User login
ColCORONA: More questions than answers for colchicine in COVID-19
Science by press release and preprint has cooled clinician enthusiasm for the use of colchicine in nonhospitalized patients with COVID-19, despite a pressing need for early treatments.
As previously reported by this news organization, a Jan. 22 press release announced that the massive ColCORONA study missed its primary endpoint of hospitalization or death among 4,488 newly diagnosed patients at increased risk for hospitalization.
But it also touted that use of the anti-inflammatory drug significantly reduced the primary endpoint in 4,159 of those patients with polymerase chain reaction–confirmed COVID and led to reductions of 25%, 50%, and 44%, respectively, for hospitalizations, ventilations, and death.
Lead investigator Jean-Claude Tardif, MD, director of the Montreal Heart Institute Research Centre, deemed the findings a “medical breakthrough.”
When the preprint released a few days later, however, newly revealed confidence intervals showed colchicine did not meaningfully reduce the need for mechanical ventilation (odds ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.23-1.07) or death alone (OR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.19-1.66).
Further, the significant benefit on the primary outcome came at the cost of a fivefold increase in pulmonary embolism (11 vs. 2; P = .01), which was not mentioned in the press release.
“Whether this represents a real phenomenon or simply the play of chance is not known,” Dr. Tardif and colleagues noted later in the preprint.
“I read the preprint on colchicine and I have so many questions,” Aaron E. Glatt, MD, spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America and chief of infectious diseases, Mount Sinai South Nassau, Hewlett, N.Y., said in an interview. “I’ve been burned too many times with COVID and prefer to see better data.
“People sometimes say if you wait for perfect data, people are going to die,” he said. “Yeah, but we have no idea if people are going to die from getting this drug more than not getting it. That’s what concerns me. How many pulmonary emboli are going to be fatal versus the slight benefit that the study showed?”
The pushback to the non–peer-reviewed data on social media and via emails was so strong that Dr. Tardif posted a nearly 2,000-word letter responding to the many questions at play.
Chief among them was why the trial, originally planned for 6,000 patients, was stopped early by the investigators without consultation with the data safety monitoring board (DSMB).
The explanation in the letter that logistical issues like running the study call center, budget constraints, and a perceived need to quickly communicate the results left some calling foul that the study wasn’t allowed to finish and come to a more definitive conclusion.
“I can be a little bit sympathetic to their cause but at the same time the DSMB should have said no,” said David Boulware, MD, MPH, who led a recent hydroxychloroquine trial in COVID-19. “The problem is we’re sort of left in limbo, where some people kind of believe it and some say it’s not really a thing. So it’s not really moving the needle, as far as guidelines go.”
Indeed, a Twitter poll by cardiologist James Januzzi Jr., MD, captured the uncertainty, with 28% of respondents saying the trial was “neutral,” 58% saying “maybe but meh,” and 14% saying “colchicine for all.”
Another poll cheekily asked whether ColCORONA was the Gamestop/Reddit equivalent of COVID.
“The press release really didn’t help things because it very much oversold the effect. That, I think, poisoned the well,” said Dr. Boulware, professor of medicine in infectious diseases at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
“The question I’m left with is not whether colchicine works, but who does it work in,” he said. “That’s really the fundamental question because it does seem that there are probably high-risk groups in their trial and others where they benefit, whereas other groups don’t benefit. In the subgroup analysis, there was absolutely no beneficial effect in women.”
According to the authors, the number needed to treat to prevent one death or hospitalization was 71 overall, but 29 for patients with diabetes, 31 for those aged 70 years and older, 53 for patients with respiratory disease, and 25 for those with coronary disease or heart failure.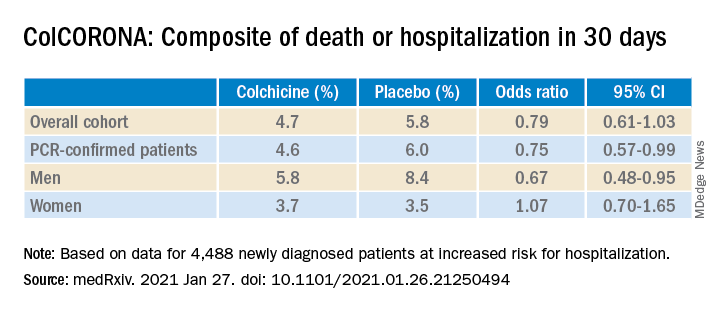
Men are at higher risk overall for poor outcomes. But “the authors didn’t present a multivariable analysis, so it is unclear if another factor, such as a differential prevalence of smoking or cardiovascular risk factors, contributed to the differential benefit,” Rachel Bender Ignacio, MD, MPH, infectious disease specialist, University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview.
Importantly, in this pragmatic study, duration and severity of symptoms were not reported, observed Dr. Bender Ignacio, who is also a STOP-COVID-2 investigator. “We don’t yet have data as to whether colchicine shortens duration or severity of symptoms or prevents long COVID, so we need more data on that.”
The overall risk for serious adverse events was lower in the colchicine group, but the difference in pulmonary embolism (PE) was striking, she said. This could be caused by a real biologic effect, or it’s possible that persons with shortness of breath and hypoxia, without evident viral pneumonia on chest x-ray after a positive COVID-19 test, were more likely to receive a CT-PE study.
The press release also failed to include information, later noted in the preprint, that the MHI has submitted two patents related to colchicine: “Methods of treating a coronavirus infection using colchicine” and “Early administration of low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction.”
Reached for clarification, MHI communications adviser Camille Turbide said in an interview that the first patent “simply refers to the novel concept of preventing complications of COVID-19, such as admission to the hospital, with colchicine as tested in the ColCORONA study.”
The second patent, she said, refers to the “novel concept that administering colchicine early after a major adverse cardiovascular event is better than waiting several days,” as supported by the COLCOT study, which Dr. Tardif also led.
The patents are being reviewed by authorities and “Dr. Tardif has waived his rights in these patents and does not stand to benefit financially at all if colchicine becomes used as a treatment for COVID-19,” Ms. Turbide said.
Dr. Tardif did not respond to interview requests for this story. Dr. Glatt said conflicts of interest must be assessed and are “something that is of great concern in any scientific study.”
Cardiologist Steve Nissen, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic said in an interview that, “despite the negative results, the study does suggest that colchicine might have a benefit and should be studied in future trials. These findings are not sufficient evidence to suggest use of the drug in patients infected with COVID-19.”
He noted that adverse effects like diarrhea were expected but that the excess PE was unexpected and needs greater clarification.
“Stopping the trial for administrative reasons is puzzling and undermined the ability of the trial to give a reliable answer,” Dr. Nissen said. “This is a reasonable pilot study that should be viewed as hypothesis generating but inconclusive.”
Several sources said a new trial is unlikely, particularly given the cost and 28 trials already evaluating colchicine. Among these are RECOVERY and COLCOVID, testing whether colchicine can reduce the duration of hospitalization or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
Because there are so many trials ongoing right now, including for antivirals and other immunomodulators, it’s important that, if colchicine comes to routine clinical use, it provides access to treatment for those not able or willing to access clinical trials, rather than impeding clinical trial enrollment, Dr. Bender Ignacio suggested.
“We have already learned the lesson in the pandemic that early adoption of potentially promising therapies can negatively impact our ability to study and develop other promising treatments,” she said.
The trial was coordinated by the Montreal Heart Institute and funded by the government of Quebec; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health; Montreal philanthropist Sophie Desmarais, and the COVID-19 Therapeutics Accelerator launched by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Wellcome, and Mastercard. CGI, Dacima, and Pharmascience of Montreal were also collaborators. Dr. Glatt reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Boulware reported receiving $18 in food and beverages from Gilead Sciences in 2018.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Science by press release and preprint has cooled clinician enthusiasm for the use of colchicine in nonhospitalized patients with COVID-19, despite a pressing need for early treatments.
As previously reported by this news organization, a Jan. 22 press release announced that the massive ColCORONA study missed its primary endpoint of hospitalization or death among 4,488 newly diagnosed patients at increased risk for hospitalization.
But it also touted that use of the anti-inflammatory drug significantly reduced the primary endpoint in 4,159 of those patients with polymerase chain reaction–confirmed COVID and led to reductions of 25%, 50%, and 44%, respectively, for hospitalizations, ventilations, and death.
Lead investigator Jean-Claude Tardif, MD, director of the Montreal Heart Institute Research Centre, deemed the findings a “medical breakthrough.”
When the preprint released a few days later, however, newly revealed confidence intervals showed colchicine did not meaningfully reduce the need for mechanical ventilation (odds ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.23-1.07) or death alone (OR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.19-1.66).
Further, the significant benefit on the primary outcome came at the cost of a fivefold increase in pulmonary embolism (11 vs. 2; P = .01), which was not mentioned in the press release.
“Whether this represents a real phenomenon or simply the play of chance is not known,” Dr. Tardif and colleagues noted later in the preprint.
“I read the preprint on colchicine and I have so many questions,” Aaron E. Glatt, MD, spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America and chief of infectious diseases, Mount Sinai South Nassau, Hewlett, N.Y., said in an interview. “I’ve been burned too many times with COVID and prefer to see better data.
“People sometimes say if you wait for perfect data, people are going to die,” he said. “Yeah, but we have no idea if people are going to die from getting this drug more than not getting it. That’s what concerns me. How many pulmonary emboli are going to be fatal versus the slight benefit that the study showed?”
The pushback to the non–peer-reviewed data on social media and via emails was so strong that Dr. Tardif posted a nearly 2,000-word letter responding to the many questions at play.
Chief among them was why the trial, originally planned for 6,000 patients, was stopped early by the investigators without consultation with the data safety monitoring board (DSMB).
The explanation in the letter that logistical issues like running the study call center, budget constraints, and a perceived need to quickly communicate the results left some calling foul that the study wasn’t allowed to finish and come to a more definitive conclusion.
“I can be a little bit sympathetic to their cause but at the same time the DSMB should have said no,” said David Boulware, MD, MPH, who led a recent hydroxychloroquine trial in COVID-19. “The problem is we’re sort of left in limbo, where some people kind of believe it and some say it’s not really a thing. So it’s not really moving the needle, as far as guidelines go.”
Indeed, a Twitter poll by cardiologist James Januzzi Jr., MD, captured the uncertainty, with 28% of respondents saying the trial was “neutral,” 58% saying “maybe but meh,” and 14% saying “colchicine for all.”
Another poll cheekily asked whether ColCORONA was the Gamestop/Reddit equivalent of COVID.
“The press release really didn’t help things because it very much oversold the effect. That, I think, poisoned the well,” said Dr. Boulware, professor of medicine in infectious diseases at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
“The question I’m left with is not whether colchicine works, but who does it work in,” he said. “That’s really the fundamental question because it does seem that there are probably high-risk groups in their trial and others where they benefit, whereas other groups don’t benefit. In the subgroup analysis, there was absolutely no beneficial effect in women.”
According to the authors, the number needed to treat to prevent one death or hospitalization was 71 overall, but 29 for patients with diabetes, 31 for those aged 70 years and older, 53 for patients with respiratory disease, and 25 for those with coronary disease or heart failure.
Men are at higher risk overall for poor outcomes. But “the authors didn’t present a multivariable analysis, so it is unclear if another factor, such as a differential prevalence of smoking or cardiovascular risk factors, contributed to the differential benefit,” Rachel Bender Ignacio, MD, MPH, infectious disease specialist, University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview.
Importantly, in this pragmatic study, duration and severity of symptoms were not reported, observed Dr. Bender Ignacio, who is also a STOP-COVID-2 investigator. “We don’t yet have data as to whether colchicine shortens duration or severity of symptoms or prevents long COVID, so we need more data on that.”
The overall risk for serious adverse events was lower in the colchicine group, but the difference in pulmonary embolism (PE) was striking, she said. This could be caused by a real biologic effect, or it’s possible that persons with shortness of breath and hypoxia, without evident viral pneumonia on chest x-ray after a positive COVID-19 test, were more likely to receive a CT-PE study.
The press release also failed to include information, later noted in the preprint, that the MHI has submitted two patents related to colchicine: “Methods of treating a coronavirus infection using colchicine” and “Early administration of low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction.”
Reached for clarification, MHI communications adviser Camille Turbide said in an interview that the first patent “simply refers to the novel concept of preventing complications of COVID-19, such as admission to the hospital, with colchicine as tested in the ColCORONA study.”
The second patent, she said, refers to the “novel concept that administering colchicine early after a major adverse cardiovascular event is better than waiting several days,” as supported by the COLCOT study, which Dr. Tardif also led.
The patents are being reviewed by authorities and “Dr. Tardif has waived his rights in these patents and does not stand to benefit financially at all if colchicine becomes used as a treatment for COVID-19,” Ms. Turbide said.
Dr. Tardif did not respond to interview requests for this story. Dr. Glatt said conflicts of interest must be assessed and are “something that is of great concern in any scientific study.”
Cardiologist Steve Nissen, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic said in an interview that, “despite the negative results, the study does suggest that colchicine might have a benefit and should be studied in future trials. These findings are not sufficient evidence to suggest use of the drug in patients infected with COVID-19.”
He noted that adverse effects like diarrhea were expected but that the excess PE was unexpected and needs greater clarification.
“Stopping the trial for administrative reasons is puzzling and undermined the ability of the trial to give a reliable answer,” Dr. Nissen said. “This is a reasonable pilot study that should be viewed as hypothesis generating but inconclusive.”
Several sources said a new trial is unlikely, particularly given the cost and 28 trials already evaluating colchicine. Among these are RECOVERY and COLCOVID, testing whether colchicine can reduce the duration of hospitalization or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
Because there are so many trials ongoing right now, including for antivirals and other immunomodulators, it’s important that, if colchicine comes to routine clinical use, it provides access to treatment for those not able or willing to access clinical trials, rather than impeding clinical trial enrollment, Dr. Bender Ignacio suggested.
“We have already learned the lesson in the pandemic that early adoption of potentially promising therapies can negatively impact our ability to study and develop other promising treatments,” she said.
The trial was coordinated by the Montreal Heart Institute and funded by the government of Quebec; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health; Montreal philanthropist Sophie Desmarais, and the COVID-19 Therapeutics Accelerator launched by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Wellcome, and Mastercard. CGI, Dacima, and Pharmascience of Montreal were also collaborators. Dr. Glatt reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Boulware reported receiving $18 in food and beverages from Gilead Sciences in 2018.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Science by press release and preprint has cooled clinician enthusiasm for the use of colchicine in nonhospitalized patients with COVID-19, despite a pressing need for early treatments.
As previously reported by this news organization, a Jan. 22 press release announced that the massive ColCORONA study missed its primary endpoint of hospitalization or death among 4,488 newly diagnosed patients at increased risk for hospitalization.
But it also touted that use of the anti-inflammatory drug significantly reduced the primary endpoint in 4,159 of those patients with polymerase chain reaction–confirmed COVID and led to reductions of 25%, 50%, and 44%, respectively, for hospitalizations, ventilations, and death.
Lead investigator Jean-Claude Tardif, MD, director of the Montreal Heart Institute Research Centre, deemed the findings a “medical breakthrough.”
