User login
Decreasing burnout for hospitalists
How one hospital benefited from applying LEAN principles
The symptoms of burnout include emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and reduced personal efficacy, and burnout is a widespread problem among hospitalists; recent data suggest that half of physicians are experiencing at least one such symptom.
Health care leaders are increasingly concerned that these levels of physician burnout pose a threat to patient quality and safety. “As a result, some health care systems are shifting emphasis from the Triple Aim – population health, reduced costs, and patient satisfaction – to the Quadruple Aim, which incorporates health care provider wellness,” according to a recent abstract.
The authors began their own attempt to address the problem when Penn State Health in Dauphin County, Pa., built a stand-alone children’s hospital and experienced bed demands that exceeded bed availability, creating decreased organizational efficiency, high stress, and elevated physician burnout.
The LEAN principles offer a process-focused, customer-centered methodology that improves efficiency and quality. “We redesigned our service line using LEAN principles, such as ‘staff to demand’ and ‘standardize work,’ ” the authors wrote. “To ‘staff to demand,’ we hired three additional FTE [full-time equivalent employees]. This allowed creation of two rounding teams ([up] from one) and reduced our patient-to-attending ratio from 15:1 to 8:1. Workflow was resequenced and standardized, which enabled teams to see discharges at the start of rounds. We also provided in-house evening and overnight resident supervision. Our model permitted flexibility in physicians’ schedules, deemphasized reliance on RVUs, and heightened purpose and efficiency in work as determinants of providers’ value-adding capacity.”
As a result, both service line and hospital efficiency improved and faculty stress decreased in their hospital. “Mean stress scores decreased from 23 (preintervention) to 15 over the first 2 years, and has remained steady for a period of 3 years. Our divisional work-life balance measurement 2 years after the intervention was 85%, well above the reported average of 41%. We have maintained a low physician turnover rate at 3.5% over the last 3 years.”
Reference
Keefer L et al. LEAN in: Our secrets to decreasing provider stress, maximizing efficiency on a pediatric hospitalist service [abstract]. Accessed April 6, 2018.
How one hospital benefited from applying LEAN principles
How one hospital benefited from applying LEAN principles
The symptoms of burnout include emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and reduced personal efficacy, and burnout is a widespread problem among hospitalists; recent data suggest that half of physicians are experiencing at least one such symptom.
Health care leaders are increasingly concerned that these levels of physician burnout pose a threat to patient quality and safety. “As a result, some health care systems are shifting emphasis from the Triple Aim – population health, reduced costs, and patient satisfaction – to the Quadruple Aim, which incorporates health care provider wellness,” according to a recent abstract.
The authors began their own attempt to address the problem when Penn State Health in Dauphin County, Pa., built a stand-alone children’s hospital and experienced bed demands that exceeded bed availability, creating decreased organizational efficiency, high stress, and elevated physician burnout.
The LEAN principles offer a process-focused, customer-centered methodology that improves efficiency and quality. “We redesigned our service line using LEAN principles, such as ‘staff to demand’ and ‘standardize work,’ ” the authors wrote. “To ‘staff to demand,’ we hired three additional FTE [full-time equivalent employees]. This allowed creation of two rounding teams ([up] from one) and reduced our patient-to-attending ratio from 15:1 to 8:1. Workflow was resequenced and standardized, which enabled teams to see discharges at the start of rounds. We also provided in-house evening and overnight resident supervision. Our model permitted flexibility in physicians’ schedules, deemphasized reliance on RVUs, and heightened purpose and efficiency in work as determinants of providers’ value-adding capacity.”
As a result, both service line and hospital efficiency improved and faculty stress decreased in their hospital. “Mean stress scores decreased from 23 (preintervention) to 15 over the first 2 years, and has remained steady for a period of 3 years. Our divisional work-life balance measurement 2 years after the intervention was 85%, well above the reported average of 41%. We have maintained a low physician turnover rate at 3.5% over the last 3 years.”
Reference
Keefer L et al. LEAN in: Our secrets to decreasing provider stress, maximizing efficiency on a pediatric hospitalist service [abstract]. Accessed April 6, 2018.
The symptoms of burnout include emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and reduced personal efficacy, and burnout is a widespread problem among hospitalists; recent data suggest that half of physicians are experiencing at least one such symptom.
Health care leaders are increasingly concerned that these levels of physician burnout pose a threat to patient quality and safety. “As a result, some health care systems are shifting emphasis from the Triple Aim – population health, reduced costs, and patient satisfaction – to the Quadruple Aim, which incorporates health care provider wellness,” according to a recent abstract.
The authors began their own attempt to address the problem when Penn State Health in Dauphin County, Pa., built a stand-alone children’s hospital and experienced bed demands that exceeded bed availability, creating decreased organizational efficiency, high stress, and elevated physician burnout.
The LEAN principles offer a process-focused, customer-centered methodology that improves efficiency and quality. “We redesigned our service line using LEAN principles, such as ‘staff to demand’ and ‘standardize work,’ ” the authors wrote. “To ‘staff to demand,’ we hired three additional FTE [full-time equivalent employees]. This allowed creation of two rounding teams ([up] from one) and reduced our patient-to-attending ratio from 15:1 to 8:1. Workflow was resequenced and standardized, which enabled teams to see discharges at the start of rounds. We also provided in-house evening and overnight resident supervision. Our model permitted flexibility in physicians’ schedules, deemphasized reliance on RVUs, and heightened purpose and efficiency in work as determinants of providers’ value-adding capacity.”
As a result, both service line and hospital efficiency improved and faculty stress decreased in their hospital. “Mean stress scores decreased from 23 (preintervention) to 15 over the first 2 years, and has remained steady for a period of 3 years. Our divisional work-life balance measurement 2 years after the intervention was 85%, well above the reported average of 41%. We have maintained a low physician turnover rate at 3.5% over the last 3 years.”
Reference
Keefer L et al. LEAN in: Our secrets to decreasing provider stress, maximizing efficiency on a pediatric hospitalist service [abstract]. Accessed April 6, 2018.
Bring Schwartz Rounds to your hospital
A more emotional approach to rounds
If you are not doing Schwartz Rounds, get them started. ASAP.
I recently completed a 4-year tenure as physician moderator for our hospital’s Schwartz Rounds. An amazing team at my hospital helped pull the bimonthly sessions together. These compassionate care rounds are a national initiative to help foster empathy and compassion in the health care setting.
We gather a panel of two to three people involved in our patient presentation who share and move quickly through the clinical details, and head on toward the thornier ethical issues, emotional triggers, and responses. The best sessions are when the audience’s voice is heard for the bulk of the time.
The emotional cadence flows from boiling in frustration, drowning in tears, followed by comfort, and ending in thoughts for the next session. It is a more powerful arc than an episode of the television program “This is Us.” Largely, because this was us. This was real life. Real-time catharsis in the hospital.
In the daily grind, we often skip the step of processing our frustration, sadness, and anger, moving right on to the next patient and walking into the next room with that stoic layer of equanimity. I walk the hallways and find I grab my phone to catch up on emails, walking to the wrong floor because I’m not paying attention. Always something to do, someone to talk to, a family to call, pagers going off, phone calls. When do we sit and reflect?
These Schwartz Rounds are those moments of reflection – a slowdown in the day to think more deeply about the case. We talk about everything and anything. We have discussions with opposing views:
“Everything should have been done!”
“How did you not stop care?!”
“I agree with the doctors.”
“I can see the patient’s view more clearly now.”
Our first Schwartz Rounds tended to be end-of-life stories, particularly regarding the family mantra of “Do everything.” The health care team watches the suffering of a patient, a family, in a seemingly futile situation. Conversations around the end of life, choices, and quality of life are cut short daily by family members who simply recite, “Do everything.”
After several of these sessions, a case swings us in the other direction. The elderly gentleman with treatable cancer, who could easily survive another 20 years, declines treatment. “I’m fine, doc; I’ve lived long enough.” His wife at his bedside, shaking her head, tells us, “I don’t know why he wants to give up. He’s been as stubborn as a mule since the day I met him.” I spend 30 minutes convincing him to stay. The nurse does the same. Now we have a patient with a “Do nothing.” The patient’s decisions conflict with the family and the health care team.
Every day in the hospital provides a new ethical dilemma, a frustrating case, a challenging patient. Fodder for rounds.
Read the full post at hospitalleader.org.
Dr. Messler is a hospitalist at Morton Plant Hospitalist group in Clearwater, Fla. He previously chaired SHM’s Quality and Patient Safety Committee and has been active in several SHM mentoring programs, most recently with Project BOOST and Glycemic Control.
Also on The Hospital Leader
- Incubating Success: How We Used Structured Feedback to Reduce A Dangerous Practice by Rich Bottner, PA-C & Victoria Valencia, MPH
- New SoHM Report Provides Unique Window into Hospital Medicine Practice Trends by Leslie Flores, MHA, SFHM
- IGNITE Change: Improving Care via Interprofessional Clinical Learning Environments by Vineet Arora, MD, MAPP, MHM
A more emotional approach to rounds
A more emotional approach to rounds
If you are not doing Schwartz Rounds, get them started. ASAP.
I recently completed a 4-year tenure as physician moderator for our hospital’s Schwartz Rounds. An amazing team at my hospital helped pull the bimonthly sessions together. These compassionate care rounds are a national initiative to help foster empathy and compassion in the health care setting.
We gather a panel of two to three people involved in our patient presentation who share and move quickly through the clinical details, and head on toward the thornier ethical issues, emotional triggers, and responses. The best sessions are when the audience’s voice is heard for the bulk of the time.
The emotional cadence flows from boiling in frustration, drowning in tears, followed by comfort, and ending in thoughts for the next session. It is a more powerful arc than an episode of the television program “This is Us.” Largely, because this was us. This was real life. Real-time catharsis in the hospital.
In the daily grind, we often skip the step of processing our frustration, sadness, and anger, moving right on to the next patient and walking into the next room with that stoic layer of equanimity. I walk the hallways and find I grab my phone to catch up on emails, walking to the wrong floor because I’m not paying attention. Always something to do, someone to talk to, a family to call, pagers going off, phone calls. When do we sit and reflect?
These Schwartz Rounds are those moments of reflection – a slowdown in the day to think more deeply about the case. We talk about everything and anything. We have discussions with opposing views:
“Everything should have been done!”
“How did you not stop care?!”
“I agree with the doctors.”
“I can see the patient’s view more clearly now.”
Our first Schwartz Rounds tended to be end-of-life stories, particularly regarding the family mantra of “Do everything.” The health care team watches the suffering of a patient, a family, in a seemingly futile situation. Conversations around the end of life, choices, and quality of life are cut short daily by family members who simply recite, “Do everything.”
After several of these sessions, a case swings us in the other direction. The elderly gentleman with treatable cancer, who could easily survive another 20 years, declines treatment. “I’m fine, doc; I’ve lived long enough.” His wife at his bedside, shaking her head, tells us, “I don’t know why he wants to give up. He’s been as stubborn as a mule since the day I met him.” I spend 30 minutes convincing him to stay. The nurse does the same. Now we have a patient with a “Do nothing.” The patient’s decisions conflict with the family and the health care team.
Every day in the hospital provides a new ethical dilemma, a frustrating case, a challenging patient. Fodder for rounds.
Read the full post at hospitalleader.org.
Dr. Messler is a hospitalist at Morton Plant Hospitalist group in Clearwater, Fla. He previously chaired SHM’s Quality and Patient Safety Committee and has been active in several SHM mentoring programs, most recently with Project BOOST and Glycemic Control.
Also on The Hospital Leader
- Incubating Success: How We Used Structured Feedback to Reduce A Dangerous Practice by Rich Bottner, PA-C & Victoria Valencia, MPH
- New SoHM Report Provides Unique Window into Hospital Medicine Practice Trends by Leslie Flores, MHA, SFHM
- IGNITE Change: Improving Care via Interprofessional Clinical Learning Environments by Vineet Arora, MD, MAPP, MHM
If you are not doing Schwartz Rounds, get them started. ASAP.
I recently completed a 4-year tenure as physician moderator for our hospital’s Schwartz Rounds. An amazing team at my hospital helped pull the bimonthly sessions together. These compassionate care rounds are a national initiative to help foster empathy and compassion in the health care setting.
We gather a panel of two to three people involved in our patient presentation who share and move quickly through the clinical details, and head on toward the thornier ethical issues, emotional triggers, and responses. The best sessions are when the audience’s voice is heard for the bulk of the time.
The emotional cadence flows from boiling in frustration, drowning in tears, followed by comfort, and ending in thoughts for the next session. It is a more powerful arc than an episode of the television program “This is Us.” Largely, because this was us. This was real life. Real-time catharsis in the hospital.
In the daily grind, we often skip the step of processing our frustration, sadness, and anger, moving right on to the next patient and walking into the next room with that stoic layer of equanimity. I walk the hallways and find I grab my phone to catch up on emails, walking to the wrong floor because I’m not paying attention. Always something to do, someone to talk to, a family to call, pagers going off, phone calls. When do we sit and reflect?
These Schwartz Rounds are those moments of reflection – a slowdown in the day to think more deeply about the case. We talk about everything and anything. We have discussions with opposing views:
“Everything should have been done!”
“How did you not stop care?!”
“I agree with the doctors.”
“I can see the patient’s view more clearly now.”
Our first Schwartz Rounds tended to be end-of-life stories, particularly regarding the family mantra of “Do everything.” The health care team watches the suffering of a patient, a family, in a seemingly futile situation. Conversations around the end of life, choices, and quality of life are cut short daily by family members who simply recite, “Do everything.”
After several of these sessions, a case swings us in the other direction. The elderly gentleman with treatable cancer, who could easily survive another 20 years, declines treatment. “I’m fine, doc; I’ve lived long enough.” His wife at his bedside, shaking her head, tells us, “I don’t know why he wants to give up. He’s been as stubborn as a mule since the day I met him.” I spend 30 minutes convincing him to stay. The nurse does the same. Now we have a patient with a “Do nothing.” The patient’s decisions conflict with the family and the health care team.
Every day in the hospital provides a new ethical dilemma, a frustrating case, a challenging patient. Fodder for rounds.
Read the full post at hospitalleader.org.
Dr. Messler is a hospitalist at Morton Plant Hospitalist group in Clearwater, Fla. He previously chaired SHM’s Quality and Patient Safety Committee and has been active in several SHM mentoring programs, most recently with Project BOOST and Glycemic Control.
Also on The Hospital Leader
- Incubating Success: How We Used Structured Feedback to Reduce A Dangerous Practice by Rich Bottner, PA-C & Victoria Valencia, MPH
- New SoHM Report Provides Unique Window into Hospital Medicine Practice Trends by Leslie Flores, MHA, SFHM
- IGNITE Change: Improving Care via Interprofessional Clinical Learning Environments by Vineet Arora, MD, MAPP, MHM
Unit-based assignments: Pros and cons
Geographic cohorting shows ‘varying success’
A relatively recent practice catching on in many different hospitalist groups is geographic cohorting, or unit-based assignments. Traditionally, most hospitalists have had patients assigned on multiple different units. Unit-based assignments have been touted as a way of improving interdisciplinary communication and provider and patient satisfaction.1
How frequently are hospital medicine groups using unit-based assignments? SHM sought to quantify this trend in the recently published 2018 State of Hospital Medicine Report. Overall, among hospital medicine groups serving adults only, a little over one-third (36.4%) of groups reported utilizing unit-based assignments. However, there was significant variation, particularly dependent on group size. Geographic cohorting was used only in 7.6% of groups with 4 or fewer full-time equivalents, and in 68.8% of groups with 30 or more FTE. These data seem logical, as the potential gains from cohorting likely increase with group/hospital size, where physicians would otherwise round on an increasingly large number of units.
As has been shared in the hospital medicine literature, groups have experienced variable success with geographic cohorting. Improvements have been achieved in interprofessional collaboration, efficiency, nursing satisfaction,2 and, in some instances, length of stay. Unit-based assignments have allowed some groups to pilot other interventions, such as interdisciplinary rounds.
