User login
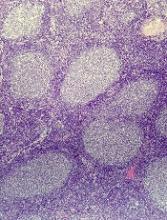
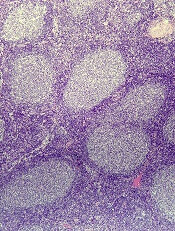
GALEN safe and effective in relapsed and refractory follicular lymphoma
LUGANO, SWITZERLAND – For patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma, a pairing of lenalidomide (Revlimid) and obinutuzumab (Gazyva) appeared to be especially useful among patients who had disease progression within 24 months, based on results from a Lymphoma Academic Research Organisation trial.
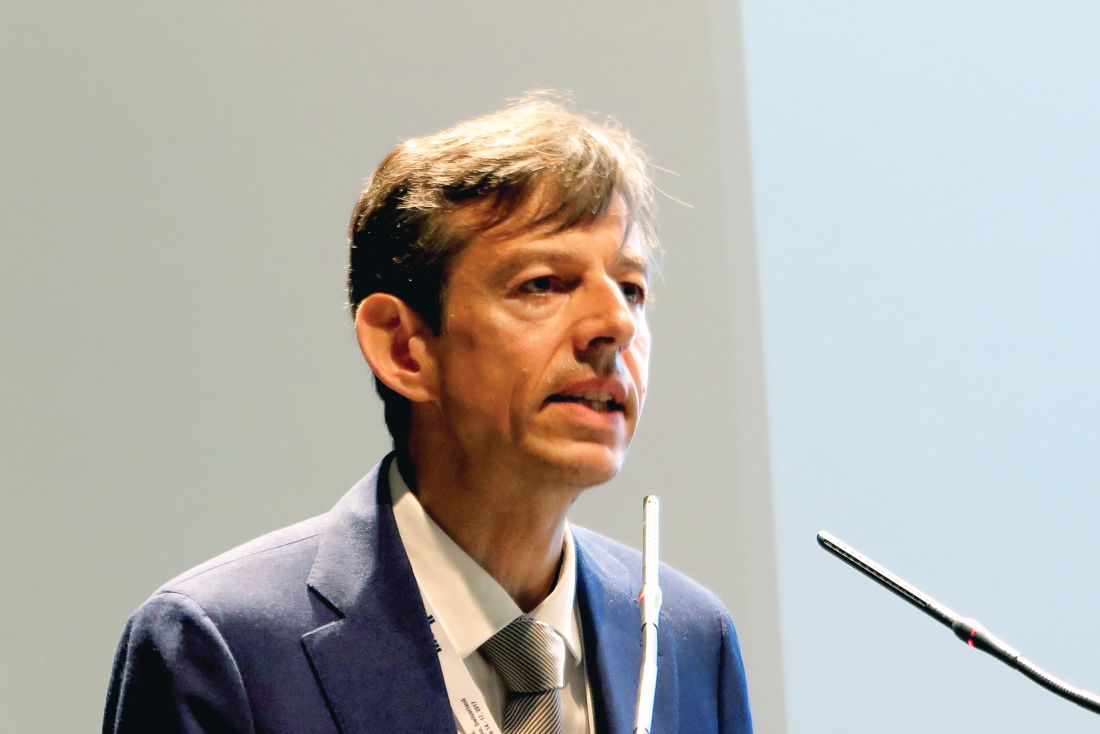
Among 86 patients who were enrolled in a phase II trial and were assessable for efficacy, overall response rates (ORR) with the combination therapy, nicknamed “GALEN,” were 80.2% by 1999 International Working Group criteria, and 74.4% according to the 2007 IWG criteria, reported Franck Morschhauser, MD, PhD, of the University of Lille, France.
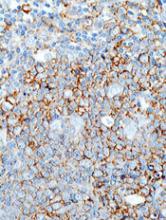
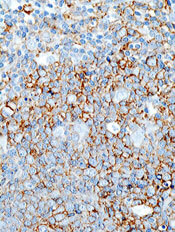
The rationale for this combination is the known synergy between lenalidomide and rituximab in relapsed refractory non-Hodgkin lymphomas and in the frontline setting for patients with follicular lymphoma. Obinutuzumab, a follow-on to rituximab, is a unique type II glycoengineered monoclonal antibody directed against CD20, but with increased antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity and increased direct cytotoxicity, compared with rituximab, he explained.
In the phase Ib part of the study, researchers settled on a dose of obinutuzumab 1000 mg and lenalidomide 20 mg. Obinutuzumab was administered on days 8, 15 and 22 and lenalidomide on days 1 to 21 of each 28 day cycle. Patients were evaluated for response after three cycles and at the end of induction (after completion of 4 to 6 cycles).
The maintenance phase consisted of obinutuzumab on day 1 of every other cycle beginning with cycle 1, and lenalidomide on days 1 through 22 for cycles 7 through 18. From cycles 19 through 24, obinutuzumab was given alone on the first day of every 56-day cycle.
The overall response rate (ORR) at the end of induction according to the IWG 1999 criteria, the primary endpoint, was 80.2%, including 39.5% complete or unconfirmed complete responses.
When the same patients were assessed according to 2007 IWG criteria, the ORR rate was slightly lower, at 74.4%, but the complete or unconfirmed complete response rate was slightly higher, at 44.2%.
