User login
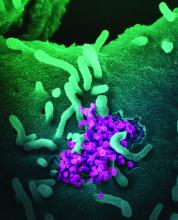
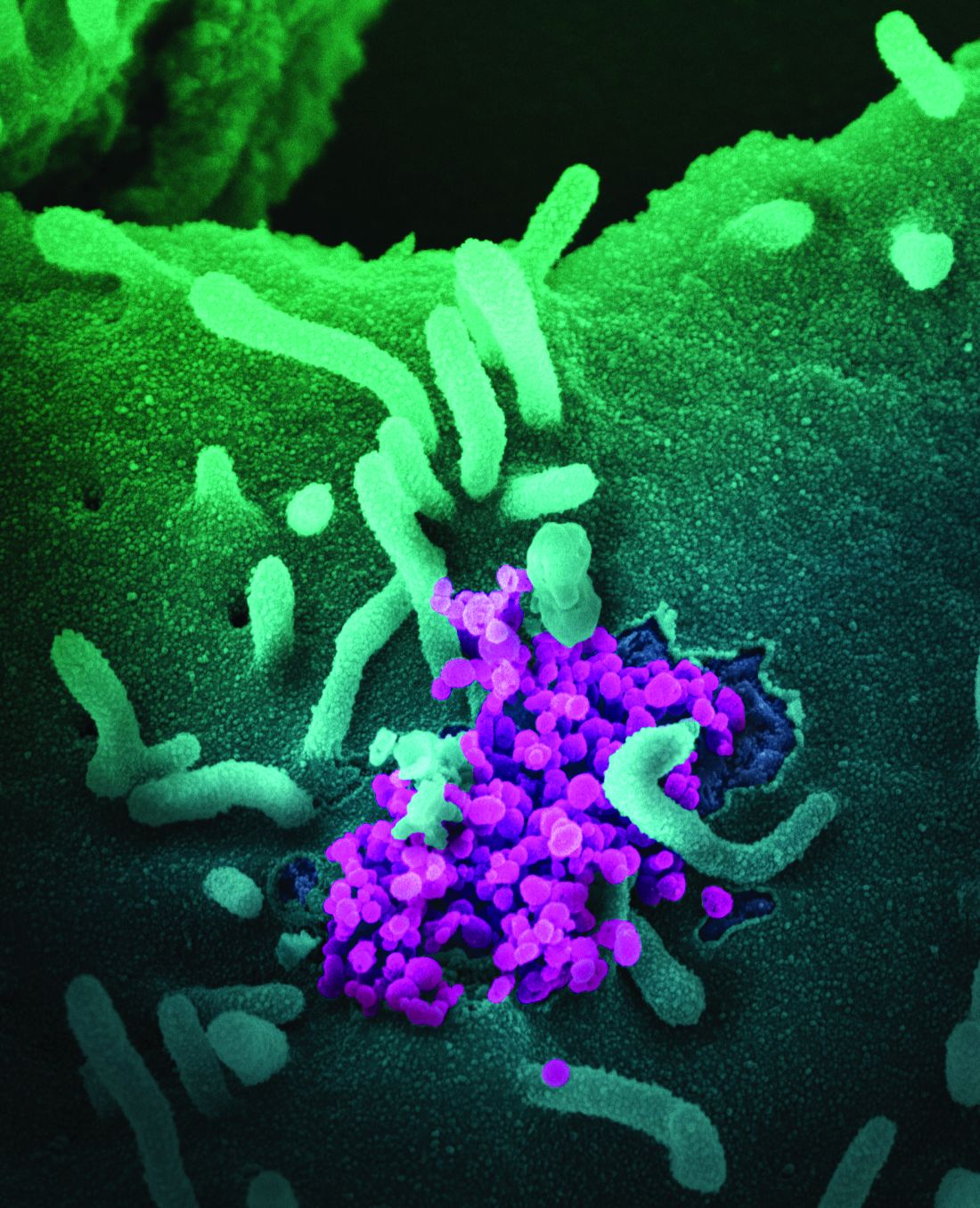
CDC chief lays out attack plan for COVID variants
earlier this week.
As part of JAMA’s Q&A series with JAMA editor in chief Howard Bauchner, MD, Dr. Walensky referenced the blueprint she coathored with Anthony Fauci, MD, the nation’s top infectious disease expert, and Henry T. Walke, MD, MPH, of the CDC, which was published on Feb. 17 in JAMA.
In the viewpoint article, they explain that the Department of Health & Human Services has established the SARS-CoV-2 Interagency Group to improve coordination among the CDC, the National Institutes of Health, the Food and Drug Administration, the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority, the Department of Agriculture, and the Department of Defense.
Dr. Walensky said the first objective is to reinforce vigilance regarding public health mitigation strategies to decrease the amount of virus that’s circulating.
As part of that strategy, she said, the CDC strongly urges against nonessential travel.
In addition, public health leaders are working on a surveillance system to better understand the SARS-CoV-2 variants. That will take ramping up genome sequencing of the SARS-CoV-2 virus and ensuring that sampling is geographically representative.
She said the CDC is partnering with state health labs to obtain about 750 samples every week and is teaming up with commercial labs and academic centers to obtain an interim target of 6,000 samples per week.
She acknowledged the United States “is not where we need to be” with sequencing but has come a long way since January. At that time, they were sequencing 250 samples every week; they are currently sequencing thousands each week.
Data analysis is another concern: “We need to be able to understand at the basic science level what the information means,” Dr. Walensky said.
Researchers aren’t sure how the variants might affect use of convalescent plasma or monoclonal antibody treatments. It is expected that 5% of persons who are vaccinated against COVID-19 will nevertheless contract the disease. Sequencing will help answer whether such persons who have been vaccinated and who subsequently contract the virus are among those 5% or whether have been infected by a variant that evades the vaccine.
Accelerating vaccine administration globally and in the United States is essential, Dr. Walensky said.
As of Feb. 17, 56 million doses had been administered in the United States.
Top three threats
She updated the numbers on the three biggest variant threats.
Regarding B.1.1.7, which originated in the United Kingdom, she said: “So far, we’ve had over 1,200 cases in 41 states.” She noted that the variant is likely to be about 50% more transmissible and 30% to 50% more virulent.
“So far, it looks like that strain doesn’t have any real decrease in susceptibility to our vaccines,” she said.
The strain from South Africa (B.1.351) has been found in 19 cases in the United States.
The P.1. variant, which originated in Brazil, has been identified in two cases in two states.
Outlook for March and April
Dr. Bauchner asked Dr. Walensky what she envisions for March and April. He noted that public optimism is high in light of the continued reductions in COVID-19 case numbers, hospitalizations, and deaths, as well as the fact that warmer weather is coming and that more vaccinations are on the horizon.
“While I really am hopeful for what could happen in March and April,” Dr. Walensky said, “I really do know that this could go bad so fast. We saw it in November. We saw it in December.”
CDC models have projected that, by March, the more transmissible B.1.1.7 strain is likely to be the dominant strain, she reiterated.
“I worry that it will be spring, and we will all have had enough,” Dr. Walensky said. She noted that some states are already relaxing mask mandates.
“Around that time, life will look and feel a little better, and the motivation for those who might be vaccine hesitant may be diminished,” she said.
Dr. Bauchner also asked her to weigh in on whether a third vaccine, from Johnson & Johnson (J&J), may soon gain FDA emergency-use authorization – and whether its lower expected efficacy rate may result in a tiered system of vaccinations, with higher-risk populations receiving the more efficacious vaccines.
Dr. Walensky said more data are needed before that question can be answered.
“It may very well be that the data point us to the best populations in which to use this vaccine,” she said.
In phase 3 data, the J&J vaccine was shown to be 72% effective in the United States for moderate to severe disease.
Dr. Walensky said it’s important to remember that the projected efficacy for that vaccine is higher than that for the flu shot as well as many other vaccines currently in use for other diseases.
She said it also has several advantages. The vaccine has less-stringent storage requirements, requires just one dose, and protects against hospitalization and death, although it’s less efficacious in protecting against contracting the disease.
“I think many people would opt to get that one if they could get it sooner,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
earlier this week.
As part of JAMA’s Q&A series with JAMA editor in chief Howard Bauchner, MD, Dr. Walensky referenced the blueprint she coathored with Anthony Fauci, MD, the nation’s top infectious disease expert, and Henry T. Walke, MD, MPH, of the CDC, which was published on Feb. 17 in JAMA.
In the viewpoint article, they explain that the Department of Health & Human Services has established the SARS-CoV-2 Interagency Group to improve coordination among the CDC, the National Institutes of Health, the Food and Drug Administration, the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority, the Department of Agriculture, and the Department of Defense.
Dr. Walensky said the first objective is to reinforce vigilance regarding public health mitigation strategies to decrease the amount of virus that’s circulating.
As part of that strategy, she said, the CDC strongly urges against nonessential travel.
In addition, public health leaders are working on a surveillance system to better understand the SARS-CoV-2 variants. That will take ramping up genome sequencing of the SARS-CoV-2 virus and ensuring that sampling is geographically representative.
She said the CDC is partnering with state health labs to obtain about 750 samples every week and is teaming up with commercial labs and academic centers to obtain an interim target of 6,000 samples per week.
She acknowledged the United States “is not where we need to be” with sequencing but has come a long way since January. At that time, they were sequencing 250 samples every week; they are currently sequencing thousands each week.
Data analysis is another concern: “We need to be able to understand at the basic science level what the information means,” Dr. Walensky said.
Researchers aren’t sure how the variants might affect use of convalescent plasma or monoclonal antibody treatments. It is expected that 5% of persons who are vaccinated against COVID-19 will nevertheless contract the disease. Sequencing will help answer whether such persons who have been vaccinated and who subsequently contract the virus are among those 5% or whether have been infected by a variant that evades the vaccine.
Accelerating vaccine administration globally and in the United States is essential, Dr. Walensky said.
As of Feb. 17, 56 million doses had been administered in the United States.
Top three threats
She updated the numbers on the three biggest variant threats.
Regarding B.1.1.7, which originated in the United Kingdom, she said: “So far, we’ve had over 1,200 cases in 41 states.” She noted that the variant is likely to be about 50% more transmissible and 30% to 50% more virulent.
“So far, it looks like that strain doesn’t have any real decrease in susceptibility to our vaccines,” she said.
The strain from South Africa (B.1.351) has been found in 19 cases in the United States.
The P.1. variant, which originated in Brazil, has been identified in two cases in two states.
Outlook for March and April
Dr. Bauchner asked Dr. Walensky what she envisions for March and April. He noted that public optimism is high in light of the continued reductions in COVID-19 case numbers, hospitalizations, and deaths, as well as the fact that warmer weather is coming and that more vaccinations are on the horizon.
“While I really am hopeful for what could happen in March and April,” Dr. Walensky said, “I really do know that this could go bad so fast. We saw it in November. We saw it in December.”
CDC models have projected that, by March, the more transmissible B.1.1.7 strain is likely to be the dominant strain, she reiterated.
“I worry that it will be spring, and we will all have had enough,” Dr. Walensky said. She noted that some states are already relaxing mask mandates.
“Around that time, life will look and feel a little better, and the motivation for those who might be vaccine hesitant may be diminished,” she said.
Dr. Bauchner also asked her to weigh in on whether a third vaccine, from Johnson & Johnson (J&J), may soon gain FDA emergency-use authorization – and whether its lower expected efficacy rate may result in a tiered system of vaccinations, with higher-risk populations receiving the more efficacious vaccines.
Dr. Walensky said more data are needed before that question can be answered.
“It may very well be that the data point us to the best populations in which to use this vaccine,” she said.
In phase 3 data, the J&J vaccine was shown to be 72% effective in the United States for moderate to severe disease.
Dr. Walensky said it’s important to remember that the projected efficacy for that vaccine is higher than that for the flu shot as well as many other vaccines currently in use for other diseases.
She said it also has several advantages. The vaccine has less-stringent storage requirements, requires just one dose, and protects against hospitalization and death, although it’s less efficacious in protecting against contracting the disease.
“I think many people would opt to get that one if they could get it sooner,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
earlier this week.
As part of JAMA’s Q&A series with JAMA editor in chief Howard Bauchner, MD, Dr. Walensky referenced the blueprint she coathored with Anthony Fauci, MD, the nation’s top infectious disease expert, and Henry T. Walke, MD, MPH, of the CDC, which was published on Feb. 17 in JAMA.
In the viewpoint article, they explain that the Department of Health & Human Services has established the SARS-CoV-2 Interagency Group to improve coordination among the CDC, the National Institutes of Health, the Food and Drug Administration, the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority, the Department of Agriculture, and the Department of Defense.
Dr. Walensky said the first objective is to reinforce vigilance regarding public health mitigation strategies to decrease the amount of virus that’s circulating.
As part of that strategy, she said, the CDC strongly urges against nonessential travel.
In addition, public health leaders are working on a surveillance system to better understand the SARS-CoV-2 variants. That will take ramping up genome sequencing of the SARS-CoV-2 virus and ensuring that sampling is geographically representative.
She said the CDC is partnering with state health labs to obtain about 750 samples every week and is teaming up with commercial labs and academic centers to obtain an interim target of 6,000 samples per week.
She acknowledged the United States “is not where we need to be” with sequencing but has come a long way since January. At that time, they were sequencing 250 samples every week; they are currently sequencing thousands each week.
Data analysis is another concern: “We need to be able to understand at the basic science level what the information means,” Dr. Walensky said.
Researchers aren’t sure how the variants might affect use of convalescent plasma or monoclonal antibody treatments. It is expected that 5% of persons who are vaccinated against COVID-19 will nevertheless contract the disease. Sequencing will help answer whether such persons who have been vaccinated and who subsequently contract the virus are among those 5% or whether have been infected by a variant that evades the vaccine.
Accelerating vaccine administration globally and in the United States is essential, Dr. Walensky said.
As of Feb. 17, 56 million doses had been administered in the United States.
Top three threats
She updated the numbers on the three biggest variant threats.
Regarding B.1.1.7, which originated in the United Kingdom, she said: “So far, we’ve had over 1,200 cases in 41 states.” She noted that the variant is likely to be about 50% more transmissible and 30% to 50% more virulent.
“So far, it looks like that strain doesn’t have any real decrease in susceptibility to our vaccines,” she said.
The strain from South Africa (B.1.351) has been found in 19 cases in the United States.
The P.1. variant, which originated in Brazil, has been identified in two cases in two states.
Outlook for March and April
Dr. Bauchner asked Dr. Walensky what she envisions for March and April. He noted that public optimism is high in light of the continued reductions in COVID-19 case numbers, hospitalizations, and deaths, as well as the fact that warmer weather is coming and that more vaccinations are on the horizon.
“While I really am hopeful for what could happen in March and April,” Dr. Walensky said, “I really do know that this could go bad so fast. We saw it in November. We saw it in December.”
CDC models have projected that, by March, the more transmissible B.1.1.7 strain is likely to be the dominant strain, she reiterated.
“I worry that it will be spring, and we will all have had enough,” Dr. Walensky said. She noted that some states are already relaxing mask mandates.
“Around that time, life will look and feel a little better, and the motivation for those who might be vaccine hesitant may be diminished,” she said.
Dr. Bauchner also asked her to weigh in on whether a third vaccine, from Johnson & Johnson (J&J), may soon gain FDA emergency-use authorization – and whether its lower expected efficacy rate may result in a tiered system of vaccinations, with higher-risk populations receiving the more efficacious vaccines.
Dr. Walensky said more data are needed before that question can be answered.
“It may very well be that the data point us to the best populations in which to use this vaccine,” she said.
In phase 3 data, the J&J vaccine was shown to be 72% effective in the United States for moderate to severe disease.