When the preprint released a few days later, however, newly revealed confidence intervals showed colchicine did not meaningfully reduce the need for mechanical ventilation (odds ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.23-1.07) or death alone (OR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.19-1.66).
Further, the significant benefit on the primary outcome came at the cost of a fivefold increase in pulmonary embolism (11 vs. 2; P = .01), which was not mentioned in the press release.
“Whether this represents a real phenomenon or simply the play of chance is not known,” Dr. Tardif and colleagues noted later in the preprint.
“I read the preprint on colchicine and I have so many questions,” Aaron E. Glatt, MD, spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America and chief of infectious diseases, Mount Sinai South Nassau, Hewlett, N.Y., said in an interview. “I’ve been burned too many times with COVID and prefer to see better data.
“People sometimes say if you wait for perfect data, people are going to die,” he said. “Yeah, but we have no idea if people are going to die from getting this drug more than not getting it. That’s what concerns me. How many pulmonary emboli are going to be fatal versus the slight benefit that the study showed?”
The pushback to the non–peer-reviewed data on social media and via emails was so strong that Dr. Tardif posted a nearly 2,000-word letter responding to the many questions at play.
Chief among them was why the trial, originally planned for 6,000 patients, was stopped early by the investigators without consultation with the data safety monitoring board (DSMB).
The explanation in the letter that logistical issues like running the study call center, budget constraints, and a perceived need to quickly communicate the results left some calling foul that the study wasn’t allowed to finish and come to a more definitive conclusion.
“I can be a little bit sympathetic to their cause but at the same time the DSMB should have said no,” said David Boulware, MD, MPH, who led a recent hydroxychloroquine trial in COVID-19. “The problem is we’re sort of left in limbo, where some people kind of believe it and some say it’s not really a thing. So it’s not really moving the needle, as far as guidelines go.”
Indeed, a Twitter poll by cardiologist James Januzzi Jr., MD, captured the uncertainty, with 28% of respondents saying the trial was “neutral,” 58% saying “maybe but meh,” and 14% saying “colchicine for all.”
Another poll cheekily asked whether ColCORONA was the Gamestop/Reddit equivalent of COVID.
“The press release really didn’t help things because it very much oversold the effect. That, I think, poisoned the well,” said Dr. Boulware, professor of medicine in infectious diseases at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
“The question I’m left with is not whether colchicine works, but who does it work in,” he said. “That’s really the fundamental question because it does seem that there are probably high-risk groups in their trial and others where they benefit, whereas other groups don’t benefit. In the subgroup analysis, there was absolutely no beneficial effect in women.”
According to the authors, the number needed to treat to prevent one death or hospitalization was 71 overall, but 29 for patients with diabetes, 31 for those aged 70 years and older, 53 for patients with respiratory disease, and 25 for those with coronary disease or heart failure.
Men are at higher risk overall for poor outcomes. But “the authors didn’t present a multivariable analysis, so it is unclear if another factor, such as a differential prevalence of smoking or cardiovascular risk factors, contributed to the differential benefit,” Rachel Bender Ignacio, MD, MPH, infectious disease specialist, University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview.
Importantly, in this pragmatic study, duration and severity of symptoms were not reported, observed Dr. Bender Ignacio, who is also a STOP-COVID-2 investigator. “We don’t yet have data as to whether colchicine shortens duration or severity of symptoms or prevents long COVID, so we need more data on that.”
The overall risk for serious adverse events was lower in the colchicine group, but the difference in pulmonary embolism (PE) was striking, she said. This could be caused by a real biologic effect, or it’s possible that persons with shortness of breath and hypoxia, without evident viral pneumonia on chest x-ray after a positive COVID-19 test, were more likely to receive a CT-PE study.
The press release also failed to include information, later noted in the preprint, that the MHI has submitted two patents related to colchicine: “Methods of treating a coronavirus infection using colchicine” and “Early administration of low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction.”
Reached for clarification, MHI communications adviser Camille Turbide said in an interview that the first patent “simply refers to the novel concept of preventing complications of COVID-19, such as admission to the hospital, with colchicine as tested in the ColCORONA study.”
The second patent, she said, refers to the “novel concept that administering colchicine early after a major adverse cardiovascular event is better than waiting several days,” as supported by the COLCOT study, which Dr. Tardif also led.
The patents are being reviewed by authorities and “Dr. Tardif has waived his rights in these patents and does not stand to benefit financially at all if colchicine becomes used as a treatment for COVID-19,” Ms. Turbide said.
Dr. Tardif did not respond to interview requests for this story. Dr. Glatt said conflicts of interest must be assessed and are “something that is of great concern in any scientific study.”
Cardiologist Steve Nissen, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic said in an interview that, “despite the negative results, the study does suggest that colchicine might have a benefit and should be studied in future trials. These findings are not sufficient evidence to suggest use of the drug in patients infected with COVID-19.”
He noted that adverse effects like diarrhea were expected but that the excess PE was unexpected and needs greater clarification.
“Stopping the trial for administrative reasons is puzzling and undermined the ability of the trial to give a reliable answer,” Dr. Nissen said. “This is a reasonable pilot study that should be viewed as hypothesis generating but inconclusive.”
Several sources said a new trial is unlikely, particularly given the cost and 28 trials already evaluating colchicine. Among these are RECOVERY and COLCOVID, testing whether colchicine can reduce the duration of hospitalization or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
Because there are so many trials ongoing right now, including for antivirals and other immunomodulators, it’s important that, if colchicine comes to routine clinical use, it provides access to treatment for those not able or willing to access clinical trials, rather than impeding clinical trial enrollment, Dr. Bender Ignacio suggested.
“We have already learned the lesson in the pandemic that early adoption of potentially promising therapies can negatively impact our ability to study and develop other promising treatments,” she said.
The trial was coordinated by the Montreal Heart Institute and funded by the government of Quebec; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health; Montreal philanthropist Sophie Desmarais, and the COVID-19 Therapeutics Accelerator launched by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Wellcome, and Mastercard. CGI, Dacima, and Pharmascience of Montreal were also collaborators. Dr. Glatt reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Boulware reported receiving $18 in food and beverages from Gilead Sciences in 2018.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Finding a new approach to difficult diagnoses
Reducing – or managing – uncertainty
Beyond its clinical objective, the Socrates Project also seeks to further the discovery of previously unrecognized disease processes.
Many patients do not have a diagnosis that explains their signs and symptoms, despite a thorough evaluation, said Benjamin Singer, MD, assistant professor of pulmonology and critical care at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago. To address that problem, he and his colleagues launched the Socrates Project. The service is intended for difficult diagnoses and is based on Socratic principles, particularly the role of iterative hypothesis testing in the process of diagnosis.
“We began the Socrates Project to assist physicians caring for patients who lack a specific diagnosis. In creating this service, we have found ourselves to be doctors for doctors – formalizing the curbside consultation,” Dr. Singer said.
Northwestern Medicine launched the Socrates Project in 2015. It’s a physician-to-physician consultation service that assists doctors working to diagnose conditions that have so far eluded detection. “Our service’s goal is to improve patient care by providing an opinion to the referring physician on diagnostic possibilities for a particular case and ideas to reduce – or at least manage – diagnostic uncertainty,” they write. “Our service model is similar to a tumor board, which exists as an interdisciplinary group operating in parallel to the clinical services, to provide consensus-based recommendations.”
Hospitalists at other institutions may be interested in starting a similar type of service at their own institution or collaborating with institutions who offer this type of service, Dr. Singer said.
At Northwestern Medicine, they are at work on the project’s next steps. “We are working to generate systematic data about our practice, particularly the types of referrals and outcomes,” he said.
Reference
1. Singer BD, et al. The Socrates Project for Difficult Diagnosis at Northwestern Medicine. J Hosp Med. 2020 February;15(2):116-125. doi:10.12788/jhm.3335.
Reducing – or managing – uncertainty
Reducing – or managing – uncertainty
Beyond its clinical objective, the Socrates Project also seeks to further the discovery of previously unrecognized disease processes.
Many patients do not have a diagnosis that explains their signs and symptoms, despite a thorough evaluation, said Benjamin Singer, MD, assistant professor of pulmonology and critical care at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago. To address that problem, he and his colleagues launched the Socrates Project. The service is intended for difficult diagnoses and is based on Socratic principles, particularly the role of iterative hypothesis testing in the process of diagnosis.
“We began the Socrates Project to assist physicians caring for patients who lack a specific diagnosis. In creating this service, we have found ourselves to be doctors for doctors – formalizing the curbside consultation,” Dr. Singer said.
Northwestern Medicine launched the Socrates Project in 2015. It’s a physician-to-physician consultation service that assists doctors working to diagnose conditions that have so far eluded detection. “Our service’s goal is to improve patient care by providing an opinion to the referring physician on diagnostic possibilities for a particular case and ideas to reduce – or at least manage – diagnostic uncertainty,” they write. “Our service model is similar to a tumor board, which exists as an interdisciplinary group operating in parallel to the clinical services, to provide consensus-based recommendations.”
Hospitalists at other institutions may be interested in starting a similar type of service at their own institution or collaborating with institutions who offer this type of service, Dr. Singer said.
At Northwestern Medicine, they are at work on the project’s next steps. “We are working to generate systematic data about our practice, particularly the types of referrals and outcomes,” he said.
Reference
1. Singer BD, et al. The Socrates Project for Difficult Diagnosis at Northwestern Medicine. J Hosp Med. 2020 February;15(2):116-125. doi:10.12788/jhm.3335.
Beyond its clinical objective, the Socrates Project also seeks to further the discovery of previously unrecognized disease processes.
Many patients do not have a diagnosis that explains their signs and symptoms, despite a thorough evaluation, said Benjamin Singer, MD, assistant professor of pulmonology and critical care at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago. To address that problem, he and his colleagues launched the Socrates Project. The service is intended for difficult diagnoses and is based on Socratic principles, particularly the role of iterative hypothesis testing in the process of diagnosis.
“We began the Socrates Project to assist physicians caring for patients who lack a specific diagnosis. In creating this service, we have found ourselves to be doctors for doctors – formalizing the curbside consultation,” Dr. Singer said.
Northwestern Medicine launched the Socrates Project in 2015. It’s a physician-to-physician consultation service that assists doctors working to diagnose conditions that have so far eluded detection. “Our service’s goal is to improve patient care by providing an opinion to the referring physician on diagnostic possibilities for a particular case and ideas to reduce – or at least manage – diagnostic uncertainty,” they write. “Our service model is similar to a tumor board, which exists as an interdisciplinary group operating in parallel to the clinical services, to provide consensus-based recommendations.”
Hospitalists at other institutions may be interested in starting a similar type of service at their own institution or collaborating with institutions who offer this type of service, Dr. Singer said.
At Northwestern Medicine, they are at work on the project’s next steps. “We are working to generate systematic data about our practice, particularly the types of referrals and outcomes,” he said.
Reference
1. Singer BD, et al. The Socrates Project for Difficult Diagnosis at Northwestern Medicine. J Hosp Med. 2020 February;15(2):116-125. doi:10.12788/jhm.3335.
Study: COVID cases have been ‘severely undercounted’
Large numbers of COVID-19 cases have been undetected and unreported, which has resulted in severe undercounting of the total number of people who have been infected during the pandemic, according to a new study published Monday in the journal PLOS ONE.
In the United States, the number of COVID-19 cases is likely three times that of reported cases. According to the study, more than 71 million Americans have contracted the virus during the pandemic, and 7 million were infected or potentially contagious last week.
Public health officials rely on case counts to guide decisions, so the undercounting should be considered while trying to end the pandemic.
“The estimates of actual infections reveal for the first time the true severity of COVID-19 across the U.S. and in countries worldwide,” Jungsik Noh, PhD, a bioinformatics professor at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, said in a statement.
Dr. Noh and colleague Gaudenz Danuser created a computational model that uses machine-learning strategies to estimate the actual number of daily cases in the United States and the 50 most-infected countries.
The model pulls data from the Johns Hopkins University database and the COVID Tracking Project, as well as large-scale surveys conducted by the CDC and several states. The algorithm uses the number of reported deaths, which is thought to be more accurate than the number of lab-confirmed cases, as the basis for calculations.
In 25 of the 50 countries, the “actual” cumulative cases were estimated to be 5-20 times greater than the confirmed cases. In the United States, Belgium, and Brazil, about 10% of the population has contracted the coronavirus, according to the model. At the beginning of February, about 11% of the population in Pennsylvania had current infections, which was the highest rate of any state. About 0.15% of residents in Minnesota had infections, and about 2.5% of residents in New York and Texas had infections.
“Knowing the true severity in different regions will help us effectively fight against the virus spreading,” Dr. Noh said. “The currently infected population is the cause of future infections and deaths. Its actual size in a region is a crucial variable required when determining the severity of COVID-19 and building strategies against regional outbreaks.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Large numbers of COVID-19 cases have been undetected and unreported, which has resulted in severe undercounting of the total number of people who have been infected during the pandemic, according to a new study published Monday in the journal PLOS ONE.
In the United States, the number of COVID-19 cases is likely three times that of reported cases. According to the study, more than 71 million Americans have contracted the virus during the pandemic, and 7 million were infected or potentially contagious last week.
Public health officials rely on case counts to guide decisions, so the undercounting should be considered while trying to end the pandemic.
“The estimates of actual infections reveal for the first time the true severity of COVID-19 across the U.S. and in countries worldwide,” Jungsik Noh, PhD, a bioinformatics professor at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, said in a statement.
Dr. Noh and colleague Gaudenz Danuser created a computational model that uses machine-learning strategies to estimate the actual number of daily cases in the United States and the 50 most-infected countries.
The model pulls data from the Johns Hopkins University database and the COVID Tracking Project, as well as large-scale surveys conducted by the CDC and several states. The algorithm uses the number of reported deaths, which is thought to be more accurate than the number of lab-confirmed cases, as the basis for calculations.
In 25 of the 50 countries, the “actual” cumulative cases were estimated to be 5-20 times greater than the confirmed cases. In the United States, Belgium, and Brazil, about 10% of the population has contracted the coronavirus, according to the model. At the beginning of February, about 11% of the population in Pennsylvania had current infections, which was the highest rate of any state. About 0.15% of residents in Minnesota had infections, and about 2.5% of residents in New York and Texas had infections.
“Knowing the true severity in different regions will help us effectively fight against the virus spreading,” Dr. Noh said. “The currently infected population is the cause of future infections and deaths. Its actual size in a region is a crucial variable required when determining the severity of COVID-19 and building strategies against regional outbreaks.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Large numbers of COVID-19 cases have been undetected and unreported, which has resulted in severe undercounting of the total number of people who have been infected during the pandemic, according to a new study published Monday in the journal PLOS ONE.
In the United States, the number of COVID-19 cases is likely three times that of reported cases. According to the study, more than 71 million Americans have contracted the virus during the pandemic, and 7 million were infected or potentially contagious last week.
Public health officials rely on case counts to guide decisions, so the undercounting should be considered while trying to end the pandemic.
“The estimates of actual infections reveal for the first time the true severity of COVID-19 across the U.S. and in countries worldwide,” Jungsik Noh, PhD, a bioinformatics professor at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, said in a statement.
