User login
Statins Raise Diabetes Risk, but CV Benefit Outweighs It
Statins raise the risks for increased glucose levels and the development of type 2 diabetes among people who don’t have it at baseline, but those risks are outweighed by the cardiovascular benefit, new data suggested.
The findings come from an analysis of individual participant data from a total of 23 randomized trials of statin therapy involving 154,664 individuals. In people without diabetes at baseline, statin therapy produces a dose-dependent increase in the risk for diabetes diagnosis, particularly among those whose glycemia marker levels are already at the diagnostic threshold.
Statins also tend to raise glucose levels in people who already have diabetes, but “the diabetes-related risks arising from the small changes in glycemia resulting from statin therapy are greatly outweighed by the benefits of statins on major vascular events when the direct clinical consequences of these outcomes are taken into consideration,” wrote the authors of the Cholesterol Treatment Trialists’ (CTT) Collaboration in their paper, published online in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
Moreover, they say, “since the effect of statin therapy on measures of glycemia within an individual is small, there is likely to be little clinical benefit in measuring glucose concentrations and A1c values routinely after starting statin therapy with the aim of making comparisons to values taken before the initiation of a statin. However, people should continue to be screened for diabetes and associated risk factors and have their glycemic control monitored in accordance with current clinical guidelines.”
The CTT is co-led by Christina Reith, MBChB, PhD, and David Preiss, PhD, FRCPath, MRCP, both of the Nuffield Department of Population Health, University of Oxford, England.
In an accompanying editorial,
Dr. Gerstein and Dr. Pigeyre also said “these findings emphasize the importance of holistic care. As people at risk for cardiovascular outcomes are also at risk for type 2 diabetes, any prescription of a statin should be accompanied by promoting proven strategies to prevent or delay diabetes, such as modest weight reduction and increased physical activity. Finally, these findings emphasize the importance of always being alert for harmful adverse effects, even with the most beneficial and successful preventive therapies.”
Statins Raise Diabetes Risk, Glucose Levels Slightly
The meta-analysis of trials in the CTT Collaboration included individual participant data from 19 double-blind randomized, controlled trials with a median follow-up of 4.3 years comparing statins with placebo in a total of 123,940 participants, including 18% who had known type 2 diabetes at randomization. Also analyzed were another four double-blind trials of lower- vs higher-intensity statins involving a total of 30,724 participants followed for a median of 4.9 years, with 15% having diabetes at baseline.
In the 19 trials of low- or moderate-intensity statins vs placebo, statins resulted in a significant 10% increase in new-onset diabetes compared with placebo (rate ratio, 1.10), while high-intensity statins raised the risk by an also significant 36% (1.36). This translated to a mean absolute excess of 0.12% per year of treatment.
Compared with less intensive statin therapy, more intensive statin therapy resulted in a significant 10% proportional increase in new-onset diabetes (1.10), giving an absolute annual excess of 0.22%.
In the statin vs placebo trials, differences in A1c values from placebo were 0.06 percentage points higher for low- or moderate-intensity statins and 0.08 points greater for high-intensity statins.
Nearly two thirds (62%) of the excess cases of new-onset diabetes occurred among participants in the highest quarter of the baseline glycemia distribution for both low-intensity or moderate-intensity and high-intensity statin therapy.
And among participants who already had diabetes at baseline, there was a significant 10% relative increase in worsening glycemia (defined by adverse glycemic event, A1c increase of ≥ 0.5 percentage points, or medication escalation) with low- or moderate-intensity statins compared with placebo and a 24% relative increase in the high-intensity trials.
The Nuffield Department of Population Health has an explicit policy of not accepting any personal honoraria payments directly or indirectly from the pharmaceutical and food industries. It seeks reimbursement to the University of Oxford for the costs of travel and accommodation to participate in scientific meetings. Dr. Reith reported receiving funding to the University of Oxford from the UK National Institute for Health and Care Research Health Technology Assessment Programme and holding unpaid roles on the Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium as a board member and WHO as a scientific advisor. Dr. Preiss reported receiving funding to his research institution (but no personal funding) from Novartis for the ORION 4 trial of inclisiran, Novo Nordisk for the ASCEND PLUS trial of semaglutide, and Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly for the EMPA-KIDNEY trial and being a committee member for a National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guideline.
Dr. Gerstein holds the McMaster-Sanofi Population Health Institute Chair in Diabetes Research and Care. He reported research grants from Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Novo Nordisk, Hanmi, and Merck; continuing medical education grants to McMaster University from Eli Lilly, Abbott, Sanofi, Novo Nordisk, and Boehringer Ingelheim; honoraria for speaking from AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, DKSH, Zuellig Pharma, Sanofi, and Jiangsu Hanson; and consulting fees from Abbott, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Carbon Brand, Sanofi, Kowa, and Hanmi. Pigeyre had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Statins raise the risks for increased glucose levels and the development of type 2 diabetes among people who don’t have it at baseline, but those risks are outweighed by the cardiovascular benefit, new data suggested.
The findings come from an analysis of individual participant data from a total of 23 randomized trials of statin therapy involving 154,664 individuals. In people without diabetes at baseline, statin therapy produces a dose-dependent increase in the risk for diabetes diagnosis, particularly among those whose glycemia marker levels are already at the diagnostic threshold.
Statins also tend to raise glucose levels in people who already have diabetes, but “the diabetes-related risks arising from the small changes in glycemia resulting from statin therapy are greatly outweighed by the benefits of statins on major vascular events when the direct clinical consequences of these outcomes are taken into consideration,” wrote the authors of the Cholesterol Treatment Trialists’ (CTT) Collaboration in their paper, published online in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
Moreover, they say, “since the effect of statin therapy on measures of glycemia within an individual is small, there is likely to be little clinical benefit in measuring glucose concentrations and A1c values routinely after starting statin therapy with the aim of making comparisons to values taken before the initiation of a statin. However, people should continue to be screened for diabetes and associated risk factors and have their glycemic control monitored in accordance with current clinical guidelines.”
The CTT is co-led by Christina Reith, MBChB, PhD, and David Preiss, PhD, FRCPath, MRCP, both of the Nuffield Department of Population Health, University of Oxford, England.
In an accompanying editorial,
Dr. Gerstein and Dr. Pigeyre also said “these findings emphasize the importance of holistic care. As people at risk for cardiovascular outcomes are also at risk for type 2 diabetes, any prescription of a statin should be accompanied by promoting proven strategies to prevent or delay diabetes, such as modest weight reduction and increased physical activity. Finally, these findings emphasize the importance of always being alert for harmful adverse effects, even with the most beneficial and successful preventive therapies.”
Statins Raise Diabetes Risk, Glucose Levels Slightly
The meta-analysis of trials in the CTT Collaboration included individual participant data from 19 double-blind randomized, controlled trials with a median follow-up of 4.3 years comparing statins with placebo in a total of 123,940 participants, including 18% who had known type 2 diabetes at randomization. Also analyzed were another four double-blind trials of lower- vs higher-intensity statins involving a total of 30,724 participants followed for a median of 4.9 years, with 15% having diabetes at baseline.
In the 19 trials of low- or moderate-intensity statins vs placebo, statins resulted in a significant 10% increase in new-onset diabetes compared with placebo (rate ratio, 1.10), while high-intensity statins raised the risk by an also significant 36% (1.36). This translated to a mean absolute excess of 0.12% per year of treatment.
Compared with less intensive statin therapy, more intensive statin therapy resulted in a significant 10% proportional increase in new-onset diabetes (1.10), giving an absolute annual excess of 0.22%.
In the statin vs placebo trials, differences in A1c values from placebo were 0.06 percentage points higher for low- or moderate-intensity statins and 0.08 points greater for high-intensity statins.
Nearly two thirds (62%) of the excess cases of new-onset diabetes occurred among participants in the highest quarter of the baseline glycemia distribution for both low-intensity or moderate-intensity and high-intensity statin therapy.
And among participants who already had diabetes at baseline, there was a significant 10% relative increase in worsening glycemia (defined by adverse glycemic event, A1c increase of ≥ 0.5 percentage points, or medication escalation) with low- or moderate-intensity statins compared with placebo and a 24% relative increase in the high-intensity trials.
The Nuffield Department of Population Health has an explicit policy of not accepting any personal honoraria payments directly or indirectly from the pharmaceutical and food industries. It seeks reimbursement to the University of Oxford for the costs of travel and accommodation to participate in scientific meetings. Dr. Reith reported receiving funding to the University of Oxford from the UK National Institute for Health and Care Research Health Technology Assessment Programme and holding unpaid roles on the Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium as a board member and WHO as a scientific advisor. Dr. Preiss reported receiving funding to his research institution (but no personal funding) from Novartis for the ORION 4 trial of inclisiran, Novo Nordisk for the ASCEND PLUS trial of semaglutide, and Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly for the EMPA-KIDNEY trial and being a committee member for a National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guideline.
Dr. Gerstein holds the McMaster-Sanofi Population Health Institute Chair in Diabetes Research and Care. He reported research grants from Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Novo Nordisk, Hanmi, and Merck; continuing medical education grants to McMaster University from Eli Lilly, Abbott, Sanofi, Novo Nordisk, and Boehringer Ingelheim; honoraria for speaking from AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, DKSH, Zuellig Pharma, Sanofi, and Jiangsu Hanson; and consulting fees from Abbott, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Carbon Brand, Sanofi, Kowa, and Hanmi. Pigeyre had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Statins raise the risks for increased glucose levels and the development of type 2 diabetes among people who don’t have it at baseline, but those risks are outweighed by the cardiovascular benefit, new data suggested.
The findings come from an analysis of individual participant data from a total of 23 randomized trials of statin therapy involving 154,664 individuals. In people without diabetes at baseline, statin therapy produces a dose-dependent increase in the risk for diabetes diagnosis, particularly among those whose glycemia marker levels are already at the diagnostic threshold.
Statins also tend to raise glucose levels in people who already have diabetes, but “the diabetes-related risks arising from the small changes in glycemia resulting from statin therapy are greatly outweighed by the benefits of statins on major vascular events when the direct clinical consequences of these outcomes are taken into consideration,” wrote the authors of the Cholesterol Treatment Trialists’ (CTT) Collaboration in their paper, published online in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
Moreover, they say, “since the effect of statin therapy on measures of glycemia within an individual is small, there is likely to be little clinical benefit in measuring glucose concentrations and A1c values routinely after starting statin therapy with the aim of making comparisons to values taken before the initiation of a statin. However, people should continue to be screened for diabetes and associated risk factors and have their glycemic control monitored in accordance with current clinical guidelines.”
The CTT is co-led by Christina Reith, MBChB, PhD, and David Preiss, PhD, FRCPath, MRCP, both of the Nuffield Department of Population Health, University of Oxford, England.
In an accompanying editorial,
Dr. Gerstein and Dr. Pigeyre also said “these findings emphasize the importance of holistic care. As people at risk for cardiovascular outcomes are also at risk for type 2 diabetes, any prescription of a statin should be accompanied by promoting proven strategies to prevent or delay diabetes, such as modest weight reduction and increased physical activity. Finally, these findings emphasize the importance of always being alert for harmful adverse effects, even with the most beneficial and successful preventive therapies.”
Statins Raise Diabetes Risk, Glucose Levels Slightly
The meta-analysis of trials in the CTT Collaboration included individual participant data from 19 double-blind randomized, controlled trials with a median follow-up of 4.3 years comparing statins with placebo in a total of 123,940 participants, including 18% who had known type 2 diabetes at randomization. Also analyzed were another four double-blind trials of lower- vs higher-intensity statins involving a total of 30,724 participants followed for a median of 4.9 years, with 15% having diabetes at baseline.
In the 19 trials of low- or moderate-intensity statins vs placebo, statins resulted in a significant 10% increase in new-onset diabetes compared with placebo (rate ratio, 1.10), while high-intensity statins raised the risk by an also significant 36% (1.36). This translated to a mean absolute excess of 0.12% per year of treatment.
Compared with less intensive statin therapy, more intensive statin therapy resulted in a significant 10% proportional increase in new-onset diabetes (1.10), giving an absolute annual excess of 0.22%.
In the statin vs placebo trials, differences in A1c values from placebo were 0.06 percentage points higher for low- or moderate-intensity statins and 0.08 points greater for high-intensity statins.
Nearly two thirds (62%) of the excess cases of new-onset diabetes occurred among participants in the highest quarter of the baseline glycemia distribution for both low-intensity or moderate-intensity and high-intensity statin therapy.
And among participants who already had diabetes at baseline, there was a significant 10% relative increase in worsening glycemia (defined by adverse glycemic event, A1c increase of ≥ 0.5 percentage points, or medication escalation) with low- or moderate-intensity statins compared with placebo and a 24% relative increase in the high-intensity trials.
The Nuffield Department of Population Health has an explicit policy of not accepting any personal honoraria payments directly or indirectly from the pharmaceutical and food industries. It seeks reimbursement to the University of Oxford for the costs of travel and accommodation to participate in scientific meetings. Dr. Reith reported receiving funding to the University of Oxford from the UK National Institute for Health and Care Research Health Technology Assessment Programme and holding unpaid roles on the Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium as a board member and WHO as a scientific advisor. Dr. Preiss reported receiving funding to his research institution (but no personal funding) from Novartis for the ORION 4 trial of inclisiran, Novo Nordisk for the ASCEND PLUS trial of semaglutide, and Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly for the EMPA-KIDNEY trial and being a committee member for a National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guideline.
Dr. Gerstein holds the McMaster-Sanofi Population Health Institute Chair in Diabetes Research and Care. He reported research grants from Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Novo Nordisk, Hanmi, and Merck; continuing medical education grants to McMaster University from Eli Lilly, Abbott, Sanofi, Novo Nordisk, and Boehringer Ingelheim; honoraria for speaking from AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, DKSH, Zuellig Pharma, Sanofi, and Jiangsu Hanson; and consulting fees from Abbott, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Carbon Brand, Sanofi, Kowa, and Hanmi. Pigeyre had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Early Olezarsen Results Show 50% Reduction in Triglycerides
ATLANTA — A novel antisense therapy called olezarsen reduced triglycerides (TGs) by approximately 50% with either of the two study doses relative to placebo and did so with a low relative risk for adverse events, new data from a phase 2b trial showed.
“The reduction in triglycerides was greater than that currently possible with any available therapy,” reported Brian A. Bergmark, MD, an interventional cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
The drug also produced meaningful improvements in multiple other lipid subfractions associated with increased cardiovascular (CV) risk, including ApoC-III, very low–density lipoprotein (VLDL) cholesterol, ApoB, and non-LDL cholesterol. High-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels were significantly raised.
The results were presented on April 7 as a late breaker at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) Scientific Session 2024 and published online simultaneously in The New England Journal of Medicine.
No Major Subgroup Failed to Respond
The effect was seen across all the key subgroups evaluated, including women and patients with diabetes, obesity, and severe as well as moderate elevations in TGs at baseline, Dr. Bergmark reported.
Olezarsen is a N-acetylgalactosamine–conjugated antisense oligonucleotide targeting APOC3 RNA.
In this study, 154 patients at 24 sites in North America were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to 50 or 80 mg olezarsen. Those in each of these cohorts were then randomized in a 3:1 ratio to active therapy or placebo. All therapies were administered by subcutaneous injection once per month.
Patients were eligible for the trial if they had moderate hypertriglyceridemia, defined as a level of 150-499 mg/dL, and elevated CV risk or if they had severe hypertriglyceridemia (≥ 500 mg/dL) with or without other evidence of elevated CV risk. The primary endpoint was a change in TGs at 6 months. Complete follow-up was available in about 97% of patients regardless of treatment assignment.
With a slight numerical advantage for the higher dose, the TG reductions were 49.1% for the 50-mg dose and 53.1% for the 80-mg dose relative to no significant change in the placebo group (P < .001 for both olezarsen doses). The reductions in ApoC-III, an upstream driver of TG production and a CV risk factor, were 64.2% and 73.2% relative to placebo (both P < .001), respectively, Dr. Bergmark reported.
In those with moderate hypertriglyceridemia, normal TG levels, defined as < 150 mg/dL, were reached at 6 months in 85.7% and 93.3% in the 40-mg and 80-mg dose groups, respectively. Relative to these reductions, normalization was seen in only 11.8% of placebo patients (P < .001).
TG Lowering Might Not Be Best Endpoint
The primary endpoint in this trial was a change in TGs, but this target was questioned by an invited ACC discussant, Daniel Soffer, MD, who is both an adjunct professor assistant professor of medicine at Penn Medicine, Philadelphia, and current president of the National Lipid Association.
Dr. Soffer noted that highly elevated TGs are a major risk factor for acute pancreatitis, so this predicts a clinical benefit for this purpose, but he thought the other lipid subfractions are far more important for the goal of reducing atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Indeed, he said categorically that it is not TGs that drive ASCVD risk and therefore not what is the real importance of these data. Rather, “it is the non-HDL cholesterol and ApoB lowering” that will drive the likely benefits from this therapy in CV disease.
In addition to the TG reductions, olezarsen did, in fact, produce significant reductions in many of the lipid subfractions associated with increased CV risk. While slightly more favorable in most cases with the higher dose of olezarsen, even the lower dose reduced Apo C-III from baseline by 64.2% (P < .001), VLDL by 46.2% (P < .001), remnant cholesterol by 46.6% (P < .001), ApoB by 18.2% (P < .001), and non-HDL cholesterol by 25.4% (P < .001). HDL cholesterol was increased by 39.6% (P < .001).
These favorable effects on TG and other lipid subfractions were achieved with a safety profile that was reassuring, Dr. Bergmark said. Serious adverse events leading to discontinuation occurred in 0%, 1.7%, and 1.8% of the placebo, lower-dose, and higher-dose arms, respectively. These rates did not differ significantly.
Increased Liver Enzymes Is Common
Liver enzymes were significantly elevated (P < .001) for both doses of olezarsen vs placebo, but liver enzymes > 3× the upper limit of normal did not reach significance on either dose of olezarsen relative to placebo. Low platelet counts and reductions in kidney function were observed in a minority of patients but were generally manageable, according to Dr. Bergmark. There was no impact on hemoglobin A1c levels.
Further evaluation of change in hepatic function is planned in the ongoing extension studies.
Characterizing these results as “exciting,” Neha J. Pagidipati, MD, a member of the Duke Clinical Research Institute and an assistant professor at the Duke School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina, said that identifying a drug effective for hypertriglyceridemia is likely to be a major advance. While elevated TGs are “one of the toughest” lipid abnormalities to manage, “there is not much out there to offer for treatment.”
She, like Dr. Soffer, was encouraged by the favorable effects on multiple lipid abnormalities associated with increased CV risk, but she said the ultimate clinical utility of this or other agents that lower TGs for ASCVD requires a study showing a change in CV events.
Dr. Bergmark reported financial relationships with 15 pharmaceutical companies, including Ionis, which provided funding for the BRIDGE-TIMI 73a trial. Soffer had financial relationships with Akcea, Amgen, Amryt, AstraZeneca, Ionis, Novartis, Regeneron, and Verve. Dr. Pagidipati had financial relationships with more than 10 pharmaceutical companies but was not involved in the design of management of the BRIDGE-TIMI 73a trial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ATLANTA — A novel antisense therapy called olezarsen reduced triglycerides (TGs) by approximately 50% with either of the two study doses relative to placebo and did so with a low relative risk for adverse events, new data from a phase 2b trial showed.
“The reduction in triglycerides was greater than that currently possible with any available therapy,” reported Brian A. Bergmark, MD, an interventional cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
The drug also produced meaningful improvements in multiple other lipid subfractions associated with increased cardiovascular (CV) risk, including ApoC-III, very low–density lipoprotein (VLDL) cholesterol, ApoB, and non-LDL cholesterol. High-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels were significantly raised.
The results were presented on April 7 as a late breaker at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) Scientific Session 2024 and published online simultaneously in The New England Journal of Medicine.
No Major Subgroup Failed to Respond
The effect was seen across all the key subgroups evaluated, including women and patients with diabetes, obesity, and severe as well as moderate elevations in TGs at baseline, Dr. Bergmark reported.
Olezarsen is a N-acetylgalactosamine–conjugated antisense oligonucleotide targeting APOC3 RNA.
In this study, 154 patients at 24 sites in North America were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to 50 or 80 mg olezarsen. Those in each of these cohorts were then randomized in a 3:1 ratio to active therapy or placebo. All therapies were administered by subcutaneous injection once per month.
Patients were eligible for the trial if they had moderate hypertriglyceridemia, defined as a level of 150-499 mg/dL, and elevated CV risk or if they had severe hypertriglyceridemia (≥ 500 mg/dL) with or without other evidence of elevated CV risk. The primary endpoint was a change in TGs at 6 months. Complete follow-up was available in about 97% of patients regardless of treatment assignment.
