User login
MitraClip improves survival and health status for at least 2 years
, based on results from a substudy of the COAPT trial.
Significant improvements seen at 1 month in the TMVr group had waned only slightly by the 2-year time point, reported lead author Suzanne V. Arnold, MD, of Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute and University of Missouri–Kansas City, who presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology. The study was simultaneously published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“Considering the previously reported benefits of TMVr on survival and heart failure hospitalization, these health status findings further support the device as a valuable treatment option for heart failure patients with severe secondary mitral regurgitation who remain symptomatic despite maximally-tolerated guideline-directed medical therapy,” Dr. Arnold and her colleagues concluded.
Primary findings from the COAPT (Cardiovascular Outcomes Assessment of the MitraClip Percutaneous Therapy for Heart Failure Patients with Functional Mitral Regurgitation) trial showed that TMVr reduced hospitalizations due to heart failure and all-cause mortality over 2 years, leading the Food and Drug Administration to grant an extended indication to MitraClip. With the present substudy, the investigators sought to learn more about impacts of TMVr on overall health.
“Beyond prolonging survival and reducing hospitalizations, improving patients’ health status (i.e., symptoms, functional status, quality of life) is a key treatment goal of TMVr,” the investigators wrote. “In fact, among older patients with comorbidities and high symptom burden, health status improvement may be of greater importance to patients than improved survival.”
To measure these outcomes, the investigators employed the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) and the SF-36 health status survey, which they administered to 302 patients in the TMVr group and 312 patients in the standard care group. The primary endpoint was the KCCQ overall summary score (KCCQ-OS), which ranges from 0 to 100, with higher scores indicating better health status.
Across all patients, the average baseline KCCQ-OS score was 52.4 ± 23.0. After 1 month, the average KCCQ-OS score rose 2.1 points in the standard care group, while the TMVr group saw a 16.9-point increase, most heavily through the questionnaire’s quality of life domain. These figures translate to a mean between-group difference of 15.9 points, a value that decreased only slightly after 2 years, to 12.8 points. Further suggesting that TMVr had beneficial and lasting effects, a significantly greater percentage of patients in the TMVr group than in the standard care group were alive with a moderately large health improvement after 2 years (36.4% vs 16.6%; P less than .001).
The study was funded by Abbott Vascular. Several of the investigators reported financial relationships with Abbott as well as Novartis, Bayer, V-wave, Corvia, and others.
SOURCE: Arnold et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Mar 17.
, based on results from a substudy of the COAPT trial.
Significant improvements seen at 1 month in the TMVr group had waned only slightly by the 2-year time point, reported lead author Suzanne V. Arnold, MD, of Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute and University of Missouri–Kansas City, who presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology. The study was simultaneously published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“Considering the previously reported benefits of TMVr on survival and heart failure hospitalization, these health status findings further support the device as a valuable treatment option for heart failure patients with severe secondary mitral regurgitation who remain symptomatic despite maximally-tolerated guideline-directed medical therapy,” Dr. Arnold and her colleagues concluded.
Primary findings from the COAPT (Cardiovascular Outcomes Assessment of the MitraClip Percutaneous Therapy for Heart Failure Patients with Functional Mitral Regurgitation) trial showed that TMVr reduced hospitalizations due to heart failure and all-cause mortality over 2 years, leading the Food and Drug Administration to grant an extended indication to MitraClip. With the present substudy, the investigators sought to learn more about impacts of TMVr on overall health.
“Beyond prolonging survival and reducing hospitalizations, improving patients’ health status (i.e., symptoms, functional status, quality of life) is a key treatment goal of TMVr,” the investigators wrote. “In fact, among older patients with comorbidities and high symptom burden, health status improvement may be of greater importance to patients than improved survival.”
To measure these outcomes, the investigators employed the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) and the SF-36 health status survey, which they administered to 302 patients in the TMVr group and 312 patients in the standard care group. The primary endpoint was the KCCQ overall summary score (KCCQ-OS), which ranges from 0 to 100, with higher scores indicating better health status.
Across all patients, the average baseline KCCQ-OS score was 52.4 ± 23.0. After 1 month, the average KCCQ-OS score rose 2.1 points in the standard care group, while the TMVr group saw a 16.9-point increase, most heavily through the questionnaire’s quality of life domain. These figures translate to a mean between-group difference of 15.9 points, a value that decreased only slightly after 2 years, to 12.8 points. Further suggesting that TMVr had beneficial and lasting effects, a significantly greater percentage of patients in the TMVr group than in the standard care group were alive with a moderately large health improvement after 2 years (36.4% vs 16.6%; P less than .001).
The study was funded by Abbott Vascular. Several of the investigators reported financial relationships with Abbott as well as Novartis, Bayer, V-wave, Corvia, and others.
SOURCE: Arnold et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Mar 17.
, based on results from a substudy of the COAPT trial.
Significant improvements seen at 1 month in the TMVr group had waned only slightly by the 2-year time point, reported lead author Suzanne V. Arnold, MD, of Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute and University of Missouri–Kansas City, who presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology. The study was simultaneously published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“Considering the previously reported benefits of TMVr on survival and heart failure hospitalization, these health status findings further support the device as a valuable treatment option for heart failure patients with severe secondary mitral regurgitation who remain symptomatic despite maximally-tolerated guideline-directed medical therapy,” Dr. Arnold and her colleagues concluded.
Primary findings from the COAPT (Cardiovascular Outcomes Assessment of the MitraClip Percutaneous Therapy for Heart Failure Patients with Functional Mitral Regurgitation) trial showed that TMVr reduced hospitalizations due to heart failure and all-cause mortality over 2 years, leading the Food and Drug Administration to grant an extended indication to MitraClip. With the present substudy, the investigators sought to learn more about impacts of TMVr on overall health.
“Beyond prolonging survival and reducing hospitalizations, improving patients’ health status (i.e., symptoms, functional status, quality of life) is a key treatment goal of TMVr,” the investigators wrote. “In fact, among older patients with comorbidities and high symptom burden, health status improvement may be of greater importance to patients than improved survival.”
To measure these outcomes, the investigators employed the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) and the SF-36 health status survey, which they administered to 302 patients in the TMVr group and 312 patients in the standard care group. The primary endpoint was the KCCQ overall summary score (KCCQ-OS), which ranges from 0 to 100, with higher scores indicating better health status.
Across all patients, the average baseline KCCQ-OS score was 52.4 ± 23.0. After 1 month, the average KCCQ-OS score rose 2.1 points in the standard care group, while the TMVr group saw a 16.9-point increase, most heavily through the questionnaire’s quality of life domain. These figures translate to a mean between-group difference of 15.9 points, a value that decreased only slightly after 2 years, to 12.8 points. Further suggesting that TMVr had beneficial and lasting effects, a significantly greater percentage of patients in the TMVr group than in the standard care group were alive with a moderately large health improvement after 2 years (36.4% vs 16.6%; P less than .001).
The study was funded by Abbott Vascular. Several of the investigators reported financial relationships with Abbott as well as Novartis, Bayer, V-wave, Corvia, and others.
SOURCE: Arnold et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Mar 17.
FROM JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Practice makes better: Robotic lobectomy can shorten OR times
A new single-surgeon study suggests that and shave about 90 minutes off adjusted operating time.
The findings provide “further support to the adaptation of formalized robotic training and credentialing procedures,” wrote the authors of the retrospective, single-center study, which was presented at the 2018 Academic Surgical Congress and published in Surgery.
According to the study authors, advantages of robotic surgery, compared with thoracoscopic surgery, include “3-dimensional visualization, enhanced maneuverability in small spaces, and the ease of the hilar and mediastinal dissection. Disadvantages include the lack of haptic feedback, increased cost, and increased operative time.”
In the new study, the authors, led by thoracic surgeon Brian N. Arnold, MD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., attempted to quantify the learning curve in RATS pulmonary lobectomies by using a more “statistically rigorous” technique than previous studies.
The study tracked 101 of 116 consecutive patients who underwent RATS pulmonary lobectomy at a single unnamed center from 2010 to 2016. Some patients, such as those who underwent a right middle lobectomy that is considered an easier procedure, were excluded. All patients were treated by the same unidentified surgeon.
Researchers identified three phases of the RATS learning curve: cases 1-22, cases 23-63, and cases 64-101.
On average, the patients were aged 69 years; 52% were female. Overall, a third of the patients developed complications.
After controlling for various factors, the researchers found that adjusted operating time and estimated blood loss were statistically different between the first and second phases (P less than .05 and P = .016, respectively). They were also different between the first and third phases (P less than .05 and P = .006, respectively).
Specifically, operating time in the first phase was a mean of 256 minutes versus 195 minutes in the second phase (P = .0002) and 168 minutes in the third phase (P less than .0001). Blood loss was 200 mL (interquartile range, 150-300 mL) in the first phase versus 150 mL (IQR, 75-200 mL; P = .0219) in the second phase and 150 mL (IQR, 100-150 mL; P = .0096) in the third phase.
The researchers found no statistically significant evidence that the surgeon’s growing experience affected length of stay, postoperative complications, chest tube duration, or conversion rate. No patients died within 30 or 90 days.
The researchers also compared operating time, length of stay, and complication rate in the RATS procedures with those in video-assisted thoracoscopic (VATS) lobectomies performed at the same institution from 2008 to 2014. There was only a statistically significant difference in mean operating time (RATS, 319 minutes; VATS, 253 minutes; P less than .001)
The study authors noted that the surgeon had extensive previous experience with VATS procedures. “Therefore, for better or for worse, the results may not apply to surgeons without this experience who move from open surgery to robotic surgery.”
Study funding and disclosures were not reported.
SOURCE: Arnold BN et al. Surgery. 2019 Feb;165(2):450-4.
A new single-surgeon study suggests that and shave about 90 minutes off adjusted operating time.
The findings provide “further support to the adaptation of formalized robotic training and credentialing procedures,” wrote the authors of the retrospective, single-center study, which was presented at the 2018 Academic Surgical Congress and published in Surgery.
According to the study authors, advantages of robotic surgery, compared with thoracoscopic surgery, include “3-dimensional visualization, enhanced maneuverability in small spaces, and the ease of the hilar and mediastinal dissection. Disadvantages include the lack of haptic feedback, increased cost, and increased operative time.”
In the new study, the authors, led by thoracic surgeon Brian N. Arnold, MD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., attempted to quantify the learning curve in RATS pulmonary lobectomies by using a more “statistically rigorous” technique than previous studies.
The study tracked 101 of 116 consecutive patients who underwent RATS pulmonary lobectomy at a single unnamed center from 2010 to 2016. Some patients, such as those who underwent a right middle lobectomy that is considered an easier procedure, were excluded. All patients were treated by the same unidentified surgeon.
Researchers identified three phases of the RATS learning curve: cases 1-22, cases 23-63, and cases 64-101.
On average, the patients were aged 69 years; 52% were female. Overall, a third of the patients developed complications.
After controlling for various factors, the researchers found that adjusted operating time and estimated blood loss were statistically different between the first and second phases (P less than .05 and P = .016, respectively). They were also different between the first and third phases (P less than .05 and P = .006, respectively).
Specifically, operating time in the first phase was a mean of 256 minutes versus 195 minutes in the second phase (P = .0002) and 168 minutes in the third phase (P less than .0001). Blood loss was 200 mL (interquartile range, 150-300 mL) in the first phase versus 150 mL (IQR, 75-200 mL; P = .0219) in the second phase and 150 mL (IQR, 100-150 mL; P = .0096) in the third phase.
The researchers found no statistically significant evidence that the surgeon’s growing experience affected length of stay, postoperative complications, chest tube duration, or conversion rate. No patients died within 30 or 90 days.
The researchers also compared operating time, length of stay, and complication rate in the RATS procedures with those in video-assisted thoracoscopic (VATS) lobectomies performed at the same institution from 2008 to 2014. There was only a statistically significant difference in mean operating time (RATS, 319 minutes; VATS, 253 minutes; P less than .001)
The study authors noted that the surgeon had extensive previous experience with VATS procedures. “Therefore, for better or for worse, the results may not apply to surgeons without this experience who move from open surgery to robotic surgery.”
Study funding and disclosures were not reported.
