User login
Life after death, and the case of the disappearing digit
It’s alive!!!
Calling all “The Walking Dead” fans! Did you know that, after death, certain cells in the brain can stay active and even become colossal?
Researchers evaluated brain tissue to feign the gene expression during autopsy and death. By doing this, they found that these inflammatory cells, called glial cells, can increase gene expression and “grow and sprout long arm-like appendages for many hours after death.”
According to Dr. Jeffrey Loeb, the study’s senior author, the continued growth after death doesn’t come as a shock since these are the cells that do damage control after certain brain injuries, such as stroke.
Maybe those mindless zombies aren’t so mindless after all. We’re not sure if we should be more scared of a zombie that can think, or a zombie that can’t. We’re sensing a spin-off!
Beam me up, Doc!
In the realm of Star Trek, Dr. Leonard “Bones” McCoy isn’t the only physician who seems to find merit in the adventures of the starship Enterprise.
Pediatric cardiologist Victor Grech, it was reported, has been so influenced by the generational hit that the show made special guest appearances in his medical writing.
The alarm was sounded by a student at Oxford University who had suspicions about more than 100 articles published in Early Human Development. Of the articles eventually withdrawn by the journal’s publisher, Elsevier, 26 were on COVID-19 alone.
Just like a Romulan cloaking device, where the stories once stood Elsevier has left a “withdrawn” statement, making the articles vanish out of thin air.
Along with articles on COVID-19, Dr. Grech’s 48-article series with coauthors on how to write a scientific paper rightfully came into question. Elsevier’s statement on the incident says that the journal’s editorial work flow has been redesigned “to ensure that this will not happen again in the future.”
The number of retracted articles boldly puts Dr. Grech in a lane where few men have gone before.
Something’s wrong, but I can’t put my finger on it
Mixed martial arts is not a sport for the faint of heart. However, we doubt fans who were watching the Khetag Pliev/Devin Goodale fight on April 1 were prepared for the announcement that a search was commencing for a missing finger. Not broken, in case you think that was a misprint. Completely 100% removed from the rest of the hand.
One would think that pinpointing the exact moment when the finger, belonging to Mr. Pliev, was severed would be easy, but the video evidence is unclear, with the best guess being that a kick in the first round broke the finger and a grapple in the second severed it completely. Mr. Pliev was not helpful in clearing up the matter; not only did he fail to immediately notice the fact that his finger had broken or severed, he tried to keep the fight going after the second round when the referee noticed some blood where his left ring finger should have been. He thought he was winning. Unfortunately, the doctor on hand, who was clearly a complete drag, felt differently, ending the fight and awarding it to Mr. Goodale in a technical knockout.
Rest assured, there is a happy ending to this gruesome story. After a frantic search, the missing finger was found deep within Mr. Pliev’s glove and was successfully reattached in a Philadelphia emergency room.
The LOTME team commends Mr. Pliev’s commitment to his craft by wanting to continue the fight, but we respectfully disagree with his assertion that he was winning. We’re fairly confident that body part removal is an automatic loss (pun intended), unless you’re the Black Knight from “Monty Python and the Holy Grail.” Then it’s a draw.
Take two cookies and call me in the morning
The placebo effect is a well-known phenomenon. A pharmacologically inactive treatment can help people if they don’t know it’s pharmacologically inactive. But what if they did know? Would it still work?
That’s what researchers at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston wanted to find out. They divided a cohort of patients with irritable bowel syndrome into three groups. One group got pill bottles containing “open-label placebo,” so the subjects knew they were getting a placebo. The second received bottles labeled “double-blind placebo or peppermint oil.” The third got no pills but followed the rest of the study protocol.
Can you see where this is going? Two-thirds of the open-label placebo group had meaningful improvement of their symptoms, there was no difference in improvement between the two placebo groups, and both did significantly better than the no-pill group.
“If the presumption that deception is necessary for placebos to be effective is false, then many theories about the mechanisms that drive placebo effects may need modification,” investigator Ted J. Kaptchuk said in a written statement.
In other words, this changes everything. Who needs real drugs when anything that a doctor gives to a patient will help? Someone who has trouble swallowing pills can get a milkshake instead. Kid doesn’t like the taste of amoxicillin? Prescribe a slice of therapeutic pizza. Vaccine deniers can get a shot of vitamin C … or bourbon. And just imagine all the good that can be done in this crazy, mixed up world with a batch of chocolate chip cookies.
It’s alive!!!
Calling all “The Walking Dead” fans! Did you know that, after death, certain cells in the brain can stay active and even become colossal?
Researchers evaluated brain tissue to feign the gene expression during autopsy and death. By doing this, they found that these inflammatory cells, called glial cells, can increase gene expression and “grow and sprout long arm-like appendages for many hours after death.”
According to Dr. Jeffrey Loeb, the study’s senior author, the continued growth after death doesn’t come as a shock since these are the cells that do damage control after certain brain injuries, such as stroke.
Maybe those mindless zombies aren’t so mindless after all. We’re not sure if we should be more scared of a zombie that can think, or a zombie that can’t. We’re sensing a spin-off!
Beam me up, Doc!
In the realm of Star Trek, Dr. Leonard “Bones” McCoy isn’t the only physician who seems to find merit in the adventures of the starship Enterprise.
Pediatric cardiologist Victor Grech, it was reported, has been so influenced by the generational hit that the show made special guest appearances in his medical writing.
The alarm was sounded by a student at Oxford University who had suspicions about more than 100 articles published in Early Human Development. Of the articles eventually withdrawn by the journal’s publisher, Elsevier, 26 were on COVID-19 alone.
Just like a Romulan cloaking device, where the stories once stood Elsevier has left a “withdrawn” statement, making the articles vanish out of thin air.
Along with articles on COVID-19, Dr. Grech’s 48-article series with coauthors on how to write a scientific paper rightfully came into question. Elsevier’s statement on the incident says that the journal’s editorial work flow has been redesigned “to ensure that this will not happen again in the future.”
The number of retracted articles boldly puts Dr. Grech in a lane where few men have gone before.
Something’s wrong, but I can’t put my finger on it
Mixed martial arts is not a sport for the faint of heart. However, we doubt fans who were watching the Khetag Pliev/Devin Goodale fight on April 1 were prepared for the announcement that a search was commencing for a missing finger. Not broken, in case you think that was a misprint. Completely 100% removed from the rest of the hand.
One would think that pinpointing the exact moment when the finger, belonging to Mr. Pliev, was severed would be easy, but the video evidence is unclear, with the best guess being that a kick in the first round broke the finger and a grapple in the second severed it completely. Mr. Pliev was not helpful in clearing up the matter; not only did he fail to immediately notice the fact that his finger had broken or severed, he tried to keep the fight going after the second round when the referee noticed some blood where his left ring finger should have been. He thought he was winning. Unfortunately, the doctor on hand, who was clearly a complete drag, felt differently, ending the fight and awarding it to Mr. Goodale in a technical knockout.
Rest assured, there is a happy ending to this gruesome story. After a frantic search, the missing finger was found deep within Mr. Pliev’s glove and was successfully reattached in a Philadelphia emergency room.
The LOTME team commends Mr. Pliev’s commitment to his craft by wanting to continue the fight, but we respectfully disagree with his assertion that he was winning. We’re fairly confident that body part removal is an automatic loss (pun intended), unless you’re the Black Knight from “Monty Python and the Holy Grail.” Then it’s a draw.
Take two cookies and call me in the morning
The placebo effect is a well-known phenomenon. A pharmacologically inactive treatment can help people if they don’t know it’s pharmacologically inactive. But what if they did know? Would it still work?
That’s what researchers at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston wanted to find out. They divided a cohort of patients with irritable bowel syndrome into three groups. One group got pill bottles containing “open-label placebo,” so the subjects knew they were getting a placebo. The second received bottles labeled “double-blind placebo or peppermint oil.” The third got no pills but followed the rest of the study protocol.
Can you see where this is going? Two-thirds of the open-label placebo group had meaningful improvement of their symptoms, there was no difference in improvement between the two placebo groups, and both did significantly better than the no-pill group.
“If the presumption that deception is necessary for placebos to be effective is false, then many theories about the mechanisms that drive placebo effects may need modification,” investigator Ted J. Kaptchuk said in a written statement.
In other words, this changes everything. Who needs real drugs when anything that a doctor gives to a patient will help? Someone who has trouble swallowing pills can get a milkshake instead. Kid doesn’t like the taste of amoxicillin? Prescribe a slice of therapeutic pizza. Vaccine deniers can get a shot of vitamin C … or bourbon. And just imagine all the good that can be done in this crazy, mixed up world with a batch of chocolate chip cookies.
It’s alive!!!
Calling all “The Walking Dead” fans! Did you know that, after death, certain cells in the brain can stay active and even become colossal?
Researchers evaluated brain tissue to feign the gene expression during autopsy and death. By doing this, they found that these inflammatory cells, called glial cells, can increase gene expression and “grow and sprout long arm-like appendages for many hours after death.”
According to Dr. Jeffrey Loeb, the study’s senior author, the continued growth after death doesn’t come as a shock since these are the cells that do damage control after certain brain injuries, such as stroke.
Maybe those mindless zombies aren’t so mindless after all. We’re not sure if we should be more scared of a zombie that can think, or a zombie that can’t. We’re sensing a spin-off!
Beam me up, Doc!
In the realm of Star Trek, Dr. Leonard “Bones” McCoy isn’t the only physician who seems to find merit in the adventures of the starship Enterprise.
Pediatric cardiologist Victor Grech, it was reported, has been so influenced by the generational hit that the show made special guest appearances in his medical writing.
The alarm was sounded by a student at Oxford University who had suspicions about more than 100 articles published in Early Human Development. Of the articles eventually withdrawn by the journal’s publisher, Elsevier, 26 were on COVID-19 alone.
Just like a Romulan cloaking device, where the stories once stood Elsevier has left a “withdrawn” statement, making the articles vanish out of thin air.
Along with articles on COVID-19, Dr. Grech’s 48-article series with coauthors on how to write a scientific paper rightfully came into question. Elsevier’s statement on the incident says that the journal’s editorial work flow has been redesigned “to ensure that this will not happen again in the future.”
The number of retracted articles boldly puts Dr. Grech in a lane where few men have gone before.
Something’s wrong, but I can’t put my finger on it
Mixed martial arts is not a sport for the faint of heart. However, we doubt fans who were watching the Khetag Pliev/Devin Goodale fight on April 1 were prepared for the announcement that a search was commencing for a missing finger. Not broken, in case you think that was a misprint. Completely 100% removed from the rest of the hand.
One would think that pinpointing the exact moment when the finger, belonging to Mr. Pliev, was severed would be easy, but the video evidence is unclear, with the best guess being that a kick in the first round broke the finger and a grapple in the second severed it completely. Mr. Pliev was not helpful in clearing up the matter; not only did he fail to immediately notice the fact that his finger had broken or severed, he tried to keep the fight going after the second round when the referee noticed some blood where his left ring finger should have been. He thought he was winning. Unfortunately, the doctor on hand, who was clearly a complete drag, felt differently, ending the fight and awarding it to Mr. Goodale in a technical knockout.
Rest assured, there is a happy ending to this gruesome story. After a frantic search, the missing finger was found deep within Mr. Pliev’s glove and was successfully reattached in a Philadelphia emergency room.
The LOTME team commends Mr. Pliev’s commitment to his craft by wanting to continue the fight, but we respectfully disagree with his assertion that he was winning. We’re fairly confident that body part removal is an automatic loss (pun intended), unless you’re the Black Knight from “Monty Python and the Holy Grail.” Then it’s a draw.
Take two cookies and call me in the morning
The placebo effect is a well-known phenomenon. A pharmacologically inactive treatment can help people if they don’t know it’s pharmacologically inactive. But what if they did know? Would it still work?
That’s what researchers at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston wanted to find out. They divided a cohort of patients with irritable bowel syndrome into three groups. One group got pill bottles containing “open-label placebo,” so the subjects knew they were getting a placebo. The second received bottles labeled “double-blind placebo or peppermint oil.” The third got no pills but followed the rest of the study protocol.
Can you see where this is going? Two-thirds of the open-label placebo group had meaningful improvement of their symptoms, there was no difference in improvement between the two placebo groups, and both did significantly better than the no-pill group.
“If the presumption that deception is necessary for placebos to be effective is false, then many theories about the mechanisms that drive placebo effects may need modification,” investigator Ted J. Kaptchuk said in a written statement.
In other words, this changes everything. Who needs real drugs when anything that a doctor gives to a patient will help? Someone who has trouble swallowing pills can get a milkshake instead. Kid doesn’t like the taste of amoxicillin? Prescribe a slice of therapeutic pizza. Vaccine deniers can get a shot of vitamin C … or bourbon. And just imagine all the good that can be done in this crazy, mixed up world with a batch of chocolate chip cookies.
Disparities and racism in health care
From Anarcha Westcott to George Floyd to the Atlanta massacre
The Atlanta spa massacre, the commencement of the George Floyd trial, and COVID-19 highlight societal inequalities and health disparities among minority groups. We can only hope that we have arrived at the tipping point to address historical institutional racism and structural violence in this country.
Admittedly, we, as health care professionals, have been at best apathetic and at worst complicit with this tragedy. Dr. James Sims, the father of gynecology, perfected his surgical techniques of vaginal fistula on slaves. Starting in 1845, he performed over thirty surgeries without anesthesia on Anarcha Westcott.1 Moreover, the past century was dotted with similar transgressions such as the Tuskegee Untreated Syphilis Experiment from 1932 to 1972, the use of the cells of Henrietta Lack in 1951, and the disproportionate lack of funding of sickle cell research.2 We must move from complicit/apathetic to being part of the discourse and solution.
The juxtaposition of George Floyd’s cry of “I can’t breathe” and the disproportionate way in which COVID-19 has affected Black communities and people of color highlights how deeply entrenched the problem of systemic racism is in this country. The innumerable reported hate crimes against Asian Americans stemming from xenophobia linked to the COVID-19 pandemic and the stereotyping of Hispanic Americans as criminals during the last U.S. administration demonstrate that all minority racial/ethnic groups are affected. As clinicians who care for the health of our communities and strive to reduce suffering, we have a responsibility to identify discrimination that exists in the health care system – ranging from subtle implicit bias to overt discrimination.3
Unconscious bias and its effect on diversity and inclusion has only recently been recognized and addressed in the realm of health care as applied to clinicians. This is key to structural racism as providers inadvertently use unconscious bias every day to make their medical decisions quick and efficient. As Dayna Bowen Matthews points out in her book, “Just Medicine,” “where health and health care are concerned, even when implicit biases are based on seemingly benign distinctions, or supported by apparently rational or widely held observations, these biases can cause grave individual, group, and societal harm that is commensurate to and even exceeds the harm caused by outright racism.” To deny the prejudices that providers have when making decisions for patients will perpetuate the racism and hinder our ability to overcome health inequity. Americans of racial and ethnic minorities have a higher incidence of chronic diseases and premature death when compared to white Americans.4 These disparities exist even when controlling for individual variations such as availability of health insurance, education, and socioeconomic status.5 Social determinants of health because of racial differences is often talked about as a cause of health care inequity, but given the evidence that providers play a much more active role in this, we need to become more comfortable with the discomfort of using the word “racism” if we intend to bring awareness and create change.
In order to tackle structural racism in health care, organizations must take a multifaceted approach. Evidence-based strategies include: creation of an inclusive workforce, diversification of the workforce to better represent patient populations, and education/training on the effect of implicit bias on equitable health care.6 These aspirations can provide a framework for interventions at all levels of health care organizations.
The JEDI (justice, equity, diversity, and inclusion) committee of the section of hospital medicine at Wake Forest Baptist Health System came into existence in November 2019. The objective for JEDI was to use evidence-based methods to help create an environment that would lead to the creation of a diverse and inclusive hospital medicine group. Prior to establishing our committee, we interviewed providers from traditional minority groups who were part of our practice to bring clarity to the discrimination faced by our providers from colleagues, staff, and patients. The discrimination varied from microaggressions caused by implicit biases to macroaggression from overt discrimination. We initiated our work on this burning platform by following the evidence-based methods mentioned earlier.
Creation of an inclusive workforce. Our working committee included members of varied backgrounds and experiences who were passionate about enhancing equity while focusing on inclusion and wellness. The committee brainstormed ideas for interventions that could make a positive impact for our teammates. Individual providers voted to choose the interventions that would positively impact their inclusion and health. Using a validated survey,7 we were able to measure the degree of inclusion of our work group based on multiple demographics including age, gender, race/ethnicity, training (physician vs. APP), etc. Our intention is to complete the proposed interventions before remeasuring inclusion to understand the effect of our work.
Diversifying the workforce. Although our section of hospital medicine at Wake Forest Baptist Health System consists of providers self-identifying as people of color, we do not adequately mirror the racial composition of the population we serve. To achieve the desired result, we have made changes to our recruiting program. The section of hospital medicine visibly demonstrates our commitment to diversity and displays our values on our website. We intend for this to attract diverse individuals who would intend to be part of our group.
Education and training on impact of implicit bias on equitable health care. Implicit bias training will have to consist of actions that would help our clinicians recognize their own prejudices and find means to mitigate them. We have committed to bystander education that would give practice and words to our providers to speak up in situations where they see discrimination in the workplace that is directed against patients, staff, and colleagues. A series of open and honest conversations about racial and gender discrimination in health care that involves inviting accomplished speakers from around the country has been planned. Continued attention to opportunities to further awareness on this subject is vital.
On Jan. 6, 2021, a day that should have filled citizens with pride and hope with the election of the first Black minister and the first Jewish man to the U.S. Senate in a historically conservative state, as well as the confirmation of the election of a president who pledged to address racial disparities, we instead saw another stark reminder of where we came from and just how far we have to go. White supremacists incited by their perceived threat to a legacy of centuries of suppression transformed into a mob of insurrectionists, blatantly bearing Confederate and Nazi flags, and seemingly easily invaded and desecrated the U.S. Capitol. On March 16, 2021, a white male who was “having a bad day” ended the lives of eight individuals, including six Asian Americans.
These instances have brought forth the reality that many of our interventions have been directed towards subtle prejudices and microaggressions alone. We have skirted around calling out overt discrimination of minority groups and failed to openly acknowledge our own contribution to the problem. This newly found awareness has created an opportunity for more impactful work. The equitable delivery of health care is dependent on creating a patient-provider relationship based on trust; addressing overt discrimination respectfully; and overcoming unconscious bias.
While we have made the commitment to confront structural racism in our workplace and taken important steps to work towards this goal with the initiatives set forth by our JEDI committee, we certainly have a long way to go. George Floyd spent the last 8 minutes and 46 seconds of his life struggling to breathe and asking for his mother. Let’s not waste another second and instead be the change that we seek in health care.
Dr. Nagaraj is medical director, Hospital Medicine, at Lexington (N.C.) Medical Center, assistant professor at Wake Forest School of Medicine, and cochair, JEDI committee for diversity and inclusion, hospital medicine, at Wake Forest Baptist Health, Winston-Salem, NC. Ms. Haller is cochair, JEDI committee for diversity and inclusion, hospital medicine, Wake Forest Baptist Health. Dr. Huang is the executive medical director and service line director of general medicine and hospital medicine within the Wake Forest Baptist Health System and associate professor at Wake Forest School of Medicine. The authors would like to acknowledge Dr. Julie Freischlag, Dr. Kevin High, and Dr. David McIntosh at Wake Forest Baptist Health System for the support of the JEDI committee and the section on hospital medicine.
References
1. Holland B. The “father of modern gynecology” performed shocking experiments on enslaved women. History. 2017 Aug 29. www.history.com/news/the-father-of-modern-gynecology-performed-shocking-experiments-on-slaves.
2. Buseh AG et al. Community leaders’ perspectives on engaging African Americans in biobanks and other human genetics initiatives. J Community Genet. 2013 Oct;4(4):483-94. doi: 10.1007/s12687-013-0155-z.
3. National Center for Health Statistics. Health, United States, 2015: With special feature on racial and ethnic health disparities. 2016 May. www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hus/hus15.pdf.
4. Bailey ZD et al. Structural racism and health inequities in the USA: evidence and interventions. Lancet. 2017 Apr 8;389(10077):1453-63. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30569-X.
5. Arvizo C and Garrison E. Diversity and inclusion: the role of unconscious bias on patient care, health outcomes and the workforce in obstetrics and gynaecology. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Oct;31(5):356-62. doi: 10.1097/GCO.0000000000000566.
6. Chung BG et al. Work group inclusion: test of a scale and model. Group & Organization Management. 2020;45(1):75-102. doi: 10.1177/1059601119839858.
From Anarcha Westcott to George Floyd to the Atlanta massacre
From Anarcha Westcott to George Floyd to the Atlanta massacre
The Atlanta spa massacre, the commencement of the George Floyd trial, and COVID-19 highlight societal inequalities and health disparities among minority groups. We can only hope that we have arrived at the tipping point to address historical institutional racism and structural violence in this country.
Admittedly, we, as health care professionals, have been at best apathetic and at worst complicit with this tragedy. Dr. James Sims, the father of gynecology, perfected his surgical techniques of vaginal fistula on slaves. Starting in 1845, he performed over thirty surgeries without anesthesia on Anarcha Westcott.1 Moreover, the past century was dotted with similar transgressions such as the Tuskegee Untreated Syphilis Experiment from 1932 to 1972, the use of the cells of Henrietta Lack in 1951, and the disproportionate lack of funding of sickle cell research.2 We must move from complicit/apathetic to being part of the discourse and solution.