But geographic cohorting comes with its implementation challenges, too. For example, in many hospitals, some units have differing telemetry or nursing capabilities. And, in other institutions, there are units providing specialized care, such as care for neurology or oncology patients. The workload for hospitalists caring for particular types of patients may vary, and with specialty units, it may be more difficult to keep a similar census assigned to each hospitalist.
While some groups have noted increased professional satisfaction, others have noted decreases in satisfaction. One reason is that, while the frequency of paging may decrease, this is replaced by an increase in face-to-face interruptions. Also, unit-based assignments in some groups have resulted in hospitalists perceiving they are working in silos because of a decrease in interactions and camaraderie among providers in the same hospital medicine group.
At my home institution, University of California, San Diego, geographic cohorting has largely been a successful and positively perceived change. Our efforts have been particularly successful at one of our two campuses where most units have telemetry capabilities and where we have a dedicated daytime admitter (there are data on this in the Report as well, and a dedicated daytime admitter is the topic of a future Survey Insights column). Unit-based assignments have allowed the implementation of what we’ve termed focused interdisciplinary rounds.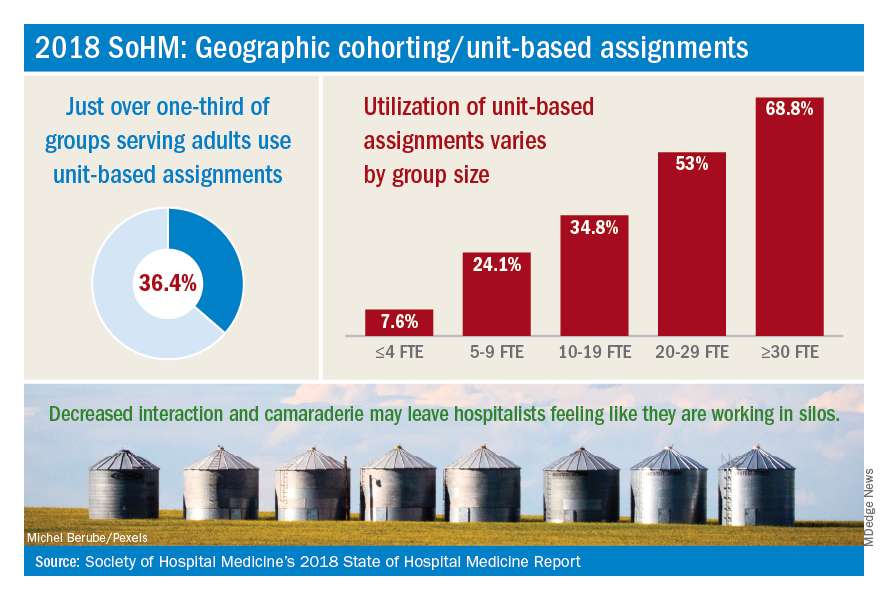
Our unit-based assignments are not perfect – we re-cohort each week when new hospitalists come on service, and some hospitalists are assigned a small number of patients off their home unit. Our internal data have shown a significant increase in patient satisfaction scores, but we have not realized a decrease in length of stay. Despite an overall positive perception, hospitalists have sometimes noted an imbalanced workload – we have a particularly challenging oncology/palliative unit and a daytime admitter that is at times very busy. Our system also requires the use of physician time to assign patients each morning and each week.
In contrast, while we’ve aimed to achieve the same success with unit-based assignments at our other campus, we’ve faced more challenges there. Our other facility is older, and fewer units have telemetry capabilities. A more traditional teaching structure also means that teams take turns with on-call admitting days, as opposed to a daytime admitter structure, and there may not be beds available in the unit assigned to the admitting team of the day.
Overall, geographic cohorting is likely to be considered or implemented in many hospital medicine groups, and efforts have met with varying success. There are certainly pros and cons to every model, and if your group is looking at redesigning services to include unit-based assignments, it’s worth examining the intended outcomes. While unit-based assignments are not for every group, there’s no doubt that this trend has been driven by our specialty’s commitment to outcome-driven process improvement.
Addendum added Feb. 15, 2019: The impact of UC San Diego's efforts discussed in this article are the author's own opinions through limited participation in focused interdisciplinary rounds, and have not been validated with formal data analysis. More study is in progress on the impact of focused interdiscplinary rounds on communication, utilization, and quality metrics. Sarah Horman, MD ([email protected]), Daniel Bouland, MD ([email protected]), and William Frederick, MD ([email protected]), have led efforts at UC San Diego to develop and implement focused interdisciplinary rounds, and may be contacted for further information.
Dr. Huang is physician advisor for care management and associate clinical professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of California, San Diego. He is a member of SHM’s practice analysis subcommittee.
References
1. O’Leary KJ et al. Interdisciplinary teamwork in hospitals: A review and practical recommendations for improvement. J Hosp Med. 2012 Jan;7(1):48-54.
2. Kara A et al. Hospital-based clinicians’ perceptions of geographic cohorting: Identifying opportunities for improvement. Am J Med Qual. 2018 May/Jun;33(3):303-12.
Geographic cohorting shows ‘varying success’
Geographic cohorting shows ‘varying success’
A relatively recent practice catching on in many different hospitalist groups is geographic cohorting, or unit-based assignments. Traditionally, most hospitalists have had patients assigned on multiple different units. Unit-based assignments have been touted as a way of improving interdisciplinary communication and provider and patient satisfaction.1
How frequently are hospital medicine groups using unit-based assignments? SHM sought to quantify this trend in the recently published 2018 State of Hospital Medicine Report. Overall, among hospital medicine groups serving adults only, a little over one-third (36.4%) of groups reported utilizing unit-based assignments. However, there was significant variation, particularly dependent on group size. Geographic cohorting was used only in 7.6% of groups with 4 or fewer full-time equivalents, and in 68.8% of groups with 30 or more FTE. These data seem logical, as the potential gains from cohorting likely increase with group/hospital size, where physicians would otherwise round on an increasingly large number of units.
As has been shared in the hospital medicine literature, groups have experienced variable success with geographic cohorting. Improvements have been achieved in interprofessional collaboration, efficiency, nursing satisfaction,2 and, in some instances, length of stay. Unit-based assignments have allowed some groups to pilot other interventions, such as interdisciplinary rounds.
But geographic cohorting comes with its implementation challenges, too. For example, in many hospitals, some units have differing telemetry or nursing capabilities. And, in other institutions, there are units providing specialized care, such as care for neurology or oncology patients. The workload for hospitalists caring for particular types of patients may vary, and with specialty units, it may be more difficult to keep a similar census assigned to each hospitalist.
While some groups have noted increased professional satisfaction, others have noted decreases in satisfaction. One reason is that, while the frequency of paging may decrease, this is replaced by an increase in face-to-face interruptions. Also, unit-based assignments in some groups have resulted in hospitalists perceiving they are working in silos because of a decrease in interactions and camaraderie among providers in the same hospital medicine group.
At my home institution, University of California, San Diego, geographic cohorting has largely been a successful and positively perceived change. Our efforts have been particularly successful at one of our two campuses where most units have telemetry capabilities and where we have a dedicated daytime admitter (there are data on this in the Report as well, and a dedicated daytime admitter is the topic of a future Survey Insights column). Unit-based assignments have allowed the implementation of what we’ve termed focused interdisciplinary rounds.
Our unit-based assignments are not perfect – we re-cohort each week when new hospitalists come on service, and some hospitalists are assigned a small number of patients off their home unit. Our internal data have shown a significant increase in patient satisfaction scores, but we have not realized a decrease in length of stay. Despite an overall positive perception, hospitalists have sometimes noted an imbalanced workload – we have a particularly challenging oncology/palliative unit and a daytime admitter that is at times very busy. Our system also requires the use of physician time to assign patients each morning and each week.
In contrast, while we’ve aimed to achieve the same success with unit-based assignments at our other campus, we’ve faced more challenges there. Our other facility is older, and fewer units have telemetry capabilities. A more traditional teaching structure also means that teams take turns with on-call admitting days, as opposed to a daytime admitter structure, and there may not be beds available in the unit assigned to the admitting team of the day.
Overall, geographic cohorting is likely to be considered or implemented in many hospital medicine groups, and efforts have met with varying success. There are certainly pros and cons to every model, and if your group is looking at redesigning services to include unit-based assignments, it’s worth examining the intended outcomes. While unit-based assignments are not for every group, there’s no doubt that this trend has been driven by our specialty’s commitment to outcome-driven process improvement.
Addendum added Feb. 15, 2019: The impact of UC San Diego's efforts discussed in this article are the author's own opinions through limited participation in focused interdisciplinary rounds, and have not been validated with formal data analysis. More study is in progress on the impact of focused interdiscplinary rounds on communication, utilization, and quality metrics. Sarah Horman, MD ([email protected]), Daniel Bouland, MD ([email protected]), and William Frederick, MD ([email protected]), have led efforts at UC San Diego to develop and implement focused interdisciplinary rounds, and may be contacted for further information.
Dr. Huang is physician advisor for care management and associate clinical professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of California, San Diego. He is a member of SHM’s practice analysis subcommittee.
References
1. O’Leary KJ et al. Interdisciplinary teamwork in hospitals: A review and practical recommendations for improvement. J Hosp Med. 2012 Jan;7(1):48-54.
2. Kara A et al. Hospital-based clinicians’ perceptions of geographic cohorting: Identifying opportunities for improvement. Am J Med Qual. 2018 May/Jun;33(3):303-12.
A relatively recent practice catching on in many different hospitalist groups is geographic cohorting, or unit-based assignments. Traditionally, most hospitalists have had patients assigned on multiple different units. Unit-based assignments have been touted as a way of improving interdisciplinary communication and provider and patient satisfaction.1
How frequently are hospital medicine groups using unit-based assignments? SHM sought to quantify this trend in the recently published 2018 State of Hospital Medicine Report. Overall, among hospital medicine groups serving adults only, a little over one-third (36.4%) of groups reported utilizing unit-based assignments. However, there was significant variation, particularly dependent on group size. Geographic cohorting was used only in 7.6% of groups with 4 or fewer full-time equivalents, and in 68.8% of groups with 30 or more FTE. These data seem logical, as the potential gains from cohorting likely increase with group/hospital size, where physicians would otherwise round on an increasingly large number of units.
As has been shared in the hospital medicine literature, groups have experienced variable success with geographic cohorting. Improvements have been achieved in interprofessional collaboration, efficiency, nursing satisfaction,2 and, in some instances, length of stay. Unit-based assignments have allowed some groups to pilot other interventions, such as interdisciplinary rounds.
But geographic cohorting comes with its implementation challenges, too. For example, in many hospitals, some units have differing telemetry or nursing capabilities. And, in other institutions, there are units providing specialized care, such as care for neurology or oncology patients. The workload for hospitalists caring for particular types of patients may vary, and with specialty units, it may be more difficult to keep a similar census assigned to each hospitalist.
While some groups have noted increased professional satisfaction, others have noted decreases in satisfaction. One reason is that, while the frequency of paging may decrease, this is replaced by an increase in face-to-face interruptions. Also, unit-based assignments in some groups have resulted in hospitalists perceiving they are working in silos because of a decrease in interactions and camaraderie among providers in the same hospital medicine group.
At my home institution, University of California, San Diego, geographic cohorting has largely been a successful and positively perceived change. Our efforts have been particularly successful at one of our two campuses where most units have telemetry capabilities and where we have a dedicated daytime admitter (there are data on this in the Report as well, and a dedicated daytime admitter is the topic of a future Survey Insights column). Unit-based assignments have allowed the implementation of what we’ve termed focused interdisciplinary rounds.
Our unit-based assignments are not perfect – we re-cohort each week when new hospitalists come on service, and some hospitalists are assigned a small number of patients off their home unit. Our internal data have shown a significant increase in patient satisfaction scores, but we have not realized a decrease in length of stay. Despite an overall positive perception, hospitalists have sometimes noted an imbalanced workload – we have a particularly challenging oncology/palliative unit and a daytime admitter that is at times very busy. Our system also requires the use of physician time to assign patients each morning and each week.
In contrast, while we’ve aimed to achieve the same success with unit-based assignments at our other campus, we’ve faced more challenges there. Our other facility is older, and fewer units have telemetry capabilities. A more traditional teaching structure also means that teams take turns with on-call admitting days, as opposed to a daytime admitter structure, and there may not be beds available in the unit assigned to the admitting team of the day.
Overall, geographic cohorting is likely to be considered or implemented in many hospital medicine groups, and efforts have met with varying success. There are certainly pros and cons to every model, and if your group is looking at redesigning services to include unit-based assignments, it’s worth examining the intended outcomes. While unit-based assignments are not for every group, there’s no doubt that this trend has been driven by our specialty’s commitment to outcome-driven process improvement.
Addendum added Feb. 15, 2019: The impact of UC San Diego's efforts discussed in this article are the author's own opinions through limited participation in focused interdisciplinary rounds, and have not been validated with formal data analysis. More study is in progress on the impact of focused interdiscplinary rounds on communication, utilization, and quality metrics. Sarah Horman, MD ([email protected]), Daniel Bouland, MD ([email protected]), and William Frederick, MD ([email protected]), have led efforts at UC San Diego to develop and implement focused interdisciplinary rounds, and may be contacted for further information.
Dr. Huang is physician advisor for care management and associate clinical professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of California, San Diego. He is a member of SHM’s practice analysis subcommittee.
References
1. O’Leary KJ et al. Interdisciplinary teamwork in hospitals: A review and practical recommendations for improvement. J Hosp Med. 2012 Jan;7(1):48-54.
2. Kara A et al. Hospital-based clinicians’ perceptions of geographic cohorting: Identifying opportunities for improvement. Am J Med Qual. 2018 May/Jun;33(3):303-12.
Giving hospitalists a larger clinical footprint
Something you did not know about warm handoffs
I am going to teach you something you do not know. I am almost sure of it.
Warm handoffs – a term you often hear within the confines of hospital walls when transferring a patient service to service or ward to ward. You do it in-house, but it’s unlikely you make the same connection when you discharge the same patient or transfer them to an outside entity.
But you have to be asleep under a rock not to have heard or read the changes afoot in the skilled nursing facility (SNF) realm, including the rise of the “SNFist”. Too much variation in use and spending; plus, we are learning patients do not need 25 days cooped up in a rehabilitation facility when 15 might do with a segue into home health for another 10 or 14. Patients like being home, and it costs a lot less.
Unfortunately, we do not do SNF handoffs in the same manner as ICUs. Our bad, and inpatient providers better adapt.
As hospitals decant and quality measures get an intimate look in the rehab space, SNFs will notice sicker patients, and the staff there will be more mindful of the sign outs and the data they receive. Know a Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services value-based program started on October 1 (just like hospitals – penalties and all) and SNFists, whoever they might be – NP/PA/DO/MD – will also require of hospitals a step-up in information transfer, both in quality and timeliness.
Read the full post at hospitalleader.org.
Also on The Hospital Leader
- “Immigration & the Future of Healthcare: Looking to a Greater Good,” by Jordan Messler, MD, SFHM
- “We Must Become Comfortable Talking about Physician Suicide,” by Tracy Cardin, ACNP-BC, SFHM
- “A New Light in the Darkness: Using Hospital-Based Medication-Assisted Treatment to Tackle the Opioid Crisis,” by Richard Bottner, PA-C
Something you did not know about warm handoffs
Something you did not know about warm handoffs
I am going to teach you something you do not know. I am almost sure of it.
Warm handoffs – a term you often hear within the confines of hospital walls when transferring a patient service to service or ward to ward. You do it in-house, but it’s unlikely you make the same connection when you discharge the same patient or transfer them to an outside entity.
But you have to be asleep under a rock not to have heard or read the changes afoot in the skilled nursing facility (SNF) realm, including the rise of the “SNFist”. Too much variation in use and spending; plus, we are learning patients do not need 25 days cooped up in a rehabilitation facility when 15 might do with a segue into home health for another 10 or 14. Patients like being home, and it costs a lot less.
Unfortunately, we do not do SNF handoffs in the same manner as ICUs. Our bad, and inpatient providers better adapt.
