User login
COVID-19 fears tied to dangerous drop in child vaccinations
The social distancing and sheltering in place mandated because of the COVID-19 pandemic are keeping parents and kids out of their doctors’ offices, and that has prompted a steep decline in recommended routine vaccinations for U.S. children, according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention researchers.
Pediatric vaccinations dropped sharply after the national emergency was declared on March 13, suggesting that some children may be at increased risk for other serious infectious diseases, such as measles.
The researchers compared weekly orders for federally funded vaccines from Jan. 6 to April 19, 2020, with those during the same period in 2019.
They noted that, by the end of the study period, there was a cumulative COVID-19–related decline of 2.5 million doses in orders for routine noninfluenza pediatric childhood vaccines recommended by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, as well as a cumulative decline in orders of 250,000 doses of measles vaccines.
Although the overall decrease in vaccinations during the study period was larger, according to CDC spokesperson Richard Quartarone, the above figures represent declines clearly associated with the pandemic.
The weekly number of measles vaccines ordered for children aged 24 months or older fell dramatically to about 500 during the week beginning March 16, 2020, and fell further to approximately 250 during the week beginning March 23. It stayed at that level until the week beginning April 13. By comparison, more than 2,500 were ordered during the week starting March 2, before the emergency was declared.
The decline was notably less for children younger than 2 years. For those children, orders dropped to about 750 during the week starting March 23 and climbed slightly for 3 weeks. By comparison, during the week of March 2, about 2,000 vaccines were ordered.
The findings, which were published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, stem from an analysis of ordering data from the federal Vaccines for Children (VFC) Program, as well as from vaccine administration data from the CDC’s Vaccine Tracking System and the collaborative Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD).
The VFC provides federally purchased vaccines at no cost to about half of persons aged 18 years or younger. The VSD collaborates on vaccine coverage with the CDC’s Immunization Safety Office and eight large health care organizations across the country. Vaccination coverage is the usual metric for assessing vaccine usage; providers’ orders and the number of doses administered are two proxy measures, the authors explained.
“The substantial reduction in VFC-funded pediatric vaccine ordering after the COVID-19 emergency declaration is consistent with changes in vaccine administration among children in the VSD population receiving care through eight large U.S. health care organizations,” wrote Jeanne M. Santoli, MD, and colleagues, of the immunization services division at the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases. “The smaller decline in measles-containing vaccine administration among children aged ≤24 months suggests that system-level strategies to prioritize well child care and immunization for this age group are being implemented.”
Dr. Santoli, who is an Atlanta-based pediatrician, and associates stressed the importance of maintaining regular vaccinations during the pandemic. “The identified declines in routine pediatric vaccine ordering and doses administered might indicate that U.S. children and their communities face increased risks for outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases,” they wrote. “Parental concerns about potentially exposing their children to COVID-19 during well child visits might contribute to the declines observed.” Parents should therefore be reminded of the necessity of protecting their children against vaccine-preventable diseases.
In 2019, a Gallup survey reported that overall support for vaccination continued to decline in the United States.
The researchers predicted that, as social distancing relaxes, unvaccinated children will be more susceptible to other serious diseases. “In response, continued coordinated efforts between health care providers and public health officials at the local, state, and federal levels will be necessary to achieve rapid catch-up vaccination,” they concluded.
The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The social distancing and sheltering in place mandated because of the COVID-19 pandemic are keeping parents and kids out of their doctors’ offices, and that has prompted a steep decline in recommended routine vaccinations for U.S. children, according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention researchers.
Pediatric vaccinations dropped sharply after the national emergency was declared on March 13, suggesting that some children may be at increased risk for other serious infectious diseases, such as measles.
The researchers compared weekly orders for federally funded vaccines from Jan. 6 to April 19, 2020, with those during the same period in 2019.
They noted that, by the end of the study period, there was a cumulative COVID-19–related decline of 2.5 million doses in orders for routine noninfluenza pediatric childhood vaccines recommended by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, as well as a cumulative decline in orders of 250,000 doses of measles vaccines.
Although the overall decrease in vaccinations during the study period was larger, according to CDC spokesperson Richard Quartarone, the above figures represent declines clearly associated with the pandemic.
The weekly number of measles vaccines ordered for children aged 24 months or older fell dramatically to about 500 during the week beginning March 16, 2020, and fell further to approximately 250 during the week beginning March 23. It stayed at that level until the week beginning April 13. By comparison, more than 2,500 were ordered during the week starting March 2, before the emergency was declared.
The decline was notably less for children younger than 2 years. For those children, orders dropped to about 750 during the week starting March 23 and climbed slightly for 3 weeks. By comparison, during the week of March 2, about 2,000 vaccines were ordered.
The findings, which were published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, stem from an analysis of ordering data from the federal Vaccines for Children (VFC) Program, as well as from vaccine administration data from the CDC’s Vaccine Tracking System and the collaborative Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD).
The VFC provides federally purchased vaccines at no cost to about half of persons aged 18 years or younger. The VSD collaborates on vaccine coverage with the CDC’s Immunization Safety Office and eight large health care organizations across the country. Vaccination coverage is the usual metric for assessing vaccine usage; providers’ orders and the number of doses administered are two proxy measures, the authors explained.
“The substantial reduction in VFC-funded pediatric vaccine ordering after the COVID-19 emergency declaration is consistent with changes in vaccine administration among children in the VSD population receiving care through eight large U.S. health care organizations,” wrote Jeanne M. Santoli, MD, and colleagues, of the immunization services division at the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases. “The smaller decline in measles-containing vaccine administration among children aged ≤24 months suggests that system-level strategies to prioritize well child care and immunization for this age group are being implemented.”
Dr. Santoli, who is an Atlanta-based pediatrician, and associates stressed the importance of maintaining regular vaccinations during the pandemic. “The identified declines in routine pediatric vaccine ordering and doses administered might indicate that U.S. children and their communities face increased risks for outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases,” they wrote. “Parental concerns about potentially exposing their children to COVID-19 during well child visits might contribute to the declines observed.” Parents should therefore be reminded of the necessity of protecting their children against vaccine-preventable diseases.
In 2019, a Gallup survey reported that overall support for vaccination continued to decline in the United States.
The researchers predicted that, as social distancing relaxes, unvaccinated children will be more susceptible to other serious diseases. “In response, continued coordinated efforts between health care providers and public health officials at the local, state, and federal levels will be necessary to achieve rapid catch-up vaccination,” they concluded.
The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The social distancing and sheltering in place mandated because of the COVID-19 pandemic are keeping parents and kids out of their doctors’ offices, and that has prompted a steep decline in recommended routine vaccinations for U.S. children, according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention researchers.
Pediatric vaccinations dropped sharply after the national emergency was declared on March 13, suggesting that some children may be at increased risk for other serious infectious diseases, such as measles.
The researchers compared weekly orders for federally funded vaccines from Jan. 6 to April 19, 2020, with those during the same period in 2019.
They noted that, by the end of the study period, there was a cumulative COVID-19–related decline of 2.5 million doses in orders for routine noninfluenza pediatric childhood vaccines recommended by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, as well as a cumulative decline in orders of 250,000 doses of measles vaccines.
Although the overall decrease in vaccinations during the study period was larger, according to CDC spokesperson Richard Quartarone, the above figures represent declines clearly associated with the pandemic.
The weekly number of measles vaccines ordered for children aged 24 months or older fell dramatically to about 500 during the week beginning March 16, 2020, and fell further to approximately 250 during the week beginning March 23. It stayed at that level until the week beginning April 13. By comparison, more than 2,500 were ordered during the week starting March 2, before the emergency was declared.
The decline was notably less for children younger than 2 years. For those children, orders dropped to about 750 during the week starting March 23 and climbed slightly for 3 weeks. By comparison, during the week of March 2, about 2,000 vaccines were ordered.
The findings, which were published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, stem from an analysis of ordering data from the federal Vaccines for Children (VFC) Program, as well as from vaccine administration data from the CDC’s Vaccine Tracking System and the collaborative Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD).
The VFC provides federally purchased vaccines at no cost to about half of persons aged 18 years or younger. The VSD collaborates on vaccine coverage with the CDC’s Immunization Safety Office and eight large health care organizations across the country. Vaccination coverage is the usual metric for assessing vaccine usage; providers’ orders and the number of doses administered are two proxy measures, the authors explained.