An analysis of responses by time to relapse showed that the ORR among 24 patients with disease progression within 24 months was 70.8%, including 33.3% complete or unconfirmed complete responses by the 1999 criteria, and 66.7% with 54.2% complete or unconfirmed complete responses by the 2007 criteria.
ORR among the 64 patients with disease progression after more than 24 months was 83.9% with 41.9% complete or unconfirmed complete responses by 1999 criteria, and 77.4% with 40.3% complete or unconfirmed complete responses by 2007 criteria. The differences between the groups with disease progression within 24 months and later relapse groups were not significant.
A subanalysis by refractory status, however, showed that the 63 nonrefractory patients fared significantly better, with 87.3% ORR and 41.3% complete or unconfirmed complete responses by 1999 criteria, and 81.0% with 49.2% complete or unconfirmed complete response rate by 2007 determinations, compared with respective rates among 23 refractory patients of 60.9%/34.8% complete or unconfirmed complete response rate and 56.5% with 30.4% complete or unconfirmed complete responses (P = .0212 by 1999 criteria, and P = .022 by 2007 criteria).
After a median follow-up of 18 months, 1-year progression-free survival (PFS) among all patients was 75.5%, and 1-year overall survival (OS) was 88.8%.
There were no significant differences in either progression-free survival or overall survival by time to relapse. Although there appeared to be a nonsignificant trend toward worse outcomes among patients with refractory vs. nonrefractory disease, there was a significantly lower 1-year overall survival rate among refractory patients, at 71.5% compared with 95% for nonrefractory patients (censored logrank P = .0098).
Dr. Morschhauser said that the combination had no unexpected toxicities. Hematologic toxicities of grade 3 or greater included neutropenia in 28.4%, thrombocytopenia in 11.4%, and anemia and lymphopenia in 3.4% each.
The most common nonhematologic toxicities of all grades included infections in 62.5% of patients (grade 3 or greater in 6.8%), and asthenia in 52.3% of patients (grade 3 or greater in 2.3%). The only other grade 3 or greater toxicities were peripheral neuropathy in 1.1%, and infusion related rash in 3.4%.
Additional follow-up will be need for evaluation of the full impact of maintenance on outcomes, he added.
The study was funded by Celgene and Roche. Dr. Morschhauser disclosed receiving honoraria from and serving on advisory boards for both companies.
LUGANO, SWITZERLAND – For patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma, a pairing of lenalidomide (Revlimid) and obinutuzumab (Gazyva) appeared to be especially useful among patients who had disease progression within 24 months, based on results from a Lymphoma Academic Research Organisation trial.
Among 86 patients who were enrolled in a phase II trial and were assessable for efficacy, overall response rates (ORR) with the combination therapy, nicknamed “GALEN,” were 80.2% by 1999 International Working Group criteria, and 74.4% according to the 2007 IWG criteria, reported Franck Morschhauser, MD, PhD, of the University of Lille, France.
The rationale for this combination is the known synergy between lenalidomide and rituximab in relapsed refractory non-Hodgkin lymphomas and in the frontline setting for patients with follicular lymphoma. Obinutuzumab, a follow-on to rituximab, is a unique type II glycoengineered monoclonal antibody directed against CD20, but with increased antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity and increased direct cytotoxicity, compared with rituximab, he explained.
In the phase Ib part of the study, researchers settled on a dose of obinutuzumab 1000 mg and lenalidomide 20 mg. Obinutuzumab was administered on days 8, 15 and 22 and lenalidomide on days 1 to 21 of each 28 day cycle. Patients were evaluated for response after three cycles and at the end of induction (after completion of 4 to 6 cycles).
The maintenance phase consisted of obinutuzumab on day 1 of every other cycle beginning with cycle 1, and lenalidomide on days 1 through 22 for cycles 7 through 18. From cycles 19 through 24, obinutuzumab was given alone on the first day of every 56-day cycle.
The overall response rate (ORR) at the end of induction according to the IWG 1999 criteria, the primary endpoint, was 80.2%, including 39.5% complete or unconfirmed complete responses.
When the same patients were assessed according to 2007 IWG criteria, the ORR rate was slightly lower, at 74.4%, but the complete or unconfirmed complete response rate was slightly higher, at 44.2%.
An analysis of responses by time to relapse showed that the ORR among 24 patients with disease progression within 24 months was 70.8%, including 33.3% complete or unconfirmed complete responses by the 1999 criteria, and 66.7% with 54.2% complete or unconfirmed complete responses by the 2007 criteria.
ORR among the 64 patients with disease progression after more than 24 months was 83.9% with 41.9% complete or unconfirmed complete responses by 1999 criteria, and 77.4% with 40.3% complete or unconfirmed complete responses by 2007 criteria. The differences between the groups with disease progression within 24 months and later relapse groups were not significant.
A subanalysis by refractory status, however, showed that the 63 nonrefractory patients fared significantly better, with 87.3% ORR and 41.3% complete or unconfirmed complete responses by 1999 criteria, and 81.0% with 49.2% complete or unconfirmed complete response rate by 2007 determinations, compared with respective rates among 23 refractory patients of 60.9%/34.8% complete or unconfirmed complete response rate and 56.5% with 30.4% complete or unconfirmed complete responses (P = .0212 by 1999 criteria, and P = .022 by 2007 criteria).
After a median follow-up of 18 months, 1-year progression-free survival (PFS) among all patients was 75.5%, and 1-year overall survival (OS) was 88.8%.
