User login
A 61-year-old with bipolar disorder and cognitive impairment: Dementia or polypharmacy?
A 61-year-old man presents for evaluation of new-onset cognitive impairment, which has developed over the past 6 to 8 months. He has bipolar disorder, for which he has been taking lithium carbonate (Eskalith) for the past 15 years. This therapy kept his mood stable until a relapse of depression and mania 1 year ago required hospitalization and an increase in the lithium dose, which was then lowered somewhat after he improved (see below). His cognitive symptoms appeared gradually within 2 months after his release from the hospital.
He now has difficulty concentrating, a tendency to substitute words incorrectly during conversation, and difficulty recalling names and “retrieving memories.” He also reports a worsening tremor in his dominant hand that compromises his ability to eat with a spoon or a fork. He complains of increasing daytime somnolence, which began when his lithium dose was increased and improved when the dose was decreased.
The patient is a mathematician and recently finished revising the curriculum for an undergraduate course in advanced mathematics that he teaches. He does not smoke cigarettes, and he drinks alcohol only socially. He has no other medical conditions and no known cardiovascular risk factors.
Current and recent medications
- Lithium carbonate 600 mg twice daily (before his hospitalization he had been taking 600 mg twice daily; this was increased to 1,500 mg/day during the hospitalization and then decreased to the current dose as maintenance therapy)
- Divalproex (Depakote) 250 mg every night
- Gabapentin (Neurontin) 400 mg every night (the dosages of divalproex and gabapentin have remained unchanged since before his hospitalization)
- A multivitamin daily
- Naproxen (Naprosyn, Aleve) 250 mg up to two times a week for arthritic knee pain
- Aripiprazole (Abilify). This antipsychotic drug was recently discontinued because of parkinsonian symptoms, which then gradually improved.
- Memantine (Namenda), which is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe Alzheimer disease. The patient reports that he stopped taking it after 3 weeks because he did not perceive it to be helping.
THE INITIAL EVALUATION
Physical examination
Temperature 98.3°F (36.8°C), pulse 60 beats per minute, respirations 16 per minute, blood pressure 126/64 mm Hg sitting and 118/71 mm Hg standing.
The patient is well groomed, alert, and cooperative. His head, eyes, ears, nose, and throat are normal. His teeth are in good condition. His skin is normal. We note no thyromegaly, carotid bruits, or palpable lymphadenopathy. His lungs are clear to auscultation. Results of cardiac, abdominal, and musculoskeletal examinations are all normal.
His deep tendon reflexes, sensory and motor testing, and gait are normal. The cerebellar examination is normal, aside from a mild tremor in his right hand when it is outstretched, with no resting tremor or cogwheel rigidity.
On the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) he scores a perfect 30/30 (normal 24–30). He can draw a clock normally. His score on the short-form Geriatric Depression Scale is 4/15 (a score of 6 or higher indicates depression).
Laboratory tests
- Serum lithium level 0.8 mmol/L (therapeutic range 0.5–1.5 mmol/L) (his previous values are not available)
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone level 1.61 μU/mL (normal 0.40–5.50)
- Complete blood cell count and comprehensive metabolic panel values are within normal limits.
Magnetic resonance imaging
Noncontrast magnetic resonance imaging of the head reveals two nonspecific punctate foci of high signal intensity on T2-weighted images in the left frontal white matter, but the results are otherwise normal.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
1. On the basis of this information, which is the most likely cause of this patient’s cogitive impairment?
- Dementia with Lewy bodies
- Early-onset Alzheimer disease
- Stroke with vascular cognitive impairment
- Lithium neurotoxicity
Lithium neurotoxicity is the most likely cause of this patient’s symptoms, given the temporal relationship between the adjusting of his lithium dose and the onset of his symptoms. Lithium therapy causes subtle cognitive deficits. Its dosing in older patients requires careful monitoring because of age-related alterations in its pharmacology and its various drug interactions; both mechanisms played a role in precipitating lithium toxicity in this patient.
Although his lithium levels are in the broadly accepted therapeutic range, there is much debate about the best maintenance level for patients with bipolar disorder. A level in the range of 1 to 1.2 mmol/L may be best in acute mania, while a lower level of around 0.8 mmol/L is preferred in the depressive phase. Once the patient’s mood has stabilized, the best maintenance level may be in the range of 0.2 to 0.6 mmol/L.
Dementia with Lewy bodies, although suggested by the patient’s cognitive impairment, history of parkinsonian symptoms, and somnolence, is an unlikely cause because his motor symptoms resolved after the aripiprazole was discontinued, his somnolence improved after the dose of lithium was reduced, and his alertness did not fluctuate thereafter as would be expected in dementia with Lewy bodies.
Alzheimer disease usually manifests as gradually progressive cognitive deficits involving memory impairment with one or more of the following: aphasia, apraxia, agnosia, and disturbance in executive functioning. In contrast, this patient’s memory loss was fairly abrupt and not slowly progressive.
Stroke is also unlikely, as he has no history of stroke or focal neurologic deficits. Although a magnetic resonance scan of the brain showed some evidence of small-vessel ischemic changes, it showed no cortical infarcts.
MECHANISMS OF LITHIUM NEUROTOXICITY
2. What are the possible mechanisms of lithium neurotoxicity in this patient?
- The increased dose of lithium
- The interaction of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and lithium
- The interaction of the other psychotropic medications with lithium
- All of the above
- None of the above
All of the above could be contributing.
Although lithium is thought to cause side effects in as many as 60% of patients of any age who take it, the rate of serious adverse effects is reportedly higher in older patients than in younger patients.1
That said, cognitive deficits are common in bipolar disorder irrespective of lithium use.
COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT IN BIPOLAR DISORDER
3. If cognitive impairment in bipolar disorder is common, when does it occur?
- Only in the remission phase
- Only in the manic phase
- Only in the depression phase
- In all phases of the disease
Cognitive impairment occurs in all phases of bipolar disorder. Neuropsychological testing of bipolar patients in remission uncovers subtle, persistent cognitive impairment in executive function and in visuospatial memory without mood symptoms.3–5 Impaired executive functioning, predominantly frontal lobe dysfunction, interferes with one’s ability to initiate, plan, perform, and successfully complete a task and challenges one’s ability to function effectively in society and to comply with medical advice and instructions on taking medications.
RECOMMENDATIONS
4. What should we recommend to this patient?
- Decrease the current dose of lithium
- Stop all medications
- Undergo detailed neuropsychological testing
- Follow up with a psychiatrist, if needed
The patient’s lithium level was within the therapeutic range and his bipolar symptoms were well controlled. In older patients, however, the optimal serum level of lithium is often unclear, making it advisable to reduce the dose when an adverse effect is suspected.
His other medications should be reviewed. Gabapentin is not indicated for use as a mood stabilizer, and his divalproex dose (250 mg) is well below the usual therapeutic dose of 1,000 to 2,000 mg/day.6 The gabapentin could be discontinued, and the divalproex could be increased to a therapeutic dose.
NSAIDs can increase serum lithium levels, diminish renal lithium clearance, and possibly induce lithium toxicity, but the effect varies considerably among drugs and individuals.7 We would advise this patient to stop taking naproxen and switch to acetaminophen (Tylenol) for his arthritis pain, and we would inform him of the risk of lithium toxicity with continuous use of NSAIDs.
We would also recommend additional neuropsychological testing. The patient noticed subtle difficulties in his cognitive abilities that were not apparent on the MMSE. While the MMSE is an acceptable cognitive test, it is often not sensitive enough to detect milder forms of cognitive impairment, especially in well-educated patients at the usual cut-point of 24. A comprehensive neuropsychological examination is a more sensitive measure of cognition, involving the detailed testing of various cognitive domains. It can reveal a pattern of cognitive impairment that helps to differentiate between normal and mood disorders and also can detect subtle executive dysfunction.
However, detailed neuropsychological testing is time-consuming and may not be obtained rapidly enough to help in making clinical decisions quickly. In this patient’s case, immediate collaboration and follow-up with the patient’s psychiatrist would be the most expeditious way to reassess the patient’s medication regimen.
FOLLOW-UP COURSE
We informed the patient’s psychiatrist that we thought the patient had increased sensitivity to lithium (even at “therapeutic” levels), possibly related to a drug-drug interaction.
His dose of lithium was kept at 600 mg twice daily, as the lithium toxicity was most likely due to a drug-drug interaction.
We discontinued his memantine, since he did not have Alzheimer disease and since he wasn’t taking it anyway. He continued taking gabapentin and divalproex at the same doses, and he stopped taking naproxyn and substituted acetaminophen for his arthritis pain. We advised him about about health maintenance, including proper nutrition, mineral and vitamin supplements, and exercise.
The patient underwent neuropsychological testing to better characterize his cognitive impairment. The findings did not suggest dementia, but were consistent with minor cognitive deficits caused by lithium.
When seen at a follow-up visit 6 weeks later the patient was free of symptoms except for the tremor in his dominant hand. His mood was stable and his cognition was better. No further changes were required in his psychotropic drug regimen.
