User login
CAR T for all R/R DLBCL patients: The jury is still out
Is it time to consider chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy for all relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients? Maybe not, according to Andrew Zelenetz, MD, PhD.
CAR T-cell therapy has demonstrated activity in relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), transformed indolent NHL, and mantle cell lymphoma, and can provide durable complete responses in a portion of patients with chemorefractory disease, Dr. Zelenetz, chair of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Lymphoma Guidelines Panel and a specialist in lymphoma at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, said at the NCCN Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
In chemosensitive patients, however, its role requires further examination, especially given findings from a recent analysis of patients from the Center for International Blood & Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR) registry showing comparable outcomes with high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell rescue for patients with a positron emission testing–positive partial response (PR) after second-line chemotherapy, he said.
Of 249 patients who underwent a first autologous transplant for DLBCL between 2003 and 2018, received front-line rituximab chemotherapy, and had PET– or computed tomography–positive disease prior to transplant, 182 had early chemotherapy failure (within 12 months) and 67 had late chemotherapy failure (at 12 months or later) after therapy, according to findings from the study as reported at ASCO 2020.
The adjusted nonrelapse mortality rates in the early- and late-failure patients, respectively, were not significantly different at 7% and 3% at 1 year, and at 10% and 8% at 5 years. The corresponding progression/relapse rates were 41% and 35% at 1 year and 48% and 57% at 5 years; these were also not significantly different.
The adjusted progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in the groups at 5 years also did not differ significantly (PFS of 41% in both the early- and late-failure groups, and OS of 51% and 63%, respectively).
These outcomes are comparable to those seen with CAR T-cell therapy in refractory DLBCL patients in trials of CAR T-cell products, including the ZUMA-1 study of axicabtagene cyloleucel (Yescarta), which, in a 2019 update, showed survival plateaus of about 40% vs. the 5%-10% expected rate based on pre-CAR-T outcomes data; the JULIET trial of tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah), which showed survival plateaus in the range of 30%-35%; and the recently published TRANSCEND study of the investigational modified CAR-T product, lisocabtagene maraleucel, which also showed survival plateaus “in the range of 40%.”
“So all three agents are showing that CAR T cells represent a new treatment for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the relapsed/refractory setting,” Dr. Zelenetz said. “And as a result, [CAR T-cell therapy has] been included in the NCCN guidelines for transformed follicular lymphoma, for transformed marginal zone lymphoma, and for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, as well as for refractory large B-cell lymphoma.
“But are CAR T cells absolutely required? Generally what we consider these days is that if you’re not in a PET-negative CR prior to high-dose therapy stem cell rescue, you should go on to CAR T cells,” Dr. Zelenetz said.
The analysis based on the CIBMTR registry data, however, suggests there may be other alternatives.
“The bottom line is that nonrelapse mortality was very low. Progression occurred in about half of the patients, but if we look at the overall and progression-free survival curves, there’s a plateau at around 45%,” Dr. Zelenetz said, explaining that the results are “very similar to the results that we’re getting in third-line treatment with CAR T cells, and this is a very similar population [of] PET-positive patients after second-line chemotherapy.”
CAR T-cell therapy can provide a durable CR in a portion of chemorefractory patients, and although there is room for improvement, “this represents a major step forward for these patients,” he said.
However, it’s not clear that CAR T cells are clearly superior to high-dose therapy and stem cell rescue for chemosensitive patients, he added, noting that “additional randomized trials are needed to answer this question, and they are ongoing as we speak.”
Dr. Zelenetz reported clinical research support or data safety monitoring board activity for BeiGene, Genentech, Juno Therapeutics, and MEI Pharma, and scientific advisory board, consulting, or expert witness activity for Celgene Corporation, Curries, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Janssen Pharmaceutical Products, and several other pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies.
Is it time to consider chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy for all relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients? Maybe not, according to Andrew Zelenetz, MD, PhD.
CAR T-cell therapy has demonstrated activity in relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), transformed indolent NHL, and mantle cell lymphoma, and can provide durable complete responses in a portion of patients with chemorefractory disease, Dr. Zelenetz, chair of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Lymphoma Guidelines Panel and a specialist in lymphoma at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, said at the NCCN Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
In chemosensitive patients, however, its role requires further examination, especially given findings from a recent analysis of patients from the Center for International Blood & Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR) registry showing comparable outcomes with high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell rescue for patients with a positron emission testing–positive partial response (PR) after second-line chemotherapy, he said.
Of 249 patients who underwent a first autologous transplant for DLBCL between 2003 and 2018, received front-line rituximab chemotherapy, and had PET– or computed tomography–positive disease prior to transplant, 182 had early chemotherapy failure (within 12 months) and 67 had late chemotherapy failure (at 12 months or later) after therapy, according to findings from the study as reported at ASCO 2020.
The adjusted nonrelapse mortality rates in the early- and late-failure patients, respectively, were not significantly different at 7% and 3% at 1 year, and at 10% and 8% at 5 years. The corresponding progression/relapse rates were 41% and 35% at 1 year and 48% and 57% at 5 years; these were also not significantly different.
The adjusted progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in the groups at 5 years also did not differ significantly (PFS of 41% in both the early- and late-failure groups, and OS of 51% and 63%, respectively).
These outcomes are comparable to those seen with CAR T-cell therapy in refractory DLBCL patients in trials of CAR T-cell products, including the ZUMA-1 study of axicabtagene cyloleucel (Yescarta), which, in a 2019 update, showed survival plateaus of about 40% vs. the 5%-10% expected rate based on pre-CAR-T outcomes data; the JULIET trial of tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah), which showed survival plateaus in the range of 30%-35%; and the recently published TRANSCEND study of the investigational modified CAR-T product, lisocabtagene maraleucel, which also showed survival plateaus “in the range of 40%.”
“So all three agents are showing that CAR T cells represent a new treatment for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the relapsed/refractory setting,” Dr. Zelenetz said. “And as a result, [CAR T-cell therapy has] been included in the NCCN guidelines for transformed follicular lymphoma, for transformed marginal zone lymphoma, and for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, as well as for refractory large B-cell lymphoma.
“But are CAR T cells absolutely required? Generally what we consider these days is that if you’re not in a PET-negative CR prior to high-dose therapy stem cell rescue, you should go on to CAR T cells,” Dr. Zelenetz said.
The analysis based on the CIBMTR registry data, however, suggests there may be other alternatives.
“The bottom line is that nonrelapse mortality was very low. Progression occurred in about half of the patients, but if we look at the overall and progression-free survival curves, there’s a plateau at around 45%,” Dr. Zelenetz said, explaining that the results are “very similar to the results that we’re getting in third-line treatment with CAR T cells, and this is a very similar population [of] PET-positive patients after second-line chemotherapy.”
CAR T-cell therapy can provide a durable CR in a portion of chemorefractory patients, and although there is room for improvement, “this represents a major step forward for these patients,” he said.
However, it’s not clear that CAR T cells are clearly superior to high-dose therapy and stem cell rescue for chemosensitive patients, he added, noting that “additional randomized trials are needed to answer this question, and they are ongoing as we speak.”
Dr. Zelenetz reported clinical research support or data safety monitoring board activity for BeiGene, Genentech, Juno Therapeutics, and MEI Pharma, and scientific advisory board, consulting, or expert witness activity for Celgene Corporation, Curries, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Janssen Pharmaceutical Products, and several other pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies.
Is it time to consider chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy for all relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients? Maybe not, according to Andrew Zelenetz, MD, PhD.
CAR T-cell therapy has demonstrated activity in relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), transformed indolent NHL, and mantle cell lymphoma, and can provide durable complete responses in a portion of patients with chemorefractory disease, Dr. Zelenetz, chair of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Lymphoma Guidelines Panel and a specialist in lymphoma at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, said at the NCCN Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
In chemosensitive patients, however, its role requires further examination, especially given findings from a recent analysis of patients from the Center for International Blood & Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR) registry showing comparable outcomes with high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell rescue for patients with a positron emission testing–positive partial response (PR) after second-line chemotherapy, he said.
Of 249 patients who underwent a first autologous transplant for DLBCL between 2003 and 2018, received front-line rituximab chemotherapy, and had PET– or computed tomography–positive disease prior to transplant, 182 had early chemotherapy failure (within 12 months) and 67 had late chemotherapy failure (at 12 months or later) after therapy, according to findings from the study as reported at ASCO 2020.
The adjusted nonrelapse mortality rates in the early- and late-failure patients, respectively, were not significantly different at 7% and 3% at 1 year, and at 10% and 8% at 5 years. The corresponding progression/relapse rates were 41% and 35% at 1 year and 48% and 57% at 5 years; these were also not significantly different.
The adjusted progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in the groups at 5 years also did not differ significantly (PFS of 41% in both the early- and late-failure groups, and OS of 51% and 63%, respectively).
These outcomes are comparable to those seen with CAR T-cell therapy in refractory DLBCL patients in trials of CAR T-cell products, including the ZUMA-1 study of axicabtagene cyloleucel (Yescarta), which, in a 2019 update, showed survival plateaus of about 40% vs. the 5%-10% expected rate based on pre-CAR-T outcomes data; the JULIET trial of tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah), which showed survival plateaus in the range of 30%-35%; and the recently published TRANSCEND study of the investigational modified CAR-T product, lisocabtagene maraleucel, which also showed survival plateaus “in the range of 40%.”
“So all three agents are showing that CAR T cells represent a new treatment for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the relapsed/refractory setting,” Dr. Zelenetz said. “And as a result, [CAR T-cell therapy has] been included in the NCCN guidelines for transformed follicular lymphoma, for transformed marginal zone lymphoma, and for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, as well as for refractory large B-cell lymphoma.
“But are CAR T cells absolutely required? Generally what we consider these days is that if you’re not in a PET-negative CR prior to high-dose therapy stem cell rescue, you should go on to CAR T cells,” Dr. Zelenetz said.
The analysis based on the CIBMTR registry data, however, suggests there may be other alternatives.
“The bottom line is that nonrelapse mortality was very low. Progression occurred in about half of the patients, but if we look at the overall and progression-free survival curves, there’s a plateau at around 45%,” Dr. Zelenetz said, explaining that the results are “very similar to the results that we’re getting in third-line treatment with CAR T cells, and this is a very similar population [of] PET-positive patients after second-line chemotherapy.”
CAR T-cell therapy can provide a durable CR in a portion of chemorefractory patients, and although there is room for improvement, “this represents a major step forward for these patients,” he said.
However, it’s not clear that CAR T cells are clearly superior to high-dose therapy and stem cell rescue for chemosensitive patients, he added, noting that “additional randomized trials are needed to answer this question, and they are ongoing as we speak.”
Dr. Zelenetz reported clinical research support or data safety monitoring board activity for BeiGene, Genentech, Juno Therapeutics, and MEI Pharma, and scientific advisory board, consulting, or expert witness activity for Celgene Corporation, Curries, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Janssen Pharmaceutical Products, and several other pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies.
FROM NCCN HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES
Older age, r/r disease in lymphoma patients tied to increased COVID-19 death rate
Patients with B-cell lymphoma are immunocompromised because of the disease and its treatments. This presents the question of their outcomes upon infection with SARS-CoV-2. Researchers assessed the characteristics of patients with lymphoma hospitalized for COVID-19 and analyzed determinants of mortality in a retrospective database study. The investigators looked at data from adult patients with lymphoma who were hospitalized for COVID-19 in March and April 2020 in three French regions.
Older age and relapsed/refractory (r/r) disease in B-cell lymphoma patients were both found to be independent risk factors of increased death rate from COVID-19, according to the online report in EClinicalMedicine, published by The Lancet.
These results encourage “the application of standard Covid-19 treatment, including intubation, for lymphoma patients with Covid-19 lymphoma diagnosis, under first- or second-line chemotherapy, or in remission,” according to Sylvain Lamure, MD, of Montellier (France) University, and colleagues.
The study examined a series of 89 consecutive patients from three French regions who had lymphoma and were hospitalized for COVID-19 in March and April 2020. The population was homogeneous; most patients were diagnosed with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and had been treated for their lymphoma within 1 year.
Promising results for many
There were a significant associations between 30-day mortality and increasing age (over age 70 years) and r/r lymphoma. However, in the absence of those factors, mortality of the lymphoma patients with COVID-19 was comparable with that of the reference French COVID-19 population. In addition, there was no significant impact of active lymphoma treatment that had been given within 1 year, except for those patients who received bendamustine, which was associated with greater mortality, according to the researchers.
With a median follow-up of 33 days from admission, the Kaplan-Meier estimate of 30-day overall survival was 71% (95% confidence interval, 62%-81%). According to histological type of the lymphoma, 30-day overall survival rates were 80% (95% CI, 45%-100%) for Hodgkin lymphoma, 71% (95% CI, 61%-82%) for B-cell non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, and 71% (95% CI, 38%-100%) for T-cell non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.
The main factors associated with mortality were age 70 years and older (hazard ratio, 3.78; 95% CI, 1.73-8.25; P = .0009), hypertension (HR, 2.20; 95% CI, 1.06-4.59; P = .03), previous cancer (HR, 2.11; 95% CI, 0.90-4.92; P = .08), use of bendamustine within 12 months before admission to hospital (HR, 3.05; 95% CI, 1.31-7.11; P = .01), and r/r lymphoma (HR, 2.62; 95% CI, 1.20-5.72; P = .02).
Overall, the Kaplan-Meier estimates of 30-day overall survival were 61% for patients with r/r lymphoma, 52% in patients age 70 years with non–r/r lymphoma, and 88% for patients younger than 70 years with non–r/r, which was comparable with general population survival data among French populations, according to the researchers.
“Longer term clinical follow-up and biological monitoring of immune responses is warranted to explore the impact of lymphoma and its treatment on the immunity and prolonged outcome of Covid-19 patients,” they concluded.
The study was unsponsored. Several of the authors reported financial relationships with a number of biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Lamure S et al. EClinicalMedicine. 2020 Oct 12. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100549.
Patients with B-cell lymphoma are immunocompromised because of the disease and its treatments. This presents the question of their outcomes upon infection with SARS-CoV-2. Researchers assessed the characteristics of patients with lymphoma hospitalized for COVID-19 and analyzed determinants of mortality in a retrospective database study. The investigators looked at data from adult patients with lymphoma who were hospitalized for COVID-19 in March and April 2020 in three French regions.
Older age and relapsed/refractory (r/r) disease in B-cell lymphoma patients were both found to be independent risk factors of increased death rate from COVID-19, according to the online report in EClinicalMedicine, published by The Lancet.
These results encourage “the application of standard Covid-19 treatment, including intubation, for lymphoma patients with Covid-19 lymphoma diagnosis, under first- or second-line chemotherapy, or in remission,” according to Sylvain Lamure, MD, of Montellier (France) University, and colleagues.
The study examined a series of 89 consecutive patients from three French regions who had lymphoma and were hospitalized for COVID-19 in March and April 2020. The population was homogeneous; most patients were diagnosed with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and had been treated for their lymphoma within 1 year.
Promising results for many
There were a significant associations between 30-day mortality and increasing age (over age 70 years) and r/r lymphoma. However, in the absence of those factors, mortality of the lymphoma patients with COVID-19 was comparable with that of the reference French COVID-19 population. In addition, there was no significant impact of active lymphoma treatment that had been given within 1 year, except for those patients who received bendamustine, which was associated with greater mortality, according to the researchers.