There were no significant differences in either progression-free survival or overall survival by time to relapse. Although there appeared to be a nonsignificant trend toward worse outcomes among patients with refractory vs. nonrefractory disease, there was a significantly lower 1-year overall survival rate among refractory patients, at 71.5% compared with 95% for nonrefractory patients (censored logrank P = .0098).
Dr. Morschhauser said that the combination had no unexpected toxicities. Hematologic toxicities of grade 3 or greater included neutropenia in 28.4%, thrombocytopenia in 11.4%, and anemia and lymphopenia in 3.4% each.
The most common nonhematologic toxicities of all grades included infections in 62.5% of patients (grade 3 or greater in 6.8%), and asthenia in 52.3% of patients (grade 3 or greater in 2.3%). The only other grade 3 or greater toxicities were peripheral neuropathy in 1.1%, and infusion related rash in 3.4%.
Additional follow-up will be need for evaluation of the full impact of maintenance on outcomes, he added.
The study was funded by Celgene and Roche. Dr. Morschhauser disclosed receiving honoraria from and serving on advisory boards for both companies.
LUGANO, SWITZERLAND – For patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma, a pairing of lenalidomide (Revlimid) and obinutuzumab (Gazyva) appeared to be especially useful among patients who had disease progression within 24 months, based on results from a Lymphoma Academic Research Organisation trial.
Among 86 patients who were enrolled in a phase II trial and were assessable for efficacy, overall response rates (ORR) with the combination therapy, nicknamed “GALEN,” were 80.2% by 1999 International Working Group criteria, and 74.4% according to the 2007 IWG criteria, reported Franck Morschhauser, MD, PhD, of the University of Lille, France.
The rationale for this combination is the known synergy between lenalidomide and rituximab in relapsed refractory non-Hodgkin lymphomas and in the frontline setting for patients with follicular lymphoma. Obinutuzumab, a follow-on to rituximab, is a unique type II glycoengineered monoclonal antibody directed against CD20, but with increased antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity and increased direct cytotoxicity, compared with rituximab, he explained.
In the phase Ib part of the study, researchers settled on a dose of obinutuzumab 1000 mg and lenalidomide 20 mg. Obinutuzumab was administered on days 8, 15 and 22 and lenalidomide on days 1 to 21 of each 28 day cycle. Patients were evaluated for response after three cycles and at the end of induction (after completion of 4 to 6 cycles).
The maintenance phase consisted of obinutuzumab on day 1 of every other cycle beginning with cycle 1, and lenalidomide on days 1 through 22 for cycles 7 through 18. From cycles 19 through 24, obinutuzumab was given alone on the first day of every 56-day cycle.
The overall response rate (ORR) at the end of induction according to the IWG 1999 criteria, the primary endpoint, was 80.2%, including 39.5% complete or unconfirmed complete responses.
When the same patients were assessed according to 2007 IWG criteria, the ORR rate was slightly lower, at 74.4%, but the complete or unconfirmed complete response rate was slightly higher, at 44.2%.
An analysis of responses by time to relapse showed that the ORR among 24 patients with disease progression within 24 months was 70.8%, including 33.3% complete or unconfirmed complete responses by the 1999 criteria, and 66.7% with 54.2% complete or unconfirmed complete responses by the 2007 criteria.
ORR among the 64 patients with disease progression after more than 24 months was 83.9% with 41.9% complete or unconfirmed complete responses by 1999 criteria, and 77.4% with 40.3% complete or unconfirmed complete responses by 2007 criteria. The differences between the groups with disease progression within 24 months and later relapse groups were not significant.
A subanalysis by refractory status, however, showed that the 63 nonrefractory patients fared significantly better, with 87.3% ORR and 41.3% complete or unconfirmed complete responses by 1999 criteria, and 81.0% with 49.2% complete or unconfirmed complete response rate by 2007 determinations, compared with respective rates among 23 refractory patients of 60.9%/34.8% complete or unconfirmed complete response rate and 56.5% with 30.4% complete or unconfirmed complete responses (P = .0212 by 1999 criteria, and P = .022 by 2007 criteria).
After a median follow-up of 18 months, 1-year progression-free survival (PFS) among all patients was 75.5%, and 1-year overall survival (OS) was 88.8%.
There were no significant differences in either progression-free survival or overall survival by time to relapse. Although there appeared to be a nonsignificant trend toward worse outcomes among patients with refractory vs. nonrefractory disease, there was a significantly lower 1-year overall survival rate among refractory patients, at 71.5% compared with 95% for nonrefractory patients (censored logrank P = .0098).
Dr. Morschhauser said that the combination had no unexpected toxicities. Hematologic toxicities of grade 3 or greater included neutropenia in 28.4%, thrombocytopenia in 11.4%, and anemia and lymphopenia in 3.4% each.
The most common nonhematologic toxicities of all grades included infections in 62.5% of patients (grade 3 or greater in 6.8%), and asthenia in 52.3% of patients (grade 3 or greater in 2.3%). The only other grade 3 or greater toxicities were peripheral neuropathy in 1.1%, and infusion related rash in 3.4%.
Additional follow-up will be need for evaluation of the full impact of maintenance on outcomes, he added.
The study was funded by Celgene and Roche. Dr. Morschhauser disclosed receiving honoraria from and serving on advisory boards for both companies.
AT 14-ICML
Key clinical point: A combination of lenalidomide and obinutuzumab was safe and effective in patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma.