With a slight numerical advantage for the higher dose, the TG reductions were 49.1% for the 50-mg dose and 53.1% for the 80-mg dose relative to no significant change in the placebo group (P < .001 for both olezarsen doses). The reductions in ApoC-III, an upstream driver of TG production and a CV risk factor, were 64.2% and 73.2% relative to placebo (both P < .001), respectively, Dr. Bergmark reported.
In those with moderate hypertriglyceridemia, normal TG levels, defined as < 150 mg/dL, were reached at 6 months in 85.7% and 93.3% in the 40-mg and 80-mg dose groups, respectively. Relative to these reductions, normalization was seen in only 11.8% of placebo patients (P < .001).
TG Lowering Might Not Be Best Endpoint
The primary endpoint in this trial was a change in TGs, but this target was questioned by an invited ACC discussant, Daniel Soffer, MD, who is both an adjunct professor assistant professor of medicine at Penn Medicine, Philadelphia, and current president of the National Lipid Association.
Dr. Soffer noted that highly elevated TGs are a major risk factor for acute pancreatitis, so this predicts a clinical benefit for this purpose, but he thought the other lipid subfractions are far more important for the goal of reducing atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Indeed, he said categorically that it is not TGs that drive ASCVD risk and therefore not what is the real importance of these data. Rather, “it is the non-HDL cholesterol and ApoB lowering” that will drive the likely benefits from this therapy in CV disease.
In addition to the TG reductions, olezarsen did, in fact, produce significant reductions in many of the lipid subfractions associated with increased CV risk. While slightly more favorable in most cases with the higher dose of olezarsen, even the lower dose reduced Apo C-III from baseline by 64.2% (P < .001), VLDL by 46.2% (P < .001), remnant cholesterol by 46.6% (P < .001), ApoB by 18.2% (P < .001), and non-HDL cholesterol by 25.4% (P < .001). HDL cholesterol was increased by 39.6% (P < .001).
These favorable effects on TG and other lipid subfractions were achieved with a safety profile that was reassuring, Dr. Bergmark said. Serious adverse events leading to discontinuation occurred in 0%, 1.7%, and 1.8% of the placebo, lower-dose, and higher-dose arms, respectively. These rates did not differ significantly.
Increased Liver Enzymes Is Common
Liver enzymes were significantly elevated (P < .001) for both doses of olezarsen vs placebo, but liver enzymes > 3× the upper limit of normal did not reach significance on either dose of olezarsen relative to placebo. Low platelet counts and reductions in kidney function were observed in a minority of patients but were generally manageable, according to Dr. Bergmark. There was no impact on hemoglobin A1c levels.
Further evaluation of change in hepatic function is planned in the ongoing extension studies.
Characterizing these results as “exciting,” Neha J. Pagidipati, MD, a member of the Duke Clinical Research Institute and an assistant professor at the Duke School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina, said that identifying a drug effective for hypertriglyceridemia is likely to be a major advance. While elevated TGs are “one of the toughest” lipid abnormalities to manage, “there is not much out there to offer for treatment.”
She, like Dr. Soffer, was encouraged by the favorable effects on multiple lipid abnormalities associated with increased CV risk, but she said the ultimate clinical utility of this or other agents that lower TGs for ASCVD requires a study showing a change in CV events.
Dr. Bergmark reported financial relationships with 15 pharmaceutical companies, including Ionis, which provided funding for the BRIDGE-TIMI 73a trial. Soffer had financial relationships with Akcea, Amgen, Amryt, AstraZeneca, Ionis, Novartis, Regeneron, and Verve. Dr. Pagidipati had financial relationships with more than 10 pharmaceutical companies but was not involved in the design of management of the BRIDGE-TIMI 73a trial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ATLANTA — A novel antisense therapy called olezarsen reduced triglycerides (TGs) by approximately 50% with either of the two study doses relative to placebo and did so with a low relative risk for adverse events, new data from a phase 2b trial showed.
“The reduction in triglycerides was greater than that currently possible with any available therapy,” reported Brian A. Bergmark, MD, an interventional cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
The drug also produced meaningful improvements in multiple other lipid subfractions associated with increased cardiovascular (CV) risk, including ApoC-III, very low–density lipoprotein (VLDL) cholesterol, ApoB, and non-LDL cholesterol. High-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels were significantly raised.
The results were presented on April 7 as a late breaker at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) Scientific Session 2024 and published online simultaneously in The New England Journal of Medicine.
No Major Subgroup Failed to Respond
The effect was seen across all the key subgroups evaluated, including women and patients with diabetes, obesity, and severe as well as moderate elevations in TGs at baseline, Dr. Bergmark reported.
Olezarsen is a N-acetylgalactosamine–conjugated antisense oligonucleotide targeting APOC3 RNA.
In this study, 154 patients at 24 sites in North America were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to 50 or 80 mg olezarsen. Those in each of these cohorts were then randomized in a 3:1 ratio to active therapy or placebo. All therapies were administered by subcutaneous injection once per month.
Patients were eligible for the trial if they had moderate hypertriglyceridemia, defined as a level of 150-499 mg/dL, and elevated CV risk or if they had severe hypertriglyceridemia (≥ 500 mg/dL) with or without other evidence of elevated CV risk. The primary endpoint was a change in TGs at 6 months. Complete follow-up was available in about 97% of patients regardless of treatment assignment.
With a slight numerical advantage for the higher dose, the TG reductions were 49.1% for the 50-mg dose and 53.1% for the 80-mg dose relative to no significant change in the placebo group (P < .001 for both olezarsen doses). The reductions in ApoC-III, an upstream driver of TG production and a CV risk factor, were 64.2% and 73.2% relative to placebo (both P < .001), respectively, Dr. Bergmark reported.
In those with moderate hypertriglyceridemia, normal TG levels, defined as < 150 mg/dL, were reached at 6 months in 85.7% and 93.3% in the 40-mg and 80-mg dose groups, respectively. Relative to these reductions, normalization was seen in only 11.8% of placebo patients (P < .001).
TG Lowering Might Not Be Best Endpoint
The primary endpoint in this trial was a change in TGs, but this target was questioned by an invited ACC discussant, Daniel Soffer, MD, who is both an adjunct professor assistant professor of medicine at Penn Medicine, Philadelphia, and current president of the National Lipid Association.
Dr. Soffer noted that highly elevated TGs are a major risk factor for acute pancreatitis, so this predicts a clinical benefit for this purpose, but he thought the other lipid subfractions are far more important for the goal of reducing atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Indeed, he said categorically that it is not TGs that drive ASCVD risk and therefore not what is the real importance of these data. Rather, “it is the non-HDL cholesterol and ApoB lowering” that will drive the likely benefits from this therapy in CV disease.
In addition to the TG reductions, olezarsen did, in fact, produce significant reductions in many of the lipid subfractions associated with increased CV risk. While slightly more favorable in most cases with the higher dose of olezarsen, even the lower dose reduced Apo C-III from baseline by 64.2% (P < .001), VLDL by 46.2% (P < .001), remnant cholesterol by 46.6% (P < .001), ApoB by 18.2% (P < .001), and non-HDL cholesterol by 25.4% (P < .001). HDL cholesterol was increased by 39.6% (P < .001).
These favorable effects on TG and other lipid subfractions were achieved with a safety profile that was reassuring, Dr. Bergmark said. Serious adverse events leading to discontinuation occurred in 0%, 1.7%, and 1.8% of the placebo, lower-dose, and higher-dose arms, respectively. These rates did not differ significantly.
Increased Liver Enzymes Is Common
Liver enzymes were significantly elevated (P < .001) for both doses of olezarsen vs placebo, but liver enzymes > 3× the upper limit of normal did not reach significance on either dose of olezarsen relative to placebo. Low platelet counts and reductions in kidney function were observed in a minority of patients but were generally manageable, according to Dr. Bergmark. There was no impact on hemoglobin A1c levels.
Further evaluation of change in hepatic function is planned in the ongoing extension studies.
Characterizing these results as “exciting,” Neha J. Pagidipati, MD, a member of the Duke Clinical Research Institute and an assistant professor at the Duke School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina, said that identifying a drug effective for hypertriglyceridemia is likely to be a major advance. While elevated TGs are “one of the toughest” lipid abnormalities to manage, “there is not much out there to offer for treatment.”
She, like Dr. Soffer, was encouraged by the favorable effects on multiple lipid abnormalities associated with increased CV risk, but she said the ultimate clinical utility of this or other agents that lower TGs for ASCVD requires a study showing a change in CV events.
Dr. Bergmark reported financial relationships with 15 pharmaceutical companies, including Ionis, which provided funding for the BRIDGE-TIMI 73a trial. Soffer had financial relationships with Akcea, Amgen, Amryt, AstraZeneca, Ionis, Novartis, Regeneron, and Verve. Dr. Pagidipati had financial relationships with more than 10 pharmaceutical companies but was not involved in the design of management of the BRIDGE-TIMI 73a trial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Arm Fat Raises CVD Risk in People With Type 2 Diabetes
TOPLINE:
In people with type 2 diabetes (T2D), higher levels of arm and trunk fat are associated with an increased risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD) and mortality, while higher levels of leg fat are associated with a reduced risk for these conditions.
METHODOLOGY:
- People with T2D have a twofold to fourfold higher risk for CVD and mortality, and evidence shows obesity management helps delay complications and premature death, but an elevated body mass index (BMI) may be insufficient to measure obesity.
- In the “obesity paradox,” people with elevated BMI may have a lower CVD risk than people of normal weight.
- Researchers prospectively investigated how regional body fat accumulation was associated with CVD risk in 21,472 people with T2D (mean age, 58.9 years; 60.7% men; BMI about 29-33) from the UK Biobank (2006-2010), followed up for a median of 7.7 years.
- The regional body fat distribution in arms, trunk, and legs was assessed using bioelectrical impedance analysis.
- The primary outcomes were the incidence of CVD, all-cause mortality, and CVD mortality.
TAKEAWAY:
- However, participants in the highest quartile of leg fat percentage had a lower risk for CVD than those in the lowest quartile (HR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.58-0.90).
- A nonlinear relationship was observed between higher leg fat percentage and lower CVD risk and between higher trunk fat percentage and higher CVD risk, whereas a linear relationship was noted between higher arm fat percentage and higher CVD risk.
- The patterns of association were similar for both all-cause mortality and CVD mortality. Overall patterns were similar for men and women.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings add to the understanding of body fat distribution in patients with T2D, which highlights the importance of considering both the amount and the location of body fat when assessing CVD and mortality risk among patients with T2D,” wrote the authors.
SOURCE:
The study led by Zixin Qiu, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, was published online in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
As body fat was measured only once at the beginning of the study, its changing association over time could not be assessed. Moreover, the findings were primarily based on predominantly White UK adults, potentially restricting their generalizability to other population groups. Furthermore, diabetes was diagnosed using self-reported medical history, medication, and hemoglobin A1c levels, implying that some cases may have gone undetected at baseline.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Hubei Province Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars, and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In people with type 2 diabetes (T2D), higher levels of arm and trunk fat are associated with an increased risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD) and mortality, while higher levels of leg fat are associated with a reduced risk for these conditions.
METHODOLOGY:
- People with T2D have a twofold to fourfold higher risk for CVD and mortality, and evidence shows obesity management helps delay complications and premature death, but an elevated body mass index (BMI) may be insufficient to measure obesity.
- In the “obesity paradox,” people with elevated BMI may have a lower CVD risk than people of normal weight.
- Researchers prospectively investigated how regional body fat accumulation was associated with CVD risk in 21,472 people with T2D (mean age, 58.9 years; 60.7% men; BMI about 29-33) from the UK Biobank (2006-2010), followed up for a median of 7.7 years.
- The regional body fat distribution in arms, trunk, and legs was assessed using bioelectrical impedance analysis.
- The primary outcomes were the incidence of CVD, all-cause mortality, and CVD mortality.
TAKEAWAY:
- However, participants in the highest quartile of leg fat percentage had a lower risk for CVD than those in the lowest quartile (HR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.58-0.90).
- A nonlinear relationship was observed between higher leg fat percentage and lower CVD risk and between higher trunk fat percentage and higher CVD risk, whereas a linear relationship was noted between higher arm fat percentage and higher CVD risk.
- The patterns of association were similar for both all-cause mortality and CVD mortality. Overall patterns were similar for men and women.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings add to the understanding of body fat distribution in patients with T2D, which highlights the importance of considering both the amount and the location of body fat when assessing CVD and mortality risk among patients with T2D,” wrote the authors.
SOURCE:
The study led by Zixin Qiu, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, was published online in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
As body fat was measured only once at the beginning of the study, its changing association over time could not be assessed. Moreover, the findings were primarily based on predominantly White UK adults, potentially restricting their generalizability to other population groups. Furthermore, diabetes was diagnosed using self-reported medical history, medication, and hemoglobin A1c levels, implying that some cases may have gone undetected at baseline.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Hubei Province Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars, and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In people with type 2 diabetes (T2D), higher levels of arm and trunk fat are associated with an increased risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD) and mortality, while higher levels of leg fat are associated with a reduced risk for these conditions.
METHODOLOGY:
- People with T2D have a twofold to fourfold higher risk for CVD and mortality, and evidence shows obesity management helps delay complications and premature death, but an elevated body mass index (BMI) may be insufficient to measure obesity.
- In the “obesity paradox,” people with elevated BMI may have a lower CVD risk than people of normal weight.
- Researchers prospectively investigated how regional body fat accumulation was associated with CVD risk in 21,472 people with T2D (mean age, 58.9 years; 60.7% men; BMI about 29-33) from the UK Biobank (2006-2010), followed up for a median of 7.7 years.
- The regional body fat distribution in arms, trunk, and legs was assessed using bioelectrical impedance analysis.
- The primary outcomes were the incidence of CVD, all-cause mortality, and CVD mortality.
TAKEAWAY:
- However, participants in the highest quartile of leg fat percentage had a lower risk for CVD than those in the lowest quartile (HR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.58-0.90).
- A nonlinear relationship was observed between higher leg fat percentage and lower CVD risk and between higher trunk fat percentage and higher CVD risk, whereas a linear relationship was noted between higher arm fat percentage and higher CVD risk.
- The patterns of association were similar for both all-cause mortality and CVD mortality. Overall patterns were similar for men and women.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings add to the understanding of body fat distribution in patients with T2D, which highlights the importance of considering both the amount and the location of body fat when assessing CVD and mortality risk among patients with T2D,” wrote the authors.
SOURCE:
The study led by Zixin Qiu, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, was published online in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
As body fat was measured only once at the beginning of the study, its changing association over time could not be assessed. Moreover, the findings were primarily based on predominantly White UK adults, potentially restricting their generalizability to other population groups. Furthermore, diabetes was diagnosed using self-reported medical history, medication, and hemoglobin A1c levels, implying that some cases may have gone undetected at baseline.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Hubei Province Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars, and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Telemedicine Reduces Rehospitalization, Revascularization in Post-PCI ACS Patients
ATLANTA — Patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) who had a myocardial infarction or unstable angina and underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) had a 76% lower rate of hospital readmission after 6 months if they participated in a remote monitoring protocol compared with similar patients who had standard post-discharge care, results of a new trial suggest.
The TELE-ACS trial showed that at 6 months, telemedicine patients also had statistically significantly lower rates of post-discharge emergency department visits, unplanned coronary revascularizations, and cardiovascular symptoms, such as chest pain, shortness of breath and dizziness. However, the rates of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) were similar between the two groups. The protocol included consultation with a cardiologist who reviewed home-monitoring data.
“The team was able to aid in preventing unnecessary presentations and advised the patients to seek emergency care whenever was necessary,” Nasser Alshahrani, MSc, a clinical research fellow at Imperial College London, said while presenting the results at the American College of Cardiology meeting. “The TELE-ACS protocol provided a significant reduction in readmission rates post-ACS and other adverse events.”
The study findings were published online simultaneously in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Telemedicine Protocol
The trial, conducted from January 2022 to April 2023, randomly assigned 337 patients to telemedicine or standard care when they were discharged after PCI and had at least one cardiovascular risk factor. The telemedicine protocol consisted of 12-lead electrocardiogram belt, an automated blood-pressure monitor, and a pulse oximeter.
Patients in the telemedicine arm initiated the remote monitoring protocol if they thought they had cardiac symptoms. The majority (86%) were men with what the study described as “a high preponderance of cardiovascular risk factors.” Average age was 58.1 years.
If a telemedicine patient initiated the protocol, a cardiologist remotely assessed the patient’s symptoms and channeled the patient to the appropriate care pathway, whether reassuring the patient or sending them to a primary care physician or emergency department, or to call emergency services. Patients who didn’t get a call back from the cardiologist within 15 minutes were told to seek care in the standard clinical pathway.
Telemedicine patients were given the telemonitoring package and training in how to use the devices before they were discharged. They also received three follow-up quality control calls in the first two months to ensure they were using the equipment correctly. They kept the telemonitoring equipment for 8 months, but were followed out to 9 months. Six telemedicine patients dropped out while one standard care patient withdrew from the study.
Results showed that at 6 months, telemedicine patients had statistically significantly lower rates of post-discharge emergency department visits (25% vs 37%, P < .001), unplanned coronary revascularizations (3% vs 9%, P < .01) and cardiovascular symptoms, such as chest pain, shortness of breath and dizziness (a 13% to 18% difference for each symptom, P < .01).
MACE rates were similar between the two groups.
At 9 months, 3 months after the protocol ended, 20 telemedicine patients and 50 standard-care patients were readmitted to the hospital, while 52 and 73, respectively, went to the emergency department.
The telemedicine patients also had shorter hospital stays: an average of 0.5 and 1.2 days at 6 and 9 months, respectively, vs 1.5 and 1.8 days in the standard treatment arm (P < .001 for both).
Mr. Alshahrani noted several limitations with the study, namely that 86% of participants were men, and that the intervention was only offered to people who had smartphones. “The high level of support for the telemedicine group, with prompt cardiology responses, may be challenging to replicate outside a trial setting, requiring significant investment and training,” he added.
Human Element Key
In an interview from London after the presentation, lead author Ramzi Khamis, MB ChB, PhD, said, “This was quite a basic study. Really what we did was we integrated a clinical decision-making algorithm that we perfected with some quite novel but basic technology.” Future research should strive to add a home troponin test to the protocol and an artificial intelligence component, he said.
However, Dr. Khamis noted that human interaction was key to the success of the TELE-ACS trial. “The human factor is very important here and I think it would be really interesting to have a head-to-head comparison of human interaction with remote monitoring vs an AI-driven interaction,” he said. “I have my doubts that AI would be able to beat the human factor here.”
Lawrence Phillips, MD, medical director of outpatient cardiology at NYU Langone Heart, told this news organization that the study was appropriately powered to evaluate the telemedicine protocol, and that it could serve as a template for other studies of remote monitoring in cardiology.
“I think that this study is forming the foundation of evolving telemedicine data,” he said. “It shows really interesting results, and I’m sure it’s going to be reproduced in different ways going forward.”
While other studies have shown the utility of telemedicine to decrease unnecessary hospitalizations, this study went one step further, Dr. Phillips said. “What was unique about this study was the package that they put together,” he added. “It was a combination of telehealth and being able to speak with someone when you have concerns with objective data of an electrocardiogram, blood-pressure cuff, and oxygen level assessment, which is an interesting approach having that ejective data with [a] subjective element.”
The trial received funding from the British Heart Foundation; King Khalid University, Abha, Saudi Arabia via The Saudi Arabian Cultural Bureau; Sansour Fund, Imperial Healthcare Charity; and Safwan Sobhan Fund at Imperial College London. Mr. Alshahrani and Dr. Khamis have no relevant relationships to disclose. Dr. Phillips has no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ATLANTA — Patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) who had a myocardial infarction or unstable angina and underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) had a 76% lower rate of hospital readmission after 6 months if they participated in a remote monitoring protocol compared with similar patients who had standard post-discharge care, results of a new trial suggest.
The TELE-ACS trial showed that at 6 months, telemedicine patients also had statistically significantly lower rates of post-discharge emergency department visits, unplanned coronary revascularizations, and cardiovascular symptoms, such as chest pain, shortness of breath and dizziness. However, the rates of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) were similar between the two groups. The protocol included consultation with a cardiologist who reviewed home-monitoring data.
“The team was able to aid in preventing unnecessary presentations and advised the patients to seek emergency care whenever was necessary,” Nasser Alshahrani, MSc, a clinical research fellow at Imperial College London, said while presenting the results at the American College of Cardiology meeting. “The TELE-ACS protocol provided a significant reduction in readmission rates post-ACS and other adverse events.”
The study findings were published online simultaneously in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Telemedicine Protocol
The trial, conducted from January 2022 to April 2023, randomly assigned 337 patients to telemedicine or standard care when they were discharged after PCI and had at least one cardiovascular risk factor. The telemedicine protocol consisted of 12-lead electrocardiogram belt, an automated blood-pressure monitor, and a pulse oximeter.