SOURCE: Arnold BN et al. Surgery. 2019 Feb;165(2):450-4.
A new single-surgeon study suggests that and shave about 90 minutes off adjusted operating time.
The findings provide “further support to the adaptation of formalized robotic training and credentialing procedures,” wrote the authors of the retrospective, single-center study, which was presented at the 2018 Academic Surgical Congress and published in Surgery.
According to the study authors, advantages of robotic surgery, compared with thoracoscopic surgery, include “3-dimensional visualization, enhanced maneuverability in small spaces, and the ease of the hilar and mediastinal dissection. Disadvantages include the lack of haptic feedback, increased cost, and increased operative time.”
In the new study, the authors, led by thoracic surgeon Brian N. Arnold, MD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., attempted to quantify the learning curve in RATS pulmonary lobectomies by using a more “statistically rigorous” technique than previous studies.
The study tracked 101 of 116 consecutive patients who underwent RATS pulmonary lobectomy at a single unnamed center from 2010 to 2016. Some patients, such as those who underwent a right middle lobectomy that is considered an easier procedure, were excluded. All patients were treated by the same unidentified surgeon.
Researchers identified three phases of the RATS learning curve: cases 1-22, cases 23-63, and cases 64-101.
On average, the patients were aged 69 years; 52% were female. Overall, a third of the patients developed complications.
After controlling for various factors, the researchers found that adjusted operating time and estimated blood loss were statistically different between the first and second phases (P less than .05 and P = .016, respectively). They were also different between the first and third phases (P less than .05 and P = .006, respectively).
Specifically, operating time in the first phase was a mean of 256 minutes versus 195 minutes in the second phase (P = .0002) and 168 minutes in the third phase (P less than .0001). Blood loss was 200 mL (interquartile range, 150-300 mL) in the first phase versus 150 mL (IQR, 75-200 mL; P = .0219) in the second phase and 150 mL (IQR, 100-150 mL; P = .0096) in the third phase.
The researchers found no statistically significant evidence that the surgeon’s growing experience affected length of stay, postoperative complications, chest tube duration, or conversion rate. No patients died within 30 or 90 days.
The researchers also compared operating time, length of stay, and complication rate in the RATS procedures with those in video-assisted thoracoscopic (VATS) lobectomies performed at the same institution from 2008 to 2014. There was only a statistically significant difference in mean operating time (RATS, 319 minutes; VATS, 253 minutes; P less than .001)
The study authors noted that the surgeon had extensive previous experience with VATS procedures. “Therefore, for better or for worse, the results may not apply to surgeons without this experience who move from open surgery to robotic surgery.”
Study funding and disclosures were not reported.
SOURCE: Arnold BN et al. Surgery. 2019 Feb;165(2):450-4.
FROM SURGERY
Key clinical point: Extensive experience in robot-assisted thoracoscopic (RATS) pulmonary lobectomies could lead to dramatically shorter adjusted operating time.
Major finding: From a surgeon’s first 22 surgeries to cases 64-101, mean operating time fell from 256 minutes to 168 minutes, (P less than .05).
Study details: A retrospective, single-center, single-surgeon study of 101 patients who underwent robot-assisted thoracoscopic pulmonary lobectomies from 2010 to 2016.
Disclosures: Study funding and disclosures were not reported.
Source: Arnold BN et al. Surgery. 2019 Feb;165(2):450-4.
Impella RP shows higher mortality in postapproval study
The Food and Drug Administration issued a letter on Feb. 4, 2019, to health care providers regarding interim results from a postapproval study for Abiomed’s Impella RP System because these results appear to have a higher mortality rate than was seen in premarket clinical studies.
As a condition of its approval, the FDA mandated Abiomed to perform a postapproval study (PAS); this study reflects use in a broader population than the premarket studies, which adhered to stricter inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Earlier in January, Abiomed submitted data to the FDA suggesting that differences in preimplant characteristics between patients in the PAS and those in the premarket clinical studies may explain the difference in mortality. Specifically, 16 of the 23 patients enrolled in the PAS would not have met the enrollment criteria for the premarket clinical studies because they were in cardiogenic shock for longer than 48 hours, experienced an in-hospital cardiac arrest, were treated with an intra-aortic balloon pump, or suffered a preimplant hypoxic or ischemic neurologic event.
“Although the FDA is concerned about the high mortality rate from the interim PAS results,” they wrote in the letter, which is available on the FDA website, “we believe that, when the device is used for the currently approved indication in appropriately selected patients, the benefits of the Impella RP system continue to outweigh the risks.”
The Food and Drug Administration issued a letter on Feb. 4, 2019, to health care providers regarding interim results from a postapproval study for Abiomed’s Impella RP System because these results appear to have a higher mortality rate than was seen in premarket clinical studies.
As a condition of its approval, the FDA mandated Abiomed to perform a postapproval study (PAS); this study reflects use in a broader population than the premarket studies, which adhered to stricter inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Earlier in January, Abiomed submitted data to the FDA suggesting that differences in preimplant characteristics between patients in the PAS and those in the premarket clinical studies may explain the difference in mortality. Specifically, 16 of the 23 patients enrolled in the PAS would not have met the enrollment criteria for the premarket clinical studies because they were in cardiogenic shock for longer than 48 hours, experienced an in-hospital cardiac arrest, were treated with an intra-aortic balloon pump, or suffered a preimplant hypoxic or ischemic neurologic event.
“Although the FDA is concerned about the high mortality rate from the interim PAS results,” they wrote in the letter, which is available on the FDA website, “we believe that, when the device is used for the currently approved indication in appropriately selected patients, the benefits of the Impella RP system continue to outweigh the risks.”
The Food and Drug Administration issued a letter on Feb. 4, 2019, to health care providers regarding interim results from a postapproval study for Abiomed’s Impella RP System because these results appear to have a higher mortality rate than was seen in premarket clinical studies.
As a condition of its approval, the FDA mandated Abiomed to perform a postapproval study (PAS); this study reflects use in a broader population than the premarket studies, which adhered to stricter inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Earlier in January, Abiomed submitted data to the FDA suggesting that differences in preimplant characteristics between patients in the PAS and those in the premarket clinical studies may explain the difference in mortality. Specifically, 16 of the 23 patients enrolled in the PAS would not have met the enrollment criteria for the premarket clinical studies because they were in cardiogenic shock for longer than 48 hours, experienced an in-hospital cardiac arrest, were treated with an intra-aortic balloon pump, or suffered a preimplant hypoxic or ischemic neurologic event.
“Although the FDA is concerned about the high mortality rate from the interim PAS results,” they wrote in the letter, which is available on the FDA website, “we believe that, when the device is used for the currently approved indication in appropriately selected patients, the benefits of the Impella RP system continue to outweigh the risks.”
Pulmonary hypertension linked to complications after head and neck procedures
SAN DIEGO – Patients with , compared with their counterparts who do not have the condition. They also face an increase in total charges and length of stay.
The findings come from what is believed to be the first study of its kind to investigate the impact of pulmonary hypertension (PHTN) on major head and neck procedures. “PHTN is a common condition which affects the caliber of lung vasculature, with varied symptom presentation from shortness of breath to syncope, with an estimated prevalence of 2.5 to 7.1 million new cases each year worldwide,” one of the study authors, Nirali M. Patel, said at the Triological Society’s Combined Sections Meeting. “Due to improved therapeutic options, there is an enhanced survival of PHTN patients and higher prevalence of this disease. PHTN has some significant systemic implications. Therefore, cardiopulmonary clearance and a clear understanding of postoperative complications are very important.”
Previous studies have shown PHTN to be an independent predictor of morbidity and mortality in noncardiac procedures, said Ms. Patel, a fourth-year medical student at New Jersey Medical School, Newark. Furthermore, the rate of pulmonary complications is reported to be between 11% and 44.8% following radical head and neck cancer resection. “Despite these findings, there is currently a lack of information regarding perioperative morbidity and mortality of patients with PHTN undergoing major head and neck procedures,” she said.
The researchers queried the National Inpatient Survey from 2002 to 2013 for all cases of major head and neck surgery based on the ICD-9 codes for esophagectomy, glossectomy, laryngectomy, mandibulectomy, and pharyngectomy. They divided patients into two groups: those who had PHTN and those who did not, and performed demographic analyses as well as univariate and multivariate regression analyses.
Ms. Patel reported findings from a cohort of 46,311 patients. Of these, 46,073 had PHTN and 238 did not. The two groups were similar in age (a mean of 69 vs. 60 years in those with and without PHTN, respectively) and race (80% white vs. 79% white, respectively), but there were significantly fewer male patients in the PHTN group (57% vs. 70%; P less than .0001).
Several patient comorbidities were increased in the PHTN group, compared with the non-PHTN group, including coagulopathy (8.4% vs. 3.1%; P less than .0001), chronic heart failure (22.4% vs. 4.1%; P less than .0001), complicated diabetes (4.6% vs. 1.2%; P less than .0001), fluid and electrolyte disorders (30% vs. 18.3%; P less than .0001), and hypertension (63.3% vs. 43.7%; P less than .0001).
Postoperatively, patients with PHTN had a longer length of stay (a mean of 15.80 vs. 11.50 days, respectively; P less than .0001) as well as significantly higher total charges (a mean of $162,021.06 vs. $107,309.46, respectively; P less than .0001). When the researchers evaluated postoperative outcomes between the two cohorts, patients with PHTN had significantly higher rates of cardiac complications (9.2% vs. 3.5%; P less than .0001), iatrogenic pulmonary embolism (2.1% vs. 0.3%; P = .001), pulmonary edema (2.1% vs. 0.4%; P = .003), venous thrombotic events (4.6% vs. 1%; P less than. 0001), pulmonary insufficiency (17.2% vs. 9.7%; P less than .0001), and pneumonia (9.7% vs. 6%; P = .027), as well as higher rates of postoperative tracheostomy (8.4% vs. 4.5%; P = .007).
Multivariate analysis revealed that the following factors predicted in-hospital mortality: coagulopathy, chronic heart failure, fluid and electrolyte disorders, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, hypothyroidism, liver disease, obesity, paralysis, and renal failure. Despite these findings, there was no significant change in overall hospital mortality for those with PHTN, with an odds ratio of 1.055.
“Our study is not without its limitations, many of which are inherent to the use of a database, which is subject to errors in coding and sampling,” Ms. Patel noted at the meeting, which was jointly sponsored by the Triological Society and the American College of Surgeons. “Despite these limitations, the study provides valuable information on the impact of PHTN on major head and neck procedures.
She reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Patel N et al. Triological CSM, Abstracts.
SAN DIEGO – Patients with , compared with their counterparts who do not have the condition. They also face an increase in total charges and length of stay.
The findings come from what is believed to be the first study of its kind to investigate the impact of pulmonary hypertension (PHTN) on major head and neck procedures. “PHTN is a common condition which affects the caliber of lung vasculature, with varied symptom presentation from shortness of breath to syncope, with an estimated prevalence of 2.5 to 7.1 million new cases each year worldwide,” one of the study authors, Nirali M. Patel, said at the Triological Society’s Combined Sections Meeting. “Due to improved therapeutic options, there is an enhanced survival of PHTN patients and higher prevalence of this disease. PHTN has some significant systemic implications. Therefore, cardiopulmonary clearance and a clear understanding of postoperative complications are very important.”
Previous studies have shown PHTN to be an independent predictor of morbidity and mortality in noncardiac procedures, said Ms. Patel, a fourth-year medical student at New Jersey Medical School, Newark. Furthermore, the rate of pulmonary complications is reported to be between 11% and 44.8% following radical head and neck cancer resection. “Despite these findings, there is currently a lack of information regarding perioperative morbidity and mortality of patients with PHTN undergoing major head and neck procedures,” she said.
The researchers queried the National Inpatient Survey from 2002 to 2013 for all cases of major head and neck surgery based on the ICD-9 codes for esophagectomy, glossectomy, laryngectomy, mandibulectomy, and pharyngectomy. They divided patients into two groups: those who had PHTN and those who did not, and performed demographic analyses as well as univariate and multivariate regression analyses.