Dr. Walensky said it’s important to remember that the projected efficacy for that vaccine is higher than that for the flu shot as well as many other vaccines currently in use for other diseases.
She said it also has several advantages. The vaccine has less-stringent storage requirements, requires just one dose, and protects against hospitalization and death, although it’s less efficacious in protecting against contracting the disease.
“I think many people would opt to get that one if they could get it sooner,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Alien cells may explain COVID-19 brain fog
, a new report suggests.
The authors report five separate post-mortem cases from patients who died with COVID-19 in which large cells resembling megakaryocytes were identified in cortical capillaries. Immunohistochemistry subsequently confirmed their megakaryocyte identity.
They point out that the finding is of interest as – to their knowledge – megakaryocytes have not been found in the brain before.
The observations are described in a research letter published online Feb. 12 in JAMA Neurology.
Bone marrow cells in the brain
Lead author David Nauen, MD, PhD, a neuropathologist from Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, reported that he identified these cells in the first analysis of post-mortem brain tissue from a patient who had COVID-19.
“Some other viruses cause changes in the brain such as encephalopathy, and as neurologic symptoms are often reported in COVID-19, I was curious to see if similar effects were seen in brain post-mortem samples from patients who had died with the infection,” Dr. Nauen said.
On his first analysis of the brain tissue of a patient who had COVID-19, Dr. Nauen saw no evidence of viral encephalitis, but he observed some “unusually large” cells in the brain capillaries.
“I was taken aback; I couldn’t figure out what they were. Then I realized these cells were megakaryocytes from the bone marrow. I have never seen these cells in the brain before. I asked several colleagues and none of them had either. After extensive literature searches, I could find no evidence of megakaryocytes being in the brain,” Dr. Nauen noted.
Megakaryocytes, he explained, are “very large cells, and the brain capillaries are very small – just large enough to let red blood cells and lymphocytes pass through. To see these very large cells in such vessels is extremely unusual. It looks like they are causing occlusions.”
By occluding flow through individual capillaries, these large cells could cause ischemic alteration in a distinct pattern, potentially resulting in an atypical form of neurologic impairment, the authors suggest.
“This might alter the hemodynamics and put pressure on other vessels, possibly contributing to the increased risk of stroke that has been reported in COVID-19,” Dr. Nauen said. None of the samples he examined came from patients with COVID-19 who had had a stroke, he reported.
Other than the presence of megakaryocytes in the capillaries, the brain looked normal, he said. He has now examined samples from 15 brains of patients who had COVID-19 and megakaryocytes have been found in the brain capillaries in five cases.
New neurologic complication
Classic encephalitis found with other viruses has not been reported in brain post-mortem examinations from patients who had COVID-19, Dr. Nauen noted. “The cognitive issues such as grogginess associated with COVID-19 would indicate problems with the cortex but that hasn’t been documented. This occlusion of a multitude of tiny vessels by megalokaryocytes may offer some explanation of the cognitive issues. This is a new kind of vascular insult seen on pathology, and suggests a new kind of neurologic complication,” he added.
The big question is what these megakaryocytes are doing in the brain.
“Megakaryocytes are bone marrow cells. They are not immune cells. Their job is to produce platelets to help the blood clot. They are not normally found outside the bone marrow, but they have been reported in other organs in COVID-19 patients.
“But the big puzzle associated with finding them in the brain is how they get through the very fine network of blood vessels in the lungs. The geometry just doesn’t work. We don’t know which part of the COVID inflammatory response makes this happen,” said Dr. Nauen.
The authors suggest one possibility is that altered endothelial or other signaling is recruiting megakaryocytes into the circulation and somehow permitting them to pass through the lungs.
“We need to try and understand if there is anything distinctive about these megakaryocytes – which proteins are they expressing that may explain why they are behaving in such an unusual way,” said Dr. Nauen.
Noting that many patients with severe COVID-19 have problems with clotting, and megakaryocytes are part of the clotting system, he speculated that some sort of aberrant message is being sent to these cells.
“It is notable that we found megakaryocytes in cortical capillaries in 33% of cases examined. Because the standard brain autopsy sections taken sampled at random [are] only a minute portion of the cortical volume, finding these cells suggests the total burden could be considerable,” the authors wrote.
Dr. Nauen added that to his knowledge, this is the first report of such observations, and the next step is to look for similar findings in larger sample sizes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new report suggests.
The authors report five separate post-mortem cases from patients who died with COVID-19 in which large cells resembling megakaryocytes were identified in cortical capillaries. Immunohistochemistry subsequently confirmed their megakaryocyte identity.
They point out that the finding is of interest as – to their knowledge – megakaryocytes have not been found in the brain before.
The observations are described in a research letter published online Feb. 12 in JAMA Neurology.
Bone marrow cells in the brain
Lead author David Nauen, MD, PhD, a neuropathologist from Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, reported that he identified these cells in the first analysis of post-mortem brain tissue from a patient who had COVID-19.
“Some other viruses cause changes in the brain such as encephalopathy, and as neurologic symptoms are often reported in COVID-19, I was curious to see if similar effects were seen in brain post-mortem samples from patients who had died with the infection,” Dr. Nauen said.
On his first analysis of the brain tissue of a patient who had COVID-19, Dr. Nauen saw no evidence of viral encephalitis, but he observed some “unusually large” cells in the brain capillaries.
“I was taken aback; I couldn’t figure out what they were. Then I realized these cells were megakaryocytes from the bone marrow. I have never seen these cells in the brain before. I asked several colleagues and none of them had either. After extensive literature searches, I could find no evidence of megakaryocytes being in the brain,” Dr. Nauen noted.
Megakaryocytes, he explained, are “very large cells, and the brain capillaries are very small – just large enough to let red blood cells and lymphocytes pass through. To see these very large cells in such vessels is extremely unusual. It looks like they are causing occlusions.”
By occluding flow through individual capillaries, these large cells could cause ischemic alteration in a distinct pattern, potentially resulting in an atypical form of neurologic impairment, the authors suggest.
“This might alter the hemodynamics and put pressure on other vessels, possibly contributing to the increased risk of stroke that has been reported in COVID-19,” Dr. Nauen said. None of the samples he examined came from patients with COVID-19 who had had a stroke, he reported.
Other than the presence of megakaryocytes in the capillaries, the brain looked normal, he said. He has now examined samples from 15 brains of patients who had COVID-19 and megakaryocytes have been found in the brain capillaries in five cases.
New neurologic complication
Classic encephalitis found with other viruses has not been reported in brain post-mortem examinations from patients who had COVID-19, Dr. Nauen noted. “The cognitive issues such as grogginess associated with COVID-19 would indicate problems with the cortex but that hasn’t been documented. This occlusion of a multitude of tiny vessels by megalokaryocytes may offer some explanation of the cognitive issues. This is a new kind of vascular insult seen on pathology, and suggests a new kind of neurologic complication,” he added.
The big question is what these megakaryocytes are doing in the brain.
“Megakaryocytes are bone marrow cells. They are not immune cells. Their job is to produce platelets to help the blood clot. They are not normally found outside the bone marrow, but they have been reported in other organs in COVID-19 patients.
“But the big puzzle associated with finding them in the brain is how they get through the very fine network of blood vessels in the lungs. The geometry just doesn’t work. We don’t know which part of the COVID inflammatory response makes this happen,” said Dr. Nauen.
The authors suggest one possibility is that altered endothelial or other signaling is recruiting megakaryocytes into the circulation and somehow permitting them to pass through the lungs.
“We need to try and understand if there is anything distinctive about these megakaryocytes – which proteins are they expressing that may explain why they are behaving in such an unusual way,” said Dr. Nauen.
Noting that many patients with severe COVID-19 have problems with clotting, and megakaryocytes are part of the clotting system, he speculated that some sort of aberrant message is being sent to these cells.
“It is notable that we found megakaryocytes in cortical capillaries in 33% of cases examined. Because the standard brain autopsy sections taken sampled at random [are] only a minute portion of the cortical volume, finding these cells suggests the total burden could be considerable,” the authors wrote.
Dr. Nauen added that to his knowledge, this is the first report of such observations, and the next step is to look for similar findings in larger sample sizes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new report suggests.
The authors report five separate post-mortem cases from patients who died with COVID-19 in which large cells resembling megakaryocytes were identified in cortical capillaries. Immunohistochemistry subsequently confirmed their megakaryocyte identity.
They point out that the finding is of interest as – to their knowledge – megakaryocytes have not been found in the brain before.
The observations are described in a research letter published online Feb. 12 in JAMA Neurology.
Bone marrow cells in the brain
Lead author David Nauen, MD, PhD, a neuropathologist from Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, reported that he identified these cells in the first analysis of post-mortem brain tissue from a patient who had COVID-19.
“Some other viruses cause changes in the brain such as encephalopathy, and as neurologic symptoms are often reported in COVID-19, I was curious to see if similar effects were seen in brain post-mortem samples from patients who had died with the infection,” Dr. Nauen said.
On his first analysis of the brain tissue of a patient who had COVID-19, Dr. Nauen saw no evidence of viral encephalitis, but he observed some “unusually large” cells in the brain capillaries.
“I was taken aback; I couldn’t figure out what they were. Then I realized these cells were megakaryocytes from the bone marrow. I have never seen these cells in the brain before. I asked several colleagues and none of them had either. After extensive literature searches, I could find no evidence of megakaryocytes being in the brain,” Dr. Nauen noted.
Megakaryocytes, he explained, are “very large cells, and the brain capillaries are very small – just large enough to let red blood cells and lymphocytes pass through. To see these very large cells in such vessels is extremely unusual. It looks like they are causing occlusions.”
By occluding flow through individual capillaries, these large cells could cause ischemic alteration in a distinct pattern, potentially resulting in an atypical form of neurologic impairment, the authors suggest.
“This might alter the hemodynamics and put pressure on other vessels, possibly contributing to the increased risk of stroke that has been reported in COVID-19,” Dr. Nauen said. None of the samples he examined came from patients with COVID-19 who had had a stroke, he reported.
Other than the presence of megakaryocytes in the capillaries, the brain looked normal, he said. He has now examined samples from 15 brains of patients who had COVID-19 and megakaryocytes have been found in the brain capillaries in five cases.
New neurologic complication
Classic encephalitis found with other viruses has not been reported in brain post-mortem examinations from patients who had COVID-19, Dr. Nauen noted. “The cognitive issues such as grogginess associated with COVID-19 would indicate problems with the cortex but that hasn’t been documented. This occlusion of a multitude of tiny vessels by megalokaryocytes may offer some explanation of the cognitive issues. This is a new kind of vascular insult seen on pathology, and suggests a new kind of neurologic complication,” he added.
The big question is what these megakaryocytes are doing in the brain.
“Megakaryocytes are bone marrow cells. They are not immune cells. Their job is to produce platelets to help the blood clot. They are not normally found outside the bone marrow, but they have been reported in other organs in COVID-19 patients.
“But the big puzzle associated with finding them in the brain is how they get through the very fine network of blood vessels in the lungs. The geometry just doesn’t work. We don’t know which part of the COVID inflammatory response makes this happen,” said Dr. Nauen.
The authors suggest one possibility is that altered endothelial or other signaling is recruiting megakaryocytes into the circulation and somehow permitting them to pass through the lungs.
“We need to try and understand if there is anything distinctive about these megakaryocytes – which proteins are they expressing that may explain why they are behaving in such an unusual way,” said Dr. Nauen.
Noting that many patients with severe COVID-19 have problems with clotting, and megakaryocytes are part of the clotting system, he speculated that some sort of aberrant message is being sent to these cells.
“It is notable that we found megakaryocytes in cortical capillaries in 33% of cases examined. Because the standard brain autopsy sections taken sampled at random [are] only a minute portion of the cortical volume, finding these cells suggests the total burden could be considerable,” the authors wrote.
Dr. Nauen added that to his knowledge, this is the first report of such observations, and the next step is to look for similar findings in larger sample sizes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY
When the X-Waiver gets X’ed: Implications for hospitalists
There are two pandemics permeating the United States: COVID-19 and addiction. To date, more than 468,000 people have died from COVID-19 in the U.S. In the 12-month period ending in May 2020, over 80,000 died from a drug related cause – the highest number ever recorded in a year. Many of these deaths involved opioids.
COVID-19 has worsened outcomes for people with addiction. There is less access to treatment, increased isolation, and worsening psychosocial and economic stressors. These factors may drive new, increased, or more risky substance use and return to use for people in recovery. As hospitalists, we have been responders in both COVID-19 and our country’s worsening overdose and addiction crisis.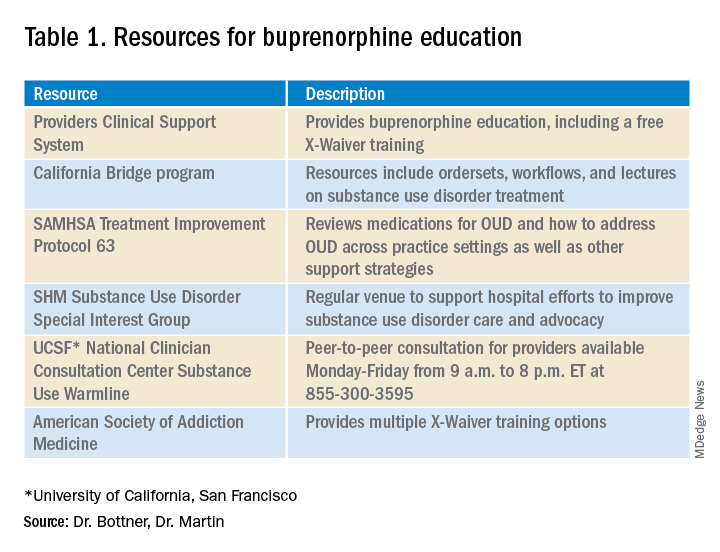
In December 2020’s Journal of Hospital Medicine article “Converging Crises: Caring for hospitalized adults with substance use disorder in the time of COVID-19”, Dr. Honora Englander and her coauthors called on hospitalists to actively engage patients with substance use disorders during hospitalization. The article highlights the colliding crises of addiction and COVID-19 and provides eight practical approaches for hospitalists to address substance use disorders during the pandemic, including initiating buprenorphine for opioid withdrawal and prescribing it for opioid use disorder (OUD) treatment.
Buprenorphine effectively treats opioid withdrawal, reduces OUD-related mortality, and decreases hospital readmissions related to OUD. To prescribe buprenorphine for OUD in the outpatient setting or on hospital discharge, providers need an X-Waiver. The X-Waiver is a result of the Drug Addiction Treatment Act 2000 (DATA 2000), which was enacted in 2000. It permits physicians to prescribe buprenorphine for OUD treatment after an 8-hour training. In 2016, the Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act extended buprenorphine prescribing to physician assistants (PAs) and advanced-practice nurses (APNs). However, PAs and APNs are required to complete a 24-hour training to receive the waiver.
On Jan. 14, 2021, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services under the Trump administration announced it was removing the X-Waiver training previously required for physicians to prescribe this life-saving medication. However, on Jan. 20, 2021, the Biden administration froze the training requirement removal pending a 60-day review. The excitement about the waiver’s eradication further dampened on Jan. 25, when the plan was halted due to procedural factors coupled with the concern that HHS may not have the authority to void requirements mandated by Congress.
Many of us continue to be hopeful that the X-Waiver will soon be gone. The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has committed to working with federal agencies to increase access to buprenorphine. The Biden administration also committed to addressing our country’s addiction crisis, including a plan to “make effective prevention, treatment, and recovery services available to all, including through a $125 billion federal investment.”
Despite the pause on HHS’s recent attempt to “X the X-Waiver,” we now have renewed attention and interest in this critical issue and an opportunity for greater and longer-lasting legislative impact. SHM supports that Congress repeal the legislative requirement for buprenorphine training dictated by DATA 2000 so that it cannot be rolled back by future administrations. To further increase access to buprenorphine treatment, the training requirement should be removed for all providers who care for individuals with OUD.
