User login
Mavyret approved for children with any HCV genotype
The Food and Drug Administration has approved glecaprevir/pibrentasvir tablets (Mavyret) for treating any of six identified genotypes of hepatitis C virus in children ages 12-17 years.
The agency noted in its press announcement that, Dosing information now will be provided for patients aged 12 years and older or weighing at least 99 lbs, without cirrhosis or who have compensated cirrhosis. It is not recommended for patients with moderate cirrhosis, and it is contraindicated in patients with severe cirrhosis, as well as patients taking atazanavir and rifampin.
In clinical trials of 47 patients with genotype 1, 2, 3, or 4 HCV without cirrhosis or with only mild cirrhosis, results at 12 weeks after 8 or 16 weeks’ treatment suggested patients’ infections had been cured – 100% had no virus detected in their blood. Adverse reactions observed were consistent with those previously observed in adults during clinical trials.
The most common reactions were headache and fatigue. Hepatitis B virus reactivation has been reported in coinfected adults during or after treatment with direct-acting antivirals, and in those who were not receiving HBV antiviral treatment. Full prescribing information can be found on the FDA website, and more information about this approval can be found in the agency’s announcement.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved glecaprevir/pibrentasvir tablets (Mavyret) for treating any of six identified genotypes of hepatitis C virus in children ages 12-17 years.
The agency noted in its press announcement that, Dosing information now will be provided for patients aged 12 years and older or weighing at least 99 lbs, without cirrhosis or who have compensated cirrhosis. It is not recommended for patients with moderate cirrhosis, and it is contraindicated in patients with severe cirrhosis, as well as patients taking atazanavir and rifampin.
In clinical trials of 47 patients with genotype 1, 2, 3, or 4 HCV without cirrhosis or with only mild cirrhosis, results at 12 weeks after 8 or 16 weeks’ treatment suggested patients’ infections had been cured – 100% had no virus detected in their blood. Adverse reactions observed were consistent with those previously observed in adults during clinical trials.
The most common reactions were headache and fatigue. Hepatitis B virus reactivation has been reported in coinfected adults during or after treatment with direct-acting antivirals, and in those who were not receiving HBV antiviral treatment. Full prescribing information can be found on the FDA website, and more information about this approval can be found in the agency’s announcement.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved glecaprevir/pibrentasvir tablets (Mavyret) for treating any of six identified genotypes of hepatitis C virus in children ages 12-17 years.
The agency noted in its press announcement that, Dosing information now will be provided for patients aged 12 years and older or weighing at least 99 lbs, without cirrhosis or who have compensated cirrhosis. It is not recommended for patients with moderate cirrhosis, and it is contraindicated in patients with severe cirrhosis, as well as patients taking atazanavir and rifampin.
In clinical trials of 47 patients with genotype 1, 2, 3, or 4 HCV without cirrhosis or with only mild cirrhosis, results at 12 weeks after 8 or 16 weeks’ treatment suggested patients’ infections had been cured – 100% had no virus detected in their blood. Adverse reactions observed were consistent with those previously observed in adults during clinical trials.
The most common reactions were headache and fatigue. Hepatitis B virus reactivation has been reported in coinfected adults during or after treatment with direct-acting antivirals, and in those who were not receiving HBV antiviral treatment. Full prescribing information can be found on the FDA website, and more information about this approval can be found in the agency’s announcement.
Long-term antibiotic use may heighten stroke, CHD risk
, according to a study in the European Heart Journal.
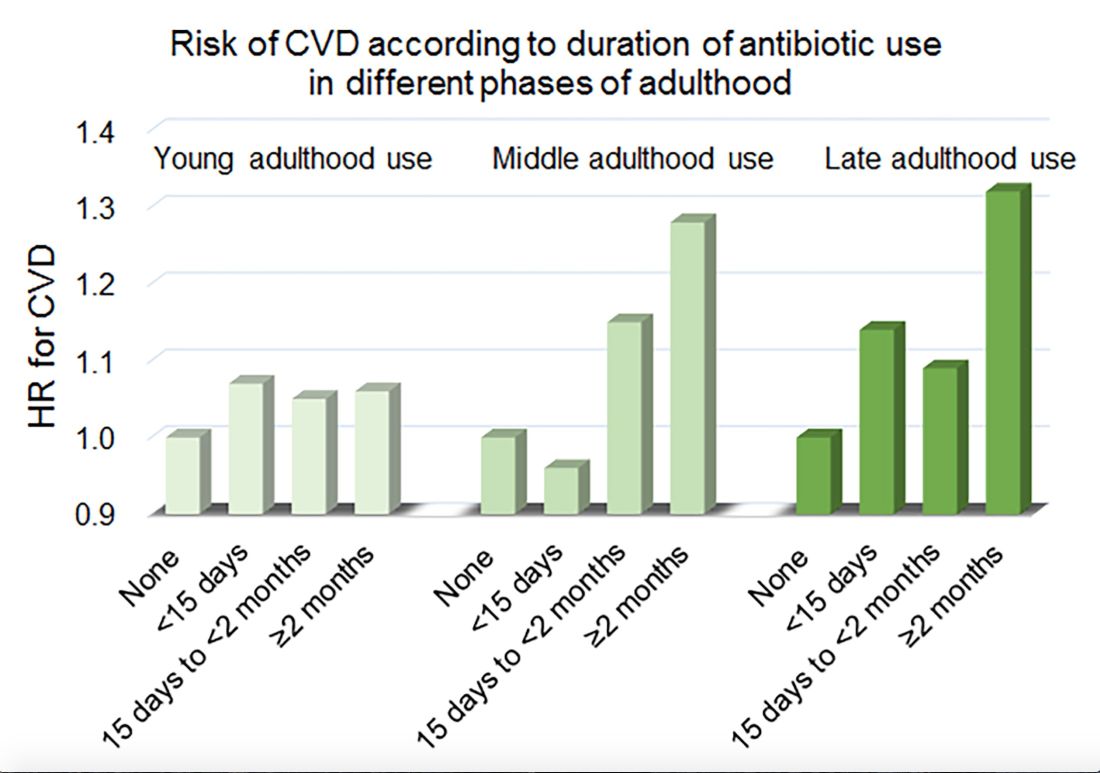
Women in the Nurses’ Health Study who used antibiotics for 2 or more months between ages 40 and 59 years or at age 60 years and older had a significantly increased risk of cardiovascular disease, compared with those who did not use antibiotics. Antibiotic use between 20 and 39 years old was not significantly related to cardiovascular disease.
Prior research has found that antibiotics may have long-lasting effects on gut microbiota and relate to cardiovascular disease risk.
“Antibiotic use is the most critical factor in altering the balance of microorganisms in the gut,” said lead investigator Lu Qi, MD, PhD, in a news release. “Previous studies have shown a link between alterations in the microbiotic environment of the gut and inflammation and narrowing of the blood vessels, stroke, and heart disease,” said Dr. Qi, who is the director of the Tulane University Obesity Research Center in New Orleans and an adjunct professor of nutrition at Harvard T.C. Chan School of Public Health in Boston.
To evaluate associations between life stage, antibiotic exposure, and subsequent cardiovascular disease, researchers analyzed data from 36,429 participants in the Nurses’ Health Study. The women were at least 60 years old and had no history of cardiovascular disease or cancer when they completed a 2004 questionnaire about antibiotic usage during young, middle, and late adulthood. The questionnaire asked participants to indicate the total time using antibiotics with eight categories ranging from none to 5 or more years.
The researchers defined incident cardiovascular disease as a composite endpoint of coronary heart disease (nonfatal myocardial infarction or fatal coronary heart disease) and stroke (nonfatal or fatal). They calculated person-years of follow-up from the questionnaire return date until date of cardiovascular disease diagnosis, death, or end of follow-up in 2012.
Women with longer duration of antibiotic use were more likely to use other medications and have unfavorable cardiovascular risk profiles, including family history of myocardial infarction and higher body mass index. Antibiotics most often were used to treat respiratory infections. During an average follow-up of 7.6 years, 1,056 participants developed cardiovascular disease.
In a multivariable model that adjusted for demographics, diet, lifestyle, reason for antibiotic use, medications, overweight status, and other factors, long-term antibiotic use – 2 months or more – in late adulthood was associated with significantly increased risk of cardiovascular disease (hazard ratio, 1.32), as was long-term antibiotic use in middle adulthood (HR, 1.28).
Although antibiotic use was self-reported, which could lead to misclassification, the participants were health professionals, which may mitigate this limitation, the authors noted. Whether these findings apply to men and other populations requires further study, they said.
Because of the study’s observational design, the results “cannot show that antibiotics cause heart disease and stroke, only that there is a link between them,” Dr. Qi said. “It’s possible that women who reported more antibiotic use might be sicker in other ways that we were unable to measure, or there may be other factors that could affect the results that we have not been able take account of.”
“Our study suggests that antibiotics should be used only when they are absolutely needed,” he concluded. “Considering the potentially cumulative adverse effects, the shorter time of antibiotic use the better.”
The study was supported by National Institutes of Health grants, the Boston Obesity Nutrition Research Center, and the United States–Israel Binational Science Foundation. One author received support from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. The authors had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Heianza Y et al. Eur Heart J. 2019 Apr 24. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz231.
, according to a study in the European Heart Journal.

Women in the Nurses’ Health Study who used antibiotics for 2 or more months between ages 40 and 59 years or at age 60 years and older had a significantly increased risk of cardiovascular disease, compared with those who did not use antibiotics. Antibiotic use between 20 and 39 years old was not significantly related to cardiovascular disease.
Prior research has found that antibiotics may have long-lasting effects on gut microbiota and relate to cardiovascular disease risk.
“Antibiotic use is the most critical factor in altering the balance of microorganisms in the gut,” said lead investigator Lu Qi, MD, PhD, in a news release. “Previous studies have shown a link between alterations in the microbiotic environment of the gut and inflammation and narrowing of the blood vessels, stroke, and heart disease,” said Dr. Qi, who is the director of the Tulane University Obesity Research Center in New Orleans and an adjunct professor of nutrition at Harvard T.C. Chan School of Public Health in Boston.
To evaluate associations between life stage, antibiotic exposure, and subsequent cardiovascular disease, researchers analyzed data from 36,429 participants in the Nurses’ Health Study. The women were at least 60 years old and had no history of cardiovascular disease or cancer when they completed a 2004 questionnaire about antibiotic usage during young, middle, and late adulthood. The questionnaire asked participants to indicate the total time using antibiotics with eight categories ranging from none to 5 or more years.
The researchers defined incident cardiovascular disease as a composite endpoint of coronary heart disease (nonfatal myocardial infarction or fatal coronary heart disease) and stroke (nonfatal or fatal). They calculated person-years of follow-up from the questionnaire return date until date of cardiovascular disease diagnosis, death, or end of follow-up in 2012.
Women with longer duration of antibiotic use were more likely to use other medications and have unfavorable cardiovascular risk profiles, including family history of myocardial infarction and higher body mass index. Antibiotics most often were used to treat respiratory infections. During an average follow-up of 7.6 years, 1,056 participants developed cardiovascular disease.
In a multivariable model that adjusted for demographics, diet, lifestyle, reason for antibiotic use, medications, overweight status, and other factors, long-term antibiotic use – 2 months or more – in late adulthood was associated with significantly increased risk of cardiovascular disease (hazard ratio, 1.32), as was long-term antibiotic use in middle adulthood (HR, 1.28).
Although antibiotic use was self-reported, which could lead to misclassification, the participants were health professionals, which may mitigate this limitation, the authors noted. Whether these findings apply to men and other populations requires further study, they said.
Because of the study’s observational design, the results “cannot show that antibiotics cause heart disease and stroke, only that there is a link between them,” Dr. Qi said. “It’s possible that women who reported more antibiotic use might be sicker in other ways that we were unable to measure, or there may be other factors that could affect the results that we have not been able take account of.”
“Our study suggests that antibiotics should be used only when they are absolutely needed,” he concluded. “Considering the potentially cumulative adverse effects, the shorter time of antibiotic use the better.”
The study was supported by National Institutes of Health grants, the Boston Obesity Nutrition Research Center, and the United States–Israel Binational Science Foundation. One author received support from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. The authors had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Heianza Y et al. Eur Heart J. 2019 Apr 24. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz231.
, according to a study in the European Heart Journal.

Women in the Nurses’ Health Study who used antibiotics for 2 or more months between ages 40 and 59 years or at age 60 years and older had a significantly increased risk of cardiovascular disease, compared with those who did not use antibiotics. Antibiotic use between 20 and 39 years old was not significantly related to cardiovascular disease.
Prior research has found that antibiotics may have long-lasting effects on gut microbiota and relate to cardiovascular disease risk.
“Antibiotic use is the most critical factor in altering the balance of microorganisms in the gut,” said lead investigator Lu Qi, MD, PhD, in a news release. “Previous studies have shown a link between alterations in the microbiotic environment of the gut and inflammation and narrowing of the blood vessels, stroke, and heart disease,” said Dr. Qi, who is the director of the Tulane University Obesity Research Center in New Orleans and an adjunct professor of nutrition at Harvard T.C. Chan School of Public Health in Boston.
To evaluate associations between life stage, antibiotic exposure, and subsequent cardiovascular disease, researchers analyzed data from 36,429 participants in the Nurses’ Health Study. The women were at least 60 years old and had no history of cardiovascular disease or cancer when they completed a 2004 questionnaire about antibiotic usage during young, middle, and late adulthood. The questionnaire asked participants to indicate the total time using antibiotics with eight categories ranging from none to 5 or more years.
The researchers defined incident cardiovascular disease as a composite endpoint of coronary heart disease (nonfatal myocardial infarction or fatal coronary heart disease) and stroke (nonfatal or fatal). They calculated person-years of follow-up from the questionnaire return date until date of cardiovascular disease diagnosis, death, or end of follow-up in 2012.
Women with longer duration of antibiotic use were more likely to use other medications and have unfavorable cardiovascular risk profiles, including family history of myocardial infarction and higher body mass index. Antibiotics most often were used to treat respiratory infections. During an average follow-up of 7.6 years, 1,056 participants developed cardiovascular disease.
In a multivariable model that adjusted for demographics, diet, lifestyle, reason for antibiotic use, medications, overweight status, and other factors, long-term antibiotic use – 2 months or more – in late adulthood was associated with significantly increased risk of cardiovascular disease (hazard ratio, 1.32), as was long-term antibiotic use in middle adulthood (HR, 1.28).
Although antibiotic use was self-reported, which could lead to misclassification, the participants were health professionals, which may mitigate this limitation, the authors noted. Whether these findings apply to men and other populations requires further study, they said.
Because of the study’s observational design, the results “cannot show that antibiotics cause heart disease and stroke, only that there is a link between them,” Dr. Qi said. “It’s possible that women who reported more antibiotic use might be sicker in other ways that we were unable to measure, or there may be other factors that could affect the results that we have not been able take account of.”
“Our study suggests that antibiotics should be used only when they are absolutely needed,” he concluded. “Considering the potentially cumulative adverse effects, the shorter time of antibiotic use the better.”
The study was supported by National Institutes of Health grants, the Boston Obesity Nutrition Research Center, and the United States–Israel Binational Science Foundation. One author received support from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. The authors had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Heianza Y et al. Eur Heart J. 2019 Apr 24. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz231.
FROM THE EUROPEAN HEART JOURNAL
Key clinical point: Among middle-aged and older women, 2 or more months’ exposure to antibiotics is associated with an increased risk of coronary heart disease or stroke.
Major finding: Long-term antibiotic use in late adulthood was associated with significantly increased risk of cardiovascular disease (hazard ratio, 1.32), as was long-term antibiotic use in middle adulthood (HR, 1.28).
Study details: An analysis of data from nearly 36,500 women in the Nurses’ Health Study.
Disclosures: The study was supported by National Institutes of Health grants, the Boston Obesity Nutrition Research Center, and the United States–Israel Binational Science Foundation. One author received support from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. The authors had no conflicts of interest.
Source: Heianza Y et al. Eur Heart J. 2019 Apr 24. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz231.