Major finding: The overall response rate according to 1999 International Working Group criteria was 80.2%, including 39.5% CR/CRu.
Data source: Single-arm phase II study with 86 patients evaluable for efficacy and 88 evaluable for safety.
Disclosures: The study was funded by Celgene and Roche. Dr. Morschhauser disclosed receiving honoraria from and serving on advisory boards for both companies.
Biosimilar rituximab approved in Europe
The European Commission (EC) has approved the Sandoz biosimilar rituximab (Rixathon®) for use in the European Economic Area.
Rixathon is approved for all indications of the reference medicine, MabThera®, including follicular lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and immunologic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, and microscopic polyangiitis.
This approval allows Rixathon to be marketed in the member states of the European Union and Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway, members of the European Free Trade Association.
The approval “represents a big win for patients in Europe with blood cancers or immunological diseases,” according to Carol Lynch, global head of Biopharmaceuticals at Sandoz.
“Rixathon will be one of the 5 major launches we plan in the next 4 years,” she said.
Earlier in the year, the European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use had recommended marketing authorization for Rixathon.
The EC based its approval on a comprehensive development program generating analytical, preclinical, and clinical data. Clinical studies included ASSIST-RA and ASSIST-FL.
ASSIST-RA demonstrated that the biosimilar product has equivalent pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles to the reference medicine, with no clinically meaningful differences in safety, tolerability, or immunogenicity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
ASSIST-FL was a phase 3 study confirming efficacy and safety. The study met its primary endpoint of equivalence in overall response rate between the biosimilar product and the reference medicine after 6 months.
ASSIST-FL also confirmed the comparable safety profiles of the 2 medicines.
Sandoz is a division of the Swiss pharmaceutical company Novartis. MabThera is a registered trademark of F. Hoffmann-La-Roche AG.
Another Sandoz biosimilar rituximab has been approved in the EU as Riximyo® under a duplicate marketing authorization. ![]()
The European Commission (EC) has approved the Sandoz biosimilar rituximab (Rixathon®) for use in the European Economic Area.
Rixathon is approved for all indications of the reference medicine, MabThera®, including follicular lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and immunologic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, and microscopic polyangiitis.
This approval allows Rixathon to be marketed in the member states of the European Union and Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway, members of the European Free Trade Association.
The approval “represents a big win for patients in Europe with blood cancers or immunological diseases,” according to Carol Lynch, global head of Biopharmaceuticals at Sandoz.
“Rixathon will be one of the 5 major launches we plan in the next 4 years,” she said.
Earlier in the year, the European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use had recommended marketing authorization for Rixathon.
The EC based its approval on a comprehensive development program generating analytical, preclinical, and clinical data. Clinical studies included ASSIST-RA and ASSIST-FL.
ASSIST-RA demonstrated that the biosimilar product has equivalent pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles to the reference medicine, with no clinically meaningful differences in safety, tolerability, or immunogenicity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
ASSIST-FL was a phase 3 study confirming efficacy and safety. The study met its primary endpoint of equivalence in overall response rate between the biosimilar product and the reference medicine after 6 months.
ASSIST-FL also confirmed the comparable safety profiles of the 2 medicines.
Sandoz is a division of the Swiss pharmaceutical company Novartis. MabThera is a registered trademark of F. Hoffmann-La-Roche AG.
Another Sandoz biosimilar rituximab has been approved in the EU as Riximyo® under a duplicate marketing authorization. ![]()
The European Commission (EC) has approved the Sandoz biosimilar rituximab (Rixathon®) for use in the European Economic Area.
Rixathon is approved for all indications of the reference medicine, MabThera®, including follicular lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and immunologic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, and microscopic polyangiitis.
This approval allows Rixathon to be marketed in the member states of the European Union and Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway, members of the European Free Trade Association.
The approval “represents a big win for patients in Europe with blood cancers or immunological diseases,” according to Carol Lynch, global head of Biopharmaceuticals at Sandoz.
“Rixathon will be one of the 5 major launches we plan in the next 4 years,” she said.
Earlier in the year, the European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use had recommended marketing authorization for Rixathon.
The EC based its approval on a comprehensive development program generating analytical, preclinical, and clinical data. Clinical studies included ASSIST-RA and ASSIST-FL.
ASSIST-RA demonstrated that the biosimilar product has equivalent pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles to the reference medicine, with no clinically meaningful differences in safety, tolerability, or immunogenicity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
ASSIST-FL was a phase 3 study confirming efficacy and safety. The study met its primary endpoint of equivalence in overall response rate between the biosimilar product and the reference medicine after 6 months.
ASSIST-FL also confirmed the comparable safety profiles of the 2 medicines.
Sandoz is a division of the Swiss pharmaceutical company Novartis. MabThera is a registered trademark of F. Hoffmann-La-Roche AG.
Another Sandoz biosimilar rituximab has been approved in the EU as Riximyo® under a duplicate marketing authorization. ![]()
BLA for CAR T-cell therapy granted priority review
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has accepted for priority review the biologics license application (BLA) for axicabtagene ciloleucel (formerly KTE-C19), a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy.
Kite Pharma, Inc. is seeking approval for axicabtagene ciloleucel as a treatment for patients with relapsed or refractory, aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) who are ineligible for autologous stem cell transplant.
The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that may provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions.
The agency’s goal is to take action on a priority review application within 6 months of receiving it, rather than the standard 10 months.