The juxtaposition of George Floyd’s cry of “I can’t breathe” and the disproportionate way in which COVID-19 has affected Black communities and people of color highlights how deeply entrenched the problem of systemic racism is in this country. The innumerable reported hate crimes against Asian Americans stemming from xenophobia linked to the COVID-19 pandemic and the stereotyping of Hispanic Americans as criminals during the last U.S. administration demonstrate that all minority racial/ethnic groups are affected. As clinicians who care for the health of our communities and strive to reduce suffering, we have a responsibility to identify discrimination that exists in the health care system – ranging from subtle implicit bias to overt discrimination.3
Unconscious bias and its effect on diversity and inclusion has only recently been recognized and addressed in the realm of health care as applied to clinicians. This is key to structural racism as providers inadvertently use unconscious bias every day to make their medical decisions quick and efficient. As Dayna Bowen Matthews points out in her book, “Just Medicine,” “where health and health care are concerned, even when implicit biases are based on seemingly benign distinctions, or supported by apparently rational or widely held observations, these biases can cause grave individual, group, and societal harm that is commensurate to and even exceeds the harm caused by outright racism.” To deny the prejudices that providers have when making decisions for patients will perpetuate the racism and hinder our ability to overcome health inequity. Americans of racial and ethnic minorities have a higher incidence of chronic diseases and premature death when compared to white Americans.4 These disparities exist even when controlling for individual variations such as availability of health insurance, education, and socioeconomic status.5 Social determinants of health because of racial differences is often talked about as a cause of health care inequity, but given the evidence that providers play a much more active role in this, we need to become more comfortable with the discomfort of using the word “racism” if we intend to bring awareness and create change.
In order to tackle structural racism in health care, organizations must take a multifaceted approach. Evidence-based strategies include: creation of an inclusive workforce, diversification of the workforce to better represent patient populations, and education/training on the effect of implicit bias on equitable health care.6 These aspirations can provide a framework for interventions at all levels of health care organizations.
The JEDI (justice, equity, diversity, and inclusion) committee of the section of hospital medicine at Wake Forest Baptist Health System came into existence in November 2019. The objective for JEDI was to use evidence-based methods to help create an environment that would lead to the creation of a diverse and inclusive hospital medicine group. Prior to establishing our committee, we interviewed providers from traditional minority groups who were part of our practice to bring clarity to the discrimination faced by our providers from colleagues, staff, and patients. The discrimination varied from microaggressions caused by implicit biases to macroaggression from overt discrimination. We initiated our work on this burning platform by following the evidence-based methods mentioned earlier.
Creation of an inclusive workforce. Our working committee included members of varied backgrounds and experiences who were passionate about enhancing equity while focusing on inclusion and wellness. The committee brainstormed ideas for interventions that could make a positive impact for our teammates. Individual providers voted to choose the interventions that would positively impact their inclusion and health. Using a validated survey,7 we were able to measure the degree of inclusion of our work group based on multiple demographics including age, gender, race/ethnicity, training (physician vs. APP), etc. Our intention is to complete the proposed interventions before remeasuring inclusion to understand the effect of our work.
Diversifying the workforce. Although our section of hospital medicine at Wake Forest Baptist Health System consists of providers self-identifying as people of color, we do not adequately mirror the racial composition of the population we serve. To achieve the desired result, we have made changes to our recruiting program. The section of hospital medicine visibly demonstrates our commitment to diversity and displays our values on our website. We intend for this to attract diverse individuals who would intend to be part of our group.
Education and training on impact of implicit bias on equitable health care. Implicit bias training will have to consist of actions that would help our clinicians recognize their own prejudices and find means to mitigate them. We have committed to bystander education that would give practice and words to our providers to speak up in situations where they see discrimination in the workplace that is directed against patients, staff, and colleagues. A series of open and honest conversations about racial and gender discrimination in health care that involves inviting accomplished speakers from around the country has been planned. Continued attention to opportunities to further awareness on this subject is vital.
On Jan. 6, 2021, a day that should have filled citizens with pride and hope with the election of the first Black minister and the first Jewish man to the U.S. Senate in a historically conservative state, as well as the confirmation of the election of a president who pledged to address racial disparities, we instead saw another stark reminder of where we came from and just how far we have to go. White supremacists incited by their perceived threat to a legacy of centuries of suppression transformed into a mob of insurrectionists, blatantly bearing Confederate and Nazi flags, and seemingly easily invaded and desecrated the U.S. Capitol. On March 16, 2021, a white male who was “having a bad day” ended the lives of eight individuals, including six Asian Americans.
These instances have brought forth the reality that many of our interventions have been directed towards subtle prejudices and microaggressions alone. We have skirted around calling out overt discrimination of minority groups and failed to openly acknowledge our own contribution to the problem. This newly found awareness has created an opportunity for more impactful work. The equitable delivery of health care is dependent on creating a patient-provider relationship based on trust; addressing overt discrimination respectfully; and overcoming unconscious bias.
While we have made the commitment to confront structural racism in our workplace and taken important steps to work towards this goal with the initiatives set forth by our JEDI committee, we certainly have a long way to go. George Floyd spent the last 8 minutes and 46 seconds of his life struggling to breathe and asking for his mother. Let’s not waste another second and instead be the change that we seek in health care.
Dr. Nagaraj is medical director, Hospital Medicine, at Lexington (N.C.) Medical Center, assistant professor at Wake Forest School of Medicine, and cochair, JEDI committee for diversity and inclusion, hospital medicine, at Wake Forest Baptist Health, Winston-Salem, NC. Ms. Haller is cochair, JEDI committee for diversity and inclusion, hospital medicine, Wake Forest Baptist Health. Dr. Huang is the executive medical director and service line director of general medicine and hospital medicine within the Wake Forest Baptist Health System and associate professor at Wake Forest School of Medicine. The authors would like to acknowledge Dr. Julie Freischlag, Dr. Kevin High, and Dr. David McIntosh at Wake Forest Baptist Health System for the support of the JEDI committee and the section on hospital medicine.
References
1. Holland B. The “father of modern gynecology” performed shocking experiments on enslaved women. History. 2017 Aug 29. www.history.com/news/the-father-of-modern-gynecology-performed-shocking-experiments-on-slaves.
2. Buseh AG et al. Community leaders’ perspectives on engaging African Americans in biobanks and other human genetics initiatives. J Community Genet. 2013 Oct;4(4):483-94. doi: 10.1007/s12687-013-0155-z.
3. National Center for Health Statistics. Health, United States, 2015: With special feature on racial and ethnic health disparities. 2016 May. www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hus/hus15.pdf.
4. Bailey ZD et al. Structural racism and health inequities in the USA: evidence and interventions. Lancet. 2017 Apr 8;389(10077):1453-63. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30569-X.
5. Arvizo C and Garrison E. Diversity and inclusion: the role of unconscious bias on patient care, health outcomes and the workforce in obstetrics and gynaecology. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Oct;31(5):356-62. doi: 10.1097/GCO.0000000000000566.
6. Chung BG et al. Work group inclusion: test of a scale and model. Group & Organization Management. 2020;45(1):75-102. doi: 10.1177/1059601119839858.
The Atlanta spa massacre, the commencement of the George Floyd trial, and COVID-19 highlight societal inequalities and health disparities among minority groups. We can only hope that we have arrived at the tipping point to address historical institutional racism and structural violence in this country.
Admittedly, we, as health care professionals, have been at best apathetic and at worst complicit with this tragedy. Dr. James Sims, the father of gynecology, perfected his surgical techniques of vaginal fistula on slaves. Starting in 1845, he performed over thirty surgeries without anesthesia on Anarcha Westcott.1 Moreover, the past century was dotted with similar transgressions such as the Tuskegee Untreated Syphilis Experiment from 1932 to 1972, the use of the cells of Henrietta Lack in 1951, and the disproportionate lack of funding of sickle cell research.2 We must move from complicit/apathetic to being part of the discourse and solution.
The juxtaposition of George Floyd’s cry of “I can’t breathe” and the disproportionate way in which COVID-19 has affected Black communities and people of color highlights how deeply entrenched the problem of systemic racism is in this country. The innumerable reported hate crimes against Asian Americans stemming from xenophobia linked to the COVID-19 pandemic and the stereotyping of Hispanic Americans as criminals during the last U.S. administration demonstrate that all minority racial/ethnic groups are affected. As clinicians who care for the health of our communities and strive to reduce suffering, we have a responsibility to identify discrimination that exists in the health care system – ranging from subtle implicit bias to overt discrimination.3
Unconscious bias and its effect on diversity and inclusion has only recently been recognized and addressed in the realm of health care as applied to clinicians. This is key to structural racism as providers inadvertently use unconscious bias every day to make their medical decisions quick and efficient. As Dayna Bowen Matthews points out in her book, “Just Medicine,” “where health and health care are concerned, even when implicit biases are based on seemingly benign distinctions, or supported by apparently rational or widely held observations, these biases can cause grave individual, group, and societal harm that is commensurate to and even exceeds the harm caused by outright racism.” To deny the prejudices that providers have when making decisions for patients will perpetuate the racism and hinder our ability to overcome health inequity. Americans of racial and ethnic minorities have a higher incidence of chronic diseases and premature death when compared to white Americans.4 These disparities exist even when controlling for individual variations such as availability of health insurance, education, and socioeconomic status.5 Social determinants of health because of racial differences is often talked about as a cause of health care inequity, but given the evidence that providers play a much more active role in this, we need to become more comfortable with the discomfort of using the word “racism” if we intend to bring awareness and create change.
In order to tackle structural racism in health care, organizations must take a multifaceted approach. Evidence-based strategies include: creation of an inclusive workforce, diversification of the workforce to better represent patient populations, and education/training on the effect of implicit bias on equitable health care.6 These aspirations can provide a framework for interventions at all levels of health care organizations.
The JEDI (justice, equity, diversity, and inclusion) committee of the section of hospital medicine at Wake Forest Baptist Health System came into existence in November 2019. The objective for JEDI was to use evidence-based methods to help create an environment that would lead to the creation of a diverse and inclusive hospital medicine group. Prior to establishing our committee, we interviewed providers from traditional minority groups who were part of our practice to bring clarity to the discrimination faced by our providers from colleagues, staff, and patients. The discrimination varied from microaggressions caused by implicit biases to macroaggression from overt discrimination. We initiated our work on this burning platform by following the evidence-based methods mentioned earlier.
Creation of an inclusive workforce. Our working committee included members of varied backgrounds and experiences who were passionate about enhancing equity while focusing on inclusion and wellness. The committee brainstormed ideas for interventions that could make a positive impact for our teammates. Individual providers voted to choose the interventions that would positively impact their inclusion and health. Using a validated survey,7 we were able to measure the degree of inclusion of our work group based on multiple demographics including age, gender, race/ethnicity, training (physician vs. APP), etc. Our intention is to complete the proposed interventions before remeasuring inclusion to understand the effect of our work.
Diversifying the workforce. Although our section of hospital medicine at Wake Forest Baptist Health System consists of providers self-identifying as people of color, we do not adequately mirror the racial composition of the population we serve. To achieve the desired result, we have made changes to our recruiting program. The section of hospital medicine visibly demonstrates our commitment to diversity and displays our values on our website. We intend for this to attract diverse individuals who would intend to be part of our group.
Education and training on impact of implicit bias on equitable health care. Implicit bias training will have to consist of actions that would help our clinicians recognize their own prejudices and find means to mitigate them. We have committed to bystander education that would give practice and words to our providers to speak up in situations where they see discrimination in the workplace that is directed against patients, staff, and colleagues. A series of open and honest conversations about racial and gender discrimination in health care that involves inviting accomplished speakers from around the country has been planned. Continued attention to opportunities to further awareness on this subject is vital.
On Jan. 6, 2021, a day that should have filled citizens with pride and hope with the election of the first Black minister and the first Jewish man to the U.S. Senate in a historically conservative state, as well as the confirmation of the election of a president who pledged to address racial disparities, we instead saw another stark reminder of where we came from and just how far we have to go. White supremacists incited by their perceived threat to a legacy of centuries of suppression transformed into a mob of insurrectionists, blatantly bearing Confederate and Nazi flags, and seemingly easily invaded and desecrated the U.S. Capitol. On March 16, 2021, a white male who was “having a bad day” ended the lives of eight individuals, including six Asian Americans.
These instances have brought forth the reality that many of our interventions have been directed towards subtle prejudices and microaggressions alone. We have skirted around calling out overt discrimination of minority groups and failed to openly acknowledge our own contribution to the problem. This newly found awareness has created an opportunity for more impactful work. The equitable delivery of health care is dependent on creating a patient-provider relationship based on trust; addressing overt discrimination respectfully; and overcoming unconscious bias.
While we have made the commitment to confront structural racism in our workplace and taken important steps to work towards this goal with the initiatives set forth by our JEDI committee, we certainly have a long way to go. George Floyd spent the last 8 minutes and 46 seconds of his life struggling to breathe and asking for his mother. Let’s not waste another second and instead be the change that we seek in health care.
Dr. Nagaraj is medical director, Hospital Medicine, at Lexington (N.C.) Medical Center, assistant professor at Wake Forest School of Medicine, and cochair, JEDI committee for diversity and inclusion, hospital medicine, at Wake Forest Baptist Health, Winston-Salem, NC. Ms. Haller is cochair, JEDI committee for diversity and inclusion, hospital medicine, Wake Forest Baptist Health. Dr. Huang is the executive medical director and service line director of general medicine and hospital medicine within the Wake Forest Baptist Health System and associate professor at Wake Forest School of Medicine. The authors would like to acknowledge Dr. Julie Freischlag, Dr. Kevin High, and Dr. David McIntosh at Wake Forest Baptist Health System for the support of the JEDI committee and the section on hospital medicine.
References
1. Holland B. The “father of modern gynecology” performed shocking experiments on enslaved women. History. 2017 Aug 29. www.history.com/news/the-father-of-modern-gynecology-performed-shocking-experiments-on-slaves.
2. Buseh AG et al. Community leaders’ perspectives on engaging African Americans in biobanks and other human genetics initiatives. J Community Genet. 2013 Oct;4(4):483-94. doi: 10.1007/s12687-013-0155-z.
3. National Center for Health Statistics. Health, United States, 2015: With special feature on racial and ethnic health disparities. 2016 May. www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hus/hus15.pdf.
4. Bailey ZD et al. Structural racism and health inequities in the USA: evidence and interventions. Lancet. 2017 Apr 8;389(10077):1453-63. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30569-X.
5. Arvizo C and Garrison E. Diversity and inclusion: the role of unconscious bias on patient care, health outcomes and the workforce in obstetrics and gynaecology. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Oct;31(5):356-62. doi: 10.1097/GCO.0000000000000566.
6. Chung BG et al. Work group inclusion: test of a scale and model. Group & Organization Management. 2020;45(1):75-102. doi: 10.1177/1059601119839858.
Antimicrobial, pH-modulating gel shows promise in preventing common STIs
An investigational vaginal gel significantly reduced urogenital chlamydia and gonorrhea in women at high risk for infection, compared with placebo, opening up new possibilities for an on-demand prevention option. Investigators of a randomized trial reported these findings in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Rates of Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) and Neisseria gonorrhoeae (GC) are on the rise in the United States, despite wide availability of male and female condoms to prevent sexually transmitted infections. This suggests that women need a more discrete method that they can better control. Other vaginal microbicides developed over the last few decades haven’t performed well in protecting against STIs or HIV in clinical trials.
The slightly alkaline nature of human semen has the potential to neutralize vaginal pH after intercourse, creating a more vulnerable environment for STIs. EVO100 is an investigational antimicrobial, bioadhesive vaginal gel that contains L-lactic acid, citric acid, and potassium bitartrate. In preclinical studies, it was highly effective at buffering the alkaline properties of human semen and maintaining vaginal pH levels. Patients generally tolerated it well, aside from some reports of vaginal itching and burning.
In the AMPREVENCE study, a double-blinded, placebo-controlled, randomized, phase 2b/3 trial, Todd Chappell, MD, of Adams Patterson Gynecology & Obstetrics, Memphis, and colleagues tested the efficacy and safety of EVO100 to prevent chlamydia and gonorrhea.
Investigators randomized 1:1,860 healthy, sexually active women to receive either EVO100 (n = 426) or placebo (n = 434). Participants had either been diagnosed or treated for these STIs up to 16 weeks prior to enrollment. Among those enrolled, 335 women in the EVO100 arm and 335 women in the placebo arm completed the study.
From this cohort, 764 women (EVO100: n = 376; placebo: n = 388) reported any use of either product. These women represented the “safety analysis population,” a predefined population for statistical analysis.
Participants averaged nearly 28 years of age, had a median body mass index of 28.9 kg/m2, and represented several racial/ethnic groups: White (54.3% [467/860]), African American (41.6% [358/860]), and non-Hispanic/Latinx ethnicity (67.1% [577/860]).
The women were instructed to apply the drug within 1 hour of initiating sexual intercourse. Investigators scheduled follow-up visits every 4 weeks during the 16-week study period, to obtain repeat CT/GC assessments, review diary entries, and to collect information about adverse effects and use of concomitant medications. During enrollment, participants consented to return to the clinic at each study visit. If a woman missed a visit, the study site would follow-up by telephone after the missed assessment visit.
Participants reported a mean number of 16 coital events (EVO100, 15.7 [13.5]; placebo, 16.3 [15.8]). EVO100 significantly reduced STI incidence for both types of STIs. CT infection rates among EVO100 users was 4.8% (14/289), half of what it was in placebo users (9.7% [28/290]) (P = .0256). The investigational method was even more successful in GC-analysis–eligible women: infection rates averaged 0.7% (2/280), compared with 3.2% (9/277) in the placebo group, a relative risk reduction of 78% (P = .0316).
Examining electronic diary entries of the participants, investigators reported similar adherence rates among the two treatment arms. However, additional sensitivity analyses in CT-eligible and GC-eligible populations on adherence yielded notably different results.
EVO100 users in the CT population who used the product as directed 100% of the time were significantly less likely to become infected, compared with the placebo group (2.3% vs. 16.9%, P = .0012). However, investigators found no significant differences in infection rates among women with poorer adherence rates in the two groups. Comparatively, they found no major differences in GC infection rates between the control and EVO100 groups, regardless of adherence rates, likely because of the small number of GC infections reported. Observed adverse events correlated with the drug’s known safety profile.
Most of the participants said they would likely recommend EVO100 to other women and continue using this preventive treatment.
A small GC subgroup caused by fewer infection cases and reliance on participant self-reporting of coital incidents may have limited the study’s results. “While use of the electronic diaries is helpful for collection of study data, it may encourage compliance and efficacy that may be higher in the ‘real-world’ population outside of the setting of a clinical trial,” noted Dr. Chappell and colleagues.
According to the investigators, this is the first prospective, randomized trial to study the use of an antimicrobial bioadhesive vaginal gel for preventing CT and GC infection. “EVO100 has the potential of fulfilling an unmet need in women’s sexual health as a new on-demand, woman-controlled option that reduces the risk of urogenital CT and GC infections,” the authors concluded.
The Food and Drug Administration has already approved EVO100 as a contraceptive option (Phexxi), Dr. Chappell said in an interview. Next steps are to conduct a phase 3 trial, which is currently underway. “If the findings are positive, we will submit to the FDA for review and approval of EVO100” for preventing these STIs.
These are promising results, Catherine Cansino, MD, MPH, an associate clinical professor with the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of California, Davis, said in an interview. It’s always helpful to look at effective treatments, “especially those that aren’t traditional antibiotics in order to decrease the risk of antibiotic resistance,” said Dr. Cansino, who was not part of the study. This is why EVO100 is such an attractive option.
Future studies should look at a broader population, she continued. “The population this study looked at is not the general population – these women had an infection at some point, previously,” which means they are potentially at higher risk for reinfection. “Looking at what their likelihood is of getting infected again, it’s hard to know if this would be the same or different from the general population.” If the drug appears to cause a decrease in new infections, the relative risk reduction is actually greater than what’s reported. If the reinfection rate for this population is lower because people who’ve had infections are practicing safer sex, the relative risk reduction would be lower, explained Dr. Cansino.
Dr. Chappell and several coauthors received research funding from Evofem Biosciences.
An investigational vaginal gel significantly reduced urogenital chlamydia and gonorrhea in women at high risk for infection, compared with placebo, opening up new possibilities for an on-demand prevention option. Investigators of a randomized trial reported these findings in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Rates of Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) and Neisseria gonorrhoeae (GC) are on the rise in the United States, despite wide availability of male and female condoms to prevent sexually transmitted infections. This suggests that women need a more discrete method that they can better control. Other vaginal microbicides developed over the last few decades haven’t performed well in protecting against STIs or HIV in clinical trials.
The slightly alkaline nature of human semen has the potential to neutralize vaginal pH after intercourse, creating a more vulnerable environment for STIs. EVO100 is an investigational antimicrobial, bioadhesive vaginal gel that contains L-lactic acid, citric acid, and potassium bitartrate. In preclinical studies, it was highly effective at buffering the alkaline properties of human semen and maintaining vaginal pH levels. Patients generally tolerated it well, aside from some reports of vaginal itching and burning.
In the AMPREVENCE study, a double-blinded, placebo-controlled, randomized, phase 2b/3 trial, Todd Chappell, MD, of Adams Patterson Gynecology & Obstetrics, Memphis, and colleagues tested the efficacy and safety of EVO100 to prevent chlamydia and gonorrhea.
Investigators randomized 1:1,860 healthy, sexually active women to receive either EVO100 (n = 426) or placebo (n = 434). Participants had either been diagnosed or treated for these STIs up to 16 weeks prior to enrollment. Among those enrolled, 335 women in the EVO100 arm and 335 women in the placebo arm completed the study.
