User login
What to do if you encounter Candida auris
Closely monitor patients for treatment failure
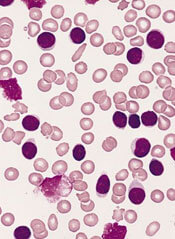
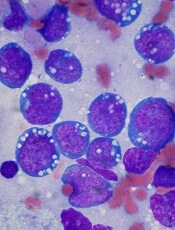
Candida auris is an emerging, often multidrug-resistant yeast that causes invasive infections (such as bloodstream, intra-abdominal) and is transmitted in health care settings. It is difficult to diagnose using traditional yeast identification methods. C. auris also has been found in noninvasive body sites and can colonize a person without causing active infection and hence permitting transmission of the pathogen between patients. These sites include skin, urine, external ear, wounds, and respiratory specimens.
This fungus was first described in 2009 in an ear-discharge culture from a patient in Japan. The first clinical cases were described in South Korea in 2011. An unknown pathogen before 2009, C. auris caused 4%-8% of candidemia in Indian ICUs during 2011-2012 and 38% of candidemia in one Kenyan hospital during 2010-2013. It has now spread across Asia and Europe, only to arrive in the United States in 2016.
As of Aug. 31, 2017, a total of 153 clinical cases of C. auris infection have been reported to CDC from 10 U.S. states; most have occurred in New York and New Jersey. An additional 143 patients have been found to be colonized with C. auris. Based on epidemiologic and molecular information, including whole genome sequencing, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention infers that most U.S. cases likely resulted from local transmission of C. auris following previous introduction from other countries in Asia.
The majority of infections within the United States have been in blood streams. The reported all-cause mortality from these infections has been up to 60%. Most C. auris isolates in the United States have been resistant to at least one antifungal, most commonly fluconazole, and patients have developed resistance to echinocandin drugs while on treatment. Amphotericin B resistance also has been seen in about 30% of isolates.
In response to global reports and a large outbreak in a specialty hospital in the United Kingdom, the CDC issued its first advisory and clinical alert to health care facilities in June 2016. It is essential for hospitalist physicians to be aware of this emerging pathogen and also of the interventions needed to curb its spread, given they are the frontline warriors in the fight against hospital-acquired infections.
The first step in controlling C. auris is identification. C. auris can be misidentified when using traditional biochemical methods. They are most commonly misidentified as Candida haemulonii. Currently, accurate identification for C. auris can be performed by Vitek MS and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight using research use–only databases. Hospitalists should be aware of the diagnostic instruments used in their hospital laboratories and their ability to detect C. auris. Clinical laboratories should request testing of suspect C. auris isolates from their state or regional public health laboratory or the CDC. Laboratories should also consider reviewing historical microbiology records for suspect isolates (e.g., C. haemulonii) to identify missed cases of C. auris.
All cultures positive for Candida should be further speciated and antifungal susceptibilities should be reported as per new Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines for candidiasis from 2016. As many clinical laboratories do not determine the species of Candida from noninvasive sites, C. auris colonization may go unrecognized and lead to transmission. About 54% of recognized U.S. clinical cases have been identified from blood cultures. The remaining patients with positive C. auris cultures, including those with recent hospitalizations abroad, have had the organism isolated from other body sites, including skin wounds, urine, respiratory specimens, bile fluid, and ears. Determining the species of Candida for isolates from these noninvasive sites in certain situations may allow for more rapid identification of C. auris and allow for timely implementation of targeted infection control measures to reduce transmission.
Patients have been persistently colonized with C. auris, posing long-term risk of transmission. Currently, data on effective decolonization methods are lacking. Patients with suspected or confirmed C. auris infection should be placed in a single room if possible and standard and contact precautions should be initiated and thorough environmental cleaning and disinfection of the patient care area should be undertaken. Using an Environmental Protection Agency–registered antimicrobial product active against Clostridium difficile for routine and terminal disinfection is recommended.
Implement contact tracing and testing to identify other patients colonized with C. auris. Review past microbiology records (at least for the preceding 1 year) for suspect or confirmed cases of C. auris at the institution. Set up enhanced surveillance for C. auris in the laboratory setting.
Echinocandin drugs are the first-line treatment for most invasive Candida infections, making resistance to this class of antifungal drugs particularly concerning. As of Sept. 15, 2017, at least five patients in the United States had echinocandin-resistant isolates. In one patient, resistance to echinocandin drugs developed while being treated with echinocandins.
Based on these findings, CDC is concerned that echinocandin-resistant C. auris could become more common. Patients with C. auris infection should be closely monitored for treatment failure, as indicated by persistently positive clinical cultures (lasting more than 5 days). Consultation with an infectious disease specialist is highly recommended.
Dr. Tirupathi is medical director, infectious diseases/HIV at Keystone Health, and chair, infection prevention, at Summit Health, both in Chambersburg, Pa. He is clinical assistant professor of medicine at Penn State University, Hershey.
Closely monitor patients for treatment failure
Closely monitor patients for treatment failure
Candida auris is an emerging, often multidrug-resistant yeast that causes invasive infections (such as bloodstream, intra-abdominal) and is transmitted in health care settings. It is difficult to diagnose using traditional yeast identification methods. C. auris also has been found in noninvasive body sites and can colonize a person without causing active infection and hence permitting transmission of the pathogen between patients. These sites include skin, urine, external ear, wounds, and respiratory specimens.
This fungus was first described in 2009 in an ear-discharge culture from a patient in Japan. The first clinical cases were described in South Korea in 2011. An unknown pathogen before 2009, C. auris caused 4%-8% of candidemia in Indian ICUs during 2011-2012 and 38% of candidemia in one Kenyan hospital during 2010-2013. It has now spread across Asia and Europe, only to arrive in the United States in 2016.
As of Aug. 31, 2017, a total of 153 clinical cases of C. auris infection have been reported to CDC from 10 U.S. states; most have occurred in New York and New Jersey. An additional 143 patients have been found to be colonized with C. auris. Based on epidemiologic and molecular information, including whole genome sequencing, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention infers that most U.S. cases likely resulted from local transmission of C. auris following previous introduction from other countries in Asia.
The majority of infections within the United States have been in blood streams. The reported all-cause mortality from these infections has been up to 60%. Most C. auris isolates in the United States have been resistant to at least one antifungal, most commonly fluconazole, and patients have developed resistance to echinocandin drugs while on treatment. Amphotericin B resistance also has been seen in about 30% of isolates.
In response to global reports and a large outbreak in a specialty hospital in the United Kingdom, the CDC issued its first advisory and clinical alert to health care facilities in June 2016. It is essential for hospitalist physicians to be aware of this emerging pathogen and also of the interventions needed to curb its spread, given they are the frontline warriors in the fight against hospital-acquired infections.
The first step in controlling C. auris is identification. C. auris can be misidentified when using traditional biochemical methods. They are most commonly misidentified as Candida haemulonii. Currently, accurate identification for C. auris can be performed by Vitek MS and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight using research use–only databases. Hospitalists should be aware of the diagnostic instruments used in their hospital laboratories and their ability to detect C. auris. Clinical laboratories should request testing of suspect C. auris isolates from their state or regional public health laboratory or the CDC. Laboratories should also consider reviewing historical microbiology records for suspect isolates (e.g., C. haemulonii) to identify missed cases of C. auris.
All cultures positive for Candida should be further speciated and antifungal susceptibilities should be reported as per new Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines for candidiasis from 2016. As many clinical laboratories do not determine the species of Candida from noninvasive sites, C. auris colonization may go unrecognized and lead to transmission. About 54% of recognized U.S. clinical cases have been identified from blood cultures. The remaining patients with positive C. auris cultures, including those with recent hospitalizations abroad, have had the organism isolated from other body sites, including skin wounds, urine, respiratory specimens, bile fluid, and ears. Determining the species of Candida for isolates from these noninvasive sites in certain situations may allow for more rapid identification of C. auris and allow for timely implementation of targeted infection control measures to reduce transmission.
Patients have been persistently colonized with C. auris, posing long-term risk of transmission. Currently, data on effective decolonization methods are lacking. Patients with suspected or confirmed C. auris infection should be placed in a single room if possible and standard and contact precautions should be initiated and thorough environmental cleaning and disinfection of the patient care area should be undertaken. Using an Environmental Protection Agency–registered antimicrobial product active against Clostridium difficile for routine and terminal disinfection is recommended.
Implement contact tracing and testing to identify other patients colonized with C. auris. Review past microbiology records (at least for the preceding 1 year) for suspect or confirmed cases of C. auris at the institution. Set up enhanced surveillance for C. auris in the laboratory setting.
Echinocandin drugs are the first-line treatment for most invasive Candida infections, making resistance to this class of antifungal drugs particularly concerning. As of Sept. 15, 2017, at least five patients in the United States had echinocandin-resistant isolates. In one patient, resistance to echinocandin drugs developed while being treated with echinocandins.
Based on these findings, CDC is concerned that echinocandin-resistant C. auris could become more common. Patients with C. auris infection should be closely monitored for treatment failure, as indicated by persistently positive clinical cultures (lasting more than 5 days). Consultation with an infectious disease specialist is highly recommended.
Dr. Tirupathi is medical director, infectious diseases/HIV at Keystone Health, and chair, infection prevention, at Summit Health, both in Chambersburg, Pa. He is clinical assistant professor of medicine at Penn State University, Hershey.
Candida auris is an emerging, often multidrug-resistant yeast that causes invasive infections (such as bloodstream, intra-abdominal) and is transmitted in health care settings. It is difficult to diagnose using traditional yeast identification methods. C. auris also has been found in noninvasive body sites and can colonize a person without causing active infection and hence permitting transmission of the pathogen between patients. These sites include skin, urine, external ear, wounds, and respiratory specimens.
This fungus was first described in 2009 in an ear-discharge culture from a patient in Japan. The first clinical cases were described in South Korea in 2011. An unknown pathogen before 2009, C. auris caused 4%-8% of candidemia in Indian ICUs during 2011-2012 and 38% of candidemia in one Kenyan hospital during 2010-2013. It has now spread across Asia and Europe, only to arrive in the United States in 2016.
As of Aug. 31, 2017, a total of 153 clinical cases of C. auris infection have been reported to CDC from 10 U.S. states; most have occurred in New York and New Jersey. An additional 143 patients have been found to be colonized with C. auris. Based on epidemiologic and molecular information, including whole genome sequencing, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention infers that most U.S. cases likely resulted from local transmission of C. auris following previous introduction from other countries in Asia.
The majority of infections within the United States have been in blood streams. The reported all-cause mortality from these infections has been up to 60%. Most C. auris isolates in the United States have been resistant to at least one antifungal, most commonly fluconazole, and patients have developed resistance to echinocandin drugs while on treatment. Amphotericin B resistance also has been seen in about 30% of isolates.
In response to global reports and a large outbreak in a specialty hospital in the United Kingdom, the CDC issued its first advisory and clinical alert to health care facilities in June 2016. It is essential for hospitalist physicians to be aware of this emerging pathogen and also of the interventions needed to curb its spread, given they are the frontline warriors in the fight against hospital-acquired infections.
The first step in controlling C. auris is identification. C. auris can be misidentified when using traditional biochemical methods. They are most commonly misidentified as Candida haemulonii. Currently, accurate identification for C. auris can be performed by Vitek MS and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight using research use–only databases. Hospitalists should be aware of the diagnostic instruments used in their hospital laboratories and their ability to detect C. auris. Clinical laboratories should request testing of suspect C. auris isolates from their state or regional public health laboratory or the CDC. Laboratories should also consider reviewing historical microbiology records for suspect isolates (e.g., C. haemulonii) to identify missed cases of C. auris.