The FDA has set a review deadline of November 29, 2017, for the axicabtagene ciloleucel BLA.
Axicabtagene ciloleucel also has breakthrough therapy designation from the FDA as a treatment for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, transformed follicular lymphoma, and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma.
ZUMA-1 trial
The BLA for axicabtagene ciloleucel is supported by data from the phase 2 ZUMA-1 trial, which enrolled 111 patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell NHL.
After a single infusion of axicabtagene ciloleucel, the objective response rate was 82%. At a median follow-up of 8.7 months, 44% of patients were still in response, which included 39% of patients in complete response.
The most common grade 3 or higher adverse events were anemia (43%), neutropenia (39%), decreased neutrophil count (32%), febrile neutropenia (31%), decreased white blood cell count (29%), thrombocytopenia (24%), encephalopathy (21%), and decreased lymphocyte count (20%).
There were 3 deaths during the trial that were not due to disease progression. Two of these deaths were deemed related to axicabtagene ciloleucel. ![]()
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has accepted for priority review the biologics license application (BLA) for axicabtagene ciloleucel (formerly KTE-C19), a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy.
Kite Pharma, Inc. is seeking approval for axicabtagene ciloleucel as a treatment for patients with relapsed or refractory, aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) who are ineligible for autologous stem cell transplant.
The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that may provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions.
The agency’s goal is to take action on a priority review application within 6 months of receiving it, rather than the standard 10 months.
The FDA has set a review deadline of November 29, 2017, for the axicabtagene ciloleucel BLA.
Axicabtagene ciloleucel also has breakthrough therapy designation from the FDA as a treatment for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, transformed follicular lymphoma, and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma.
ZUMA-1 trial
The BLA for axicabtagene ciloleucel is supported by data from the phase 2 ZUMA-1 trial, which enrolled 111 patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell NHL.
After a single infusion of axicabtagene ciloleucel, the objective response rate was 82%. At a median follow-up of 8.7 months, 44% of patients were still in response, which included 39% of patients in complete response.
The most common grade 3 or higher adverse events were anemia (43%), neutropenia (39%), decreased neutrophil count (32%), febrile neutropenia (31%), decreased white blood cell count (29%), thrombocytopenia (24%), encephalopathy (21%), and decreased lymphocyte count (20%).
There were 3 deaths during the trial that were not due to disease progression. Two of these deaths were deemed related to axicabtagene ciloleucel. ![]()
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has accepted for priority review the biologics license application (BLA) for axicabtagene ciloleucel (formerly KTE-C19), a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy.
Kite Pharma, Inc. is seeking approval for axicabtagene ciloleucel as a treatment for patients with relapsed or refractory, aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) who are ineligible for autologous stem cell transplant.
The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that may provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions.
The agency’s goal is to take action on a priority review application within 6 months of receiving it, rather than the standard 10 months.
The FDA has set a review deadline of November 29, 2017, for the axicabtagene ciloleucel BLA.
Axicabtagene ciloleucel also has breakthrough therapy designation from the FDA as a treatment for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, transformed follicular lymphoma, and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma.
ZUMA-1 trial
The BLA for axicabtagene ciloleucel is supported by data from the phase 2 ZUMA-1 trial, which enrolled 111 patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell NHL.
After a single infusion of axicabtagene ciloleucel, the objective response rate was 82%. At a median follow-up of 8.7 months, 44% of patients were still in response, which included 39% of patients in complete response.
The most common grade 3 or higher adverse events were anemia (43%), neutropenia (39%), decreased neutrophil count (32%), febrile neutropenia (31%), decreased white blood cell count (29%), thrombocytopenia (24%), encephalopathy (21%), and decreased lymphocyte count (20%).
There were 3 deaths during the trial that were not due to disease progression. Two of these deaths were deemed related to axicabtagene ciloleucel. ![]()
FDA grants priority review to NDA for copanlisib
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted priority review to the new drug application (NDA) for copanlisib, an intravenous PI3K inhibitor.
The NDA is for copanlisib as a treatment for patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma (FL) who have received at least 2 prior therapies.
The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that may provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions.
The agency’s goal is to take action on a priority review application within 6 months of receiving it, rather than the standard 10 months.
The application for copanlisib is supported by data from the CHRONOS-1 trial. This phase 2 trial enrolled 141 patients with relapsed/refractory, indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Most of these patients had FL (n=104).
In all patients, copanlisib produced an objective response rate of 59.2%, with a complete response rate of 12%. The median duration of response exceeded 98 weeks.
In the FL subset, copanlisib produced an overall response rate of 58.7%, with a complete response rate of 14.4%. The median duration of response exceeded 52 weeks.
In the entire cohort, there were 3 deaths considered related to copanlisib.
The most common treatment-related adverse events were transient hyperglycemia (all grades: 49%/grade 3-4: 40%) and hypertension (all grades: 29%/grade 3: 23%).
“Patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma have a poor prognosis, and new treatment options which are well tolerated and effective are needed to prolong progression-free survival and improve quality of life for these patients,” said Martin Dreyling, MD, a professor at the University of Munich Hospital (Grosshadern) in Germany and lead investigator of the CHRONOS-1 study.
“Based on the CHRONOS-1 results, where copanlisib showed durable efficacy with a manageable and distinct safety profile, the compound may have the potential to address this unmet medical need.”
Data from CHRONOS-1 were presented at the AACR Annual Meeting 2017.