TAKE-HOME POINTS
When a bipolar patient develops acute changes in cognition, we should suspect adverse effects of lithium as the cause, because of its narrow therapeutic window and interactions with other prescribed drugs. The case presented here reminds us to consider adverse drug effects any time an older patient develops acute changes in cognition. One should also consider the potential for a drug-drug interaction when reviewing the patient’s medication list and be especially vigilant in monitoring patients taking lithium, since its safety and effectiveness are affected by aging and by the co-administration of drugs that influence its clearance.
Despite these caveats, lithium remains an effective treatment in elderly patients, provided we are aware of the risks and benefits of its use.
- Juurlink DN, Mamdani MM, Kopp A, Rochon PA, Shulman KI, Redelmeier DA. Drug-induced lithium toxicity in the elderly: a population-based study. J Am Geriatr Soc 2004; 52:794–798.
- Sproule BA, Hardy BG, Shulman KI. Differential pharma-cokinetics of lithium in elderly patients. Drugs Aging 2000; 16:165–177.
- Martinez-Aran A, Vieta E, Colom F, et al. Cognitive impairment in euthymic bipolar patients: implications for clinical and functional outcome. Bipolar Disord 2004; 6:224–232.
- Martinez-Aran A, Vieta E, Reinares M, et al. Cognitive function across manic or hypomanic, depressed, and euthymic states in bipolar disorder. Am J Psychiatry 2004; 161:262–270.
- Rubinsztein JS, Michael A, Paykel ES, Sahakian BJ. Cognitive impairment in remission in bipolar affective disorder. Psychol Med 2000; 30:1025–1036.
- Sajatovic M, Madhusoodanan S, Coconcea N. Managing bipolar disorder in the elderly: defining the role of the newer agents. Drugs Aging 2005; 22:39–54.
- Ragheb M. The clinical significance of lithium-non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug interactions. J Clin Psychopharmacol 1990; 10:350–354.
A 61-year-old man presents for evaluation of new-onset cognitive impairment, which has developed over the past 6 to 8 months. He has bipolar disorder, for which he has been taking lithium carbonate (Eskalith) for the past 15 years. This therapy kept his mood stable until a relapse of depression and mania 1 year ago required hospitalization and an increase in the lithium dose, which was then lowered somewhat after he improved (see below). His cognitive symptoms appeared gradually within 2 months after his release from the hospital.
He now has difficulty concentrating, a tendency to substitute words incorrectly during conversation, and difficulty recalling names and “retrieving memories.” He also reports a worsening tremor in his dominant hand that compromises his ability to eat with a spoon or a fork. He complains of increasing daytime somnolence, which began when his lithium dose was increased and improved when the dose was decreased.
The patient is a mathematician and recently finished revising the curriculum for an undergraduate course in advanced mathematics that he teaches. He does not smoke cigarettes, and he drinks alcohol only socially. He has no other medical conditions and no known cardiovascular risk factors.
Current and recent medications
- Lithium carbonate 600 mg twice daily (before his hospitalization he had been taking 600 mg twice daily; this was increased to 1,500 mg/day during the hospitalization and then decreased to the current dose as maintenance therapy)
- Divalproex (Depakote) 250 mg every night
- Gabapentin (Neurontin) 400 mg every night (the dosages of divalproex and gabapentin have remained unchanged since before his hospitalization)
- A multivitamin daily
- Naproxen (Naprosyn, Aleve) 250 mg up to two times a week for arthritic knee pain
- Aripiprazole (Abilify). This antipsychotic drug was recently discontinued because of parkinsonian symptoms, which then gradually improved.
- Memantine (Namenda), which is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe Alzheimer disease. The patient reports that he stopped taking it after 3 weeks because he did not perceive it to be helping.
THE INITIAL EVALUATION
Physical examination
Temperature 98.3°F (36.8°C), pulse 60 beats per minute, respirations 16 per minute, blood pressure 126/64 mm Hg sitting and 118/71 mm Hg standing.
The patient is well groomed, alert, and cooperative. His head, eyes, ears, nose, and throat are normal. His teeth are in good condition. His skin is normal. We note no thyromegaly, carotid bruits, or palpable lymphadenopathy. His lungs are clear to auscultation. Results of cardiac, abdominal, and musculoskeletal examinations are all normal.
His deep tendon reflexes, sensory and motor testing, and gait are normal. The cerebellar examination is normal, aside from a mild tremor in his right hand when it is outstretched, with no resting tremor or cogwheel rigidity.
On the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) he scores a perfect 30/30 (normal 24–30). He can draw a clock normally. His score on the short-form Geriatric Depression Scale is 4/15 (a score of 6 or higher indicates depression).
Laboratory tests
- Serum lithium level 0.8 mmol/L (therapeutic range 0.5–1.5 mmol/L) (his previous values are not available)
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone level 1.61 μU/mL (normal 0.40–5.50)
- Complete blood cell count and comprehensive metabolic panel values are within normal limits.
Magnetic resonance imaging
Noncontrast magnetic resonance imaging of the head reveals two nonspecific punctate foci of high signal intensity on T2-weighted images in the left frontal white matter, but the results are otherwise normal.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
1. On the basis of this information, which is the most likely cause of this patient’s cogitive impairment?
- Dementia with Lewy bodies
- Early-onset Alzheimer disease
- Stroke with vascular cognitive impairment
- Lithium neurotoxicity
Lithium neurotoxicity is the most likely cause of this patient’s symptoms, given the temporal relationship between the adjusting of his lithium dose and the onset of his symptoms. Lithium therapy causes subtle cognitive deficits. Its dosing in older patients requires careful monitoring because of age-related alterations in its pharmacology and its various drug interactions; both mechanisms played a role in precipitating lithium toxicity in this patient.
Although his lithium levels are in the broadly accepted therapeutic range, there is much debate about the best maintenance level for patients with bipolar disorder. A level in the range of 1 to 1.2 mmol/L may be best in acute mania, while a lower level of around 0.8 mmol/L is preferred in the depressive phase. Once the patient’s mood has stabilized, the best maintenance level may be in the range of 0.2 to 0.6 mmol/L.
Dementia with Lewy bodies, although suggested by the patient’s cognitive impairment, history of parkinsonian symptoms, and somnolence, is an unlikely cause because his motor symptoms resolved after the aripiprazole was discontinued, his somnolence improved after the dose of lithium was reduced, and his alertness did not fluctuate thereafter as would be expected in dementia with Lewy bodies.
Alzheimer disease usually manifests as gradually progressive cognitive deficits involving memory impairment with one or more of the following: aphasia, apraxia, agnosia, and disturbance in executive functioning. In contrast, this patient’s memory loss was fairly abrupt and not slowly progressive.
Stroke is also unlikely, as he has no history of stroke or focal neurologic deficits. Although a magnetic resonance scan of the brain showed some evidence of small-vessel ischemic changes, it showed no cortical infarcts.
MECHANISMS OF LITHIUM NEUROTOXICITY
2. What are the possible mechanisms of lithium neurotoxicity in this patient?
- The increased dose of lithium
- The interaction of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and lithium
- The interaction of the other psychotropic medications with lithium
- All of the above
- None of the above
All of the above could be contributing.
Although lithium is thought to cause side effects in as many as 60% of patients of any age who take it, the rate of serious adverse effects is reportedly higher in older patients than in younger patients.1
That said, cognitive deficits are common in bipolar disorder irrespective of lithium use.
COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT IN BIPOLAR DISORDER
3. If cognitive impairment in bipolar disorder is common, when does it occur?
- Only in the remission phase
- Only in the manic phase
- Only in the depression phase
- In all phases of the disease
Cognitive impairment occurs in all phases of bipolar disorder. Neuropsychological testing of bipolar patients in remission uncovers subtle, persistent cognitive impairment in executive function and in visuospatial memory without mood symptoms.3–5 Impaired executive functioning, predominantly frontal lobe dysfunction, interferes with one’s ability to initiate, plan, perform, and successfully complete a task and challenges one’s ability to function effectively in society and to comply with medical advice and instructions on taking medications.
RECOMMENDATIONS
4. What should we recommend to this patient?
- Decrease the current dose of lithium
- Stop all medications
- Undergo detailed neuropsychological testing
- Follow up with a psychiatrist, if needed
The patient’s lithium level was within the therapeutic range and his bipolar symptoms were well controlled. In older patients, however, the optimal serum level of lithium is often unclear, making it advisable to reduce the dose when an adverse effect is suspected.
His other medications should be reviewed. Gabapentin is not indicated for use as a mood stabilizer, and his divalproex dose (250 mg) is well below the usual therapeutic dose of 1,000 to 2,000 mg/day.6 The gabapentin could be discontinued, and the divalproex could be increased to a therapeutic dose.
NSAIDs can increase serum lithium levels, diminish renal lithium clearance, and possibly induce lithium toxicity, but the effect varies considerably among drugs and individuals.7 We would advise this patient to stop taking naproxen and switch to acetaminophen (Tylenol) for his arthritis pain, and we would inform him of the risk of lithium toxicity with continuous use of NSAIDs.
We would also recommend additional neuropsychological testing. The patient noticed subtle difficulties in his cognitive abilities that were not apparent on the MMSE. While the MMSE is an acceptable cognitive test, it is often not sensitive enough to detect milder forms of cognitive impairment, especially in well-educated patients at the usual cut-point of 24. A comprehensive neuropsychological examination is a more sensitive measure of cognition, involving the detailed testing of various cognitive domains. It can reveal a pattern of cognitive impairment that helps to differentiate between normal and mood disorders and also can detect subtle executive dysfunction.