From this cohort, 764 women (EVO100: n = 376; placebo: n = 388) reported any use of either product. These women represented the “safety analysis population,” a predefined population for statistical analysis.
Participants averaged nearly 28 years of age, had a median body mass index of 28.9 kg/m2, and represented several racial/ethnic groups: White (54.3% [467/860]), African American (41.6% [358/860]), and non-Hispanic/Latinx ethnicity (67.1% [577/860]).
The women were instructed to apply the drug within 1 hour of initiating sexual intercourse. Investigators scheduled follow-up visits every 4 weeks during the 16-week study period, to obtain repeat CT/GC assessments, review diary entries, and to collect information about adverse effects and use of concomitant medications. During enrollment, participants consented to return to the clinic at each study visit. If a woman missed a visit, the study site would follow-up by telephone after the missed assessment visit.
Participants reported a mean number of 16 coital events (EVO100, 15.7 [13.5]; placebo, 16.3 [15.8]). EVO100 significantly reduced STI incidence for both types of STIs. CT infection rates among EVO100 users was 4.8% (14/289), half of what it was in placebo users (9.7% [28/290]) (P = .0256). The investigational method was even more successful in GC-analysis–eligible women: infection rates averaged 0.7% (2/280), compared with 3.2% (9/277) in the placebo group, a relative risk reduction of 78% (P = .0316).
Examining electronic diary entries of the participants, investigators reported similar adherence rates among the two treatment arms. However, additional sensitivity analyses in CT-eligible and GC-eligible populations on adherence yielded notably different results.
EVO100 users in the CT population who used the product as directed 100% of the time were significantly less likely to become infected, compared with the placebo group (2.3% vs. 16.9%, P = .0012). However, investigators found no significant differences in infection rates among women with poorer adherence rates in the two groups. Comparatively, they found no major differences in GC infection rates between the control and EVO100 groups, regardless of adherence rates, likely because of the small number of GC infections reported. Observed adverse events correlated with the drug’s known safety profile.
Most of the participants said they would likely recommend EVO100 to other women and continue using this preventive treatment.
A small GC subgroup caused by fewer infection cases and reliance on participant self-reporting of coital incidents may have limited the study’s results. “While use of the electronic diaries is helpful for collection of study data, it may encourage compliance and efficacy that may be higher in the ‘real-world’ population outside of the setting of a clinical trial,” noted Dr. Chappell and colleagues.
According to the investigators, this is the first prospective, randomized trial to study the use of an antimicrobial bioadhesive vaginal gel for preventing CT and GC infection. “EVO100 has the potential of fulfilling an unmet need in women’s sexual health as a new on-demand, woman-controlled option that reduces the risk of urogenital CT and GC infections,” the authors concluded.
The Food and Drug Administration has already approved EVO100 as a contraceptive option (Phexxi), Dr. Chappell said in an interview. Next steps are to conduct a phase 3 trial, which is currently underway. “If the findings are positive, we will submit to the FDA for review and approval of EVO100” for preventing these STIs.
These are promising results, Catherine Cansino, MD, MPH, an associate clinical professor with the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of California, Davis, said in an interview. It’s always helpful to look at effective treatments, “especially those that aren’t traditional antibiotics in order to decrease the risk of antibiotic resistance,” said Dr. Cansino, who was not part of the study. This is why EVO100 is such an attractive option.
Future studies should look at a broader population, she continued. “The population this study looked at is not the general population – these women had an infection at some point, previously,” which means they are potentially at higher risk for reinfection. “Looking at what their likelihood is of getting infected again, it’s hard to know if this would be the same or different from the general population.” If the drug appears to cause a decrease in new infections, the relative risk reduction is actually greater than what’s reported. If the reinfection rate for this population is lower because people who’ve had infections are practicing safer sex, the relative risk reduction would be lower, explained Dr. Cansino.
Dr. Chappell and several coauthors received research funding from Evofem Biosciences.
An investigational vaginal gel significantly reduced urogenital chlamydia and gonorrhea in women at high risk for infection, compared with placebo, opening up new possibilities for an on-demand prevention option. Investigators of a randomized trial reported these findings in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Rates of Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) and Neisseria gonorrhoeae (GC) are on the rise in the United States, despite wide availability of male and female condoms to prevent sexually transmitted infections. This suggests that women need a more discrete method that they can better control. Other vaginal microbicides developed over the last few decades haven’t performed well in protecting against STIs or HIV in clinical trials.
The slightly alkaline nature of human semen has the potential to neutralize vaginal pH after intercourse, creating a more vulnerable environment for STIs. EVO100 is an investigational antimicrobial, bioadhesive vaginal gel that contains L-lactic acid, citric acid, and potassium bitartrate. In preclinical studies, it was highly effective at buffering the alkaline properties of human semen and maintaining vaginal pH levels. Patients generally tolerated it well, aside from some reports of vaginal itching and burning.
In the AMPREVENCE study, a double-blinded, placebo-controlled, randomized, phase 2b/3 trial, Todd Chappell, MD, of Adams Patterson Gynecology & Obstetrics, Memphis, and colleagues tested the efficacy and safety of EVO100 to prevent chlamydia and gonorrhea.
Investigators randomized 1:1,860 healthy, sexually active women to receive either EVO100 (n = 426) or placebo (n = 434). Participants had either been diagnosed or treated for these STIs up to 16 weeks prior to enrollment. Among those enrolled, 335 women in the EVO100 arm and 335 women in the placebo arm completed the study.
From this cohort, 764 women (EVO100: n = 376; placebo: n = 388) reported any use of either product. These women represented the “safety analysis population,” a predefined population for statistical analysis.
Participants averaged nearly 28 years of age, had a median body mass index of 28.9 kg/m2, and represented several racial/ethnic groups: White (54.3% [467/860]), African American (41.6% [358/860]), and non-Hispanic/Latinx ethnicity (67.1% [577/860]).
The women were instructed to apply the drug within 1 hour of initiating sexual intercourse. Investigators scheduled follow-up visits every 4 weeks during the 16-week study period, to obtain repeat CT/GC assessments, review diary entries, and to collect information about adverse effects and use of concomitant medications. During enrollment, participants consented to return to the clinic at each study visit. If a woman missed a visit, the study site would follow-up by telephone after the missed assessment visit.
Participants reported a mean number of 16 coital events (EVO100, 15.7 [13.5]; placebo, 16.3 [15.8]). EVO100 significantly reduced STI incidence for both types of STIs. CT infection rates among EVO100 users was 4.8% (14/289), half of what it was in placebo users (9.7% [28/290]) (P = .0256). The investigational method was even more successful in GC-analysis–eligible women: infection rates averaged 0.7% (2/280), compared with 3.2% (9/277) in the placebo group, a relative risk reduction of 78% (P = .0316).
Examining electronic diary entries of the participants, investigators reported similar adherence rates among the two treatment arms. However, additional sensitivity analyses in CT-eligible and GC-eligible populations on adherence yielded notably different results.
EVO100 users in the CT population who used the product as directed 100% of the time were significantly less likely to become infected, compared with the placebo group (2.3% vs. 16.9%, P = .0012). However, investigators found no significant differences in infection rates among women with poorer adherence rates in the two groups. Comparatively, they found no major differences in GC infection rates between the control and EVO100 groups, regardless of adherence rates, likely because of the small number of GC infections reported. Observed adverse events correlated with the drug’s known safety profile.
Most of the participants said they would likely recommend EVO100 to other women and continue using this preventive treatment.
A small GC subgroup caused by fewer infection cases and reliance on participant self-reporting of coital incidents may have limited the study’s results. “While use of the electronic diaries is helpful for collection of study data, it may encourage compliance and efficacy that may be higher in the ‘real-world’ population outside of the setting of a clinical trial,” noted Dr. Chappell and colleagues.
According to the investigators, this is the first prospective, randomized trial to study the use of an antimicrobial bioadhesive vaginal gel for preventing CT and GC infection. “EVO100 has the potential of fulfilling an unmet need in women’s sexual health as a new on-demand, woman-controlled option that reduces the risk of urogenital CT and GC infections,” the authors concluded.
The Food and Drug Administration has already approved EVO100 as a contraceptive option (Phexxi), Dr. Chappell said in an interview. Next steps are to conduct a phase 3 trial, which is currently underway. “If the findings are positive, we will submit to the FDA for review and approval of EVO100” for preventing these STIs.
These are promising results, Catherine Cansino, MD, MPH, an associate clinical professor with the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of California, Davis, said in an interview. It’s always helpful to look at effective treatments, “especially those that aren’t traditional antibiotics in order to decrease the risk of antibiotic resistance,” said Dr. Cansino, who was not part of the study. This is why EVO100 is such an attractive option.
Future studies should look at a broader population, she continued. “The population this study looked at is not the general population – these women had an infection at some point, previously,” which means they are potentially at higher risk for reinfection. “Looking at what their likelihood is of getting infected again, it’s hard to know if this would be the same or different from the general population.” If the drug appears to cause a decrease in new infections, the relative risk reduction is actually greater than what’s reported. If the reinfection rate for this population is lower because people who’ve had infections are practicing safer sex, the relative risk reduction would be lower, explained Dr. Cansino.
Dr. Chappell and several coauthors received research funding from Evofem Biosciences.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY
COVID-19 leaves thousands of U.S. children without a parent
Approximately 40,000 children in the United States have lost a parent to COVID-19, based on data from a combination of death counts and simulation models.
The scale of mortality from COVID-19 among adults in the United States merits efforts to monitor how many children have lost a parent as a result of the pandemic, wrote Rachel Kidman, PhD, of Stony Brook (N.Y.) University and colleagues.
In a study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers used kinship networks of White and Black individuals in the United States to estimate parental bereavement. They combined deaths from COVID-19 as of February 2021 and combined them with excess deaths, and estimated future bereavement based on a herd immunity scenario.
Overall, the model suggested that each death from COVID-19 results in potential parental bereavement for 0.78 children aged 0-17 years, representing an increase of 17.5%-20.2% in parental bereavement. The model indicated that, as of February 2021, 37,337 children aged 0-17 years had lost a parent to COVID-19, including 11,366 children age 0-9 years and 31,661 children and teens aged 10-17 years. A total of 20,600 of these children were non-Hispanic White and 7,600 were Black. Black children accounted for 20% of the bereaved children, although they account for approximately 14% of children aged 0-17 years in the United States, the researchers noted.
Including the excess death estimate, which refers to the difference between observed and expected deaths for the remainder of the pandemic, raised the total bereaved children to 43,000. A future mortality scenario using a total of 1,500,000 deaths from COVID-19 based on a natural herd immunity strategy increased the total estimate of bereaved children to 116,922.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of data on nonparental primary caregivers, and the use of demographic models rather than survey or administrative data, the researchers noted.
However, the huge number of children who have experienced the death of a parent because of COVID-19 emphasizes the need for reforms to address health, educational, and economic impacts of this mass bereavement on children and teens, they said.
“Parentally bereaved children will also need targeted support to help with grief, particularly during this period of heightened social isolation,” they emphasized.
Establishment of a national child bereavement cohort could identify children early in the bereavement process to help ensure that they are connected to local supportive care and monitored for health and behavior problems, the researchers said. In addition, such a cohort could be used as a basis for a longitudinal study of the impact of mass parental bereavement during a unique period of social isolation and economic uncertainty, they concluded.
Study spotlights gaps in mental health care
The study is an important reminder of how COVID-19 has disrupted children’s lives, said Herschel Lessin, MD, of Children’s Medical Group in Poughkeepsie, N.Y., in an interview. Losing a parent because of COVID-19 is one more tragedy on the list of social and emotional disasters the pandemic has wrought on children, he said.
“There has to be some sort of national response to help children through all of this, not just one item at a time,” Dr. Lessin said. However, the management of children’s mental health in the United States has been subpar for decades, he noted, with few clinicians trained to specialize in treating behavioral and mental health issues in children. Consequently, more general pediatricians will continue to be faced with the mental health issues of bereaved children who desperately need support, he said.
Money remains a key barrier, as it keeps qualified clinicians from entering the field of pediatric mental and behavioral health, and even where there are mental health providers, most do not take insurance and have long waiting lists, Dr. Lessin noted.
General pediatricians were seeing more patients with ADHD, anxiety, and depression before the advent of COVID-19, though most are not trained in managing these conditions, said Dr. Lessin. “Approximately 25%-30% of my visits now are mental health related, and the pandemic will make it geometrically worse,” he said.
The current study, with its dramatic estimates of the number of children who have lost a parent because of COVID-19, may bring attention to the fact that more training and money are needed to support mental health programs for children, he said.
Lead author Dr. Kidman had no financial conflicts to disclose. The study was supported by grants to corresponding author Ashton M. Verdery, PhD, from the National Institute on Aging and the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Lessin had no financial conflicts but serves on the Pediatric News editorial advisory board.
SOURCE: Kidman R et al. JAMA Pediatr. .
Approximately 40,000 children in the United States have lost a parent to COVID-19, based on data from a combination of death counts and simulation models.
The scale of mortality from COVID-19 among adults in the United States merits efforts to monitor how many children have lost a parent as a result of the pandemic, wrote Rachel Kidman, PhD, of Stony Brook (N.Y.) University and colleagues.
In a study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers used kinship networks of White and Black individuals in the United States to estimate parental bereavement. They combined deaths from COVID-19 as of February 2021 and combined them with excess deaths, and estimated future bereavement based on a herd immunity scenario.
Overall, the model suggested that each death from COVID-19 results in potential parental bereavement for 0.78 children aged 0-17 years, representing an increase of 17.5%-20.2% in parental bereavement. The model indicated that, as of February 2021, 37,337 children aged 0-17 years had lost a parent to COVID-19, including 11,366 children age 0-9 years and 31,661 children and teens aged 10-17 years. A total of 20,600 of these children were non-Hispanic White and 7,600 were Black. Black children accounted for 20% of the bereaved children, although they account for approximately 14% of children aged 0-17 years in the United States, the researchers noted.
Including the excess death estimate, which refers to the difference between observed and expected deaths for the remainder of the pandemic, raised the total bereaved children to 43,000. A future mortality scenario using a total of 1,500,000 deaths from COVID-19 based on a natural herd immunity strategy increased the total estimate of bereaved children to 116,922.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of data on nonparental primary caregivers, and the use of demographic models rather than survey or administrative data, the researchers noted.
However, the huge number of children who have experienced the death of a parent because of COVID-19 emphasizes the need for reforms to address health, educational, and economic impacts of this mass bereavement on children and teens, they said.
“Parentally bereaved children will also need targeted support to help with grief, particularly during this period of heightened social isolation,” they emphasized.
Establishment of a national child bereavement cohort could identify children early in the bereavement process to help ensure that they are connected to local supportive care and monitored for health and behavior problems, the researchers said. In addition, such a cohort could be used as a basis for a longitudinal study of the impact of mass parental bereavement during a unique period of social isolation and economic uncertainty, they concluded.
Study spotlights gaps in mental health care
The study is an important reminder of how COVID-19 has disrupted children’s lives, said Herschel Lessin, MD, of Children’s Medical Group in Poughkeepsie, N.Y., in an interview. Losing a parent because of COVID-19 is one more tragedy on the list of social and emotional disasters the pandemic has wrought on children, he said.
“There has to be some sort of national response to help children through all of this, not just one item at a time,” Dr. Lessin said. However, the management of children’s mental health in the United States has been subpar for decades, he noted, with few clinicians trained to specialize in treating behavioral and mental health issues in children. Consequently, more general pediatricians will continue to be faced with the mental health issues of bereaved children who desperately need support, he said.
Money remains a key barrier, as it keeps qualified clinicians from entering the field of pediatric mental and behavioral health, and even where there are mental health providers, most do not take insurance and have long waiting lists, Dr. Lessin noted.
General pediatricians were seeing more patients with ADHD, anxiety, and depression before the advent of COVID-19, though most are not trained in managing these conditions, said Dr. Lessin. “Approximately 25%-30% of my visits now are mental health related, and the pandemic will make it geometrically worse,” he said.
The current study, with its dramatic estimates of the number of children who have lost a parent because of COVID-19, may bring attention to the fact that more training and money are needed to support mental health programs for children, he said.
Lead author Dr. Kidman had no financial conflicts to disclose. The study was supported by grants to corresponding author Ashton M. Verdery, PhD, from the National Institute on Aging and the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Lessin had no financial conflicts but serves on the Pediatric News editorial advisory board.
SOURCE: Kidman R et al. JAMA Pediatr. .
Approximately 40,000 children in the United States have lost a parent to COVID-19, based on data from a combination of death counts and simulation models.
The scale of mortality from COVID-19 among adults in the United States merits efforts to monitor how many children have lost a parent as a result of the pandemic, wrote Rachel Kidman, PhD, of Stony Brook (N.Y.) University and colleagues.
In a study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers used kinship networks of White and Black individuals in the United States to estimate parental bereavement. They combined deaths from COVID-19 as of February 2021 and combined them with excess deaths, and estimated future bereavement based on a herd immunity scenario.
Overall, the model suggested that each death from COVID-19 results in potential parental bereavement for 0.78 children aged 0-17 years, representing an increase of 17.5%-20.2% in parental bereavement. The model indicated that, as of February 2021, 37,337 children aged 0-17 years had lost a parent to COVID-19, including 11,366 children age 0-9 years and 31,661 children and teens aged 10-17 years. A total of 20,600 of these children were non-Hispanic White and 7,600 were Black. Black children accounted for 20% of the bereaved children, although they account for approximately 14% of children aged 0-17 years in the United States, the researchers noted.
Including the excess death estimate, which refers to the difference between observed and expected deaths for the remainder of the pandemic, raised the total bereaved children to 43,000. A future mortality scenario using a total of 1,500,000 deaths from COVID-19 based on a natural herd immunity strategy increased the total estimate of bereaved children to 116,922.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of data on nonparental primary caregivers, and the use of demographic models rather than survey or administrative data, the researchers noted.
However, the huge number of children who have experienced the death of a parent because of COVID-19 emphasizes the need for reforms to address health, educational, and economic impacts of this mass bereavement on children and teens, they said.
“Parentally bereaved children will also need targeted support to help with grief, particularly during this period of heightened social isolation,” they emphasized.
Establishment of a national child bereavement cohort could identify children early in the bereavement process to help ensure that they are connected to local supportive care and monitored for health and behavior problems, the researchers said. In addition, such a cohort could be used as a basis for a longitudinal study of the impact of mass parental bereavement during a unique period of social isolation and economic uncertainty, they concluded.
Study spotlights gaps in mental health care
The study is an important reminder of how COVID-19 has disrupted children’s lives, said Herschel Lessin, MD, of Children’s Medical Group in Poughkeepsie, N.Y., in an interview. Losing a parent because of COVID-19 is one more tragedy on the list of social and emotional disasters the pandemic has wrought on children, he said.
“There has to be some sort of national response to help children through all of this, not just one item at a time,” Dr. Lessin said. However, the management of children’s mental health in the United States has been subpar for decades, he noted, with few clinicians trained to specialize in treating behavioral and mental health issues in children. Consequently, more general pediatricians will continue to be faced with the mental health issues of bereaved children who desperately need support, he said.
Money remains a key barrier, as it keeps qualified clinicians from entering the field of pediatric mental and behavioral health, and even where there are mental health providers, most do not take insurance and have long waiting lists, Dr. Lessin noted.
General pediatricians were seeing more patients with ADHD, anxiety, and depression before the advent of COVID-19, though most are not trained in managing these conditions, said Dr. Lessin. “Approximately 25%-30% of my visits now are mental health related, and the pandemic will make it geometrically worse,” he said.
The current study, with its dramatic estimates of the number of children who have lost a parent because of COVID-19, may bring attention to the fact that more training and money are needed to support mental health programs for children, he said.
Lead author Dr. Kidman had no financial conflicts to disclose. The study was supported by grants to corresponding author Ashton M. Verdery, PhD, from the National Institute on Aging and the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Lessin had no financial conflicts but serves on the Pediatric News editorial advisory board.
SOURCE: Kidman R et al. JAMA Pediatr. .
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
Itchy rash on back
A unilateral, neuropathic itch accompanied by postinflammatory pigmentation changes or lichenification at the medial inferior tip of the scapula are the hallmarks of notalgia paresthetica (NP).
NP is thought to result from nerve impingement or chronic nerve trauma to the posterior rami of the upper thoracic spinal nerves. The hyperpigmentation and lichenification arise from repeated scratching or rubbing of the skin.
NP is a clinical diagnosis and does not require biopsy or imaging. The differential diagnosis includes brachioradial pruritus, postherpetic neuralgia, multiple sclerosis, and other small fiber neuropathies.
The standard treatment is topical capsaicin 0.025% tid for 5 weeks, with repeat treatments (for a few days or weeks) if there are relapses. Higher doses (0.075%) may work more quickly but may also lead to more burning. A lidocaine 5% patch bid can also be considered. Second-line treatment options include cutaneous electrical field stimulation or transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, gabapentin, or oxcarbazepine. Topical steroids are considered ineffective for this condition.1
The patient in this case was started on capsaicin 0.025%. She was encouraged to keep her skin moisturized and well hydrated because dyshidrosis can exacerbate itching. A prescription for gabapentin was offered in case topical treatments were unsuccessful, but she declined after she weighed the risks of adverse effects against her current symptoms.
Photo courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, and text courtesy of Nathan Birnbaum, MD, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque
1. Lebwohl MG, Heymann WR, Berth-Jones J, et al, eds. Treatment of Skin Disease: Comprehensive Therapeutic Strategies. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2017.

A unilateral, neuropathic itch accompanied by postinflammatory pigmentation changes or lichenification at the medial inferior tip of the scapula are the hallmarks of notalgia paresthetica (NP).