All cultures positive for Candida should be further speciated and antifungal susceptibilities should be reported as per new Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines for candidiasis from 2016. As many clinical laboratories do not determine the species of Candida from noninvasive sites, C. auris colonization may go unrecognized and lead to transmission. About 54% of recognized U.S. clinical cases have been identified from blood cultures. The remaining patients with positive C. auris cultures, including those with recent hospitalizations abroad, have had the organism isolated from other body sites, including skin wounds, urine, respiratory specimens, bile fluid, and ears. Determining the species of Candida for isolates from these noninvasive sites in certain situations may allow for more rapid identification of C. auris and allow for timely implementation of targeted infection control measures to reduce transmission.
Patients have been persistently colonized with C. auris, posing long-term risk of transmission. Currently, data on effective decolonization methods are lacking. Patients with suspected or confirmed C. auris infection should be placed in a single room if possible and standard and contact precautions should be initiated and thorough environmental cleaning and disinfection of the patient care area should be undertaken. Using an Environmental Protection Agency–registered antimicrobial product active against Clostridium difficile for routine and terminal disinfection is recommended.
Implement contact tracing and testing to identify other patients colonized with C. auris. Review past microbiology records (at least for the preceding 1 year) for suspect or confirmed cases of C. auris at the institution. Set up enhanced surveillance for C. auris in the laboratory setting.
Echinocandin drugs are the first-line treatment for most invasive Candida infections, making resistance to this class of antifungal drugs particularly concerning. As of Sept. 15, 2017, at least five patients in the United States had echinocandin-resistant isolates. In one patient, resistance to echinocandin drugs developed while being treated with echinocandins.
Based on these findings, CDC is concerned that echinocandin-resistant C. auris could become more common. Patients with C. auris infection should be closely monitored for treatment failure, as indicated by persistently positive clinical cultures (lasting more than 5 days). Consultation with an infectious disease specialist is highly recommended.
Dr. Tirupathi is medical director, infectious diseases/HIV at Keystone Health, and chair, infection prevention, at Summit Health, both in Chambersburg, Pa. He is clinical assistant professor of medicine at Penn State University, Hershey.
Noninvasive ventilation during exercise benefited a subgroup of COPD patients
SAN DIEGO – Use of noninvasive ventilation during an exercise session in hypercapnic patients with very severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) led to a clinically relevant increase in endurance time, a randomized trial showed.
At an international conference of the American Thoracic Society, lead study author Tessa Schneeberger noted that nocturnal noninvasive ventilation (NIV) in hypercapnic COPD patients has been shown to improve quality of life and survival (Lancet Resp Med. 2014;2[9]:698-705). Another study found that NIV with unchanged nocturnal settings during a 6-minute walk test in hypercapnic COPD patients can increase oxygenation, decrease dyspnea, and increase walking distance (Eur Respir J. 2007;29:930-6).
For the current study, Ms. Schneeberger, a physiotherapist at the Institute for Pulmonary Rehabilitation Research, Schoenau am Koenigssee, Germany, and her associates set out to investigate short-term effects of using NIV during exercise in hypercapnic patients with very severe COPD, as part of a 3-week inpatient physical rehabilitation program. The researchers limited their analysis to 20 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease stage IV patients aged 40-80 years with a carbon dioxide partial pressure (PCO2) of greater than 50 mm Hg at rest and/or during exercise and who were non-naive to NIV, and excluded patients with concomitant conditions that make cycling impossible, those with acute exacerbations, and those with exercise-limiting cardiovascular diseases.
The day after an initial incremental cycle ergometer test, patients performed two constant work rate tests (CWRT) at 60% of the peak work rate, with and without NIV, in randomized order and with a resting time of 1 hour between tests. The inspiratory positive airway pressure (IPAP) was individually adjusted from each patient’s nocturnal settings to provide sufficient pressure to relieve the work on breathing muscles and to decrease transcutaneous PCO2 (TcPCO2) levels during NIV. The primary outcome was cycle endurance time. Other outcomes of interest were TcPCO2, oxygen saturation (SpO2) and perceived dyspnea/leg fatigue via the 10-point Borg scale during CWRTs.
The mean age of the study participants was 60 years, their mean body mass index was 23 kg/m2, their mean forced expiratory volume in1 second was 19% predicted, their mean PaCO2 was 51 mm Hg, their mean PaO2 was 54.5 mm Hg, their mean distance on the 6-minute walk test was 243 meters, and their mean peak work rate was 42 watts.
NIV via full face mask and assisted pressure control ventilation mode was performed with mean IPAP/expiratory PAP levels of 27/6 cm H2O.
During CWRTs patients cycled with NIV for 663 seconds and without NIV for 476 seconds, a significant difference (P = .013) and one that was clinically relevant. At isotime (the time of CWRT with shortest duration), TcPCO2 was significantly lower with NIV (a mean of –6.1 mm Hg), while SpO2 was significantly higher with NIV (a mean of 3.6%). In addition, after CWRT, NIV patients perceived less dyspnea (P = .008) with comparable leg fatigue (P = .79).
“We found that NIV during cycling exercise in hypercapnic patients with very severe COPD can lead to an acutely significant increase in exercise duration, with lower TcPCO2 and a reduced sensation of dyspnea,” Ms. Schneeberger concluded. “It can be performed with high-pressure assisted-controlled ventilation comparable as that used nocturnally to effectively reduce TcPCO2 in people with COPD.”
She emphasized that this approach requires appropriate equipment and special staff expertise for setup titration. “We will continue this research to look into the underlying physiological mechanisms to define nonresponders and responders, and also to look how at this might improve outcomes of an exercise training program.”
Ms. Schneeberger reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Schneeberger T et al. ATS 2018, Abstract A2453.
SAN DIEGO – Use of noninvasive ventilation during an exercise session in hypercapnic patients with very severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) led to a clinically relevant increase in endurance time, a randomized trial showed.
At an international conference of the American Thoracic Society, lead study author Tessa Schneeberger noted that nocturnal noninvasive ventilation (NIV) in hypercapnic COPD patients has been shown to improve quality of life and survival (Lancet Resp Med. 2014;2[9]:698-705). Another study found that NIV with unchanged nocturnal settings during a 6-minute walk test in hypercapnic COPD patients can increase oxygenation, decrease dyspnea, and increase walking distance (Eur Respir J. 2007;29:930-6).
For the current study, Ms. Schneeberger, a physiotherapist at the Institute for Pulmonary Rehabilitation Research, Schoenau am Koenigssee, Germany, and her associates set out to investigate short-term effects of using NIV during exercise in hypercapnic patients with very severe COPD, as part of a 3-week inpatient physical rehabilitation program. The researchers limited their analysis to 20 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease stage IV patients aged 40-80 years with a carbon dioxide partial pressure (PCO2) of greater than 50 mm Hg at rest and/or during exercise and who were non-naive to NIV, and excluded patients with concomitant conditions that make cycling impossible, those with acute exacerbations, and those with exercise-limiting cardiovascular diseases.
The day after an initial incremental cycle ergometer test, patients performed two constant work rate tests (CWRT) at 60% of the peak work rate, with and without NIV, in randomized order and with a resting time of 1 hour between tests. The inspiratory positive airway pressure (IPAP) was individually adjusted from each patient’s nocturnal settings to provide sufficient pressure to relieve the work on breathing muscles and to decrease transcutaneous PCO2 (TcPCO2) levels during NIV. The primary outcome was cycle endurance time. Other outcomes of interest were TcPCO2, oxygen saturation (SpO2) and perceived dyspnea/leg fatigue via the 10-point Borg scale during CWRTs.
The mean age of the study participants was 60 years, their mean body mass index was 23 kg/m2, their mean forced expiratory volume in1 second was 19% predicted, their mean PaCO2 was 51 mm Hg, their mean PaO2 was 54.5 mm Hg, their mean distance on the 6-minute walk test was 243 meters, and their mean peak work rate was 42 watts.
NIV via full face mask and assisted pressure control ventilation mode was performed with mean IPAP/expiratory PAP levels of 27/6 cm H2O.
During CWRTs patients cycled with NIV for 663 seconds and without NIV for 476 seconds, a significant difference (P = .013) and one that was clinically relevant. At isotime (the time of CWRT with shortest duration), TcPCO2 was significantly lower with NIV (a mean of –6.1 mm Hg), while SpO2 was significantly higher with NIV (a mean of 3.6%). In addition, after CWRT, NIV patients perceived less dyspnea (P = .008) with comparable leg fatigue (P = .79).
“We found that NIV during cycling exercise in hypercapnic patients with very severe COPD can lead to an acutely significant increase in exercise duration, with lower TcPCO2 and a reduced sensation of dyspnea,” Ms. Schneeberger concluded. “It can be performed with high-pressure assisted-controlled ventilation comparable as that used nocturnally to effectively reduce TcPCO2 in people with COPD.”
She emphasized that this approach requires appropriate equipment and special staff expertise for setup titration. “We will continue this research to look into the underlying physiological mechanisms to define nonresponders and responders, and also to look how at this might improve outcomes of an exercise training program.”
Ms. Schneeberger reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Schneeberger T et al. ATS 2018, Abstract A2453.
SAN DIEGO – Use of noninvasive ventilation during an exercise session in hypercapnic patients with very severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) led to a clinically relevant increase in endurance time, a randomized trial showed.
At an international conference of the American Thoracic Society, lead study author Tessa Schneeberger noted that nocturnal noninvasive ventilation (NIV) in hypercapnic COPD patients has been shown to improve quality of life and survival (Lancet Resp Med. 2014;2[9]:698-705). Another study found that NIV with unchanged nocturnal settings during a 6-minute walk test in hypercapnic COPD patients can increase oxygenation, decrease dyspnea, and increase walking distance (Eur Respir J. 2007;29:930-6).
For the current study, Ms. Schneeberger, a physiotherapist at the Institute for Pulmonary Rehabilitation Research, Schoenau am Koenigssee, Germany, and her associates set out to investigate short-term effects of using NIV during exercise in hypercapnic patients with very severe COPD, as part of a 3-week inpatient physical rehabilitation program. The researchers limited their analysis to 20 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease stage IV patients aged 40-80 years with a carbon dioxide partial pressure (PCO2) of greater than 50 mm Hg at rest and/or during exercise and who were non-naive to NIV, and excluded patients with concomitant conditions that make cycling impossible, those with acute exacerbations, and those with exercise-limiting cardiovascular diseases.
The day after an initial incremental cycle ergometer test, patients performed two constant work rate tests (CWRT) at 60% of the peak work rate, with and without NIV, in randomized order and with a resting time of 1 hour between tests. The inspiratory positive airway pressure (IPAP) was individually adjusted from each patient’s nocturnal settings to provide sufficient pressure to relieve the work on breathing muscles and to decrease transcutaneous PCO2 (TcPCO2) levels during NIV. The primary outcome was cycle endurance time. Other outcomes of interest were TcPCO2, oxygen saturation (SpO2) and perceived dyspnea/leg fatigue via the 10-point Borg scale during CWRTs.
The mean age of the study participants was 60 years, their mean body mass index was 23 kg/m2, their mean forced expiratory volume in1 second was 19% predicted, their mean PaCO2 was 51 mm Hg, their mean PaO2 was 54.5 mm Hg, their mean distance on the 6-minute walk test was 243 meters, and their mean peak work rate was 42 watts.