Ms. Patel reported findings from a cohort of 46,311 patients. Of these, 46,073 had PHTN and 238 did not. The two groups were similar in age (a mean of 69 vs. 60 years in those with and without PHTN, respectively) and race (80% white vs. 79% white, respectively), but there were significantly fewer male patients in the PHTN group (57% vs. 70%; P less than .0001).
Several patient comorbidities were increased in the PHTN group, compared with the non-PHTN group, including coagulopathy (8.4% vs. 3.1%; P less than .0001), chronic heart failure (22.4% vs. 4.1%; P less than .0001), complicated diabetes (4.6% vs. 1.2%; P less than .0001), fluid and electrolyte disorders (30% vs. 18.3%; P less than .0001), and hypertension (63.3% vs. 43.7%; P less than .0001).
Postoperatively, patients with PHTN had a longer length of stay (a mean of 15.80 vs. 11.50 days, respectively; P less than .0001) as well as significantly higher total charges (a mean of $162,021.06 vs. $107,309.46, respectively; P less than .0001). When the researchers evaluated postoperative outcomes between the two cohorts, patients with PHTN had significantly higher rates of cardiac complications (9.2% vs. 3.5%; P less than .0001), iatrogenic pulmonary embolism (2.1% vs. 0.3%; P = .001), pulmonary edema (2.1% vs. 0.4%; P = .003), venous thrombotic events (4.6% vs. 1%; P less than. 0001), pulmonary insufficiency (17.2% vs. 9.7%; P less than .0001), and pneumonia (9.7% vs. 6%; P = .027), as well as higher rates of postoperative tracheostomy (8.4% vs. 4.5%; P = .007).
Multivariate analysis revealed that the following factors predicted in-hospital mortality: coagulopathy, chronic heart failure, fluid and electrolyte disorders, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, hypothyroidism, liver disease, obesity, paralysis, and renal failure. Despite these findings, there was no significant change in overall hospital mortality for those with PHTN, with an odds ratio of 1.055.
“Our study is not without its limitations, many of which are inherent to the use of a database, which is subject to errors in coding and sampling,” Ms. Patel noted at the meeting, which was jointly sponsored by the Triological Society and the American College of Surgeons. “Despite these limitations, the study provides valuable information on the impact of PHTN on major head and neck procedures.
She reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Patel N et al. Triological CSM, Abstracts.
SAN DIEGO – Patients with , compared with their counterparts who do not have the condition. They also face an increase in total charges and length of stay.
The findings come from what is believed to be the first study of its kind to investigate the impact of pulmonary hypertension (PHTN) on major head and neck procedures. “PHTN is a common condition which affects the caliber of lung vasculature, with varied symptom presentation from shortness of breath to syncope, with an estimated prevalence of 2.5 to 7.1 million new cases each year worldwide,” one of the study authors, Nirali M. Patel, said at the Triological Society’s Combined Sections Meeting. “Due to improved therapeutic options, there is an enhanced survival of PHTN patients and higher prevalence of this disease. PHTN has some significant systemic implications. Therefore, cardiopulmonary clearance and a clear understanding of postoperative complications are very important.”
Previous studies have shown PHTN to be an independent predictor of morbidity and mortality in noncardiac procedures, said Ms. Patel, a fourth-year medical student at New Jersey Medical School, Newark. Furthermore, the rate of pulmonary complications is reported to be between 11% and 44.8% following radical head and neck cancer resection. “Despite these findings, there is currently a lack of information regarding perioperative morbidity and mortality of patients with PHTN undergoing major head and neck procedures,” she said.
The researchers queried the National Inpatient Survey from 2002 to 2013 for all cases of major head and neck surgery based on the ICD-9 codes for esophagectomy, glossectomy, laryngectomy, mandibulectomy, and pharyngectomy. They divided patients into two groups: those who had PHTN and those who did not, and performed demographic analyses as well as univariate and multivariate regression analyses.
Ms. Patel reported findings from a cohort of 46,311 patients. Of these, 46,073 had PHTN and 238 did not. The two groups were similar in age (a mean of 69 vs. 60 years in those with and without PHTN, respectively) and race (80% white vs. 79% white, respectively), but there were significantly fewer male patients in the PHTN group (57% vs. 70%; P less than .0001).
Several patient comorbidities were increased in the PHTN group, compared with the non-PHTN group, including coagulopathy (8.4% vs. 3.1%; P less than .0001), chronic heart failure (22.4% vs. 4.1%; P less than .0001), complicated diabetes (4.6% vs. 1.2%; P less than .0001), fluid and electrolyte disorders (30% vs. 18.3%; P less than .0001), and hypertension (63.3% vs. 43.7%; P less than .0001).
Postoperatively, patients with PHTN had a longer length of stay (a mean of 15.80 vs. 11.50 days, respectively; P less than .0001) as well as significantly higher total charges (a mean of $162,021.06 vs. $107,309.46, respectively; P less than .0001). When the researchers evaluated postoperative outcomes between the two cohorts, patients with PHTN had significantly higher rates of cardiac complications (9.2% vs. 3.5%; P less than .0001), iatrogenic pulmonary embolism (2.1% vs. 0.3%; P = .001), pulmonary edema (2.1% vs. 0.4%; P = .003), venous thrombotic events (4.6% vs. 1%; P less than. 0001), pulmonary insufficiency (17.2% vs. 9.7%; P less than .0001), and pneumonia (9.7% vs. 6%; P = .027), as well as higher rates of postoperative tracheostomy (8.4% vs. 4.5%; P = .007).
Multivariate analysis revealed that the following factors predicted in-hospital mortality: coagulopathy, chronic heart failure, fluid and electrolyte disorders, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, hypothyroidism, liver disease, obesity, paralysis, and renal failure. Despite these findings, there was no significant change in overall hospital mortality for those with PHTN, with an odds ratio of 1.055.
“Our study is not without its limitations, many of which are inherent to the use of a database, which is subject to errors in coding and sampling,” Ms. Patel noted at the meeting, which was jointly sponsored by the Triological Society and the American College of Surgeons. “Despite these limitations, the study provides valuable information on the impact of PHTN on major head and neck procedures.
She reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Patel N et al. Triological CSM, Abstracts.
REPORTING FROM THE TRIOLOGICAL CSM
Key clinical point: Pulmonary hypertension (PHTN) is linked with certain head and neck surgical complications.
Major finding: For patients undergoing head and neck surgery, PHTN is associated with an increased risk of cardiac complications (9.2% vs. 3.5%) and iatrogenic pulmonary embolism (2.1% vs. 0.3%).
Study details: A retrospective analysis of 46,311 patient records from the National Inpatient Survey.
Disclosures: The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
Source: Patel N et al. Triological CSM, Abstracts.
For CABG, multiple and single arterial grafts show no survival difference
No significant difference in rate of death was found in patients who underwent either bilateral or single internal thoracic artery grafting during coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery, according to a randomized trial of patients who were scheduled to undergo CABG.
“At 10 years, in intention-to-treat analyses, there were no significant between-group differences in all-cause mortality,” wrote lead author David P. Taggart, MD, PhD, of the University of Oxford (England), and his coauthors, adding that “the results of this trial are not consistent with data from previous, nonrandomized studies.” The study was published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
In the multicenter, unblinded Arterial Revascularization Trial (ART), 3,102 patients with multivessel coronary artery disease were divided into two groups: the bilateral-graft group (1,548 patients) and the single-graft group (1,554). They were assigned to receive bilateral internal thoracic artery grafts or a standard single left internal thoracic artery graft during CABG, respectively. However, 13.9% of the patients in the bilateral-graft group received only a single internal thoracic artery graft, while 21.8% of those in the single-graft group also received a radial artery graft.
At 10-year follow-up, 644 patients (20.8%) had died; 315 deaths (20.3%) occurred in the bilateral-graft group and 329 (21.2%) occurred in the single-graft group. A total of 385 patients (24.9%) suffered MI, stroke, or death in the bilateral-graft group, compared with 425 (27.3%) in the single-graft group (hazard ratio, 0.90; 95% confidence interval, 0.79-1.03).
The coauthors noted several reasons that the results of their trial may not have matched previous data, including conflicting evidence about vein graft failure’s clinical effect on survival and the aforementioned patients who were assigned to a specific group but received alternate grafting. In addition, they acknowledged that ART was an unblinded trial and “biases may be introduced in the treatment of patients, depending on their randomization assignment.”
The study was supported by grants from the British Heart Foundation, the U.K. Medical Research Council, and the National Institute of Health Research Efficacy and Mechanistic Evaluation Program. No relevant conflicts of interest were reported.
SOURCE: Taggart DP et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 31. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1808783.
Do the results of the Arterial Revascularization Trial undercut observational studies that elevated bilateral internal thoracic artery grafting? Not just yet, according to Stuart J. Head, MD, PhD, and Arie Pieter Kappetein, MD, PhD, of Erasmus Medical Center, the Netherlands.
They also recognized the study’s limitations in regard to groups receiving unassigned grafts and potential selection bias. Until another ongoing study on multiple arterial grafts is completed, the authors recommended that “CABG [coronary artery bypass grafting] with both internal thoracic arteries should not be abandoned. It should still be performed in patients with a low risk of sternal wound complications and a good long-term survival prognosis and by surgeons who are experienced in performing multiarterial CABG procedures.”
These comments are adapted from an accompanying editorial (N Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 31. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1814681). No conflicts of interest were reported.
Do the results of the Arterial Revascularization Trial undercut observational studies that elevated bilateral internal thoracic artery grafting? Not just yet, according to Stuart J. Head, MD, PhD, and Arie Pieter Kappetein, MD, PhD, of Erasmus Medical Center, the Netherlands.
They also recognized the study’s limitations in regard to groups receiving unassigned grafts and potential selection bias. Until another ongoing study on multiple arterial grafts is completed, the authors recommended that “CABG [coronary artery bypass grafting] with both internal thoracic arteries should not be abandoned. It should still be performed in patients with a low risk of sternal wound complications and a good long-term survival prognosis and by surgeons who are experienced in performing multiarterial CABG procedures.”
These comments are adapted from an accompanying editorial (N Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 31. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1814681). No conflicts of interest were reported.
Do the results of the Arterial Revascularization Trial undercut observational studies that elevated bilateral internal thoracic artery grafting? Not just yet, according to Stuart J. Head, MD, PhD, and Arie Pieter Kappetein, MD, PhD, of Erasmus Medical Center, the Netherlands.
They also recognized the study’s limitations in regard to groups receiving unassigned grafts and potential selection bias. Until another ongoing study on multiple arterial grafts is completed, the authors recommended that “CABG [coronary artery bypass grafting] with both internal thoracic arteries should not be abandoned. It should still be performed in patients with a low risk of sternal wound complications and a good long-term survival prognosis and by surgeons who are experienced in performing multiarterial CABG procedures.”
These comments are adapted from an accompanying editorial (N Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 31. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1814681). No conflicts of interest were reported.
No significant difference in rate of death was found in patients who underwent either bilateral or single internal thoracic artery grafting during coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery, according to a randomized trial of patients who were scheduled to undergo CABG.
“At 10 years, in intention-to-treat analyses, there were no significant between-group differences in all-cause mortality,” wrote lead author David P. Taggart, MD, PhD, of the University of Oxford (England), and his coauthors, adding that “the results of this trial are not consistent with data from previous, nonrandomized studies.” The study was published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
In the multicenter, unblinded Arterial Revascularization Trial (ART), 3,102 patients with multivessel coronary artery disease were divided into two groups: the bilateral-graft group (1,548 patients) and the single-graft group (1,554). They were assigned to receive bilateral internal thoracic artery grafts or a standard single left internal thoracic artery graft during CABG, respectively. However, 13.9% of the patients in the bilateral-graft group received only a single internal thoracic artery graft, while 21.8% of those in the single-graft group also received a radial artery graft.
At 10-year follow-up, 644 patients (20.8%) had died; 315 deaths (20.3%) occurred in the bilateral-graft group and 329 (21.2%) occurred in the single-graft group. A total of 385 patients (24.9%) suffered MI, stroke, or death in the bilateral-graft group, compared with 425 (27.3%) in the single-graft group (hazard ratio, 0.90; 95% confidence interval, 0.79-1.03).