As hospitals decant and quality measures get an intimate look in the rehab space, SNFs will notice sicker patients, and the staff there will be more mindful of the sign outs and the data they receive. Know a Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services value-based program started on October 1 (just like hospitals – penalties and all) and SNFists, whoever they might be – NP/PA/DO/MD – will also require of hospitals a step-up in information transfer, both in quality and timeliness.
Read the full post at hospitalleader.org.
Also on The Hospital Leader
- “Immigration & the Future of Healthcare: Looking to a Greater Good,” by Jordan Messler, MD, SFHM
- “We Must Become Comfortable Talking about Physician Suicide,” by Tracy Cardin, ACNP-BC, SFHM
- “A New Light in the Darkness: Using Hospital-Based Medication-Assisted Treatment to Tackle the Opioid Crisis,” by Richard Bottner, PA-C
I am going to teach you something you do not know. I am almost sure of it.
Warm handoffs – a term you often hear within the confines of hospital walls when transferring a patient service to service or ward to ward. You do it in-house, but it’s unlikely you make the same connection when you discharge the same patient or transfer them to an outside entity.
But you have to be asleep under a rock not to have heard or read the changes afoot in the skilled nursing facility (SNF) realm, including the rise of the “SNFist”. Too much variation in use and spending; plus, we are learning patients do not need 25 days cooped up in a rehabilitation facility when 15 might do with a segue into home health for another 10 or 14. Patients like being home, and it costs a lot less.
Unfortunately, we do not do SNF handoffs in the same manner as ICUs. Our bad, and inpatient providers better adapt.
As hospitals decant and quality measures get an intimate look in the rehab space, SNFs will notice sicker patients, and the staff there will be more mindful of the sign outs and the data they receive. Know a Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services value-based program started on October 1 (just like hospitals – penalties and all) and SNFists, whoever they might be – NP/PA/DO/MD – will also require of hospitals a step-up in information transfer, both in quality and timeliness.
Read the full post at hospitalleader.org.
Also on The Hospital Leader
- “Immigration & the Future of Healthcare: Looking to a Greater Good,” by Jordan Messler, MD, SFHM
- “We Must Become Comfortable Talking about Physician Suicide,” by Tracy Cardin, ACNP-BC, SFHM
- “A New Light in the Darkness: Using Hospital-Based Medication-Assisted Treatment to Tackle the Opioid Crisis,” by Richard Bottner, PA-C
Building on diversity
Maryland SHM chapter follows expansive vision
Nidhi Goel, MD, MHS, is a Med-Peds hospitalist and assistant professor of internal medicine and pediatrics at the University of Maryland, Baltimore. Since August 2017, she has been the president of the Maryland chapter of SHM.
The Hospitalist recently sat down with her to discuss some of the initiatives that the large and active Maryland chapter is focused on.
Can you talk about your background and how you became interested in hospital medicine?
I grew up in the Baltimore area, and I went to medical school at the University of Maryland in Baltimore. I trained in internal medicine and pediatrics, also at the University of Maryland. Then I joined the faculty after I finished residency in 2014. I practiced as a hospitalist in internal medicine and pediatrics and was also a teaching hospitalist.
Early in my residency, I worked with teaching hospitalists. I rotated on the hospitalist teams, and I was inspired by their perspective on taking care of patients through a lens of quality and safety. I gained a greater appreciation for the risks associated with taking care of a patient in the hospital setting, and the opportunities to mitigate those risks and provide really high quality patient care. It made me realize that was what I wanted to do – and also to teach residents and students how to do the same.
So it was a philosophical attraction to the hospitalist approach?
Yes, and intellectually I’d say that I liked taking care of really complicated, very sick patients. I found that to be interesting – and rewarding when they got better.
Tell us more about what kind of research you do.
I work primarily on projects centered on quality and safety; they involve both adult internal medicine and pediatric patients. Currently on the adult medicine side, we have a project looking at improving outcomes for sepsis in the hospital setting. On the pediatric side, I’ve done a lot of work related to throughput – trying to increase the efficiency of our admissions – and especially our discharge process. Moving patients through the system efficiently has become a significant quality issue, especially during the winter months when our volumes pick up.
How long have you been involved in the Maryland SHM chapter, and what are the rewards of participation?
Early in my residency, I got involved in the chapter because some of the hospitalist faculty I worked with were chapter officers. They believed that the chapter was a good place for residents to be exposed to research and to other hospitalists for networking and camaraderie. So they began inviting us to Maryland chapter meetings, and I found those meetings to be very enlightening – from the practical and research content related to hospital medicine, and to networking with other hospitalists.
I was invited to be part of the Maryland chapter advisory board when I was still a resident, so that I might present trainee perspectives on how the chapter could continue to grow and target some of their activities for the benefit of residents. I stayed involved with the chapter after I finished residency, and when the opportunity presented itself to become an officer, and I decided to take it. I thought serving as a chapter officer would be a really interesting chance to meet more people in the field and to continue to innovate within the chapter setting.
Tell us more about the Maryland chapter.
We are a large chapter and we’re very, very active. Around 7 or 8 years ago, the Maryland chapter reached a significant turning point because the officers that were in place at that time had a vision for building the chapter. That was a major inflexion point in how active the chapter became, leading to the kinds of activities that we do now, and the variety of memberships.
One thing that I’m super proud of our chapter for is that we’ve really tried to continue building on the diversity that is represented in our membership. We have members stretching geographically all through the Baltimore and the Washington corridor, as well as out to western Maryland and the Eastern shore. The Maryland chapter has been able to attract members from different organizations throughout the state and from a diversity of practice settings. We have active members who are not just physicians, but also a nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and clinical pharmacists. We have members from throughout the health care delivery process, which really enriches the discussion and the value of the chapter as a whole.
What kind of initiatives and programs is the chapter working on?
Every year we have an abstracts competition at our fall meeting. Whoever wins that competition is allowed to present at the national SHM conference, which is a great opportunity. We’re really pushing that competition to make it an even more robust experience.
One thing that we had heard from some of our members, and that we recognized as a need as well, was to make our career guidance a little bit more robust. To that end, we’re creating a separate job fair that is almost like an employment workshop – to help people to buff up their CVs, to talk about interviewing skills, contracts, salary negotiations, as well as exposing job candidates to various hospital groups from throughout the area. That’s something that we’re really excited about. It’s going to take a lot of work, but I think it could be a really high-yield event for our members.
We’re also encouraging our nonphysician members to take more active leadership roles in the chapter; several of our nonphysician members on our chapter advisory board, including pharmacists and physician assistants, and we are trying to make sure that we’re also liaising with some of the professional organizations that represent our nonphysician members. So, for example, the clinical pharmacist who’s on our advisory board also is president of the Maryland chapter of the Society for Hospital Pharmacists. She brings a lot of really great ideas and interesting perspectives, and she’s brought a lot of exposure of our SHM chapter to the clinical pharmacy community as well.
What about more long-term goals for your chapter? What’s on the horizon?
We’re targeting early-career hospitalists and helping them to develop their career goals in whatever fashion they see as appropriate.
So, as someone who’s in academics, obviously research and publications are very important for me, but they’re not necessarily as important for other hospitalists. I think our early-career hospitalists are increasingly looking to incorporate things into their practice aside from direct patient care. Our members have interests in various elements of hospital medicine, including patient safety and quality improvement initiatives, clinical informatics, advocacy (especially related to the myriad aspects of health care reform), and strategies surrounding billing and denials. I think having our chapter help our members to realize some of those opportunities and develop their skills in a way that’s personally meaningful to them, as well as good for their marketability as they build their careers, would be a really positive step.
The ultimate goal of the chapter is to service members, so whatever long-term goals we have right now could definitely be fluid as time goes on.
What are some concerns of the chapter?
One area of significant discussion among hospitalists in Maryland has been global budgets. Our system of reimbursement is unique in the nation. It’s a system that aims to emphasize high-value care: the idea is to prioritize quality over quantity.
This system requires that hospitals rethink how we provide care in the inpatient setting, and how we create a continuum of care to the post-acute setting. It poses a lot of challenges, but also a lot of opportunities. Hospitalists are positioned perfectly to play a substantial role in implementing solutions.
Why might readers want to consider getting involved in their local SHM chapters?
I think it’s really beneficial to have the exposure that being involved with an SHM chapter brings – to people, to perspectives, to knowledge. There’s not really a downside to being involved with a chapter. You can take as little or as much as you want out of it, but I think most of our members find it to be a very enriching experience. Being involved in a chapter means you can have a voice, so that the chapter ends up serving you and your needs as well.
Maryland SHM chapter follows expansive vision
Maryland SHM chapter follows expansive vision
Nidhi Goel, MD, MHS, is a Med-Peds hospitalist and assistant professor of internal medicine and pediatrics at the University of Maryland, Baltimore. Since August 2017, she has been the president of the Maryland chapter of SHM.
The Hospitalist recently sat down with her to discuss some of the initiatives that the large and active Maryland chapter is focused on.
Can you talk about your background and how you became interested in hospital medicine?
I grew up in the Baltimore area, and I went to medical school at the University of Maryland in Baltimore. I trained in internal medicine and pediatrics, also at the University of Maryland. Then I joined the faculty after I finished residency in 2014. I practiced as a hospitalist in internal medicine and pediatrics and was also a teaching hospitalist.
Early in my residency, I worked with teaching hospitalists. I rotated on the hospitalist teams, and I was inspired by their perspective on taking care of patients through a lens of quality and safety. I gained a greater appreciation for the risks associated with taking care of a patient in the hospital setting, and the opportunities to mitigate those risks and provide really high quality patient care. It made me realize that was what I wanted to do – and also to teach residents and students how to do the same.
So it was a philosophical attraction to the hospitalist approach?
Yes, and intellectually I’d say that I liked taking care of really complicated, very sick patients. I found that to be interesting – and rewarding when they got better.
Tell us more about what kind of research you do.
I work primarily on projects centered on quality and safety; they involve both adult internal medicine and pediatric patients. Currently on the adult medicine side, we have a project looking at improving outcomes for sepsis in the hospital setting. On the pediatric side, I’ve done a lot of work related to throughput – trying to increase the efficiency of our admissions – and especially our discharge process. Moving patients through the system efficiently has become a significant quality issue, especially during the winter months when our volumes pick up.
How long have you been involved in the Maryland SHM chapter, and what are the rewards of participation?
Early in my residency, I got involved in the chapter because some of the hospitalist faculty I worked with were chapter officers. They believed that the chapter was a good place for residents to be exposed to research and to other hospitalists for networking and camaraderie. So they began inviting us to Maryland chapter meetings, and I found those meetings to be very enlightening – from the practical and research content related to hospital medicine, and to networking with other hospitalists.
I was invited to be part of the Maryland chapter advisory board when I was still a resident, so that I might present trainee perspectives on how the chapter could continue to grow and target some of their activities for the benefit of residents. I stayed involved with the chapter after I finished residency, and when the opportunity presented itself to become an officer, and I decided to take it. I thought serving as a chapter officer would be a really interesting chance to meet more people in the field and to continue to innovate within the chapter setting.
Tell us more about the Maryland chapter.
We are a large chapter and we’re very, very active. Around 7 or 8 years ago, the Maryland chapter reached a significant turning point because the officers that were in place at that time had a vision for building the chapter. That was a major inflexion point in how active the chapter became, leading to the kinds of activities that we do now, and the variety of memberships.
One thing that I’m super proud of our chapter for is that we’ve really tried to continue building on the diversity that is represented in our membership. We have members stretching geographically all through the Baltimore and the Washington corridor, as well as out to western Maryland and the Eastern shore. The Maryland chapter has been able to attract members from different organizations throughout the state and from a diversity of practice settings. We have active members who are not just physicians, but also a nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and clinical pharmacists. We have members from throughout the health care delivery process, which really enriches the discussion and the value of the chapter as a whole.
What kind of initiatives and programs is the chapter working on?
Every year we have an abstracts competition at our fall meeting. Whoever wins that competition is allowed to present at the national SHM conference, which is a great opportunity. We’re really pushing that competition to make it an even more robust experience.
One thing that we had heard from some of our members, and that we recognized as a need as well, was to make our career guidance a little bit more robust. To that end, we’re creating a separate job fair that is almost like an employment workshop – to help people to buff up their CVs, to talk about interviewing skills, contracts, salary negotiations, as well as exposing job candidates to various hospital groups from throughout the area. That’s something that we’re really excited about. It’s going to take a lot of work, but I think it could be a really high-yield event for our members.
We’re also encouraging our nonphysician members to take more active leadership roles in the chapter; several of our nonphysician members on our chapter advisory board, including pharmacists and physician assistants, and we are trying to make sure that we’re also liaising with some of the professional organizations that represent our nonphysician members. So, for example, the clinical pharmacist who’s on our advisory board also is president of the Maryland chapter of the Society for Hospital Pharmacists. She brings a lot of really great ideas and interesting perspectives, and she’s brought a lot of exposure of our SHM chapter to the clinical pharmacy community as well.
What about more long-term goals for your chapter? What’s on the horizon?
We’re targeting early-career hospitalists and helping them to develop their career goals in whatever fashion they see as appropriate.
So, as someone who’s in academics, obviously research and publications are very important for me, but they’re not necessarily as important for other hospitalists. I think our early-career hospitalists are increasingly looking to incorporate things into their practice aside from direct patient care. Our members have interests in various elements of hospital medicine, including patient safety and quality improvement initiatives, clinical informatics, advocacy (especially related to the myriad aspects of health care reform), and strategies surrounding billing and denials. I think having our chapter help our members to realize some of those opportunities and develop their skills in a way that’s personally meaningful to them, as well as good for their marketability as they build their careers, would be a really positive step.
The ultimate goal of the chapter is to service members, so whatever long-term goals we have right now could definitely be fluid as time goes on.
What are some concerns of the chapter?
One area of significant discussion among hospitalists in Maryland has been global budgets. Our system of reimbursement is unique in the nation. It’s a system that aims to emphasize high-value care: the idea is to prioritize quality over quantity.
This system requires that hospitals rethink how we provide care in the inpatient setting, and how we create a continuum of care to the post-acute setting. It poses a lot of challenges, but also a lot of opportunities. Hospitalists are positioned perfectly to play a substantial role in implementing solutions.
Why might readers want to consider getting involved in their local SHM chapters?
I think it’s really beneficial to have the exposure that being involved with an SHM chapter brings – to people, to perspectives, to knowledge. There’s not really a downside to being involved with a chapter. You can take as little or as much as you want out of it, but I think most of our members find it to be a very enriching experience. Being involved in a chapter means you can have a voice, so that the chapter ends up serving you and your needs as well.
Nidhi Goel, MD, MHS, is a Med-Peds hospitalist and assistant professor of internal medicine and pediatrics at the University of Maryland, Baltimore. Since August 2017, she has been the president of the Maryland chapter of SHM.
The Hospitalist recently sat down with her to discuss some of the initiatives that the large and active Maryland chapter is focused on.
Can you talk about your background and how you became interested in hospital medicine?
I grew up in the Baltimore area, and I went to medical school at the University of Maryland in Baltimore. I trained in internal medicine and pediatrics, also at the University of Maryland. Then I joined the faculty after I finished residency in 2014. I practiced as a hospitalist in internal medicine and pediatrics and was also a teaching hospitalist.
Early in my residency, I worked with teaching hospitalists. I rotated on the hospitalist teams, and I was inspired by their perspective on taking care of patients through a lens of quality and safety. I gained a greater appreciation for the risks associated with taking care of a patient in the hospital setting, and the opportunities to mitigate those risks and provide really high quality patient care. It made me realize that was what I wanted to do – and also to teach residents and students how to do the same.
So it was a philosophical attraction to the hospitalist approach?
Yes, and intellectually I’d say that I liked taking care of really complicated, very sick patients. I found that to be interesting – and rewarding when they got better.
Tell us more about what kind of research you do.