Patients in the telemedicine arm initiated the remote monitoring protocol if they thought they had cardiac symptoms. The majority (86%) were men with what the study described as “a high preponderance of cardiovascular risk factors.” Average age was 58.1 years.
If a telemedicine patient initiated the protocol, a cardiologist remotely assessed the patient’s symptoms and channeled the patient to the appropriate care pathway, whether reassuring the patient or sending them to a primary care physician or emergency department, or to call emergency services. Patients who didn’t get a call back from the cardiologist within 15 minutes were told to seek care in the standard clinical pathway.
Telemedicine patients were given the telemonitoring package and training in how to use the devices before they were discharged. They also received three follow-up quality control calls in the first two months to ensure they were using the equipment correctly. They kept the telemonitoring equipment for 8 months, but were followed out to 9 months. Six telemedicine patients dropped out while one standard care patient withdrew from the study.
Results showed that at 6 months, telemedicine patients had statistically significantly lower rates of post-discharge emergency department visits (25% vs 37%, P < .001), unplanned coronary revascularizations (3% vs 9%, P < .01) and cardiovascular symptoms, such as chest pain, shortness of breath and dizziness (a 13% to 18% difference for each symptom, P < .01).
MACE rates were similar between the two groups.
At 9 months, 3 months after the protocol ended, 20 telemedicine patients and 50 standard-care patients were readmitted to the hospital, while 52 and 73, respectively, went to the emergency department.
The telemedicine patients also had shorter hospital stays: an average of 0.5 and 1.2 days at 6 and 9 months, respectively, vs 1.5 and 1.8 days in the standard treatment arm (P < .001 for both).
Mr. Alshahrani noted several limitations with the study, namely that 86% of participants were men, and that the intervention was only offered to people who had smartphones. “The high level of support for the telemedicine group, with prompt cardiology responses, may be challenging to replicate outside a trial setting, requiring significant investment and training,” he added.
Human Element Key
In an interview from London after the presentation, lead author Ramzi Khamis, MB ChB, PhD, said, “This was quite a basic study. Really what we did was we integrated a clinical decision-making algorithm that we perfected with some quite novel but basic technology.” Future research should strive to add a home troponin test to the protocol and an artificial intelligence component, he said.
However, Dr. Khamis noted that human interaction was key to the success of the TELE-ACS trial. “The human factor is very important here and I think it would be really interesting to have a head-to-head comparison of human interaction with remote monitoring vs an AI-driven interaction,” he said. “I have my doubts that AI would be able to beat the human factor here.”
Lawrence Phillips, MD, medical director of outpatient cardiology at NYU Langone Heart, told this news organization that the study was appropriately powered to evaluate the telemedicine protocol, and that it could serve as a template for other studies of remote monitoring in cardiology.
“I think that this study is forming the foundation of evolving telemedicine data,” he said. “It shows really interesting results, and I’m sure it’s going to be reproduced in different ways going forward.”
While other studies have shown the utility of telemedicine to decrease unnecessary hospitalizations, this study went one step further, Dr. Phillips said. “What was unique about this study was the package that they put together,” he added. “It was a combination of telehealth and being able to speak with someone when you have concerns with objective data of an electrocardiogram, blood-pressure cuff, and oxygen level assessment, which is an interesting approach having that ejective data with [a] subjective element.”
The trial received funding from the British Heart Foundation; King Khalid University, Abha, Saudi Arabia via The Saudi Arabian Cultural Bureau; Sansour Fund, Imperial Healthcare Charity; and Safwan Sobhan Fund at Imperial College London. Mr. Alshahrani and Dr. Khamis have no relevant relationships to disclose. Dr. Phillips has no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ATLANTA — Patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) who had a myocardial infarction or unstable angina and underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) had a 76% lower rate of hospital readmission after 6 months if they participated in a remote monitoring protocol compared with similar patients who had standard post-discharge care, results of a new trial suggest.
The TELE-ACS trial showed that at 6 months, telemedicine patients also had statistically significantly lower rates of post-discharge emergency department visits, unplanned coronary revascularizations, and cardiovascular symptoms, such as chest pain, shortness of breath and dizziness. However, the rates of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) were similar between the two groups. The protocol included consultation with a cardiologist who reviewed home-monitoring data.
“The team was able to aid in preventing unnecessary presentations and advised the patients to seek emergency care whenever was necessary,” Nasser Alshahrani, MSc, a clinical research fellow at Imperial College London, said while presenting the results at the American College of Cardiology meeting. “The TELE-ACS protocol provided a significant reduction in readmission rates post-ACS and other adverse events.”
The study findings were published online simultaneously in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Telemedicine Protocol
The trial, conducted from January 2022 to April 2023, randomly assigned 337 patients to telemedicine or standard care when they were discharged after PCI and had at least one cardiovascular risk factor. The telemedicine protocol consisted of 12-lead electrocardiogram belt, an automated blood-pressure monitor, and a pulse oximeter.
Patients in the telemedicine arm initiated the remote monitoring protocol if they thought they had cardiac symptoms. The majority (86%) were men with what the study described as “a high preponderance of cardiovascular risk factors.” Average age was 58.1 years.
If a telemedicine patient initiated the protocol, a cardiologist remotely assessed the patient’s symptoms and channeled the patient to the appropriate care pathway, whether reassuring the patient or sending them to a primary care physician or emergency department, or to call emergency services. Patients who didn’t get a call back from the cardiologist within 15 minutes were told to seek care in the standard clinical pathway.
Telemedicine patients were given the telemonitoring package and training in how to use the devices before they were discharged. They also received three follow-up quality control calls in the first two months to ensure they were using the equipment correctly. They kept the telemonitoring equipment for 8 months, but were followed out to 9 months. Six telemedicine patients dropped out while one standard care patient withdrew from the study.
Results showed that at 6 months, telemedicine patients had statistically significantly lower rates of post-discharge emergency department visits (25% vs 37%, P < .001), unplanned coronary revascularizations (3% vs 9%, P < .01) and cardiovascular symptoms, such as chest pain, shortness of breath and dizziness (a 13% to 18% difference for each symptom, P < .01).
MACE rates were similar between the two groups.
At 9 months, 3 months after the protocol ended, 20 telemedicine patients and 50 standard-care patients were readmitted to the hospital, while 52 and 73, respectively, went to the emergency department.
The telemedicine patients also had shorter hospital stays: an average of 0.5 and 1.2 days at 6 and 9 months, respectively, vs 1.5 and 1.8 days in the standard treatment arm (P < .001 for both).
Mr. Alshahrani noted several limitations with the study, namely that 86% of participants were men, and that the intervention was only offered to people who had smartphones. “The high level of support for the telemedicine group, with prompt cardiology responses, may be challenging to replicate outside a trial setting, requiring significant investment and training,” he added.
Human Element Key
In an interview from London after the presentation, lead author Ramzi Khamis, MB ChB, PhD, said, “This was quite a basic study. Really what we did was we integrated a clinical decision-making algorithm that we perfected with some quite novel but basic technology.” Future research should strive to add a home troponin test to the protocol and an artificial intelligence component, he said.
However, Dr. Khamis noted that human interaction was key to the success of the TELE-ACS trial. “The human factor is very important here and I think it would be really interesting to have a head-to-head comparison of human interaction with remote monitoring vs an AI-driven interaction,” he said. “I have my doubts that AI would be able to beat the human factor here.”
Lawrence Phillips, MD, medical director of outpatient cardiology at NYU Langone Heart, told this news organization that the study was appropriately powered to evaluate the telemedicine protocol, and that it could serve as a template for other studies of remote monitoring in cardiology.
“I think that this study is forming the foundation of evolving telemedicine data,” he said. “It shows really interesting results, and I’m sure it’s going to be reproduced in different ways going forward.”
While other studies have shown the utility of telemedicine to decrease unnecessary hospitalizations, this study went one step further, Dr. Phillips said. “What was unique about this study was the package that they put together,” he added. “It was a combination of telehealth and being able to speak with someone when you have concerns with objective data of an electrocardiogram, blood-pressure cuff, and oxygen level assessment, which is an interesting approach having that ejective data with [a] subjective element.”
The trial received funding from the British Heart Foundation; King Khalid University, Abha, Saudi Arabia via The Saudi Arabian Cultural Bureau; Sansour Fund, Imperial Healthcare Charity; and Safwan Sobhan Fund at Imperial College London. Mr. Alshahrani and Dr. Khamis have no relevant relationships to disclose. Dr. Phillips has no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
An App for ED?
Little blue pill meets a little blue light.
A digital application can improve erectile function, according to new research presented at the European Association of Urology (EAU) Annual Congress on April 8, 2024.
Researchers developed a 12-week, self-managed program to treat erectile dysfunction (ED). The program is delivered to patients’ mobile devices and encourages users to do cardiovascular training, pelvic floor exercises, and physiotherapy. It also provides information about ED, sexual therapy, and stress management.
“The treatment of ED through physical activity and/or lifestyle changes is recommended in current European guidelines but is not well established in clinical practice,” according to the researchers.
App or Waitlist
The app, known as Kranus Edera, was created by Kranus Health. It is available by prescription in Germany and France.
To study the effectiveness of the app, investigators conducted a randomized controlled trial at the University Hospital Münster in Germany.
The study included 241 men who had scores of 21 or less on the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5).
About half of the participants were randomly assigned to get the app. The rest were placed on a waiting list for the technology and served as a control group.
Men who received the app also reported gains in measures of quality of life (20.5 vs −0.04) and patient activation (11.1 vs 0.64).
Nearly nine in 10 people who used the app did so several times per week, the researchers reported.
Sabine Kliesch, MD, with University Hospital Münster, led the study, which was presented at a poster session on April 8 at the EAU Congress in Paris.
Fully Reimbursed in Germany
In Germany, Kranus Edera has been included on a government list of digital health apps that are fully reimbursed by insurers, partly based on the results of the clinical trial. The cost there is €235 (about $255).
Patients typically notice improvements in 2-4 weeks, according to the company’s website. Patients who are taking a phosphodiesterase-5 enzyme inhibitor for ED may continue taking the medication, although they may no longer need it or they may be able to reduce the dose after treatment with the app, it says.
Kranus also has virtual treatments for incontinence in women and voiding dysfunction.
The app is meant to save doctors time by providing patients with detailed explanations and guidance within the app itself, said Laura Wiemer, MD, senior medical director of Kranus.
The app’s modules help reinforce guideline-recommended approaches to the treatment of ED “in playful ways with awards, motivational messages, and individual adjustments to help achieve better adherence and compliance of the patient,” Dr. Wiemer told this news organization.
Kranus plans to expand to the United States in 2024, she said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Little blue pill meets a little blue light.
A digital application can improve erectile function, according to new research presented at the European Association of Urology (EAU) Annual Congress on April 8, 2024.
Researchers developed a 12-week, self-managed program to treat erectile dysfunction (ED). The program is delivered to patients’ mobile devices and encourages users to do cardiovascular training, pelvic floor exercises, and physiotherapy. It also provides information about ED, sexual therapy, and stress management.
“The treatment of ED through physical activity and/or lifestyle changes is recommended in current European guidelines but is not well established in clinical practice,” according to the researchers.
App or Waitlist
The app, known as Kranus Edera, was created by Kranus Health. It is available by prescription in Germany and France.
To study the effectiveness of the app, investigators conducted a randomized controlled trial at the University Hospital Münster in Germany.
The study included 241 men who had scores of 21 or less on the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5).
About half of the participants were randomly assigned to get the app. The rest were placed on a waiting list for the technology and served as a control group.
Men who received the app also reported gains in measures of quality of life (20.5 vs −0.04) and patient activation (11.1 vs 0.64).
Nearly nine in 10 people who used the app did so several times per week, the researchers reported.
Sabine Kliesch, MD, with University Hospital Münster, led the study, which was presented at a poster session on April 8 at the EAU Congress in Paris.
Fully Reimbursed in Germany
In Germany, Kranus Edera has been included on a government list of digital health apps that are fully reimbursed by insurers, partly based on the results of the clinical trial. The cost there is €235 (about $255).
Patients typically notice improvements in 2-4 weeks, according to the company’s website. Patients who are taking a phosphodiesterase-5 enzyme inhibitor for ED may continue taking the medication, although they may no longer need it or they may be able to reduce the dose after treatment with the app, it says.
Kranus also has virtual treatments for incontinence in women and voiding dysfunction.
The app is meant to save doctors time by providing patients with detailed explanations and guidance within the app itself, said Laura Wiemer, MD, senior medical director of Kranus.
The app’s modules help reinforce guideline-recommended approaches to the treatment of ED “in playful ways with awards, motivational messages, and individual adjustments to help achieve better adherence and compliance of the patient,” Dr. Wiemer told this news organization.
Kranus plans to expand to the United States in 2024, she said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Little blue pill meets a little blue light.
A digital application can improve erectile function, according to new research presented at the European Association of Urology (EAU) Annual Congress on April 8, 2024.
Researchers developed a 12-week, self-managed program to treat erectile dysfunction (ED). The program is delivered to patients’ mobile devices and encourages users to do cardiovascular training, pelvic floor exercises, and physiotherapy. It also provides information about ED, sexual therapy, and stress management.
“The treatment of ED through physical activity and/or lifestyle changes is recommended in current European guidelines but is not well established in clinical practice,” according to the researchers.
App or Waitlist
The app, known as Kranus Edera, was created by Kranus Health. It is available by prescription in Germany and France.
To study the effectiveness of the app, investigators conducted a randomized controlled trial at the University Hospital Münster in Germany.
The study included 241 men who had scores of 21 or less on the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5).
About half of the participants were randomly assigned to get the app. The rest were placed on a waiting list for the technology and served as a control group.
Men who received the app also reported gains in measures of quality of life (20.5 vs −0.04) and patient activation (11.1 vs 0.64).
Nearly nine in 10 people who used the app did so several times per week, the researchers reported.
Sabine Kliesch, MD, with University Hospital Münster, led the study, which was presented at a poster session on April 8 at the EAU Congress in Paris.
Fully Reimbursed in Germany
In Germany, Kranus Edera has been included on a government list of digital health apps that are fully reimbursed by insurers, partly based on the results of the clinical trial. The cost there is €235 (about $255).
Patients typically notice improvements in 2-4 weeks, according to the company’s website. Patients who are taking a phosphodiesterase-5 enzyme inhibitor for ED may continue taking the medication, although they may no longer need it or they may be able to reduce the dose after treatment with the app, it says.
Kranus also has virtual treatments for incontinence in women and voiding dysfunction.
The app is meant to save doctors time by providing patients with detailed explanations and guidance within the app itself, said Laura Wiemer, MD, senior medical director of Kranus.
The app’s modules help reinforce guideline-recommended approaches to the treatment of ED “in playful ways with awards, motivational messages, and individual adjustments to help achieve better adherence and compliance of the patient,” Dr. Wiemer told this news organization.
Kranus plans to expand to the United States in 2024, she said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
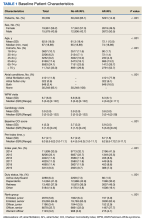
Association of Atrial Fibrillation and/or Flutter With Adverse Cardiac Outcomes and Mortality in Patients With Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome is characterized by the presence of ≥ 1 accessory pathways and the development of both recurrent paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) and supraventricular tachycardia that can lead to further malignant arrhythmias resulting in sudden cardiac death (SCD).1-7 Historically, incidental, ventricular pre-excitation on electrocardiogram has conferred a relatively low SCD risk in adults; however, newer WPW syndrome data suggest the endpoint may not be as benign as previously thought.7 The current literature has defined atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia triggering AF, rather than symptoms, as an independent risk factor for malignant arrhythmias. Still, long-term data detailing the association of AF with serious cardiac events and death in patients with WPW syndrome are still limited.1-7
While previous guidelines for the treatment of WPW syndrome only recommended routine electrophysiology testing (EPT) with liberal catheter ablation for symptomatic individuals, the 2015 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association/Heart Rhythm Society guidelines now suggest its potential benefit for risk stratification in the asymptomatic population.8-12 Given the limited existing data, more long-term studies are needed to corroborate the latest EPT recommendations before routinely applying them in practice. Furthermore, since concomitant AF can lead to adverse cardiac outcomes in patients with WPW syndrome, additional data evaluating this association are also necessary. In this study, we aimed to determine the impact of atrial fibrillation and/or flutter (AF/AFL) on adverse cardiac outcomes and mortality in patients with WPW syndrome.
METHODS
This study used data from the Military Health System (MHS) Database Repository. The MHS is one of the largest health care systems in the country and includes information on about 10 million active duty and retired military service members and their families (51% male; 49% female).13,14 Data were fully anonymized and complied in accordance with federal and state laws, including the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996. The Naval Medical Center Portsmouth Institutional Review Board approved this study.
Study Design
This retrospective, observational cohort study identified MHS patients with WPW syndrome from January 1, 2014, to December 31, 2019. Patients were included if they had ≥ 2 International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9) or International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) diagnosis codes for WPW syndrome (ICD-9, 426.7; ICD-10, I45.6) on separate dates; were aged ≥ 18 years at index date; and had ≥ 1 year of continuous eligibility prior to the index date (enrollment gaps ≤ 30 days were considered continuous). Patients were then divided into 2 subgroups by the presence or absence of AF/AFL using diagnostic codes. Patients were excluded if they had evidence of an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator, permanent pacemaker or were missing age or sex data. Patients were followed from index date until the first occurrence of the outcome of interest, MHS disenrollment, or the end of the study period.
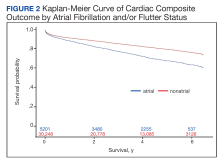
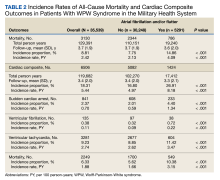
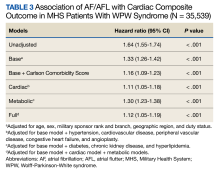
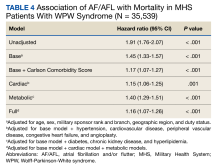
Cardiac composite outcomes comprised of sudden cardiac arrest (SCA), ventricular fibrillation (VF), ventricular tachycardia and death, as well as death specifically, were the outcomes of interest and assessed after index date using ICD-9 and ICD-10 codes. Death was defined as all-cause mortality. Time to event was calculated based on the date of the initial component from the composite outcome and date of death specifically for mortality. Those not experiencing an outcome were followed until MHS disenrollment or the end of the study period.
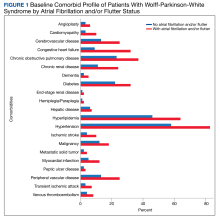
Various patient characteristics were assessed at index including age, sex, military sponsor (the patient’s active or retired duty member through which their dependent receives TRICARE benefits) rank and branch, geographic region, type of US Department of Defense beneficiary, and index year. Clinical characteristics were assessed over a 1-year baseline period prior to index date and included the number of cardiologist and clinical visits for WPW syndrome, Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) scores calculated from diagnostic codes outlined in the Quan coding method, and preindex time.15 Comorbidities were assessed at baseline and defined as having ≥ 1 ICD-9 or ICD-10 code for a corresponding condition within 1 year prior to index.
Statistical Analysis
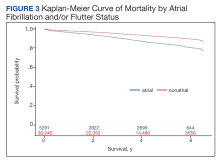
Baseline characteristics were assessed and descriptive statistics for categorical and continuous variables were presented accordingly. To assess bivariate association with exposure, χ2 tests were used to compare categorical variables, while t tests were used to compare continuous variables by exposure status. Incidence proportions and rates were reported for each outcome of interest. Kaplan-Meier curves were constructed to assess the bivariate association between exposure and study outcomes. Cox proportional hazard modeling was performed to estimate the association between AF/AFL and time to each of the outcomes. Multiple models were designed to assess cardiac and metabolic covariates, in addition to baseline characteristics. This included a base model adjusted for age, sex, military sponsor rank and branch, geographic region, and duty status.
Additional models adjusted for cardiac and metabolic confounders and CCI score. A comprehensive model included the base, cardiac, and metabolic covariates. Multicollinearity between covariates was assessed. Variables with a variance inflation factor > 4 or a tolerance level < 0.1 were added to the models. Cox proportional hazard models were used to estimate the unadjusted and adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% CIs of the association between AF/AFL and the study outcomes. Data were analyzed using SAS, version 9.4 for Windows.
RESULTS
From 2014 through 2019, 35,539 patients with WPW syndrome were identified in the MHS, 5291 had AF/AFL (14.9%); 19,961 were female (56.2%), the mean (SD) age was 62.9 (18.0) years, and 11,742 were aged ≥ 75 years (33.0%) (Table 1).
