User login
The VA, California, and NYC requiring employee vaccinations
-- or, in the case of California and New York City, undergo regular testing.
The VA becomes the first federal agency to mandate COVID vaccinations for workers. In a news release, VA Secretary Denis McDonough said the mandate is “the best way to keep Veterans safe, especially as the Delta variant spreads across the country.”
VA health care personnel -- including doctors, dentists, podiatrists, optometrists, registered nurses, physician assistants, and chiropractors -- have 8 weeks to become fully vaccinated, the news release said. The New York Times reported that about 115,000 workers will be affected.
The trifecta of federal-state-municipal vaccine requirements arrived as the nation searches for ways to get more people vaccinated to tamp down the Delta variant.
Some organizations, including the military, have already said vaccinations will be required as soon as the Food and Drug Administration formally approves the vaccines, which are now given under emergency use authorizations. The FDA has said the Pfizer vaccine could receive full approval within months.
California Gov. Gavin Newsom said the requirements he announced July 27 were the first in the nation on the state level.
“As the state’s largest employer, we are leading by example and requiring all state and health care workers to show proof of vaccination or be tested regularly, and we are encouraging local governments and businesses to do the same,” he said in a news release.
California employees must provide proof of vaccination or get tested at least once a week. The policy starts Aug. 2 for state employees and Aug. 9 for state health care workers and employees of congregate facilities, such as jails or homeless shelters.
California, especially the southern part of the state, is grappling with a COVID-19 surge. The state’s daily case rate more than quadrupled, from a low of 1.9 cases per 100,000 in May to at least 9.5 cases per 100,000 today, the release said.
In New York City, Mayor Bill de Blasio had previously announced that city health and hospital employees and those working in Department of Health and Mental Hygiene clinical settings would be required to provide proof of vaccination or have regular testing.
On July 27 he expanded the rule to cover all city employees, with a Sept. 13 deadline for most of them, according to a news release.
“This is what it takes to continue our recovery for all of us while fighting back the Delta variant,” Mayor de Blasio said. “It’s going to take all of us to finally end the fight against COVID-19.”
“We have a moral responsibility to take every precaution possible to ensure we keep ourselves, our colleagues and loved ones safe,” NYC Health + Hospitals President and CEO Mitchell Katz, MD, said in the release. “Our city’s new testing requirement for city workers provides more [peace] of mind until more people get their safe and effective COVID-19 vaccine.”
NBC News reported the plan would affect about 340,000 employees.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
-- or, in the case of California and New York City, undergo regular testing.
The VA becomes the first federal agency to mandate COVID vaccinations for workers. In a news release, VA Secretary Denis McDonough said the mandate is “the best way to keep Veterans safe, especially as the Delta variant spreads across the country.”
VA health care personnel -- including doctors, dentists, podiatrists, optometrists, registered nurses, physician assistants, and chiropractors -- have 8 weeks to become fully vaccinated, the news release said. The New York Times reported that about 115,000 workers will be affected.
The trifecta of federal-state-municipal vaccine requirements arrived as the nation searches for ways to get more people vaccinated to tamp down the Delta variant.
Some organizations, including the military, have already said vaccinations will be required as soon as the Food and Drug Administration formally approves the vaccines, which are now given under emergency use authorizations. The FDA has said the Pfizer vaccine could receive full approval within months.
California Gov. Gavin Newsom said the requirements he announced July 27 were the first in the nation on the state level.
“As the state’s largest employer, we are leading by example and requiring all state and health care workers to show proof of vaccination or be tested regularly, and we are encouraging local governments and businesses to do the same,” he said in a news release.
California employees must provide proof of vaccination or get tested at least once a week. The policy starts Aug. 2 for state employees and Aug. 9 for state health care workers and employees of congregate facilities, such as jails or homeless shelters.
California, especially the southern part of the state, is grappling with a COVID-19 surge. The state’s daily case rate more than quadrupled, from a low of 1.9 cases per 100,000 in May to at least 9.5 cases per 100,000 today, the release said.
In New York City, Mayor Bill de Blasio had previously announced that city health and hospital employees and those working in Department of Health and Mental Hygiene clinical settings would be required to provide proof of vaccination or have regular testing.
On July 27 he expanded the rule to cover all city employees, with a Sept. 13 deadline for most of them, according to a news release.
“This is what it takes to continue our recovery for all of us while fighting back the Delta variant,” Mayor de Blasio said. “It’s going to take all of us to finally end the fight against COVID-19.”
“We have a moral responsibility to take every precaution possible to ensure we keep ourselves, our colleagues and loved ones safe,” NYC Health + Hospitals President and CEO Mitchell Katz, MD, said in the release. “Our city’s new testing requirement for city workers provides more [peace] of mind until more people get their safe and effective COVID-19 vaccine.”
NBC News reported the plan would affect about 340,000 employees.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
-- or, in the case of California and New York City, undergo regular testing.
The VA becomes the first federal agency to mandate COVID vaccinations for workers. In a news release, VA Secretary Denis McDonough said the mandate is “the best way to keep Veterans safe, especially as the Delta variant spreads across the country.”
VA health care personnel -- including doctors, dentists, podiatrists, optometrists, registered nurses, physician assistants, and chiropractors -- have 8 weeks to become fully vaccinated, the news release said. The New York Times reported that about 115,000 workers will be affected.
The trifecta of federal-state-municipal vaccine requirements arrived as the nation searches for ways to get more people vaccinated to tamp down the Delta variant.
Some organizations, including the military, have already said vaccinations will be required as soon as the Food and Drug Administration formally approves the vaccines, which are now given under emergency use authorizations. The FDA has said the Pfizer vaccine could receive full approval within months.
California Gov. Gavin Newsom said the requirements he announced July 27 were the first in the nation on the state level.
“As the state’s largest employer, we are leading by example and requiring all state and health care workers to show proof of vaccination or be tested regularly, and we are encouraging local governments and businesses to do the same,” he said in a news release.
California employees must provide proof of vaccination or get tested at least once a week. The policy starts Aug. 2 for state employees and Aug. 9 for state health care workers and employees of congregate facilities, such as jails or homeless shelters.
California, especially the southern part of the state, is grappling with a COVID-19 surge. The state’s daily case rate more than quadrupled, from a low of 1.9 cases per 100,000 in May to at least 9.5 cases per 100,000 today, the release said.
In New York City, Mayor Bill de Blasio had previously announced that city health and hospital employees and those working in Department of Health and Mental Hygiene clinical settings would be required to provide proof of vaccination or have regular testing.
On July 27 he expanded the rule to cover all city employees, with a Sept. 13 deadline for most of them, according to a news release.
“This is what it takes to continue our recovery for all of us while fighting back the Delta variant,” Mayor de Blasio said. “It’s going to take all of us to finally end the fight against COVID-19.”
“We have a moral responsibility to take every precaution possible to ensure we keep ourselves, our colleagues and loved ones safe,” NYC Health + Hospitals President and CEO Mitchell Katz, MD, said in the release. “Our city’s new testing requirement for city workers provides more [peace] of mind until more people get their safe and effective COVID-19 vaccine.”
NBC News reported the plan would affect about 340,000 employees.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Children and COVID: Vaccinations, new cases both rising
COVID-19 vaccine initiations rose in U.S. children for the second consecutive week, but new pediatric cases jumped by 64% in just 1 week, according to new data.
the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
“After decreases in weekly reported cases over the past couple of months, in July we have seen steady increases in cases added to the cumulative total,” the AAP noted. In this latest reversal of COVID fortunes, the steady increase in new cases is in its fourth consecutive week since hitting a low of 8,447 in late June.
As of July 22, the total number of reported cases was over 4.12 million in 49 states, the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, and there have been 349 deaths in children in the 46 jurisdictions reporting age distributions of COVID-19 deaths, the AAP and CHA said in their report.
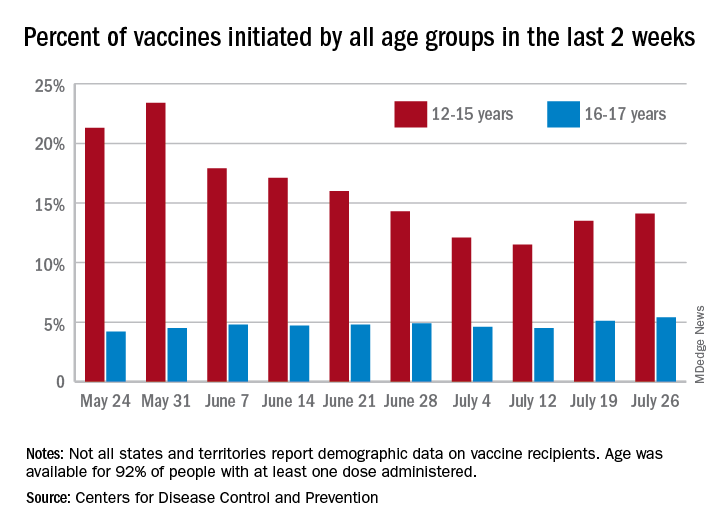
Meanwhile, over 9.3 million children received at least one dose of COVID vaccine as of July 26, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Vaccine initiation rose for the second week in a row after falling for several weeks as 301,000 children aged 12-15 years and almost 115,000 children aged 16-17 got their first dose during the week ending July 26. Children aged 12-15 represented 14.1% (up from 13.5% a week before) of all first vaccinations and 16- to 17-year-olds were 5.4% (up from 5.1%) of all vaccine initiators, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
Just over 37% of all 12- to 15-year-olds have received at least one dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine since the CDC approved its use for children under age 16 in May, and almost 28% are fully vaccinated. Use in children aged 16-17 started earlier (December 2020), and 48% of that age group have received a first dose and over 39% have completed the vaccine regimen, the CDC said.
COVID-19 vaccine initiations rose in U.S. children for the second consecutive week, but new pediatric cases jumped by 64% in just 1 week, according to new data.

the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
“After decreases in weekly reported cases over the past couple of months, in July we have seen steady increases in cases added to the cumulative total,” the AAP noted. In this latest reversal of COVID fortunes, the steady increase in new cases is in its fourth consecutive week since hitting a low of 8,447 in late June.
