). Safety profiles were similar across groups and management strategies.
Rhythm control well supported from statistical perspective
“We think that physicians should pursue early rhythm control in all patients diagnosed with AF[ib],” principal author Boyoung Joung, MD, PhD, of Yonsei University said in an interview. “Like catheter ablation, we support the idea that early rhythm control can be more effective and safely performed in younger and less frail populations.”
Xiaoxi Yao, PhD, MPH, associate professor of health services research at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., agreed that rhythm control is now well supported from a statistical perspective, but patients and physicians need to look beyond relative risk improvements, and remain pragmatic.
“There is a benefit, but the benefit is consistent in terms of hazard ratio, or relative risk,” Dr. Yao said in an interview. “You still find a smaller absolute risk difference.”
Patients in the United States – versus Korea where the investigators are based – also need to consider the out-of-pocket costs involved in rhythm control, Dr. Yao said, noting that unclear cost effectiveness may also prevent changes to American guidelines. Medication side effects and procedural risks should also be considered, she added, as well as time off from work needed for ablation.
Dr. Yao, who published a similar paper in June and previously evaluated the role of catheter ablation in routine practice, suggested that the youngest patients may have the most to gain from rhythm control. This is because even a small absolute benefit is magnified with time, she said.
“Since [younger patients] have another several decades to live ... then yes, there might be very significant long-term effects in terms of both symptom control and cardiovascular death and stroke,” Dr. Yao said.
For optimal patient selection, however, more advanced tools are needed, which is why Dr. Yao and her colleagues are exploring new technologies to improve risk-benefit analysis.
“We are not only interested in [a patient’s] baseline high or low risk, but also the extent of risk reduction [that rhythm control provides],” Dr. Yao said. “We are trying to see if there is an [artificial intelligence] or machine-learning approach that can help us provide each patient with a more accurate, individualized estimate to help them make their decision.”
Until then, Dr. Yao encouraged physicians to engage in shared decision-making with patients, making sure to discuss both statistical and practical considerations.
The study was funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare and the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety of the Republic of Korea. The investigators and Dr. Yao reported no conflicts.
These findings broaden support for early rhythm control, suggesting that physicians should be presenting the option to all patients diagnosed with AFib in routine clinical practice, lead author Daehoon Kim, MD, of Yonsei University, Seoul, South Korea, and colleagues reported.
In 2020, the EAST-AFNET 4 trial showed that early rhythm control was better than rate control for reducing adverse cardiovascular outcomes, but the trial only included patients at risk of stroke with a CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 2, leaving it unclear whether healthier patients might benefit from the same approach.
“Although the primary indication for rhythm control is to alleviate AF[ib]-related symptoms and improve quality of life, the current guidelines suggest younger age and no or few comorbid conditions as factors favoring rhythm control,” the investigators wrote in Annals of Internal Medicine. “Thus, the effect of rhythm control on cardiovascular outcomes in this population requires elucidation.”
Methods and results
The present study aimed to address this knowledge gap by reviewing data from 54,216 patients with AFib who had rhythm control (ablation or medication) or rate control within one year of diagnosis. Among these patients, 69.3% would have qualified for the EAST-AFNET 4 trial based on higher stroke risk, while the remaining 30.7% of patients would not have been eligible because of lower stroke risk. Median age, consequently, was higher in the former group, at 70 years, versus 54 years in the latter group.
Evaluating the same primary composite outcome as the EAST-AFNET 4 trial (cardiovascular death, ischemic stroke, hospitalization for heart failure, or MI) showed that patients benefited from rhythm control over rate control regardless of risk group.
Those in the higher risk group had a 14% reduced risk of negative cardiovascular outcomes (weighted hazard ratio, 0.86; 95% confidence interval, 0.81-0.92), while those in the lower risk group had a 19% reduced risk of adverse cardiovascular outcomes (weighted HR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.66-0.98). Safety profiles were similar across groups and management strategies.
Rhythm control well supported from statistical perspective
“We think that physicians should pursue early rhythm control in all patients diagnosed with AF[ib],” principal author Boyoung Joung, MD, PhD, of Yonsei University said in an interview. “Like catheter ablation, we support the idea that early rhythm control can be more effective and safely performed in younger and less frail populations.”
Xiaoxi Yao, PhD, MPH, associate professor of health services research at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., agreed that rhythm control is now well supported from a statistical perspective, but patients and physicians need to look beyond relative risk improvements, and remain pragmatic.
“There is a benefit, but the benefit is consistent in terms of hazard ratio, or relative risk,” Dr. Yao said in an interview. “You still find a smaller absolute risk difference.”
Patients in the United States – versus Korea where the investigators are based – also need to consider the out-of-pocket costs involved in rhythm control, Dr. Yao said, noting that unclear cost effectiveness may also prevent changes to American guidelines. Medication side effects and procedural risks should also be considered, she added, as well as time off from work needed for ablation.
Dr. Yao, who published a similar paper in June and previously evaluated the role of catheter ablation in routine practice, suggested that the youngest patients may have the most to gain from rhythm control. This is because even a small absolute benefit is magnified with time, she said.
“Since [younger patients] have another several decades to live ... then yes, there might be very significant long-term effects in terms of both symptom control and cardiovascular death and stroke,” Dr. Yao said.
For optimal patient selection, however, more advanced tools are needed, which is why Dr. Yao and her colleagues are exploring new technologies to improve risk-benefit analysis.
“We are not only interested in [a patient’s] baseline high or low risk, but also the extent of risk reduction [that rhythm control provides],” Dr. Yao said. “We are trying to see if there is an [artificial intelligence] or machine-learning approach that can help us provide each patient with a more accurate, individualized estimate to help them make their decision.”
Until then, Dr. Yao encouraged physicians to engage in shared decision-making with patients, making sure to discuss both statistical and practical considerations.
The study was funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare and the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety of the Republic of Korea. The investigators and Dr. Yao reported no conflicts.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Hepatitis C meds linked to improved PTSD symptoms
The combination of the two antiviral medications glecaprevir and pibrentasvir (Mavyret) is linked to improved symptoms in posttraumatic stress disorder, new research suggests.
A national cohort study of U.S. Veterans Affairs patients included more than 250 participants with PTSD and comorbid hepatitis C virus.
Results showed in the study, including ledipasvir/sofosbuvir.
“While there are great treatments available for PTSD, there’s a lot of desire in the field to find a new medication that will be helpful,” lead author Brian Shiner, MD, acting associate chief of staff for research, VA Medical Center, White River Junction, Vt., told this news organization.
“We had a great opportunity to use a novel data mining method to look in a wonderful database for a new treatment and we found something very promising,” said Dr. Shiner, who is also an associate professor of psychiatry at the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H.
The findings were published online in the American Journal of Epidemiology.
Common psychiatric disorder
PTSD is one of the most common psychiatric disorders, with an estimated lifetime prevalence of 6.4% in the United States. Yet only two drugs, the SSRIs sertraline (Zoloft) and paroxetine (Paxil), have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat PTSD.
The VA recommends trauma-based psychotherapy, such as prolonged exposure and cognitive processing therapy, as first-line treatments for PTSD. However, not all patents respond to or have access to these approaches, said Dr. Shiner.
The investigators wanted to examine whether existing medications might reduce PTSD symptoms. Their previous exploratory study used “data mining” of national VA medical records.
Results from that study showed the three hepatitis C antivirals of GLE (an NS3/4A protease inhibitor), PIB (a NS5A protein inhibitor), and velpatasvir (another NS5A protein inhibitor) were associated with more than double the expected number of patients experiencing a clinically meaningful improvement in PTSD symptoms.
Sertraline was associated with only a slightly higher than expected improvement.
“SSRIs are effective, better than placebo, but the effects are not as good as we would hope,” Dr. Shiner said.
He noted that GLE and PIB are always prescribed together (Mavyret), whereas velpatasvir is commonly prescribed with the NS5B polymerase inhibitor sofosbuvir under the brand name Epclusa. Sofosbuvir is also commonly prescribed with the NS5A protein inhibitor ledipasvir under the brand name Harvoni.
Strong association
The new study included 253 VA users with a diagnosis of PTSD and hepatitis C. Of these, 54 were receiving GLE/PIB, 145 were receiving ledipasvir/sofosbuvir, and 54 were receiving sofosbuvir/velpatasvir.
Researchers compared the groups with respect to change over 8-12 weeks on the PTSD Checklist (PCL), a 20-item self-report scale.
In adjusted analyses, the largest mean improvement on the PCL was 14.9 points for the GLE/PIB group and the smallest adjusted mean improvement on the PCL was 7.5 points for the ledipasvir/sofosbuvir group (mean difference, 7.34 points; 95% confidence interval, 1.05-13.63).
The adjusted proportion of patients improving by 15 points or more on the PCL was highest for the GLE/PIB group at 43.6% and lowest for the ledipasvir/sofosbuvir group at 26.3%.
Even when accounting for patients receiving trauma-based therapy or SSRIs, “it still looks like there’s a strong association of the hepatitis C antivirals with PTSD symptom improvement,” said Dr. Shiner.
Researchers also carried out a sensitivity analysis among only patients who were cured of HCV (over 90% of the total sample), defined as having an undetectable HCV viral load up to a year after completion of therapy. The analysis showed PTSD outcomes were still superior for participants receiving GLE/PIB.
“The sensitivity analysis was not that robust because almost everyone was cured, so it included almost everybody, but it didn’t point us away from the possibility of an off-target effect,” Dr. Shiner said.
Why antivirals may improve PTSD symptoms is not clear, but they may affect the immune response in patients with hepatitis C – and there may also be an immune response in PTSD, he noted. “Some of those factors may be shared, and that could explain some of the off-target effect.”
However, he noted the GLE/PIB drug combination is costly and patients with PTSD can probably access it only through enrolling in a study.
“We are not recommending that people go out and purchase this very expensive drug to treat their PTSD at this point,” Dr. Shiner said.