There were 4121 (11.6%), 322 (0.9%), and 848 (2.4%) patients with AF, AFL, and both arrhythmias, respectively. The mean (SD) number of cardiology visits was 3.9 (3.0). The mean (SD) baseline CCI score for the AF/AFL subgroup was 5.9 (3.5) vs 3.7 (2.2) for the non-AF/AFL subgroup (P < .001). The most prevalent comorbid conditions were hypertension, hyperlipidemia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and diabetes (P < .001) (Figure 1).
Composite Outcomes
In the overall cohort, during a mean (SD) follow-up time of 3.4 (2.0) years comprising 119,682 total person-years, the components of the composite outcome occurred 6506 times with an incidence rate of 5.44 per 100 person-years. Ventricular tachycardia was the most common event, occurring 3281 times with an incidence rate of 2.74 per 100 person-years. SCA and VF occurred 841 and 135 times with incidence rates of 0.70 and 0.11 per 100 person-years, respectively. Death was the initial event 2249 times with an incidence rate of 1.88 per 100 person-years. Figure 2 shows the Kaplan-Meier curve of cardiac composite outcome by AF/AFL status.
The subgroup with AF/AFL comprised 17,412 total person-years and 1424 cardiac composite incidences compared with 102,270 person years and 5082 incidences in the no AF/AFL group (Table 2). Comparing AF/AFL vs no AF/AFL incidence rates were 8.18 vs 4.97 per 100 person-years, respectively (P < .001). SCA and VF occurred 233 and 38 times and respectively had incidence rates of 1.34 and 0.22 per 100 person-years in the AF/AFL group vs 0.59 and 0.09 per 100 person-years in the no AF/AFL group (P < .001). There were 549 deaths and a 3.15 per 100 person-years incidence rate in the AF/AFL group vs 1700 deaths and a 1.66 incidence rate in the no AF/AFL group (P < .001).
The HR for the composite outcome in the base model was 1.33 (95% CI, 1.26-1.42, P < .001) (Table 3). The association between AF/AFL and the composite outcome remained significant after adjusting for additional metabolic and cardiac covariates. The HRs for the metabolic and cardiac models were 1.30 (95% CI, 1.23-1.38, P < .001) and 1.11 (95% CI, 1.05-1.18, P < .001), respectively. After adjusting for the full model, the HR was 1.12 (95% CI, 1.05-1.19, P < .001).
Mortality
Over the 6-year study period, there was a lower survival probability for patients with AF/AFL. In the overall cohort, during a mean (SD) follow-up time of 3.7 (1.9) years comprising 129,391 total person-years, there were 3130 (8.8%) deaths and an incidence rate of 2.42 per 100 person-years. Death occurred 786 times with a 4.09 incidence rate per 100 person-years in the AF/AFL vs 2344 deaths and a 2.13 incidence rate per 100 person-years in the no AF/AFL group (P < .001). In the non-AF/AFL subgroup, death occurred 2344 times during a mean (SD) follow-up of 3.7 (1.9) years comprising 110,151 total person-years. Figure 3 shows the Kaplan-Meier curve of mortality by AF/AFL status.
After adjusting for the base, metabolic and cardiac covariates, the HRs for mortality were 1.45 (95% CI, 1.33-1.57, P < .001), 1.40 (95% CI, 1.29-1.51, P < .001) and 1.15 (95% CI, 1.06-1.25, P = .001), respectively (Table 4). The HR after adjusting for the full model was 1.16 (95% CI, 1.07-1.26, P < .001).
DISCUSSION
In this large retrospective cohort study, patients with WPW syndrome and comorbid AF/AFL had a significantly higher association with the cardiac composite outcome and death during a 3-year follow-up period when compared with patients without AF/AFL. After adjusting for confounding variables, the AF/AFL subgroup maintained a 12% and 16% higher association with the composite outcome and mortality, respectively. There was minimal difference in confounding effects between demographic data and metabolic profiles, suggesting one may serve as a proxy for the other.
To our knowledge, this is the largest WPW syndrome cohort study evaluating cardiac outcomes and mortality to date. Although previous research has shown the relatively low and mostly anecdotal SCD incidence within this population, our results demonstrate a higher association of adverse cardiac outcomes and death in an AF/AFL subgroup.16-18 Notably, in this study the AF/AFL cohort was older and had higher CCI scores than their counterparts (P < .001), thus inferring an inherently greater degree of morbidity and 10-year mortality risk. Our study is also unique in that the mean patient age was significantly older than previously reported (63 vs 27 years), which may suggest a longer living history of both ventricular pre-excitation and the comorbidities outlined in Figure 1.19 Given these age discrepancies, it is possible that our overall study population was still relatively low risk and that not all reported deaths were necessarily related to WPW syndrome. Despite these assumptions, when comparing the WPW syndrome subgroups, we still found the AF/AFL cohort maintained a statistically significant higher association with the 2 study outcomes, even after adjusting for the greater presence of comorbidities. This suggests that the presence of AF/AFL may still portend a worse prognosis in patients with WPW syndrome.
Although the association of AF and development of VF in patients with WPW syndrome—due to rapid conduction over the accessory pathway(s)—was first reported > 40 years ago, there has still been few large, long-term data studies exploring mortality in this cohort.19-25 Furthermore, even though the current literature attributes the development of AF with the electrophysiologic properties of the accessory pathway, as well as intrinsic atrial architecture and muscle vulnerability, there is still equivocal consensus regarding EPT screening and ablation indications for asymptomatic patients with WPW syndrome.26-28 Notably, Pappone and colleagues demonstrated the potential benefit of liberal ablation indications for asymptomatic patients, arguing that the intrinsic electrophysiologic properties of the accessory pathway—ie, short accessory-pathway antegrade effective refractory period, inducibility of atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia triggering AF, and multiple accessory pathway—rather than symptoms, are independent predictors of developing malignant arrhythmia.1-5
These findings contradict those reported by Obeyesekere and colleagues, who concluded that the low SCD incidence rates in patients with WPW syndrome precluded routine invasive screening.19,28 They argued that Pappone and colleagues used malignant arrhythmia as a surrogate marker for death, and that the positive predictive value of a short accessory-pathway antegrade effective refractory period for developing malignant arrhythmia was lower than reported (15% vs 82%, respectively) and that its negative predictive value was 100%.1,19,28 Given these conflicting recommendations, we hope our data elucidates the higher association of adverse outcomes and support considerations for more intensive EPT indications in patients with WPW syndrome.
While our study does not report SCD incidence, it does provide robust and reliable mortality data that suggests a greater association of death within an AF/AFL subgroup. Our findings would support more liberal EPT recommendations in patients with WPW syndrome.1-5,8,9 In this study, the SCA incidence rate was more than double the rate in the AF/AFL cohort (P < .001) and is commonly the initial presenting event in WPW syndrome.9 Even though the reported SCD incidence rate is low in WPW syndrome, our data demonstrated an increased association of death within the AF/AFL cohort. Physicians should consider early risk stratification and ablation to prevent potential recurrent malignant arrhythmia leading to death.1-5,8,9,12,19,20
Limitations
As a retrospective study and without access to the National Death Index, we were unable to determine the exact cause or events leading to death and instead utilized all-cause mortality data. Subsequently, our observations may only demonstrate association, rather than causality, between AF/AFL and death in patients with WPW syndrome. Additionally, we could not distinguish between AF and AFL as the arrhythmia leading to death. However, since overall survivability was the outcome of interest, our adjusted HR models were still able to demonstrate the increased association of the composite outcome and death within an AF/AFL cohort.
Although a large cohort was analyzed, due to the constraints of utilizing diagnostic codes to determine study outcomes, we could not distinguish between symptomatic and asymptomatic patients, nor how they were managed prior to the outcome event. However, as recent literature demonstrates, updated predictors of malignant arrhythmia and decisions for early EPT are similar for both symptomatic and asymptomatic patients and should be driven by the intrinsic electrophysiologic properties of the accessory pathway, rather than symptomatology; thus, our inability to discern this should have negligible consequence in determining when to perform risk stratification and ablation.1
MHS eligible patients have direct access to care; the generalizability of our data may not necessarily correspond to a community population with lower socioeconomic status (we did adjust for military sponsor rank which has been used as a proxy), reduced access to care, or uninsured individuals. However, the prevalence of WPW syndrome within our cohort was comparable to the general population, 0.4% vs 0.1%-0.3%, respectively.13,14,19 Similarly, the incidence of AF within our population was comparable to the general population, 15% vs 16%-26%, respectively.23 These similar data points suggest our results may apply beyond MHS patients.
CONCLUSIONS
Patients with WPW syndrome and AF/AFL have a higher association with adverse cardiac outcomes and death. Despite previously reported low SCD incidence rates in this population, our study demonstrates the increased association of mortality in an AF/AFL cohort. The limitations of utilizing all-cause mortality data necessitate further investigation into the etiology behind the deaths in our study population. Since ventricular pre-excitation can predispose patients to AF and potentially lead to malignant arrhythmia and SCD, understanding the cause of mortality will allow physicians to determine the appropriate monitoring and intervention strategies to improve outcomes in this population. Our results suggest consideration for more aggressive EPT screening and ablation recommendations in patients with WPW syndrome may be warranted.
1. Pappone C, Vicedomini G, Manguso F, et al. The natural history of WPW syndrome. Eur Heart J Suppl. 2015; 17 (Supplement A):A8-A11.doi:10.1093/eurheartj/suv004
2. Pappone C, Vicedomini G, Manguso F, et al. Risk of malignant arrhythmias in initially symptomatic patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: results of a prospective long-term electrophysiological follow-up study. Circulation. 2012;125(5):661-668. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.065722
3. Pappone C, Santinelli V, Rosanio S, et al. Usefulness of invasive electrophysiologic testing to stratify the risk of arrhythmic events in asymptomatic patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White pattern: results from a large prospective long-term follow-up study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;41(2):239-244. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(02)02706-7
4. Pappone C, Vicedomini G, Manguso F, et al. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome in the era of catheter ablation: insights from a registry study of 2169 patients. Circulation. 2014;130(10):811-819. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.011154
5. Pappone C, Santinelli V, Manguso F, et al. A randomized study of prophylactic catheter ablation in asymptomatic patients with the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(19):1803-1811. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa035345
6. Santinelli V, Radinovic A, Manguso F, et al. Asymptomatic ventricular preexcitation: a long-term prospective follow-up study of 293 adult patients. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2009;2(2):102-107. doi:10.1161/CIRCEP.108.827550
7. Santinelli V, Radinovic A, Manguso F, et al. The natural history of asymptomatic ventricular pre-excitation a long-term prospective follow-up study of 184 asymptomatic children. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53(3):275-280. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2008.09.037
8. Al-Khatib SM, Arshad A, Balk EM, et al. Risk Stratification for Arrhythmic Events in Patients With Asymptomatic Pre-Excitation: A Systematic Review for the 2015 ACC/AHA/HRS Guideline for the Management of Adult Patients With Supraventricular Tachycardia: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;67(13):1624-1638. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2015.09.018
9. Blomström-Lundqvist C, Scheinman MM, Aliot EM, et al. ACC/AHA/ESC guidelines for the management of patients with supraventricular arrhythmias--executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Develop Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Supraventricular Arrhythmias). Circulation. 2003;108(15):1871-1909.doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000091380.04100.84
10. Pediatric and Congenital Electrophysiology Society (PACES); Heart Rhythm Society (HRS); American College of Cardiology Foundation (ACCF); PACES/HRS expert consensus statement on the management of the asymptomatic young patient with a Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW, ventricular preexcitation) electrocardiographic pattern: developed in partnership between the Pediatric and Congenital Electrophysiology Society (PACES) and the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS). Endorsed by the governing bodies of PACES, HRS, the American College of Cardiology Foundation (ACCF), the American Heart Association (AHA), the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), and the Canadian Heart Rhythm Society (CHRS). Heart Rhythm. 2012;9(6):1006-1024. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2012.03.050
11. Cohen M, Triedman J. Guidelines for management of asymptomatic ventricular pre-excitation: brave new world or Pandora’s box?. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2014;7(2):187-189. doi:10.1161/CIRCEP.114.001528
12. Svendsen JH, Dagres N, Dobreanu D, et al. Current strategy for treatment of patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome and asymptomatic preexcitation in Europe: European Heart Rhythm Association survey. Europace. 2013;15(5):750-753. doi:10.1093/europace/eut094
13. Gimbel RW, Pangaro L, Barbour G. America’s “undiscovered” laboratory for health services research. Med Care. 2010;48(8):751-756. doi:10.1097/MLR.0b013e3181e35be8
14. Dorrance KA, Ramchandani S, Neil N, Fisher H. Leveraging the military health system as a laboratory for health care reform. Mil Med. 2013;178(2):142-145. doi:10.7205/milmed-d-12-00168
15. Quan H, Sundararajan V, Halfon P, et al. Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data. Med Care. 2005;43(11):1130-1139. doi:10.1097/01.mlr.0000182534.19832.83
16. Finocchiaro G, Papadakis M, Behr ER, Sharma S, Sheppard M. Sudden Cardiac Death in Pre-Excitation and Wolff-Parkinson-White: Demographic and Clinical Features. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;69(12):1644-1645. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2017.01.023
17. Munger TM, Packer DL, Hammill SC, et al. A population study of the natural history of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1953-1989. Circulation. 1993;87(3):866-873. doi:10.1161/01.cir.87.3.866
18. Fitzsimmons PJ, McWhirter PD, Peterson DW, Kruyer WB. The natural history of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome in 228 military aviators: a long-term follow-up of 22 years. Am Heart J. 2001;142(3):530-536. doi:10.1067/mhj.2001.117779
19. Obeyesekere MN, Leong-Sit P, Massel D, et al. Risk of arrhythmia and sudden death in patients with asymptomatic preexcitation: a meta-analysis. Circulation. 2012;125(19):2308-2315. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.055350
20. Waspe LE, Brodman R, Kim SG, Fisher JD. Susceptibility to atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachyarrhythmia in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: role of the accessory pathway. Am Heart J. 1986;112(6):1141-1152. doi:10.1016/0002-8703(86)90342-x
21. Pietersen AH, Andersen ED, Sandøe E. Atrial fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 1992;70(5):38A-43A. doi:10.1016/0002-9149(92)91076-g
22. Della Bella P, Brugada P, Talajic M, et al. Atrial fibrillation in patients with an accessory pathway: importance of the conduction properties of the accessory pathway. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1991;17(6):1352-1356. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(10)80146-9
23. Fujimura O, Klein GJ, Yee R, Sharma AD. Mode of onset of atrial fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: how important is the accessory pathway?. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1990;15(5):1082-1086. doi:10.1016/0735-1097(90)90244-j
24. Montoya PT, Brugada P, Smeets J, et al. Ventricular fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Eur Heart J. 1991;12(2):144-150. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a059860
25. Klein GJ, Bashore TM, Sellers TD, Pritchett EL, Smith WM, Gallagher JJ. Ventricular fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1979;301(20):1080-1085. doi:10.1056/NEJM197911153012003
26. Centurion OA. Atrial Fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome. J Atr Fibrillation. 2011;4(1):287. Published 2011 May 4. doi:10.4022/jafib.287
27. Song C, Guo Y, Zheng X, et al. Prognostic Significance and Risk of Atrial Fibrillation of Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome in Patients With Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol. 2018;122(9):1546-1550. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2018.07.021
28. Obeyesekere M, Gula LJ, Skanes AC, Leong-Sit P, Klein GJ. Risk of sudden death in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: how high is the risk?. Circulation. 2012;125(5):659-660. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.085159
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome is characterized by the presence of ≥ 1 accessory pathways and the development of both recurrent paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) and supraventricular tachycardia that can lead to further malignant arrhythmias resulting in sudden cardiac death (SCD).1-7 Historically, incidental, ventricular pre-excitation on electrocardiogram has conferred a relatively low SCD risk in adults; however, newer WPW syndrome data suggest the endpoint may not be as benign as previously thought.7 The current literature has defined atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia triggering AF, rather than symptoms, as an independent risk factor for malignant arrhythmias. Still, long-term data detailing the association of AF with serious cardiac events and death in patients with WPW syndrome are still limited.1-7
While previous guidelines for the treatment of WPW syndrome only recommended routine electrophysiology testing (EPT) with liberal catheter ablation for symptomatic individuals, the 2015 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association/Heart Rhythm Society guidelines now suggest its potential benefit for risk stratification in the asymptomatic population.8-12 Given the limited existing data, more long-term studies are needed to corroborate the latest EPT recommendations before routinely applying them in practice. Furthermore, since concomitant AF can lead to adverse cardiac outcomes in patients with WPW syndrome, additional data evaluating this association are also necessary. In this study, we aimed to determine the impact of atrial fibrillation and/or flutter (AF/AFL) on adverse cardiac outcomes and mortality in patients with WPW syndrome.
METHODS
This study used data from the Military Health System (MHS) Database Repository. The MHS is one of the largest health care systems in the country and includes information on about 10 million active duty and retired military service members and their families (51% male; 49% female).13,14 Data were fully anonymized and complied in accordance with federal and state laws, including the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996. The Naval Medical Center Portsmouth Institutional Review Board approved this study.
Study Design
This retrospective, observational cohort study identified MHS patients with WPW syndrome from January 1, 2014, to December 31, 2019. Patients were included if they had ≥ 2 International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9) or International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) diagnosis codes for WPW syndrome (ICD-9, 426.7; ICD-10, I45.6) on separate dates; were aged ≥ 18 years at index date; and had ≥ 1 year of continuous eligibility prior to the index date (enrollment gaps ≤ 30 days were considered continuous). Patients were then divided into 2 subgroups by the presence or absence of AF/AFL using diagnostic codes. Patients were excluded if they had evidence of an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator, permanent pacemaker or were missing age or sex data. Patients were followed from index date until the first occurrence of the outcome of interest, MHS disenrollment, or the end of the study period.
Cardiac composite outcomes comprised of sudden cardiac arrest (SCA), ventricular fibrillation (VF), ventricular tachycardia and death, as well as death specifically, were the outcomes of interest and assessed after index date using ICD-9 and ICD-10 codes. Death was defined as all-cause mortality. Time to event was calculated based on the date of the initial component from the composite outcome and date of death specifically for mortality. Those not experiencing an outcome were followed until MHS disenrollment or the end of the study period.
Various patient characteristics were assessed at index including age, sex, military sponsor (the patient’s active or retired duty member through which their dependent receives TRICARE benefits) rank and branch, geographic region, type of US Department of Defense beneficiary, and index year. Clinical characteristics were assessed over a 1-year baseline period prior to index date and included the number of cardiologist and clinical visits for WPW syndrome, Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) scores calculated from diagnostic codes outlined in the Quan coding method, and preindex time.15 Comorbidities were assessed at baseline and defined as having ≥ 1 ICD-9 or ICD-10 code for a corresponding condition within 1 year prior to index.
Statistical Analysis
Baseline characteristics were assessed and descriptive statistics for categorical and continuous variables were presented accordingly. To assess bivariate association with exposure, χ2 tests were used to compare categorical variables, while t tests were used to compare continuous variables by exposure status. Incidence proportions and rates were reported for each outcome of interest. Kaplan-Meier curves were constructed to assess the bivariate association between exposure and study outcomes. Cox proportional hazard modeling was performed to estimate the association between AF/AFL and time to each of the outcomes. Multiple models were designed to assess cardiac and metabolic covariates, in addition to baseline characteristics. This included a base model adjusted for age, sex, military sponsor rank and branch, geographic region, and duty status.
Additional models adjusted for cardiac and metabolic confounders and CCI score. A comprehensive model included the base, cardiac, and metabolic covariates. Multicollinearity between covariates was assessed. Variables with a variance inflation factor > 4 or a tolerance level < 0.1 were added to the models. Cox proportional hazard models were used to estimate the unadjusted and adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% CIs of the association between AF/AFL and the study outcomes. Data were analyzed using SAS, version 9.4 for Windows.
RESULTS
From 2014 through 2019, 35,539 patients with WPW syndrome were identified in the MHS, 5291 had AF/AFL (14.9%); 19,961 were female (56.2%), the mean (SD) age was 62.9 (18.0) years, and 11,742 were aged ≥ 75 years (33.0%) (Table 1).
There were 4121 (11.6%), 322 (0.9%), and 848 (2.4%) patients with AF, AFL, and both arrhythmias, respectively. The mean (SD) number of cardiology visits was 3.9 (3.0). The mean (SD) baseline CCI score for the AF/AFL subgroup was 5.9 (3.5) vs 3.7 (2.2) for the non-AF/AFL subgroup (P < .001). The most prevalent comorbid conditions were hypertension, hyperlipidemia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and diabetes (P < .001) (Figure 1).