As of July 22, the total number of reported cases was over 4.12 million in 49 states, the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, and there have been 349 deaths in children in the 46 jurisdictions reporting age distributions of COVID-19 deaths, the AAP and CHA said in their report.
Meanwhile, over 9.3 million children received at least one dose of COVID vaccine as of July 26, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Vaccine initiation rose for the second week in a row after falling for several weeks as 301,000 children aged 12-15 years and almost 115,000 children aged 16-17 got their first dose during the week ending July 26. Children aged 12-15 represented 14.1% (up from 13.5% a week before) of all first vaccinations and 16- to 17-year-olds were 5.4% (up from 5.1%) of all vaccine initiators, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
Just over 37% of all 12- to 15-year-olds have received at least one dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine since the CDC approved its use for children under age 16 in May, and almost 28% are fully vaccinated. Use in children aged 16-17 started earlier (December 2020), and 48% of that age group have received a first dose and over 39% have completed the vaccine regimen, the CDC said.
COVID-19 vaccine initiations rose in U.S. children for the second consecutive week, but new pediatric cases jumped by 64% in just 1 week, according to new data.

the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
“After decreases in weekly reported cases over the past couple of months, in July we have seen steady increases in cases added to the cumulative total,” the AAP noted. In this latest reversal of COVID fortunes, the steady increase in new cases is in its fourth consecutive week since hitting a low of 8,447 in late June.
As of July 22, the total number of reported cases was over 4.12 million in 49 states, the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, and there have been 349 deaths in children in the 46 jurisdictions reporting age distributions of COVID-19 deaths, the AAP and CHA said in their report.
Meanwhile, over 9.3 million children received at least one dose of COVID vaccine as of July 26, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Vaccine initiation rose for the second week in a row after falling for several weeks as 301,000 children aged 12-15 years and almost 115,000 children aged 16-17 got their first dose during the week ending July 26. Children aged 12-15 represented 14.1% (up from 13.5% a week before) of all first vaccinations and 16- to 17-year-olds were 5.4% (up from 5.1%) of all vaccine initiators, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
Just over 37% of all 12- to 15-year-olds have received at least one dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine since the CDC approved its use for children under age 16 in May, and almost 28% are fully vaccinated. Use in children aged 16-17 started earlier (December 2020), and 48% of that age group have received a first dose and over 39% have completed the vaccine regimen, the CDC said.
Accelerated surgery for hip fracture did not lower risk of mortality or major complications
Background: Patients diagnosed with a hip fracture are at substantial risk of major complications and mortality. Observational studies have suggested that accelerated surgery for a hip fracture is associated with lower risk of mortality and major complications.
Study design: International, randomized, controlled trial (RCT).
Setting: 69 hospitals in 17 countries.
Synopsis: This RCT enrolled 2,970 patients with a hip fracture, aged 45 years and older. The median time from hip fracture diagnosis to surgery was 6 h in the accelerated surgery group (n = 1,487) and 24 h in the standard-care group (n = 1,483). A total of 140 (9%) patients assigned to accelerated surgery and 154 (10%) assigned to standard care died at 90 days after randomization (P = .40). Composite of major complications (mortality, nonfatal MI, stroke, venous thromboembolism, sepsis, pneumonia, life-threatening bleeding, and major bleeding) occurred in 321 (22%) patients assigned to accelerated surgery and 331 (22%) assigned to standard care at 90 days after randomization (p = .71). However, accelerated surgery was associated with lower risk of delirium, urinary tract infection, andmoderate to severe pain and resulted in faster mobilization and shorter length of stay.
Practical limitations include the additional resources needed for an accelerated surgical pathway such as staffing and operating room time. Furthermore, this study included only patients diagnosed during regular working hours.
Bottom line: Among patients with a hip fracture, accelerated surgery did not lower the risk of the coprimary outcomes of mortality or a composite of major complications at 90 days compared with standard care.
Citation: Borges F et al. Accelerated surgery versus standard care in hip fracture (HIP ATTACK): An international, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet. 2020 Feb 29; 395(10225), 698-708.
Dr. Miller is assistant professor of medicine, section of hospital medicine, at the University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville.
Background: Patients diagnosed with a hip fracture are at substantial risk of major complications and mortality. Observational studies have suggested that accelerated surgery for a hip fracture is associated with lower risk of mortality and major complications.
Study design: International, randomized, controlled trial (RCT).
Setting: 69 hospitals in 17 countries.
Synopsis: This RCT enrolled 2,970 patients with a hip fracture, aged 45 years and older. The median time from hip fracture diagnosis to surgery was 6 h in the accelerated surgery group (n = 1,487) and 24 h in the standard-care group (n = 1,483). A total of 140 (9%) patients assigned to accelerated surgery and 154 (10%) assigned to standard care died at 90 days after randomization (P = .40). Composite of major complications (mortality, nonfatal MI, stroke, venous thromboembolism, sepsis, pneumonia, life-threatening bleeding, and major bleeding) occurred in 321 (22%) patients assigned to accelerated surgery and 331 (22%) assigned to standard care at 90 days after randomization (p = .71). However, accelerated surgery was associated with lower risk of delirium, urinary tract infection, andmoderate to severe pain and resulted in faster mobilization and shorter length of stay.
Practical limitations include the additional resources needed for an accelerated surgical pathway such as staffing and operating room time. Furthermore, this study included only patients diagnosed during regular working hours.
Bottom line: Among patients with a hip fracture, accelerated surgery did not lower the risk of the coprimary outcomes of mortality or a composite of major complications at 90 days compared with standard care.
Citation: Borges F et al. Accelerated surgery versus standard care in hip fracture (HIP ATTACK): An international, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet. 2020 Feb 29; 395(10225), 698-708.
Dr. Miller is assistant professor of medicine, section of hospital medicine, at the University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville.
Background: Patients diagnosed with a hip fracture are at substantial risk of major complications and mortality. Observational studies have suggested that accelerated surgery for a hip fracture is associated with lower risk of mortality and major complications.
Study design: International, randomized, controlled trial (RCT).
Setting: 69 hospitals in 17 countries.
Synopsis: This RCT enrolled 2,970 patients with a hip fracture, aged 45 years and older. The median time from hip fracture diagnosis to surgery was 6 h in the accelerated surgery group (n = 1,487) and 24 h in the standard-care group (n = 1,483). A total of 140 (9%) patients assigned to accelerated surgery and 154 (10%) assigned to standard care died at 90 days after randomization (P = .40). Composite of major complications (mortality, nonfatal MI, stroke, venous thromboembolism, sepsis, pneumonia, life-threatening bleeding, and major bleeding) occurred in 321 (22%) patients assigned to accelerated surgery and 331 (22%) assigned to standard care at 90 days after randomization (p = .71). However, accelerated surgery was associated with lower risk of delirium, urinary tract infection, andmoderate to severe pain and resulted in faster mobilization and shorter length of stay.
Practical limitations include the additional resources needed for an accelerated surgical pathway such as staffing and operating room time. Furthermore, this study included only patients diagnosed during regular working hours.
Bottom line: Among patients with a hip fracture, accelerated surgery did not lower the risk of the coprimary outcomes of mortality or a composite of major complications at 90 days compared with standard care.
Citation: Borges F et al. Accelerated surgery versus standard care in hip fracture (HIP ATTACK): An international, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet. 2020 Feb 29; 395(10225), 698-708.
Dr. Miller is assistant professor of medicine, section of hospital medicine, at the University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville.
Direct oral anticoagulants: Competition brought no cost relief
Medicare Part D spending for oral anticoagulants has risen by almost 1,600% since 2011, while the number of users has increased by just 95%, according to a new study.
In 2011, the year after the first direct oral anticoagulant (DOACs) was approved, Medicare Part D spent $0.44 billion on all oral anticoagulants. By 2019, when there a total of four DOACs on the market, spending was $7.38 billion, an increase of 1,577%, Aaron Troy, MD, MPH, and Timothy S. Anderson, MD, MAS, said in JAMA Health Forum.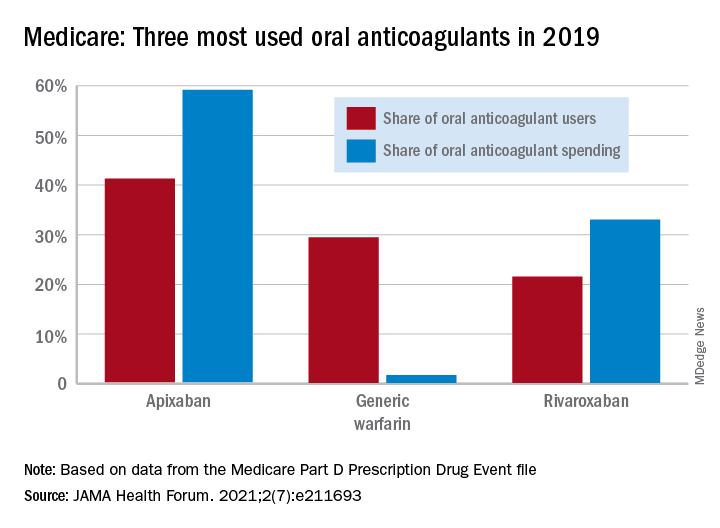
Over that same time, the number of beneficiaries using oral anticoagulants went from 2.68 million to 5.24 million, they said, based on data from the Medicare Part D Prescription Drug Event file.
“While higher prices for novel therapeutics like DOACs, which offer clear benefits, such as decreased drug-drug interactions and improved persistence, may partly reflect value and help drive innovation, the patterns and effects of spending on novel medications still merit attention,” they noted.
One pattern of use looked like this: 0.2 million Medicare beneficiaries took DOACs in 2011,compared with 3.5 million in 2019, while the number of warfarin users dropped from 2.48 million to 1.74 million, the investigators reported.
As for spending over the study period, the cost to treat one beneficiary with atrial fibrillation increased by 9.3% each year for apixaban (a DOAC that was the most popular oral anticoagulant in 2019), decreased 27.6% per year for generic warfarin, and increased 9.5% per year for rivaroxaban, said Dr. Troy and Dr. Anderson of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston.