“The substantial reduction in VFC-funded pediatric vaccine ordering after the COVID-19 emergency declaration is consistent with changes in vaccine administration among children in the VSD population receiving care through eight large U.S. health care organizations,” wrote Jeanne M. Santoli, MD, and colleagues, of the immunization services division at the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases. “The smaller decline in measles-containing vaccine administration among children aged ≤24 months suggests that system-level strategies to prioritize well child care and immunization for this age group are being implemented.”
Dr. Santoli, who is an Atlanta-based pediatrician, and associates stressed the importance of maintaining regular vaccinations during the pandemic. “The identified declines in routine pediatric vaccine ordering and doses administered might indicate that U.S. children and their communities face increased risks for outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases,” they wrote. “Parental concerns about potentially exposing their children to COVID-19 during well child visits might contribute to the declines observed.” Parents should therefore be reminded of the necessity of protecting their children against vaccine-preventable diseases.
In 2019, a Gallup survey reported that overall support for vaccination continued to decline in the United States.
The researchers predicted that, as social distancing relaxes, unvaccinated children will be more susceptible to other serious diseases. “In response, continued coordinated efforts between health care providers and public health officials at the local, state, and federal levels will be necessary to achieve rapid catch-up vaccination,” they concluded.
The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves olaparib/bevacizumab maintenance
The Food and Drug Administration has announced a new approved indication for olaparib (Lynparza) in adults with advanced epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer.
Olaparib is now FDA-approved for use in combination with bevacizumab as maintenance therapy in patients who responded to first-line platinum-based chemotherapy and whose cancer is homologous recombination deficiency positive, as defined by a deleterious or suspected deleterious BRCA mutation and/or genomic instability.
The FDA also approved the Myriad myChoice CDx test as a companion diagnostic for olaparib.
Trial results
The efficacy of olaparib and the myChoice CDx test were assessed in patients in the phase 3 PAOLA-1 trial (NCT02477644). The study enrolled patients with advanced high-grade epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer who had received first-line platinum-based chemotherapy and bevacizumab.
Patients were stratified by first-line treatment outcome and BRCA mutation status, as determined by prospective local testing. All available clinical samples were retrospectively tested with the Myriad myChoice CDx test.
The patients were randomized to receive olaparib at 300 mg orally twice daily in combination with bevacizumab at 15 mg/kg every 3 weeks (n = 537) or placebo plus bevacizumab (n = 269). Patients continued bevacizumab in the maintenance setting and started olaparib 3-9 weeks after their last chemotherapy dose. Olaparib could be continued for up to 2 years or until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The median progression-free survival among the 387 patients with homologous recombination deficiency-positive tumors was 37.2 months in the olaparib arm and 17.7 months in the placebo arm (hazard ratio, 0.33), according to the prescribing information for olaparib.
Serious adverse events occurred in 31% of patients in the olaparib arm. The most common were hypertension (19%) and anemia (17%).
Dose interruptions from adverse events occurred in 54% of patients in the olaparib arm, and dose reductions from adverse events occurred in 41%.
The Food and Drug Administration has announced a new approved indication for olaparib (Lynparza) in adults with advanced epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer.
Olaparib is now FDA-approved for use in combination with bevacizumab as maintenance therapy in patients who responded to first-line platinum-based chemotherapy and whose cancer is homologous recombination deficiency positive, as defined by a deleterious or suspected deleterious BRCA mutation and/or genomic instability.
The FDA also approved the Myriad myChoice CDx test as a companion diagnostic for olaparib.
Trial results
The efficacy of olaparib and the myChoice CDx test were assessed in patients in the phase 3 PAOLA-1 trial (NCT02477644). The study enrolled patients with advanced high-grade epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer who had received first-line platinum-based chemotherapy and bevacizumab.
Patients were stratified by first-line treatment outcome and BRCA mutation status, as determined by prospective local testing. All available clinical samples were retrospectively tested with the Myriad myChoice CDx test.
The patients were randomized to receive olaparib at 300 mg orally twice daily in combination with bevacizumab at 15 mg/kg every 3 weeks (n = 537) or placebo plus bevacizumab (n = 269). Patients continued bevacizumab in the maintenance setting and started olaparib 3-9 weeks after their last chemotherapy dose. Olaparib could be continued for up to 2 years or until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The median progression-free survival among the 387 patients with homologous recombination deficiency-positive tumors was 37.2 months in the olaparib arm and 17.7 months in the placebo arm (hazard ratio, 0.33), according to the prescribing information for olaparib.
Serious adverse events occurred in 31% of patients in the olaparib arm. The most common were hypertension (19%) and anemia (17%).
Dose interruptions from adverse events occurred in 54% of patients in the olaparib arm, and dose reductions from adverse events occurred in 41%.
The Food and Drug Administration has announced a new approved indication for olaparib (Lynparza) in adults with advanced epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer.
Olaparib is now FDA-approved for use in combination with bevacizumab as maintenance therapy in patients who responded to first-line platinum-based chemotherapy and whose cancer is homologous recombination deficiency positive, as defined by a deleterious or suspected deleterious BRCA mutation and/or genomic instability.
The FDA also approved the Myriad myChoice CDx test as a companion diagnostic for olaparib.
Trial results
The efficacy of olaparib and the myChoice CDx test were assessed in patients in the phase 3 PAOLA-1 trial (NCT02477644). The study enrolled patients with advanced high-grade epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer who had received first-line platinum-based chemotherapy and bevacizumab.
Patients were stratified by first-line treatment outcome and BRCA mutation status, as determined by prospective local testing. All available clinical samples were retrospectively tested with the Myriad myChoice CDx test.
The patients were randomized to receive olaparib at 300 mg orally twice daily in combination with bevacizumab at 15 mg/kg every 3 weeks (n = 537) or placebo plus bevacizumab (n = 269). Patients continued bevacizumab in the maintenance setting and started olaparib 3-9 weeks after their last chemotherapy dose. Olaparib could be continued for up to 2 years or until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The median progression-free survival among the 387 patients with homologous recombination deficiency-positive tumors was 37.2 months in the olaparib arm and 17.7 months in the placebo arm (hazard ratio, 0.33), according to the prescribing information for olaparib.
Serious adverse events occurred in 31% of patients in the olaparib arm. The most common were hypertension (19%) and anemia (17%).
Dose interruptions from adverse events occurred in 54% of patients in the olaparib arm, and dose reductions from adverse events occurred in 41%.
FDA approves selpercatinib for lung and thyroid RET tumors
Selpercatinib (Retevmo) becomes the first targeted therapy to be approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in patients with cancer who have certain tumors that have an alteration (mutation or fusion) in the RET gene.
The drug is indicated for use in RET-positive tumors found in the following:
- Non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that has spread in adult patients
- Advanced medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) or MTC that has spread in adult and pediatric patients (older than 12 years) who require systemic therapy
- Thyroid cancer that requires systemic therapy and that has stopped responding to or is not appropriate for radioactive iodine therapy in adult and pediatric (older than 12 years) patients.
Before initiating treatment, a RET gene alteration must be determined via laboratory testing, the FDA emphasized. However, no FDA-approved test is currently available for detecting RET fusions/mutations.
Approval based on responses in open-label trial
This was an accelerated approval based on the overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR) seen in an open-label clinical trial (the phase 1/2 LIBRETTO-001 study), which involved patients with each of the three types of tumors.
All patients received selpercatinib 160 mg orally twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurred.
For this trial, identification of a RET gene alteration was prospectively determined in plasma or tumor tissue by local laboratories using next-generation sequencing, polymerase chain reaction testing, or fluorescence in situ hybridization, according to Eli Lilly, the company marketing selpercatinib. Immunohistochemistry was not used in the clinical trial.
Efficacy for NSCLC was evaluated in 105 adult patients with RET fusion-positive NSCLC who were previously treated with platinum chemotherapy. The ORR was 64%.
Efficacy was also evaluated in 39 patients with RET fusion-positive NSCLC who had not received any previous treatment. The ORR for these patients was 84%.
For both groups, among patients who responded to treatment, the response lasted more than 6 months.
“In the clinical trial, we observed that the majority of metastatic lung cancer patients experienced clinically meaningful responses when treated with selpercatinib, including responses in difficult-to-treat brain metastases,” LIBRETTO-001 lead investigator Alexander Drilon, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, N.Y., said in an Eli Lilly press release.