NP is thought to result from nerve impingement or chronic nerve trauma to the posterior rami of the upper thoracic spinal nerves. The hyperpigmentation and lichenification arise from repeated scratching or rubbing of the skin.
NP is a clinical diagnosis and does not require biopsy or imaging. The differential diagnosis includes brachioradial pruritus, postherpetic neuralgia, multiple sclerosis, and other small fiber neuropathies.
The standard treatment is topical capsaicin 0.025% tid for 5 weeks, with repeat treatments (for a few days or weeks) if there are relapses. Higher doses (0.075%) may work more quickly but may also lead to more burning. A lidocaine 5% patch bid can also be considered. Second-line treatment options include cutaneous electrical field stimulation or transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, gabapentin, or oxcarbazepine. Topical steroids are considered ineffective for this condition.1
The patient in this case was started on capsaicin 0.025%. She was encouraged to keep her skin moisturized and well hydrated because dyshidrosis can exacerbate itching. A prescription for gabapentin was offered in case topical treatments were unsuccessful, but she declined after she weighed the risks of adverse effects against her current symptoms.
Photo courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, and text courtesy of Nathan Birnbaum, MD, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque

A unilateral, neuropathic itch accompanied by postinflammatory pigmentation changes or lichenification at the medial inferior tip of the scapula are the hallmarks of notalgia paresthetica (NP).
NP is thought to result from nerve impingement or chronic nerve trauma to the posterior rami of the upper thoracic spinal nerves. The hyperpigmentation and lichenification arise from repeated scratching or rubbing of the skin.
NP is a clinical diagnosis and does not require biopsy or imaging. The differential diagnosis includes brachioradial pruritus, postherpetic neuralgia, multiple sclerosis, and other small fiber neuropathies.
The standard treatment is topical capsaicin 0.025% tid for 5 weeks, with repeat treatments (for a few days or weeks) if there are relapses. Higher doses (0.075%) may work more quickly but may also lead to more burning. A lidocaine 5% patch bid can also be considered. Second-line treatment options include cutaneous electrical field stimulation or transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, gabapentin, or oxcarbazepine. Topical steroids are considered ineffective for this condition.1
The patient in this case was started on capsaicin 0.025%. She was encouraged to keep her skin moisturized and well hydrated because dyshidrosis can exacerbate itching. A prescription for gabapentin was offered in case topical treatments were unsuccessful, but she declined after she weighed the risks of adverse effects against her current symptoms.
Photo courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, and text courtesy of Nathan Birnbaum, MD, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque
1. Lebwohl MG, Heymann WR, Berth-Jones J, et al, eds. Treatment of Skin Disease: Comprehensive Therapeutic Strategies. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2017.
1. Lebwohl MG, Heymann WR, Berth-Jones J, et al, eds. Treatment of Skin Disease: Comprehensive Therapeutic Strategies. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2017.
TAVR feasible, comparable with surgery in rheumatic heart disease
Patients with rheumatic heart disease (RHD) appear to have comparable outcomes, whether undergoing transcatheter or surgical aortic valve replacement (TAVR/SAVR), and when compared with TAVR in patients with nonrheumatic aortic stenosis, a new Medicare study finds.
An analysis of data from 1,159 Medicare beneficiaries with rheumatic aortic stenosis revealed that, over a median follow-up of 19 months, there was no difference in all-cause mortality with TAVR vs. SAVR (11.2 vs. 7.0 per 100 person-years; adjusted hazard ratio, 1.53; P = .2).
Mortality was also similar after a median follow-up of 17 months between TAVR in patients with rheumatic aortic stenosis and 88,554 additional beneficiaries with nonrheumatic aortic stenosis (15.2 vs. 17.7 deaths per 100 person-years; aHR, 0.87; P = .2).
“We need collaboration between industry and society leaders in developed countries to initiate a randomized, controlled trial to address the feasibility of TAVR in rheumatic heart disease in younger populations who aren’t surgical candidates or if there’s a lack of surgical capabilities in countries, but this is an encouraging first sign,” lead author Amgad Mentias, MD, MSc, Cleveland Clinic Foundation, said in an interview.
Although the prevalence of rheumatic heart disease (RHD) has fallen to less than 5% or so in the United States and Europe, it remains a significant problem in developing and low-income countries, with more than 1 million deaths per year, he noted. RHD patients typically present at younger ages, often with concomitant aortic regurgitation and mitral valve disease, but have less calcification than degenerative calcific aortic stenosis.
Commenting on the results, published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, David F. Williams, PhD, said in an interview that “it is only now becoming possible to entertain the use of TAVR in such patients, and this paper demonstrates the feasibility of doing so.
“Although the study is based on geriatric patients of an industrialized country, it opens the door to the massive unmet clinical needs in poorer regions as well as emerging economies,” said Dr. Williams, a professor at the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine, Winston-Salem, N.C., and coauthor of an accompanying editorial.
The study included Medicare beneficiaries treated from October 2015 to December 2017 for rheumatic aortic stenosis (TAVR, n = 605; SAVR, n = 55) or nonrheumatic aortic stenosis (n = 88,554).
Among those with rheumatic disease, SAVR patients were younger than TAVR patients (73.4 vs. 79.4 years), had a lower prevalence of most comorbidities, and were less frail (median frailty score, 5.3 vs. 11.3).
SAVR was associated with significantly higher weighted risk for in-hospital acute kidney injury (22.3% vs. 11.9%), blood transfusion (19.8% vs. 7.6%), cardiogenic shock (5.7% vs. 1.5%), new-onset atrial fibrillation (21.1% vs. 2.2%), and had longer hospital stays (median, 8 vs. 3 days), whereas new permanent pacemaker implantations trended higher with TAVR (12.5% vs 7.2%).
The TAVR and SAVR groups had comparable rates of adjusted in-hospital mortality (2.4% vs. 3.5%), 30-day mortality (3.6% vs. 3.2%), 30-day stroke (2.4% vs. 2.8%), and 1-year mortality (13.1% vs. 8.9%).
Among the two TAVR cohorts, patients with rheumatic disease were younger than those with nonrheumatic aortic stenosis (79.4 vs. 81.2 years); had a higher prevalence of heart failure, ischemic stroke, atrial fibrillation, and lung disease; and were more frail (median score, 11.3 vs. 6.9).
Still, there was no difference in weighted risk of in-hospital mortality (2.2% vs. 2.6%), 30-day mortality (3.6% vs. 3.7%), 30-day stroke (2.0% vs. 3.3%), or 1-year mortality (16.0% vs. 17.1%) between TAVR patients with and without rheumatic stenosis.
“We didn’t have specific information on echo[cardiography], so we don’t know how that affected our results, but one of the encouraging points is that after a median follow-up of almost 2 years, none of the patients who had TAVR in the rheumatic valve and who survived required redo aortic valve replacement,” Dr. Mentias said. “It’s still short term but it shows that for the short to mid term, the valve is durable.”
Data were not available on paravalvular regurgitation, an Achilles heel for TAVR, but Dr. Mentias said rates of this complication have come down significantly in the past 2 years with modifications to newer-generation TAVR valves.
Dr. Williams and colleagues say one main limitation of the study also highlights the major shortcoming of contemporary TAVRs when treating patients with RHD: “namely, their inadequate suitability for AR [aortic regurgitation], the predominant rheumatic lesion of the aortic valve” in low- to middle-income countries.
They pointed out that patients needing an aortic valve where RHD is rampant are at least 30 years younger than the 79-year-old TAVR recipients in the study.
In a comment, Dr. Williams said there are several unanswered questions about the full impact TAVR could have in the treatment of young RHD patients in underprivileged regions. “These mainly concern the durability of the valves in individuals who could expect greater longevity than the typical heart valve patient in the USA, and the adaptation of transcatheter techniques to provide cost-effective treatment in regions that lack the usual sophisticated clinical infrastructure.”
Dr. Mentias received support from a National Research Service Award institutional grant to the Abboud Cardiovascular Research Center. Dr. Williams and coauthors are directors of Strait Access Technologies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with rheumatic heart disease (RHD) appear to have comparable outcomes, whether undergoing transcatheter or surgical aortic valve replacement (TAVR/SAVR), and when compared with TAVR in patients with nonrheumatic aortic stenosis, a new Medicare study finds.
An analysis of data from 1,159 Medicare beneficiaries with rheumatic aortic stenosis revealed that, over a median follow-up of 19 months, there was no difference in all-cause mortality with TAVR vs. SAVR (11.2 vs. 7.0 per 100 person-years; adjusted hazard ratio, 1.53; P = .2).
Mortality was also similar after a median follow-up of 17 months between TAVR in patients with rheumatic aortic stenosis and 88,554 additional beneficiaries with nonrheumatic aortic stenosis (15.2 vs. 17.7 deaths per 100 person-years; aHR, 0.87; P = .2).
“We need collaboration between industry and society leaders in developed countries to initiate a randomized, controlled trial to address the feasibility of TAVR in rheumatic heart disease in younger populations who aren’t surgical candidates or if there’s a lack of surgical capabilities in countries, but this is an encouraging first sign,” lead author Amgad Mentias, MD, MSc, Cleveland Clinic Foundation, said in an interview.
Although the prevalence of rheumatic heart disease (RHD) has fallen to less than 5% or so in the United States and Europe, it remains a significant problem in developing and low-income countries, with more than 1 million deaths per year, he noted. RHD patients typically present at younger ages, often with concomitant aortic regurgitation and mitral valve disease, but have less calcification than degenerative calcific aortic stenosis.
Commenting on the results, published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, David F. Williams, PhD, said in an interview that “it is only now becoming possible to entertain the use of TAVR in such patients, and this paper demonstrates the feasibility of doing so.
“Although the study is based on geriatric patients of an industrialized country, it opens the door to the massive unmet clinical needs in poorer regions as well as emerging economies,” said Dr. Williams, a professor at the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine, Winston-Salem, N.C., and coauthor of an accompanying editorial.
The study included Medicare beneficiaries treated from October 2015 to December 2017 for rheumatic aortic stenosis (TAVR, n = 605; SAVR, n = 55) or nonrheumatic aortic stenosis (n = 88,554).
Among those with rheumatic disease, SAVR patients were younger than TAVR patients (73.4 vs. 79.4 years), had a lower prevalence of most comorbidities, and were less frail (median frailty score, 5.3 vs. 11.3).
SAVR was associated with significantly higher weighted risk for in-hospital acute kidney injury (22.3% vs. 11.9%), blood transfusion (19.8% vs. 7.6%), cardiogenic shock (5.7% vs. 1.5%), new-onset atrial fibrillation (21.1% vs. 2.2%), and had longer hospital stays (median, 8 vs. 3 days), whereas new permanent pacemaker implantations trended higher with TAVR (12.5% vs 7.2%).
The TAVR and SAVR groups had comparable rates of adjusted in-hospital mortality (2.4% vs. 3.5%), 30-day mortality (3.6% vs. 3.2%), 30-day stroke (2.4% vs. 2.8%), and 1-year mortality (13.1% vs. 8.9%).
Among the two TAVR cohorts, patients with rheumatic disease were younger than those with nonrheumatic aortic stenosis (79.4 vs. 81.2 years); had a higher prevalence of heart failure, ischemic stroke, atrial fibrillation, and lung disease; and were more frail (median score, 11.3 vs. 6.9).
Still, there was no difference in weighted risk of in-hospital mortality (2.2% vs. 2.6%), 30-day mortality (3.6% vs. 3.7%), 30-day stroke (2.0% vs. 3.3%), or 1-year mortality (16.0% vs. 17.1%) between TAVR patients with and without rheumatic stenosis.
“We didn’t have specific information on echo[cardiography], so we don’t know how that affected our results, but one of the encouraging points is that after a median follow-up of almost 2 years, none of the patients who had TAVR in the rheumatic valve and who survived required redo aortic valve replacement,” Dr. Mentias said. “It’s still short term but it shows that for the short to mid term, the valve is durable.”
Data were not available on paravalvular regurgitation, an Achilles heel for TAVR, but Dr. Mentias said rates of this complication have come down significantly in the past 2 years with modifications to newer-generation TAVR valves.
Dr. Williams and colleagues say one main limitation of the study also highlights the major shortcoming of contemporary TAVRs when treating patients with RHD: “namely, their inadequate suitability for AR [aortic regurgitation], the predominant rheumatic lesion of the aortic valve” in low- to middle-income countries.
They pointed out that patients needing an aortic valve where RHD is rampant are at least 30 years younger than the 79-year-old TAVR recipients in the study.
In a comment, Dr. Williams said there are several unanswered questions about the full impact TAVR could have in the treatment of young RHD patients in underprivileged regions. “These mainly concern the durability of the valves in individuals who could expect greater longevity than the typical heart valve patient in the USA, and the adaptation of transcatheter techniques to provide cost-effective treatment in regions that lack the usual sophisticated clinical infrastructure.”
Dr. Mentias received support from a National Research Service Award institutional grant to the Abboud Cardiovascular Research Center. Dr. Williams and coauthors are directors of Strait Access Technologies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with rheumatic heart disease (RHD) appear to have comparable outcomes, whether undergoing transcatheter or surgical aortic valve replacement (TAVR/SAVR), and when compared with TAVR in patients with nonrheumatic aortic stenosis, a new Medicare study finds.
An analysis of data from 1,159 Medicare beneficiaries with rheumatic aortic stenosis revealed that, over a median follow-up of 19 months, there was no difference in all-cause mortality with TAVR vs. SAVR (11.2 vs. 7.0 per 100 person-years; adjusted hazard ratio, 1.53; P = .2).
Mortality was also similar after a median follow-up of 17 months between TAVR in patients with rheumatic aortic stenosis and 88,554 additional beneficiaries with nonrheumatic aortic stenosis (15.2 vs. 17.7 deaths per 100 person-years; aHR, 0.87; P = .2).
“We need collaboration between industry and society leaders in developed countries to initiate a randomized, controlled trial to address the feasibility of TAVR in rheumatic heart disease in younger populations who aren’t surgical candidates or if there’s a lack of surgical capabilities in countries, but this is an encouraging first sign,” lead author Amgad Mentias, MD, MSc, Cleveland Clinic Foundation, said in an interview.
Although the prevalence of rheumatic heart disease (RHD) has fallen to less than 5% or so in the United States and Europe, it remains a significant problem in developing and low-income countries, with more than 1 million deaths per year, he noted. RHD patients typically present at younger ages, often with concomitant aortic regurgitation and mitral valve disease, but have less calcification than degenerative calcific aortic stenosis.
Commenting on the results, published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, David F. Williams, PhD, said in an interview that “it is only now becoming possible to entertain the use of TAVR in such patients, and this paper demonstrates the feasibility of doing so.
“Although the study is based on geriatric patients of an industrialized country, it opens the door to the massive unmet clinical needs in poorer regions as well as emerging economies,” said Dr. Williams, a professor at the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine, Winston-Salem, N.C., and coauthor of an accompanying editorial.
The study included Medicare beneficiaries treated from October 2015 to December 2017 for rheumatic aortic stenosis (TAVR, n = 605; SAVR, n = 55) or nonrheumatic aortic stenosis (n = 88,554).
Among those with rheumatic disease, SAVR patients were younger than TAVR patients (73.4 vs. 79.4 years), had a lower prevalence of most comorbidities, and were less frail (median frailty score, 5.3 vs. 11.3).
SAVR was associated with significantly higher weighted risk for in-hospital acute kidney injury (22.3% vs. 11.9%), blood transfusion (19.8% vs. 7.6%), cardiogenic shock (5.7% vs. 1.5%), new-onset atrial fibrillation (21.1% vs. 2.2%), and had longer hospital stays (median, 8 vs. 3 days), whereas new permanent pacemaker implantations trended higher with TAVR (12.5% vs 7.2%).
The TAVR and SAVR groups had comparable rates of adjusted in-hospital mortality (2.4% vs. 3.5%), 30-day mortality (3.6% vs. 3.2%), 30-day stroke (2.4% vs. 2.8%), and 1-year mortality (13.1% vs. 8.9%).
Among the two TAVR cohorts, patients with rheumatic disease were younger than those with nonrheumatic aortic stenosis (79.4 vs. 81.2 years); had a higher prevalence of heart failure, ischemic stroke, atrial fibrillation, and lung disease; and were more frail (median score, 11.3 vs. 6.9).
Still, there was no difference in weighted risk of in-hospital mortality (2.2% vs. 2.6%), 30-day mortality (3.6% vs. 3.7%), 30-day stroke (2.0% vs. 3.3%), or 1-year mortality (16.0% vs. 17.1%) between TAVR patients with and without rheumatic stenosis.
“We didn’t have specific information on echo[cardiography], so we don’t know how that affected our results, but one of the encouraging points is that after a median follow-up of almost 2 years, none of the patients who had TAVR in the rheumatic valve and who survived required redo aortic valve replacement,” Dr. Mentias said. “It’s still short term but it shows that for the short to mid term, the valve is durable.”
Data were not available on paravalvular regurgitation, an Achilles heel for TAVR, but Dr. Mentias said rates of this complication have come down significantly in the past 2 years with modifications to newer-generation TAVR valves.
Dr. Williams and colleagues say one main limitation of the study also highlights the major shortcoming of contemporary TAVRs when treating patients with RHD: “namely, their inadequate suitability for AR [aortic regurgitation], the predominant rheumatic lesion of the aortic valve” in low- to middle-income countries.
They pointed out that patients needing an aortic valve where RHD is rampant are at least 30 years younger than the 79-year-old TAVR recipients in the study.
In a comment, Dr. Williams said there are several unanswered questions about the full impact TAVR could have in the treatment of young RHD patients in underprivileged regions. “These mainly concern the durability of the valves in individuals who could expect greater longevity than the typical heart valve patient in the USA, and the adaptation of transcatheter techniques to provide cost-effective treatment in regions that lack the usual sophisticated clinical infrastructure.”
Dr. Mentias received support from a National Research Service Award institutional grant to the Abboud Cardiovascular Research Center. Dr. Williams and coauthors are directors of Strait Access Technologies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Beyond a reasonable doubt’: COVID-19 brain health fallout is real, severe
COVID-19 survivors face a sharply elevated risk of developing psychiatric or neurologic disorders in the 6 months after they contract the virus – a danger that mounts with symptom severity, new research shows.
In what is purported to be the largest study of its kind to date, results showed that among 236,379 COVID-19 patients, one-third were diagnosed with at least 1 of 14 psychiatric or neurologic disorders within a 6-month span.
The rate of illnesses, which ranged from depression to stroke, rose sharply among those with COVID-19 symptoms acute enough to require hospitalization.
“If we look at patients who were hospitalized, that rate increased to 39%, and then increased to about just under 1 in 2 patients who needed ICU admission at the time of the COVID-19 diagnosis,” Maxime Taquet, PhD, University of Oxford (England) department of psychiatry, said at a media briefing.
Incidence jumps to almost two-thirds in patients with encephalopathy at the time of COVID-19 diagnosis, he added.
The study, which examined the brain health of 236,379 survivors of COVID-19 via a U.S. database of 81 million electronic health records, was published online April 6 in The Lancet Psychiatry.
High rate of neurologic, psychiatric disorders
The research team looked at the first-time diagnosis or recurrence of 14 neurologic and psychiatric outcomes in patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infections. They also compared the brain health of this cohort with a control group of those with influenza or with non–COVID-19 respiratory infections over the same period.
All study participants were older than 10 years, diagnosed with COVID-19 on or after Jan. 20, 2020, and still alive as of Dec. 13, 2020.
The psychiatric and neurologic conditions examined included intracranial hemorrhage; ischemic stroke; parkinsonism; Guillain-Barré syndrome; nerve, nerve root and plexus disorders; myoneural junction and muscle disease; encephalitis; dementia; psychotic, mood, and anxiety disorders; substance use disorder; and insomnia.
The investigators used hospitalization, intensive care admissions, and encephalopathy as an indication of the severity of COVID-19 symptoms.
The study benchmarked the primary cohort with four populations of patients diagnosed in the same period with nonrespiratory illnesses, including skin infection, urolithiasis, bone fractures, and pulmonary embolisms.
Results showed that substantially more COVID-19 patients were diagnosed with a neurologic or psychiatric disorder compared with those with other respiratory illnesses.
“On average, in terms of the relative numbers, there was a 44% increased risk of having a neurological or psychiatric diagnosis after COVID-19 than after the flu and a 16% increased risk compared to other respiratory tract infections,” Dr. Taquet told reporters.
Health services should be prepared for an increase in psychiatric and neurologic issues in the months to come, he said, adding that further investigations are needed into why, and how, the coronavirus affects brain health.
Largest study to date
Although previous research suggests a link between the two, this is the largest study of its kind, examines a wider range of neurologic outcomes, and spans the longest time frame to date, said study coinvestigator Paul Harrison, BM BCh, associate head of the University of Oxford department of psychiatry.
There was a lower incidence of mood and anxiety disorders vs. neurologic disorders in patients with severe COVID-19 symptoms, a finding that Dr. Harrison said may indicate pandemic-related psychological stress is driving these disorders vs. biological factors.
“This paper follows up on an earlier study we did where we found much the same association, and our view is that a lot of the mental health consequences of COVID are … to do with the stress of knowing that one has had COVID and all the implications that go with that, rather than its being a direct effect, for example, of the virus on the brain, or of the immune response to the virus on the brain,” he added.
In contrast, neurologic diagnoses were more likely to be “mediated by some direct consequence of the COVID infection,” he added.
Psychosis and dementia, for instance, were less frequent in the overall COVID-19 population but became much more frequent among those with severe symptoms. The research team said these findings, along with those related to the incidence of ischemic stroke, were “concerning.”