The X-Waiver has been a barrier to hospitalist adoption of this critical, life-saving medication. HHS’s stance to nix the waiver, though fleeting, should be interpreted as an urgent call to the medical community, including us as hospitalists, to learn about buprenorphine with the many resources available (see table 1). As hospital medicine providers, we can order buprenorphine for patients with OUD during hospitalization. It is discharge prescriptions that have been limited to providers with an X-Waiver.
What can we do now to prepare for the eventual X-Waiver training removal? We can start by educating ourselves with the resources listed in table 1. Those of us who are already buprenorphine champions could lead trainings in our home institutions. In a future without the waiver there will be more flexibility to develop hospitalist-focused buprenorphine trainings, as the previous ones were geared for outpatient providers. Hospitalist organizations could support hospitalist-specific buprenorphine trainings and extend the models to include additional medications for addiction.
There is a large body of evidence regarding buprenorphine’s safety and efficacy in OUD treatment. With a worsening overdose crisis, there have been increasing opioid-related hospitalizations. When new medications for diabetes, hypertension, or DVT treatment become available, as hospitalists we incorporate them into our toolbox. As buprenorphine becomes more accessible, we can be leaders in further adopting it (and other substance use disorder medications while we are at it) as our standard of care for people with OUD.
Dr. Bottner is a physician assistant in the Division of Hospital Medicine at Dell Medical School at The University of Texas at Austin and director of the hospital’s Buprenorphine Team. Dr. Martin is a board-certified addiction medicine physician and hospitalist at University of California, San Francisco, and director of the Addiction Care Team at San Francisco General Hospital. Dr. Bottner and Dr. Martin colead the SHM Substance Use Disorder Special Interest Group.
There are two pandemics permeating the United States: COVID-19 and addiction. To date, more than 468,000 people have died from COVID-19 in the U.S. In the 12-month period ending in May 2020, over 80,000 died from a drug related cause – the highest number ever recorded in a year. Many of these deaths involved opioids.
COVID-19 has worsened outcomes for people with addiction. There is less access to treatment, increased isolation, and worsening psychosocial and economic stressors. These factors may drive new, increased, or more risky substance use and return to use for people in recovery. As hospitalists, we have been responders in both COVID-19 and our country’s worsening overdose and addiction crisis.
In December 2020’s Journal of Hospital Medicine article “Converging Crises: Caring for hospitalized adults with substance use disorder in the time of COVID-19”, Dr. Honora Englander and her coauthors called on hospitalists to actively engage patients with substance use disorders during hospitalization. The article highlights the colliding crises of addiction and COVID-19 and provides eight practical approaches for hospitalists to address substance use disorders during the pandemic, including initiating buprenorphine for opioid withdrawal and prescribing it for opioid use disorder (OUD) treatment.
Buprenorphine effectively treats opioid withdrawal, reduces OUD-related mortality, and decreases hospital readmissions related to OUD. To prescribe buprenorphine for OUD in the outpatient setting or on hospital discharge, providers need an X-Waiver. The X-Waiver is a result of the Drug Addiction Treatment Act 2000 (DATA 2000), which was enacted in 2000. It permits physicians to prescribe buprenorphine for OUD treatment after an 8-hour training. In 2016, the Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act extended buprenorphine prescribing to physician assistants (PAs) and advanced-practice nurses (APNs). However, PAs and APNs are required to complete a 24-hour training to receive the waiver.
On Jan. 14, 2021, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services under the Trump administration announced it was removing the X-Waiver training previously required for physicians to prescribe this life-saving medication. However, on Jan. 20, 2021, the Biden administration froze the training requirement removal pending a 60-day review. The excitement about the waiver’s eradication further dampened on Jan. 25, when the plan was halted due to procedural factors coupled with the concern that HHS may not have the authority to void requirements mandated by Congress.
Many of us continue to be hopeful that the X-Waiver will soon be gone. The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has committed to working with federal agencies to increase access to buprenorphine. The Biden administration also committed to addressing our country’s addiction crisis, including a plan to “make effective prevention, treatment, and recovery services available to all, including through a $125 billion federal investment.”
Despite the pause on HHS’s recent attempt to “X the X-Waiver,” we now have renewed attention and interest in this critical issue and an opportunity for greater and longer-lasting legislative impact. SHM supports that Congress repeal the legislative requirement for buprenorphine training dictated by DATA 2000 so that it cannot be rolled back by future administrations. To further increase access to buprenorphine treatment, the training requirement should be removed for all providers who care for individuals with OUD.
The X-Waiver has been a barrier to hospitalist adoption of this critical, life-saving medication. HHS’s stance to nix the waiver, though fleeting, should be interpreted as an urgent call to the medical community, including us as hospitalists, to learn about buprenorphine with the many resources available (see table 1). As hospital medicine providers, we can order buprenorphine for patients with OUD during hospitalization. It is discharge prescriptions that have been limited to providers with an X-Waiver.
What can we do now to prepare for the eventual X-Waiver training removal? We can start by educating ourselves with the resources listed in table 1. Those of us who are already buprenorphine champions could lead trainings in our home institutions. In a future without the waiver there will be more flexibility to develop hospitalist-focused buprenorphine trainings, as the previous ones were geared for outpatient providers. Hospitalist organizations could support hospitalist-specific buprenorphine trainings and extend the models to include additional medications for addiction.
There is a large body of evidence regarding buprenorphine’s safety and efficacy in OUD treatment. With a worsening overdose crisis, there have been increasing opioid-related hospitalizations. When new medications for diabetes, hypertension, or DVT treatment become available, as hospitalists we incorporate them into our toolbox. As buprenorphine becomes more accessible, we can be leaders in further adopting it (and other substance use disorder medications while we are at it) as our standard of care for people with OUD.
Dr. Bottner is a physician assistant in the Division of Hospital Medicine at Dell Medical School at The University of Texas at Austin and director of the hospital’s Buprenorphine Team. Dr. Martin is a board-certified addiction medicine physician and hospitalist at University of California, San Francisco, and director of the Addiction Care Team at San Francisco General Hospital. Dr. Bottner and Dr. Martin colead the SHM Substance Use Disorder Special Interest Group.
There are two pandemics permeating the United States: COVID-19 and addiction. To date, more than 468,000 people have died from COVID-19 in the U.S. In the 12-month period ending in May 2020, over 80,000 died from a drug related cause – the highest number ever recorded in a year. Many of these deaths involved opioids.
COVID-19 has worsened outcomes for people with addiction. There is less access to treatment, increased isolation, and worsening psychosocial and economic stressors. These factors may drive new, increased, or more risky substance use and return to use for people in recovery. As hospitalists, we have been responders in both COVID-19 and our country’s worsening overdose and addiction crisis.
In December 2020’s Journal of Hospital Medicine article “Converging Crises: Caring for hospitalized adults with substance use disorder in the time of COVID-19”, Dr. Honora Englander and her coauthors called on hospitalists to actively engage patients with substance use disorders during hospitalization. The article highlights the colliding crises of addiction and COVID-19 and provides eight practical approaches for hospitalists to address substance use disorders during the pandemic, including initiating buprenorphine for opioid withdrawal and prescribing it for opioid use disorder (OUD) treatment.
Buprenorphine effectively treats opioid withdrawal, reduces OUD-related mortality, and decreases hospital readmissions related to OUD. To prescribe buprenorphine for OUD in the outpatient setting or on hospital discharge, providers need an X-Waiver. The X-Waiver is a result of the Drug Addiction Treatment Act 2000 (DATA 2000), which was enacted in 2000. It permits physicians to prescribe buprenorphine for OUD treatment after an 8-hour training. In 2016, the Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act extended buprenorphine prescribing to physician assistants (PAs) and advanced-practice nurses (APNs). However, PAs and APNs are required to complete a 24-hour training to receive the waiver.
On Jan. 14, 2021, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services under the Trump administration announced it was removing the X-Waiver training previously required for physicians to prescribe this life-saving medication. However, on Jan. 20, 2021, the Biden administration froze the training requirement removal pending a 60-day review. The excitement about the waiver’s eradication further dampened on Jan. 25, when the plan was halted due to procedural factors coupled with the concern that HHS may not have the authority to void requirements mandated by Congress.
Many of us continue to be hopeful that the X-Waiver will soon be gone. The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has committed to working with federal agencies to increase access to buprenorphine. The Biden administration also committed to addressing our country’s addiction crisis, including a plan to “make effective prevention, treatment, and recovery services available to all, including through a $125 billion federal investment.”
Despite the pause on HHS’s recent attempt to “X the X-Waiver,” we now have renewed attention and interest in this critical issue and an opportunity for greater and longer-lasting legislative impact. SHM supports that Congress repeal the legislative requirement for buprenorphine training dictated by DATA 2000 so that it cannot be rolled back by future administrations. To further increase access to buprenorphine treatment, the training requirement should be removed for all providers who care for individuals with OUD.
The X-Waiver has been a barrier to hospitalist adoption of this critical, life-saving medication. HHS’s stance to nix the waiver, though fleeting, should be interpreted as an urgent call to the medical community, including us as hospitalists, to learn about buprenorphine with the many resources available (see table 1). As hospital medicine providers, we can order buprenorphine for patients with OUD during hospitalization. It is discharge prescriptions that have been limited to providers with an X-Waiver.
What can we do now to prepare for the eventual X-Waiver training removal? We can start by educating ourselves with the resources listed in table 1. Those of us who are already buprenorphine champions could lead trainings in our home institutions. In a future without the waiver there will be more flexibility to develop hospitalist-focused buprenorphine trainings, as the previous ones were geared for outpatient providers. Hospitalist organizations could support hospitalist-specific buprenorphine trainings and extend the models to include additional medications for addiction.
There is a large body of evidence regarding buprenorphine’s safety and efficacy in OUD treatment. With a worsening overdose crisis, there have been increasing opioid-related hospitalizations. When new medications for diabetes, hypertension, or DVT treatment become available, as hospitalists we incorporate them into our toolbox. As buprenorphine becomes more accessible, we can be leaders in further adopting it (and other substance use disorder medications while we are at it) as our standard of care for people with OUD.
Dr. Bottner is a physician assistant in the Division of Hospital Medicine at Dell Medical School at The University of Texas at Austin and director of the hospital’s Buprenorphine Team. Dr. Martin is a board-certified addiction medicine physician and hospitalist at University of California, San Francisco, and director of the Addiction Care Team at San Francisco General Hospital. Dr. Bottner and Dr. Martin colead the SHM Substance Use Disorder Special Interest Group.
New child COVID-19 cases decline as total passes 3 million
New COVID-19 cases in children continue to drop each week, but the total number of cases has now surpassed 3 million since the start of the pandemic, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
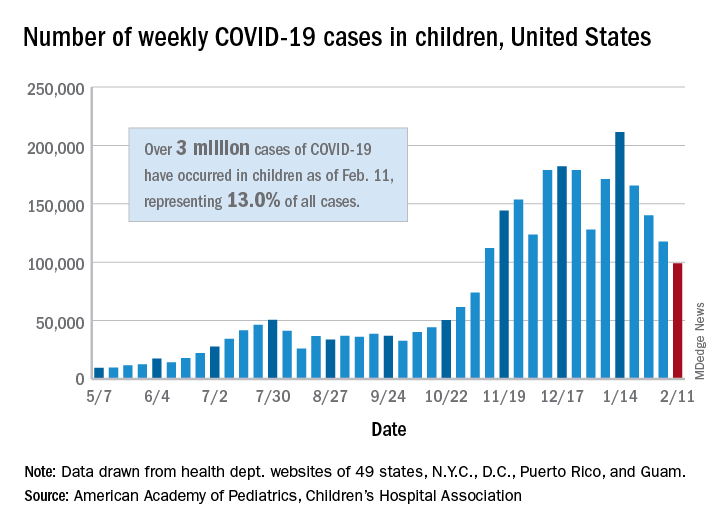
It was still enough, though, to bring the total to 3.03 million children infected with SARS-CoV-19 in the United States, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly report.
The nation also hit a couple of other ignominious milestones. The cumulative rate of COVID-19 infection now stands at 4,030 per 100,000, so 4% of all children have been infected. Also, children represented 16.9% of all new cases for the week, which equals the highest proportion seen throughout the pandemic, based on data from health departments in 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
There have been 241 COVID-19–related deaths in children so far, with 14 reported during the week of Feb. 5-11. Kansas just recorded its first pediatric death, which leaves 10 states that have had no fatalities. Texas, with 39 deaths, has had more than any other state, among the 43 that are reporting mortality by age, the AAP/CHA report showed.
New COVID-19 cases in children continue to drop each week, but the total number of cases has now surpassed 3 million since the start of the pandemic, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

It was still enough, though, to bring the total to 3.03 million children infected with SARS-CoV-19 in the United States, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly report.
The nation also hit a couple of other ignominious milestones. The cumulative rate of COVID-19 infection now stands at 4,030 per 100,000, so 4% of all children have been infected. Also, children represented 16.9% of all new cases for the week, which equals the highest proportion seen throughout the pandemic, based on data from health departments in 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
There have been 241 COVID-19–related deaths in children so far, with 14 reported during the week of Feb. 5-11. Kansas just recorded its first pediatric death, which leaves 10 states that have had no fatalities. Texas, with 39 deaths, has had more than any other state, among the 43 that are reporting mortality by age, the AAP/CHA report showed.
New COVID-19 cases in children continue to drop each week, but the total number of cases has now surpassed 3 million since the start of the pandemic, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

It was still enough, though, to bring the total to 3.03 million children infected with SARS-CoV-19 in the United States, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly report.
The nation also hit a couple of other ignominious milestones. The cumulative rate of COVID-19 infection now stands at 4,030 per 100,000, so 4% of all children have been infected. Also, children represented 16.9% of all new cases for the week, which equals the highest proportion seen throughout the pandemic, based on data from health departments in 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
There have been 241 COVID-19–related deaths in children so far, with 14 reported during the week of Feb. 5-11. Kansas just recorded its first pediatric death, which leaves 10 states that have had no fatalities. Texas, with 39 deaths, has had more than any other state, among the 43 that are reporting mortality by age, the AAP/CHA report showed.
FDA expands sacubitril/valsartan indication to embrace some HFpEF
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a groundbreaking expanded indication for sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto), making it the first drug in the United States indicated for chronic heart failure not specifically characterized by ejection fraction.
The new labeling, as provided by Novartis, grants physicians a good deal of discretion in prescribing sacubitril/valsartan for patients with HF beyond those with HF and reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), for which the drug was approved in 2015 primarily on the basis of the PARADIGM-HF trial.
The indication now reads, “to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in adult patients with chronic heart failure. Benefits are most clearly evident in patients with left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) below normal.”
Of note, the labeling cautions that “LVEF is a variable measure, so use clinical judgment in deciding whom to treat.”
The expanded indication essentially extends the sacubitril/valsartan option to many patients with HF and preserved LVEF (HFpEF), who in practice are most likely to have an LVEF in the range adjacent to “reduced,” long defined as “preserved” but lately categorized as “mid-range.”
But the FDA did not get so specific. In granting the expanded indication, which Novartis announced Feb. 16 in a press release, the agency accommodated the Dec. 15 majority recommendation of its Cardiovascular and Renal Drugs Advisory Committee that the PARAGON-HF trial “provided sufficient evidence to support” an indication beyond HFrEF.
The nature of the PARAGON-HF trial, along with detailed discussion among committee members after their vote tally, made it clear that the 12-to-1 majority favored an indication that would include clinically appropriate patients with “below normal” LVEF.