“The approval of selpercatinib marks an important milestone in the treatment of NSCLC, making RET-driven cancers now specifically targetable in the same manner as cancers with activating EGFR and ALK alterations, across all lines of therapy,” Dr. Drilon added.
About 1% to 2% of NSCLC tumors are thought to have a RET alteration.
The same trial also included patients with thyroid cancer.
Efficacy for MTC was evaluated in 55 adult and pediatric (older than 12 years) patients with advanced or metastatic RET-mutant MTC who had previously been treated with cabozantinib, vandetanib, or both. The ORR in these patients was 69%.
In addition, selpercatinib was evaluated in 88 patients with advanced or metastatic RET-mutant MTC who had not received prior treatment with cabozantinib or vandetanib. The ORR for these patients was 73%.
The trial also enrolled 19 patients with RET-positive thyroid cancer whose condition was refractory to radioactive iodine (RAI) treatment and who had received another prior systemic treatment. The ORR was 79%. Eight patients had received only RAI. The ORR for these patients was 100%.
In all the cases of thyroid cancer and lung cancer, among the patients who responded to treatment, the response lasted longer than 6 months.
“RET alterations account for the majority of medullary thyroid cancers and a meaningful percentage of other thyroid cancers,” Lori J. Wirth, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center in Boston, noted in the company release.
A fact sheet from Eli Lilly notes that RET mutations are found in about 60% of sporadic MTC cases and in over 90% of familial MTC cases, and that RET fusions are found in approximately 10% to 20% of papillary thyroid cancers.
“For patients living with these cancers, the approval of selpercatinib means they now have a treatment option that selectively and potently inhibits RET,” Dr. Wirth commented. “Based on the published data for this new medicine, as well as my personal experience treating patients, this may be a good treatment option.”
In the LIBRETTO-001 trial, the rate of discontinuations because of adverse reactions (ARs) was 5%, the company reported. The most common ARs, including laboratory abnormalities (≥25%), were increased aspartate aminotransferase level, increased alanine aminotransferase level, increased glucose level, decreased leukocyte count, decreased albumin level, decreased calcium level, dry mouth, diarrhea, increased creatinine level, increased alkaline phosphatase level, hypertension, fatigue, edema, decreased platelet count, increased total cholesterol level, rash, decreased sodium levels, and constipation. The most frequent serious AR (≥2%) was pneumonia.
The FDA warned that selpercatinib can cause hepatotoxicity, elevation in blood pressure, QT prolongation, bleeding, and allergic reactions. It may also be toxic to a fetus or newborn baby so should not be taken by pregnant or breastfeeding women.
Selpercatinib is currently being assessed in two phase 3 confirmatory trials. LIBRETTO-431 will test the drug in previously untreated patients with RET-positive NSCLC. LIBRETTO-531 involves treatment-naive patients with RET-positive MTC.
The company that developed selpercaptinib, Loxo Oncology, was acquired by Eli Lilly last year in an $8 billion takeover. This drug was billed as the most promising asset in that deal, alongside oral BTK inhibitor LOXO-305, according to a report in Pharmaphorum.
Loxo developed Vitrakvi (larotrectinib), the first TRK inhibitor to reach the market, as well as the follow-up drug LOXO-195. Both were acquired by Bayer ahead of the Lilly takeover, that report notes.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Selpercatinib (Retevmo) becomes the first targeted therapy to be approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in patients with cancer who have certain tumors that have an alteration (mutation or fusion) in the RET gene.
The drug is indicated for use in RET-positive tumors found in the following:
- Non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that has spread in adult patients
- Advanced medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) or MTC that has spread in adult and pediatric patients (older than 12 years) who require systemic therapy
- Thyroid cancer that requires systemic therapy and that has stopped responding to or is not appropriate for radioactive iodine therapy in adult and pediatric (older than 12 years) patients.
Before initiating treatment, a RET gene alteration must be determined via laboratory testing, the FDA emphasized. However, no FDA-approved test is currently available for detecting RET fusions/mutations.
Approval based on responses in open-label trial
This was an accelerated approval based on the overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR) seen in an open-label clinical trial (the phase 1/2 LIBRETTO-001 study), which involved patients with each of the three types of tumors.
All patients received selpercatinib 160 mg orally twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurred.
For this trial, identification of a RET gene alteration was prospectively determined in plasma or tumor tissue by local laboratories using next-generation sequencing, polymerase chain reaction testing, or fluorescence in situ hybridization, according to Eli Lilly, the company marketing selpercatinib. Immunohistochemistry was not used in the clinical trial.
Efficacy for NSCLC was evaluated in 105 adult patients with RET fusion-positive NSCLC who were previously treated with platinum chemotherapy. The ORR was 64%.
Efficacy was also evaluated in 39 patients with RET fusion-positive NSCLC who had not received any previous treatment. The ORR for these patients was 84%.
For both groups, among patients who responded to treatment, the response lasted more than 6 months.
“In the clinical trial, we observed that the majority of metastatic lung cancer patients experienced clinically meaningful responses when treated with selpercatinib, including responses in difficult-to-treat brain metastases,” LIBRETTO-001 lead investigator Alexander Drilon, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, N.Y., said in an Eli Lilly press release.
“The approval of selpercatinib marks an important milestone in the treatment of NSCLC, making RET-driven cancers now specifically targetable in the same manner as cancers with activating EGFR and ALK alterations, across all lines of therapy,” Dr. Drilon added.
About 1% to 2% of NSCLC tumors are thought to have a RET alteration.
The same trial also included patients with thyroid cancer.
Efficacy for MTC was evaluated in 55 adult and pediatric (older than 12 years) patients with advanced or metastatic RET-mutant MTC who had previously been treated with cabozantinib, vandetanib, or both. The ORR in these patients was 69%.
In addition, selpercatinib was evaluated in 88 patients with advanced or metastatic RET-mutant MTC who had not received prior treatment with cabozantinib or vandetanib. The ORR for these patients was 73%.
The trial also enrolled 19 patients with RET-positive thyroid cancer whose condition was refractory to radioactive iodine (RAI) treatment and who had received another prior systemic treatment. The ORR was 79%. Eight patients had received only RAI. The ORR for these patients was 100%.
In all the cases of thyroid cancer and lung cancer, among the patients who responded to treatment, the response lasted longer than 6 months.
“RET alterations account for the majority of medullary thyroid cancers and a meaningful percentage of other thyroid cancers,” Lori J. Wirth, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center in Boston, noted in the company release.
A fact sheet from Eli Lilly notes that RET mutations are found in about 60% of sporadic MTC cases and in over 90% of familial MTC cases, and that RET fusions are found in approximately 10% to 20% of papillary thyroid cancers.
“For patients living with these cancers, the approval of selpercatinib means they now have a treatment option that selectively and potently inhibits RET,” Dr. Wirth commented. “Based on the published data for this new medicine, as well as my personal experience treating patients, this may be a good treatment option.”
In the LIBRETTO-001 trial, the rate of discontinuations because of adverse reactions (ARs) was 5%, the company reported. The most common ARs, including laboratory abnormalities (≥25%), were increased aspartate aminotransferase level, increased alanine aminotransferase level, increased glucose level, decreased leukocyte count, decreased albumin level, decreased calcium level, dry mouth, diarrhea, increased creatinine level, increased alkaline phosphatase level, hypertension, fatigue, edema, decreased platelet count, increased total cholesterol level, rash, decreased sodium levels, and constipation. The most frequent serious AR (≥2%) was pneumonia.
The FDA warned that selpercatinib can cause hepatotoxicity, elevation in blood pressure, QT prolongation, bleeding, and allergic reactions. It may also be toxic to a fetus or newborn baby so should not be taken by pregnant or breastfeeding women.
Selpercatinib is currently being assessed in two phase 3 confirmatory trials. LIBRETTO-431 will test the drug in previously untreated patients with RET-positive NSCLC. LIBRETTO-531 involves treatment-naive patients with RET-positive MTC.
The company that developed selpercaptinib, Loxo Oncology, was acquired by Eli Lilly last year in an $8 billion takeover. This drug was billed as the most promising asset in that deal, alongside oral BTK inhibitor LOXO-305, according to a report in Pharmaphorum.
Loxo developed Vitrakvi (larotrectinib), the first TRK inhibitor to reach the market, as well as the follow-up drug LOXO-195. Both were acquired by Bayer ahead of the Lilly takeover, that report notes.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Selpercatinib (Retevmo) becomes the first targeted therapy to be approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in patients with cancer who have certain tumors that have an alteration (mutation or fusion) in the RET gene.