Data from the FL subset of the trial are scheduled to be presented at the 2017 ASCO Annual Meeting in June.
Copanlisib is being developed by Bayer. The compound has fast track and orphan drug designations from the FDA.
The FDA grants orphan designation to products intended to treat, diagnose, or prevent diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the US.
The designation provides incentives for sponsors to develop products for rare diseases. This may include tax credits toward the cost of clinical trials, prescription drug user fee waivers, and 7 years of market exclusivity if the product is approved.
The FDA’s fast track program is designed to facilitate the development and expedite the review of products intended to treat or prevent serious or life-threatening conditions and address unmet medical need.
Through the fast track program, a product may be eligible for priority review. In addition, the company developing the product may be allowed to submit sections of the NDA or biologic license application on a rolling basis as data become available.
Fast track designation also provides the company with opportunities for more frequent meetings and written communications with the FDA. ![]()
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted priority review to the new drug application (NDA) for copanlisib, an intravenous PI3K inhibitor.
The NDA is for copanlisib as a treatment for patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma (FL) who have received at least 2 prior therapies.
The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that may provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions.
The agency’s goal is to take action on a priority review application within 6 months of receiving it, rather than the standard 10 months.
The application for copanlisib is supported by data from the CHRONOS-1 trial. This phase 2 trial enrolled 141 patients with relapsed/refractory, indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Most of these patients had FL (n=104).
In all patients, copanlisib produced an objective response rate of 59.2%, with a complete response rate of 12%. The median duration of response exceeded 98 weeks.
In the FL subset, copanlisib produced an overall response rate of 58.7%, with a complete response rate of 14.4%. The median duration of response exceeded 52 weeks.
In the entire cohort, there were 3 deaths considered related to copanlisib.
The most common treatment-related adverse events were transient hyperglycemia (all grades: 49%/grade 3-4: 40%) and hypertension (all grades: 29%/grade 3: 23%).
“Patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma have a poor prognosis, and new treatment options which are well tolerated and effective are needed to prolong progression-free survival and improve quality of life for these patients,” said Martin Dreyling, MD, a professor at the University of Munich Hospital (Grosshadern) in Germany and lead investigator of the CHRONOS-1 study.
“Based on the CHRONOS-1 results, where copanlisib showed durable efficacy with a manageable and distinct safety profile, the compound may have the potential to address this unmet medical need.”
Data from CHRONOS-1 were presented at the AACR Annual Meeting 2017.
Data from the FL subset of the trial are scheduled to be presented at the 2017 ASCO Annual Meeting in June.
Copanlisib is being developed by Bayer. The compound has fast track and orphan drug designations from the FDA.
The FDA grants orphan designation to products intended to treat, diagnose, or prevent diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the US.
The designation provides incentives for sponsors to develop products for rare diseases. This may include tax credits toward the cost of clinical trials, prescription drug user fee waivers, and 7 years of market exclusivity if the product is approved.
The FDA’s fast track program is designed to facilitate the development and expedite the review of products intended to treat or prevent serious or life-threatening conditions and address unmet medical need.
Through the fast track program, a product may be eligible for priority review. In addition, the company developing the product may be allowed to submit sections of the NDA or biologic license application on a rolling basis as data become available.
Fast track designation also provides the company with opportunities for more frequent meetings and written communications with the FDA. ![]()
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted priority review to the new drug application (NDA) for copanlisib, an intravenous PI3K inhibitor.
The NDA is for copanlisib as a treatment for patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma (FL) who have received at least 2 prior therapies.
The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that may provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions.
The agency’s goal is to take action on a priority review application within 6 months of receiving it, rather than the standard 10 months.
The application for copanlisib is supported by data from the CHRONOS-1 trial. This phase 2 trial enrolled 141 patients with relapsed/refractory, indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Most of these patients had FL (n=104).
In all patients, copanlisib produced an objective response rate of 59.2%, with a complete response rate of 12%. The median duration of response exceeded 98 weeks.
In the FL subset, copanlisib produced an overall response rate of 58.7%, with a complete response rate of 14.4%. The median duration of response exceeded 52 weeks.
In the entire cohort, there were 3 deaths considered related to copanlisib.
The most common treatment-related adverse events were transient hyperglycemia (all grades: 49%/grade 3-4: 40%) and hypertension (all grades: 29%/grade 3: 23%).
“Patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma have a poor prognosis, and new treatment options which are well tolerated and effective are needed to prolong progression-free survival and improve quality of life for these patients,” said Martin Dreyling, MD, a professor at the University of Munich Hospital (Grosshadern) in Germany and lead investigator of the CHRONOS-1 study.
“Based on the CHRONOS-1 results, where copanlisib showed durable efficacy with a manageable and distinct safety profile, the compound may have the potential to address this unmet medical need.”
Data from CHRONOS-1 were presented at the AACR Annual Meeting 2017.
Data from the FL subset of the trial are scheduled to be presented at the 2017 ASCO Annual Meeting in June.
Copanlisib is being developed by Bayer. The compound has fast track and orphan drug designations from the FDA.
The FDA grants orphan designation to products intended to treat, diagnose, or prevent diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the US.
The designation provides incentives for sponsors to develop products for rare diseases. This may include tax credits toward the cost of clinical trials, prescription drug user fee waivers, and 7 years of market exclusivity if the product is approved.