He added that the research team has now received funding from the Department of Defense to conduct a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of GLE/PIB as a potential treatment for PTSD.
Promising potential treatment
PTSD expert Elspeth Cameron Ritchie, MD, chief of psychiatry at Medstar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, D.C., said the results suggest GLE/PIB is a promising potential treatment for PTSD.
“I definitely think this should be looked at further,” said Dr. Ritchie, who was not involved with the research.
She noted that current PTSD therapies have drawbacks. SSRIs have side effects, the most “troubling” being sexual dysfunction. And although cognitive-behavioral therapy is effective, “people have to stick with it” and studies show about two thirds of patients drop out, she said.
Potentially effective PTSD treatment approaches include “self-soothing” or “self-regulating” techniques such as exercise, meditation, yoga, and working with animals, she added.
Dr. Ritchie pointed out the numbers of participants in the study were relatively small, including two groups that had only 54 patients each.
And while the GLE/PIB combination should be explored further, cost, availability, and side effects of this medication need to be taken into consideration, she said.
Dr. Ritchie added she is not overly concerned that the mechanism of action for the combination on PTSD may not be well understood. She noted several psychiatric medications fall into that category, including electroconvulsive therapy and lithium.
“When lithium was first found to be effective against bipolar disorder, we had no clue why,” she said. “So I would not discount the antiviral based on us not knowing how it works.”
However, “we’re a long way off” from starting a patient with PTSD on an antiviral, said Dr. Ritchie, adding there are “a lot of steps to go through” to get FDA approval.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Mental Health. The cohort used for this study was developed through support from the Department of Defense. Dr. Shiner is a coinventor on a provisional patent application covering the use of glecaprevir, pibrentasvir, and velpatasvir for PTSD and other psychiatric indications. Dr. Ritchie reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The combination of the two antiviral medications glecaprevir and pibrentasvir (Mavyret) is linked to improved symptoms in posttraumatic stress disorder, new research suggests.
A national cohort study of U.S. Veterans Affairs patients included more than 250 participants with PTSD and comorbid hepatitis C virus.
Results showed in the study, including ledipasvir/sofosbuvir.
“While there are great treatments available for PTSD, there’s a lot of desire in the field to find a new medication that will be helpful,” lead author Brian Shiner, MD, acting associate chief of staff for research, VA Medical Center, White River Junction, Vt., told this news organization.
“We had a great opportunity to use a novel data mining method to look in a wonderful database for a new treatment and we found something very promising,” said Dr. Shiner, who is also an associate professor of psychiatry at the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H.
The findings were published online in the American Journal of Epidemiology.
Common psychiatric disorder
PTSD is one of the most common psychiatric disorders, with an estimated lifetime prevalence of 6.4% in the United States. Yet only two drugs, the SSRIs sertraline (Zoloft) and paroxetine (Paxil), have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat PTSD.
The VA recommends trauma-based psychotherapy, such as prolonged exposure and cognitive processing therapy, as first-line treatments for PTSD. However, not all patents respond to or have access to these approaches, said Dr. Shiner.
The investigators wanted to examine whether existing medications might reduce PTSD symptoms. Their previous exploratory study used “data mining” of national VA medical records.
Results from that study showed the three hepatitis C antivirals of GLE (an NS3/4A protease inhibitor), PIB (a NS5A protein inhibitor), and velpatasvir (another NS5A protein inhibitor) were associated with more than double the expected number of patients experiencing a clinically meaningful improvement in PTSD symptoms.
Sertraline was associated with only a slightly higher than expected improvement.
“SSRIs are effective, better than placebo, but the effects are not as good as we would hope,” Dr. Shiner said.
He noted that GLE and PIB are always prescribed together (Mavyret), whereas velpatasvir is commonly prescribed with the NS5B polymerase inhibitor sofosbuvir under the brand name Epclusa. Sofosbuvir is also commonly prescribed with the NS5A protein inhibitor ledipasvir under the brand name Harvoni.
Strong association
The new study included 253 VA users with a diagnosis of PTSD and hepatitis C. Of these, 54 were receiving GLE/PIB, 145 were receiving ledipasvir/sofosbuvir, and 54 were receiving sofosbuvir/velpatasvir.
Researchers compared the groups with respect to change over 8-12 weeks on the PTSD Checklist (PCL), a 20-item self-report scale.
In adjusted analyses, the largest mean improvement on the PCL was 14.9 points for the GLE/PIB group and the smallest adjusted mean improvement on the PCL was 7.5 points for the ledipasvir/sofosbuvir group (mean difference, 7.34 points; 95% confidence interval, 1.05-13.63).
The adjusted proportion of patients improving by 15 points or more on the PCL was highest for the GLE/PIB group at 43.6% and lowest for the ledipasvir/sofosbuvir group at 26.3%.
Even when accounting for patients receiving trauma-based therapy or SSRIs, “it still looks like there’s a strong association of the hepatitis C antivirals with PTSD symptom improvement,” said Dr. Shiner.
Researchers also carried out a sensitivity analysis among only patients who were cured of HCV (over 90% of the total sample), defined as having an undetectable HCV viral load up to a year after completion of therapy. The analysis showed PTSD outcomes were still superior for participants receiving GLE/PIB.
“The sensitivity analysis was not that robust because almost everyone was cured, so it included almost everybody, but it didn’t point us away from the possibility of an off-target effect,” Dr. Shiner said.
Why antivirals may improve PTSD symptoms is not clear, but they may affect the immune response in patients with hepatitis C – and there may also be an immune response in PTSD, he noted. “Some of those factors may be shared, and that could explain some of the off-target effect.”
However, he noted the GLE/PIB drug combination is costly and patients with PTSD can probably access it only through enrolling in a study.
“We are not recommending that people go out and purchase this very expensive drug to treat their PTSD at this point,” Dr. Shiner said.
He added that the research team has now received funding from the Department of Defense to conduct a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of GLE/PIB as a potential treatment for PTSD.
Promising potential treatment
PTSD expert Elspeth Cameron Ritchie, MD, chief of psychiatry at Medstar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, D.C., said the results suggest GLE/PIB is a promising potential treatment for PTSD.
“I definitely think this should be looked at further,” said Dr. Ritchie, who was not involved with the research.
She noted that current PTSD therapies have drawbacks. SSRIs have side effects, the most “troubling” being sexual dysfunction. And although cognitive-behavioral therapy is effective, “people have to stick with it” and studies show about two thirds of patients drop out, she said.
Potentially effective PTSD treatment approaches include “self-soothing” or “self-regulating” techniques such as exercise, meditation, yoga, and working with animals, she added.
Dr. Ritchie pointed out the numbers of participants in the study were relatively small, including two groups that had only 54 patients each.
And while the GLE/PIB combination should be explored further, cost, availability, and side effects of this medication need to be taken into consideration, she said.
Dr. Ritchie added she is not overly concerned that the mechanism of action for the combination on PTSD may not be well understood. She noted several psychiatric medications fall into that category, including electroconvulsive therapy and lithium.
“When lithium was first found to be effective against bipolar disorder, we had no clue why,” she said. “So I would not discount the antiviral based on us not knowing how it works.”
However, “we’re a long way off” from starting a patient with PTSD on an antiviral, said Dr. Ritchie, adding there are “a lot of steps to go through” to get FDA approval.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Mental Health. The cohort used for this study was developed through support from the Department of Defense. Dr. Shiner is a coinventor on a provisional patent application covering the use of glecaprevir, pibrentasvir, and velpatasvir for PTSD and other psychiatric indications. Dr. Ritchie reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The combination of the two antiviral medications glecaprevir and pibrentasvir (Mavyret) is linked to improved symptoms in posttraumatic stress disorder, new research suggests.
A national cohort study of U.S. Veterans Affairs patients included more than 250 participants with PTSD and comorbid hepatitis C virus.
Results showed in the study, including ledipasvir/sofosbuvir.
“While there are great treatments available for PTSD, there’s a lot of desire in the field to find a new medication that will be helpful,” lead author Brian Shiner, MD, acting associate chief of staff for research, VA Medical Center, White River Junction, Vt., told this news organization.
“We had a great opportunity to use a novel data mining method to look in a wonderful database for a new treatment and we found something very promising,” said Dr. Shiner, who is also an associate professor of psychiatry at the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H.
The findings were published online in the American Journal of Epidemiology.
Common psychiatric disorder
PTSD is one of the most common psychiatric disorders, with an estimated lifetime prevalence of 6.4% in the United States. Yet only two drugs, the SSRIs sertraline (Zoloft) and paroxetine (Paxil), have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat PTSD.
The VA recommends trauma-based psychotherapy, such as prolonged exposure and cognitive processing therapy, as first-line treatments for PTSD. However, not all patents respond to or have access to these approaches, said Dr. Shiner.
The investigators wanted to examine whether existing medications might reduce PTSD symptoms. Their previous exploratory study used “data mining” of national VA medical records.
Results from that study showed the three hepatitis C antivirals of GLE (an NS3/4A protease inhibitor), PIB (a NS5A protein inhibitor), and velpatasvir (another NS5A protein inhibitor) were associated with more than double the expected number of patients experiencing a clinically meaningful improvement in PTSD symptoms.
Sertraline was associated with only a slightly higher than expected improvement.
“SSRIs are effective, better than placebo, but the effects are not as good as we would hope,” Dr. Shiner said.
He noted that GLE and PIB are always prescribed together (Mavyret), whereas velpatasvir is commonly prescribed with the NS5B polymerase inhibitor sofosbuvir under the brand name Epclusa. Sofosbuvir is also commonly prescribed with the NS5A protein inhibitor ledipasvir under the brand name Harvoni.
Strong association
The new study included 253 VA users with a diagnosis of PTSD and hepatitis C. Of these, 54 were receiving GLE/PIB, 145 were receiving ledipasvir/sofosbuvir, and 54 were receiving sofosbuvir/velpatasvir.
Researchers compared the groups with respect to change over 8-12 weeks on the PTSD Checklist (PCL), a 20-item self-report scale.