With a median follow-up of 33 days from admission, the Kaplan-Meier estimate of 30-day overall survival was 71% (95% confidence interval, 62%-81%). According to histological type of the lymphoma, 30-day overall survival rates were 80% (95% CI, 45%-100%) for Hodgkin lymphoma, 71% (95% CI, 61%-82%) for B-cell non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, and 71% (95% CI, 38%-100%) for T-cell non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.
The main factors associated with mortality were age 70 years and older (hazard ratio, 3.78; 95% CI, 1.73-8.25; P = .0009), hypertension (HR, 2.20; 95% CI, 1.06-4.59; P = .03), previous cancer (HR, 2.11; 95% CI, 0.90-4.92; P = .08), use of bendamustine within 12 months before admission to hospital (HR, 3.05; 95% CI, 1.31-7.11; P = .01), and r/r lymphoma (HR, 2.62; 95% CI, 1.20-5.72; P = .02).
Overall, the Kaplan-Meier estimates of 30-day overall survival were 61% for patients with r/r lymphoma, 52% in patients age 70 years with non–r/r lymphoma, and 88% for patients younger than 70 years with non–r/r, which was comparable with general population survival data among French populations, according to the researchers.
“Longer term clinical follow-up and biological monitoring of immune responses is warranted to explore the impact of lymphoma and its treatment on the immunity and prolonged outcome of Covid-19 patients,” they concluded.
The study was unsponsored. Several of the authors reported financial relationships with a number of biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Lamure S et al. EClinicalMedicine. 2020 Oct 12. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100549.
Patients with B-cell lymphoma are immunocompromised because of the disease and its treatments. This presents the question of their outcomes upon infection with SARS-CoV-2. Researchers assessed the characteristics of patients with lymphoma hospitalized for COVID-19 and analyzed determinants of mortality in a retrospective database study. The investigators looked at data from adult patients with lymphoma who were hospitalized for COVID-19 in March and April 2020 in three French regions.
Older age and relapsed/refractory (r/r) disease in B-cell lymphoma patients were both found to be independent risk factors of increased death rate from COVID-19, according to the online report in EClinicalMedicine, published by The Lancet.
These results encourage “the application of standard Covid-19 treatment, including intubation, for lymphoma patients with Covid-19 lymphoma diagnosis, under first- or second-line chemotherapy, or in remission,” according to Sylvain Lamure, MD, of Montellier (France) University, and colleagues.
The study examined a series of 89 consecutive patients from three French regions who had lymphoma and were hospitalized for COVID-19 in March and April 2020. The population was homogeneous; most patients were diagnosed with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and had been treated for their lymphoma within 1 year.
Promising results for many
There were a significant associations between 30-day mortality and increasing age (over age 70 years) and r/r lymphoma. However, in the absence of those factors, mortality of the lymphoma patients with COVID-19 was comparable with that of the reference French COVID-19 population. In addition, there was no significant impact of active lymphoma treatment that had been given within 1 year, except for those patients who received bendamustine, which was associated with greater mortality, according to the researchers.
With a median follow-up of 33 days from admission, the Kaplan-Meier estimate of 30-day overall survival was 71% (95% confidence interval, 62%-81%). According to histological type of the lymphoma, 30-day overall survival rates were 80% (95% CI, 45%-100%) for Hodgkin lymphoma, 71% (95% CI, 61%-82%) for B-cell non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, and 71% (95% CI, 38%-100%) for T-cell non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.
The main factors associated with mortality were age 70 years and older (hazard ratio, 3.78; 95% CI, 1.73-8.25; P = .0009), hypertension (HR, 2.20; 95% CI, 1.06-4.59; P = .03), previous cancer (HR, 2.11; 95% CI, 0.90-4.92; P = .08), use of bendamustine within 12 months before admission to hospital (HR, 3.05; 95% CI, 1.31-7.11; P = .01), and r/r lymphoma (HR, 2.62; 95% CI, 1.20-5.72; P = .02).
Overall, the Kaplan-Meier estimates of 30-day overall survival were 61% for patients with r/r lymphoma, 52% in patients age 70 years with non–r/r lymphoma, and 88% for patients younger than 70 years with non–r/r, which was comparable with general population survival data among French populations, according to the researchers.
“Longer term clinical follow-up and biological monitoring of immune responses is warranted to explore the impact of lymphoma and its treatment on the immunity and prolonged outcome of Covid-19 patients,” they concluded.
The study was unsponsored. Several of the authors reported financial relationships with a number of biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Lamure S et al. EClinicalMedicine. 2020 Oct 12. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100549.
FROM ECLINICALMEDICINE
Efforts to close the ‘AYA gap’ in lymphoma
In the 1970s, cancer survival was poor for young children and older adults in the United States, as shown by data published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Great progress has been made since the 1970s, but improvements in outcome have been less impressive for cancer patients aged 15-39 years, as shown by research published in Cancer.
Patients aged 15-39 years have been designated by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) as “adolescents and young adults (AYAs),” and the lag in survival benefit has been termed “the AYA gap.”
The AYA gap persists in lymphoma patients, and an expert panel recently outlined differences between lymphoma in AYAs and lymphoma in other age groups.
The experts spoke at a special session of the AACR Virtual Meeting: Advances in Malignant Lymphoma moderated by Somali M. Smith, MD, of the University of Chicago.
Factors that contribute to the AYA gap
About 89,000 AYAs are diagnosed with cancer each year in the United States, according to data from the National Cancer Institute (NCI). Lymphomas and thyroid cancer are the most common cancers among younger AYAs, aged 15-24 years.
In a report commissioned by the NIH in 2006, many factors contributing to the AYA gap were identified. Chief among them were:
- Limitations in access to care.
- Delayed diagnosis.
- Inconsistency in treatment and follow-up.
- Long-term toxicity (fertility, second malignancies, and cardiovascular disease).
These factors compromise health-related survival, even when cancer-specific survival is improved.
Panelist Kara Kelly, MD, of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center in Buffalo, N.Y., noted that there are additional unique challenges for AYAs with cancer. These include:
- Pubertal changes.
- Developmental transition to independence.
- Societal impediments such as insurance coverage and disparities in access to specialized centers.
- Psychosocial factors such as health literacy and adherence to treatment and follow-up.
Focusing on lymphoma specifically, Dr. Kelly noted that lymphoma biology differs across the age spectrum and by race and ethnicity. Both tumor and host factors require further study, she said.
Clinical trial access for AYAs
Dr. Kelly emphasized that, unfortunately, clinical research participation is low among AYAs. A major impediment is that adult clinical trials historically required participants to be at least 18 years old.
In addition, there has not been a focused effort to educate AYAs about regulatory safeguards to ensure safety and the promise of enhanced benefit to them in NCI Cancer Trials Network (NCTN) trials. As a result, the refusal rate is high.
A multi-stakeholder workshop, convened in May 2016 by the American Society of Clinical Oncology and Friends of Cancer Research, outlined opportunities for expanding trial eligibility to include children younger than 18 years in first-in-human and other adult cancer clinical trials, enhancing their access to new agents, without compromising safety.
Recently, collaborative efforts between the adult and children’s NCTN research groups have included AYAs in studies addressing cancers that span the age spectrum, including lymphoma.
However, as Dr. Kelly noted, there are differences in AYA lymphoid malignancy types with a transition from more pediatric to more adult types.
Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma
Panelist Lisa G. Roth, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, reviewed the genomic landscape of Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL).
Dr. Roth explained that both HL and PMBCL are derived from thymic B cells, predominantly affect the mediastinum, and are CD30-positive lymphomas. Both are characterized by upregulation of JAK/STAT and NF-kappaB as well as overexpression of PD-L1.
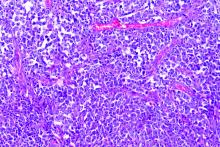
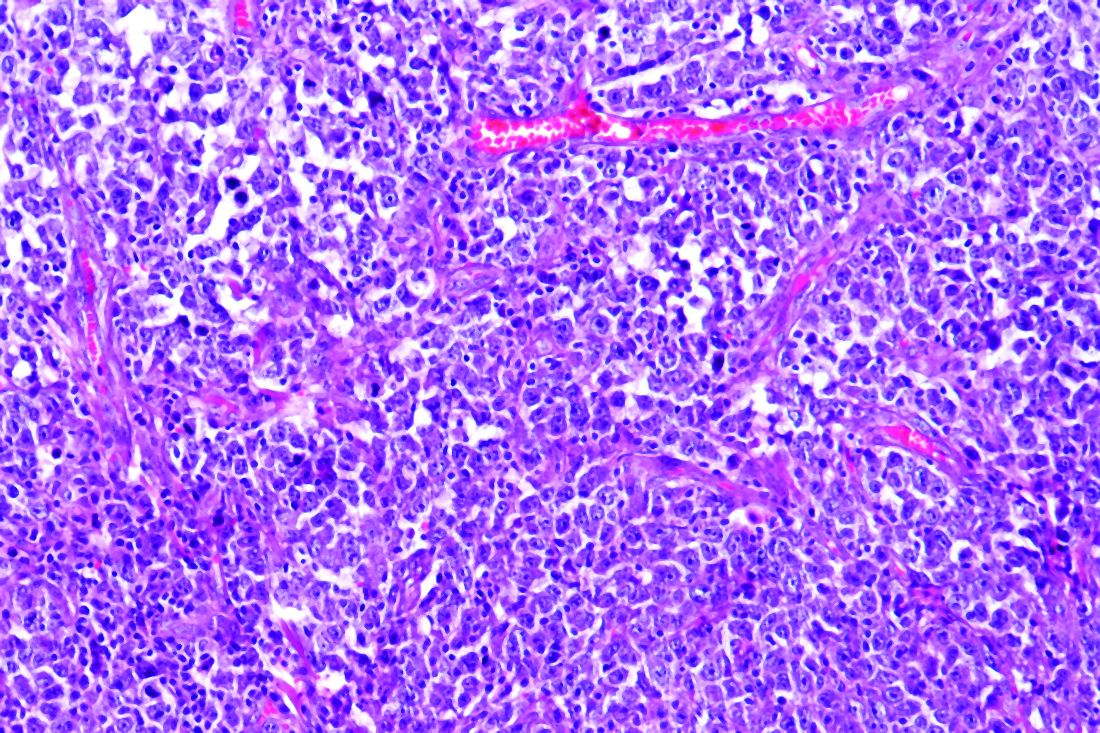
Dr. Roth noted that HL is challenging to sequence by standard methods because Reed Sternberg (HRS) cells represent less than 1% of the cellular infiltrate. Recurrently mutated genes in HL cluster by histologic subtype.
Whole-exome sequencing of HRS cells show loss of beta-2 microglobulin and MHC-1 expression, HLA-B, NF-kappaB signaling, and JAK-STAT signaling, according to data published in Blood Advances in 2019.
Dr. Roth’s lab performed immunohistochemistry on tissue microarrays in 145 cases of HL (unpublished data). Results showed that loss of beta-2 microglobulin is more common in younger HL patients. For other alterations, there were too few cases to know.
Dr. Roth’s lab is a member of a pediatric/AYA HL sequencing multi-institutional consortium that has been able to extract DNA and RNA from samples submitted for whole-exome sequencing. The consortium’s goal is to shed light on implications of other genomic alterations that may differ by age in HL patients.
Dr. Roth cited research showing that PMBCL shares molecular alterations similar to those of HL. Alterations in PMBCL suggest dysregulated cellular signaling and immune evasion mechanisms (e.g., deletions in MHC type 1 and 2, beta-2 microglobulin, JAK-STAT, and NF-kappaB mutations) that provide opportunities to study novel agents, according to data published in Blood in 2019.
By early 2021, the S1826 and ANHL1931 studies, which have no age restriction, will be available to AYA lymphoma patients with HL and PMBCL, respectively, Dr. Roth said.
Follicular lymphoma: Clinical features by age
Panelist Abner Louissaint Jr, MD, PhD, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, discussed age-related differences in follicular lymphoma (FL).
He noted that FL typically presents at an advanced stage, with low- or high-grade histology. It is increasingly common in adults in their 50s and 60s, representing 20% of all lymphomas. FL is rare in children and AYAs.
Dr. Louissaint explained that the typical flow cytometric findings in FL are BCL2 translocations, occurring in up to 85%-90% of low-grade and 50% of high-grade cases. The t(14;18)(q32;q21) translocation juxtaposes BCL2 on 18q21 to regulatory sequences and enhances the expression of elements of the Ig heavy chain.
Malignant cells in FL patients express CD20, CD10, CD21, and BCL2 (in contrast to normal germinal centers) and overexpress BCL6 (in contrast to normal follicles), Dr. Louissaint noted. He said the Ki-67 proliferative index of the malignant cells is typically low.
Pediatric-type FL is rare, but case series show clinical, pathologic, and molecular features that are distinctive from adult FL, Dr. Louissaint explained.
He then discussed the features of pediatric-type FL in multiple domains. In the clinical domain, there is a male predilection, and stage tends to be low. There is frequent involvement of nodes of the head and neck region and rare involvement of internal lymph node chains.
Pathologically, the malignant cells appear high grade, with architectural effacement, expansile follicular pattern, large lymphocyte size, and an elevated proliferation index. In contrast to adult FL, malignant cells in pediatric-type FL lack aberrant BCL2 expression.
Most importantly, for pediatric-type FL, the prognosis is excellent with durable remissions after surgical excision, Dr. Louissaint said.
Follicular lymphoma: Molecular features by age
Because of the excellent prognosis in pediatric-type FL, it is important to assess whether young adults with FL have adult-type or pediatric-type lesions, Dr. Louissaint said.
He cited many studies showing differences in adult and pediatric-type FL. In adult FL, the mutational landscape is characterized by frequent chromatin-modifying mutations in genes such as CREBBP, KM22D, and EP300.
In contrast, in pediatric-type FL, there are frequent activating MAPK pathway mutations, including mutations in the negative regulatory domain of MAP2K1. These mutations are not seen in adult FL.
Dr. Louissaint noted that there may be mutations in epigenetic modifiers (CREBBP, TNFRSF14) in both adult and pediatric-type FL. However, CREBBP is very unusual in pediatric-type FL and common in adult FL. This suggests the alterations in pediatric-type FL do not simply represent an early stage of the same disease as adult FL.
Despite a high proliferating fraction and absence of BCL2/BCL6/IRF4 rearrangements in pediatric-type FL, the presence of these features was associated with dramatic difference in progression-free survival, according to research published in Blood in 2012.
A distinct entity
In 2016, the World Health Organization recognized pediatric-type FL as a distinct entity, with the following diagnostic criteria (published in Blood):
- At least partial effacement of nodal architecture, expansile follicles, intermediate-size blastoid cells, and no component of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
- Immunohistochemistry showing BCL6 positivity, BCL2 negativity or weak positivity, and a high proliferative fraction.
- Genomic studies showing no BCL2 amplification.
- Clinical features of nodal disease in the head and neck region, early clinical stage, age younger than 40 years, typically in a male with no internal nodes involved.
When FL occurs in AYAs, the diagnostic findings of pediatric-type FL suggest the patient will do well with conservative management (e.g., excision alone), Dr. Louissaint noted.
Two sizes do not fit all
The strategies that have improved cancer outcomes since the 1970s for children and older adults have been much less successful for AYAs with cancer.