Medical cannabis relieved pain, decreased opioid use in elderly
results of a recent retrospective chart review suggest. Treatment with medical cannabis improved pain, sleep, anxiety, and neuropathy in patients aged 75 years of age and older, and was associated with reduced use of opioids in about one-third of cases, according to authors of the study, which will be presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
“Our findings are promising and can help fuel further research into medical marijuana as an additional option for this group of people who often have chronic conditions,” said lead investigator Laszlo Mechtler, MD, of Dent Neurologic Institute in Buffalo, N.Y., in a news release. However, additional randomized, placebo-controlled studies are needed to confirm results of this study, Dr. Mechtler added.
The chart review focused on 204 elderly patients who participated in New York State’s medical marijuana program and were followed in a neurologic outpatient setting. The cohort included 129 female and 75 male patients, ranging in age from 75 to 102 years, with a mean age of 81 years. The medical marijuana was taken by mouth as a liquid extract tincture, capsule, or in an electronic vaporizer.
With an average exposure time of 16.8 weeks, 69% of patients experienced symptomatic benefit, according to patient self-report. The most commonly reported benefit was relief of chronic pain in 49%, while improvements in sleep, neuropathy, and anxiety were reported in 18%, 15%, and 10%, respectively. Reductions in opioid pain medication were noted in about one-third of cases, they found.
While 34% of patients had adverse effects on medical marijuana, only 21% reported adverse effects after cannabinoid doses were adjusted, investigators said. Adverse effects led to discontinuation of medical cannabis in seven patients, or 3.4% of the overall cohort. Somnolence, disequilibrium, and gastrointestinal disturbance were the most common adverse effects, occurring in 13%, 7%, and 7% of patients, respectively. Euphoria was reported in 3% of patients.
Among patients who had no reported adverse effects, the most commonly used formulation was a balanced 1:1 tincture of tetrahydrocannabinol to cannabidiol, investigators said.
Further trials could explore optimal dosing of medical cannabis in elderly patients and shed more light on adverse effects such as somnolence and disequilibrium, according to Dr. Mechtler and colleagues.
The study was supported by the Dent Family Foundation.
SOURCE: Bargnes V et al. AAN 2019, Abstract P4.1-014.
results of a recent retrospective chart review suggest. Treatment with medical cannabis improved pain, sleep, anxiety, and neuropathy in patients aged 75 years of age and older, and was associated with reduced use of opioids in about one-third of cases, according to authors of the study, which will be presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
“Our findings are promising and can help fuel further research into medical marijuana as an additional option for this group of people who often have chronic conditions,” said lead investigator Laszlo Mechtler, MD, of Dent Neurologic Institute in Buffalo, N.Y., in a news release. However, additional randomized, placebo-controlled studies are needed to confirm results of this study, Dr. Mechtler added.
The chart review focused on 204 elderly patients who participated in New York State’s medical marijuana program and were followed in a neurologic outpatient setting. The cohort included 129 female and 75 male patients, ranging in age from 75 to 102 years, with a mean age of 81 years. The medical marijuana was taken by mouth as a liquid extract tincture, capsule, or in an electronic vaporizer.
With an average exposure time of 16.8 weeks, 69% of patients experienced symptomatic benefit, according to patient self-report. The most commonly reported benefit was relief of chronic pain in 49%, while improvements in sleep, neuropathy, and anxiety were reported in 18%, 15%, and 10%, respectively. Reductions in opioid pain medication were noted in about one-third of cases, they found.
While 34% of patients had adverse effects on medical marijuana, only 21% reported adverse effects after cannabinoid doses were adjusted, investigators said. Adverse effects led to discontinuation of medical cannabis in seven patients, or 3.4% of the overall cohort. Somnolence, disequilibrium, and gastrointestinal disturbance were the most common adverse effects, occurring in 13%, 7%, and 7% of patients, respectively. Euphoria was reported in 3% of patients.
Among patients who had no reported adverse effects, the most commonly used formulation was a balanced 1:1 tincture of tetrahydrocannabinol to cannabidiol, investigators said.
Further trials could explore optimal dosing of medical cannabis in elderly patients and shed more light on adverse effects such as somnolence and disequilibrium, according to Dr. Mechtler and colleagues.
The study was supported by the Dent Family Foundation.
SOURCE: Bargnes V et al. AAN 2019, Abstract P4.1-014.
results of a recent retrospective chart review suggest. Treatment with medical cannabis improved pain, sleep, anxiety, and neuropathy in patients aged 75 years of age and older, and was associated with reduced use of opioids in about one-third of cases, according to authors of the study, which will be presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
“Our findings are promising and can help fuel further research into medical marijuana as an additional option for this group of people who often have chronic conditions,” said lead investigator Laszlo Mechtler, MD, of Dent Neurologic Institute in Buffalo, N.Y., in a news release. However, additional randomized, placebo-controlled studies are needed to confirm results of this study, Dr. Mechtler added.
The chart review focused on 204 elderly patients who participated in New York State’s medical marijuana program and were followed in a neurologic outpatient setting. The cohort included 129 female and 75 male patients, ranging in age from 75 to 102 years, with a mean age of 81 years. The medical marijuana was taken by mouth as a liquid extract tincture, capsule, or in an electronic vaporizer.
With an average exposure time of 16.8 weeks, 69% of patients experienced symptomatic benefit, according to patient self-report. The most commonly reported benefit was relief of chronic pain in 49%, while improvements in sleep, neuropathy, and anxiety were reported in 18%, 15%, and 10%, respectively. Reductions in opioid pain medication were noted in about one-third of cases, they found.
While 34% of patients had adverse effects on medical marijuana, only 21% reported adverse effects after cannabinoid doses were adjusted, investigators said. Adverse effects led to discontinuation of medical cannabis in seven patients, or 3.4% of the overall cohort. Somnolence, disequilibrium, and gastrointestinal disturbance were the most common adverse effects, occurring in 13%, 7%, and 7% of patients, respectively. Euphoria was reported in 3% of patients.
Among patients who had no reported adverse effects, the most commonly used formulation was a balanced 1:1 tincture of tetrahydrocannabinol to cannabidiol, investigators said.
Further trials could explore optimal dosing of medical cannabis in elderly patients and shed more light on adverse effects such as somnolence and disequilibrium, according to Dr. Mechtler and colleagues.
The study was supported by the Dent Family Foundation.
SOURCE: Bargnes V et al. AAN 2019, Abstract P4.1-014.
FROM AAN 2019
FDA approves IL-23 inhibitor risankizumab for treating plaque psoriasis
Risankizumab, an interleukin-23 inhibitor, has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adults who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy, the manufacturer announced on April 23.
Risankizumab selectively inhibits interleukin-23 (IL-23), a key inflammatory protein, by binding to its p19 subunit. The drug is administered at a dose of 150 mg, in two subcutaneous injections, every 12 weeks, after starting doses at weeks 0 and 4. It will be available in early May, according to an AbbVie press release announcing the approval.
The approval was based in part on data from two phase 3, 2-year studies, In UltIMMA-1 and UltIMMA-2, at 16 weeks, 75% of risankizumab patients in both studies achieved a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI 90), compared with 5% and 2% of those on placebo, respectively. These results were published in 2018 (Lancet. 2018 Aug 25;392[10148]:650-61).
At 1 year, 82% and 81% of those treated with risankizumab in the two studies achieved a PASI 90, and 56% and 60% achieved a PASI 100, respectively, according to the company.
Approval was also based on additional phase 3 studies, IMMhance and IMMvent.
Upper respiratory infections were among the most common adverse events associated with risankizumab in trials, reported in 13%, according to the company. Other adverse events associated with treatment included headache (3.5 %), fatigue (2.5 %), injection site reactions (1.5%) and tinea infections (1.1%). The AbbVie release states that candidates for treatment should be evaluated for tuberculosis before starting therapy, and patients should be instructed to report signs and symptoms of infection.
Risankizumab, which will be marketed as Skyrizi, was recently approved in Canada for the same indication, and in Japan, for plaque psoriasis, generalized pustular psoriasis, erythrodermic psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis in adults. It currently is under review in Europe.
AbbVie and Boehringer Ingelheim are collaborating on the development of risankizumab, according to an AbbVie press release. Studies of risankizumab for treatment of psoriatic arthritis and Crohn’s disease are underway.
Risankizumab, an interleukin-23 inhibitor, has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adults who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy, the manufacturer announced on April 23.
Risankizumab selectively inhibits interleukin-23 (IL-23), a key inflammatory protein, by binding to its p19 subunit. The drug is administered at a dose of 150 mg, in two subcutaneous injections, every 12 weeks, after starting doses at weeks 0 and 4. It will be available in early May, according to an AbbVie press release announcing the approval.
The approval was based in part on data from two phase 3, 2-year studies, In UltIMMA-1 and UltIMMA-2, at 16 weeks, 75% of risankizumab patients in both studies achieved a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI 90), compared with 5% and 2% of those on placebo, respectively. These results were published in 2018 (Lancet. 2018 Aug 25;392[10148]:650-61).
At 1 year, 82% and 81% of those treated with risankizumab in the two studies achieved a PASI 90, and 56% and 60% achieved a PASI 100, respectively, according to the company.
Approval was also based on additional phase 3 studies, IMMhance and IMMvent.
Upper respiratory infections were among the most common adverse events associated with risankizumab in trials, reported in 13%, according to the company. Other adverse events associated with treatment included headache (3.5 %), fatigue (2.5 %), injection site reactions (1.5%) and tinea infections (1.1%). The AbbVie release states that candidates for treatment should be evaluated for tuberculosis before starting therapy, and patients should be instructed to report signs and symptoms of infection.
Risankizumab, which will be marketed as Skyrizi, was recently approved in Canada for the same indication, and in Japan, for plaque psoriasis, generalized pustular psoriasis, erythrodermic psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis in adults. It currently is under review in Europe.
AbbVie and Boehringer Ingelheim are collaborating on the development of risankizumab, according to an AbbVie press release. Studies of risankizumab for treatment of psoriatic arthritis and Crohn’s disease are underway.
Risankizumab, an interleukin-23 inhibitor, has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adults who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy, the manufacturer announced on April 23.
Risankizumab selectively inhibits interleukin-23 (IL-23), a key inflammatory protein, by binding to its p19 subunit. The drug is administered at a dose of 150 mg, in two subcutaneous injections, every 12 weeks, after starting doses at weeks 0 and 4. It will be available in early May, according to an AbbVie press release announcing the approval.
The approval was based in part on data from two phase 3, 2-year studies, In UltIMMA-1 and UltIMMA-2, at 16 weeks, 75% of risankizumab patients in both studies achieved a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI 90), compared with 5% and 2% of those on placebo, respectively. These results were published in 2018 (Lancet. 2018 Aug 25;392[10148]:650-61).
At 1 year, 82% and 81% of those treated with risankizumab in the two studies achieved a PASI 90, and 56% and 60% achieved a PASI 100, respectively, according to the company.
Approval was also based on additional phase 3 studies, IMMhance and IMMvent.
Upper respiratory infections were among the most common adverse events associated with risankizumab in trials, reported in 13%, according to the company. Other adverse events associated with treatment included headache (3.5 %), fatigue (2.5 %), injection site reactions (1.5%) and tinea infections (1.1%). The AbbVie release states that candidates for treatment should be evaluated for tuberculosis before starting therapy, and patients should be instructed to report signs and symptoms of infection.
Risankizumab, which will be marketed as Skyrizi, was recently approved in Canada for the same indication, and in Japan, for plaque psoriasis, generalized pustular psoriasis, erythrodermic psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis in adults. It currently is under review in Europe.
AbbVie and Boehringer Ingelheim are collaborating on the development of risankizumab, according to an AbbVie press release. Studies of risankizumab for treatment of psoriatic arthritis and Crohn’s disease are underway.
Alvogen issues recall for mislabeled fentanyl patches
Alvogen has issued a voluntary recall of two lots of its Fentanyl Transdermal System 12-mcg/h transdermal patches because of a product mislabeling, according to the Food and Drug Administration.
The recall was issued because a small number of cartons labeled as containing 12-mcg/h patches contained 50-mcg/h patches. The 50-mcg/h patches were labeled as such within the package.
Application of a 50-mcg/h patch instead of a 12-mcg/h patch could result in serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression. Groups at potential risk for such adverse events include first-time users of the patch, children, and the elderly. No reports of serious adverse events have yet been reported.
“Pharmacies are requested not to dispense any product subject to this recall,” the FDA said in a press release. Patients who “have product subject to this recall should immediately remove any patch currently in use and contact their health care provider. Patients with unused product should return it to point of purchase for replacement.”
Find more information on the recall at the FDA website.
Alvogen has issued a voluntary recall of two lots of its Fentanyl Transdermal System 12-mcg/h transdermal patches because of a product mislabeling, according to the Food and Drug Administration.
The recall was issued because a small number of cartons labeled as containing 12-mcg/h patches contained 50-mcg/h patches. The 50-mcg/h patches were labeled as such within the package.
Application of a 50-mcg/h patch instead of a 12-mcg/h patch could result in serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression. Groups at potential risk for such adverse events include first-time users of the patch, children, and the elderly. No reports of serious adverse events have yet been reported.
“Pharmacies are requested not to dispense any product subject to this recall,” the FDA said in a press release. Patients who “have product subject to this recall should immediately remove any patch currently in use and contact their health care provider. Patients with unused product should return it to point of purchase for replacement.”
Find more information on the recall at the FDA website.
Alvogen has issued a voluntary recall of two lots of its Fentanyl Transdermal System 12-mcg/h transdermal patches because of a product mislabeling, according to the Food and Drug Administration.
The recall was issued because a small number of cartons labeled as containing 12-mcg/h patches contained 50-mcg/h patches. The 50-mcg/h patches were labeled as such within the package.
Application of a 50-mcg/h patch instead of a 12-mcg/h patch could result in serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression. Groups at potential risk for such adverse events include first-time users of the patch, children, and the elderly. No reports of serious adverse events have yet been reported.
“Pharmacies are requested not to dispense any product subject to this recall,” the FDA said in a press release. Patients who “have product subject to this recall should immediately remove any patch currently in use and contact their health care provider. Patients with unused product should return it to point of purchase for replacement.”
Find more information on the recall at the FDA website.
Restricting opioids after knee surgery did not increase refills
according to a study in the Journal of Arthroplasty.
Contrary to concerns that restrictive opioid prescribing might increase the number of patient call-ins and refill requests, one academic institution had significantly fewer call-ins and refills after it implemented a strict postoperative opioid prescribing protocol on Jan. 1, 2018.
“Orthopedic surgeons might be reluctant to change practice without evidence that new, more-restrictive practice will not impede patient care,” the researchers wrote. “As the current study demonstrates, there is room to significantly decrease postoperative opioid prescriptions in total joint arthroplasty. This places patients at lower risk of opioid abuse and diversion without significantly altering the risk of postoperative complications or compromising postoperative pain control.”
Opioid overuse is a major public health concern, and orthopedic surgeons may overprescribe opioids after surgery. The University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics in Iowa City implemented strict postoperative opioid prescription guidelines that are based on the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons Clinical Practice Guidelines. As part of the protocol, patients receive a preoperative education session that emphasizes risks associated with opioid use. Before initiating this protocol, postoperative drug choice and quantity had not been standardized.
To examine changes in opioid prescriptions and the number of call-ins, postoperative complications, and prescription refill requests after the implementation of the restrictive opioid prescribing protocol, investigators at the institution conducted a retrospective study.
Andrew J. Holte, a researcher in the department of orthopedics and rehabilitation, and his colleagues reviewed cases from June 2017 to February 2018. Their analysis included 399 patients who underwent total hip arthroplasty or total knee arthroplasty.
In all, 282 patients underwent surgery before the restrictive protocol (the historical cohort) and 117 after (the restrictive cohort). In the historical cohort, about 48% of the patients underwent total knee arthroplasty. In the restrictive cohort, about 44% underwent total knee arthroplasty. Patients had an average age of about 61 years, and approximately 52% were women.
According to comparisons of morphine mg equivalents (MME), the historical cohort received significantly larger mean initial opioid prescriptions (752 MME vs. 387 MME), significantly more refills per patient (0.5 vs. 0.3), and significantly more medication through refills (253 MME vs. 84 MME).
“For reference, 50 pills of 5 mg oxycodone is equivalent to 300 MMEs,” the authors noted.
A multivariable model found that younger age and total knee arthroplasty, compared with total hip arthroplasty, were associated with increased likelihood of requests for refills and patient call-ins.