“We found that 1 in 50 patients with COVID-19 go on to have an ischemic stroke in the 6 months after the COVID-19 illness,” Dr. Taquet told reporters. “And that rate increased to 1 in 11 patients if we look at patients with encephalopathy at the time of the COVID-19 diagnosis.”
Rates of brain hemorrhages also rose sharply among those with acute symptoms. Just over 1 in 200 total COVID-19 patients were diagnosed with this neurological condition, but that jumped to 1 in 25 of those who experienced encephalopathy at the time of their COVID-19 diagnosis.
Need for replication
Study coauthor Masud Husain, PhD, of University of Oxford’s cognitive neurology department, told reporters that while there is evidence from other neurologic studies that the virus can access the brain, there has been little sign the neurons themselves are affected.
“There isn’t much evidence that the virus itself attacks neurons in the brain, but it can cause inflammation, and it can activate inflammatory cells in the brain,” he said.
“And those effects are probably very important in some of the biological effects on the brain. In addition, of course, we know that the virus can change clotting and the likelihood of thrombosis in the blood, and those effects can also impact upon the brain,” he added.
Dr. Harrison said it would be helpful to replicate the results garnered from the U.S. database in other populations.
“It goes without saying that replication of these results with other electronic health records and in other countries is a priority,” he said, adding that investigations are essential into how and why the virus affects brain health.
Dr. Harrison cited a U.K. Research and Innovation–funded study called COVID CNS that will follow patients with neurologic and/or psychiatric issues during acute COVID-19 in hopes of exploring possible causes.
Beyond a reasonable doubt
Commenting on the findings, Sir Simon Wessely, MD, Regius chair of psychiatry, King’s College London, said in a release: “This is a very important paper. It confirms beyond any reasonable doubt that COVID-19 affects both brain and mind in equal measure.”
Some of these effects, including stroke and anxiety disorders, were already known, but others such as dementia and psychosis were less well known, he added.
“What is very new is the comparisons with all respiratory viruses or influenza, which suggests that these increases are specifically related to COVID-19, and not a general impact of viral infection,” Dr. Wessely said. “In general, the worse the illness, the greater the neurological or psychiatric outcomes, which is perhaps not surprising.
“The worst outcomes were in those with encephalopathy – inflammation of the brain – again, not surprising. The association with dementia was, however, small and might reflect diagnostic issues, whilst so far there doesn’t seem early evidence of a link with parkinsonism, which was a major factor after the great Spanish Flu pandemic, although the authors caution that it is too early to rule this out.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 survivors face a sharply elevated risk of developing psychiatric or neurologic disorders in the 6 months after they contract the virus – a danger that mounts with symptom severity, new research shows.
In what is purported to be the largest study of its kind to date, results showed that among 236,379 COVID-19 patients, one-third were diagnosed with at least 1 of 14 psychiatric or neurologic disorders within a 6-month span.
The rate of illnesses, which ranged from depression to stroke, rose sharply among those with COVID-19 symptoms acute enough to require hospitalization.
“If we look at patients who were hospitalized, that rate increased to 39%, and then increased to about just under 1 in 2 patients who needed ICU admission at the time of the COVID-19 diagnosis,” Maxime Taquet, PhD, University of Oxford (England) department of psychiatry, said at a media briefing.
Incidence jumps to almost two-thirds in patients with encephalopathy at the time of COVID-19 diagnosis, he added.
The study, which examined the brain health of 236,379 survivors of COVID-19 via a U.S. database of 81 million electronic health records, was published online April 6 in The Lancet Psychiatry.
High rate of neurologic, psychiatric disorders
The research team looked at the first-time diagnosis or recurrence of 14 neurologic and psychiatric outcomes in patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infections. They also compared the brain health of this cohort with a control group of those with influenza or with non–COVID-19 respiratory infections over the same period.
All study participants were older than 10 years, diagnosed with COVID-19 on or after Jan. 20, 2020, and still alive as of Dec. 13, 2020.
The psychiatric and neurologic conditions examined included intracranial hemorrhage; ischemic stroke; parkinsonism; Guillain-Barré syndrome; nerve, nerve root and plexus disorders; myoneural junction and muscle disease; encephalitis; dementia; psychotic, mood, and anxiety disorders; substance use disorder; and insomnia.
The investigators used hospitalization, intensive care admissions, and encephalopathy as an indication of the severity of COVID-19 symptoms.
The study benchmarked the primary cohort with four populations of patients diagnosed in the same period with nonrespiratory illnesses, including skin infection, urolithiasis, bone fractures, and pulmonary embolisms.
Results showed that substantially more COVID-19 patients were diagnosed with a neurologic or psychiatric disorder compared with those with other respiratory illnesses.
“On average, in terms of the relative numbers, there was a 44% increased risk of having a neurological or psychiatric diagnosis after COVID-19 than after the flu and a 16% increased risk compared to other respiratory tract infections,” Dr. Taquet told reporters.
Health services should be prepared for an increase in psychiatric and neurologic issues in the months to come, he said, adding that further investigations are needed into why, and how, the coronavirus affects brain health.
Largest study to date
Although previous research suggests a link between the two, this is the largest study of its kind, examines a wider range of neurologic outcomes, and spans the longest time frame to date, said study coinvestigator Paul Harrison, BM BCh, associate head of the University of Oxford department of psychiatry.
There was a lower incidence of mood and anxiety disorders vs. neurologic disorders in patients with severe COVID-19 symptoms, a finding that Dr. Harrison said may indicate pandemic-related psychological stress is driving these disorders vs. biological factors.
“This paper follows up on an earlier study we did where we found much the same association, and our view is that a lot of the mental health consequences of COVID are … to do with the stress of knowing that one has had COVID and all the implications that go with that, rather than its being a direct effect, for example, of the virus on the brain, or of the immune response to the virus on the brain,” he added.
In contrast, neurologic diagnoses were more likely to be “mediated by some direct consequence of the COVID infection,” he added.
Psychosis and dementia, for instance, were less frequent in the overall COVID-19 population but became much more frequent among those with severe symptoms. The research team said these findings, along with those related to the incidence of ischemic stroke, were “concerning.”
“We found that 1 in 50 patients with COVID-19 go on to have an ischemic stroke in the 6 months after the COVID-19 illness,” Dr. Taquet told reporters. “And that rate increased to 1 in 11 patients if we look at patients with encephalopathy at the time of the COVID-19 diagnosis.”
Rates of brain hemorrhages also rose sharply among those with acute symptoms. Just over 1 in 200 total COVID-19 patients were diagnosed with this neurological condition, but that jumped to 1 in 25 of those who experienced encephalopathy at the time of their COVID-19 diagnosis.
Need for replication
Study coauthor Masud Husain, PhD, of University of Oxford’s cognitive neurology department, told reporters that while there is evidence from other neurologic studies that the virus can access the brain, there has been little sign the neurons themselves are affected.
“There isn’t much evidence that the virus itself attacks neurons in the brain, but it can cause inflammation, and it can activate inflammatory cells in the brain,” he said.
“And those effects are probably very important in some of the biological effects on the brain. In addition, of course, we know that the virus can change clotting and the likelihood of thrombosis in the blood, and those effects can also impact upon the brain,” he added.
Dr. Harrison said it would be helpful to replicate the results garnered from the U.S. database in other populations.
“It goes without saying that replication of these results with other electronic health records and in other countries is a priority,” he said, adding that investigations are essential into how and why the virus affects brain health.
Dr. Harrison cited a U.K. Research and Innovation–funded study called COVID CNS that will follow patients with neurologic and/or psychiatric issues during acute COVID-19 in hopes of exploring possible causes.
Beyond a reasonable doubt
Commenting on the findings, Sir Simon Wessely, MD, Regius chair of psychiatry, King’s College London, said in a release: “This is a very important paper. It confirms beyond any reasonable doubt that COVID-19 affects both brain and mind in equal measure.”
Some of these effects, including stroke and anxiety disorders, were already known, but others such as dementia and psychosis were less well known, he added.
“What is very new is the comparisons with all respiratory viruses or influenza, which suggests that these increases are specifically related to COVID-19, and not a general impact of viral infection,” Dr. Wessely said. “In general, the worse the illness, the greater the neurological or psychiatric outcomes, which is perhaps not surprising.
“The worst outcomes were in those with encephalopathy – inflammation of the brain – again, not surprising. The association with dementia was, however, small and might reflect diagnostic issues, whilst so far there doesn’t seem early evidence of a link with parkinsonism, which was a major factor after the great Spanish Flu pandemic, although the authors caution that it is too early to rule this out.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 survivors face a sharply elevated risk of developing psychiatric or neurologic disorders in the 6 months after they contract the virus – a danger that mounts with symptom severity, new research shows.
In what is purported to be the largest study of its kind to date, results showed that among 236,379 COVID-19 patients, one-third were diagnosed with at least 1 of 14 psychiatric or neurologic disorders within a 6-month span.
The rate of illnesses, which ranged from depression to stroke, rose sharply among those with COVID-19 symptoms acute enough to require hospitalization.
“If we look at patients who were hospitalized, that rate increased to 39%, and then increased to about just under 1 in 2 patients who needed ICU admission at the time of the COVID-19 diagnosis,” Maxime Taquet, PhD, University of Oxford (England) department of psychiatry, said at a media briefing.
Incidence jumps to almost two-thirds in patients with encephalopathy at the time of COVID-19 diagnosis, he added.
The study, which examined the brain health of 236,379 survivors of COVID-19 via a U.S. database of 81 million electronic health records, was published online April 6 in The Lancet Psychiatry.
High rate of neurologic, psychiatric disorders
The research team looked at the first-time diagnosis or recurrence of 14 neurologic and psychiatric outcomes in patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infections. They also compared the brain health of this cohort with a control group of those with influenza or with non–COVID-19 respiratory infections over the same period.
All study participants were older than 10 years, diagnosed with COVID-19 on or after Jan. 20, 2020, and still alive as of Dec. 13, 2020.
The psychiatric and neurologic conditions examined included intracranial hemorrhage; ischemic stroke; parkinsonism; Guillain-Barré syndrome; nerve, nerve root and plexus disorders; myoneural junction and muscle disease; encephalitis; dementia; psychotic, mood, and anxiety disorders; substance use disorder; and insomnia.
The investigators used hospitalization, intensive care admissions, and encephalopathy as an indication of the severity of COVID-19 symptoms.
The study benchmarked the primary cohort with four populations of patients diagnosed in the same period with nonrespiratory illnesses, including skin infection, urolithiasis, bone fractures, and pulmonary embolisms.
Results showed that substantially more COVID-19 patients were diagnosed with a neurologic or psychiatric disorder compared with those with other respiratory illnesses.
“On average, in terms of the relative numbers, there was a 44% increased risk of having a neurological or psychiatric diagnosis after COVID-19 than after the flu and a 16% increased risk compared to other respiratory tract infections,” Dr. Taquet told reporters.
Health services should be prepared for an increase in psychiatric and neurologic issues in the months to come, he said, adding that further investigations are needed into why, and how, the coronavirus affects brain health.
Largest study to date
Although previous research suggests a link between the two, this is the largest study of its kind, examines a wider range of neurologic outcomes, and spans the longest time frame to date, said study coinvestigator Paul Harrison, BM BCh, associate head of the University of Oxford department of psychiatry.
There was a lower incidence of mood and anxiety disorders vs. neurologic disorders in patients with severe COVID-19 symptoms, a finding that Dr. Harrison said may indicate pandemic-related psychological stress is driving these disorders vs. biological factors.
“This paper follows up on an earlier study we did where we found much the same association, and our view is that a lot of the mental health consequences of COVID are … to do with the stress of knowing that one has had COVID and all the implications that go with that, rather than its being a direct effect, for example, of the virus on the brain, or of the immune response to the virus on the brain,” he added.
In contrast, neurologic diagnoses were more likely to be “mediated by some direct consequence of the COVID infection,” he added.
Psychosis and dementia, for instance, were less frequent in the overall COVID-19 population but became much more frequent among those with severe symptoms. The research team said these findings, along with those related to the incidence of ischemic stroke, were “concerning.”
“We found that 1 in 50 patients with COVID-19 go on to have an ischemic stroke in the 6 months after the COVID-19 illness,” Dr. Taquet told reporters. “And that rate increased to 1 in 11 patients if we look at patients with encephalopathy at the time of the COVID-19 diagnosis.”
Rates of brain hemorrhages also rose sharply among those with acute symptoms. Just over 1 in 200 total COVID-19 patients were diagnosed with this neurological condition, but that jumped to 1 in 25 of those who experienced encephalopathy at the time of their COVID-19 diagnosis.
Need for replication
Study coauthor Masud Husain, PhD, of University of Oxford’s cognitive neurology department, told reporters that while there is evidence from other neurologic studies that the virus can access the brain, there has been little sign the neurons themselves are affected.
“There isn’t much evidence that the virus itself attacks neurons in the brain, but it can cause inflammation, and it can activate inflammatory cells in the brain,” he said.
“And those effects are probably very important in some of the biological effects on the brain. In addition, of course, we know that the virus can change clotting and the likelihood of thrombosis in the blood, and those effects can also impact upon the brain,” he added.
Dr. Harrison said it would be helpful to replicate the results garnered from the U.S. database in other populations.
“It goes without saying that replication of these results with other electronic health records and in other countries is a priority,” he said, adding that investigations are essential into how and why the virus affects brain health.
Dr. Harrison cited a U.K. Research and Innovation–funded study called COVID CNS that will follow patients with neurologic and/or psychiatric issues during acute COVID-19 in hopes of exploring possible causes.
Beyond a reasonable doubt
Commenting on the findings, Sir Simon Wessely, MD, Regius chair of psychiatry, King’s College London, said in a release: “This is a very important paper. It confirms beyond any reasonable doubt that COVID-19 affects both brain and mind in equal measure.”
Some of these effects, including stroke and anxiety disorders, were already known, but others such as dementia and psychosis were less well known, he added.
“What is very new is the comparisons with all respiratory viruses or influenza, which suggests that these increases are specifically related to COVID-19, and not a general impact of viral infection,” Dr. Wessely said. “In general, the worse the illness, the greater the neurological or psychiatric outcomes, which is perhaps not surprising.
“The worst outcomes were in those with encephalopathy – inflammation of the brain – again, not surprising. The association with dementia was, however, small and might reflect diagnostic issues, whilst so far there doesn’t seem early evidence of a link with parkinsonism, which was a major factor after the great Spanish Flu pandemic, although the authors caution that it is too early to rule this out.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
About one in five clinicians considers quitting because of pandemic
a new survey of more than 5,000 clinicians at an academic medical center illustrates.
About one in five people reported considering leaving the workforce because of the challenges of working during the COVID-19 pandemic. In addition, 30% reported they are considering cutting back work hours.
“There are a substantial number of employees and trainees who are experiencing major stress and work disruptions because of the pandemic,” lead author Rebecca K. Delaney, PhD, said in an interview. “It is particularly alarming that people who have spent 5 or more years in training for their specialty are struggling with their work, so much so that they have even considered leaving the workforce or reducing their hours.”
“Being a caregiver adds another layer of difficulty for faculty, staff, and trainees who are trying to manage work and child care,” added Dr. Delaney, a researcher in the department of population health sciences, University of Utah, Salt Lake City.
The study was published online April 2 in JAMA Network Open.
“This looks like an excellent survey,” Carol A Bernstein, MD, said in an interview when asked to comment. “I do not think it provides particularly new information as these challenges in the workplace, especially for women during COVID, have been well documented in the media and the medical literature to date.”
“That said, to the extent that data helps drive solutions, I would hope that information such as this would be considered as strong further evidence that health care systems must pay close attention to the wellbeing of the workforce,” added Dr. Bernstein, professor and vice chair of faculty development and well-being, departments of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and obstetrics and gynecology and women’s health, Montefiore Medical Center/Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York.
When the pandemic hits home
A total of 42% of the American workforce rapidly transitioned to working from home at the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. At the same time, many employees had to provide child care and assistance with schoolwork. This placed a burden on many individuals at academic medical centers, and women in particular.
“Women comprise 74.9% of hospital employees, many of whom are essential clinical workers,” the researchers noted. “The extent of the needs and difficulties for these workers during the pandemic remain largely unknown.”
To learn more, Dr. Delaney, senior author Angie Fagerlin, PhD, and their colleagues emailed a Qualtrics survey to 27,700 faculty, staff, and trainees at University of Utah Health. The survey was conducted Aug. 5-20, 2020 as part of a quality improvement initiative. All responses were anonymous.
Survey questions included if, because of the pandemic, people had considered leaving the workforce, considered reducing their hours, or experienced reduced productivity. The researchers also asked about career impacts and potential solutions in terms of “work culture adaptations.”
Respondents with children aged under 18 years also were asked about child care options. Dr. Delaney and colleagues also inquired about race and ethnicity because they hypothesized that employees from underrepresented groups would likely experience the pandemic differently.
The mean age of the 5,951 (21%) faculty, staff, and trainees who completed the survey was 40 years. A majority of respondents were women, reflecting the higher proportion of women within the health system.
A majority (86%) identified as White or European American. About two-thirds of respondents (66%) were staff, 16% were faculty, and 13% were trainees.
COVID-19 career concerns
Overall, 1,061 respondents (21%) “moderately or very seriously” considered leaving the workforce and 1,505 (30%) considered reducing hours. Respondents who were younger, married, a member of an underrepresented racial/ethnic group, and worked in a clinical setting were more likely to consider leaving the workforce.
The survey showed 27% felt their productivity increased whereas 39% believed their productivity decreased.
Of the 2,412 survey participants with children aged 18 years or younger, 66% reported that they did not have child care fully available.
“Failure to address and provide for child care has long been one of the many significant deficits in U.S. health care systems,” said Dr. Bernstein, lead author of a March 2021 report evaluating staff emotional support at Montefiore Medical Center during the pandemic in The Joint Commission Journal on Quality and Patient Safety.
Furthermore, 47% were “moderately or very seriously worried” about COVID-19 impacting their career development.
Women trainees were significantly more likely than male counterparts to consider leaving the workforce and reducing their work hours. Women in a faculty or trainee role were also more likely to worry about COVID-19’s impact on their career, compared with men, and compared with women in staff positions.
“It was disheartening to have our data support the gender and racial/ethnic disparity that has been highlighted in the media during the pandemic,” Dr. Delaney said. “Women and in some cases racial/ethnic groups that are underrepresented in medicine were most likely to consider leaving the workforce, reducing hours, and were worried about their career development.
“It is critical that we strategically address these important disparities,” she said.
Women also are disproportionately affected by burnout, particularly during the pandemic, according to an analysis of Medscape’s Physician Burnout and Suicide Report.
Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has shifted the medical specialties now considered highest risk for burnout: critical care physicians ranked first in the report, followed by rheumatologists and infectious disease specialists.
Potential solutions
“Given the disproportionate impact COVID-19 has on employees of health systems, institutions must find ways to support their employees, both in terms of workplace cultural adaptations and assistance with familial responsibilities,” the researchers noted.
Telecommuting policies, scheduling flexibility, and expanding employee support programs are potential solutions. Institutional policies also could address the educational and direct care needs of employee children.
Limitations of the study include its generalizability beyond employees of University of Utah Health. Also, respondents included a lower proportion of racial and ethnic groups, compared with national figures, “although this is mostly accounted for by the overall low population of such groups in the state of Utah,” the researchers added.
“Our results suggest that respondents were struggling during the COVID-19 pandemic,” the researchers noted. “As a result, even after investing substantial amounts of time in years of training, many were considering leaving the workforce because of stress and caregiving responsibilities related to the pandemic.”
The Jon M. Huntsman Presidential Endowed Chair supported the work with a financial award to Dr. Fagerlin. Dr. Delaney and Dr. Bernstein disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
a new survey of more than 5,000 clinicians at an academic medical center illustrates.
About one in five people reported considering leaving the workforce because of the challenges of working during the COVID-19 pandemic. In addition, 30% reported they are considering cutting back work hours.
“There are a substantial number of employees and trainees who are experiencing major stress and work disruptions because of the pandemic,” lead author Rebecca K. Delaney, PhD, said in an interview. “It is particularly alarming that people who have spent 5 or more years in training for their specialty are struggling with their work, so much so that they have even considered leaving the workforce or reducing their hours.”
“Being a caregiver adds another layer of difficulty for faculty, staff, and trainees who are trying to manage work and child care,” added Dr. Delaney, a researcher in the department of population health sciences, University of Utah, Salt Lake City.
The study was published online April 2 in JAMA Network Open.
“This looks like an excellent survey,” Carol A Bernstein, MD, said in an interview when asked to comment. “I do not think it provides particularly new information as these challenges in the workplace, especially for women during COVID, have been well documented in the media and the medical literature to date.”
“That said, to the extent that data helps drive solutions, I would hope that information such as this would be considered as strong further evidence that health care systems must pay close attention to the wellbeing of the workforce,” added Dr. Bernstein, professor and vice chair of faculty development and well-being, departments of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and obstetrics and gynecology and women’s health, Montefiore Medical Center/Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York.
When the pandemic hits home
A total of 42% of the American workforce rapidly transitioned to working from home at the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. At the same time, many employees had to provide child care and assistance with schoolwork. This placed a burden on many individuals at academic medical centers, and women in particular.
“Women comprise 74.9% of hospital employees, many of whom are essential clinical workers,” the researchers noted. “The extent of the needs and difficulties for these workers during the pandemic remain largely unknown.”
To learn more, Dr. Delaney, senior author Angie Fagerlin, PhD, and their colleagues emailed a Qualtrics survey to 27,700 faculty, staff, and trainees at University of Utah Health. The survey was conducted Aug. 5-20, 2020 as part of a quality improvement initiative. All responses were anonymous.