The coauthors noted several reasons that the results of their trial may not have matched previous data, including conflicting evidence about vein graft failure’s clinical effect on survival and the aforementioned patients who were assigned to a specific group but received alternate grafting. In addition, they acknowledged that ART was an unblinded trial and “biases may be introduced in the treatment of patients, depending on their randomization assignment.”
The study was supported by grants from the British Heart Foundation, the U.K. Medical Research Council, and the National Institute of Health Research Efficacy and Mechanistic Evaluation Program. No relevant conflicts of interest were reported.
SOURCE: Taggart DP et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 31. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1808783.
No significant difference in rate of death was found in patients who underwent either bilateral or single internal thoracic artery grafting during coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery, according to a randomized trial of patients who were scheduled to undergo CABG.
“At 10 years, in intention-to-treat analyses, there were no significant between-group differences in all-cause mortality,” wrote lead author David P. Taggart, MD, PhD, of the University of Oxford (England), and his coauthors, adding that “the results of this trial are not consistent with data from previous, nonrandomized studies.” The study was published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
In the multicenter, unblinded Arterial Revascularization Trial (ART), 3,102 patients with multivessel coronary artery disease were divided into two groups: the bilateral-graft group (1,548 patients) and the single-graft group (1,554). They were assigned to receive bilateral internal thoracic artery grafts or a standard single left internal thoracic artery graft during CABG, respectively. However, 13.9% of the patients in the bilateral-graft group received only a single internal thoracic artery graft, while 21.8% of those in the single-graft group also received a radial artery graft.
At 10-year follow-up, 644 patients (20.8%) had died; 315 deaths (20.3%) occurred in the bilateral-graft group and 329 (21.2%) occurred in the single-graft group. A total of 385 patients (24.9%) suffered MI, stroke, or death in the bilateral-graft group, compared with 425 (27.3%) in the single-graft group (hazard ratio, 0.90; 95% confidence interval, 0.79-1.03).
The coauthors noted several reasons that the results of their trial may not have matched previous data, including conflicting evidence about vein graft failure’s clinical effect on survival and the aforementioned patients who were assigned to a specific group but received alternate grafting. In addition, they acknowledged that ART was an unblinded trial and “biases may be introduced in the treatment of patients, depending on their randomization assignment.”
The study was supported by grants from the British Heart Foundation, the U.K. Medical Research Council, and the National Institute of Health Research Efficacy and Mechanistic Evaluation Program. No relevant conflicts of interest were reported.
SOURCE: Taggart DP et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 31. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1808783.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Key clinical point:
Major finding: At 10-year follow-up, there were 315 deaths (20.3% of patients) in the bilateral-graft group and 329 deaths (21.2%) in the single-graft group.
Study details: A two-group, multicenter, randomized, unblinded trial of 3,102 patients who were scheduled to undergo coronary artery bypass grafting.
Disclosures: The study was supported by grants from the British Heart Foundation, the U.K. Medical Research Council, and the National Institute of Health Research Efficacy and Mechanistic Evaluation Program. No relevant conflicts of interest were reported.
Source: Taggart DP et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 31. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1808783.
U.S. vs. Europe: Costs of cardiac implant devices compared
Prices that hospitals pay for cardiac implant devices are two to six times higher in the United States than in Europe, according to analysis of a large hospital panel survey.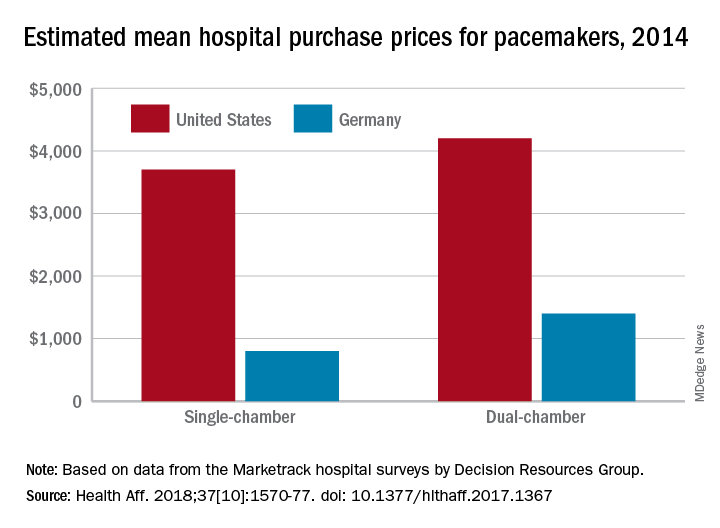
U.S. hospitals had an estimated mean cost of $670 for a bare-metal stent in 2014, compared with $120 in Germany, and the mean costs for dual-chamber pacemakers that year were $4,200 in the United States and $1,400 in Germany, which had lower costs for cardiac devices than the other three European countries – United Kingdom, France, and Italy – included in the study, Martin Wenzl, MSc, and Elias Mossialos, MD, PhD, reported in Health Affairs.
France generally had the highest costs among the European countries, with Italy next and then the United Kingdom. The estimated cost of bare-metal stents was actually higher for French hospitals ($750) than for those in the United States, and Italy had mean prices similar to the United Sates for dual-chamber implantable cardioverter-defibrillators. The prices of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators and cardiac resynchronization devices with defibrillating function were the other exceptions, with the United Kingdom similar to or higher than the United States, said Mr. Wenzl and Dr. Mossialos, both of the London School of Economics and Political Science.
The analysis of data from Decision Resources Group’s Marketrack hospital surveys also showed significant variation between the hospitals in each country, with the exception of France, where payments are based on the specific device rather than the procedure and the system “creates weak incentives for hospitals to negotiate lower prices,” they said. In most of the device categories, “variation between hospitals in each country was similar to variation between countries,” they wrote, adding that prices in general “were only weakly correlated with volumes purchased by hospitals.”
The study was supported by a grant from the Commonwealth Fund. The investigators did not disclose any possible conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Wenzi M, Mossialos E. Health Aff. 2018;37[10]:1570-77. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2017.1367.
Prices that hospitals pay for cardiac implant devices are two to six times higher in the United States than in Europe, according to analysis of a large hospital panel survey.
U.S. hospitals had an estimated mean cost of $670 for a bare-metal stent in 2014, compared with $120 in Germany, and the mean costs for dual-chamber pacemakers that year were $4,200 in the United States and $1,400 in Germany, which had lower costs for cardiac devices than the other three European countries – United Kingdom, France, and Italy – included in the study, Martin Wenzl, MSc, and Elias Mossialos, MD, PhD, reported in Health Affairs.
France generally had the highest costs among the European countries, with Italy next and then the United Kingdom. The estimated cost of bare-metal stents was actually higher for French hospitals ($750) than for those in the United States, and Italy had mean prices similar to the United Sates for dual-chamber implantable cardioverter-defibrillators. The prices of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators and cardiac resynchronization devices with defibrillating function were the other exceptions, with the United Kingdom similar to or higher than the United States, said Mr. Wenzl and Dr. Mossialos, both of the London School of Economics and Political Science.
The analysis of data from Decision Resources Group’s Marketrack hospital surveys also showed significant variation between the hospitals in each country, with the exception of France, where payments are based on the specific device rather than the procedure and the system “creates weak incentives for hospitals to negotiate lower prices,” they said. In most of the device categories, “variation between hospitals in each country was similar to variation between countries,” they wrote, adding that prices in general “were only weakly correlated with volumes purchased by hospitals.”
The study was supported by a grant from the Commonwealth Fund. The investigators did not disclose any possible conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Wenzi M, Mossialos E. Health Aff. 2018;37[10]:1570-77. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2017.1367.
Prices that hospitals pay for cardiac implant devices are two to six times higher in the United States than in Europe, according to analysis of a large hospital panel survey.
U.S. hospitals had an estimated mean cost of $670 for a bare-metal stent in 2014, compared with $120 in Germany, and the mean costs for dual-chamber pacemakers that year were $4,200 in the United States and $1,400 in Germany, which had lower costs for cardiac devices than the other three European countries – United Kingdom, France, and Italy – included in the study, Martin Wenzl, MSc, and Elias Mossialos, MD, PhD, reported in Health Affairs.
France generally had the highest costs among the European countries, with Italy next and then the United Kingdom. The estimated cost of bare-metal stents was actually higher for French hospitals ($750) than for those in the United States, and Italy had mean prices similar to the United Sates for dual-chamber implantable cardioverter-defibrillators. The prices of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators and cardiac resynchronization devices with defibrillating function were the other exceptions, with the United Kingdom similar to or higher than the United States, said Mr. Wenzl and Dr. Mossialos, both of the London School of Economics and Political Science.
The analysis of data from Decision Resources Group’s Marketrack hospital surveys also showed significant variation between the hospitals in each country, with the exception of France, where payments are based on the specific device rather than the procedure and the system “creates weak incentives for hospitals to negotiate lower prices,” they said. In most of the device categories, “variation between hospitals in each country was similar to variation between countries,” they wrote, adding that prices in general “were only weakly correlated with volumes purchased by hospitals.”
The study was supported by a grant from the Commonwealth Fund. The investigators did not disclose any possible conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Wenzi M, Mossialos E. Health Aff. 2018;37[10]:1570-77. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2017.1367.
FROM HEALTH AFFAIRS
Prosthesis-patient mismatch post TAVR ups death risk 19%
SAN DIEGO – Severe prosthesis-patient mismatch (PPM) after transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) increases risk of adverse outcomes and may be preventable in some cases with careful preprocedural planning, suggests a registry-based retrospective cohort study of 62,125 patients treated in the contemporary era.
The study – the largest to date of this patient population – determined that about one in every eight patients undergoing TAVR ultimately had a severe mismatch between the hemodynamics of the valve prosthesis and the requirements for cardiac output. Compared with counterparts that have moderate or no PPM, these patients with severe PPM had a 12% higher adjusted risk of heart failure rehospitalization and a 19% higher adjusted risk of death, according to results reported at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting and simultaneously published online (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Sep 23. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.09.001).
Notably, some of the predictors of severe PPM, such as use of smaller-diameter valves and performance of a valve-in-valve procedure, were potentially modifiable.
“Our findings suggest that efforts should be made to identify this problem and limit the risk for PPM after TAVR,” concluded lead investigator Howard C. Herrmann, MD, a professor at the University of Pennsylvania and director of the cardiac catheterization laboratories, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, both in Philadelphia. “Awareness is really the first step in trying to fix it.”
“We spend a lot of time in the heart-team meetings looking at the CT scans for annular dimensions and the vascular access, but we don’t really talk too much about severe PPM or the risk of that,” he elaborated. “This [study] allows us to start to predict it, based on patient factors and what prosthesis we might be choosing for a patient, and it allows us to have that conversation and think about alternatives.
“There are alternatives to try to avoid PPM, everything from which prosthesis we choose to the size of the prosthesis, to whether we fracture a patient’s valve if we are doing a valve-in-valve procedure. In the future, in some situations, we might even choose a low-risk or low-intermediate-risk patient for surgery with an enlargement operation in order to get a larger effective orifice area. So there are choices that we can make, and we should start thinking about that in the heart-team approach.”
Findings in context
The new study reinforces the message “that hemodynamics matter,” he said. “To the extent that we can get larger valves in and get better results from those valves, it will reduce the frequency of PPM. That’s something as operators we don’t spend as much time focusing on, and this will refocus our attention in trying to prevent PPM by being more diligent in terms of prosthesis choice and some operator characteristics, to try to reduce the gradients and improve the effective orifice areas as much as we can.”
Panelist Jeffrey J. Popma, MD, an interventional cardiologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, noted that he and his colleagues have observed similar trends in their smaller studies but had difficulty teasing out contributors. “It really goes back to the preprocedural planning about what valve you can get in, and larger orifice area is certainly better,” he concurred. “So I do think that this is a phenomenal addition.”
Study details
For the study, Dr. Herrmann and his colleagues analyzed 2014-2107 data from the STS/ACC Transcatheter Valve Therapy Registry, a national surveillance and quality improvement system. They identified enrollees aged 65 years or older at the time of their TAVR procedure who had fee-for-service Medicare and linked them to Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services claims data to assess outcomes.