I work primarily on projects centered on quality and safety; they involve both adult internal medicine and pediatric patients. Currently on the adult medicine side, we have a project looking at improving outcomes for sepsis in the hospital setting. On the pediatric side, I’ve done a lot of work related to throughput – trying to increase the efficiency of our admissions – and especially our discharge process. Moving patients through the system efficiently has become a significant quality issue, especially during the winter months when our volumes pick up.
How long have you been involved in the Maryland SHM chapter, and what are the rewards of participation?
Early in my residency, I got involved in the chapter because some of the hospitalist faculty I worked with were chapter officers. They believed that the chapter was a good place for residents to be exposed to research and to other hospitalists for networking and camaraderie. So they began inviting us to Maryland chapter meetings, and I found those meetings to be very enlightening – from the practical and research content related to hospital medicine, and to networking with other hospitalists.
I was invited to be part of the Maryland chapter advisory board when I was still a resident, so that I might present trainee perspectives on how the chapter could continue to grow and target some of their activities for the benefit of residents. I stayed involved with the chapter after I finished residency, and when the opportunity presented itself to become an officer, and I decided to take it. I thought serving as a chapter officer would be a really interesting chance to meet more people in the field and to continue to innovate within the chapter setting.
Tell us more about the Maryland chapter.
We are a large chapter and we’re very, very active. Around 7 or 8 years ago, the Maryland chapter reached a significant turning point because the officers that were in place at that time had a vision for building the chapter. That was a major inflexion point in how active the chapter became, leading to the kinds of activities that we do now, and the variety of memberships.
One thing that I’m super proud of our chapter for is that we’ve really tried to continue building on the diversity that is represented in our membership. We have members stretching geographically all through the Baltimore and the Washington corridor, as well as out to western Maryland and the Eastern shore. The Maryland chapter has been able to attract members from different organizations throughout the state and from a diversity of practice settings. We have active members who are not just physicians, but also a nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and clinical pharmacists. We have members from throughout the health care delivery process, which really enriches the discussion and the value of the chapter as a whole.
What kind of initiatives and programs is the chapter working on?
Every year we have an abstracts competition at our fall meeting. Whoever wins that competition is allowed to present at the national SHM conference, which is a great opportunity. We’re really pushing that competition to make it an even more robust experience.
One thing that we had heard from some of our members, and that we recognized as a need as well, was to make our career guidance a little bit more robust. To that end, we’re creating a separate job fair that is almost like an employment workshop – to help people to buff up their CVs, to talk about interviewing skills, contracts, salary negotiations, as well as exposing job candidates to various hospital groups from throughout the area. That’s something that we’re really excited about. It’s going to take a lot of work, but I think it could be a really high-yield event for our members.
We’re also encouraging our nonphysician members to take more active leadership roles in the chapter; several of our nonphysician members on our chapter advisory board, including pharmacists and physician assistants, and we are trying to make sure that we’re also liaising with some of the professional organizations that represent our nonphysician members. So, for example, the clinical pharmacist who’s on our advisory board also is president of the Maryland chapter of the Society for Hospital Pharmacists. She brings a lot of really great ideas and interesting perspectives, and she’s brought a lot of exposure of our SHM chapter to the clinical pharmacy community as well.
What about more long-term goals for your chapter? What’s on the horizon?
We’re targeting early-career hospitalists and helping them to develop their career goals in whatever fashion they see as appropriate.
So, as someone who’s in academics, obviously research and publications are very important for me, but they’re not necessarily as important for other hospitalists. I think our early-career hospitalists are increasingly looking to incorporate things into their practice aside from direct patient care. Our members have interests in various elements of hospital medicine, including patient safety and quality improvement initiatives, clinical informatics, advocacy (especially related to the myriad aspects of health care reform), and strategies surrounding billing and denials. I think having our chapter help our members to realize some of those opportunities and develop their skills in a way that’s personally meaningful to them, as well as good for their marketability as they build their careers, would be a really positive step.
The ultimate goal of the chapter is to service members, so whatever long-term goals we have right now could definitely be fluid as time goes on.
What are some concerns of the chapter?
One area of significant discussion among hospitalists in Maryland has been global budgets. Our system of reimbursement is unique in the nation. It’s a system that aims to emphasize high-value care: the idea is to prioritize quality over quantity.
This system requires that hospitals rethink how we provide care in the inpatient setting, and how we create a continuum of care to the post-acute setting. It poses a lot of challenges, but also a lot of opportunities. Hospitalists are positioned perfectly to play a substantial role in implementing solutions.
Why might readers want to consider getting involved in their local SHM chapters?
I think it’s really beneficial to have the exposure that being involved with an SHM chapter brings – to people, to perspectives, to knowledge. There’s not really a downside to being involved with a chapter. You can take as little or as much as you want out of it, but I think most of our members find it to be a very enriching experience. Being involved in a chapter means you can have a voice, so that the chapter ends up serving you and your needs as well.
Hospitalist movers and shakers – Nov. 2018
George Kasarala, MD, recently was named the hospitalist medical director at Nash UNC Health Care in Rocky Mount, N.C. Dr. Kasarala will guide Nash UNC’s team of hospitalists, a program that has partnered with Sound Physicians.
Dr. Kasarala has a wealth of hospitalist experience, serving in a variety of positions since 2012. He comes to Nash UNC from Vidant Medical Center in Greenville, N.C. Prior to that, he was the associate hospitalist program director at the Apogee Hospitalist program in Elkhart, Ind.
In addition to his medical degree from Saint Louis University, Dr. Kasarala holds a master of business administration from the University of Findlay (Ohio).
Donald W. Woodburn, MD, has been selected as the new medical director at Carolinas Primary Care in Wadesboro, S.C. The longtime internist and hospitalist will stay in his role directing primary care for the facility, which is operated by Atrium Health.
A 35-year veteran in the medical field, Dr. Woodburn most recently was medical director for AnMed Hospitalist Services in Anderson, S.C. He has been a medical director in New York, Florida, and South Carolina since earning his medical degree from Howard University in Washington.
Rita Goyal, MD, has been hired as chief medical officer of ConcertCare, a health care technology company based in Birmingham, Ala. Dr. Goyal has expertise in both medicine and business was cited as the key to her appointment. She founded a Web-based medical consultation business in 2017, virtualMDvisit.net.
Dr. Goyal is an academic hospitalist at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, and will continue to serve as a hospitalist and in the University’s urgent care system.
Nirupma Sharma, MD, has been named chief of the newly minted division of pediatric hospital medicine at Augusta (Ga.) University Health. Dr. Sharma will oversee the pediatric hospitalist staff, including education, research, and clinical assistance.
Dr. Sharma has been the medical director of the 4C unit at Children’s Hospital of Georgia in Augusta. She also has served as associate director of the Medical College of Georgia’s department of pediatrics clerkship program.
Vineet Arora, MD, MHM, was recently named one of the top 10 doctors to follow on Twitter by Becker’s Hospital Review. Dr. Arora is an academic hospitalist at University of Chicago Medicine.
Using the hashtag #meded, Dr. Arora provides a wealth of medical knowledge on Twitter, currently boasting more than 29,000 followers on that social media platform. She also serves as the Journal of Hospital Medicine’s deputy social media editor, and blogs about topics trending in resident education.
BUSINESS MOVES
Aspirus Iron River (Mich.) Hospital has partnered with iNDIGO Health Partners to create a telehealth hospitalist program at night. iNDIGO, a private hospitalist group, will utilize two-way video to treat Aspirus patients during overnight hours.
The telehealth providers with iNDIGO are part of the staff at Aspirus Iron River and are familiar with the facility’s procedures. The remote physicians will be in contact with staff at the hospital, providing direction after meeting with patients via the video system.
The Hospitals of Providence Memorial Campus in El Paso, Tex., intends to have specialists on site at all times for expectant mothers after recently adopting an obstetric hospitalist program. The OB hospitalists will be available to treat patient concerns and medical emergencies that occur outside of normal hours for patients’ primary obstetricians.
All OB hospitalists will be board-certified OB physicians. The goal is to decrease wait times for expectant mothers, who can receive immediate assessments and treatment upon arrival in the emergency department.
George Kasarala, MD, recently was named the hospitalist medical director at Nash UNC Health Care in Rocky Mount, N.C. Dr. Kasarala will guide Nash UNC’s team of hospitalists, a program that has partnered with Sound Physicians.
Dr. Kasarala has a wealth of hospitalist experience, serving in a variety of positions since 2012. He comes to Nash UNC from Vidant Medical Center in Greenville, N.C. Prior to that, he was the associate hospitalist program director at the Apogee Hospitalist program in Elkhart, Ind.
In addition to his medical degree from Saint Louis University, Dr. Kasarala holds a master of business administration from the University of Findlay (Ohio).
Donald W. Woodburn, MD, has been selected as the new medical director at Carolinas Primary Care in Wadesboro, S.C. The longtime internist and hospitalist will stay in his role directing primary care for the facility, which is operated by Atrium Health.
A 35-year veteran in the medical field, Dr. Woodburn most recently was medical director for AnMed Hospitalist Services in Anderson, S.C. He has been a medical director in New York, Florida, and South Carolina since earning his medical degree from Howard University in Washington.
Rita Goyal, MD, has been hired as chief medical officer of ConcertCare, a health care technology company based in Birmingham, Ala. Dr. Goyal has expertise in both medicine and business was cited as the key to her appointment. She founded a Web-based medical consultation business in 2017, virtualMDvisit.net.
Dr. Goyal is an academic hospitalist at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, and will continue to serve as a hospitalist and in the University’s urgent care system.
Nirupma Sharma, MD, has been named chief of the newly minted division of pediatric hospital medicine at Augusta (Ga.) University Health. Dr. Sharma will oversee the pediatric hospitalist staff, including education, research, and clinical assistance.
Dr. Sharma has been the medical director of the 4C unit at Children’s Hospital of Georgia in Augusta. She also has served as associate director of the Medical College of Georgia’s department of pediatrics clerkship program.
Vineet Arora, MD, MHM, was recently named one of the top 10 doctors to follow on Twitter by Becker’s Hospital Review. Dr. Arora is an academic hospitalist at University of Chicago Medicine.
Using the hashtag #meded, Dr. Arora provides a wealth of medical knowledge on Twitter, currently boasting more than 29,000 followers on that social media platform. She also serves as the Journal of Hospital Medicine’s deputy social media editor, and blogs about topics trending in resident education.
BUSINESS MOVES
Aspirus Iron River (Mich.) Hospital has partnered with iNDIGO Health Partners to create a telehealth hospitalist program at night. iNDIGO, a private hospitalist group, will utilize two-way video to treat Aspirus patients during overnight hours.
The telehealth providers with iNDIGO are part of the staff at Aspirus Iron River and are familiar with the facility’s procedures. The remote physicians will be in contact with staff at the hospital, providing direction after meeting with patients via the video system.
The Hospitals of Providence Memorial Campus in El Paso, Tex., intends to have specialists on site at all times for expectant mothers after recently adopting an obstetric hospitalist program. The OB hospitalists will be available to treat patient concerns and medical emergencies that occur outside of normal hours for patients’ primary obstetricians.
All OB hospitalists will be board-certified OB physicians. The goal is to decrease wait times for expectant mothers, who can receive immediate assessments and treatment upon arrival in the emergency department.
George Kasarala, MD, recently was named the hospitalist medical director at Nash UNC Health Care in Rocky Mount, N.C. Dr. Kasarala will guide Nash UNC’s team of hospitalists, a program that has partnered with Sound Physicians.
Dr. Kasarala has a wealth of hospitalist experience, serving in a variety of positions since 2012. He comes to Nash UNC from Vidant Medical Center in Greenville, N.C. Prior to that, he was the associate hospitalist program director at the Apogee Hospitalist program in Elkhart, Ind.
In addition to his medical degree from Saint Louis University, Dr. Kasarala holds a master of business administration from the University of Findlay (Ohio).
Donald W. Woodburn, MD, has been selected as the new medical director at Carolinas Primary Care in Wadesboro, S.C. The longtime internist and hospitalist will stay in his role directing primary care for the facility, which is operated by Atrium Health.
A 35-year veteran in the medical field, Dr. Woodburn most recently was medical director for AnMed Hospitalist Services in Anderson, S.C. He has been a medical director in New York, Florida, and South Carolina since earning his medical degree from Howard University in Washington.
Rita Goyal, MD, has been hired as chief medical officer of ConcertCare, a health care technology company based in Birmingham, Ala. Dr. Goyal has expertise in both medicine and business was cited as the key to her appointment. She founded a Web-based medical consultation business in 2017, virtualMDvisit.net.
Dr. Goyal is an academic hospitalist at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, and will continue to serve as a hospitalist and in the University’s urgent care system.
Nirupma Sharma, MD, has been named chief of the newly minted division of pediatric hospital medicine at Augusta (Ga.) University Health. Dr. Sharma will oversee the pediatric hospitalist staff, including education, research, and clinical assistance.
Dr. Sharma has been the medical director of the 4C unit at Children’s Hospital of Georgia in Augusta. She also has served as associate director of the Medical College of Georgia’s department of pediatrics clerkship program.
Vineet Arora, MD, MHM, was recently named one of the top 10 doctors to follow on Twitter by Becker’s Hospital Review. Dr. Arora is an academic hospitalist at University of Chicago Medicine.
Using the hashtag #meded, Dr. Arora provides a wealth of medical knowledge on Twitter, currently boasting more than 29,000 followers on that social media platform. She also serves as the Journal of Hospital Medicine’s deputy social media editor, and blogs about topics trending in resident education.
BUSINESS MOVES
Aspirus Iron River (Mich.) Hospital has partnered with iNDIGO Health Partners to create a telehealth hospitalist program at night. iNDIGO, a private hospitalist group, will utilize two-way video to treat Aspirus patients during overnight hours.
The telehealth providers with iNDIGO are part of the staff at Aspirus Iron River and are familiar with the facility’s procedures. The remote physicians will be in contact with staff at the hospital, providing direction after meeting with patients via the video system.
The Hospitals of Providence Memorial Campus in El Paso, Tex., intends to have specialists on site at all times for expectant mothers after recently adopting an obstetric hospitalist program. The OB hospitalists will be available to treat patient concerns and medical emergencies that occur outside of normal hours for patients’ primary obstetricians.
All OB hospitalists will be board-certified OB physicians. The goal is to decrease wait times for expectant mothers, who can receive immediate assessments and treatment upon arrival in the emergency department.
Hospitalists can meet the demand for physician executives
HM provides “foundational leadership skills”
Hospitals and health systems are increasingly looking to physicians to provide leadership at the most senior executive level. While the chief medical officer (CMO) or similar role has given physicians a seat at the executive table at many organizations, physicians are also being sought for the CEO role at the head of that table.
A commonly referenced study from 2011 by Amanda Goodall, MD, in Social Science & Medicine concluded that, among a cohort of highly ranked hospitals, overall quality metrics were approximately 25% higher in hospitals where a physician was CEO, in comparison to hospitals with non-physician CEOs (2011 Aug;73[4]:535-9). In addition, new positions at both the hospital and health system level are coming into existence: Examples include chief (or VP) of population health, chief innovation officer, chief quality officer, chief patient experience officer, and others.
There is every reason to think that these senior executive physician roles can – and in many cases perhaps should – be filled by hospitalists. Hospital medicine is an ideal “proving ground” for future physician executives and leaders. I believe that the best practitioners of hospital medicine are also the best candidates for hospital, health care, and health system physician executive leadership, because many of the characteristics essential for success as an executive are the same characteristics that are essential for success as a hospitalist. Strong candidates should have the following characteristics:
- A patient-centered perspective. Perhaps the most important characteristic of a leader is empathy. To appreciate the complex, and often (if not usual) challenging emotional states of our patients keeps us connected at the most fundamental, human level to the work we do and to our patients and families. Empathy can – and should – extend to fellow caregivers as well, and allows us to practice and lead teams in the most human of professions. No leader – in health care, anyway – can last long without being able to demonstrate empathy, through words and behavior.