The drug is indicated for use in RET-positive tumors found in the following:
- Non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that has spread in adult patients
- Advanced medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) or MTC that has spread in adult and pediatric patients (older than 12 years) who require systemic therapy
- Thyroid cancer that requires systemic therapy and that has stopped responding to or is not appropriate for radioactive iodine therapy in adult and pediatric (older than 12 years) patients.
Before initiating treatment, a RET gene alteration must be determined via laboratory testing, the FDA emphasized. However, no FDA-approved test is currently available for detecting RET fusions/mutations.
Approval based on responses in open-label trial
This was an accelerated approval based on the overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR) seen in an open-label clinical trial (the phase 1/2 LIBRETTO-001 study), which involved patients with each of the three types of tumors.
All patients received selpercatinib 160 mg orally twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurred.
For this trial, identification of a RET gene alteration was prospectively determined in plasma or tumor tissue by local laboratories using next-generation sequencing, polymerase chain reaction testing, or fluorescence in situ hybridization, according to Eli Lilly, the company marketing selpercatinib. Immunohistochemistry was not used in the clinical trial.
Efficacy for NSCLC was evaluated in 105 adult patients with RET fusion-positive NSCLC who were previously treated with platinum chemotherapy. The ORR was 64%.
Efficacy was also evaluated in 39 patients with RET fusion-positive NSCLC who had not received any previous treatment. The ORR for these patients was 84%.
For both groups, among patients who responded to treatment, the response lasted more than 6 months.
“In the clinical trial, we observed that the majority of metastatic lung cancer patients experienced clinically meaningful responses when treated with selpercatinib, including responses in difficult-to-treat brain metastases,” LIBRETTO-001 lead investigator Alexander Drilon, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, N.Y., said in an Eli Lilly press release.
“The approval of selpercatinib marks an important milestone in the treatment of NSCLC, making RET-driven cancers now specifically targetable in the same manner as cancers with activating EGFR and ALK alterations, across all lines of therapy,” Dr. Drilon added.
About 1% to 2% of NSCLC tumors are thought to have a RET alteration.
The same trial also included patients with thyroid cancer.
Efficacy for MTC was evaluated in 55 adult and pediatric (older than 12 years) patients with advanced or metastatic RET-mutant MTC who had previously been treated with cabozantinib, vandetanib, or both. The ORR in these patients was 69%.
In addition, selpercatinib was evaluated in 88 patients with advanced or metastatic RET-mutant MTC who had not received prior treatment with cabozantinib or vandetanib. The ORR for these patients was 73%.
The trial also enrolled 19 patients with RET-positive thyroid cancer whose condition was refractory to radioactive iodine (RAI) treatment and who had received another prior systemic treatment. The ORR was 79%. Eight patients had received only RAI. The ORR for these patients was 100%.
In all the cases of thyroid cancer and lung cancer, among the patients who responded to treatment, the response lasted longer than 6 months.
“RET alterations account for the majority of medullary thyroid cancers and a meaningful percentage of other thyroid cancers,” Lori J. Wirth, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center in Boston, noted in the company release.
A fact sheet from Eli Lilly notes that RET mutations are found in about 60% of sporadic MTC cases and in over 90% of familial MTC cases, and that RET fusions are found in approximately 10% to 20% of papillary thyroid cancers.
“For patients living with these cancers, the approval of selpercatinib means they now have a treatment option that selectively and potently inhibits RET,” Dr. Wirth commented. “Based on the published data for this new medicine, as well as my personal experience treating patients, this may be a good treatment option.”
In the LIBRETTO-001 trial, the rate of discontinuations because of adverse reactions (ARs) was 5%, the company reported. The most common ARs, including laboratory abnormalities (≥25%), were increased aspartate aminotransferase level, increased alanine aminotransferase level, increased glucose level, decreased leukocyte count, decreased albumin level, decreased calcium level, dry mouth, diarrhea, increased creatinine level, increased alkaline phosphatase level, hypertension, fatigue, edema, decreased platelet count, increased total cholesterol level, rash, decreased sodium levels, and constipation. The most frequent serious AR (≥2%) was pneumonia.
The FDA warned that selpercatinib can cause hepatotoxicity, elevation in blood pressure, QT prolongation, bleeding, and allergic reactions. It may also be toxic to a fetus or newborn baby so should not be taken by pregnant or breastfeeding women.
Selpercatinib is currently being assessed in two phase 3 confirmatory trials. LIBRETTO-431 will test the drug in previously untreated patients with RET-positive NSCLC. LIBRETTO-531 involves treatment-naive patients with RET-positive MTC.
The company that developed selpercaptinib, Loxo Oncology, was acquired by Eli Lilly last year in an $8 billion takeover. This drug was billed as the most promising asset in that deal, alongside oral BTK inhibitor LOXO-305, according to a report in Pharmaphorum.
Loxo developed Vitrakvi (larotrectinib), the first TRK inhibitor to reach the market, as well as the follow-up drug LOXO-195. Both were acquired by Bayer ahead of the Lilly takeover, that report notes.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
E-cigarette users topped 8 million in 2018
according to a report from the National Center for Health Statistics.
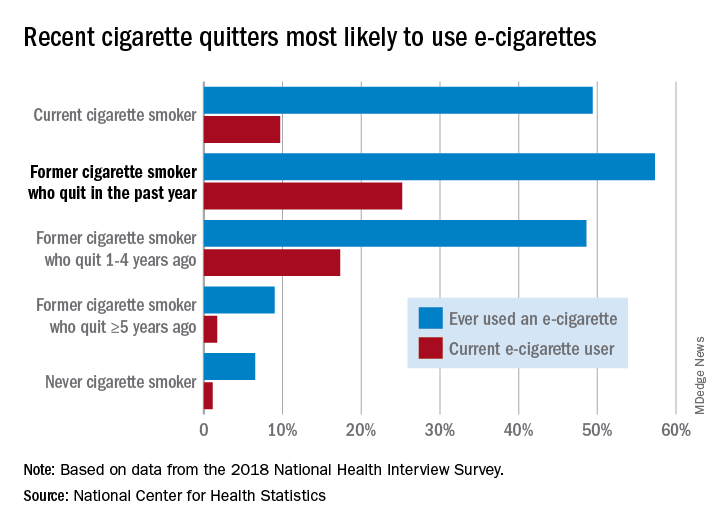
Those 8.1 million individuals who were using e-cigarettes either every day or some days represented 3.2% of the total adult population, based on data from the 2018 National Health Interview Survey. An even larger proportion, 14.9%, said that they had at least tried an e-cigarette, Maria A. Villarroel, PhD, and associates at the NCHS said in a recent data brief.
Most cigarette smokers, both current and former, were even more likely to use e-cigarettes, they noted.
Former cigarette smokers who had quit within the last year were the most likely to use e-cigarettes – 57.3% had ever used one and 25.2% were current users – while current cigarette users (49.4% ever use and 9.7% current use) and former smokers who had quit 1-5 years before (48.6% ever use, 17.3% current) also were above-average e-cigarette consumers, they reported.
Use was significantly lower, however, among former cigarette smokers who had quit 5 or more years earlier (9.0% and 1.7%, respectively) and those who had never smoked (6.5% and 1.1%), the NCHS investigators said.
The survey data also showed much variation among the sociodemographic subgroups:
- E-cigarette ever/current use was significantly higher in men (17.9% and 4.2%) than women (12.3% and 2.3%).
- Whites were significantly more likely to use e-cigarettes (16.9% and 3.7%), compared with Hispanic (11.5% and 2.5%), black (10.0% and 1.6%), and Asian (10.2% and 2.2%) adults.
- There was significant trend of decreasing use from age 18-24 years (25.8% and 7.6%) to 65 years and older (4.7% and 0.8%).
SOURCE: Villarroel MA et al. NCHS Data Brief No. 365, April 2020.
according to a report from the National Center for Health Statistics.

Those 8.1 million individuals who were using e-cigarettes either every day or some days represented 3.2% of the total adult population, based on data from the 2018 National Health Interview Survey. An even larger proportion, 14.9%, said that they had at least tried an e-cigarette, Maria A. Villarroel, PhD, and associates at the NCHS said in a recent data brief.
Most cigarette smokers, both current and former, were even more likely to use e-cigarettes, they noted.