As an oncologic community, we should not allow the AYA gap to persist. As always, the solutions are likely to involve focused clinical research, education, and communication. Effort will need to be targeted specifically to the AYA population.
Since health-related mortality is high even when cancer-specific outcomes improve, adopting and maintaining a healthy lifestyle must be a key part of the discussion with these young patients.
The biologic differences associated with AYA lymphomas demand participation in clinical trials.
Oncologists should vigorously support removing impediments to the participation of AYAs in prospective clinical trials, stratified (but unrestricted) by age, with careful analysis of patient-reported outcomes, late adverse effects, and biospecimen collection.
As Dr. Kelly noted in the question-and-answer period, the Children’s Oncology Group has an existing biobank of paraffin-embedded tumor samples, DNA from lymphoma specimens, plasma, and sera with clinically annotated data that can be given to investigators upon request and justification.
Going beyond eligibility for clinical trials
Unfortunately, we will likely find that broadening eligibility criteria is the “low-hanging fruit.” There are protocol-, patient-, and physician-related obstacles, according to a review published in Cancer in 2019.
Patient-related obstacles include fear of toxicity, uncertainty about placebos, a steep learning curve for health literacy, insurance-related impediments, and other access-related issues.
Discussions will need to be tailored to the AYA population. Frank, early conversations about fertility, sexuality, financial hardship, career advancement, work-life balance, and cognitive risks may not only facilitate treatment planning but also encourage the trust that is essential for patients to enroll in trials.
The investment in time, multidisciplinary staff and physician involvement, and potential delays in treatment initiation may be painful and inconvenient, but the benefits for long-term health outcomes and personal-professional relationships will be gratifying beyond measure.
Dr. Smith disclosed relationships with Genentech/Roche, Celgene, TGTX, Karyopharm, Janssen, and Bantem. Dr. Roth disclosed relationships with Janssen, ADC Therapeutics, and Celgene. Dr. Kelly and Dr. Louissaint had no financial relationships to disclose.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers, as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
In the 1970s, cancer survival was poor for young children and older adults in the United States, as shown by data published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Great progress has been made since the 1970s, but improvements in outcome have been less impressive for cancer patients aged 15-39 years, as shown by research published in Cancer.
Patients aged 15-39 years have been designated by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) as “adolescents and young adults (AYAs),” and the lag in survival benefit has been termed “the AYA gap.”
The AYA gap persists in lymphoma patients, and an expert panel recently outlined differences between lymphoma in AYAs and lymphoma in other age groups.
The experts spoke at a special session of the AACR Virtual Meeting: Advances in Malignant Lymphoma moderated by Somali M. Smith, MD, of the University of Chicago.
Factors that contribute to the AYA gap
About 89,000 AYAs are diagnosed with cancer each year in the United States, according to data from the National Cancer Institute (NCI). Lymphomas and thyroid cancer are the most common cancers among younger AYAs, aged 15-24 years.
In a report commissioned by the NIH in 2006, many factors contributing to the AYA gap were identified. Chief among them were:
- Limitations in access to care.
- Delayed diagnosis.
- Inconsistency in treatment and follow-up.
- Long-term toxicity (fertility, second malignancies, and cardiovascular disease).
These factors compromise health-related survival, even when cancer-specific survival is improved.
Panelist Kara Kelly, MD, of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center in Buffalo, N.Y., noted that there are additional unique challenges for AYAs with cancer. These include:
- Pubertal changes.
- Developmental transition to independence.
- Societal impediments such as insurance coverage and disparities in access to specialized centers.
- Psychosocial factors such as health literacy and adherence to treatment and follow-up.
Focusing on lymphoma specifically, Dr. Kelly noted that lymphoma biology differs across the age spectrum and by race and ethnicity. Both tumor and host factors require further study, she said.
Clinical trial access for AYAs
Dr. Kelly emphasized that, unfortunately, clinical research participation is low among AYAs. A major impediment is that adult clinical trials historically required participants to be at least 18 years old.
In addition, there has not been a focused effort to educate AYAs about regulatory safeguards to ensure safety and the promise of enhanced benefit to them in NCI Cancer Trials Network (NCTN) trials. As a result, the refusal rate is high.
A multi-stakeholder workshop, convened in May 2016 by the American Society of Clinical Oncology and Friends of Cancer Research, outlined opportunities for expanding trial eligibility to include children younger than 18 years in first-in-human and other adult cancer clinical trials, enhancing their access to new agents, without compromising safety.
Recently, collaborative efforts between the adult and children’s NCTN research groups have included AYAs in studies addressing cancers that span the age spectrum, including lymphoma.
However, as Dr. Kelly noted, there are differences in AYA lymphoid malignancy types with a transition from more pediatric to more adult types.
Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma
Panelist Lisa G. Roth, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, reviewed the genomic landscape of Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL).
Dr. Roth explained that both HL and PMBCL are derived from thymic B cells, predominantly affect the mediastinum, and are CD30-positive lymphomas. Both are characterized by upregulation of JAK/STAT and NF-kappaB as well as overexpression of PD-L1.
Dr. Roth noted that HL is challenging to sequence by standard methods because Reed Sternberg (HRS) cells represent less than 1% of the cellular infiltrate. Recurrently mutated genes in HL cluster by histologic subtype.
Whole-exome sequencing of HRS cells show loss of beta-2 microglobulin and MHC-1 expression, HLA-B, NF-kappaB signaling, and JAK-STAT signaling, according to data published in Blood Advances in 2019.
Dr. Roth’s lab performed immunohistochemistry on tissue microarrays in 145 cases of HL (unpublished data). Results showed that loss of beta-2 microglobulin is more common in younger HL patients. For other alterations, there were too few cases to know.
Dr. Roth’s lab is a member of a pediatric/AYA HL sequencing multi-institutional consortium that has been able to extract DNA and RNA from samples submitted for whole-exome sequencing. The consortium’s goal is to shed light on implications of other genomic alterations that may differ by age in HL patients.
Dr. Roth cited research showing that PMBCL shares molecular alterations similar to those of HL. Alterations in PMBCL suggest dysregulated cellular signaling and immune evasion mechanisms (e.g., deletions in MHC type 1 and 2, beta-2 microglobulin, JAK-STAT, and NF-kappaB mutations) that provide opportunities to study novel agents, according to data published in Blood in 2019.
By early 2021, the S1826 and ANHL1931 studies, which have no age restriction, will be available to AYA lymphoma patients with HL and PMBCL, respectively, Dr. Roth said.
Follicular lymphoma: Clinical features by age
Panelist Abner Louissaint Jr, MD, PhD, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, discussed age-related differences in follicular lymphoma (FL).
He noted that FL typically presents at an advanced stage, with low- or high-grade histology. It is increasingly common in adults in their 50s and 60s, representing 20% of all lymphomas. FL is rare in children and AYAs.
Dr. Louissaint explained that the typical flow cytometric findings in FL are BCL2 translocations, occurring in up to 85%-90% of low-grade and 50% of high-grade cases. The t(14;18)(q32;q21) translocation juxtaposes BCL2 on 18q21 to regulatory sequences and enhances the expression of elements of the Ig heavy chain.
Malignant cells in FL patients express CD20, CD10, CD21, and BCL2 (in contrast to normal germinal centers) and overexpress BCL6 (in contrast to normal follicles), Dr. Louissaint noted. He said the Ki-67 proliferative index of the malignant cells is typically low.
Pediatric-type FL is rare, but case series show clinical, pathologic, and molecular features that are distinctive from adult FL, Dr. Louissaint explained.
He then discussed the features of pediatric-type FL in multiple domains. In the clinical domain, there is a male predilection, and stage tends to be low. There is frequent involvement of nodes of the head and neck region and rare involvement of internal lymph node chains.
Pathologically, the malignant cells appear high grade, with architectural effacement, expansile follicular pattern, large lymphocyte size, and an elevated proliferation index. In contrast to adult FL, malignant cells in pediatric-type FL lack aberrant BCL2 expression.
Most importantly, for pediatric-type FL, the prognosis is excellent with durable remissions after surgical excision, Dr. Louissaint said.
Follicular lymphoma: Molecular features by age
Because of the excellent prognosis in pediatric-type FL, it is important to assess whether young adults with FL have adult-type or pediatric-type lesions, Dr. Louissaint said.
He cited many studies showing differences in adult and pediatric-type FL. In adult FL, the mutational landscape is characterized by frequent chromatin-modifying mutations in genes such as CREBBP, KM22D, and EP300.
In contrast, in pediatric-type FL, there are frequent activating MAPK pathway mutations, including mutations in the negative regulatory domain of MAP2K1. These mutations are not seen in adult FL.
Dr. Louissaint noted that there may be mutations in epigenetic modifiers (CREBBP, TNFRSF14) in both adult and pediatric-type FL. However, CREBBP is very unusual in pediatric-type FL and common in adult FL. This suggests the alterations in pediatric-type FL do not simply represent an early stage of the same disease as adult FL.
Despite a high proliferating fraction and absence of BCL2/BCL6/IRF4 rearrangements in pediatric-type FL, the presence of these features was associated with dramatic difference in progression-free survival, according to research published in Blood in 2012.
A distinct entity
In 2016, the World Health Organization recognized pediatric-type FL as a distinct entity, with the following diagnostic criteria (published in Blood):
- At least partial effacement of nodal architecture, expansile follicles, intermediate-size blastoid cells, and no component of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
- Immunohistochemistry showing BCL6 positivity, BCL2 negativity or weak positivity, and a high proliferative fraction.
- Genomic studies showing no BCL2 amplification.
- Clinical features of nodal disease in the head and neck region, early clinical stage, age younger than 40 years, typically in a male with no internal nodes involved.
When FL occurs in AYAs, the diagnostic findings of pediatric-type FL suggest the patient will do well with conservative management (e.g., excision alone), Dr. Louissaint noted.
Two sizes do not fit all
The strategies that have improved cancer outcomes since the 1970s for children and older adults have been much less successful for AYAs with cancer.
As an oncologic community, we should not allow the AYA gap to persist. As always, the solutions are likely to involve focused clinical research, education, and communication. Effort will need to be targeted specifically to the AYA population.
Since health-related mortality is high even when cancer-specific outcomes improve, adopting and maintaining a healthy lifestyle must be a key part of the discussion with these young patients.
The biologic differences associated with AYA lymphomas demand participation in clinical trials.
Oncologists should vigorously support removing impediments to the participation of AYAs in prospective clinical trials, stratified (but unrestricted) by age, with careful analysis of patient-reported outcomes, late adverse effects, and biospecimen collection.
As Dr. Kelly noted in the question-and-answer period, the Children’s Oncology Group has an existing biobank of paraffin-embedded tumor samples, DNA from lymphoma specimens, plasma, and sera with clinically annotated data that can be given to investigators upon request and justification.
Going beyond eligibility for clinical trials
Unfortunately, we will likely find that broadening eligibility criteria is the “low-hanging fruit.” There are protocol-, patient-, and physician-related obstacles, according to a review published in Cancer in 2019.
Patient-related obstacles include fear of toxicity, uncertainty about placebos, a steep learning curve for health literacy, insurance-related impediments, and other access-related issues.
Discussions will need to be tailored to the AYA population. Frank, early conversations about fertility, sexuality, financial hardship, career advancement, work-life balance, and cognitive risks may not only facilitate treatment planning but also encourage the trust that is essential for patients to enroll in trials.
The investment in time, multidisciplinary staff and physician involvement, and potential delays in treatment initiation may be painful and inconvenient, but the benefits for long-term health outcomes and personal-professional relationships will be gratifying beyond measure.
Dr. Smith disclosed relationships with Genentech/Roche, Celgene, TGTX, Karyopharm, Janssen, and Bantem. Dr. Roth disclosed relationships with Janssen, ADC Therapeutics, and Celgene. Dr. Kelly and Dr. Louissaint had no financial relationships to disclose.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers, as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
In the 1970s, cancer survival was poor for young children and older adults in the United States, as shown by data published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Great progress has been made since the 1970s, but improvements in outcome have been less impressive for cancer patients aged 15-39 years, as shown by research published in Cancer.
Patients aged 15-39 years have been designated by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) as “adolescents and young adults (AYAs),” and the lag in survival benefit has been termed “the AYA gap.”
The AYA gap persists in lymphoma patients, and an expert panel recently outlined differences between lymphoma in AYAs and lymphoma in other age groups.
The experts spoke at a special session of the AACR Virtual Meeting: Advances in Malignant Lymphoma moderated by Somali M. Smith, MD, of the University of Chicago.
Factors that contribute to the AYA gap
About 89,000 AYAs are diagnosed with cancer each year in the United States, according to data from the National Cancer Institute (NCI). Lymphomas and thyroid cancer are the most common cancers among younger AYAs, aged 15-24 years.
In a report commissioned by the NIH in 2006, many factors contributing to the AYA gap were identified. Chief among them were:
- Limitations in access to care.
- Delayed diagnosis.
- Inconsistency in treatment and follow-up.
- Long-term toxicity (fertility, second malignancies, and cardiovascular disease).
These factors compromise health-related survival, even when cancer-specific survival is improved.
Panelist Kara Kelly, MD, of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center in Buffalo, N.Y., noted that there are additional unique challenges for AYAs with cancer. These include:
- Pubertal changes.
- Developmental transition to independence.
- Societal impediments such as insurance coverage and disparities in access to specialized centers.
- Psychosocial factors such as health literacy and adherence to treatment and follow-up.
Focusing on lymphoma specifically, Dr. Kelly noted that lymphoma biology differs across the age spectrum and by race and ethnicity. Both tumor and host factors require further study, she said.
Clinical trial access for AYAs
Dr. Kelly emphasized that, unfortunately, clinical research participation is low among AYAs. A major impediment is that adult clinical trials historically required participants to be at least 18 years old.
In addition, there has not been a focused effort to educate AYAs about regulatory safeguards to ensure safety and the promise of enhanced benefit to them in NCI Cancer Trials Network (NCTN) trials. As a result, the refusal rate is high.
A multi-stakeholder workshop, convened in May 2016 by the American Society of Clinical Oncology and Friends of Cancer Research, outlined opportunities for expanding trial eligibility to include children younger than 18 years in first-in-human and other adult cancer clinical trials, enhancing their access to new agents, without compromising safety.
Recently, collaborative efforts between the adult and children’s NCTN research groups have included AYAs in studies addressing cancers that span the age spectrum, including lymphoma.
However, as Dr. Kelly noted, there are differences in AYA lymphoid malignancy types with a transition from more pediatric to more adult types.
Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma
Panelist Lisa G. Roth, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, reviewed the genomic landscape of Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL).
Dr. Roth explained that both HL and PMBCL are derived from thymic B cells, predominantly affect the mediastinum, and are CD30-positive lymphomas. Both are characterized by upregulation of JAK/STAT and NF-kappaB as well as overexpression of PD-L1.
Dr. Roth noted that HL is challenging to sequence by standard methods because Reed Sternberg (HRS) cells represent less than 1% of the cellular infiltrate. Recurrently mutated genes in HL cluster by histologic subtype.
Whole-exome sequencing of HRS cells show loss of beta-2 microglobulin and MHC-1 expression, HLA-B, NF-kappaB signaling, and JAK-STAT signaling, according to data published in Blood Advances in 2019.
Dr. Roth’s lab performed immunohistochemistry on tissue microarrays in 145 cases of HL (unpublished data). Results showed that loss of beta-2 microglobulin is more common in younger HL patients. For other alterations, there were too few cases to know.