- A systems-based practice: A hospitalist must be able to have a foot in each of two canoes – to be able to see each patient and their family individually and develop preference-based plans of care, and also to be able to focus on process, structure, and outcomes for the hospital system as a whole. The former trait is imbued in us during training and is the critical foundation for the patient-physician relationship. The latter, however, is something different entirely and reflects an ability to have perspective on the entire ecosystem of care – and apply principles of process and quality improvement to achieve forward looking results. That’s leadership.
- Team leadership: Another fundamental attribute of leaders is to assemble a talented and diverse team around an objective, and then to delegate both tasks and their ownership, deferring to expertise. Hospitalists – the best ones, anyway – similarly recognize that for the vast majority of a patient’s hospital stay, the most important caregiver in a patient’s care is someone other than themselves. At any given time, it might be the nurse, aide, pharmacist, care manager, transporter, radiology tech, urologist, housekeeper, surgical resident, or anyone involved in that patient’s care. The hospitalist’s greatest value is in developing the plan of care with the patient and their family, and then communicating – and therefore delegating – that plan to individuals with the expertise to execute that plan. I believe the biggest difficulty hospitalists have in assuming leadership roles is getting out of the comfortable weeds of daily clinical operations and instead focusing on goals, strategies, and teams to accomplish them. The best hospitalists are doing this already as part of their daily care.
- The ability to manage relationships: Hospitalists manage and work among a team of diverse talents. They also often have accountability relationships to a myriad of clinical and administrative leaders in the hospital, each of whom may be in a position of authority to place demands on the hospitalists: A partial list might include the CEO, the chief medical officer, chief nurse, chief of staff, other medical staff departments, academic leaders, and of course, patients and their families. Functioning in a “matrixed” organization – in which lines of authority can go in many directions, depending on the situation – is standard fare, even at the executive level, and the key competency is open and frequent communication.
- Experience: Already, hospitalists assume leadership roles in their hospitals – leaders in quality, medical informatics, patient experience, and continuous improvement. In these roles, physicians work with senior executives and other hospital leaders to both set goals and implement strategies, providing visibility and working relationships that can be helpful to aspiring leaders.
Perhaps more so than most other specialties, then, hospitalists demonstrate foundational leadership skills in their day-to-day practice – an ideal start to a leadership path. This is not to say or suggest that a career devoted purely to clinical practice is somehow inferior – far from it. However, as health care organizations turn to the medical community to provider leadership, hospitalists are well positioned to develop and be developed as executive leaders.
How can the Society of Hospital Medicine help? While management degrees become a common pathway for many, some health systems and professional organizations support their membership with a leadership development curriculum which may be a better place to start. In my opinion, SHM provides one of the most thorough and relevant experiences available. The SHM Leadership Academy focuses on developing a broad set of additional leadership competencies across a spectrum of experience. The format varies depending on the course, but all rely heavily upon experienced hospitalist leaders – in fact, many current and former Board members and officers volunteer their time to facilitate and teach at the Academy, including at the entry level. It’s a powerful way to learn from others who have started walking the leadership path.
Dr. Harte is a past president of SHM and president of Cleveland Clinic Akron General and Southern Region.
HM provides “foundational leadership skills”
HM provides “foundational leadership skills”
Hospitals and health systems are increasingly looking to physicians to provide leadership at the most senior executive level. While the chief medical officer (CMO) or similar role has given physicians a seat at the executive table at many organizations, physicians are also being sought for the CEO role at the head of that table.
A commonly referenced study from 2011 by Amanda Goodall, MD, in Social Science & Medicine concluded that, among a cohort of highly ranked hospitals, overall quality metrics were approximately 25% higher in hospitals where a physician was CEO, in comparison to hospitals with non-physician CEOs (2011 Aug;73[4]:535-9). In addition, new positions at both the hospital and health system level are coming into existence: Examples include chief (or VP) of population health, chief innovation officer, chief quality officer, chief patient experience officer, and others.
There is every reason to think that these senior executive physician roles can – and in many cases perhaps should – be filled by hospitalists. Hospital medicine is an ideal “proving ground” for future physician executives and leaders. I believe that the best practitioners of hospital medicine are also the best candidates for hospital, health care, and health system physician executive leadership, because many of the characteristics essential for success as an executive are the same characteristics that are essential for success as a hospitalist. Strong candidates should have the following characteristics:
- A patient-centered perspective. Perhaps the most important characteristic of a leader is empathy. To appreciate the complex, and often (if not usual) challenging emotional states of our patients keeps us connected at the most fundamental, human level to the work we do and to our patients and families. Empathy can – and should – extend to fellow caregivers as well, and allows us to practice and lead teams in the most human of professions. No leader – in health care, anyway – can last long without being able to demonstrate empathy, through words and behavior.
- A systems-based practice: A hospitalist must be able to have a foot in each of two canoes – to be able to see each patient and their family individually and develop preference-based plans of care, and also to be able to focus on process, structure, and outcomes for the hospital system as a whole. The former trait is imbued in us during training and is the critical foundation for the patient-physician relationship. The latter, however, is something different entirely and reflects an ability to have perspective on the entire ecosystem of care – and apply principles of process and quality improvement to achieve forward looking results. That’s leadership.
- Team leadership: Another fundamental attribute of leaders is to assemble a talented and diverse team around an objective, and then to delegate both tasks and their ownership, deferring to expertise. Hospitalists – the best ones, anyway – similarly recognize that for the vast majority of a patient’s hospital stay, the most important caregiver in a patient’s care is someone other than themselves. At any given time, it might be the nurse, aide, pharmacist, care manager, transporter, radiology tech, urologist, housekeeper, surgical resident, or anyone involved in that patient’s care. The hospitalist’s greatest value is in developing the plan of care with the patient and their family, and then communicating – and therefore delegating – that plan to individuals with the expertise to execute that plan. I believe the biggest difficulty hospitalists have in assuming leadership roles is getting out of the comfortable weeds of daily clinical operations and instead focusing on goals, strategies, and teams to accomplish them. The best hospitalists are doing this already as part of their daily care.
- The ability to manage relationships: Hospitalists manage and work among a team of diverse talents. They also often have accountability relationships to a myriad of clinical and administrative leaders in the hospital, each of whom may be in a position of authority to place demands on the hospitalists: A partial list might include the CEO, the chief medical officer, chief nurse, chief of staff, other medical staff departments, academic leaders, and of course, patients and their families. Functioning in a “matrixed” organization – in which lines of authority can go in many directions, depending on the situation – is standard fare, even at the executive level, and the key competency is open and frequent communication.
- Experience: Already, hospitalists assume leadership roles in their hospitals – leaders in quality, medical informatics, patient experience, and continuous improvement. In these roles, physicians work with senior executives and other hospital leaders to both set goals and implement strategies, providing visibility and working relationships that can be helpful to aspiring leaders.
Perhaps more so than most other specialties, then, hospitalists demonstrate foundational leadership skills in their day-to-day practice – an ideal start to a leadership path. This is not to say or suggest that a career devoted purely to clinical practice is somehow inferior – far from it. However, as health care organizations turn to the medical community to provider leadership, hospitalists are well positioned to develop and be developed as executive leaders.
How can the Society of Hospital Medicine help? While management degrees become a common pathway for many, some health systems and professional organizations support their membership with a leadership development curriculum which may be a better place to start. In my opinion, SHM provides one of the most thorough and relevant experiences available. The SHM Leadership Academy focuses on developing a broad set of additional leadership competencies across a spectrum of experience. The format varies depending on the course, but all rely heavily upon experienced hospitalist leaders – in fact, many current and former Board members and officers volunteer their time to facilitate and teach at the Academy, including at the entry level. It’s a powerful way to learn from others who have started walking the leadership path.
Dr. Harte is a past president of SHM and president of Cleveland Clinic Akron General and Southern Region.
Hospitals and health systems are increasingly looking to physicians to provide leadership at the most senior executive level. While the chief medical officer (CMO) or similar role has given physicians a seat at the executive table at many organizations, physicians are also being sought for the CEO role at the head of that table.
A commonly referenced study from 2011 by Amanda Goodall, MD, in Social Science & Medicine concluded that, among a cohort of highly ranked hospitals, overall quality metrics were approximately 25% higher in hospitals where a physician was CEO, in comparison to hospitals with non-physician CEOs (2011 Aug;73[4]:535-9). In addition, new positions at both the hospital and health system level are coming into existence: Examples include chief (or VP) of population health, chief innovation officer, chief quality officer, chief patient experience officer, and others.
There is every reason to think that these senior executive physician roles can – and in many cases perhaps should – be filled by hospitalists. Hospital medicine is an ideal “proving ground” for future physician executives and leaders. I believe that the best practitioners of hospital medicine are also the best candidates for hospital, health care, and health system physician executive leadership, because many of the characteristics essential for success as an executive are the same characteristics that are essential for success as a hospitalist. Strong candidates should have the following characteristics:
- A patient-centered perspective. Perhaps the most important characteristic of a leader is empathy. To appreciate the complex, and often (if not usual) challenging emotional states of our patients keeps us connected at the most fundamental, human level to the work we do and to our patients and families. Empathy can – and should – extend to fellow caregivers as well, and allows us to practice and lead teams in the most human of professions. No leader – in health care, anyway – can last long without being able to demonstrate empathy, through words and behavior.
- A systems-based practice: A hospitalist must be able to have a foot in each of two canoes – to be able to see each patient and their family individually and develop preference-based plans of care, and also to be able to focus on process, structure, and outcomes for the hospital system as a whole. The former trait is imbued in us during training and is the critical foundation for the patient-physician relationship. The latter, however, is something different entirely and reflects an ability to have perspective on the entire ecosystem of care – and apply principles of process and quality improvement to achieve forward looking results. That’s leadership.
- Team leadership: Another fundamental attribute of leaders is to assemble a talented and diverse team around an objective, and then to delegate both tasks and their ownership, deferring to expertise. Hospitalists – the best ones, anyway – similarly recognize that for the vast majority of a patient’s hospital stay, the most important caregiver in a patient’s care is someone other than themselves. At any given time, it might be the nurse, aide, pharmacist, care manager, transporter, radiology tech, urologist, housekeeper, surgical resident, or anyone involved in that patient’s care. The hospitalist’s greatest value is in developing the plan of care with the patient and their family, and then communicating – and therefore delegating – that plan to individuals with the expertise to execute that plan. I believe the biggest difficulty hospitalists have in assuming leadership roles is getting out of the comfortable weeds of daily clinical operations and instead focusing on goals, strategies, and teams to accomplish them. The best hospitalists are doing this already as part of their daily care.
- The ability to manage relationships: Hospitalists manage and work among a team of diverse talents. They also often have accountability relationships to a myriad of clinical and administrative leaders in the hospital, each of whom may be in a position of authority to place demands on the hospitalists: A partial list might include the CEO, the chief medical officer, chief nurse, chief of staff, other medical staff departments, academic leaders, and of course, patients and their families. Functioning in a “matrixed” organization – in which lines of authority can go in many directions, depending on the situation – is standard fare, even at the executive level, and the key competency is open and frequent communication.
- Experience: Already, hospitalists assume leadership roles in their hospitals – leaders in quality, medical informatics, patient experience, and continuous improvement. In these roles, physicians work with senior executives and other hospital leaders to both set goals and implement strategies, providing visibility and working relationships that can be helpful to aspiring leaders.
Perhaps more so than most other specialties, then, hospitalists demonstrate foundational leadership skills in their day-to-day practice – an ideal start to a leadership path. This is not to say or suggest that a career devoted purely to clinical practice is somehow inferior – far from it. However, as health care organizations turn to the medical community to provider leadership, hospitalists are well positioned to develop and be developed as executive leaders.
How can the Society of Hospital Medicine help? While management degrees become a common pathway for many, some health systems and professional organizations support their membership with a leadership development curriculum which may be a better place to start. In my opinion, SHM provides one of the most thorough and relevant experiences available. The SHM Leadership Academy focuses on developing a broad set of additional leadership competencies across a spectrum of experience. The format varies depending on the course, but all rely heavily upon experienced hospitalist leaders – in fact, many current and former Board members and officers volunteer their time to facilitate and teach at the Academy, including at the entry level. It’s a powerful way to learn from others who have started walking the leadership path.
Dr. Harte is a past president of SHM and president of Cleveland Clinic Akron General and Southern Region.
What is the ‘meta’ in ‘metaleadership’?
The knowns and the unknowns
Over the course of a career, it is not uncommon for people to become narrower and more focused in their work purview and interests. Competence in select procedures and practices imparts confidence and reliability in performance and results. One develops a reputation for those skills and capabilities, and others call upon them.
Rewards and incentives encourage advancement and promotion along established career paths, further accelerating specialization and concentration. At the top of your game, you advocate for and ease into your comfort zone. That zone is defined by the knowns of practice and the certainties they provide.
For those who prefer to practice in the confines of a narrow clinical sphere, that strategy could be the pathway to career success.
However, for those promoted to leadership positions, the inward and insulated focus today is counterproductive and even dangerous. Many times, physicians advance to a senior position because it is the next step in a preset career ladder, the reward for acumen in clinical skills, or simply out of boredom, with hope for a new landscape and a higher wage. But just because one has a high rank or impressive title does not mean that one is fulfilling the mandates of leadership. It takes more than that. You must be attuned to what is known and unknown in building stability and progress for those you lead.
A brief historic angle: For years, medicine occupied a sweet spot within the health care system. The profession protected its perks and privileges deriving from its untouchable status. With it came superiority, dominance, and protectionism. It was an inward, parochial focus of thinking, status, and reward. The problem was: This insulated mindset prompted a blind spot. The profession missed changes and transformation that were occurring just beyond the comfort zone. Those changes were unknowns in planning and perspective.
In the 1990s, medicine as a whole woke up to calls for change and a new order. The rise of the hospitalist was in part an outgrowth of that wake-up call. It reshaped power structures, status, and lucrative business arrangements within the profession. For many, the sweet spot soured.
The problem with collapsing into a sweet spot today is that so much is changing: all that is known and much that is unknown. Finances, technology, and demand are all in flux. The health care system finds itself in a quantity/quality/cost paradox. Volume accelerates, but at what cost to quality and morale? If someone or something can accomplish similar outcomes at less cost, why not go with the cheaper option? These questions can best be addressed by seeing them in the context of larger changes happening in the health system.
A new view for leaders
The “meta” in metaleadership hopes to provide a broader, disciplined slant on this phenomenon. That prefix – used to modify many concepts and terms – refers to a wider, more expansive view or a more comprehensive and transcendent perch on a topic. A “meta-” prefix invites a critical analysis of the original topic with the addition of new perspectives and insights, as with a meta-analysis.
Why then the need now for a “meta” view among health care leaders? It is easy in the course of career progression to lose track of the bigger picture of what you are doing and how it fits into changes occurring in society and for the profession. Even if your focus is on a particular clinical procedure, how does what you are doing fit into larger metatrends and changes? How might you tangibly contribute to the evolution of those trends? If you are in a leadership position, how do you fit your practice or department into the bigger picture? How might this enterprise perspective speak to your career trajectory?
To inform these questions, build your platform for knowns and unknowns. There are four combinations in the “known-unknown” equation. They are each important and provocative for leaders. Your awareness of them prompts curiosity about “meta” problems and problem solving.
- There are the “known-knowns”: what you know and you know you know it. The problem here is that you may assume that you know something that you don’t.
- There are the “known-unknowns”: Clear and curious about what you need to learn, you develop pathways to find out.
- There are the “unknown-knowns”: what others know and you don’t; a point of vulnerability if you are not careful to discover and figure this out.
- And finally, the “unknown-unknowns”: the mysteries of what could lie ahead that no one yet fully comprehends.
The task for the “metaleader”? Be clear on what you know, and seek always to learn and discover those unknowns. The better you factor them into your assessments, the better you are able to shape trends and the less likely you are to be overrun by them.
Just as you become more specialized with time, as a leader, you can leverage your experience to widen your lens and see more, understand it better, and – with that knowledge – chart a pathway that corresponds with where the health system is going. With this wider mindset, you fashion a fresh and innovative perspective on what is happening with health care and the options for constructively addressing new constraints and opportunities. You think big, reach far, and with this broader understanding, foment a lively set of perspectives and options that would otherwise not be available for those you lead. And when seen as a puzzle to learn and solve, the “meta” perch provides an engaging angle on the game of health care change. You too can be a player.