Rising Part D enrollment had an effect on spending growth, as did increased use of oral anticoagulants in general. The introduction of competing DOACs, however, “did not substantially curb annual spending increases, suggesting a lack of price competition, which is consistent with trends observed in other therapeutic categories,” they wrote.
Dr. Anderson has received research grants from the National Institute on Aging and the American College of Cardiology outside of this study and honoraria from Alosa Health. No other disclosures were reported.
Medicare Part D spending for oral anticoagulants has risen by almost 1,600% since 2011, while the number of users has increased by just 95%, according to a new study.
In 2011, the year after the first direct oral anticoagulant (DOACs) was approved, Medicare Part D spent $0.44 billion on all oral anticoagulants. By 2019, when there a total of four DOACs on the market, spending was $7.38 billion, an increase of 1,577%, Aaron Troy, MD, MPH, and Timothy S. Anderson, MD, MAS, said in JAMA Health Forum.
Over that same time, the number of beneficiaries using oral anticoagulants went from 2.68 million to 5.24 million, they said, based on data from the Medicare Part D Prescription Drug Event file.
“While higher prices for novel therapeutics like DOACs, which offer clear benefits, such as decreased drug-drug interactions and improved persistence, may partly reflect value and help drive innovation, the patterns and effects of spending on novel medications still merit attention,” they noted.
One pattern of use looked like this: 0.2 million Medicare beneficiaries took DOACs in 2011,compared with 3.5 million in 2019, while the number of warfarin users dropped from 2.48 million to 1.74 million, the investigators reported.
As for spending over the study period, the cost to treat one beneficiary with atrial fibrillation increased by 9.3% each year for apixaban (a DOAC that was the most popular oral anticoagulant in 2019), decreased 27.6% per year for generic warfarin, and increased 9.5% per year for rivaroxaban, said Dr. Troy and Dr. Anderson of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston.
Rising Part D enrollment had an effect on spending growth, as did increased use of oral anticoagulants in general. The introduction of competing DOACs, however, “did not substantially curb annual spending increases, suggesting a lack of price competition, which is consistent with trends observed in other therapeutic categories,” they wrote.
Dr. Anderson has received research grants from the National Institute on Aging and the American College of Cardiology outside of this study and honoraria from Alosa Health. No other disclosures were reported.
Medicare Part D spending for oral anticoagulants has risen by almost 1,600% since 2011, while the number of users has increased by just 95%, according to a new study.
In 2011, the year after the first direct oral anticoagulant (DOACs) was approved, Medicare Part D spent $0.44 billion on all oral anticoagulants. By 2019, when there a total of four DOACs on the market, spending was $7.38 billion, an increase of 1,577%, Aaron Troy, MD, MPH, and Timothy S. Anderson, MD, MAS, said in JAMA Health Forum.
Over that same time, the number of beneficiaries using oral anticoagulants went from 2.68 million to 5.24 million, they said, based on data from the Medicare Part D Prescription Drug Event file.
“While higher prices for novel therapeutics like DOACs, which offer clear benefits, such as decreased drug-drug interactions and improved persistence, may partly reflect value and help drive innovation, the patterns and effects of spending on novel medications still merit attention,” they noted.
One pattern of use looked like this: 0.2 million Medicare beneficiaries took DOACs in 2011,compared with 3.5 million in 2019, while the number of warfarin users dropped from 2.48 million to 1.74 million, the investigators reported.
As for spending over the study period, the cost to treat one beneficiary with atrial fibrillation increased by 9.3% each year for apixaban (a DOAC that was the most popular oral anticoagulant in 2019), decreased 27.6% per year for generic warfarin, and increased 9.5% per year for rivaroxaban, said Dr. Troy and Dr. Anderson of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston.
Rising Part D enrollment had an effect on spending growth, as did increased use of oral anticoagulants in general. The introduction of competing DOACs, however, “did not substantially curb annual spending increases, suggesting a lack of price competition, which is consistent with trends observed in other therapeutic categories,” they wrote.
Dr. Anderson has received research grants from the National Institute on Aging and the American College of Cardiology outside of this study and honoraria from Alosa Health. No other disclosures were reported.
FROM JAMA HEALTH FORUM
C. Diff eradication not necessary for clinical cure of recurrent infections with fecal transplant
It’s not necessary to completely eradicate all Clostridioides difficile to successfully treat recurrent C. difficile infections with fecal microbiota transplant (FMT), according to a study presented online July 12 at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases.
C. difficile colonization persisted for 3 weeks after FMT in about one-quarter of patients, but it’s not clear whether this is a persistent infection, a newly acquired infection, or partial persistence of a mixed infection, said Elisabeth Terveer, MD, a medical microbiologist at Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center. In addition, “82% of patients with detectable C. diff do not relapse, so it’s absolutely not necessary for a cure,” she said.
Several mechanisms explain why FMT is a highly effective therapy for recurrent C. difficile infections, including restoration of bacterial metabolism in the gut, immune modulation, and direct competition between bacteria, Dr. Terveer said, but it’s less clear whether eradication of C. difficile spores is among these mechanisms.
Between May 2016 and April 2020, the researchers analyzed fecal samples from 84 patients who took vancomycin for at least 4 days before undergoing FMT. The researchers took fecal samples from patients before FMT and 3 weeks after FMT to culture them and the donor samples for presence of C. difficile, and they assessed clinical outcomes at 3 weeks and 6 months after FMT.
After antibiotic treatment but prior to FMT, 19% of patients (n = 16) still had a toxigenic C. difficile culture while the other 81% had a negative culture. None of the donor samples had a positive C. difficile culture. After FMT treatment, five patients who had a positive pre-FMT culture remained positive, and the other 11 were negative. Among the 81% of patients (n = 68) who had a negative culture just before FMT, 22 had a positive culture and 46 had a negative culture after FMT. Overall, 26% of patients post FMT had a positive C. difficile culture, a finding that was 10-fold higher than another study that assessed C. difficile with PCR testing, Dr. Terveer said.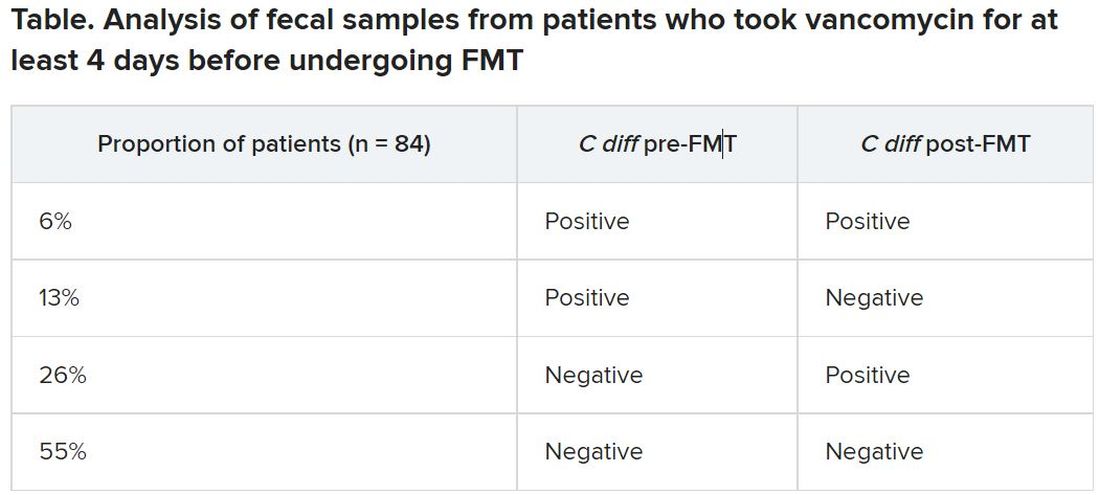
The clinical cure rate after FMT was 94%, and five patients had relapses within 2 months of their FMT. These relapses were more prevalent in patients with a positive C. difficile culture prior to FMT (odds ratio [OR], 7.6; P = .045) and a positive C. difficile culture after FMT (OR, 13.6; P = .016). Still, 82% of patients who had a positive C. difficile culture post FMT remained clinically cured 2 months later.
It’s unclear why 19% of patients had a positive culture after their antibiotic pretreatment prior to FMT, Dr. Terveer said, but it may be because the pretreatment was of such a short duration.
“I think the advice should be: Give a full anti–C. diff antibiotic course to treat the C. diff infection, and then give FMT afterward to restore the microbiota and prevent further relapses,” Dr. Terveer told attendees.
Dimitri Drekonja, MD, chief of the Minneapolis VA Infectious Disease Section, said the findings were not necessarily surprising, but it would have been interesting for the researchers to have conducted DNA sequencing of the patients’ fecal samples post FMT to see what the biological diversity looked like.
“One school of thought has been that you have to repopulate the normal diverse microbiota of the colon” with FMT, and the other “is that you need to get rid of the C. diff that›s there,” Dr. Drekonja, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview. “I think more people think it’s the diverse microbiota because if it’s just getting rid of C. diff, we can get do that with antibiotics – but that gets rid of the other organisms.”
As long as you have a diverse microbiota post FMT, Dr. Drekonja said, then “having a few residual organisms, even if they get magnified in the culture process, is probably not that big a deal.”
But there’s a third school of thought that Dr. Drekonja said he himself falls into: “I don’t really care how it works, just that in well-done trials, it does work.” As long as large, robust, well-blinded trials show that FMT works, “I’m open to all sorts of ideas of what the mechanism is,” he said. “The main thing is that it does or doesn’t work.”
These findings basically reinforce current guidance not to test patients’ stools if they are asymptomatic, Dr. Drekonja said. In the past, clinicians sometimes tested patients’ stool after therapy to ensure the C. difficile was eradicated, regardless of whether the patient had symptoms of infection, he said.
“We’ve since become much more attuned that there are lots of people who have detectable C. diff in their stool without any symptoms,” whether detectable by culture or PCR, Dr. Drekonja said. “Generally, if you’re doing well and you’re not having diarrhea, don’t test, and if someone does test and finds it, pretend you didn’t see the test,” he advised. “This is a big part of diagnostic stewardship, which is: You don’t go testing people who are doing well.”