“Surprisingly, there were significantly more patient call-ins and requests for refills of opioids in the historical cohort,” Mr. Holte and his colleagues said. “Although this study did not collect direct data on patient pain scores, we believe that call-ins and requests for refills are sufficient surrogate markers for inadequate pain control.”
The study does not account for prescriptions from other providers or whether patients took none, some, or all of their filled prescriptions. Future studies are needed to assess how reduced opioid prescriptions affect pain and functional outcomes in the long term, the researchers said.
One or more study authors disclosed potential conflicts of interest. The disclosures can be found in Appendix A, Supplementary Data, at the end of the journal article.
SOURCE: Holte AJ et al. J Arthroplasty. 2019 Feb 20. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2019.02.022.
according to a study in the Journal of Arthroplasty.
Contrary to concerns that restrictive opioid prescribing might increase the number of patient call-ins and refill requests, one academic institution had significantly fewer call-ins and refills after it implemented a strict postoperative opioid prescribing protocol on Jan. 1, 2018.
“Orthopedic surgeons might be reluctant to change practice without evidence that new, more-restrictive practice will not impede patient care,” the researchers wrote. “As the current study demonstrates, there is room to significantly decrease postoperative opioid prescriptions in total joint arthroplasty. This places patients at lower risk of opioid abuse and diversion without significantly altering the risk of postoperative complications or compromising postoperative pain control.”
Opioid overuse is a major public health concern, and orthopedic surgeons may overprescribe opioids after surgery. The University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics in Iowa City implemented strict postoperative opioid prescription guidelines that are based on the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons Clinical Practice Guidelines. As part of the protocol, patients receive a preoperative education session that emphasizes risks associated with opioid use. Before initiating this protocol, postoperative drug choice and quantity had not been standardized.
To examine changes in opioid prescriptions and the number of call-ins, postoperative complications, and prescription refill requests after the implementation of the restrictive opioid prescribing protocol, investigators at the institution conducted a retrospective study.
Andrew J. Holte, a researcher in the department of orthopedics and rehabilitation, and his colleagues reviewed cases from June 2017 to February 2018. Their analysis included 399 patients who underwent total hip arthroplasty or total knee arthroplasty.
In all, 282 patients underwent surgery before the restrictive protocol (the historical cohort) and 117 after (the restrictive cohort). In the historical cohort, about 48% of the patients underwent total knee arthroplasty. In the restrictive cohort, about 44% underwent total knee arthroplasty. Patients had an average age of about 61 years, and approximately 52% were women.
According to comparisons of morphine mg equivalents (MME), the historical cohort received significantly larger mean initial opioid prescriptions (752 MME vs. 387 MME), significantly more refills per patient (0.5 vs. 0.3), and significantly more medication through refills (253 MME vs. 84 MME).
“For reference, 50 pills of 5 mg oxycodone is equivalent to 300 MMEs,” the authors noted.
A multivariable model found that younger age and total knee arthroplasty, compared with total hip arthroplasty, were associated with increased likelihood of requests for refills and patient call-ins.
“Surprisingly, there were significantly more patient call-ins and requests for refills of opioids in the historical cohort,” Mr. Holte and his colleagues said. “Although this study did not collect direct data on patient pain scores, we believe that call-ins and requests for refills are sufficient surrogate markers for inadequate pain control.”
The study does not account for prescriptions from other providers or whether patients took none, some, or all of their filled prescriptions. Future studies are needed to assess how reduced opioid prescriptions affect pain and functional outcomes in the long term, the researchers said.
One or more study authors disclosed potential conflicts of interest. The disclosures can be found in Appendix A, Supplementary Data, at the end of the journal article.
SOURCE: Holte AJ et al. J Arthroplasty. 2019 Feb 20. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2019.02.022.
according to a study in the Journal of Arthroplasty.
Contrary to concerns that restrictive opioid prescribing might increase the number of patient call-ins and refill requests, one academic institution had significantly fewer call-ins and refills after it implemented a strict postoperative opioid prescribing protocol on Jan. 1, 2018.
“Orthopedic surgeons might be reluctant to change practice without evidence that new, more-restrictive practice will not impede patient care,” the researchers wrote. “As the current study demonstrates, there is room to significantly decrease postoperative opioid prescriptions in total joint arthroplasty. This places patients at lower risk of opioid abuse and diversion without significantly altering the risk of postoperative complications or compromising postoperative pain control.”
Opioid overuse is a major public health concern, and orthopedic surgeons may overprescribe opioids after surgery. The University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics in Iowa City implemented strict postoperative opioid prescription guidelines that are based on the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons Clinical Practice Guidelines. As part of the protocol, patients receive a preoperative education session that emphasizes risks associated with opioid use. Before initiating this protocol, postoperative drug choice and quantity had not been standardized.
To examine changes in opioid prescriptions and the number of call-ins, postoperative complications, and prescription refill requests after the implementation of the restrictive opioid prescribing protocol, investigators at the institution conducted a retrospective study.
Andrew J. Holte, a researcher in the department of orthopedics and rehabilitation, and his colleagues reviewed cases from June 2017 to February 2018. Their analysis included 399 patients who underwent total hip arthroplasty or total knee arthroplasty.
In all, 282 patients underwent surgery before the restrictive protocol (the historical cohort) and 117 after (the restrictive cohort). In the historical cohort, about 48% of the patients underwent total knee arthroplasty. In the restrictive cohort, about 44% underwent total knee arthroplasty. Patients had an average age of about 61 years, and approximately 52% were women.
According to comparisons of morphine mg equivalents (MME), the historical cohort received significantly larger mean initial opioid prescriptions (752 MME vs. 387 MME), significantly more refills per patient (0.5 vs. 0.3), and significantly more medication through refills (253 MME vs. 84 MME).
“For reference, 50 pills of 5 mg oxycodone is equivalent to 300 MMEs,” the authors noted.
A multivariable model found that younger age and total knee arthroplasty, compared with total hip arthroplasty, were associated with increased likelihood of requests for refills and patient call-ins.
“Surprisingly, there were significantly more patient call-ins and requests for refills of opioids in the historical cohort,” Mr. Holte and his colleagues said. “Although this study did not collect direct data on patient pain scores, we believe that call-ins and requests for refills are sufficient surrogate markers for inadequate pain control.”
The study does not account for prescriptions from other providers or whether patients took none, some, or all of their filled prescriptions. Future studies are needed to assess how reduced opioid prescriptions affect pain and functional outcomes in the long term, the researchers said.
One or more study authors disclosed potential conflicts of interest. The disclosures can be found in Appendix A, Supplementary Data, at the end of the journal article.
SOURCE: Holte AJ et al. J Arthroplasty. 2019 Feb 20. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2019.02.022.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF ARTHROPLASTY
FDA approves generic naloxone spray for opioid overdose treatment
The Food and Drug Administration on April 19 approved the first generic naloxone hydrochloride nasal spray (Narcan) as treatment for stopping or reversing an opioid overdose.
“In the wake of the opioid crisis, a number of efforts are underway to make this emergency overdose reversal treatment more readily available and more accessible,” said Douglas Throckmorton, MD, deputy center director for regulatory programs in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, in a press release. “In addition to this approval of the first generic naloxone nasal spray, moving forward, we will prioritize our review of generic drug applications for naloxone.”
The agency said the naloxone nasal spray does not need assembly and can be used by anyone, regardless of medical training. If the spray is administered quickly after the overdose begins, the effect of the opioid will be countered, often within minutes. However, patients should still seek immediate medical attention.
The FDA cautioned that, when used on a patient with an opioid dependence, naloxone can cause severe opioid withdrawal, characterized by symptoms such as body aches, diarrhea, tachycardia, fever, runny nose, sneezing, goose bumps, sweating, yawning, nausea or vomiting, nervousness, restlessness or irritability, shivering or trembling, abdominal cramps, weakness, and increased blood pressure.
Find the full press release on the FDA website.
The Food and Drug Administration on April 19 approved the first generic naloxone hydrochloride nasal spray (Narcan) as treatment for stopping or reversing an opioid overdose.
“In the wake of the opioid crisis, a number of efforts are underway to make this emergency overdose reversal treatment more readily available and more accessible,” said Douglas Throckmorton, MD, deputy center director for regulatory programs in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, in a press release. “In addition to this approval of the first generic naloxone nasal spray, moving forward, we will prioritize our review of generic drug applications for naloxone.”
The agency said the naloxone nasal spray does not need assembly and can be used by anyone, regardless of medical training. If the spray is administered quickly after the overdose begins, the effect of the opioid will be countered, often within minutes. However, patients should still seek immediate medical attention.
The FDA cautioned that, when used on a patient with an opioid dependence, naloxone can cause severe opioid withdrawal, characterized by symptoms such as body aches, diarrhea, tachycardia, fever, runny nose, sneezing, goose bumps, sweating, yawning, nausea or vomiting, nervousness, restlessness or irritability, shivering or trembling, abdominal cramps, weakness, and increased blood pressure.
Find the full press release on the FDA website.
The Food and Drug Administration on April 19 approved the first generic naloxone hydrochloride nasal spray (Narcan) as treatment for stopping or reversing an opioid overdose.
“In the wake of the opioid crisis, a number of efforts are underway to make this emergency overdose reversal treatment more readily available and more accessible,” said Douglas Throckmorton, MD, deputy center director for regulatory programs in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, in a press release. “In addition to this approval of the first generic naloxone nasal spray, moving forward, we will prioritize our review of generic drug applications for naloxone.”
The agency said the naloxone nasal spray does not need assembly and can be used by anyone, regardless of medical training. If the spray is administered quickly after the overdose begins, the effect of the opioid will be countered, often within minutes. However, patients should still seek immediate medical attention.
The FDA cautioned that, when used on a patient with an opioid dependence, naloxone can cause severe opioid withdrawal, characterized by symptoms such as body aches, diarrhea, tachycardia, fever, runny nose, sneezing, goose bumps, sweating, yawning, nausea or vomiting, nervousness, restlessness or irritability, shivering or trembling, abdominal cramps, weakness, and increased blood pressure.
Find the full press release on the FDA website.
Calcium supplement use linked to cancer death
PHILADELPHIA – a nutrition specialist noted at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
The report, published (Ann Intern Med. 2019 Apr 9. doi: 10.7326/M18-2478) just 2 days before the start of the Internal Medicine meeting, found no mortality benefits associated with any reported dietary supplement use among nearly 31,000 adults in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
On the contrary, they found that excess calcium consumption was associated with increased risk for cancer-related deaths. Calcium supplements were specifically implicated in the excess of mortality, according to the investigators, with a rate ratio of 1.53 (95% confidence interval, 1.04-2.25) for intakes of 1,000 mg/day versus no intake.
“It’s better to get all of your vitamins from your food, over supplements,” said Marijane Hynes, MD, director of weight management at George Washington University, Washington, in a meet-the-professor session at the conference.
The amount of calcium patients are getting from food can be estimated with one rule of thumb: Multiply the number of dairy servings per day by 300 mg, Dr. Hynes said, who added that a serving is 8 ounces of milk or 1 ounce of hard cheese. Dark green vegetables, breads, cereals, and some nuts can provide 100-200 mg of calcium per day.
Calcium carbonate can be taken with food to enhance calcium absorption, according to Dr. Hynes, while calcium citrate can be taken without food, and is preferred for patients taking acid reflux medications.
Because calcium absorption is reduced at higher doses, patients who need more than 600 mg/day should be taking divided doses, she said.
Bone health goes beyond the dairy aisle, Dr. Hynes added. High vitamin K intake was linked to reduced hip fracture risk among the Framingham Heart Study participants. To get the recommended amount of vitamin K in the diet, patients can consume one or more servings of broccoli, kale, collard greens, or dark green lettuce.
Dr. Hynes reported she that had no relationships with entities producing, marketing, reselling, or distributing health care goods or services consumed by, or used on, patients.
These are observational data. This is not saying we put someone on calcium, and they ended up with cancer, and when you look at this whole thing it’s amazing to me that nobody is discussing the benefits that were found in patients taking magnesium, vitamin K2, and other vitamins. The other thing I would like to point out is that, for at least a decade, it has been really well established that we shouldn’t be using more than 1,000 milligrams of calcium a day, especially from a supplements source. In this study, supplemental calcium intake of 1,000 mg/d or higher was associated with increased risk of cancer death, so what’s the big deal?
The big thing with calcium is calcium comes in 7 different forms. When you eat a variety of fruits and vegetables the source of calcium you get is mixed. The problem with supplements is you are using one or maybe two forms of calcium, but if your body doesn’t recognize that form of calcium then you aren’t getting calcium and it may not be beneficial to you.
What we need to do here, in my opinion, is we need to look at the whole picture. We know that dieting alone or exercising alone does not improve outcomes. It’s the combination of diet, exercise, hormone balance, nutrients from supplements, and emotional balance that makes you healthy. Similarly, you can’t say if you just take this one nutrient you are going to improve your quality of life.
With calcium and vitamin D, you have to take vitamin K2, because vitamin K2 activates osteocalcin, a protein that rebuilds the matrix of the bone. Without vitamin K2, you can’t deposit calcium in the bones. K2 also prevents the deposition of calcium in the blood vessels.
Magnesium is another tremendously important mineral, and magnesium deficiency is the most common mineral deficiency in the United States.
Probably one of the most common causes of magnesium deficiency is the use of acid blockers. I would be very curious to know how many people were taking proton pump inhibitors or acid blockers in general. I bet you most of them were.
Derrick DeSilva Jr., MD, is an internist, practicing in Edison, N.J. He made these comments in an interview. He reported serving as a consultant for Common Sense Supplements, a company that produces dietary supplements.
These are observational data. This is not saying we put someone on calcium, and they ended up with cancer, and when you look at this whole thing it’s amazing to me that nobody is discussing the benefits that were found in patients taking magnesium, vitamin K2, and other vitamins. The other thing I would like to point out is that, for at least a decade, it has been really well established that we shouldn’t be using more than 1,000 milligrams of calcium a day, especially from a supplements source. In this study, supplemental calcium intake of 1,000 mg/d or higher was associated with increased risk of cancer death, so what’s the big deal?
The big thing with calcium is calcium comes in 7 different forms. When you eat a variety of fruits and vegetables the source of calcium you get is mixed. The problem with supplements is you are using one or maybe two forms of calcium, but if your body doesn’t recognize that form of calcium then you aren’t getting calcium and it may not be beneficial to you.
What we need to do here, in my opinion, is we need to look at the whole picture. We know that dieting alone or exercising alone does not improve outcomes. It’s the combination of diet, exercise, hormone balance, nutrients from supplements, and emotional balance that makes you healthy. Similarly, you can’t say if you just take this one nutrient you are going to improve your quality of life.
With calcium and vitamin D, you have to take vitamin K2, because vitamin K2 activates osteocalcin, a protein that rebuilds the matrix of the bone. Without vitamin K2, you can’t deposit calcium in the bones. K2 also prevents the deposition of calcium in the blood vessels.
Magnesium is another tremendously important mineral, and magnesium deficiency is the most common mineral deficiency in the United States.
Probably one of the most common causes of magnesium deficiency is the use of acid blockers. I would be very curious to know how many people were taking proton pump inhibitors or acid blockers in general. I bet you most of them were.
Derrick DeSilva Jr., MD, is an internist, practicing in Edison, N.J. He made these comments in an interview. He reported serving as a consultant for Common Sense Supplements, a company that produces dietary supplements.
These are observational data. This is not saying we put someone on calcium, and they ended up with cancer, and when you look at this whole thing it’s amazing to me that nobody is discussing the benefits that were found in patients taking magnesium, vitamin K2, and other vitamins. The other thing I would like to point out is that, for at least a decade, it has been really well established that we shouldn’t be using more than 1,000 milligrams of calcium a day, especially from a supplements source. In this study, supplemental calcium intake of 1,000 mg/d or higher was associated with increased risk of cancer death, so what’s the big deal?
The big thing with calcium is calcium comes in 7 different forms. When you eat a variety of fruits and vegetables the source of calcium you get is mixed. The problem with supplements is you are using one or maybe two forms of calcium, but if your body doesn’t recognize that form of calcium then you aren’t getting calcium and it may not be beneficial to you.
What we need to do here, in my opinion, is we need to look at the whole picture. We know that dieting alone or exercising alone does not improve outcomes. It’s the combination of diet, exercise, hormone balance, nutrients from supplements, and emotional balance that makes you healthy. Similarly, you can’t say if you just take this one nutrient you are going to improve your quality of life.