PARAGON-HF had assigned more than 4,800 patients whose LVEF was 45% or higher and were in NYHA class 2-4 to receive sacubitril/valsartan or valsartan only. Those taking the combo drug showed a 13% drop in risk for HF hospitalization or cardiovascular deaths over an average of 3 years, which narrowly missed significance (P = .059).
But a subgroup analysis garnered attention for its hint of benefit for patients with “mid-range” LVEF, in this case, below the median of 57%. The finding was supported by a later PARAGON-HF and PARADIGM-HF meta-analysis that pointed to a significant benefit for patients with HFpEF at its lowest LVEF levels, especially in women.
The expanded approval “is a significant advancement, providing a treatment to many patients who were not eligible for treatment before, because their ejection fraction was above the region we normally considered reduced,” Scott Solomon, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in the Novartis press release. “We can now offer a treatment to a wider range of patients who have an LVEF below normal,” added Dr. Solomon, PARAGON-HF executive committee cochair.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a groundbreaking expanded indication for sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto), making it the first drug in the United States indicated for chronic heart failure not specifically characterized by ejection fraction.
The new labeling, as provided by Novartis, grants physicians a good deal of discretion in prescribing sacubitril/valsartan for patients with HF beyond those with HF and reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), for which the drug was approved in 2015 primarily on the basis of the PARADIGM-HF trial.
The indication now reads, “to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in adult patients with chronic heart failure. Benefits are most clearly evident in patients with left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) below normal.”
Of note, the labeling cautions that “LVEF is a variable measure, so use clinical judgment in deciding whom to treat.”
The expanded indication essentially extends the sacubitril/valsartan option to many patients with HF and preserved LVEF (HFpEF), who in practice are most likely to have an LVEF in the range adjacent to “reduced,” long defined as “preserved” but lately categorized as “mid-range.”
But the FDA did not get so specific. In granting the expanded indication, which Novartis announced Feb. 16 in a press release, the agency accommodated the Dec. 15 majority recommendation of its Cardiovascular and Renal Drugs Advisory Committee that the PARAGON-HF trial “provided sufficient evidence to support” an indication beyond HFrEF.
The nature of the PARAGON-HF trial, along with detailed discussion among committee members after their vote tally, made it clear that the 12-to-1 majority favored an indication that would include clinically appropriate patients with “below normal” LVEF.
PARAGON-HF had assigned more than 4,800 patients whose LVEF was 45% or higher and were in NYHA class 2-4 to receive sacubitril/valsartan or valsartan only. Those taking the combo drug showed a 13% drop in risk for HF hospitalization or cardiovascular deaths over an average of 3 years, which narrowly missed significance (P = .059).
But a subgroup analysis garnered attention for its hint of benefit for patients with “mid-range” LVEF, in this case, below the median of 57%. The finding was supported by a later PARAGON-HF and PARADIGM-HF meta-analysis that pointed to a significant benefit for patients with HFpEF at its lowest LVEF levels, especially in women.
The expanded approval “is a significant advancement, providing a treatment to many patients who were not eligible for treatment before, because their ejection fraction was above the region we normally considered reduced,” Scott Solomon, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in the Novartis press release. “We can now offer a treatment to a wider range of patients who have an LVEF below normal,” added Dr. Solomon, PARAGON-HF executive committee cochair.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a groundbreaking expanded indication for sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto), making it the first drug in the United States indicated for chronic heart failure not specifically characterized by ejection fraction.
The new labeling, as provided by Novartis, grants physicians a good deal of discretion in prescribing sacubitril/valsartan for patients with HF beyond those with HF and reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), for which the drug was approved in 2015 primarily on the basis of the PARADIGM-HF trial.
The indication now reads, “to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in adult patients with chronic heart failure. Benefits are most clearly evident in patients with left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) below normal.”
Of note, the labeling cautions that “LVEF is a variable measure, so use clinical judgment in deciding whom to treat.”
The expanded indication essentially extends the sacubitril/valsartan option to many patients with HF and preserved LVEF (HFpEF), who in practice are most likely to have an LVEF in the range adjacent to “reduced,” long defined as “preserved” but lately categorized as “mid-range.”
But the FDA did not get so specific. In granting the expanded indication, which Novartis announced Feb. 16 in a press release, the agency accommodated the Dec. 15 majority recommendation of its Cardiovascular and Renal Drugs Advisory Committee that the PARAGON-HF trial “provided sufficient evidence to support” an indication beyond HFrEF.
The nature of the PARAGON-HF trial, along with detailed discussion among committee members after their vote tally, made it clear that the 12-to-1 majority favored an indication that would include clinically appropriate patients with “below normal” LVEF.
PARAGON-HF had assigned more than 4,800 patients whose LVEF was 45% or higher and were in NYHA class 2-4 to receive sacubitril/valsartan or valsartan only. Those taking the combo drug showed a 13% drop in risk for HF hospitalization or cardiovascular deaths over an average of 3 years, which narrowly missed significance (P = .059).
But a subgroup analysis garnered attention for its hint of benefit for patients with “mid-range” LVEF, in this case, below the median of 57%. The finding was supported by a later PARAGON-HF and PARADIGM-HF meta-analysis that pointed to a significant benefit for patients with HFpEF at its lowest LVEF levels, especially in women.
The expanded approval “is a significant advancement, providing a treatment to many patients who were not eligible for treatment before, because their ejection fraction was above the region we normally considered reduced,” Scott Solomon, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in the Novartis press release. “We can now offer a treatment to a wider range of patients who have an LVEF below normal,” added Dr. Solomon, PARAGON-HF executive committee cochair.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One-third of health care workers leery of getting COVID-19 vaccine, survey shows
Moreover, 54% of direct care providers indicated that they would take the vaccine if offered, compared with 60% of noncare providers.
The findings come from what is believed to be the largest survey of health care provider attitudes toward COVID-19 vaccination, published online Jan. 25 in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
“We have shown that self-reported willingness to receive vaccination against COVID-19 differs by age, gender, race and hospital role, with physicians and research scientists showing the highest acceptance,” Jana Shaw, MD, MPH, State University of New York, Syracuse, N.Y, the study’s corresponding author, told this news organization. “Building trust in authorities and confidence in vaccines is a complex and time-consuming process that requires commitment and resources. We have to make those investments as hesitancy can severely undermine vaccination coverage. Because health care providers are members of our communities, it is possible that their views are shared by the public at large. Our findings can assist public health professionals as a starting point of discussion and engagement with communities to ensure that we vaccinate at least 80% of the public to end the pandemic.”
For the study, Dr. Shaw and her colleagues emailed an anonymous survey to 9,565 employees of State University of New York Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, an academic medical center that cares for an estimated 1.8 million people. The survey, which contained questions intended to evaluate attitudes, belief, and willingness to get vaccinated, took place between Nov. 23 and Dec. 5, about a week before the U.S. Food and Drug Administration granted the first emergency use authorization for the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine.
Survey recipients included physicians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, nurses, pharmacists, medical and nursing students, allied health professionals, and nonclinical ancillary staff.
Of the 9,565 surveys sent, 5,287 responses were collected and used in the final analysis, for a response rate of 55%. The mean age of respondents was 43, 73% were female, 85% were White, 6% were Asian, 5% were Black/African American, and the rest were Native American, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, or from other races. More than half of respondents (59%) reported that they provided direct patient care, and 32% said they provided care for patients with COVID-19.
Of all survey respondents, 58% expressed their intent to receive a COVID-19 vaccine, but this varied by their role in the health care system. For example, in response to the statement, “If a vaccine were offered free of charge, I would take it,” 80% of scientists and physicians agreed that they would, while colleagues in other roles were unsure whether they would take the vaccine, including 34% of registered nurses, 32% of allied health professionals, and 32% of master’s-level clinicians. These differences across roles were significant (P less than .001).
The researchers also found that direct patient care or care for COVID-19 patients was associated with lower vaccination intent. For example, 54% of direct care providers and 62% of non-care providers indicated they would take the vaccine if offered, compared with 52% of those who had provided care for COVID-19 patients vs. 61% of those who had not (P less than .001).
“This was a really surprising finding,” said Dr. Shaw, who is a pediatric infectious diseases physician at SUNY Upstate. “In general, one would expect that perceived severity of disease would lead to a greater desire to get vaccinated. Because our question did not address severity of disease, it is possible that we oversampled respondents who took care of patients with mild disease (i.e., in an outpatient setting). This could have led to an underestimation of disease severity and resulted in lower vaccination intent.”
A focus on rebuilding trust
Survey respondents who agreed or strongly agreed that they would accept a vaccine were older (a mean age of 44 years), compared with those who were not sure or who disagreed (a mean age of 42 vs. 38 years, respectively; P less than .001). In addition, fewer females agreed or strongly agreed that they would accept a vaccine (54% vs. 73% of males), whereas those who self-identified as Black/African American were least likely to want to get vaccinated, compared with those from other ethnic groups (31%, compared with 74% of Asians, 58% of Whites, and 39% of American Indians or Alaska Natives).
“We are deeply aware of the poor decisions scientists made in the past, which led to a prevailing skepticism and ‘feeling like guinea pigs’ among people of color, especially Black adults,” Dr. Shaw said. “Black adults are less likely, compared [with] White adults, to have confidence that scientists act in the public interest. Rebuilding trust will take time and has to start with addressing health care disparities. In addition, we need to acknowledge contributions of Black researchers to science. For example, until recently very few knew that the Moderna vaccine was developed [with the help of] Dr. Kizzmekia Corbett, who is Black.”
The top five main areas of unease that all respondents expressed about a COVID-19 vaccine were concern about adverse events/side effects (47%), efficacy (15%), rushed release (11%), safety (11%), and the research and authorization process (3%).
“I think it is important that fellow clinicians recognize that, in order to boost vaccine confidence we will need careful, individually tailored communication strategies,” Dr. Shaw said. “A consideration should be given to those [strategies] that utilize interpersonal channels that deliver leadership by example and leverage influencers in the institution to encourage wider adoption of vaccination.”
Aaron M. Milstone, MD, MHS, asked to comment on the research, recommended that health care workers advocate for the vaccine and encourage their patients, friends, and loved ones to get vaccinated. “Soon, COVID-19 will have taken more than half a million lives in the U.S.,” said Dr. Milstone, a pediatric epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. “Although vaccines can have side effects like fever and muscle aches, and very, very rare more serious side effects, the risks of dying from COVID are much greater than the risk of a serious vaccine reaction. The study’s authors shed light on the ongoing need for leaders of all communities to support the COVID vaccines, not just the scientific community, but religious leaders, political leaders, and community leaders.”
Addressing vaccine hesitancy
Informed by their own survey, Dr. Shaw and her colleagues have developed a plan to address vaccine hesitancy to ensure high vaccine uptake at SUNY Upstate. Those strategies include, but aren’t limited to, institution-wide forums for all employees on COVID-19 vaccine safety, risks, and benefits followed by Q&A sessions, grand rounds for providers summarizing clinical trial data on mRNA vaccines, development of an Ask COVID email line for staff to ask vaccine-related questions, and a detailed vaccine-specific FAQ document.
In addition, SUNY Upstate experts have engaged in numerous media interviews to provide education and updates on the benefits of vaccination to public and staff, stationary vaccine locations, and mobile COVID-19 vaccine carts. “To date, the COVID-19 vaccination process has been well received, and we anticipate strong vaccine uptake,” she said.
Dr. Shaw acknowledged certain limitations of the survey, including its cross-sectional design and the fact that it was conducted in a single health care system in the northeastern United States. “Thus, generalizability to other regions of the U.S. and other countries may be limited,” Dr. Shaw said. “The study was also conducted before EUA [emergency use authorization] was granted to either the Moderna or Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines. It is therefore likely that vaccine acceptance will change over time as more people get vaccinated.”
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Milstone disclosed that he has received a research grant from Merck, but it is not related to vaccines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Moreover, 54% of direct care providers indicated that they would take the vaccine if offered, compared with 60% of noncare providers.
The findings come from what is believed to be the largest survey of health care provider attitudes toward COVID-19 vaccination, published online Jan. 25 in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
“We have shown that self-reported willingness to receive vaccination against COVID-19 differs by age, gender, race and hospital role, with physicians and research scientists showing the highest acceptance,” Jana Shaw, MD, MPH, State University of New York, Syracuse, N.Y, the study’s corresponding author, told this news organization. “Building trust in authorities and confidence in vaccines is a complex and time-consuming process that requires commitment and resources. We have to make those investments as hesitancy can severely undermine vaccination coverage. Because health care providers are members of our communities, it is possible that their views are shared by the public at large. Our findings can assist public health professionals as a starting point of discussion and engagement with communities to ensure that we vaccinate at least 80% of the public to end the pandemic.”
For the study, Dr. Shaw and her colleagues emailed an anonymous survey to 9,565 employees of State University of New York Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, an academic medical center that cares for an estimated 1.8 million people. The survey, which contained questions intended to evaluate attitudes, belief, and willingness to get vaccinated, took place between Nov. 23 and Dec. 5, about a week before the U.S. Food and Drug Administration granted the first emergency use authorization for the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine.
Survey recipients included physicians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, nurses, pharmacists, medical and nursing students, allied health professionals, and nonclinical ancillary staff.
Of the 9,565 surveys sent, 5,287 responses were collected and used in the final analysis, for a response rate of 55%. The mean age of respondents was 43, 73% were female, 85% were White, 6% were Asian, 5% were Black/African American, and the rest were Native American, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, or from other races. More than half of respondents (59%) reported that they provided direct patient care, and 32% said they provided care for patients with COVID-19.
Of all survey respondents, 58% expressed their intent to receive a COVID-19 vaccine, but this varied by their role in the health care system. For example, in response to the statement, “If a vaccine were offered free of charge, I would take it,” 80% of scientists and physicians agreed that they would, while colleagues in other roles were unsure whether they would take the vaccine, including 34% of registered nurses, 32% of allied health professionals, and 32% of master’s-level clinicians. These differences across roles were significant (P less than .001).
The researchers also found that direct patient care or care for COVID-19 patients was associated with lower vaccination intent. For example, 54% of direct care providers and 62% of non-care providers indicated they would take the vaccine if offered, compared with 52% of those who had provided care for COVID-19 patients vs. 61% of those who had not (P less than .001).
“This was a really surprising finding,” said Dr. Shaw, who is a pediatric infectious diseases physician at SUNY Upstate. “In general, one would expect that perceived severity of disease would lead to a greater desire to get vaccinated. Because our question did not address severity of disease, it is possible that we oversampled respondents who took care of patients with mild disease (i.e., in an outpatient setting). This could have led to an underestimation of disease severity and resulted in lower vaccination intent.”
A focus on rebuilding trust
Survey respondents who agreed or strongly agreed that they would accept a vaccine were older (a mean age of 44 years), compared with those who were not sure or who disagreed (a mean age of 42 vs. 38 years, respectively; P less than .001). In addition, fewer females agreed or strongly agreed that they would accept a vaccine (54% vs. 73% of males), whereas those who self-identified as Black/African American were least likely to want to get vaccinated, compared with those from other ethnic groups (31%, compared with 74% of Asians, 58% of Whites, and 39% of American Indians or Alaska Natives).
“We are deeply aware of the poor decisions scientists made in the past, which led to a prevailing skepticism and ‘feeling like guinea pigs’ among people of color, especially Black adults,” Dr. Shaw said. “Black adults are less likely, compared [with] White adults, to have confidence that scientists act in the public interest. Rebuilding trust will take time and has to start with addressing health care disparities. In addition, we need to acknowledge contributions of Black researchers to science. For example, until recently very few knew that the Moderna vaccine was developed [with the help of] Dr. Kizzmekia Corbett, who is Black.”
The top five main areas of unease that all respondents expressed about a COVID-19 vaccine were concern about adverse events/side effects (47%), efficacy (15%), rushed release (11%), safety (11%), and the research and authorization process (3%).