However, detailed neuropsychological testing is time-consuming and may not be obtained rapidly enough to help in making clinical decisions quickly. In this patient’s case, immediate collaboration and follow-up with the patient’s psychiatrist would be the most expeditious way to reassess the patient’s medication regimen.
FOLLOW-UP COURSE
We informed the patient’s psychiatrist that we thought the patient had increased sensitivity to lithium (even at “therapeutic” levels), possibly related to a drug-drug interaction.
His dose of lithium was kept at 600 mg twice daily, as the lithium toxicity was most likely due to a drug-drug interaction.
We discontinued his memantine, since he did not have Alzheimer disease and since he wasn’t taking it anyway. He continued taking gabapentin and divalproex at the same doses, and he stopped taking naproxyn and substituted acetaminophen for his arthritis pain. We advised him about about health maintenance, including proper nutrition, mineral and vitamin supplements, and exercise.
The patient underwent neuropsychological testing to better characterize his cognitive impairment. The findings did not suggest dementia, but were consistent with minor cognitive deficits caused by lithium.
When seen at a follow-up visit 6 weeks later the patient was free of symptoms except for the tremor in his dominant hand. His mood was stable and his cognition was better. No further changes were required in his psychotropic drug regimen.
TAKE-HOME POINTS
When a bipolar patient develops acute changes in cognition, we should suspect adverse effects of lithium as the cause, because of its narrow therapeutic window and interactions with other prescribed drugs. The case presented here reminds us to consider adverse drug effects any time an older patient develops acute changes in cognition. One should also consider the potential for a drug-drug interaction when reviewing the patient’s medication list and be especially vigilant in monitoring patients taking lithium, since its safety and effectiveness are affected by aging and by the co-administration of drugs that influence its clearance.
Despite these caveats, lithium remains an effective treatment in elderly patients, provided we are aware of the risks and benefits of its use.
A 61-year-old man presents for evaluation of new-onset cognitive impairment, which has developed over the past 6 to 8 months. He has bipolar disorder, for which he has been taking lithium carbonate (Eskalith) for the past 15 years. This therapy kept his mood stable until a relapse of depression and mania 1 year ago required hospitalization and an increase in the lithium dose, which was then lowered somewhat after he improved (see below). His cognitive symptoms appeared gradually within 2 months after his release from the hospital.
He now has difficulty concentrating, a tendency to substitute words incorrectly during conversation, and difficulty recalling names and “retrieving memories.” He also reports a worsening tremor in his dominant hand that compromises his ability to eat with a spoon or a fork. He complains of increasing daytime somnolence, which began when his lithium dose was increased and improved when the dose was decreased.
The patient is a mathematician and recently finished revising the curriculum for an undergraduate course in advanced mathematics that he teaches. He does not smoke cigarettes, and he drinks alcohol only socially. He has no other medical conditions and no known cardiovascular risk factors.
Current and recent medications
- Lithium carbonate 600 mg twice daily (before his hospitalization he had been taking 600 mg twice daily; this was increased to 1,500 mg/day during the hospitalization and then decreased to the current dose as maintenance therapy)
- Divalproex (Depakote) 250 mg every night
- Gabapentin (Neurontin) 400 mg every night (the dosages of divalproex and gabapentin have remained unchanged since before his hospitalization)
- A multivitamin daily
- Naproxen (Naprosyn, Aleve) 250 mg up to two times a week for arthritic knee pain
- Aripiprazole (Abilify). This antipsychotic drug was recently discontinued because of parkinsonian symptoms, which then gradually improved.
- Memantine (Namenda), which is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe Alzheimer disease. The patient reports that he stopped taking it after 3 weeks because he did not perceive it to be helping.
THE INITIAL EVALUATION
Physical examination
Temperature 98.3°F (36.8°C), pulse 60 beats per minute, respirations 16 per minute, blood pressure 126/64 mm Hg sitting and 118/71 mm Hg standing.
The patient is well groomed, alert, and cooperative. His head, eyes, ears, nose, and throat are normal. His teeth are in good condition. His skin is normal. We note no thyromegaly, carotid bruits, or palpable lymphadenopathy. His lungs are clear to auscultation. Results of cardiac, abdominal, and musculoskeletal examinations are all normal.
His deep tendon reflexes, sensory and motor testing, and gait are normal. The cerebellar examination is normal, aside from a mild tremor in his right hand when it is outstretched, with no resting tremor or cogwheel rigidity.
On the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) he scores a perfect 30/30 (normal 24–30). He can draw a clock normally. His score on the short-form Geriatric Depression Scale is 4/15 (a score of 6 or higher indicates depression).
Laboratory tests
- Serum lithium level 0.8 mmol/L (therapeutic range 0.5–1.5 mmol/L) (his previous values are not available)
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone level 1.61 μU/mL (normal 0.40–5.50)
- Complete blood cell count and comprehensive metabolic panel values are within normal limits.
Magnetic resonance imaging
Noncontrast magnetic resonance imaging of the head reveals two nonspecific punctate foci of high signal intensity on T2-weighted images in the left frontal white matter, but the results are otherwise normal.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
1. On the basis of this information, which is the most likely cause of this patient’s cogitive impairment?
- Dementia with Lewy bodies
- Early-onset Alzheimer disease
- Stroke with vascular cognitive impairment
- Lithium neurotoxicity
Lithium neurotoxicity is the most likely cause of this patient’s symptoms, given the temporal relationship between the adjusting of his lithium dose and the onset of his symptoms. Lithium therapy causes subtle cognitive deficits. Its dosing in older patients requires careful monitoring because of age-related alterations in its pharmacology and its various drug interactions; both mechanisms played a role in precipitating lithium toxicity in this patient.
Although his lithium levels are in the broadly accepted therapeutic range, there is much debate about the best maintenance level for patients with bipolar disorder. A level in the range of 1 to 1.2 mmol/L may be best in acute mania, while a lower level of around 0.8 mmol/L is preferred in the depressive phase. Once the patient’s mood has stabilized, the best maintenance level may be in the range of 0.2 to 0.6 mmol/L.
Dementia with Lewy bodies, although suggested by the patient’s cognitive impairment, history of parkinsonian symptoms, and somnolence, is an unlikely cause because his motor symptoms resolved after the aripiprazole was discontinued, his somnolence improved after the dose of lithium was reduced, and his alertness did not fluctuate thereafter as would be expected in dementia with Lewy bodies.
Alzheimer disease usually manifests as gradually progressive cognitive deficits involving memory impairment with one or more of the following: aphasia, apraxia, agnosia, and disturbance in executive functioning. In contrast, this patient’s memory loss was fairly abrupt and not slowly progressive.
Stroke is also unlikely, as he has no history of stroke or focal neurologic deficits. Although a magnetic resonance scan of the brain showed some evidence of small-vessel ischemic changes, it showed no cortical infarcts.
MECHANISMS OF LITHIUM NEUROTOXICITY
2. What are the possible mechanisms of lithium neurotoxicity in this patient?
- The increased dose of lithium
- The interaction of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and lithium
- The interaction of the other psychotropic medications with lithium
- All of the above
- None of the above
All of the above could be contributing.
Although lithium is thought to cause side effects in as many as 60% of patients of any age who take it, the rate of serious adverse effects is reportedly higher in older patients than in younger patients.1
That said, cognitive deficits are common in bipolar disorder irrespective of lithium use.
COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT IN BIPOLAR DISORDER
3. If cognitive impairment in bipolar disorder is common, when does it occur?
- Only in the remission phase
- Only in the manic phase
- Only in the depression phase
- In all phases of the disease
Cognitive impairment occurs in all phases of bipolar disorder. Neuropsychological testing of bipolar patients in remission uncovers subtle, persistent cognitive impairment in executive function and in visuospatial memory without mood symptoms.3–5 Impaired executive functioning, predominantly frontal lobe dysfunction, interferes with one’s ability to initiate, plan, perform, and successfully complete a task and challenges one’s ability to function effectively in society and to comply with medical advice and instructions on taking medications.
RECOMMENDATIONS
4. What should we recommend to this patient?
- Decrease the current dose of lithium
- Stop all medications
- Undergo detailed neuropsychological testing
- Follow up with a psychiatrist, if needed
The patient’s lithium level was within the therapeutic range and his bipolar symptoms were well controlled. In older patients, however, the optimal serum level of lithium is often unclear, making it advisable to reduce the dose when an adverse effect is suspected.
His other medications should be reviewed. Gabapentin is not indicated for use as a mood stabilizer, and his divalproex dose (250 mg) is well below the usual therapeutic dose of 1,000 to 2,000 mg/day.6 The gabapentin could be discontinued, and the divalproex could be increased to a therapeutic dose.
NSAIDs can increase serum lithium levels, diminish renal lithium clearance, and possibly induce lithium toxicity, but the effect varies considerably among drugs and individuals.7 We would advise this patient to stop taking naproxen and switch to acetaminophen (Tylenol) for his arthritis pain, and we would inform him of the risk of lithium toxicity with continuous use of NSAIDs.