With calcium and vitamin D, you have to take vitamin K2, because vitamin K2 activates osteocalcin, a protein that rebuilds the matrix of the bone. Without vitamin K2, you can’t deposit calcium in the bones. K2 also prevents the deposition of calcium in the blood vessels.
Magnesium is another tremendously important mineral, and magnesium deficiency is the most common mineral deficiency in the United States.
Probably one of the most common causes of magnesium deficiency is the use of acid blockers. I would be very curious to know how many people were taking proton pump inhibitors or acid blockers in general. I bet you most of them were.
Derrick DeSilva Jr., MD, is an internist, practicing in Edison, N.J. He made these comments in an interview. He reported serving as a consultant for Common Sense Supplements, a company that produces dietary supplements.
PHILADELPHIA – a nutrition specialist noted at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
The report, published (Ann Intern Med. 2019 Apr 9. doi: 10.7326/M18-2478) just 2 days before the start of the Internal Medicine meeting, found no mortality benefits associated with any reported dietary supplement use among nearly 31,000 adults in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
On the contrary, they found that excess calcium consumption was associated with increased risk for cancer-related deaths. Calcium supplements were specifically implicated in the excess of mortality, according to the investigators, with a rate ratio of 1.53 (95% confidence interval, 1.04-2.25) for intakes of 1,000 mg/day versus no intake.
“It’s better to get all of your vitamins from your food, over supplements,” said Marijane Hynes, MD, director of weight management at George Washington University, Washington, in a meet-the-professor session at the conference.
The amount of calcium patients are getting from food can be estimated with one rule of thumb: Multiply the number of dairy servings per day by 300 mg, Dr. Hynes said, who added that a serving is 8 ounces of milk or 1 ounce of hard cheese. Dark green vegetables, breads, cereals, and some nuts can provide 100-200 mg of calcium per day.
Calcium carbonate can be taken with food to enhance calcium absorption, according to Dr. Hynes, while calcium citrate can be taken without food, and is preferred for patients taking acid reflux medications.
Because calcium absorption is reduced at higher doses, patients who need more than 600 mg/day should be taking divided doses, she said.
Bone health goes beyond the dairy aisle, Dr. Hynes added. High vitamin K intake was linked to reduced hip fracture risk among the Framingham Heart Study participants. To get the recommended amount of vitamin K in the diet, patients can consume one or more servings of broccoli, kale, collard greens, or dark green lettuce.
Dr. Hynes reported she that had no relationships with entities producing, marketing, reselling, or distributing health care goods or services consumed by, or used on, patients.
PHILADELPHIA – a nutrition specialist noted at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
The report, published (Ann Intern Med. 2019 Apr 9. doi: 10.7326/M18-2478) just 2 days before the start of the Internal Medicine meeting, found no mortality benefits associated with any reported dietary supplement use among nearly 31,000 adults in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
On the contrary, they found that excess calcium consumption was associated with increased risk for cancer-related deaths. Calcium supplements were specifically implicated in the excess of mortality, according to the investigators, with a rate ratio of 1.53 (95% confidence interval, 1.04-2.25) for intakes of 1,000 mg/day versus no intake.
“It’s better to get all of your vitamins from your food, over supplements,” said Marijane Hynes, MD, director of weight management at George Washington University, Washington, in a meet-the-professor session at the conference.
The amount of calcium patients are getting from food can be estimated with one rule of thumb: Multiply the number of dairy servings per day by 300 mg, Dr. Hynes said, who added that a serving is 8 ounces of milk or 1 ounce of hard cheese. Dark green vegetables, breads, cereals, and some nuts can provide 100-200 mg of calcium per day.
Calcium carbonate can be taken with food to enhance calcium absorption, according to Dr. Hynes, while calcium citrate can be taken without food, and is preferred for patients taking acid reflux medications.
Because calcium absorption is reduced at higher doses, patients who need more than 600 mg/day should be taking divided doses, she said.
Bone health goes beyond the dairy aisle, Dr. Hynes added. High vitamin K intake was linked to reduced hip fracture risk among the Framingham Heart Study participants. To get the recommended amount of vitamin K in the diet, patients can consume one or more servings of broccoli, kale, collard greens, or dark green lettuce.
Dr. Hynes reported she that had no relationships with entities producing, marketing, reselling, or distributing health care goods or services consumed by, or used on, patients.
REPORTING FROM INTERNAL MEDICINE 2019
Clinical Pharmacist Credentialing and Privileging: A Process for Ensuring High-Quality Patient Care
The Red Lake Indian Health Service (IHS) health care facility is in north-central Minnesota within the Red Lake Nation. The facility supports primary care, emergency, urgent care, pharmacy, inpatient, optometry, dental, radiology, laboratory, physical therapy, and behavioral health services to about 10,000 Red Lake Band of Chippewa Indian patients. The Red Lake pharmacy provides inpatient and outpatient medication services and pharmacist-managed clinical patient care.
In 2013, the Red Lake IHS medical staff endorsed the implementation of comprehensive clinical pharmacy services to increase health care access and optimize clinical outcomes for patients. During the evolution of pharmacy-based patient-centric care, the clinical programs offered by Red Lake IHS pharmacy expanded from 1 anticoagulation clinic to multiple advanced-practice clinical pharmacy services. This included pharmacy primary care, medication-assisted therapy, naloxone, hepatitis C, and behavioral health medication management clinics.
The immense clinical growth of the pharmacy department demonstrated a need to assess and monitor pharmacist competency to ensure the delivery of quality patient care. Essential quality improvement processes were lacking. To fill these quality improvement gaps, a robust pharmacist credentialing and privileging program was implemented in 2015.
Patient Care
As efforts within health care establishments across the US focus on the delivery of efficient, high-quality, affordable health care, pharmacists have become increasingly instrumental in providing patient care within expanded clinical roles.1-8 Many clinical pharmacy models have evolved into interdisciplinary approaches to care.9 Within these models, abiding by state and federal laws, pharmacists practice under the indirect supervision of licensed independent practitioners (LIPs), such as physicians, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants.8 Under collaborative practice agreements (CPAs), patients are initially diagnosed by LIPs, then referred to clinical pharmacists for therapeutic management.5,7
Clinical pharmacist functions encompass comprehensive medication management (ie, prescribing, monitoring, and adjustment of medications), nonpharmacologic guidance, and coordination of care. Interdisciplinary collaboration allows pharmacists opportunities to provide direct patient care or consultations by telecommunication in many different clinical environments, including disease management, primary care, or specialty care. Pharmacists may manage chronic or acute illnesses associated with endocrine, cardiovascular, respiratory, gastrointestinal, or other systems.
Pharmacists may also provide comprehensive medication review services, such as medication therapy management (MTM), transitions of care, or chronic care management. Examples of specialized areas include psychiatric, opioid use disorder, palliative care, infectious disease, chronic pain, or oncology services. For hospitalized patients, pharmacists may monitor pharmacokinetics and adjust dosing, transition patients from IV to oral medications, or complete medication reconciliation.10 Within these clinical roles, pharmacists assist in providing patient care during shortages of other health care providers (HCPs), improve patient outcomes, decrease health care-associated costs by preventing emergency department and hospital admissions or readmissions, increase access to patient care, and increase revenue through pharmacist-managed clinics and services.11
Pharmacist Credentialing
With the advancement of modern clinical pharmacy practice, many pharmacists have undertaken responsibilities to fulfill the complex duties of clinical care and diverse patient situations, but with few or no requirements to prove initial or ongoing clinical competency.2 Traditionally, pharmacist credentialing is limited to a onetime or periodic review of education and licensure, with little to no involvement in privileging and ongoing monitoring of clinical proficiency.10 These quality assurance disparities can be met and satisfied through credentialing and privileging processes. Credentialing and privileging are systematic, evidence-based processes that provide validation to HCPs, employers, and patients that pharmacists are qualified to practice clinically. 2,9 According to the Council on Credentialing in Pharmacy, clinical pharmacists should be held accountable for demonstrating competency and providing quality care through credentialing and privileging, as required for other HCPs.2,12
Credentialing and recredentialing is a primary source verification process. These processes ensure that there are no license restrictions or revocations; certifications are current; mandatory courses, certificates, and continuing education are complete; training and orientation are satisfactory; and any disciplinary action, malpractice claims, or history of impairment is reported. Privileging is the review of credentials and evaluation of clinical training and competence by the Clinical Director and Medical Executive Committee to determine whether a clinical pharmacist is competent to practice within requested privileges.11
Credentialing and privileging processes are designed not only to initially confirm that a pharmacist is competent to practice clinically, but also monitor ongoing performance.2,13 Participation in professional practice evaluations, which includes peer reviews, ongoing professional practice evaluations, and focused professional practice evaluations, is required for all credentialed and privileged practitioners. These evaluations are used to identify, assess, and correct unsatisfactory trends. Individual practices, documentation, and processes are evaluated against existing department standards (eg, CPAs, policies, processes)11,13 The results of individual professional practice evaluations are reviewed with practitioners on a regular basis and performance improvement plans implemented as needed.
Since 2015, 17 pharmacists at the Red Lake IHS health care facility have been granted membership to the medical staff as credentialed and privileged practitioners. In a retrospective review of professional practice evaluations by the Red Lake IHS pharmacy clinical coordinator, 971 outpatient clinical peer reviews, including the evaluation of 21,526 peer-review elements were completed by pharmacists from fiscal year 2015 through 2018. Peer-review elements assessed
Conclusion
Pharmacists have become increasingly instrumental in providing effective, cost-efficient, and accessible clinical services by continuing to move toward expanding and evolving roles within comprehensive, patient-centered clinical pharmacy practice settings.5,6 Multifaceted clinical responsibilities associated with health care delivery necessitate assessment and monitoring of pharmacist performance. Credentialing and privileging is an established and trusted systematic process that assures HCPs, employers, and patients that pharmacists are qualified and competent to practice clinically.2,4,12 Implementation of professional practice evaluations suggest improved staff compliance with visit documentation, patient care standards, and clinic processes required by CPAs, policies, and department standards to ensure the delivery of safe, high-quality patient care.
1. Giberson S, Yoder S, Lee MP. Improving patient and health system outcomes through advanced pharmacy practice. https://www.accp.com/docs/positions/misc/Improving_Patient_and_Health_System_Outcomes.pdf. Published December 2011. Accessed March 15, 2019.
2. Rouse MJ, Vlasses PH, Webb CE; Council on Credentialing in Pharmacy. Credentialing and privileging of pharmacists: a resource paper from the Council on Credentialing in Pharmacy. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2014;71(21):e109-e118.
3. Berwick DM, Nolan TW, Whittington J. The triple aim: care, health, and cost. Health Aff (Millwood). 2008;27(3):759-769.
4. Blair MM, Carmichael J, Young E, Thrasher K; Qualified Provider Model Ad Hoc Committee. Pharmacist privileging in a health system: report of the Qualified Provider Model Ad Hoc Committee. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2007;64(22):2373-2381.
5. Claxton KI, Wojtal P. Design and implementation of a credentialing and privileging model for ambulatory care pharmacists. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2006;63(17):1627-1632.
6. Jordan TA, Hennenfent JA, Lewin JJ III, Nesbit TW, Weber R. Elevating pharmacists’ scope of practice through a health-system clinical privileging process. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(18):1395-1405.
7. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Collaborative practice agreements and pharmacists’ patient care services: a resource for doctors, nurses, physician assistants, and other providers. https://www.cdc.gov/dhdsp/pubs/docs/Translational_Tools_Providers.pdf. Published October 2013. Accessed March 18, 2019.
8. Council on Credentialing in Pharmacy, Albanese NP, Rouse MJ. Scope of contemporary pharmacy practice: roles, responsibilities, and functions of practitioners and pharmacy technicians. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2010;50(2):e35-e69.
9. Philip B, Weber R. Enhancing pharmacy practice models through pharmacists’ privileging. Hosp Pharm. 2013; 48(2):160-165.
10. Galt KA. Credentialing and privileging of pharmacists. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2004;61(7):661-670.
11. Smith ML, Gemelas MF; US Public Health Service; Indian Health Service. Indian Health Service medical staff credentialing and privileging guide. https://www.ihs.gov/riskmanagement/includes/themes/newihstheme/display_objects/documents/IHS-Medical-Staff-Credentialing-and-Privileging-Guide.pdf. Published September 2005. Accessed March 15, 2019.
12. US Department of Health and Human Services, Indian Health Service. Indian health manual: medical credentials and privileges review process. https://www.ihs.gov/ihm/pc/part-3/p3c1. Accessed March 15, 2019.
13. Holley SL, Ketel C. Ongoing professional practice evaluation and focused professional practice evaluation: an overview for advanced practice clinicians. J Midwifery Women Health. 2014;59(4):452-459.
The Red Lake Indian Health Service (IHS) health care facility is in north-central Minnesota within the Red Lake Nation. The facility supports primary care, emergency, urgent care, pharmacy, inpatient, optometry, dental, radiology, laboratory, physical therapy, and behavioral health services to about 10,000 Red Lake Band of Chippewa Indian patients. The Red Lake pharmacy provides inpatient and outpatient medication services and pharmacist-managed clinical patient care.
In 2013, the Red Lake IHS medical staff endorsed the implementation of comprehensive clinical pharmacy services to increase health care access and optimize clinical outcomes for patients. During the evolution of pharmacy-based patient-centric care, the clinical programs offered by Red Lake IHS pharmacy expanded from 1 anticoagulation clinic to multiple advanced-practice clinical pharmacy services. This included pharmacy primary care, medication-assisted therapy, naloxone, hepatitis C, and behavioral health medication management clinics.
The immense clinical growth of the pharmacy department demonstrated a need to assess and monitor pharmacist competency to ensure the delivery of quality patient care. Essential quality improvement processes were lacking. To fill these quality improvement gaps, a robust pharmacist credentialing and privileging program was implemented in 2015.
Patient Care
As efforts within health care establishments across the US focus on the delivery of efficient, high-quality, affordable health care, pharmacists have become increasingly instrumental in providing patient care within expanded clinical roles.1-8 Many clinical pharmacy models have evolved into interdisciplinary approaches to care.9 Within these models, abiding by state and federal laws, pharmacists practice under the indirect supervision of licensed independent practitioners (LIPs), such as physicians, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants.8 Under collaborative practice agreements (CPAs), patients are initially diagnosed by LIPs, then referred to clinical pharmacists for therapeutic management.5,7
Clinical pharmacist functions encompass comprehensive medication management (ie, prescribing, monitoring, and adjustment of medications), nonpharmacologic guidance, and coordination of care. Interdisciplinary collaboration allows pharmacists opportunities to provide direct patient care or consultations by telecommunication in many different clinical environments, including disease management, primary care, or specialty care. Pharmacists may manage chronic or acute illnesses associated with endocrine, cardiovascular, respiratory, gastrointestinal, or other systems.
Pharmacists may also provide comprehensive medication review services, such as medication therapy management (MTM), transitions of care, or chronic care management. Examples of specialized areas include psychiatric, opioid use disorder, palliative care, infectious disease, chronic pain, or oncology services. For hospitalized patients, pharmacists may monitor pharmacokinetics and adjust dosing, transition patients from IV to oral medications, or complete medication reconciliation.10 Within these clinical roles, pharmacists assist in providing patient care during shortages of other health care providers (HCPs), improve patient outcomes, decrease health care-associated costs by preventing emergency department and hospital admissions or readmissions, increase access to patient care, and increase revenue through pharmacist-managed clinics and services.11
Pharmacist Credentialing
With the advancement of modern clinical pharmacy practice, many pharmacists have undertaken responsibilities to fulfill the complex duties of clinical care and diverse patient situations, but with few or no requirements to prove initial or ongoing clinical competency.2 Traditionally, pharmacist credentialing is limited to a onetime or periodic review of education and licensure, with little to no involvement in privileging and ongoing monitoring of clinical proficiency.10 These quality assurance disparities can be met and satisfied through credentialing and privileging processes. Credentialing and privileging are systematic, evidence-based processes that provide validation to HCPs, employers, and patients that pharmacists are qualified to practice clinically. 2,9 According to the Council on Credentialing in Pharmacy, clinical pharmacists should be held accountable for demonstrating competency and providing quality care through credentialing and privileging, as required for other HCPs.2,12
Credentialing and recredentialing is a primary source verification process. These processes ensure that there are no license restrictions or revocations; certifications are current; mandatory courses, certificates, and continuing education are complete; training and orientation are satisfactory; and any disciplinary action, malpractice claims, or history of impairment is reported. Privileging is the review of credentials and evaluation of clinical training and competence by the Clinical Director and Medical Executive Committee to determine whether a clinical pharmacist is competent to practice within requested privileges.11
Credentialing and privileging processes are designed not only to initially confirm that a pharmacist is competent to practice clinically, but also monitor ongoing performance.2,13 Participation in professional practice evaluations, which includes peer reviews, ongoing professional practice evaluations, and focused professional practice evaluations, is required for all credentialed and privileged practitioners. These evaluations are used to identify, assess, and correct unsatisfactory trends. Individual practices, documentation, and processes are evaluated against existing department standards (eg, CPAs, policies, processes)11,13 The results of individual professional practice evaluations are reviewed with practitioners on a regular basis and performance improvement plans implemented as needed.