NIV via full face mask and assisted pressure control ventilation mode was performed with mean IPAP/expiratory PAP levels of 27/6 cm H2O.
During CWRTs patients cycled with NIV for 663 seconds and without NIV for 476 seconds, a significant difference (P = .013) and one that was clinically relevant. At isotime (the time of CWRT with shortest duration), TcPCO2 was significantly lower with NIV (a mean of –6.1 mm Hg), while SpO2 was significantly higher with NIV (a mean of 3.6%). In addition, after CWRT, NIV patients perceived less dyspnea (P = .008) with comparable leg fatigue (P = .79).
“We found that NIV during cycling exercise in hypercapnic patients with very severe COPD can lead to an acutely significant increase in exercise duration, with lower TcPCO2 and a reduced sensation of dyspnea,” Ms. Schneeberger concluded. “It can be performed with high-pressure assisted-controlled ventilation comparable as that used nocturnally to effectively reduce TcPCO2 in people with COPD.”
She emphasized that this approach requires appropriate equipment and special staff expertise for setup titration. “We will continue this research to look into the underlying physiological mechanisms to define nonresponders and responders, and also to look how at this might improve outcomes of an exercise training program.”
Ms. Schneeberger reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Schneeberger T et al. ATS 2018, Abstract A2453.
REPORTING FROM ATS 2018
Key clinical point: Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) during exercise seems feasible and could provide an opportunity to improve endurance training outcomes in selected chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients.
Major finding: During constant work rate tests patients cycled with NIV for 663 seconds and without NIV for 476 seconds, a significant difference (P = .013).
Study details: A randomized trial of short-term effects of NIV during exercise in 20 hypercapnic patients with very severe COPD.
Disclosures: Ms. Schneeberger reported having no financial disclosures.
Source: Schneeberger T et al. ATS 2018, Abstract A2453.
Effort to phenotype pulmonary hypertension patients under way
SAN DIEGO – A massive effort to better understand and treat patients with pulmonary hypertension and right heart dysfunction is underway.
The endeavor, funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association and known as Redefining Pulmonary Hypertension Through Pulmonary Vascular Disease Phenomics (PVDOMICS), began recruiting participants in 2017, with a goal of 1,500 by 2019. The aim is to perform comprehensive phenotyping and endophenotyping across the World Health Organization–classified pulmonary hypertension (PH) clinical groups 1 through 5 in order to deconstruct the traditional classification and define new meaningful subclassifications of patients with pulmonary vascular disease.
At an international conference of the American Thoracic Society, one of the study’s investigators, Robert P. Frantz, MD, discussed the role of echocardiography and MRI in the overall PVDOMICS program, which he characterized as a work in progress. “Imaging is critically important as we try to integrate severity of pulmonary vascular disease along with how well the ventricle functions as way to try and understand why some patients have a failing RV at a given pulmonary resistance and others don’t,” said Dr. Frantz, who directs the Mayo Pulmonary Hypertension Clinic in Rochester, Minn. The goals are to be able to integrate cardiac morphology and function with contemporaneous hemodynamics, he said. This will allow for validation of noninvasive hemodynamics versus right heart catheterization across all the phenotypes.
“In addition, we’ll have imaging parameters as predictors of hemodynamics at rest and with exercise, particularly in conditions like heart failure with preserved ejection fraction or concerns about left atrial stiffness,” he said. “In these cases, our ability on the basis of echocardiography or MRI to guess what the wedge pressure is at rest or exercise, or to think about other more recently described phenotypes like left atrial stiffness in patients who have left atrial ablation procedures, will be enabled by looking at parameters such as left atrial strain.”
Ultimately, he continued, a key goal of PVDOMICS is to be able to correlate the “-omics” with markers of RV compensation in an effort to understand what the determinants of RV compensation are across the varying types of pulmonary vascular disease.
“If we could do that, we might be able to develop new targets for therapy,” said Dr. Frantz. To illustrate how this might work, he cited findings from researchers who set out to identify and characterize homogeneous phenotypes by a cluster analysis in scleroderma patients with pulmonary hypertension, who were identified from two prospective cohorts in the United States and France (PLoS One 2018 May 15;13[5]:e0197112).
The researchers identified four different clusters of scleroderma patients: those with mild to moderate PAH with no or minimal interstitial lung disease and low-diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide; those with precapillary PH with severe ILD and worse survival; those with severe PAH, who trended toward worse survival, and those similar to the first cluster but with higher DLCO.
Dr. Frantz then shared preliminary findings of echocardiographic parameters by primary WHO group in PVDOMICS, on behalf of his PVDOMICS collaborators. They found, for example, that the mean right ventricular systolic pressure in group 3 was 45 mm Hg, as opposed to group 1, which was 64 mm Hg. “In general we had some patients in group 3 with less severe elevation of PA pressures,” he said.
Other parameters that can be compared across WHO groups include ventricular fractional area change, tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion, and RV free wall strain. “That strain of the right ventricle is one of the most important ways of looking at how the right ventricle works,” Dr. Frantz explained. “With this, we can integrate the concept of severity of RV dysfunction with severity of pulmonary vascular disease. This is where the rubber hits the road. It’s going to be very complicated and time consuming, but I think critically important. Ultimately, we can make proteomic heat maps that track these correlates, and ultimately identify pathways that may be driving RV compensation in pulmonary vascular disease.”
Dr. Frantz reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – A massive effort to better understand and treat patients with pulmonary hypertension and right heart dysfunction is underway.
The endeavor, funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association and known as Redefining Pulmonary Hypertension Through Pulmonary Vascular Disease Phenomics (PVDOMICS), began recruiting participants in 2017, with a goal of 1,500 by 2019. The aim is to perform comprehensive phenotyping and endophenotyping across the World Health Organization–classified pulmonary hypertension (PH) clinical groups 1 through 5 in order to deconstruct the traditional classification and define new meaningful subclassifications of patients with pulmonary vascular disease.
At an international conference of the American Thoracic Society, one of the study’s investigators, Robert P. Frantz, MD, discussed the role of echocardiography and MRI in the overall PVDOMICS program, which he characterized as a work in progress. “Imaging is critically important as we try to integrate severity of pulmonary vascular disease along with how well the ventricle functions as way to try and understand why some patients have a failing RV at a given pulmonary resistance and others don’t,” said Dr. Frantz, who directs the Mayo Pulmonary Hypertension Clinic in Rochester, Minn. The goals are to be able to integrate cardiac morphology and function with contemporaneous hemodynamics, he said. This will allow for validation of noninvasive hemodynamics versus right heart catheterization across all the phenotypes.
“In addition, we’ll have imaging parameters as predictors of hemodynamics at rest and with exercise, particularly in conditions like heart failure with preserved ejection fraction or concerns about left atrial stiffness,” he said. “In these cases, our ability on the basis of echocardiography or MRI to guess what the wedge pressure is at rest or exercise, or to think about other more recently described phenotypes like left atrial stiffness in patients who have left atrial ablation procedures, will be enabled by looking at parameters such as left atrial strain.”
Ultimately, he continued, a key goal of PVDOMICS is to be able to correlate the “-omics” with markers of RV compensation in an effort to understand what the determinants of RV compensation are across the varying types of pulmonary vascular disease.
“If we could do that, we might be able to develop new targets for therapy,” said Dr. Frantz. To illustrate how this might work, he cited findings from researchers who set out to identify and characterize homogeneous phenotypes by a cluster analysis in scleroderma patients with pulmonary hypertension, who were identified from two prospective cohorts in the United States and France (PLoS One 2018 May 15;13[5]:e0197112).
The researchers identified four different clusters of scleroderma patients: those with mild to moderate PAH with no or minimal interstitial lung disease and low-diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide; those with precapillary PH with severe ILD and worse survival; those with severe PAH, who trended toward worse survival, and those similar to the first cluster but with higher DLCO.
Dr. Frantz then shared preliminary findings of echocardiographic parameters by primary WHO group in PVDOMICS, on behalf of his PVDOMICS collaborators. They found, for example, that the mean right ventricular systolic pressure in group 3 was 45 mm Hg, as opposed to group 1, which was 64 mm Hg. “In general we had some patients in group 3 with less severe elevation of PA pressures,” he said.
Other parameters that can be compared across WHO groups include ventricular fractional area change, tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion, and RV free wall strain. “That strain of the right ventricle is one of the most important ways of looking at how the right ventricle works,” Dr. Frantz explained. “With this, we can integrate the concept of severity of RV dysfunction with severity of pulmonary vascular disease. This is where the rubber hits the road. It’s going to be very complicated and time consuming, but I think critically important. Ultimately, we can make proteomic heat maps that track these correlates, and ultimately identify pathways that may be driving RV compensation in pulmonary vascular disease.”
Dr. Frantz reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – A massive effort to better understand and treat patients with pulmonary hypertension and right heart dysfunction is underway.
The endeavor, funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association and known as Redefining Pulmonary Hypertension Through Pulmonary Vascular Disease Phenomics (PVDOMICS), began recruiting participants in 2017, with a goal of 1,500 by 2019. The aim is to perform comprehensive phenotyping and endophenotyping across the World Health Organization–classified pulmonary hypertension (PH) clinical groups 1 through 5 in order to deconstruct the traditional classification and define new meaningful subclassifications of patients with pulmonary vascular disease.
At an international conference of the American Thoracic Society, one of the study’s investigators, Robert P. Frantz, MD, discussed the role of echocardiography and MRI in the overall PVDOMICS program, which he characterized as a work in progress. “Imaging is critically important as we try to integrate severity of pulmonary vascular disease along with how well the ventricle functions as way to try and understand why some patients have a failing RV at a given pulmonary resistance and others don’t,” said Dr. Frantz, who directs the Mayo Pulmonary Hypertension Clinic in Rochester, Minn. The goals are to be able to integrate cardiac morphology and function with contemporaneous hemodynamics, he said. This will allow for validation of noninvasive hemodynamics versus right heart catheterization across all the phenotypes.
“In addition, we’ll have imaging parameters as predictors of hemodynamics at rest and with exercise, particularly in conditions like heart failure with preserved ejection fraction or concerns about left atrial stiffness,” he said. “In these cases, our ability on the basis of echocardiography or MRI to guess what the wedge pressure is at rest or exercise, or to think about other more recently described phenotypes like left atrial stiffness in patients who have left atrial ablation procedures, will be enabled by looking at parameters such as left atrial strain.”
Ultimately, he continued, a key goal of PVDOMICS is to be able to correlate the “-omics” with markers of RV compensation in an effort to understand what the determinants of RV compensation are across the varying types of pulmonary vascular disease.
“If we could do that, we might be able to develop new targets for therapy,” said Dr. Frantz. To illustrate how this might work, he cited findings from researchers who set out to identify and characterize homogeneous phenotypes by a cluster analysis in scleroderma patients with pulmonary hypertension, who were identified from two prospective cohorts in the United States and France (PLoS One 2018 May 15;13[5]:e0197112).
The researchers identified four different clusters of scleroderma patients: those with mild to moderate PAH with no or minimal interstitial lung disease and low-diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide; those with precapillary PH with severe ILD and worse survival; those with severe PAH, who trended toward worse survival, and those similar to the first cluster but with higher DLCO.
Dr. Frantz then shared preliminary findings of echocardiographic parameters by primary WHO group in PVDOMICS, on behalf of his PVDOMICS collaborators. They found, for example, that the mean right ventricular systolic pressure in group 3 was 45 mm Hg, as opposed to group 1, which was 64 mm Hg. “In general we had some patients in group 3 with less severe elevation of PA pressures,” he said.