The Netherlands Donor Feces Bank used in the research is funded by a grant from Vedanta Biosciences. Dr. Drekonja had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s not necessary to completely eradicate all Clostridioides difficile to successfully treat recurrent C. difficile infections with fecal microbiota transplant (FMT), according to a study presented online July 12 at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases.
C. difficile colonization persisted for 3 weeks after FMT in about one-quarter of patients, but it’s not clear whether this is a persistent infection, a newly acquired infection, or partial persistence of a mixed infection, said Elisabeth Terveer, MD, a medical microbiologist at Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center. In addition, “82% of patients with detectable C. diff do not relapse, so it’s absolutely not necessary for a cure,” she said.
Several mechanisms explain why FMT is a highly effective therapy for recurrent C. difficile infections, including restoration of bacterial metabolism in the gut, immune modulation, and direct competition between bacteria, Dr. Terveer said, but it’s less clear whether eradication of C. difficile spores is among these mechanisms.
Between May 2016 and April 2020, the researchers analyzed fecal samples from 84 patients who took vancomycin for at least 4 days before undergoing FMT. The researchers took fecal samples from patients before FMT and 3 weeks after FMT to culture them and the donor samples for presence of C. difficile, and they assessed clinical outcomes at 3 weeks and 6 months after FMT.
After antibiotic treatment but prior to FMT, 19% of patients (n = 16) still had a toxigenic C. difficile culture while the other 81% had a negative culture. None of the donor samples had a positive C. difficile culture. After FMT treatment, five patients who had a positive pre-FMT culture remained positive, and the other 11 were negative. Among the 81% of patients (n = 68) who had a negative culture just before FMT, 22 had a positive culture and 46 had a negative culture after FMT. Overall, 26% of patients post FMT had a positive C. difficile culture, a finding that was 10-fold higher than another study that assessed C. difficile with PCR testing, Dr. Terveer said.
The clinical cure rate after FMT was 94%, and five patients had relapses within 2 months of their FMT. These relapses were more prevalent in patients with a positive C. difficile culture prior to FMT (odds ratio [OR], 7.6; P = .045) and a positive C. difficile culture after FMT (OR, 13.6; P = .016). Still, 82% of patients who had a positive C. difficile culture post FMT remained clinically cured 2 months later.
It’s unclear why 19% of patients had a positive culture after their antibiotic pretreatment prior to FMT, Dr. Terveer said, but it may be because the pretreatment was of such a short duration.
“I think the advice should be: Give a full anti–C. diff antibiotic course to treat the C. diff infection, and then give FMT afterward to restore the microbiota and prevent further relapses,” Dr. Terveer told attendees.
Dimitri Drekonja, MD, chief of the Minneapolis VA Infectious Disease Section, said the findings were not necessarily surprising, but it would have been interesting for the researchers to have conducted DNA sequencing of the patients’ fecal samples post FMT to see what the biological diversity looked like.
“One school of thought has been that you have to repopulate the normal diverse microbiota of the colon” with FMT, and the other “is that you need to get rid of the C. diff that›s there,” Dr. Drekonja, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview. “I think more people think it’s the diverse microbiota because if it’s just getting rid of C. diff, we can get do that with antibiotics – but that gets rid of the other organisms.”
As long as you have a diverse microbiota post FMT, Dr. Drekonja said, then “having a few residual organisms, even if they get magnified in the culture process, is probably not that big a deal.”
But there’s a third school of thought that Dr. Drekonja said he himself falls into: “I don’t really care how it works, just that in well-done trials, it does work.” As long as large, robust, well-blinded trials show that FMT works, “I’m open to all sorts of ideas of what the mechanism is,” he said. “The main thing is that it does or doesn’t work.”
These findings basically reinforce current guidance not to test patients’ stools if they are asymptomatic, Dr. Drekonja said. In the past, clinicians sometimes tested patients’ stool after therapy to ensure the C. difficile was eradicated, regardless of whether the patient had symptoms of infection, he said.
“We’ve since become much more attuned that there are lots of people who have detectable C. diff in their stool without any symptoms,” whether detectable by culture or PCR, Dr. Drekonja said. “Generally, if you’re doing well and you’re not having diarrhea, don’t test, and if someone does test and finds it, pretend you didn’t see the test,” he advised. “This is a big part of diagnostic stewardship, which is: You don’t go testing people who are doing well.”
The Netherlands Donor Feces Bank used in the research is funded by a grant from Vedanta Biosciences. Dr. Drekonja had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s not necessary to completely eradicate all Clostridioides difficile to successfully treat recurrent C. difficile infections with fecal microbiota transplant (FMT), according to a study presented online July 12 at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases.
C. difficile colonization persisted for 3 weeks after FMT in about one-quarter of patients, but it’s not clear whether this is a persistent infection, a newly acquired infection, or partial persistence of a mixed infection, said Elisabeth Terveer, MD, a medical microbiologist at Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center. In addition, “82% of patients with detectable C. diff do not relapse, so it’s absolutely not necessary for a cure,” she said.
Several mechanisms explain why FMT is a highly effective therapy for recurrent C. difficile infections, including restoration of bacterial metabolism in the gut, immune modulation, and direct competition between bacteria, Dr. Terveer said, but it’s less clear whether eradication of C. difficile spores is among these mechanisms.
Between May 2016 and April 2020, the researchers analyzed fecal samples from 84 patients who took vancomycin for at least 4 days before undergoing FMT. The researchers took fecal samples from patients before FMT and 3 weeks after FMT to culture them and the donor samples for presence of C. difficile, and they assessed clinical outcomes at 3 weeks and 6 months after FMT.
After antibiotic treatment but prior to FMT, 19% of patients (n = 16) still had a toxigenic C. difficile culture while the other 81% had a negative culture. None of the donor samples had a positive C. difficile culture. After FMT treatment, five patients who had a positive pre-FMT culture remained positive, and the other 11 were negative. Among the 81% of patients (n = 68) who had a negative culture just before FMT, 22 had a positive culture and 46 had a negative culture after FMT. Overall, 26% of patients post FMT had a positive C. difficile culture, a finding that was 10-fold higher than another study that assessed C. difficile with PCR testing, Dr. Terveer said.
The clinical cure rate after FMT was 94%, and five patients had relapses within 2 months of their FMT. These relapses were more prevalent in patients with a positive C. difficile culture prior to FMT (odds ratio [OR], 7.6; P = .045) and a positive C. difficile culture after FMT (OR, 13.6; P = .016). Still, 82% of patients who had a positive C. difficile culture post FMT remained clinically cured 2 months later.
It’s unclear why 19% of patients had a positive culture after their antibiotic pretreatment prior to FMT, Dr. Terveer said, but it may be because the pretreatment was of such a short duration.
“I think the advice should be: Give a full anti–C. diff antibiotic course to treat the C. diff infection, and then give FMT afterward to restore the microbiota and prevent further relapses,” Dr. Terveer told attendees.
Dimitri Drekonja, MD, chief of the Minneapolis VA Infectious Disease Section, said the findings were not necessarily surprising, but it would have been interesting for the researchers to have conducted DNA sequencing of the patients’ fecal samples post FMT to see what the biological diversity looked like.
“One school of thought has been that you have to repopulate the normal diverse microbiota of the colon” with FMT, and the other “is that you need to get rid of the C. diff that›s there,” Dr. Drekonja, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview. “I think more people think it’s the diverse microbiota because if it’s just getting rid of C. diff, we can get do that with antibiotics – but that gets rid of the other organisms.”
As long as you have a diverse microbiota post FMT, Dr. Drekonja said, then “having a few residual organisms, even if they get magnified in the culture process, is probably not that big a deal.”
But there’s a third school of thought that Dr. Drekonja said he himself falls into: “I don’t really care how it works, just that in well-done trials, it does work.” As long as large, robust, well-blinded trials show that FMT works, “I’m open to all sorts of ideas of what the mechanism is,” he said. “The main thing is that it does or doesn’t work.”
These findings basically reinforce current guidance not to test patients’ stools if they are asymptomatic, Dr. Drekonja said. In the past, clinicians sometimes tested patients’ stool after therapy to ensure the C. difficile was eradicated, regardless of whether the patient had symptoms of infection, he said.
“We’ve since become much more attuned that there are lots of people who have detectable C. diff in their stool without any symptoms,” whether detectable by culture or PCR, Dr. Drekonja said. “Generally, if you’re doing well and you’re not having diarrhea, don’t test, and if someone does test and finds it, pretend you didn’t see the test,” he advised. “This is a big part of diagnostic stewardship, which is: You don’t go testing people who are doing well.”
The Netherlands Donor Feces Bank used in the research is funded by a grant from Vedanta Biosciences. Dr. Drekonja had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AMA, 55 other groups urge health care vax mandate
As COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths mount again across the country, the American Medical Association (AMA), the American Nursing Association, and 54 other
This injunction, issued July 26, covers everyone in healthcare, Emanuel Ezekiel, MD, PhD, chair of the department of medical ethics and health policy at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and the organizer of the joint statement, said in an interview.
That includes not only hospitals, but also physician offices, ambulatory surgery centers, home care agencies, skilled nursing facilities, pharmacies, laboratories, and imaging centers, he said.
The exhortation to get vaccinated also extends to federal and state healthcare facilities, including those of the military health system — TRICARE and the Department of Veterans Affairs — which instituted a mandate the same day.
The American Hospital Association (AHA) and other hospital groups recently said they supported hospitals and health systems that required their personnel to get vaccinated. Several dozen healthcare organizations have already done so, including some of the nation’s largest health systems.
A substantial fraction of U.S. healthcare workers have not yet gotten vaccinated, although how many are unvaccinated is unclear. An analysis by WebMD and Medscape Medical News estimated that 25% of hospital workers who had contact with patients were unvaccinated at the end of May.
More than 38% of nursing workers were not fully vaccinated by July 11, according to an analysis of Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services data by LeadingAge, which was cited by the Washington Post. And more than 40% of nursing home employees have not been fully vaccinated, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The joint statement did not give any indication of how many employees of physician practices have failed to get COVID shots. However, a recent AMA survey shows that 96% of physicians have been fully vaccinated.