“I think it is important that fellow clinicians recognize that, in order to boost vaccine confidence we will need careful, individually tailored communication strategies,” Dr. Shaw said. “A consideration should be given to those [strategies] that utilize interpersonal channels that deliver leadership by example and leverage influencers in the institution to encourage wider adoption of vaccination.”
Aaron M. Milstone, MD, MHS, asked to comment on the research, recommended that health care workers advocate for the vaccine and encourage their patients, friends, and loved ones to get vaccinated. “Soon, COVID-19 will have taken more than half a million lives in the U.S.,” said Dr. Milstone, a pediatric epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. “Although vaccines can have side effects like fever and muscle aches, and very, very rare more serious side effects, the risks of dying from COVID are much greater than the risk of a serious vaccine reaction. The study’s authors shed light on the ongoing need for leaders of all communities to support the COVID vaccines, not just the scientific community, but religious leaders, political leaders, and community leaders.”
Addressing vaccine hesitancy
Informed by their own survey, Dr. Shaw and her colleagues have developed a plan to address vaccine hesitancy to ensure high vaccine uptake at SUNY Upstate. Those strategies include, but aren’t limited to, institution-wide forums for all employees on COVID-19 vaccine safety, risks, and benefits followed by Q&A sessions, grand rounds for providers summarizing clinical trial data on mRNA vaccines, development of an Ask COVID email line for staff to ask vaccine-related questions, and a detailed vaccine-specific FAQ document.
In addition, SUNY Upstate experts have engaged in numerous media interviews to provide education and updates on the benefits of vaccination to public and staff, stationary vaccine locations, and mobile COVID-19 vaccine carts. “To date, the COVID-19 vaccination process has been well received, and we anticipate strong vaccine uptake,” she said.
Dr. Shaw acknowledged certain limitations of the survey, including its cross-sectional design and the fact that it was conducted in a single health care system in the northeastern United States. “Thus, generalizability to other regions of the U.S. and other countries may be limited,” Dr. Shaw said. “The study was also conducted before EUA [emergency use authorization] was granted to either the Moderna or Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines. It is therefore likely that vaccine acceptance will change over time as more people get vaccinated.”
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Milstone disclosed that he has received a research grant from Merck, but it is not related to vaccines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Moreover, 54% of direct care providers indicated that they would take the vaccine if offered, compared with 60% of noncare providers.
The findings come from what is believed to be the largest survey of health care provider attitudes toward COVID-19 vaccination, published online Jan. 25 in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
“We have shown that self-reported willingness to receive vaccination against COVID-19 differs by age, gender, race and hospital role, with physicians and research scientists showing the highest acceptance,” Jana Shaw, MD, MPH, State University of New York, Syracuse, N.Y, the study’s corresponding author, told this news organization. “Building trust in authorities and confidence in vaccines is a complex and time-consuming process that requires commitment and resources. We have to make those investments as hesitancy can severely undermine vaccination coverage. Because health care providers are members of our communities, it is possible that their views are shared by the public at large. Our findings can assist public health professionals as a starting point of discussion and engagement with communities to ensure that we vaccinate at least 80% of the public to end the pandemic.”
For the study, Dr. Shaw and her colleagues emailed an anonymous survey to 9,565 employees of State University of New York Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, an academic medical center that cares for an estimated 1.8 million people. The survey, which contained questions intended to evaluate attitudes, belief, and willingness to get vaccinated, took place between Nov. 23 and Dec. 5, about a week before the U.S. Food and Drug Administration granted the first emergency use authorization for the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine.
Survey recipients included physicians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, nurses, pharmacists, medical and nursing students, allied health professionals, and nonclinical ancillary staff.
Of the 9,565 surveys sent, 5,287 responses were collected and used in the final analysis, for a response rate of 55%. The mean age of respondents was 43, 73% were female, 85% were White, 6% were Asian, 5% were Black/African American, and the rest were Native American, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, or from other races. More than half of respondents (59%) reported that they provided direct patient care, and 32% said they provided care for patients with COVID-19.
Of all survey respondents, 58% expressed their intent to receive a COVID-19 vaccine, but this varied by their role in the health care system. For example, in response to the statement, “If a vaccine were offered free of charge, I would take it,” 80% of scientists and physicians agreed that they would, while colleagues in other roles were unsure whether they would take the vaccine, including 34% of registered nurses, 32% of allied health professionals, and 32% of master’s-level clinicians. These differences across roles were significant (P less than .001).
The researchers also found that direct patient care or care for COVID-19 patients was associated with lower vaccination intent. For example, 54% of direct care providers and 62% of non-care providers indicated they would take the vaccine if offered, compared with 52% of those who had provided care for COVID-19 patients vs. 61% of those who had not (P less than .001).
“This was a really surprising finding,” said Dr. Shaw, who is a pediatric infectious diseases physician at SUNY Upstate. “In general, one would expect that perceived severity of disease would lead to a greater desire to get vaccinated. Because our question did not address severity of disease, it is possible that we oversampled respondents who took care of patients with mild disease (i.e., in an outpatient setting). This could have led to an underestimation of disease severity and resulted in lower vaccination intent.”
A focus on rebuilding trust
Survey respondents who agreed or strongly agreed that they would accept a vaccine were older (a mean age of 44 years), compared with those who were not sure or who disagreed (a mean age of 42 vs. 38 years, respectively; P less than .001). In addition, fewer females agreed or strongly agreed that they would accept a vaccine (54% vs. 73% of males), whereas those who self-identified as Black/African American were least likely to want to get vaccinated, compared with those from other ethnic groups (31%, compared with 74% of Asians, 58% of Whites, and 39% of American Indians or Alaska Natives).
“We are deeply aware of the poor decisions scientists made in the past, which led to a prevailing skepticism and ‘feeling like guinea pigs’ among people of color, especially Black adults,” Dr. Shaw said. “Black adults are less likely, compared [with] White adults, to have confidence that scientists act in the public interest. Rebuilding trust will take time and has to start with addressing health care disparities. In addition, we need to acknowledge contributions of Black researchers to science. For example, until recently very few knew that the Moderna vaccine was developed [with the help of] Dr. Kizzmekia Corbett, who is Black.”
The top five main areas of unease that all respondents expressed about a COVID-19 vaccine were concern about adverse events/side effects (47%), efficacy (15%), rushed release (11%), safety (11%), and the research and authorization process (3%).
“I think it is important that fellow clinicians recognize that, in order to boost vaccine confidence we will need careful, individually tailored communication strategies,” Dr. Shaw said. “A consideration should be given to those [strategies] that utilize interpersonal channels that deliver leadership by example and leverage influencers in the institution to encourage wider adoption of vaccination.”
Aaron M. Milstone, MD, MHS, asked to comment on the research, recommended that health care workers advocate for the vaccine and encourage their patients, friends, and loved ones to get vaccinated. “Soon, COVID-19 will have taken more than half a million lives in the U.S.,” said Dr. Milstone, a pediatric epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. “Although vaccines can have side effects like fever and muscle aches, and very, very rare more serious side effects, the risks of dying from COVID are much greater than the risk of a serious vaccine reaction. The study’s authors shed light on the ongoing need for leaders of all communities to support the COVID vaccines, not just the scientific community, but religious leaders, political leaders, and community leaders.”
Addressing vaccine hesitancy
Informed by their own survey, Dr. Shaw and her colleagues have developed a plan to address vaccine hesitancy to ensure high vaccine uptake at SUNY Upstate. Those strategies include, but aren’t limited to, institution-wide forums for all employees on COVID-19 vaccine safety, risks, and benefits followed by Q&A sessions, grand rounds for providers summarizing clinical trial data on mRNA vaccines, development of an Ask COVID email line for staff to ask vaccine-related questions, and a detailed vaccine-specific FAQ document.
In addition, SUNY Upstate experts have engaged in numerous media interviews to provide education and updates on the benefits of vaccination to public and staff, stationary vaccine locations, and mobile COVID-19 vaccine carts. “To date, the COVID-19 vaccination process has been well received, and we anticipate strong vaccine uptake,” she said.
Dr. Shaw acknowledged certain limitations of the survey, including its cross-sectional design and the fact that it was conducted in a single health care system in the northeastern United States. “Thus, generalizability to other regions of the U.S. and other countries may be limited,” Dr. Shaw said. “The study was also conducted before EUA [emergency use authorization] was granted to either the Moderna or Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines. It is therefore likely that vaccine acceptance will change over time as more people get vaccinated.”
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Milstone disclosed that he has received a research grant from Merck, but it is not related to vaccines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More Americans hospitalized, readmitted for heart failure
Overall primary HF hospitalization rates per 1,000 adults declined from 4.4 in 2010 to 4.1 in 2013, and then increased from 4.2 in 2014 to 4.9 in 2017.
Rates of unique patient visits for HF were also on the way down – falling from 3.4 in 2010 to 3.2 in 2013 and 2014 – before climbing to 3.8 in 2017.
Similar trends were observed for rates of postdischarge HF readmissions (from 1.0 in 2010 to 0.9 in 2014 to 1.1 in 2017) and all-cause 30-day readmissions (from 0.8 in 2010 to 0.7 in 2014 to 0.9 in 2017).
“We should be emphasizing the things we know work to reduce heart failure hospitalization, which is, No. 1, prevention,” senior author Boback Ziaeian, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Comorbidities that can lead to heart failure crept up over the study period, such that by 2017, hypertension was present in 91.4% of patients, diabetes in 48.9%, and lipid disorders in 53.1%, up from 76.5%, 44.9%, and 40.4%, respectively, in 2010. Half of all patients had coronary artery disease at both time points. Renal disease shot up from 45.9% to 60.6% by 2017.
“If we did a better job of controlling our known risk factors, we would really cut down on the incidence of heart failure being developed and then, among those estimated 6.6 million heart failure patients, we need to get them on our cornerstone therapies,” said Dr. Ziaeian, of the Veterans Affairts Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System and the University of California, Los Angeles.
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, which have shown clear efficacy and safety in trials like DAPA-HF and EMPEROR-Reduced, provide a “huge opportunity” to add on to standard therapies, he noted. Competition for VA contracts has brought the price down to about $50 a month for veterans, compared with a cash price of about $500-$600 a month.
Yet in routine practice, only 8% of veterans with HF at his center are on an SGLT2 inhibitor, compared with 80% on ACE inhibitors or beta blockers, observed Dr. Ziaeian. “This medication has been indicated for the last year and a half and we’re only at 8% in a system where we have pretty easy access to medications.”
As reported online Feb. 10 in JAMA Cardiology, notable sex differences were found in hospitalization, with higher rates per 1,000 persons among men.
In contrast, a 2020 report on HF trends in the VA system showed a 2% decrease in unadjusted 30-day readmissions from 2007 to 2017 and a decline in the adjusted 30-day readmission risk.
The present study did not risk-adjust readmission risk and included a population that was 51% male, compared with about 98% male in the VA, the investigators noted.
“The increasing hospitalization rate in our study may represent an actual increase in HF hospitalizations or shifts in administrative coding practices, increased use of HF biomarkers, or lower thresholds for diagnosis of HF with preserved ejection fraction,” they wrote.
The analysis was based on data from the Nationwide Readmission Database, which included 35,197,725 hospitalizations with a primary or secondary diagnosis of HF and 8,273,270 primary HF hospitalizations from January 2010 to December 2017.
A single primary HF admission occurred in 5,092,626 unique patients and 1,269,109 had two or more HF hospitalizations. The mean age was 72.1 years.
The administrative database did not include clinical data, so it wasn’t possible to differentiate between HF with preserved or reduced ejection fraction, the authors noted. Patient race and ethnicity data also were not available.
“Future studies are needed to verify our findings to better develop and improve individualized strategies for HF prevention, management, and surveillance for men and women,” the investigators concluded.
One coauthor reporting receiving personal fees from Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, CHF Solutions, Edwards Lifesciences, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Overall primary HF hospitalization rates per 1,000 adults declined from 4.4 in 2010 to 4.1 in 2013, and then increased from 4.2 in 2014 to 4.9 in 2017.
Rates of unique patient visits for HF were also on the way down – falling from 3.4 in 2010 to 3.2 in 2013 and 2014 – before climbing to 3.8 in 2017.
Similar trends were observed for rates of postdischarge HF readmissions (from 1.0 in 2010 to 0.9 in 2014 to 1.1 in 2017) and all-cause 30-day readmissions (from 0.8 in 2010 to 0.7 in 2014 to 0.9 in 2017).
“We should be emphasizing the things we know work to reduce heart failure hospitalization, which is, No. 1, prevention,” senior author Boback Ziaeian, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Comorbidities that can lead to heart failure crept up over the study period, such that by 2017, hypertension was present in 91.4% of patients, diabetes in 48.9%, and lipid disorders in 53.1%, up from 76.5%, 44.9%, and 40.4%, respectively, in 2010. Half of all patients had coronary artery disease at both time points. Renal disease shot up from 45.9% to 60.6% by 2017.
“If we did a better job of controlling our known risk factors, we would really cut down on the incidence of heart failure being developed and then, among those estimated 6.6 million heart failure patients, we need to get them on our cornerstone therapies,” said Dr. Ziaeian, of the Veterans Affairts Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System and the University of California, Los Angeles.
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, which have shown clear efficacy and safety in trials like DAPA-HF and EMPEROR-Reduced, provide a “huge opportunity” to add on to standard therapies, he noted. Competition for VA contracts has brought the price down to about $50 a month for veterans, compared with a cash price of about $500-$600 a month.
Yet in routine practice, only 8% of veterans with HF at his center are on an SGLT2 inhibitor, compared with 80% on ACE inhibitors or beta blockers, observed Dr. Ziaeian. “This medication has been indicated for the last year and a half and we’re only at 8% in a system where we have pretty easy access to medications.”
As reported online Feb. 10 in JAMA Cardiology, notable sex differences were found in hospitalization, with higher rates per 1,000 persons among men.
In contrast, a 2020 report on HF trends in the VA system showed a 2% decrease in unadjusted 30-day readmissions from 2007 to 2017 and a decline in the adjusted 30-day readmission risk.
The present study did not risk-adjust readmission risk and included a population that was 51% male, compared with about 98% male in the VA, the investigators noted.
“The increasing hospitalization rate in our study may represent an actual increase in HF hospitalizations or shifts in administrative coding practices, increased use of HF biomarkers, or lower thresholds for diagnosis of HF with preserved ejection fraction,” they wrote.
The analysis was based on data from the Nationwide Readmission Database, which included 35,197,725 hospitalizations with a primary or secondary diagnosis of HF and 8,273,270 primary HF hospitalizations from January 2010 to December 2017.
A single primary HF admission occurred in 5,092,626 unique patients and 1,269,109 had two or more HF hospitalizations. The mean age was 72.1 years.
The administrative database did not include clinical data, so it wasn’t possible to differentiate between HF with preserved or reduced ejection fraction, the authors noted. Patient race and ethnicity data also were not available.
“Future studies are needed to verify our findings to better develop and improve individualized strategies for HF prevention, management, and surveillance for men and women,” the investigators concluded.
One coauthor reporting receiving personal fees from Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, CHF Solutions, Edwards Lifesciences, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Overall primary HF hospitalization rates per 1,000 adults declined from 4.4 in 2010 to 4.1 in 2013, and then increased from 4.2 in 2014 to 4.9 in 2017.
Rates of unique patient visits for HF were also on the way down – falling from 3.4 in 2010 to 3.2 in 2013 and 2014 – before climbing to 3.8 in 2017.
Similar trends were observed for rates of postdischarge HF readmissions (from 1.0 in 2010 to 0.9 in 2014 to 1.1 in 2017) and all-cause 30-day readmissions (from 0.8 in 2010 to 0.7 in 2014 to 0.9 in 2017).