Survey questions included if, because of the pandemic, people had considered leaving the workforce, considered reducing their hours, or experienced reduced productivity. The researchers also asked about career impacts and potential solutions in terms of “work culture adaptations.”
Respondents with children aged under 18 years also were asked about child care options. Dr. Delaney and colleagues also inquired about race and ethnicity because they hypothesized that employees from underrepresented groups would likely experience the pandemic differently.
The mean age of the 5,951 (21%) faculty, staff, and trainees who completed the survey was 40 years. A majority of respondents were women, reflecting the higher proportion of women within the health system.
A majority (86%) identified as White or European American. About two-thirds of respondents (66%) were staff, 16% were faculty, and 13% were trainees.
COVID-19 career concerns
Overall, 1,061 respondents (21%) “moderately or very seriously” considered leaving the workforce and 1,505 (30%) considered reducing hours. Respondents who were younger, married, a member of an underrepresented racial/ethnic group, and worked in a clinical setting were more likely to consider leaving the workforce.
The survey showed 27% felt their productivity increased whereas 39% believed their productivity decreased.
Of the 2,412 survey participants with children aged 18 years or younger, 66% reported that they did not have child care fully available.
“Failure to address and provide for child care has long been one of the many significant deficits in U.S. health care systems,” said Dr. Bernstein, lead author of a March 2021 report evaluating staff emotional support at Montefiore Medical Center during the pandemic in The Joint Commission Journal on Quality and Patient Safety.
Furthermore, 47% were “moderately or very seriously worried” about COVID-19 impacting their career development.
Women trainees were significantly more likely than male counterparts to consider leaving the workforce and reducing their work hours. Women in a faculty or trainee role were also more likely to worry about COVID-19’s impact on their career, compared with men, and compared with women in staff positions.
“It was disheartening to have our data support the gender and racial/ethnic disparity that has been highlighted in the media during the pandemic,” Dr. Delaney said. “Women and in some cases racial/ethnic groups that are underrepresented in medicine were most likely to consider leaving the workforce, reducing hours, and were worried about their career development.
“It is critical that we strategically address these important disparities,” she said.
Women also are disproportionately affected by burnout, particularly during the pandemic, according to an analysis of Medscape’s Physician Burnout and Suicide Report.
Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has shifted the medical specialties now considered highest risk for burnout: critical care physicians ranked first in the report, followed by rheumatologists and infectious disease specialists.
Potential solutions
“Given the disproportionate impact COVID-19 has on employees of health systems, institutions must find ways to support their employees, both in terms of workplace cultural adaptations and assistance with familial responsibilities,” the researchers noted.
Telecommuting policies, scheduling flexibility, and expanding employee support programs are potential solutions. Institutional policies also could address the educational and direct care needs of employee children.
Limitations of the study include its generalizability beyond employees of University of Utah Health. Also, respondents included a lower proportion of racial and ethnic groups, compared with national figures, “although this is mostly accounted for by the overall low population of such groups in the state of Utah,” the researchers added.
“Our results suggest that respondents were struggling during the COVID-19 pandemic,” the researchers noted. “As a result, even after investing substantial amounts of time in years of training, many were considering leaving the workforce because of stress and caregiving responsibilities related to the pandemic.”
The Jon M. Huntsman Presidential Endowed Chair supported the work with a financial award to Dr. Fagerlin. Dr. Delaney and Dr. Bernstein disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
a new survey of more than 5,000 clinicians at an academic medical center illustrates.
About one in five people reported considering leaving the workforce because of the challenges of working during the COVID-19 pandemic. In addition, 30% reported they are considering cutting back work hours.
“There are a substantial number of employees and trainees who are experiencing major stress and work disruptions because of the pandemic,” lead author Rebecca K. Delaney, PhD, said in an interview. “It is particularly alarming that people who have spent 5 or more years in training for their specialty are struggling with their work, so much so that they have even considered leaving the workforce or reducing their hours.”
“Being a caregiver adds another layer of difficulty for faculty, staff, and trainees who are trying to manage work and child care,” added Dr. Delaney, a researcher in the department of population health sciences, University of Utah, Salt Lake City.
The study was published online April 2 in JAMA Network Open.
“This looks like an excellent survey,” Carol A Bernstein, MD, said in an interview when asked to comment. “I do not think it provides particularly new information as these challenges in the workplace, especially for women during COVID, have been well documented in the media and the medical literature to date.”
“That said, to the extent that data helps drive solutions, I would hope that information such as this would be considered as strong further evidence that health care systems must pay close attention to the wellbeing of the workforce,” added Dr. Bernstein, professor and vice chair of faculty development and well-being, departments of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and obstetrics and gynecology and women’s health, Montefiore Medical Center/Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York.
When the pandemic hits home
A total of 42% of the American workforce rapidly transitioned to working from home at the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. At the same time, many employees had to provide child care and assistance with schoolwork. This placed a burden on many individuals at academic medical centers, and women in particular.
“Women comprise 74.9% of hospital employees, many of whom are essential clinical workers,” the researchers noted. “The extent of the needs and difficulties for these workers during the pandemic remain largely unknown.”
To learn more, Dr. Delaney, senior author Angie Fagerlin, PhD, and their colleagues emailed a Qualtrics survey to 27,700 faculty, staff, and trainees at University of Utah Health. The survey was conducted Aug. 5-20, 2020 as part of a quality improvement initiative. All responses were anonymous.
Survey questions included if, because of the pandemic, people had considered leaving the workforce, considered reducing their hours, or experienced reduced productivity. The researchers also asked about career impacts and potential solutions in terms of “work culture adaptations.”
Respondents with children aged under 18 years also were asked about child care options. Dr. Delaney and colleagues also inquired about race and ethnicity because they hypothesized that employees from underrepresented groups would likely experience the pandemic differently.
The mean age of the 5,951 (21%) faculty, staff, and trainees who completed the survey was 40 years. A majority of respondents were women, reflecting the higher proportion of women within the health system.
A majority (86%) identified as White or European American. About two-thirds of respondents (66%) were staff, 16% were faculty, and 13% were trainees.
COVID-19 career concerns
Overall, 1,061 respondents (21%) “moderately or very seriously” considered leaving the workforce and 1,505 (30%) considered reducing hours. Respondents who were younger, married, a member of an underrepresented racial/ethnic group, and worked in a clinical setting were more likely to consider leaving the workforce.
The survey showed 27% felt their productivity increased whereas 39% believed their productivity decreased.
Of the 2,412 survey participants with children aged 18 years or younger, 66% reported that they did not have child care fully available.
“Failure to address and provide for child care has long been one of the many significant deficits in U.S. health care systems,” said Dr. Bernstein, lead author of a March 2021 report evaluating staff emotional support at Montefiore Medical Center during the pandemic in The Joint Commission Journal on Quality and Patient Safety.
Furthermore, 47% were “moderately or very seriously worried” about COVID-19 impacting their career development.
Women trainees were significantly more likely than male counterparts to consider leaving the workforce and reducing their work hours. Women in a faculty or trainee role were also more likely to worry about COVID-19’s impact on their career, compared with men, and compared with women in staff positions.
“It was disheartening to have our data support the gender and racial/ethnic disparity that has been highlighted in the media during the pandemic,” Dr. Delaney said. “Women and in some cases racial/ethnic groups that are underrepresented in medicine were most likely to consider leaving the workforce, reducing hours, and were worried about their career development.
“It is critical that we strategically address these important disparities,” she said.
Women also are disproportionately affected by burnout, particularly during the pandemic, according to an analysis of Medscape’s Physician Burnout and Suicide Report.
Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has shifted the medical specialties now considered highest risk for burnout: critical care physicians ranked first in the report, followed by rheumatologists and infectious disease specialists.
Potential solutions
“Given the disproportionate impact COVID-19 has on employees of health systems, institutions must find ways to support their employees, both in terms of workplace cultural adaptations and assistance with familial responsibilities,” the researchers noted.
Telecommuting policies, scheduling flexibility, and expanding employee support programs are potential solutions. Institutional policies also could address the educational and direct care needs of employee children.
Limitations of the study include its generalizability beyond employees of University of Utah Health. Also, respondents included a lower proportion of racial and ethnic groups, compared with national figures, “although this is mostly accounted for by the overall low population of such groups in the state of Utah,” the researchers added.
“Our results suggest that respondents were struggling during the COVID-19 pandemic,” the researchers noted. “As a result, even after investing substantial amounts of time in years of training, many were considering leaving the workforce because of stress and caregiving responsibilities related to the pandemic.”
The Jon M. Huntsman Presidential Endowed Chair supported the work with a financial award to Dr. Fagerlin. Dr. Delaney and Dr. Bernstein disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Hidradenitis Suppurativa Lesions Following Tumor Necrosis Factor α Inhibitors
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition with high morbidity rates. Symptoms typically develop between puberty and the third decade of life, affecting twice as many females as males, with an overall disease prevalence of 1% to 4%.1 The pathogenesis is theorized to be related to an immune response to follicular occlusion and rupture in genetically susceptible individuals.
Among the complications associated with HS, the development of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is 4.6-times more likely within HS lesions than in normal skin and typically is seen in the setting of long-standing disease, particularly in men with HS lesions located on the buttocks and genital region for more than 20 years.2 In 2015, the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor adalimumab was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of HS. Tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors have been associated with an increased risk for skin cancer in other clinical settings.3,4 We present a case of locally advanced SCC that developed in a patient with HS who was treated with adalimumab and infliximab (both TNF-α inhibitors), ultimately leading to the patient’s death.
A 59-year-old man who smoked with a 40-year history of severe HS, who previously was lost to follow-up, presented to our dermatology clinic with lesions on the buttocks. Physical examination demonstrated confluent, indurated, boggy plaques; scattered sinus tracts with purulent drainage; scattered cystlike nodules; and tenderness to palpation consistent with Hurley stage III disease (Figure 1A). No involvement of the axillae or groin was noted. He was started on doxycycline and a prednisone taper with minimal improvement and subsequently was switched to adalimumab 3 months later. Adalimumab provided little relief and was discontinued; therapy was transitioned to infliximab 3 months later.
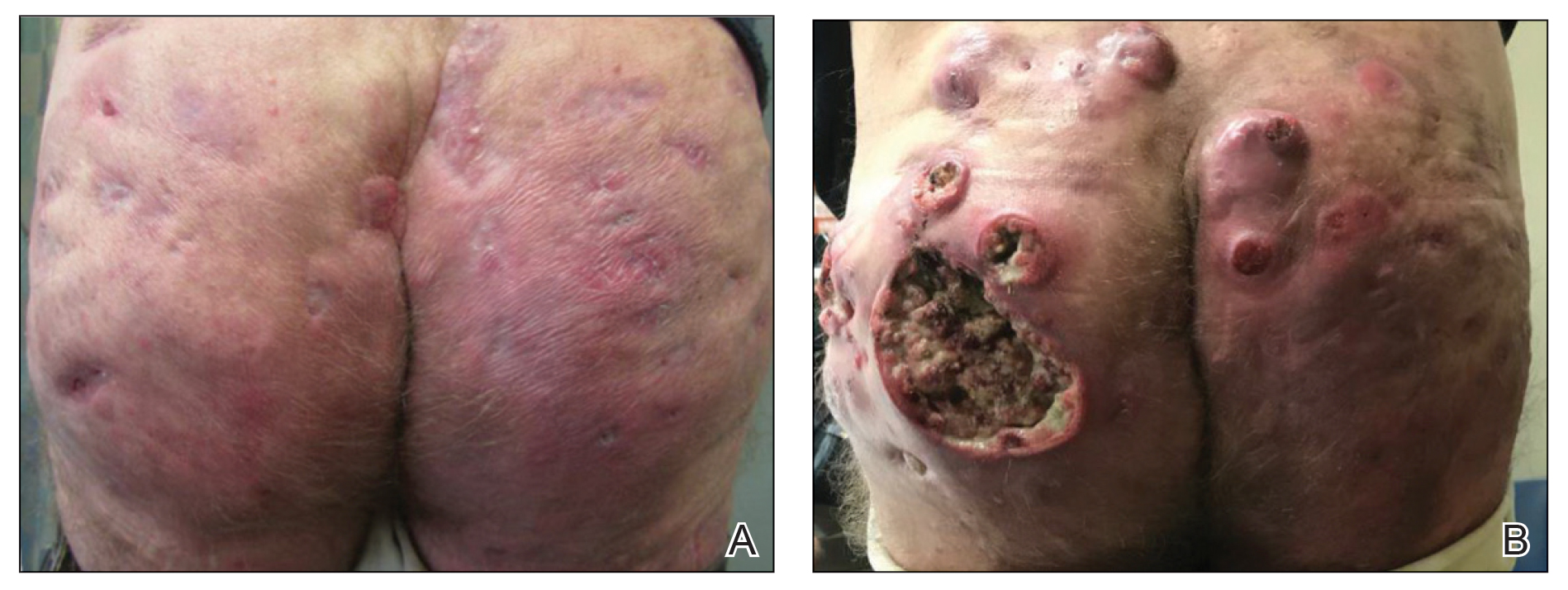
The patient returned to our clinic 3 months later with a severe flare and intractable pain after 4 infusions of infliximab. Physical examination showed a 7×5-cm deep malodorous ulcer with fibrinous exudate on the left buttock, several 2- to 3-cm shallow ulcers draining yellow exudate, and numerous fluctuant subcutaneous nodules on a background of scarring and sinus tracts. He was started again on doxycycline and a prednisone taper. At follow-up 2 weeks later, the largest ulcer had increased to 8 cm, and more indurated and tender subcutaneous nodules and scattered ulcerations developed (Figure 1B). Two punch biopsies of the left buttock revealed an invasive keratinizing carcinoma with no connection to the epidermis, consistent with SCC (Figure 2). Human papillomavirus (HPV) test results with probes for 37 HPV types—13 that were high risk (HPV-16, −18, −31, −33, −35, −39, −45, −51, −52, −56, −58, −59, −68)—were negative. Computerized tomography demonstrated diffuse thickening of the skin on the buttocks, inguinal adenopathy suspicious for nodal metastases, and no evidence of distant metastatic disease. Given the extent of the disease, surgical treatment was not an option, and he began receiving palliative radiotherapy. However, his health declined, and he developed aspiration pneumonia and hypotension requiring pressor support. He was transitioned to hospice care and died 3 months after presentation.
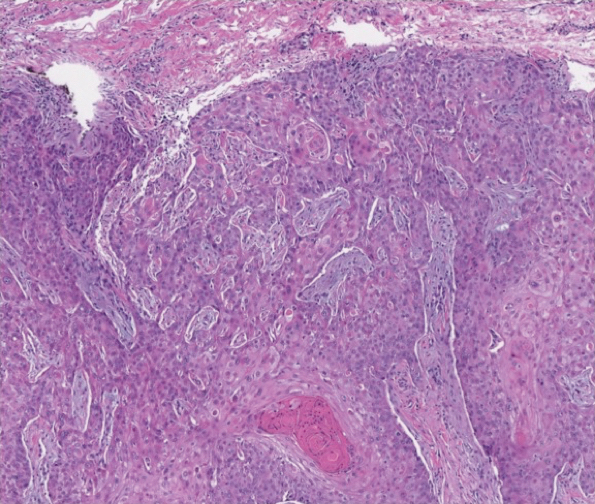
Tumor necrosis factor α antagonist treatment is being increasingly used to control HS but also may increase the risk for SCC development. We performed a search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE as well as Web of Science using the terms hidradenitis suppurativa or acne inversa and one of the following—tumor necrosis factor inhibitor, infliximab, adalimumab, or etanercept—and squamous cell carcinoma or Marjolin ulcer. Seven cases of SCC arising in an HS patient treated with a TNF-α inhibitor have been reported (Table).5-10 Four cases were associated with infliximab use, 2 with adalimumab, and our case occurred after both adalimumab and infliximab treatment. All individuals were men with severe, long-standing disease of the anogenital region. In addition to smoking, HPV-16 positivity also has been reported as a risk factor for developing SCC in the setting of HS.11 In our patient, however, HPV testing did not cover all HPV strains, but several high-risk strains, including HPV-16, were negative.
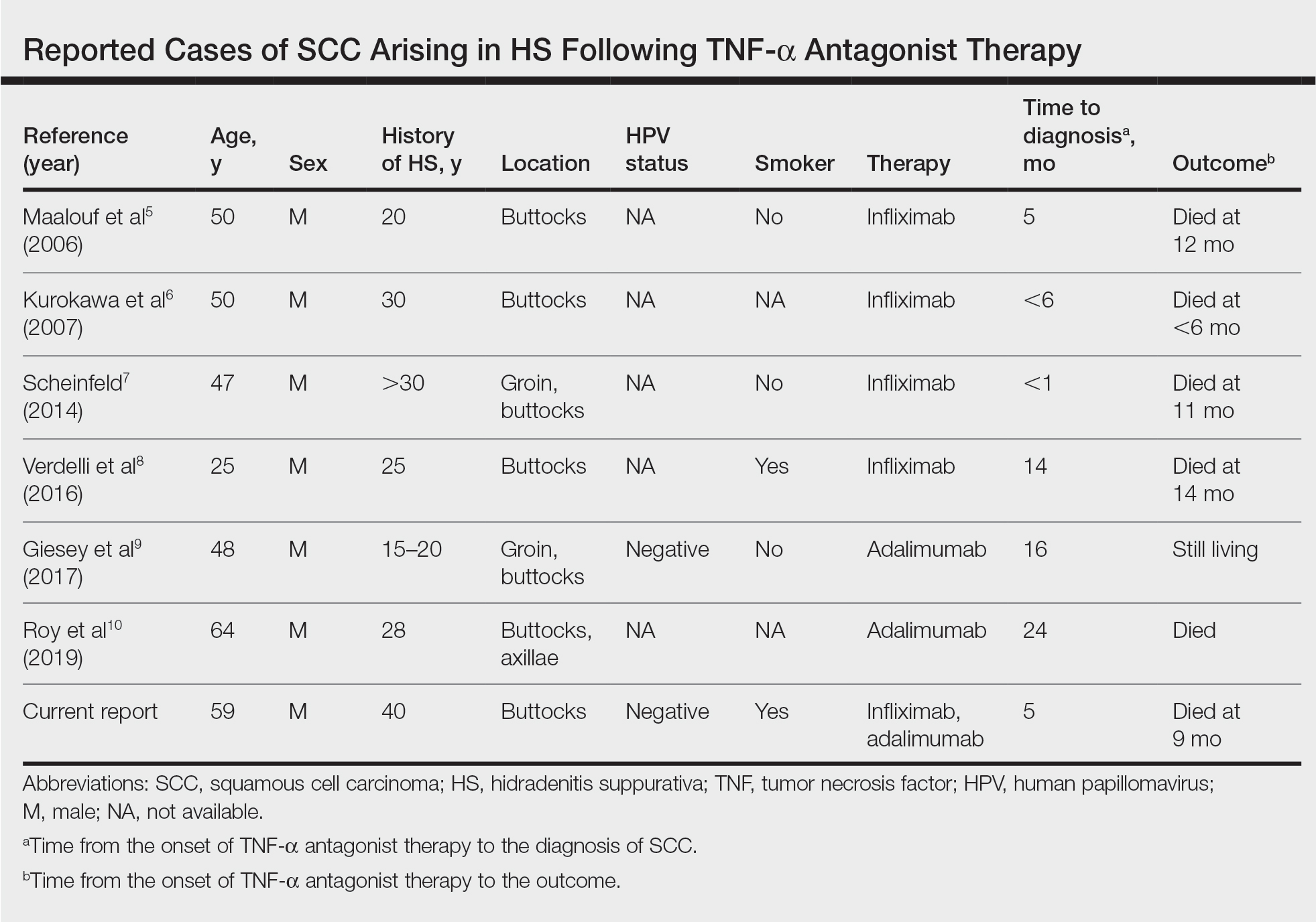
Hidradenitis suppurativa is caused by an immune response to ruptured follicles and TNF-α antagonists are useful in suppressing this response; however, immunosuppression can lead to an increased susceptibility to malignancy, especially in SCC. It is unclear whether the use of infliximab or adalimumab is causal, additive, or a confounder in the development of SCC in patients with severe HS. It is possible that these agents increase the rapidity of the development of SCC in already-susceptible patients. Although TNF-α antagonists can be an effective therapeutic option for patients with moderate to severe HS, the potential risk for contributing to skin cancer development should raise provider suspicion in high-risk patients. Given the findings in this report, it may be suitable for providers to consider a biopsy prior to initiating TNF-α therapy in men older than 20 years with moderate to severe HS of the groin or buttocks, in addition to more frequent monitoring and a lower threshold to biopsy lesions with rapid growth or ulceration.
- Alikhan A, Lynch PJ, Eisen DB. Hidradenitis suppurativa: a comprehensive review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:539-561; quiz 562-533.
- Lapins J, Ye W, Nyren O, et al. Incidence of cancer among patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:730-734.
- Askling J, Fahrbach K, Nordstrom B, et al. Cancer risk with tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF) inhibitors: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab using patient level data. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2011;20:119-130.
- Mariette X, Matucci-Cerinic M, Pavelka K, et al. Malignancies associated with tumour necrosis factor inhibitors in registries and prospective observational studies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:1895-1904.
- Maalouf E, Faye O, Poli F, et al. Fatal epidermoid carcinoma in hidradenitis suppurativa following treatment with infliximab. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2006;133(5 pt 1):473-474.
- Kurokawa I, Nishimura K, Yamanaka K, et al. Cytokeratin expression in squamous cell carcinoma arising from hidradenitis suppurativa (acne inversa). J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34:675-678.