In adjusted analyses, the largest mean improvement on the PCL was 14.9 points for the GLE/PIB group and the smallest adjusted mean improvement on the PCL was 7.5 points for the ledipasvir/sofosbuvir group (mean difference, 7.34 points; 95% confidence interval, 1.05-13.63).
The adjusted proportion of patients improving by 15 points or more on the PCL was highest for the GLE/PIB group at 43.6% and lowest for the ledipasvir/sofosbuvir group at 26.3%.
Even when accounting for patients receiving trauma-based therapy or SSRIs, “it still looks like there’s a strong association of the hepatitis C antivirals with PTSD symptom improvement,” said Dr. Shiner.
Researchers also carried out a sensitivity analysis among only patients who were cured of HCV (over 90% of the total sample), defined as having an undetectable HCV viral load up to a year after completion of therapy. The analysis showed PTSD outcomes were still superior for participants receiving GLE/PIB.
“The sensitivity analysis was not that robust because almost everyone was cured, so it included almost everybody, but it didn’t point us away from the possibility of an off-target effect,” Dr. Shiner said.
Why antivirals may improve PTSD symptoms is not clear, but they may affect the immune response in patients with hepatitis C – and there may also be an immune response in PTSD, he noted. “Some of those factors may be shared, and that could explain some of the off-target effect.”
However, he noted the GLE/PIB drug combination is costly and patients with PTSD can probably access it only through enrolling in a study.
“We are not recommending that people go out and purchase this very expensive drug to treat their PTSD at this point,” Dr. Shiner said.
He added that the research team has now received funding from the Department of Defense to conduct a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of GLE/PIB as a potential treatment for PTSD.
Promising potential treatment
PTSD expert Elspeth Cameron Ritchie, MD, chief of psychiatry at Medstar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, D.C., said the results suggest GLE/PIB is a promising potential treatment for PTSD.
“I definitely think this should be looked at further,” said Dr. Ritchie, who was not involved with the research.
She noted that current PTSD therapies have drawbacks. SSRIs have side effects, the most “troubling” being sexual dysfunction. And although cognitive-behavioral therapy is effective, “people have to stick with it” and studies show about two thirds of patients drop out, she said.
Potentially effective PTSD treatment approaches include “self-soothing” or “self-regulating” techniques such as exercise, meditation, yoga, and working with animals, she added.
Dr. Ritchie pointed out the numbers of participants in the study were relatively small, including two groups that had only 54 patients each.
And while the GLE/PIB combination should be explored further, cost, availability, and side effects of this medication need to be taken into consideration, she said.
Dr. Ritchie added she is not overly concerned that the mechanism of action for the combination on PTSD may not be well understood. She noted several psychiatric medications fall into that category, including electroconvulsive therapy and lithium.
“When lithium was first found to be effective against bipolar disorder, we had no clue why,” she said. “So I would not discount the antiviral based on us not knowing how it works.”
However, “we’re a long way off” from starting a patient with PTSD on an antiviral, said Dr. Ritchie, adding there are “a lot of steps to go through” to get FDA approval.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Mental Health. The cohort used for this study was developed through support from the Department of Defense. Dr. Shiner is a coinventor on a provisional patent application covering the use of glecaprevir, pibrentasvir, and velpatasvir for PTSD and other psychiatric indications. Dr. Ritchie reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Acute myocarditis a possible complication of monkeypox
Clinicians in Portugal say a 31-year-old man with confirmed monkeypox developed acute myocarditis roughly 1 week after the eruption of the characteristic skin lesions of the disease.
Ana Isabel Pinho, MD, department of cardiology, São João University Hospital Centre, Porto, Portugal, said in a news release.
“We believe that reporting this potential causal relationship can raise more awareness of the scientific community and health professionals for acute myocarditis as a possible complication associated with monkeypox and might be helpful for close monitoring of affected patients for further recognition of other complications in the future,” Dr. Pinho adds.
Dr. Pinho and colleagues describe the case in a report published in JACC: Case Reports.
Case details
The patient presented with a 5-day history of malaise, myalgias, and fever followed by the eruption of multiple swollen skin lesions on his face, hands, and genitalia.
Monkeypox was confirmed by positive polymerase chain reaction assay of a swab sample from a skin lesion.
Three days later, the patient developed chest tightness that radiated through the left arm and which awoke him during the night. He was admitted to an intensive care unit with clinical suspicion of acute myocarditis.
The patient’s initial electrocardiogram showed sinus rhythm with nonspecific ventricular repolarization abnormalities.
On chest x-ray, the cardiothoracic index was normal, with no interstitial infiltrates, pleural effusion, or masses. On transthoracic echocardigraphy, biventricular systolic function was preserved, and there was no pericardial effusion.
Routine laboratory tests revealed elevated levels of C-reactive protein, creatine phosphokinase, high-sensitivity troponin I, and brain natriuretic peptide, suggesting stress injury to the heart.
Findings on cardiac magnetic resonance were consistent with myocardial inflammation and acute myocarditis.
The patient was treated with supportive care, and he made a full clinical recovery. He was discharged after 1 week. On discharge, cardiac enzymes were within the normal range. The patient showed sustained electric and hemodynamic stability, and the skin lesions had healed.
“Through this important case study, we are developing a deeper understanding of monkeypox, viral myocarditis, and how to accurately diagnose and manage this disease,” Julia Grapsa, MD, PhD, editor-in-chief of JACC: Case Reports, commented in the news release.
“I commend the authors on this valuable clinical case during a critical time as monkeypox continues to spread globally,” Dr. Grapsa added.
The researchers say further research is needed to identify the pathologic mechanism underlying monkeypox-associated cardiac injury.
By the numbers
According to the latest data, California has reported 3,629 cases, followed closely by New York with 3,367 cases, Florida with 1,957 cases, Texas with 1,698, Georgia with 1,418, and Illinois with 1,081. The other states have reported fewer than 600 cases.
The CDC says that globally, more than 52,000 monkeypox cases have been reported.
Monkeypox case counts appear to be slowing in the United States and globally.
Last week, the World Health Organization said the number of new cases worldwide declined by 21% between Aug. 15 and 21 after increasing for 4 straight weeks.
The research had no funding. Dr. Pinho and colleagues have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinicians in Portugal say a 31-year-old man with confirmed monkeypox developed acute myocarditis roughly 1 week after the eruption of the characteristic skin lesions of the disease.
Ana Isabel Pinho, MD, department of cardiology, São João University Hospital Centre, Porto, Portugal, said in a news release.
“We believe that reporting this potential causal relationship can raise more awareness of the scientific community and health professionals for acute myocarditis as a possible complication associated with monkeypox and might be helpful for close monitoring of affected patients for further recognition of other complications in the future,” Dr. Pinho adds.
Dr. Pinho and colleagues describe the case in a report published in JACC: Case Reports.
Case details
The patient presented with a 5-day history of malaise, myalgias, and fever followed by the eruption of multiple swollen skin lesions on his face, hands, and genitalia.
Monkeypox was confirmed by positive polymerase chain reaction assay of a swab sample from a skin lesion.
Three days later, the patient developed chest tightness that radiated through the left arm and which awoke him during the night. He was admitted to an intensive care unit with clinical suspicion of acute myocarditis.
The patient’s initial electrocardiogram showed sinus rhythm with nonspecific ventricular repolarization abnormalities.
On chest x-ray, the cardiothoracic index was normal, with no interstitial infiltrates, pleural effusion, or masses. On transthoracic echocardigraphy, biventricular systolic function was preserved, and there was no pericardial effusion.
Routine laboratory tests revealed elevated levels of C-reactive protein, creatine phosphokinase, high-sensitivity troponin I, and brain natriuretic peptide, suggesting stress injury to the heart.
Findings on cardiac magnetic resonance were consistent with myocardial inflammation and acute myocarditis.
The patient was treated with supportive care, and he made a full clinical recovery. He was discharged after 1 week. On discharge, cardiac enzymes were within the normal range. The patient showed sustained electric and hemodynamic stability, and the skin lesions had healed.
“Through this important case study, we are developing a deeper understanding of monkeypox, viral myocarditis, and how to accurately diagnose and manage this disease,” Julia Grapsa, MD, PhD, editor-in-chief of JACC: Case Reports, commented in the news release.
“I commend the authors on this valuable clinical case during a critical time as monkeypox continues to spread globally,” Dr. Grapsa added.
The researchers say further research is needed to identify the pathologic mechanism underlying monkeypox-associated cardiac injury.
By the numbers
According to the latest data, California has reported 3,629 cases, followed closely by New York with 3,367 cases, Florida with 1,957 cases, Texas with 1,698, Georgia with 1,418, and Illinois with 1,081. The other states have reported fewer than 600 cases.
The CDC says that globally, more than 52,000 monkeypox cases have been reported.
Monkeypox case counts appear to be slowing in the United States and globally.
Last week, the World Health Organization said the number of new cases worldwide declined by 21% between Aug. 15 and 21 after increasing for 4 straight weeks.
The research had no funding. Dr. Pinho and colleagues have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinicians in Portugal say a 31-year-old man with confirmed monkeypox developed acute myocarditis roughly 1 week after the eruption of the characteristic skin lesions of the disease.
Ana Isabel Pinho, MD, department of cardiology, São João University Hospital Centre, Porto, Portugal, said in a news release.
“We believe that reporting this potential causal relationship can raise more awareness of the scientific community and health professionals for acute myocarditis as a possible complication associated with monkeypox and might be helpful for close monitoring of affected patients for further recognition of other complications in the future,” Dr. Pinho adds.
Dr. Pinho and colleagues describe the case in a report published in JACC: Case Reports.
Case details
The patient presented with a 5-day history of malaise, myalgias, and fever followed by the eruption of multiple swollen skin lesions on his face, hands, and genitalia.
Monkeypox was confirmed by positive polymerase chain reaction assay of a swab sample from a skin lesion.
Three days later, the patient developed chest tightness that radiated through the left arm and which awoke him during the night. He was admitted to an intensive care unit with clinical suspicion of acute myocarditis.