Former cigarette smokers who had quit within the last year were the most likely to use e-cigarettes – 57.3% had ever used one and 25.2% were current users – while current cigarette users (49.4% ever use and 9.7% current use) and former smokers who had quit 1-5 years before (48.6% ever use, 17.3% current) also were above-average e-cigarette consumers, they reported.
Use was significantly lower, however, among former cigarette smokers who had quit 5 or more years earlier (9.0% and 1.7%, respectively) and those who had never smoked (6.5% and 1.1%), the NCHS investigators said.
The survey data also showed much variation among the sociodemographic subgroups:
- E-cigarette ever/current use was significantly higher in men (17.9% and 4.2%) than women (12.3% and 2.3%).
- Whites were significantly more likely to use e-cigarettes (16.9% and 3.7%), compared with Hispanic (11.5% and 2.5%), black (10.0% and 1.6%), and Asian (10.2% and 2.2%) adults.
- There was significant trend of decreasing use from age 18-24 years (25.8% and 7.6%) to 65 years and older (4.7% and 0.8%).
SOURCE: Villarroel MA et al. NCHS Data Brief No. 365, April 2020.
according to a report from the National Center for Health Statistics.

Those 8.1 million individuals who were using e-cigarettes either every day or some days represented 3.2% of the total adult population, based on data from the 2018 National Health Interview Survey. An even larger proportion, 14.9%, said that they had at least tried an e-cigarette, Maria A. Villarroel, PhD, and associates at the NCHS said in a recent data brief.
Most cigarette smokers, both current and former, were even more likely to use e-cigarettes, they noted.
Former cigarette smokers who had quit within the last year were the most likely to use e-cigarettes – 57.3% had ever used one and 25.2% were current users – while current cigarette users (49.4% ever use and 9.7% current use) and former smokers who had quit 1-5 years before (48.6% ever use, 17.3% current) also were above-average e-cigarette consumers, they reported.
Use was significantly lower, however, among former cigarette smokers who had quit 5 or more years earlier (9.0% and 1.7%, respectively) and those who had never smoked (6.5% and 1.1%), the NCHS investigators said.
The survey data also showed much variation among the sociodemographic subgroups:
- E-cigarette ever/current use was significantly higher in men (17.9% and 4.2%) than women (12.3% and 2.3%).
- Whites were significantly more likely to use e-cigarettes (16.9% and 3.7%), compared with Hispanic (11.5% and 2.5%), black (10.0% and 1.6%), and Asian (10.2% and 2.2%) adults.
- There was significant trend of decreasing use from age 18-24 years (25.8% and 7.6%) to 65 years and older (4.7% and 0.8%).
SOURCE: Villarroel MA et al. NCHS Data Brief No. 365, April 2020.
Operation Quack Hack: FDA moves to stop fraudulent COVID-19 products
No form of human misery can be allowed to go unexploited, and the pandemic, it seems, is no exception.
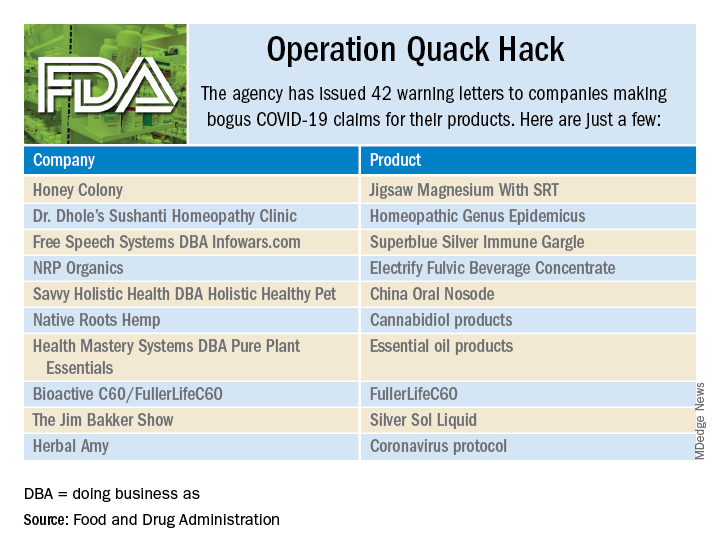
As part of Operation Quack Hack, the Food and Drug Administration has stepped up its investigation and enforcement efforts against companies and individuals that are “taking advantage of widespread fear among consumers during the COVID-19 pandemic” by selling fake products and treatments for coronavirus.
As of May 7, 2020, the agency had issued 42 warning letters to companies that were “selling unapproved products that fraudulently claim to mitigate, prevent, treat, diagnose or cure COVID-19,” the FDA announced in a written statement. Of those 42 products, 29 are no longer being sold with any sort of COVID-19 claim.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, Operation Quack Hack has uncovered hundreds of such products – drugs, testing kits, and personal protective equipment – being sold online, and complaints were sent to domain-name registrars and Internet marketplaces that have, in most cases, removed the postings, the FDA said.
“We will continue to monitor the online ecosystem for fraudulent products peddled by bad actors seeking to profit from this global pandemic. We encourage anyone aware of suspected fraudulent medical products for COVID-19 to report them to the FDA,” the statement said.
No form of human misery can be allowed to go unexploited, and the pandemic, it seems, is no exception.

As part of Operation Quack Hack, the Food and Drug Administration has stepped up its investigation and enforcement efforts against companies and individuals that are “taking advantage of widespread fear among consumers during the COVID-19 pandemic” by selling fake products and treatments for coronavirus.
As of May 7, 2020, the agency had issued 42 warning letters to companies that were “selling unapproved products that fraudulently claim to mitigate, prevent, treat, diagnose or cure COVID-19,” the FDA announced in a written statement. Of those 42 products, 29 are no longer being sold with any sort of COVID-19 claim.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, Operation Quack Hack has uncovered hundreds of such products – drugs, testing kits, and personal protective equipment – being sold online, and complaints were sent to domain-name registrars and Internet marketplaces that have, in most cases, removed the postings, the FDA said.
“We will continue to monitor the online ecosystem for fraudulent products peddled by bad actors seeking to profit from this global pandemic. We encourage anyone aware of suspected fraudulent medical products for COVID-19 to report them to the FDA,” the statement said.
No form of human misery can be allowed to go unexploited, and the pandemic, it seems, is no exception.

As part of Operation Quack Hack, the Food and Drug Administration has stepped up its investigation and enforcement efforts against companies and individuals that are “taking advantage of widespread fear among consumers during the COVID-19 pandemic” by selling fake products and treatments for coronavirus.
As of May 7, 2020, the agency had issued 42 warning letters to companies that were “selling unapproved products that fraudulently claim to mitigate, prevent, treat, diagnose or cure COVID-19,” the FDA announced in a written statement. Of those 42 products, 29 are no longer being sold with any sort of COVID-19 claim.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, Operation Quack Hack has uncovered hundreds of such products – drugs, testing kits, and personal protective equipment – being sold online, and complaints were sent to domain-name registrars and Internet marketplaces that have, in most cases, removed the postings, the FDA said.
“We will continue to monitor the online ecosystem for fraudulent products peddled by bad actors seeking to profit from this global pandemic. We encourage anyone aware of suspected fraudulent medical products for COVID-19 to report them to the FDA,” the statement said.
NSCLC: FDA approves capmatinib and companion assay
as detected by an FDA-approved test.
The FDA also approved the FoundationOne CDx assay (F1CDx) as a companion diagnostic for capmatinib. F1CDx is a next-generation sequencing-based, in vitro diagnostic device that detects several mutations, including MET exon 14 skipping mutations.
Capmatinib is a selective, reversible inhibitor of MET tyrosine kinase and the first treatment FDA-approved for NSCLC with MET exon 14 skipping mutations.
Capmatinib was granted accelerated approval based on overall response rate and response duration in the GEOMETRY mono-1 trial, the FDA said. Results from this trial were recently presented at the AACR Virtual Annual Meeting I.
The phase 2 trial enrolled 97 patients with metastatic NSCLC and confirmed MET exon 14 skipping mutations, 69 of whom were previously treated and 28 of whom were treatment naive. The patients received capmatinib at 400 mg orally twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The overall response rate was 68% in the treatment-naive patients and 41% in the previously treated patients. The median duration of response was 12.6 months and 9.7 months, respectively, according to the FDA.