Ethical commitment
The main reason for vaccine mandates, according to the healthcare associations’ statement, is “the ethical commitment to put patients as well as residents of long-term care facilities first and take all steps necessary to ensure their health and well-being.”
In addition, the statement noted, vaccination can protect healthcare workers and their families from getting COVID-19.
The statement also pointed out that many healthcare and long-term care organizations already require vaccinations for influenza, hepatitis B, and pertussis.
Workers who have certain medical conditions should be exempt from the vaccination mandates, the statement added.
While recognizing the “historical mistrust of health care institutions” among some healthcare workers, the statement said, “We must continue to address workers’ concerns, engage with marginalized populations, and work with trusted messengers to improve vaccine acceptance.”
There has been some skepticism about the legality of requiring healthcare workers to get vaccinated as a condition of employment, partly because the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has not yet fully authorized any of the COVID-19 vaccines.
But in June, a federal judge turned down a legal challenge to Houston Methodist’s vaccination mandate.
“It is critical that all people in the health care workforce get vaccinated against COVID-19 for the safety of our patients and our colleagues. With more than 300 million doses administered in the United States and nearly 4 billion doses administered worldwide, we know the vaccines are safe and highly effective at preventing severe illness and death from COVID-19.
“Increased vaccinations among health care personnel will not only reduce the spread of COVID-19 but also reduce the harmful toll this virus is taking within the health care workforce and those we are striving to serve,” Susan Bailey, MD, immediate past president of the AMA, said in a news release.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths mount again across the country, the American Medical Association (AMA), the American Nursing Association, and 54 other
This injunction, issued July 26, covers everyone in healthcare, Emanuel Ezekiel, MD, PhD, chair of the department of medical ethics and health policy at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and the organizer of the joint statement, said in an interview.
That includes not only hospitals, but also physician offices, ambulatory surgery centers, home care agencies, skilled nursing facilities, pharmacies, laboratories, and imaging centers, he said.
The exhortation to get vaccinated also extends to federal and state healthcare facilities, including those of the military health system — TRICARE and the Department of Veterans Affairs — which instituted a mandate the same day.
The American Hospital Association (AHA) and other hospital groups recently said they supported hospitals and health systems that required their personnel to get vaccinated. Several dozen healthcare organizations have already done so, including some of the nation’s largest health systems.
A substantial fraction of U.S. healthcare workers have not yet gotten vaccinated, although how many are unvaccinated is unclear. An analysis by WebMD and Medscape Medical News estimated that 25% of hospital workers who had contact with patients were unvaccinated at the end of May.
More than 38% of nursing workers were not fully vaccinated by July 11, according to an analysis of Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services data by LeadingAge, which was cited by the Washington Post. And more than 40% of nursing home employees have not been fully vaccinated, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The joint statement did not give any indication of how many employees of physician practices have failed to get COVID shots. However, a recent AMA survey shows that 96% of physicians have been fully vaccinated.
Ethical commitment
The main reason for vaccine mandates, according to the healthcare associations’ statement, is “the ethical commitment to put patients as well as residents of long-term care facilities first and take all steps necessary to ensure their health and well-being.”
In addition, the statement noted, vaccination can protect healthcare workers and their families from getting COVID-19.
The statement also pointed out that many healthcare and long-term care organizations already require vaccinations for influenza, hepatitis B, and pertussis.
Workers who have certain medical conditions should be exempt from the vaccination mandates, the statement added.
While recognizing the “historical mistrust of health care institutions” among some healthcare workers, the statement said, “We must continue to address workers’ concerns, engage with marginalized populations, and work with trusted messengers to improve vaccine acceptance.”
There has been some skepticism about the legality of requiring healthcare workers to get vaccinated as a condition of employment, partly because the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has not yet fully authorized any of the COVID-19 vaccines.
But in June, a federal judge turned down a legal challenge to Houston Methodist’s vaccination mandate.
“It is critical that all people in the health care workforce get vaccinated against COVID-19 for the safety of our patients and our colleagues. With more than 300 million doses administered in the United States and nearly 4 billion doses administered worldwide, we know the vaccines are safe and highly effective at preventing severe illness and death from COVID-19.
“Increased vaccinations among health care personnel will not only reduce the spread of COVID-19 but also reduce the harmful toll this virus is taking within the health care workforce and those we are striving to serve,” Susan Bailey, MD, immediate past president of the AMA, said in a news release.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths mount again across the country, the American Medical Association (AMA), the American Nursing Association, and 54 other
This injunction, issued July 26, covers everyone in healthcare, Emanuel Ezekiel, MD, PhD, chair of the department of medical ethics and health policy at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and the organizer of the joint statement, said in an interview.
That includes not only hospitals, but also physician offices, ambulatory surgery centers, home care agencies, skilled nursing facilities, pharmacies, laboratories, and imaging centers, he said.
The exhortation to get vaccinated also extends to federal and state healthcare facilities, including those of the military health system — TRICARE and the Department of Veterans Affairs — which instituted a mandate the same day.
The American Hospital Association (AHA) and other hospital groups recently said they supported hospitals and health systems that required their personnel to get vaccinated. Several dozen healthcare organizations have already done so, including some of the nation’s largest health systems.
A substantial fraction of U.S. healthcare workers have not yet gotten vaccinated, although how many are unvaccinated is unclear. An analysis by WebMD and Medscape Medical News estimated that 25% of hospital workers who had contact with patients were unvaccinated at the end of May.
More than 38% of nursing workers were not fully vaccinated by July 11, according to an analysis of Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services data by LeadingAge, which was cited by the Washington Post. And more than 40% of nursing home employees have not been fully vaccinated, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The joint statement did not give any indication of how many employees of physician practices have failed to get COVID shots. However, a recent AMA survey shows that 96% of physicians have been fully vaccinated.
Ethical commitment
The main reason for vaccine mandates, according to the healthcare associations’ statement, is “the ethical commitment to put patients as well as residents of long-term care facilities first and take all steps necessary to ensure their health and well-being.”
In addition, the statement noted, vaccination can protect healthcare workers and their families from getting COVID-19.
The statement also pointed out that many healthcare and long-term care organizations already require vaccinations for influenza, hepatitis B, and pertussis.
Workers who have certain medical conditions should be exempt from the vaccination mandates, the statement added.
While recognizing the “historical mistrust of health care institutions” among some healthcare workers, the statement said, “We must continue to address workers’ concerns, engage with marginalized populations, and work with trusted messengers to improve vaccine acceptance.”
There has been some skepticism about the legality of requiring healthcare workers to get vaccinated as a condition of employment, partly because the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has not yet fully authorized any of the COVID-19 vaccines.
But in June, a federal judge turned down a legal challenge to Houston Methodist’s vaccination mandate.
“It is critical that all people in the health care workforce get vaccinated against COVID-19 for the safety of our patients and our colleagues. With more than 300 million doses administered in the United States and nearly 4 billion doses administered worldwide, we know the vaccines are safe and highly effective at preventing severe illness and death from COVID-19.
“Increased vaccinations among health care personnel will not only reduce the spread of COVID-19 but also reduce the harmful toll this virus is taking within the health care workforce and those we are striving to serve,” Susan Bailey, MD, immediate past president of the AMA, said in a news release.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Vaccine breakthrough cases rising with Delta: Here’s what that means
At a recent town hall meeting in Cincinnati, President Joe Biden was asked about COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths rising in response to the Delta variant.
Touting the importance of vaccination, “We have a pandemic for those who haven’t gotten a vaccination. It’s that basic, that simple,” President Biden said at the event, which was broadcast live on CNN.
“If you’re vaccinated, you’re not going to be hospitalized, not going to the ICU unit, and not going to die,” he said, adding “you’re not going to get COVID if you have these vaccinations.”
Unfortunately, it’s not so simple. Fully vaccinated people continue to be well protected against severe disease and death, even with Delta, Because of that, many experts continue to advise caution, even if fully vaccinated.
“I was disappointed,” Leana Wen, MD, MSc, an emergency physician and visiting professor of health policy and management at George Washington University’s Milken School of Public Health in Washington, told CNN in response to the president’s statement.
“I actually thought he was answering questions as if it were a month ago. He’s not really meeting the realities of what’s happening on the ground,” she said. “I think he may have led people astray.”
Vaccines still work
Recent cases support Dr. Wen’s claim. Fully vaccinated Olympic athletes, wedding guests, healthcare workers, and even White House staff have recently tested positive. So what gives?
The vast majority of these illnesses are mild, and public health officials say they are to be expected.
“The vaccines were designed to keep us out of the hospital and to keep us from dying. That was the whole purpose of the vaccine and they’re even more successful than we anticipated,” says William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert at Vanderbilt University in Nashville.
As good as they are, these shots aren’t perfect. Their protection differs from person to person depending on age and underlying health. People with immune function that’s weakened because of age or a health condition can still become seriously ill, and, in very rare cases, die after vaccination.
When people are infected with Delta, they carry approximately 1,000 times more virus compared with previous versions of the virus, according to a recent study. All that virus can overwhelm even the strong protection from the vaccines.
“Three months ago, breakthroughs didn’t occur nearly at this rate because there was just so much less virus exposure in the community,” said Michael Osterholm, PhD, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota in Minneapolis.
Breakthroughs by the numbers
In Los Angeles County, where 69% of residents over age 12 have been fully vaccinated, COVID-19 cases are rising, and so, too, are cases that break through the protection of the vaccine.
In June, fully vaccinated people accounted for 20%, or 1 in 5, COVID cases in the county, which is the most populous in the United States. The increase mirrors Delta’s rise. The proportion of breakthrough cases is up from 11% in May, 5% in April, and 2% in March, according to the Los Angeles County Department of Public Health.
In the United Kingdom, which is collecting the best information on infections caused by variants, the estimated effectiveness of the vaccines to prevent an illness that causes symptoms dropped by about 10 points against Delta compared with Alpha (or B.1.1.7).
After two doses, vaccines prevent symptomatic infection about 79% of the time against Delta, according to data compiled by Public Health England. They are still highly effective at preventing hospitalization, 96% after two doses.