The patient’s initial electrocardiogram showed sinus rhythm with nonspecific ventricular repolarization abnormalities.
On chest x-ray, the cardiothoracic index was normal, with no interstitial infiltrates, pleural effusion, or masses. On transthoracic echocardigraphy, biventricular systolic function was preserved, and there was no pericardial effusion.
Routine laboratory tests revealed elevated levels of C-reactive protein, creatine phosphokinase, high-sensitivity troponin I, and brain natriuretic peptide, suggesting stress injury to the heart.
Findings on cardiac magnetic resonance were consistent with myocardial inflammation and acute myocarditis.
The patient was treated with supportive care, and he made a full clinical recovery. He was discharged after 1 week. On discharge, cardiac enzymes were within the normal range. The patient showed sustained electric and hemodynamic stability, and the skin lesions had healed.
“Through this important case study, we are developing a deeper understanding of monkeypox, viral myocarditis, and how to accurately diagnose and manage this disease,” Julia Grapsa, MD, PhD, editor-in-chief of JACC: Case Reports, commented in the news release.
“I commend the authors on this valuable clinical case during a critical time as monkeypox continues to spread globally,” Dr. Grapsa added.
The researchers say further research is needed to identify the pathologic mechanism underlying monkeypox-associated cardiac injury.
By the numbers
According to the latest data, California has reported 3,629 cases, followed closely by New York with 3,367 cases, Florida with 1,957 cases, Texas with 1,698, Georgia with 1,418, and Illinois with 1,081. The other states have reported fewer than 600 cases.
The CDC says that globally, more than 52,000 monkeypox cases have been reported.
Monkeypox case counts appear to be slowing in the United States and globally.
Last week, the World Health Organization said the number of new cases worldwide declined by 21% between Aug. 15 and 21 after increasing for 4 straight weeks.
The research had no funding. Dr. Pinho and colleagues have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
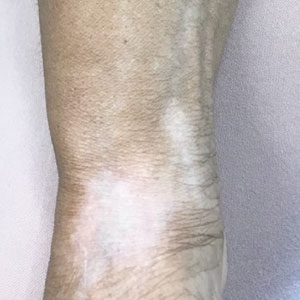
Linear Hypopigmentation on the Right Arm
The Diagnosis: Chemical Leukoderma
A clinical diagnosis of chemical leukoderma was made. In our patient, the observed linear hypopigmentation likely resulted from the prior treatment for De Quervain tenosynovitis in which an intralesional corticosteroid entered the lymphatic channel causing a linear distribution of chemical leukoderma. The hypopigmentation self-resolved at 6-month follow-up, and the patient was counseled to continue steroid injections if indicated.
Chemical leukoderma is an acquired depigmenting dermatosis that displays vitiligolike patterning. Detailed personal and family history in addition to complete physical examination are crucial given the inability to distinguish chemical leukoderma from vitiligo on histopathology. A set of clinical criteria proposed by Ghosh and Mukhopadhyay1 includes the presence of acquired depigmented macules and patches resembling vitiligo, history of repeat exposure to certain chemical substances, hypopigmentation at the site of exposure, and/ or confettilike white macules. Three of these 4 clinical findings must be present to establish a diagnosis of chemical leukoderma. The extent of disease involvement may be graded as follows: Stage I is defined as leukoderma only at the site of contact to the offending agent. Stage II involvement is characterized by local spread beyond the exposure site via the lymphatic system. Stages IIIA and IIIB leukoderma entail hematogenous spread distant to the site of chemical exposure. Although stage IIIA leukoderma is limited to cutaneous involvement, stage IIIB findings are marked by systemic organ involvement. Stage IV disease is defined by the distant spread of hypopigmented macules and patches that continues following 1 year of strict avoidance of the causative agent.1
The pathogenesis behind chemical leukoderma is not completely understood. Studies have suggested that individuals with certain genetic susceptibilities are predisposed to developing the condition after being exposed to chemicals with melanocytotoxic properties.2,3 It has been proposed that the chemicals accelerate pre-existing cellular stress cascades within melanocytes to levels higher than what healthy cells can tolerate. Genetic factors can increase an individual’s total melanocytic stress or establish a lower cellular threshold for stress than what the immune system can manage.4 These influences culminate in an inflammatory response that results in melanocytic destruction and subsequent cutaneous hypopigmentation.
The most well-known offending chemical agents are phenol and catechol derivatives, such as hydroquinone, which is used in topical bleaching agents to treat diseases of hyperpigmentation, including melasma.2 Potent topical or intralesional corticosteroids also may precipitate chemical leukoderma, most notably in individuals with darker skin tones. Hypomelanosis induced by intralesional steroids frequently occurs weeks to months after administration and commonly is observed in a stellate or linear pattern with an irregular outline.5 Other offending chemical agents include sulfhydryls, mercurials, arsenic, benzoyl peroxide, azelaic acid, imiquimod, chloroquine, and tyrosine kinase inhibitors.2,5
Segmental vitiligo is characterized by unilateral hypopigmentation in a linear or blocklike distribution that does not cross the midline. However, onset of segmental vitiligo classically occurs prior to 30 years of age and frequently is related with early leukotrichia.6 Additionally, the hypomelanosis associated with segmental vitiligo more often presents as broad bands or patches that occasionally have a blaschkoid distribution and most commonly appear on the face.5 Lichen striatus is a lichenoid dermatosis that presents as asymptomatic pink or hypopigmented papules that follow the Blaschko lines, often favoring the extremities. Postinflammatory hypopigmentation also may occur as an associated sequela of resolved lichen striatus. Although the disease onset of lichen striatus may occur in adulthood, it typically appears in childhood and is triggered by factors such as trauma, hypersensitivity reactions, viral infections, and medications. Physical injuries such as trauma following surgical procedures also can lead to hypomelanosis; however, our patient denied any relevant surgical history. Progressive macular hypomelanosis is a skin condition presenting as ill-defined, nummular, hypopigmented macules or patches that commonly affects women with darker skin tones with an ethnic background from a tropical location or residing in a tropical environment.5 Lesions frequently appear on the trunk and rarely progress to the proximal extremities, making it an unlikely diagnosis for our patient.
In most cases of chemical leukoderma, spontaneous repigmentation often occurs within 12 months after the elimination of the offending substance; however, hypopigmented lesions may persist or continue to develop at sites distant from the initial site despite discontinuing the causative agent.1 Therapies for vitiligo, such as topical corticosteroids, topical immunosuppressants, narrowband UVB phototherapy, and psoralen plus UVA photochemotherapy, may be utilized for chemical leukoderma that does not self-resolve.
- Ghosh S, Mukhopadhyay S. Chemical leucoderma: a clinicoaetiological study of 864 cases in the perspective of a developing country [published online September 6, 2008]. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160:40-47.
- Ghosh S. Chemical leukoderma: what’s new on etiopathological and clinical aspects? Indian J Dermatol. 2010;55:255.
- Boissy RE, Manga P. On the etiology of contact/occupational vitiligo. Pigment Cell Res. 2004;17:208-214.
- Harris J. Chemical-induced vitiligo. Dermatol Clin. 2017; 35:151-161.
- Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, et al. Vitiligo and other disorders of hypopigmentation. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Mosby/Elsevier; 2018:1087-1114.
- Rodrigues M, Ezzedine K, Hamzavi I, et al. New discoveries in the pathogenesis and classification of vitiligo. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:1-13.
The Diagnosis: Chemical Leukoderma
A clinical diagnosis of chemical leukoderma was made. In our patient, the observed linear hypopigmentation likely resulted from the prior treatment for De Quervain tenosynovitis in which an intralesional corticosteroid entered the lymphatic channel causing a linear distribution of chemical leukoderma. The hypopigmentation self-resolved at 6-month follow-up, and the patient was counseled to continue steroid injections if indicated.
Chemical leukoderma is an acquired depigmenting dermatosis that displays vitiligolike patterning. Detailed personal and family history in addition to complete physical examination are crucial given the inability to distinguish chemical leukoderma from vitiligo on histopathology. A set of clinical criteria proposed by Ghosh and Mukhopadhyay1 includes the presence of acquired depigmented macules and patches resembling vitiligo, history of repeat exposure to certain chemical substances, hypopigmentation at the site of exposure, and/ or confettilike white macules. Three of these 4 clinical findings must be present to establish a diagnosis of chemical leukoderma. The extent of disease involvement may be graded as follows: Stage I is defined as leukoderma only at the site of contact to the offending agent. Stage II involvement is characterized by local spread beyond the exposure site via the lymphatic system. Stages IIIA and IIIB leukoderma entail hematogenous spread distant to the site of chemical exposure. Although stage IIIA leukoderma is limited to cutaneous involvement, stage IIIB findings are marked by systemic organ involvement. Stage IV disease is defined by the distant spread of hypopigmented macules and patches that continues following 1 year of strict avoidance of the causative agent.1
The pathogenesis behind chemical leukoderma is not completely understood. Studies have suggested that individuals with certain genetic susceptibilities are predisposed to developing the condition after being exposed to chemicals with melanocytotoxic properties.2,3 It has been proposed that the chemicals accelerate pre-existing cellular stress cascades within melanocytes to levels higher than what healthy cells can tolerate. Genetic factors can increase an individual’s total melanocytic stress or establish a lower cellular threshold for stress than what the immune system can manage.4 These influences culminate in an inflammatory response that results in melanocytic destruction and subsequent cutaneous hypopigmentation.