Composite Outcomes
In the overall cohort, during a mean (SD) follow-up time of 3.4 (2.0) years comprising 119,682 total person-years, the components of the composite outcome occurred 6506 times with an incidence rate of 5.44 per 100 person-years. Ventricular tachycardia was the most common event, occurring 3281 times with an incidence rate of 2.74 per 100 person-years. SCA and VF occurred 841 and 135 times with incidence rates of 0.70 and 0.11 per 100 person-years, respectively. Death was the initial event 2249 times with an incidence rate of 1.88 per 100 person-years. Figure 2 shows the Kaplan-Meier curve of cardiac composite outcome by AF/AFL status.
The subgroup with AF/AFL comprised 17,412 total person-years and 1424 cardiac composite incidences compared with 102,270 person years and 5082 incidences in the no AF/AFL group (Table 2). Comparing AF/AFL vs no AF/AFL incidence rates were 8.18 vs 4.97 per 100 person-years, respectively (P < .001). SCA and VF occurred 233 and 38 times and respectively had incidence rates of 1.34 and 0.22 per 100 person-years in the AF/AFL group vs 0.59 and 0.09 per 100 person-years in the no AF/AFL group (P < .001). There were 549 deaths and a 3.15 per 100 person-years incidence rate in the AF/AFL group vs 1700 deaths and a 1.66 incidence rate in the no AF/AFL group (P < .001).
The HR for the composite outcome in the base model was 1.33 (95% CI, 1.26-1.42, P < .001) (Table 3). The association between AF/AFL and the composite outcome remained significant after adjusting for additional metabolic and cardiac covariates. The HRs for the metabolic and cardiac models were 1.30 (95% CI, 1.23-1.38, P < .001) and 1.11 (95% CI, 1.05-1.18, P < .001), respectively. After adjusting for the full model, the HR was 1.12 (95% CI, 1.05-1.19, P < .001).
Mortality
Over the 6-year study period, there was a lower survival probability for patients with AF/AFL. In the overall cohort, during a mean (SD) follow-up time of 3.7 (1.9) years comprising 129,391 total person-years, there were 3130 (8.8%) deaths and an incidence rate of 2.42 per 100 person-years. Death occurred 786 times with a 4.09 incidence rate per 100 person-years in the AF/AFL vs 2344 deaths and a 2.13 incidence rate per 100 person-years in the no AF/AFL group (P < .001). In the non-AF/AFL subgroup, death occurred 2344 times during a mean (SD) follow-up of 3.7 (1.9) years comprising 110,151 total person-years. Figure 3 shows the Kaplan-Meier curve of mortality by AF/AFL status.
After adjusting for the base, metabolic and cardiac covariates, the HRs for mortality were 1.45 (95% CI, 1.33-1.57, P < .001), 1.40 (95% CI, 1.29-1.51, P < .001) and 1.15 (95% CI, 1.06-1.25, P = .001), respectively (Table 4). The HR after adjusting for the full model was 1.16 (95% CI, 1.07-1.26, P < .001).
DISCUSSION
In this large retrospective cohort study, patients with WPW syndrome and comorbid AF/AFL had a significantly higher association with the cardiac composite outcome and death during a 3-year follow-up period when compared with patients without AF/AFL. After adjusting for confounding variables, the AF/AFL subgroup maintained a 12% and 16% higher association with the composite outcome and mortality, respectively. There was minimal difference in confounding effects between demographic data and metabolic profiles, suggesting one may serve as a proxy for the other.
To our knowledge, this is the largest WPW syndrome cohort study evaluating cardiac outcomes and mortality to date. Although previous research has shown the relatively low and mostly anecdotal SCD incidence within this population, our results demonstrate a higher association of adverse cardiac outcomes and death in an AF/AFL subgroup.16-18 Notably, in this study the AF/AFL cohort was older and had higher CCI scores than their counterparts (P < .001), thus inferring an inherently greater degree of morbidity and 10-year mortality risk. Our study is also unique in that the mean patient age was significantly older than previously reported (63 vs 27 years), which may suggest a longer living history of both ventricular pre-excitation and the comorbidities outlined in Figure 1.19 Given these age discrepancies, it is possible that our overall study population was still relatively low risk and that not all reported deaths were necessarily related to WPW syndrome. Despite these assumptions, when comparing the WPW syndrome subgroups, we still found the AF/AFL cohort maintained a statistically significant higher association with the 2 study outcomes, even after adjusting for the greater presence of comorbidities. This suggests that the presence of AF/AFL may still portend a worse prognosis in patients with WPW syndrome.
Although the association of AF and development of VF in patients with WPW syndrome—due to rapid conduction over the accessory pathway(s)—was first reported > 40 years ago, there has still been few large, long-term data studies exploring mortality in this cohort.19-25 Furthermore, even though the current literature attributes the development of AF with the electrophysiologic properties of the accessory pathway, as well as intrinsic atrial architecture and muscle vulnerability, there is still equivocal consensus regarding EPT screening and ablation indications for asymptomatic patients with WPW syndrome.26-28 Notably, Pappone and colleagues demonstrated the potential benefit of liberal ablation indications for asymptomatic patients, arguing that the intrinsic electrophysiologic properties of the accessory pathway—ie, short accessory-pathway antegrade effective refractory period, inducibility of atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia triggering AF, and multiple accessory pathway—rather than symptoms, are independent predictors of developing malignant arrhythmia.1-5
These findings contradict those reported by Obeyesekere and colleagues, who concluded that the low SCD incidence rates in patients with WPW syndrome precluded routine invasive screening.19,28 They argued that Pappone and colleagues used malignant arrhythmia as a surrogate marker for death, and that the positive predictive value of a short accessory-pathway antegrade effective refractory period for developing malignant arrhythmia was lower than reported (15% vs 82%, respectively) and that its negative predictive value was 100%.1,19,28 Given these conflicting recommendations, we hope our data elucidates the higher association of adverse outcomes and support considerations for more intensive EPT indications in patients with WPW syndrome.
While our study does not report SCD incidence, it does provide robust and reliable mortality data that suggests a greater association of death within an AF/AFL subgroup. Our findings would support more liberal EPT recommendations in patients with WPW syndrome.1-5,8,9 In this study, the SCA incidence rate was more than double the rate in the AF/AFL cohort (P < .001) and is commonly the initial presenting event in WPW syndrome.9 Even though the reported SCD incidence rate is low in WPW syndrome, our data demonstrated an increased association of death within the AF/AFL cohort. Physicians should consider early risk stratification and ablation to prevent potential recurrent malignant arrhythmia leading to death.1-5,8,9,12,19,20
Limitations
As a retrospective study and without access to the National Death Index, we were unable to determine the exact cause or events leading to death and instead utilized all-cause mortality data. Subsequently, our observations may only demonstrate association, rather than causality, between AF/AFL and death in patients with WPW syndrome. Additionally, we could not distinguish between AF and AFL as the arrhythmia leading to death. However, since overall survivability was the outcome of interest, our adjusted HR models were still able to demonstrate the increased association of the composite outcome and death within an AF/AFL cohort.
Although a large cohort was analyzed, due to the constraints of utilizing diagnostic codes to determine study outcomes, we could not distinguish between symptomatic and asymptomatic patients, nor how they were managed prior to the outcome event. However, as recent literature demonstrates, updated predictors of malignant arrhythmia and decisions for early EPT are similar for both symptomatic and asymptomatic patients and should be driven by the intrinsic electrophysiologic properties of the accessory pathway, rather than symptomatology; thus, our inability to discern this should have negligible consequence in determining when to perform risk stratification and ablation.1
MHS eligible patients have direct access to care; the generalizability of our data may not necessarily correspond to a community population with lower socioeconomic status (we did adjust for military sponsor rank which has been used as a proxy), reduced access to care, or uninsured individuals. However, the prevalence of WPW syndrome within our cohort was comparable to the general population, 0.4% vs 0.1%-0.3%, respectively.13,14,19 Similarly, the incidence of AF within our population was comparable to the general population, 15% vs 16%-26%, respectively.23 These similar data points suggest our results may apply beyond MHS patients.
CONCLUSIONS
Patients with WPW syndrome and AF/AFL have a higher association with adverse cardiac outcomes and death. Despite previously reported low SCD incidence rates in this population, our study demonstrates the increased association of mortality in an AF/AFL cohort. The limitations of utilizing all-cause mortality data necessitate further investigation into the etiology behind the deaths in our study population. Since ventricular pre-excitation can predispose patients to AF and potentially lead to malignant arrhythmia and SCD, understanding the cause of mortality will allow physicians to determine the appropriate monitoring and intervention strategies to improve outcomes in this population. Our results suggest consideration for more aggressive EPT screening and ablation recommendations in patients with WPW syndrome may be warranted.
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome is characterized by the presence of ≥ 1 accessory pathways and the development of both recurrent paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) and supraventricular tachycardia that can lead to further malignant arrhythmias resulting in sudden cardiac death (SCD).1-7 Historically, incidental, ventricular pre-excitation on electrocardiogram has conferred a relatively low SCD risk in adults; however, newer WPW syndrome data suggest the endpoint may not be as benign as previously thought.7 The current literature has defined atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia triggering AF, rather than symptoms, as an independent risk factor for malignant arrhythmias. Still, long-term data detailing the association of AF with serious cardiac events and death in patients with WPW syndrome are still limited.1-7
While previous guidelines for the treatment of WPW syndrome only recommended routine electrophysiology testing (EPT) with liberal catheter ablation for symptomatic individuals, the 2015 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association/Heart Rhythm Society guidelines now suggest its potential benefit for risk stratification in the asymptomatic population.8-12 Given the limited existing data, more long-term studies are needed to corroborate the latest EPT recommendations before routinely applying them in practice. Furthermore, since concomitant AF can lead to adverse cardiac outcomes in patients with WPW syndrome, additional data evaluating this association are also necessary. In this study, we aimed to determine the impact of atrial fibrillation and/or flutter (AF/AFL) on adverse cardiac outcomes and mortality in patients with WPW syndrome.
METHODS
This study used data from the Military Health System (MHS) Database Repository. The MHS is one of the largest health care systems in the country and includes information on about 10 million active duty and retired military service members and their families (51% male; 49% female).13,14 Data were fully anonymized and complied in accordance with federal and state laws, including the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996. The Naval Medical Center Portsmouth Institutional Review Board approved this study.
Study Design
This retrospective, observational cohort study identified MHS patients with WPW syndrome from January 1, 2014, to December 31, 2019. Patients were included if they had ≥ 2 International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9) or International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) diagnosis codes for WPW syndrome (ICD-9, 426.7; ICD-10, I45.6) on separate dates; were aged ≥ 18 years at index date; and had ≥ 1 year of continuous eligibility prior to the index date (enrollment gaps ≤ 30 days were considered continuous). Patients were then divided into 2 subgroups by the presence or absence of AF/AFL using diagnostic codes. Patients were excluded if they had evidence of an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator, permanent pacemaker or were missing age or sex data. Patients were followed from index date until the first occurrence of the outcome of interest, MHS disenrollment, or the end of the study period.
Cardiac composite outcomes comprised of sudden cardiac arrest (SCA), ventricular fibrillation (VF), ventricular tachycardia and death, as well as death specifically, were the outcomes of interest and assessed after index date using ICD-9 and ICD-10 codes. Death was defined as all-cause mortality. Time to event was calculated based on the date of the initial component from the composite outcome and date of death specifically for mortality. Those not experiencing an outcome were followed until MHS disenrollment or the end of the study period.
Various patient characteristics were assessed at index including age, sex, military sponsor (the patient’s active or retired duty member through which their dependent receives TRICARE benefits) rank and branch, geographic region, type of US Department of Defense beneficiary, and index year. Clinical characteristics were assessed over a 1-year baseline period prior to index date and included the number of cardiologist and clinical visits for WPW syndrome, Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) scores calculated from diagnostic codes outlined in the Quan coding method, and preindex time.15 Comorbidities were assessed at baseline and defined as having ≥ 1 ICD-9 or ICD-10 code for a corresponding condition within 1 year prior to index.
Statistical Analysis
Baseline characteristics were assessed and descriptive statistics for categorical and continuous variables were presented accordingly. To assess bivariate association with exposure, χ2 tests were used to compare categorical variables, while t tests were used to compare continuous variables by exposure status. Incidence proportions and rates were reported for each outcome of interest. Kaplan-Meier curves were constructed to assess the bivariate association between exposure and study outcomes. Cox proportional hazard modeling was performed to estimate the association between AF/AFL and time to each of the outcomes. Multiple models were designed to assess cardiac and metabolic covariates, in addition to baseline characteristics. This included a base model adjusted for age, sex, military sponsor rank and branch, geographic region, and duty status.
Additional models adjusted for cardiac and metabolic confounders and CCI score. A comprehensive model included the base, cardiac, and metabolic covariates. Multicollinearity between covariates was assessed. Variables with a variance inflation factor > 4 or a tolerance level < 0.1 were added to the models. Cox proportional hazard models were used to estimate the unadjusted and adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% CIs of the association between AF/AFL and the study outcomes. Data were analyzed using SAS, version 9.4 for Windows.
RESULTS
From 2014 through 2019, 35,539 patients with WPW syndrome were identified in the MHS, 5291 had AF/AFL (14.9%); 19,961 were female (56.2%), the mean (SD) age was 62.9 (18.0) years, and 11,742 were aged ≥ 75 years (33.0%) (Table 1).
There were 4121 (11.6%), 322 (0.9%), and 848 (2.4%) patients with AF, AFL, and both arrhythmias, respectively. The mean (SD) number of cardiology visits was 3.9 (3.0). The mean (SD) baseline CCI score for the AF/AFL subgroup was 5.9 (3.5) vs 3.7 (2.2) for the non-AF/AFL subgroup (P < .001). The most prevalent comorbid conditions were hypertension, hyperlipidemia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and diabetes (P < .001) (Figure 1).
Composite Outcomes
In the overall cohort, during a mean (SD) follow-up time of 3.4 (2.0) years comprising 119,682 total person-years, the components of the composite outcome occurred 6506 times with an incidence rate of 5.44 per 100 person-years. Ventricular tachycardia was the most common event, occurring 3281 times with an incidence rate of 2.74 per 100 person-years. SCA and VF occurred 841 and 135 times with incidence rates of 0.70 and 0.11 per 100 person-years, respectively. Death was the initial event 2249 times with an incidence rate of 1.88 per 100 person-years. Figure 2 shows the Kaplan-Meier curve of cardiac composite outcome by AF/AFL status.
The subgroup with AF/AFL comprised 17,412 total person-years and 1424 cardiac composite incidences compared with 102,270 person years and 5082 incidences in the no AF/AFL group (Table 2). Comparing AF/AFL vs no AF/AFL incidence rates were 8.18 vs 4.97 per 100 person-years, respectively (P < .001). SCA and VF occurred 233 and 38 times and respectively had incidence rates of 1.34 and 0.22 per 100 person-years in the AF/AFL group vs 0.59 and 0.09 per 100 person-years in the no AF/AFL group (P < .001). There were 549 deaths and a 3.15 per 100 person-years incidence rate in the AF/AFL group vs 1700 deaths and a 1.66 incidence rate in the no AF/AFL group (P < .001).
The HR for the composite outcome in the base model was 1.33 (95% CI, 1.26-1.42, P < .001) (Table 3). The association between AF/AFL and the composite outcome remained significant after adjusting for additional metabolic and cardiac covariates. The HRs for the metabolic and cardiac models were 1.30 (95% CI, 1.23-1.38, P < .001) and 1.11 (95% CI, 1.05-1.18, P < .001), respectively. After adjusting for the full model, the HR was 1.12 (95% CI, 1.05-1.19, P < .001).
Mortality
Over the 6-year study period, there was a lower survival probability for patients with AF/AFL. In the overall cohort, during a mean (SD) follow-up time of 3.7 (1.9) years comprising 129,391 total person-years, there were 3130 (8.8%) deaths and an incidence rate of 2.42 per 100 person-years. Death occurred 786 times with a 4.09 incidence rate per 100 person-years in the AF/AFL vs 2344 deaths and a 2.13 incidence rate per 100 person-years in the no AF/AFL group (P < .001). In the non-AF/AFL subgroup, death occurred 2344 times during a mean (SD) follow-up of 3.7 (1.9) years comprising 110,151 total person-years. Figure 3 shows the Kaplan-Meier curve of mortality by AF/AFL status.
After adjusting for the base, metabolic and cardiac covariates, the HRs for mortality were 1.45 (95% CI, 1.33-1.57, P < .001), 1.40 (95% CI, 1.29-1.51, P < .001) and 1.15 (95% CI, 1.06-1.25, P = .001), respectively (Table 4). The HR after adjusting for the full model was 1.16 (95% CI, 1.07-1.26, P < .001).
DISCUSSION
In this large retrospective cohort study, patients with WPW syndrome and comorbid AF/AFL had a significantly higher association with the cardiac composite outcome and death during a 3-year follow-up period when compared with patients without AF/AFL. After adjusting for confounding variables, the AF/AFL subgroup maintained a 12% and 16% higher association with the composite outcome and mortality, respectively. There was minimal difference in confounding effects between demographic data and metabolic profiles, suggesting one may serve as a proxy for the other.
To our knowledge, this is the largest WPW syndrome cohort study evaluating cardiac outcomes and mortality to date. Although previous research has shown the relatively low and mostly anecdotal SCD incidence within this population, our results demonstrate a higher association of adverse cardiac outcomes and death in an AF/AFL subgroup.16-18 Notably, in this study the AF/AFL cohort was older and had higher CCI scores than their counterparts (P < .001), thus inferring an inherently greater degree of morbidity and 10-year mortality risk. Our study is also unique in that the mean patient age was significantly older than previously reported (63 vs 27 years), which may suggest a longer living history of both ventricular pre-excitation and the comorbidities outlined in Figure 1.19 Given these age discrepancies, it is possible that our overall study population was still relatively low risk and that not all reported deaths were necessarily related to WPW syndrome. Despite these assumptions, when comparing the WPW syndrome subgroups, we still found the AF/AFL cohort maintained a statistically significant higher association with the 2 study outcomes, even after adjusting for the greater presence of comorbidities. This suggests that the presence of AF/AFL may still portend a worse prognosis in patients with WPW syndrome.
Although the association of AF and development of VF in patients with WPW syndrome—due to rapid conduction over the accessory pathway(s)—was first reported > 40 years ago, there has still been few large, long-term data studies exploring mortality in this cohort.19-25 Furthermore, even though the current literature attributes the development of AF with the electrophysiologic properties of the accessory pathway, as well as intrinsic atrial architecture and muscle vulnerability, there is still equivocal consensus regarding EPT screening and ablation indications for asymptomatic patients with WPW syndrome.26-28 Notably, Pappone and colleagues demonstrated the potential benefit of liberal ablation indications for asymptomatic patients, arguing that the intrinsic electrophysiologic properties of the accessory pathway—ie, short accessory-pathway antegrade effective refractory period, inducibility of atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia triggering AF, and multiple accessory pathway—rather than symptoms, are independent predictors of developing malignant arrhythmia.1-5
These findings contradict those reported by Obeyesekere and colleagues, who concluded that the low SCD incidence rates in patients with WPW syndrome precluded routine invasive screening.19,28 They argued that Pappone and colleagues used malignant arrhythmia as a surrogate marker for death, and that the positive predictive value of a short accessory-pathway antegrade effective refractory period for developing malignant arrhythmia was lower than reported (15% vs 82%, respectively) and that its negative predictive value was 100%.1,19,28 Given these conflicting recommendations, we hope our data elucidates the higher association of adverse outcomes and support considerations for more intensive EPT indications in patients with WPW syndrome.
While our study does not report SCD incidence, it does provide robust and reliable mortality data that suggests a greater association of death within an AF/AFL subgroup. Our findings would support more liberal EPT recommendations in patients with WPW syndrome.1-5,8,9 In this study, the SCA incidence rate was more than double the rate in the AF/AFL cohort (P < .001) and is commonly the initial presenting event in WPW syndrome.9 Even though the reported SCD incidence rate is low in WPW syndrome, our data demonstrated an increased association of death within the AF/AFL cohort. Physicians should consider early risk stratification and ablation to prevent potential recurrent malignant arrhythmia leading to death.1-5,8,9,12,19,20
Limitations
As a retrospective study and without access to the National Death Index, we were unable to determine the exact cause or events leading to death and instead utilized all-cause mortality data. Subsequently, our observations may only demonstrate association, rather than causality, between AF/AFL and death in patients with WPW syndrome. Additionally, we could not distinguish between AF and AFL as the arrhythmia leading to death. However, since overall survivability was the outcome of interest, our adjusted HR models were still able to demonstrate the increased association of the composite outcome and death within an AF/AFL cohort.