- Scheinfeld N. A case of a patient with stage III familial hidradenitis suppurativa treated with 3 courses of infliximab and died of metastatic squamous cell carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20(3).
- Verdelli A, Antiga E, Bonciani D, et al. A fatal case of hidradenitis suppurativa associated with sepsis and squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:E52-E53.
- Giesey R, Delost GR, Honaker J, et al. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma in a patient treated with adalimumab for hidradenitis suppurativa. JAAD Case Rep. 2017;3:489-491.
- Roy C, Roy S, Ghazawi F, et al. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma arising in hidradenitis suppurativa: a case report. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2019;7:2050313X19847359.
- Lavogiez C, Delaporte E, Darras-Vercambre S, et al. Clinicopathological study of 13 cases of squamous cell carcinoma complicating hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatology. 2010;220:147-153.
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition with high morbidity rates. Symptoms typically develop between puberty and the third decade of life, affecting twice as many females as males, with an overall disease prevalence of 1% to 4%.1 The pathogenesis is theorized to be related to an immune response to follicular occlusion and rupture in genetically susceptible individuals.
Among the complications associated with HS, the development of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is 4.6-times more likely within HS lesions than in normal skin and typically is seen in the setting of long-standing disease, particularly in men with HS lesions located on the buttocks and genital region for more than 20 years.2 In 2015, the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor adalimumab was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of HS. Tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors have been associated with an increased risk for skin cancer in other clinical settings.3,4 We present a case of locally advanced SCC that developed in a patient with HS who was treated with adalimumab and infliximab (both TNF-α inhibitors), ultimately leading to the patient’s death.
A 59-year-old man who smoked with a 40-year history of severe HS, who previously was lost to follow-up, presented to our dermatology clinic with lesions on the buttocks. Physical examination demonstrated confluent, indurated, boggy plaques; scattered sinus tracts with purulent drainage; scattered cystlike nodules; and tenderness to palpation consistent with Hurley stage III disease (Figure 1A). No involvement of the axillae or groin was noted. He was started on doxycycline and a prednisone taper with minimal improvement and subsequently was switched to adalimumab 3 months later. Adalimumab provided little relief and was discontinued; therapy was transitioned to infliximab 3 months later.

The patient returned to our clinic 3 months later with a severe flare and intractable pain after 4 infusions of infliximab. Physical examination showed a 7×5-cm deep malodorous ulcer with fibrinous exudate on the left buttock, several 2- to 3-cm shallow ulcers draining yellow exudate, and numerous fluctuant subcutaneous nodules on a background of scarring and sinus tracts. He was started again on doxycycline and a prednisone taper. At follow-up 2 weeks later, the largest ulcer had increased to 8 cm, and more indurated and tender subcutaneous nodules and scattered ulcerations developed (Figure 1B). Two punch biopsies of the left buttock revealed an invasive keratinizing carcinoma with no connection to the epidermis, consistent with SCC (Figure 2). Human papillomavirus (HPV) test results with probes for 37 HPV types—13 that were high risk (HPV-16, −18, −31, −33, −35, −39, −45, −51, −52, −56, −58, −59, −68)—were negative. Computerized tomography demonstrated diffuse thickening of the skin on the buttocks, inguinal adenopathy suspicious for nodal metastases, and no evidence of distant metastatic disease. Given the extent of the disease, surgical treatment was not an option, and he began receiving palliative radiotherapy. However, his health declined, and he developed aspiration pneumonia and hypotension requiring pressor support. He was transitioned to hospice care and died 3 months after presentation.

Tumor necrosis factor α antagonist treatment is being increasingly used to control HS but also may increase the risk for SCC development. We performed a search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE as well as Web of Science using the terms hidradenitis suppurativa or acne inversa and one of the following—tumor necrosis factor inhibitor, infliximab, adalimumab, or etanercept—and squamous cell carcinoma or Marjolin ulcer. Seven cases of SCC arising in an HS patient treated with a TNF-α inhibitor have been reported (Table).5-10 Four cases were associated with infliximab use, 2 with adalimumab, and our case occurred after both adalimumab and infliximab treatment. All individuals were men with severe, long-standing disease of the anogenital region. In addition to smoking, HPV-16 positivity also has been reported as a risk factor for developing SCC in the setting of HS.11 In our patient, however, HPV testing did not cover all HPV strains, but several high-risk strains, including HPV-16, were negative.

Hidradenitis suppurativa is caused by an immune response to ruptured follicles and TNF-α antagonists are useful in suppressing this response; however, immunosuppression can lead to an increased susceptibility to malignancy, especially in SCC. It is unclear whether the use of infliximab or adalimumab is causal, additive, or a confounder in the development of SCC in patients with severe HS. It is possible that these agents increase the rapidity of the development of SCC in already-susceptible patients. Although TNF-α antagonists can be an effective therapeutic option for patients with moderate to severe HS, the potential risk for contributing to skin cancer development should raise provider suspicion in high-risk patients. Given the findings in this report, it may be suitable for providers to consider a biopsy prior to initiating TNF-α therapy in men older than 20 years with moderate to severe HS of the groin or buttocks, in addition to more frequent monitoring and a lower threshold to biopsy lesions with rapid growth or ulceration.
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition with high morbidity rates. Symptoms typically develop between puberty and the third decade of life, affecting twice as many females as males, with an overall disease prevalence of 1% to 4%.1 The pathogenesis is theorized to be related to an immune response to follicular occlusion and rupture in genetically susceptible individuals.
Among the complications associated with HS, the development of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is 4.6-times more likely within HS lesions than in normal skin and typically is seen in the setting of long-standing disease, particularly in men with HS lesions located on the buttocks and genital region for more than 20 years.2 In 2015, the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor adalimumab was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of HS. Tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors have been associated with an increased risk for skin cancer in other clinical settings.3,4 We present a case of locally advanced SCC that developed in a patient with HS who was treated with adalimumab and infliximab (both TNF-α inhibitors), ultimately leading to the patient’s death.
A 59-year-old man who smoked with a 40-year history of severe HS, who previously was lost to follow-up, presented to our dermatology clinic with lesions on the buttocks. Physical examination demonstrated confluent, indurated, boggy plaques; scattered sinus tracts with purulent drainage; scattered cystlike nodules; and tenderness to palpation consistent with Hurley stage III disease (Figure 1A). No involvement of the axillae or groin was noted. He was started on doxycycline and a prednisone taper with minimal improvement and subsequently was switched to adalimumab 3 months later. Adalimumab provided little relief and was discontinued; therapy was transitioned to infliximab 3 months later.

The patient returned to our clinic 3 months later with a severe flare and intractable pain after 4 infusions of infliximab. Physical examination showed a 7×5-cm deep malodorous ulcer with fibrinous exudate on the left buttock, several 2- to 3-cm shallow ulcers draining yellow exudate, and numerous fluctuant subcutaneous nodules on a background of scarring and sinus tracts. He was started again on doxycycline and a prednisone taper. At follow-up 2 weeks later, the largest ulcer had increased to 8 cm, and more indurated and tender subcutaneous nodules and scattered ulcerations developed (Figure 1B). Two punch biopsies of the left buttock revealed an invasive keratinizing carcinoma with no connection to the epidermis, consistent with SCC (Figure 2). Human papillomavirus (HPV) test results with probes for 37 HPV types—13 that were high risk (HPV-16, −18, −31, −33, −35, −39, −45, −51, −52, −56, −58, −59, −68)—were negative. Computerized tomography demonstrated diffuse thickening of the skin on the buttocks, inguinal adenopathy suspicious for nodal metastases, and no evidence of distant metastatic disease. Given the extent of the disease, surgical treatment was not an option, and he began receiving palliative radiotherapy. However, his health declined, and he developed aspiration pneumonia and hypotension requiring pressor support. He was transitioned to hospice care and died 3 months after presentation.

Tumor necrosis factor α antagonist treatment is being increasingly used to control HS but also may increase the risk for SCC development. We performed a search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE as well as Web of Science using the terms hidradenitis suppurativa or acne inversa and one of the following—tumor necrosis factor inhibitor, infliximab, adalimumab, or etanercept—and squamous cell carcinoma or Marjolin ulcer. Seven cases of SCC arising in an HS patient treated with a TNF-α inhibitor have been reported (Table).5-10 Four cases were associated with infliximab use, 2 with adalimumab, and our case occurred after both adalimumab and infliximab treatment. All individuals were men with severe, long-standing disease of the anogenital region. In addition to smoking, HPV-16 positivity also has been reported as a risk factor for developing SCC in the setting of HS.11 In our patient, however, HPV testing did not cover all HPV strains, but several high-risk strains, including HPV-16, were negative.

Hidradenitis suppurativa is caused by an immune response to ruptured follicles and TNF-α antagonists are useful in suppressing this response; however, immunosuppression can lead to an increased susceptibility to malignancy, especially in SCC. It is unclear whether the use of infliximab or adalimumab is causal, additive, or a confounder in the development of SCC in patients with severe HS. It is possible that these agents increase the rapidity of the development of SCC in already-susceptible patients. Although TNF-α antagonists can be an effective therapeutic option for patients with moderate to severe HS, the potential risk for contributing to skin cancer development should raise provider suspicion in high-risk patients. Given the findings in this report, it may be suitable for providers to consider a biopsy prior to initiating TNF-α therapy in men older than 20 years with moderate to severe HS of the groin or buttocks, in addition to more frequent monitoring and a lower threshold to biopsy lesions with rapid growth or ulceration.
- Alikhan A, Lynch PJ, Eisen DB. Hidradenitis suppurativa: a comprehensive review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:539-561; quiz 562-533.
- Lapins J, Ye W, Nyren O, et al. Incidence of cancer among patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:730-734.
- Askling J, Fahrbach K, Nordstrom B, et al. Cancer risk with tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF) inhibitors: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab using patient level data. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2011;20:119-130.
- Mariette X, Matucci-Cerinic M, Pavelka K, et al. Malignancies associated with tumour necrosis factor inhibitors in registries and prospective observational studies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:1895-1904.
- Maalouf E, Faye O, Poli F, et al. Fatal epidermoid carcinoma in hidradenitis suppurativa following treatment with infliximab. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2006;133(5 pt 1):473-474.
- Kurokawa I, Nishimura K, Yamanaka K, et al. Cytokeratin expression in squamous cell carcinoma arising from hidradenitis suppurativa (acne inversa). J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34:675-678.
- Scheinfeld N. A case of a patient with stage III familial hidradenitis suppurativa treated with 3 courses of infliximab and died of metastatic squamous cell carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20(3).
- Verdelli A, Antiga E, Bonciani D, et al. A fatal case of hidradenitis suppurativa associated with sepsis and squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:E52-E53.
- Giesey R, Delost GR, Honaker J, et al. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma in a patient treated with adalimumab for hidradenitis suppurativa. JAAD Case Rep. 2017;3:489-491.
- Roy C, Roy S, Ghazawi F, et al. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma arising in hidradenitis suppurativa: a case report. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2019;7:2050313X19847359.
- Lavogiez C, Delaporte E, Darras-Vercambre S, et al. Clinicopathological study of 13 cases of squamous cell carcinoma complicating hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatology. 2010;220:147-153.
- Alikhan A, Lynch PJ, Eisen DB. Hidradenitis suppurativa: a comprehensive review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:539-561; quiz 562-533.
- Lapins J, Ye W, Nyren O, et al. Incidence of cancer among patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:730-734.
- Askling J, Fahrbach K, Nordstrom B, et al. Cancer risk with tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF) inhibitors: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab using patient level data. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2011;20:119-130.
- Mariette X, Matucci-Cerinic M, Pavelka K, et al. Malignancies associated with tumour necrosis factor inhibitors in registries and prospective observational studies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:1895-1904.
- Maalouf E, Faye O, Poli F, et al. Fatal epidermoid carcinoma in hidradenitis suppurativa following treatment with infliximab. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2006;133(5 pt 1):473-474.
- Kurokawa I, Nishimura K, Yamanaka K, et al. Cytokeratin expression in squamous cell carcinoma arising from hidradenitis suppurativa (acne inversa). J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34:675-678.
- Scheinfeld N. A case of a patient with stage III familial hidradenitis suppurativa treated with 3 courses of infliximab and died of metastatic squamous cell carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20(3).
- Verdelli A, Antiga E, Bonciani D, et al. A fatal case of hidradenitis suppurativa associated with sepsis and squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:E52-E53.
- Giesey R, Delost GR, Honaker J, et al. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma in a patient treated with adalimumab for hidradenitis suppurativa. JAAD Case Rep. 2017;3:489-491.
- Roy C, Roy S, Ghazawi F, et al. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma arising in hidradenitis suppurativa: a case report. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2019;7:2050313X19847359.
- Lavogiez C, Delaporte E, Darras-Vercambre S, et al. Clinicopathological study of 13 cases of squamous cell carcinoma complicating hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatology. 2010;220:147-153.
Practice Points
- Consider biopsy of representative lesions in men older than 20 years with moderate to severe disease of the groin and/or buttocks prior to initiation of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.
- Consider more frequent clinical monitoring with a decrease in threshold to perform biopsy of any new or ulcerating lesions.
VEXAS: A novel rheumatologic, hematologic syndrome that’s making waves
Older men with a novel adult-onset, severe autoinflammatory syndrome known by the acronym VEXAS are likely hiding in plain sight in many adult rheumatology, hematology, and dermatology practices. New clinical features are being described to fill out the clinical profile of such patients who may be currently misdiagnosed with other conditions, according to researchers who first described the syndrome in the last quarter of 2020.
VEXAS is often misdiagnosed as treatment-refractory relapsing polychondritis, polyarteritis nodosa, Sweet syndrome, or giant cell arteritis. These seemingly unrelated disorders are actually tied together by a single thread recently unraveled by David B. Beck, MD, PhD, a clinical fellow at the National Human Genome Research Institute, and colleagues, including rheumatologist Marcela Ferrada, MD, and others at institutes of the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md. The connection between these disparate clinical presentations lies in somatic mutations in UBA1, a gene that initiates cytoplasmic ubiquitylation, a process by which misfolded proteins are tagged for degradation. VEXAS appears primarily limited to men because the UBA1 gene lies on the X chromosome, although it may be possible for women to have it because of an acquired loss of X chromosome.
VEXAS is an acronym for:
- Vacuoles in bone marrow cells
- E-1 activating enzyme, which is what UBA1 encodes for
- X-linked
- Autoinflammatory
- Somatic mutation featuring hematologic mosaicism
Dr. Beck said that VEXAS is “probably affecting thousands of Americans,” but it is tough to say this early in the understanding of the disease. He estimated that the prevalence of VEXAS could be 1 per 20,000-30,000 individuals.
A new way of looking for disease
VEXAS has caused a major stir among geneticists because of the novel manner in which Dr. Beck and his coinvestigators made their discovery. Instead of starting out in the traditional path to discovery of a new genetic disease – that is, by looking for clinical similarities among patients with undiagnosed diseases and then conducting a search for a gene or genes that might explain the shared patient symptoms – the investigators took a genotype-first approach. They scanned the mapped genomic sequences of patients in the National Institutes of Health Undiagnosed Diseases Network, which led them to zero in on mutations in UBA1 as their top candidate.
“We targeted the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, because it has been implicated in many autoinflammatory diseases – for example, HA20 [A20 haploinsufficiency] and CANDLE syndrome [Chronic Atypical Neutrophilic Dermatosis with Lipodystrophy and Elevated temperature]. Many of these recurrent inflammatory diseases are caused by mutations within this pathway,” Dr. Beck said in an interview.
Next, they analyzed the genomes of patients in other NIH databases and patients from other study populations at the University College London and Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust in the United Kingdom in a search for UBA1 somatic mutations, eventually identifying 25 men with the shared features they called VEXAS. These 25 formed the basis for their initial report on the syndrome in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Most autoinflammatory diseases appear in childhood because they stem from germline mutations. VEXAS syndrome, because of somatic mutations with mosaicism, appears to manifest later in life: The median age of the initial 25-man cohort was 64 years, ranging from 45 to 80 years. It’s a severe disorder. By the time the investigators were preparing their paper for publication, 10 of the 25 patients, or 40%, had died.
“I think that somatic mutations may account for a significant percentage of severe. adult-onset rheumatologic diseases, and it may change the way we think about treating them based on having a genetic diagnosis,” Dr. Beck said.
“This approach could be expanded to look at other pathways we know are important in inflammation, or alternatively, it could be completely unbiased and look for any shared variation that occurs across undiagnosed patients with inflammatory diseases. I think that one thing that’s important about our study is that previously we had been looking for mutations that really in most cases were the same sort of germline mutations present in [pediatric] patients who have disease at early onset, but now we’re thinking about things differently. There may be a different type of genetics that drives adult-onset rheumatologic disease, and this would be somatic mutations which are not present in every cell of the body, just in the blood, and that’s why there’s just this blood-based disease.”
When to suspect VEXAS syndrome
Consider the possibility of VEXAS in middle-aged or older men in a rheumatology clinic with characteristics suggestive of treatment-refractory relapsing polychondritis, giant cell arteritis, polyarteritis nodosa, or Sweet syndrome. In the original series of 25 men, 15 were diagnosed with relapsing polychondritis, 8 with Sweet syndrome, 3 with polyarteritis nodosa, and 1 with giant cell arteritis.
Men with VEXAS often have periodic fevers, pulmonary infiltrates, a history of unprovoked venous thromboembolic events, neutrophilic dermatoses, and/or hematologic abnormalities such as myelodysplastic syndrome, multiple myeloma, or monoclonal gammopathy of unknown origin.
Bone marrow biopsy will show vacuoles in myeloid and erythroid precursor cells. Inflammatory marker levels are very high: In the NIH series, the median C-reactive protein was 73 mg/L and median erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 97 mm/hr. The diagnosis of VEXAS can be confirmed by genetic testing performed by Dr. Beck and his NIH coworkers ([email protected]).
In interviews, Dr. Beck and Dr. Ferrada emphasized that management of VEXAS requires a multidisciplinary team of clinicians including rheumatologists, hematologists, and dermatologists.
Dr. Ferrada said that rheumatologists could suspect VEXAS in patients who have very high inflammatory markers and do not have a clear diagnosis or do not meet all criteria for other rheumatologic diseases, particularly in older men, but it’s possible in younger men as well. Hematologists could also consider VEXAS in patients with macrocytic anemia or macrocytosis without an explanation and inflammatory features, she said.
Dr. Ferrada, Dr. Beck, and colleagues also published a study in Arthritis & Rheumatology that presents a useful clinical algorithm for deciding whether to order genetic screening for VEXAS in patients with relapsing polychondritis.
First off, Dr. Ferrada and colleagues performed whole-exome sequencing and testing for UBA1 variants in an observational cohort of 92 relapsing polychondritis patients to determine the prevalence of VEXAS, which turned out to be 8%. They added an additional 6 patients with relapsing polychondritis and VEXAS from other cohorts, for a total of 13. The investigators determined that patients with VEXAS were older at disease onset, and more likely to have fever, ear chondritis, DVT, pulmonary infiltrates, skin involvement, and periorbital edema. In contrast, the RP cohort had a significantly higher prevalence of airway chondritis, joint involvement, and vestibular symptoms.
Dr. Ferrada’s algorithm for picking out VEXAS in patients who meet diagnostic criteria for relapsing polychondritis is based upon a few simple factors readily apparent in screening patient charts: male sex; age at onset older than 50 years; macrocytic anemia; and thrombocytopenia. Those four variables, when present, identify VEXAS within an RP cohort with 100% sensitivity and 96% specificity. “As we learn more about [VEXAS] and how it presents earlier, I think we are going to be able to find different manifestations or laboratory data that are going to allow us to diagnose these patients earlier,” she said. “The whole role of that algorithm was to guide clinicians who see patients with relapsing polychondritis to test these patients for the mutation, but I think over time that is going to evolve.”
Researchers are taking similar approaches for other clinical diagnoses to see which should be referred for UBA1 testing, Dr. Beck said.
Myelodysplastic syndrome and hematologic abnormalities
While patients with both myelodysplastic syndrome and relapsing polychondritis have been known in the literature for many years, it’s not until now that researchers are seeing a connection between the two, Dr. Ferrada said.
A majority of the VEXAS patients in the NEJM study had a workup for myelodysplastic syndrome, but only 24% met criteria. However, many were within the spectrum of myelodysplastic disease and some did not meet criteria because their anemia was attributed to a rheumatologic diagnosis and they did not have a known genetic driver of myelodysplastic syndrome, Dr. Beck said. It also fits with this new evidence that UBA1 is probably a driver of myelodysplastic syndrome in and of itself, and that anemia and hematologic involvement are not secondary to the rheumatologic disease; they are linked to the same disease process.
Dr. Beck said that there may be a subset of patients who present with primarily hematologic manifestations, noting the NEJM study could have ascertainment bias because the researchers analyzed mainly patients presenting to their clinic with relapsing polychondritis and severe inflammation. NIH researchers also are still looking in their cohort for any association with hematologic malignancies that preceded clinical manifestations, he said.
More cases reported
As of early April, another 27 cases had been reported in the literature as more researchers have begun to look for patients with UBA1 mutations, some with additional presenting clinical features associated with VEXAS, including chronic progressive inflammatory arthritis, Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease, spondyloarthritis, and bacterial pneumonia.
“Many times with rare diseases, we can’t get enough patients to understand the full spectrum of the disease, but this disease seems to be far more common than we would have expected. We’re actually getting many referrals,” Dr. Beck said.