Dr. Roth’s lab is a member of a pediatric/AYA HL sequencing multi-institutional consortium that has been able to extract DNA and RNA from samples submitted for whole-exome sequencing. The consortium’s goal is to shed light on implications of other genomic alterations that may differ by age in HL patients.
Dr. Roth cited research showing that PMBCL shares molecular alterations similar to those of HL. Alterations in PMBCL suggest dysregulated cellular signaling and immune evasion mechanisms (e.g., deletions in MHC type 1 and 2, beta-2 microglobulin, JAK-STAT, and NF-kappaB mutations) that provide opportunities to study novel agents, according to data published in Blood in 2019.
By early 2021, the S1826 and ANHL1931 studies, which have no age restriction, will be available to AYA lymphoma patients with HL and PMBCL, respectively, Dr. Roth said.
Follicular lymphoma: Clinical features by age
Panelist Abner Louissaint Jr, MD, PhD, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, discussed age-related differences in follicular lymphoma (FL).
He noted that FL typically presents at an advanced stage, with low- or high-grade histology. It is increasingly common in adults in their 50s and 60s, representing 20% of all lymphomas. FL is rare in children and AYAs.
Dr. Louissaint explained that the typical flow cytometric findings in FL are BCL2 translocations, occurring in up to 85%-90% of low-grade and 50% of high-grade cases. The t(14;18)(q32;q21) translocation juxtaposes BCL2 on 18q21 to regulatory sequences and enhances the expression of elements of the Ig heavy chain.
Malignant cells in FL patients express CD20, CD10, CD21, and BCL2 (in contrast to normal germinal centers) and overexpress BCL6 (in contrast to normal follicles), Dr. Louissaint noted. He said the Ki-67 proliferative index of the malignant cells is typically low.
Pediatric-type FL is rare, but case series show clinical, pathologic, and molecular features that are distinctive from adult FL, Dr. Louissaint explained.
He then discussed the features of pediatric-type FL in multiple domains. In the clinical domain, there is a male predilection, and stage tends to be low. There is frequent involvement of nodes of the head and neck region and rare involvement of internal lymph node chains.
Pathologically, the malignant cells appear high grade, with architectural effacement, expansile follicular pattern, large lymphocyte size, and an elevated proliferation index. In contrast to adult FL, malignant cells in pediatric-type FL lack aberrant BCL2 expression.
Most importantly, for pediatric-type FL, the prognosis is excellent with durable remissions after surgical excision, Dr. Louissaint said.
Follicular lymphoma: Molecular features by age
Because of the excellent prognosis in pediatric-type FL, it is important to assess whether young adults with FL have adult-type or pediatric-type lesions, Dr. Louissaint said.
He cited many studies showing differences in adult and pediatric-type FL. In adult FL, the mutational landscape is characterized by frequent chromatin-modifying mutations in genes such as CREBBP, KM22D, and EP300.
In contrast, in pediatric-type FL, there are frequent activating MAPK pathway mutations, including mutations in the negative regulatory domain of MAP2K1. These mutations are not seen in adult FL.
Dr. Louissaint noted that there may be mutations in epigenetic modifiers (CREBBP, TNFRSF14) in both adult and pediatric-type FL. However, CREBBP is very unusual in pediatric-type FL and common in adult FL. This suggests the alterations in pediatric-type FL do not simply represent an early stage of the same disease as adult FL.
Despite a high proliferating fraction and absence of BCL2/BCL6/IRF4 rearrangements in pediatric-type FL, the presence of these features was associated with dramatic difference in progression-free survival, according to research published in Blood in 2012.
A distinct entity
In 2016, the World Health Organization recognized pediatric-type FL as a distinct entity, with the following diagnostic criteria (published in Blood):
- At least partial effacement of nodal architecture, expansile follicles, intermediate-size blastoid cells, and no component of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
- Immunohistochemistry showing BCL6 positivity, BCL2 negativity or weak positivity, and a high proliferative fraction.
- Genomic studies showing no BCL2 amplification.
- Clinical features of nodal disease in the head and neck region, early clinical stage, age younger than 40 years, typically in a male with no internal nodes involved.
When FL occurs in AYAs, the diagnostic findings of pediatric-type FL suggest the patient will do well with conservative management (e.g., excision alone), Dr. Louissaint noted.
Two sizes do not fit all
The strategies that have improved cancer outcomes since the 1970s for children and older adults have been much less successful for AYAs with cancer.
As an oncologic community, we should not allow the AYA gap to persist. As always, the solutions are likely to involve focused clinical research, education, and communication. Effort will need to be targeted specifically to the AYA population.
Since health-related mortality is high even when cancer-specific outcomes improve, adopting and maintaining a healthy lifestyle must be a key part of the discussion with these young patients.
The biologic differences associated with AYA lymphomas demand participation in clinical trials.
Oncologists should vigorously support removing impediments to the participation of AYAs in prospective clinical trials, stratified (but unrestricted) by age, with careful analysis of patient-reported outcomes, late adverse effects, and biospecimen collection.
As Dr. Kelly noted in the question-and-answer period, the Children’s Oncology Group has an existing biobank of paraffin-embedded tumor samples, DNA from lymphoma specimens, plasma, and sera with clinically annotated data that can be given to investigators upon request and justification.
Going beyond eligibility for clinical trials
Unfortunately, we will likely find that broadening eligibility criteria is the “low-hanging fruit.” There are protocol-, patient-, and physician-related obstacles, according to a review published in Cancer in 2019.
Patient-related obstacles include fear of toxicity, uncertainty about placebos, a steep learning curve for health literacy, insurance-related impediments, and other access-related issues.
Discussions will need to be tailored to the AYA population. Frank, early conversations about fertility, sexuality, financial hardship, career advancement, work-life balance, and cognitive risks may not only facilitate treatment planning but also encourage the trust that is essential for patients to enroll in trials.
The investment in time, multidisciplinary staff and physician involvement, and potential delays in treatment initiation may be painful and inconvenient, but the benefits for long-term health outcomes and personal-professional relationships will be gratifying beyond measure.
Dr. Smith disclosed relationships with Genentech/Roche, Celgene, TGTX, Karyopharm, Janssen, and Bantem. Dr. Roth disclosed relationships with Janssen, ADC Therapeutics, and Celgene. Dr. Kelly and Dr. Louissaint had no financial relationships to disclose.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers, as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
FROM AACR ADVANCES IN MALIGNANT LYMPHOMA 2020
Seven things to know about new lymphoma drug tafasitamab
The Food and Drug Administration recently approved tafasitamab-cxix (Monjuvi) in combination with lenalidomide for the treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) not otherwise specified, including DLBCL arising from low-grade lymphoma, who are not eligible for autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT).
In an interview, Ann S. LaCasce, MD, a lymphoma specialist, associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, and director of the Dana-Farber/Massachusetts General Brigham fellowship in hematology/oncology, discussed the drug and its approval:
Question: How common is relapsed or refractory DLBCL? Have there been any changes in the rates of this disease in recent years?
Dr. LaCasce: Approximately 40% of patients with DLBCL will have relapsed or refractory disease. The rates of lymphoma have been rising over the past several decades for unclear reasons. As this is a disease predominantly of older adults, increasing life expectancy likely plays a role. Environmental factors may also be contributing.
Q: How long do patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL who are not eligible for stem cell transplant usually survive?
Dr. LaCasce: This is highly variable, though it’s estimated to be approximately 1 year. Some patients will be cured with autologous transplantation or CAR-T cells. The pace of the disease can be highly variable, with some patients responding to multiple lines of therapy whereas others may have rapidly progressive refractory disease.
Q: What makes patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL ineligible for ASCT?
Dr. LaCasce: To be eligible, patients need to be younger than 70-75 years or so without significant comorbidities and must have chemotherapy-responsive disease. More than half of patients will not fit these criteria.
Q: Can you briefly describe the L-MIND study that led to the approval of tafasitamab-cxix?
Dr. LaCasce: This was a single-arm, phase 2 study of tafasitamab plus lenalidomide in patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL status after one to three prior regimens who were not candidates for ASCT. Patients received tafasitamab until progression and up to 1 year of lenalidomide. The median age was 72 years, and 50% of patients had received only one prior line of therapy.
The overall and complete response rates in 80 patients treated were 60% and 43%, respectively. The median progression-free survival was approximately 1 year. Nearly half of patients required dose reduction of lenalidomide, and about a quarter discontinued the drug. Twenty-five percent of patients discontinued therapy for adverse events.
Q: What’s the toxicity profile of tafasitamab-cxix?
Dr. LaCasce: The most common adverse events were infusion reactions and myelosuppression, which are managed with standard approaches to incident rate ratios with steroids, antihistamines, etc. Myelosuppression can occur, but in this combination is mostly driven by lenalidomide, which is dose reduced or discontinued.
Q: Where does tafasitamab-cxix fit in the treatment paradigm for relapsed or refractory DLBCL? How does it compare with other available options?
Dr. LaCasce: This is an option for patients who are not candidates for potentially curative approaches, including ASCT and CAR T-cell therapy. There are patients not eligible for ASCT who may be appropriate for CAR-T.
Tafasitamab plus lenalidomide requires frequent visits, particularly during the first 3 months, and then every other week until progression. The dose of lenalidomide will not be tolerable for many of these patients.
Other options in this population include polatuzumab plus bendamustine/rituximab or possibly selinexor. The former has similar activity and is time limited, though many patients will not tolerate the full dose of bendamustine. In the study leading to approval, selinexor had a much lower response rate of approximately 30%, and the patient population was much more favorable, given that eligibility required 60-98 days after last therapy before enrolling.
The only approval specific for nontransplant patients is tafasitamab/lenalidomide.
Q: From a cost standpoint, how does tafasitamab compare with other options in this patient population?
Dr. LaCasce: I don’t have exact figures, but all options are very expensive. CAR-T is the most expensive. Given the ongoing therapy of tafasitamab until progression, the cumulative cost could be very high. Polatuzumab plus bendamustine/rituximab and selinexor are also very costly.
Q: What other drugs are in development for relapsed or refractory DLBCL?
Dr. LaCasce: Novel CAR T-cell therapies, including lisocabtagene maraleucel that is at the FDA, are in development. Bispecific antibodies (REGN1979 and mosunetuzumab), combinations with CD47 antibodies, and loncastuximab tesirine are all in phase 2 trials.
Dr. LaCasce has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration recently approved tafasitamab-cxix (Monjuvi) in combination with lenalidomide for the treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) not otherwise specified, including DLBCL arising from low-grade lymphoma, who are not eligible for autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT).
In an interview, Ann S. LaCasce, MD, a lymphoma specialist, associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, and director of the Dana-Farber/Massachusetts General Brigham fellowship in hematology/oncology, discussed the drug and its approval:
Question: How common is relapsed or refractory DLBCL? Have there been any changes in the rates of this disease in recent years?
Dr. LaCasce: Approximately 40% of patients with DLBCL will have relapsed or refractory disease. The rates of lymphoma have been rising over the past several decades for unclear reasons. As this is a disease predominantly of older adults, increasing life expectancy likely plays a role. Environmental factors may also be contributing.
Q: How long do patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL who are not eligible for stem cell transplant usually survive?
Dr. LaCasce: This is highly variable, though it’s estimated to be approximately 1 year. Some patients will be cured with autologous transplantation or CAR-T cells. The pace of the disease can be highly variable, with some patients responding to multiple lines of therapy whereas others may have rapidly progressive refractory disease.
Q: What makes patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL ineligible for ASCT?
Dr. LaCasce: To be eligible, patients need to be younger than 70-75 years or so without significant comorbidities and must have chemotherapy-responsive disease. More than half of patients will not fit these criteria.
Q: Can you briefly describe the L-MIND study that led to the approval of tafasitamab-cxix?
Dr. LaCasce: This was a single-arm, phase 2 study of tafasitamab plus lenalidomide in patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL status after one to three prior regimens who were not candidates for ASCT. Patients received tafasitamab until progression and up to 1 year of lenalidomide. The median age was 72 years, and 50% of patients had received only one prior line of therapy.
The overall and complete response rates in 80 patients treated were 60% and 43%, respectively. The median progression-free survival was approximately 1 year. Nearly half of patients required dose reduction of lenalidomide, and about a quarter discontinued the drug. Twenty-five percent of patients discontinued therapy for adverse events.
Q: What’s the toxicity profile of tafasitamab-cxix?
Dr. LaCasce: The most common adverse events were infusion reactions and myelosuppression, which are managed with standard approaches to incident rate ratios with steroids, antihistamines, etc. Myelosuppression can occur, but in this combination is mostly driven by lenalidomide, which is dose reduced or discontinued.
Q: Where does tafasitamab-cxix fit in the treatment paradigm for relapsed or refractory DLBCL? How does it compare with other available options?
Dr. LaCasce: This is an option for patients who are not candidates for potentially curative approaches, including ASCT and CAR T-cell therapy. There are patients not eligible for ASCT who may be appropriate for CAR-T.
Tafasitamab plus lenalidomide requires frequent visits, particularly during the first 3 months, and then every other week until progression. The dose of lenalidomide will not be tolerable for many of these patients.
Other options in this population include polatuzumab plus bendamustine/rituximab or possibly selinexor. The former has similar activity and is time limited, though many patients will not tolerate the full dose of bendamustine. In the study leading to approval, selinexor had a much lower response rate of approximately 30%, and the patient population was much more favorable, given that eligibility required 60-98 days after last therapy before enrolling.
The only approval specific for nontransplant patients is tafasitamab/lenalidomide.
Q: From a cost standpoint, how does tafasitamab compare with other options in this patient population?
Dr. LaCasce: I don’t have exact figures, but all options are very expensive. CAR-T is the most expensive. Given the ongoing therapy of tafasitamab until progression, the cumulative cost could be very high. Polatuzumab plus bendamustine/rituximab and selinexor are also very costly.
Q: What other drugs are in development for relapsed or refractory DLBCL?
Dr. LaCasce: Novel CAR T-cell therapies, including lisocabtagene maraleucel that is at the FDA, are in development. Bispecific antibodies (REGN1979 and mosunetuzumab), combinations with CD47 antibodies, and loncastuximab tesirine are all in phase 2 trials.
Dr. LaCasce has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration recently approved tafasitamab-cxix (Monjuvi) in combination with lenalidomide for the treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) not otherwise specified, including DLBCL arising from low-grade lymphoma, who are not eligible for autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT).
In an interview, Ann S. LaCasce, MD, a lymphoma specialist, associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, and director of the Dana-Farber/Massachusetts General Brigham fellowship in hematology/oncology, discussed the drug and its approval:
Question: How common is relapsed or refractory DLBCL? Have there been any changes in the rates of this disease in recent years?
Dr. LaCasce: Approximately 40% of patients with DLBCL will have relapsed or refractory disease. The rates of lymphoma have been rising over the past several decades for unclear reasons. As this is a disease predominantly of older adults, increasing life expectancy likely plays a role. Environmental factors may also be contributing.
Q: How long do patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL who are not eligible for stem cell transplant usually survive?
Dr. LaCasce: This is highly variable, though it’s estimated to be approximately 1 year. Some patients will be cured with autologous transplantation or CAR-T cells. The pace of the disease can be highly variable, with some patients responding to multiple lines of therapy whereas others may have rapidly progressive refractory disease.