Dr. Noh and colleague Gaudenz Danuser created a computational model that uses machine-learning strategies to estimate the actual number of daily cases in the United States and the 50 most-infected countries.
The model pulls data from the Johns Hopkins University database and the COVID Tracking Project, as well as large-scale surveys conducted by the CDC and several states. The algorithm uses the number of reported deaths, which is thought to be more accurate than the number of lab-confirmed cases, as the basis for calculations.
In 25 of the 50 countries, the “actual” cumulative cases were estimated to be 5-20 times greater than the confirmed cases. In the United States, Belgium, and Brazil, about 10% of the population has contracted the coronavirus, according to the model. At the beginning of February, about 11% of the population in Pennsylvania had current infections, which was the highest rate of any state. About 0.15% of residents in Minnesota had infections, and about 2.5% of residents in New York and Texas had infections.
“Knowing the true severity in different regions will help us effectively fight against the virus spreading,” Dr. Noh said. “The currently infected population is the cause of future infections and deaths. Its actual size in a region is a crucial variable required when determining the severity of COVID-19 and building strategies against regional outbreaks.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Some COVID-19 vaccine reactions could be pseudoallergic, experts say
On Jan. 13, 2 days after a drive-through vaccination “superstation” opened in San Diego, six people were treated for anaphylaxis after they received the Moderna vaccine, leading the California state epidemiologist to recommend pausing the administration of that particular lot.
A group of allergy and immunology experts and public health officials reviewed the cases, as well as an incident that occurred the day before, and concluded that at least some of the responses were angioedema, or swelling — a serious allergic reaction — but none were actually anaphylaxis. No similar clusters had occurred with the same vaccine lot in other states, and California resumed using the doses.
Yet questions remain about the reactions and the mechanisms for them. Some might have been triggered by an allergy to a vaccine component, most likely the polyethylene glycol (PEG) that stabilizes the lipid surrounding the mRNA, the key vaccine component in both the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines. Another possible explanation is that some could be pseudoallergic reactions to a blood protein known as complement, a little-understood process that resembles an antigen-based reaction but doesn’t leave an immune memory and might not recur.
Cases of complement-activation-related pseudoallergy look like a severe allergic reaction but occur through a different mechanism and don’t require previous exposure to an allergen.
“It has the same signs and symptoms and is treated the same way, but it occurs through a different pathway,” explained Neal Halsey, MD, director emeritus of the Institute for Vaccine Safety and emeritus professor at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore.
Pseudoallergies are not well understood, but they have been associated with reactions to the contrast media used in imaging, such as with MRI. “If people have had an anaphylaxis-type reaction following the injection of contrast-dye material, that is a strong signal that it might be a complement-activation-related pseudoallergy,” said Dr. Halsey, a member of the Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment Network. “Those are the people who definitely need to consider seeing an allergist before getting the COVID vaccines.”
When Aleena Banerji, MD, clinical director of the allergy and clinical immunology unit at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, talks to patients about vaccine reactions, she addresses the risk for COVID-19 infection. All of the people who developed allergies after the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines recovered, but more than 445,000 Americans have died from COVID-19.
Most people with common allergies, such as to food or oral medications, don’t need to worry about reactions, said Dr. Banerji, lead author of a review that assessed the risk for allergic reactions to the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines.
Investigating reactions
As investigators search for the answers to what causes reactions, transparency is crucial to trust, said Kathryn Edwards, MD, principal investigator of the Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment Project, a vaccine safety network funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Unless the public knows that we’re really investigating and we’re taking this seriously, then I think the vaccine hesitancy is going to increase,” said Dr. Edwards, professor of pediatrics at Vanderbilt University Medical Center and scientific director of the Vanderbilt Vaccine Research Program in Nashville, Tenn.
First reports of anaphylaxis came quickly after COVID-19 vaccinations began. In the 2 weeks before the holidays, almost 2 million health care workers received the Pfizer vaccine, and 21 of them developed anaphylaxis, according to CDC researchers who reviewed case reports from the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS). That rate of about 1 in 100,000 is 10 times higher than the occurrence with other vaccines. No deaths from anaphylaxis were reported.
As the vaccinations ramped up, the rate declined. As of Jan. 18, 50 cases of anaphylaxis were reported to VAERS after the administration of 9,943,247 Pfizer doses, for a rate of 5.0 per million, according to data presented at the Jan. 27 meeting of the CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. And 21 cases of anaphylaxis were reported to VAERS after the administration of 7,581,429 Moderna doses, for a rate of 2.8 per million.
The anaphylaxis occurred almost exclusively in women; only three of the VAERS anaphylaxis reports were from men. Only 24% had a history of anaphylaxis.
The earlier CDC report explored the potential link to allergies. One person with anaphylaxis had a history of allergy to iodinated contrast media, and others had allergies to various medications, vaccines, foods, and animals. The researchers reported 86 nonanaphylaxis allergic reactions and 61 nonallergic adverse events among the 175 case reports they reviewed as possible cases of severe allergic reaction.
Of 1,266 reports that VAERS received from Dec. 21 to Jan. 10, the CDC identified 108 possible cases of severe allergic reaction after the Moderna vaccine. Only 10 met the case definition of anaphylaxis put forward by the Brighton Collaboration, a vaccine safety organization. All but one case involved a history of allergies or allergic reactions; only five had a previously experienced anaphylaxis.
There were 47 nonanaphylaxis allergic reactions.
The San Diego cluster also met the Brighton case definition for anaphylaxis, Dr. Edwards reported. This discrepancy highlights the difficulties in characterizing vaccine reactions.
Measuring a pseudoallergic reaction is a challenge. It requires that a blood sample be drawn soon after the incident and then frozen to protect heat-sensitive blood markers, Dr. Edwards explained.
And as vaccinations rise, so do adverse-event reports. But unlike in clinical trials, there is no control group for comparison. That is why vaccine safety experts urge caution when evaluating events and, where possible, advise looking at background rates.
“A major way to determine whether the adverse event is causally related is to assess the incidence of the adverse event in vaccines versus nonvaccines,” said Walter Orenstein, MD, who directed the U.S. Immunization Program from 1988 to 2004 and is now associate director of the Emory Vaccine Center and professor of infectious diseases at Emory University in Atlanta. Public health officials could then identify vaccine risk factors, he said.
When a reaction occurs almost immediately after vaccination, vaccine safety investigators look for probable triggers. If allergy to PEG is the culprit in anaphylactic reactions, then the individuals would have had a previous exposure, perhaps from injectable medications, Dr. Edwards said.
It might be feasible to perform a skin test for allergy to PEG. “If the skin testing is negative, that doesn’t completely rule out allergy, but it can be used in the decision-making about giving the first or second vaccine dose,” Dr. Banerji said.
Other vaccines, such as childhood vaccines, contain polysorbate as a stabilizer, which has a similar chemical structure, and it’s not clear why someone would react to PEG but not to polysorbate, Dr. Edwards said.
Meanwhile, other illnesses and even deaths sometimes occur in the days after vaccination, but that doesn’t mean the vaccine caused them, cautioned Steve Black, MD, emeritus professor of pediatrics at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and cofounder of the Global Vaccine Data Network, an international vaccine safety collaboration.
“Different events and clusters of events will occur by chance alone, as these events can occur without vaccines. We need to not immediately assume that they’re due to the vaccine,” he said. “You don’t want to undermine the whole vaccine program every time something comes up and assume that it’s associated with the vaccine.”
The CDC only has three contraindications for the vaccines:
- Severe allergic reaction (such as anaphylaxis) after a previous dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine or any of its components.
- Immediate allergic reaction of any severity to a previous dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine or any of its components (including PEG).
- Immediate allergic reaction of any severity to polysorbate (due to potential cross-reactive hypersensitivity with PEG).
People who have had an immediate allergic reaction to other vaccines or injectable therapies should consider consulting with an allergist or immunologist before getting the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines, the CDC advises.
The CDC also says that people with a history of anaphylaxis from any cause should be observed for 30 minutes after vaccination. Vaccination protocol calls for everyone else to wait on site for 15 minutes after vaccination.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On Jan. 13, 2 days after a drive-through vaccination “superstation” opened in San Diego, six people were treated for anaphylaxis after they received the Moderna vaccine, leading the California state epidemiologist to recommend pausing the administration of that particular lot.
A group of allergy and immunology experts and public health officials reviewed the cases, as well as an incident that occurred the day before, and concluded that at least some of the responses were angioedema, or swelling — a serious allergic reaction — but none were actually anaphylaxis. No similar clusters had occurred with the same vaccine lot in other states, and California resumed using the doses.
Yet questions remain about the reactions and the mechanisms for them. Some might have been triggered by an allergy to a vaccine component, most likely the polyethylene glycol (PEG) that stabilizes the lipid surrounding the mRNA, the key vaccine component in both the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines. Another possible explanation is that some could be pseudoallergic reactions to a blood protein known as complement, a little-understood process that resembles an antigen-based reaction but doesn’t leave an immune memory and might not recur.
Cases of complement-activation-related pseudoallergy look like a severe allergic reaction but occur through a different mechanism and don’t require previous exposure to an allergen.
“It has the same signs and symptoms and is treated the same way, but it occurs through a different pathway,” explained Neal Halsey, MD, director emeritus of the Institute for Vaccine Safety and emeritus professor at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore.
Pseudoallergies are not well understood, but they have been associated with reactions to the contrast media used in imaging, such as with MRI. “If people have had an anaphylaxis-type reaction following the injection of contrast-dye material, that is a strong signal that it might be a complement-activation-related pseudoallergy,” said Dr. Halsey, a member of the Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment Network. “Those are the people who definitely need to consider seeing an allergist before getting the COVID vaccines.”
When Aleena Banerji, MD, clinical director of the allergy and clinical immunology unit at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, talks to patients about vaccine reactions, she addresses the risk for COVID-19 infection. All of the people who developed allergies after the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines recovered, but more than 445,000 Americans have died from COVID-19.
Most people with common allergies, such as to food or oral medications, don’t need to worry about reactions, said Dr. Banerji, lead author of a review that assessed the risk for allergic reactions to the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines.
Investigating reactions
As investigators search for the answers to what causes reactions, transparency is crucial to trust, said Kathryn Edwards, MD, principal investigator of the Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment Project, a vaccine safety network funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Unless the public knows that we’re really investigating and we’re taking this seriously, then I think the vaccine hesitancy is going to increase,” said Dr. Edwards, professor of pediatrics at Vanderbilt University Medical Center and scientific director of the Vanderbilt Vaccine Research Program in Nashville, Tenn.
First reports of anaphylaxis came quickly after COVID-19 vaccinations began. In the 2 weeks before the holidays, almost 2 million health care workers received the Pfizer vaccine, and 21 of them developed anaphylaxis, according to CDC researchers who reviewed case reports from the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS). That rate of about 1 in 100,000 is 10 times higher than the occurrence with other vaccines. No deaths from anaphylaxis were reported.
As the vaccinations ramped up, the rate declined. As of Jan. 18, 50 cases of anaphylaxis were reported to VAERS after the administration of 9,943,247 Pfizer doses, for a rate of 5.0 per million, according to data presented at the Jan. 27 meeting of the CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. And 21 cases of anaphylaxis were reported to VAERS after the administration of 7,581,429 Moderna doses, for a rate of 2.8 per million.
The anaphylaxis occurred almost exclusively in women; only three of the VAERS anaphylaxis reports were from men. Only 24% had a history of anaphylaxis.
The earlier CDC report explored the potential link to allergies. One person with anaphylaxis had a history of allergy to iodinated contrast media, and others had allergies to various medications, vaccines, foods, and animals. The researchers reported 86 nonanaphylaxis allergic reactions and 61 nonallergic adverse events among the 175 case reports they reviewed as possible cases of severe allergic reaction.
Of 1,266 reports that VAERS received from Dec. 21 to Jan. 10, the CDC identified 108 possible cases of severe allergic reaction after the Moderna vaccine. Only 10 met the case definition of anaphylaxis put forward by the Brighton Collaboration, a vaccine safety organization. All but one case involved a history of allergies or allergic reactions; only five had a previously experienced anaphylaxis.
There were 47 nonanaphylaxis allergic reactions.
The San Diego cluster also met the Brighton case definition for anaphylaxis, Dr. Edwards reported. This discrepancy highlights the difficulties in characterizing vaccine reactions.
Measuring a pseudoallergic reaction is a challenge. It requires that a blood sample be drawn soon after the incident and then frozen to protect heat-sensitive blood markers, Dr. Edwards explained.
And as vaccinations rise, so do adverse-event reports. But unlike in clinical trials, there is no control group for comparison. That is why vaccine safety experts urge caution when evaluating events and, where possible, advise looking at background rates.
“A major way to determine whether the adverse event is causally related is to assess the incidence of the adverse event in vaccines versus nonvaccines,” said Walter Orenstein, MD, who directed the U.S. Immunization Program from 1988 to 2004 and is now associate director of the Emory Vaccine Center and professor of infectious diseases at Emory University in Atlanta. Public health officials could then identify vaccine risk factors, he said.
When a reaction occurs almost immediately after vaccination, vaccine safety investigators look for probable triggers. If allergy to PEG is the culprit in anaphylactic reactions, then the individuals would have had a previous exposure, perhaps from injectable medications, Dr. Edwards said.
It might be feasible to perform a skin test for allergy to PEG. “If the skin testing is negative, that doesn’t completely rule out allergy, but it can be used in the decision-making about giving the first or second vaccine dose,” Dr. Banerji said.
Other vaccines, such as childhood vaccines, contain polysorbate as a stabilizer, which has a similar chemical structure, and it’s not clear why someone would react to PEG but not to polysorbate, Dr. Edwards said.
Meanwhile, other illnesses and even deaths sometimes occur in the days after vaccination, but that doesn’t mean the vaccine caused them, cautioned Steve Black, MD, emeritus professor of pediatrics at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and cofounder of the Global Vaccine Data Network, an international vaccine safety collaboration.
“Different events and clusters of events will occur by chance alone, as these events can occur without vaccines. We need to not immediately assume that they’re due to the vaccine,” he said. “You don’t want to undermine the whole vaccine program every time something comes up and assume that it’s associated with the vaccine.”
The CDC only has three contraindications for the vaccines:
- Severe allergic reaction (such as anaphylaxis) after a previous dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine or any of its components.
- Immediate allergic reaction of any severity to a previous dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine or any of its components (including PEG).
- Immediate allergic reaction of any severity to polysorbate (due to potential cross-reactive hypersensitivity with PEG).
People who have had an immediate allergic reaction to other vaccines or injectable therapies should consider consulting with an allergist or immunologist before getting the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines, the CDC advises.
The CDC also says that people with a history of anaphylaxis from any cause should be observed for 30 minutes after vaccination. Vaccination protocol calls for everyone else to wait on site for 15 minutes after vaccination.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On Jan. 13, 2 days after a drive-through vaccination “superstation” opened in San Diego, six people were treated for anaphylaxis after they received the Moderna vaccine, leading the California state epidemiologist to recommend pausing the administration of that particular lot.