The most well-known offending chemical agents are phenol and catechol derivatives, such as hydroquinone, which is used in topical bleaching agents to treat diseases of hyperpigmentation, including melasma.2 Potent topical or intralesional corticosteroids also may precipitate chemical leukoderma, most notably in individuals with darker skin tones. Hypomelanosis induced by intralesional steroids frequently occurs weeks to months after administration and commonly is observed in a stellate or linear pattern with an irregular outline.5 Other offending chemical agents include sulfhydryls, mercurials, arsenic, benzoyl peroxide, azelaic acid, imiquimod, chloroquine, and tyrosine kinase inhibitors.2,5
Segmental vitiligo is characterized by unilateral hypopigmentation in a linear or blocklike distribution that does not cross the midline. However, onset of segmental vitiligo classically occurs prior to 30 years of age and frequently is related with early leukotrichia.6 Additionally, the hypomelanosis associated with segmental vitiligo more often presents as broad bands or patches that occasionally have a blaschkoid distribution and most commonly appear on the face.5 Lichen striatus is a lichenoid dermatosis that presents as asymptomatic pink or hypopigmented papules that follow the Blaschko lines, often favoring the extremities. Postinflammatory hypopigmentation also may occur as an associated sequela of resolved lichen striatus. Although the disease onset of lichen striatus may occur in adulthood, it typically appears in childhood and is triggered by factors such as trauma, hypersensitivity reactions, viral infections, and medications. Physical injuries such as trauma following surgical procedures also can lead to hypomelanosis; however, our patient denied any relevant surgical history. Progressive macular hypomelanosis is a skin condition presenting as ill-defined, nummular, hypopigmented macules or patches that commonly affects women with darker skin tones with an ethnic background from a tropical location or residing in a tropical environment.5 Lesions frequently appear on the trunk and rarely progress to the proximal extremities, making it an unlikely diagnosis for our patient.
In most cases of chemical leukoderma, spontaneous repigmentation often occurs within 12 months after the elimination of the offending substance; however, hypopigmented lesions may persist or continue to develop at sites distant from the initial site despite discontinuing the causative agent.1 Therapies for vitiligo, such as topical corticosteroids, topical immunosuppressants, narrowband UVB phototherapy, and psoralen plus UVA photochemotherapy, may be utilized for chemical leukoderma that does not self-resolve.
The Diagnosis: Chemical Leukoderma
A clinical diagnosis of chemical leukoderma was made. In our patient, the observed linear hypopigmentation likely resulted from the prior treatment for De Quervain tenosynovitis in which an intralesional corticosteroid entered the lymphatic channel causing a linear distribution of chemical leukoderma. The hypopigmentation self-resolved at 6-month follow-up, and the patient was counseled to continue steroid injections if indicated.
Chemical leukoderma is an acquired depigmenting dermatosis that displays vitiligolike patterning. Detailed personal and family history in addition to complete physical examination are crucial given the inability to distinguish chemical leukoderma from vitiligo on histopathology. A set of clinical criteria proposed by Ghosh and Mukhopadhyay1 includes the presence of acquired depigmented macules and patches resembling vitiligo, history of repeat exposure to certain chemical substances, hypopigmentation at the site of exposure, and/ or confettilike white macules. Three of these 4 clinical findings must be present to establish a diagnosis of chemical leukoderma. The extent of disease involvement may be graded as follows: Stage I is defined as leukoderma only at the site of contact to the offending agent. Stage II involvement is characterized by local spread beyond the exposure site via the lymphatic system. Stages IIIA and IIIB leukoderma entail hematogenous spread distant to the site of chemical exposure. Although stage IIIA leukoderma is limited to cutaneous involvement, stage IIIB findings are marked by systemic organ involvement. Stage IV disease is defined by the distant spread of hypopigmented macules and patches that continues following 1 year of strict avoidance of the causative agent.1
The pathogenesis behind chemical leukoderma is not completely understood. Studies have suggested that individuals with certain genetic susceptibilities are predisposed to developing the condition after being exposed to chemicals with melanocytotoxic properties.2,3 It has been proposed that the chemicals accelerate pre-existing cellular stress cascades within melanocytes to levels higher than what healthy cells can tolerate. Genetic factors can increase an individual’s total melanocytic stress or establish a lower cellular threshold for stress than what the immune system can manage.4 These influences culminate in an inflammatory response that results in melanocytic destruction and subsequent cutaneous hypopigmentation.
The most well-known offending chemical agents are phenol and catechol derivatives, such as hydroquinone, which is used in topical bleaching agents to treat diseases of hyperpigmentation, including melasma.2 Potent topical or intralesional corticosteroids also may precipitate chemical leukoderma, most notably in individuals with darker skin tones. Hypomelanosis induced by intralesional steroids frequently occurs weeks to months after administration and commonly is observed in a stellate or linear pattern with an irregular outline.5 Other offending chemical agents include sulfhydryls, mercurials, arsenic, benzoyl peroxide, azelaic acid, imiquimod, chloroquine, and tyrosine kinase inhibitors.2,5
Segmental vitiligo is characterized by unilateral hypopigmentation in a linear or blocklike distribution that does not cross the midline. However, onset of segmental vitiligo classically occurs prior to 30 years of age and frequently is related with early leukotrichia.6 Additionally, the hypomelanosis associated with segmental vitiligo more often presents as broad bands or patches that occasionally have a blaschkoid distribution and most commonly appear on the face.5 Lichen striatus is a lichenoid dermatosis that presents as asymptomatic pink or hypopigmented papules that follow the Blaschko lines, often favoring the extremities. Postinflammatory hypopigmentation also may occur as an associated sequela of resolved lichen striatus. Although the disease onset of lichen striatus may occur in adulthood, it typically appears in childhood and is triggered by factors such as trauma, hypersensitivity reactions, viral infections, and medications. Physical injuries such as trauma following surgical procedures also can lead to hypomelanosis; however, our patient denied any relevant surgical history. Progressive macular hypomelanosis is a skin condition presenting as ill-defined, nummular, hypopigmented macules or patches that commonly affects women with darker skin tones with an ethnic background from a tropical location or residing in a tropical environment.5 Lesions frequently appear on the trunk and rarely progress to the proximal extremities, making it an unlikely diagnosis for our patient.
In most cases of chemical leukoderma, spontaneous repigmentation often occurs within 12 months after the elimination of the offending substance; however, hypopigmented lesions may persist or continue to develop at sites distant from the initial site despite discontinuing the causative agent.1 Therapies for vitiligo, such as topical corticosteroids, topical immunosuppressants, narrowband UVB phototherapy, and psoralen plus UVA photochemotherapy, may be utilized for chemical leukoderma that does not self-resolve.
- Ghosh S, Mukhopadhyay S. Chemical leucoderma: a clinicoaetiological study of 864 cases in the perspective of a developing country [published online September 6, 2008]. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160:40-47.
- Ghosh S. Chemical leukoderma: what’s new on etiopathological and clinical aspects? Indian J Dermatol. 2010;55:255.
- Boissy RE, Manga P. On the etiology of contact/occupational vitiligo. Pigment Cell Res. 2004;17:208-214.
- Harris J. Chemical-induced vitiligo. Dermatol Clin. 2017; 35:151-161.
- Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, et al. Vitiligo and other disorders of hypopigmentation. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Mosby/Elsevier; 2018:1087-1114.
- Rodrigues M, Ezzedine K, Hamzavi I, et al. New discoveries in the pathogenesis and classification of vitiligo. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:1-13.
- Ghosh S, Mukhopadhyay S. Chemical leucoderma: a clinicoaetiological study of 864 cases in the perspective of a developing country [published online September 6, 2008]. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160:40-47.
- Ghosh S. Chemical leukoderma: what’s new on etiopathological and clinical aspects? Indian J Dermatol. 2010;55:255.
- Boissy RE, Manga P. On the etiology of contact/occupational vitiligo. Pigment Cell Res. 2004;17:208-214.
- Harris J. Chemical-induced vitiligo. Dermatol Clin. 2017; 35:151-161.
- Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, et al. Vitiligo and other disorders of hypopigmentation. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Mosby/Elsevier; 2018:1087-1114.
- Rodrigues M, Ezzedine K, Hamzavi I, et al. New discoveries in the pathogenesis and classification of vitiligo. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:1-13.
A 73-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic with hypopigmentation along the right arm. Her medical history was notable for prior treatment with intralesional triamcinolone injections for De Quervain tenosynovitis. Two months after receiving the steroid injections she noted progressive spreading of an asymptomatic white discoloration originating on the right wrist. Physical examination revealed a hypopigmented atrophic patch on the medial aspect of the right wrist (left) with linear hypopigmented patches extending proximally up the forearm (right).