Q: What makes patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL ineligible for ASCT?
Dr. LaCasce: To be eligible, patients need to be younger than 70-75 years or so without significant comorbidities and must have chemotherapy-responsive disease. More than half of patients will not fit these criteria.
Q: Can you briefly describe the L-MIND study that led to the approval of tafasitamab-cxix?
Dr. LaCasce: This was a single-arm, phase 2 study of tafasitamab plus lenalidomide in patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL status after one to three prior regimens who were not candidates for ASCT. Patients received tafasitamab until progression and up to 1 year of lenalidomide. The median age was 72 years, and 50% of patients had received only one prior line of therapy.
The overall and complete response rates in 80 patients treated were 60% and 43%, respectively. The median progression-free survival was approximately 1 year. Nearly half of patients required dose reduction of lenalidomide, and about a quarter discontinued the drug. Twenty-five percent of patients discontinued therapy for adverse events.
Q: What’s the toxicity profile of tafasitamab-cxix?
Dr. LaCasce: The most common adverse events were infusion reactions and myelosuppression, which are managed with standard approaches to incident rate ratios with steroids, antihistamines, etc. Myelosuppression can occur, but in this combination is mostly driven by lenalidomide, which is dose reduced or discontinued.
Q: Where does tafasitamab-cxix fit in the treatment paradigm for relapsed or refractory DLBCL? How does it compare with other available options?
Dr. LaCasce: This is an option for patients who are not candidates for potentially curative approaches, including ASCT and CAR T-cell therapy. There are patients not eligible for ASCT who may be appropriate for CAR-T.
Tafasitamab plus lenalidomide requires frequent visits, particularly during the first 3 months, and then every other week until progression. The dose of lenalidomide will not be tolerable for many of these patients.
Other options in this population include polatuzumab plus bendamustine/rituximab or possibly selinexor. The former has similar activity and is time limited, though many patients will not tolerate the full dose of bendamustine. In the study leading to approval, selinexor had a much lower response rate of approximately 30%, and the patient population was much more favorable, given that eligibility required 60-98 days after last therapy before enrolling.
The only approval specific for nontransplant patients is tafasitamab/lenalidomide.
Q: From a cost standpoint, how does tafasitamab compare with other options in this patient population?
Dr. LaCasce: I don’t have exact figures, but all options are very expensive. CAR-T is the most expensive. Given the ongoing therapy of tafasitamab until progression, the cumulative cost could be very high. Polatuzumab plus bendamustine/rituximab and selinexor are also very costly.
Q: What other drugs are in development for relapsed or refractory DLBCL?
Dr. LaCasce: Novel CAR T-cell therapies, including lisocabtagene maraleucel that is at the FDA, are in development. Bispecific antibodies (REGN1979 and mosunetuzumab), combinations with CD47 antibodies, and loncastuximab tesirine are all in phase 2 trials.
Dr. LaCasce has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Survey quantifies COVID-19’s impact on oncology
An international survey provides new insights into how COVID-19 has affected, and may continue to affect, the field of oncology.
The survey showed that “COVID-19 has had a major impact on the organization of patient care, on the well-being of caregivers, on continued medical education, and on clinical trial activities in oncology,” stated Guy Jerusalem, MD, PhD, of Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Liège (Belgium).
Dr. Jerusalem presented these findings at the European Society for Medical Oncology Virtual Congress 2020.
The survey was distributed by 20 oncologists from 10 of the countries most affected by COVID-19. Responses were obtained from 109 oncologists representing centers in 18 countries. The responses were recorded between June 17 and July 14, 2020.
The survey consisted of 95 items intended to evaluate the impact of COVID-19 on the organization of oncologic care. Questions encompassed the capacity and service offered at each center, the magnitude of COVID-19–based care interruptions and the reasons for them, the ensuing challenges faced, interventions implemented, and the estimated harms to patients during the pandemic.
The 109 oncologists surveyed had a median of 20 years of oncology experience. A majority of respondents were men (61.5%), and the median age was 48.5 years.
The respondents had worked predominantly (62.4%) at academic hospitals, with 29.6% at community hospitals. Most respondents worked at general hospitals with an oncology unit (66.1%) rather than a specialized separate cancer center (32.1%).
The most common specialty was breast cancer (60.6%), followed by gastrointestinal cancer (10.1%), urogenital cancer (9.2%), and lung cancer (8.3%).
Impact on treatment
The treatment modalities affected by the pandemic – through cancellations or delays in more than 10% of patients – included surgery (in 34% of centers), chemotherapy (22%), radiotherapy (13.7%), checkpoint inhibitor therapy (9.1%), monoclonal antibodies (9%), and oral targeted therapy (3.7%).
Among oncologists treating breast cancer, cancellations/delays in more than 10% of patients were reported for everolimus (18%), CDK4/6 inhibitors (8.9%), and endocrine therapy (2.2%).
Overall, 34.8% of respondents reported increased use of granulocyte colony–stimulating factor, and 6.4% reported increased use of erythropoietin.
On the other hand, 11.1% of respondents reported a decrease in the use of double immunotherapy, and 21.9% reported decreased use of corticosteroids.
Not only can the immunosuppressive effects of steroid use increase infection risks, Dr. Jerusalem noted, fever suppression can lead to a delayed diagnosis of COVID-19.
“To circumvent potential higher infection risks or greater disease severity, we use lower doses of steroids, but this is not based on studies,” he said.
“Previous exposure to steroids or being on steroids at the time of COVID-19 infection is a detrimental factor for complications and mortality,” commented ESMO President Solange Peters, MD, PhD, of Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois in Lausanne, Switzerland.
Dr. Peters noted that the observation was based on lung cancer registry findings. Furthermore, because data from smaller outbreaks of other coronavirus infections suggested worse prognosis and increased mortality, steroid use was already feared in the very early days of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Lastly, earlier cessation of palliative treatment was observed in 32.1% of centers, and 64.2% of respondents agreed that undertreatment because of COVID-19 is a major concern.
Dr. Jerusalem noted that the survey data do not explain the early cessation of palliative treatment. “I suspect that many patients died at home rather than alone in institutions because it was the only way they could die with their families around them.”
Telehealth, meetings, and trials
The survey also revealed rationales for the use of teleconsultation, including follow-up (94.5%), oral therapy (92.7%), immunotherapy (57.8%), and chemotherapy (55%).
Most respondents reported more frequent use of virtual meetings for continuing medical education (94%), oncologic team meetings (92%), and tumor boards (82%).
While about 82% of respondents said they were likely to continue the use of telemedicine, 45% said virtual conferences are not an acceptable alternative to live international conferences such as ESMO, Dr. Jerusalem said.
Finally, nearly three-quarters of respondents (72.5%) said all clinical trial activities are or will soon be activated, or never stopped, at their centers. On the other hand, 27.5% of respondents reported that their centers had major protocol violations or deviations, and 37% of respondents said they expect significant reductions in clinical trial activities this year.
Dr. Jerusalem concluded that COVID-19 is having a major, long-term impact on the organization of patient care, caregivers, continued medical education, and clinical trial activities in oncology.
He cautioned that “the risk of a delayed diagnosis of new cancers and economic consequences of COVID-19 on access to health care and cancer treatments have to be carefully evaluated.”
This research was funded by Fondation Léon Fredericq. Dr. Jerusalem disclosed relationships with Novartis, Roche, Lilly, Pfizer, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, AbbVie, MedImmune, and Merck. Dr. Peters disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, and many other companies.
SOURCE: Jerusalem G et al. ESMO 2020, Abstract LBA76.
An international survey provides new insights into how COVID-19 has affected, and may continue to affect, the field of oncology.
The survey showed that “COVID-19 has had a major impact on the organization of patient care, on the well-being of caregivers, on continued medical education, and on clinical trial activities in oncology,” stated Guy Jerusalem, MD, PhD, of Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Liège (Belgium).
Dr. Jerusalem presented these findings at the European Society for Medical Oncology Virtual Congress 2020.
The survey was distributed by 20 oncologists from 10 of the countries most affected by COVID-19. Responses were obtained from 109 oncologists representing centers in 18 countries. The responses were recorded between June 17 and July 14, 2020.
The survey consisted of 95 items intended to evaluate the impact of COVID-19 on the organization of oncologic care. Questions encompassed the capacity and service offered at each center, the magnitude of COVID-19–based care interruptions and the reasons for them, the ensuing challenges faced, interventions implemented, and the estimated harms to patients during the pandemic.
The 109 oncologists surveyed had a median of 20 years of oncology experience. A majority of respondents were men (61.5%), and the median age was 48.5 years.
The respondents had worked predominantly (62.4%) at academic hospitals, with 29.6% at community hospitals. Most respondents worked at general hospitals with an oncology unit (66.1%) rather than a specialized separate cancer center (32.1%).
The most common specialty was breast cancer (60.6%), followed by gastrointestinal cancer (10.1%), urogenital cancer (9.2%), and lung cancer (8.3%).
Impact on treatment
The treatment modalities affected by the pandemic – through cancellations or delays in more than 10% of patients – included surgery (in 34% of centers), chemotherapy (22%), radiotherapy (13.7%), checkpoint inhibitor therapy (9.1%), monoclonal antibodies (9%), and oral targeted therapy (3.7%).
Among oncologists treating breast cancer, cancellations/delays in more than 10% of patients were reported for everolimus (18%), CDK4/6 inhibitors (8.9%), and endocrine therapy (2.2%).
Overall, 34.8% of respondents reported increased use of granulocyte colony–stimulating factor, and 6.4% reported increased use of erythropoietin.
On the other hand, 11.1% of respondents reported a decrease in the use of double immunotherapy, and 21.9% reported decreased use of corticosteroids.
Not only can the immunosuppressive effects of steroid use increase infection risks, Dr. Jerusalem noted, fever suppression can lead to a delayed diagnosis of COVID-19.
“To circumvent potential higher infection risks or greater disease severity, we use lower doses of steroids, but this is not based on studies,” he said.
“Previous exposure to steroids or being on steroids at the time of COVID-19 infection is a detrimental factor for complications and mortality,” commented ESMO President Solange Peters, MD, PhD, of Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois in Lausanne, Switzerland.
Dr. Peters noted that the observation was based on lung cancer registry findings. Furthermore, because data from smaller outbreaks of other coronavirus infections suggested worse prognosis and increased mortality, steroid use was already feared in the very early days of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Lastly, earlier cessation of palliative treatment was observed in 32.1% of centers, and 64.2% of respondents agreed that undertreatment because of COVID-19 is a major concern.
Dr. Jerusalem noted that the survey data do not explain the early cessation of palliative treatment. “I suspect that many patients died at home rather than alone in institutions because it was the only way they could die with their families around them.”
Telehealth, meetings, and trials
The survey also revealed rationales for the use of teleconsultation, including follow-up (94.5%), oral therapy (92.7%), immunotherapy (57.8%), and chemotherapy (55%).
Most respondents reported more frequent use of virtual meetings for continuing medical education (94%), oncologic team meetings (92%), and tumor boards (82%).
While about 82% of respondents said they were likely to continue the use of telemedicine, 45% said virtual conferences are not an acceptable alternative to live international conferences such as ESMO, Dr. Jerusalem said.
Finally, nearly three-quarters of respondents (72.5%) said all clinical trial activities are or will soon be activated, or never stopped, at their centers. On the other hand, 27.5% of respondents reported that their centers had major protocol violations or deviations, and 37% of respondents said they expect significant reductions in clinical trial activities this year.
Dr. Jerusalem concluded that COVID-19 is having a major, long-term impact on the organization of patient care, caregivers, continued medical education, and clinical trial activities in oncology.
He cautioned that “the risk of a delayed diagnosis of new cancers and economic consequences of COVID-19 on access to health care and cancer treatments have to be carefully evaluated.”
This research was funded by Fondation Léon Fredericq. Dr. Jerusalem disclosed relationships with Novartis, Roche, Lilly, Pfizer, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, AbbVie, MedImmune, and Merck. Dr. Peters disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, and many other companies.
SOURCE: Jerusalem G et al. ESMO 2020, Abstract LBA76.
An international survey provides new insights into how COVID-19 has affected, and may continue to affect, the field of oncology.
The survey showed that “COVID-19 has had a major impact on the organization of patient care, on the well-being of caregivers, on continued medical education, and on clinical trial activities in oncology,” stated Guy Jerusalem, MD, PhD, of Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Liège (Belgium).
Dr. Jerusalem presented these findings at the European Society for Medical Oncology Virtual Congress 2020.
The survey was distributed by 20 oncologists from 10 of the countries most affected by COVID-19. Responses were obtained from 109 oncologists representing centers in 18 countries. The responses were recorded between June 17 and July 14, 2020.
The survey consisted of 95 items intended to evaluate the impact of COVID-19 on the organization of oncologic care. Questions encompassed the capacity and service offered at each center, the magnitude of COVID-19–based care interruptions and the reasons for them, the ensuing challenges faced, interventions implemented, and the estimated harms to patients during the pandemic.
The 109 oncologists surveyed had a median of 20 years of oncology experience. A majority of respondents were men (61.5%), and the median age was 48.5 years.
The respondents had worked predominantly (62.4%) at academic hospitals, with 29.6% at community hospitals. Most respondents worked at general hospitals with an oncology unit (66.1%) rather than a specialized separate cancer center (32.1%).
The most common specialty was breast cancer (60.6%), followed by gastrointestinal cancer (10.1%), urogenital cancer (9.2%), and lung cancer (8.3%).
Impact on treatment
The treatment modalities affected by the pandemic – through cancellations or delays in more than 10% of patients – included surgery (in 34% of centers), chemotherapy (22%), radiotherapy (13.7%), checkpoint inhibitor therapy (9.1%), monoclonal antibodies (9%), and oral targeted therapy (3.7%).
Among oncologists treating breast cancer, cancellations/delays in more than 10% of patients were reported for everolimus (18%), CDK4/6 inhibitors (8.9%), and endocrine therapy (2.2%).
Overall, 34.8% of respondents reported increased use of granulocyte colony–stimulating factor, and 6.4% reported increased use of erythropoietin.
On the other hand, 11.1% of respondents reported a decrease in the use of double immunotherapy, and 21.9% reported decreased use of corticosteroids.
Not only can the immunosuppressive effects of steroid use increase infection risks, Dr. Jerusalem noted, fever suppression can lead to a delayed diagnosis of COVID-19.
“To circumvent potential higher infection risks or greater disease severity, we use lower doses of steroids, but this is not based on studies,” he said.
“Previous exposure to steroids or being on steroids at the time of COVID-19 infection is a detrimental factor for complications and mortality,” commented ESMO President Solange Peters, MD, PhD, of Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois in Lausanne, Switzerland.
Dr. Peters noted that the observation was based on lung cancer registry findings. Furthermore, because data from smaller outbreaks of other coronavirus infections suggested worse prognosis and increased mortality, steroid use was already feared in the very early days of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Lastly, earlier cessation of palliative treatment was observed in 32.1% of centers, and 64.2% of respondents agreed that undertreatment because of COVID-19 is a major concern.
Dr. Jerusalem noted that the survey data do not explain the early cessation of palliative treatment. “I suspect that many patients died at home rather than alone in institutions because it was the only way they could die with their families around them.”
Telehealth, meetings, and trials
The survey also revealed rationales for the use of teleconsultation, including follow-up (94.5%), oral therapy (92.7%), immunotherapy (57.8%), and chemotherapy (55%).