Overall, 12.1% of patients had severe PPM, defined as an effective valve orifice area indexed to body surface area of less than 0.65 cm2/m2 on discharge echocardiography, and another 24.6% had moderate PPM, Dr. Herrmann reported at the meeting, sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
The strongest multivariate predictors of severe PPM were small prosthetic valve size (up to 23 mm in diameter) (odds ratio, 2.77), a valve-in-valve procedure (OR, 2.78), larger body surface area (OR, 1.71 per 0.2-U increase), and female sex (OR, 1.46). Odds also increased with decreasing age and were elevated for patients of nonwhite/Hispanic race and those having a lower ejection fraction, atrial fibrillation or flutter, or severe mitral or tricuspid regurgitation.
It was not possible to assess specific valves as predictors of mismatch because the registry prohibits comparisons across manufacturers, according to Dr. Herrmann.
One-year mortality, the study’s primary endpoint, was 17.2% in patients with severe PPM, compared with 15.8% in patients with moderate or no PPM (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.19; P less than .001). Findings were similar across subgroups.
The 1-year rate of heart failure rehospitalization was 14.7% in patients with severe PPM, compared with 12.2% in patients with moderate or no PPM (AHR, 1.12; P = .017).
“I would point out that these [outcome] curves are divergent at 1 year,” Dr. Herrmann noted. “So if we look at low-intermediate-risk and low-risk patients and younger patients, who may be more active and who see the effects of PPM more commonly and who are going to be living more than 1 year, we are going to have to consider this going forward in a more important way.”
Severe PPM did not significantly influence the rate of stroke (which stood at about 4% in each group) or worsen quality of life score at 1 year.
Dr. Herrmann disclosed receiving institutional grant/research support from Abbott Vascular, Bayer, Boston Scientific, Corvia Medical, Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic, and St. Jude Medical, as well as consulting fees/honoraria from Edwards, Medtronic, and Siemens Healthineers.
SAN DIEGO – Severe prosthesis-patient mismatch (PPM) after transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) increases risk of adverse outcomes and may be preventable in some cases with careful preprocedural planning, suggests a registry-based retrospective cohort study of 62,125 patients treated in the contemporary era.
The study – the largest to date of this patient population – determined that about one in every eight patients undergoing TAVR ultimately had a severe mismatch between the hemodynamics of the valve prosthesis and the requirements for cardiac output. Compared with counterparts that have moderate or no PPM, these patients with severe PPM had a 12% higher adjusted risk of heart failure rehospitalization and a 19% higher adjusted risk of death, according to results reported at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting and simultaneously published online (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Sep 23. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.09.001).
Notably, some of the predictors of severe PPM, such as use of smaller-diameter valves and performance of a valve-in-valve procedure, were potentially modifiable.
“Our findings suggest that efforts should be made to identify this problem and limit the risk for PPM after TAVR,” concluded lead investigator Howard C. Herrmann, MD, a professor at the University of Pennsylvania and director of the cardiac catheterization laboratories, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, both in Philadelphia. “Awareness is really the first step in trying to fix it.”
“We spend a lot of time in the heart-team meetings looking at the CT scans for annular dimensions and the vascular access, but we don’t really talk too much about severe PPM or the risk of that,” he elaborated. “This [study] allows us to start to predict it, based on patient factors and what prosthesis we might be choosing for a patient, and it allows us to have that conversation and think about alternatives.
“There are alternatives to try to avoid PPM, everything from which prosthesis we choose to the size of the prosthesis, to whether we fracture a patient’s valve if we are doing a valve-in-valve procedure. In the future, in some situations, we might even choose a low-risk or low-intermediate-risk patient for surgery with an enlargement operation in order to get a larger effective orifice area. So there are choices that we can make, and we should start thinking about that in the heart-team approach.”
Findings in context
The new study reinforces the message “that hemodynamics matter,” he said. “To the extent that we can get larger valves in and get better results from those valves, it will reduce the frequency of PPM. That’s something as operators we don’t spend as much time focusing on, and this will refocus our attention in trying to prevent PPM by being more diligent in terms of prosthesis choice and some operator characteristics, to try to reduce the gradients and improve the effective orifice areas as much as we can.”
Panelist Jeffrey J. Popma, MD, an interventional cardiologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, noted that he and his colleagues have observed similar trends in their smaller studies but had difficulty teasing out contributors. “It really goes back to the preprocedural planning about what valve you can get in, and larger orifice area is certainly better,” he concurred. “So I do think that this is a phenomenal addition.”
Study details
For the study, Dr. Herrmann and his colleagues analyzed 2014-2107 data from the STS/ACC Transcatheter Valve Therapy Registry, a national surveillance and quality improvement system. They identified enrollees aged 65 years or older at the time of their TAVR procedure who had fee-for-service Medicare and linked them to Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services claims data to assess outcomes.
Overall, 12.1% of patients had severe PPM, defined as an effective valve orifice area indexed to body surface area of less than 0.65 cm2/m2 on discharge echocardiography, and another 24.6% had moderate PPM, Dr. Herrmann reported at the meeting, sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
The strongest multivariate predictors of severe PPM were small prosthetic valve size (up to 23 mm in diameter) (odds ratio, 2.77), a valve-in-valve procedure (OR, 2.78), larger body surface area (OR, 1.71 per 0.2-U increase), and female sex (OR, 1.46). Odds also increased with decreasing age and were elevated for patients of nonwhite/Hispanic race and those having a lower ejection fraction, atrial fibrillation or flutter, or severe mitral or tricuspid regurgitation.
It was not possible to assess specific valves as predictors of mismatch because the registry prohibits comparisons across manufacturers, according to Dr. Herrmann.
One-year mortality, the study’s primary endpoint, was 17.2% in patients with severe PPM, compared with 15.8% in patients with moderate or no PPM (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.19; P less than .001). Findings were similar across subgroups.
The 1-year rate of heart failure rehospitalization was 14.7% in patients with severe PPM, compared with 12.2% in patients with moderate or no PPM (AHR, 1.12; P = .017).
“I would point out that these [outcome] curves are divergent at 1 year,” Dr. Herrmann noted. “So if we look at low-intermediate-risk and low-risk patients and younger patients, who may be more active and who see the effects of PPM more commonly and who are going to be living more than 1 year, we are going to have to consider this going forward in a more important way.”
Severe PPM did not significantly influence the rate of stroke (which stood at about 4% in each group) or worsen quality of life score at 1 year.
Dr. Herrmann disclosed receiving institutional grant/research support from Abbott Vascular, Bayer, Boston Scientific, Corvia Medical, Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic, and St. Jude Medical, as well as consulting fees/honoraria from Edwards, Medtronic, and Siemens Healthineers.
SAN DIEGO – Severe prosthesis-patient mismatch (PPM) after transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) increases risk of adverse outcomes and may be preventable in some cases with careful preprocedural planning, suggests a registry-based retrospective cohort study of 62,125 patients treated in the contemporary era.
The study – the largest to date of this patient population – determined that about one in every eight patients undergoing TAVR ultimately had a severe mismatch between the hemodynamics of the valve prosthesis and the requirements for cardiac output. Compared with counterparts that have moderate or no PPM, these patients with severe PPM had a 12% higher adjusted risk of heart failure rehospitalization and a 19% higher adjusted risk of death, according to results reported at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting and simultaneously published online (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Sep 23. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.09.001).
Notably, some of the predictors of severe PPM, such as use of smaller-diameter valves and performance of a valve-in-valve procedure, were potentially modifiable.
“Our findings suggest that efforts should be made to identify this problem and limit the risk for PPM after TAVR,” concluded lead investigator Howard C. Herrmann, MD, a professor at the University of Pennsylvania and director of the cardiac catheterization laboratories, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, both in Philadelphia. “Awareness is really the first step in trying to fix it.”
“We spend a lot of time in the heart-team meetings looking at the CT scans for annular dimensions and the vascular access, but we don’t really talk too much about severe PPM or the risk of that,” he elaborated. “This [study] allows us to start to predict it, based on patient factors and what prosthesis we might be choosing for a patient, and it allows us to have that conversation and think about alternatives.
“There are alternatives to try to avoid PPM, everything from which prosthesis we choose to the size of the prosthesis, to whether we fracture a patient’s valve if we are doing a valve-in-valve procedure. In the future, in some situations, we might even choose a low-risk or low-intermediate-risk patient for surgery with an enlargement operation in order to get a larger effective orifice area. So there are choices that we can make, and we should start thinking about that in the heart-team approach.”
Findings in context
The new study reinforces the message “that hemodynamics matter,” he said. “To the extent that we can get larger valves in and get better results from those valves, it will reduce the frequency of PPM. That’s something as operators we don’t spend as much time focusing on, and this will refocus our attention in trying to prevent PPM by being more diligent in terms of prosthesis choice and some operator characteristics, to try to reduce the gradients and improve the effective orifice areas as much as we can.”
Panelist Jeffrey J. Popma, MD, an interventional cardiologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, noted that he and his colleagues have observed similar trends in their smaller studies but had difficulty teasing out contributors. “It really goes back to the preprocedural planning about what valve you can get in, and larger orifice area is certainly better,” he concurred. “So I do think that this is a phenomenal addition.”
Study details
For the study, Dr. Herrmann and his colleagues analyzed 2014-2107 data from the STS/ACC Transcatheter Valve Therapy Registry, a national surveillance and quality improvement system. They identified enrollees aged 65 years or older at the time of their TAVR procedure who had fee-for-service Medicare and linked them to Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services claims data to assess outcomes.
Overall, 12.1% of patients had severe PPM, defined as an effective valve orifice area indexed to body surface area of less than 0.65 cm2/m2 on discharge echocardiography, and another 24.6% had moderate PPM, Dr. Herrmann reported at the meeting, sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
The strongest multivariate predictors of severe PPM were small prosthetic valve size (up to 23 mm in diameter) (odds ratio, 2.77), a valve-in-valve procedure (OR, 2.78), larger body surface area (OR, 1.71 per 0.2-U increase), and female sex (OR, 1.46). Odds also increased with decreasing age and were elevated for patients of nonwhite/Hispanic race and those having a lower ejection fraction, atrial fibrillation or flutter, or severe mitral or tricuspid regurgitation.
It was not possible to assess specific valves as predictors of mismatch because the registry prohibits comparisons across manufacturers, according to Dr. Herrmann.
One-year mortality, the study’s primary endpoint, was 17.2% in patients with severe PPM, compared with 15.8% in patients with moderate or no PPM (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.19; P less than .001). Findings were similar across subgroups.
The 1-year rate of heart failure rehospitalization was 14.7% in patients with severe PPM, compared with 12.2% in patients with moderate or no PPM (AHR, 1.12; P = .017).
“I would point out that these [outcome] curves are divergent at 1 year,” Dr. Herrmann noted. “So if we look at low-intermediate-risk and low-risk patients and younger patients, who may be more active and who see the effects of PPM more commonly and who are going to be living more than 1 year, we are going to have to consider this going forward in a more important way.”
Severe PPM did not significantly influence the rate of stroke (which stood at about 4% in each group) or worsen quality of life score at 1 year.
Dr. Herrmann disclosed receiving institutional grant/research support from Abbott Vascular, Bayer, Boston Scientific, Corvia Medical, Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic, and St. Jude Medical, as well as consulting fees/honoraria from Edwards, Medtronic, and Siemens Healthineers.
REPORTING FROM TCT 2018
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Patients with severe PPM after TAVR had elevated risks of heart failure rehospitalization (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.12) and death (AHR, 1.19).
Study details: A retrospective cohort study of 62,125 patients aged 65 years or older who underwent TAVR and were captured in the national STS/ACC Transcatheter Valve Therapy Registry.
Disclosures: Dr. Herrmann disclosed receiving institutional grant/research support from Abbott Vascular, Bayer, Boston Scientific, Corvia Medical, Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic, and St. Jude Medical, as well as consulting fees/honoraria from Edwards, Medtronic, and Siemens Healthineers.
Novel device improves mitral regurgitation 30% in REDUCE-FMR
SAN DIEGO – In patients with heart failure and functional mitral regurgitation, implantation of an investigational device led to reduced MR and improved left ventricular remodeling at 1 year, compared with patients who received sham treatment in the REDUCE-FMR trial.