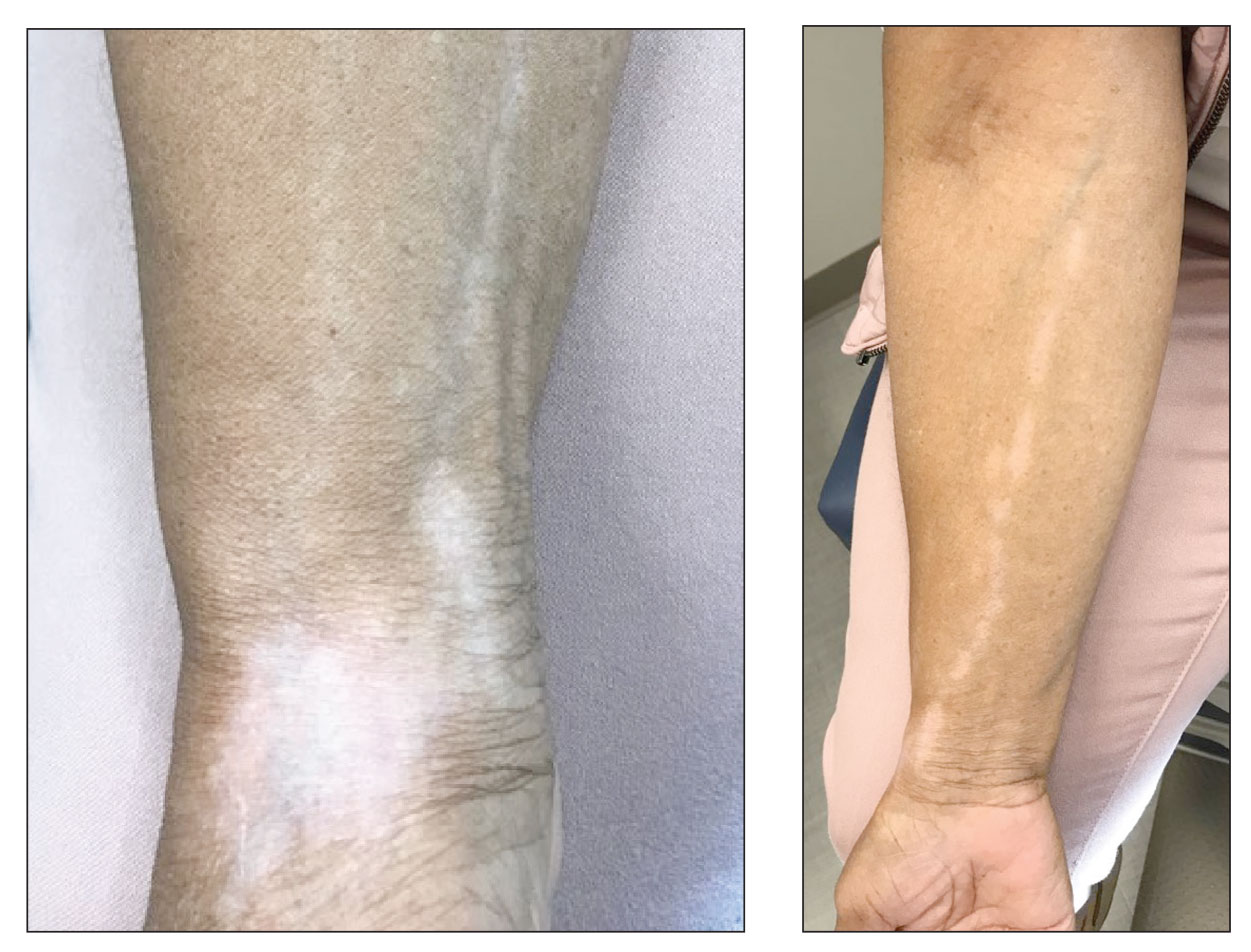
Blue light from cell phones and other devices could be causing wrinkles
Blue light from screens on smartphones, computers, and other gadgets “may have detrimental effects on a wide range of cells in our body, from skin and fat cells to sensory neurons,” Oregon State University scientist Jadwiga Giebultowicz, PhD, said of the study, which was published in the journal Frontiers in Aging.
“Our study suggests that avoidance of excessive blue light exposure may be a good anti-aging strategy,” Dr. Giebultowicz added.
Ultraviolet rays from the sun harm skin appearance and health. Doctors are continuing to study the damage caused by the screens of devices that most people are exposed to throughout the day. These devices emit blue light.
“Aging occurs in various ways, but on a cellular level, we age when cells stop repairing and producing new healthy cells. And cells that aren’t functioning properly are more likely to self destruct – which has ramifications not only in terms of appearance but for the whole body,” the New York Post wrote. “It’s the reason why the elderly take longer to heal, and their bones and organs begin to deteriorate.”
Dr. Giebultowicz said the study shows that certain substances in the body, called metabolites, are essential indicators of how a cell functions. These metabolites are naturally occurring as the body converts food and drinks into energy. Research indicates that these substances are altered by blue light exposure.
More specifically, researchers found that levels of succinate, or succinic acid, in fruit flies increased under excessive blue light, while glutamate decreased, the newspaper wrote.
Researchers said the insects “make an appropriate analog for humans” because the same signaling devices are shared.
The flies were exposed with more blue light than people usually get. Dr. Giebultowicz said future research is needed on human cells.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Blue light from screens on smartphones, computers, and other gadgets “may have detrimental effects on a wide range of cells in our body, from skin and fat cells to sensory neurons,” Oregon State University scientist Jadwiga Giebultowicz, PhD, said of the study, which was published in the journal Frontiers in Aging.
“Our study suggests that avoidance of excessive blue light exposure may be a good anti-aging strategy,” Dr. Giebultowicz added.
Ultraviolet rays from the sun harm skin appearance and health. Doctors are continuing to study the damage caused by the screens of devices that most people are exposed to throughout the day. These devices emit blue light.
“Aging occurs in various ways, but on a cellular level, we age when cells stop repairing and producing new healthy cells. And cells that aren’t functioning properly are more likely to self destruct – which has ramifications not only in terms of appearance but for the whole body,” the New York Post wrote. “It’s the reason why the elderly take longer to heal, and their bones and organs begin to deteriorate.”
Dr. Giebultowicz said the study shows that certain substances in the body, called metabolites, are essential indicators of how a cell functions. These metabolites are naturally occurring as the body converts food and drinks into energy. Research indicates that these substances are altered by blue light exposure.
More specifically, researchers found that levels of succinate, or succinic acid, in fruit flies increased under excessive blue light, while glutamate decreased, the newspaper wrote.
Researchers said the insects “make an appropriate analog for humans” because the same signaling devices are shared.
The flies were exposed with more blue light than people usually get. Dr. Giebultowicz said future research is needed on human cells.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Blue light from screens on smartphones, computers, and other gadgets “may have detrimental effects on a wide range of cells in our body, from skin and fat cells to sensory neurons,” Oregon State University scientist Jadwiga Giebultowicz, PhD, said of the study, which was published in the journal Frontiers in Aging.
“Our study suggests that avoidance of excessive blue light exposure may be a good anti-aging strategy,” Dr. Giebultowicz added.
Ultraviolet rays from the sun harm skin appearance and health. Doctors are continuing to study the damage caused by the screens of devices that most people are exposed to throughout the day. These devices emit blue light.
“Aging occurs in various ways, but on a cellular level, we age when cells stop repairing and producing new healthy cells. And cells that aren’t functioning properly are more likely to self destruct – which has ramifications not only in terms of appearance but for the whole body,” the New York Post wrote. “It’s the reason why the elderly take longer to heal, and their bones and organs begin to deteriorate.”
Dr. Giebultowicz said the study shows that certain substances in the body, called metabolites, are essential indicators of how a cell functions. These metabolites are naturally occurring as the body converts food and drinks into energy. Research indicates that these substances are altered by blue light exposure.
More specifically, researchers found that levels of succinate, or succinic acid, in fruit flies increased under excessive blue light, while glutamate decreased, the newspaper wrote.
Researchers said the insects “make an appropriate analog for humans” because the same signaling devices are shared.
The flies were exposed with more blue light than people usually get. Dr. Giebultowicz said future research is needed on human cells.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM FRONTIERS IN AGING
Low physical function tied to cardiac events in older adults
including coronary heart disease (CHD), stroke, and heart failure (HF) in older adults, according to new observational data from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study.
“We found that physical function in older adults predicts future cardiovascular disease (CVD) beyond traditional heart disease risk factors, regardless of whether an individual has a history of cardiovascular disease,” senior author Kunihiro Matsushita, MD, PhD, division of cardiology, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said in a news release.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Keeping fit with age
The researchers analyzed health data collected between 2011 and 2013 for 5,570 ARIC participants (mean age, 75 years; 58% women, 22% Black persons). They assessed physical function using the Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB), which measures walking speed, leg strength, and balance.
On the basis of the results, participants were categorized into three physical function groups: low (score, 0-6; 13% of the cohort), intermediate (score, 7-9; 30%) and high (score, 10-12; 57%).
During a median follow up of 7 years, there were 930 composite CVD events (386 CHD, 251 stroke, and 529 HF).
Adults with lower SPPB scores had a higher cumulative incidence of composite CVD outcomes.
The 5-year cumulative incidence of the composite CVD outcome in the low- and intermediate-SPPB categories was about three times (23.4%) and two times (15.3%) higher than in the high-SPPB category (8.6%), the researchers reported.
In addition, continuous SPPB scores showed significant associations with composite and individual CVD outcomes in all models. A 1-point lower SPPB score was associated with 6%-10% higher risk for CVD events after adjusting for potential confounders.
In the fully adjusted model, the risk for composite CVD outcomes was 47% higher (hazard ratio, 1.47; 95% confidence interval, 1.20-1.79) in those with low physical function and 25% higher in those with intermediate physical function (HR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.07-1.46) compared with peers with high physical function.
For the individual outcomes, low physical function was associated with higher risk for stroke (HR, 1.81; 95% CI, 1.24-2.64) and HF (HR, 1.33; 95% CI, 1.02-1.73), whereas the association for CHD was not significant.
The associations were largely consistent across subgroups, including those with CVD at baseline.
The addition of SPPB scores significantly improved risk prediction of CVD events beyond traditional CVD risk factors in adults regardless of prior CVD history, suggesting that this tool may be useful for classifying CVD risk in older adults, the researchers said.
Meaningful impact on care?
“Our findings highlight the value of assessing the physical function level of older adults in clinical practice,” lead author Xiao Hu, MHS, with the department of epidemiology at Johns Hopkins, said in the news release. “In addition to heart health, older adults are at higher risk for falls and disability. The assessment of physical function may also inform the risk of these concerning conditions in older adults.”
Weighing in on the study, Jonathan Halperin, MD, cardiologist at Mount Sinai Heart and professor of medicine (cardiology) at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, both in New York, said that “It’s known that cardiorespiratory fitness is an important predictor of cardiovascular risk, but it is one of the few physiological risk factors that are subjectively queried but not objectively assessed in routine clinical practice.”
In this study, Dr. Halperin noted, the investigators found that a battery of physical performance assessments, including a walk test, chair standing, and balance testing, improved cardiovascular risk prediction.
Dr. Halperin cautioned, however, that “since even the short sequence of tests takes time to perform and interpret, and is not currently reimbursed under most health insurance policies, it is not clear whether the report will have a meaningful impact on patient care.”
This research was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Matsushita and Dr. Halperin have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
including coronary heart disease (CHD), stroke, and heart failure (HF) in older adults, according to new observational data from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study.