Most respondents reported more frequent use of virtual meetings for continuing medical education (94%), oncologic team meetings (92%), and tumor boards (82%).
While about 82% of respondents said they were likely to continue the use of telemedicine, 45% said virtual conferences are not an acceptable alternative to live international conferences such as ESMO, Dr. Jerusalem said.
Finally, nearly three-quarters of respondents (72.5%) said all clinical trial activities are or will soon be activated, or never stopped, at their centers. On the other hand, 27.5% of respondents reported that their centers had major protocol violations or deviations, and 37% of respondents said they expect significant reductions in clinical trial activities this year.
Dr. Jerusalem concluded that COVID-19 is having a major, long-term impact on the organization of patient care, caregivers, continued medical education, and clinical trial activities in oncology.
He cautioned that “the risk of a delayed diagnosis of new cancers and economic consequences of COVID-19 on access to health care and cancer treatments have to be carefully evaluated.”
This research was funded by Fondation Léon Fredericq. Dr. Jerusalem disclosed relationships with Novartis, Roche, Lilly, Pfizer, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, AbbVie, MedImmune, and Merck. Dr. Peters disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, and many other companies.
SOURCE: Jerusalem G et al. ESMO 2020, Abstract LBA76.
FROM ESMO 2020
Napabucasin suppressed tumor growth in DLBCL cell lines
The STAT3 pathway is important to the development of many cancers, but so far, no Food and Drug Administration–approved drugs are ready for clinical use. Napabucasin, a novel oral small-molecule inhibitor of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), blocks tumor growth and resists metastasis in a broad spectrum of solid tumors. Napabucasin was now found to be effective in inhibiting diffuse large beta cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in cell lines and in in vitro testing, as reported by Xue Li of the West China Hospital, Sichuan (China) University, and colleagues.
In addition, the effects of napabucasin were found to be synergistic with the use of doxorubicin, a standard DLBCL therapy agent, according to the report, published online in Cancer Letters.
‘Dramatic’ results
The researchers found that 34% (23/69) of DLBCL patients expressed STAT3 in tumor tissues. When they tested napabucasin in a variety of DLBCL cell lines they found that the drug exhibited potent cytotoxicity in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, they found that napabucasin induced intrinsic and extrinsic cell apoptosis, downregulated the expression of STAT3 target genes, including the antiapoptotic protein Mcl-1, and regulated the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, all important indicators of antitumor effectiveness in vitro.
In cells treated with napabucasin and doxorubicin alone and in combination, napabucasin alone significantly suppressed tumor growth, compared with that of the control (P < .01), achieving tumor growth inhibition (TGI) of 78.8%. The combination treatment, “with a dramatic TGI of 98.2%,” was more effective than doxorubicin monotherapy (TGI = 63.2%; P < .05), according to the researchers.
“Our study provided evidence that napabucasin is an attractive candidate drug either as a monotherapy or in combination therapies for DLBCL treatment. Further work studying the clinical efficacy and combination treatment schedule should be performed for personalized therapy,” the researchers concluded.
The work was supported by grants from the Chinese government. The authors stated that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Li X et al. Cancer Lett. 2020 Aug 14. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.07.032.
The STAT3 pathway is important to the development of many cancers, but so far, no Food and Drug Administration–approved drugs are ready for clinical use. Napabucasin, a novel oral small-molecule inhibitor of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), blocks tumor growth and resists metastasis in a broad spectrum of solid tumors. Napabucasin was now found to be effective in inhibiting diffuse large beta cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in cell lines and in in vitro testing, as reported by Xue Li of the West China Hospital, Sichuan (China) University, and colleagues.
In addition, the effects of napabucasin were found to be synergistic with the use of doxorubicin, a standard DLBCL therapy agent, according to the report, published online in Cancer Letters.
‘Dramatic’ results
The researchers found that 34% (23/69) of DLBCL patients expressed STAT3 in tumor tissues. When they tested napabucasin in a variety of DLBCL cell lines they found that the drug exhibited potent cytotoxicity in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, they found that napabucasin induced intrinsic and extrinsic cell apoptosis, downregulated the expression of STAT3 target genes, including the antiapoptotic protein Mcl-1, and regulated the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, all important indicators of antitumor effectiveness in vitro.
In cells treated with napabucasin and doxorubicin alone and in combination, napabucasin alone significantly suppressed tumor growth, compared with that of the control (P < .01), achieving tumor growth inhibition (TGI) of 78.8%. The combination treatment, “with a dramatic TGI of 98.2%,” was more effective than doxorubicin monotherapy (TGI = 63.2%; P < .05), according to the researchers.
“Our study provided evidence that napabucasin is an attractive candidate drug either as a monotherapy or in combination therapies for DLBCL treatment. Further work studying the clinical efficacy and combination treatment schedule should be performed for personalized therapy,” the researchers concluded.
The work was supported by grants from the Chinese government. The authors stated that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Li X et al. Cancer Lett. 2020 Aug 14. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.07.032.
The STAT3 pathway is important to the development of many cancers, but so far, no Food and Drug Administration–approved drugs are ready for clinical use. Napabucasin, a novel oral small-molecule inhibitor of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), blocks tumor growth and resists metastasis in a broad spectrum of solid tumors. Napabucasin was now found to be effective in inhibiting diffuse large beta cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in cell lines and in in vitro testing, as reported by Xue Li of the West China Hospital, Sichuan (China) University, and colleagues.
In addition, the effects of napabucasin were found to be synergistic with the use of doxorubicin, a standard DLBCL therapy agent, according to the report, published online in Cancer Letters.
‘Dramatic’ results
The researchers found that 34% (23/69) of DLBCL patients expressed STAT3 in tumor tissues. When they tested napabucasin in a variety of DLBCL cell lines they found that the drug exhibited potent cytotoxicity in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, they found that napabucasin induced intrinsic and extrinsic cell apoptosis, downregulated the expression of STAT3 target genes, including the antiapoptotic protein Mcl-1, and regulated the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, all important indicators of antitumor effectiveness in vitro.
In cells treated with napabucasin and doxorubicin alone and in combination, napabucasin alone significantly suppressed tumor growth, compared with that of the control (P < .01), achieving tumor growth inhibition (TGI) of 78.8%. The combination treatment, “with a dramatic TGI of 98.2%,” was more effective than doxorubicin monotherapy (TGI = 63.2%; P < .05), according to the researchers.
“Our study provided evidence that napabucasin is an attractive candidate drug either as a monotherapy or in combination therapies for DLBCL treatment. Further work studying the clinical efficacy and combination treatment schedule should be performed for personalized therapy,” the researchers concluded.
The work was supported by grants from the Chinese government. The authors stated that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Li X et al. Cancer Lett. 2020 Aug 14. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.07.032.
FROM CANCER LETTERS
Hepatitis screening now for all patients with cancer on therapy
All patients with cancer who are candidates for systemic anticancer therapy should be screened for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection prior to or at the start of therapy, according to an updated provisional clinical opinion (PCO) from the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
“This is a new approach [that] will actively take system changes ... but it will ultimately be safer for patients – and that is crucial,” commented Jessica P. Hwang, MD, MPH, cochair of the American Society of Clinical Oncology HBV Screening Expert Panel and the first author of the PCO.
Uptake of this universal screening approach would streamline testing protocols and identify more patients at risk for HBV reactivation who should receive prophylactic antiviral therapy, Dr. Hwang said in an interview.
The PCO calls for antiviral prophylaxis during and for at least 12 months after therapy for those with chronic HBV infection who are receiving any systemic anticancer treatment and for those with have had HBV in the past and are receiving any therapies that pose a risk for HBV reactivation.
“Hepatitis B reactivation can cause really terrible outcomes, like organ failure and even death,” Dr. Hwang, who is also a professor at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, commented in an interview.
“This whole [issue of] reactivation and adverse outcomes with anticancer therapies is completely preventable with good planning, good communication, comanagement with specialists, and antiviral therapy and monitoring,” she added.
The updated opinion was published online July 27 in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
It was developed in response to new data that call into question the previously recommended risk-adaptive approach to HBV screening of cancer patients, say the authors.
ASCO PCOs are developed “to provide timely clinical guidance” on the basis of emerging practice-changing information. This is the second update to follow the initial HBV screening PCO, published in 2010. In the absence of clear consensus because of limited data, the original PCO called for a risk-based approach to screening. A 2015 update extended the recommendation for screening to patients starting anti-CD20 therapy or who are to undergo stem cell transplant and to those with risk factors for HBV exposure.
The current update provides “a clinically pragmatic approach to HBV screening and management” that is based on the latest findings, say the authors. These include findings from a multicenter prospective cohort study of more than 3000 patients. In that study, 21% of patients with chronic HBV had no known risk factors for the infection. In another large prospective observational cohort study, led by Dr. Hwang, which included more than 2100 patients with cancer, 90% had one or more significant risk factors for HBV infection, making selective screening “inefficient and impractical,” she said.
“The results of these two studies suggest that a universal screening approach, its potential harms (e.g., patient and clinician anxiety about management, financial burden associated with antiviral therapy) notwithstanding, is the most efficient, clinically pragmatic approach to HBV screening in persons anticipating systemic anticancer treatment,” the authors comment.
The screening recommended in the PCO requires three tests: hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), core antibody total immunoglobulin or IgG, and antibody to HBsAg tests.
Anticancer therapy should not be delayed pending the results, they write.
Planning for monitoring and long-term prophylaxis for chronic HBV infection should involve a clinician experienced in HBV management, the authors write. Management of those with past infection should be individualized. Alternatively, patients with past infection can be carefully monitored rather than given prophylactic treatment, as long as frequent and consistent follow-up is possible to allow for rapid initiation of antiviral therapy in the event of reactivation, they say.
Hormonal therapy without systemic anticancer therapy is not likely to lead to HBV reactivation in patients with chronic or past infection; antiviral therapy and management of these patients should follow relevant national HBV guidelines, they note.
Challenges in implementing universal HBV screening
The expert panel acknowledges the challenges associated with implementation of universal HBV screening as recommended in their report and notes that electronic health record–based approaches that use alerts to prompt screening have demonstrated success. In one study of high-risk primary care patients, an EHR alert system significantly increased testing rates (odds ratio, 2.64 in comparison with a control group without alerts), and another study that used a simple “sticky-note” alert system to promote referral of HBsAg patients to hepatologists increased referrals from 28% to 73%.
In a cancer population, a “comprehensive set of multimodal interventions,” including pharmacy staff checks for screening prior to anti-CD20 therapy administration and electronic medication order reviews to assess for appropriate testing and treatment before anti-CD20 therapy, increased testing rates to greater than 90% and antiviral prophylaxis rates to more than 80%.
A study of 965 patients in Taiwan showed that a computer-assisted reminder system that prompted for testing prior to ordering anticancer therapy increased screening from 8% to 86% but was less effective for improving the rates of antiviral prophylaxis for those who tested positive for HBV, particularly among physicians treating patients with nonhematologic malignancies.
“Future studies will be needed to make universal HBV screening and linkage to care efficient and systematic, likely based in EHR systems,” the panel says. The authors note that “[o]ngoing studies of HBV tests such as ultrasensitive HBsAg, HBV RNA, and hepatitis B core antigen are being studied and may be useful in predicting risk of HBV reactivation.”
The panel also identified a research gap related to HBV reactivation risks “for the growing list of agents that deplete or modulate B cells.” It notes a need for additional research on the cost-effectiveness of HBV screening. The results of prior cost analyses have been inconsistent and vary with respect to the population studied. For example, universal screening and antiviral prophylaxis approaches have been shown to be cost-effective for patients with hematologic malignancies and high HBV reactivation risk but are less so for patients with solid tumors and lower reactivation risk, they explain.
Dr. Hwang said that not one of the more than 2100 patients in her HBV screening cohort study encountered problems with receiving insurance payment for their HBV screening.
“That’s a really strong statement that insurance payers are accepting of this kind of preventative service,” she said.
Expert panel cochair Andrew Artz, MD, commented that there is now greater acceptance of the need for HBV screening across medical specialties.
“There’s growing consensus among hepatologists, infectious disease specialists, oncologists, and HBV specialists that we need to do a better job of finding patients with hepatitis B [who are] about to receive immunocompromising treatment,” Dr. Artz said in an interview.
Dr. Artz is director of the Program for Aging and Blood Cancers and deputy director of the Center for Cancer and Aging at City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center, Duarte, California.
He suggested that the growing acceptance is due in part to the increasing number of anticancer therapies available and the resulting increase in the likelihood of patients receiving therapies that could cause reactivation.
More therapies – and more lines of therapy – could mean greater risk, he explained. He said that testing is easy and that universal screening is the simplest approach to determining who needs it. “There’s no question we will have to change practice,” Dr. Artz said in an interview. “But this is easier than the previous approach that essentially wasn’t being followed because it was too difficult to follow and patients were being missed.”
Most clinicians will appreciate having an approach that’s easier to follow, Dr. Artz predicted.
If there’s a challenge it will be in developing partnerships with HBV specialists, particularly in rural areas. In areas where there is a paucity of subspecialists, oncologists will have to “take some ownership of the issue,” as they often do in such settings, he said.
However, with support from pharmacists, administrators, and others in embracing this guidance, implementation can take place at a systems level rather than an individual clinician level, he added.
The recommendations in this updated PCO were all rated as “strong,” with the exception of the recommendation on hormonal therapy in the absence of systemic anticancer therapy, which was rated as “moderate.” All were based on “informal consensus,” with the exception of the key recommendation for universal HBV screening – use of three specific tests – which was “evidence based.”
The expert panel agreed that the benefits outweigh the harms for each recommendation in the update.
Dr. Hwang received research funding to her institution from Gilead Sciences and Merck Sharp & Dohme. She also has a relationship with the Asian Health Foundation. Dr. Artz received research funding from Miltenyi Biotec. All expert panel members’ disclosures are available in the PCO update.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
All patients with cancer who are candidates for systemic anticancer therapy should be screened for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection prior to or at the start of therapy, according to an updated provisional clinical opinion (PCO) from the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
“This is a new approach [that] will actively take system changes ... but it will ultimately be safer for patients – and that is crucial,” commented Jessica P. Hwang, MD, MPH, cochair of the American Society of Clinical Oncology HBV Screening Expert Panel and the first author of the PCO.
Uptake of this universal screening approach would streamline testing protocols and identify more patients at risk for HBV reactivation who should receive prophylactic antiviral therapy, Dr. Hwang said in an interview.
The PCO calls for antiviral prophylaxis during and for at least 12 months after therapy for those with chronic HBV infection who are receiving any systemic anticancer treatment and for those with have had HBV in the past and are receiving any therapies that pose a risk for HBV reactivation.
“Hepatitis B reactivation can cause really terrible outcomes, like organ failure and even death,” Dr. Hwang, who is also a professor at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, commented in an interview.
“This whole [issue of] reactivation and adverse outcomes with anticancer therapies is completely preventable with good planning, good communication, comanagement with specialists, and antiviral therapy and monitoring,” she added.
The updated opinion was published online July 27 in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
It was developed in response to new data that call into question the previously recommended risk-adaptive approach to HBV screening of cancer patients, say the authors.
ASCO PCOs are developed “to provide timely clinical guidance” on the basis of emerging practice-changing information. This is the second update to follow the initial HBV screening PCO, published in 2010. In the absence of clear consensus because of limited data, the original PCO called for a risk-based approach to screening. A 2015 update extended the recommendation for screening to patients starting anti-CD20 therapy or who are to undergo stem cell transplant and to those with risk factors for HBV exposure.