We would also recommend additional neuropsychological testing. The patient noticed subtle difficulties in his cognitive abilities that were not apparent on the MMSE. While the MMSE is an acceptable cognitive test, it is often not sensitive enough to detect milder forms of cognitive impairment, especially in well-educated patients at the usual cut-point of 24. A comprehensive neuropsychological examination is a more sensitive measure of cognition, involving the detailed testing of various cognitive domains. It can reveal a pattern of cognitive impairment that helps to differentiate between normal and mood disorders and also can detect subtle executive dysfunction.
However, detailed neuropsychological testing is time-consuming and may not be obtained rapidly enough to help in making clinical decisions quickly. In this patient’s case, immediate collaboration and follow-up with the patient’s psychiatrist would be the most expeditious way to reassess the patient’s medication regimen.
FOLLOW-UP COURSE
We informed the patient’s psychiatrist that we thought the patient had increased sensitivity to lithium (even at “therapeutic” levels), possibly related to a drug-drug interaction.
His dose of lithium was kept at 600 mg twice daily, as the lithium toxicity was most likely due to a drug-drug interaction.
We discontinued his memantine, since he did not have Alzheimer disease and since he wasn’t taking it anyway. He continued taking gabapentin and divalproex at the same doses, and he stopped taking naproxyn and substituted acetaminophen for his arthritis pain. We advised him about about health maintenance, including proper nutrition, mineral and vitamin supplements, and exercise.
The patient underwent neuropsychological testing to better characterize his cognitive impairment. The findings did not suggest dementia, but were consistent with minor cognitive deficits caused by lithium.
When seen at a follow-up visit 6 weeks later the patient was free of symptoms except for the tremor in his dominant hand. His mood was stable and his cognition was better. No further changes were required in his psychotropic drug regimen.
TAKE-HOME POINTS
When a bipolar patient develops acute changes in cognition, we should suspect adverse effects of lithium as the cause, because of its narrow therapeutic window and interactions with other prescribed drugs. The case presented here reminds us to consider adverse drug effects any time an older patient develops acute changes in cognition. One should also consider the potential for a drug-drug interaction when reviewing the patient’s medication list and be especially vigilant in monitoring patients taking lithium, since its safety and effectiveness are affected by aging and by the co-administration of drugs that influence its clearance.
Despite these caveats, lithium remains an effective treatment in elderly patients, provided we are aware of the risks and benefits of its use.
- Juurlink DN, Mamdani MM, Kopp A, Rochon PA, Shulman KI, Redelmeier DA. Drug-induced lithium toxicity in the elderly: a population-based study. J Am Geriatr Soc 2004; 52:794–798.
- Sproule BA, Hardy BG, Shulman KI. Differential pharma-cokinetics of lithium in elderly patients. Drugs Aging 2000; 16:165–177.
- Martinez-Aran A, Vieta E, Colom F, et al. Cognitive impairment in euthymic bipolar patients: implications for clinical and functional outcome. Bipolar Disord 2004; 6:224–232.
- Martinez-Aran A, Vieta E, Reinares M, et al. Cognitive function across manic or hypomanic, depressed, and euthymic states in bipolar disorder. Am J Psychiatry 2004; 161:262–270.
- Rubinsztein JS, Michael A, Paykel ES, Sahakian BJ. Cognitive impairment in remission in bipolar affective disorder. Psychol Med 2000; 30:1025–1036.
- Sajatovic M, Madhusoodanan S, Coconcea N. Managing bipolar disorder in the elderly: defining the role of the newer agents. Drugs Aging 2005; 22:39–54.
- Ragheb M. The clinical significance of lithium-non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug interactions. J Clin Psychopharmacol 1990; 10:350–354.
- Juurlink DN, Mamdani MM, Kopp A, Rochon PA, Shulman KI, Redelmeier DA. Drug-induced lithium toxicity in the elderly: a population-based study. J Am Geriatr Soc 2004; 52:794–798.
- Sproule BA, Hardy BG, Shulman KI. Differential pharma-cokinetics of lithium in elderly patients. Drugs Aging 2000; 16:165–177.
- Martinez-Aran A, Vieta E, Colom F, et al. Cognitive impairment in euthymic bipolar patients: implications for clinical and functional outcome. Bipolar Disord 2004; 6:224–232.
- Martinez-Aran A, Vieta E, Reinares M, et al. Cognitive function across manic or hypomanic, depressed, and euthymic states in bipolar disorder. Am J Psychiatry 2004; 161:262–270.
- Rubinsztein JS, Michael A, Paykel ES, Sahakian BJ. Cognitive impairment in remission in bipolar affective disorder. Psychol Med 2000; 30:1025–1036.
- Sajatovic M, Madhusoodanan S, Coconcea N. Managing bipolar disorder in the elderly: defining the role of the newer agents. Drugs Aging 2005; 22:39–54.
- Ragheb M. The clinical significance of lithium-non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug interactions. J Clin Psychopharmacol 1990; 10:350–354.
A young woman with fatigue
A 22-year-old woman presents to the clinic for evaluation of fatigue. She has not felt well for the past few years. Her current symptoms include generalized fatigue and diarrhea, characterized as two to three semi-formed, nonbloody bowel movements each day and occasional episodes of watery diarrhea. Her bowel movements are usually precipitated by meals. She consumes a regular diet and has not recognized any intolerance to any particular foods. She denies having any abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, recent travel, joint pain, rash, or change in the texture of her hair. She has been seen by several internists in her hometown, who have not provided her with a specific diagnosis.
Her medical history is significant for anemia, anxiety, and depression. Menarche occurred at age 16. Her menstrual cycle has been regular, with bleeding noted to be only modest. Her medications include oral contraceptive pills. She has not had previous surgeries.
On examination, she appears well. She is afebrile, weighs 128 lbs, and is 63 inches tall. The physical examination is normal, including a rectal examination and fecal occult blood testing.
Routine laboratory tests are performed. Results:
- White blood cell count 3.88 × 109/L (normal 4.0–11)
- Hemoglobin 10.4 g/dL (normal 12–16)
- Hematocrit 34% (normal 37%–47%)
- Mean corpuscular volume 80.2 fL (normal 80–100)
- Mean corpuscular hemoglobin 24.5 pG (normal 27–34)
- Platelet count 365 × 109/L (normal 150–400)
- Sodium 141 mmol/L (normal 132–148)
- Potassium 4.2 mmol/L (normal 3.5–5.0)
- Chloride 107 mmol/L (normal 98–110)
- Alanine aminotransferase 22 U/L (normal 0–45)
- Glucose 66 mg/dL (normal 65–100)
- Blood urea nitrogen 6 mg/dL (normal 8–25)
- Creatinine 0.6 mg/dL (normal 0.7–1.4)
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone 2.860 mIU/L (normal 0.4–5.5)
- Red blood cell folate 539 ng/mL (normal 257–800)
- Vitamin B12 321 pg/mL (normal 221–700)
- Iron/total iron-binding capacity 21/445 μg/dL (normal 30–140, 210–415)
- Ferritin 5 ng/mL (normal 9–150).
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
1. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her diarrhea?
- Thyroid disease
- Functional bowel disease
- Gluten-sensitive enteropathy (celiac disease)
Given her constellation of symptoms (fatigue, neuropsychiatric changes, iron deficiency anemia, and diarrhea), celiac disease is the most likely diagnosis. Hyperthyroidism can cause diarrhea, but this is unlikely since her thyroid tests are normal. Functional bowel disease is a diagnosis of exclusion and usually has a more chronic, fluctuating course.
CELIAC DISEASE HAS VARIOUS PRESENTATIONS
Celiac disease has various presentations and therefore has been classified into several types1,2:
Classic disease is dominated by symptoms of malabsorption. The diagnosis is established by serologic testing, findings of villous atrophy on biopsy, and improvement of symptoms on a gluten-free diet. However, the presentation of celiac disease has changed, and now atypical presentations are more common in adults (see below). The reason for the change in presentation is not known, but some have hypothesized that it is related to an increase in breast-feeding and the later introduction of cereals into infants’ diets.
Celiac disease with atypical symptoms is characterized by extraintestinal manifestations with few or no gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms. Patients may present with iron-deficiency anemia; osteoporosis or vitamin D deficiency; arthritis; neurologic symptoms such as ataxia, headaches, or depression or anxiety; myocarditis; infertility; or elevated aminotransferase levels. As in classic celiac disease, the diagnosis is established with serologic testing, findings of villous atrophy on biopsy, and improvement of symptoms on a gluten-free diet.
Latent disease includes cases in patients with positive serologic tests but no villous atrophy on biopsy. These patients have no symptoms but may develop symptoms or histologic changes later.
Silent disease refers to cases in patients who have no symptoms but have a positive serologic test and villous atrophy on biopsy. These cases are usually detected via screening of people at high risk, ie, relatives of patients with celiac disease.
It is important that clinicians be aware of the various symptoms and presentations of celiac disease in order to make the diagnosis.