Other parameters that can be compared across WHO groups include ventricular fractional area change, tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion, and RV free wall strain. “That strain of the right ventricle is one of the most important ways of looking at how the right ventricle works,” Dr. Frantz explained. “With this, we can integrate the concept of severity of RV dysfunction with severity of pulmonary vascular disease. This is where the rubber hits the road. It’s going to be very complicated and time consuming, but I think critically important. Ultimately, we can make proteomic heat maps that track these correlates, and ultimately identify pathways that may be driving RV compensation in pulmonary vascular disease.”
Dr. Frantz reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
AT ATS 2018
FDA approves topical anticholinergic for primary axillary hyperhidrosis
The in adults and children aged 9 years and older.
Glycopyrronium, which is formulated in a cloth wipe, will be marketed as Qbrexza and is expected to be available in October, according to the approval announcement June 29, which was made by Dermira, the manufacturer. The instructions for use section in the prescribing information states that patients are advised to use one cloth to apply the medication to both axillae, wiping the cloth across each underarm. Each cloth, intended for single use, is pre-moistened with 2.4% glycopyrronium solution.
Glycopyrronium blocks sweat production “by inhibiting the interaction between acetylcholine and the cholinergic receptors responsible for sweat gland activation,” the company said in a February press release.
The approval was based on the results of two phase 3 clinical studies, ATMOS-1 and ATMOS-2, which were multicenter, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, 4-week studies in patients 9 years of age or older with primary axillary hyperhidrosis for 6 months or longer. Study subjects had production of at least 50 mg of underarm sweat over 5 minutes, and scores of four or higher on the 11-point Axillary Sweating Daily Diary (ASDD) or the Children’s ASDD (ASDD-C) – an instrument developed by the company in consultation with the FDA – and scores of three or four on the four-grade Hyperhidrosis Disease Severity Scale (HDSS). In total, 463 patients were randomized to receive glycopyrronium and 234 to vehicle. Forty four of these patients were aged 9-16 years, with 25 receiving glycopyrronium and 19 receiving vehicle.
According to the February release, the ASDD/ASDD-C severity scale responder rates were about 60% in the pediatric and adult groups treated with glycopyrronium, compared with 13.0% and 28.8% for children and adults, respectively, in the vehicle group. At week 4, the median absolute change in sweat production was a reduction of 64.2 mg in children and a reduction of 80.6 mg among adults treated with glycopyrronium, compared with reductions of 53.7 mg and 62 mg among those in the vehicle group, respectively.
In the glycopyrronium-treated group, almost 80% of the pediatric patients and 74.3% of the adults experienced at least a 50% reduction in sweat production at week 4, compared with almost 55% and 53%, respectively, in the vehicle group.
Among pediatric patients, the mean decrease from baseline in the Children’s Dermatology Quality of Life Index was 8.1 in glycopyrronium-treated patients, compared with 1.9 in the vehicle group. In adults, scores on the Dermatology Life Quality Index measure were reduced by 8.4 and 4.7 in glycopyrronium- and vehicle-treated adult patients, respectively.
Nearly 57% of adults and 44% of pediatric patients treated with glycopyrronium experienced treatment-emergent adverse events, compared with 34.3% of adults and 10.5% of the pediatric patients in the vehicle group. The majority were related to anticholinergic activity and were mild, and rarely led to drug discontinuation, according to the company.
The press release announcing the approval stated that the most common adverse effects observed after application of glycopyrronium were dry mouth, mydriasis, sore throat, headache, urinary hesitation, blurred vision, dry nose, dry throat, dry eye, dry skin and constipation. Erythema, burning/stinging, and pruritus were the most common skin reactions.
The product is contraindicated in patients with glaucoma, paralytic ileus, and other medical conditions that can be exacerbated by its anticholinergic effects, according to the prescribing information. Patients should be advised that they should wash their hands thoroughly after application, and that it can cause temporary dilation of the pupils and blurred vision if glycopyrronium comes into contact with their eyes.
The in adults and children aged 9 years and older.
Glycopyrronium, which is formulated in a cloth wipe, will be marketed as Qbrexza and is expected to be available in October, according to the approval announcement June 29, which was made by Dermira, the manufacturer. The instructions for use section in the prescribing information states that patients are advised to use one cloth to apply the medication to both axillae, wiping the cloth across each underarm. Each cloth, intended for single use, is pre-moistened with 2.4% glycopyrronium solution.
Glycopyrronium blocks sweat production “by inhibiting the interaction between acetylcholine and the cholinergic receptors responsible for sweat gland activation,” the company said in a February press release.
The approval was based on the results of two phase 3 clinical studies, ATMOS-1 and ATMOS-2, which were multicenter, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, 4-week studies in patients 9 years of age or older with primary axillary hyperhidrosis for 6 months or longer. Study subjects had production of at least 50 mg of underarm sweat over 5 minutes, and scores of four or higher on the 11-point Axillary Sweating Daily Diary (ASDD) or the Children’s ASDD (ASDD-C) – an instrument developed by the company in consultation with the FDA – and scores of three or four on the four-grade Hyperhidrosis Disease Severity Scale (HDSS). In total, 463 patients were randomized to receive glycopyrronium and 234 to vehicle. Forty four of these patients were aged 9-16 years, with 25 receiving glycopyrronium and 19 receiving vehicle.
According to the February release, the ASDD/ASDD-C severity scale responder rates were about 60% in the pediatric and adult groups treated with glycopyrronium, compared with 13.0% and 28.8% for children and adults, respectively, in the vehicle group. At week 4, the median absolute change in sweat production was a reduction of 64.2 mg in children and a reduction of 80.6 mg among adults treated with glycopyrronium, compared with reductions of 53.7 mg and 62 mg among those in the vehicle group, respectively.
In the glycopyrronium-treated group, almost 80% of the pediatric patients and 74.3% of the adults experienced at least a 50% reduction in sweat production at week 4, compared with almost 55% and 53%, respectively, in the vehicle group.
Among pediatric patients, the mean decrease from baseline in the Children’s Dermatology Quality of Life Index was 8.1 in glycopyrronium-treated patients, compared with 1.9 in the vehicle group. In adults, scores on the Dermatology Life Quality Index measure were reduced by 8.4 and 4.7 in glycopyrronium- and vehicle-treated adult patients, respectively.
Nearly 57% of adults and 44% of pediatric patients treated with glycopyrronium experienced treatment-emergent adverse events, compared with 34.3% of adults and 10.5% of the pediatric patients in the vehicle group. The majority were related to anticholinergic activity and were mild, and rarely led to drug discontinuation, according to the company.
The press release announcing the approval stated that the most common adverse effects observed after application of glycopyrronium were dry mouth, mydriasis, sore throat, headache, urinary hesitation, blurred vision, dry nose, dry throat, dry eye, dry skin and constipation. Erythema, burning/stinging, and pruritus were the most common skin reactions.
The product is contraindicated in patients with glaucoma, paralytic ileus, and other medical conditions that can be exacerbated by its anticholinergic effects, according to the prescribing information. Patients should be advised that they should wash their hands thoroughly after application, and that it can cause temporary dilation of the pupils and blurred vision if glycopyrronium comes into contact with their eyes.
The in adults and children aged 9 years and older.
Glycopyrronium, which is formulated in a cloth wipe, will be marketed as Qbrexza and is expected to be available in October, according to the approval announcement June 29, which was made by Dermira, the manufacturer. The instructions for use section in the prescribing information states that patients are advised to use one cloth to apply the medication to both axillae, wiping the cloth across each underarm. Each cloth, intended for single use, is pre-moistened with 2.4% glycopyrronium solution.
Glycopyrronium blocks sweat production “by inhibiting the interaction between acetylcholine and the cholinergic receptors responsible for sweat gland activation,” the company said in a February press release.
The approval was based on the results of two phase 3 clinical studies, ATMOS-1 and ATMOS-2, which were multicenter, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, 4-week studies in patients 9 years of age or older with primary axillary hyperhidrosis for 6 months or longer. Study subjects had production of at least 50 mg of underarm sweat over 5 minutes, and scores of four or higher on the 11-point Axillary Sweating Daily Diary (ASDD) or the Children’s ASDD (ASDD-C) – an instrument developed by the company in consultation with the FDA – and scores of three or four on the four-grade Hyperhidrosis Disease Severity Scale (HDSS). In total, 463 patients were randomized to receive glycopyrronium and 234 to vehicle. Forty four of these patients were aged 9-16 years, with 25 receiving glycopyrronium and 19 receiving vehicle.
According to the February release, the ASDD/ASDD-C severity scale responder rates were about 60% in the pediatric and adult groups treated with glycopyrronium, compared with 13.0% and 28.8% for children and adults, respectively, in the vehicle group. At week 4, the median absolute change in sweat production was a reduction of 64.2 mg in children and a reduction of 80.6 mg among adults treated with glycopyrronium, compared with reductions of 53.7 mg and 62 mg among those in the vehicle group, respectively.
In the glycopyrronium-treated group, almost 80% of the pediatric patients and 74.3% of the adults experienced at least a 50% reduction in sweat production at week 4, compared with almost 55% and 53%, respectively, in the vehicle group.
Among pediatric patients, the mean decrease from baseline in the Children’s Dermatology Quality of Life Index was 8.1 in glycopyrronium-treated patients, compared with 1.9 in the vehicle group. In adults, scores on the Dermatology Life Quality Index measure were reduced by 8.4 and 4.7 in glycopyrronium- and vehicle-treated adult patients, respectively.
Nearly 57% of adults and 44% of pediatric patients treated with glycopyrronium experienced treatment-emergent adverse events, compared with 34.3% of adults and 10.5% of the pediatric patients in the vehicle group. The majority were related to anticholinergic activity and were mild, and rarely led to drug discontinuation, according to the company.
The press release announcing the approval stated that the most common adverse effects observed after application of glycopyrronium were dry mouth, mydriasis, sore throat, headache, urinary hesitation, blurred vision, dry nose, dry throat, dry eye, dry skin and constipation. Erythema, burning/stinging, and pruritus were the most common skin reactions.
The product is contraindicated in patients with glaucoma, paralytic ileus, and other medical conditions that can be exacerbated by its anticholinergic effects, according to the prescribing information. Patients should be advised that they should wash their hands thoroughly after application, and that it can cause temporary dilation of the pupils and blurred vision if glycopyrronium comes into contact with their eyes.
Elderly patients with psoriasis can benefit from biologics with low rates of adverse events
according to a new retrospective study.
Among 266 older patients, 65% achieved a 75% improvement in Psoriasis Area Severity Index score (PASI 75) after 1 year of therapy; 50% reached a PASI 90, and 40% a PASI 100, Francesca Prignano MD, PhD, and her colleagues reported in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. The rate of serious adverse events was less than 10%.
Elderly patients – those aged 65 years and older – are commonly excluded from studies on biologic treatments because they have more medical comorbidities and are thought to be more at risk for serious adverse events, like infections and malignancy, wrote Dr. Prignano of the dermatology unit, University of Florence, Italy, and her colleagues.
As a result, they noted, there is a “lack of information concerning safety and effectiveness of available treatments for psoriasis in the elderly, particularly about new biologic agents. Disease remission should be an objective for both younger patients and older patients, and biologic therapy should be considered a treatment option for all patients.”
To examine both the benefit and risk of biologics in this population, the team reviewed the records of 266 elderly psoriasis patients; everyone had been on a biologic treatment for at least 1 year.
The primary outcome was PASI score at weeks 8, 16, 28, and 52. The secondary outcomes were the rate and types of biologic-associated adverse events.