The current update provides “a clinically pragmatic approach to HBV screening and management” that is based on the latest findings, say the authors. These include findings from a multicenter prospective cohort study of more than 3000 patients. In that study, 21% of patients with chronic HBV had no known risk factors for the infection. In another large prospective observational cohort study, led by Dr. Hwang, which included more than 2100 patients with cancer, 90% had one or more significant risk factors for HBV infection, making selective screening “inefficient and impractical,” she said.
“The results of these two studies suggest that a universal screening approach, its potential harms (e.g., patient and clinician anxiety about management, financial burden associated with antiviral therapy) notwithstanding, is the most efficient, clinically pragmatic approach to HBV screening in persons anticipating systemic anticancer treatment,” the authors comment.
The screening recommended in the PCO requires three tests: hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), core antibody total immunoglobulin or IgG, and antibody to HBsAg tests.
Anticancer therapy should not be delayed pending the results, they write.
Planning for monitoring and long-term prophylaxis for chronic HBV infection should involve a clinician experienced in HBV management, the authors write. Management of those with past infection should be individualized. Alternatively, patients with past infection can be carefully monitored rather than given prophylactic treatment, as long as frequent and consistent follow-up is possible to allow for rapid initiation of antiviral therapy in the event of reactivation, they say.
Hormonal therapy without systemic anticancer therapy is not likely to lead to HBV reactivation in patients with chronic or past infection; antiviral therapy and management of these patients should follow relevant national HBV guidelines, they note.
Challenges in implementing universal HBV screening
The expert panel acknowledges the challenges associated with implementation of universal HBV screening as recommended in their report and notes that electronic health record–based approaches that use alerts to prompt screening have demonstrated success. In one study of high-risk primary care patients, an EHR alert system significantly increased testing rates (odds ratio, 2.64 in comparison with a control group without alerts), and another study that used a simple “sticky-note” alert system to promote referral of HBsAg patients to hepatologists increased referrals from 28% to 73%.
In a cancer population, a “comprehensive set of multimodal interventions,” including pharmacy staff checks for screening prior to anti-CD20 therapy administration and electronic medication order reviews to assess for appropriate testing and treatment before anti-CD20 therapy, increased testing rates to greater than 90% and antiviral prophylaxis rates to more than 80%.
A study of 965 patients in Taiwan showed that a computer-assisted reminder system that prompted for testing prior to ordering anticancer therapy increased screening from 8% to 86% but was less effective for improving the rates of antiviral prophylaxis for those who tested positive for HBV, particularly among physicians treating patients with nonhematologic malignancies.
“Future studies will be needed to make universal HBV screening and linkage to care efficient and systematic, likely based in EHR systems,” the panel says. The authors note that “[o]ngoing studies of HBV tests such as ultrasensitive HBsAg, HBV RNA, and hepatitis B core antigen are being studied and may be useful in predicting risk of HBV reactivation.”
The panel also identified a research gap related to HBV reactivation risks “for the growing list of agents that deplete or modulate B cells.” It notes a need for additional research on the cost-effectiveness of HBV screening. The results of prior cost analyses have been inconsistent and vary with respect to the population studied. For example, universal screening and antiviral prophylaxis approaches have been shown to be cost-effective for patients with hematologic malignancies and high HBV reactivation risk but are less so for patients with solid tumors and lower reactivation risk, they explain.
Dr. Hwang said that not one of the more than 2100 patients in her HBV screening cohort study encountered problems with receiving insurance payment for their HBV screening.
“That’s a really strong statement that insurance payers are accepting of this kind of preventative service,” she said.
Expert panel cochair Andrew Artz, MD, commented that there is now greater acceptance of the need for HBV screening across medical specialties.
“There’s growing consensus among hepatologists, infectious disease specialists, oncologists, and HBV specialists that we need to do a better job of finding patients with hepatitis B [who are] about to receive immunocompromising treatment,” Dr. Artz said in an interview.
Dr. Artz is director of the Program for Aging and Blood Cancers and deputy director of the Center for Cancer and Aging at City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center, Duarte, California.
He suggested that the growing acceptance is due in part to the increasing number of anticancer therapies available and the resulting increase in the likelihood of patients receiving therapies that could cause reactivation.
More therapies – and more lines of therapy – could mean greater risk, he explained. He said that testing is easy and that universal screening is the simplest approach to determining who needs it. “There’s no question we will have to change practice,” Dr. Artz said in an interview. “But this is easier than the previous approach that essentially wasn’t being followed because it was too difficult to follow and patients were being missed.”
Most clinicians will appreciate having an approach that’s easier to follow, Dr. Artz predicted.
If there’s a challenge it will be in developing partnerships with HBV specialists, particularly in rural areas. In areas where there is a paucity of subspecialists, oncologists will have to “take some ownership of the issue,” as they often do in such settings, he said.
However, with support from pharmacists, administrators, and others in embracing this guidance, implementation can take place at a systems level rather than an individual clinician level, he added.
The recommendations in this updated PCO were all rated as “strong,” with the exception of the recommendation on hormonal therapy in the absence of systemic anticancer therapy, which was rated as “moderate.” All were based on “informal consensus,” with the exception of the key recommendation for universal HBV screening – use of three specific tests – which was “evidence based.”
The expert panel agreed that the benefits outweigh the harms for each recommendation in the update.
Dr. Hwang received research funding to her institution from Gilead Sciences and Merck Sharp & Dohme. She also has a relationship with the Asian Health Foundation. Dr. Artz received research funding from Miltenyi Biotec. All expert panel members’ disclosures are available in the PCO update.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
All patients with cancer who are candidates for systemic anticancer therapy should be screened for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection prior to or at the start of therapy, according to an updated provisional clinical opinion (PCO) from the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
“This is a new approach [that] will actively take system changes ... but it will ultimately be safer for patients – and that is crucial,” commented Jessica P. Hwang, MD, MPH, cochair of the American Society of Clinical Oncology HBV Screening Expert Panel and the first author of the PCO.
Uptake of this universal screening approach would streamline testing protocols and identify more patients at risk for HBV reactivation who should receive prophylactic antiviral therapy, Dr. Hwang said in an interview.
The PCO calls for antiviral prophylaxis during and for at least 12 months after therapy for those with chronic HBV infection who are receiving any systemic anticancer treatment and for those with have had HBV in the past and are receiving any therapies that pose a risk for HBV reactivation.
“Hepatitis B reactivation can cause really terrible outcomes, like organ failure and even death,” Dr. Hwang, who is also a professor at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, commented in an interview.
“This whole [issue of] reactivation and adverse outcomes with anticancer therapies is completely preventable with good planning, good communication, comanagement with specialists, and antiviral therapy and monitoring,” she added.
The updated opinion was published online July 27 in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
It was developed in response to new data that call into question the previously recommended risk-adaptive approach to HBV screening of cancer patients, say the authors.
ASCO PCOs are developed “to provide timely clinical guidance” on the basis of emerging practice-changing information. This is the second update to follow the initial HBV screening PCO, published in 2010. In the absence of clear consensus because of limited data, the original PCO called for a risk-based approach to screening. A 2015 update extended the recommendation for screening to patients starting anti-CD20 therapy or who are to undergo stem cell transplant and to those with risk factors for HBV exposure.
The current update provides “a clinically pragmatic approach to HBV screening and management” that is based on the latest findings, say the authors. These include findings from a multicenter prospective cohort study of more than 3000 patients. In that study, 21% of patients with chronic HBV had no known risk factors for the infection. In another large prospective observational cohort study, led by Dr. Hwang, which included more than 2100 patients with cancer, 90% had one or more significant risk factors for HBV infection, making selective screening “inefficient and impractical,” she said.
“The results of these two studies suggest that a universal screening approach, its potential harms (e.g., patient and clinician anxiety about management, financial burden associated with antiviral therapy) notwithstanding, is the most efficient, clinically pragmatic approach to HBV screening in persons anticipating systemic anticancer treatment,” the authors comment.
The screening recommended in the PCO requires three tests: hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), core antibody total immunoglobulin or IgG, and antibody to HBsAg tests.
Anticancer therapy should not be delayed pending the results, they write.
Planning for monitoring and long-term prophylaxis for chronic HBV infection should involve a clinician experienced in HBV management, the authors write. Management of those with past infection should be individualized. Alternatively, patients with past infection can be carefully monitored rather than given prophylactic treatment, as long as frequent and consistent follow-up is possible to allow for rapid initiation of antiviral therapy in the event of reactivation, they say.
Hormonal therapy without systemic anticancer therapy is not likely to lead to HBV reactivation in patients with chronic or past infection; antiviral therapy and management of these patients should follow relevant national HBV guidelines, they note.
Challenges in implementing universal HBV screening
The expert panel acknowledges the challenges associated with implementation of universal HBV screening as recommended in their report and notes that electronic health record–based approaches that use alerts to prompt screening have demonstrated success. In one study of high-risk primary care patients, an EHR alert system significantly increased testing rates (odds ratio, 2.64 in comparison with a control group without alerts), and another study that used a simple “sticky-note” alert system to promote referral of HBsAg patients to hepatologists increased referrals from 28% to 73%.
In a cancer population, a “comprehensive set of multimodal interventions,” including pharmacy staff checks for screening prior to anti-CD20 therapy administration and electronic medication order reviews to assess for appropriate testing and treatment before anti-CD20 therapy, increased testing rates to greater than 90% and antiviral prophylaxis rates to more than 80%.
A study of 965 patients in Taiwan showed that a computer-assisted reminder system that prompted for testing prior to ordering anticancer therapy increased screening from 8% to 86% but was less effective for improving the rates of antiviral prophylaxis for those who tested positive for HBV, particularly among physicians treating patients with nonhematologic malignancies.
“Future studies will be needed to make universal HBV screening and linkage to care efficient and systematic, likely based in EHR systems,” the panel says. The authors note that “[o]ngoing studies of HBV tests such as ultrasensitive HBsAg, HBV RNA, and hepatitis B core antigen are being studied and may be useful in predicting risk of HBV reactivation.”
The panel also identified a research gap related to HBV reactivation risks “for the growing list of agents that deplete or modulate B cells.” It notes a need for additional research on the cost-effectiveness of HBV screening. The results of prior cost analyses have been inconsistent and vary with respect to the population studied. For example, universal screening and antiviral prophylaxis approaches have been shown to be cost-effective for patients with hematologic malignancies and high HBV reactivation risk but are less so for patients with solid tumors and lower reactivation risk, they explain.
Dr. Hwang said that not one of the more than 2100 patients in her HBV screening cohort study encountered problems with receiving insurance payment for their HBV screening.
“That’s a really strong statement that insurance payers are accepting of this kind of preventative service,” she said.
Expert panel cochair Andrew Artz, MD, commented that there is now greater acceptance of the need for HBV screening across medical specialties.
“There’s growing consensus among hepatologists, infectious disease specialists, oncologists, and HBV specialists that we need to do a better job of finding patients with hepatitis B [who are] about to receive immunocompromising treatment,” Dr. Artz said in an interview.
Dr. Artz is director of the Program for Aging and Blood Cancers and deputy director of the Center for Cancer and Aging at City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center, Duarte, California.
He suggested that the growing acceptance is due in part to the increasing number of anticancer therapies available and the resulting increase in the likelihood of patients receiving therapies that could cause reactivation.
More therapies – and more lines of therapy – could mean greater risk, he explained. He said that testing is easy and that universal screening is the simplest approach to determining who needs it. “There’s no question we will have to change practice,” Dr. Artz said in an interview. “But this is easier than the previous approach that essentially wasn’t being followed because it was too difficult to follow and patients were being missed.”
Most clinicians will appreciate having an approach that’s easier to follow, Dr. Artz predicted.
If there’s a challenge it will be in developing partnerships with HBV specialists, particularly in rural areas. In areas where there is a paucity of subspecialists, oncologists will have to “take some ownership of the issue,” as they often do in such settings, he said.
However, with support from pharmacists, administrators, and others in embracing this guidance, implementation can take place at a systems level rather than an individual clinician level, he added.
The recommendations in this updated PCO were all rated as “strong,” with the exception of the recommendation on hormonal therapy in the absence of systemic anticancer therapy, which was rated as “moderate.” All were based on “informal consensus,” with the exception of the key recommendation for universal HBV screening – use of three specific tests – which was “evidence based.”
The expert panel agreed that the benefits outweigh the harms for each recommendation in the update.
Dr. Hwang received research funding to her institution from Gilead Sciences and Merck Sharp & Dohme. She also has a relationship with the Asian Health Foundation. Dr. Artz received research funding from Miltenyi Biotec. All expert panel members’ disclosures are available in the PCO update.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves new drug for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
A novel drug, tafasitamab-cxix (Monjuvi, MorphoSys US), has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
The product is a humanized Fc-modified cytolytic CD19 targeting monoclonal antibody. It mediates B-cell lysis through apoptosis and immune effector mechanism, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP).
It is indicated for use in combination with lenalidomide for adult patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL that is not otherwise specified, including DLBCL arising from low-grade lymphoma, and in patients who are not eligible for autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT).
Tafasitamab-cxix in combination with lenalidomide is the first treatment that approved by the FDA for second-line use for patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL, notes the manufacturer.
The approval “brings a new treatment option to patients in dire need across the United States,” said Gilles Salles, MD, chair of the clinical hematology department at the University of Lyon (France), and lead investigator of the L-MIND study.
The FDA granted an accelerated approval on the basis of overall response rate from an open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial in 81 patients (known as L-MIND). Further trials are underway to confirm clinical benefit.
The L-MIND trial was conducted in patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL who had received at least one, but no more than three, prior lines of therapy, including an anti-CD20 targeting therapy (e.g., rituximab), who were not eligible for high-dose chemotherapy or who refused subsequent ASCT.
All patients received tafasitamab-cxix 12 mg/kg intravenously with lenalidomide (25 mg orally on days 1-21 of each 28-day cycle) for a maximum of 12 cycles, followed by tafasitamab-cxix as monotherapy.
The best ORR (defined as complete and partial responders) in 71 patients with a diagnosis of DLBCL confirmed by central pathology was 55%, with complete responses in 37% and partial responses in 18% of patients. The median response duration was 21.7 months (range, 0-24).
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) were neutropenia, fatigue, anemia, diarrhea, thrombocytopenia, cough, fever, peripheral edema, respiratory tract infection, and decreased appetite.
Precautions and warnings include infusion-related reactions (6%), serious or severe myelosuppression (including neutropenia [50%], thrombocytopenia [18%], and anemia [7%]), infections (73%), and embryo-fetal toxicity.
DLBCL is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in adults worldwide, characterized by rapidly growing masses of malignant B-cells in the lymph nodes, spleen, liver, bone marrow or other organs. It is an aggressive disease with about one in three patients not responding to initial therapy or relapsing thereafter, notes the manufacturer. In the United States each year approximately 10,000 patients who are not eligible for ASCT are diagnosed with relapsed or refractory DLBCL.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A novel drug, tafasitamab-cxix (Monjuvi, MorphoSys US), has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
The product is a humanized Fc-modified cytolytic CD19 targeting monoclonal antibody. It mediates B-cell lysis through apoptosis and immune effector mechanism, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP).