“We found that physical function in older adults predicts future cardiovascular disease (CVD) beyond traditional heart disease risk factors, regardless of whether an individual has a history of cardiovascular disease,” senior author Kunihiro Matsushita, MD, PhD, division of cardiology, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said in a news release.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Keeping fit with age
The researchers analyzed health data collected between 2011 and 2013 for 5,570 ARIC participants (mean age, 75 years; 58% women, 22% Black persons). They assessed physical function using the Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB), which measures walking speed, leg strength, and balance.
On the basis of the results, participants were categorized into three physical function groups: low (score, 0-6; 13% of the cohort), intermediate (score, 7-9; 30%) and high (score, 10-12; 57%).
During a median follow up of 7 years, there were 930 composite CVD events (386 CHD, 251 stroke, and 529 HF).
Adults with lower SPPB scores had a higher cumulative incidence of composite CVD outcomes.
The 5-year cumulative incidence of the composite CVD outcome in the low- and intermediate-SPPB categories was about three times (23.4%) and two times (15.3%) higher than in the high-SPPB category (8.6%), the researchers reported.
In addition, continuous SPPB scores showed significant associations with composite and individual CVD outcomes in all models. A 1-point lower SPPB score was associated with 6%-10% higher risk for CVD events after adjusting for potential confounders.
In the fully adjusted model, the risk for composite CVD outcomes was 47% higher (hazard ratio, 1.47; 95% confidence interval, 1.20-1.79) in those with low physical function and 25% higher in those with intermediate physical function (HR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.07-1.46) compared with peers with high physical function.
For the individual outcomes, low physical function was associated with higher risk for stroke (HR, 1.81; 95% CI, 1.24-2.64) and HF (HR, 1.33; 95% CI, 1.02-1.73), whereas the association for CHD was not significant.
The associations were largely consistent across subgroups, including those with CVD at baseline.
The addition of SPPB scores significantly improved risk prediction of CVD events beyond traditional CVD risk factors in adults regardless of prior CVD history, suggesting that this tool may be useful for classifying CVD risk in older adults, the researchers said.
Meaningful impact on care?
“Our findings highlight the value of assessing the physical function level of older adults in clinical practice,” lead author Xiao Hu, MHS, with the department of epidemiology at Johns Hopkins, said in the news release. “In addition to heart health, older adults are at higher risk for falls and disability. The assessment of physical function may also inform the risk of these concerning conditions in older adults.”
Weighing in on the study, Jonathan Halperin, MD, cardiologist at Mount Sinai Heart and professor of medicine (cardiology) at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, both in New York, said that “It’s known that cardiorespiratory fitness is an important predictor of cardiovascular risk, but it is one of the few physiological risk factors that are subjectively queried but not objectively assessed in routine clinical practice.”
In this study, Dr. Halperin noted, the investigators found that a battery of physical performance assessments, including a walk test, chair standing, and balance testing, improved cardiovascular risk prediction.
Dr. Halperin cautioned, however, that “since even the short sequence of tests takes time to perform and interpret, and is not currently reimbursed under most health insurance policies, it is not clear whether the report will have a meaningful impact on patient care.”
This research was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Matsushita and Dr. Halperin have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
including coronary heart disease (CHD), stroke, and heart failure (HF) in older adults, according to new observational data from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study.
“We found that physical function in older adults predicts future cardiovascular disease (CVD) beyond traditional heart disease risk factors, regardless of whether an individual has a history of cardiovascular disease,” senior author Kunihiro Matsushita, MD, PhD, division of cardiology, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said in a news release.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Keeping fit with age
The researchers analyzed health data collected between 2011 and 2013 for 5,570 ARIC participants (mean age, 75 years; 58% women, 22% Black persons). They assessed physical function using the Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB), which measures walking speed, leg strength, and balance.
On the basis of the results, participants were categorized into three physical function groups: low (score, 0-6; 13% of the cohort), intermediate (score, 7-9; 30%) and high (score, 10-12; 57%).
During a median follow up of 7 years, there were 930 composite CVD events (386 CHD, 251 stroke, and 529 HF).
Adults with lower SPPB scores had a higher cumulative incidence of composite CVD outcomes.
The 5-year cumulative incidence of the composite CVD outcome in the low- and intermediate-SPPB categories was about three times (23.4%) and two times (15.3%) higher than in the high-SPPB category (8.6%), the researchers reported.
In addition, continuous SPPB scores showed significant associations with composite and individual CVD outcomes in all models. A 1-point lower SPPB score was associated with 6%-10% higher risk for CVD events after adjusting for potential confounders.
In the fully adjusted model, the risk for composite CVD outcomes was 47% higher (hazard ratio, 1.47; 95% confidence interval, 1.20-1.79) in those with low physical function and 25% higher in those with intermediate physical function (HR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.07-1.46) compared with peers with high physical function.
For the individual outcomes, low physical function was associated with higher risk for stroke (HR, 1.81; 95% CI, 1.24-2.64) and HF (HR, 1.33; 95% CI, 1.02-1.73), whereas the association for CHD was not significant.
The associations were largely consistent across subgroups, including those with CVD at baseline.
The addition of SPPB scores significantly improved risk prediction of CVD events beyond traditional CVD risk factors in adults regardless of prior CVD history, suggesting that this tool may be useful for classifying CVD risk in older adults, the researchers said.
Meaningful impact on care?
“Our findings highlight the value of assessing the physical function level of older adults in clinical practice,” lead author Xiao Hu, MHS, with the department of epidemiology at Johns Hopkins, said in the news release. “In addition to heart health, older adults are at higher risk for falls and disability. The assessment of physical function may also inform the risk of these concerning conditions in older adults.”
Weighing in on the study, Jonathan Halperin, MD, cardiologist at Mount Sinai Heart and professor of medicine (cardiology) at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, both in New York, said that “It’s known that cardiorespiratory fitness is an important predictor of cardiovascular risk, but it is one of the few physiological risk factors that are subjectively queried but not objectively assessed in routine clinical practice.”
In this study, Dr. Halperin noted, the investigators found that a battery of physical performance assessments, including a walk test, chair standing, and balance testing, improved cardiovascular risk prediction.
Dr. Halperin cautioned, however, that “since even the short sequence of tests takes time to perform and interpret, and is not currently reimbursed under most health insurance policies, it is not clear whether the report will have a meaningful impact on patient care.”
This research was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Matsushita and Dr. Halperin have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION
Robots better than humans at detecting mental well-being issues in children
Robots can be better at detecting mental well-being issues in children than parent-reported or self-reported testing, say U.K. researchers.
The researchers behind a new study, presented at the 31st IEEE International Conference on Robot & Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN) in Naples, Italy, have suggested that robots could be a useful addition to traditional methods of mental health assessment.
“There are times when traditional methods aren’t able to catch mental well-being lapses in children, as sometimes the changes are incredibly subtle,” said Nida Itrat Abbasi, a PhD student at Cambridge (England) Affective Computing and Robotics Group, University of Cambridge, and the study’s first author. “We wanted to see whether robots might be able to help with this process,” she explained.
The authors highlighted how, during the COVID-19 pandemic, home schooling, financial pressures, and isolation from peers and friends impacted the mental health of many children. Even before the pandemic however, anxiety and depression among children in the United Kingdom has been on the rise, but the resources and support to address mental well-being are severely limited.
Children engage with robots
For their study the research team – which comprised roboticists, computer scientists, and psychiatrists from the University of Cambridge – enrolled 28 participants between ages 8 and 13 years. While being observed from an adjacent room by a parent or guardian, along with members of the research team, the participants took part in a one-to-one 45-minute session with a Nao robot – a humanoid robot about 60 cm tall – that administered a series of standard psychological questionnaires to assess the mental well-being of each participant.
Participants interacted with the robot throughout the session by speaking with it or by touching sensors on the robot’s hands and feet. Additional sensors tracked participants’ heartbeat, head, and eye movements during the session.
Professor Hatice Gunes, affective intelligence and robotics laboratory, department of computer science, University of Cambridge, said: “Children are quite tactile, and they’re drawn to technology. If they’re using a screen-based tool, they’re withdrawn from the physical world,” she said. “But robots are perfect because they’re in the physical world – they’re more interactive, so the children are more engaged.”
Prior to each session the children and their parent or guardian completed standard online questionnaires to assess each child’s mental well-being.
During each session, the robot performed four different tasks:
- Asked open-ended questions about happy and sad memories over the last week.
- Administered the Short Mood and Feelings Questionnaire (SMFQ).
- Administered a picture task inspired by the Children’s Apperception Test (CAT), where children are asked to answer questions related to pictures shown.
- Administered the Revised Children’s Anxiety and Depression Scale (RCADS) for generalized anxiety, panic disorder, and low mood.
Following the SMFQ children were divided into three different groups according to how likely they were to be struggling with their mental well-being.
The researchers found that children with varying levels of well-being concerns interacted differently with the robot. For children that might not be experiencing mental well-being–related problems, the researchers found that interacting with the robot led to more positive response ratings to the questionnaires. However, for children that might be experiencing well-being–related concerns, the robot may have enabled them to divulge their true feelings and experiences, leading to more negative response ratings to the questionnaire.
Robots an addition not a replacement
“Since the robot we use is child-sized, and completely nonthreatening, children might see the robot as a confidant – they feel like they won’t get into trouble if they share secrets with it,” said Ms. Abbasi. “Other researchers have found that children are more likely to divulge private information – like that they’re being bullied, for example – to a robot than they would be to an adult,” she said.
Study participants all said they “enjoyed talking with the robot,” commented the authors, who added that, “the children were willing to confide in the robot, in some cases sharing information with the robot that they had not yet shared via the standard assessment method of online or in-person questionnaires.”
This is the first time that robots have been used to assess mental well-being in children, the researchers pointed out. “Robots could be a useful addition to traditional methods of mental health assessment,” they said, though they emphasized that robots are “not intended to be a substitute for professional mental health support.”
“We don’t have any intention of replacing psychologists or other mental health professionals with robots, since their expertise far surpasses anything a robot can do,” said Dr. Micol Spitale, affective computing and robotics laboratory, University of Cambridge, and study coauthor. “However, our work suggests that robots could be a useful tool in helping children to open up and share things they might not be comfortable sharing at first.”