The study comprised 266 patients (mean age 72 years). Their mean psoriasis duration was 25.7 years. Comorbidities included psoriatic arthritis; hypertension and dyslipidemia; diabetes mellitus; cardiovascular, gastrointestinal and respiratory diseases; osteoporosis; thyroid dysfunction; depression; and cancer.
Adalimumab was the most commonly prescribed biologic (31%), followed by ustekinumab (28.9%), etanercept (20%), and secukinumab (15%). A smaller proportion of patients were taking infliximab, golimumab, or certolizumab pegol.
The mean baseline PASI was 16.5, although the range was wide (4-54). At the time of review, the average biologic treatment duration was 44 months. Almost half of the cohort (128) were on their second biologic, and 20 more had been on three biologics. A few patients were taking concomitant medications, including steroids, cyclosporine, and acitretin.
The mean PASI scores decreased to 3.7 at week 16, 1.6 at week 28, and 1.2 at week 52. The group exhibited a rapid response to biologic treatment. By 16 weeks, about 55% had achieved a PASI 75, about 28% a PASI 90, and about 20% a PASI 100. By 28 weeks, these numbers were about 64%, 45%, and 35%, respectively. At 1 year, they were about 65%, 50%, and 40%, respectively.
The rate of adverse events was 9.4%. There were 25 events in the cohort, the majority of which (48%) were infections; these included four respiratory infections, three urinary tract infections, two cases of mucocutaneous candidiasis, two cases of herpes zoster infection, and one case of erysipelas.
There were four malignancies: three nonmelanoma skin cancers and one vocal cord cancer.
Noting that, to date, their study represented “the broadest experience on the use of biological drugs” for elderly patients with psoriasis, they wrote that while “comorbidities should be taken into consideration when a long-term treatment is proposed, for the higher risk of side effects and drug interactions,” they wrote, noting that none of the 266 patients had a serious infection and the malignancy rate was low (1.5%).
None of the authors had financial disclosures, and the study had no funding source.
SOURCE: Ricceri F et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018 Jun 15. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15139.
according to a new retrospective study.
Among 266 older patients, 65% achieved a 75% improvement in Psoriasis Area Severity Index score (PASI 75) after 1 year of therapy; 50% reached a PASI 90, and 40% a PASI 100, Francesca Prignano MD, PhD, and her colleagues reported in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. The rate of serious adverse events was less than 10%.
Elderly patients – those aged 65 years and older – are commonly excluded from studies on biologic treatments because they have more medical comorbidities and are thought to be more at risk for serious adverse events, like infections and malignancy, wrote Dr. Prignano of the dermatology unit, University of Florence, Italy, and her colleagues.
As a result, they noted, there is a “lack of information concerning safety and effectiveness of available treatments for psoriasis in the elderly, particularly about new biologic agents. Disease remission should be an objective for both younger patients and older patients, and biologic therapy should be considered a treatment option for all patients.”
To examine both the benefit and risk of biologics in this population, the team reviewed the records of 266 elderly psoriasis patients; everyone had been on a biologic treatment for at least 1 year.
The primary outcome was PASI score at weeks 8, 16, 28, and 52. The secondary outcomes were the rate and types of biologic-associated adverse events.
The study comprised 266 patients (mean age 72 years). Their mean psoriasis duration was 25.7 years. Comorbidities included psoriatic arthritis; hypertension and dyslipidemia; diabetes mellitus; cardiovascular, gastrointestinal and respiratory diseases; osteoporosis; thyroid dysfunction; depression; and cancer.
Adalimumab was the most commonly prescribed biologic (31%), followed by ustekinumab (28.9%), etanercept (20%), and secukinumab (15%). A smaller proportion of patients were taking infliximab, golimumab, or certolizumab pegol.
The mean baseline PASI was 16.5, although the range was wide (4-54). At the time of review, the average biologic treatment duration was 44 months. Almost half of the cohort (128) were on their second biologic, and 20 more had been on three biologics. A few patients were taking concomitant medications, including steroids, cyclosporine, and acitretin.
The mean PASI scores decreased to 3.7 at week 16, 1.6 at week 28, and 1.2 at week 52. The group exhibited a rapid response to biologic treatment. By 16 weeks, about 55% had achieved a PASI 75, about 28% a PASI 90, and about 20% a PASI 100. By 28 weeks, these numbers were about 64%, 45%, and 35%, respectively. At 1 year, they were about 65%, 50%, and 40%, respectively.
The rate of adverse events was 9.4%. There were 25 events in the cohort, the majority of which (48%) were infections; these included four respiratory infections, three urinary tract infections, two cases of mucocutaneous candidiasis, two cases of herpes zoster infection, and one case of erysipelas.
There were four malignancies: three nonmelanoma skin cancers and one vocal cord cancer.
Noting that, to date, their study represented “the broadest experience on the use of biological drugs” for elderly patients with psoriasis, they wrote that while “comorbidities should be taken into consideration when a long-term treatment is proposed, for the higher risk of side effects and drug interactions,” they wrote, noting that none of the 266 patients had a serious infection and the malignancy rate was low (1.5%).
None of the authors had financial disclosures, and the study had no funding source.
SOURCE: Ricceri F et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018 Jun 15. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15139.
according to a new retrospective study.
Among 266 older patients, 65% achieved a 75% improvement in Psoriasis Area Severity Index score (PASI 75) after 1 year of therapy; 50% reached a PASI 90, and 40% a PASI 100, Francesca Prignano MD, PhD, and her colleagues reported in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. The rate of serious adverse events was less than 10%.
Elderly patients – those aged 65 years and older – are commonly excluded from studies on biologic treatments because they have more medical comorbidities and are thought to be more at risk for serious adverse events, like infections and malignancy, wrote Dr. Prignano of the dermatology unit, University of Florence, Italy, and her colleagues.
As a result, they noted, there is a “lack of information concerning safety and effectiveness of available treatments for psoriasis in the elderly, particularly about new biologic agents. Disease remission should be an objective for both younger patients and older patients, and biologic therapy should be considered a treatment option for all patients.”
To examine both the benefit and risk of biologics in this population, the team reviewed the records of 266 elderly psoriasis patients; everyone had been on a biologic treatment for at least 1 year.
The primary outcome was PASI score at weeks 8, 16, 28, and 52. The secondary outcomes were the rate and types of biologic-associated adverse events.
The study comprised 266 patients (mean age 72 years). Their mean psoriasis duration was 25.7 years. Comorbidities included psoriatic arthritis; hypertension and dyslipidemia; diabetes mellitus; cardiovascular, gastrointestinal and respiratory diseases; osteoporosis; thyroid dysfunction; depression; and cancer.
Adalimumab was the most commonly prescribed biologic (31%), followed by ustekinumab (28.9%), etanercept (20%), and secukinumab (15%). A smaller proportion of patients were taking infliximab, golimumab, or certolizumab pegol.
The mean baseline PASI was 16.5, although the range was wide (4-54). At the time of review, the average biologic treatment duration was 44 months. Almost half of the cohort (128) were on their second biologic, and 20 more had been on three biologics. A few patients were taking concomitant medications, including steroids, cyclosporine, and acitretin.
The mean PASI scores decreased to 3.7 at week 16, 1.6 at week 28, and 1.2 at week 52. The group exhibited a rapid response to biologic treatment. By 16 weeks, about 55% had achieved a PASI 75, about 28% a PASI 90, and about 20% a PASI 100. By 28 weeks, these numbers were about 64%, 45%, and 35%, respectively. At 1 year, they were about 65%, 50%, and 40%, respectively.
The rate of adverse events was 9.4%. There were 25 events in the cohort, the majority of which (48%) were infections; these included four respiratory infections, three urinary tract infections, two cases of mucocutaneous candidiasis, two cases of herpes zoster infection, and one case of erysipelas.
There were four malignancies: three nonmelanoma skin cancers and one vocal cord cancer.
Noting that, to date, their study represented “the broadest experience on the use of biological drugs” for elderly patients with psoriasis, they wrote that while “comorbidities should be taken into consideration when a long-term treatment is proposed, for the higher risk of side effects and drug interactions,” they wrote, noting that none of the 266 patients had a serious infection and the malignancy rate was low (1.5%).
None of the authors had financial disclosures, and the study had no funding source.
SOURCE: Ricceri F et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018 Jun 15. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15139.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE EUROPEAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY AND VENEREOLOGY
Key clinical point: Patients aged 65 years and older responded well to biologics and had a low rate of serious adverse events.
Major finding: At 1 year, 65% achieved a PASI 75, 50% achieved a reached PASI 90, and 40% achieved a PASI 100, with a 9.4% rate of serious adverse events.
Study details: The retrospective study comprised 266 patients aged 65 years and older treated with biologics for psoriasis.
Disclosures: None of the authors had financial disclosures, and the study had no funding source.
Source: Ricceri F et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15139.
Low risk of complications from sedation-associated GI endoscopies
Background: Most GI endoscopies use sedation to keep patients comfortable during procedures, but sedation puts patients at increased risk of complications. Most of the available studies reporting sedation-related complications are retrospective and dated. There is a lack of prospective studies investigating sedation-related complications and their associated risk factors.
Study design: Prospective study.
Setting: Thirty-nine hospitals in Germany.
Synopsis: Using data collected from 314,190 adult endoscopies in which sedation was used, this study identified that there was only a 0.01% rate of major complications. Major complications for this study included intubation, ICU admission, resuscitation, or death. Propofol was the most commonly used sedative (61.7% of cases) and had the lowest risk of complications (odds ratio, 0.7509; P = .028). The top risk factors for complications were an American Society of Anesthesiologists class greater than 2 (OR, 2.2998; P less than .001), emergent need for the endoscopy (9 of the 13 fatal cases), and longer procedure length (P less than .001).
Bottom line: GI endoscopic procedures with sedation are tolerated well in the general population and have low risk of complications.
Citation: Behrens A et al. Acute sedation-associated complications in GI endoscopy (ProSed 2 Study): Results from the prospective multicentre electronic registry of sedation-associated complications. Gut. 2018 Jan 3. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-311037.
Dr. Ally is a hospitalist at UC San Diego Health and an assistant clinical professor at the University of California, San Diego.
Background: Most GI endoscopies use sedation to keep patients comfortable during procedures, but sedation puts patients at increased risk of complications. Most of the available studies reporting sedation-related complications are retrospective and dated. There is a lack of prospective studies investigating sedation-related complications and their associated risk factors.
Study design: Prospective study.
Setting: Thirty-nine hospitals in Germany.
Synopsis: Using data collected from 314,190 adult endoscopies in which sedation was used, this study identified that there was only a 0.01% rate of major complications. Major complications for this study included intubation, ICU admission, resuscitation, or death. Propofol was the most commonly used sedative (61.7% of cases) and had the lowest risk of complications (odds ratio, 0.7509; P = .028). The top risk factors for complications were an American Society of Anesthesiologists class greater than 2 (OR, 2.2998; P less than .001), emergent need for the endoscopy (9 of the 13 fatal cases), and longer procedure length (P less than .001).
Bottom line: GI endoscopic procedures with sedation are tolerated well in the general population and have low risk of complications.
Citation: Behrens A et al. Acute sedation-associated complications in GI endoscopy (ProSed 2 Study): Results from the prospective multicentre electronic registry of sedation-associated complications. Gut. 2018 Jan 3. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-311037.
Dr. Ally is a hospitalist at UC San Diego Health and an assistant clinical professor at the University of California, San Diego.