A group of allergy and immunology experts and public health officials reviewed the cases, as well as an incident that occurred the day before, and concluded that at least some of the responses were angioedema, or swelling — a serious allergic reaction — but none were actually anaphylaxis. No similar clusters had occurred with the same vaccine lot in other states, and California resumed using the doses.
Yet questions remain about the reactions and the mechanisms for them. Some might have been triggered by an allergy to a vaccine component, most likely the polyethylene glycol (PEG) that stabilizes the lipid surrounding the mRNA, the key vaccine component in both the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines. Another possible explanation is that some could be pseudoallergic reactions to a blood protein known as complement, a little-understood process that resembles an antigen-based reaction but doesn’t leave an immune memory and might not recur.
Cases of complement-activation-related pseudoallergy look like a severe allergic reaction but occur through a different mechanism and don’t require previous exposure to an allergen.
“It has the same signs and symptoms and is treated the same way, but it occurs through a different pathway,” explained Neal Halsey, MD, director emeritus of the Institute for Vaccine Safety and emeritus professor at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore.
Pseudoallergies are not well understood, but they have been associated with reactions to the contrast media used in imaging, such as with MRI. “If people have had an anaphylaxis-type reaction following the injection of contrast-dye material, that is a strong signal that it might be a complement-activation-related pseudoallergy,” said Dr. Halsey, a member of the Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment Network. “Those are the people who definitely need to consider seeing an allergist before getting the COVID vaccines.”
When Aleena Banerji, MD, clinical director of the allergy and clinical immunology unit at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, talks to patients about vaccine reactions, she addresses the risk for COVID-19 infection. All of the people who developed allergies after the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines recovered, but more than 445,000 Americans have died from COVID-19.
Most people with common allergies, such as to food or oral medications, don’t need to worry about reactions, said Dr. Banerji, lead author of a review that assessed the risk for allergic reactions to the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines.
Investigating reactions
As investigators search for the answers to what causes reactions, transparency is crucial to trust, said Kathryn Edwards, MD, principal investigator of the Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment Project, a vaccine safety network funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Unless the public knows that we’re really investigating and we’re taking this seriously, then I think the vaccine hesitancy is going to increase,” said Dr. Edwards, professor of pediatrics at Vanderbilt University Medical Center and scientific director of the Vanderbilt Vaccine Research Program in Nashville, Tenn.
First reports of anaphylaxis came quickly after COVID-19 vaccinations began. In the 2 weeks before the holidays, almost 2 million health care workers received the Pfizer vaccine, and 21 of them developed anaphylaxis, according to CDC researchers who reviewed case reports from the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS). That rate of about 1 in 100,000 is 10 times higher than the occurrence with other vaccines. No deaths from anaphylaxis were reported.
As the vaccinations ramped up, the rate declined. As of Jan. 18, 50 cases of anaphylaxis were reported to VAERS after the administration of 9,943,247 Pfizer doses, for a rate of 5.0 per million, according to data presented at the Jan. 27 meeting of the CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. And 21 cases of anaphylaxis were reported to VAERS after the administration of 7,581,429 Moderna doses, for a rate of 2.8 per million.
The anaphylaxis occurred almost exclusively in women; only three of the VAERS anaphylaxis reports were from men. Only 24% had a history of anaphylaxis.
The earlier CDC report explored the potential link to allergies. One person with anaphylaxis had a history of allergy to iodinated contrast media, and others had allergies to various medications, vaccines, foods, and animals. The researchers reported 86 nonanaphylaxis allergic reactions and 61 nonallergic adverse events among the 175 case reports they reviewed as possible cases of severe allergic reaction.
Of 1,266 reports that VAERS received from Dec. 21 to Jan. 10, the CDC identified 108 possible cases of severe allergic reaction after the Moderna vaccine. Only 10 met the case definition of anaphylaxis put forward by the Brighton Collaboration, a vaccine safety organization. All but one case involved a history of allergies or allergic reactions; only five had a previously experienced anaphylaxis.
There were 47 nonanaphylaxis allergic reactions.
The San Diego cluster also met the Brighton case definition for anaphylaxis, Dr. Edwards reported. This discrepancy highlights the difficulties in characterizing vaccine reactions.
Measuring a pseudoallergic reaction is a challenge. It requires that a blood sample be drawn soon after the incident and then frozen to protect heat-sensitive blood markers, Dr. Edwards explained.
And as vaccinations rise, so do adverse-event reports. But unlike in clinical trials, there is no control group for comparison. That is why vaccine safety experts urge caution when evaluating events and, where possible, advise looking at background rates.
“A major way to determine whether the adverse event is causally related is to assess the incidence of the adverse event in vaccines versus nonvaccines,” said Walter Orenstein, MD, who directed the U.S. Immunization Program from 1988 to 2004 and is now associate director of the Emory Vaccine Center and professor of infectious diseases at Emory University in Atlanta. Public health officials could then identify vaccine risk factors, he said.
When a reaction occurs almost immediately after vaccination, vaccine safety investigators look for probable triggers. If allergy to PEG is the culprit in anaphylactic reactions, then the individuals would have had a previous exposure, perhaps from injectable medications, Dr. Edwards said.
It might be feasible to perform a skin test for allergy to PEG. “If the skin testing is negative, that doesn’t completely rule out allergy, but it can be used in the decision-making about giving the first or second vaccine dose,” Dr. Banerji said.
Other vaccines, such as childhood vaccines, contain polysorbate as a stabilizer, which has a similar chemical structure, and it’s not clear why someone would react to PEG but not to polysorbate, Dr. Edwards said.
Meanwhile, other illnesses and even deaths sometimes occur in the days after vaccination, but that doesn’t mean the vaccine caused them, cautioned Steve Black, MD, emeritus professor of pediatrics at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and cofounder of the Global Vaccine Data Network, an international vaccine safety collaboration.
“Different events and clusters of events will occur by chance alone, as these events can occur without vaccines. We need to not immediately assume that they’re due to the vaccine,” he said. “You don’t want to undermine the whole vaccine program every time something comes up and assume that it’s associated with the vaccine.”
The CDC only has three contraindications for the vaccines:
- Severe allergic reaction (such as anaphylaxis) after a previous dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine or any of its components.
- Immediate allergic reaction of any severity to a previous dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine or any of its components (including PEG).
- Immediate allergic reaction of any severity to polysorbate (due to potential cross-reactive hypersensitivity with PEG).
People who have had an immediate allergic reaction to other vaccines or injectable therapies should consider consulting with an allergist or immunologist before getting the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines, the CDC advises.
The CDC also says that people with a history of anaphylaxis from any cause should be observed for 30 minutes after vaccination. Vaccination protocol calls for everyone else to wait on site for 15 minutes after vaccination.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 in children: New cases down for third straight week
New COVID-19 cases in children dropped for the third consecutive week, even as children continue to make up a larger share of all cases, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
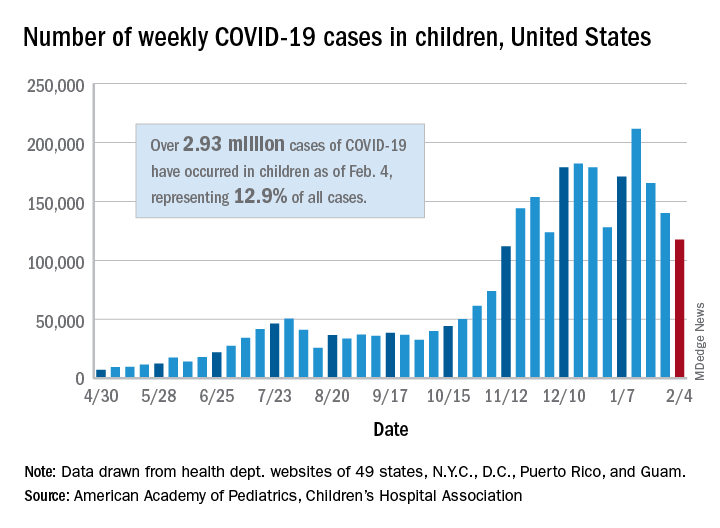
New child cases totaled almost 118,000 for the week of Jan. 29-Feb. 4, continuing the decline that began right after the United States topped 200,000 cases for the only time Jan. 8-14, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
For the latest week, however, children represented 16.0% of all new COVID-19 cases, continuing a 5-week increase that began in early December 2020, after the proportion had dropped to 12.6%, based on data collected from the health departments of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. During the week of Sept. 11-17, children made up 16.9% of all cases, the highest level seen during the pandemic.
The 2.93 million cases that have been reported in children make up 12.9% of all cases since the pandemic began, and the overall rate of pediatric coronavirus infection is 3,899 cases per 100,000 children in the population. Taking a step down from the national level, 30 states are above that rate and 18 are below it, along with D.C., New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam (New York and Texas are excluded), the AAP and CHA reported.
There were 12 new COVID-19–related child deaths in the 43 states, along with New York City and Guam, that are reporting such data, bringing the total to 227. Nationally, 0.06% of all deaths have occurred in children, with rates ranging from 0.00% (11 states) to 0.26% (Nebraska) in the 45 jurisdictions, the AAP/CHA report shows.
Child hospitalizations rose to 1.9% of all hospitalizations after holding at 1.8% since mid-November in 25 reporting jurisdictions (24 states and New York City), but the hospitalization rate among children with COVID held at 0.8%, where it has been for the last 4 weeks. Hospitalization rates as high as 3.8% were recorded early in the pandemic, the AAP and CHA noted.
New COVID-19 cases in children dropped for the third consecutive week, even as children continue to make up a larger share of all cases, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

New child cases totaled almost 118,000 for the week of Jan. 29-Feb. 4, continuing the decline that began right after the United States topped 200,000 cases for the only time Jan. 8-14, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
For the latest week, however, children represented 16.0% of all new COVID-19 cases, continuing a 5-week increase that began in early December 2020, after the proportion had dropped to 12.6%, based on data collected from the health departments of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. During the week of Sept. 11-17, children made up 16.9% of all cases, the highest level seen during the pandemic.
The 2.93 million cases that have been reported in children make up 12.9% of all cases since the pandemic began, and the overall rate of pediatric coronavirus infection is 3,899 cases per 100,000 children in the population. Taking a step down from the national level, 30 states are above that rate and 18 are below it, along with D.C., New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam (New York and Texas are excluded), the AAP and CHA reported.
There were 12 new COVID-19–related child deaths in the 43 states, along with New York City and Guam, that are reporting such data, bringing the total to 227. Nationally, 0.06% of all deaths have occurred in children, with rates ranging from 0.00% (11 states) to 0.26% (Nebraska) in the 45 jurisdictions, the AAP/CHA report shows.
Child hospitalizations rose to 1.9% of all hospitalizations after holding at 1.8% since mid-November in 25 reporting jurisdictions (24 states and New York City), but the hospitalization rate among children with COVID held at 0.8%, where it has been for the last 4 weeks. Hospitalization rates as high as 3.8% were recorded early in the pandemic, the AAP and CHA noted.
New COVID-19 cases in children dropped for the third consecutive week, even as children continue to make up a larger share of all cases, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

New child cases totaled almost 118,000 for the week of Jan. 29-Feb. 4, continuing the decline that began right after the United States topped 200,000 cases for the only time Jan. 8-14, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
For the latest week, however, children represented 16.0% of all new COVID-19 cases, continuing a 5-week increase that began in early December 2020, after the proportion had dropped to 12.6%, based on data collected from the health departments of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. During the week of Sept. 11-17, children made up 16.9% of all cases, the highest level seen during the pandemic.
The 2.93 million cases that have been reported in children make up 12.9% of all cases since the pandemic began, and the overall rate of pediatric coronavirus infection is 3,899 cases per 100,000 children in the population. Taking a step down from the national level, 30 states are above that rate and 18 are below it, along with D.C., New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam (New York and Texas are excluded), the AAP and CHA reported.
There were 12 new COVID-19–related child deaths in the 43 states, along with New York City and Guam, that are reporting such data, bringing the total to 227. Nationally, 0.06% of all deaths have occurred in children, with rates ranging from 0.00% (11 states) to 0.26% (Nebraska) in the 45 jurisdictions, the AAP/CHA report shows.
Child hospitalizations rose to 1.9% of all hospitalizations after holding at 1.8% since mid-November in 25 reporting jurisdictions (24 states and New York City), but the hospitalization rate among children with COVID held at 0.8%, where it has been for the last 4 weeks. Hospitalization rates as high as 3.8% were recorded early in the pandemic, the AAP and CHA noted.
U.K. COVID-19 variant doubling every 10 days in the U.S.: Study
The SARS-CoV-2 variant first detected in the United Kingdom is rapidly becoming the dominant strain in several countries and is doubling every 10 days in the United States, according to new data.
The findings by Nicole L. Washington, PhD, associate director of research at the genomics company Helix, and colleagues were posted Feb. 7, 2021, on the preprint server medRxiv. The paper has not been peer-reviewed in a scientific journal.
The researchers also found that the transmission rate in the United States of the variant, labeled B.1.1.7, is 30%-40% higher than that of more common lineages.
While clinical outcomes initially were thought to be similar to those of other SARS-CoV-2 variants, early reports suggest that infection with the B.1.1.7 variant may increase death risk by about 30%.
A coauthor of the current study, Kristian Andersen, PhD, told the New York Times , “Nothing in this paper is surprising, but people need to see it.”
Dr. Andersen, a virologist at the Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla, Calif., added that “we should probably prepare for this being the predominant lineage in most places in the United States by March.”
The study of the B.1.1.7 variant adds support for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention prediction in January that it would dominate by March.
“Our study shows that the U.S. is on a similar trajectory as other countries where B.1.1.7 rapidly became the dominant SARS-CoV-2 variant, requiring immediate and decisive action to minimize COVID-19 morbidity and mortality,” the researchers wrote.
The authors pointed out that the B.1.1.7 variant became the dominant SARS-CoV-2 strain in the United Kingdom within a couple of months of its detection.
“Since then, the variant has been increasingly observed across many European countries, including Portugal and Ireland, which, like the U.K., observed devastating waves of COVID-19 after B.1.1.7 became dominant,” the authors wrote.
“Category 5” storm
The B.1.1.7 variant has likely been spreading between U.S. states since at least December, they wrote.
This news organization reported on Jan. 15 that, as of Jan. 13, the B.1.1.7 variant was seen in 76 cases across 12 U.S. states, according to an early release of the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
As of Feb. 7, there were 690 cases of the B.1.1.7 variant in the US in 33 states, according to the CDC.
Dr. Washington and colleagues examined more than 500,000 coronavirus test samples from cases across the United States that were tested at San Mateo, Calif.–based Helix facilities since July.
In the study, they found inconsistent prevalence of the variant across states. By the last week in January, the researchers estimated the proportion of B.1.1.7 in the U.S. population to be about 2.1% of all COVID-19 cases, though they found it made up about 2% of all COVID-19 cases in California and about 4.5% of cases in Florida. The authors acknowledged that their data is less robust outside of those two states.
Though that seems a relatively low frequency, “our estimates show that its growth rate is at least 35%-45% increased and doubling every week and a half,” the authors wrote.