“We should be emphasizing the things we know work to reduce heart failure hospitalization, which is, No. 1, prevention,” senior author Boback Ziaeian, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Comorbidities that can lead to heart failure crept up over the study period, such that by 2017, hypertension was present in 91.4% of patients, diabetes in 48.9%, and lipid disorders in 53.1%, up from 76.5%, 44.9%, and 40.4%, respectively, in 2010. Half of all patients had coronary artery disease at both time points. Renal disease shot up from 45.9% to 60.6% by 2017.
“If we did a better job of controlling our known risk factors, we would really cut down on the incidence of heart failure being developed and then, among those estimated 6.6 million heart failure patients, we need to get them on our cornerstone therapies,” said Dr. Ziaeian, of the Veterans Affairts Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System and the University of California, Los Angeles.
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, which have shown clear efficacy and safety in trials like DAPA-HF and EMPEROR-Reduced, provide a “huge opportunity” to add on to standard therapies, he noted. Competition for VA contracts has brought the price down to about $50 a month for veterans, compared with a cash price of about $500-$600 a month.
Yet in routine practice, only 8% of veterans with HF at his center are on an SGLT2 inhibitor, compared with 80% on ACE inhibitors or beta blockers, observed Dr. Ziaeian. “This medication has been indicated for the last year and a half and we’re only at 8% in a system where we have pretty easy access to medications.”
As reported online Feb. 10 in JAMA Cardiology, notable sex differences were found in hospitalization, with higher rates per 1,000 persons among men.
In contrast, a 2020 report on HF trends in the VA system showed a 2% decrease in unadjusted 30-day readmissions from 2007 to 2017 and a decline in the adjusted 30-day readmission risk.
The present study did not risk-adjust readmission risk and included a population that was 51% male, compared with about 98% male in the VA, the investigators noted.
“The increasing hospitalization rate in our study may represent an actual increase in HF hospitalizations or shifts in administrative coding practices, increased use of HF biomarkers, or lower thresholds for diagnosis of HF with preserved ejection fraction,” they wrote.
The analysis was based on data from the Nationwide Readmission Database, which included 35,197,725 hospitalizations with a primary or secondary diagnosis of HF and 8,273,270 primary HF hospitalizations from January 2010 to December 2017.
A single primary HF admission occurred in 5,092,626 unique patients and 1,269,109 had two or more HF hospitalizations. The mean age was 72.1 years.
The administrative database did not include clinical data, so it wasn’t possible to differentiate between HF with preserved or reduced ejection fraction, the authors noted. Patient race and ethnicity data also were not available.
“Future studies are needed to verify our findings to better develop and improve individualized strategies for HF prevention, management, and surveillance for men and women,” the investigators concluded.
One coauthor reporting receiving personal fees from Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, CHF Solutions, Edwards Lifesciences, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Steroid and immunoglobulin standard of care for MIS-C
The combination of methylprednisolone and intravenous immunoglobulins works better than intravenous immunoglobulins alone for multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), researchers say.
“I’m not sure it’s the best treatment because we have not studied every possible treatment,” François Angoulvant, MD, PhD, told this news organization, “but right now, it’s the standard of care.”
Dr. Angoulvant, a professor of pediatrics at University of Paris, and colleagues published a comparison of the two treatments in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
A small percentage of children infected with SARS-CoV-2 develop MIS-C about 2 to 4 weeks later. It is considered a separate disease entity from COVID-19 and is associated with persistent fever, digestive symptoms, rash, bilateral nonpurulent conjunctivitis, mucocutaneous inflammation signs, and frequent cardiovascular involvement. In more than 60% of cases, it leads to hemodynamic failure, with acute cardiac dysfunction.
Because MIS-C resembles Kawasaki disease, clinicians modeled their treatment on that condition and started with immunoglobulins alone, Dr. Angoulvant said.
Based on expert opinion, the National Health Service in the United Kingdom published a consensus statement in Sept. listing immunoglobulins alone as the first-line treatment.
But anecdotal reports have emerged that combining the immunoglobulins with a corticosteroid worked better. To investigate this possibility, Dr. Angoulvant and colleagues analyzed records of MIS-C cases in France, where physicians are required to report all suspected cases of MIS-C to the French National Public Health Agency.
Among the 181 cases they scrutinized, 111 fulfilled the World Health Organization criteria for MIS-C. Of these, the researchers were able to match 64 patients who had received immunoglobulins alone with 32 who had received the combined therapy and could be matched using propensity scores.
The researchers defined treatment failure as persistence of fever for 2 days after the start of therapy or recurrence of fever within a week. By this measure, the combination treatment failed in only 9% of cases while immunoglobulins alone failed in 38% of cases. The difference was statistically significant (P = .008). Most of those for whom these treatments failed received second-line treatments such as steroids or biological agents.
Patients treated with the combination therapy also had a lower risk of secondary acute left ventricular dysfunction (odds ratio, 0.20; 95% confidence interval, 0.06-0.66) and a lower risk of needing hemodynamic support (OR, 0.21; 95% CI, 0.06-0.76).
Those receiving the combination therapy spent a mean of 4 days in the pediatric intensive care unit compared with 6 days for those receiving immunoglobulins alone. (Difference in days, −2.4; 95% CI, −4.0 to −0.7; P = .005).
There are few drawbacks to the combination approach, Dr. Angoulvant said, as the side effects of corticosteroids are generally not severe and they can be anticipated because this class of medications has been used for many years.
The study raises the question of whether corticosteroids might work as well by themselves, but it could not be answered with this database as no one is using that approach in France, Dr. Angoulvant said. “I hope other teams around the world could bring us the answer.”
In the United States, most physicians appear to already be using the combination therapy, said David Teachey, MD, an associate professor of pediatrics at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
The reduction in time in pediatric intensive care and the reduced risk of cardiac dysfunction are important findings, he said.
This retrospective study falls short of the evidence provided by a randomized clinical trial, Dr. Teachey noted. But he acknowledged that few families would agree to participate in such a trial as they would have to take a chance that the sick children would receive a less effective therapy than what they would otherwise get. “It’s hard to [talk] about a therapy reduction,” he told this news organization.
Given that impediment, he agreed with Dr. Angoulvant that the current study and others like it may provide the best data available pointing to a treatment approach for MIS-C.
The study received an unrestricted grant from Pfizer. The French COVID-19 Paediatric Inflammation Consortium received an unrestricted grant from the Square Foundation (Grandir–Fonds de Solidarité pour L’Enfance). Dr. Angoulvant and Dr. Teachey have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The combination of methylprednisolone and intravenous immunoglobulins works better than intravenous immunoglobulins alone for multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), researchers say.
“I’m not sure it’s the best treatment because we have not studied every possible treatment,” François Angoulvant, MD, PhD, told this news organization, “but right now, it’s the standard of care.”
Dr. Angoulvant, a professor of pediatrics at University of Paris, and colleagues published a comparison of the two treatments in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
A small percentage of children infected with SARS-CoV-2 develop MIS-C about 2 to 4 weeks later. It is considered a separate disease entity from COVID-19 and is associated with persistent fever, digestive symptoms, rash, bilateral nonpurulent conjunctivitis, mucocutaneous inflammation signs, and frequent cardiovascular involvement. In more than 60% of cases, it leads to hemodynamic failure, with acute cardiac dysfunction.
Because MIS-C resembles Kawasaki disease, clinicians modeled their treatment on that condition and started with immunoglobulins alone, Dr. Angoulvant said.
Based on expert opinion, the National Health Service in the United Kingdom published a consensus statement in Sept. listing immunoglobulins alone as the first-line treatment.
But anecdotal reports have emerged that combining the immunoglobulins with a corticosteroid worked better. To investigate this possibility, Dr. Angoulvant and colleagues analyzed records of MIS-C cases in France, where physicians are required to report all suspected cases of MIS-C to the French National Public Health Agency.
Among the 181 cases they scrutinized, 111 fulfilled the World Health Organization criteria for MIS-C. Of these, the researchers were able to match 64 patients who had received immunoglobulins alone with 32 who had received the combined therapy and could be matched using propensity scores.
The researchers defined treatment failure as persistence of fever for 2 days after the start of therapy or recurrence of fever within a week. By this measure, the combination treatment failed in only 9% of cases while immunoglobulins alone failed in 38% of cases. The difference was statistically significant (P = .008). Most of those for whom these treatments failed received second-line treatments such as steroids or biological agents.
Patients treated with the combination therapy also had a lower risk of secondary acute left ventricular dysfunction (odds ratio, 0.20; 95% confidence interval, 0.06-0.66) and a lower risk of needing hemodynamic support (OR, 0.21; 95% CI, 0.06-0.76).
Those receiving the combination therapy spent a mean of 4 days in the pediatric intensive care unit compared with 6 days for those receiving immunoglobulins alone. (Difference in days, −2.4; 95% CI, −4.0 to −0.7; P = .005).
There are few drawbacks to the combination approach, Dr. Angoulvant said, as the side effects of corticosteroids are generally not severe and they can be anticipated because this class of medications has been used for many years.
The study raises the question of whether corticosteroids might work as well by themselves, but it could not be answered with this database as no one is using that approach in France, Dr. Angoulvant said. “I hope other teams around the world could bring us the answer.”
In the United States, most physicians appear to already be using the combination therapy, said David Teachey, MD, an associate professor of pediatrics at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
The reduction in time in pediatric intensive care and the reduced risk of cardiac dysfunction are important findings, he said.
This retrospective study falls short of the evidence provided by a randomized clinical trial, Dr. Teachey noted. But he acknowledged that few families would agree to participate in such a trial as they would have to take a chance that the sick children would receive a less effective therapy than what they would otherwise get. “It’s hard to [talk] about a therapy reduction,” he told this news organization.
Given that impediment, he agreed with Dr. Angoulvant that the current study and others like it may provide the best data available pointing to a treatment approach for MIS-C.
The study received an unrestricted grant from Pfizer. The French COVID-19 Paediatric Inflammation Consortium received an unrestricted grant from the Square Foundation (Grandir–Fonds de Solidarité pour L’Enfance). Dr. Angoulvant and Dr. Teachey have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The combination of methylprednisolone and intravenous immunoglobulins works better than intravenous immunoglobulins alone for multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), researchers say.
“I’m not sure it’s the best treatment because we have not studied every possible treatment,” François Angoulvant, MD, PhD, told this news organization, “but right now, it’s the standard of care.”
Dr. Angoulvant, a professor of pediatrics at University of Paris, and colleagues published a comparison of the two treatments in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
A small percentage of children infected with SARS-CoV-2 develop MIS-C about 2 to 4 weeks later. It is considered a separate disease entity from COVID-19 and is associated with persistent fever, digestive symptoms, rash, bilateral nonpurulent conjunctivitis, mucocutaneous inflammation signs, and frequent cardiovascular involvement. In more than 60% of cases, it leads to hemodynamic failure, with acute cardiac dysfunction.
Because MIS-C resembles Kawasaki disease, clinicians modeled their treatment on that condition and started with immunoglobulins alone, Dr. Angoulvant said.
Based on expert opinion, the National Health Service in the United Kingdom published a consensus statement in Sept. listing immunoglobulins alone as the first-line treatment.
But anecdotal reports have emerged that combining the immunoglobulins with a corticosteroid worked better. To investigate this possibility, Dr. Angoulvant and colleagues analyzed records of MIS-C cases in France, where physicians are required to report all suspected cases of MIS-C to the French National Public Health Agency.
Among the 181 cases they scrutinized, 111 fulfilled the World Health Organization criteria for MIS-C. Of these, the researchers were able to match 64 patients who had received immunoglobulins alone with 32 who had received the combined therapy and could be matched using propensity scores.
The researchers defined treatment failure as persistence of fever for 2 days after the start of therapy or recurrence of fever within a week. By this measure, the combination treatment failed in only 9% of cases while immunoglobulins alone failed in 38% of cases. The difference was statistically significant (P = .008). Most of those for whom these treatments failed received second-line treatments such as steroids or biological agents.
Patients treated with the combination therapy also had a lower risk of secondary acute left ventricular dysfunction (odds ratio, 0.20; 95% confidence interval, 0.06-0.66) and a lower risk of needing hemodynamic support (OR, 0.21; 95% CI, 0.06-0.76).
Those receiving the combination therapy spent a mean of 4 days in the pediatric intensive care unit compared with 6 days for those receiving immunoglobulins alone. (Difference in days, −2.4; 95% CI, −4.0 to −0.7; P = .005).
There are few drawbacks to the combination approach, Dr. Angoulvant said, as the side effects of corticosteroids are generally not severe and they can be anticipated because this class of medications has been used for many years.
The study raises the question of whether corticosteroids might work as well by themselves, but it could not be answered with this database as no one is using that approach in France, Dr. Angoulvant said. “I hope other teams around the world could bring us the answer.”
In the United States, most physicians appear to already be using the combination therapy, said David Teachey, MD, an associate professor of pediatrics at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
The reduction in time in pediatric intensive care and the reduced risk of cardiac dysfunction are important findings, he said.
This retrospective study falls short of the evidence provided by a randomized clinical trial, Dr. Teachey noted. But he acknowledged that few families would agree to participate in such a trial as they would have to take a chance that the sick children would receive a less effective therapy than what they would otherwise get. “It’s hard to [talk] about a therapy reduction,” he told this news organization.
Given that impediment, he agreed with Dr. Angoulvant that the current study and others like it may provide the best data available pointing to a treatment approach for MIS-C.
The study received an unrestricted grant from Pfizer. The French COVID-19 Paediatric Inflammation Consortium received an unrestricted grant from the Square Foundation (Grandir–Fonds de Solidarité pour L’Enfance). Dr. Angoulvant and Dr. Teachey have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PPE protected critical care staff from COVID-19 transmission
, a new study has found.
“Other staff, other areas of the hospital, and the wider community are more likely sources of infection,” said lead author Kate El Bouzidi, MRCP, South London Specialist Virology Centre, King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, London.
She noted that 60% of critical care staff were symptomatic during the first wave of the coronavirus pandemic and 20% were antibody positive, with 10% asymptomatic. “Staff acquisition peaked 3 weeks before the peak of COVID-19 ICU admission, and personal protective equipment (PPE) was effective at preventing transmission from patients.” Working in other areas of the hospital was associated with higher seroprevalence, Dr. El Bouzidi noted.
The findings were presented at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
The novel coronavirus was spreading around the world, and when it reached northern Italy, medical authorities began to think in terms of how it might overwhelm the health care system in the United Kingdom, explained Dr. El Bouzidi.
“There was a lot of interest at this time about health care workers who were particularly vulnerable and also about the allocation of resources and rationing of care, particularly in intensive care,” she said. “And this only intensified when our prime minister was admitted to intensive care. About this time, antibody testing also became available.”
The goal of their study was to determine the SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence in critical care staff, as well as look at the correlation between antibody status, prior swab testing, and COVID-19 symptoms.
The survey was conducted at Kings College Hospital in London, which is a tertiary-care teaching center. The critical care department is one of the largest in the United Kingdom. The authors estimate that more than 800 people worked in the critical care units, and between March and April 2020, more than 2,000 patients with COVID-19 were admitted, of whom 180 required care in the ICU.
“There was good PPE available in the ICU units right from the start,” she said, “and staff testing was available.”
All staff working in the critical care department participated in the study, which required serum samples and completion of a questionnaire. The samples were tested via six different assays to measure receptor-binding domain, nucleoprotein, and tri-spike, with one antibody result determined for each sample.
Of the 625 staff members, 384 (61.4%) had previously reported experiencing symptoms and 124 (19.8%) had sent a swab for testing. COVID-19 infection had been confirmed in 37 of those health care workers (29.8%).
Overall, 21% were positive for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, of whom 9.9% had been asymptomatic.