CONFIRMING CELIAC DISEASE
2. Which of the following is used to test for celiac disease?
- Immunoglobulin G (IgG) and immunoglobulin A (IgA) antigliadin antibody testing
- IgA antiendomysial antibody and IgA antitransglutaminase antibody testing
- HLA DQ2/DQ8 testing
The sensitivity of antigliadin antibody testing is only about 70% to 85%, and its specificity is about 70% to 90%. Better serologic tests are those for IgA antiendomysial and antitransglutaminase antibodies, which have sensitivities greater than 90% and specificities greater than 95%.3 HLA DQ2/DQ8 testing has a high sensitivity (> 90%–95%), but because about 30% of the general population also carry these markers, the specificity of this test is not ideal. This test is best used for its negative predictive value—ie, to rule out the diagnosis of celiac disease.
Of note: 1% to 2% of patients with celiac disease have a deficiency of IgA.4 Therefore, if the clinical suspicion for celiac disease is high but the IgA antibody tests are negative or equivocal, IgG antitransglutaminase and IgG antiendomysial antibody tests can help establish the diagnosis. HLA testing in this situation can also help rule out the diagnosis.
CONFIRMING CELIAC DISEASE—CONTINUED
3. What test should be performed next in this patient?
- Upper GI series with small-bowel follow-through
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy with biopsies
- Small-bowel barium study
- Video capsule endoscopy
Today, the presumptive diagnosis of celiac disease requires positive serologic testing and biopsy results. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy with biopsies should be ordered. Upper GI series and barium studies do not provide a tissue diagnosis. Barium studies and other radiologic tests can be considered if a patient does not have the expected response to a strict gluten-free diet or if one suspects complications of celiac disease, such as GI lymphoma.
Video capsule endoscopy is an emerging tool for diagnosing celiac disease, as suggested in several trials.5 Some findings seen on video capsule endoscopy in patients with celiac disease include mosaicism, nodularity, visible vessels, and loss of mucosal folds. However, the role of this test continues to be investigated, and biopsy is still required to confirm the diagnosis.
WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CELIAC DISEASE?
The reported prevalence of symptomatic celiac disease is about 1 in 1,000 live births in populations of northern European ancestry, ranging from 1 in 250 (in Sweden) to 1 in 4,000 (in Denmark).6 The prevalence appears to be higher in women than in men.7
In a large US study, the prevalence of celiac disease was 1 in 22 in first-degree relatives of celiac patients, 1 in 39 in second-degree relatives, 1 in 56 in patients with either GI symptoms or a condition associated with celiac disease, and 1 in 133 in groups not at risk.8 Another study found that the prevalence of antiendomysial antibodies in US blood donors was as high as 1 in 2,502.
Given that patients with celiac disease may not present with classic symptoms, it has been suggested that the following groups of patients be tested for it1:
- Patients with GI symptoms such as chronic diarrhea, malabsorption, weight loss, or abdominal symptoms
- Patients without diarrhea but with other unexplained signs or symptoms that could be due to celiac disease, such as iron-deficiency anemia, elevated aminotransferase levels, short stature, delayed puberty, or infertility
- Symptomatic patients at high risk for celiac disease. Risk factors include type 1 diabetes or other autoimmune endocrinopathies, first- and second-degree relatives of people with celiac disease, and patients with Turner, Down, or Williams syndromes.
Screening of the general population is not recommended, even in populations at high risk (eg, white people of northern European ancestry).
WHAT CAN CELIAC PATIENTS EAT?
4. Patients with celiac disease should avoid eating which of the following?
- Wheat
- Barley
- Rye
- Oats
Patients with celiac disease should follow a gluten-free diet and should initially eliminate all of these substances.
Some recent studies have suggested that pure oat powder can be tolerated without disease recurrence, although the long-term safety of oat consumption in patients with celiac disease is uncertain.9 It may be reasonable for patients to reintroduce oats when the disease is under control, especially since uncontaminated oats can be obtained from reliable retail or wholesale stores. The definitive diagnosis of celiac disease requires clinical suspicion, serologic tests, biopsy, and documented clinical and histologic improvement after a gluten-free diet is started.
All patients with celiac disease should receive dietary counseling and referral to a nutritionist who is experienced in the treatment of this disease. Because of the significant lifestyle and dietary changes involved in treating this disease, many patients may also benefit from participating in a celiac support group.
COMPLICATIONS OF CELIAC DISEASE
5. What are the complications of untreated celiac disease?
- Anemia
- Osteoporosis
- Intestinal lymphoma
- Infertility
- Neuropsychiatric symptoms
- Rash
All of the above are complications of untreated celiac disease and are often clinical features at presentation. Patients with celiac disease should be tested for anemia and nutritional deficiencies, including iron, folate, calcium, and vitamin D deficiency.
All patients should also undergo dual-energy x-ray absorptiometric scanning. Bone loss is thought to be related to vitamin D deficiency and secondary hyperparathyroidism, and may be partially reversed with a gluten-free diet.
Celiac disease is associated with hyposplenism, so pneumococcal vaccination should be considered. Celiac disease is also frequently associated with the rash of dermatitis herpetiformis, and diagnosis of this rash should prompt an evaluation for celiac disease.
Other associated conditions include Down syndrome, selective IgA deficiency, and other autoimmune diseases such as type 1 diabetes, thyroid disease, and liver disease.
WHAT HAPPENED TO OUR PATIENT?
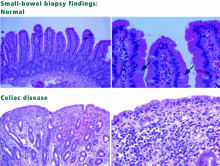
Our patient tested positive for antiendomysial and antitransglutaminase antibodies and underwent small-bowel biopsy, which confirmed the diagnosis of celiac disease. She was started on a gluten-free diet, and within 2 weeks she noted an improvement in her symptoms of fatigue, GI upset, mood disorders, and difficulty with concentration. She met with a nutritionist who specializes in celiac disease and joined a celiac support group.
However, about 2 months later, her symptoms recurred. She again met with her nutritionist, who confirmed that she was adhering to a gluten-free and lactose-free diet. Even so, when she was tested again for antitransglutaminase antibodies, the titer was elevated. Stool cultures were obtained and were negative. She was started on a course of prednisone, and her symptoms resolved.
WHAT IF PATIENTS DO NOT RESPOND TO TREATMENT?
The most common cause of recurrent symptoms or nonresponse to treatment is noncompliance with the gluten-free diet or inadvertent ingestion of gluten. Patients who do not respond to treatment or who have a period of response but then relapse should be referred back to a nutritionist who specializes in celiac disease.
If a patient continues to have symptoms despite strict adherence to a gluten-free diet, other disorders should be considered, such as concomitant lactose intolerance, small-bowel bacterial overgrowth, pancreatic insufficiency, or irritable bowel syndrome. If these conditions are ruled out, patients can be considered for treatment with prednisone or other immunosuppressive agents. Patients with refractory symptoms are at higher risk of more severe complications of celiac disease, such as intestinal lymphoma, intestinal strictures, and collagenous colitis.
TAKE-HOME POINTS
- Celiac disease classically presents with symptoms of malabsorption, but nonclassic presentations are much more common.
- Celiac disease should be tested for in patients with or without symptoms of mal-absorption and other associated signs or symptoms including unexplained iron-deficiency anemia, infertility, short stature, delayed puberty, or elevated transaminases. Testing should be considered for symptomatic patients with type 1 diabetes or other autoimmune endocrinopathies, first- and second-degree relatives of patients with known disease, and those with certain chromosomal abnormalities.
- Heightened physician awareness is important in the diagnosis of celiac disease.
- Diagnosis depends on serologic testing, biopsy, and clinical improvement on a gluten-free diet.
- Treatment should consist of education about the disease, consultation with a nutritionist experienced in celiac disease, and lifelong adherence to a gluten-free diet. Referral to a celiac support group should be considered.
- Long-term follow-up should include heightened vigilance and awareness of the complications of celiac disease such as osteoporosis, vitamin D deficiency and other nutritional deficiencies, increased risk of malignancy, association with low birth-weight infants and preterm labor, and occurrence of autoimmune disorders.
Acknowledgments: I would like to extend a special thank you to Dr. Walter Henricks, Director, Center for Pathology Informatics, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Cleveland Clinic, for providing biopsy slides and interpretation. I would also like to extend thanks to Dr. Derek Abbott, Department of Pathology, Case Western University Hospitals, for his helpful criticisms.
- National Institutes of Health. NIH Consensus Development Conference on Celiac Disease, 2004 Accessed 1/29/2008. http://consensus.nih.gov/2004/2004CeliacDisease118html.htm.
- Rostom A, Murray JA, Kagnoff MF. American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) Institute technical review on the diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Gastroenterology 2006; 131:1981–2002.
- Hellekson K. AHRQ releases practice guidelines for celiac disease screening. Am Fam Phys 2005; 71:1–3.
- Cataldo F, Marino V, Bottaro G, Greco P, Ventura A. Celiac disease and selective immunoglobulin A deficiency. J Pediatr 1997; 131:306–308.
- Kesari A, Bobba RK, Arsura EL. Video capsule endoscopy and celiac disease. Gastrointest Endosc 2005; 62:796–797.
- Branski D, Fasano A, Troncone R. Latest developments in the pathogenesis and treatment of celiac disease. J Pediatr 2006; 149:295–300.
- Rampertab SD, Pooran N, Brar P, Singh P, Green PH. Trends in the presentation of celiac disease. Am J Med 2006; 119 4:355.e9–e14.
- Fasano A, Berti I, Gerarduzzi T, et al. Prevalence of celiac disease in at-risk and not-at-risk groups in the United States: a large multicenter study. Arch Intern Med 2003; 163:286–292.