“Because laboratories in the U.S. are only sequencing a small subset of SARS-CoV-2 samples, the true sequence diversity of SARS-CoV-2 in this country is still unknown,” they noted.
Michael Osterholm, PhD, MPH, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, said last week that the United States is facing a “Category 5” storm with the spread of the B.1.1.7 variant as well as the variants first identified in South Africa and Brazil.
“We are going to see something like we have not seen yet in this country,” Dr. Osterholm said recently on NBC’s Meet the Press.
Lead author Nicole L. Washington and many of the coauthors are employees of Helix. Other coauthors are employees of Illumina. Three coauthors own stock in ILMN. The work was funded by Illumina, Helix, the Innovative Genomics Institute, and the New Frontiers in Research Fund provided by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The SARS-CoV-2 variant first detected in the United Kingdom is rapidly becoming the dominant strain in several countries and is doubling every 10 days in the United States, according to new data.
The findings by Nicole L. Washington, PhD, associate director of research at the genomics company Helix, and colleagues were posted Feb. 7, 2021, on the preprint server medRxiv. The paper has not been peer-reviewed in a scientific journal.
The researchers also found that the transmission rate in the United States of the variant, labeled B.1.1.7, is 30%-40% higher than that of more common lineages.
While clinical outcomes initially were thought to be similar to those of other SARS-CoV-2 variants, early reports suggest that infection with the B.1.1.7 variant may increase death risk by about 30%.
A coauthor of the current study, Kristian Andersen, PhD, told the New York Times , “Nothing in this paper is surprising, but people need to see it.”
Dr. Andersen, a virologist at the Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla, Calif., added that “we should probably prepare for this being the predominant lineage in most places in the United States by March.”
The study of the B.1.1.7 variant adds support for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention prediction in January that it would dominate by March.
“Our study shows that the U.S. is on a similar trajectory as other countries where B.1.1.7 rapidly became the dominant SARS-CoV-2 variant, requiring immediate and decisive action to minimize COVID-19 morbidity and mortality,” the researchers wrote.
The authors pointed out that the B.1.1.7 variant became the dominant SARS-CoV-2 strain in the United Kingdom within a couple of months of its detection.
“Since then, the variant has been increasingly observed across many European countries, including Portugal and Ireland, which, like the U.K., observed devastating waves of COVID-19 after B.1.1.7 became dominant,” the authors wrote.
“Category 5” storm
The B.1.1.7 variant has likely been spreading between U.S. states since at least December, they wrote.
This news organization reported on Jan. 15 that, as of Jan. 13, the B.1.1.7 variant was seen in 76 cases across 12 U.S. states, according to an early release of the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
As of Feb. 7, there were 690 cases of the B.1.1.7 variant in the US in 33 states, according to the CDC.
Dr. Washington and colleagues examined more than 500,000 coronavirus test samples from cases across the United States that were tested at San Mateo, Calif.–based Helix facilities since July.
In the study, they found inconsistent prevalence of the variant across states. By the last week in January, the researchers estimated the proportion of B.1.1.7 in the U.S. population to be about 2.1% of all COVID-19 cases, though they found it made up about 2% of all COVID-19 cases in California and about 4.5% of cases in Florida. The authors acknowledged that their data is less robust outside of those two states.
Though that seems a relatively low frequency, “our estimates show that its growth rate is at least 35%-45% increased and doubling every week and a half,” the authors wrote.
“Because laboratories in the U.S. are only sequencing a small subset of SARS-CoV-2 samples, the true sequence diversity of SARS-CoV-2 in this country is still unknown,” they noted.
Michael Osterholm, PhD, MPH, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, said last week that the United States is facing a “Category 5” storm with the spread of the B.1.1.7 variant as well as the variants first identified in South Africa and Brazil.
“We are going to see something like we have not seen yet in this country,” Dr. Osterholm said recently on NBC’s Meet the Press.
Lead author Nicole L. Washington and many of the coauthors are employees of Helix. Other coauthors are employees of Illumina. Three coauthors own stock in ILMN. The work was funded by Illumina, Helix, the Innovative Genomics Institute, and the New Frontiers in Research Fund provided by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The SARS-CoV-2 variant first detected in the United Kingdom is rapidly becoming the dominant strain in several countries and is doubling every 10 days in the United States, according to new data.
The findings by Nicole L. Washington, PhD, associate director of research at the genomics company Helix, and colleagues were posted Feb. 7, 2021, on the preprint server medRxiv. The paper has not been peer-reviewed in a scientific journal.
The researchers also found that the transmission rate in the United States of the variant, labeled B.1.1.7, is 30%-40% higher than that of more common lineages.
While clinical outcomes initially were thought to be similar to those of other SARS-CoV-2 variants, early reports suggest that infection with the B.1.1.7 variant may increase death risk by about 30%.
A coauthor of the current study, Kristian Andersen, PhD, told the New York Times , “Nothing in this paper is surprising, but people need to see it.”
Dr. Andersen, a virologist at the Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla, Calif., added that “we should probably prepare for this being the predominant lineage in most places in the United States by March.”
The study of the B.1.1.7 variant adds support for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention prediction in January that it would dominate by March.
“Our study shows that the U.S. is on a similar trajectory as other countries where B.1.1.7 rapidly became the dominant SARS-CoV-2 variant, requiring immediate and decisive action to minimize COVID-19 morbidity and mortality,” the researchers wrote.
The authors pointed out that the B.1.1.7 variant became the dominant SARS-CoV-2 strain in the United Kingdom within a couple of months of its detection.
“Since then, the variant has been increasingly observed across many European countries, including Portugal and Ireland, which, like the U.K., observed devastating waves of COVID-19 after B.1.1.7 became dominant,” the authors wrote.
“Category 5” storm
The B.1.1.7 variant has likely been spreading between U.S. states since at least December, they wrote.
This news organization reported on Jan. 15 that, as of Jan. 13, the B.1.1.7 variant was seen in 76 cases across 12 U.S. states, according to an early release of the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
As of Feb. 7, there were 690 cases of the B.1.1.7 variant in the US in 33 states, according to the CDC.
Dr. Washington and colleagues examined more than 500,000 coronavirus test samples from cases across the United States that were tested at San Mateo, Calif.–based Helix facilities since July.
In the study, they found inconsistent prevalence of the variant across states. By the last week in January, the researchers estimated the proportion of B.1.1.7 in the U.S. population to be about 2.1% of all COVID-19 cases, though they found it made up about 2% of all COVID-19 cases in California and about 4.5% of cases in Florida. The authors acknowledged that their data is less robust outside of those two states.
Though that seems a relatively low frequency, “our estimates show that its growth rate is at least 35%-45% increased and doubling every week and a half,” the authors wrote.
“Because laboratories in the U.S. are only sequencing a small subset of SARS-CoV-2 samples, the true sequence diversity of SARS-CoV-2 in this country is still unknown,” they noted.
Michael Osterholm, PhD, MPH, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, said last week that the United States is facing a “Category 5” storm with the spread of the B.1.1.7 variant as well as the variants first identified in South Africa and Brazil.
“We are going to see something like we have not seen yet in this country,” Dr. Osterholm said recently on NBC’s Meet the Press.
Lead author Nicole L. Washington and many of the coauthors are employees of Helix. Other coauthors are employees of Illumina. Three coauthors own stock in ILMN. The work was funded by Illumina, Helix, the Innovative Genomics Institute, and the New Frontiers in Research Fund provided by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Are diagnosticians chasing COVID-linked zebras and missing horses?
The emergence of multiple inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) in association with COVID-19 may be complicating the investigation and diagnosis of more common viral and bacterial infections, potentially delaying treatment and prolonging hospital stays.
Two recent articles published online in Hospital Pediatrics provide evidence of this phenomenon. The articles outlined case studies of children who underwent extensive investigation for MIS-C when in fact they had less severe and more common infections. MIS-C is a severe but rare syndrome that involves systemic hyperinflammation with fever and multisystem organ dysfunction similar to that of Kawasaki disease (KD).
In one of the articles, Matthew Molloy, MD, MPH, of the division of pediatric hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, and colleagues aptly asked: “What are we missing in our search for MIS-C?”
E. coli, not SARS-CoV-2
That question arose from a case involving a 3-year-old boy who had a 6-day history of fever and fatigue. Three days earlier, he had tested negative for strep antigen and COVID-19. He had a persistent, high fever, reduced appetite, and reduced urine output and was taken to the ED. On physical examination, there was no rash, skin peeling, redness of the eye or oral mucosa, congestion, rhinorrhea, cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
Urinalysis results and exam findings were suspicious for pyelonephritis. Other findings from an extensive laboratory workup raised the alarm that the boy was suffering from MIS-C as opposed to incomplete KD. After admission to hospital medicine, the cardiology, rheumatology, and infectious disease teams were called in to consult.
Repeat labs were planned for the following day before initiating therapy. On day 2, the child’s urine culture was positive for gram-negative rods, later identified as Escherichia coli. The boy was started on ceftriaxone. Left renal scarring was apparent on ultrasound. The patient’s condition resolved after 36 hours, and he was discharged home with antibiotics.
‘Diagnosis derailed’
Calling this a case of “diagnosis derailed,” the authors noted that, in the pre-COVID era, this child’s signs and symptoms would likely have triggered a more targeted and less costly evaluation for more common infectious and noninfectious causes, including pyelonephritis, absent any physical exam findings consistent with KD.
“However, the patient presented in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic with growing awareness of a new clinical entity,” Dr. Molloy and colleagues wrote. “Anchored to the patient’s persistent fever, the medical team initiated an extensive, costly, and ultimately unnecessary workup to avoid missing the diagnosis of MIS-C; a not yet well-described diagnosis with potentially severe morbidity.”
Confirmation bias and diagnostic momentum likely contributed to the early focus on MIS-C rather than more common alternatives, the authors acknowledged. The addition of mildly abnormal laboratory data not typically obtained in the evaluation of fever led the team astray. “The diagnosis and definitive treatment may have been made earlier had the focus on concern for MIS-C not been present,” Dr. Molloy said in an interview.
Keeping value in care
The authors recognized that their initial approach to evaluating for MIS-C provided low-value care. “In our desire to not ‘miss’ MIS-C, we were performing costly evaluations that at times produced mildly abnormal, nonspecific results,” they wrote. That triggered a cascade of specialty consultations, follow-up testing, and an unwarranted diagnostic preoccupation with MIS-C.
Determining the extra price tag for the child’s workup would be complex and difficult because there is a difference in the cost to the hospital and the cost to the family, Dr. Molloy said. “However, there are potential cost savings that would be related to making a correct diagnosis in a timely manner in terms of preventing downstream effects from delayed diagnoses.”
Even as clinicians struggle with the challenging SARS-CoV-2 learning curve, Dr. Molloy and associates urged them to continue to strive for high-value care, with an unwavering focus on using only necessary resources, a stewardship the pandemic has shown to be critical.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has been an incredibly stressful time for physicians and for families,” Dr. Molloy said. “COVID-19 and related conditions like MIS-C are new, and we are learning more and more about them every week. These diagnoses are understandably on the minds of physicians and families when children present with fever.” Notwithstanding, the boy’s case underscores the need for clinicians to consider alternate diagnoses and the value of the care provided.
Impact of bias
Dr. Molloy’s group brings home the cognitive biases practitioners often suffer from, including anchoring and confirmation bias and diagnostic momentum, according to J. Howard Smart, MD, chief of pediatrics at Sharp Mary Birch Hospital for Women and Newborns, San Diego, and an assistant clinical professor of pediatrics at University of California, San Diego.
“But it is one thing to recognize these in retrospect and quite another to consider whether they may be happening to you yourself in real time,” he said in an interview. “It is almost as if we need to have a ‘time out,’ where we stop and ask ourselves whether there is something else that could be explaining our patient’s presentation, something that would be more common and more likely to be occurring.”
According to Dr. Smart, who was not involved in Dr. Molloy’s study, the team’s premature diagnostic focus on MIS-C was almost the inverse of what typically happens with KD. “It is usually the case that Kawasaki disease does not enter the differential diagnosis until late in the course of the fever, typically on day 5 or later, when it may have been better to think of it earlier,” he said.
In the second article, Andrea Dean, MD, of the department of pediatrics at Baylor College of Medicine and Texas Children’s Hospital, both in Houston, and colleagues outlined the cases of five patients aged 8-17 years who were hospitalized in May 2020 for suspected MIS-C. They exhibited inflammatory and other concerning indicators but were eventually discharged with a diagnosis of murine typhus.
This flea-borne infection, most commonly reported in the United States in the southeastern Gulf Coast region, Hawaii, and California, is often associated with a triad of fever, rash, and headache.
Cases have been rising in southern Texas, and Dr. Dean and colleagues postulated that school closures and social distancing may have increased exposure as a result of children spending more time outdoors or with pets. “Alternatively, parental concern for SARS-CoV-2 infection could mean children with symptoms are presenting to care and being referred or admitted to the hospital more frequently due to provider concern for MIS-C,” they wrote.
Cardiac involvement
The most concerning of the five cases in terms of possible MIS-C, Dr. Dean said in an interview, was that of a 12-year-old boy who had fever for 6 days in association with headache, eczematous rash, dry lips, and conjunctivitis. Laboratory tests showed a mildly elevated C-reactive protein level, hyponatremia, and thrombocytopenia, as well as sterile pyuria and mildly elevated prothrombin time. He was treated empirically with doxycycline, and his fever resolved over the next 24 hours.
An echocardiogram at initial evaluation, however, revealed mild dilation of the left anterior descending and right coronary arteries, which led to the administration of intravenous immunoglobulin and aspirin for atypical KD, in contrast to MIS-C. The authors postulated that mild cardiac involvement in disorders other than MIS-C and KD may be underrecognized.
The lesson from these cases, Dr. Dean and associates concluded, is that hospitalists must maintain a wide differential diagnosis when assessing a child with prolonged fever and evidence of systemic inflammation. The CDC stipulates that a diagnosis of MIS-C requires the absence of a plausible alternative diagnosis.
In addition to common viral, bacterial, and noninfectious disorders, a range of regional endemic rickettsial and parasitic infections must be considered as alternative diagnoses to MIS-C. “Many of these diseases cannot be reliably differentiated from MIS-C on presentation, and as community exposure to SARS-CoV-2 grows, hospitalists should be prepared to admit febrile children with evidence of systemic inflammation for brief observation periods to evaluate for MIS-C,” Dr. Dean’s group wrote. In this context, however, empiric treatment for common or even uncommon infectious diseases may avoid overdiagnosis and overtreatment of MIS-C as well as improve patient outcomes.
“We do have specific MIS-C guidelines at our institution,” Dr. Dean said, “but like all institutions, we are dealing with the broad definition of MIS-C according to the World Health Organization and the CDC, which is really the takeaway from this paper.”
More difficult differentiation
Both groups of authors pointed out that, as SARS-CoV-2 spreads throughout a community, a higher percentage of the population will have positive results on antibody testing, and such results will become less useful for differentiating between MIS-C and other conditions.