Dr. Marcus is coauthor of “Renegotiating Health Care: Resolving Conflict to Build Collaboration,” 2nd ed. (San Francisco: Jossey-Bass Publishers, 2011) and is director of the program for health care negotiation and conflict resolution at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. Dr. Marcus teaches regularly in the SHM Leadership Academy. He can be reached at [email protected].
The knowns and the unknowns
The knowns and the unknowns
Over the course of a career, it is not uncommon for people to become narrower and more focused in their work purview and interests. Competence in select procedures and practices imparts confidence and reliability in performance and results. One develops a reputation for those skills and capabilities, and others call upon them.
Rewards and incentives encourage advancement and promotion along established career paths, further accelerating specialization and concentration. At the top of your game, you advocate for and ease into your comfort zone. That zone is defined by the knowns of practice and the certainties they provide.
For those who prefer to practice in the confines of a narrow clinical sphere, that strategy could be the pathway to career success.
However, for those promoted to leadership positions, the inward and insulated focus today is counterproductive and even dangerous. Many times, physicians advance to a senior position because it is the next step in a preset career ladder, the reward for acumen in clinical skills, or simply out of boredom, with hope for a new landscape and a higher wage. But just because one has a high rank or impressive title does not mean that one is fulfilling the mandates of leadership. It takes more than that. You must be attuned to what is known and unknown in building stability and progress for those you lead.
A brief historic angle: For years, medicine occupied a sweet spot within the health care system. The profession protected its perks and privileges deriving from its untouchable status. With it came superiority, dominance, and protectionism. It was an inward, parochial focus of thinking, status, and reward. The problem was: This insulated mindset prompted a blind spot. The profession missed changes and transformation that were occurring just beyond the comfort zone. Those changes were unknowns in planning and perspective.
In the 1990s, medicine as a whole woke up to calls for change and a new order. The rise of the hospitalist was in part an outgrowth of that wake-up call. It reshaped power structures, status, and lucrative business arrangements within the profession. For many, the sweet spot soured.
The problem with collapsing into a sweet spot today is that so much is changing: all that is known and much that is unknown. Finances, technology, and demand are all in flux. The health care system finds itself in a quantity/quality/cost paradox. Volume accelerates, but at what cost to quality and morale? If someone or something can accomplish similar outcomes at less cost, why not go with the cheaper option? These questions can best be addressed by seeing them in the context of larger changes happening in the health system.
A new view for leaders
The “meta” in metaleadership hopes to provide a broader, disciplined slant on this phenomenon. That prefix – used to modify many concepts and terms – refers to a wider, more expansive view or a more comprehensive and transcendent perch on a topic. A “meta-” prefix invites a critical analysis of the original topic with the addition of new perspectives and insights, as with a meta-analysis.
Why then the need now for a “meta” view among health care leaders? It is easy in the course of career progression to lose track of the bigger picture of what you are doing and how it fits into changes occurring in society and for the profession. Even if your focus is on a particular clinical procedure, how does what you are doing fit into larger metatrends and changes? How might you tangibly contribute to the evolution of those trends? If you are in a leadership position, how do you fit your practice or department into the bigger picture? How might this enterprise perspective speak to your career trajectory?
To inform these questions, build your platform for knowns and unknowns. There are four combinations in the “known-unknown” equation. They are each important and provocative for leaders. Your awareness of them prompts curiosity about “meta” problems and problem solving.
- There are the “known-knowns”: what you know and you know you know it. The problem here is that you may assume that you know something that you don’t.
- There are the “known-unknowns”: Clear and curious about what you need to learn, you develop pathways to find out.
- There are the “unknown-knowns”: what others know and you don’t; a point of vulnerability if you are not careful to discover and figure this out.
- And finally, the “unknown-unknowns”: the mysteries of what could lie ahead that no one yet fully comprehends.
The task for the “metaleader”? Be clear on what you know, and seek always to learn and discover those unknowns. The better you factor them into your assessments, the better you are able to shape trends and the less likely you are to be overrun by them.
Just as you become more specialized with time, as a leader, you can leverage your experience to widen your lens and see more, understand it better, and – with that knowledge – chart a pathway that corresponds with where the health system is going. With this wider mindset, you fashion a fresh and innovative perspective on what is happening with health care and the options for constructively addressing new constraints and opportunities. You think big, reach far, and with this broader understanding, foment a lively set of perspectives and options that would otherwise not be available for those you lead. And when seen as a puzzle to learn and solve, the “meta” perch provides an engaging angle on the game of health care change. You too can be a player.
Dr. Marcus is coauthor of “Renegotiating Health Care: Resolving Conflict to Build Collaboration,” 2nd ed. (San Francisco: Jossey-Bass Publishers, 2011) and is director of the program for health care negotiation and conflict resolution at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. Dr. Marcus teaches regularly in the SHM Leadership Academy. He can be reached at [email protected].
Over the course of a career, it is not uncommon for people to become narrower and more focused in their work purview and interests. Competence in select procedures and practices imparts confidence and reliability in performance and results. One develops a reputation for those skills and capabilities, and others call upon them.
Rewards and incentives encourage advancement and promotion along established career paths, further accelerating specialization and concentration. At the top of your game, you advocate for and ease into your comfort zone. That zone is defined by the knowns of practice and the certainties they provide.
For those who prefer to practice in the confines of a narrow clinical sphere, that strategy could be the pathway to career success.
However, for those promoted to leadership positions, the inward and insulated focus today is counterproductive and even dangerous. Many times, physicians advance to a senior position because it is the next step in a preset career ladder, the reward for acumen in clinical skills, or simply out of boredom, with hope for a new landscape and a higher wage. But just because one has a high rank or impressive title does not mean that one is fulfilling the mandates of leadership. It takes more than that. You must be attuned to what is known and unknown in building stability and progress for those you lead.
A brief historic angle: For years, medicine occupied a sweet spot within the health care system. The profession protected its perks and privileges deriving from its untouchable status. With it came superiority, dominance, and protectionism. It was an inward, parochial focus of thinking, status, and reward. The problem was: This insulated mindset prompted a blind spot. The profession missed changes and transformation that were occurring just beyond the comfort zone. Those changes were unknowns in planning and perspective.
In the 1990s, medicine as a whole woke up to calls for change and a new order. The rise of the hospitalist was in part an outgrowth of that wake-up call. It reshaped power structures, status, and lucrative business arrangements within the profession. For many, the sweet spot soured.
The problem with collapsing into a sweet spot today is that so much is changing: all that is known and much that is unknown. Finances, technology, and demand are all in flux. The health care system finds itself in a quantity/quality/cost paradox. Volume accelerates, but at what cost to quality and morale? If someone or something can accomplish similar outcomes at less cost, why not go with the cheaper option? These questions can best be addressed by seeing them in the context of larger changes happening in the health system.
A new view for leaders
The “meta” in metaleadership hopes to provide a broader, disciplined slant on this phenomenon. That prefix – used to modify many concepts and terms – refers to a wider, more expansive view or a more comprehensive and transcendent perch on a topic. A “meta-” prefix invites a critical analysis of the original topic with the addition of new perspectives and insights, as with a meta-analysis.
Why then the need now for a “meta” view among health care leaders? It is easy in the course of career progression to lose track of the bigger picture of what you are doing and how it fits into changes occurring in society and for the profession. Even if your focus is on a particular clinical procedure, how does what you are doing fit into larger metatrends and changes? How might you tangibly contribute to the evolution of those trends? If you are in a leadership position, how do you fit your practice or department into the bigger picture? How might this enterprise perspective speak to your career trajectory?
To inform these questions, build your platform for knowns and unknowns. There are four combinations in the “known-unknown” equation. They are each important and provocative for leaders. Your awareness of them prompts curiosity about “meta” problems and problem solving.
- There are the “known-knowns”: what you know and you know you know it. The problem here is that you may assume that you know something that you don’t.
- There are the “known-unknowns”: Clear and curious about what you need to learn, you develop pathways to find out.
- There are the “unknown-knowns”: what others know and you don’t; a point of vulnerability if you are not careful to discover and figure this out.
- And finally, the “unknown-unknowns”: the mysteries of what could lie ahead that no one yet fully comprehends.
The task for the “metaleader”? Be clear on what you know, and seek always to learn and discover those unknowns. The better you factor them into your assessments, the better you are able to shape trends and the less likely you are to be overrun by them.
Just as you become more specialized with time, as a leader, you can leverage your experience to widen your lens and see more, understand it better, and – with that knowledge – chart a pathway that corresponds with where the health system is going. With this wider mindset, you fashion a fresh and innovative perspective on what is happening with health care and the options for constructively addressing new constraints and opportunities. You think big, reach far, and with this broader understanding, foment a lively set of perspectives and options that would otherwise not be available for those you lead. And when seen as a puzzle to learn and solve, the “meta” perch provides an engaging angle on the game of health care change. You too can be a player.
Dr. Marcus is coauthor of “Renegotiating Health Care: Resolving Conflict to Build Collaboration,” 2nd ed. (San Francisco: Jossey-Bass Publishers, 2011) and is director of the program for health care negotiation and conflict resolution at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. Dr. Marcus teaches regularly in the SHM Leadership Academy. He can be reached at [email protected].
ASH releases new VTE guidelines
The new guidelines, released on Nov. 27, contain more than 150 individual recommendations, including sections devoted to managing venous thromboembolism (VTE) during pregnancy and in pediatric patients. Guideline highlights cited by some of the writing-panel participants included a high reliance on low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) agents as the preferred treatment for many patients, reliance on the D-dimer test to rule out VTE in patients with a low pretest probability of disease, and reliance on the 4Ts score to identify patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia.
The guidelines took more than 3 years to develop, an effort that began in 2015.
An updated set of VTE guidelines were needed because clinicians now have a “greater understanding of risk factors” for VTE as well as having “more options available for treating VTE, including new medications,” Adam C. Cuker, MD, cochair of the guideline-writing group and a hematologist and thrombosis specialist at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said during a webcast to unveil the new guidelines.
Prevention
For preventing VTE in hospitalized medical patients the guidelines recommended initial assessment of the patient’s risk for both VTE and bleeding. Patients with a high bleeding risk who need VTE prevention should preferentially receive mechanical prophylaxis, either compression stockings or pneumatic sleeves. But in patients with a high VTE risk and an “acceptable” bleeding risk, prophylaxis with an anticoagulant is preferred over mechanical measures, said Mary Cushman, MD, professor and medical director of the thrombosis and hemostasis program at the University of Vermont, Burlington.
For prevention of VTE in medical inpatients, LMWH is preferred over unfractionated heparin because of its once-daily dosing and fewer complications, said Dr. Cushman, a member of the writing group. The panel also endorsed LMWH over a direct-acting oral anticoagulant, both during hospitalization and following discharge. The guidelines for prevention in medical patients explicitly “recommended against” using a direct-acting oral anticoagulant “over other treatments” both for hospitalized medical patients and after discharge, and the guidelines further recommend against extended prophylaxis after discharge with any other anticoagulant.
Another important takeaway from the prevention section was a statement that combining both mechanical and medical prophylaxis was not needed for medical inpatients. And once patients are discharged, if they take a long air trip they have no need for compression stockings or aspirin if their risk for thrombosis is not elevated. People with a “substantially increased” thrombosis risk “may benefit” from compression stockings or treatment with LMWH, Dr. Cushman said.
Diagnosis
For diagnosis, Wendy Lim, MD, highlighted the need for first categorizing patients as having a low or high probability for VTE, a judgment that can aid the accuracy of the diagnosis and helps avoid unnecessary testing.
For patients with low pretest probability, the guidelines recommended the D-dimer test as the best first step. Further testing isn’t needed when the D-dimer is negative, noted Dr. Lim, a hematologist and professor at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont.
The guidelines also recommended using ventilation-perfusion scintigraphy (V/Q scan) for imaging a pulmonary embolism over a CT scan, which uses more radiation. But V/Q scans are not ideal for assessing older patients or patients with lung disease, Dr. Lim cautioned.
Management
Management of VTE should occur, when feasible, through a specialized anticoagulation management service center, which can provide care that is best suited to the complexities of anticoagulation therapy. But it’s a level of care that many U.S. patients don’t currently receive and hence is an area ripe for growth, said Daniel M. Witt, PharmD, professor and vice-chair of pharmacotherapy at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City.
The guidelines recommended against bridging therapy with LMWH for most patients who need to stop warfarin when undergoing an invasive procedure. The guidelines also called for “thoughtful” use of anticoagulant reversal agents and advised that patients who survive a major bleed while on anticoagulation should often resume the anticoagulant once they are stabilized.
For patients who develop heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, the 4Ts score is the best way to make a more accurate diagnosis and boost the prospects for recovery, said Dr. Cuker (Blood. 2012 Nov 15;120[20]:4160-7). The guidelines cite several agents now available to treat this common complication, which affects about 1% of the 12 million Americans treated with heparin annually: argatroban, bivalirudin, danaparoid, fondaparinux, apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban, and rivaroxaban.
ASH has a VTE website with links to detailed information for each of the guideline subcategories: prophylaxis in medical patients, diagnosis, therapy, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, VTE in pregnancy, and VTE in children. The website indicates that additional guidelines will soon be released on managing VTE in patients with cancer, in patients with thrombophilia, and for prophylaxis in surgical patients, as well as further information on treatment. A spokesperson for ASH said that these additional documents will post sometime in 2019.
At the time of the release, the guidelines panel published six articles in the journal Blood Advances that detailed the guidelines and their documentation.
The articles include prophylaxis of medical patients (Blood Advances. 2018 Nov 27;2[22]:3198-225), diagnosis (Blood Advances. 2018 Nov 27;2[22]:3226-56), anticoagulation therapy (Blood Advances. 2018 Nov 27;2[22]:3257-91), pediatrics (Blood Advances. 2018 Nov 27;2[22]:3292-316), pregnancy (Blood Advances. 2018 Nov 27;2[22]:3317-59), and heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (Blood Advances. 2018 Nov 27;2[22]:3360-92).
Dr. Cushman, Dr. Lim, and Dr. Witt reported having no relevant disclosures. Dr. Cuker reported receiving research support from T2 Biosystems.
The new guidelines, released on Nov. 27, contain more than 150 individual recommendations, including sections devoted to managing venous thromboembolism (VTE) during pregnancy and in pediatric patients. Guideline highlights cited by some of the writing-panel participants included a high reliance on low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) agents as the preferred treatment for many patients, reliance on the D-dimer test to rule out VTE in patients with a low pretest probability of disease, and reliance on the 4Ts score to identify patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia.
The guidelines took more than 3 years to develop, an effort that began in 2015.
An updated set of VTE guidelines were needed because clinicians now have a “greater understanding of risk factors” for VTE as well as having “more options available for treating VTE, including new medications,” Adam C. Cuker, MD, cochair of the guideline-writing group and a hematologist and thrombosis specialist at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said during a webcast to unveil the new guidelines.
Prevention
For preventing VTE in hospitalized medical patients the guidelines recommended initial assessment of the patient’s risk for both VTE and bleeding. Patients with a high bleeding risk who need VTE prevention should preferentially receive mechanical prophylaxis, either compression stockings or pneumatic sleeves. But in patients with a high VTE risk and an “acceptable” bleeding risk, prophylaxis with an anticoagulant is preferred over mechanical measures, said Mary Cushman, MD, professor and medical director of the thrombosis and hemostasis program at the University of Vermont, Burlington.
For prevention of VTE in medical inpatients, LMWH is preferred over unfractionated heparin because of its once-daily dosing and fewer complications, said Dr. Cushman, a member of the writing group. The panel also endorsed LMWH over a direct-acting oral anticoagulant, both during hospitalization and following discharge. The guidelines for prevention in medical patients explicitly “recommended against” using a direct-acting oral anticoagulant “over other treatments” both for hospitalized medical patients and after discharge, and the guidelines further recommend against extended prophylaxis after discharge with any other anticoagulant.