It is indicated for use in combination with lenalidomide for adult patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL that is not otherwise specified, including DLBCL arising from low-grade lymphoma, and in patients who are not eligible for autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT).
Tafasitamab-cxix in combination with lenalidomide is the first treatment that approved by the FDA for second-line use for patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL, notes the manufacturer.
The approval “brings a new treatment option to patients in dire need across the United States,” said Gilles Salles, MD, chair of the clinical hematology department at the University of Lyon (France), and lead investigator of the L-MIND study.
The FDA granted an accelerated approval on the basis of overall response rate from an open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial in 81 patients (known as L-MIND). Further trials are underway to confirm clinical benefit.
The L-MIND trial was conducted in patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL who had received at least one, but no more than three, prior lines of therapy, including an anti-CD20 targeting therapy (e.g., rituximab), who were not eligible for high-dose chemotherapy or who refused subsequent ASCT.
All patients received tafasitamab-cxix 12 mg/kg intravenously with lenalidomide (25 mg orally on days 1-21 of each 28-day cycle) for a maximum of 12 cycles, followed by tafasitamab-cxix as monotherapy.
The best ORR (defined as complete and partial responders) in 71 patients with a diagnosis of DLBCL confirmed by central pathology was 55%, with complete responses in 37% and partial responses in 18% of patients. The median response duration was 21.7 months (range, 0-24).
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) were neutropenia, fatigue, anemia, diarrhea, thrombocytopenia, cough, fever, peripheral edema, respiratory tract infection, and decreased appetite.
Precautions and warnings include infusion-related reactions (6%), serious or severe myelosuppression (including neutropenia [50%], thrombocytopenia [18%], and anemia [7%]), infections (73%), and embryo-fetal toxicity.
DLBCL is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in adults worldwide, characterized by rapidly growing masses of malignant B-cells in the lymph nodes, spleen, liver, bone marrow or other organs. It is an aggressive disease with about one in three patients not responding to initial therapy or relapsing thereafter, notes the manufacturer. In the United States each year approximately 10,000 patients who are not eligible for ASCT are diagnosed with relapsed or refractory DLBCL.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A novel drug, tafasitamab-cxix (Monjuvi, MorphoSys US), has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
The product is a humanized Fc-modified cytolytic CD19 targeting monoclonal antibody. It mediates B-cell lysis through apoptosis and immune effector mechanism, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP).
It is indicated for use in combination with lenalidomide for adult patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL that is not otherwise specified, including DLBCL arising from low-grade lymphoma, and in patients who are not eligible for autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT).
Tafasitamab-cxix in combination with lenalidomide is the first treatment that approved by the FDA for second-line use for patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL, notes the manufacturer.
The approval “brings a new treatment option to patients in dire need across the United States,” said Gilles Salles, MD, chair of the clinical hematology department at the University of Lyon (France), and lead investigator of the L-MIND study.
The FDA granted an accelerated approval on the basis of overall response rate from an open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial in 81 patients (known as L-MIND). Further trials are underway to confirm clinical benefit.
The L-MIND trial was conducted in patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL who had received at least one, but no more than three, prior lines of therapy, including an anti-CD20 targeting therapy (e.g., rituximab), who were not eligible for high-dose chemotherapy or who refused subsequent ASCT.
All patients received tafasitamab-cxix 12 mg/kg intravenously with lenalidomide (25 mg orally on days 1-21 of each 28-day cycle) for a maximum of 12 cycles, followed by tafasitamab-cxix as monotherapy.
The best ORR (defined as complete and partial responders) in 71 patients with a diagnosis of DLBCL confirmed by central pathology was 55%, with complete responses in 37% and partial responses in 18% of patients. The median response duration was 21.7 months (range, 0-24).
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) were neutropenia, fatigue, anemia, diarrhea, thrombocytopenia, cough, fever, peripheral edema, respiratory tract infection, and decreased appetite.
Precautions and warnings include infusion-related reactions (6%), serious or severe myelosuppression (including neutropenia [50%], thrombocytopenia [18%], and anemia [7%]), infections (73%), and embryo-fetal toxicity.
DLBCL is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in adults worldwide, characterized by rapidly growing masses of malignant B-cells in the lymph nodes, spleen, liver, bone marrow or other organs. It is an aggressive disease with about one in three patients not responding to initial therapy or relapsing thereafter, notes the manufacturer. In the United States each year approximately 10,000 patients who are not eligible for ASCT are diagnosed with relapsed or refractory DLBCL.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HSCT or systemic treatment should be offered to HIV+ patients with lymphoma
Systemic or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) treatment of HIV-positive lymphoma patients resulted in improved outcomes, compared with nonsystemic treatment, according to the results of a large database study.
Researchers Thejus T. Jayakrishnan, MD, and colleagues examined patients with lymphoma diagnosed between 2004 and 2015 from the National Cancer Database. Patients were categorized as HIV positive and HIV negative. First-line lymphoma treatment was categorized as no systemic therapy reported, systemic therapy, or HSCT. Multivariate analysis was used to predict treatment and survival, according to Dr. Jayakrishnan, a resident at the department of internal medicine, Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh.
A total of 11,160 HIV-positive vs. 349,607 HIV-negative patients were analyzed, including mostly men, with a comorbidity index of 0. The most common lymphoma among HIV-positive patients was diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, according to the report in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
Among HIV-positive patients, 792 had no systemic treatment, 10,328 underwent systemic treatment, and 40 received HSCT treatment. The results showed that treatment of HIV-positive lymphoma patients resulted in improved outcomes: 3-year overall survival was 43.6% for nonsystemic treatment versus 58.1% for systemic (hazard ratio, 0.56; 95% confidence interval, 0.52-0.61; P < .005) versus 62.2% for HSCT therapy (HR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.14-1.3; P = .08), the lack of significance in the latter could be caused in part by the small number of patients treated. Outcomes for both treatment regimens were lower, however, compared with non-HIV patients.
“The present study demonstrates improvement in survival outcomes for HIV-positive patients with lymphoma with treatments when feasible, but these outcomes are poor when compared to HIV-negative patients,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jayakrishnan TT et al. Clin Lymph Myeloma Leuk. 2020 Feb 20. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2020.06.003.
Systemic or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) treatment of HIV-positive lymphoma patients resulted in improved outcomes, compared with nonsystemic treatment, according to the results of a large database study.
Researchers Thejus T. Jayakrishnan, MD, and colleagues examined patients with lymphoma diagnosed between 2004 and 2015 from the National Cancer Database. Patients were categorized as HIV positive and HIV negative. First-line lymphoma treatment was categorized as no systemic therapy reported, systemic therapy, or HSCT. Multivariate analysis was used to predict treatment and survival, according to Dr. Jayakrishnan, a resident at the department of internal medicine, Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh.
A total of 11,160 HIV-positive vs. 349,607 HIV-negative patients were analyzed, including mostly men, with a comorbidity index of 0. The most common lymphoma among HIV-positive patients was diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, according to the report in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
Among HIV-positive patients, 792 had no systemic treatment, 10,328 underwent systemic treatment, and 40 received HSCT treatment. The results showed that treatment of HIV-positive lymphoma patients resulted in improved outcomes: 3-year overall survival was 43.6% for nonsystemic treatment versus 58.1% for systemic (hazard ratio, 0.56; 95% confidence interval, 0.52-0.61; P < .005) versus 62.2% for HSCT therapy (HR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.14-1.3; P = .08), the lack of significance in the latter could be caused in part by the small number of patients treated. Outcomes for both treatment regimens were lower, however, compared with non-HIV patients.
“The present study demonstrates improvement in survival outcomes for HIV-positive patients with lymphoma with treatments when feasible, but these outcomes are poor when compared to HIV-negative patients,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jayakrishnan TT et al. Clin Lymph Myeloma Leuk. 2020 Feb 20. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2020.06.003.
Systemic or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) treatment of HIV-positive lymphoma patients resulted in improved outcomes, compared with nonsystemic treatment, according to the results of a large database study.
Researchers Thejus T. Jayakrishnan, MD, and colleagues examined patients with lymphoma diagnosed between 2004 and 2015 from the National Cancer Database. Patients were categorized as HIV positive and HIV negative. First-line lymphoma treatment was categorized as no systemic therapy reported, systemic therapy, or HSCT. Multivariate analysis was used to predict treatment and survival, according to Dr. Jayakrishnan, a resident at the department of internal medicine, Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh.
A total of 11,160 HIV-positive vs. 349,607 HIV-negative patients were analyzed, including mostly men, with a comorbidity index of 0. The most common lymphoma among HIV-positive patients was diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, according to the report in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
Among HIV-positive patients, 792 had no systemic treatment, 10,328 underwent systemic treatment, and 40 received HSCT treatment. The results showed that treatment of HIV-positive lymphoma patients resulted in improved outcomes: 3-year overall survival was 43.6% for nonsystemic treatment versus 58.1% for systemic (hazard ratio, 0.56; 95% confidence interval, 0.52-0.61; P < .005) versus 62.2% for HSCT therapy (HR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.14-1.3; P = .08), the lack of significance in the latter could be caused in part by the small number of patients treated. Outcomes for both treatment regimens were lower, however, compared with non-HIV patients.
“The present study demonstrates improvement in survival outcomes for HIV-positive patients with lymphoma with treatments when feasible, but these outcomes are poor when compared to HIV-negative patients,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jayakrishnan TT et al. Clin Lymph Myeloma Leuk. 2020 Feb 20. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2020.06.003.
FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA & LEUKEMIA
FDA approves selinexor for relapsed/refractory DLBCL
The Food and Drug Administration has granted accelerated approval of selinexor, a nuclear transport inhibitor, for the treatment of relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Selinexor (marketed as XPOVIO by Karyopharm Therapeutics) is intended for adult patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, not otherwise specified, including DLBCL arising from follicular lymphoma, after at least two lines of systemic therapy, according to the FDA’s announcement.
The FDA granted selinexor accelerated approval for this indication based on the response rate seen in the SADAL trial. Continued approval for this indication “may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials,” according to the FDA.
The SADAL trial (NCT02227251) was a phase 2, single-arm, open-label study of patients with DLBCL who had previously received two to five systemic regimens. The patients received selinexor at 60 mg orally on days 1 and 3 of each week.
Results in 134 patients showed an overall response rate of 29% (95% confidence interval: 22-38), with complete responses in 13% of patients. Of 39 patients who achieved a partial or complete response, 38% had a response duration of at least 6 months, and 15% had a response duration of at least 12 months, according to the FDA announcement.
The most common adverse reactions in this trial were fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, appetite decrease, weight decrease, constipation, vomiting, and pyrexia. Grade 3-4 laboratory abnormalities occurred in 15% or more of the patients, and comprised thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia, neutropenia, anemia, and hyponatremia.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 46% of patients, most often from infection. Gastrointestinal toxicity occurred in 80% of patients, and any-grade hyponatremia occurred in 61%. Central neurological adverse reactions occurred in 25% of patients, including dizziness and mental status changes, according to the announcement.
Warnings and precautions for adverse events – including thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, gastrointestinal toxicity, hyponatremia, serious infection, neurological toxicity, and embryo-fetal toxicity – are provided in the prescribing information.
Selinexor acts through the inhibition of exportin-1 and leads to an accumulation of tumor suppressor proteins, a reduction in oncoproteins, and apoptosis of cancer cells. The drug was previously approved in 2019 for the treatment of relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.
The SADAL trial was sponsored by Karyopharm Therapeutics.
SOURCE: U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 2020. Approval announcement.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted accelerated approval of selinexor, a nuclear transport inhibitor, for the treatment of relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Selinexor (marketed as XPOVIO by Karyopharm Therapeutics) is intended for adult patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, not otherwise specified, including DLBCL arising from follicular lymphoma, after at least two lines of systemic therapy, according to the FDA’s announcement.
The FDA granted selinexor accelerated approval for this indication based on the response rate seen in the SADAL trial. Continued approval for this indication “may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials,” according to the FDA.
The SADAL trial (NCT02227251) was a phase 2, single-arm, open-label study of patients with DLBCL who had previously received two to five systemic regimens. The patients received selinexor at 60 mg orally on days 1 and 3 of each week.
Results in 134 patients showed an overall response rate of 29% (95% confidence interval: 22-38), with complete responses in 13% of patients. Of 39 patients who achieved a partial or complete response, 38% had a response duration of at least 6 months, and 15% had a response duration of at least 12 months, according to the FDA announcement.
The most common adverse reactions in this trial were fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, appetite decrease, weight decrease, constipation, vomiting, and pyrexia. Grade 3-4 laboratory abnormalities occurred in 15% or more of the patients, and comprised thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia, neutropenia, anemia, and hyponatremia.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 46% of patients, most often from infection. Gastrointestinal toxicity occurred in 80% of patients, and any-grade hyponatremia occurred in 61%. Central neurological adverse reactions occurred in 25% of patients, including dizziness and mental status changes, according to the announcement.
Warnings and precautions for adverse events – including thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, gastrointestinal toxicity, hyponatremia, serious infection, neurological toxicity, and embryo-fetal toxicity – are provided in the prescribing information.
Selinexor acts through the inhibition of exportin-1 and leads to an accumulation of tumor suppressor proteins, a reduction in oncoproteins, and apoptosis of cancer cells. The drug was previously approved in 2019 for the treatment of relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.
The SADAL trial was sponsored by Karyopharm Therapeutics.
SOURCE: U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 2020. Approval announcement.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted accelerated approval of selinexor, a nuclear transport inhibitor, for the treatment of relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Selinexor (marketed as XPOVIO by Karyopharm Therapeutics) is intended for adult patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, not otherwise specified, including DLBCL arising from follicular lymphoma, after at least two lines of systemic therapy, according to the FDA’s announcement.
The FDA granted selinexor accelerated approval for this indication based on the response rate seen in the SADAL trial. Continued approval for this indication “may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials,” according to the FDA.
The SADAL trial (NCT02227251) was a phase 2, single-arm, open-label study of patients with DLBCL who had previously received two to five systemic regimens. The patients received selinexor at 60 mg orally on days 1 and 3 of each week.
Results in 134 patients showed an overall response rate of 29% (95% confidence interval: 22-38), with complete responses in 13% of patients. Of 39 patients who achieved a partial or complete response, 38% had a response duration of at least 6 months, and 15% had a response duration of at least 12 months, according to the FDA announcement.
The most common adverse reactions in this trial were fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, appetite decrease, weight decrease, constipation, vomiting, and pyrexia. Grade 3-4 laboratory abnormalities occurred in 15% or more of the patients, and comprised thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia, neutropenia, anemia, and hyponatremia.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 46% of patients, most often from infection. Gastrointestinal toxicity occurred in 80% of patients, and any-grade hyponatremia occurred in 61%. Central neurological adverse reactions occurred in 25% of patients, including dizziness and mental status changes, according to the announcement.
Warnings and precautions for adverse events – including thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, gastrointestinal toxicity, hyponatremia, serious infection, neurological toxicity, and embryo-fetal toxicity – are provided in the prescribing information.
Selinexor acts through the inhibition of exportin-1 and leads to an accumulation of tumor suppressor proteins, a reduction in oncoproteins, and apoptosis of cancer cells. The drug was previously approved in 2019 for the treatment of relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.
The SADAL trial was sponsored by Karyopharm Therapeutics.
SOURCE: U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 2020. Approval announcement.
FROM THE FDA