The most common adverse events (occurring in at least 20% of patients) were peripheral edema, nausea, fatigue, vomiting, dyspnea, and decreased appetite.
The full prescribing information for capmatinib is available for download from the FDA website.
The FDA granted the approval of capmatinib to Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation and the approval of the F1CDx companion diagnostic to Foundation Medicine.
as detected by an FDA-approved test.
The FDA also approved the FoundationOne CDx assay (F1CDx) as a companion diagnostic for capmatinib. F1CDx is a next-generation sequencing-based, in vitro diagnostic device that detects several mutations, including MET exon 14 skipping mutations.
Capmatinib is a selective, reversible inhibitor of MET tyrosine kinase and the first treatment FDA-approved for NSCLC with MET exon 14 skipping mutations.
Capmatinib was granted accelerated approval based on overall response rate and response duration in the GEOMETRY mono-1 trial, the FDA said. Results from this trial were recently presented at the AACR Virtual Annual Meeting I.
The phase 2 trial enrolled 97 patients with metastatic NSCLC and confirmed MET exon 14 skipping mutations, 69 of whom were previously treated and 28 of whom were treatment naive. The patients received capmatinib at 400 mg orally twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The overall response rate was 68% in the treatment-naive patients and 41% in the previously treated patients. The median duration of response was 12.6 months and 9.7 months, respectively, according to the FDA.
The most common adverse events (occurring in at least 20% of patients) were peripheral edema, nausea, fatigue, vomiting, dyspnea, and decreased appetite.
The full prescribing information for capmatinib is available for download from the FDA website.
The FDA granted the approval of capmatinib to Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation and the approval of the F1CDx companion diagnostic to Foundation Medicine.
as detected by an FDA-approved test.
The FDA also approved the FoundationOne CDx assay (F1CDx) as a companion diagnostic for capmatinib. F1CDx is a next-generation sequencing-based, in vitro diagnostic device that detects several mutations, including MET exon 14 skipping mutations.
Capmatinib is a selective, reversible inhibitor of MET tyrosine kinase and the first treatment FDA-approved for NSCLC with MET exon 14 skipping mutations.
Capmatinib was granted accelerated approval based on overall response rate and response duration in the GEOMETRY mono-1 trial, the FDA said. Results from this trial were recently presented at the AACR Virtual Annual Meeting I.
The phase 2 trial enrolled 97 patients with metastatic NSCLC and confirmed MET exon 14 skipping mutations, 69 of whom were previously treated and 28 of whom were treatment naive. The patients received capmatinib at 400 mg orally twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The overall response rate was 68% in the treatment-naive patients and 41% in the previously treated patients. The median duration of response was 12.6 months and 9.7 months, respectively, according to the FDA.
The most common adverse events (occurring in at least 20% of patients) were peripheral edema, nausea, fatigue, vomiting, dyspnea, and decreased appetite.
The full prescribing information for capmatinib is available for download from the FDA website.
The FDA granted the approval of capmatinib to Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation and the approval of the F1CDx companion diagnostic to Foundation Medicine.
FDA grants EUA to muscle stimulator to reduce mechanical ventilator usage
The Food and Drug Administration has issued an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for the VentFree Respiratory Muscle Stimulator in order to potentially reduce the number of days adult patients, including those with COVID-19, require mechanical ventilation, according to a press release from Liberate Medical.
In comparison with mechanical ventilation, which is invasive and commonly weakens the breathing muscles, the VentFree system uses noninvasive neuromuscular electrical stimulation to contract the abdominal wall muscles in synchrony with exhalation during mechanical ventilation, according to the press release. This allows patients to begin treatment during the early stages of ventilation while they are sedated and to continue until they are weaned off of ventilation.
A pair of pilot randomized, controlled studies, completed in Europe and Australia, showed that VentFree helped to reduce ventilation duration and ICU length of stay, compared with placebo stimulation. The FDA granted VentFree Breakthrough Device status in 2019.
“We are grateful to the FDA for recognizing the potential of VentFree and feel privileged to have the opportunity to help patients on mechanical ventilation during the COVID-19 pandemic,” Angus McLachlan PhD, cofounder and CEO of Liberate Medical, said in the press release.
VentFree has been authorized for use only for the duration of the current COVID-19 emergency, as it has not yet been approved or cleared for usage by primary care providers.
The Food and Drug Administration has issued an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for the VentFree Respiratory Muscle Stimulator in order to potentially reduce the number of days adult patients, including those with COVID-19, require mechanical ventilation, according to a press release from Liberate Medical.
In comparison with mechanical ventilation, which is invasive and commonly weakens the breathing muscles, the VentFree system uses noninvasive neuromuscular electrical stimulation to contract the abdominal wall muscles in synchrony with exhalation during mechanical ventilation, according to the press release. This allows patients to begin treatment during the early stages of ventilation while they are sedated and to continue until they are weaned off of ventilation.
A pair of pilot randomized, controlled studies, completed in Europe and Australia, showed that VentFree helped to reduce ventilation duration and ICU length of stay, compared with placebo stimulation. The FDA granted VentFree Breakthrough Device status in 2019.
“We are grateful to the FDA for recognizing the potential of VentFree and feel privileged to have the opportunity to help patients on mechanical ventilation during the COVID-19 pandemic,” Angus McLachlan PhD, cofounder and CEO of Liberate Medical, said in the press release.
VentFree has been authorized for use only for the duration of the current COVID-19 emergency, as it has not yet been approved or cleared for usage by primary care providers.
The Food and Drug Administration has issued an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for the VentFree Respiratory Muscle Stimulator in order to potentially reduce the number of days adult patients, including those with COVID-19, require mechanical ventilation, according to a press release from Liberate Medical.
In comparison with mechanical ventilation, which is invasive and commonly weakens the breathing muscles, the VentFree system uses noninvasive neuromuscular electrical stimulation to contract the abdominal wall muscles in synchrony with exhalation during mechanical ventilation, according to the press release. This allows patients to begin treatment during the early stages of ventilation while they are sedated and to continue until they are weaned off of ventilation.
A pair of pilot randomized, controlled studies, completed in Europe and Australia, showed that VentFree helped to reduce ventilation duration and ICU length of stay, compared with placebo stimulation. The FDA granted VentFree Breakthrough Device status in 2019.
“We are grateful to the FDA for recognizing the potential of VentFree and feel privileged to have the opportunity to help patients on mechanical ventilation during the COVID-19 pandemic,” Angus McLachlan PhD, cofounder and CEO of Liberate Medical, said in the press release.
VentFree has been authorized for use only for the duration of the current COVID-19 emergency, as it has not yet been approved or cleared for usage by primary care providers.
FDA tightens requirements for COVID-19 antibody tests
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration is tightening requirements for companies that develop COVID-19 antibody tests in an effort to combat fraud and better regulate the frenzy of tests coming to market.
The updated policy, announced May 4, requires commercial antibody test developers to apply for Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) from the FDA under a tight time frame and also provides specific performance threshold recommendations for test specificity and sensitivity. The revised requirements follow a March 16 policy that allowed developers to validate their own tests and bring them to market without an agency review. More than 100 coronavirus antibody tests have since entered the market, fueling a congressional investigation into the accuracy of tests.
When the March policy was issued, FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said it was critical for the FDA to provide regulatory flexibility for serology test developers, given the nature of the COVID-19 public health emergency and an understanding that the tests were not meant to be used as the sole basis for COVID-19 diagnosis.
“As FDA has authorized more antibody tests and validation data has become available, including through the capability at [the National Cancer Institute] the careful balancing of risks and benefits has shifted to the approach we have outlined today and our policy update,” Dr. Hahn said during a May 4 press conference.
The new approach requires all commercial manufacturers to submit EUA requests with their validation data within 10 business days from the date they notified the FDA of their validation testing or from the date of the May 4 policy, whichever is later. Additionally, the FDA has provided specific performance threshold recommendations for specificity and sensitivity for all serology test developers.
In a statement released May 4, FDA leaders acknowledged the widespread fraud that is occurring in connection to antibody tests entering the market.
“We unfortunately see unscrupulous actors marketing fraudulent test kits and using the pandemic as an opportunity to take advantage of Americans’ anxiety,” wrote Anand Shah, MD, FDA deputy commissioner for medical and scientific affairs in a joint statement with Jeff E. Shuren, MD, director for the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “Some test developers have falsely claimed their serological tests are FDA approved or authorized. Others have falsely claimed that their tests can diagnose COVID-19 or that they are for at-home testing, which would fall outside of the policies outlined in our March 16 guidance, as well as the updated guidance.”