The FDA’s fast track program is designed to facilitate the development and expedite the review of products intended to treat or prevent serious or life-threatening conditions and address unmet medical need.
Through the fast track program, a product may be eligible for priority review. In addition, the company developing the product may be allowed to submit sections of the NDA or biologic license application on a rolling basis as data become available.
Fast track designation also provides the company with opportunities for more frequent meetings and written communications with the FDA. ![]()
Subcutaneous rituximab safe, effective for follicular lymphoma
Efficacy and safety profiles were similar for subcutaneous and standard IV rituximab when given as first-line therapy to adults with follicular lymphoma, based on results of a phase III clinical trial published online in Lancet Haematology.
Administering rituximab by IV infusion can take up to 6 hours to complete and requires continuous monitoring. Subcutaneous delivery takes approximately 6 minutes using a new rituximab formulation that is 12 times more concentrated to reduce the administered volume. The new formulation is expected to reduce the burden of treatment for patients, as well as for the health care system, said Andrew Davies, PhD, of the Cancer Research UK Centre, Southampton, and his associates.
They compared the two agents in an international open-label trial funded by Hoffmann-La Roche, maker of the subcutaneous formulation. Adult patients at 113 medical centers in 30 countries were randomly assigned to receive either IV (205 patients) or subcutaneous (205 patients) rituximab during induction therapy with six to eight cycles of CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) or CVP (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone). They continued with rituximab as maintenance therapy every 2 months for 2 years. The median duration of treatment was 27 months, and median follow-up was 37 months.
The primary efficacy end point – overall (complete or partial) response rate at the end of induction, based on investigator assessment confirmed by an independent review panel of radiologists – was 84.9% with IV and 84.4% with subcutaneous rituximab, a nonsignificant difference. Similarly, the overall response rate at the end of maintenance therapy was not significantly different between the two groups, at 78.1% and 77.9%, respectively.
Progression-free survival (hazard ratio, 0.84) and event-free survival (HR, 0.91) also did not differ significantly between the two study groups, the investigators said (Lancet Haematol. 2017 doi: 10.1016/S2352.3026(17)30078-9).
The rates of adverse events, grade 3 or higher adverse events, and serious adverse events also were similar for IV and subcutaneous formulations of rituximab. “Administration-related reactions were more common in the subcutaneous group but were predominantly mild-to-moderate local injection-site reactions, such as mild pain, swelling and erythema, reflecting the expected change in safety profile when switching to the subcutaneous route of administration,” Dr. Davies and his associates said.
These results indicate that subcutaneous administration of rituximab along with chemotherapy doesn’t compromise the agent’s antilymphoma activity, they added.
Efficacy and safety profiles were similar for subcutaneous and standard IV rituximab when given as first-line therapy to adults with follicular lymphoma, based on results of a phase III clinical trial published online in Lancet Haematology.
Administering rituximab by IV infusion can take up to 6 hours to complete and requires continuous monitoring. Subcutaneous delivery takes approximately 6 minutes using a new rituximab formulation that is 12 times more concentrated to reduce the administered volume. The new formulation is expected to reduce the burden of treatment for patients, as well as for the health care system, said Andrew Davies, PhD, of the Cancer Research UK Centre, Southampton, and his associates.
They compared the two agents in an international open-label trial funded by Hoffmann-La Roche, maker of the subcutaneous formulation. Adult patients at 113 medical centers in 30 countries were randomly assigned to receive either IV (205 patients) or subcutaneous (205 patients) rituximab during induction therapy with six to eight cycles of CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) or CVP (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone). They continued with rituximab as maintenance therapy every 2 months for 2 years. The median duration of treatment was 27 months, and median follow-up was 37 months.
The primary efficacy end point – overall (complete or partial) response rate at the end of induction, based on investigator assessment confirmed by an independent review panel of radiologists – was 84.9% with IV and 84.4% with subcutaneous rituximab, a nonsignificant difference. Similarly, the overall response rate at the end of maintenance therapy was not significantly different between the two groups, at 78.1% and 77.9%, respectively.
Progression-free survival (hazard ratio, 0.84) and event-free survival (HR, 0.91) also did not differ significantly between the two study groups, the investigators said (Lancet Haematol. 2017 doi: 10.1016/S2352.3026(17)30078-9).
The rates of adverse events, grade 3 or higher adverse events, and serious adverse events also were similar for IV and subcutaneous formulations of rituximab. “Administration-related reactions were more common in the subcutaneous group but were predominantly mild-to-moderate local injection-site reactions, such as mild pain, swelling and erythema, reflecting the expected change in safety profile when switching to the subcutaneous route of administration,” Dr. Davies and his associates said.
These results indicate that subcutaneous administration of rituximab along with chemotherapy doesn’t compromise the agent’s antilymphoma activity, they added.
Efficacy and safety profiles were similar for subcutaneous and standard IV rituximab when given as first-line therapy to adults with follicular lymphoma, based on results of a phase III clinical trial published online in Lancet Haematology.
Administering rituximab by IV infusion can take up to 6 hours to complete and requires continuous monitoring. Subcutaneous delivery takes approximately 6 minutes using a new rituximab formulation that is 12 times more concentrated to reduce the administered volume. The new formulation is expected to reduce the burden of treatment for patients, as well as for the health care system, said Andrew Davies, PhD, of the Cancer Research UK Centre, Southampton, and his associates.