Despite these series’ cautionary lessons, other experts point to the critical importance of including MIS-C early on in the interest of efficient diagnosis and therapy. “In the cases cited, other pathologies were evaluated for and treated accordingly,” said Kara Gross Margolis, MD, AGAF, an associate professor of pediatrics in the division of pediatric gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Morgan Stanley Children’s Hospital,New York. “These papers stress the need for a balance that is important, and all potential diagnoses need to be considered, but MIS-C, due to its potential severe consequences, also needs to be on our differential now.”
In her view, as this new high-morbidity entity becomes more widespread during the pandemic, it will be increasingly important to keep this condition on the diagnostic radar.
Interestingly, in a converse example of diagnostic clouding, Dr. Gross Margolis’s group reported (Gastroenterology. 2020 Oct;159[4]:1571-4.e2) last year on a pediatric case series in which the presence of gastrointestinal symptoms in children with COVID-19–related MIS-C muddied the diagnosis by confusing this potentially severe syndrome with more common and less toxic gastrointestinal infections.
According to Dr. Smart, although the two reports don’t offer evidence for a particular diagnostic practice, they can inform the decision-making process. “It may be that we will have enough evidence shortly to say what the best practice is regarding diagnostic evaluation of possible MIS-C cases,” he said. “Until then, we must remember that common things occur commonly, even during a global pandemic.”
Neither of the two reports received any specific funding. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The emergence of multiple inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) in association with COVID-19 may be complicating the investigation and diagnosis of more common viral and bacterial infections, potentially delaying treatment and prolonging hospital stays.
Two recent articles published online in Hospital Pediatrics provide evidence of this phenomenon. The articles outlined case studies of children who underwent extensive investigation for MIS-C when in fact they had less severe and more common infections. MIS-C is a severe but rare syndrome that involves systemic hyperinflammation with fever and multisystem organ dysfunction similar to that of Kawasaki disease (KD).
In one of the articles, Matthew Molloy, MD, MPH, of the division of pediatric hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, and colleagues aptly asked: “What are we missing in our search for MIS-C?”
E. coli, not SARS-CoV-2
That question arose from a case involving a 3-year-old boy who had a 6-day history of fever and fatigue. Three days earlier, he had tested negative for strep antigen and COVID-19. He had a persistent, high fever, reduced appetite, and reduced urine output and was taken to the ED. On physical examination, there was no rash, skin peeling, redness of the eye or oral mucosa, congestion, rhinorrhea, cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
Urinalysis results and exam findings were suspicious for pyelonephritis. Other findings from an extensive laboratory workup raised the alarm that the boy was suffering from MIS-C as opposed to incomplete KD. After admission to hospital medicine, the cardiology, rheumatology, and infectious disease teams were called in to consult.
Repeat labs were planned for the following day before initiating therapy. On day 2, the child’s urine culture was positive for gram-negative rods, later identified as Escherichia coli. The boy was started on ceftriaxone. Left renal scarring was apparent on ultrasound. The patient’s condition resolved after 36 hours, and he was discharged home with antibiotics.
‘Diagnosis derailed’
Calling this a case of “diagnosis derailed,” the authors noted that, in the pre-COVID era, this child’s signs and symptoms would likely have triggered a more targeted and less costly evaluation for more common infectious and noninfectious causes, including pyelonephritis, absent any physical exam findings consistent with KD.
“However, the patient presented in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic with growing awareness of a new clinical entity,” Dr. Molloy and colleagues wrote. “Anchored to the patient’s persistent fever, the medical team initiated an extensive, costly, and ultimately unnecessary workup to avoid missing the diagnosis of MIS-C; a not yet well-described diagnosis with potentially severe morbidity.”
Confirmation bias and diagnostic momentum likely contributed to the early focus on MIS-C rather than more common alternatives, the authors acknowledged. The addition of mildly abnormal laboratory data not typically obtained in the evaluation of fever led the team astray. “The diagnosis and definitive treatment may have been made earlier had the focus on concern for MIS-C not been present,” Dr. Molloy said in an interview.
Keeping value in care
The authors recognized that their initial approach to evaluating for MIS-C provided low-value care. “In our desire to not ‘miss’ MIS-C, we were performing costly evaluations that at times produced mildly abnormal, nonspecific results,” they wrote. That triggered a cascade of specialty consultations, follow-up testing, and an unwarranted diagnostic preoccupation with MIS-C.
Determining the extra price tag for the child’s workup would be complex and difficult because there is a difference in the cost to the hospital and the cost to the family, Dr. Molloy said. “However, there are potential cost savings that would be related to making a correct diagnosis in a timely manner in terms of preventing downstream effects from delayed diagnoses.”
Even as clinicians struggle with the challenging SARS-CoV-2 learning curve, Dr. Molloy and associates urged them to continue to strive for high-value care, with an unwavering focus on using only necessary resources, a stewardship the pandemic has shown to be critical.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has been an incredibly stressful time for physicians and for families,” Dr. Molloy said. “COVID-19 and related conditions like MIS-C are new, and we are learning more and more about them every week. These diagnoses are understandably on the minds of physicians and families when children present with fever.” Notwithstanding, the boy’s case underscores the need for clinicians to consider alternate diagnoses and the value of the care provided.
Impact of bias
Dr. Molloy’s group brings home the cognitive biases practitioners often suffer from, including anchoring and confirmation bias and diagnostic momentum, according to J. Howard Smart, MD, chief of pediatrics at Sharp Mary Birch Hospital for Women and Newborns, San Diego, and an assistant clinical professor of pediatrics at University of California, San Diego.
“But it is one thing to recognize these in retrospect and quite another to consider whether they may be happening to you yourself in real time,” he said in an interview. “It is almost as if we need to have a ‘time out,’ where we stop and ask ourselves whether there is something else that could be explaining our patient’s presentation, something that would be more common and more likely to be occurring.”
According to Dr. Smart, who was not involved in Dr. Molloy’s study, the team’s premature diagnostic focus on MIS-C was almost the inverse of what typically happens with KD. “It is usually the case that Kawasaki disease does not enter the differential diagnosis until late in the course of the fever, typically on day 5 or later, when it may have been better to think of it earlier,” he said.
In the second article, Andrea Dean, MD, of the department of pediatrics at Baylor College of Medicine and Texas Children’s Hospital, both in Houston, and colleagues outlined the cases of five patients aged 8-17 years who were hospitalized in May 2020 for suspected MIS-C. They exhibited inflammatory and other concerning indicators but were eventually discharged with a diagnosis of murine typhus.
This flea-borne infection, most commonly reported in the United States in the southeastern Gulf Coast region, Hawaii, and California, is often associated with a triad of fever, rash, and headache.
Cases have been rising in southern Texas, and Dr. Dean and colleagues postulated that school closures and social distancing may have increased exposure as a result of children spending more time outdoors or with pets. “Alternatively, parental concern for SARS-CoV-2 infection could mean children with symptoms are presenting to care and being referred or admitted to the hospital more frequently due to provider concern for MIS-C,” they wrote.
Cardiac involvement
The most concerning of the five cases in terms of possible MIS-C, Dr. Dean said in an interview, was that of a 12-year-old boy who had fever for 6 days in association with headache, eczematous rash, dry lips, and conjunctivitis. Laboratory tests showed a mildly elevated C-reactive protein level, hyponatremia, and thrombocytopenia, as well as sterile pyuria and mildly elevated prothrombin time. He was treated empirically with doxycycline, and his fever resolved over the next 24 hours.
An echocardiogram at initial evaluation, however, revealed mild dilation of the left anterior descending and right coronary arteries, which led to the administration of intravenous immunoglobulin and aspirin for atypical KD, in contrast to MIS-C. The authors postulated that mild cardiac involvement in disorders other than MIS-C and KD may be underrecognized.
The lesson from these cases, Dr. Dean and associates concluded, is that hospitalists must maintain a wide differential diagnosis when assessing a child with prolonged fever and evidence of systemic inflammation. The CDC stipulates that a diagnosis of MIS-C requires the absence of a plausible alternative diagnosis.
In addition to common viral, bacterial, and noninfectious disorders, a range of regional endemic rickettsial and parasitic infections must be considered as alternative diagnoses to MIS-C. “Many of these diseases cannot be reliably differentiated from MIS-C on presentation, and as community exposure to SARS-CoV-2 grows, hospitalists should be prepared to admit febrile children with evidence of systemic inflammation for brief observation periods to evaluate for MIS-C,” Dr. Dean’s group wrote. In this context, however, empiric treatment for common or even uncommon infectious diseases may avoid overdiagnosis and overtreatment of MIS-C as well as improve patient outcomes.
“We do have specific MIS-C guidelines at our institution,” Dr. Dean said, “but like all institutions, we are dealing with the broad definition of MIS-C according to the World Health Organization and the CDC, which is really the takeaway from this paper.”
More difficult differentiation
Both groups of authors pointed out that, as SARS-CoV-2 spreads throughout a community, a higher percentage of the population will have positive results on antibody testing, and such results will become less useful for differentiating between MIS-C and other conditions.
Despite these series’ cautionary lessons, other experts point to the critical importance of including MIS-C early on in the interest of efficient diagnosis and therapy. “In the cases cited, other pathologies were evaluated for and treated accordingly,” said Kara Gross Margolis, MD, AGAF, an associate professor of pediatrics in the division of pediatric gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Morgan Stanley Children’s Hospital,New York. “These papers stress the need for a balance that is important, and all potential diagnoses need to be considered, but MIS-C, due to its potential severe consequences, also needs to be on our differential now.”
In her view, as this new high-morbidity entity becomes more widespread during the pandemic, it will be increasingly important to keep this condition on the diagnostic radar.
Interestingly, in a converse example of diagnostic clouding, Dr. Gross Margolis’s group reported (Gastroenterology. 2020 Oct;159[4]:1571-4.e2) last year on a pediatric case series in which the presence of gastrointestinal symptoms in children with COVID-19–related MIS-C muddied the diagnosis by confusing this potentially severe syndrome with more common and less toxic gastrointestinal infections.
According to Dr. Smart, although the two reports don’t offer evidence for a particular diagnostic practice, they can inform the decision-making process. “It may be that we will have enough evidence shortly to say what the best practice is regarding diagnostic evaluation of possible MIS-C cases,” he said. “Until then, we must remember that common things occur commonly, even during a global pandemic.”
Neither of the two reports received any specific funding. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The emergence of multiple inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) in association with COVID-19 may be complicating the investigation and diagnosis of more common viral and bacterial infections, potentially delaying treatment and prolonging hospital stays.
Two recent articles published online in Hospital Pediatrics provide evidence of this phenomenon. The articles outlined case studies of children who underwent extensive investigation for MIS-C when in fact they had less severe and more common infections. MIS-C is a severe but rare syndrome that involves systemic hyperinflammation with fever and multisystem organ dysfunction similar to that of Kawasaki disease (KD).
In one of the articles, Matthew Molloy, MD, MPH, of the division of pediatric hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, and colleagues aptly asked: “What are we missing in our search for MIS-C?”
E. coli, not SARS-CoV-2
That question arose from a case involving a 3-year-old boy who had a 6-day history of fever and fatigue. Three days earlier, he had tested negative for strep antigen and COVID-19. He had a persistent, high fever, reduced appetite, and reduced urine output and was taken to the ED. On physical examination, there was no rash, skin peeling, redness of the eye or oral mucosa, congestion, rhinorrhea, cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
Urinalysis results and exam findings were suspicious for pyelonephritis. Other findings from an extensive laboratory workup raised the alarm that the boy was suffering from MIS-C as opposed to incomplete KD. After admission to hospital medicine, the cardiology, rheumatology, and infectious disease teams were called in to consult.
Repeat labs were planned for the following day before initiating therapy. On day 2, the child’s urine culture was positive for gram-negative rods, later identified as Escherichia coli. The boy was started on ceftriaxone. Left renal scarring was apparent on ultrasound. The patient’s condition resolved after 36 hours, and he was discharged home with antibiotics.
‘Diagnosis derailed’
Calling this a case of “diagnosis derailed,” the authors noted that, in the pre-COVID era, this child’s signs and symptoms would likely have triggered a more targeted and less costly evaluation for more common infectious and noninfectious causes, including pyelonephritis, absent any physical exam findings consistent with KD.
“However, the patient presented in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic with growing awareness of a new clinical entity,” Dr. Molloy and colleagues wrote. “Anchored to the patient’s persistent fever, the medical team initiated an extensive, costly, and ultimately unnecessary workup to avoid missing the diagnosis of MIS-C; a not yet well-described diagnosis with potentially severe morbidity.”
Confirmation bias and diagnostic momentum likely contributed to the early focus on MIS-C rather than more common alternatives, the authors acknowledged. The addition of mildly abnormal laboratory data not typically obtained in the evaluation of fever led the team astray. “The diagnosis and definitive treatment may have been made earlier had the focus on concern for MIS-C not been present,” Dr. Molloy said in an interview.
Keeping value in care
The authors recognized that their initial approach to evaluating for MIS-C provided low-value care. “In our desire to not ‘miss’ MIS-C, we were performing costly evaluations that at times produced mildly abnormal, nonspecific results,” they wrote. That triggered a cascade of specialty consultations, follow-up testing, and an unwarranted diagnostic preoccupation with MIS-C.
Determining the extra price tag for the child’s workup would be complex and difficult because there is a difference in the cost to the hospital and the cost to the family, Dr. Molloy said. “However, there are potential cost savings that would be related to making a correct diagnosis in a timely manner in terms of preventing downstream effects from delayed diagnoses.”
Even as clinicians struggle with the challenging SARS-CoV-2 learning curve, Dr. Molloy and associates urged them to continue to strive for high-value care, with an unwavering focus on using only necessary resources, a stewardship the pandemic has shown to be critical.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has been an incredibly stressful time for physicians and for families,” Dr. Molloy said. “COVID-19 and related conditions like MIS-C are new, and we are learning more and more about them every week. These diagnoses are understandably on the minds of physicians and families when children present with fever.” Notwithstanding, the boy’s case underscores the need for clinicians to consider alternate diagnoses and the value of the care provided.
Impact of bias
Dr. Molloy’s group brings home the cognitive biases practitioners often suffer from, including anchoring and confirmation bias and diagnostic momentum, according to J. Howard Smart, MD, chief of pediatrics at Sharp Mary Birch Hospital for Women and Newborns, San Diego, and an assistant clinical professor of pediatrics at University of California, San Diego.
“But it is one thing to recognize these in retrospect and quite another to consider whether they may be happening to you yourself in real time,” he said in an interview. “It is almost as if we need to have a ‘time out,’ where we stop and ask ourselves whether there is something else that could be explaining our patient’s presentation, something that would be more common and more likely to be occurring.”
According to Dr. Smart, who was not involved in Dr. Molloy’s study, the team’s premature diagnostic focus on MIS-C was almost the inverse of what typically happens with KD. “It is usually the case that Kawasaki disease does not enter the differential diagnosis until late in the course of the fever, typically on day 5 or later, when it may have been better to think of it earlier,” he said.
In the second article, Andrea Dean, MD, of the department of pediatrics at Baylor College of Medicine and Texas Children’s Hospital, both in Houston, and colleagues outlined the cases of five patients aged 8-17 years who were hospitalized in May 2020 for suspected MIS-C. They exhibited inflammatory and other concerning indicators but were eventually discharged with a diagnosis of murine typhus.