Out of 229,218 COVID infections in the United Kingdom between February and July 19, 28,773 — or 12.5% — were in fully vaccinated people. Of those breakthrough infections, 1,101, or 3.8%, required a visit to an emergency room, according to Public Health England. Just 474, or 2.9%, of fully vaccinated people required hospital admission, and 229, or less than 1%, died.
Unanswered questions
One of the biggest questions about breakthrough cases is how often people who have it may pass the virus to others.
“We know the vaccine reduces the likelihood of carrying the virus and the amount of virus you would carry,” Dr. Wen told CNN. But we don’t yet know whether a vaccinated person with a breakthrough infection may still be contagious to others.
For that reason, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says that fully vaccinated people still need to be tested if they have symptoms and shouldn’t be out in public for at least 10 days after a positive test.
How should fully vaccinated people behave? That depends a lot on their underlying health and whether or not they have vulnerable people around them.
If you’re older or immunocompromised, Dr. Schaffner recommends what he calls the “belt-and-suspenders approach,” in other words, do everything you can to stay safe.
“Get vaccinated for sure, but since we can’t be absolutely certain that the vaccines are going to be optimally protective and you are particularly susceptible to serious disease, you would be well advised to adopt at least one and perhaps more of the other mitigation measures,” he said.
These include wearing a mask, social distancing, making sure your spaces are well ventilated, and not spending prolonged periods of time indoors in crowded places.
Taking young children to visit vaccinated, elderly grandparents demands extra caution, again, with Delta circulating, particularly as they go back to school and start mixing with other kids.
Dr. Schaffner recommends explaining the ground rules before the visit: Hugs around the waist. No kissing. Wearing a mask while indoors with them.
Other important unanswered questions are whether breakthrough infections can lead to prolonged symptoms, or “long covid.” Most experts think that’s less likely in vaccinated people.
And Dr. Osterholm said it will be important to see whether there’s anything unusual about the breakthrough cases happening in the community.
“I think some of us have been challenged by the number of clusters that we’ve seen,” he said. “I think that really needs to be examined more.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
At a recent town hall meeting in Cincinnati, President Joe Biden was asked about COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths rising in response to the Delta variant.
Touting the importance of vaccination, “We have a pandemic for those who haven’t gotten a vaccination. It’s that basic, that simple,” President Biden said at the event, which was broadcast live on CNN.
“If you’re vaccinated, you’re not going to be hospitalized, not going to the ICU unit, and not going to die,” he said, adding “you’re not going to get COVID if you have these vaccinations.”
Unfortunately, it’s not so simple. Fully vaccinated people continue to be well protected against severe disease and death, even with Delta, Because of that, many experts continue to advise caution, even if fully vaccinated.
“I was disappointed,” Leana Wen, MD, MSc, an emergency physician and visiting professor of health policy and management at George Washington University’s Milken School of Public Health in Washington, told CNN in response to the president’s statement.
“I actually thought he was answering questions as if it were a month ago. He’s not really meeting the realities of what’s happening on the ground,” she said. “I think he may have led people astray.”
Vaccines still work
Recent cases support Dr. Wen’s claim. Fully vaccinated Olympic athletes, wedding guests, healthcare workers, and even White House staff have recently tested positive. So what gives?
The vast majority of these illnesses are mild, and public health officials say they are to be expected.
“The vaccines were designed to keep us out of the hospital and to keep us from dying. That was the whole purpose of the vaccine and they’re even more successful than we anticipated,” says William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert at Vanderbilt University in Nashville.
As good as they are, these shots aren’t perfect. Their protection differs from person to person depending on age and underlying health. People with immune function that’s weakened because of age or a health condition can still become seriously ill, and, in very rare cases, die after vaccination.
When people are infected with Delta, they carry approximately 1,000 times more virus compared with previous versions of the virus, according to a recent study. All that virus can overwhelm even the strong protection from the vaccines.
“Three months ago, breakthroughs didn’t occur nearly at this rate because there was just so much less virus exposure in the community,” said Michael Osterholm, PhD, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota in Minneapolis.
Breakthroughs by the numbers
In Los Angeles County, where 69% of residents over age 12 have been fully vaccinated, COVID-19 cases are rising, and so, too, are cases that break through the protection of the vaccine.
In June, fully vaccinated people accounted for 20%, or 1 in 5, COVID cases in the county, which is the most populous in the United States. The increase mirrors Delta’s rise. The proportion of breakthrough cases is up from 11% in May, 5% in April, and 2% in March, according to the Los Angeles County Department of Public Health.
In the United Kingdom, which is collecting the best information on infections caused by variants, the estimated effectiveness of the vaccines to prevent an illness that causes symptoms dropped by about 10 points against Delta compared with Alpha (or B.1.1.7).
After two doses, vaccines prevent symptomatic infection about 79% of the time against Delta, according to data compiled by Public Health England. They are still highly effective at preventing hospitalization, 96% after two doses.
Out of 229,218 COVID infections in the United Kingdom between February and July 19, 28,773 — or 12.5% — were in fully vaccinated people. Of those breakthrough infections, 1,101, or 3.8%, required a visit to an emergency room, according to Public Health England. Just 474, or 2.9%, of fully vaccinated people required hospital admission, and 229, or less than 1%, died.
Unanswered questions
One of the biggest questions about breakthrough cases is how often people who have it may pass the virus to others.
“We know the vaccine reduces the likelihood of carrying the virus and the amount of virus you would carry,” Dr. Wen told CNN. But we don’t yet know whether a vaccinated person with a breakthrough infection may still be contagious to others.
For that reason, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says that fully vaccinated people still need to be tested if they have symptoms and shouldn’t be out in public for at least 10 days after a positive test.
How should fully vaccinated people behave? That depends a lot on their underlying health and whether or not they have vulnerable people around them.
If you’re older or immunocompromised, Dr. Schaffner recommends what he calls the “belt-and-suspenders approach,” in other words, do everything you can to stay safe.
“Get vaccinated for sure, but since we can’t be absolutely certain that the vaccines are going to be optimally protective and you are particularly susceptible to serious disease, you would be well advised to adopt at least one and perhaps more of the other mitigation measures,” he said.
These include wearing a mask, social distancing, making sure your spaces are well ventilated, and not spending prolonged periods of time indoors in crowded places.
Taking young children to visit vaccinated, elderly grandparents demands extra caution, again, with Delta circulating, particularly as they go back to school and start mixing with other kids.
Dr. Schaffner recommends explaining the ground rules before the visit: Hugs around the waist. No kissing. Wearing a mask while indoors with them.
Other important unanswered questions are whether breakthrough infections can lead to prolonged symptoms, or “long covid.” Most experts think that’s less likely in vaccinated people.
And Dr. Osterholm said it will be important to see whether there’s anything unusual about the breakthrough cases happening in the community.
“I think some of us have been challenged by the number of clusters that we’ve seen,” he said. “I think that really needs to be examined more.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
At a recent town hall meeting in Cincinnati, President Joe Biden was asked about COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths rising in response to the Delta variant.
Touting the importance of vaccination, “We have a pandemic for those who haven’t gotten a vaccination. It’s that basic, that simple,” President Biden said at the event, which was broadcast live on CNN.
“If you’re vaccinated, you’re not going to be hospitalized, not going to the ICU unit, and not going to die,” he said, adding “you’re not going to get COVID if you have these vaccinations.”
Unfortunately, it’s not so simple. Fully vaccinated people continue to be well protected against severe disease and death, even with Delta, Because of that, many experts continue to advise caution, even if fully vaccinated.
“I was disappointed,” Leana Wen, MD, MSc, an emergency physician and visiting professor of health policy and management at George Washington University’s Milken School of Public Health in Washington, told CNN in response to the president’s statement.
“I actually thought he was answering questions as if it were a month ago. He’s not really meeting the realities of what’s happening on the ground,” she said. “I think he may have led people astray.”
Vaccines still work
Recent cases support Dr. Wen’s claim. Fully vaccinated Olympic athletes, wedding guests, healthcare workers, and even White House staff have recently tested positive. So what gives?
The vast majority of these illnesses are mild, and public health officials say they are to be expected.
“The vaccines were designed to keep us out of the hospital and to keep us from dying. That was the whole purpose of the vaccine and they’re even more successful than we anticipated,” says William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert at Vanderbilt University in Nashville.
As good as they are, these shots aren’t perfect. Their protection differs from person to person depending on age and underlying health. People with immune function that’s weakened because of age or a health condition can still become seriously ill, and, in very rare cases, die after vaccination.
When people are infected with Delta, they carry approximately 1,000 times more virus compared with previous versions of the virus, according to a recent study. All that virus can overwhelm even the strong protection from the vaccines.
“Three months ago, breakthroughs didn’t occur nearly at this rate because there was just so much less virus exposure in the community,” said Michael Osterholm, PhD, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota in Minneapolis.
Breakthroughs by the numbers
In Los Angeles County, where 69% of residents over age 12 have been fully vaccinated, COVID-19 cases are rising, and so, too, are cases that break through the protection of the vaccine.
In June, fully vaccinated people accounted for 20%, or 1 in 5, COVID cases in the county, which is the most populous in the United States. The increase mirrors Delta’s rise. The proportion of breakthrough cases is up from 11% in May, 5% in April, and 2% in March, according to the Los Angeles County Department of Public Health.
In the United Kingdom, which is collecting the best information on infections caused by variants, the estimated effectiveness of the vaccines to prevent an illness that causes symptoms dropped by about 10 points against Delta compared with Alpha (or B.1.1.7).
After two doses, vaccines prevent symptomatic infection about 79% of the time against Delta, according to data compiled by Public Health England. They are still highly effective at preventing hospitalization, 96% after two doses.
Out of 229,218 COVID infections in the United Kingdom between February and July 19, 28,773 — or 12.5% — were in fully vaccinated people. Of those breakthrough infections, 1,101, or 3.8%, required a visit to an emergency room, according to Public Health England. Just 474, or 2.9%, of fully vaccinated people required hospital admission, and 229, or less than 1%, died.
Unanswered questions
One of the biggest questions about breakthrough cases is how often people who have it may pass the virus to others.
“We know the vaccine reduces the likelihood of carrying the virus and the amount of virus you would carry,” Dr. Wen told CNN. But we don’t yet know whether a vaccinated person with a breakthrough infection may still be contagious to others.