“We were surprised to find that 61% of staff reported symptoms they felt could be consistent with COVID-19,” she said, noting that fatigue, headache, and cough were the most common symptoms reported. “Seroprevalence was reported in 31% of symptomatic staff and in 5% of those without symptoms.”
Seroprevalence differed by role in a critical care unit, although it did not significantly differ by factors such as age, sex, ethnicity, or underlying conditions. Consultants, who are senior physicians, were twice as likely to test positive, compared with junior doctors. The reason for this finding is not clear, but it may lie in the nature of their work responsibilities, such as performing more aerosol-generating procedures in the ICU or in other departments.
The investigators looked at the timing of infections and found that they preceded peak of patient admissions by 3 weeks, with peak onset of staff symptoms in early March. At this time, Dr. El Bouzidi noted, there were very few patients with COVID-19 in the hospital, and good PPE was available throughout this time period.
“Staff were unlikely to be infected by ICU patients, and therefore PPE was largely effective,” she said. “Other sources of infection were more likely to be the cause, such as interactions with other staff, meetings, or contact in break rooms. Routine mask-wearing throughout the hospital was only encouraged as of June 15.”
There were several limitations to the study, such as the cross-sectional design, reliance on response/recall, the fact that antibody tests are unlikely to detect all previous infections, and no genomic data were available to confirm infections. Even though the study had limitations, Dr. El Bouzidi concluded that ICU staff are unlikely to contract COVID-19 from patients but that other staff, other areas of the hospital, and the wider community are more likely sources of infection.
These findings, she added, demonstrate that PPE was effective at preventing transmission from patients and that protective measures need to be maintained when staff is away from the bedside.
In commenting on the study, Greg S. Martin, MD, professor of medicine in the division of pulmonary, allergy, critical care and sleep medicine, Emory University, Atlanta, noted that, even though the study was conducted almost a year ago, the results are still relevant with regard to the effectiveness of PPE.
“There was a huge amount of uncertainty about PPE – what was most effective, could we reuse it, how to sterilize it, what about surfaces, and so on,” he said. “Even for people who work in ICU and who are familiar with the environment and familiar with the patients, there was 1,000 times more uncertainty about everything they were doing.”
Dr. Martin believes that the situation has improved. “It’s not that we take COVID more lightly, but I think the staff is more comfortable dealing with it,” he said. “They now know what they need to do on an hourly and daily basis to stay safe. The PPE had become second nature to them now, with all the other precautions.”
, a new study has found.
“Other staff, other areas of the hospital, and the wider community are more likely sources of infection,” said lead author Kate El Bouzidi, MRCP, South London Specialist Virology Centre, King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, London.
She noted that 60% of critical care staff were symptomatic during the first wave of the coronavirus pandemic and 20% were antibody positive, with 10% asymptomatic. “Staff acquisition peaked 3 weeks before the peak of COVID-19 ICU admission, and personal protective equipment (PPE) was effective at preventing transmission from patients.” Working in other areas of the hospital was associated with higher seroprevalence, Dr. El Bouzidi noted.
The findings were presented at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
The novel coronavirus was spreading around the world, and when it reached northern Italy, medical authorities began to think in terms of how it might overwhelm the health care system in the United Kingdom, explained Dr. El Bouzidi.
“There was a lot of interest at this time about health care workers who were particularly vulnerable and also about the allocation of resources and rationing of care, particularly in intensive care,” she said. “And this only intensified when our prime minister was admitted to intensive care. About this time, antibody testing also became available.”
The goal of their study was to determine the SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence in critical care staff, as well as look at the correlation between antibody status, prior swab testing, and COVID-19 symptoms.
The survey was conducted at Kings College Hospital in London, which is a tertiary-care teaching center. The critical care department is one of the largest in the United Kingdom. The authors estimate that more than 800 people worked in the critical care units, and between March and April 2020, more than 2,000 patients with COVID-19 were admitted, of whom 180 required care in the ICU.
“There was good PPE available in the ICU units right from the start,” she said, “and staff testing was available.”
All staff working in the critical care department participated in the study, which required serum samples and completion of a questionnaire. The samples were tested via six different assays to measure receptor-binding domain, nucleoprotein, and tri-spike, with one antibody result determined for each sample.
Of the 625 staff members, 384 (61.4%) had previously reported experiencing symptoms and 124 (19.8%) had sent a swab for testing. COVID-19 infection had been confirmed in 37 of those health care workers (29.8%).
Overall, 21% were positive for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, of whom 9.9% had been asymptomatic.
“We were surprised to find that 61% of staff reported symptoms they felt could be consistent with COVID-19,” she said, noting that fatigue, headache, and cough were the most common symptoms reported. “Seroprevalence was reported in 31% of symptomatic staff and in 5% of those without symptoms.”
Seroprevalence differed by role in a critical care unit, although it did not significantly differ by factors such as age, sex, ethnicity, or underlying conditions. Consultants, who are senior physicians, were twice as likely to test positive, compared with junior doctors. The reason for this finding is not clear, but it may lie in the nature of their work responsibilities, such as performing more aerosol-generating procedures in the ICU or in other departments.
The investigators looked at the timing of infections and found that they preceded peak of patient admissions by 3 weeks, with peak onset of staff symptoms in early March. At this time, Dr. El Bouzidi noted, there were very few patients with COVID-19 in the hospital, and good PPE was available throughout this time period.
“Staff were unlikely to be infected by ICU patients, and therefore PPE was largely effective,” she said. “Other sources of infection were more likely to be the cause, such as interactions with other staff, meetings, or contact in break rooms. Routine mask-wearing throughout the hospital was only encouraged as of June 15.”
There were several limitations to the study, such as the cross-sectional design, reliance on response/recall, the fact that antibody tests are unlikely to detect all previous infections, and no genomic data were available to confirm infections. Even though the study had limitations, Dr. El Bouzidi concluded that ICU staff are unlikely to contract COVID-19 from patients but that other staff, other areas of the hospital, and the wider community are more likely sources of infection.
These findings, she added, demonstrate that PPE was effective at preventing transmission from patients and that protective measures need to be maintained when staff is away from the bedside.
In commenting on the study, Greg S. Martin, MD, professor of medicine in the division of pulmonary, allergy, critical care and sleep medicine, Emory University, Atlanta, noted that, even though the study was conducted almost a year ago, the results are still relevant with regard to the effectiveness of PPE.
“There was a huge amount of uncertainty about PPE – what was most effective, could we reuse it, how to sterilize it, what about surfaces, and so on,” he said. “Even for people who work in ICU and who are familiar with the environment and familiar with the patients, there was 1,000 times more uncertainty about everything they were doing.”
Dr. Martin believes that the situation has improved. “It’s not that we take COVID more lightly, but I think the staff is more comfortable dealing with it,” he said. “They now know what they need to do on an hourly and daily basis to stay safe. The PPE had become second nature to them now, with all the other precautions.”
, a new study has found.
“Other staff, other areas of the hospital, and the wider community are more likely sources of infection,” said lead author Kate El Bouzidi, MRCP, South London Specialist Virology Centre, King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, London.
She noted that 60% of critical care staff were symptomatic during the first wave of the coronavirus pandemic and 20% were antibody positive, with 10% asymptomatic. “Staff acquisition peaked 3 weeks before the peak of COVID-19 ICU admission, and personal protective equipment (PPE) was effective at preventing transmission from patients.” Working in other areas of the hospital was associated with higher seroprevalence, Dr. El Bouzidi noted.
The findings were presented at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
The novel coronavirus was spreading around the world, and when it reached northern Italy, medical authorities began to think in terms of how it might overwhelm the health care system in the United Kingdom, explained Dr. El Bouzidi.
“There was a lot of interest at this time about health care workers who were particularly vulnerable and also about the allocation of resources and rationing of care, particularly in intensive care,” she said. “And this only intensified when our prime minister was admitted to intensive care. About this time, antibody testing also became available.”
The goal of their study was to determine the SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence in critical care staff, as well as look at the correlation between antibody status, prior swab testing, and COVID-19 symptoms.
The survey was conducted at Kings College Hospital in London, which is a tertiary-care teaching center. The critical care department is one of the largest in the United Kingdom. The authors estimate that more than 800 people worked in the critical care units, and between March and April 2020, more than 2,000 patients with COVID-19 were admitted, of whom 180 required care in the ICU.
“There was good PPE available in the ICU units right from the start,” she said, “and staff testing was available.”
All staff working in the critical care department participated in the study, which required serum samples and completion of a questionnaire. The samples were tested via six different assays to measure receptor-binding domain, nucleoprotein, and tri-spike, with one antibody result determined for each sample.
Of the 625 staff members, 384 (61.4%) had previously reported experiencing symptoms and 124 (19.8%) had sent a swab for testing. COVID-19 infection had been confirmed in 37 of those health care workers (29.8%).
Overall, 21% were positive for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, of whom 9.9% had been asymptomatic.
“We were surprised to find that 61% of staff reported symptoms they felt could be consistent with COVID-19,” she said, noting that fatigue, headache, and cough were the most common symptoms reported. “Seroprevalence was reported in 31% of symptomatic staff and in 5% of those without symptoms.”
Seroprevalence differed by role in a critical care unit, although it did not significantly differ by factors such as age, sex, ethnicity, or underlying conditions. Consultants, who are senior physicians, were twice as likely to test positive, compared with junior doctors. The reason for this finding is not clear, but it may lie in the nature of their work responsibilities, such as performing more aerosol-generating procedures in the ICU or in other departments.
The investigators looked at the timing of infections and found that they preceded peak of patient admissions by 3 weeks, with peak onset of staff symptoms in early March. At this time, Dr. El Bouzidi noted, there were very few patients with COVID-19 in the hospital, and good PPE was available throughout this time period.
“Staff were unlikely to be infected by ICU patients, and therefore PPE was largely effective,” she said. “Other sources of infection were more likely to be the cause, such as interactions with other staff, meetings, or contact in break rooms. Routine mask-wearing throughout the hospital was only encouraged as of June 15.”
There were several limitations to the study, such as the cross-sectional design, reliance on response/recall, the fact that antibody tests are unlikely to detect all previous infections, and no genomic data were available to confirm infections. Even though the study had limitations, Dr. El Bouzidi concluded that ICU staff are unlikely to contract COVID-19 from patients but that other staff, other areas of the hospital, and the wider community are more likely sources of infection.
These findings, she added, demonstrate that PPE was effective at preventing transmission from patients and that protective measures need to be maintained when staff is away from the bedside.
In commenting on the study, Greg S. Martin, MD, professor of medicine in the division of pulmonary, allergy, critical care and sleep medicine, Emory University, Atlanta, noted that, even though the study was conducted almost a year ago, the results are still relevant with regard to the effectiveness of PPE.
“There was a huge amount of uncertainty about PPE – what was most effective, could we reuse it, how to sterilize it, what about surfaces, and so on,” he said. “Even for people who work in ICU and who are familiar with the environment and familiar with the patients, there was 1,000 times more uncertainty about everything they were doing.”
Dr. Martin believes that the situation has improved. “It’s not that we take COVID more lightly, but I think the staff is more comfortable dealing with it,” he said. “They now know what they need to do on an hourly and daily basis to stay safe. The PPE had become second nature to them now, with all the other precautions.”
FROM CCC50
Burnout rates in ICU staff fueled by shortages, overtime
Health care professionals working in critical care settings have been overburdened because of the plethora of COVID-19 cases, which has led to symptoms of burnout in both physicians and nurses, findings from a new study show.
“Overburdening ICU professionals during an extended period of time leads to burnout,” said lead study author Niek Kok, MSc, of IQ healthcare, Radboud University Medical Center, Radboud Institute for Health Sciences, Nijmegen, the Netherlands. “All ICU professionals are at the risk of this, and in our study, the incidence of physicians experiencing burnout was significantly higher than that of nurses in June 2020.”
This burnout can be explained by conditions caused by the pandemic, he noted, such as the scarcity of staff and resources and having to work with colleagues who were not qualified to work in critical care but who were there out of necessity.
Mr. Kok presented the findings of the study at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
Burnout highest among critical care physicians
The ICU can be a stressful environment for both patients and health care personnel, and burnout is not uncommon among ICU clinicians. However, COVID-19 has amplified the degree of burnout being experienced by clinicians working in this setting. Critical care physicians now top the list of physicians experiencing burnout, at 51%, up from 44% last year, according to the Medscape report ‘Death by 1000 Thousand Cuts’: Physician Burnout and Suicide Report 2021.
The Medscape Nurse Career Satisfaction Report 2020, while not restricted to those working in critical care, also reported higher rates of burnout, compared with the prepandemic period. The percentage of nurses reporting being “very burned out” prior to the pandemic was 4%. Six months into the pandemic, that percentage soared to 18%.
In this study, Mr. Kok and colleagues examined the prevalence and incidence of burnout symptoms and moral distress in health care professionals working in the ICU, both before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“When the COVID-19 pandemic surfaced in the Netherlands, the health care professionals in our hospitals were motivated to do everything they could to provide the best care possible,” said Mr. Kok. “Many of the ICU professionals immediately realized that they would have to work longer hours.”
However, the health care professionals that he spoke with did have mixed feelings. Some were afraid of being infected with the virus, while others said that “it was very interesting times for them and that gave them extra motivation to do the work.
“Some physicians [and] the WHO warned that COVID-19 is not going to weathered by a heroic sprint – it is an arduous marathon that is going to go hand in hand with burnout symptoms,” Mr. Kok added. “It will eat away at our qualified ICU staff.”
Before and after data on burnout
It was widely believed that the COVID-19 pandemic would increase burnout symptoms, as had been demonstrated in studies of previous pandemics. However, Mr. Kok emphasized that there are no before and after measurements that transcend cross-sectional designs.
“The claim [has been] that it increases burnout – but there are no assessments of how it progresses in ICU professionals through time,” he said. “So what we really need is a comparison [of] before and after the pandemic.”
It is quite difficult to obtain this type of information because disruptive events like the COVID-19 pandemic cannot be predicted, he said. Thus, it is challenging to get a baseline measurement. But Mr. Kok pointed out that the study has both “before and after” measurements.
“By coincidence really, we had baseline data to measure the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and had information that was collected before the pandemic,” he said.
In January 2020, a study began looking at the effects of ethics meetings on moral distress in ICU professionals. Data had been collected on moral distress and burnout on ICU professionals in December 2019. The first COVID-19 cases appeared in the Netherlands in February 2020.
A follow-up study was then conducted in May and June 2020, several months into the pandemic.
The longitudinal open cohort study included all ICU personnel who were working in five units within a single university medical center, plus another adult ICU that was based in a separate teaching hospital.
A total of 352 health care professionals responded to a baseline survey in October through December 2019, and then 233 responded to a follow-up survey sent in May and June 2020. The authors measured burnout symptoms and moral distress with the Maslach Burnout Inventory and the Moral Distress Scale, respectively.
Findings
The overall prevalence of burnout symptoms was 23.0% prior to the pandemic, and that jumped to 36.1% at post-peak time. Higher rates of burnout were reported by nurses (38.0%) than physicians (28.6%).
However, the incidence rate of new burnout cases was higher among physicians, compared with nurses (26.7% vs 21.9%). Not surprisingly, a higher prevalence of burnout symptoms was observed in the post-peak period for all clinicians (odds ratio, 1.83; 95% confidence interval, 1.32-2.53), and was higher for nurses (odds ratio, 1.77; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-3.04), for those working overtime (OR, 2.11; 95% CI, 1.48-3.02), and for personnel who directly engaged in patient care (OR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.35-2.60).
Physicians in general were much more likely to develop burnout symptoms related to the pandemic, compared with nurses (OR, 3.56; 95% CI, 1.06-12.21).