This flea-borne infection, most commonly reported in the United States in the southeastern Gulf Coast region, Hawaii, and California, is often associated with a triad of fever, rash, and headache.
Cases have been rising in southern Texas, and Dr. Dean and colleagues postulated that school closures and social distancing may have increased exposure as a result of children spending more time outdoors or with pets. “Alternatively, parental concern for SARS-CoV-2 infection could mean children with symptoms are presenting to care and being referred or admitted to the hospital more frequently due to provider concern for MIS-C,” they wrote.
Cardiac involvement
The most concerning of the five cases in terms of possible MIS-C, Dr. Dean said in an interview, was that of a 12-year-old boy who had fever for 6 days in association with headache, eczematous rash, dry lips, and conjunctivitis. Laboratory tests showed a mildly elevated C-reactive protein level, hyponatremia, and thrombocytopenia, as well as sterile pyuria and mildly elevated prothrombin time. He was treated empirically with doxycycline, and his fever resolved over the next 24 hours.
An echocardiogram at initial evaluation, however, revealed mild dilation of the left anterior descending and right coronary arteries, which led to the administration of intravenous immunoglobulin and aspirin for atypical KD, in contrast to MIS-C. The authors postulated that mild cardiac involvement in disorders other than MIS-C and KD may be underrecognized.
The lesson from these cases, Dr. Dean and associates concluded, is that hospitalists must maintain a wide differential diagnosis when assessing a child with prolonged fever and evidence of systemic inflammation. The CDC stipulates that a diagnosis of MIS-C requires the absence of a plausible alternative diagnosis.
In addition to common viral, bacterial, and noninfectious disorders, a range of regional endemic rickettsial and parasitic infections must be considered as alternative diagnoses to MIS-C. “Many of these diseases cannot be reliably differentiated from MIS-C on presentation, and as community exposure to SARS-CoV-2 grows, hospitalists should be prepared to admit febrile children with evidence of systemic inflammation for brief observation periods to evaluate for MIS-C,” Dr. Dean’s group wrote. In this context, however, empiric treatment for common or even uncommon infectious diseases may avoid overdiagnosis and overtreatment of MIS-C as well as improve patient outcomes.
“We do have specific MIS-C guidelines at our institution,” Dr. Dean said, “but like all institutions, we are dealing with the broad definition of MIS-C according to the World Health Organization and the CDC, which is really the takeaway from this paper.”
More difficult differentiation
Both groups of authors pointed out that, as SARS-CoV-2 spreads throughout a community, a higher percentage of the population will have positive results on antibody testing, and such results will become less useful for differentiating between MIS-C and other conditions.
Despite these series’ cautionary lessons, other experts point to the critical importance of including MIS-C early on in the interest of efficient diagnosis and therapy. “In the cases cited, other pathologies were evaluated for and treated accordingly,” said Kara Gross Margolis, MD, AGAF, an associate professor of pediatrics in the division of pediatric gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Morgan Stanley Children’s Hospital,New York. “These papers stress the need for a balance that is important, and all potential diagnoses need to be considered, but MIS-C, due to its potential severe consequences, also needs to be on our differential now.”
In her view, as this new high-morbidity entity becomes more widespread during the pandemic, it will be increasingly important to keep this condition on the diagnostic radar.
Interestingly, in a converse example of diagnostic clouding, Dr. Gross Margolis’s group reported (Gastroenterology. 2020 Oct;159[4]:1571-4.e2) last year on a pediatric case series in which the presence of gastrointestinal symptoms in children with COVID-19–related MIS-C muddied the diagnosis by confusing this potentially severe syndrome with more common and less toxic gastrointestinal infections.
According to Dr. Smart, although the two reports don’t offer evidence for a particular diagnostic practice, they can inform the decision-making process. “It may be that we will have enough evidence shortly to say what the best practice is regarding diagnostic evaluation of possible MIS-C cases,” he said. “Until then, we must remember that common things occur commonly, even during a global pandemic.”
Neither of the two reports received any specific funding. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SARS-CoV-2 in hospitalized children and youth
Clinical syndromes and predictors of disease severity
Clinical questions: What are the demographics and clinical features of pediatric severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) syndromes, and which admitting demographics and clinical features are predictive of disease severity?
Background: In children, SARS-CoV-2 causes respiratory disease and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) as well as other clinical manifestations. The authors of this study chose to address the gap of identifying characteristics for severe disease caused by SARS-CoV-2, including respiratory disease, MIS-C and other manifestations.
Study design: Retrospective and prospective cohort analysis of hospitalized children
Setting: Participating hospitals in Tri-State Pediatric COVID-19 Consortium, including hospitals in New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut.
Synopsis: The authors identified hospitalized patients 22 years old or younger who had a positive SARS-CoV-2 test or met the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Preventions’ MIS-C case definition. For comparative analysis, patients were divided into a respiratory disease group (based on the World Health Organization’s criteria for COVID-19), MIS-C group or other group (based on the primary reason for hospitalization).
The authors included 281 patients in the study. 51% of the patients presented with respiratory disease, 25% with MIS-C and 25% with other symptoms, including gastrointestinal, or fever. 51% of all patients were Hispanic and 23% were non-Black Hispanic. The most common pre-existing comorbidities amongst all groups were obesity (34%) and asthma (14%).
Patients with respiratory disease had a median age of 14 years while those with MIS-C had a median age of 7 years. Patients more commonly identified as non-Hispanic Black in the MIS-C group vs the respiratory group (35% vs. 18%). Obesity and medical complexity were more prevalent in the respiratory group relative to the MIS-C group. 75% of patients with MIS-C had gastrointestinal symptoms. 44% of respiratory patients had a chest radiograph with bilateral infiltrates on admission, and 18% or respiratory patients required invasive mechanical ventilation. The most common complications in the respiratory group were acute respiratory distress syndrome (17%) and acute kidney injury (11%), whereas shock (35%) and cardiac dysfunction (25%) were the most common complications in the MIS-C group. The median length of stay for all patients was 4 days (IQR 2-8 days).
Patients with MIS-C were more likely to be admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) but all deaths (7 patients) occurred in the respiratory group. 40% of patients with respiratory disease, 56% of patients with MIS-C, and 6% of other patients met the authors’ definition of severe disease (ICU admission > 48 hours). For the respiratory group, younger age, obesity, increasing white blood cell count, hypoxia, and bilateral infiltrates on chest radiograph were independent predictors of severe disease based on multivariate analyses. For the MIS-C group, lower absolute lymphocyte count and increasing CRP at admission were independent predictors of severity.
Bottom line: Mortality in pediatric patients is low. Ethnicity and race were not predictive of disease severity in this model, even though 51% of the patients studied were Hispanic and 23% were non-Hispanic Black. Severity of illness for patients with respiratory disease was found to be associated with younger age, obesity, increasing white blood cell count, hypoxia, and bilateral infiltrates on chest radiograph. Severity of illness in patients with MIS-C was associated with lower absolute lymphocyte count and increasing CRP.
Citation: Fernandes DM, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 clinical syndromes and predictors of disease severity in hospitalized children and youth. J Pediatr. 2020 Nov 14;S0022-3476(20):31393-7. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.11.016.
Dr. Kumar is an assistant professor of pediatrics at the Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine of Case Western Reserve University and a pediatric hospitalist at Cleveland Clinic Children’s. She is the pediatric editor of The Hospitalist.
Clinical syndromes and predictors of disease severity
Clinical syndromes and predictors of disease severity
Clinical questions: What are the demographics and clinical features of pediatric severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) syndromes, and which admitting demographics and clinical features are predictive of disease severity?
Background: In children, SARS-CoV-2 causes respiratory disease and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) as well as other clinical manifestations. The authors of this study chose to address the gap of identifying characteristics for severe disease caused by SARS-CoV-2, including respiratory disease, MIS-C and other manifestations.
Study design: Retrospective and prospective cohort analysis of hospitalized children
Setting: Participating hospitals in Tri-State Pediatric COVID-19 Consortium, including hospitals in New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut.
Synopsis: The authors identified hospitalized patients 22 years old or younger who had a positive SARS-CoV-2 test or met the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Preventions’ MIS-C case definition. For comparative analysis, patients were divided into a respiratory disease group (based on the World Health Organization’s criteria for COVID-19), MIS-C group or other group (based on the primary reason for hospitalization).
The authors included 281 patients in the study. 51% of the patients presented with respiratory disease, 25% with MIS-C and 25% with other symptoms, including gastrointestinal, or fever. 51% of all patients were Hispanic and 23% were non-Black Hispanic. The most common pre-existing comorbidities amongst all groups were obesity (34%) and asthma (14%).
Patients with respiratory disease had a median age of 14 years while those with MIS-C had a median age of 7 years. Patients more commonly identified as non-Hispanic Black in the MIS-C group vs the respiratory group (35% vs. 18%). Obesity and medical complexity were more prevalent in the respiratory group relative to the MIS-C group. 75% of patients with MIS-C had gastrointestinal symptoms. 44% of respiratory patients had a chest radiograph with bilateral infiltrates on admission, and 18% or respiratory patients required invasive mechanical ventilation. The most common complications in the respiratory group were acute respiratory distress syndrome (17%) and acute kidney injury (11%), whereas shock (35%) and cardiac dysfunction (25%) were the most common complications in the MIS-C group. The median length of stay for all patients was 4 days (IQR 2-8 days).
Patients with MIS-C were more likely to be admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) but all deaths (7 patients) occurred in the respiratory group. 40% of patients with respiratory disease, 56% of patients with MIS-C, and 6% of other patients met the authors’ definition of severe disease (ICU admission > 48 hours). For the respiratory group, younger age, obesity, increasing white blood cell count, hypoxia, and bilateral infiltrates on chest radiograph were independent predictors of severe disease based on multivariate analyses. For the MIS-C group, lower absolute lymphocyte count and increasing CRP at admission were independent predictors of severity.
Bottom line: Mortality in pediatric patients is low. Ethnicity and race were not predictive of disease severity in this model, even though 51% of the patients studied were Hispanic and 23% were non-Hispanic Black. Severity of illness for patients with respiratory disease was found to be associated with younger age, obesity, increasing white blood cell count, hypoxia, and bilateral infiltrates on chest radiograph. Severity of illness in patients with MIS-C was associated with lower absolute lymphocyte count and increasing CRP.
Citation: Fernandes DM, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 clinical syndromes and predictors of disease severity in hospitalized children and youth. J Pediatr. 2020 Nov 14;S0022-3476(20):31393-7. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.11.016.
Dr. Kumar is an assistant professor of pediatrics at the Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine of Case Western Reserve University and a pediatric hospitalist at Cleveland Clinic Children’s. She is the pediatric editor of The Hospitalist.
Clinical questions: What are the demographics and clinical features of pediatric severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) syndromes, and which admitting demographics and clinical features are predictive of disease severity?
Background: In children, SARS-CoV-2 causes respiratory disease and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) as well as other clinical manifestations. The authors of this study chose to address the gap of identifying characteristics for severe disease caused by SARS-CoV-2, including respiratory disease, MIS-C and other manifestations.
Study design: Retrospective and prospective cohort analysis of hospitalized children
Setting: Participating hospitals in Tri-State Pediatric COVID-19 Consortium, including hospitals in New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut.
Synopsis: The authors identified hospitalized patients 22 years old or younger who had a positive SARS-CoV-2 test or met the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Preventions’ MIS-C case definition. For comparative analysis, patients were divided into a respiratory disease group (based on the World Health Organization’s criteria for COVID-19), MIS-C group or other group (based on the primary reason for hospitalization).
The authors included 281 patients in the study. 51% of the patients presented with respiratory disease, 25% with MIS-C and 25% with other symptoms, including gastrointestinal, or fever. 51% of all patients were Hispanic and 23% were non-Black Hispanic. The most common pre-existing comorbidities amongst all groups were obesity (34%) and asthma (14%).
Patients with respiratory disease had a median age of 14 years while those with MIS-C had a median age of 7 years. Patients more commonly identified as non-Hispanic Black in the MIS-C group vs the respiratory group (35% vs. 18%). Obesity and medical complexity were more prevalent in the respiratory group relative to the MIS-C group. 75% of patients with MIS-C had gastrointestinal symptoms. 44% of respiratory patients had a chest radiograph with bilateral infiltrates on admission, and 18% or respiratory patients required invasive mechanical ventilation. The most common complications in the respiratory group were acute respiratory distress syndrome (17%) and acute kidney injury (11%), whereas shock (35%) and cardiac dysfunction (25%) were the most common complications in the MIS-C group. The median length of stay for all patients was 4 days (IQR 2-8 days).
Patients with MIS-C were more likely to be admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) but all deaths (7 patients) occurred in the respiratory group. 40% of patients with respiratory disease, 56% of patients with MIS-C, and 6% of other patients met the authors’ definition of severe disease (ICU admission > 48 hours). For the respiratory group, younger age, obesity, increasing white blood cell count, hypoxia, and bilateral infiltrates on chest radiograph were independent predictors of severe disease based on multivariate analyses. For the MIS-C group, lower absolute lymphocyte count and increasing CRP at admission were independent predictors of severity.
Bottom line: Mortality in pediatric patients is low. Ethnicity and race were not predictive of disease severity in this model, even though 51% of the patients studied were Hispanic and 23% were non-Hispanic Black. Severity of illness for patients with respiratory disease was found to be associated with younger age, obesity, increasing white blood cell count, hypoxia, and bilateral infiltrates on chest radiograph. Severity of illness in patients with MIS-C was associated with lower absolute lymphocyte count and increasing CRP.
Citation: Fernandes DM, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 clinical syndromes and predictors of disease severity in hospitalized children and youth. J Pediatr. 2020 Nov 14;S0022-3476(20):31393-7. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.11.016.
Dr. Kumar is an assistant professor of pediatrics at the Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine of Case Western Reserve University and a pediatric hospitalist at Cleveland Clinic Children’s. She is the pediatric editor of The Hospitalist.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF PEDIATRICS
Mask mandates reduced COVID-19 hospitalizations
States that implemented mask mandates in 2020 saw a decline in the growth of COVID-19 hospitalizations between March and October 2020, according to a new study published Feb. 5 in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Hospitalization growth rates declined by 5.5 percentage points for adults between ages 18-64 about 3 weeks after the mandates were implemented, compared with climbing growth rates in the 4 weeks before mandates.
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky said she was pleased to see the results, but that it’s “too early” to tell whether President Joe Biden’s recent mask orders have had an effect on cases and hospitalizations in 2021.
“We’re going to be watching the mask data very carefully,” she said during a news briefing with the White House COVID-19 Response Team on Feb. 5. “I think it’s probably still a bit too early to tell, but I’m encouraged with the decrease in case rates right now.”
In another study published Feb. 5 in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, trained observers tracked mask use at six universities with mask mandates between September and November 2020. Overall, observers reported that about 92% of people wore masks correctly indoors, which varied based on the type of mask.
About 97% of people used N95 masks correctly, compared with 92% who used cloth masks, and 79% who used bandanas, scarves, or neck gaiters. Cloth masks were most common, and bandanas and scarves were least common.