For that reason, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says that fully vaccinated people still need to be tested if they have symptoms and shouldn’t be out in public for at least 10 days after a positive test.
How should fully vaccinated people behave? That depends a lot on their underlying health and whether or not they have vulnerable people around them.
If you’re older or immunocompromised, Dr. Schaffner recommends what he calls the “belt-and-suspenders approach,” in other words, do everything you can to stay safe.
“Get vaccinated for sure, but since we can’t be absolutely certain that the vaccines are going to be optimally protective and you are particularly susceptible to serious disease, you would be well advised to adopt at least one and perhaps more of the other mitigation measures,” he said.
These include wearing a mask, social distancing, making sure your spaces are well ventilated, and not spending prolonged periods of time indoors in crowded places.
Taking young children to visit vaccinated, elderly grandparents demands extra caution, again, with Delta circulating, particularly as they go back to school and start mixing with other kids.
Dr. Schaffner recommends explaining the ground rules before the visit: Hugs around the waist. No kissing. Wearing a mask while indoors with them.
Other important unanswered questions are whether breakthrough infections can lead to prolonged symptoms, or “long covid.” Most experts think that’s less likely in vaccinated people.
And Dr. Osterholm said it will be important to see whether there’s anything unusual about the breakthrough cases happening in the community.
“I think some of us have been challenged by the number of clusters that we’ve seen,” he said. “I think that really needs to be examined more.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Antibiotic prophylaxis to prevent spontaneous bacterial peritonitis may not be effective
Background: Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis is common and is associated with significant short-term mortality. Antibiotic prophylaxis is the mainstay preventive treatment, but there is concern about development of drug resistance and other adverse events. There is uncertainty regarding relative efficacy and optimal combination of the different available prophylactic treatments.
Study design: 29 randomized clinical trials.
Synopsis: Across 29 randomized clinical trials (total of 3,896 participants) looking at nine different antibiotic regimens for prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, there was no evidence of differences between any of the antibiotics and no intervention in terms of mortality or serious adverse events, though there was very low certainty of evidence. The authors felt only two small studies were conducted without flaws. There was no difference between any of the antibiotics and no intervention in the proportion of people who developed spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Overall, 10% of trial participants developed spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and 15% of trial participants died. The lack of effectiveness of across several outcomes may be because of sparse data and selective reporting bias.
Bottom line: Whether antibiotics are effective prophylaxis to prevent spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and which antibiotics should be used is still uncertain; future well-designed studies are needed.
Citation: Komolafe O et al. Antibiotic prophylaxis to prevent spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in people with liver cirrhosis: A network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 16;1:CD013125. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013125.pub2.
Dr. Millard is assistant professor of medicine, section of hospital medicine, at the University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville.
Background: Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis is common and is associated with significant short-term mortality. Antibiotic prophylaxis is the mainstay preventive treatment, but there is concern about development of drug resistance and other adverse events. There is uncertainty regarding relative efficacy and optimal combination of the different available prophylactic treatments.
Study design: 29 randomized clinical trials.
Synopsis: Across 29 randomized clinical trials (total of 3,896 participants) looking at nine different antibiotic regimens for prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, there was no evidence of differences between any of the antibiotics and no intervention in terms of mortality or serious adverse events, though there was very low certainty of evidence. The authors felt only two small studies were conducted without flaws. There was no difference between any of the antibiotics and no intervention in the proportion of people who developed spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Overall, 10% of trial participants developed spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and 15% of trial participants died. The lack of effectiveness of across several outcomes may be because of sparse data and selective reporting bias.
Bottom line: Whether antibiotics are effective prophylaxis to prevent spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and which antibiotics should be used is still uncertain; future well-designed studies are needed.
Citation: Komolafe O et al. Antibiotic prophylaxis to prevent spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in people with liver cirrhosis: A network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 16;1:CD013125. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013125.pub2.
Dr. Millard is assistant professor of medicine, section of hospital medicine, at the University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville.
Background: Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis is common and is associated with significant short-term mortality. Antibiotic prophylaxis is the mainstay preventive treatment, but there is concern about development of drug resistance and other adverse events. There is uncertainty regarding relative efficacy and optimal combination of the different available prophylactic treatments.
Study design: 29 randomized clinical trials.
Synopsis: Across 29 randomized clinical trials (total of 3,896 participants) looking at nine different antibiotic regimens for prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, there was no evidence of differences between any of the antibiotics and no intervention in terms of mortality or serious adverse events, though there was very low certainty of evidence. The authors felt only two small studies were conducted without flaws. There was no difference between any of the antibiotics and no intervention in the proportion of people who developed spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Overall, 10% of trial participants developed spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and 15% of trial participants died. The lack of effectiveness of across several outcomes may be because of sparse data and selective reporting bias.
Bottom line: Whether antibiotics are effective prophylaxis to prevent spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and which antibiotics should be used is still uncertain; future well-designed studies are needed.
Citation: Komolafe O et al. Antibiotic prophylaxis to prevent spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in people with liver cirrhosis: A network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 16;1:CD013125. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013125.pub2.
Dr. Millard is assistant professor of medicine, section of hospital medicine, at the University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville.
Aspirin efficacious and safe for VTE prophylaxis in total hip and knee replacement
Background: Most patients undergoing total hip replacement (THR) and total knee replacement (TKR) require anticoagulant therapy to reduce venous thromboembolism (VTE) risk. Compared with injectable low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH), warfarin, and newer oral agents, aspirin is easily administered, inexpensive, and well tolerated and requires no monitoring. There are observational data to support aspirin as VTE prophylaxis after THR and TKR. However, high-quality randomized, clinical trials (RCT) in favor of aspirin have been limited. Recently, a large RCT (n = 3,224) that compared aspirin to rivaroxaban after THR and TKR has been published that supports aspirin use for VTE prophylaxis.
Study design: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Setting: Seven studies from North America, four from Asia, and two from Europe.
Synopsis: In a meta-analysis comprising 13 RCT including 6,060 participants (2,969 aspirin and 3,091 comparator), there was no statistically significant difference in the risk of venous thromboembolism (including deep-vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism) when comparing aspirin with other anticoagulants (LMWH, rivaroxaban) in patients undergoing THR and TKR. Also, there were no differences in the risk of adverse events, such as bleeding, wound complications, MI, and death, when aspirin was compared with other anticoagulants.
This systematic review and meta-analysis included trials from around the world, including the most recent and largest in this area. However, because of the heterogeneity and high risk of bias encountered in most RCTs included in this analysis, additional large, well-designed RCTs are needed to validate findings of this review.
Bottom line: Findings of the current meta-analysis support the use of aspirin for VTE prophylaxis after THR and TKR, in line with the 2012 recommendations of the American College of Chest Physicians.
Citation: Matharu GS et al. Clinical effectiveness and safety of aspirin for venous thromboembolism prophylaxis after total hip and knee replacement. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 Feb 3;180(3):376-84.
Dr. Mehta is assistant professor of medicine, section of hospital medicine, at the University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville.
Background: Most patients undergoing total hip replacement (THR) and total knee replacement (TKR) require anticoagulant therapy to reduce venous thromboembolism (VTE) risk. Compared with injectable low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH), warfarin, and newer oral agents, aspirin is easily administered, inexpensive, and well tolerated and requires no monitoring. There are observational data to support aspirin as VTE prophylaxis after THR and TKR. However, high-quality randomized, clinical trials (RCT) in favor of aspirin have been limited. Recently, a large RCT (n = 3,224) that compared aspirin to rivaroxaban after THR and TKR has been published that supports aspirin use for VTE prophylaxis.
Study design: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Setting: Seven studies from North America, four from Asia, and two from Europe.
Synopsis: In a meta-analysis comprising 13 RCT including 6,060 participants (2,969 aspirin and 3,091 comparator), there was no statistically significant difference in the risk of venous thromboembolism (including deep-vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism) when comparing aspirin with other anticoagulants (LMWH, rivaroxaban) in patients undergoing THR and TKR. Also, there were no differences in the risk of adverse events, such as bleeding, wound complications, MI, and death, when aspirin was compared with other anticoagulants.
This systematic review and meta-analysis included trials from around the world, including the most recent and largest in this area. However, because of the heterogeneity and high risk of bias encountered in most RCTs included in this analysis, additional large, well-designed RCTs are needed to validate findings of this review.
Bottom line: Findings of the current meta-analysis support the use of aspirin for VTE prophylaxis after THR and TKR, in line with the 2012 recommendations of the American College of Chest Physicians.
Citation: Matharu GS et al. Clinical effectiveness and safety of aspirin for venous thromboembolism prophylaxis after total hip and knee replacement. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 Feb 3;180(3):376-84.
Dr. Mehta is assistant professor of medicine, section of hospital medicine, at the University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville.
Background: Most patients undergoing total hip replacement (THR) and total knee replacement (TKR) require anticoagulant therapy to reduce venous thromboembolism (VTE) risk. Compared with injectable low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH), warfarin, and newer oral agents, aspirin is easily administered, inexpensive, and well tolerated and requires no monitoring. There are observational data to support aspirin as VTE prophylaxis after THR and TKR. However, high-quality randomized, clinical trials (RCT) in favor of aspirin have been limited. Recently, a large RCT (n = 3,224) that compared aspirin to rivaroxaban after THR and TKR has been published that supports aspirin use for VTE prophylaxis.
Study design: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Setting: Seven studies from North America, four from Asia, and two from Europe.
Synopsis: In a meta-analysis comprising 13 RCT including 6,060 participants (2,969 aspirin and 3,091 comparator), there was no statistically significant difference in the risk of venous thromboembolism (including deep-vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism) when comparing aspirin with other anticoagulants (LMWH, rivaroxaban) in patients undergoing THR and TKR. Also, there were no differences in the risk of adverse events, such as bleeding, wound complications, MI, and death, when aspirin was compared with other anticoagulants.
This systematic review and meta-analysis included trials from around the world, including the most recent and largest in this area. However, because of the heterogeneity and high risk of bias encountered in most RCTs included in this analysis, additional large, well-designed RCTs are needed to validate findings of this review.