Background: Most GI endoscopies use sedation to keep patients comfortable during procedures, but sedation puts patients at increased risk of complications. Most of the available studies reporting sedation-related complications are retrospective and dated. There is a lack of prospective studies investigating sedation-related complications and their associated risk factors.
Study design: Prospective study.
Setting: Thirty-nine hospitals in Germany.
Synopsis: Using data collected from 314,190 adult endoscopies in which sedation was used, this study identified that there was only a 0.01% rate of major complications. Major complications for this study included intubation, ICU admission, resuscitation, or death. Propofol was the most commonly used sedative (61.7% of cases) and had the lowest risk of complications (odds ratio, 0.7509; P = .028). The top risk factors for complications were an American Society of Anesthesiologists class greater than 2 (OR, 2.2998; P less than .001), emergent need for the endoscopy (9 of the 13 fatal cases), and longer procedure length (P less than .001).
Bottom line: GI endoscopic procedures with sedation are tolerated well in the general population and have low risk of complications.
Citation: Behrens A et al. Acute sedation-associated complications in GI endoscopy (ProSed 2 Study): Results from the prospective multicentre electronic registry of sedation-associated complications. Gut. 2018 Jan 3. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-311037.
Dr. Ally is a hospitalist at UC San Diego Health and an assistant clinical professor at the University of California, San Diego.
What's your diagnosis? - July 2018
Polycystic pancreas
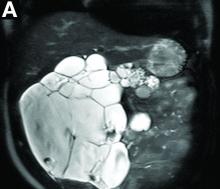
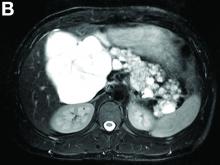
Cross-sectional imaging revealed the diagnosis of polycystic pancreas (diffuse cystic degeneration of the whole organ) with giant cysts in the head and multiple cysts across the whole organ in the absence of concomitant kidney or liver cysts (Figure A, B).
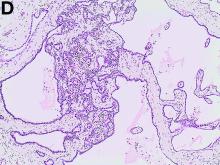
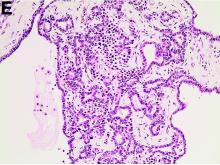
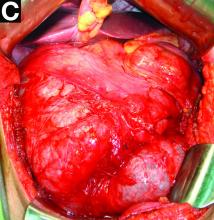
The patient underwent an endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration before the operation, and a mucinous cystic neoplasm was documented. A total duodenopancreatosplenectomy followed. The postoperative course was uneventful. Histology showed multiple cysts of variable diameter lined by monolayer flattened or cuboidal epithelium without atypia and confirmed the diagnosis of polycystic pancreas (Figures D, E; stain: hematoxylin and eosin; original magnifications: ×100 and ×200, respectively).
Genetic testing was negative for von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease. The patient remains in good general condition under diabetes management and oral administration of pancreatic enzymes 45 months 4 years after pancreatectomy. Magnetic resonance imaging of the central nervous system and abdomen were without pathologic findings.
Although pancreatic cysts are very common, a diffuse cystic degeneration of the pancreas in the form of polycystic pancreas is very infrequent and has been described in patients with VHL disease.1 It is almost always associated with multiple renal cysts.1 Genetic testing for VHL disease is suggested in all cases presenting with multiple pancreatic cysts by some investigators.2 It has an accuracy greater than 80%, which reaches 95%-100% in patients who fulfill the clinical criteria for VHL disease.3
The novelty of this case is double; to the best of our knowledge, polycystic pancreas with such a volume (cysts up to 25 cm) has not yet been documented in the literature and has not been at all described in the absence of VHL disease up to now.
References
1. Leung R., Biswas S., Duncan M. et al. Imaging features of Von Hippel-Lindau disease. Radiographics. 2008;28:65-79.
2. Kapur V. Brower S.T. Cystic replacement of pancreas in patient with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome. Gastrointest Cancer Res. 2013;6:25-6.
3. Nielsen S.M., Rhodes L., Blanco I. et al. Von Hippel-Lindau disease: genetics and role of genetic counseling in a multiple neoplasia syndrome. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:2172-81.
Polycystic pancreas
Cross-sectional imaging revealed the diagnosis of polycystic pancreas (diffuse cystic degeneration of the whole organ) with giant cysts in the head and multiple cysts across the whole organ in the absence of concomitant kidney or liver cysts (Figure A, B).
The patient underwent an endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration before the operation, and a mucinous cystic neoplasm was documented. A total duodenopancreatosplenectomy followed. The postoperative course was uneventful. Histology showed multiple cysts of variable diameter lined by monolayer flattened or cuboidal epithelium without atypia and confirmed the diagnosis of polycystic pancreas (Figures D, E; stain: hematoxylin and eosin; original magnifications: ×100 and ×200, respectively).
Genetic testing was negative for von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease. The patient remains in good general condition under diabetes management and oral administration of pancreatic enzymes 45 months 4 years after pancreatectomy. Magnetic resonance imaging of the central nervous system and abdomen were without pathologic findings.
Although pancreatic cysts are very common, a diffuse cystic degeneration of the pancreas in the form of polycystic pancreas is very infrequent and has been described in patients with VHL disease.1 It is almost always associated with multiple renal cysts.1 Genetic testing for VHL disease is suggested in all cases presenting with multiple pancreatic cysts by some investigators.2 It has an accuracy greater than 80%, which reaches 95%-100% in patients who fulfill the clinical criteria for VHL disease.3
The novelty of this case is double; to the best of our knowledge, polycystic pancreas with such a volume (cysts up to 25 cm) has not yet been documented in the literature and has not been at all described in the absence of VHL disease up to now.
References
1. Leung R., Biswas S., Duncan M. et al. Imaging features of Von Hippel-Lindau disease. Radiographics. 2008;28:65-79.
2. Kapur V. Brower S.T. Cystic replacement of pancreas in patient with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome. Gastrointest Cancer Res. 2013;6:25-6.
3. Nielsen S.M., Rhodes L., Blanco I. et al. Von Hippel-Lindau disease: genetics and role of genetic counseling in a multiple neoplasia syndrome. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:2172-81.
Polycystic pancreas
Cross-sectional imaging revealed the diagnosis of polycystic pancreas (diffuse cystic degeneration of the whole organ) with giant cysts in the head and multiple cysts across the whole organ in the absence of concomitant kidney or liver cysts (Figure A, B).
The patient underwent an endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration before the operation, and a mucinous cystic neoplasm was documented. A total duodenopancreatosplenectomy followed. The postoperative course was uneventful. Histology showed multiple cysts of variable diameter lined by monolayer flattened or cuboidal epithelium without atypia and confirmed the diagnosis of polycystic pancreas (Figures D, E; stain: hematoxylin and eosin; original magnifications: ×100 and ×200, respectively).
Genetic testing was negative for von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease. The patient remains in good general condition under diabetes management and oral administration of pancreatic enzymes 45 months 4 years after pancreatectomy. Magnetic resonance imaging of the central nervous system and abdomen were without pathologic findings.
Although pancreatic cysts are very common, a diffuse cystic degeneration of the pancreas in the form of polycystic pancreas is very infrequent and has been described in patients with VHL disease.1 It is almost always associated with multiple renal cysts.1 Genetic testing for VHL disease is suggested in all cases presenting with multiple pancreatic cysts by some investigators.2 It has an accuracy greater than 80%, which reaches 95%-100% in patients who fulfill the clinical criteria for VHL disease.3
The novelty of this case is double; to the best of our knowledge, polycystic pancreas with such a volume (cysts up to 25 cm) has not yet been documented in the literature and has not been at all described in the absence of VHL disease up to now.
References
1. Leung R., Biswas S., Duncan M. et al. Imaging features of Von Hippel-Lindau disease. Radiographics. 2008;28:65-79.
2. Kapur V. Brower S.T. Cystic replacement of pancreas in patient with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome. Gastrointest Cancer Res. 2013;6:25-6.
3. Nielsen S.M., Rhodes L., Blanco I. et al. Von Hippel-Lindau disease: genetics and role of genetic counseling in a multiple neoplasia syndrome. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:2172-81.
Doc reports favorable results from trial on hold
STOCKHOLM—Interim trial results suggest the EZH2 inhibitor tazemetostat can produce durable responses in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma (FL).
In patients with EZH2 mutations, the overall response rate (ORR) was 71%, and the median duration of response (DOR) was 32 weeks.
For patients with wild-type (WT) EZH2, the ORR was 33%, and the median DOR was 76 weeks.
Tazemetostat was considered generally well tolerated in this phase 2 trial, which is currently on partial clinical hold.
Gilles Salles, MD, PhD, of the University Hospital of Lyon France, presented results from the trial at the 23rd Congress of the European Hematology Association (EHA) as abstract S100.
The trial is sponsored by Epizyme, Inc.
In April, Epizyme announced that all US-based trials of tazemetostat had been placed on partial hold after a pediatric patient on a phase 1 trial developed secondary T-cell lymphoma.
Enrollment was stopped in all the trials, but patients could continue receiving tazemetostat if they had not progressed on the drug.
The phase 2 trial of tazemetostat in non-Hodgkin lymphoma has enrolled 89 adults with relapsed/refractory FL.
At EHA, Dr Salles presented results in 82 of these patients. There were 28 patients with EZH2-mutated FL and 54 with EZH2-WT FL.
The median age was 61 in both cohorts. Forty-three percent of EZH2-mutated and 63% of WT patients were male.
EZH2-mutated patients had a median of 3 prior therapies, and WT patients had a median of 4. Thirty-eight percent and 42%, respectively, were refractory to their last therapy. Eleven percent and 39%, respectively, had received prior transplant.
The median time from diagnosis was 5.1 years for EZH2-mutated patients and 6.4 years for WT patients. The median time from last prior therapy was 18.4 weeks and 28.1 weeks, respectively.
The patients received tazemetostat at 800 mg twice daily until disease progression or withdrawal.
Safety
In all 82 patients, the rate of treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) was 95%, and the rate of treatment-related AEs was 78%. The rate of grade 3 or higher treatment-related AEs was 17%, and the rate of serious treatment-related AEs was 4%.
Six percent of patients discontinued treatment due to a related AE, 18% had a dose interruption, and 5% had a dose reduction due to a related AE.
Treatment-related AEs included nausea (20%), fatigue (13%), anemia (13%), diarrhea (11%), alopecia (11%), asthenia (10%), thrombocytopenia (10%), muscle spasms (6%), bronchitis (5%), vomiting (5%), headache (5%), abdominal pain (2%), pyrexia (1%), and cough (1%).
Grade 3 or higher treatment-related AEs included thrombocytopenia (4%), anemia (4%), fatigue (1%), and asthenia (1%).
Efficacy
In the EZH2-mutated cohort, the ORR was 71% (n=20). Eleven percent of patients (n=3) achieved a complete response, and 61% (n=17) had a partial response.
Twenty-nine percent (n=8) had stable disease as their best response. And 21% (n=6) of patients are still on study with stable disease.
All patients in this cohort experienced a reduction in tumor burden. None of the patients had progressive disease as their best response.
At the time of analysis (May 1, 2018), the median DOR was 32.3 weeks, and 55% of responders (n=11) had an ongoing response.
The median progression-free survival was 48.6 weeks.
In patients with WT EZH2 (n=54), the ORR was 33% (n=18). Six percent of patients (n=3) achieved a complete response, and 28% (n=15) had a partial response.
Thirty-one percent of patients (n=17) had stable disease as their best response, including 1 patient who is still receiving treatment.
Thirty-one percent of patients (n=17) progressed. For 4% (n=2), their response status was unknown.