The Biden administration is considering whether to send masks directly to American households to encourage people to wear them, according to NBC News. The White House COVID-19 Response Team is debating the logistics of mailing out masks, including how many to send and what the mask material would be, the news outlet reported.
Wisconsin Gov. Tony Evers reissued a new statewide mask mandate on Feb. 4, just an hour after the Republican-controlled legislature voted to repeal his previous mandate, according to The Associated Press. Gov. Evers said his priority is to keep people safe and that wearing a mask is the easiest way to do so.
“If the legislature keeps playing politics and we don’t keep wearing masks, we’re going to see more preventable deaths,” he said. “It’s going to take even longer to get our state and our economy back on track.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
States that implemented mask mandates in 2020 saw a decline in the growth of COVID-19 hospitalizations between March and October 2020, according to a new study published Feb. 5 in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Hospitalization growth rates declined by 5.5 percentage points for adults between ages 18-64 about 3 weeks after the mandates were implemented, compared with climbing growth rates in the 4 weeks before mandates.
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky said she was pleased to see the results, but that it’s “too early” to tell whether President Joe Biden’s recent mask orders have had an effect on cases and hospitalizations in 2021.
“We’re going to be watching the mask data very carefully,” she said during a news briefing with the White House COVID-19 Response Team on Feb. 5. “I think it’s probably still a bit too early to tell, but I’m encouraged with the decrease in case rates right now.”
In another study published Feb. 5 in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, trained observers tracked mask use at six universities with mask mandates between September and November 2020. Overall, observers reported that about 92% of people wore masks correctly indoors, which varied based on the type of mask.
About 97% of people used N95 masks correctly, compared with 92% who used cloth masks, and 79% who used bandanas, scarves, or neck gaiters. Cloth masks were most common, and bandanas and scarves were least common.
The Biden administration is considering whether to send masks directly to American households to encourage people to wear them, according to NBC News. The White House COVID-19 Response Team is debating the logistics of mailing out masks, including how many to send and what the mask material would be, the news outlet reported.
Wisconsin Gov. Tony Evers reissued a new statewide mask mandate on Feb. 4, just an hour after the Republican-controlled legislature voted to repeal his previous mandate, according to The Associated Press. Gov. Evers said his priority is to keep people safe and that wearing a mask is the easiest way to do so.
“If the legislature keeps playing politics and we don’t keep wearing masks, we’re going to see more preventable deaths,” he said. “It’s going to take even longer to get our state and our economy back on track.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
States that implemented mask mandates in 2020 saw a decline in the growth of COVID-19 hospitalizations between March and October 2020, according to a new study published Feb. 5 in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Hospitalization growth rates declined by 5.5 percentage points for adults between ages 18-64 about 3 weeks after the mandates were implemented, compared with climbing growth rates in the 4 weeks before mandates.
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky said she was pleased to see the results, but that it’s “too early” to tell whether President Joe Biden’s recent mask orders have had an effect on cases and hospitalizations in 2021.
“We’re going to be watching the mask data very carefully,” she said during a news briefing with the White House COVID-19 Response Team on Feb. 5. “I think it’s probably still a bit too early to tell, but I’m encouraged with the decrease in case rates right now.”
In another study published Feb. 5 in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, trained observers tracked mask use at six universities with mask mandates between September and November 2020. Overall, observers reported that about 92% of people wore masks correctly indoors, which varied based on the type of mask.
About 97% of people used N95 masks correctly, compared with 92% who used cloth masks, and 79% who used bandanas, scarves, or neck gaiters. Cloth masks were most common, and bandanas and scarves were least common.
The Biden administration is considering whether to send masks directly to American households to encourage people to wear them, according to NBC News. The White House COVID-19 Response Team is debating the logistics of mailing out masks, including how many to send and what the mask material would be, the news outlet reported.
Wisconsin Gov. Tony Evers reissued a new statewide mask mandate on Feb. 4, just an hour after the Republican-controlled legislature voted to repeal his previous mandate, according to The Associated Press. Gov. Evers said his priority is to keep people safe and that wearing a mask is the easiest way to do so.
“If the legislature keeps playing politics and we don’t keep wearing masks, we’re going to see more preventable deaths,” he said. “It’s going to take even longer to get our state and our economy back on track.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Children in ICU for COVID-19 likely to be older, Black, and asthmatic
Little has been known about children sick enough with COVID-19 to require intensive care because such patients are relatively few, but preliminary data analyzed from a nationwide registry indicate that they are more likely to be older, to be Black, and to have asthma.
Gastrointestinal distress is also more common in children with severe COVID-19, according to research by Sandeep Tripathi, MD. Dr. Tripathi, a pediatric intensivist and associate professor at the University of Illinois at Peoria, presented the findings on Feb. 3 at the Society for Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) 2021 Critical Care Congress.
Registry data gathered from 49 sites
Results from the SCCM’s VIRUS: COVID-19 Registry, which involved data from 49 sites, included 181 children admitted to an intensive care unit between February and July 2020. Those in the ICU were older than patients who did not receive care in the ICU (10 years vs. 3.67 years; P < .01) and were more likely to be Black (28.8% vs. 17.8%; P = .02).
More of the patients who required intensive care had preexisting conditions (58.2% vs. 44.3%; P = .01), the most common of which was asthma.
For both the ICU patients and the non-ICU group, the most common presenting symptom was fever.
Symptoms that were more common among children needing ICU care included nausea/vomiting (38.4% vs. 22.1%; P < .01), dyspnea (31.8% vs. 17.7%; P < .01), and abdominal pain (25.2% vs. 14.1%; P < .01).
Significantly higher proportions of ICU patients had multisystem inflammatory syndrome of childhood (MIS-C) (44.2% vs. 6.8%; P < .01) and acute kidney injury (9.34% vs. 1.7%; P < .01).
“The children who presented with MIS-C tended to be much sicker than children who present with just COVID,” Dr. Tripathi said in an interview.
In this analysis, among children in ICUs with COVID, the mortality rate was 4%, Dr. Tripathi said.
He said he hopes the information, which will be periodically published with updated data, will raise awareness of which children might be likely to experience progression to severe disease.
“The information may help physicians be more mindful of deterioration in those patients and be more aggressive in their management,” he said. When children are brought to the emergency department with the features this analysis highlights, he said, “physicians should have a low threshold for treating or admitting the patients.”
Another study that was presented on Feb. 3 in parallel with the registry study described patterns of illness among 68 children hospitalized with COVID-19 in a tertiary-care pediatric center.
In that analysis, Meghana Nadiger, MD, a critical care fellow with Nicklaus Children’s Hospital in Miami, found that all patients admitted to the pediatric ICU (n = 17) had either MIS-C or severe illness and COVID-19-related Kawasaki-like disease.
The investigators also found that the patients with serious illness were more commonly adolescents with elevated body mass index (73%). In this study, 83.8% of the hospitalized children were Hispanic. They also found that 88.8% of the children older than 2 years who had been hospitalized with COVID-19 were overweight or obese, with a BMI >25 kg/m2.
Jerry Zimmerman, MD, PhD, SCCM’s immediate past president, said in an interview that he found it interesting that in the Nadiger study, “All of the children with severe illness had MIS-C as compared to adults, who typically are critically ill with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome.” Dr. Zimmerman was not involved in either study.
He said that although the high percentage of Hispanic patients in the hospitalized population may reflect the high percentage of Hispanic children in the Miami area, it may also reflect challenges of controlling the disease in the Hispanic community. Such challenges might include shortages of personal protective equipment, poorer access to health care, and difficulty in social distancing.
Dr. Zimmerman pointed out that obesity is an important risk factor for COVID-19 and that according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, childhood obesity is much more common among Hispanics (25.8%) and non-Hispanic Blacks persons (22.0%) compared with non-Hispanic White persons (14.1%).
The VIRUS registry is funded in part by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation and Janssen Research and Development. Dr. Tripathi, Dr. Nadiger, and Dr. Zimmerman have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Little has been known about children sick enough with COVID-19 to require intensive care because such patients are relatively few, but preliminary data analyzed from a nationwide registry indicate that they are more likely to be older, to be Black, and to have asthma.
Gastrointestinal distress is also more common in children with severe COVID-19, according to research by Sandeep Tripathi, MD. Dr. Tripathi, a pediatric intensivist and associate professor at the University of Illinois at Peoria, presented the findings on Feb. 3 at the Society for Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) 2021 Critical Care Congress.
Registry data gathered from 49 sites
Results from the SCCM’s VIRUS: COVID-19 Registry, which involved data from 49 sites, included 181 children admitted to an intensive care unit between February and July 2020. Those in the ICU were older than patients who did not receive care in the ICU (10 years vs. 3.67 years; P < .01) and were more likely to be Black (28.8% vs. 17.8%; P = .02).
More of the patients who required intensive care had preexisting conditions (58.2% vs. 44.3%; P = .01), the most common of which was asthma.
For both the ICU patients and the non-ICU group, the most common presenting symptom was fever.
Symptoms that were more common among children needing ICU care included nausea/vomiting (38.4% vs. 22.1%; P < .01), dyspnea (31.8% vs. 17.7%; P < .01), and abdominal pain (25.2% vs. 14.1%; P < .01).
Significantly higher proportions of ICU patients had multisystem inflammatory syndrome of childhood (MIS-C) (44.2% vs. 6.8%; P < .01) and acute kidney injury (9.34% vs. 1.7%; P < .01).
“The children who presented with MIS-C tended to be much sicker than children who present with just COVID,” Dr. Tripathi said in an interview.
In this analysis, among children in ICUs with COVID, the mortality rate was 4%, Dr. Tripathi said.
He said he hopes the information, which will be periodically published with updated data, will raise awareness of which children might be likely to experience progression to severe disease.
“The information may help physicians be more mindful of deterioration in those patients and be more aggressive in their management,” he said. When children are brought to the emergency department with the features this analysis highlights, he said, “physicians should have a low threshold for treating or admitting the patients.”
Another study that was presented on Feb. 3 in parallel with the registry study described patterns of illness among 68 children hospitalized with COVID-19 in a tertiary-care pediatric center.
In that analysis, Meghana Nadiger, MD, a critical care fellow with Nicklaus Children’s Hospital in Miami, found that all patients admitted to the pediatric ICU (n = 17) had either MIS-C or severe illness and COVID-19-related Kawasaki-like disease.
The investigators also found that the patients with serious illness were more commonly adolescents with elevated body mass index (73%). In this study, 83.8% of the hospitalized children were Hispanic. They also found that 88.8% of the children older than 2 years who had been hospitalized with COVID-19 were overweight or obese, with a BMI >25 kg/m2.
Jerry Zimmerman, MD, PhD, SCCM’s immediate past president, said in an interview that he found it interesting that in the Nadiger study, “All of the children with severe illness had MIS-C as compared to adults, who typically are critically ill with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome.” Dr. Zimmerman was not involved in either study.
He said that although the high percentage of Hispanic patients in the hospitalized population may reflect the high percentage of Hispanic children in the Miami area, it may also reflect challenges of controlling the disease in the Hispanic community. Such challenges might include shortages of personal protective equipment, poorer access to health care, and difficulty in social distancing.
Dr. Zimmerman pointed out that obesity is an important risk factor for COVID-19 and that according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, childhood obesity is much more common among Hispanics (25.8%) and non-Hispanic Blacks persons (22.0%) compared with non-Hispanic White persons (14.1%).
The VIRUS registry is funded in part by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation and Janssen Research and Development. Dr. Tripathi, Dr. Nadiger, and Dr. Zimmerman have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Little has been known about children sick enough with COVID-19 to require intensive care because such patients are relatively few, but preliminary data analyzed from a nationwide registry indicate that they are more likely to be older, to be Black, and to have asthma.
Gastrointestinal distress is also more common in children with severe COVID-19, according to research by Sandeep Tripathi, MD. Dr. Tripathi, a pediatric intensivist and associate professor at the University of Illinois at Peoria, presented the findings on Feb. 3 at the Society for Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) 2021 Critical Care Congress.
Registry data gathered from 49 sites
Results from the SCCM’s VIRUS: COVID-19 Registry, which involved data from 49 sites, included 181 children admitted to an intensive care unit between February and July 2020. Those in the ICU were older than patients who did not receive care in the ICU (10 years vs. 3.67 years; P < .01) and were more likely to be Black (28.8% vs. 17.8%; P = .02).
More of the patients who required intensive care had preexisting conditions (58.2% vs. 44.3%; P = .01), the most common of which was asthma.
For both the ICU patients and the non-ICU group, the most common presenting symptom was fever.
Symptoms that were more common among children needing ICU care included nausea/vomiting (38.4% vs. 22.1%; P < .01), dyspnea (31.8% vs. 17.7%; P < .01), and abdominal pain (25.2% vs. 14.1%; P < .01).
Significantly higher proportions of ICU patients had multisystem inflammatory syndrome of childhood (MIS-C) (44.2% vs. 6.8%; P < .01) and acute kidney injury (9.34% vs. 1.7%; P < .01).
“The children who presented with MIS-C tended to be much sicker than children who present with just COVID,” Dr. Tripathi said in an interview.
In this analysis, among children in ICUs with COVID, the mortality rate was 4%, Dr. Tripathi said.
He said he hopes the information, which will be periodically published with updated data, will raise awareness of which children might be likely to experience progression to severe disease.
“The information may help physicians be more mindful of deterioration in those patients and be more aggressive in their management,” he said. When children are brought to the emergency department with the features this analysis highlights, he said, “physicians should have a low threshold for treating or admitting the patients.”
Another study that was presented on Feb. 3 in parallel with the registry study described patterns of illness among 68 children hospitalized with COVID-19 in a tertiary-care pediatric center.
In that analysis, Meghana Nadiger, MD, a critical care fellow with Nicklaus Children’s Hospital in Miami, found that all patients admitted to the pediatric ICU (n = 17) had either MIS-C or severe illness and COVID-19-related Kawasaki-like disease.
The investigators also found that the patients with serious illness were more commonly adolescents with elevated body mass index (73%). In this study, 83.8% of the hospitalized children were Hispanic. They also found that 88.8% of the children older than 2 years who had been hospitalized with COVID-19 were overweight or obese, with a BMI >25 kg/m2.
Jerry Zimmerman, MD, PhD, SCCM’s immediate past president, said in an interview that he found it interesting that in the Nadiger study, “All of the children with severe illness had MIS-C as compared to adults, who typically are critically ill with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome.” Dr. Zimmerman was not involved in either study.
He said that although the high percentage of Hispanic patients in the hospitalized population may reflect the high percentage of Hispanic children in the Miami area, it may also reflect challenges of controlling the disease in the Hispanic community. Such challenges might include shortages of personal protective equipment, poorer access to health care, and difficulty in social distancing.
Dr. Zimmerman pointed out that obesity is an important risk factor for COVID-19 and that according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, childhood obesity is much more common among Hispanics (25.8%) and non-Hispanic Blacks persons (22.0%) compared with non-Hispanic White persons (14.1%).
The VIRUS registry is funded in part by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation and Janssen Research and Development. Dr. Tripathi, Dr. Nadiger, and Dr. Zimmerman have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.