At the same time, FDA officials said they are aware of a “concerning number” of commercial serology tests that are being inappropriately marketed, including for diagnostic use, or that are performing poorly based on an independent evaluation by the National Institutes of Health, according to the May 4 statement.
In addition to tightening its requirements for test developers, the FDA also is introducing a more streamlined process to support EUA submissions and review. Two voluntary EUA templates for antibody tests are now available – one for commercial manufacturers and one for Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments-certified high-complexity labs seeking FDA authorization. The templates will facilitate the preparation and submission of EUA requests and can be used by any interested developer, according to the FDA.
To date, 12 antibody tests have been authorized under an individual EUA, and more than 200 antibody tests are currently the subject of a pre-EUA or EUA review, according to the FDA.
Many unknowns remain about antibody tests and how they might help researchers and clinicians understand and/or potentially treat COVID-19. Antibody tests may be able to provide information on disease prevalence and frequency of asymptomatic infection, as well as identify potential donors of “convalescent plasma,” an approach in which blood plasma containing antibodies from a recovered individual serves as a therapy for an infected patient with severe disease, Dr. Shah wrote in the May 4 statement.
“There are a lot of unanswered questions about this particular issue,” Dr. Hahn said during the press conference. “We need the data because we need to understand this particular aspect of the disease and put it as part of the puzzle around COVID-19.”
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration is tightening requirements for companies that develop COVID-19 antibody tests in an effort to combat fraud and better regulate the frenzy of tests coming to market.
The updated policy, announced May 4, requires commercial antibody test developers to apply for Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) from the FDA under a tight time frame and also provides specific performance threshold recommendations for test specificity and sensitivity. The revised requirements follow a March 16 policy that allowed developers to validate their own tests and bring them to market without an agency review. More than 100 coronavirus antibody tests have since entered the market, fueling a congressional investigation into the accuracy of tests.
When the March policy was issued, FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said it was critical for the FDA to provide regulatory flexibility for serology test developers, given the nature of the COVID-19 public health emergency and an understanding that the tests were not meant to be used as the sole basis for COVID-19 diagnosis.
“As FDA has authorized more antibody tests and validation data has become available, including through the capability at [the National Cancer Institute] the careful balancing of risks and benefits has shifted to the approach we have outlined today and our policy update,” Dr. Hahn said during a May 4 press conference.
The new approach requires all commercial manufacturers to submit EUA requests with their validation data within 10 business days from the date they notified the FDA of their validation testing or from the date of the May 4 policy, whichever is later. Additionally, the FDA has provided specific performance threshold recommendations for specificity and sensitivity for all serology test developers.
In a statement released May 4, FDA leaders acknowledged the widespread fraud that is occurring in connection to antibody tests entering the market.
“We unfortunately see unscrupulous actors marketing fraudulent test kits and using the pandemic as an opportunity to take advantage of Americans’ anxiety,” wrote Anand Shah, MD, FDA deputy commissioner for medical and scientific affairs in a joint statement with Jeff E. Shuren, MD, director for the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “Some test developers have falsely claimed their serological tests are FDA approved or authorized. Others have falsely claimed that their tests can diagnose COVID-19 or that they are for at-home testing, which would fall outside of the policies outlined in our March 16 guidance, as well as the updated guidance.”
At the same time, FDA officials said they are aware of a “concerning number” of commercial serology tests that are being inappropriately marketed, including for diagnostic use, or that are performing poorly based on an independent evaluation by the National Institutes of Health, according to the May 4 statement.
In addition to tightening its requirements for test developers, the FDA also is introducing a more streamlined process to support EUA submissions and review. Two voluntary EUA templates for antibody tests are now available – one for commercial manufacturers and one for Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments-certified high-complexity labs seeking FDA authorization. The templates will facilitate the preparation and submission of EUA requests and can be used by any interested developer, according to the FDA.
To date, 12 antibody tests have been authorized under an individual EUA, and more than 200 antibody tests are currently the subject of a pre-EUA or EUA review, according to the FDA.
Many unknowns remain about antibody tests and how they might help researchers and clinicians understand and/or potentially treat COVID-19. Antibody tests may be able to provide information on disease prevalence and frequency of asymptomatic infection, as well as identify potential donors of “convalescent plasma,” an approach in which blood plasma containing antibodies from a recovered individual serves as a therapy for an infected patient with severe disease, Dr. Shah wrote in the May 4 statement.
“There are a lot of unanswered questions about this particular issue,” Dr. Hahn said during the press conference. “We need the data because we need to understand this particular aspect of the disease and put it as part of the puzzle around COVID-19.”
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration is tightening requirements for companies that develop COVID-19 antibody tests in an effort to combat fraud and better regulate the frenzy of tests coming to market.
The updated policy, announced May 4, requires commercial antibody test developers to apply for Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) from the FDA under a tight time frame and also provides specific performance threshold recommendations for test specificity and sensitivity. The revised requirements follow a March 16 policy that allowed developers to validate their own tests and bring them to market without an agency review. More than 100 coronavirus antibody tests have since entered the market, fueling a congressional investigation into the accuracy of tests.
When the March policy was issued, FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said it was critical for the FDA to provide regulatory flexibility for serology test developers, given the nature of the COVID-19 public health emergency and an understanding that the tests were not meant to be used as the sole basis for COVID-19 diagnosis.
“As FDA has authorized more antibody tests and validation data has become available, including through the capability at [the National Cancer Institute] the careful balancing of risks and benefits has shifted to the approach we have outlined today and our policy update,” Dr. Hahn said during a May 4 press conference.
The new approach requires all commercial manufacturers to submit EUA requests with their validation data within 10 business days from the date they notified the FDA of their validation testing or from the date of the May 4 policy, whichever is later. Additionally, the FDA has provided specific performance threshold recommendations for specificity and sensitivity for all serology test developers.
In a statement released May 4, FDA leaders acknowledged the widespread fraud that is occurring in connection to antibody tests entering the market.
“We unfortunately see unscrupulous actors marketing fraudulent test kits and using the pandemic as an opportunity to take advantage of Americans’ anxiety,” wrote Anand Shah, MD, FDA deputy commissioner for medical and scientific affairs in a joint statement with Jeff E. Shuren, MD, director for the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “Some test developers have falsely claimed their serological tests are FDA approved or authorized. Others have falsely claimed that their tests can diagnose COVID-19 or that they are for at-home testing, which would fall outside of the policies outlined in our March 16 guidance, as well as the updated guidance.”
At the same time, FDA officials said they are aware of a “concerning number” of commercial serology tests that are being inappropriately marketed, including for diagnostic use, or that are performing poorly based on an independent evaluation by the National Institutes of Health, according to the May 4 statement.
In addition to tightening its requirements for test developers, the FDA also is introducing a more streamlined process to support EUA submissions and review. Two voluntary EUA templates for antibody tests are now available – one for commercial manufacturers and one for Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments-certified high-complexity labs seeking FDA authorization. The templates will facilitate the preparation and submission of EUA requests and can be used by any interested developer, according to the FDA.
To date, 12 antibody tests have been authorized under an individual EUA, and more than 200 antibody tests are currently the subject of a pre-EUA or EUA review, according to the FDA.
Many unknowns remain about antibody tests and how they might help researchers and clinicians understand and/or potentially treat COVID-19. Antibody tests may be able to provide information on disease prevalence and frequency of asymptomatic infection, as well as identify potential donors of “convalescent plasma,” an approach in which blood plasma containing antibodies from a recovered individual serves as a therapy for an infected patient with severe disease, Dr. Shah wrote in the May 4 statement.
“There are a lot of unanswered questions about this particular issue,” Dr. Hahn said during the press conference. “We need the data because we need to understand this particular aspect of the disease and put it as part of the puzzle around COVID-19.”