The device showed promise in this trial, despite a small sample size, and its nature makes it possible to follow up with other procedures if the disease progresses. “The advantage of this technique is that all other options are still open,” Horst Sievert, MD, director of the CardioVascular Center in Frankfurt, said during a press conference at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting.
The Carillon Mitral Counter System includes two anchors, one in the great cardiac vein and one in the coronary sinus, connected by a shaping ribbon. The tension of the ribbon bolsters the mitral annulus, which in turn reduces mitral regurgitation.
REDUCE-FMR recruited 120 patients from centers in eight countries and randomized 87 to the Carillon device (73 implanted) and 33 to a sham procedure. Sham patients were sedated and received a coronary sinus angiogram. Patients were included if they had dilated ischemic or nonischemic cardiomyopathy and moderate to severe functional MR, among other requirements. Exclusion criteria included existing coronary artery stents in the implant target zone, severe mitral annular calcification, and significant organic mitral valve pathology.
The primary endpoint was the mean reduction of regurgitant volume at 1 year. The treated patients had a 22% reduction of 7.1 mL, while the sham group on average had an 8% increase of 3.3 mL (P = .03). In the as-treated subpopulation, which comprised 45 patients in the treatment group and 13 controls, the values were –7.5 mL and +3.3 mL (P = .02). A per-protocol analysis, which excluded patients who did not meet protocol criteria, led to an amplification of the effect when the study design was adhered to (–12.5 mL vs. +1.3 mL), though this result did not achieve statistical significance owing to the small sample size.
For the safety endpoints, the researchers examined the frequency of major adverse events (MAE), including death, myocardial infarction, cardiac perforation, device embolism, and surgery or percutaneous coronary intervention related to the device at 1 year. In the treatment group, 16.1% experienced a MAE, compared with 18.2% of control patients, a statistically nonsignificant difference.
A secondary efficacy endpoint of change in left ventricular end-diastolic volume showed improvements in the treatment group at 6 months (–12.4 mL) and 12 months (–8.6 mL), compared with increases in the sham group at 6 months (+5.4 mL) and 12 months (+6.5 mL). A similar trend occurred in left ventricular end-systolic volume (–7.8 mL and –4.8 mL; +3.4 mL and +6.1 mL, respectively).
The study was conducted in a patient population similar to that of the COAPT trial, which examined implantation of Abbott’s MitraClip. That study, presented here at TCT 2018 and simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine, also examined patients with heart failure and secondary MR.
However, in REDUCE-FMR, many of the patients had milder heart failure than the researchers had expected: 44.8% in the treatment group had NYHA class II, as did 48.5% in the sham group. That surprise may help identify an appropriate patient population. “I think this device may have a nice spot in between medical therapy and MitraClip implantation, because we have, by chance, a patient population with mild heart insufficiency and mild MR,” said Dr. Sievert.
The two devices also showed different physiologic effects, Michael Mack, MD, said at a press conference. “One subtle difference is that, in this trial, the difference is due to both positive left ventricular remodeling in the treatment arm and continued progression in the sham control. In COAPT, the difference in improvement that we saw was totally due to prevention of progression of disease. We just stabilized the disease to where it was at. So that’s an intriguing difference here, that you actually were able to demonstrate positive left ventricular remodeling,” noted Dr. Mack, medical director for cardiovascular surgery at Baylor Scott & White Medical Center, Plano, Tex. He was a coinvestigator in the COAPT trial.
REDUCE-FMR was funded by Cardiac Dimensions. Dr. Sievert has received consulting fees, travel expenses, and study honoraria from Cardiac Dimensions, and 35 other companies. Dr. Mack has received grant support or had a research contract with Abbott Vascular, Medtronic, and Edwards Lifesciences.
SAN DIEGO – In patients with heart failure and functional mitral regurgitation, implantation of an investigational device led to reduced MR and improved left ventricular remodeling at 1 year, compared with patients who received sham treatment in the REDUCE-FMR trial.
The device showed promise in this trial, despite a small sample size, and its nature makes it possible to follow up with other procedures if the disease progresses. “The advantage of this technique is that all other options are still open,” Horst Sievert, MD, director of the CardioVascular Center in Frankfurt, said during a press conference at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting.
The Carillon Mitral Counter System includes two anchors, one in the great cardiac vein and one in the coronary sinus, connected by a shaping ribbon. The tension of the ribbon bolsters the mitral annulus, which in turn reduces mitral regurgitation.
REDUCE-FMR recruited 120 patients from centers in eight countries and randomized 87 to the Carillon device (73 implanted) and 33 to a sham procedure. Sham patients were sedated and received a coronary sinus angiogram. Patients were included if they had dilated ischemic or nonischemic cardiomyopathy and moderate to severe functional MR, among other requirements. Exclusion criteria included existing coronary artery stents in the implant target zone, severe mitral annular calcification, and significant organic mitral valve pathology.
The primary endpoint was the mean reduction of regurgitant volume at 1 year. The treated patients had a 22% reduction of 7.1 mL, while the sham group on average had an 8% increase of 3.3 mL (P = .03). In the as-treated subpopulation, which comprised 45 patients in the treatment group and 13 controls, the values were –7.5 mL and +3.3 mL (P = .02). A per-protocol analysis, which excluded patients who did not meet protocol criteria, led to an amplification of the effect when the study design was adhered to (–12.5 mL vs. +1.3 mL), though this result did not achieve statistical significance owing to the small sample size.
For the safety endpoints, the researchers examined the frequency of major adverse events (MAE), including death, myocardial infarction, cardiac perforation, device embolism, and surgery or percutaneous coronary intervention related to the device at 1 year. In the treatment group, 16.1% experienced a MAE, compared with 18.2% of control patients, a statistically nonsignificant difference.
A secondary efficacy endpoint of change in left ventricular end-diastolic volume showed improvements in the treatment group at 6 months (–12.4 mL) and 12 months (–8.6 mL), compared with increases in the sham group at 6 months (+5.4 mL) and 12 months (+6.5 mL). A similar trend occurred in left ventricular end-systolic volume (–7.8 mL and –4.8 mL; +3.4 mL and +6.1 mL, respectively).
The study was conducted in a patient population similar to that of the COAPT trial, which examined implantation of Abbott’s MitraClip. That study, presented here at TCT 2018 and simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine, also examined patients with heart failure and secondary MR.
However, in REDUCE-FMR, many of the patients had milder heart failure than the researchers had expected: 44.8% in the treatment group had NYHA class II, as did 48.5% in the sham group. That surprise may help identify an appropriate patient population. “I think this device may have a nice spot in between medical therapy and MitraClip implantation, because we have, by chance, a patient population with mild heart insufficiency and mild MR,” said Dr. Sievert.
The two devices also showed different physiologic effects, Michael Mack, MD, said at a press conference. “One subtle difference is that, in this trial, the difference is due to both positive left ventricular remodeling in the treatment arm and continued progression in the sham control. In COAPT, the difference in improvement that we saw was totally due to prevention of progression of disease. We just stabilized the disease to where it was at. So that’s an intriguing difference here, that you actually were able to demonstrate positive left ventricular remodeling,” noted Dr. Mack, medical director for cardiovascular surgery at Baylor Scott & White Medical Center, Plano, Tex. He was a coinvestigator in the COAPT trial.
REDUCE-FMR was funded by Cardiac Dimensions. Dr. Sievert has received consulting fees, travel expenses, and study honoraria from Cardiac Dimensions, and 35 other companies. Dr. Mack has received grant support or had a research contract with Abbott Vascular, Medtronic, and Edwards Lifesciences.
SAN DIEGO – In patients with heart failure and functional mitral regurgitation, implantation of an investigational device led to reduced MR and improved left ventricular remodeling at 1 year, compared with patients who received sham treatment in the REDUCE-FMR trial.
The device showed promise in this trial, despite a small sample size, and its nature makes it possible to follow up with other procedures if the disease progresses. “The advantage of this technique is that all other options are still open,” Horst Sievert, MD, director of the CardioVascular Center in Frankfurt, said during a press conference at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting.
The Carillon Mitral Counter System includes two anchors, one in the great cardiac vein and one in the coronary sinus, connected by a shaping ribbon. The tension of the ribbon bolsters the mitral annulus, which in turn reduces mitral regurgitation.
REDUCE-FMR recruited 120 patients from centers in eight countries and randomized 87 to the Carillon device (73 implanted) and 33 to a sham procedure. Sham patients were sedated and received a coronary sinus angiogram. Patients were included if they had dilated ischemic or nonischemic cardiomyopathy and moderate to severe functional MR, among other requirements. Exclusion criteria included existing coronary artery stents in the implant target zone, severe mitral annular calcification, and significant organic mitral valve pathology.
The primary endpoint was the mean reduction of regurgitant volume at 1 year. The treated patients had a 22% reduction of 7.1 mL, while the sham group on average had an 8% increase of 3.3 mL (P = .03). In the as-treated subpopulation, which comprised 45 patients in the treatment group and 13 controls, the values were –7.5 mL and +3.3 mL (P = .02). A per-protocol analysis, which excluded patients who did not meet protocol criteria, led to an amplification of the effect when the study design was adhered to (–12.5 mL vs. +1.3 mL), though this result did not achieve statistical significance owing to the small sample size.
For the safety endpoints, the researchers examined the frequency of major adverse events (MAE), including death, myocardial infarction, cardiac perforation, device embolism, and surgery or percutaneous coronary intervention related to the device at 1 year. In the treatment group, 16.1% experienced a MAE, compared with 18.2% of control patients, a statistically nonsignificant difference.
A secondary efficacy endpoint of change in left ventricular end-diastolic volume showed improvements in the treatment group at 6 months (–12.4 mL) and 12 months (–8.6 mL), compared with increases in the sham group at 6 months (+5.4 mL) and 12 months (+6.5 mL). A similar trend occurred in left ventricular end-systolic volume (–7.8 mL and –4.8 mL; +3.4 mL and +6.1 mL, respectively).
The study was conducted in a patient population similar to that of the COAPT trial, which examined implantation of Abbott’s MitraClip. That study, presented here at TCT 2018 and simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine, also examined patients with heart failure and secondary MR.
However, in REDUCE-FMR, many of the patients had milder heart failure than the researchers had expected: 44.8% in the treatment group had NYHA class II, as did 48.5% in the sham group. That surprise may help identify an appropriate patient population. “I think this device may have a nice spot in between medical therapy and MitraClip implantation, because we have, by chance, a patient population with mild heart insufficiency and mild MR,” said Dr. Sievert.
The two devices also showed different physiologic effects, Michael Mack, MD, said at a press conference. “One subtle difference is that, in this trial, the difference is due to both positive left ventricular remodeling in the treatment arm and continued progression in the sham control. In COAPT, the difference in improvement that we saw was totally due to prevention of progression of disease. We just stabilized the disease to where it was at. So that’s an intriguing difference here, that you actually were able to demonstrate positive left ventricular remodeling,” noted Dr. Mack, medical director for cardiovascular surgery at Baylor Scott & White Medical Center, Plano, Tex. He was a coinvestigator in the COAPT trial.
REDUCE-FMR was funded by Cardiac Dimensions. Dr. Sievert has received consulting fees, travel expenses, and study honoraria from Cardiac Dimensions, and 35 other companies. Dr. Mack has received grant support or had a research contract with Abbott Vascular, Medtronic, and Edwards Lifesciences.
REPORTING FROM TCT 2018
Key clinical point: The device led to improvement in mitral regurgitation as well as ventricular remodeling.
Major finding:
Study details: REDUCE-FMR, a randomized, sham controlled trial of 120 patients from 8 countries.
Disclosures: REDUCE-FMR was funded by Cardiac Dimensions. Dr. Sievert has received consulting fees, travel expenses, and study honoraria from Cardiac Dimensions, and 35 other companies. Dr. Mack has received grant support or had a research contract with Abbott Vascular, Medtronic, and Edwards Lifesciences.
COAPT: MitraClip prolongs life in selected HF patients
SAN DIEGO – Among a carefully selected subset of heart failure patients and severe secondary mitral regurgitation, transcatheter mitral valve repair with the MitraClip reduced hospitalizations for heart failure by 47%, and death from any cause by 38% over 24 months, compared with maximal medical therapy alone.