Since 2015, 17 pharmacists at the Red Lake IHS health care facility have been granted membership to the medical staff as credentialed and privileged practitioners. In a retrospective review of professional practice evaluations by the Red Lake IHS pharmacy clinical coordinator, 971 outpatient clinical peer reviews, including the evaluation of 21,526 peer-review elements were completed by pharmacists from fiscal year 2015 through 2018. Peer-review elements assessed
Conclusion
Pharmacists have become increasingly instrumental in providing effective, cost-efficient, and accessible clinical services by continuing to move toward expanding and evolving roles within comprehensive, patient-centered clinical pharmacy practice settings.5,6 Multifaceted clinical responsibilities associated with health care delivery necessitate assessment and monitoring of pharmacist performance. Credentialing and privileging is an established and trusted systematic process that assures HCPs, employers, and patients that pharmacists are qualified and competent to practice clinically.2,4,12 Implementation of professional practice evaluations suggest improved staff compliance with visit documentation, patient care standards, and clinic processes required by CPAs, policies, and department standards to ensure the delivery of safe, high-quality patient care.
The Red Lake Indian Health Service (IHS) health care facility is in north-central Minnesota within the Red Lake Nation. The facility supports primary care, emergency, urgent care, pharmacy, inpatient, optometry, dental, radiology, laboratory, physical therapy, and behavioral health services to about 10,000 Red Lake Band of Chippewa Indian patients. The Red Lake pharmacy provides inpatient and outpatient medication services and pharmacist-managed clinical patient care.
In 2013, the Red Lake IHS medical staff endorsed the implementation of comprehensive clinical pharmacy services to increase health care access and optimize clinical outcomes for patients. During the evolution of pharmacy-based patient-centric care, the clinical programs offered by Red Lake IHS pharmacy expanded from 1 anticoagulation clinic to multiple advanced-practice clinical pharmacy services. This included pharmacy primary care, medication-assisted therapy, naloxone, hepatitis C, and behavioral health medication management clinics.
The immense clinical growth of the pharmacy department demonstrated a need to assess and monitor pharmacist competency to ensure the delivery of quality patient care. Essential quality improvement processes were lacking. To fill these quality improvement gaps, a robust pharmacist credentialing and privileging program was implemented in 2015.
Patient Care
As efforts within health care establishments across the US focus on the delivery of efficient, high-quality, affordable health care, pharmacists have become increasingly instrumental in providing patient care within expanded clinical roles.1-8 Many clinical pharmacy models have evolved into interdisciplinary approaches to care.9 Within these models, abiding by state and federal laws, pharmacists practice under the indirect supervision of licensed independent practitioners (LIPs), such as physicians, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants.8 Under collaborative practice agreements (CPAs), patients are initially diagnosed by LIPs, then referred to clinical pharmacists for therapeutic management.5,7
Clinical pharmacist functions encompass comprehensive medication management (ie, prescribing, monitoring, and adjustment of medications), nonpharmacologic guidance, and coordination of care. Interdisciplinary collaboration allows pharmacists opportunities to provide direct patient care or consultations by telecommunication in many different clinical environments, including disease management, primary care, or specialty care. Pharmacists may manage chronic or acute illnesses associated with endocrine, cardiovascular, respiratory, gastrointestinal, or other systems.
Pharmacists may also provide comprehensive medication review services, such as medication therapy management (MTM), transitions of care, or chronic care management. Examples of specialized areas include psychiatric, opioid use disorder, palliative care, infectious disease, chronic pain, or oncology services. For hospitalized patients, pharmacists may monitor pharmacokinetics and adjust dosing, transition patients from IV to oral medications, or complete medication reconciliation.10 Within these clinical roles, pharmacists assist in providing patient care during shortages of other health care providers (HCPs), improve patient outcomes, decrease health care-associated costs by preventing emergency department and hospital admissions or readmissions, increase access to patient care, and increase revenue through pharmacist-managed clinics and services.11
Pharmacist Credentialing
With the advancement of modern clinical pharmacy practice, many pharmacists have undertaken responsibilities to fulfill the complex duties of clinical care and diverse patient situations, but with few or no requirements to prove initial or ongoing clinical competency.2 Traditionally, pharmacist credentialing is limited to a onetime or periodic review of education and licensure, with little to no involvement in privileging and ongoing monitoring of clinical proficiency.10 These quality assurance disparities can be met and satisfied through credentialing and privileging processes. Credentialing and privileging are systematic, evidence-based processes that provide validation to HCPs, employers, and patients that pharmacists are qualified to practice clinically. 2,9 According to the Council on Credentialing in Pharmacy, clinical pharmacists should be held accountable for demonstrating competency and providing quality care through credentialing and privileging, as required for other HCPs.2,12
Credentialing and recredentialing is a primary source verification process. These processes ensure that there are no license restrictions or revocations; certifications are current; mandatory courses, certificates, and continuing education are complete; training and orientation are satisfactory; and any disciplinary action, malpractice claims, or history of impairment is reported. Privileging is the review of credentials and evaluation of clinical training and competence by the Clinical Director and Medical Executive Committee to determine whether a clinical pharmacist is competent to practice within requested privileges.11
Credentialing and privileging processes are designed not only to initially confirm that a pharmacist is competent to practice clinically, but also monitor ongoing performance.2,13 Participation in professional practice evaluations, which includes peer reviews, ongoing professional practice evaluations, and focused professional practice evaluations, is required for all credentialed and privileged practitioners. These evaluations are used to identify, assess, and correct unsatisfactory trends. Individual practices, documentation, and processes are evaluated against existing department standards (eg, CPAs, policies, processes)11,13 The results of individual professional practice evaluations are reviewed with practitioners on a regular basis and performance improvement plans implemented as needed.
Since 2015, 17 pharmacists at the Red Lake IHS health care facility have been granted membership to the medical staff as credentialed and privileged practitioners. In a retrospective review of professional practice evaluations by the Red Lake IHS pharmacy clinical coordinator, 971 outpatient clinical peer reviews, including the evaluation of 21,526 peer-review elements were completed by pharmacists from fiscal year 2015 through 2018. Peer-review elements assessed
Conclusion
Pharmacists have become increasingly instrumental in providing effective, cost-efficient, and accessible clinical services by continuing to move toward expanding and evolving roles within comprehensive, patient-centered clinical pharmacy practice settings.5,6 Multifaceted clinical responsibilities associated with health care delivery necessitate assessment and monitoring of pharmacist performance. Credentialing and privileging is an established and trusted systematic process that assures HCPs, employers, and patients that pharmacists are qualified and competent to practice clinically.2,4,12 Implementation of professional practice evaluations suggest improved staff compliance with visit documentation, patient care standards, and clinic processes required by CPAs, policies, and department standards to ensure the delivery of safe, high-quality patient care.
1. Giberson S, Yoder S, Lee MP. Improving patient and health system outcomes through advanced pharmacy practice. https://www.accp.com/docs/positions/misc/Improving_Patient_and_Health_System_Outcomes.pdf. Published December 2011. Accessed March 15, 2019.
2. Rouse MJ, Vlasses PH, Webb CE; Council on Credentialing in Pharmacy. Credentialing and privileging of pharmacists: a resource paper from the Council on Credentialing in Pharmacy. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2014;71(21):e109-e118.
3. Berwick DM, Nolan TW, Whittington J. The triple aim: care, health, and cost. Health Aff (Millwood). 2008;27(3):759-769.
4. Blair MM, Carmichael J, Young E, Thrasher K; Qualified Provider Model Ad Hoc Committee. Pharmacist privileging in a health system: report of the Qualified Provider Model Ad Hoc Committee. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2007;64(22):2373-2381.
5. Claxton KI, Wojtal P. Design and implementation of a credentialing and privileging model for ambulatory care pharmacists. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2006;63(17):1627-1632.
6. Jordan TA, Hennenfent JA, Lewin JJ III, Nesbit TW, Weber R. Elevating pharmacists’ scope of practice through a health-system clinical privileging process. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(18):1395-1405.
7. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Collaborative practice agreements and pharmacists’ patient care services: a resource for doctors, nurses, physician assistants, and other providers. https://www.cdc.gov/dhdsp/pubs/docs/Translational_Tools_Providers.pdf. Published October 2013. Accessed March 18, 2019.
8. Council on Credentialing in Pharmacy, Albanese NP, Rouse MJ. Scope of contemporary pharmacy practice: roles, responsibilities, and functions of practitioners and pharmacy technicians. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2010;50(2):e35-e69.
9. Philip B, Weber R. Enhancing pharmacy practice models through pharmacists’ privileging. Hosp Pharm. 2013; 48(2):160-165.
10. Galt KA. Credentialing and privileging of pharmacists. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2004;61(7):661-670.
11. Smith ML, Gemelas MF; US Public Health Service; Indian Health Service. Indian Health Service medical staff credentialing and privileging guide. https://www.ihs.gov/riskmanagement/includes/themes/newihstheme/display_objects/documents/IHS-Medical-Staff-Credentialing-and-Privileging-Guide.pdf. Published September 2005. Accessed March 15, 2019.
12. US Department of Health and Human Services, Indian Health Service. Indian health manual: medical credentials and privileges review process. https://www.ihs.gov/ihm/pc/part-3/p3c1. Accessed March 15, 2019.
13. Holley SL, Ketel C. Ongoing professional practice evaluation and focused professional practice evaluation: an overview for advanced practice clinicians. J Midwifery Women Health. 2014;59(4):452-459.
1. Giberson S, Yoder S, Lee MP. Improving patient and health system outcomes through advanced pharmacy practice. https://www.accp.com/docs/positions/misc/Improving_Patient_and_Health_System_Outcomes.pdf. Published December 2011. Accessed March 15, 2019.
2. Rouse MJ, Vlasses PH, Webb CE; Council on Credentialing in Pharmacy. Credentialing and privileging of pharmacists: a resource paper from the Council on Credentialing in Pharmacy. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2014;71(21):e109-e118.
3. Berwick DM, Nolan TW, Whittington J. The triple aim: care, health, and cost. Health Aff (Millwood). 2008;27(3):759-769.
4. Blair MM, Carmichael J, Young E, Thrasher K; Qualified Provider Model Ad Hoc Committee. Pharmacist privileging in a health system: report of the Qualified Provider Model Ad Hoc Committee. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2007;64(22):2373-2381.
5. Claxton KI, Wojtal P. Design and implementation of a credentialing and privileging model for ambulatory care pharmacists. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2006;63(17):1627-1632.
6. Jordan TA, Hennenfent JA, Lewin JJ III, Nesbit TW, Weber R. Elevating pharmacists’ scope of practice through a health-system clinical privileging process. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(18):1395-1405.
7. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Collaborative practice agreements and pharmacists’ patient care services: a resource for doctors, nurses, physician assistants, and other providers. https://www.cdc.gov/dhdsp/pubs/docs/Translational_Tools_Providers.pdf. Published October 2013. Accessed March 18, 2019.
8. Council on Credentialing in Pharmacy, Albanese NP, Rouse MJ. Scope of contemporary pharmacy practice: roles, responsibilities, and functions of practitioners and pharmacy technicians. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2010;50(2):e35-e69.
9. Philip B, Weber R. Enhancing pharmacy practice models through pharmacists’ privileging. Hosp Pharm. 2013; 48(2):160-165.
10. Galt KA. Credentialing and privileging of pharmacists. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2004;61(7):661-670.
11. Smith ML, Gemelas MF; US Public Health Service; Indian Health Service. Indian Health Service medical staff credentialing and privileging guide. https://www.ihs.gov/riskmanagement/includes/themes/newihstheme/display_objects/documents/IHS-Medical-Staff-Credentialing-and-Privileging-Guide.pdf. Published September 2005. Accessed March 15, 2019.
12. US Department of Health and Human Services, Indian Health Service. Indian health manual: medical credentials and privileges review process. https://www.ihs.gov/ihm/pc/part-3/p3c1. Accessed March 15, 2019.
13. Holley SL, Ketel C. Ongoing professional practice evaluation and focused professional practice evaluation: an overview for advanced practice clinicians. J Midwifery Women Health. 2014;59(4):452-459.
Pharmacist Interventions to Reduce Modifiable Bleeding Risk Factors Using HAS-BLED in Patients Taking Warfarin (FULL)
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia and is associated with a 5-fold increase in the risk of ischemic stroke and the risk increases with age.1-3 Oral anticoagulation (OAC) therapy effectively reduces the risk of ischemic stroke in patients with nonvalvular AF. However, OAC therapy carries a bleeding risk.4
Several bleeding risk scores have been developed and validated for patients with AF who are taking warfarin: HEMORR2HAGES (Hepatic or renal disease, Ethanol abuse, Malignancy, Older age, Reduced platelet count or function, Re-bleeding, Hypertension, Anemia, Genetic factors, Excessive fall risk, Stroke), ATRIA (Anticoagulation and Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation), and HAS-BLED (Hypertension, Abnormal renal and/or liver function, Stroke, Bleeding history or predisposition, Labile international normalized ratio [INR], Elderly, and Drugs and/or alcohol excess concomitantly).4,5 All 3 bleeding risk scores demonstrate only modest ability to predict clinically relevant bleeding in patients taking warfarin. The HAS-BLED score was superior to HEMORR2HAGES and ATRIA for predicting any clinically relevant bleeding and was the only bleeding risk score that demonstrated significant predictive performance for intracranial hemorrhage.5 Compared with HEMORR2HAGES, the HAS-BLED score is simpler to use and to assess risk factors that can be gathered from medical history or routinely tested in patients with AF.4 Unlike HAS-BLED, HEMORR2HAGES and ATRIA do not consider medications that could increase the risk of bleeding.
Despite the availability of validated bleeding risk scores, clinical application of these measures should not be used to exclude a patient from OAC therapy for patients who reach a threshold score. Rather, current guideline and expert consensus agree with the recommendation to use bleeding risk scores to identify risk factors and address those factors that are modifiable to reduce the risk of anticoagulant-associated major bleeding.6-8
The authors identified modifiable bleeding risk factors using the HAS-BLED score and evaluated pharmacist interventions to correct these factors in patients with nonvalvular AF who are taking warfarin. To the authors’ knowledge, there have been no published studies evaluating interventions to reduce modifiable bleeding risk factors identified by the HAS-BLED score.
Methods
Clinical pharmacy specialists (CPSs) in the primary care (PC) clinics at the Clement J. Zablocki VAMC (CJZVAMC) in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, have prescriptive authority within their scope of practice to manage smoking cessation and diseases, including anticoagulation, diabetes mellitus, heart failure, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. Patients who are on OAC therapy, including warfarin, receive comprehensive anticoagulation management from PC CPSs, including prescribing OAC therapy, education, dosage adjustments, and laboratory monitoring.
Patients were included in the HAS-BLED risk scoring and intervention if their warfarin therapy was managed by a PC CPS, had an active warfarin prescription with a diagnosis of nonvalvular AF in their problem list, and had ≥ 1 modifiable risk factor(s) from the HAS-BLED risk score. Modifiable risk factors evaluated were systolic blood pressure (SBP) > 160 mm Hg, an active prescription for VA or non-VA (which generally indicates over-the-counter [OTC] medication use) aspirin, clopidogrel, or a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). Excess alcohol consumption was not listed as a modifiable risk factor in this assessment because nearly all the anticoagulation patients already receive regular recommendations to minimize alcohol use from the PC CPSs.