At the time of analysis, the median DOR was 76 weeks, and 56% of responders (n=10) had an ongoing response.
The median progression-free survival was 29.9 weeks.
“I am impressed by the sustained clinical activity and the good tolerability of tazemetostat in this heavily pretreated patient population,” Dr Salles said. “This is important for patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma, as both the response rates and durations of response usually tend to decrease with each successive line of treatment.”
“I believe tazemetostat has the potential to fill a significant unmet need for these patients, and continued investigation of tazemetostat as a single agent or in combination with other agents is warranted.”
Epizyme’s president and chief executive officer, Robert Bazemore, said the company is still working to resolve the partial clinical hold on tazemetostat trials and is “making good progress.”
STOCKHOLM—Interim trial results suggest the EZH2 inhibitor tazemetostat can produce durable responses in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma (FL).
In patients with EZH2 mutations, the overall response rate (ORR) was 71%, and the median duration of response (DOR) was 32 weeks.
For patients with wild-type (WT) EZH2, the ORR was 33%, and the median DOR was 76 weeks.
Tazemetostat was considered generally well tolerated in this phase 2 trial, which is currently on partial clinical hold.
Gilles Salles, MD, PhD, of the University Hospital of Lyon France, presented results from the trial at the 23rd Congress of the European Hematology Association (EHA) as abstract S100.
The trial is sponsored by Epizyme, Inc.
In April, Epizyme announced that all US-based trials of tazemetostat had been placed on partial hold after a pediatric patient on a phase 1 trial developed secondary T-cell lymphoma.
Enrollment was stopped in all the trials, but patients could continue receiving tazemetostat if they had not progressed on the drug.
The phase 2 trial of tazemetostat in non-Hodgkin lymphoma has enrolled 89 adults with relapsed/refractory FL.
At EHA, Dr Salles presented results in 82 of these patients. There were 28 patients with EZH2-mutated FL and 54 with EZH2-WT FL.
The median age was 61 in both cohorts. Forty-three percent of EZH2-mutated and 63% of WT patients were male.
EZH2-mutated patients had a median of 3 prior therapies, and WT patients had a median of 4. Thirty-eight percent and 42%, respectively, were refractory to their last therapy. Eleven percent and 39%, respectively, had received prior transplant.
The median time from diagnosis was 5.1 years for EZH2-mutated patients and 6.4 years for WT patients. The median time from last prior therapy was 18.4 weeks and 28.1 weeks, respectively.
The patients received tazemetostat at 800 mg twice daily until disease progression or withdrawal.
Safety
In all 82 patients, the rate of treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) was 95%, and the rate of treatment-related AEs was 78%. The rate of grade 3 or higher treatment-related AEs was 17%, and the rate of serious treatment-related AEs was 4%.
Six percent of patients discontinued treatment due to a related AE, 18% had a dose interruption, and 5% had a dose reduction due to a related AE.
Treatment-related AEs included nausea (20%), fatigue (13%), anemia (13%), diarrhea (11%), alopecia (11%), asthenia (10%), thrombocytopenia (10%), muscle spasms (6%), bronchitis (5%), vomiting (5%), headache (5%), abdominal pain (2%), pyrexia (1%), and cough (1%).
Grade 3 or higher treatment-related AEs included thrombocytopenia (4%), anemia (4%), fatigue (1%), and asthenia (1%).
Efficacy
In the EZH2-mutated cohort, the ORR was 71% (n=20). Eleven percent of patients (n=3) achieved a complete response, and 61% (n=17) had a partial response.
Twenty-nine percent (n=8) had stable disease as their best response. And 21% (n=6) of patients are still on study with stable disease.
All patients in this cohort experienced a reduction in tumor burden. None of the patients had progressive disease as their best response.
At the time of analysis (May 1, 2018), the median DOR was 32.3 weeks, and 55% of responders (n=11) had an ongoing response.
The median progression-free survival was 48.6 weeks.
In patients with WT EZH2 (n=54), the ORR was 33% (n=18). Six percent of patients (n=3) achieved a complete response, and 28% (n=15) had a partial response.
Thirty-one percent of patients (n=17) had stable disease as their best response, including 1 patient who is still receiving treatment.
Thirty-one percent of patients (n=17) progressed. For 4% (n=2), their response status was unknown.
At the time of analysis, the median DOR was 76 weeks, and 56% of responders (n=10) had an ongoing response.
The median progression-free survival was 29.9 weeks.
“I am impressed by the sustained clinical activity and the good tolerability of tazemetostat in this heavily pretreated patient population,” Dr Salles said. “This is important for patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma, as both the response rates and durations of response usually tend to decrease with each successive line of treatment.”
“I believe tazemetostat has the potential to fill a significant unmet need for these patients, and continued investigation of tazemetostat as a single agent or in combination with other agents is warranted.”
Epizyme’s president and chief executive officer, Robert Bazemore, said the company is still working to resolve the partial clinical hold on tazemetostat trials and is “making good progress.”
STOCKHOLM—Interim trial results suggest the EZH2 inhibitor tazemetostat can produce durable responses in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma (FL).
In patients with EZH2 mutations, the overall response rate (ORR) was 71%, and the median duration of response (DOR) was 32 weeks.
For patients with wild-type (WT) EZH2, the ORR was 33%, and the median DOR was 76 weeks.
Tazemetostat was considered generally well tolerated in this phase 2 trial, which is currently on partial clinical hold.
Gilles Salles, MD, PhD, of the University Hospital of Lyon France, presented results from the trial at the 23rd Congress of the European Hematology Association (EHA) as abstract S100.
The trial is sponsored by Epizyme, Inc.
In April, Epizyme announced that all US-based trials of tazemetostat had been placed on partial hold after a pediatric patient on a phase 1 trial developed secondary T-cell lymphoma.
Enrollment was stopped in all the trials, but patients could continue receiving tazemetostat if they had not progressed on the drug.
The phase 2 trial of tazemetostat in non-Hodgkin lymphoma has enrolled 89 adults with relapsed/refractory FL.
At EHA, Dr Salles presented results in 82 of these patients. There were 28 patients with EZH2-mutated FL and 54 with EZH2-WT FL.
The median age was 61 in both cohorts. Forty-three percent of EZH2-mutated and 63% of WT patients were male.
EZH2-mutated patients had a median of 3 prior therapies, and WT patients had a median of 4. Thirty-eight percent and 42%, respectively, were refractory to their last therapy. Eleven percent and 39%, respectively, had received prior transplant.
The median time from diagnosis was 5.1 years for EZH2-mutated patients and 6.4 years for WT patients. The median time from last prior therapy was 18.4 weeks and 28.1 weeks, respectively.
The patients received tazemetostat at 800 mg twice daily until disease progression or withdrawal.
Safety
In all 82 patients, the rate of treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) was 95%, and the rate of treatment-related AEs was 78%. The rate of grade 3 or higher treatment-related AEs was 17%, and the rate of serious treatment-related AEs was 4%.
Six percent of patients discontinued treatment due to a related AE, 18% had a dose interruption, and 5% had a dose reduction due to a related AE.
Treatment-related AEs included nausea (20%), fatigue (13%), anemia (13%), diarrhea (11%), alopecia (11%), asthenia (10%), thrombocytopenia (10%), muscle spasms (6%), bronchitis (5%), vomiting (5%), headache (5%), abdominal pain (2%), pyrexia (1%), and cough (1%).
Grade 3 or higher treatment-related AEs included thrombocytopenia (4%), anemia (4%), fatigue (1%), and asthenia (1%).
Efficacy
In the EZH2-mutated cohort, the ORR was 71% (n=20). Eleven percent of patients (n=3) achieved a complete response, and 61% (n=17) had a partial response.
Twenty-nine percent (n=8) had stable disease as their best response. And 21% (n=6) of patients are still on study with stable disease.
All patients in this cohort experienced a reduction in tumor burden. None of the patients had progressive disease as their best response.
At the time of analysis (May 1, 2018), the median DOR was 32.3 weeks, and 55% of responders (n=11) had an ongoing response.
The median progression-free survival was 48.6 weeks.
In patients with WT EZH2 (n=54), the ORR was 33% (n=18). Six percent of patients (n=3) achieved a complete response, and 28% (n=15) had a partial response.
Thirty-one percent of patients (n=17) had stable disease as their best response, including 1 patient who is still receiving treatment.
Thirty-one percent of patients (n=17) progressed. For 4% (n=2), their response status was unknown.
At the time of analysis, the median DOR was 76 weeks, and 56% of responders (n=10) had an ongoing response.
The median progression-free survival was 29.9 weeks.
“I am impressed by the sustained clinical activity and the good tolerability of tazemetostat in this heavily pretreated patient population,” Dr Salles said. “This is important for patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma, as both the response rates and durations of response usually tend to decrease with each successive line of treatment.”
“I believe tazemetostat has the potential to fill a significant unmet need for these patients, and continued investigation of tazemetostat as a single agent or in combination with other agents is warranted.”
Epizyme’s president and chief executive officer, Robert Bazemore, said the company is still working to resolve the partial clinical hold on tazemetostat trials and is “making good progress.”
Group updates guidelines on CLL
Recent advances in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) have prompted an update to the 2008 International Workshop in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (iwCLL) consensus guidelines.
The updated iwCLL guidelines include new information on genomic alterations, the use of clinical staging and prognostic markers/scores, response assessment, minimal residual disease (MRD), and viral diseases in CLL patients.
The update was recently published in Blood.
Diagnosis, prognosis, and staging
To verify CLL diagnosis, the iwCLL guidelines recommend obtaining complete blood counts and differential counts as well as immunophenotyping of peripheral blood lymphocytes. A panel of CD19, CD5, CD20, CD23, κ, and λ typically suffices to establish a diagnosis.
Other tests that may help in prognosis or assessing tumor burden include molecular cytogenetics for del(13q), del(11q), del(17p), and add(12) in peripheral blood lymphocytes and determining TP53 and IGHV mutational status.
These tests can help identify poor-prognosis patients who are not likely to benefit from standard chemotherapy but are likely to benefit from small-molecule inhibitors of BTK, PI3K, or BCL2.
In addition, serum markers such as β2-microglogulin provide insight into overall survival and progression-free survival.
With regard to clinical staging, the guidelines highlight the Binet and Rai systems, which are routinely used in clinical practice and clinical trials.
However, the guidelines also note that “there are a large number of biomarkers that can provide additional prognostic information,” and, recently, “several prognostic scores and stratification systems have been proposed based on multivariate analyses.”
For example, the CLL international prognostic index (CLL-IPI) provides a weighted score that uses clinical stage, age, IGHV mutational status, β2-microglogulin, and the presence of del(17p) and/or TP53 mutations.
Indications for treatment
The guidelines note that active disease must be documented to initiate therapy. At least 1 of the following criteria must be met:
- Evidence of progressive marrow failure
- Massive, progressive, or symptomatic splenomegaly
- Progressive/symptomatic lymphadenopathy or massive nodes
- Progressive lymphocytosis
- Autoimmune complications
- Extranodal involvement
- Disease-related symptoms (unintentional weight loss, significant fatigue, fevers, night sweats for over a month without evidence of infection).
Following relapse, subsequent lines of treatment should follow the same principles as those used for initial treatment decisions.
Response, MRD, and more
The guidelines say 2 groups of parameters must be assessed to determine response to therapy:
- Group A: lymphoid tumor load and constitutional symptoms, including liver and/or spleen size, lymph node evaluation, and circulating lymphocyte count
- Group B: the hematopoietic system (platelet count, hemoglobin, and marrow).