Although a large cohort was analyzed, due to the constraints of utilizing diagnostic codes to determine study outcomes, we could not distinguish between symptomatic and asymptomatic patients, nor how they were managed prior to the outcome event. However, as recent literature demonstrates, updated predictors of malignant arrhythmia and decisions for early EPT are similar for both symptomatic and asymptomatic patients and should be driven by the intrinsic electrophysiologic properties of the accessory pathway, rather than symptomatology; thus, our inability to discern this should have negligible consequence in determining when to perform risk stratification and ablation.1
MHS eligible patients have direct access to care; the generalizability of our data may not necessarily correspond to a community population with lower socioeconomic status (we did adjust for military sponsor rank which has been used as a proxy), reduced access to care, or uninsured individuals. However, the prevalence of WPW syndrome within our cohort was comparable to the general population, 0.4% vs 0.1%-0.3%, respectively.13,14,19 Similarly, the incidence of AF within our population was comparable to the general population, 15% vs 16%-26%, respectively.23 These similar data points suggest our results may apply beyond MHS patients.
CONCLUSIONS
Patients with WPW syndrome and AF/AFL have a higher association with adverse cardiac outcomes and death. Despite previously reported low SCD incidence rates in this population, our study demonstrates the increased association of mortality in an AF/AFL cohort. The limitations of utilizing all-cause mortality data necessitate further investigation into the etiology behind the deaths in our study population. Since ventricular pre-excitation can predispose patients to AF and potentially lead to malignant arrhythmia and SCD, understanding the cause of mortality will allow physicians to determine the appropriate monitoring and intervention strategies to improve outcomes in this population. Our results suggest consideration for more aggressive EPT screening and ablation recommendations in patients with WPW syndrome may be warranted.
1. Pappone C, Vicedomini G, Manguso F, et al. The natural history of WPW syndrome. Eur Heart J Suppl. 2015; 17 (Supplement A):A8-A11.doi:10.1093/eurheartj/suv004
2. Pappone C, Vicedomini G, Manguso F, et al. Risk of malignant arrhythmias in initially symptomatic patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: results of a prospective long-term electrophysiological follow-up study. Circulation. 2012;125(5):661-668. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.065722
3. Pappone C, Santinelli V, Rosanio S, et al. Usefulness of invasive electrophysiologic testing to stratify the risk of arrhythmic events in asymptomatic patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White pattern: results from a large prospective long-term follow-up study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;41(2):239-244. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(02)02706-7
4. Pappone C, Vicedomini G, Manguso F, et al. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome in the era of catheter ablation: insights from a registry study of 2169 patients. Circulation. 2014;130(10):811-819. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.011154
5. Pappone C, Santinelli V, Manguso F, et al. A randomized study of prophylactic catheter ablation in asymptomatic patients with the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(19):1803-1811. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa035345
6. Santinelli V, Radinovic A, Manguso F, et al. Asymptomatic ventricular preexcitation: a long-term prospective follow-up study of 293 adult patients. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2009;2(2):102-107. doi:10.1161/CIRCEP.108.827550
7. Santinelli V, Radinovic A, Manguso F, et al. The natural history of asymptomatic ventricular pre-excitation a long-term prospective follow-up study of 184 asymptomatic children. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53(3):275-280. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2008.09.037
8. Al-Khatib SM, Arshad A, Balk EM, et al. Risk Stratification for Arrhythmic Events in Patients With Asymptomatic Pre-Excitation: A Systematic Review for the 2015 ACC/AHA/HRS Guideline for the Management of Adult Patients With Supraventricular Tachycardia: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;67(13):1624-1638. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2015.09.018
9. Blomström-Lundqvist C, Scheinman MM, Aliot EM, et al. ACC/AHA/ESC guidelines for the management of patients with supraventricular arrhythmias--executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Develop Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Supraventricular Arrhythmias). Circulation. 2003;108(15):1871-1909.doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000091380.04100.84
10. Pediatric and Congenital Electrophysiology Society (PACES); Heart Rhythm Society (HRS); American College of Cardiology Foundation (ACCF); PACES/HRS expert consensus statement on the management of the asymptomatic young patient with a Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW, ventricular preexcitation) electrocardiographic pattern: developed in partnership between the Pediatric and Congenital Electrophysiology Society (PACES) and the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS). Endorsed by the governing bodies of PACES, HRS, the American College of Cardiology Foundation (ACCF), the American Heart Association (AHA), the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), and the Canadian Heart Rhythm Society (CHRS). Heart Rhythm. 2012;9(6):1006-1024. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2012.03.050
11. Cohen M, Triedman J. Guidelines for management of asymptomatic ventricular pre-excitation: brave new world or Pandora’s box?. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2014;7(2):187-189. doi:10.1161/CIRCEP.114.001528
12. Svendsen JH, Dagres N, Dobreanu D, et al. Current strategy for treatment of patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome and asymptomatic preexcitation in Europe: European Heart Rhythm Association survey. Europace. 2013;15(5):750-753. doi:10.1093/europace/eut094
13. Gimbel RW, Pangaro L, Barbour G. America’s “undiscovered” laboratory for health services research. Med Care. 2010;48(8):751-756. doi:10.1097/MLR.0b013e3181e35be8
14. Dorrance KA, Ramchandani S, Neil N, Fisher H. Leveraging the military health system as a laboratory for health care reform. Mil Med. 2013;178(2):142-145. doi:10.7205/milmed-d-12-00168
15. Quan H, Sundararajan V, Halfon P, et al. Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data. Med Care. 2005;43(11):1130-1139. doi:10.1097/01.mlr.0000182534.19832.83
16. Finocchiaro G, Papadakis M, Behr ER, Sharma S, Sheppard M. Sudden Cardiac Death in Pre-Excitation and Wolff-Parkinson-White: Demographic and Clinical Features. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;69(12):1644-1645. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2017.01.023
17. Munger TM, Packer DL, Hammill SC, et al. A population study of the natural history of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1953-1989. Circulation. 1993;87(3):866-873. doi:10.1161/01.cir.87.3.866
18. Fitzsimmons PJ, McWhirter PD, Peterson DW, Kruyer WB. The natural history of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome in 228 military aviators: a long-term follow-up of 22 years. Am Heart J. 2001;142(3):530-536. doi:10.1067/mhj.2001.117779
19. Obeyesekere MN, Leong-Sit P, Massel D, et al. Risk of arrhythmia and sudden death in patients with asymptomatic preexcitation: a meta-analysis. Circulation. 2012;125(19):2308-2315. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.055350
20. Waspe LE, Brodman R, Kim SG, Fisher JD. Susceptibility to atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachyarrhythmia in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: role of the accessory pathway. Am Heart J. 1986;112(6):1141-1152. doi:10.1016/0002-8703(86)90342-x
21. Pietersen AH, Andersen ED, Sandøe E. Atrial fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 1992;70(5):38A-43A. doi:10.1016/0002-9149(92)91076-g
22. Della Bella P, Brugada P, Talajic M, et al. Atrial fibrillation in patients with an accessory pathway: importance of the conduction properties of the accessory pathway. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1991;17(6):1352-1356. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(10)80146-9
23. Fujimura O, Klein GJ, Yee R, Sharma AD. Mode of onset of atrial fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: how important is the accessory pathway?. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1990;15(5):1082-1086. doi:10.1016/0735-1097(90)90244-j
24. Montoya PT, Brugada P, Smeets J, et al. Ventricular fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Eur Heart J. 1991;12(2):144-150. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a059860
25. Klein GJ, Bashore TM, Sellers TD, Pritchett EL, Smith WM, Gallagher JJ. Ventricular fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1979;301(20):1080-1085. doi:10.1056/NEJM197911153012003
26. Centurion OA. Atrial Fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome. J Atr Fibrillation. 2011;4(1):287. Published 2011 May 4. doi:10.4022/jafib.287
27. Song C, Guo Y, Zheng X, et al. Prognostic Significance and Risk of Atrial Fibrillation of Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome in Patients With Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol. 2018;122(9):1546-1550. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2018.07.021
28. Obeyesekere M, Gula LJ, Skanes AC, Leong-Sit P, Klein GJ. Risk of sudden death in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: how high is the risk?. Circulation. 2012;125(5):659-660. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.085159
1. Pappone C, Vicedomini G, Manguso F, et al. The natural history of WPW syndrome. Eur Heart J Suppl. 2015; 17 (Supplement A):A8-A11.doi:10.1093/eurheartj/suv004
2. Pappone C, Vicedomini G, Manguso F, et al. Risk of malignant arrhythmias in initially symptomatic patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: results of a prospective long-term electrophysiological follow-up study. Circulation. 2012;125(5):661-668. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.065722
3. Pappone C, Santinelli V, Rosanio S, et al. Usefulness of invasive electrophysiologic testing to stratify the risk of arrhythmic events in asymptomatic patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White pattern: results from a large prospective long-term follow-up study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;41(2):239-244. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(02)02706-7
4. Pappone C, Vicedomini G, Manguso F, et al. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome in the era of catheter ablation: insights from a registry study of 2169 patients. Circulation. 2014;130(10):811-819. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.011154
5. Pappone C, Santinelli V, Manguso F, et al. A randomized study of prophylactic catheter ablation in asymptomatic patients with the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(19):1803-1811. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa035345
6. Santinelli V, Radinovic A, Manguso F, et al. Asymptomatic ventricular preexcitation: a long-term prospective follow-up study of 293 adult patients. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2009;2(2):102-107. doi:10.1161/CIRCEP.108.827550
7. Santinelli V, Radinovic A, Manguso F, et al. The natural history of asymptomatic ventricular pre-excitation a long-term prospective follow-up study of 184 asymptomatic children. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53(3):275-280. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2008.09.037
8. Al-Khatib SM, Arshad A, Balk EM, et al. Risk Stratification for Arrhythmic Events in Patients With Asymptomatic Pre-Excitation: A Systematic Review for the 2015 ACC/AHA/HRS Guideline for the Management of Adult Patients With Supraventricular Tachycardia: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;67(13):1624-1638. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2015.09.018
9. Blomström-Lundqvist C, Scheinman MM, Aliot EM, et al. ACC/AHA/ESC guidelines for the management of patients with supraventricular arrhythmias--executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Develop Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Supraventricular Arrhythmias). Circulation. 2003;108(15):1871-1909.doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000091380.04100.84
10. Pediatric and Congenital Electrophysiology Society (PACES); Heart Rhythm Society (HRS); American College of Cardiology Foundation (ACCF); PACES/HRS expert consensus statement on the management of the asymptomatic young patient with a Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW, ventricular preexcitation) electrocardiographic pattern: developed in partnership between the Pediatric and Congenital Electrophysiology Society (PACES) and the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS). Endorsed by the governing bodies of PACES, HRS, the American College of Cardiology Foundation (ACCF), the American Heart Association (AHA), the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), and the Canadian Heart Rhythm Society (CHRS). Heart Rhythm. 2012;9(6):1006-1024. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2012.03.050
11. Cohen M, Triedman J. Guidelines for management of asymptomatic ventricular pre-excitation: brave new world or Pandora’s box?. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2014;7(2):187-189. doi:10.1161/CIRCEP.114.001528
12. Svendsen JH, Dagres N, Dobreanu D, et al. Current strategy for treatment of patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome and asymptomatic preexcitation in Europe: European Heart Rhythm Association survey. Europace. 2013;15(5):750-753. doi:10.1093/europace/eut094
13. Gimbel RW, Pangaro L, Barbour G. America’s “undiscovered” laboratory for health services research. Med Care. 2010;48(8):751-756. doi:10.1097/MLR.0b013e3181e35be8
14. Dorrance KA, Ramchandani S, Neil N, Fisher H. Leveraging the military health system as a laboratory for health care reform. Mil Med. 2013;178(2):142-145. doi:10.7205/milmed-d-12-00168
15. Quan H, Sundararajan V, Halfon P, et al. Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data. Med Care. 2005;43(11):1130-1139. doi:10.1097/01.mlr.0000182534.19832.83
16. Finocchiaro G, Papadakis M, Behr ER, Sharma S, Sheppard M. Sudden Cardiac Death in Pre-Excitation and Wolff-Parkinson-White: Demographic and Clinical Features. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;69(12):1644-1645. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2017.01.023
17. Munger TM, Packer DL, Hammill SC, et al. A population study of the natural history of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1953-1989. Circulation. 1993;87(3):866-873. doi:10.1161/01.cir.87.3.866
18. Fitzsimmons PJ, McWhirter PD, Peterson DW, Kruyer WB. The natural history of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome in 228 military aviators: a long-term follow-up of 22 years. Am Heart J. 2001;142(3):530-536. doi:10.1067/mhj.2001.117779
19. Obeyesekere MN, Leong-Sit P, Massel D, et al. Risk of arrhythmia and sudden death in patients with asymptomatic preexcitation: a meta-analysis. Circulation. 2012;125(19):2308-2315. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.055350
20. Waspe LE, Brodman R, Kim SG, Fisher JD. Susceptibility to atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachyarrhythmia in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: role of the accessory pathway. Am Heart J. 1986;112(6):1141-1152. doi:10.1016/0002-8703(86)90342-x
21. Pietersen AH, Andersen ED, Sandøe E. Atrial fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 1992;70(5):38A-43A. doi:10.1016/0002-9149(92)91076-g
22. Della Bella P, Brugada P, Talajic M, et al. Atrial fibrillation in patients with an accessory pathway: importance of the conduction properties of the accessory pathway. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1991;17(6):1352-1356. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(10)80146-9
23. Fujimura O, Klein GJ, Yee R, Sharma AD. Mode of onset of atrial fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: how important is the accessory pathway?. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1990;15(5):1082-1086. doi:10.1016/0735-1097(90)90244-j
24. Montoya PT, Brugada P, Smeets J, et al. Ventricular fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Eur Heart J. 1991;12(2):144-150. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a059860
25. Klein GJ, Bashore TM, Sellers TD, Pritchett EL, Smith WM, Gallagher JJ. Ventricular fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1979;301(20):1080-1085. doi:10.1056/NEJM197911153012003
26. Centurion OA. Atrial Fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome. J Atr Fibrillation. 2011;4(1):287. Published 2011 May 4. doi:10.4022/jafib.287
27. Song C, Guo Y, Zheng X, et al. Prognostic Significance and Risk of Atrial Fibrillation of Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome in Patients With Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol. 2018;122(9):1546-1550. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2018.07.021
28. Obeyesekere M, Gula LJ, Skanes AC, Leong-Sit P, Klein GJ. Risk of sudden death in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: how high is the risk?. Circulation. 2012;125(5):659-660. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.085159
Higher BMI More CVD Protective in Older Adults With T2D?
Among adults with type 2 diabetes (T2D) older than 65 years, a body mass index (BMI) in the moderate overweight category (26-28) appears to offer better protection from cardiovascular death than does a BMI in the “normal” range, new data suggested.
On the other hand, the study findings also suggest that the “normal” range of 23-25 is optimal for middle-aged adults with T2D.
The findings reflect a previously demonstrated phenomenon called the “obesity paradox,” in which older people with overweight may have better outcomes than leaner people due to factors such as bone loss, frailty, and nutritional deficits, study lead author Shaoyong Xu, of Xiangyang Central Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Arts and Science, Xiangyang, China, told this news organization.
“In this era of population growth and aging, the question arises as to whether obesity or overweight can be beneficial in improving survival rates for older individuals with diabetes. This topic holds significant relevance due to the potential implications it has on weight management strategies for older adults. If overweight does not pose an increased risk of cardiovascular mortality, it may suggest that older individuals are not necessarily required to strive for weight loss to achieve so-called normal values.”
Moreover, Dr. Xu added, “inappropriate weight loss and being underweight could potentially elevate the risk of cardiovascular events, myocardial infarction, cerebral infarction, and all-cause mortality.”
Thus, he said, “while there are general guidelines recommending a BMI below 25, our findings suggest that personalized BMI targets may be more beneficial, particularly for different age groups and individuals with specific health conditions.”
Asked to comment, Ian J. Neeland, MD, director of cardiovascular prevention, University Hospitals Harrington Heart & Vascular Institute, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio, pointed out that older people who are underweight or in lower weight categories may be more likely to smoke or have undiagnosed cancer, or that “their BMI is not so much reflective of fat mass as of low muscle mass, or sarcopenia, and that is definitely a risk factor for adverse outcomes and risks. ... And those who have slightly higher BMIs may be maintaining muscle mass, even though they’re older, and therefore they have less risk.”
However, Dr. Neeland disagreed with the authors’ conclusions regarding “optimal” BMI. “Just because you have different risk categories based on BMI doesn’t mean that’s ‘optimal’ BMI. The way I would interpret this paper is that there’s an association of mildly overweight with better outcomes in adults who are over 65 with type 2 diabetes. We need to try to understand the mechanisms underlying that observation.”
Dr. Neeland advised that for an older person with T2D who has low muscle mass and frailty, “I wouldn’t recommend necessarily targeted weight loss in that person. But I would potentially recommend weight loss in addition to resistance training, muscle building, and endurance training, and therefore reducing fat mass. The goal would be not so much weight loss but reduction of body fat and maintaining and improving muscle health.”
U-Shaped Relationship Found Between Age, BMI, and Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Risk
The data come from the UK Biobank, a population-based prospective cohort study of adults in the United Kingdom. A total of 22,874 participants with baseline T2D were included in the current study. Baseline surveys were conducted between 2006 and 2010, and follow-up was a median of 12.52 years. During that time, 891 people died of CVD.
Hazard ratios were adjusted for baseline variables including age, sex, smoking history, alcohol consumption, level of physical exercise, and history of CVDs.
Compared with people with BMI a < 25 in the group who were aged 65 years or younger, those with a BMI of 25.0-29.9 had a 13% higher risk for cardiovascular death. However, among those older than 65 years, a BMI between 25.0 and 29.9 was associated with an 18% lower risk.
A U-shaped relationship was found between BMI and the risk for cardiovascular death, with an optimal BMI cutoff of 24.0 in the under-65 group and a 27.0 cutoff in the older group. Ranges of 23.0-25.0 in the under-65 group and 26.0-28 in the older group were associated with the lowest cardiovascular risk.
In contrast, there was a linear relationship between both waist circumference and waist-to-height ratio and the risk for cardiovascular death, making those more direct measures of adiposity, Dr. Xu told this news organization.
“For clinicians, our data underscores the importance of considering age when assessing BMI targets for cardiovascular health. Personalized treatment plans that account for age-specific BMI cutoffs and other risk factors may enhance patient outcomes and reduce CVD mortality,” Dr. Xu said.
However, he added, “while these findings suggest an optimal BMI range, it is crucial to acknowledge that these cutoff points may vary based on gender, race, and other factors. Our future studies will validate these findings in different populations and attempt to explain the mechanism by which the optimal nodal values exist in people with diabetes at different ages.”
Dr. Neeland cautioned, “I think more work needs to be done in terms of not just identifying the risk differences but understanding why and how to better risk stratify individuals and do personalized medicine. I think that’s important, but you have to have good data to support the strategies you’re going to use. These data are observational, and they’re a good start, but they wouldn’t directly impact practice at this point.”
The data will be presented at the European Congress on Obesity taking place May 12-15 in Venice, Italy.
The authors declared no competing interests. Study funding came from several sources, including the Young Talents Project of Hubei Provincial Health Commission, China, Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China, the Science and Technology Research Key Project of the Education Department of Hubei Province China, and the Sanuo Diabetes Charity Foundation, China, and the Xiangyang Science and Technology Plan Project, China. Dr. Neeland is a speaker and/or consultant for Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, Bayer, and Eli Lilly and Company.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Among adults with type 2 diabetes (T2D) older than 65 years, a body mass index (BMI) in the moderate overweight category (26-28) appears to offer better protection from cardiovascular death than does a BMI in the “normal” range, new data suggested.
On the other hand, the study findings also suggest that the “normal” range of 23-25 is optimal for middle-aged adults with T2D.
The findings reflect a previously demonstrated phenomenon called the “obesity paradox,” in which older people with overweight may have better outcomes than leaner people due to factors such as bone loss, frailty, and nutritional deficits, study lead author Shaoyong Xu, of Xiangyang Central Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Arts and Science, Xiangyang, China, told this news organization.
“In this era of population growth and aging, the question arises as to whether obesity or overweight can be beneficial in improving survival rates for older individuals with diabetes. This topic holds significant relevance due to the potential implications it has on weight management strategies for older adults. If overweight does not pose an increased risk of cardiovascular mortality, it may suggest that older individuals are not necessarily required to strive for weight loss to achieve so-called normal values.”
Moreover, Dr. Xu added, “inappropriate weight loss and being underweight could potentially elevate the risk of cardiovascular events, myocardial infarction, cerebral infarction, and all-cause mortality.”
Thus, he said, “while there are general guidelines recommending a BMI below 25, our findings suggest that personalized BMI targets may be more beneficial, particularly for different age groups and individuals with specific health conditions.”