The researchers say that they hope to expand their survey in future by including more participants and following them over time. They are also investigating whether similar results could be achieved if children interact with the robot via video chat.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
Robots can be better at detecting mental well-being issues in children than parent-reported or self-reported testing, say U.K. researchers.
The researchers behind a new study, presented at the 31st IEEE International Conference on Robot & Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN) in Naples, Italy, have suggested that robots could be a useful addition to traditional methods of mental health assessment.
“There are times when traditional methods aren’t able to catch mental well-being lapses in children, as sometimes the changes are incredibly subtle,” said Nida Itrat Abbasi, a PhD student at Cambridge (England) Affective Computing and Robotics Group, University of Cambridge, and the study’s first author. “We wanted to see whether robots might be able to help with this process,” she explained.
The authors highlighted how, during the COVID-19 pandemic, home schooling, financial pressures, and isolation from peers and friends impacted the mental health of many children. Even before the pandemic however, anxiety and depression among children in the United Kingdom has been on the rise, but the resources and support to address mental well-being are severely limited.
Children engage with robots
For their study the research team – which comprised roboticists, computer scientists, and psychiatrists from the University of Cambridge – enrolled 28 participants between ages 8 and 13 years. While being observed from an adjacent room by a parent or guardian, along with members of the research team, the participants took part in a one-to-one 45-minute session with a Nao robot – a humanoid robot about 60 cm tall – that administered a series of standard psychological questionnaires to assess the mental well-being of each participant.
Participants interacted with the robot throughout the session by speaking with it or by touching sensors on the robot’s hands and feet. Additional sensors tracked participants’ heartbeat, head, and eye movements during the session.
Professor Hatice Gunes, affective intelligence and robotics laboratory, department of computer science, University of Cambridge, said: “Children are quite tactile, and they’re drawn to technology. If they’re using a screen-based tool, they’re withdrawn from the physical world,” she said. “But robots are perfect because they’re in the physical world – they’re more interactive, so the children are more engaged.”
Prior to each session the children and their parent or guardian completed standard online questionnaires to assess each child’s mental well-being.
During each session, the robot performed four different tasks:
- Asked open-ended questions about happy and sad memories over the last week.
- Administered the Short Mood and Feelings Questionnaire (SMFQ).
- Administered a picture task inspired by the Children’s Apperception Test (CAT), where children are asked to answer questions related to pictures shown.
- Administered the Revised Children’s Anxiety and Depression Scale (RCADS) for generalized anxiety, panic disorder, and low mood.
Following the SMFQ children were divided into three different groups according to how likely they were to be struggling with their mental well-being.
The researchers found that children with varying levels of well-being concerns interacted differently with the robot. For children that might not be experiencing mental well-being–related problems, the researchers found that interacting with the robot led to more positive response ratings to the questionnaires. However, for children that might be experiencing well-being–related concerns, the robot may have enabled them to divulge their true feelings and experiences, leading to more negative response ratings to the questionnaire.
Robots an addition not a replacement
“Since the robot we use is child-sized, and completely nonthreatening, children might see the robot as a confidant – they feel like they won’t get into trouble if they share secrets with it,” said Ms. Abbasi. “Other researchers have found that children are more likely to divulge private information – like that they’re being bullied, for example – to a robot than they would be to an adult,” she said.
Study participants all said they “enjoyed talking with the robot,” commented the authors, who added that, “the children were willing to confide in the robot, in some cases sharing information with the robot that they had not yet shared via the standard assessment method of online or in-person questionnaires.”
This is the first time that robots have been used to assess mental well-being in children, the researchers pointed out. “Robots could be a useful addition to traditional methods of mental health assessment,” they said, though they emphasized that robots are “not intended to be a substitute for professional mental health support.”
“We don’t have any intention of replacing psychologists or other mental health professionals with robots, since their expertise far surpasses anything a robot can do,” said Dr. Micol Spitale, affective computing and robotics laboratory, University of Cambridge, and study coauthor. “However, our work suggests that robots could be a useful tool in helping children to open up and share things they might not be comfortable sharing at first.”
The researchers say that they hope to expand their survey in future by including more participants and following them over time. They are also investigating whether similar results could be achieved if children interact with the robot via video chat.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
Robots can be better at detecting mental well-being issues in children than parent-reported or self-reported testing, say U.K. researchers.
The researchers behind a new study, presented at the 31st IEEE International Conference on Robot & Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN) in Naples, Italy, have suggested that robots could be a useful addition to traditional methods of mental health assessment.
“There are times when traditional methods aren’t able to catch mental well-being lapses in children, as sometimes the changes are incredibly subtle,” said Nida Itrat Abbasi, a PhD student at Cambridge (England) Affective Computing and Robotics Group, University of Cambridge, and the study’s first author. “We wanted to see whether robots might be able to help with this process,” she explained.
The authors highlighted how, during the COVID-19 pandemic, home schooling, financial pressures, and isolation from peers and friends impacted the mental health of many children. Even before the pandemic however, anxiety and depression among children in the United Kingdom has been on the rise, but the resources and support to address mental well-being are severely limited.
Children engage with robots
For their study the research team – which comprised roboticists, computer scientists, and psychiatrists from the University of Cambridge – enrolled 28 participants between ages 8 and 13 years. While being observed from an adjacent room by a parent or guardian, along with members of the research team, the participants took part in a one-to-one 45-minute session with a Nao robot – a humanoid robot about 60 cm tall – that administered a series of standard psychological questionnaires to assess the mental well-being of each participant.
Participants interacted with the robot throughout the session by speaking with it or by touching sensors on the robot’s hands and feet. Additional sensors tracked participants’ heartbeat, head, and eye movements during the session.
Professor Hatice Gunes, affective intelligence and robotics laboratory, department of computer science, University of Cambridge, said: “Children are quite tactile, and they’re drawn to technology. If they’re using a screen-based tool, they’re withdrawn from the physical world,” she said. “But robots are perfect because they’re in the physical world – they’re more interactive, so the children are more engaged.”
Prior to each session the children and their parent or guardian completed standard online questionnaires to assess each child’s mental well-being.
During each session, the robot performed four different tasks:
- Asked open-ended questions about happy and sad memories over the last week.
- Administered the Short Mood and Feelings Questionnaire (SMFQ).
- Administered a picture task inspired by the Children’s Apperception Test (CAT), where children are asked to answer questions related to pictures shown.
- Administered the Revised Children’s Anxiety and Depression Scale (RCADS) for generalized anxiety, panic disorder, and low mood.
Following the SMFQ children were divided into three different groups according to how likely they were to be struggling with their mental well-being.
The researchers found that children with varying levels of well-being concerns interacted differently with the robot. For children that might not be experiencing mental well-being–related problems, the researchers found that interacting with the robot led to more positive response ratings to the questionnaires. However, for children that might be experiencing well-being–related concerns, the robot may have enabled them to divulge their true feelings and experiences, leading to more negative response ratings to the questionnaire.
Robots an addition not a replacement
“Since the robot we use is child-sized, and completely nonthreatening, children might see the robot as a confidant – they feel like they won’t get into trouble if they share secrets with it,” said Ms. Abbasi. “Other researchers have found that children are more likely to divulge private information – like that they’re being bullied, for example – to a robot than they would be to an adult,” she said.
Study participants all said they “enjoyed talking with the robot,” commented the authors, who added that, “the children were willing to confide in the robot, in some cases sharing information with the robot that they had not yet shared via the standard assessment method of online or in-person questionnaires.”
This is the first time that robots have been used to assess mental well-being in children, the researchers pointed out. “Robots could be a useful addition to traditional methods of mental health assessment,” they said, though they emphasized that robots are “not intended to be a substitute for professional mental health support.”
“We don’t have any intention of replacing psychologists or other mental health professionals with robots, since their expertise far surpasses anything a robot can do,” said Dr. Micol Spitale, affective computing and robotics laboratory, University of Cambridge, and study coauthor. “However, our work suggests that robots could be a useful tool in helping children to open up and share things they might not be comfortable sharing at first.”
The researchers say that they hope to expand their survey in future by including more participants and following them over time. They are also investigating whether similar results could be achieved if children interact with the robot via video chat.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
AVAHO 2022: A Boost of Confidence
Lauren G. Cliffel, MSW, looks forward to the upcoming 2022 Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) annual meeting and the opportunity to connect in-person with social workers, physicians, nurses, cancer navigators, and other cancer care providers who share a mission to establish and expand oncology programs for veterans.
The theme of this year's annual meeting is "Your Best Version: Self-care in Cancer Care." Sessions include a discussion by a cancer care provider who was also a cancer patient, as well as presentations on the VA Whole Health initiative, survivorship, palliative care, and the Schwartz Rounds initiative. In addition, there will be sessions on self-care that include methods to address burnout and compassion fatigue.
Lauren G. Cliffel, MSW, looks forward to the upcoming 2022 Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) annual meeting and the opportunity to connect in-person with social workers, physicians, nurses, cancer navigators, and other cancer care providers who share a mission to establish and expand oncology programs for veterans.
The theme of this year's annual meeting is "Your Best Version: Self-care in Cancer Care." Sessions include a discussion by a cancer care provider who was also a cancer patient, as well as presentations on the VA Whole Health initiative, survivorship, palliative care, and the Schwartz Rounds initiative. In addition, there will be sessions on self-care that include methods to address burnout and compassion fatigue.
Lauren G. Cliffel, MSW, looks forward to the upcoming 2022 Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) annual meeting and the opportunity to connect in-person with social workers, physicians, nurses, cancer navigators, and other cancer care providers who share a mission to establish and expand oncology programs for veterans.
The theme of this year's annual meeting is "Your Best Version: Self-care in Cancer Care." Sessions include a discussion by a cancer care provider who was also a cancer patient, as well as presentations on the VA Whole Health initiative, survivorship, palliative care, and the Schwartz Rounds initiative. In addition, there will be sessions on self-care that include methods to address burnout and compassion fatigue.