That’s according to a randomized, open-label trial presented at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting.
The number needed to treat to prevent one heart failure (HF) hospitalization within 2 years was three; the number needed to treat to save one life was six. Only about 3% of patients had a device complication within 12 months of placement in the study, dubbed COAPT (the Heart Failure Patients with Functional Mitral Regurgitation Trial).
COAPT patients had grade 3+ or 4+ secondary mitral regurgitation, with a mean effective regurgitant orifice area (EROA) of 41 mm2. Their left ventricles were dilated, but not huge, with a mean left ventricular end-diastolic volume of 101 mL/m2. “We estimate that’s about 10% of heart failure patients,” said lead investigator and interventional cardiologist Gregg W. Stone, MD, a professor of medicine at Columbia University, New York.
MitraClip placement was performed in high-volume centers by experienced operators, and patients were on maximally tolerated doses of guideline-directed medical therapy, as per the 2013 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association heart failure management guidelines. There was very little variation in treatment regimens during the 2-year trial (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70:776-803).
Those parameters matter. Among HF patients who did not fit them in the recent Mitra-FR trial in France, MitraClip did not reduce rates of death or unplanned hospitalization (N Engl J Med. 2018 Aug 27. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1805374).
COAPT and Mitra-FR investigators said at the meeting that the studies are complimentary, not conflicting, because together, they define secondary mitral regurgitation (MR) patients who will and will not benefit from the device.
MR was less severe in Mitra-FR, with a mean EROA of 31 mm2, but left ventricles were more dilated, with a mean left ventricular end-diastolic volume of 135 mL/m2. Patients were on more real-world drug regimens that varied over the course of the trial. Also, the lower implantation rates and higher complication rates in Mitra-FR “suggests perhaps greater experience of the COAPT operators,” said Dr. Stone, who also is the director of cardiovascular research and education at the Center for Interventional Vascular Therapy at New York-Presbyterian Hospital/Columbia University Medical Center.
In short, “they were a different patient population than were enrolled in COAPT,” he said at the meeting, sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation, which Dr. Stone also codirects.
There was great excitement at TCT about COAPT because there was a startling benefit for patients who previously had few options. But many speakers worried that the hype surrounding the trial will drown out the critically important message about patient selection and that the clip will be used in HF patients who don’t fit the COAPT profile.
They also said that the emerging picture of benefit in patients with less ventricular dilation but more mitral regurgitation needs to be fleshed out and better quantified.
COAPT randomized 302 patients to MitraClip on a background of guideline-directed therapy and 312 to guideline-directed therapy alone. Participants who had mitral regurgitation caused by left ventricular dysfunction, were not surgical candidates, and remained symptomatic despite optimal treatment.
The annualized rate of all hospitalizations for HF within 24 months was 35.8% per patient-year in the device group, as compared with 67.9% per patient-year in the control group, for a relative reduction of 47% (P less than .001).
Death from any cause within 24 months occurred in 29.1% of the patients in the device group and 46.1% in the control group, yielding a reduction of 38% (P less than .001).
“We didn’t cure patients by fixing their MR. They still had 29% 2-year mortality, but we did markedly improve their quality of life. The only subgroup that didn’t benefit were patients that had an EORA of less than 30 mm2 and end diastolic volume greater than the median” of 96 mL/m2, which was “fascinating,” Dr. Stone said, and fit the emerging picture.
Mitral regurgitation grade fell to 1+ or lower in 82% of patients after clip placement and remained there in the majority of survivors at 2 years.
For a long time, “HF experts thought MR was just a marker of severe left ventricular dysfunction. What I think we see here is that secondary MR is not just a bystander. It contributes to the abnormal pathophysiology of these patients,” he said.
The trial was sponsored by MitraClip’s maker, Abbott. The company participated in site selection, management, and data analysis. Dr. Stone disclosed that his employer, Columbia University, receives royalties from Abbott for sale of the clip. Several fellow investigators disclosed grants, fees, and other financial ties to the company.
Simultaneously with the COAPT presentation, the results were published online (N Engl J Med. 2018 Sep 23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1806640).
Mitra-FR was funded by the French Ministry of Health and Research and Abbott.
This is really a blockbuster trial, because you see a statistically significant reduction in cardiovascular endpoints, which is something we almost never see in device-based trials. I think this is going to change clinical practice, but the question of generalizability is tricky. This was such a well-conducted trial; it may be difficult to generalize this to the practicing public. I was impressed by the MitraClip performance: the reduction in MR [mitral regurgitation], the lack of recurrence, and the small number of complications. Perhaps more than anything else, the difference between Mitra-FR and COAPT was the quality of the operators.
Martin B. Leon, MD , is the director of the Center for Interventional Vascular Therapy at Columbia University, N.Y., and the Cardiovascular Research Foundation’s founder and codirector of medical research and education. He was not involved in COAPT, and made his comments after the study presentation.
This is really a blockbuster trial, because you see a statistically significant reduction in cardiovascular endpoints, which is something we almost never see in device-based trials. I think this is going to change clinical practice, but the question of generalizability is tricky. This was such a well-conducted trial; it may be difficult to generalize this to the practicing public. I was impressed by the MitraClip performance: the reduction in MR [mitral regurgitation], the lack of recurrence, and the small number of complications. Perhaps more than anything else, the difference between Mitra-FR and COAPT was the quality of the operators.
Martin B. Leon, MD , is the director of the Center for Interventional Vascular Therapy at Columbia University, N.Y., and the Cardiovascular Research Foundation’s founder and codirector of medical research and education. He was not involved in COAPT, and made his comments after the study presentation.
This is really a blockbuster trial, because you see a statistically significant reduction in cardiovascular endpoints, which is something we almost never see in device-based trials. I think this is going to change clinical practice, but the question of generalizability is tricky. This was such a well-conducted trial; it may be difficult to generalize this to the practicing public. I was impressed by the MitraClip performance: the reduction in MR [mitral regurgitation], the lack of recurrence, and the small number of complications. Perhaps more than anything else, the difference between Mitra-FR and COAPT was the quality of the operators.
Martin B. Leon, MD , is the director of the Center for Interventional Vascular Therapy at Columbia University, N.Y., and the Cardiovascular Research Foundation’s founder and codirector of medical research and education. He was not involved in COAPT, and made his comments after the study presentation.
SAN DIEGO – Among a carefully selected subset of heart failure patients and severe secondary mitral regurgitation, transcatheter mitral valve repair with the MitraClip reduced hospitalizations for heart failure by 47%, and death from any cause by 38% over 24 months, compared with maximal medical therapy alone.
That’s according to a randomized, open-label trial presented at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting.
The number needed to treat to prevent one heart failure (HF) hospitalization within 2 years was three; the number needed to treat to save one life was six. Only about 3% of patients had a device complication within 12 months of placement in the study, dubbed COAPT (the Heart Failure Patients with Functional Mitral Regurgitation Trial).
COAPT patients had grade 3+ or 4+ secondary mitral regurgitation, with a mean effective regurgitant orifice area (EROA) of 41 mm2. Their left ventricles were dilated, but not huge, with a mean left ventricular end-diastolic volume of 101 mL/m2. “We estimate that’s about 10% of heart failure patients,” said lead investigator and interventional cardiologist Gregg W. Stone, MD, a professor of medicine at Columbia University, New York.
MitraClip placement was performed in high-volume centers by experienced operators, and patients were on maximally tolerated doses of guideline-directed medical therapy, as per the 2013 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association heart failure management guidelines. There was very little variation in treatment regimens during the 2-year trial (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70:776-803).
Those parameters matter. Among HF patients who did not fit them in the recent Mitra-FR trial in France, MitraClip did not reduce rates of death or unplanned hospitalization (N Engl J Med. 2018 Aug 27. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1805374).
COAPT and Mitra-FR investigators said at the meeting that the studies are complimentary, not conflicting, because together, they define secondary mitral regurgitation (MR) patients who will and will not benefit from the device.
MR was less severe in Mitra-FR, with a mean EROA of 31 mm2, but left ventricles were more dilated, with a mean left ventricular end-diastolic volume of 135 mL/m2. Patients were on more real-world drug regimens that varied over the course of the trial. Also, the lower implantation rates and higher complication rates in Mitra-FR “suggests perhaps greater experience of the COAPT operators,” said Dr. Stone, who also is the director of cardiovascular research and education at the Center for Interventional Vascular Therapy at New York-Presbyterian Hospital/Columbia University Medical Center.
In short, “they were a different patient population than were enrolled in COAPT,” he said at the meeting, sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation, which Dr. Stone also codirects.
There was great excitement at TCT about COAPT because there was a startling benefit for patients who previously had few options. But many speakers worried that the hype surrounding the trial will drown out the critically important message about patient selection and that the clip will be used in HF patients who don’t fit the COAPT profile.
They also said that the emerging picture of benefit in patients with less ventricular dilation but more mitral regurgitation needs to be fleshed out and better quantified.
COAPT randomized 302 patients to MitraClip on a background of guideline-directed therapy and 312 to guideline-directed therapy alone. Participants who had mitral regurgitation caused by left ventricular dysfunction, were not surgical candidates, and remained symptomatic despite optimal treatment.
The annualized rate of all hospitalizations for HF within 24 months was 35.8% per patient-year in the device group, as compared with 67.9% per patient-year in the control group, for a relative reduction of 47% (P less than .001).
Death from any cause within 24 months occurred in 29.1% of the patients in the device group and 46.1% in the control group, yielding a reduction of 38% (P less than .001).
“We didn’t cure patients by fixing their MR. They still had 29% 2-year mortality, but we did markedly improve their quality of life. The only subgroup that didn’t benefit were patients that had an EORA of less than 30 mm2 and end diastolic volume greater than the median” of 96 mL/m2, which was “fascinating,” Dr. Stone said, and fit the emerging picture.
Mitral regurgitation grade fell to 1+ or lower in 82% of patients after clip placement and remained there in the majority of survivors at 2 years.
For a long time, “HF experts thought MR was just a marker of severe left ventricular dysfunction. What I think we see here is that secondary MR is not just a bystander. It contributes to the abnormal pathophysiology of these patients,” he said.
The trial was sponsored by MitraClip’s maker, Abbott. The company participated in site selection, management, and data analysis. Dr. Stone disclosed that his employer, Columbia University, receives royalties from Abbott for sale of the clip. Several fellow investigators disclosed grants, fees, and other financial ties to the company.
Simultaneously with the COAPT presentation, the results were published online (N Engl J Med. 2018 Sep 23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1806640).
Mitra-FR was funded by the French Ministry of Health and Research and Abbott.
SAN DIEGO – Among a carefully selected subset of heart failure patients and severe secondary mitral regurgitation, transcatheter mitral valve repair with the MitraClip reduced hospitalizations for heart failure by 47%, and death from any cause by 38% over 24 months, compared with maximal medical therapy alone.
That’s according to a randomized, open-label trial presented at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting.
The number needed to treat to prevent one heart failure (HF) hospitalization within 2 years was three; the number needed to treat to save one life was six. Only about 3% of patients had a device complication within 12 months of placement in the study, dubbed COAPT (the Heart Failure Patients with Functional Mitral Regurgitation Trial).
COAPT patients had grade 3+ or 4+ secondary mitral regurgitation, with a mean effective regurgitant orifice area (EROA) of 41 mm2. Their left ventricles were dilated, but not huge, with a mean left ventricular end-diastolic volume of 101 mL/m2. “We estimate that’s about 10% of heart failure patients,” said lead investigator and interventional cardiologist Gregg W. Stone, MD, a professor of medicine at Columbia University, New York.
MitraClip placement was performed in high-volume centers by experienced operators, and patients were on maximally tolerated doses of guideline-directed medical therapy, as per the 2013 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association heart failure management guidelines. There was very little variation in treatment regimens during the 2-year trial (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70:776-803).
Those parameters matter. Among HF patients who did not fit them in the recent Mitra-FR trial in France, MitraClip did not reduce rates of death or unplanned hospitalization (N Engl J Med. 2018 Aug 27. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1805374).
COAPT and Mitra-FR investigators said at the meeting that the studies are complimentary, not conflicting, because together, they define secondary mitral regurgitation (MR) patients who will and will not benefit from the device.