- Janatuinen EK, Pikkarainen PH, Kemppainen TA, et al. A comparison of diets with and without oats in adults with celiac disease. N Engl J Med 1995; 333:1033–1037.
A 22-year-old woman presents to the clinic for evaluation of fatigue. She has not felt well for the past few years. Her current symptoms include generalized fatigue and diarrhea, characterized as two to three semi-formed, nonbloody bowel movements each day and occasional episodes of watery diarrhea. Her bowel movements are usually precipitated by meals. She consumes a regular diet and has not recognized any intolerance to any particular foods. She denies having any abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, recent travel, joint pain, rash, or change in the texture of her hair. She has been seen by several internists in her hometown, who have not provided her with a specific diagnosis.
Her medical history is significant for anemia, anxiety, and depression. Menarche occurred at age 16. Her menstrual cycle has been regular, with bleeding noted to be only modest. Her medications include oral contraceptive pills. She has not had previous surgeries.
On examination, she appears well. She is afebrile, weighs 128 lbs, and is 63 inches tall. The physical examination is normal, including a rectal examination and fecal occult blood testing.
Routine laboratory tests are performed. Results:
- White blood cell count 3.88 × 109/L (normal 4.0–11)
- Hemoglobin 10.4 g/dL (normal 12–16)
- Hematocrit 34% (normal 37%–47%)
- Mean corpuscular volume 80.2 fL (normal 80–100)
- Mean corpuscular hemoglobin 24.5 pG (normal 27–34)
- Platelet count 365 × 109/L (normal 150–400)
- Sodium 141 mmol/L (normal 132–148)
- Potassium 4.2 mmol/L (normal 3.5–5.0)
- Chloride 107 mmol/L (normal 98–110)
- Alanine aminotransferase 22 U/L (normal 0–45)
- Glucose 66 mg/dL (normal 65–100)
- Blood urea nitrogen 6 mg/dL (normal 8–25)
- Creatinine 0.6 mg/dL (normal 0.7–1.4)
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone 2.860 mIU/L (normal 0.4–5.5)
- Red blood cell folate 539 ng/mL (normal 257–800)
- Vitamin B12 321 pg/mL (normal 221–700)
- Iron/total iron-binding capacity 21/445 μg/dL (normal 30–140, 210–415)
- Ferritin 5 ng/mL (normal 9–150).
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
1. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her diarrhea?
- Thyroid disease
- Functional bowel disease
- Gluten-sensitive enteropathy (celiac disease)
Given her constellation of symptoms (fatigue, neuropsychiatric changes, iron deficiency anemia, and diarrhea), celiac disease is the most likely diagnosis. Hyperthyroidism can cause diarrhea, but this is unlikely since her thyroid tests are normal. Functional bowel disease is a diagnosis of exclusion and usually has a more chronic, fluctuating course.
CELIAC DISEASE HAS VARIOUS PRESENTATIONS
Celiac disease has various presentations and therefore has been classified into several types1,2:
Classic disease is dominated by symptoms of malabsorption. The diagnosis is established by serologic testing, findings of villous atrophy on biopsy, and improvement of symptoms on a gluten-free diet. However, the presentation of celiac disease has changed, and now atypical presentations are more common in adults (see below). The reason for the change in presentation is not known, but some have hypothesized that it is related to an increase in breast-feeding and the later introduction of cereals into infants’ diets.
Celiac disease with atypical symptoms is characterized by extraintestinal manifestations with few or no gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms. Patients may present with iron-deficiency anemia; osteoporosis or vitamin D deficiency; arthritis; neurologic symptoms such as ataxia, headaches, or depression or anxiety; myocarditis; infertility; or elevated aminotransferase levels. As in classic celiac disease, the diagnosis is established with serologic testing, findings of villous atrophy on biopsy, and improvement of symptoms on a gluten-free diet.
Latent disease includes cases in patients with positive serologic tests but no villous atrophy on biopsy. These patients have no symptoms but may develop symptoms or histologic changes later.
Silent disease refers to cases in patients who have no symptoms but have a positive serologic test and villous atrophy on biopsy. These cases are usually detected via screening of people at high risk, ie, relatives of patients with celiac disease.
It is important that clinicians be aware of the various symptoms and presentations of celiac disease in order to make the diagnosis.
CONFIRMING CELIAC DISEASE
2. Which of the following is used to test for celiac disease?
- Immunoglobulin G (IgG) and immunoglobulin A (IgA) antigliadin antibody testing
- IgA antiendomysial antibody and IgA antitransglutaminase antibody testing
- HLA DQ2/DQ8 testing
The sensitivity of antigliadin antibody testing is only about 70% to 85%, and its specificity is about 70% to 90%. Better serologic tests are those for IgA antiendomysial and antitransglutaminase antibodies, which have sensitivities greater than 90% and specificities greater than 95%.3 HLA DQ2/DQ8 testing has a high sensitivity (> 90%–95%), but because about 30% of the general population also carry these markers, the specificity of this test is not ideal. This test is best used for its negative predictive value—ie, to rule out the diagnosis of celiac disease.
Of note: 1% to 2% of patients with celiac disease have a deficiency of IgA.4 Therefore, if the clinical suspicion for celiac disease is high but the IgA antibody tests are negative or equivocal, IgG antitransglutaminase and IgG antiendomysial antibody tests can help establish the diagnosis. HLA testing in this situation can also help rule out the diagnosis.
CONFIRMING CELIAC DISEASE—CONTINUED
3. What test should be performed next in this patient?
- Upper GI series with small-bowel follow-through
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy with biopsies
- Small-bowel barium study
- Video capsule endoscopy
Today, the presumptive diagnosis of celiac disease requires positive serologic testing and biopsy results. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy with biopsies should be ordered. Upper GI series and barium studies do not provide a tissue diagnosis. Barium studies and other radiologic tests can be considered if a patient does not have the expected response to a strict gluten-free diet or if one suspects complications of celiac disease, such as GI lymphoma.
Video capsule endoscopy is an emerging tool for diagnosing celiac disease, as suggested in several trials.5 Some findings seen on video capsule endoscopy in patients with celiac disease include mosaicism, nodularity, visible vessels, and loss of mucosal folds. However, the role of this test continues to be investigated, and biopsy is still required to confirm the diagnosis.
WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CELIAC DISEASE?
The reported prevalence of symptomatic celiac disease is about 1 in 1,000 live births in populations of northern European ancestry, ranging from 1 in 250 (in Sweden) to 1 in 4,000 (in Denmark).6 The prevalence appears to be higher in women than in men.7
In a large US study, the prevalence of celiac disease was 1 in 22 in first-degree relatives of celiac patients, 1 in 39 in second-degree relatives, 1 in 56 in patients with either GI symptoms or a condition associated with celiac disease, and 1 in 133 in groups not at risk.8 Another study found that the prevalence of antiendomysial antibodies in US blood donors was as high as 1 in 2,502.
Given that patients with celiac disease may not present with classic symptoms, it has been suggested that the following groups of patients be tested for it1:
- Patients with GI symptoms such as chronic diarrhea, malabsorption, weight loss, or abdominal symptoms
- Patients without diarrhea but with other unexplained signs or symptoms that could be due to celiac disease, such as iron-deficiency anemia, elevated aminotransferase levels, short stature, delayed puberty, or infertility
- Symptomatic patients at high risk for celiac disease. Risk factors include type 1 diabetes or other autoimmune endocrinopathies, first- and second-degree relatives of people with celiac disease, and patients with Turner, Down, or Williams syndromes.
Screening of the general population is not recommended, even in populations at high risk (eg, white people of northern European ancestry).
WHAT CAN CELIAC PATIENTS EAT?
4. Patients with celiac disease should avoid eating which of the following?
- Wheat
- Barley
- Rye
- Oats
Patients with celiac disease should follow a gluten-free diet and should initially eliminate all of these substances.
Some recent studies have suggested that pure oat powder can be tolerated without disease recurrence, although the long-term safety of oat consumption in patients with celiac disease is uncertain.9 It may be reasonable for patients to reintroduce oats when the disease is under control, especially since uncontaminated oats can be obtained from reliable retail or wholesale stores. The definitive diagnosis of celiac disease requires clinical suspicion, serologic tests, biopsy, and documented clinical and histologic improvement after a gluten-free diet is started.
All patients with celiac disease should receive dietary counseling and referral to a nutritionist who is experienced in the treatment of this disease. Because of the significant lifestyle and dietary changes involved in treating this disease, many patients may also benefit from participating in a celiac support group.
COMPLICATIONS OF CELIAC DISEASE
5. What are the complications of untreated celiac disease?
- Anemia
- Osteoporosis
- Intestinal lymphoma
- Infertility
- Neuropsychiatric symptoms
- Rash
All of the above are complications of untreated celiac disease and are often clinical features at presentation. Patients with celiac disease should be tested for anemia and nutritional deficiencies, including iron, folate, calcium, and vitamin D deficiency.
All patients should also undergo dual-energy x-ray absorptiometric scanning. Bone loss is thought to be related to vitamin D deficiency and secondary hyperparathyroidism, and may be partially reversed with a gluten-free diet.