Progress report: Elimination of neonatal tetanus
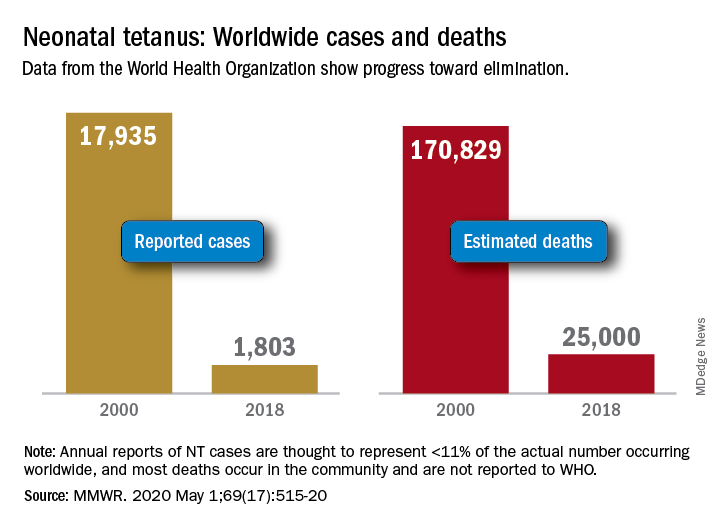
Worldwide cases of neonatal tetanus fell by 90% from 2000 to 2018, deaths dropped by 85%, and 45 countries achieved elimination of maternal and neonatal tetanus (MNT), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Despite this progress, some countries that achieved elimination are still struggling to sustain performance indicators; war and insecurity pose challenges in countries that have not achieved MNT elimination,” Henry N. Njuguna, MD, of the CDC’s global immunization division, and associates wrote in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Other worldwide measures also improved from 2000 to 2018: and the percentage of deliveries attended by a skilled birth attendant increased from 62% during 2000-2005 to 81% in 2013-2018, they reported.
The MNT elimination initiative, which began in 1999 and targeted 59 priority countries, immunized approximately 154 million women of reproductive age with at least two doses of tetanus toxoid–containing vaccine from 2000 to 2018, the investigators wrote, based on data from the World Health Organization and the United Nations Children’s Fund.
With 14 of the priority countries – including Nigeria, Pakistan, and Yemen – still dealing with MNT, however, numerous challenges remain, they noted. About 47 million women and their babies are still unprotected, and 49 million women have not received tetanus toxoid–containing vaccine.
This lack of coverage “can be attributed to weak health systems, including conflict and security issues that limit access to vaccination services, competing priorities that limit the implementation of planned MNT elimination activities, and withdrawal of donor funding,” Dr. Njuguna and associates wrote.
SOURCE: Njuguna HN et al. MMWR. 2020 May 1;69(17):515-20.
Worldwide cases of neonatal tetanus fell by 90% from 2000 to 2018, deaths dropped by 85%, and 45 countries achieved elimination of maternal and neonatal tetanus (MNT), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Despite this progress, some countries that achieved elimination are still struggling to sustain performance indicators; war and insecurity pose challenges in countries that have not achieved MNT elimination,” Henry N. Njuguna, MD, of the CDC’s global immunization division, and associates wrote in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Other worldwide measures also improved from 2000 to 2018: and the percentage of deliveries attended by a skilled birth attendant increased from 62% during 2000-2005 to 81% in 2013-2018, they reported.
The MNT elimination initiative, which began in 1999 and targeted 59 priority countries, immunized approximately 154 million women of reproductive age with at least two doses of tetanus toxoid–containing vaccine from 2000 to 2018, the investigators wrote, based on data from the World Health Organization and the United Nations Children’s Fund.
With 14 of the priority countries – including Nigeria, Pakistan, and Yemen – still dealing with MNT, however, numerous challenges remain, they noted. About 47 million women and their babies are still unprotected, and 49 million women have not received tetanus toxoid–containing vaccine.
This lack of coverage “can be attributed to weak health systems, including conflict and security issues that limit access to vaccination services, competing priorities that limit the implementation of planned MNT elimination activities, and withdrawal of donor funding,” Dr. Njuguna and associates wrote.
SOURCE: Njuguna HN et al. MMWR. 2020 May 1;69(17):515-20.
Worldwide cases of neonatal tetanus fell by 90% from 2000 to 2018, deaths dropped by 85%, and 45 countries achieved elimination of maternal and neonatal tetanus (MNT), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Despite this progress, some countries that achieved elimination are still struggling to sustain performance indicators; war and insecurity pose challenges in countries that have not achieved MNT elimination,” Henry N. Njuguna, MD, of the CDC’s global immunization division, and associates wrote in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Other worldwide measures also improved from 2000 to 2018: and the percentage of deliveries attended by a skilled birth attendant increased from 62% during 2000-2005 to 81% in 2013-2018, they reported.
The MNT elimination initiative, which began in 1999 and targeted 59 priority countries, immunized approximately 154 million women of reproductive age with at least two doses of tetanus toxoid–containing vaccine from 2000 to 2018, the investigators wrote, based on data from the World Health Organization and the United Nations Children’s Fund.
With 14 of the priority countries – including Nigeria, Pakistan, and Yemen – still dealing with MNT, however, numerous challenges remain, they noted. About 47 million women and their babies are still unprotected, and 49 million women have not received tetanus toxoid–containing vaccine.
This lack of coverage “can be attributed to weak health systems, including conflict and security issues that limit access to vaccination services, competing priorities that limit the implementation of planned MNT elimination activities, and withdrawal of donor funding,” Dr. Njuguna and associates wrote.
SOURCE: Njuguna HN et al. MMWR. 2020 May 1;69(17):515-20.
FROM MMWR
FDA grants Breakthrough Therapy status to sotatercept for PAH treatment
Approval for sotatercept, “a selective ligand trap for members of the TGF-beta [transforming growth factor-beta] superfamily which rebalances BMPR-II [bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II] signaling,” was based on two types of research. It was based on results of preclinical research indicating “reversed pulmonary vessel muscularization and improved indicators of right heart failure,” as well as results of the phase 2, placebo-controlled PULSAR study, in which sotatercept showed positive results, meeting primary and secondary endpoints.
Adverse events during PULSAR “were consistent with previously published data on sotatercept” in other diseases. The drug is also under investigation in the phase 2 SPECTRA trial, which includes patients with PAH.
“We believe that sotatercept has the potential to shift the current treatment paradigm and provide significant benefit to patients with PAH on top of currently available therapies. Thus, we’re thrilled that the FDA has granted this Breakthrough Therapy designation – a first for an Acceleron-discovered medicine and for a therapeutic candidate in PAH – as it supports and aligns with our mission to deliver novel therapeutic options to patients in need as quickly as possible,” Habib Dable, president and CEO of Acceleron Pharma, said in the press release.
Approval for sotatercept, “a selective ligand trap for members of the TGF-beta [transforming growth factor-beta] superfamily which rebalances BMPR-II [bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II] signaling,” was based on two types of research. It was based on results of preclinical research indicating “reversed pulmonary vessel muscularization and improved indicators of right heart failure,” as well as results of the phase 2, placebo-controlled PULSAR study, in which sotatercept showed positive results, meeting primary and secondary endpoints.
Adverse events during PULSAR “were consistent with previously published data on sotatercept” in other diseases. The drug is also under investigation in the phase 2 SPECTRA trial, which includes patients with PAH.
“We believe that sotatercept has the potential to shift the current treatment paradigm and provide significant benefit to patients with PAH on top of currently available therapies. Thus, we’re thrilled that the FDA has granted this Breakthrough Therapy designation – a first for an Acceleron-discovered medicine and for a therapeutic candidate in PAH – as it supports and aligns with our mission to deliver novel therapeutic options to patients in need as quickly as possible,” Habib Dable, president and CEO of Acceleron Pharma, said in the press release.
Approval for sotatercept, “a selective ligand trap for members of the TGF-beta [transforming growth factor-beta] superfamily which rebalances BMPR-II [bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II] signaling,” was based on two types of research. It was based on results of preclinical research indicating “reversed pulmonary vessel muscularization and improved indicators of right heart failure,” as well as results of the phase 2, placebo-controlled PULSAR study, in which sotatercept showed positive results, meeting primary and secondary endpoints.
Adverse events during PULSAR “were consistent with previously published data on sotatercept” in other diseases. The drug is also under investigation in the phase 2 SPECTRA trial, which includes patients with PAH.
“We believe that sotatercept has the potential to shift the current treatment paradigm and provide significant benefit to patients with PAH on top of currently available therapies. Thus, we’re thrilled that the FDA has granted this Breakthrough Therapy designation – a first for an Acceleron-discovered medicine and for a therapeutic candidate in PAH – as it supports and aligns with our mission to deliver novel therapeutic options to patients in need as quickly as possible,” Habib Dable, president and CEO of Acceleron Pharma, said in the press release.