Asked to comment, Ian J. Neeland, MD, director of cardiovascular prevention, University Hospitals Harrington Heart & Vascular Institute, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio, pointed out that older people who are underweight or in lower weight categories may be more likely to smoke or have undiagnosed cancer, or that “their BMI is not so much reflective of fat mass as of low muscle mass, or sarcopenia, and that is definitely a risk factor for adverse outcomes and risks. ... And those who have slightly higher BMIs may be maintaining muscle mass, even though they’re older, and therefore they have less risk.”
However, Dr. Neeland disagreed with the authors’ conclusions regarding “optimal” BMI. “Just because you have different risk categories based on BMI doesn’t mean that’s ‘optimal’ BMI. The way I would interpret this paper is that there’s an association of mildly overweight with better outcomes in adults who are over 65 with type 2 diabetes. We need to try to understand the mechanisms underlying that observation.”
Dr. Neeland advised that for an older person with T2D who has low muscle mass and frailty, “I wouldn’t recommend necessarily targeted weight loss in that person. But I would potentially recommend weight loss in addition to resistance training, muscle building, and endurance training, and therefore reducing fat mass. The goal would be not so much weight loss but reduction of body fat and maintaining and improving muscle health.”
U-Shaped Relationship Found Between Age, BMI, and Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Risk
The data come from the UK Biobank, a population-based prospective cohort study of adults in the United Kingdom. A total of 22,874 participants with baseline T2D were included in the current study. Baseline surveys were conducted between 2006 and 2010, and follow-up was a median of 12.52 years. During that time, 891 people died of CVD.
Hazard ratios were adjusted for baseline variables including age, sex, smoking history, alcohol consumption, level of physical exercise, and history of CVDs.
Compared with people with BMI a < 25 in the group who were aged 65 years or younger, those with a BMI of 25.0-29.9 had a 13% higher risk for cardiovascular death. However, among those older than 65 years, a BMI between 25.0 and 29.9 was associated with an 18% lower risk.
A U-shaped relationship was found between BMI and the risk for cardiovascular death, with an optimal BMI cutoff of 24.0 in the under-65 group and a 27.0 cutoff in the older group. Ranges of 23.0-25.0 in the under-65 group and 26.0-28 in the older group were associated with the lowest cardiovascular risk.
In contrast, there was a linear relationship between both waist circumference and waist-to-height ratio and the risk for cardiovascular death, making those more direct measures of adiposity, Dr. Xu told this news organization.
“For clinicians, our data underscores the importance of considering age when assessing BMI targets for cardiovascular health. Personalized treatment plans that account for age-specific BMI cutoffs and other risk factors may enhance patient outcomes and reduce CVD mortality,” Dr. Xu said.
However, he added, “while these findings suggest an optimal BMI range, it is crucial to acknowledge that these cutoff points may vary based on gender, race, and other factors. Our future studies will validate these findings in different populations and attempt to explain the mechanism by which the optimal nodal values exist in people with diabetes at different ages.”
Dr. Neeland cautioned, “I think more work needs to be done in terms of not just identifying the risk differences but understanding why and how to better risk stratify individuals and do personalized medicine. I think that’s important, but you have to have good data to support the strategies you’re going to use. These data are observational, and they’re a good start, but they wouldn’t directly impact practice at this point.”
The data will be presented at the European Congress on Obesity taking place May 12-15 in Venice, Italy.
The authors declared no competing interests. Study funding came from several sources, including the Young Talents Project of Hubei Provincial Health Commission, China, Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China, the Science and Technology Research Key Project of the Education Department of Hubei Province China, and the Sanuo Diabetes Charity Foundation, China, and the Xiangyang Science and Technology Plan Project, China. Dr. Neeland is a speaker and/or consultant for Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, Bayer, and Eli Lilly and Company.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Among adults with type 2 diabetes (T2D) older than 65 years, a body mass index (BMI) in the moderate overweight category (26-28) appears to offer better protection from cardiovascular death than does a BMI in the “normal” range, new data suggested.
On the other hand, the study findings also suggest that the “normal” range of 23-25 is optimal for middle-aged adults with T2D.
The findings reflect a previously demonstrated phenomenon called the “obesity paradox,” in which older people with overweight may have better outcomes than leaner people due to factors such as bone loss, frailty, and nutritional deficits, study lead author Shaoyong Xu, of Xiangyang Central Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Arts and Science, Xiangyang, China, told this news organization.
“In this era of population growth and aging, the question arises as to whether obesity or overweight can be beneficial in improving survival rates for older individuals with diabetes. This topic holds significant relevance due to the potential implications it has on weight management strategies for older adults. If overweight does not pose an increased risk of cardiovascular mortality, it may suggest that older individuals are not necessarily required to strive for weight loss to achieve so-called normal values.”
Moreover, Dr. Xu added, “inappropriate weight loss and being underweight could potentially elevate the risk of cardiovascular events, myocardial infarction, cerebral infarction, and all-cause mortality.”
Thus, he said, “while there are general guidelines recommending a BMI below 25, our findings suggest that personalized BMI targets may be more beneficial, particularly for different age groups and individuals with specific health conditions.”
Asked to comment, Ian J. Neeland, MD, director of cardiovascular prevention, University Hospitals Harrington Heart & Vascular Institute, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio, pointed out that older people who are underweight or in lower weight categories may be more likely to smoke or have undiagnosed cancer, or that “their BMI is not so much reflective of fat mass as of low muscle mass, or sarcopenia, and that is definitely a risk factor for adverse outcomes and risks. ... And those who have slightly higher BMIs may be maintaining muscle mass, even though they’re older, and therefore they have less risk.”
However, Dr. Neeland disagreed with the authors’ conclusions regarding “optimal” BMI. “Just because you have different risk categories based on BMI doesn’t mean that’s ‘optimal’ BMI. The way I would interpret this paper is that there’s an association of mildly overweight with better outcomes in adults who are over 65 with type 2 diabetes. We need to try to understand the mechanisms underlying that observation.”
Dr. Neeland advised that for an older person with T2D who has low muscle mass and frailty, “I wouldn’t recommend necessarily targeted weight loss in that person. But I would potentially recommend weight loss in addition to resistance training, muscle building, and endurance training, and therefore reducing fat mass. The goal would be not so much weight loss but reduction of body fat and maintaining and improving muscle health.”
U-Shaped Relationship Found Between Age, BMI, and Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Risk
The data come from the UK Biobank, a population-based prospective cohort study of adults in the United Kingdom. A total of 22,874 participants with baseline T2D were included in the current study. Baseline surveys were conducted between 2006 and 2010, and follow-up was a median of 12.52 years. During that time, 891 people died of CVD.
Hazard ratios were adjusted for baseline variables including age, sex, smoking history, alcohol consumption, level of physical exercise, and history of CVDs.
Compared with people with BMI a < 25 in the group who were aged 65 years or younger, those with a BMI of 25.0-29.9 had a 13% higher risk for cardiovascular death. However, among those older than 65 years, a BMI between 25.0 and 29.9 was associated with an 18% lower risk.
A U-shaped relationship was found between BMI and the risk for cardiovascular death, with an optimal BMI cutoff of 24.0 in the under-65 group and a 27.0 cutoff in the older group. Ranges of 23.0-25.0 in the under-65 group and 26.0-28 in the older group were associated with the lowest cardiovascular risk.
In contrast, there was a linear relationship between both waist circumference and waist-to-height ratio and the risk for cardiovascular death, making those more direct measures of adiposity, Dr. Xu told this news organization.
“For clinicians, our data underscores the importance of considering age when assessing BMI targets for cardiovascular health. Personalized treatment plans that account for age-specific BMI cutoffs and other risk factors may enhance patient outcomes and reduce CVD mortality,” Dr. Xu said.
However, he added, “while these findings suggest an optimal BMI range, it is crucial to acknowledge that these cutoff points may vary based on gender, race, and other factors. Our future studies will validate these findings in different populations and attempt to explain the mechanism by which the optimal nodal values exist in people with diabetes at different ages.”
Dr. Neeland cautioned, “I think more work needs to be done in terms of not just identifying the risk differences but understanding why and how to better risk stratify individuals and do personalized medicine. I think that’s important, but you have to have good data to support the strategies you’re going to use. These data are observational, and they’re a good start, but they wouldn’t directly impact practice at this point.”
The data will be presented at the European Congress on Obesity taking place May 12-15 in Venice, Italy.
The authors declared no competing interests. Study funding came from several sources, including the Young Talents Project of Hubei Provincial Health Commission, China, Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China, the Science and Technology Research Key Project of the Education Department of Hubei Province China, and the Sanuo Diabetes Charity Foundation, China, and the Xiangyang Science and Technology Plan Project, China. Dr. Neeland is a speaker and/or consultant for Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, Bayer, and Eli Lilly and Company.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Nontraditional Risk Factors Play an Outsized Role in Young Adult Stroke Risk
, new research showed.
The findings may offer insight into the increased incidence of stroke in adults under age 45, which has more than doubled in the past 20 years in high-income countries, while incidence in those over 45 has decreased.
Investigators believe the findings are important because most conventional prevention efforts focus on traditional risk factors.
“The younger they are at the time of stroke, the more likely their stroke is due to a nontraditional risk factor,” lead author Michelle Leppert, MD, an assistant professor of neurology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora, Colorado, said in a news release.
The findings were published online in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
Traditional Versus Nontraditional
The researchers retrospectively analyzed 2618 stroke cases (52% female; 73% ischemic stroke) that resulted in an inpatient admission and 7827 controls, all aged 18-55 years. Data came from the Colorado All Payer Claims Database between January 2012 and April 2019. Controls were matched by age, sex, and insurance type.
Traditional risk factors were defined as being a well-established risk factor for stroke that is routinely noted during stroke prevention screenings in older adults, including hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, sleep apnea, cardiovascular disease, alcohol, substance use disorder, and obesity.
Nontraditional risk factors were defined as those that are rarely cited as a cause of stroke in older adults, including migraines, malignancy, HIV, hepatitis, thrombophilia, autoimmune disease, vasculitis, sickle cell disease, heart valve disease, renal failure, and hormonal risk factors in women, such as oral contraceptives, pregnancy, or puerperium.
Overall, traditional risk factors were more common in stroke cases, with nontraditional factors playing a smaller role. However, among adults aged 18-34 years, more strokes were associated with nontraditional than traditional risk factors in men (31% vs 25%, respectively) and in women (43% vs 33%, respectively).
Migraine, the most common nontraditional risk factor for stroke in this younger age group, was found in 20% of men (odds ratio [OR], 3.9) and 35% of women (OR, 3.3).
Other notable nontraditional risk factors included heart valve disease in both men and women (OR, 3.1 and OR, 4.2, respectively); renal failure in men (OR, 8.9); and autoimmune diseases in women (OR, 8.8).
An Underestimate?
The contribution of nontraditional risk factors declined with age. After the age of 44, they were no longer significant. Hypertension was the most important traditional risk factor and increased in contribution with age.
“There have been many studies demonstrating the association between migraines and strokes, but to our knowledge, this study may be the first to demonstrate just how much stroke risk may be attributable to migraines,” Dr. Leppert said.
Overall, women had significantly more risk factors for stroke than men. Among controls, 52% and 34% of women had at least one traditional and nontraditional risk factors, respectively, compared with 48% and 22% in men.
The total contribution of nontraditional risk factors was likely an underestimate because some such factors, including the autoimmune disorder antiphospholipid syndrome and patent foramen ovale, “lacked reliable administrative algorithms” and could not be assessed in this study, the researchers noted.
Further research on how nontraditional risk factors affect strokes could lead to better prevention.
“We need to better understand the underlying mechanisms of these nontraditional risk factors to develop targeted interventions,” Dr. Leppert said.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health/National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences Colorado Clinical and Translational Science Award. Dr. Leppert reports receiving an American Heart Association Career Development Grant. Other disclosures are included in the original article.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research showed.
The findings may offer insight into the increased incidence of stroke in adults under age 45, which has more than doubled in the past 20 years in high-income countries, while incidence in those over 45 has decreased.
Investigators believe the findings are important because most conventional prevention efforts focus on traditional risk factors.
“The younger they are at the time of stroke, the more likely their stroke is due to a nontraditional risk factor,” lead author Michelle Leppert, MD, an assistant professor of neurology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora, Colorado, said in a news release.
The findings were published online in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
Traditional Versus Nontraditional
The researchers retrospectively analyzed 2618 stroke cases (52% female; 73% ischemic stroke) that resulted in an inpatient admission and 7827 controls, all aged 18-55 years. Data came from the Colorado All Payer Claims Database between January 2012 and April 2019. Controls were matched by age, sex, and insurance type.
Traditional risk factors were defined as being a well-established risk factor for stroke that is routinely noted during stroke prevention screenings in older adults, including hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, sleep apnea, cardiovascular disease, alcohol, substance use disorder, and obesity.
Nontraditional risk factors were defined as those that are rarely cited as a cause of stroke in older adults, including migraines, malignancy, HIV, hepatitis, thrombophilia, autoimmune disease, vasculitis, sickle cell disease, heart valve disease, renal failure, and hormonal risk factors in women, such as oral contraceptives, pregnancy, or puerperium.
Overall, traditional risk factors were more common in stroke cases, with nontraditional factors playing a smaller role. However, among adults aged 18-34 years, more strokes were associated with nontraditional than traditional risk factors in men (31% vs 25%, respectively) and in women (43% vs 33%, respectively).
Migraine, the most common nontraditional risk factor for stroke in this younger age group, was found in 20% of men (odds ratio [OR], 3.9) and 35% of women (OR, 3.3).
Other notable nontraditional risk factors included heart valve disease in both men and women (OR, 3.1 and OR, 4.2, respectively); renal failure in men (OR, 8.9); and autoimmune diseases in women (OR, 8.8).
An Underestimate?
The contribution of nontraditional risk factors declined with age. After the age of 44, they were no longer significant. Hypertension was the most important traditional risk factor and increased in contribution with age.
“There have been many studies demonstrating the association between migraines and strokes, but to our knowledge, this study may be the first to demonstrate just how much stroke risk may be attributable to migraines,” Dr. Leppert said.
Overall, women had significantly more risk factors for stroke than men. Among controls, 52% and 34% of women had at least one traditional and nontraditional risk factors, respectively, compared with 48% and 22% in men.
The total contribution of nontraditional risk factors was likely an underestimate because some such factors, including the autoimmune disorder antiphospholipid syndrome and patent foramen ovale, “lacked reliable administrative algorithms” and could not be assessed in this study, the researchers noted.
Further research on how nontraditional risk factors affect strokes could lead to better prevention.
“We need to better understand the underlying mechanisms of these nontraditional risk factors to develop targeted interventions,” Dr. Leppert said.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health/National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences Colorado Clinical and Translational Science Award. Dr. Leppert reports receiving an American Heart Association Career Development Grant. Other disclosures are included in the original article.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research showed.
The findings may offer insight into the increased incidence of stroke in adults under age 45, which has more than doubled in the past 20 years in high-income countries, while incidence in those over 45 has decreased.
Investigators believe the findings are important because most conventional prevention efforts focus on traditional risk factors.
“The younger they are at the time of stroke, the more likely their stroke is due to a nontraditional risk factor,” lead author Michelle Leppert, MD, an assistant professor of neurology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora, Colorado, said in a news release.
The findings were published online in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
Traditional Versus Nontraditional
The researchers retrospectively analyzed 2618 stroke cases (52% female; 73% ischemic stroke) that resulted in an inpatient admission and 7827 controls, all aged 18-55 years. Data came from the Colorado All Payer Claims Database between January 2012 and April 2019. Controls were matched by age, sex, and insurance type.
Traditional risk factors were defined as being a well-established risk factor for stroke that is routinely noted during stroke prevention screenings in older adults, including hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, sleep apnea, cardiovascular disease, alcohol, substance use disorder, and obesity.
Nontraditional risk factors were defined as those that are rarely cited as a cause of stroke in older adults, including migraines, malignancy, HIV, hepatitis, thrombophilia, autoimmune disease, vasculitis, sickle cell disease, heart valve disease, renal failure, and hormonal risk factors in women, such as oral contraceptives, pregnancy, or puerperium.
Overall, traditional risk factors were more common in stroke cases, with nontraditional factors playing a smaller role. However, among adults aged 18-34 years, more strokes were associated with nontraditional than traditional risk factors in men (31% vs 25%, respectively) and in women (43% vs 33%, respectively).
Migraine, the most common nontraditional risk factor for stroke in this younger age group, was found in 20% of men (odds ratio [OR], 3.9) and 35% of women (OR, 3.3).
Other notable nontraditional risk factors included heart valve disease in both men and women (OR, 3.1 and OR, 4.2, respectively); renal failure in men (OR, 8.9); and autoimmune diseases in women (OR, 8.8).
An Underestimate?
The contribution of nontraditional risk factors declined with age. After the age of 44, they were no longer significant. Hypertension was the most important traditional risk factor and increased in contribution with age.
“There have been many studies demonstrating the association between migraines and strokes, but to our knowledge, this study may be the first to demonstrate just how much stroke risk may be attributable to migraines,” Dr. Leppert said.
Overall, women had significantly more risk factors for stroke than men. Among controls, 52% and 34% of women had at least one traditional and nontraditional risk factors, respectively, compared with 48% and 22% in men.
The total contribution of nontraditional risk factors was likely an underestimate because some such factors, including the autoimmune disorder antiphospholipid syndrome and patent foramen ovale, “lacked reliable administrative algorithms” and could not be assessed in this study, the researchers noted.
Further research on how nontraditional risk factors affect strokes could lead to better prevention.
“We need to better understand the underlying mechanisms of these nontraditional risk factors to develop targeted interventions,” Dr. Leppert said.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health/National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences Colorado Clinical and Translational Science Award. Dr. Leppert reports receiving an American Heart Association Career Development Grant. Other disclosures are included in the original article.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CIRCULATION: CARDIOVASCULAR QUALITY AND OUTCOMES
Genetic Testing of Some Patients With Early-Onset AF Advised
Genetic testing may be considered in patients with early-onset atrial fibrillation (AF), particularly those with a positive family history and lack of conventional clinical risk factors, because specific genetic variants may underlie AF as well as “potentially more sinister cardiac conditions,” a new white paper from the Canadian Cardiovascular Society suggested.
“Given the resources and logistical challenges potentially imposed by genetic testing (that is, the majority of cardiology and arrhythmia clinics are not presently equipped to offer it), we have not recommended routine genetic testing for early-onset AF patients at this time,” lead author Jason D. Roberts, MD, associate professor of medicine at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, told this news organization.
“We do, however, recommend that early-onset AF patients undergo clinical screening for potential coexistence of a ventricular arrhythmia or cardiomyopathy syndrome through careful history, including family history, and physical examination, along with standard clinical testing, including ECG, echocardiogram, and Holter monitoring,” he said.
The white paper was published online in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology.
Routine Testing Unwarranted
The Canadian Cardiovascular Society reviewed AF research in 2022 and concluded that a guideline update was not yet warranted. One area meriting consideration but lacking sufficient evidence for a formal guideline was the clinical application of AF genetics.
Therefore, the society formed a writing group to assess the evidence linking genetic factors to AF, discuss an approach to using genetic testing for early-onset patients with AF, and consider the potential value of genetic testing in the foreseeable future.
The resulting white paper reviews familial and epidemiologic evidence for a genetic contribution to AF. As an example, the authors pointed to work from the Framingham Heart Study showing a statistically significant risk for AF among first-degree relatives of patients with AF. The overall odds ratio (OR) for AF among first-degree relatives was 1.85. But for first-degree relatives of patients with AF onset at younger than age 75 years, the OR increased to 3.23.
Other evidence included the identification of two rare genetic variants: KCNQ1 in a Chinese family and NPPA in a family with Northern European ancestry. In case-control studies, a single gene, titin (TTN), was linked to an increased burden of loss-of-function variants in patients with AF compared with controls. The variant was associated with a 2.2-fold increased risk for AF.
For example, loss-of-function SCN5A variants are implicated in Brugada syndrome and cardiac conduction system disease, whereas gain-of-function variants cause long QT syndrome type 3 and multifocal ectopic Purkinje-related premature contractions. Each of these conditions was associated with an increased prevalence of AF.
Similarly, genes implicated in various other forms of ventricular channelopathies also have been implicated in AF, as have ion channels primarily expressed in the atria and not the ventricles, such as KCNA5 and GJA5.
Nevertheless, in most cases, AF is diagnosed in the context of older age and established cardiovascular risk factors, according to the authors. The contribution of genetic factors in this population is relatively low, highlighting the limited role for genetic testing when AF develops in the presence of multiple conventional clinical risk factors.
Cardiogenetic Expertise Required
“Although significant progress has been made, additional work is needed before [beginning] routine integration of clinical genetic testing for early-onset AF patients,” Dr. Roberts said. The ideal clinical genetic testing panel for AF is still unclear, and the inclusion of genes for which there is no strong evidence of involvement in AF “creates the potential for harm.”