It appears so far that the range of somatic UBA1 mutations that have been discovered in VEXAS patients does make a difference in the severity of clinical presentation and could potentially be useful in prognosis, Dr. Beck said.
Right now, NIH researchers are asking patients about their natural clinical course, assessing disease activity, and determining which treatments get a response, with the ultimate goal of a treatment trial at the NIH.
Treatment
Developing better treatments for VEXAS syndrome is a priority. In the initial report on VEXAS, the researchers found that the only reliably effective therapy is high-dose corticosteroids. Dr. Ferrada said that NIH investigators have begun thinking about agents that target both the hematologic and inflammatory features of VEXAS. “Most patients get exposed to treatments that are targeted to decrease the inflammatory process, and some of these treatments help partially but not completely to decrease the amount of steroids that patients are taking. For example, one of the medications is tocilizumab. [It was used in] patients who had previous diagnosis of relapsing polychondritis, but they still had to take steroids and their hematologic manifestations keep progressing. We’re in the process of figuring out medications that may help in treating both.” Dr. Ferrada added that because the source of the mutation is in the bone marrow, transplantation may be an effective option.
Laboratory work to identify potential treatments for VEXAS in studies of model organisms could identify treatments outside of the classic anti-inflammatory agents, such as targeting certain cell types in the bone marrow or the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, Dr. Beck said. “We think that however UBA1 works to initiate inflammation may be important not just in VEXAS but in other diseases. Rare diseases may be informing the mechanisms in common diseases.”
The VEXAS NEJM study was sponsored by the NIH Intramural Research Programs and by an EU Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Program grant. Dr. Beck reported a patent pending on “Diagnosis and Treatment of VEXAS with Mosaic Missense Mutations in UBA1.”
Older men with a novel adult-onset, severe autoinflammatory syndrome known by the acronym VEXAS are likely hiding in plain sight in many adult rheumatology, hematology, and dermatology practices. New clinical features are being described to fill out the clinical profile of such patients who may be currently misdiagnosed with other conditions, according to researchers who first described the syndrome in the last quarter of 2020.

VEXAS is often misdiagnosed as treatment-refractory relapsing polychondritis, polyarteritis nodosa, Sweet syndrome, or giant cell arteritis. These seemingly unrelated disorders are actually tied together by a single thread recently unraveled by David B. Beck, MD, PhD, a clinical fellow at the National Human Genome Research Institute, and colleagues, including rheumatologist Marcela Ferrada, MD, and others at institutes of the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md. The connection between these disparate clinical presentations lies in somatic mutations in UBA1, a gene that initiates cytoplasmic ubiquitylation, a process by which misfolded proteins are tagged for degradation. VEXAS appears primarily limited to men because the UBA1 gene lies on the X chromosome, although it may be possible for women to have it because of an acquired loss of X chromosome.
VEXAS is an acronym for:
- Vacuoles in bone marrow cells
- E-1 activating enzyme, which is what UBA1 encodes for
- X-linked
- Autoinflammatory
- Somatic mutation featuring hematologic mosaicism
Dr. Beck said that VEXAS is “probably affecting thousands of Americans,” but it is tough to say this early in the understanding of the disease. He estimated that the prevalence of VEXAS could be 1 per 20,000-30,000 individuals.
A new way of looking for disease
VEXAS has caused a major stir among geneticists because of the novel manner in which Dr. Beck and his coinvestigators made their discovery. Instead of starting out in the traditional path to discovery of a new genetic disease – that is, by looking for clinical similarities among patients with undiagnosed diseases and then conducting a search for a gene or genes that might explain the shared patient symptoms – the investigators took a genotype-first approach. They scanned the mapped genomic sequences of patients in the National Institutes of Health Undiagnosed Diseases Network, which led them to zero in on mutations in UBA1 as their top candidate.
“We targeted the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, because it has been implicated in many autoinflammatory diseases – for example, HA20 [A20 haploinsufficiency] and CANDLE syndrome [Chronic Atypical Neutrophilic Dermatosis with Lipodystrophy and Elevated temperature]. Many of these recurrent inflammatory diseases are caused by mutations within this pathway,” Dr. Beck said in an interview.
Next, they analyzed the genomes of patients in other NIH databases and patients from other study populations at the University College London and Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust in the United Kingdom in a search for UBA1 somatic mutations, eventually identifying 25 men with the shared features they called VEXAS. These 25 formed the basis for their initial report on the syndrome in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Most autoinflammatory diseases appear in childhood because they stem from germline mutations. VEXAS syndrome, because of somatic mutations with mosaicism, appears to manifest later in life: The median age of the initial 25-man cohort was 64 years, ranging from 45 to 80 years. It’s a severe disorder. By the time the investigators were preparing their paper for publication, 10 of the 25 patients, or 40%, had died.
“I think that somatic mutations may account for a significant percentage of severe. adult-onset rheumatologic diseases, and it may change the way we think about treating them based on having a genetic diagnosis,” Dr. Beck said.
“This approach could be expanded to look at other pathways we know are important in inflammation, or alternatively, it could be completely unbiased and look for any shared variation that occurs across undiagnosed patients with inflammatory diseases. I think that one thing that’s important about our study is that previously we had been looking for mutations that really in most cases were the same sort of germline mutations present in [pediatric] patients who have disease at early onset, but now we’re thinking about things differently. There may be a different type of genetics that drives adult-onset rheumatologic disease, and this would be somatic mutations which are not present in every cell of the body, just in the blood, and that’s why there’s just this blood-based disease.”
When to suspect VEXAS syndrome
Consider the possibility of VEXAS in middle-aged or older men in a rheumatology clinic with characteristics suggestive of treatment-refractory relapsing polychondritis, giant cell arteritis, polyarteritis nodosa, or Sweet syndrome. In the original series of 25 men, 15 were diagnosed with relapsing polychondritis, 8 with Sweet syndrome, 3 with polyarteritis nodosa, and 1 with giant cell arteritis.
Men with VEXAS often have periodic fevers, pulmonary infiltrates, a history of unprovoked venous thromboembolic events, neutrophilic dermatoses, and/or hematologic abnormalities such as myelodysplastic syndrome, multiple myeloma, or monoclonal gammopathy of unknown origin.
Bone marrow biopsy will show vacuoles in myeloid and erythroid precursor cells. Inflammatory marker levels are very high: In the NIH series, the median C-reactive protein was 73 mg/L and median erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 97 mm/hr. The diagnosis of VEXAS can be confirmed by genetic testing performed by Dr. Beck and his NIH coworkers ([email protected]).
In interviews, Dr. Beck and Dr. Ferrada emphasized that management of VEXAS requires a multidisciplinary team of clinicians including rheumatologists, hematologists, and dermatologists.
Dr. Ferrada said that rheumatologists could suspect VEXAS in patients who have very high inflammatory markers and do not have a clear diagnosis or do not meet all criteria for other rheumatologic diseases, particularly in older men, but it’s possible in younger men as well. Hematologists could also consider VEXAS in patients with macrocytic anemia or macrocytosis without an explanation and inflammatory features, she said.
Dr. Ferrada, Dr. Beck, and colleagues also published a study in Arthritis & Rheumatology that presents a useful clinical algorithm for deciding whether to order genetic screening for VEXAS in patients with relapsing polychondritis.
First off, Dr. Ferrada and colleagues performed whole-exome sequencing and testing for UBA1 variants in an observational cohort of 92 relapsing polychondritis patients to determine the prevalence of VEXAS, which turned out to be 8%. They added an additional 6 patients with relapsing polychondritis and VEXAS from other cohorts, for a total of 13. The investigators determined that patients with VEXAS were older at disease onset, and more likely to have fever, ear chondritis, DVT, pulmonary infiltrates, skin involvement, and periorbital edema. In contrast, the RP cohort had a significantly higher prevalence of airway chondritis, joint involvement, and vestibular symptoms.
Dr. Ferrada’s algorithm for picking out VEXAS in patients who meet diagnostic criteria for relapsing polychondritis is based upon a few simple factors readily apparent in screening patient charts: male sex; age at onset older than 50 years; macrocytic anemia; and thrombocytopenia. Those four variables, when present, identify VEXAS within an RP cohort with 100% sensitivity and 96% specificity. “As we learn more about [VEXAS] and how it presents earlier, I think we are going to be able to find different manifestations or laboratory data that are going to allow us to diagnose these patients earlier,” she said. “The whole role of that algorithm was to guide clinicians who see patients with relapsing polychondritis to test these patients for the mutation, but I think over time that is going to evolve.”
Researchers are taking similar approaches for other clinical diagnoses to see which should be referred for UBA1 testing, Dr. Beck said.
Myelodysplastic syndrome and hematologic abnormalities
While patients with both myelodysplastic syndrome and relapsing polychondritis have been known in the literature for many years, it’s not until now that researchers are seeing a connection between the two, Dr. Ferrada said.
A majority of the VEXAS patients in the NEJM study had a workup for myelodysplastic syndrome, but only 24% met criteria. However, many were within the spectrum of myelodysplastic disease and some did not meet criteria because their anemia was attributed to a rheumatologic diagnosis and they did not have a known genetic driver of myelodysplastic syndrome, Dr. Beck said. It also fits with this new evidence that UBA1 is probably a driver of myelodysplastic syndrome in and of itself, and that anemia and hematologic involvement are not secondary to the rheumatologic disease; they are linked to the same disease process.
Dr. Beck said that there may be a subset of patients who present with primarily hematologic manifestations, noting the NEJM study could have ascertainment bias because the researchers analyzed mainly patients presenting to their clinic with relapsing polychondritis and severe inflammation. NIH researchers also are still looking in their cohort for any association with hematologic malignancies that preceded clinical manifestations, he said.
More cases reported
As of early April, another 27 cases had been reported in the literature as more researchers have begun to look for patients with UBA1 mutations, some with additional presenting clinical features associated with VEXAS, including chronic progressive inflammatory arthritis, Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease, spondyloarthritis, and bacterial pneumonia.
“Many times with rare diseases, we can’t get enough patients to understand the full spectrum of the disease, but this disease seems to be far more common than we would have expected. We’re actually getting many referrals,” Dr. Beck said.
It appears so far that the range of somatic UBA1 mutations that have been discovered in VEXAS patients does make a difference in the severity of clinical presentation and could potentially be useful in prognosis, Dr. Beck said.
Right now, NIH researchers are asking patients about their natural clinical course, assessing disease activity, and determining which treatments get a response, with the ultimate goal of a treatment trial at the NIH.
Treatment
Developing better treatments for VEXAS syndrome is a priority. In the initial report on VEXAS, the researchers found that the only reliably effective therapy is high-dose corticosteroids. Dr. Ferrada said that NIH investigators have begun thinking about agents that target both the hematologic and inflammatory features of VEXAS. “Most patients get exposed to treatments that are targeted to decrease the inflammatory process, and some of these treatments help partially but not completely to decrease the amount of steroids that patients are taking. For example, one of the medications is tocilizumab. [It was used in] patients who had previous diagnosis of relapsing polychondritis, but they still had to take steroids and their hematologic manifestations keep progressing. We’re in the process of figuring out medications that may help in treating both.” Dr. Ferrada added that because the source of the mutation is in the bone marrow, transplantation may be an effective option.
Laboratory work to identify potential treatments for VEXAS in studies of model organisms could identify treatments outside of the classic anti-inflammatory agents, such as targeting certain cell types in the bone marrow or the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, Dr. Beck said. “We think that however UBA1 works to initiate inflammation may be important not just in VEXAS but in other diseases. Rare diseases may be informing the mechanisms in common diseases.”
The VEXAS NEJM study was sponsored by the NIH Intramural Research Programs and by an EU Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Program grant. Dr. Beck reported a patent pending on “Diagnosis and Treatment of VEXAS with Mosaic Missense Mutations in UBA1.”
Older men with a novel adult-onset, severe autoinflammatory syndrome known by the acronym VEXAS are likely hiding in plain sight in many adult rheumatology, hematology, and dermatology practices. New clinical features are being described to fill out the clinical profile of such patients who may be currently misdiagnosed with other conditions, according to researchers who first described the syndrome in the last quarter of 2020.

VEXAS is often misdiagnosed as treatment-refractory relapsing polychondritis, polyarteritis nodosa, Sweet syndrome, or giant cell arteritis. These seemingly unrelated disorders are actually tied together by a single thread recently unraveled by David B. Beck, MD, PhD, a clinical fellow at the National Human Genome Research Institute, and colleagues, including rheumatologist Marcela Ferrada, MD, and others at institutes of the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md. The connection between these disparate clinical presentations lies in somatic mutations in UBA1, a gene that initiates cytoplasmic ubiquitylation, a process by which misfolded proteins are tagged for degradation. VEXAS appears primarily limited to men because the UBA1 gene lies on the X chromosome, although it may be possible for women to have it because of an acquired loss of X chromosome.
VEXAS is an acronym for:
- Vacuoles in bone marrow cells
- E-1 activating enzyme, which is what UBA1 encodes for
- X-linked
- Autoinflammatory
- Somatic mutation featuring hematologic mosaicism
Dr. Beck said that VEXAS is “probably affecting thousands of Americans,” but it is tough to say this early in the understanding of the disease. He estimated that the prevalence of VEXAS could be 1 per 20,000-30,000 individuals.
A new way of looking for disease
VEXAS has caused a major stir among geneticists because of the novel manner in which Dr. Beck and his coinvestigators made their discovery. Instead of starting out in the traditional path to discovery of a new genetic disease – that is, by looking for clinical similarities among patients with undiagnosed diseases and then conducting a search for a gene or genes that might explain the shared patient symptoms – the investigators took a genotype-first approach. They scanned the mapped genomic sequences of patients in the National Institutes of Health Undiagnosed Diseases Network, which led them to zero in on mutations in UBA1 as their top candidate.
“We targeted the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, because it has been implicated in many autoinflammatory diseases – for example, HA20 [A20 haploinsufficiency] and CANDLE syndrome [Chronic Atypical Neutrophilic Dermatosis with Lipodystrophy and Elevated temperature]. Many of these recurrent inflammatory diseases are caused by mutations within this pathway,” Dr. Beck said in an interview.
Next, they analyzed the genomes of patients in other NIH databases and patients from other study populations at the University College London and Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust in the United Kingdom in a search for UBA1 somatic mutations, eventually identifying 25 men with the shared features they called VEXAS. These 25 formed the basis for their initial report on the syndrome in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Most autoinflammatory diseases appear in childhood because they stem from germline mutations. VEXAS syndrome, because of somatic mutations with mosaicism, appears to manifest later in life: The median age of the initial 25-man cohort was 64 years, ranging from 45 to 80 years. It’s a severe disorder. By the time the investigators were preparing their paper for publication, 10 of the 25 patients, or 40%, had died.
“I think that somatic mutations may account for a significant percentage of severe. adult-onset rheumatologic diseases, and it may change the way we think about treating them based on having a genetic diagnosis,” Dr. Beck said.
“This approach could be expanded to look at other pathways we know are important in inflammation, or alternatively, it could be completely unbiased and look for any shared variation that occurs across undiagnosed patients with inflammatory diseases. I think that one thing that’s important about our study is that previously we had been looking for mutations that really in most cases were the same sort of germline mutations present in [pediatric] patients who have disease at early onset, but now we’re thinking about things differently. There may be a different type of genetics that drives adult-onset rheumatologic disease, and this would be somatic mutations which are not present in every cell of the body, just in the blood, and that’s why there’s just this blood-based disease.”
When to suspect VEXAS syndrome
Consider the possibility of VEXAS in middle-aged or older men in a rheumatology clinic with characteristics suggestive of treatment-refractory relapsing polychondritis, giant cell arteritis, polyarteritis nodosa, or Sweet syndrome. In the original series of 25 men, 15 were diagnosed with relapsing polychondritis, 8 with Sweet syndrome, 3 with polyarteritis nodosa, and 1 with giant cell arteritis.
Men with VEXAS often have periodic fevers, pulmonary infiltrates, a history of unprovoked venous thromboembolic events, neutrophilic dermatoses, and/or hematologic abnormalities such as myelodysplastic syndrome, multiple myeloma, or monoclonal gammopathy of unknown origin.
Bone marrow biopsy will show vacuoles in myeloid and erythroid precursor cells. Inflammatory marker levels are very high: In the NIH series, the median C-reactive protein was 73 mg/L and median erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 97 mm/hr. The diagnosis of VEXAS can be confirmed by genetic testing performed by Dr. Beck and his NIH coworkers ([email protected]).
In interviews, Dr. Beck and Dr. Ferrada emphasized that management of VEXAS requires a multidisciplinary team of clinicians including rheumatologists, hematologists, and dermatologists.
Dr. Ferrada said that rheumatologists could suspect VEXAS in patients who have very high inflammatory markers and do not have a clear diagnosis or do not meet all criteria for other rheumatologic diseases, particularly in older men, but it’s possible in younger men as well. Hematologists could also consider VEXAS in patients with macrocytic anemia or macrocytosis without an explanation and inflammatory features, she said.
Dr. Ferrada, Dr. Beck, and colleagues also published a study in Arthritis & Rheumatology that presents a useful clinical algorithm for deciding whether to order genetic screening for VEXAS in patients with relapsing polychondritis.
First off, Dr. Ferrada and colleagues performed whole-exome sequencing and testing for UBA1 variants in an observational cohort of 92 relapsing polychondritis patients to determine the prevalence of VEXAS, which turned out to be 8%. They added an additional 6 patients with relapsing polychondritis and VEXAS from other cohorts, for a total of 13. The investigators determined that patients with VEXAS were older at disease onset, and more likely to have fever, ear chondritis, DVT, pulmonary infiltrates, skin involvement, and periorbital edema. In contrast, the RP cohort had a significantly higher prevalence of airway chondritis, joint involvement, and vestibular symptoms.
Dr. Ferrada’s algorithm for picking out VEXAS in patients who meet diagnostic criteria for relapsing polychondritis is based upon a few simple factors readily apparent in screening patient charts: male sex; age at onset older than 50 years; macrocytic anemia; and thrombocytopenia. Those four variables, when present, identify VEXAS within an RP cohort with 100% sensitivity and 96% specificity. “As we learn more about [VEXAS] and how it presents earlier, I think we are going to be able to find different manifestations or laboratory data that are going to allow us to diagnose these patients earlier,” she said. “The whole role of that algorithm was to guide clinicians who see patients with relapsing polychondritis to test these patients for the mutation, but I think over time that is going to evolve.”
Researchers are taking similar approaches for other clinical diagnoses to see which should be referred for UBA1 testing, Dr. Beck said.
Myelodysplastic syndrome and hematologic abnormalities
While patients with both myelodysplastic syndrome and relapsing polychondritis have been known in the literature for many years, it’s not until now that researchers are seeing a connection between the two, Dr. Ferrada said.
A majority of the VEXAS patients in the NEJM study had a workup for myelodysplastic syndrome, but only 24% met criteria. However, many were within the spectrum of myelodysplastic disease and some did not meet criteria because their anemia was attributed to a rheumatologic diagnosis and they did not have a known genetic driver of myelodysplastic syndrome, Dr. Beck said. It also fits with this new evidence that UBA1 is probably a driver of myelodysplastic syndrome in and of itself, and that anemia and hematologic involvement are not secondary to the rheumatologic disease; they are linked to the same disease process.
Dr. Beck said that there may be a subset of patients who present with primarily hematologic manifestations, noting the NEJM study could have ascertainment bias because the researchers analyzed mainly patients presenting to their clinic with relapsing polychondritis and severe inflammation. NIH researchers also are still looking in their cohort for any association with hematologic malignancies that preceded clinical manifestations, he said.
More cases reported
As of early April, another 27 cases had been reported in the literature as more researchers have begun to look for patients with UBA1 mutations, some with additional presenting clinical features associated with VEXAS, including chronic progressive inflammatory arthritis, Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease, spondyloarthritis, and bacterial pneumonia.
“Many times with rare diseases, we can’t get enough patients to understand the full spectrum of the disease, but this disease seems to be far more common than we would have expected. We’re actually getting many referrals,” Dr. Beck said.
It appears so far that the range of somatic UBA1 mutations that have been discovered in VEXAS patients does make a difference in the severity of clinical presentation and could potentially be useful in prognosis, Dr. Beck said.
Right now, NIH researchers are asking patients about their natural clinical course, assessing disease activity, and determining which treatments get a response, with the ultimate goal of a treatment trial at the NIH.
Treatment
Developing better treatments for VEXAS syndrome is a priority. In the initial report on VEXAS, the researchers found that the only reliably effective therapy is high-dose corticosteroids. Dr. Ferrada said that NIH investigators have begun thinking about agents that target both the hematologic and inflammatory features of VEXAS. “Most patients get exposed to treatments that are targeted to decrease the inflammatory process, and some of these treatments help partially but not completely to decrease the amount of steroids that patients are taking. For example, one of the medications is tocilizumab. [It was used in] patients who had previous diagnosis of relapsing polychondritis, but they still had to take steroids and their hematologic manifestations keep progressing. We’re in the process of figuring out medications that may help in treating both.” Dr. Ferrada added that because the source of the mutation is in the bone marrow, transplantation may be an effective option.
Laboratory work to identify potential treatments for VEXAS in studies of model organisms could identify treatments outside of the classic anti-inflammatory agents, such as targeting certain cell types in the bone marrow or the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, Dr. Beck said. “We think that however UBA1 works to initiate inflammation may be important not just in VEXAS but in other diseases. Rare diseases may be informing the mechanisms in common diseases.”
The VEXAS NEJM study was sponsored by the NIH Intramural Research Programs and by an EU Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Program grant. Dr. Beck reported a patent pending on “Diagnosis and Treatment of VEXAS with Mosaic Missense Mutations in UBA1.”