Patients were excluded from analysis if they had an indication for warfarin use other than nonvalvular AF, such as atrial flutter, acute/chronic deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, history of venous thromboembolism, peripheral vascular disease, or aortic or mitral mechanical valve. Patients also were excluded if they were on antiplatelet therapy for unstable coronary artery disease (CAD), experienced acute coronary syndrome within the past 1 year, history of stent placement, carotid endarterectomy, carotid stenosis, or noncardioembolic stroke and no other modifiable risk factors. Last, patients were excluded if clinic SBP readings were > 160 mm Hg but there was documented white coat hypertension or home SBP readings < 160 mm Hg.
The following definitions or measurements were used for assessing the HAS-BLED bleeding risk score4:
- Uncontrolled hypertension: most recently charted SBP > 160 mm Hg;
- Abnormal renal function: dialysis, renal transplant, serum creatinine > 2.26 mg/dL;
- Abnormal liver function: chronic hepatic disease, biochemical evidence of significant hepatic derangement (bilirubin > 2 × upper limit of normal and/or AST/ALT/alkaline phosphatase > 3 × upper limit of normal);
- Stroke: including history of transient ischemic attack;
- Bleeding history or predisposition: history of major bleeding (intracranial and/or any bleeding requiring hospitalization and/or causing a decrease in hemoglobin (Hgb) level of > 2 g/dL and/or requiring blood transfusion), anemia (males: Hgb < 13 g/dL; females: Hgb < 12 g/dL);
- Labile INR: percentage of INRs in therapeutic range < 60% (using the CJZVAMC anticoagulation management tool, which calculates percentage of INRs in goal reported since the first visit);
- Geriatric: age > 65 years at initial assessment;
- Concomitant drug use (VA prescription or non-VA medication list): aspirin, clopidogrel, or NSAID; and
- Alcohol in excess: > 8 alcohol servings per week from chart documentation of the patient’s self-report.
In the HAS-BLED bleeding risk score, patients receive 1 point for each component for a maximum score of 9 points. The score is stratified into low (0 points), intermediate (1 to 2 points), and high (≥ 3 points) bleeding risk.4
The HAS-BLED risk factors were obtained from patient chart review, including problem list, laboratory results, and PC CPS anticoagulation notes. Interventions included primary care provider (PCP) notification of elevated BP and offer of BP management by a PC CPS, patient education and/or PCP contact to discontinue concurrent NSAID or addition of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) based on bleeding risk factor if the NSAID was deemed necessary, and discontinuation of concomitant antiplatelet drug(s) or reduction in aspirin dosage in consultation with patient’s PCP and cardiologist.9 In order to complete the initial HAS-BLED assessment and implement interventions, a note template was developed and entered into the electronic health record (EHR) that identified the patient’s modifiable risk factors.
Once the PCP and cardiologist (if applicable) responded to the note, by either accepting or declining the PC CPS recommendation(s), the HAS-BLED score was recalculated and recorded. If the provider did not respond to the initial note, an attempt was made to follow up at 3 months and at 6 months if necessary. If the provider did not respond at 6 months, the nonresponse was documented. For patients whose PCP requested PC CPS management of BP, the HAS-BLED score was recalculated 6 months after response from the PCP.
The primary outcome was the proportion of patients whose HAS-BLED score was reduced by at least 1 point. Secondary outcomes included the proportion of patients whose HAS-BLED score was reduced from one category of bleeding risk to a lesser one, total number of pharmacist interventions completed, number of pharmacist interventions made of each type (BP management, NSAID use, or antiplatelet drug use), and PCP acceptance rate.
Results
A total of 897 patients taking warfarin received anticoagulation management by a PC CPS at CJZVAMC in 2015. Of these, 819 patients were excluded based on the exclusion criteria (eFigure).
Seventy-eight patients were included in the assessment. Baseline HAS-BLED scores were calculated, and recommendations were made via an EHR progress note to the PCP and cardiologist (if applicable). Recommended interventions in the 78 patients resulted in 44 patients (56%) who experienced reduction in their HAS-BLED score by at least 1 point (Table 1). Twenty patients (25%) saw their HAS-BLED category reduced from a higher level of bleeding risk to a lower risk. The average HAS-BLED score in the 44 patients was 2.38 before intervention and 1.55 after the intervention.
In 10 patients, the HAS-BLED score did not decrease despite accepted PC CPS intervention. Specifically, 7 patients were on both an antiplatelet agent and NSAID. As a result of the pharmacist intervention, the NSAID was discontinued, but the antiplatelet remained because of stent placement or carotid stenosis. In 1 patient, the aspirin dosage was decreased from 325 to 81 mg/d. In 2 patients where NSAID use was deemed necessary—meloxicam in both cases—a PPI was ordered based on bleeding risk.9
A total of 82 interventions were recommended; 57 interventions were accepted, resulting in a provider acceptance rate of 69.5% (Tables 2 and 3). Thirty-five of the accepted interventions (61%) involved discontinuing an antiplatelet (aspirin or clopidogrel) in consultation with the patient’s PCP and cardiologist. Twenty-seven of these patients had no documented CAD, and 8 of the patients had stable CAD. Seventeen (30%) of the accepted recommendations were for discontinuing NSAID therapy, 2 (4%) were for BP management by a PC CPS, 2 (4%) for addition of PPI with continued NSAID use (meloxicam), and 1 (1%) for decreasing aspirin dosage from 325 to 81 mg/d. The NSAIDs that were discontinued included ibuprofen, indomethacin, meloxicam, and naproxen.
Discussion
This project is the first, to the authors’ knowledge, to evaluate pharmacist interventions to reduce modifiable bleeding risk factors identified by the HAS-BLED bleeding risk score. Most of the patients with nonvalvular AF in the PC clinics did not have modifiable bleeding risk factors. However, of the patients who received a recommendation to reduce a specific modifiable risk factor, most of the interventions were accepted by PCPs and
Most of the interventions recommended evaluating the use of antiplatelet agents, particularly aspirin. The benefits of antiplatelet therapy for secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease are well established. However, for AF patients on OAC therapy, the concomitant use of antiplatelet therapy significantly increases the risk of bleeding and should be reserved for high-risk patients.10 The 2012 American College of Chest Physicians guidelines support the use of OAC monotherapy in patients with AF with stable CAD, including patients with a myocardial infarction or percutaneous coronary intervention more than 1 year previously, which has been corroborated with guideline and expert consensus recommendations released in 2016.7,8,10,11
For patients taking warfarin for AF without CAD, the possible benefit of concomitant aspirin therapy for primary prevention is outweighed by the increased risk of major bleeding.12 Furthermore, warfarin monotherapy has been shown to be effective in primary prevention of CAD and seems to have cardiovascular benefit for secondary prevention but with increased bleeding.13,14 As a result, through the exclusion criteria this project aimed to evaluate warfarin patients with AF at low risk of cardiovascular events who might be taking unnecessary concurrent antiplatelet therapy.
More than one-half of the interventions involved discontinuing antiplatelet therapy. Chart reviews revealed a lack of documentation for the indication and intended duration of antiplatelet therapy. In many patients, it is likely that aspirin use predated AF diagnosis and warfarin initiation. In some of these cases, it would have been appropriate to discontinue aspirin when starting warfarin use. Although there is guidance to support the use of OAC monotherapy in patients with AF with stable CAD, the patient’s provider and cardiologist made the decision to discontinue an antiplatelet agent after weighing benefits and risks. Regardless of the outcome, this analysis revealed the importance and need for routine review of antiplatelet therapy and documenting the rationale for antiplatelet use in addition to anticoagulation.
The second largest category of interventions accepted was for evaluation of NSAID use. A 2014 study by Lamberts and colleagues found that concomitant use of oral anticoagulants and NSAIDs conferred an independent risk for major bleeding and thromboembolism in patients with AF.15 The increase in serious bleeding (absolute risk difference of 2.5 events per 1,000 patients) was observed even with short-term NSAID exposure of 14 days across all NSAID types (selective COX-2 inhibitors or nonselective NSAIDs). In addition, there was an incremental increase in bleeding risk with high NSAID dosages. The risk of serious bleeding was even greater when an NSAID is added to OAC therapy and aspirin. Seven out of 17 warfarin patients (41%) who were taking an NSAID also were on an antiplatelet agent. As a result of the pharmacist interventions, NSAIDs were discontinued in all of these patients, but the antiplatelet remained because of stent placement or carotid stenosis.
This analysis captured only those patients with a documented active prescription or self-reported OTC use of an NSAID. It is unknown how many patients might take OTC NSAIDs occasionally but not report this use to a provider or pharmacist. Primary care CPSs educate patients to not use NSAIDs while taking warfarin during their initial visit and periodically thereafter; however, with the number of different NSAIDs available without a prescription and the various brand and generic names offered, it can be difficult for patients to understand what they should or should not take for minor pain or fever. Therefore, it is imperative that NSAID use is reviewed regularly at anticoagulant follow-up visits and patients are educated about alternative OTC agents for pain relief (eg, acetaminophen, topical agents, heating pad) when necessary. It also is equally important for PCPs to weigh the benefit vs risk for each patient before prescribing an NSAID if alternatives have been exhausted especially if the patient also is taking an OAC and antiplatelet agent.
The smallest number of interventions completed was for BP management. According to the HAS-BLED bleeding risk score, BP management was recommended only if the most recent clinic SBP was > 160 mm Hg, excluding patients with documented white-coat syndrome or home SBP readings < 160 mm Hg. One potential explanation for the small number of patients with SBP > 160 mm Hg is that for many of the patients taking warfarin, the PC CPSs at CJZVAMC have been involved in their BP management through earlier consultation by providers.
Limitations
A limitation of the BP component of the HAS-BLED score was that the assessment of BP for this project was only one point in time. In 3 cases, the SBP was > 160 mm Hg only during the most recent measurement, and these patients had normal BP readings on return to the clinic for follow-up. This category of recommendation also took more time for follow-up because a PC CPS would need to evaluate the patient in clinic, implement changes to BP medications, and follow-up at subsequent visits. Although some PCPs felt that the patient did not need pharmacist intervention, the elevated SBPs were brought to the provider’s attention, and some patients received further monitoring by the PCP or through a specialty clinic (eg, nephrology).
Another limitation of this project was that the bleeding risk evaluation occurred at only 1 visit. Patients’ medications and medical issues often change with time. Therefore, it is important to implement a process to regularly review (eg, annually) patients’ bleeding risk factors and to identify and act on modifiable risk factors. Another limitation was a lack of a comparator group and the time frame of the evaluation. As a result, the authors were unable to evaluate bleeding outcomes because of the small sample size and limited time frame. Future studies could consider evaluating bleeding events as an outcome, including additional modifiable risk factors, such as excess alcohol and labile INR, expanding the review to patients taking warfarin for indications other than AF, and review of patients on direct-acting oral anticoagulants (DOACs) with AF; keeping in mind that currently available bleeding risk calculators were developed for patients taking warfarin, not DOACs with AF. Patients could be counselled on reducing alcohol intake or switching to a DOAC if INR is labile despite adherence.
Conclusion
This quality improvement project successfully implemented use of the HAS-BLED bleeding risk score to identify and reduce modifiable bleeding risk factors in patients with AF taking warfarin. Pharmacist intervention resulted in a reduction of HAS-BLED scores and bleeding risk categories.
Click here to read the digital edition.
1. Lloyd-Jones DM, Wang TJ, Leip EP, et al. Lifetime risk for development of atrial fibrillation: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2004;110(9):1042-1046.
2. Patel NJ, Deshmukh A, Pant S, et al. Contemporary trends of hospitalization for atrial fibrillation in the United States, 2000 through 2010: implications for healthcare planning. Circulation. 2014;129(23):2371-2379.
3. Wolf PA, Abbott RD, Kannel WB. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: the Framingham Study. Stroke. 1991;22(8):983-988.
4. Pisters R, Lane DA, Nieuwlaat R, de Vos CB, Crijns HJ, Lip GY. A novel user-friendly score (HAS-BLED) to assess 1-year risk of major bleeding in patients with atrial fibrillation: the Euro Heart Survey. Chest. 2010;138(5):1093-1100.
5. Apostolakis S, Lane DA, Guo Y, Buller H, Lip GY. Performance of the HEMORR2HAGES, ATRIA, and HAS-BLED bleeding risk-prediction scores in patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing anticoagulation: the AMADEUS (evaluating the use of SR34006 compared to warfarin or acenocoumarol in patients with atrial fibrillation) study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60(9):861-867.
6. Lane DA, Lip GY. Use of the CHA(2)DS(2)-VASc and HAS-BLED scores to aid decision making for thromboprophylaxis in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2012;126(7):860-865.
7. Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D, et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur Heart J. 2016;37(38):2893-2962.
8. Ruff CT, Ansell JE, Becker RC, et al. North American thrombosis forum, AF action initiative consensus document. Am J Med. 2016;129(suppl 5):S1-S29.
9. Lanza FL, Chan FK, Quigley EM; Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Guidelines for prevention of NSAID-related ulcer complications. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104(3):728-738.
10. You JJ, Singer DE, Howard PA, et al. Antithrombotic therapy for atrial fibrillation. Antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed. American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(suppl 2):e531S-e575S.
11. Macle L, Cairns J, Leblanc K, et al; CCS Atrial Fibrillation Guidelines Committee. 2016 focused update of the Canadian Cardiovascular Society guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation. Can J Cardiol. 2016;32(10):1170-1185.
12. Dentali F, Douketis JD, Lim W, Crowther M. Combined aspirin-oral anticoagulant therapy compared with oral anticoagulant therapy alone among patients at risk for cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167(2):117-124.
13. The Medical Research Council’s General Practice Research Framework. Thrombosis prevention trial: randomised trial of low-intensity oral anticoagulation with warfarin and low-dose aspirin in the primary prevention of ischaemic heart disease in men at increased risk. Lancet. 1998;351(9098):233-241.
14. Hurlen M, Abdelnoor M, Smith P, Erikssen J, Arnesen H. Warfarin, aspirin, or both after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(13):969-974.
15. Lamberts M, Lip GY, Hansen ML, et al. Relation of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to serious bleeding and thromboembolism risk in patients with atrial fibrillation receiving antithrombotic therapy: a nationwide cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2014;161(10):690-698.
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia and is associated with a 5-fold increase in the risk of ischemic stroke and the risk increases with age.1-3 Oral anticoagulation (OAC) therapy effectively reduces the risk of ischemic stroke in patients with nonvalvular AF. However, OAC therapy carries a bleeding risk.4
Several bleeding risk scores have been developed and validated for patients with AF who are taking warfarin: HEMORR2HAGES (Hepatic or renal disease, Ethanol abuse, Malignancy, Older age, Reduced platelet count or function, Re-bleeding, Hypertension, Anemia, Genetic factors, Excessive fall risk, Stroke), ATRIA (Anticoagulation and Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation), and HAS-BLED (Hypertension, Abnormal renal and/or liver function, Stroke, Bleeding history or predisposition, Labile international normalized ratio [INR], Elderly, and Drugs and/or alcohol excess concomitantly).4,5 All 3 bleeding risk scores demonstrate only modest ability to predict clinically relevant bleeding in patients taking warfarin. The HAS-BLED score was superior to HEMORR2HAGES and ATRIA for predicting any clinically relevant bleeding and was the only bleeding risk score that demonstrated significant predictive performance for intracranial hemorrhage.5 Compared with HEMORR2HAGES, the HAS-BLED score is simpler to use and to assess risk factors that can be gathered from medical history or routinely tested in patients with AF.4 Unlike HAS-BLED, HEMORR2HAGES and ATRIA do not consider medications that could increase the risk of bleeding.
Despite the availability of validated bleeding risk scores, clinical application of these measures should not be used to exclude a patient from OAC therapy for patients who reach a threshold score. Rather, current guideline and expert consensus agree with the recommendation to use bleeding risk scores to identify risk factors and address those factors that are modifiable to reduce the risk of anticoagulant-associated major bleeding.6-8
The authors identified modifiable bleeding risk factors using the HAS-BLED score and evaluated pharmacist interventions to correct these factors in patients with nonvalvular AF who are taking warfarin. To the authors’ knowledge, there have been no published studies evaluating interventions to reduce modifiable bleeding risk factors identified by the HAS-BLED score.