For therapies with a defined treatment duration, response should be assessed at least 2 months after treatment is completed. For continued therapies or maintenance, response should be assessed at a predefined time point or at least 2 months after patients achieve their maximum response.
The guidelines also say MRD should be assessed in clinical trials aimed at maximizing the depth of remission. Furthermore, it “may be important” to confirm MRD negativity in the blood and marrow, as there are therapies that preferentially clear the blood but not the marrow (such as monoclonal antibodies).
In addition to the aforementioned recommendations, the updated iwCLL guidelines also include information on patient eligibility for clinical trials, guidance regarding treatment-related toxicities, and recommendations for supportive care and managing complications.
Recent advances in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) have prompted an update to the 2008 International Workshop in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (iwCLL) consensus guidelines.
The updated iwCLL guidelines include new information on genomic alterations, the use of clinical staging and prognostic markers/scores, response assessment, minimal residual disease (MRD), and viral diseases in CLL patients.
The update was recently published in Blood.
Diagnosis, prognosis, and staging
To verify CLL diagnosis, the iwCLL guidelines recommend obtaining complete blood counts and differential counts as well as immunophenotyping of peripheral blood lymphocytes. A panel of CD19, CD5, CD20, CD23, κ, and λ typically suffices to establish a diagnosis.
Other tests that may help in prognosis or assessing tumor burden include molecular cytogenetics for del(13q), del(11q), del(17p), and add(12) in peripheral blood lymphocytes and determining TP53 and IGHV mutational status.
These tests can help identify poor-prognosis patients who are not likely to benefit from standard chemotherapy but are likely to benefit from small-molecule inhibitors of BTK, PI3K, or BCL2.
In addition, serum markers such as β2-microglogulin provide insight into overall survival and progression-free survival.
With regard to clinical staging, the guidelines highlight the Binet and Rai systems, which are routinely used in clinical practice and clinical trials.
However, the guidelines also note that “there are a large number of biomarkers that can provide additional prognostic information,” and, recently, “several prognostic scores and stratification systems have been proposed based on multivariate analyses.”
For example, the CLL international prognostic index (CLL-IPI) provides a weighted score that uses clinical stage, age, IGHV mutational status, β2-microglogulin, and the presence of del(17p) and/or TP53 mutations.
Indications for treatment
The guidelines note that active disease must be documented to initiate therapy. At least 1 of the following criteria must be met:
- Evidence of progressive marrow failure
- Massive, progressive, or symptomatic splenomegaly
- Progressive/symptomatic lymphadenopathy or massive nodes
- Progressive lymphocytosis
- Autoimmune complications
- Extranodal involvement
- Disease-related symptoms (unintentional weight loss, significant fatigue, fevers, night sweats for over a month without evidence of infection).
Following relapse, subsequent lines of treatment should follow the same principles as those used for initial treatment decisions.
Response, MRD, and more
The guidelines say 2 groups of parameters must be assessed to determine response to therapy:
- Group A: lymphoid tumor load and constitutional symptoms, including liver and/or spleen size, lymph node evaluation, and circulating lymphocyte count
- Group B: the hematopoietic system (platelet count, hemoglobin, and marrow).
For therapies with a defined treatment duration, response should be assessed at least 2 months after treatment is completed. For continued therapies or maintenance, response should be assessed at a predefined time point or at least 2 months after patients achieve their maximum response.
The guidelines also say MRD should be assessed in clinical trials aimed at maximizing the depth of remission. Furthermore, it “may be important” to confirm MRD negativity in the blood and marrow, as there are therapies that preferentially clear the blood but not the marrow (such as monoclonal antibodies).
In addition to the aforementioned recommendations, the updated iwCLL guidelines also include information on patient eligibility for clinical trials, guidance regarding treatment-related toxicities, and recommendations for supportive care and managing complications.
Recent advances in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) have prompted an update to the 2008 International Workshop in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (iwCLL) consensus guidelines.
The updated iwCLL guidelines include new information on genomic alterations, the use of clinical staging and prognostic markers/scores, response assessment, minimal residual disease (MRD), and viral diseases in CLL patients.
The update was recently published in Blood.
Diagnosis, prognosis, and staging
To verify CLL diagnosis, the iwCLL guidelines recommend obtaining complete blood counts and differential counts as well as immunophenotyping of peripheral blood lymphocytes. A panel of CD19, CD5, CD20, CD23, κ, and λ typically suffices to establish a diagnosis.
Other tests that may help in prognosis or assessing tumor burden include molecular cytogenetics for del(13q), del(11q), del(17p), and add(12) in peripheral blood lymphocytes and determining TP53 and IGHV mutational status.
These tests can help identify poor-prognosis patients who are not likely to benefit from standard chemotherapy but are likely to benefit from small-molecule inhibitors of BTK, PI3K, or BCL2.
In addition, serum markers such as β2-microglogulin provide insight into overall survival and progression-free survival.
With regard to clinical staging, the guidelines highlight the Binet and Rai systems, which are routinely used in clinical practice and clinical trials.
However, the guidelines also note that “there are a large number of biomarkers that can provide additional prognostic information,” and, recently, “several prognostic scores and stratification systems have been proposed based on multivariate analyses.”
For example, the CLL international prognostic index (CLL-IPI) provides a weighted score that uses clinical stage, age, IGHV mutational status, β2-microglogulin, and the presence of del(17p) and/or TP53 mutations.
Indications for treatment
The guidelines note that active disease must be documented to initiate therapy. At least 1 of the following criteria must be met:
- Evidence of progressive marrow failure
- Massive, progressive, or symptomatic splenomegaly
- Progressive/symptomatic lymphadenopathy or massive nodes
- Progressive lymphocytosis
- Autoimmune complications
- Extranodal involvement
- Disease-related symptoms (unintentional weight loss, significant fatigue, fevers, night sweats for over a month without evidence of infection).
Following relapse, subsequent lines of treatment should follow the same principles as those used for initial treatment decisions.
Response, MRD, and more
The guidelines say 2 groups of parameters must be assessed to determine response to therapy:
- Group A: lymphoid tumor load and constitutional symptoms, including liver and/or spleen size, lymph node evaluation, and circulating lymphocyte count
- Group B: the hematopoietic system (platelet count, hemoglobin, and marrow).
For therapies with a defined treatment duration, response should be assessed at least 2 months after treatment is completed. For continued therapies or maintenance, response should be assessed at a predefined time point or at least 2 months after patients achieve their maximum response.
The guidelines also say MRD should be assessed in clinical trials aimed at maximizing the depth of remission. Furthermore, it “may be important” to confirm MRD negativity in the blood and marrow, as there are therapies that preferentially clear the blood but not the marrow (such as monoclonal antibodies).
In addition to the aforementioned recommendations, the updated iwCLL guidelines also include information on patient eligibility for clinical trials, guidance regarding treatment-related toxicities, and recommendations for supportive care and managing complications.
CPI-613 receives orphan designation for BL
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted orphan drug designation to CPI-613 for the treatment of Burkitt lymphoma (BL).
CPI-613 is a novel lipoic acid analogue that inhibits multiple enzyme targets within the tricarboxylic acid cycle.
The drug is in development as a treatment for hematologic malignancies and solid tumors.
In a phase 1 trial of patients with advanced hematologic malignancies, CPI-613 produced a response in a patient with relapsed BL.
Now, Rafael Pharmaceuticals, Inc., the company developing CPI-613, is launching a phase 2 trial of the drug in patients with relapsed or refractory BL and high-grade B-cell lymphoma with rearrangements of MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6.
In the phase 1 trial, the patient with relapsed BL achieved a partial response to CPI-613 monotherapy and was ultimately cleared of disease after surgery.
The patient, a 19-year-old female, began taking CPI-613 (2940 mg/m2) after her second relapse. She achieved a radiographic partial response after the third cycle of CPI-613.
The patient completed 17 cycles of CPI-613 over 51 weeks. She decided to stop treatment after the 17th cycle to pursue a surgical resection of residual tumor. The pathology of the surgical specimen revealed BL with extensive necrosis.
Clinical follow-up on the patient showed no evidence of disease more than 36 months later. And CPI-613 was considered well tolerated in this patient.
About orphan designation
The FDA grants orphan designation to products intended to treat, diagnose, or prevent diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the US.
The designation provides incentives for sponsors to develop products for rare diseases. This may include tax credits toward the cost of clinical trials, prescription drug user fee waivers, and 7 years of market exclusivity if the product is approved.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted orphan drug designation to CPI-613 for the treatment of Burkitt lymphoma (BL).
CPI-613 is a novel lipoic acid analogue that inhibits multiple enzyme targets within the tricarboxylic acid cycle.
The drug is in development as a treatment for hematologic malignancies and solid tumors.
In a phase 1 trial of patients with advanced hematologic malignancies, CPI-613 produced a response in a patient with relapsed BL.
Now, Rafael Pharmaceuticals, Inc., the company developing CPI-613, is launching a phase 2 trial of the drug in patients with relapsed or refractory BL and high-grade B-cell lymphoma with rearrangements of MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6.
In the phase 1 trial, the patient with relapsed BL achieved a partial response to CPI-613 monotherapy and was ultimately cleared of disease after surgery.
The patient, a 19-year-old female, began taking CPI-613 (2940 mg/m2) after her second relapse. She achieved a radiographic partial response after the third cycle of CPI-613.
The patient completed 17 cycles of CPI-613 over 51 weeks. She decided to stop treatment after the 17th cycle to pursue a surgical resection of residual tumor. The pathology of the surgical specimen revealed BL with extensive necrosis.
Clinical follow-up on the patient showed no evidence of disease more than 36 months later. And CPI-613 was considered well tolerated in this patient.
About orphan designation
The FDA grants orphan designation to products intended to treat, diagnose, or prevent diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the US.
The designation provides incentives for sponsors to develop products for rare diseases. This may include tax credits toward the cost of clinical trials, prescription drug user fee waivers, and 7 years of market exclusivity if the product is approved.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted orphan drug designation to CPI-613 for the treatment of Burkitt lymphoma (BL).
CPI-613 is a novel lipoic acid analogue that inhibits multiple enzyme targets within the tricarboxylic acid cycle.
The drug is in development as a treatment for hematologic malignancies and solid tumors.
In a phase 1 trial of patients with advanced hematologic malignancies, CPI-613 produced a response in a patient with relapsed BL.
Now, Rafael Pharmaceuticals, Inc., the company developing CPI-613, is launching a phase 2 trial of the drug in patients with relapsed or refractory BL and high-grade B-cell lymphoma with rearrangements of MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6.
In the phase 1 trial, the patient with relapsed BL achieved a partial response to CPI-613 monotherapy and was ultimately cleared of disease after surgery.
The patient, a 19-year-old female, began taking CPI-613 (2940 mg/m2) after her second relapse. She achieved a radiographic partial response after the third cycle of CPI-613.
The patient completed 17 cycles of CPI-613 over 51 weeks. She decided to stop treatment after the 17th cycle to pursue a surgical resection of residual tumor. The pathology of the surgical specimen revealed BL with extensive necrosis.
Clinical follow-up on the patient showed no evidence of disease more than 36 months later. And CPI-613 was considered well tolerated in this patient.
About orphan designation
The FDA grants orphan designation to products intended to treat, diagnose, or prevent diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the US.
The designation provides incentives for sponsors to develop products for rare diseases. This may include tax credits toward the cost of clinical trials, prescription drug user fee waivers, and 7 years of market exclusivity if the product is approved.