Another important takeaway from the prevention section was a statement that combining both mechanical and medical prophylaxis was not needed for medical inpatients. And once patients are discharged, if they take a long air trip they have no need for compression stockings or aspirin if their risk for thrombosis is not elevated. People with a “substantially increased” thrombosis risk “may benefit” from compression stockings or treatment with LMWH, Dr. Cushman said.
Diagnosis
For diagnosis, Wendy Lim, MD, highlighted the need for first categorizing patients as having a low or high probability for VTE, a judgment that can aid the accuracy of the diagnosis and helps avoid unnecessary testing.
For patients with low pretest probability, the guidelines recommended the D-dimer test as the best first step. Further testing isn’t needed when the D-dimer is negative, noted Dr. Lim, a hematologist and professor at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont.
The guidelines also recommended using ventilation-perfusion scintigraphy (V/Q scan) for imaging a pulmonary embolism over a CT scan, which uses more radiation. But V/Q scans are not ideal for assessing older patients or patients with lung disease, Dr. Lim cautioned.
Management
Management of VTE should occur, when feasible, through a specialized anticoagulation management service center, which can provide care that is best suited to the complexities of anticoagulation therapy. But it’s a level of care that many U.S. patients don’t currently receive and hence is an area ripe for growth, said Daniel M. Witt, PharmD, professor and vice-chair of pharmacotherapy at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City.
The guidelines recommended against bridging therapy with LMWH for most patients who need to stop warfarin when undergoing an invasive procedure. The guidelines also called for “thoughtful” use of anticoagulant reversal agents and advised that patients who survive a major bleed while on anticoagulation should often resume the anticoagulant once they are stabilized.
For patients who develop heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, the 4Ts score is the best way to make a more accurate diagnosis and boost the prospects for recovery, said Dr. Cuker (Blood. 2012 Nov 15;120[20]:4160-7). The guidelines cite several agents now available to treat this common complication, which affects about 1% of the 12 million Americans treated with heparin annually: argatroban, bivalirudin, danaparoid, fondaparinux, apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban, and rivaroxaban.
ASH has a VTE website with links to detailed information for each of the guideline subcategories: prophylaxis in medical patients, diagnosis, therapy, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, VTE in pregnancy, and VTE in children. The website indicates that additional guidelines will soon be released on managing VTE in patients with cancer, in patients with thrombophilia, and for prophylaxis in surgical patients, as well as further information on treatment. A spokesperson for ASH said that these additional documents will post sometime in 2019.
At the time of the release, the guidelines panel published six articles in the journal Blood Advances that detailed the guidelines and their documentation.
The articles include prophylaxis of medical patients (Blood Advances. 2018 Nov 27;2[22]:3198-225), diagnosis (Blood Advances. 2018 Nov 27;2[22]:3226-56), anticoagulation therapy (Blood Advances. 2018 Nov 27;2[22]:3257-91), pediatrics (Blood Advances. 2018 Nov 27;2[22]:3292-316), pregnancy (Blood Advances. 2018 Nov 27;2[22]:3317-59), and heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (Blood Advances. 2018 Nov 27;2[22]:3360-92).
Dr. Cushman, Dr. Lim, and Dr. Witt reported having no relevant disclosures. Dr. Cuker reported receiving research support from T2 Biosystems.
The new guidelines, released on Nov. 27, contain more than 150 individual recommendations, including sections devoted to managing venous thromboembolism (VTE) during pregnancy and in pediatric patients. Guideline highlights cited by some of the writing-panel participants included a high reliance on low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) agents as the preferred treatment for many patients, reliance on the D-dimer test to rule out VTE in patients with a low pretest probability of disease, and reliance on the 4Ts score to identify patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia.
The guidelines took more than 3 years to develop, an effort that began in 2015.
An updated set of VTE guidelines were needed because clinicians now have a “greater understanding of risk factors” for VTE as well as having “more options available for treating VTE, including new medications,” Adam C. Cuker, MD, cochair of the guideline-writing group and a hematologist and thrombosis specialist at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said during a webcast to unveil the new guidelines.
Prevention
For preventing VTE in hospitalized medical patients the guidelines recommended initial assessment of the patient’s risk for both VTE and bleeding. Patients with a high bleeding risk who need VTE prevention should preferentially receive mechanical prophylaxis, either compression stockings or pneumatic sleeves. But in patients with a high VTE risk and an “acceptable” bleeding risk, prophylaxis with an anticoagulant is preferred over mechanical measures, said Mary Cushman, MD, professor and medical director of the thrombosis and hemostasis program at the University of Vermont, Burlington.
For prevention of VTE in medical inpatients, LMWH is preferred over unfractionated heparin because of its once-daily dosing and fewer complications, said Dr. Cushman, a member of the writing group. The panel also endorsed LMWH over a direct-acting oral anticoagulant, both during hospitalization and following discharge. The guidelines for prevention in medical patients explicitly “recommended against” using a direct-acting oral anticoagulant “over other treatments” both for hospitalized medical patients and after discharge, and the guidelines further recommend against extended prophylaxis after discharge with any other anticoagulant.
Another important takeaway from the prevention section was a statement that combining both mechanical and medical prophylaxis was not needed for medical inpatients. And once patients are discharged, if they take a long air trip they have no need for compression stockings or aspirin if their risk for thrombosis is not elevated. People with a “substantially increased” thrombosis risk “may benefit” from compression stockings or treatment with LMWH, Dr. Cushman said.
Diagnosis
For diagnosis, Wendy Lim, MD, highlighted the need for first categorizing patients as having a low or high probability for VTE, a judgment that can aid the accuracy of the diagnosis and helps avoid unnecessary testing.
For patients with low pretest probability, the guidelines recommended the D-dimer test as the best first step. Further testing isn’t needed when the D-dimer is negative, noted Dr. Lim, a hematologist and professor at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont.
The guidelines also recommended using ventilation-perfusion scintigraphy (V/Q scan) for imaging a pulmonary embolism over a CT scan, which uses more radiation. But V/Q scans are not ideal for assessing older patients or patients with lung disease, Dr. Lim cautioned.
Management
Management of VTE should occur, when feasible, through a specialized anticoagulation management service center, which can provide care that is best suited to the complexities of anticoagulation therapy. But it’s a level of care that many U.S. patients don’t currently receive and hence is an area ripe for growth, said Daniel M. Witt, PharmD, professor and vice-chair of pharmacotherapy at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City.
The guidelines recommended against bridging therapy with LMWH for most patients who need to stop warfarin when undergoing an invasive procedure. The guidelines also called for “thoughtful” use of anticoagulant reversal agents and advised that patients who survive a major bleed while on anticoagulation should often resume the anticoagulant once they are stabilized.
For patients who develop heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, the 4Ts score is the best way to make a more accurate diagnosis and boost the prospects for recovery, said Dr. Cuker (Blood. 2012 Nov 15;120[20]:4160-7). The guidelines cite several agents now available to treat this common complication, which affects about 1% of the 12 million Americans treated with heparin annually: argatroban, bivalirudin, danaparoid, fondaparinux, apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban, and rivaroxaban.
ASH has a VTE website with links to detailed information for each of the guideline subcategories: prophylaxis in medical patients, diagnosis, therapy, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, VTE in pregnancy, and VTE in children. The website indicates that additional guidelines will soon be released on managing VTE in patients with cancer, in patients with thrombophilia, and for prophylaxis in surgical patients, as well as further information on treatment. A spokesperson for ASH said that these additional documents will post sometime in 2019.
At the time of the release, the guidelines panel published six articles in the journal Blood Advances that detailed the guidelines and their documentation.
The articles include prophylaxis of medical patients (Blood Advances. 2018 Nov 27;2[22]:3198-225), diagnosis (Blood Advances. 2018 Nov 27;2[22]:3226-56), anticoagulation therapy (Blood Advances. 2018 Nov 27;2[22]:3257-91), pediatrics (Blood Advances. 2018 Nov 27;2[22]:3292-316), pregnancy (Blood Advances. 2018 Nov 27;2[22]:3317-59), and heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (Blood Advances. 2018 Nov 27;2[22]:3360-92).
Dr. Cushman, Dr. Lim, and Dr. Witt reported having no relevant disclosures. Dr. Cuker reported receiving research support from T2 Biosystems.
A deep commitment to veterans’ medical needs
VA hospitalist Dr. Mel Anderson loves his work
Mel C. Anderson, MD, FACP, section chief of hospital medicine for the Veterans Administration of Eastern Colorado, and his hospitalist colleagues share a mission to care for the men and women who served their country in the armed forces and are now being served by the VA.
“That mission binds us together in a deep and impactful way,” he said. “One of the greatest joys of my life has been to dedicate, with the teams I lead, our hearts and minds to serving this population of veterans.”
Approximately 400 hospitalists work nationwide in the VA, the country’s largest integrated health system, typically in groups of about a dozen. Not every VA medical center employs hospitalists; this depends on local tradition and size of the facility. Dr. Anderson was for several years the lone hospitalist at the VA Medical Center in Denver, starting in 2005, and now he heads a group of 17. The Denver facility employs five inpatient teams plus nocturnists, supported by residents, interns, and medical students in training from the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, to deliver all of its inpatient medical care.
“We also have an open ICU here. Hospitalists are able to follow their patients across the hospital, and we can make the decision to move them to the ICU,” Dr. Anderson said. The Denver group also established a hospitalist-staffed postdischarge clinic, where patients can reconnect with their hospital team. “It’s not to supplant primary care but to help promote safe transit as the patient moves back to the community,” he said. “We’ve also developed a surgery consult service for orthopedics and other surgical subspecialties.”
The VA’s integrated electronic medical record facilitates communication between hospitalists and primary care physicians, with instant messaging for updating the PCPs on the patient’s hospital stay.
The Denver VA hospitalists value their collegial culture, Dr. Anderson said. “We are invested in our group and in one another and in life-long learning. I often ask my group for their feedback. It’s one of the singular joys of my career to lead such a wonderful group, which has been built up person by person. I hired every single member. As much as their clinical skills and the achievements on their curriculum vitae were important, I also paid attention to their interpersonal communication skills.”
Members of the Denver hospitalist group also share an academic focus and commitment to scholarship and research. Dr. Anderson’s academic emphasis is on how to promote teaching and faculty development through organized bedside rounding and how to orient students to teaching as a potential career path. He is associate program director for medicine residencies at the University of Colorado and leads its Clinician/Educator Pathway.
The VA hospital’s interdisciplinary bedside rounding initiative involves the medicine team – students, residents, attending – and pharmacist, plus the patient’s bedside nurse and nurse care coordinator. “We have worked on fostering an interdisciplinary culture, and we’re very proud of the rounding model we developed here. We all round together at the bedside, and typically that might include 7 or 8 people,” Dr. Anderson explained.
“In planning this program, we used a Rapid Performance Improvement Project team with a nurse, pharmacist, and physical therapist helping us envision how to redesign rounds to overcome the time constraints,” he said. “We altered nurses’ work flow to permit them to join the rounding for their patients, and we moved morning medication administration to 7 a.m., so it wouldn’t get in the way of the rounding. We now audit rates of physician-to-nurse communication on rounds and how often we successfully achieve the nurse’s participation.”1 This approach has also cut rates of phone pages from nurses to house staff, and substantially increased job satisfaction.
What’s different in the VA?
The work of hospitalists in the VA is mostly similar to other hospital settings, but perhaps with more intensity, Dr. Anderson said. There are comorbidities such as higher rates of PTSD, alcohol use disorder, substance abuse, and mental health issues – all of which have an effect over time on patients. But veterans also have different attitudes about, for example, pain.
“When patients are asked to rate their pain on a scale of 0 to 10, for a veteran of a foreign war, 2 out of 10 is not the same as someone else’s 2 out of 10. How do we compensate for that difference?” he said. “And while awareness of PTSD and efforts to mitigate its impact have made incredible gains over the past 15 years, we still see a lot of these issues and their manifestations in social challenges such as homelessness. We are fortunate to have VA outpatient services and homeless veteran programs to help with these issues.”
There is a different paradigm for care at the VA, Dr. Anderson said. “We are a not-for-profit institution with the welfare of veterans as our primary aim. Beyond their health and wellness, that means supporting them in other ways and reaching out into the community. As doctors and nurses we feel a kinship around that mission, although we also have to be stewards of taxpayer dollars. We recognize that the VA is a large and complicated, somewhat inertia-laden organization in which making changes can be very challenging. But there are also opportunities as a national organization to effect changes on a national scale.”
Dr. Anderson chairs the VA’s Hospitalist Field Advisory Committee (HFAC), a group of about eight hospitalists empaneled to advise the system’s Office of Specialty Care Services on clinical policy and program development. They serve 3-year terms and meet monthly by phone and annually in Washington. The HFAC’s last annual meeting occurred in mid-September 2018 in Washington with a focus on developing a hospital medicine annual survey and needs assessment, revisiting strategic goals, and convening multilateral meetings with the chiefs of medicine and emergency medicine FACs.
“Our biggest emphasis is clinical – this includes clinical pathways, best practices for managing PTSD or acute coronary syndrome, and the like. We also share management issues, such as how to configure medical records or arrange night coverage. This is a national conversation to share what some sites have already experienced and learned,” Dr. Anderson said.
“We also have a VA Academic Hospitalist Subcommittee, working together on multisite research studies and on resident education protocols. Because we’re a large system, we’re able to connect with one another and leverage what we’ve learned. I get emails almost every day about research topics from colleagues across the country,” he said. A collaborative website and email distribution list allows doctors to post questions to their peers nationwide.
A calling for hospital medicine
Before moving to Denver, Dr. Anderson served as a major in the Air Force Medical Corps and was based at the David Grant US Air Force Medical Center on Travis Air Force Base in California – which is where he did his residency. In the course of a “traditionalist” internal medical training, including 4-month stints on hospital wards in addition to outpatient services, he realized he had a calling for hospital medicine.
In a job at the Providence (R.I.) VA Medical Center, he exclusively practiced outpatient care, but he found that he missed key aspects of inpatient work, such as the intensity of the clinical issues and teaching encounters. “I cold-called the hospital’s chief of medicine and volunteered to start mentoring inpatient residents,” Dr. Anderson said. “That was 17 years ago.”
Another abiding interest derived from Dr. Anderson’s military service is travel medicine. While a physician in the Air Force, he was deployed to Haiti in 1995 and to Nicaragua in 2000, where he treated thousands of patients – both U.S. service personnel and local populations.
“In Haiti, our primary mission was for U.S. troops who were still based there following the 1994 Operation Uphold Democracy intervention, but there were a lot fewer of them, so we mostly kept busy providing care to Haitian nationals,” he said. “That work was eye opening, to say the least,” and led to a professional interest in tropical illnesses. “Since then, I’ve been a visiting professor for the University of Colorado posted to the University of Zimbabwe in Harare in 2012 and 2016.”
What gives Dr. Anderson such joy and enthusiasm for his VA work? “I am a curious lifelong learner. Every day, there are 10 new things I need to learn, whether clinically or operationally in a big hospital system or just the day-to-day realities of leading a group of physicians. I never feel like I’m treading water,” he said. He is also energized by teaching – seeing “the light bulb go on” for the students he is instructing – and by serving as a role model for doctors in training.
“As I contemplate all the simultaneous balls I have in the air, including our recent move into a new hospital building, sometimes I think it is kind of crazy to be doing as much as I do,” he said. “But I also take time away, balancing work versus nonwork.” He spends quality time with his wife of 21 years, 17-year-old daughter, other relatives, and friends, as well as on physical activity, reading books about philosophy, and his hobby of rebuilding motorcycles, which he says offers a kind of meditative calm.
“I also feel a deep sense of service – to patients, colleagues, students, and to the mission of the VA,” Dr. Anderson said. “There is truly something special about caring for the veteran. It’s hard to articulate, but it really keeps us coming back for more. I’ve had vets sing to me, tell jokes, do magic tricks, share their war stories. I’ve had patients open up to me in ways that were both profound and humbling.”