When looking at findings on moral distress, Kok pointed out that it often arises in situations when the health care professional knows the right thing to do but is prevented from doing so. “Morally distressful situations all rose from December to June,” said Mr. Kok. “Scarcity was the most distressing. The other was where colleagues were perceived to be less skilled, and this had to do with the recruitment of people from outside of the ICU to provide care.”
Moral distress from scarcity and unskilled colleagues were both significantly related to burnout, he noted.
In the final model, working in a COVID-19 unit, stress from scarcity of resources and people, stress from unskilled colleagues, and stress from unsafe conditions were all related to burnout. “The stress of physicians was significantly higher,” said Kok. “Even though nurses had higher baseline burnout, it became less pronounced in June 2020. This indicates that burnout was significantly higher in physicians.”
Thus, Mr. Kok and colleagues concluded that overburdening ICU professionals during an extended period of time leads to burnout, and all ICU workers are at risk.
Burnout rates higher in physicians
Weighing in on the study, Greg S. Martin, MD, FCCP, professor of medicine in the division of pulmonary, allergy, critical care and sleep medicine, Emory University, Atlanta, noted that the differences observed between physicians and nurses may have to do with the fact that “nurses have been smoldering all along and experiencing higher rates of burnout.
“They may have adapted better to the pandemic conditions, since they are more used to working overtime and short staffed, and spending far more time at the bedside,” he said. “Because of the volume of patients, physicians may be spending more hours doing patient care and are experiencing more burnout.”
For physicians, this may be a more significant change in the workload, as well as the complexity of the situation because of the pandemic. “Many things layer into it, such as [the fact] that there are no families present to give patients support, the complexity of care of these patients, and things like lack of PPE,” Dr. Martin said.
The study did not differentiate among physician groups, so it is unclear if the affected physicians were residents, fellows, or more senior staff. “Residents are often quite busy already, and don’t usually have the capacity to add more to their schedules, and maybe attendings were having to spend more time doing patient care,” Dr. Martin said. “In the United States, at least some personnel were restricted from working with COVID-19 patients. Medical students were removed in many places as well as nonessential staff, so that may have also added to their burnout.”
The study was conducted in the Netherlands, so there may be differences in the work environment, responsibilities of nurses vs. physicians, staffing, and so on. “But it still shows that burnout is very real among doctors and nurses working in the ICU in pandemic conditions,” he said.
Health care professionals working in critical care settings have been overburdened because of the plethora of COVID-19 cases, which has led to symptoms of burnout in both physicians and nurses, findings from a new study show.
“Overburdening ICU professionals during an extended period of time leads to burnout,” said lead study author Niek Kok, MSc, of IQ healthcare, Radboud University Medical Center, Radboud Institute for Health Sciences, Nijmegen, the Netherlands. “All ICU professionals are at the risk of this, and in our study, the incidence of physicians experiencing burnout was significantly higher than that of nurses in June 2020.”
This burnout can be explained by conditions caused by the pandemic, he noted, such as the scarcity of staff and resources and having to work with colleagues who were not qualified to work in critical care but who were there out of necessity.
Mr. Kok presented the findings of the study at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
Burnout highest among critical care physicians
The ICU can be a stressful environment for both patients and health care personnel, and burnout is not uncommon among ICU clinicians. However, COVID-19 has amplified the degree of burnout being experienced by clinicians working in this setting. Critical care physicians now top the list of physicians experiencing burnout, at 51%, up from 44% last year, according to the Medscape report ‘Death by 1000 Thousand Cuts’: Physician Burnout and Suicide Report 2021.
The Medscape Nurse Career Satisfaction Report 2020, while not restricted to those working in critical care, also reported higher rates of burnout, compared with the prepandemic period. The percentage of nurses reporting being “very burned out” prior to the pandemic was 4%. Six months into the pandemic, that percentage soared to 18%.
In this study, Mr. Kok and colleagues examined the prevalence and incidence of burnout symptoms and moral distress in health care professionals working in the ICU, both before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“When the COVID-19 pandemic surfaced in the Netherlands, the health care professionals in our hospitals were motivated to do everything they could to provide the best care possible,” said Mr. Kok. “Many of the ICU professionals immediately realized that they would have to work longer hours.”
However, the health care professionals that he spoke with did have mixed feelings. Some were afraid of being infected with the virus, while others said that “it was very interesting times for them and that gave them extra motivation to do the work.
“Some physicians [and] the WHO warned that COVID-19 is not going to weathered by a heroic sprint – it is an arduous marathon that is going to go hand in hand with burnout symptoms,” Mr. Kok added. “It will eat away at our qualified ICU staff.”
Before and after data on burnout
It was widely believed that the COVID-19 pandemic would increase burnout symptoms, as had been demonstrated in studies of previous pandemics. However, Mr. Kok emphasized that there are no before and after measurements that transcend cross-sectional designs.
“The claim [has been] that it increases burnout – but there are no assessments of how it progresses in ICU professionals through time,” he said. “So what we really need is a comparison [of] before and after the pandemic.”
It is quite difficult to obtain this type of information because disruptive events like the COVID-19 pandemic cannot be predicted, he said. Thus, it is challenging to get a baseline measurement. But Mr. Kok pointed out that the study has both “before and after” measurements.
“By coincidence really, we had baseline data to measure the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and had information that was collected before the pandemic,” he said.
In January 2020, a study began looking at the effects of ethics meetings on moral distress in ICU professionals. Data had been collected on moral distress and burnout on ICU professionals in December 2019. The first COVID-19 cases appeared in the Netherlands in February 2020.
A follow-up study was then conducted in May and June 2020, several months into the pandemic.
The longitudinal open cohort study included all ICU personnel who were working in five units within a single university medical center, plus another adult ICU that was based in a separate teaching hospital.
A total of 352 health care professionals responded to a baseline survey in October through December 2019, and then 233 responded to a follow-up survey sent in May and June 2020. The authors measured burnout symptoms and moral distress with the Maslach Burnout Inventory and the Moral Distress Scale, respectively.
Findings
The overall prevalence of burnout symptoms was 23.0% prior to the pandemic, and that jumped to 36.1% at post-peak time. Higher rates of burnout were reported by nurses (38.0%) than physicians (28.6%).
However, the incidence rate of new burnout cases was higher among physicians, compared with nurses (26.7% vs 21.9%). Not surprisingly, a higher prevalence of burnout symptoms was observed in the post-peak period for all clinicians (odds ratio, 1.83; 95% confidence interval, 1.32-2.53), and was higher for nurses (odds ratio, 1.77; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-3.04), for those working overtime (OR, 2.11; 95% CI, 1.48-3.02), and for personnel who directly engaged in patient care (OR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.35-2.60).
Physicians in general were much more likely to develop burnout symptoms related to the pandemic, compared with nurses (OR, 3.56; 95% CI, 1.06-12.21).
When looking at findings on moral distress, Kok pointed out that it often arises in situations when the health care professional knows the right thing to do but is prevented from doing so. “Morally distressful situations all rose from December to June,” said Mr. Kok. “Scarcity was the most distressing. The other was where colleagues were perceived to be less skilled, and this had to do with the recruitment of people from outside of the ICU to provide care.”
Moral distress from scarcity and unskilled colleagues were both significantly related to burnout, he noted.
In the final model, working in a COVID-19 unit, stress from scarcity of resources and people, stress from unskilled colleagues, and stress from unsafe conditions were all related to burnout. “The stress of physicians was significantly higher,” said Kok. “Even though nurses had higher baseline burnout, it became less pronounced in June 2020. This indicates that burnout was significantly higher in physicians.”
Thus, Mr. Kok and colleagues concluded that overburdening ICU professionals during an extended period of time leads to burnout, and all ICU workers are at risk.
Burnout rates higher in physicians
Weighing in on the study, Greg S. Martin, MD, FCCP, professor of medicine in the division of pulmonary, allergy, critical care and sleep medicine, Emory University, Atlanta, noted that the differences observed between physicians and nurses may have to do with the fact that “nurses have been smoldering all along and experiencing higher rates of burnout.
“They may have adapted better to the pandemic conditions, since they are more used to working overtime and short staffed, and spending far more time at the bedside,” he said. “Because of the volume of patients, physicians may be spending more hours doing patient care and are experiencing more burnout.”
For physicians, this may be a more significant change in the workload, as well as the complexity of the situation because of the pandemic. “Many things layer into it, such as [the fact] that there are no families present to give patients support, the complexity of care of these patients, and things like lack of PPE,” Dr. Martin said.
The study did not differentiate among physician groups, so it is unclear if the affected physicians were residents, fellows, or more senior staff. “Residents are often quite busy already, and don’t usually have the capacity to add more to their schedules, and maybe attendings were having to spend more time doing patient care,” Dr. Martin said. “In the United States, at least some personnel were restricted from working with COVID-19 patients. Medical students were removed in many places as well as nonessential staff, so that may have also added to their burnout.”
The study was conducted in the Netherlands, so there may be differences in the work environment, responsibilities of nurses vs. physicians, staffing, and so on. “But it still shows that burnout is very real among doctors and nurses working in the ICU in pandemic conditions,” he said.
Health care professionals working in critical care settings have been overburdened because of the plethora of COVID-19 cases, which has led to symptoms of burnout in both physicians and nurses, findings from a new study show.
“Overburdening ICU professionals during an extended period of time leads to burnout,” said lead study author Niek Kok, MSc, of IQ healthcare, Radboud University Medical Center, Radboud Institute for Health Sciences, Nijmegen, the Netherlands. “All ICU professionals are at the risk of this, and in our study, the incidence of physicians experiencing burnout was significantly higher than that of nurses in June 2020.”
This burnout can be explained by conditions caused by the pandemic, he noted, such as the scarcity of staff and resources and having to work with colleagues who were not qualified to work in critical care but who were there out of necessity.
Mr. Kok presented the findings of the study at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
Burnout highest among critical care physicians
The ICU can be a stressful environment for both patients and health care personnel, and burnout is not uncommon among ICU clinicians. However, COVID-19 has amplified the degree of burnout being experienced by clinicians working in this setting. Critical care physicians now top the list of physicians experiencing burnout, at 51%, up from 44% last year, according to the Medscape report ‘Death by 1000 Thousand Cuts’: Physician Burnout and Suicide Report 2021.
The Medscape Nurse Career Satisfaction Report 2020, while not restricted to those working in critical care, also reported higher rates of burnout, compared with the prepandemic period. The percentage of nurses reporting being “very burned out” prior to the pandemic was 4%. Six months into the pandemic, that percentage soared to 18%.
In this study, Mr. Kok and colleagues examined the prevalence and incidence of burnout symptoms and moral distress in health care professionals working in the ICU, both before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“When the COVID-19 pandemic surfaced in the Netherlands, the health care professionals in our hospitals were motivated to do everything they could to provide the best care possible,” said Mr. Kok. “Many of the ICU professionals immediately realized that they would have to work longer hours.”
However, the health care professionals that he spoke with did have mixed feelings. Some were afraid of being infected with the virus, while others said that “it was very interesting times for them and that gave them extra motivation to do the work.
“Some physicians [and] the WHO warned that COVID-19 is not going to weathered by a heroic sprint – it is an arduous marathon that is going to go hand in hand with burnout symptoms,” Mr. Kok added. “It will eat away at our qualified ICU staff.”
Before and after data on burnout
It was widely believed that the COVID-19 pandemic would increase burnout symptoms, as had been demonstrated in studies of previous pandemics. However, Mr. Kok emphasized that there are no before and after measurements that transcend cross-sectional designs.
“The claim [has been] that it increases burnout – but there are no assessments of how it progresses in ICU professionals through time,” he said. “So what we really need is a comparison [of] before and after the pandemic.”
It is quite difficult to obtain this type of information because disruptive events like the COVID-19 pandemic cannot be predicted, he said. Thus, it is challenging to get a baseline measurement. But Mr. Kok pointed out that the study has both “before and after” measurements.
“By coincidence really, we had baseline data to measure the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and had information that was collected before the pandemic,” he said.
In January 2020, a study began looking at the effects of ethics meetings on moral distress in ICU professionals. Data had been collected on moral distress and burnout on ICU professionals in December 2019. The first COVID-19 cases appeared in the Netherlands in February 2020.
A follow-up study was then conducted in May and June 2020, several months into the pandemic.
The longitudinal open cohort study included all ICU personnel who were working in five units within a single university medical center, plus another adult ICU that was based in a separate teaching hospital.
A total of 352 health care professionals responded to a baseline survey in October through December 2019, and then 233 responded to a follow-up survey sent in May and June 2020. The authors measured burnout symptoms and moral distress with the Maslach Burnout Inventory and the Moral Distress Scale, respectively.
Findings
The overall prevalence of burnout symptoms was 23.0% prior to the pandemic, and that jumped to 36.1% at post-peak time. Higher rates of burnout were reported by nurses (38.0%) than physicians (28.6%).
However, the incidence rate of new burnout cases was higher among physicians, compared with nurses (26.7% vs 21.9%). Not surprisingly, a higher prevalence of burnout symptoms was observed in the post-peak period for all clinicians (odds ratio, 1.83; 95% confidence interval, 1.32-2.53), and was higher for nurses (odds ratio, 1.77; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-3.04), for those working overtime (OR, 2.11; 95% CI, 1.48-3.02), and for personnel who directly engaged in patient care (OR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.35-2.60).
Physicians in general were much more likely to develop burnout symptoms related to the pandemic, compared with nurses (OR, 3.56; 95% CI, 1.06-12.21).
When looking at findings on moral distress, Kok pointed out that it often arises in situations when the health care professional knows the right thing to do but is prevented from doing so. “Morally distressful situations all rose from December to June,” said Mr. Kok. “Scarcity was the most distressing. The other was where colleagues were perceived to be less skilled, and this had to do with the recruitment of people from outside of the ICU to provide care.”
Moral distress from scarcity and unskilled colleagues were both significantly related to burnout, he noted.
In the final model, working in a COVID-19 unit, stress from scarcity of resources and people, stress from unskilled colleagues, and stress from unsafe conditions were all related to burnout. “The stress of physicians was significantly higher,” said Kok. “Even though nurses had higher baseline burnout, it became less pronounced in June 2020. This indicates that burnout was significantly higher in physicians.”
Thus, Mr. Kok and colleagues concluded that overburdening ICU professionals during an extended period of time leads to burnout, and all ICU workers are at risk.
Burnout rates higher in physicians
Weighing in on the study, Greg S. Martin, MD, FCCP, professor of medicine in the division of pulmonary, allergy, critical care and sleep medicine, Emory University, Atlanta, noted that the differences observed between physicians and nurses may have to do with the fact that “nurses have been smoldering all along and experiencing higher rates of burnout.
“They may have adapted better to the pandemic conditions, since they are more used to working overtime and short staffed, and spending far more time at the bedside,” he said. “Because of the volume of patients, physicians may be spending more hours doing patient care and are experiencing more burnout.”
For physicians, this may be a more significant change in the workload, as well as the complexity of the situation because of the pandemic. “Many things layer into it, such as [the fact] that there are no families present to give patients support, the complexity of care of these patients, and things like lack of PPE,” Dr. Martin said.
The study did not differentiate among physician groups, so it is unclear if the affected physicians were residents, fellows, or more senior staff. “Residents are often quite busy already, and don’t usually have the capacity to add more to their schedules, and maybe attendings were having to spend more time doing patient care,” Dr. Martin said. “In the United States, at least some personnel were restricted from working with COVID-19 patients. Medical students were removed in many places as well as nonessential staff, so that may have also added to their burnout.”
The study was conducted in the Netherlands, so there may be differences in the work environment, responsibilities of nurses vs. physicians, staffing, and so on. “But it still shows that burnout is very real among doctors and nurses working in the ICU in pandemic conditions,” he said.
FROM CCC50