Methods
Clinical pharmacy specialists (CPSs) in the primary care (PC) clinics at the Clement J. Zablocki VAMC (CJZVAMC) in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, have prescriptive authority within their scope of practice to manage smoking cessation and diseases, including anticoagulation, diabetes mellitus, heart failure, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. Patients who are on OAC therapy, including warfarin, receive comprehensive anticoagulation management from PC CPSs, including prescribing OAC therapy, education, dosage adjustments, and laboratory monitoring.
Patients were included in the HAS-BLED risk scoring and intervention if their warfarin therapy was managed by a PC CPS, had an active warfarin prescription with a diagnosis of nonvalvular AF in their problem list, and had ≥ 1 modifiable risk factor(s) from the HAS-BLED risk score. Modifiable risk factors evaluated were systolic blood pressure (SBP) > 160 mm Hg, an active prescription for VA or non-VA (which generally indicates over-the-counter [OTC] medication use) aspirin, clopidogrel, or a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). Excess alcohol consumption was not listed as a modifiable risk factor in this assessment because nearly all the anticoagulation patients already receive regular recommendations to minimize alcohol use from the PC CPSs.
Patients were excluded from analysis if they had an indication for warfarin use other than nonvalvular AF, such as atrial flutter, acute/chronic deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, history of venous thromboembolism, peripheral vascular disease, or aortic or mitral mechanical valve. Patients also were excluded if they were on antiplatelet therapy for unstable coronary artery disease (CAD), experienced acute coronary syndrome within the past 1 year, history of stent placement, carotid endarterectomy, carotid stenosis, or noncardioembolic stroke and no other modifiable risk factors. Last, patients were excluded if clinic SBP readings were > 160 mm Hg but there was documented white coat hypertension or home SBP readings < 160 mm Hg.
The following definitions or measurements were used for assessing the HAS-BLED bleeding risk score4:
- Uncontrolled hypertension: most recently charted SBP > 160 mm Hg;
- Abnormal renal function: dialysis, renal transplant, serum creatinine > 2.26 mg/dL;
- Abnormal liver function: chronic hepatic disease, biochemical evidence of significant hepatic derangement (bilirubin > 2 × upper limit of normal and/or AST/ALT/alkaline phosphatase > 3 × upper limit of normal);
- Stroke: including history of transient ischemic attack;
- Bleeding history or predisposition: history of major bleeding (intracranial and/or any bleeding requiring hospitalization and/or causing a decrease in hemoglobin (Hgb) level of > 2 g/dL and/or requiring blood transfusion), anemia (males: Hgb < 13 g/dL; females: Hgb < 12 g/dL);
- Labile INR: percentage of INRs in therapeutic range < 60% (using the CJZVAMC anticoagulation management tool, which calculates percentage of INRs in goal reported since the first visit);
- Geriatric: age > 65 years at initial assessment;
- Concomitant drug use (VA prescription or non-VA medication list): aspirin, clopidogrel, or NSAID; and
- Alcohol in excess: > 8 alcohol servings per week from chart documentation of the patient’s self-report.
In the HAS-BLED bleeding risk score, patients receive 1 point for each component for a maximum score of 9 points. The score is stratified into low (0 points), intermediate (1 to 2 points), and high (≥ 3 points) bleeding risk.4
The HAS-BLED risk factors were obtained from patient chart review, including problem list, laboratory results, and PC CPS anticoagulation notes. Interventions included primary care provider (PCP) notification of elevated BP and offer of BP management by a PC CPS, patient education and/or PCP contact to discontinue concurrent NSAID or addition of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) based on bleeding risk factor if the NSAID was deemed necessary, and discontinuation of concomitant antiplatelet drug(s) or reduction in aspirin dosage in consultation with patient’s PCP and cardiologist.9 In order to complete the initial HAS-BLED assessment and implement interventions, a note template was developed and entered into the electronic health record (EHR) that identified the patient’s modifiable risk factors.
Once the PCP and cardiologist (if applicable) responded to the note, by either accepting or declining the PC CPS recommendation(s), the HAS-BLED score was recalculated and recorded. If the provider did not respond to the initial note, an attempt was made to follow up at 3 months and at 6 months if necessary. If the provider did not respond at 6 months, the nonresponse was documented. For patients whose PCP requested PC CPS management of BP, the HAS-BLED score was recalculated 6 months after response from the PCP.
The primary outcome was the proportion of patients whose HAS-BLED score was reduced by at least 1 point. Secondary outcomes included the proportion of patients whose HAS-BLED score was reduced from one category of bleeding risk to a lesser one, total number of pharmacist interventions completed, number of pharmacist interventions made of each type (BP management, NSAID use, or antiplatelet drug use), and PCP acceptance rate.
Results
A total of 897 patients taking warfarin received anticoagulation management by a PC CPS at CJZVAMC in 2015. Of these, 819 patients were excluded based on the exclusion criteria (eFigure).
Seventy-eight patients were included in the assessment. Baseline HAS-BLED scores were calculated, and recommendations were made via an EHR progress note to the PCP and cardiologist (if applicable). Recommended interventions in the 78 patients resulted in 44 patients (56%) who experienced reduction in their HAS-BLED score by at least 1 point (Table 1). Twenty patients (25%) saw their HAS-BLED category reduced from a higher level of bleeding risk to a lower risk. The average HAS-BLED score in the 44 patients was 2.38 before intervention and 1.55 after the intervention.
In 10 patients, the HAS-BLED score did not decrease despite accepted PC CPS intervention. Specifically, 7 patients were on both an antiplatelet agent and NSAID. As a result of the pharmacist intervention, the NSAID was discontinued, but the antiplatelet remained because of stent placement or carotid stenosis. In 1 patient, the aspirin dosage was decreased from 325 to 81 mg/d. In 2 patients where NSAID use was deemed necessary—meloxicam in both cases—a PPI was ordered based on bleeding risk.9
A total of 82 interventions were recommended; 57 interventions were accepted, resulting in a provider acceptance rate of 69.5% (Tables 2 and 3). Thirty-five of the accepted interventions (61%) involved discontinuing an antiplatelet (aspirin or clopidogrel) in consultation with the patient’s PCP and cardiologist. Twenty-seven of these patients had no documented CAD, and 8 of the patients had stable CAD. Seventeen (30%) of the accepted recommendations were for discontinuing NSAID therapy, 2 (4%) were for BP management by a PC CPS, 2 (4%) for addition of PPI with continued NSAID use (meloxicam), and 1 (1%) for decreasing aspirin dosage from 325 to 81 mg/d. The NSAIDs that were discontinued included ibuprofen, indomethacin, meloxicam, and naproxen.
Discussion
This project is the first, to the authors’ knowledge, to evaluate pharmacist interventions to reduce modifiable bleeding risk factors identified by the HAS-BLED bleeding risk score. Most of the patients with nonvalvular AF in the PC clinics did not have modifiable bleeding risk factors. However, of the patients who received a recommendation to reduce a specific modifiable risk factor, most of the interventions were accepted by PCPs and
Most of the interventions recommended evaluating the use of antiplatelet agents, particularly aspirin. The benefits of antiplatelet therapy for secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease are well established. However, for AF patients on OAC therapy, the concomitant use of antiplatelet therapy significantly increases the risk of bleeding and should be reserved for high-risk patients.10 The 2012 American College of Chest Physicians guidelines support the use of OAC monotherapy in patients with AF with stable CAD, including patients with a myocardial infarction or percutaneous coronary intervention more than 1 year previously, which has been corroborated with guideline and expert consensus recommendations released in 2016.7,8,10,11
For patients taking warfarin for AF without CAD, the possible benefit of concomitant aspirin therapy for primary prevention is outweighed by the increased risk of major bleeding.12 Furthermore, warfarin monotherapy has been shown to be effective in primary prevention of CAD and seems to have cardiovascular benefit for secondary prevention but with increased bleeding.13,14 As a result, through the exclusion criteria this project aimed to evaluate warfarin patients with AF at low risk of cardiovascular events who might be taking unnecessary concurrent antiplatelet therapy.
More than one-half of the interventions involved discontinuing antiplatelet therapy. Chart reviews revealed a lack of documentation for the indication and intended duration of antiplatelet therapy. In many patients, it is likely that aspirin use predated AF diagnosis and warfarin initiation. In some of these cases, it would have been appropriate to discontinue aspirin when starting warfarin use. Although there is guidance to support the use of OAC monotherapy in patients with AF with stable CAD, the patient’s provider and cardiologist made the decision to discontinue an antiplatelet agent after weighing benefits and risks. Regardless of the outcome, this analysis revealed the importance and need for routine review of antiplatelet therapy and documenting the rationale for antiplatelet use in addition to anticoagulation.
The second largest category of interventions accepted was for evaluation of NSAID use. A 2014 study by Lamberts and colleagues found that concomitant use of oral anticoagulants and NSAIDs conferred an independent risk for major bleeding and thromboembolism in patients with AF.15 The increase in serious bleeding (absolute risk difference of 2.5 events per 1,000 patients) was observed even with short-term NSAID exposure of 14 days across all NSAID types (selective COX-2 inhibitors or nonselective NSAIDs). In addition, there was an incremental increase in bleeding risk with high NSAID dosages. The risk of serious bleeding was even greater when an NSAID is added to OAC therapy and aspirin. Seven out of 17 warfarin patients (41%) who were taking an NSAID also were on an antiplatelet agent. As a result of the pharmacist interventions, NSAIDs were discontinued in all of these patients, but the antiplatelet remained because of stent placement or carotid stenosis.
This analysis captured only those patients with a documented active prescription or self-reported OTC use of an NSAID. It is unknown how many patients might take OTC NSAIDs occasionally but not report this use to a provider or pharmacist. Primary care CPSs educate patients to not use NSAIDs while taking warfarin during their initial visit and periodically thereafter; however, with the number of different NSAIDs available without a prescription and the various brand and generic names offered, it can be difficult for patients to understand what they should or should not take for minor pain or fever. Therefore, it is imperative that NSAID use is reviewed regularly at anticoagulant follow-up visits and patients are educated about alternative OTC agents for pain relief (eg, acetaminophen, topical agents, heating pad) when necessary. It also is equally important for PCPs to weigh the benefit vs risk for each patient before prescribing an NSAID if alternatives have been exhausted especially if the patient also is taking an OAC and antiplatelet agent.
The smallest number of interventions completed was for BP management. According to the HAS-BLED bleeding risk score, BP management was recommended only if the most recent clinic SBP was > 160 mm Hg, excluding patients with documented white-coat syndrome or home SBP readings < 160 mm Hg. One potential explanation for the small number of patients with SBP > 160 mm Hg is that for many of the patients taking warfarin, the PC CPSs at CJZVAMC have been involved in their BP management through earlier consultation by providers.
Limitations
A limitation of the BP component of the HAS-BLED score was that the assessment of BP for this project was only one point in time. In 3 cases, the SBP was > 160 mm Hg only during the most recent measurement, and these patients had normal BP readings on return to the clinic for follow-up. This category of recommendation also took more time for follow-up because a PC CPS would need to evaluate the patient in clinic, implement changes to BP medications, and follow-up at subsequent visits. Although some PCPs felt that the patient did not need pharmacist intervention, the elevated SBPs were brought to the provider’s attention, and some patients received further monitoring by the PCP or through a specialty clinic (eg, nephrology).
Another limitation of this project was that the bleeding risk evaluation occurred at only 1 visit. Patients’ medications and medical issues often change with time. Therefore, it is important to implement a process to regularly review (eg, annually) patients’ bleeding risk factors and to identify and act on modifiable risk factors. Another limitation was a lack of a comparator group and the time frame of the evaluation. As a result, the authors were unable to evaluate bleeding outcomes because of the small sample size and limited time frame. Future studies could consider evaluating bleeding events as an outcome, including additional modifiable risk factors, such as excess alcohol and labile INR, expanding the review to patients taking warfarin for indications other than AF, and review of patients on direct-acting oral anticoagulants (DOACs) with AF; keeping in mind that currently available bleeding risk calculators were developed for patients taking warfarin, not DOACs with AF. Patients could be counselled on reducing alcohol intake or switching to a DOAC if INR is labile despite adherence.
Conclusion
This quality improvement project successfully implemented use of the HAS-BLED bleeding risk score to identify and reduce modifiable bleeding risk factors in patients with AF taking warfarin. Pharmacist intervention resulted in a reduction of HAS-BLED scores and bleeding risk categories.
Click here to read the digital edition.
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia and is associated with a 5-fold increase in the risk of ischemic stroke and the risk increases with age.1-3 Oral anticoagulation (OAC) therapy effectively reduces the risk of ischemic stroke in patients with nonvalvular AF. However, OAC therapy carries a bleeding risk.4
Several bleeding risk scores have been developed and validated for patients with AF who are taking warfarin: HEMORR2HAGES (Hepatic or renal disease, Ethanol abuse, Malignancy, Older age, Reduced platelet count or function, Re-bleeding, Hypertension, Anemia, Genetic factors, Excessive fall risk, Stroke), ATRIA (Anticoagulation and Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation), and HAS-BLED (Hypertension, Abnormal renal and/or liver function, Stroke, Bleeding history or predisposition, Labile international normalized ratio [INR], Elderly, and Drugs and/or alcohol excess concomitantly).4,5 All 3 bleeding risk scores demonstrate only modest ability to predict clinically relevant bleeding in patients taking warfarin. The HAS-BLED score was superior to HEMORR2HAGES and ATRIA for predicting any clinically relevant bleeding and was the only bleeding risk score that demonstrated significant predictive performance for intracranial hemorrhage.5 Compared with HEMORR2HAGES, the HAS-BLED score is simpler to use and to assess risk factors that can be gathered from medical history or routinely tested in patients with AF.4 Unlike HAS-BLED, HEMORR2HAGES and ATRIA do not consider medications that could increase the risk of bleeding.
Despite the availability of validated bleeding risk scores, clinical application of these measures should not be used to exclude a patient from OAC therapy for patients who reach a threshold score. Rather, current guideline and expert consensus agree with the recommendation to use bleeding risk scores to identify risk factors and address those factors that are modifiable to reduce the risk of anticoagulant-associated major bleeding.6-8
The authors identified modifiable bleeding risk factors using the HAS-BLED score and evaluated pharmacist interventions to correct these factors in patients with nonvalvular AF who are taking warfarin. To the authors’ knowledge, there have been no published studies evaluating interventions to reduce modifiable bleeding risk factors identified by the HAS-BLED score.
Methods
Clinical pharmacy specialists (CPSs) in the primary care (PC) clinics at the Clement J. Zablocki VAMC (CJZVAMC) in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, have prescriptive authority within their scope of practice to manage smoking cessation and diseases, including anticoagulation, diabetes mellitus, heart failure, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. Patients who are on OAC therapy, including warfarin, receive comprehensive anticoagulation management from PC CPSs, including prescribing OAC therapy, education, dosage adjustments, and laboratory monitoring.
Patients were included in the HAS-BLED risk scoring and intervention if their warfarin therapy was managed by a PC CPS, had an active warfarin prescription with a diagnosis of nonvalvular AF in their problem list, and had ≥ 1 modifiable risk factor(s) from the HAS-BLED risk score. Modifiable risk factors evaluated were systolic blood pressure (SBP) > 160 mm Hg, an active prescription for VA or non-VA (which generally indicates over-the-counter [OTC] medication use) aspirin, clopidogrel, or a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). Excess alcohol consumption was not listed as a modifiable risk factor in this assessment because nearly all the anticoagulation patients already receive regular recommendations to minimize alcohol use from the PC CPSs.
Patients were excluded from analysis if they had an indication for warfarin use other than nonvalvular AF, such as atrial flutter, acute/chronic deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, history of venous thromboembolism, peripheral vascular disease, or aortic or mitral mechanical valve. Patients also were excluded if they were on antiplatelet therapy for unstable coronary artery disease (CAD), experienced acute coronary syndrome within the past 1 year, history of stent placement, carotid endarterectomy, carotid stenosis, or noncardioembolic stroke and no other modifiable risk factors. Last, patients were excluded if clinic SBP readings were > 160 mm Hg but there was documented white coat hypertension or home SBP readings < 160 mm Hg.