Celiac disease is associated with hyposplenism, so pneumococcal vaccination should be considered. Celiac disease is also frequently associated with the rash of dermatitis herpetiformis, and diagnosis of this rash should prompt an evaluation for celiac disease.
Other associated conditions include Down syndrome, selective IgA deficiency, and other autoimmune diseases such as type 1 diabetes, thyroid disease, and liver disease.
WHAT HAPPENED TO OUR PATIENT?
Our patient tested positive for antiendomysial and antitransglutaminase antibodies and underwent small-bowel biopsy, which confirmed the diagnosis of celiac disease. She was started on a gluten-free diet, and within 2 weeks she noted an improvement in her symptoms of fatigue, GI upset, mood disorders, and difficulty with concentration. She met with a nutritionist who specializes in celiac disease and joined a celiac support group.
However, about 2 months later, her symptoms recurred. She again met with her nutritionist, who confirmed that she was adhering to a gluten-free and lactose-free diet. Even so, when she was tested again for antitransglutaminase antibodies, the titer was elevated. Stool cultures were obtained and were negative. She was started on a course of prednisone, and her symptoms resolved.
WHAT IF PATIENTS DO NOT RESPOND TO TREATMENT?
The most common cause of recurrent symptoms or nonresponse to treatment is noncompliance with the gluten-free diet or inadvertent ingestion of gluten. Patients who do not respond to treatment or who have a period of response but then relapse should be referred back to a nutritionist who specializes in celiac disease.
If a patient continues to have symptoms despite strict adherence to a gluten-free diet, other disorders should be considered, such as concomitant lactose intolerance, small-bowel bacterial overgrowth, pancreatic insufficiency, or irritable bowel syndrome. If these conditions are ruled out, patients can be considered for treatment with prednisone or other immunosuppressive agents. Patients with refractory symptoms are at higher risk of more severe complications of celiac disease, such as intestinal lymphoma, intestinal strictures, and collagenous colitis.
TAKE-HOME POINTS
- Celiac disease classically presents with symptoms of malabsorption, but nonclassic presentations are much more common.
- Celiac disease should be tested for in patients with or without symptoms of mal-absorption and other associated signs or symptoms including unexplained iron-deficiency anemia, infertility, short stature, delayed puberty, or elevated transaminases. Testing should be considered for symptomatic patients with type 1 diabetes or other autoimmune endocrinopathies, first- and second-degree relatives of patients with known disease, and those with certain chromosomal abnormalities.
- Heightened physician awareness is important in the diagnosis of celiac disease.
- Diagnosis depends on serologic testing, biopsy, and clinical improvement on a gluten-free diet.
- Treatment should consist of education about the disease, consultation with a nutritionist experienced in celiac disease, and lifelong adherence to a gluten-free diet. Referral to a celiac support group should be considered.
- Long-term follow-up should include heightened vigilance and awareness of the complications of celiac disease such as osteoporosis, vitamin D deficiency and other nutritional deficiencies, increased risk of malignancy, association with low birth-weight infants and preterm labor, and occurrence of autoimmune disorders.
Acknowledgments: I would like to extend a special thank you to Dr. Walter Henricks, Director, Center for Pathology Informatics, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Cleveland Clinic, for providing biopsy slides and interpretation. I would also like to extend thanks to Dr. Derek Abbott, Department of Pathology, Case Western University Hospitals, for his helpful criticisms.
A 22-year-old woman presents to the clinic for evaluation of fatigue. She has not felt well for the past few years. Her current symptoms include generalized fatigue and diarrhea, characterized as two to three semi-formed, nonbloody bowel movements each day and occasional episodes of watery diarrhea. Her bowel movements are usually precipitated by meals. She consumes a regular diet and has not recognized any intolerance to any particular foods. She denies having any abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, recent travel, joint pain, rash, or change in the texture of her hair. She has been seen by several internists in her hometown, who have not provided her with a specific diagnosis.
Her medical history is significant for anemia, anxiety, and depression. Menarche occurred at age 16. Her menstrual cycle has been regular, with bleeding noted to be only modest. Her medications include oral contraceptive pills. She has not had previous surgeries.
On examination, she appears well. She is afebrile, weighs 128 lbs, and is 63 inches tall. The physical examination is normal, including a rectal examination and fecal occult blood testing.
Routine laboratory tests are performed. Results:
- White blood cell count 3.88 × 109/L (normal 4.0–11)
- Hemoglobin 10.4 g/dL (normal 12–16)
- Hematocrit 34% (normal 37%–47%)
- Mean corpuscular volume 80.2 fL (normal 80–100)
- Mean corpuscular hemoglobin 24.5 pG (normal 27–34)
- Platelet count 365 × 109/L (normal 150–400)
- Sodium 141 mmol/L (normal 132–148)
- Potassium 4.2 mmol/L (normal 3.5–5.0)
- Chloride 107 mmol/L (normal 98–110)
- Alanine aminotransferase 22 U/L (normal 0–45)
- Glucose 66 mg/dL (normal 65–100)
- Blood urea nitrogen 6 mg/dL (normal 8–25)
- Creatinine 0.6 mg/dL (normal 0.7–1.4)
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone 2.860 mIU/L (normal 0.4–5.5)
- Red blood cell folate 539 ng/mL (normal 257–800)
- Vitamin B12 321 pg/mL (normal 221–700)
- Iron/total iron-binding capacity 21/445 μg/dL (normal 30–140, 210–415)
- Ferritin 5 ng/mL (normal 9–150).
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
1. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her diarrhea?
- Thyroid disease
- Functional bowel disease
- Gluten-sensitive enteropathy (celiac disease)
Given her constellation of symptoms (fatigue, neuropsychiatric changes, iron deficiency anemia, and diarrhea), celiac disease is the most likely diagnosis. Hyperthyroidism can cause diarrhea, but this is unlikely since her thyroid tests are normal. Functional bowel disease is a diagnosis of exclusion and usually has a more chronic, fluctuating course.
CELIAC DISEASE HAS VARIOUS PRESENTATIONS
Celiac disease has various presentations and therefore has been classified into several types1,2:
Classic disease is dominated by symptoms of malabsorption. The diagnosis is established by serologic testing, findings of villous atrophy on biopsy, and improvement of symptoms on a gluten-free diet. However, the presentation of celiac disease has changed, and now atypical presentations are more common in adults (see below). The reason for the change in presentation is not known, but some have hypothesized that it is related to an increase in breast-feeding and the later introduction of cereals into infants’ diets.
Celiac disease with atypical symptoms is characterized by extraintestinal manifestations with few or no gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms. Patients may present with iron-deficiency anemia; osteoporosis or vitamin D deficiency; arthritis; neurologic symptoms such as ataxia, headaches, or depression or anxiety; myocarditis; infertility; or elevated aminotransferase levels. As in classic celiac disease, the diagnosis is established with serologic testing, findings of villous atrophy on biopsy, and improvement of symptoms on a gluten-free diet.
Latent disease includes cases in patients with positive serologic tests but no villous atrophy on biopsy. These patients have no symptoms but may develop symptoms or histologic changes later.
Silent disease refers to cases in patients who have no symptoms but have a positive serologic test and villous atrophy on biopsy. These cases are usually detected via screening of people at high risk, ie, relatives of patients with celiac disease.
It is important that clinicians be aware of the various symptoms and presentations of celiac disease in order to make the diagnosis.
CONFIRMING CELIAC DISEASE
2. Which of the following is used to test for celiac disease?
- Immunoglobulin G (IgG) and immunoglobulin A (IgA) antigliadin antibody testing
- IgA antiendomysial antibody and IgA antitransglutaminase antibody testing
- HLA DQ2/DQ8 testing
The sensitivity of antigliadin antibody testing is only about 70% to 85%, and its specificity is about 70% to 90%. Better serologic tests are those for IgA antiendomysial and antitransglutaminase antibodies, which have sensitivities greater than 90% and specificities greater than 95%.3 HLA DQ2/DQ8 testing has a high sensitivity (> 90%–95%), but because about 30% of the general population also carry these markers, the specificity of this test is not ideal. This test is best used for its negative predictive value—ie, to rule out the diagnosis of celiac disease.
Of note: 1% to 2% of patients with celiac disease have a deficiency of IgA.4 Therefore, if the clinical suspicion for celiac disease is high but the IgA antibody tests are negative or equivocal, IgG antitransglutaminase and IgG antiendomysial antibody tests can help establish the diagnosis. HLA testing in this situation can also help rule out the diagnosis.
CONFIRMING CELIAC DISEASE—CONTINUED
3. What test should be performed next in this patient?
- Upper GI series with small-bowel follow-through
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy with biopsies
- Small-bowel barium study
- Video capsule endoscopy
Today, the presumptive diagnosis of celiac disease requires positive serologic testing and biopsy results. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy with biopsies should be ordered. Upper GI series and barium studies do not provide a tissue diagnosis. Barium studies and other radiologic tests can be considered if a patient does not have the expected response to a strict gluten-free diet or if one suspects complications of celiac disease, such as GI lymphoma.
Video capsule endoscopy is an emerging tool for diagnosing celiac disease, as suggested in several trials.5 Some findings seen on video capsule endoscopy in patients with celiac disease include mosaicism, nodularity, visible vessels, and loss of mucosal folds. However, the role of this test continues to be investigated, and biopsy is still required to confirm the diagnosis.
WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CELIAC DISEASE?
The reported prevalence of symptomatic celiac disease is about 1 in 1,000 live births in populations of northern European ancestry, ranging from 1 in 250 (in Sweden) to 1 in 4,000 (in Denmark).6 The prevalence appears to be higher in women than in men.7
In a large US study, the prevalence of celiac disease was 1 in 22 in first-degree relatives of celiac patients, 1 in 39 in second-degree relatives, 1 in 56 in patients with either GI symptoms or a condition associated with celiac disease, and 1 in 133 in groups not at risk.8 Another study found that the prevalence of antiendomysial antibodies in US blood donors was as high as 1 in 2,502.
Given that patients with celiac disease may not present with classic symptoms, it has been suggested that the following groups of patients be tested for it1:
- Patients with GI symptoms such as chronic diarrhea, malabsorption, weight loss, or abdominal symptoms
- Patients without diarrhea but with other unexplained signs or symptoms that could be due to celiac disease, such as iron-deficiency anemia, elevated aminotransferase levels, short stature, delayed puberty, or infertility
- Symptomatic patients at high risk for celiac disease. Risk factors include type 1 diabetes or other autoimmune endocrinopathies, first- and second-degree relatives of people with celiac disease, and patients with Turner, Down, or Williams syndromes.
Screening of the general population is not recommended, even in populations at high risk (eg, white people of northern European ancestry).
WHAT CAN CELIAC PATIENTS EAT?
4. Patients with celiac disease should avoid eating which of the following?
- Wheat
- Barley
- Rye
- Oats
Patients with celiac disease should follow a gluten-free diet and should initially eliminate all of these substances.
Some recent studies have suggested that pure oat powder can be tolerated without disease recurrence, although the long-term safety of oat consumption in patients with celiac disease is uncertain.9 It may be reasonable for patients to reintroduce oats when the disease is under control, especially since uncontaminated oats can be obtained from reliable retail or wholesale stores. The definitive diagnosis of celiac disease requires clinical suspicion, serologic tests, biopsy, and documented clinical and histologic improvement after a gluten-free diet is started.
All patients with celiac disease should receive dietary counseling and referral to a nutritionist who is experienced in the treatment of this disease. Because of the significant lifestyle and dietary changes involved in treating this disease, many patients may also benefit from participating in a celiac support group.
COMPLICATIONS OF CELIAC DISEASE
5. What are the complications of untreated celiac disease?
- Anemia
- Osteoporosis
- Intestinal lymphoma
- Infertility
- Neuropsychiatric symptoms
- Rash
All of the above are complications of untreated celiac disease and are often clinical features at presentation. Patients with celiac disease should be tested for anemia and nutritional deficiencies, including iron, folate, calcium, and vitamin D deficiency.
All patients should also undergo dual-energy x-ray absorptiometric scanning. Bone loss is thought to be related to vitamin D deficiency and secondary hyperparathyroidism, and may be partially reversed with a gluten-free diet.
Celiac disease is associated with hyposplenism, so pneumococcal vaccination should be considered. Celiac disease is also frequently associated with the rash of dermatitis herpetiformis, and diagnosis of this rash should prompt an evaluation for celiac disease.
Other associated conditions include Down syndrome, selective IgA deficiency, and other autoimmune diseases such as type 1 diabetes, thyroid disease, and liver disease.
WHAT HAPPENED TO OUR PATIENT?
Our patient tested positive for antiendomysial and antitransglutaminase antibodies and underwent small-bowel biopsy, which confirmed the diagnosis of celiac disease. She was started on a gluten-free diet, and within 2 weeks she noted an improvement in her symptoms of fatigue, GI upset, mood disorders, and difficulty with concentration. She met with a nutritionist who specializes in celiac disease and joined a celiac support group.
However, about 2 months later, her symptoms recurred. She again met with her nutritionist, who confirmed that she was adhering to a gluten-free and lactose-free diet. Even so, when she was tested again for antitransglutaminase antibodies, the titer was elevated. Stool cultures were obtained and were negative. She was started on a course of prednisone, and her symptoms resolved.
WHAT IF PATIENTS DO NOT RESPOND TO TREATMENT?
The most common cause of recurrent symptoms or nonresponse to treatment is noncompliance with the gluten-free diet or inadvertent ingestion of gluten. Patients who do not respond to treatment or who have a period of response but then relapse should be referred back to a nutritionist who specializes in celiac disease.
If a patient continues to have symptoms despite strict adherence to a gluten-free diet, other disorders should be considered, such as concomitant lactose intolerance, small-bowel bacterial overgrowth, pancreatic insufficiency, or irritable bowel syndrome. If these conditions are ruled out, patients can be considered for treatment with prednisone or other immunosuppressive agents. Patients with refractory symptoms are at higher risk of more severe complications of celiac disease, such as intestinal lymphoma, intestinal strictures, and collagenous colitis.
TAKE-HOME POINTS
- Celiac disease classically presents with symptoms of malabsorption, but nonclassic presentations are much more common.
- Celiac disease should be tested for in patients with or without symptoms of mal-absorption and other associated signs or symptoms including unexplained iron-deficiency anemia, infertility, short stature, delayed puberty, or elevated transaminases. Testing should be considered for symptomatic patients with type 1 diabetes or other autoimmune endocrinopathies, first- and second-degree relatives of patients with known disease, and those with certain chromosomal abnormalities.
- Heightened physician awareness is important in the diagnosis of celiac disease.
- Diagnosis depends on serologic testing, biopsy, and clinical improvement on a gluten-free diet.
- Treatment should consist of education about the disease, consultation with a nutritionist experienced in celiac disease, and lifelong adherence to a gluten-free diet. Referral to a celiac support group should be considered.
- Long-term follow-up should include heightened vigilance and awareness of the complications of celiac disease such as osteoporosis, vitamin D deficiency and other nutritional deficiencies, increased risk of malignancy, association with low birth-weight infants and preterm labor, and occurrence of autoimmune disorders.
Acknowledgments: I would like to extend a special thank you to Dr. Walter Henricks, Director, Center for Pathology Informatics, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Cleveland Clinic, for providing biopsy slides and interpretation. I would also like to extend thanks to Dr. Derek Abbott, Department of Pathology, Case Western University Hospitals, for his helpful criticisms.
- National Institutes of Health. NIH Consensus Development Conference on Celiac Disease, 2004 Accessed 1/29/2008. http://consensus.nih.gov/2004/2004CeliacDisease118html.htm.
- Rostom A, Murray JA, Kagnoff MF. American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) Institute technical review on the diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Gastroenterology 2006; 131:1981–2002.
- Hellekson K. AHRQ releases practice guidelines for celiac disease screening. Am Fam Phys 2005; 71:1–3.
- Cataldo F, Marino V, Bottaro G, Greco P, Ventura A. Celiac disease and selective immunoglobulin A deficiency. J Pediatr 1997; 131:306–308.
- Kesari A, Bobba RK, Arsura EL. Video capsule endoscopy and celiac disease. Gastrointest Endosc 2005; 62:796–797.
- Branski D, Fasano A, Troncone R. Latest developments in the pathogenesis and treatment of celiac disease. J Pediatr 2006; 149:295–300.
- Rampertab SD, Pooran N, Brar P, Singh P, Green PH. Trends in the presentation of celiac disease. Am J Med 2006; 119 4:355.e9–e14.
- Fasano A, Berti I, Gerarduzzi T, et al. Prevalence of celiac disease in at-risk and not-at-risk groups in the United States: a large multicenter study. Arch Intern Med 2003; 163:286–292.
- Janatuinen EK, Pikkarainen PH, Kemppainen TA, et al. A comparison of diets with and without oats in adults with celiac disease. N Engl J Med 1995; 333:1033–1037.
- National Institutes of Health. NIH Consensus Development Conference on Celiac Disease, 2004 Accessed 1/29/2008. http://consensus.nih.gov/2004/2004CeliacDisease118html.htm.
- Rostom A, Murray JA, Kagnoff MF. American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) Institute technical review on the diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Gastroenterology 2006; 131:1981–2002.
- Hellekson K. AHRQ releases practice guidelines for celiac disease screening. Am Fam Phys 2005; 71:1–3.
- Cataldo F, Marino V, Bottaro G, Greco P, Ventura A. Celiac disease and selective immunoglobulin A deficiency. J Pediatr 1997; 131:306–308.
- Kesari A, Bobba RK, Arsura EL. Video capsule endoscopy and celiac disease. Gastrointest Endosc 2005; 62:796–797.
- Branski D, Fasano A, Troncone R. Latest developments in the pathogenesis and treatment of celiac disease. J Pediatr 2006; 149:295–300.
- Rampertab SD, Pooran N, Brar P, Singh P, Green PH. Trends in the presentation of celiac disease. Am J Med 2006; 119 4:355.e9–e14.
- Fasano A, Berti I, Gerarduzzi T, et al. Prevalence of celiac disease in at-risk and not-at-risk groups in the United States: a large multicenter study. Arch Intern Med 2003; 163:286–292.
- Janatuinen EK, Pikkarainen PH, Kemppainen TA, et al. A comparison of diets with and without oats in adults with celiac disease. N Engl J Med 1995; 333:1033–1037.