Specifically, “a genetic variant could be incorrectly assigned as the cause of AF, which could create confusion for the patient and family members and lead to inappropriate clinical management,” said Dr. Roberts.
“Beyond cost, routine introduction of genetic testing for AF patients will require allocation of significant resources, given that interpretation of genetic testing results can be nuanced,” he noted. “This nuance is anticipated to be heightened in AF, given that many genetic variants have low-to-intermediate penetrance and can manifest with variable clinical phenotypes.”
“Traditionally, genetic testing has been performed and interpreted, and results communicated, by dedicated cardiogenetic clinics with specialized expertise,” he added. “Existing cardiogenetic clinics, however, are unlikely to be sufficient in number to accommodate the large volume of AF patients that may be eligible for testing.”
Careful Counseling
Jim W. Cheung, MD, chair of the American College of Cardiology Electrophysiology Council, told this news organization that the white paper is consistent with the latest European Heart Rhythm Association/Heart Rhythm Society/Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society/Latin American Heart Rhythm Society expert consensus statement published in 2022.
Overall, the approach suggested for genetic testing “is a sound one, but one that requires implementation by clinicians with access to cardiogenetic expertise,” said Cheung, who was not involved in the study. “Any patient undergoing genetic testing needs to be carefully counseled about the potential uncertainties associated with the actual test results and their implications on clinical management.”
Variants of uncertain significance that are detected with genetic testing “can be a source of stress for clinicians and patients,” he said. “Therefore, patient education prior to and after genetic testing is essential.”
Furthermore, he said, “in many patients with early-onset AF who harbor pathogenic variants, initial imaging studies may not detect any signs of cardiomyopathy. In these patients, regular follow-up to assess for development of cardiomyopathy in the future is necessary.”
The white paper was drafted without outside funding. Dr. Roberts and Dr. Cheung reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Genetic testing may be considered in patients with early-onset atrial fibrillation (AF), particularly those with a positive family history and lack of conventional clinical risk factors, because specific genetic variants may underlie AF as well as “potentially more sinister cardiac conditions,” a new white paper from the Canadian Cardiovascular Society suggested.
“Given the resources and logistical challenges potentially imposed by genetic testing (that is, the majority of cardiology and arrhythmia clinics are not presently equipped to offer it), we have not recommended routine genetic testing for early-onset AF patients at this time,” lead author Jason D. Roberts, MD, associate professor of medicine at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, told this news organization.
“We do, however, recommend that early-onset AF patients undergo clinical screening for potential coexistence of a ventricular arrhythmia or cardiomyopathy syndrome through careful history, including family history, and physical examination, along with standard clinical testing, including ECG, echocardiogram, and Holter monitoring,” he said.
The white paper was published online in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology.
Routine Testing Unwarranted
The Canadian Cardiovascular Society reviewed AF research in 2022 and concluded that a guideline update was not yet warranted. One area meriting consideration but lacking sufficient evidence for a formal guideline was the clinical application of AF genetics.
Therefore, the society formed a writing group to assess the evidence linking genetic factors to AF, discuss an approach to using genetic testing for early-onset patients with AF, and consider the potential value of genetic testing in the foreseeable future.
The resulting white paper reviews familial and epidemiologic evidence for a genetic contribution to AF. As an example, the authors pointed to work from the Framingham Heart Study showing a statistically significant risk for AF among first-degree relatives of patients with AF. The overall odds ratio (OR) for AF among first-degree relatives was 1.85. But for first-degree relatives of patients with AF onset at younger than age 75 years, the OR increased to 3.23.
Other evidence included the identification of two rare genetic variants: KCNQ1 in a Chinese family and NPPA in a family with Northern European ancestry. In case-control studies, a single gene, titin (TTN), was linked to an increased burden of loss-of-function variants in patients with AF compared with controls. The variant was associated with a 2.2-fold increased risk for AF.
For example, loss-of-function SCN5A variants are implicated in Brugada syndrome and cardiac conduction system disease, whereas gain-of-function variants cause long QT syndrome type 3 and multifocal ectopic Purkinje-related premature contractions. Each of these conditions was associated with an increased prevalence of AF.
Similarly, genes implicated in various other forms of ventricular channelopathies also have been implicated in AF, as have ion channels primarily expressed in the atria and not the ventricles, such as KCNA5 and GJA5.
Nevertheless, in most cases, AF is diagnosed in the context of older age and established cardiovascular risk factors, according to the authors. The contribution of genetic factors in this population is relatively low, highlighting the limited role for genetic testing when AF develops in the presence of multiple conventional clinical risk factors.
Cardiogenetic Expertise Required
“Although significant progress has been made, additional work is needed before [beginning] routine integration of clinical genetic testing for early-onset AF patients,” Dr. Roberts said. The ideal clinical genetic testing panel for AF is still unclear, and the inclusion of genes for which there is no strong evidence of involvement in AF “creates the potential for harm.”
Specifically, “a genetic variant could be incorrectly assigned as the cause of AF, which could create confusion for the patient and family members and lead to inappropriate clinical management,” said Dr. Roberts.
“Beyond cost, routine introduction of genetic testing for AF patients will require allocation of significant resources, given that interpretation of genetic testing results can be nuanced,” he noted. “This nuance is anticipated to be heightened in AF, given that many genetic variants have low-to-intermediate penetrance and can manifest with variable clinical phenotypes.”
“Traditionally, genetic testing has been performed and interpreted, and results communicated, by dedicated cardiogenetic clinics with specialized expertise,” he added. “Existing cardiogenetic clinics, however, are unlikely to be sufficient in number to accommodate the large volume of AF patients that may be eligible for testing.”
Careful Counseling
Jim W. Cheung, MD, chair of the American College of Cardiology Electrophysiology Council, told this news organization that the white paper is consistent with the latest European Heart Rhythm Association/Heart Rhythm Society/Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society/Latin American Heart Rhythm Society expert consensus statement published in 2022.
Overall, the approach suggested for genetic testing “is a sound one, but one that requires implementation by clinicians with access to cardiogenetic expertise,” said Cheung, who was not involved in the study. “Any patient undergoing genetic testing needs to be carefully counseled about the potential uncertainties associated with the actual test results and their implications on clinical management.”
Variants of uncertain significance that are detected with genetic testing “can be a source of stress for clinicians and patients,” he said. “Therefore, patient education prior to and after genetic testing is essential.”
Furthermore, he said, “in many patients with early-onset AF who harbor pathogenic variants, initial imaging studies may not detect any signs of cardiomyopathy. In these patients, regular follow-up to assess for development of cardiomyopathy in the future is necessary.”
The white paper was drafted without outside funding. Dr. Roberts and Dr. Cheung reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Genetic testing may be considered in patients with early-onset atrial fibrillation (AF), particularly those with a positive family history and lack of conventional clinical risk factors, because specific genetic variants may underlie AF as well as “potentially more sinister cardiac conditions,” a new white paper from the Canadian Cardiovascular Society suggested.
“Given the resources and logistical challenges potentially imposed by genetic testing (that is, the majority of cardiology and arrhythmia clinics are not presently equipped to offer it), we have not recommended routine genetic testing for early-onset AF patients at this time,” lead author Jason D. Roberts, MD, associate professor of medicine at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, told this news organization.
“We do, however, recommend that early-onset AF patients undergo clinical screening for potential coexistence of a ventricular arrhythmia or cardiomyopathy syndrome through careful history, including family history, and physical examination, along with standard clinical testing, including ECG, echocardiogram, and Holter monitoring,” he said.
The white paper was published online in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology.
Routine Testing Unwarranted
The Canadian Cardiovascular Society reviewed AF research in 2022 and concluded that a guideline update was not yet warranted. One area meriting consideration but lacking sufficient evidence for a formal guideline was the clinical application of AF genetics.
Therefore, the society formed a writing group to assess the evidence linking genetic factors to AF, discuss an approach to using genetic testing for early-onset patients with AF, and consider the potential value of genetic testing in the foreseeable future.
The resulting white paper reviews familial and epidemiologic evidence for a genetic contribution to AF. As an example, the authors pointed to work from the Framingham Heart Study showing a statistically significant risk for AF among first-degree relatives of patients with AF. The overall odds ratio (OR) for AF among first-degree relatives was 1.85. But for first-degree relatives of patients with AF onset at younger than age 75 years, the OR increased to 3.23.
Other evidence included the identification of two rare genetic variants: KCNQ1 in a Chinese family and NPPA in a family with Northern European ancestry. In case-control studies, a single gene, titin (TTN), was linked to an increased burden of loss-of-function variants in patients with AF compared with controls. The variant was associated with a 2.2-fold increased risk for AF.
For example, loss-of-function SCN5A variants are implicated in Brugada syndrome and cardiac conduction system disease, whereas gain-of-function variants cause long QT syndrome type 3 and multifocal ectopic Purkinje-related premature contractions. Each of these conditions was associated with an increased prevalence of AF.
Similarly, genes implicated in various other forms of ventricular channelopathies also have been implicated in AF, as have ion channels primarily expressed in the atria and not the ventricles, such as KCNA5 and GJA5.
Nevertheless, in most cases, AF is diagnosed in the context of older age and established cardiovascular risk factors, according to the authors. The contribution of genetic factors in this population is relatively low, highlighting the limited role for genetic testing when AF develops in the presence of multiple conventional clinical risk factors.
Cardiogenetic Expertise Required
“Although significant progress has been made, additional work is needed before [beginning] routine integration of clinical genetic testing for early-onset AF patients,” Dr. Roberts said. The ideal clinical genetic testing panel for AF is still unclear, and the inclusion of genes for which there is no strong evidence of involvement in AF “creates the potential for harm.”
Specifically, “a genetic variant could be incorrectly assigned as the cause of AF, which could create confusion for the patient and family members and lead to inappropriate clinical management,” said Dr. Roberts.
“Beyond cost, routine introduction of genetic testing for AF patients will require allocation of significant resources, given that interpretation of genetic testing results can be nuanced,” he noted. “This nuance is anticipated to be heightened in AF, given that many genetic variants have low-to-intermediate penetrance and can manifest with variable clinical phenotypes.”
“Traditionally, genetic testing has been performed and interpreted, and results communicated, by dedicated cardiogenetic clinics with specialized expertise,” he added. “Existing cardiogenetic clinics, however, are unlikely to be sufficient in number to accommodate the large volume of AF patients that may be eligible for testing.”
Careful Counseling
Jim W. Cheung, MD, chair of the American College of Cardiology Electrophysiology Council, told this news organization that the white paper is consistent with the latest European Heart Rhythm Association/Heart Rhythm Society/Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society/Latin American Heart Rhythm Society expert consensus statement published in 2022.
Overall, the approach suggested for genetic testing “is a sound one, but one that requires implementation by clinicians with access to cardiogenetic expertise,” said Cheung, who was not involved in the study. “Any patient undergoing genetic testing needs to be carefully counseled about the potential uncertainties associated with the actual test results and their implications on clinical management.”
Variants of uncertain significance that are detected with genetic testing “can be a source of stress for clinicians and patients,” he said. “Therefore, patient education prior to and after genetic testing is essential.”
Furthermore, he said, “in many patients with early-onset AF who harbor pathogenic variants, initial imaging studies may not detect any signs of cardiomyopathy. In these patients, regular follow-up to assess for development of cardiomyopathy in the future is necessary.”
The white paper was drafted without outside funding. Dr. Roberts and Dr. Cheung reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE CANADIAN JOURNAL OF CARDIOLOGY
Maternal Lifestyle Interventions Boost Babies’ Heart Health
Infants born to women with obesity showed improved measures of cardiovascular health when their mothers adopted healthier lifestyles before and during pregnancy, based on data from a systematic review presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Reproductive Investigation.
Previous research has shown that children born to mothers with a high body mass index (BMI) are more likely to die from cardiovascular disease in later life, said presenting author Samuel J. Burden, PhD, in an interview.
“Surprisingly, early signs of these heart issues can start before birth and continue into childhood,” said Dr. Burden, a research associate in the Department of Women & Children’s Health, School of Life Course & Population Sciences, King’s College London, London, United Kingdom.
To examine the effect of interventions such as a healthy diet and exercise in pregnant women with obesity on the heart health of their infants, Dr. Burden and colleagues reviewed data from eight randomized, controlled trials involving diet and exercise for pregnant women with obesity. Of these, two used antenatal exercise, two used diet and physical activity, and one used preconception diet and physical activity. The studies ranged in size from 18 to 404 participants. Two studies included infants younger than 2 months of age, and four studies included children aged 3-7 years.
Overall, lifestyle interventions before conception and before birth were associated with significant changes in cardiac remodeling, specifically reduced interventricular septal wall thickness.
In addition, one of three studies of cardiac diastolic function and four of five studies of systolic function showed significant improvements. The five studies of cardiac systolic function and three studies of diastolic function also showed improvement in systolic and diastolic blood pressure in infants of mothers who took part in the interventions. The studies were limited mainly by large attrition rates, the researchers wrote in their presentation. However, more studies in larger populations that also include older children could confirm the findings and inform public health strategies to promote healthy lifestyles for pregnant women, they noted.
Encourage Healthy Lifestyle Before and During Pregnancy
The evidence supports the findings from animal studies showing that an offspring’s health is influenced by maternal lifestyle before and during pregnancy, Dr. Burden said in an interview. The data suggest that healthcare providers should encourage women with a high BMI who want to become pregnant to eat healthfully and become more active as a way to enhance the future cardiovascular health of their children, he said.
The full results of the current study are soon to be published, but more work is needed, said Dr. Burden. “While we observed a protective effect from these lifestyle programs, there is a need for more extensive studies involving a larger number of women (and their children) who were part of the initial research,” he said. “Additionally, it will be crucial to track these children into adulthood to determine whether these antenatal lifestyle interventions persist in lowering the risk of future cardiovascular disease.”
Beginning healthy lifestyle programs prior to pregnancy might yield the best results for promoting infant cardiovascular health, and more prepregnancy interventions for women with obesity are needed, Dr. Burden added.
The current study adds to the growing body of evidence that the in utero environment can have lifelong effects on offspring, Joseph R. Biggio Jr, MD, system chair of maternal fetal medicine at Ochsner Health, New Orleans, Louisiana, said in an interview.
“Several studies have previously shown that the children of mothers with diabetes, hypertension, or obesity are at increased risk for developing signs of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular changes during childhood or adolescence,” said Dr. Biggio.
The data from this systematic review support the potential value of interventions aimed at improving maternal weight gain and cardiovascular performance before and during pregnancy that may result in reduced cardiovascular remodeling and myocardial thickening in infants, he said.
The study was supported by a British Heart Foundation Special Project Grant. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Biggio had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Infants born to women with obesity showed improved measures of cardiovascular health when their mothers adopted healthier lifestyles before and during pregnancy, based on data from a systematic review presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Reproductive Investigation.
Previous research has shown that children born to mothers with a high body mass index (BMI) are more likely to die from cardiovascular disease in later life, said presenting author Samuel J. Burden, PhD, in an interview.
“Surprisingly, early signs of these heart issues can start before birth and continue into childhood,” said Dr. Burden, a research associate in the Department of Women & Children’s Health, School of Life Course & Population Sciences, King’s College London, London, United Kingdom.
To examine the effect of interventions such as a healthy diet and exercise in pregnant women with obesity on the heart health of their infants, Dr. Burden and colleagues reviewed data from eight randomized, controlled trials involving diet and exercise for pregnant women with obesity. Of these, two used antenatal exercise, two used diet and physical activity, and one used preconception diet and physical activity. The studies ranged in size from 18 to 404 participants. Two studies included infants younger than 2 months of age, and four studies included children aged 3-7 years.
Overall, lifestyle interventions before conception and before birth were associated with significant changes in cardiac remodeling, specifically reduced interventricular septal wall thickness.
In addition, one of three studies of cardiac diastolic function and four of five studies of systolic function showed significant improvements. The five studies of cardiac systolic function and three studies of diastolic function also showed improvement in systolic and diastolic blood pressure in infants of mothers who took part in the interventions. The studies were limited mainly by large attrition rates, the researchers wrote in their presentation. However, more studies in larger populations that also include older children could confirm the findings and inform public health strategies to promote healthy lifestyles for pregnant women, they noted.
Encourage Healthy Lifestyle Before and During Pregnancy
The evidence supports the findings from animal studies showing that an offspring’s health is influenced by maternal lifestyle before and during pregnancy, Dr. Burden said in an interview. The data suggest that healthcare providers should encourage women with a high BMI who want to become pregnant to eat healthfully and become more active as a way to enhance the future cardiovascular health of their children, he said.
The full results of the current study are soon to be published, but more work is needed, said Dr. Burden. “While we observed a protective effect from these lifestyle programs, there is a need for more extensive studies involving a larger number of women (and their children) who were part of the initial research,” he said. “Additionally, it will be crucial to track these children into adulthood to determine whether these antenatal lifestyle interventions persist in lowering the risk of future cardiovascular disease.”
Beginning healthy lifestyle programs prior to pregnancy might yield the best results for promoting infant cardiovascular health, and more prepregnancy interventions for women with obesity are needed, Dr. Burden added.
The current study adds to the growing body of evidence that the in utero environment can have lifelong effects on offspring, Joseph R. Biggio Jr, MD, system chair of maternal fetal medicine at Ochsner Health, New Orleans, Louisiana, said in an interview.
“Several studies have previously shown that the children of mothers with diabetes, hypertension, or obesity are at increased risk for developing signs of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular changes during childhood or adolescence,” said Dr. Biggio.
The data from this systematic review support the potential value of interventions aimed at improving maternal weight gain and cardiovascular performance before and during pregnancy that may result in reduced cardiovascular remodeling and myocardial thickening in infants, he said.
The study was supported by a British Heart Foundation Special Project Grant. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Biggio had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Infants born to women with obesity showed improved measures of cardiovascular health when their mothers adopted healthier lifestyles before and during pregnancy, based on data from a systematic review presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Reproductive Investigation.
Previous research has shown that children born to mothers with a high body mass index (BMI) are more likely to die from cardiovascular disease in later life, said presenting author Samuel J. Burden, PhD, in an interview.
“Surprisingly, early signs of these heart issues can start before birth and continue into childhood,” said Dr. Burden, a research associate in the Department of Women & Children’s Health, School of Life Course & Population Sciences, King’s College London, London, United Kingdom.
To examine the effect of interventions such as a healthy diet and exercise in pregnant women with obesity on the heart health of their infants, Dr. Burden and colleagues reviewed data from eight randomized, controlled trials involving diet and exercise for pregnant women with obesity. Of these, two used antenatal exercise, two used diet and physical activity, and one used preconception diet and physical activity. The studies ranged in size from 18 to 404 participants. Two studies included infants younger than 2 months of age, and four studies included children aged 3-7 years.
Overall, lifestyle interventions before conception and before birth were associated with significant changes in cardiac remodeling, specifically reduced interventricular septal wall thickness.
In addition, one of three studies of cardiac diastolic function and four of five studies of systolic function showed significant improvements. The five studies of cardiac systolic function and three studies of diastolic function also showed improvement in systolic and diastolic blood pressure in infants of mothers who took part in the interventions. The studies were limited mainly by large attrition rates, the researchers wrote in their presentation. However, more studies in larger populations that also include older children could confirm the findings and inform public health strategies to promote healthy lifestyles for pregnant women, they noted.
Encourage Healthy Lifestyle Before and During Pregnancy
The evidence supports the findings from animal studies showing that an offspring’s health is influenced by maternal lifestyle before and during pregnancy, Dr. Burden said in an interview. The data suggest that healthcare providers should encourage women with a high BMI who want to become pregnant to eat healthfully and become more active as a way to enhance the future cardiovascular health of their children, he said.
The full results of the current study are soon to be published, but more work is needed, said Dr. Burden. “While we observed a protective effect from these lifestyle programs, there is a need for more extensive studies involving a larger number of women (and their children) who were part of the initial research,” he said. “Additionally, it will be crucial to track these children into adulthood to determine whether these antenatal lifestyle interventions persist in lowering the risk of future cardiovascular disease.”
Beginning healthy lifestyle programs prior to pregnancy might yield the best results for promoting infant cardiovascular health, and more prepregnancy interventions for women with obesity are needed, Dr. Burden added.
The current study adds to the growing body of evidence that the in utero environment can have lifelong effects on offspring, Joseph R. Biggio Jr, MD, system chair of maternal fetal medicine at Ochsner Health, New Orleans, Louisiana, said in an interview.
“Several studies have previously shown that the children of mothers with diabetes, hypertension, or obesity are at increased risk for developing signs of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular changes during childhood or adolescence,” said Dr. Biggio.
The data from this systematic review support the potential value of interventions aimed at improving maternal weight gain and cardiovascular performance before and during pregnancy that may result in reduced cardiovascular remodeling and myocardial thickening in infants, he said.
The study was supported by a British Heart Foundation Special Project Grant. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Biggio had no financial conflicts to disclose.