The following definitions or measurements were used for assessing the HAS-BLED bleeding risk score4:
- Uncontrolled hypertension: most recently charted SBP > 160 mm Hg;
- Abnormal renal function: dialysis, renal transplant, serum creatinine > 2.26 mg/dL;
- Abnormal liver function: chronic hepatic disease, biochemical evidence of significant hepatic derangement (bilirubin > 2 × upper limit of normal and/or AST/ALT/alkaline phosphatase > 3 × upper limit of normal);
- Stroke: including history of transient ischemic attack;
- Bleeding history or predisposition: history of major bleeding (intracranial and/or any bleeding requiring hospitalization and/or causing a decrease in hemoglobin (Hgb) level of > 2 g/dL and/or requiring blood transfusion), anemia (males: Hgb < 13 g/dL; females: Hgb < 12 g/dL);
- Labile INR: percentage of INRs in therapeutic range < 60% (using the CJZVAMC anticoagulation management tool, which calculates percentage of INRs in goal reported since the first visit);
- Geriatric: age > 65 years at initial assessment;
- Concomitant drug use (VA prescription or non-VA medication list): aspirin, clopidogrel, or NSAID; and
- Alcohol in excess: > 8 alcohol servings per week from chart documentation of the patient’s self-report.
In the HAS-BLED bleeding risk score, patients receive 1 point for each component for a maximum score of 9 points. The score is stratified into low (0 points), intermediate (1 to 2 points), and high (≥ 3 points) bleeding risk.4
The HAS-BLED risk factors were obtained from patient chart review, including problem list, laboratory results, and PC CPS anticoagulation notes. Interventions included primary care provider (PCP) notification of elevated BP and offer of BP management by a PC CPS, patient education and/or PCP contact to discontinue concurrent NSAID or addition of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) based on bleeding risk factor if the NSAID was deemed necessary, and discontinuation of concomitant antiplatelet drug(s) or reduction in aspirin dosage in consultation with patient’s PCP and cardiologist.9 In order to complete the initial HAS-BLED assessment and implement interventions, a note template was developed and entered into the electronic health record (EHR) that identified the patient’s modifiable risk factors.
Once the PCP and cardiologist (if applicable) responded to the note, by either accepting or declining the PC CPS recommendation(s), the HAS-BLED score was recalculated and recorded. If the provider did not respond to the initial note, an attempt was made to follow up at 3 months and at 6 months if necessary. If the provider did not respond at 6 months, the nonresponse was documented. For patients whose PCP requested PC CPS management of BP, the HAS-BLED score was recalculated 6 months after response from the PCP.
The primary outcome was the proportion of patients whose HAS-BLED score was reduced by at least 1 point. Secondary outcomes included the proportion of patients whose HAS-BLED score was reduced from one category of bleeding risk to a lesser one, total number of pharmacist interventions completed, number of pharmacist interventions made of each type (BP management, NSAID use, or antiplatelet drug use), and PCP acceptance rate.
Results
A total of 897 patients taking warfarin received anticoagulation management by a PC CPS at CJZVAMC in 2015. Of these, 819 patients were excluded based on the exclusion criteria (eFigure).
Seventy-eight patients were included in the assessment. Baseline HAS-BLED scores were calculated, and recommendations were made via an EHR progress note to the PCP and cardiologist (if applicable). Recommended interventions in the 78 patients resulted in 44 patients (56%) who experienced reduction in their HAS-BLED score by at least 1 point (Table 1). Twenty patients (25%) saw their HAS-BLED category reduced from a higher level of bleeding risk to a lower risk. The average HAS-BLED score in the 44 patients was 2.38 before intervention and 1.55 after the intervention.
In 10 patients, the HAS-BLED score did not decrease despite accepted PC CPS intervention. Specifically, 7 patients were on both an antiplatelet agent and NSAID. As a result of the pharmacist intervention, the NSAID was discontinued, but the antiplatelet remained because of stent placement or carotid stenosis. In 1 patient, the aspirin dosage was decreased from 325 to 81 mg/d. In 2 patients where NSAID use was deemed necessary—meloxicam in both cases—a PPI was ordered based on bleeding risk.9
A total of 82 interventions were recommended; 57 interventions were accepted, resulting in a provider acceptance rate of 69.5% (Tables 2 and 3). Thirty-five of the accepted interventions (61%) involved discontinuing an antiplatelet (aspirin or clopidogrel) in consultation with the patient’s PCP and cardiologist. Twenty-seven of these patients had no documented CAD, and 8 of the patients had stable CAD. Seventeen (30%) of the accepted recommendations were for discontinuing NSAID therapy, 2 (4%) were for BP management by a PC CPS, 2 (4%) for addition of PPI with continued NSAID use (meloxicam), and 1 (1%) for decreasing aspirin dosage from 325 to 81 mg/d. The NSAIDs that were discontinued included ibuprofen, indomethacin, meloxicam, and naproxen.
Discussion
This project is the first, to the authors’ knowledge, to evaluate pharmacist interventions to reduce modifiable bleeding risk factors identified by the HAS-BLED bleeding risk score. Most of the patients with nonvalvular AF in the PC clinics did not have modifiable bleeding risk factors. However, of the patients who received a recommendation to reduce a specific modifiable risk factor, most of the interventions were accepted by PCPs and
Most of the interventions recommended evaluating the use of antiplatelet agents, particularly aspirin. The benefits of antiplatelet therapy for secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease are well established. However, for AF patients on OAC therapy, the concomitant use of antiplatelet therapy significantly increases the risk of bleeding and should be reserved for high-risk patients.10 The 2012 American College of Chest Physicians guidelines support the use of OAC monotherapy in patients with AF with stable CAD, including patients with a myocardial infarction or percutaneous coronary intervention more than 1 year previously, which has been corroborated with guideline and expert consensus recommendations released in 2016.7,8,10,11
For patients taking warfarin for AF without CAD, the possible benefit of concomitant aspirin therapy for primary prevention is outweighed by the increased risk of major bleeding.12 Furthermore, warfarin monotherapy has been shown to be effective in primary prevention of CAD and seems to have cardiovascular benefit for secondary prevention but with increased bleeding.13,14 As a result, through the exclusion criteria this project aimed to evaluate warfarin patients with AF at low risk of cardiovascular events who might be taking unnecessary concurrent antiplatelet therapy.
More than one-half of the interventions involved discontinuing antiplatelet therapy. Chart reviews revealed a lack of documentation for the indication and intended duration of antiplatelet therapy. In many patients, it is likely that aspirin use predated AF diagnosis and warfarin initiation. In some of these cases, it would have been appropriate to discontinue aspirin when starting warfarin use. Although there is guidance to support the use of OAC monotherapy in patients with AF with stable CAD, the patient’s provider and cardiologist made the decision to discontinue an antiplatelet agent after weighing benefits and risks. Regardless of the outcome, this analysis revealed the importance and need for routine review of antiplatelet therapy and documenting the rationale for antiplatelet use in addition to anticoagulation.
The second largest category of interventions accepted was for evaluation of NSAID use. A 2014 study by Lamberts and colleagues found that concomitant use of oral anticoagulants and NSAIDs conferred an independent risk for major bleeding and thromboembolism in patients with AF.15 The increase in serious bleeding (absolute risk difference of 2.5 events per 1,000 patients) was observed even with short-term NSAID exposure of 14 days across all NSAID types (selective COX-2 inhibitors or nonselective NSAIDs). In addition, there was an incremental increase in bleeding risk with high NSAID dosages. The risk of serious bleeding was even greater when an NSAID is added to OAC therapy and aspirin. Seven out of 17 warfarin patients (41%) who were taking an NSAID also were on an antiplatelet agent. As a result of the pharmacist interventions, NSAIDs were discontinued in all of these patients, but the antiplatelet remained because of stent placement or carotid stenosis.
This analysis captured only those patients with a documented active prescription or self-reported OTC use of an NSAID. It is unknown how many patients might take OTC NSAIDs occasionally but not report this use to a provider or pharmacist. Primary care CPSs educate patients to not use NSAIDs while taking warfarin during their initial visit and periodically thereafter; however, with the number of different NSAIDs available without a prescription and the various brand and generic names offered, it can be difficult for patients to understand what they should or should not take for minor pain or fever. Therefore, it is imperative that NSAID use is reviewed regularly at anticoagulant follow-up visits and patients are educated about alternative OTC agents for pain relief (eg, acetaminophen, topical agents, heating pad) when necessary. It also is equally important for PCPs to weigh the benefit vs risk for each patient before prescribing an NSAID if alternatives have been exhausted especially if the patient also is taking an OAC and antiplatelet agent.
The smallest number of interventions completed was for BP management. According to the HAS-BLED bleeding risk score, BP management was recommended only if the most recent clinic SBP was > 160 mm Hg, excluding patients with documented white-coat syndrome or home SBP readings < 160 mm Hg. One potential explanation for the small number of patients with SBP > 160 mm Hg is that for many of the patients taking warfarin, the PC CPSs at CJZVAMC have been involved in their BP management through earlier consultation by providers.
Limitations
A limitation of the BP component of the HAS-BLED score was that the assessment of BP for this project was only one point in time. In 3 cases, the SBP was > 160 mm Hg only during the most recent measurement, and these patients had normal BP readings on return to the clinic for follow-up. This category of recommendation also took more time for follow-up because a PC CPS would need to evaluate the patient in clinic, implement changes to BP medications, and follow-up at subsequent visits. Although some PCPs felt that the patient did not need pharmacist intervention, the elevated SBPs were brought to the provider’s attention, and some patients received further monitoring by the PCP or through a specialty clinic (eg, nephrology).
Another limitation of this project was that the bleeding risk evaluation occurred at only 1 visit. Patients’ medications and medical issues often change with time. Therefore, it is important to implement a process to regularly review (eg, annually) patients’ bleeding risk factors and to identify and act on modifiable risk factors. Another limitation was a lack of a comparator group and the time frame of the evaluation. As a result, the authors were unable to evaluate bleeding outcomes because of the small sample size and limited time frame. Future studies could consider evaluating bleeding events as an outcome, including additional modifiable risk factors, such as excess alcohol and labile INR, expanding the review to patients taking warfarin for indications other than AF, and review of patients on direct-acting oral anticoagulants (DOACs) with AF; keeping in mind that currently available bleeding risk calculators were developed for patients taking warfarin, not DOACs with AF. Patients could be counselled on reducing alcohol intake or switching to a DOAC if INR is labile despite adherence.
Conclusion
This quality improvement project successfully implemented use of the HAS-BLED bleeding risk score to identify and reduce modifiable bleeding risk factors in patients with AF taking warfarin. Pharmacist intervention resulted in a reduction of HAS-BLED scores and bleeding risk categories.
Click here to read the digital edition.
1. Lloyd-Jones DM, Wang TJ, Leip EP, et al. Lifetime risk for development of atrial fibrillation: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2004;110(9):1042-1046.
2. Patel NJ, Deshmukh A, Pant S, et al. Contemporary trends of hospitalization for atrial fibrillation in the United States, 2000 through 2010: implications for healthcare planning. Circulation. 2014;129(23):2371-2379.
3. Wolf PA, Abbott RD, Kannel WB. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: the Framingham Study. Stroke. 1991;22(8):983-988.
4. Pisters R, Lane DA, Nieuwlaat R, de Vos CB, Crijns HJ, Lip GY. A novel user-friendly score (HAS-BLED) to assess 1-year risk of major bleeding in patients with atrial fibrillation: the Euro Heart Survey. Chest. 2010;138(5):1093-1100.
5. Apostolakis S, Lane DA, Guo Y, Buller H, Lip GY. Performance of the HEMORR2HAGES, ATRIA, and HAS-BLED bleeding risk-prediction scores in patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing anticoagulation: the AMADEUS (evaluating the use of SR34006 compared to warfarin or acenocoumarol in patients with atrial fibrillation) study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60(9):861-867.
6. Lane DA, Lip GY. Use of the CHA(2)DS(2)-VASc and HAS-BLED scores to aid decision making for thromboprophylaxis in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2012;126(7):860-865.
7. Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D, et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur Heart J. 2016;37(38):2893-2962.
8. Ruff CT, Ansell JE, Becker RC, et al. North American thrombosis forum, AF action initiative consensus document. Am J Med. 2016;129(suppl 5):S1-S29.
9. Lanza FL, Chan FK, Quigley EM; Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Guidelines for prevention of NSAID-related ulcer complications. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104(3):728-738.
10. You JJ, Singer DE, Howard PA, et al. Antithrombotic therapy for atrial fibrillation. Antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed. American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(suppl 2):e531S-e575S.
11. Macle L, Cairns J, Leblanc K, et al; CCS Atrial Fibrillation Guidelines Committee. 2016 focused update of the Canadian Cardiovascular Society guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation. Can J Cardiol. 2016;32(10):1170-1185.
12. Dentali F, Douketis JD, Lim W, Crowther M. Combined aspirin-oral anticoagulant therapy compared with oral anticoagulant therapy alone among patients at risk for cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167(2):117-124.
13. The Medical Research Council’s General Practice Research Framework. Thrombosis prevention trial: randomised trial of low-intensity oral anticoagulation with warfarin and low-dose aspirin in the primary prevention of ischaemic heart disease in men at increased risk. Lancet. 1998;351(9098):233-241.
14. Hurlen M, Abdelnoor M, Smith P, Erikssen J, Arnesen H. Warfarin, aspirin, or both after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(13):969-974.
15. Lamberts M, Lip GY, Hansen ML, et al. Relation of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to serious bleeding and thromboembolism risk in patients with atrial fibrillation receiving antithrombotic therapy: a nationwide cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2014;161(10):690-698.
1. Lloyd-Jones DM, Wang TJ, Leip EP, et al. Lifetime risk for development of atrial fibrillation: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2004;110(9):1042-1046.
2. Patel NJ, Deshmukh A, Pant S, et al. Contemporary trends of hospitalization for atrial fibrillation in the United States, 2000 through 2010: implications for healthcare planning. Circulation. 2014;129(23):2371-2379.
3. Wolf PA, Abbott RD, Kannel WB. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: the Framingham Study. Stroke. 1991;22(8):983-988.
4. Pisters R, Lane DA, Nieuwlaat R, de Vos CB, Crijns HJ, Lip GY. A novel user-friendly score (HAS-BLED) to assess 1-year risk of major bleeding in patients with atrial fibrillation: the Euro Heart Survey. Chest. 2010;138(5):1093-1100.
5. Apostolakis S, Lane DA, Guo Y, Buller H, Lip GY. Performance of the HEMORR2HAGES, ATRIA, and HAS-BLED bleeding risk-prediction scores in patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing anticoagulation: the AMADEUS (evaluating the use of SR34006 compared to warfarin or acenocoumarol in patients with atrial fibrillation) study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60(9):861-867.
6. Lane DA, Lip GY. Use of the CHA(2)DS(2)-VASc and HAS-BLED scores to aid decision making for thromboprophylaxis in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2012;126(7):860-865.
7. Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D, et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur Heart J. 2016;37(38):2893-2962.
8. Ruff CT, Ansell JE, Becker RC, et al. North American thrombosis forum, AF action initiative consensus document. Am J Med. 2016;129(suppl 5):S1-S29.
9. Lanza FL, Chan FK, Quigley EM; Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Guidelines for prevention of NSAID-related ulcer complications. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104(3):728-738.
10. You JJ, Singer DE, Howard PA, et al. Antithrombotic therapy for atrial fibrillation. Antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed. American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(suppl 2):e531S-e575S.
11. Macle L, Cairns J, Leblanc K, et al; CCS Atrial Fibrillation Guidelines Committee. 2016 focused update of the Canadian Cardiovascular Society guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation. Can J Cardiol. 2016;32(10):1170-1185.
12. Dentali F, Douketis JD, Lim W, Crowther M. Combined aspirin-oral anticoagulant therapy compared with oral anticoagulant therapy alone among patients at risk for cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167(2):117-124.
13. The Medical Research Council’s General Practice Research Framework. Thrombosis prevention trial: randomised trial of low-intensity oral anticoagulation with warfarin and low-dose aspirin in the primary prevention of ischaemic heart disease in men at increased risk. Lancet. 1998;351(9098):233-241.
14. Hurlen M, Abdelnoor M, Smith P, Erikssen J, Arnesen H. Warfarin, aspirin, or both after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(13):969-974.
15. Lamberts M, Lip GY, Hansen ML, et al. Relation of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to serious bleeding and thromboembolism risk in patients with atrial fibrillation receiving antithrombotic therapy: a nationwide cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2014;161(10):690-698.