References
1. Young E et al. Impact of altered medication administration time on interdisciplinary bedside rounds on academic medical ward. J Nurs Care Qual. 2017 Jul/Sep;32(3):218-225.
VA hospitalist Dr. Mel Anderson loves his work
VA hospitalist Dr. Mel Anderson loves his work
Mel C. Anderson, MD, FACP, section chief of hospital medicine for the Veterans Administration of Eastern Colorado, and his hospitalist colleagues share a mission to care for the men and women who served their country in the armed forces and are now being served by the VA.
“That mission binds us together in a deep and impactful way,” he said. “One of the greatest joys of my life has been to dedicate, with the teams I lead, our hearts and minds to serving this population of veterans.”
Approximately 400 hospitalists work nationwide in the VA, the country’s largest integrated health system, typically in groups of about a dozen. Not every VA medical center employs hospitalists; this depends on local tradition and size of the facility. Dr. Anderson was for several years the lone hospitalist at the VA Medical Center in Denver, starting in 2005, and now he heads a group of 17. The Denver facility employs five inpatient teams plus nocturnists, supported by residents, interns, and medical students in training from the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, to deliver all of its inpatient medical care.
“We also have an open ICU here. Hospitalists are able to follow their patients across the hospital, and we can make the decision to move them to the ICU,” Dr. Anderson said. The Denver group also established a hospitalist-staffed postdischarge clinic, where patients can reconnect with their hospital team. “It’s not to supplant primary care but to help promote safe transit as the patient moves back to the community,” he said. “We’ve also developed a surgery consult service for orthopedics and other surgical subspecialties.”
The VA’s integrated electronic medical record facilitates communication between hospitalists and primary care physicians, with instant messaging for updating the PCPs on the patient’s hospital stay.
The Denver VA hospitalists value their collegial culture, Dr. Anderson said. “We are invested in our group and in one another and in life-long learning. I often ask my group for their feedback. It’s one of the singular joys of my career to lead such a wonderful group, which has been built up person by person. I hired every single member. As much as their clinical skills and the achievements on their curriculum vitae were important, I also paid attention to their interpersonal communication skills.”
Members of the Denver hospitalist group also share an academic focus and commitment to scholarship and research. Dr. Anderson’s academic emphasis is on how to promote teaching and faculty development through organized bedside rounding and how to orient students to teaching as a potential career path. He is associate program director for medicine residencies at the University of Colorado and leads its Clinician/Educator Pathway.
The VA hospital’s interdisciplinary bedside rounding initiative involves the medicine team – students, residents, attending – and pharmacist, plus the patient’s bedside nurse and nurse care coordinator. “We have worked on fostering an interdisciplinary culture, and we’re very proud of the rounding model we developed here. We all round together at the bedside, and typically that might include 7 or 8 people,” Dr. Anderson explained.
“In planning this program, we used a Rapid Performance Improvement Project team with a nurse, pharmacist, and physical therapist helping us envision how to redesign rounds to overcome the time constraints,” he said. “We altered nurses’ work flow to permit them to join the rounding for their patients, and we moved morning medication administration to 7 a.m., so it wouldn’t get in the way of the rounding. We now audit rates of physician-to-nurse communication on rounds and how often we successfully achieve the nurse’s participation.”1 This approach has also cut rates of phone pages from nurses to house staff, and substantially increased job satisfaction.
What’s different in the VA?
The work of hospitalists in the VA is mostly similar to other hospital settings, but perhaps with more intensity, Dr. Anderson said. There are comorbidities such as higher rates of PTSD, alcohol use disorder, substance abuse, and mental health issues – all of which have an effect over time on patients. But veterans also have different attitudes about, for example, pain.
“When patients are asked to rate their pain on a scale of 0 to 10, for a veteran of a foreign war, 2 out of 10 is not the same as someone else’s 2 out of 10. How do we compensate for that difference?” he said. “And while awareness of PTSD and efforts to mitigate its impact have made incredible gains over the past 15 years, we still see a lot of these issues and their manifestations in social challenges such as homelessness. We are fortunate to have VA outpatient services and homeless veteran programs to help with these issues.”
There is a different paradigm for care at the VA, Dr. Anderson said. “We are a not-for-profit institution with the welfare of veterans as our primary aim. Beyond their health and wellness, that means supporting them in other ways and reaching out into the community. As doctors and nurses we feel a kinship around that mission, although we also have to be stewards of taxpayer dollars. We recognize that the VA is a large and complicated, somewhat inertia-laden organization in which making changes can be very challenging. But there are also opportunities as a national organization to effect changes on a national scale.”
Dr. Anderson chairs the VA’s Hospitalist Field Advisory Committee (HFAC), a group of about eight hospitalists empaneled to advise the system’s Office of Specialty Care Services on clinical policy and program development. They serve 3-year terms and meet monthly by phone and annually in Washington. The HFAC’s last annual meeting occurred in mid-September 2018 in Washington with a focus on developing a hospital medicine annual survey and needs assessment, revisiting strategic goals, and convening multilateral meetings with the chiefs of medicine and emergency medicine FACs.
“Our biggest emphasis is clinical – this includes clinical pathways, best practices for managing PTSD or acute coronary syndrome, and the like. We also share management issues, such as how to configure medical records or arrange night coverage. This is a national conversation to share what some sites have already experienced and learned,” Dr. Anderson said.
“We also have a VA Academic Hospitalist Subcommittee, working together on multisite research studies and on resident education protocols. Because we’re a large system, we’re able to connect with one another and leverage what we’ve learned. I get emails almost every day about research topics from colleagues across the country,” he said. A collaborative website and email distribution list allows doctors to post questions to their peers nationwide.
A calling for hospital medicine
Before moving to Denver, Dr. Anderson served as a major in the Air Force Medical Corps and was based at the David Grant US Air Force Medical Center on Travis Air Force Base in California – which is where he did his residency. In the course of a “traditionalist” internal medical training, including 4-month stints on hospital wards in addition to outpatient services, he realized he had a calling for hospital medicine.
In a job at the Providence (R.I.) VA Medical Center, he exclusively practiced outpatient care, but he found that he missed key aspects of inpatient work, such as the intensity of the clinical issues and teaching encounters. “I cold-called the hospital’s chief of medicine and volunteered to start mentoring inpatient residents,” Dr. Anderson said. “That was 17 years ago.”
Another abiding interest derived from Dr. Anderson’s military service is travel medicine. While a physician in the Air Force, he was deployed to Haiti in 1995 and to Nicaragua in 2000, where he treated thousands of patients – both U.S. service personnel and local populations.
“In Haiti, our primary mission was for U.S. troops who were still based there following the 1994 Operation Uphold Democracy intervention, but there were a lot fewer of them, so we mostly kept busy providing care to Haitian nationals,” he said. “That work was eye opening, to say the least,” and led to a professional interest in tropical illnesses. “Since then, I’ve been a visiting professor for the University of Colorado posted to the University of Zimbabwe in Harare in 2012 and 2016.”
What gives Dr. Anderson such joy and enthusiasm for his VA work? “I am a curious lifelong learner. Every day, there are 10 new things I need to learn, whether clinically or operationally in a big hospital system or just the day-to-day realities of leading a group of physicians. I never feel like I’m treading water,” he said. He is also energized by teaching – seeing “the light bulb go on” for the students he is instructing – and by serving as a role model for doctors in training.
“As I contemplate all the simultaneous balls I have in the air, including our recent move into a new hospital building, sometimes I think it is kind of crazy to be doing as much as I do,” he said. “But I also take time away, balancing work versus nonwork.” He spends quality time with his wife of 21 years, 17-year-old daughter, other relatives, and friends, as well as on physical activity, reading books about philosophy, and his hobby of rebuilding motorcycles, which he says offers a kind of meditative calm.
“I also feel a deep sense of service – to patients, colleagues, students, and to the mission of the VA,” Dr. Anderson said. “There is truly something special about caring for the veteran. It’s hard to articulate, but it really keeps us coming back for more. I’ve had vets sing to me, tell jokes, do magic tricks, share their war stories. I’ve had patients open up to me in ways that were both profound and humbling.”
References
1. Young E et al. Impact of altered medication administration time on interdisciplinary bedside rounds on academic medical ward. J Nurs Care Qual. 2017 Jul/Sep;32(3):218-225.
Mel C. Anderson, MD, FACP, section chief of hospital medicine for the Veterans Administration of Eastern Colorado, and his hospitalist colleagues share a mission to care for the men and women who served their country in the armed forces and are now being served by the VA.
“That mission binds us together in a deep and impactful way,” he said. “One of the greatest joys of my life has been to dedicate, with the teams I lead, our hearts and minds to serving this population of veterans.”
Approximately 400 hospitalists work nationwide in the VA, the country’s largest integrated health system, typically in groups of about a dozen. Not every VA medical center employs hospitalists; this depends on local tradition and size of the facility. Dr. Anderson was for several years the lone hospitalist at the VA Medical Center in Denver, starting in 2005, and now he heads a group of 17. The Denver facility employs five inpatient teams plus nocturnists, supported by residents, interns, and medical students in training from the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, to deliver all of its inpatient medical care.
“We also have an open ICU here. Hospitalists are able to follow their patients across the hospital, and we can make the decision to move them to the ICU,” Dr. Anderson said. The Denver group also established a hospitalist-staffed postdischarge clinic, where patients can reconnect with their hospital team. “It’s not to supplant primary care but to help promote safe transit as the patient moves back to the community,” he said. “We’ve also developed a surgery consult service for orthopedics and other surgical subspecialties.”
The VA’s integrated electronic medical record facilitates communication between hospitalists and primary care physicians, with instant messaging for updating the PCPs on the patient’s hospital stay.
The Denver VA hospitalists value their collegial culture, Dr. Anderson said. “We are invested in our group and in one another and in life-long learning. I often ask my group for their feedback. It’s one of the singular joys of my career to lead such a wonderful group, which has been built up person by person. I hired every single member. As much as their clinical skills and the achievements on their curriculum vitae were important, I also paid attention to their interpersonal communication skills.”
Members of the Denver hospitalist group also share an academic focus and commitment to scholarship and research. Dr. Anderson’s academic emphasis is on how to promote teaching and faculty development through organized bedside rounding and how to orient students to teaching as a potential career path. He is associate program director for medicine residencies at the University of Colorado and leads its Clinician/Educator Pathway.
The VA hospital’s interdisciplinary bedside rounding initiative involves the medicine team – students, residents, attending – and pharmacist, plus the patient’s bedside nurse and nurse care coordinator. “We have worked on fostering an interdisciplinary culture, and we’re very proud of the rounding model we developed here. We all round together at the bedside, and typically that might include 7 or 8 people,” Dr. Anderson explained.
“In planning this program, we used a Rapid Performance Improvement Project team with a nurse, pharmacist, and physical therapist helping us envision how to redesign rounds to overcome the time constraints,” he said. “We altered nurses’ work flow to permit them to join the rounding for their patients, and we moved morning medication administration to 7 a.m., so it wouldn’t get in the way of the rounding. We now audit rates of physician-to-nurse communication on rounds and how often we successfully achieve the nurse’s participation.”1 This approach has also cut rates of phone pages from nurses to house staff, and substantially increased job satisfaction.
What’s different in the VA?
The work of hospitalists in the VA is mostly similar to other hospital settings, but perhaps with more intensity, Dr. Anderson said. There are comorbidities such as higher rates of PTSD, alcohol use disorder, substance abuse, and mental health issues – all of which have an effect over time on patients. But veterans also have different attitudes about, for example, pain.
“When patients are asked to rate their pain on a scale of 0 to 10, for a veteran of a foreign war, 2 out of 10 is not the same as someone else’s 2 out of 10. How do we compensate for that difference?” he said. “And while awareness of PTSD and efforts to mitigate its impact have made incredible gains over the past 15 years, we still see a lot of these issues and their manifestations in social challenges such as homelessness. We are fortunate to have VA outpatient services and homeless veteran programs to help with these issues.”
There is a different paradigm for care at the VA, Dr. Anderson said. “We are a not-for-profit institution with the welfare of veterans as our primary aim. Beyond their health and wellness, that means supporting them in other ways and reaching out into the community. As doctors and nurses we feel a kinship around that mission, although we also have to be stewards of taxpayer dollars. We recognize that the VA is a large and complicated, somewhat inertia-laden organization in which making changes can be very challenging. But there are also opportunities as a national organization to effect changes on a national scale.”
Dr. Anderson chairs the VA’s Hospitalist Field Advisory Committee (HFAC), a group of about eight hospitalists empaneled to advise the system’s Office of Specialty Care Services on clinical policy and program development. They serve 3-year terms and meet monthly by phone and annually in Washington. The HFAC’s last annual meeting occurred in mid-September 2018 in Washington with a focus on developing a hospital medicine annual survey and needs assessment, revisiting strategic goals, and convening multilateral meetings with the chiefs of medicine and emergency medicine FACs.
“Our biggest emphasis is clinical – this includes clinical pathways, best practices for managing PTSD or acute coronary syndrome, and the like. We also share management issues, such as how to configure medical records or arrange night coverage. This is a national conversation to share what some sites have already experienced and learned,” Dr. Anderson said.
“We also have a VA Academic Hospitalist Subcommittee, working together on multisite research studies and on resident education protocols. Because we’re a large system, we’re able to connect with one another and leverage what we’ve learned. I get emails almost every day about research topics from colleagues across the country,” he said. A collaborative website and email distribution list allows doctors to post questions to their peers nationwide.
A calling for hospital medicine
Before moving to Denver, Dr. Anderson served as a major in the Air Force Medical Corps and was based at the David Grant US Air Force Medical Center on Travis Air Force Base in California – which is where he did his residency. In the course of a “traditionalist” internal medical training, including 4-month stints on hospital wards in addition to outpatient services, he realized he had a calling for hospital medicine.
In a job at the Providence (R.I.) VA Medical Center, he exclusively practiced outpatient care, but he found that he missed key aspects of inpatient work, such as the intensity of the clinical issues and teaching encounters. “I cold-called the hospital’s chief of medicine and volunteered to start mentoring inpatient residents,” Dr. Anderson said. “That was 17 years ago.”
Another abiding interest derived from Dr. Anderson’s military service is travel medicine. While a physician in the Air Force, he was deployed to Haiti in 1995 and to Nicaragua in 2000, where he treated thousands of patients – both U.S. service personnel and local populations.
“In Haiti, our primary mission was for U.S. troops who were still based there following the 1994 Operation Uphold Democracy intervention, but there were a lot fewer of them, so we mostly kept busy providing care to Haitian nationals,” he said. “That work was eye opening, to say the least,” and led to a professional interest in tropical illnesses. “Since then, I’ve been a visiting professor for the University of Colorado posted to the University of Zimbabwe in Harare in 2012 and 2016.”
What gives Dr. Anderson such joy and enthusiasm for his VA work? “I am a curious lifelong learner. Every day, there are 10 new things I need to learn, whether clinically or operationally in a big hospital system or just the day-to-day realities of leading a group of physicians. I never feel like I’m treading water,” he said. He is also energized by teaching – seeing “the light bulb go on” for the students he is instructing – and by serving as a role model for doctors in training.
“As I contemplate all the simultaneous balls I have in the air, including our recent move into a new hospital building, sometimes I think it is kind of crazy to be doing as much as I do,” he said. “But I also take time away, balancing work versus nonwork.” He spends quality time with his wife of 21 years, 17-year-old daughter, other relatives, and friends, as well as on physical activity, reading books about philosophy, and his hobby of rebuilding motorcycles, which he says offers a kind of meditative calm.
“I also feel a deep sense of service – to patients, colleagues, students, and to the mission of the VA,” Dr. Anderson said. “There is truly something special about caring for the veteran. It’s hard to articulate, but it really keeps us coming back for more. I’ve had vets sing to me, tell jokes, do magic tricks, share their war stories. I’ve had patients open up to me in ways that were both profound and humbling.”
References
1. Young E et al. Impact of altered medication administration time on interdisciplinary bedside rounds on academic medical ward. J Nurs Care Qual. 2017 Jul/Sep;32(3):218-225.