MR was less severe in Mitra-FR, with a mean EROA of 31 mm2, but left ventricles were more dilated, with a mean left ventricular end-diastolic volume of 135 mL/m2. Patients were on more real-world drug regimens that varied over the course of the trial. Also, the lower implantation rates and higher complication rates in Mitra-FR “suggests perhaps greater experience of the COAPT operators,” said Dr. Stone, who also is the director of cardiovascular research and education at the Center for Interventional Vascular Therapy at New York-Presbyterian Hospital/Columbia University Medical Center.
In short, “they were a different patient population than were enrolled in COAPT,” he said at the meeting, sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation, which Dr. Stone also codirects.
There was great excitement at TCT about COAPT because there was a startling benefit for patients who previously had few options. But many speakers worried that the hype surrounding the trial will drown out the critically important message about patient selection and that the clip will be used in HF patients who don’t fit the COAPT profile.
They also said that the emerging picture of benefit in patients with less ventricular dilation but more mitral regurgitation needs to be fleshed out and better quantified.
COAPT randomized 302 patients to MitraClip on a background of guideline-directed therapy and 312 to guideline-directed therapy alone. Participants who had mitral regurgitation caused by left ventricular dysfunction, were not surgical candidates, and remained symptomatic despite optimal treatment.
The annualized rate of all hospitalizations for HF within 24 months was 35.8% per patient-year in the device group, as compared with 67.9% per patient-year in the control group, for a relative reduction of 47% (P less than .001).
Death from any cause within 24 months occurred in 29.1% of the patients in the device group and 46.1% in the control group, yielding a reduction of 38% (P less than .001).
“We didn’t cure patients by fixing their MR. They still had 29% 2-year mortality, but we did markedly improve their quality of life. The only subgroup that didn’t benefit were patients that had an EORA of less than 30 mm2 and end diastolic volume greater than the median” of 96 mL/m2, which was “fascinating,” Dr. Stone said, and fit the emerging picture.
Mitral regurgitation grade fell to 1+ or lower in 82% of patients after clip placement and remained there in the majority of survivors at 2 years.
For a long time, “HF experts thought MR was just a marker of severe left ventricular dysfunction. What I think we see here is that secondary MR is not just a bystander. It contributes to the abnormal pathophysiology of these patients,” he said.
The trial was sponsored by MitraClip’s maker, Abbott. The company participated in site selection, management, and data analysis. Dr. Stone disclosed that his employer, Columbia University, receives royalties from Abbott for sale of the clip. Several fellow investigators disclosed grants, fees, and other financial ties to the company.
Simultaneously with the COAPT presentation, the results were published online (N Engl J Med. 2018 Sep 23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1806640).
Mitra-FR was funded by the French Ministry of Health and Research and Abbott.
REPORTING FROM TCT 2018
Key clinical point: MitraClip reduced death and heart failure hospitalizations in certain patients, but
Major finding: Among a subset of heart failure patients with moderately dilated left ventricles and severe secondary mitral regurgitation, transcatheter mitral valve repair with the MitraClip reduced hospitalizations for heart failure within 24 months by 47%, and death from any cause within 24 months by 38%, compared with maximal medical therapy alone.
Study details: COAPT, a randomized, open-label trial with 614 subjects
Disclosures: The work was funded by MitraClip maker, Abbott. The company participated in site selection, management, and data analysis. The lead and several other investigators disclosed financial ties to the company.
Culprit-vessel PCI may be safer long term in cardiogenic shock
At 30 days, culprit lesion–only PCI was associated with fewer cases of death or renal replacement therapy than immediate multivessel PCI.
However, not all the news was good for culprit lesion–only PCI: At 1 year, it was associated with a higher frequency of rehospitalization for heart failure and of repeat vascularization, according to Holger Thiele, MD, of the Heart Center Leipzig at the University of Leipzig (Germany) and his colleagues.
These results from the Culprit Only Lesion PCI versus Multivessel PCI in Cardiogenic Shock (CULPRIT-SHOCK) study were presented at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The 30-day results from the study, published in the journal last year, were enough to convince the creators of the European revascularization guidelines to downgrade immediate multivessel PCI in cardiogenic shock to a class III B recommendation, which indicates that it is not effective and may cause harm.
However, the results also caused controversy because complete revascularization via immediate multivessel PCI in cardiogenic shock patients might lead to long-term benefits. In fact, evidence from nonrandomized trials and a registry study had suggested that immediate multivessel PCI may reduce mortality at 1 year.
But the new 1-year data don’t support that hypothesis of long-term benefit, Dr. Thiele and his colleagues found.
The CULPRIT-SHOCK trial randomized 684 patients at 83 centers to culprit lesion–only PCI or multivessel PCI. At 30 days, death or renal replacement therapy occurred at a lower frequency in the culprit lesion–only group (45.9% vs. 55.4%; relative risk, 0.83; P = .01).
At 1 year, all-cause mortality was 50.0% in the group that underwent culprit lesion–only PCI, compared with 56.9% in the group that underwent multivessel PCI, a result that was not statistically significant (RR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.76-1.01). There was also no significant difference in death from cardiovascular causes, 46.2% in culprit lesion–only patients, compared with 52.8% in multivessel patients (RR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.75-1.02).
Mortality rates between baseline and 1 year were similar in the intention-to-treat, per-protocol, and as-treated populations.
The researchers conducted a post hoc analysis of the original primary endpoint – death or renal replacement therapy – at 1 year, and they found results similar to those seen at 30 days: 52.0% in the culprit lesion–only group and 59.5% in the multivessel group (RR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.76-0.99).
Some results favored multivessel PCI: 32.3% of the culprit lesion–only group underwent repeat revascularization, compared with 9.4% of multivessel PCI (RR, 3.44; 95% CI, 2.39-4.95). Rehospitalizations for congestive heart failure were rare, but occurred in 5.2% of the culprit lesion–only group, compared with 1.2% of the multivessel group (RR, 4.46; 95% CI, 1.53-13.04).
The study was funded by the European Union Seventh Framework Programme, the German Heart Research Foundation, and the German Centre for Cardiovascular Research. Dr. Thiele had no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Thiele H et al. N Engl J Med. 2018 Aug 2
At 30 days, culprit lesion–only PCI was associated with fewer cases of death or renal replacement therapy than immediate multivessel PCI.
However, not all the news was good for culprit lesion–only PCI: At 1 year, it was associated with a higher frequency of rehospitalization for heart failure and of repeat vascularization, according to Holger Thiele, MD, of the Heart Center Leipzig at the University of Leipzig (Germany) and his colleagues.
These results from the Culprit Only Lesion PCI versus Multivessel PCI in Cardiogenic Shock (CULPRIT-SHOCK) study were presented at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The 30-day results from the study, published in the journal last year, were enough to convince the creators of the European revascularization guidelines to downgrade immediate multivessel PCI in cardiogenic shock to a class III B recommendation, which indicates that it is not effective and may cause harm.
However, the results also caused controversy because complete revascularization via immediate multivessel PCI in cardiogenic shock patients might lead to long-term benefits. In fact, evidence from nonrandomized trials and a registry study had suggested that immediate multivessel PCI may reduce mortality at 1 year.
But the new 1-year data don’t support that hypothesis of long-term benefit, Dr. Thiele and his colleagues found.
The CULPRIT-SHOCK trial randomized 684 patients at 83 centers to culprit lesion–only PCI or multivessel PCI. At 30 days, death or renal replacement therapy occurred at a lower frequency in the culprit lesion–only group (45.9% vs. 55.4%; relative risk, 0.83; P = .01).
At 1 year, all-cause mortality was 50.0% in the group that underwent culprit lesion–only PCI, compared with 56.9% in the group that underwent multivessel PCI, a result that was not statistically significant (RR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.76-1.01). There was also no significant difference in death from cardiovascular causes, 46.2% in culprit lesion–only patients, compared with 52.8% in multivessel patients (RR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.75-1.02).
Mortality rates between baseline and 1 year were similar in the intention-to-treat, per-protocol, and as-treated populations.
The researchers conducted a post hoc analysis of the original primary endpoint – death or renal replacement therapy – at 1 year, and they found results similar to those seen at 30 days: 52.0% in the culprit lesion–only group and 59.5% in the multivessel group (RR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.76-0.99).
Some results favored multivessel PCI: 32.3% of the culprit lesion–only group underwent repeat revascularization, compared with 9.4% of multivessel PCI (RR, 3.44; 95% CI, 2.39-4.95). Rehospitalizations for congestive heart failure were rare, but occurred in 5.2% of the culprit lesion–only group, compared with 1.2% of the multivessel group (RR, 4.46; 95% CI, 1.53-13.04).
The study was funded by the European Union Seventh Framework Programme, the German Heart Research Foundation, and the German Centre for Cardiovascular Research. Dr. Thiele had no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Thiele H et al. N Engl J Med. 2018 Aug 2
At 30 days, culprit lesion–only PCI was associated with fewer cases of death or renal replacement therapy than immediate multivessel PCI.
However, not all the news was good for culprit lesion–only PCI: At 1 year, it was associated with a higher frequency of rehospitalization for heart failure and of repeat vascularization, according to Holger Thiele, MD, of the Heart Center Leipzig at the University of Leipzig (Germany) and his colleagues.
These results from the Culprit Only Lesion PCI versus Multivessel PCI in Cardiogenic Shock (CULPRIT-SHOCK) study were presented at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The 30-day results from the study, published in the journal last year, were enough to convince the creators of the European revascularization guidelines to downgrade immediate multivessel PCI in cardiogenic shock to a class III B recommendation, which indicates that it is not effective and may cause harm.
However, the results also caused controversy because complete revascularization via immediate multivessel PCI in cardiogenic shock patients might lead to long-term benefits. In fact, evidence from nonrandomized trials and a registry study had suggested that immediate multivessel PCI may reduce mortality at 1 year.
But the new 1-year data don’t support that hypothesis of long-term benefit, Dr. Thiele and his colleagues found.
The CULPRIT-SHOCK trial randomized 684 patients at 83 centers to culprit lesion–only PCI or multivessel PCI. At 30 days, death or renal replacement therapy occurred at a lower frequency in the culprit lesion–only group (45.9% vs. 55.4%; relative risk, 0.83; P = .01).
At 1 year, all-cause mortality was 50.0% in the group that underwent culprit lesion–only PCI, compared with 56.9% in the group that underwent multivessel PCI, a result that was not statistically significant (RR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.76-1.01). There was also no significant difference in death from cardiovascular causes, 46.2% in culprit lesion–only patients, compared with 52.8% in multivessel patients (RR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.75-1.02).
Mortality rates between baseline and 1 year were similar in the intention-to-treat, per-protocol, and as-treated populations.
The researchers conducted a post hoc analysis of the original primary endpoint – death or renal replacement therapy – at 1 year, and they found results similar to those seen at 30 days: 52.0% in the culprit lesion–only group and 59.5% in the multivessel group (RR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.76-0.99).
Some results favored multivessel PCI: 32.3% of the culprit lesion–only group underwent repeat revascularization, compared with 9.4% of multivessel PCI (RR, 3.44; 95% CI, 2.39-4.95). Rehospitalizations for congestive heart failure were rare, but occurred in 5.2% of the culprit lesion–only group, compared with 1.2% of the multivessel group (RR, 4.46; 95% CI, 1.53-13.04).
The study was funded by the European Union Seventh Framework Programme, the German Heart Research Foundation, and the German Centre for Cardiovascular Research. Dr. Thiele had no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Thiele H et al. N Engl J Med. 2018 Aug 2
REPORTING FROM THE ESC CONGRESS 2018
Key clinical point: Culprit-vessel PCI may be safer than multivessel PCI.
Major finding: At 1 year, treating patients with acute MI, cardiogenic shock, and multivessel coronary artery disease with either culprit-vessel PCI or multivessel PCI had similar mortality rates.
Study details: A randomized, controlled trial of 684 patients.
Disclosures: The study was funded by the European Union Seventh Framework Programme, the German Heart Research Foundation, and the German Centre for Cardiovascular Research. Dr. Thiele had no relevant conflicts of interest.
Source: Thiele H et al. N Engl J Med. 2018 Aug 25. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1808788.