Bottom line: Findings of the current meta-analysis support the use of aspirin for VTE prophylaxis after THR and TKR, in line with the 2012 recommendations of the American College of Chest Physicians.
Citation: Matharu GS et al. Clinical effectiveness and safety of aspirin for venous thromboembolism prophylaxis after total hip and knee replacement. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 Feb 3;180(3):376-84.
Dr. Mehta is assistant professor of medicine, section of hospital medicine, at the University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville.
CDC panel updates info on rare side effect after J&J vaccine
Despite recent reports of Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) after the Johnson & Johnson vaccine,
The company also presented new data suggesting that the shots generate strong immune responses against circulating variants and that antibodies generated by the vaccine stay elevated for at least 8 months.
Members of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) did not vote, but discussed and affirmed their support for recent decisions by the Food and Drug Administration and CDC to update patient information about the very low risk of GBS that appears to be associated with the vaccine, but to continue offering the vaccine to people in the United States.
The Johnson & Johnson shot has been a minor player in the U.S. vaccination campaign, accounting for less than 4% of all vaccine doses given in this country. Still, the single-dose inoculation, which doesn’t require ultra-cold storage, has been important for reaching people in rural areas, through mobile clinics, at colleges and primary care offices, and in vulnerable populations – those who are incarcerated or homeless.
The FDA says it has received reports of 100 cases of GBS after the Johnson & Johnson vaccine in its Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System database through the end of June. The cases are still under investigation.
To date, more than 12 million doses of the vaccine have been administered, making the rate of GBS 8.1 cases for every million doses administered.
Although it is still extremely rare, that’s above the expected background rate of GBS of 1.6 cases for every million people, said Grace Lee, MD, a Stanford, Calif., pediatrician who chairs the ACIP’s Vaccine Safety Technical Work Group.
So far, most GBS cases (61%) have been among men. The midpoint age of the cases was 57 years. The average time to onset was 14 days, and 98% of cases occurred within 42 days of the shot. Facial paralysis has been associated with an estimated 30%-50% of cases. One person, who had heart failure, high blood pressure, and diabetes, has died.
Still, the benefits of the vaccine far outweigh its risks. For every million doses given to people over age 50, the vaccine prevents nearly 7,500 COVID-19 hospitalizations and nearly 100 deaths in women, and more than 13,000 COVID-19 hospitalizations and more than 2,400 deaths in men.
Rates of GBS after the mRNA vaccines made by Pfizer and Moderna were around 1 case for every 1 million doses given, which is not above the rate that would be expected without vaccination.
The link to the Johnson & Johnson vaccine prompted the FDA to add a warning to the vaccine’s patient safety information on July 12.
Also in July, the European Medicines Agency recommended a similar warning for the product information of the AstraZeneca vaccine Vaxzevria, which relies on similar technology.
Good against variants
Johnson & Johnson also presented new information showing its vaccine maintained high levels of neutralizing antibodies against four of the so-called “variants of concern” – Alpha, Gamma, Beta, and Delta. The protection generated by the vaccine lasted for at least 8 months after the shot, the company said.
“We’re still learning about the duration of protection and the breadth of coverage against this evolving variant landscape for each of the authorized vaccines,” said Mathai Mammen, MD, PhD, global head of research and development at Janssen, the company that makes the vaccine for J&J.
The company also said that its vaccine generated very strong T-cell responses. T cells destroy infected cells and, along with antibodies, are an important part of the body’s immune response.
Antibody levels and T-cell responses are markers for immunity. Measuring these levels isn’t the same as proving that shots can fend off an infection.
It’s still unclear exactly which component of the immune response is most important for fighting off COVID-19.
Dr. Mammen said the companies are still gathering that clinical data, and would present it soon.
“We will have a better view of the clinical efficacy in the coming weeks,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Despite recent reports of Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) after the Johnson & Johnson vaccine,
The company also presented new data suggesting that the shots generate strong immune responses against circulating variants and that antibodies generated by the vaccine stay elevated for at least 8 months.
Members of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) did not vote, but discussed and affirmed their support for recent decisions by the Food and Drug Administration and CDC to update patient information about the very low risk of GBS that appears to be associated with the vaccine, but to continue offering the vaccine to people in the United States.
The Johnson & Johnson shot has been a minor player in the U.S. vaccination campaign, accounting for less than 4% of all vaccine doses given in this country. Still, the single-dose inoculation, which doesn’t require ultra-cold storage, has been important for reaching people in rural areas, through mobile clinics, at colleges and primary care offices, and in vulnerable populations – those who are incarcerated or homeless.
The FDA says it has received reports of 100 cases of GBS after the Johnson & Johnson vaccine in its Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System database through the end of June. The cases are still under investigation.
To date, more than 12 million doses of the vaccine have been administered, making the rate of GBS 8.1 cases for every million doses administered.
Although it is still extremely rare, that’s above the expected background rate of GBS of 1.6 cases for every million people, said Grace Lee, MD, a Stanford, Calif., pediatrician who chairs the ACIP’s Vaccine Safety Technical Work Group.
So far, most GBS cases (61%) have been among men. The midpoint age of the cases was 57 years. The average time to onset was 14 days, and 98% of cases occurred within 42 days of the shot. Facial paralysis has been associated with an estimated 30%-50% of cases. One person, who had heart failure, high blood pressure, and diabetes, has died.
Still, the benefits of the vaccine far outweigh its risks. For every million doses given to people over age 50, the vaccine prevents nearly 7,500 COVID-19 hospitalizations and nearly 100 deaths in women, and more than 13,000 COVID-19 hospitalizations and more than 2,400 deaths in men.
Rates of GBS after the mRNA vaccines made by Pfizer and Moderna were around 1 case for every 1 million doses given, which is not above the rate that would be expected without vaccination.
The link to the Johnson & Johnson vaccine prompted the FDA to add a warning to the vaccine’s patient safety information on July 12.
Also in July, the European Medicines Agency recommended a similar warning for the product information of the AstraZeneca vaccine Vaxzevria, which relies on similar technology.
Good against variants
Johnson & Johnson also presented new information showing its vaccine maintained high levels of neutralizing antibodies against four of the so-called “variants of concern” – Alpha, Gamma, Beta, and Delta. The protection generated by the vaccine lasted for at least 8 months after the shot, the company said.
“We’re still learning about the duration of protection and the breadth of coverage against this evolving variant landscape for each of the authorized vaccines,” said Mathai Mammen, MD, PhD, global head of research and development at Janssen, the company that makes the vaccine for J&J.
The company also said that its vaccine generated very strong T-cell responses. T cells destroy infected cells and, along with antibodies, are an important part of the body’s immune response.
Antibody levels and T-cell responses are markers for immunity. Measuring these levels isn’t the same as proving that shots can fend off an infection.
It’s still unclear exactly which component of the immune response is most important for fighting off COVID-19.
Dr. Mammen said the companies are still gathering that clinical data, and would present it soon.
“We will have a better view of the clinical efficacy in the coming weeks,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Despite recent reports of Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) after the Johnson & Johnson vaccine,
The company also presented new data suggesting that the shots generate strong immune responses against circulating variants and that antibodies generated by the vaccine stay elevated for at least 8 months.
Members of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) did not vote, but discussed and affirmed their support for recent decisions by the Food and Drug Administration and CDC to update patient information about the very low risk of GBS that appears to be associated with the vaccine, but to continue offering the vaccine to people in the United States.
The Johnson & Johnson shot has been a minor player in the U.S. vaccination campaign, accounting for less than 4% of all vaccine doses given in this country. Still, the single-dose inoculation, which doesn’t require ultra-cold storage, has been important for reaching people in rural areas, through mobile clinics, at colleges and primary care offices, and in vulnerable populations – those who are incarcerated or homeless.
The FDA says it has received reports of 100 cases of GBS after the Johnson & Johnson vaccine in its Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System database through the end of June. The cases are still under investigation.
To date, more than 12 million doses of the vaccine have been administered, making the rate of GBS 8.1 cases for every million doses administered.
Although it is still extremely rare, that’s above the expected background rate of GBS of 1.6 cases for every million people, said Grace Lee, MD, a Stanford, Calif., pediatrician who chairs the ACIP’s Vaccine Safety Technical Work Group.
So far, most GBS cases (61%) have been among men. The midpoint age of the cases was 57 years. The average time to onset was 14 days, and 98% of cases occurred within 42 days of the shot. Facial paralysis has been associated with an estimated 30%-50% of cases. One person, who had heart failure, high blood pressure, and diabetes, has died.
Still, the benefits of the vaccine far outweigh its risks. For every million doses given to people over age 50, the vaccine prevents nearly 7,500 COVID-19 hospitalizations and nearly 100 deaths in women, and more than 13,000 COVID-19 hospitalizations and more than 2,400 deaths in men.
Rates of GBS after the mRNA vaccines made by Pfizer and Moderna were around 1 case for every 1 million doses given, which is not above the rate that would be expected without vaccination.
The link to the Johnson & Johnson vaccine prompted the FDA to add a warning to the vaccine’s patient safety information on July 12.
Also in July, the European Medicines Agency recommended a similar warning for the product information of the AstraZeneca vaccine Vaxzevria, which relies on similar technology.
Good against variants
Johnson & Johnson also presented new information showing its vaccine maintained high levels of neutralizing antibodies against four of the so-called “variants of concern” – Alpha, Gamma, Beta, and Delta. The protection generated by the vaccine lasted for at least 8 months after the shot, the company said.
“We’re still learning about the duration of protection and the breadth of coverage against this evolving variant landscape for each of the authorized vaccines,” said Mathai Mammen, MD, PhD, global head of research and development at Janssen, the company that makes the vaccine for J&J.
The company also said that its vaccine generated very strong T-cell responses. T cells destroy infected cells and, along with antibodies, are an important part of the body’s immune response.
Antibody levels and T-cell responses are markers for immunity. Measuring these levels isn’t the same as proving that shots can fend off an infection.
It’s still unclear exactly which component of the immune response is most important for fighting off COVID-19.
Dr. Mammen said the companies are still gathering that clinical data, and would present it soon.
“We will have a better view of the clinical efficacy in the coming weeks,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.