They compared the two agents in an international open-label trial funded by Hoffmann-La Roche, maker of the subcutaneous formulation. Adult patients at 113 medical centers in 30 countries were randomly assigned to receive either IV (205 patients) or subcutaneous (205 patients) rituximab during induction therapy with six to eight cycles of CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) or CVP (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone). They continued with rituximab as maintenance therapy every 2 months for 2 years. The median duration of treatment was 27 months, and median follow-up was 37 months.
The primary efficacy end point – overall (complete or partial) response rate at the end of induction, based on investigator assessment confirmed by an independent review panel of radiologists – was 84.9% with IV and 84.4% with subcutaneous rituximab, a nonsignificant difference. Similarly, the overall response rate at the end of maintenance therapy was not significantly different between the two groups, at 78.1% and 77.9%, respectively.
Progression-free survival (hazard ratio, 0.84) and event-free survival (HR, 0.91) also did not differ significantly between the two study groups, the investigators said (Lancet Haematol. 2017 doi: 10.1016/S2352.3026(17)30078-9).
The rates of adverse events, grade 3 or higher adverse events, and serious adverse events also were similar for IV and subcutaneous formulations of rituximab. “Administration-related reactions were more common in the subcutaneous group but were predominantly mild-to-moderate local injection-site reactions, such as mild pain, swelling and erythema, reflecting the expected change in safety profile when switching to the subcutaneous route of administration,” Dr. Davies and his associates said.
These results indicate that subcutaneous administration of rituximab along with chemotherapy doesn’t compromise the agent’s antilymphoma activity, they added.
FROM LANCET HAEMATOLOGY
Key clinical point: Subcutaneous rituximab had efficacy and safety profiles similar to those of standard IV rituximab when given as first-line therapy to adults with follicular lymphoma.
Major finding: The primary efficacy end point – overall response rate at the end of induction – was 84.9% with IV and 84.4% with subcutaneous rituximab.
Data source: An international randomized controlled phase III trial involving 410 adults followed for 3 years.
Disclosures: This trial was funded by Hoffmann-La Roche, maker of the subcutaneous formulation of rituximab. The pharmaceutical company also was involved in the design and conduct of the trial, collection and interpretation of the data, and writing of the results. Dr. Davies reported ties to Hoffmann-La Roche and numerous other drug companies.
Drug receives fast track designation for follicular lymphoma
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted fast track designation to the EZH2 inhibitor tazemetostat as a treatment for relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma, with or without EZH2-activating mutations.
The FDA’s fast track program is designed to facilitate the development and expedite the review of products intended to treat or prevent serious or life-threatening conditions and address unmet medical need.
Through the fast track program, a product may be eligible for priority review.
In addition, the company developing the product may be allowed to submit sections of the new drug application or biologic license application on a rolling basis as data become available.
Fast track designation also provides the company with opportunities for more frequent meetings and written communications with the FDA.
Tazemetostat also has fast track designation from the FDA as a treatment for patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) with EZH2-activating mutations.
Tazemetostat is under investigation as monotherapy and in combination with other agents as a treatment for multiple cancers.
Results from a phase 1 study suggested tazemetostat can produce durable responses in patients with advanced non-Hodgkin lymphomas, including follicular lymphoma and DLBCL. The study was presented at the 2015 ASH Annual Meeting.
Tazemetostat is currently under investigation in a phase 2 trial of adults with relapsed or refractory DLBCL or follicular lymphoma.
Interim efficacy and safety data from this study are scheduled to be presented at the International Conference on Malignant Lymphoma (ICML) in Lugano, Switzerland, on June 14, 2017, at 2:00 pm CET.
Tazemetostat is being developed by Epizyme, Inc. ![]()
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted fast track designation to the EZH2 inhibitor tazemetostat as a treatment for relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma, with or without EZH2-activating mutations.
The FDA’s fast track program is designed to facilitate the development and expedite the review of products intended to treat or prevent serious or life-threatening conditions and address unmet medical need.
Through the fast track program, a product may be eligible for priority review.
In addition, the company developing the product may be allowed to submit sections of the new drug application or biologic license application on a rolling basis as data become available.
Fast track designation also provides the company with opportunities for more frequent meetings and written communications with the FDA.
Tazemetostat also has fast track designation from the FDA as a treatment for patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) with EZH2-activating mutations.
Tazemetostat is under investigation as monotherapy and in combination with other agents as a treatment for multiple cancers.
Results from a phase 1 study suggested tazemetostat can produce durable responses in patients with advanced non-Hodgkin lymphomas, including follicular lymphoma and DLBCL. The study was presented at the 2015 ASH Annual Meeting.
Tazemetostat is currently under investigation in a phase 2 trial of adults with relapsed or refractory DLBCL or follicular lymphoma.
Interim efficacy and safety data from this study are scheduled to be presented at the International Conference on Malignant Lymphoma (ICML) in Lugano, Switzerland, on June 14, 2017, at 2:00 pm CET.
Tazemetostat is being developed by Epizyme, Inc. ![]()
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted fast track designation to the EZH2 inhibitor tazemetostat as a treatment for relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma, with or without EZH2-activating mutations.
The FDA’s fast track program is designed to facilitate the development and expedite the review of products intended to treat or prevent serious or life-threatening conditions and address unmet medical need.
Through the fast track program, a product may be eligible for priority review.
In addition, the company developing the product may be allowed to submit sections of the new drug application or biologic license application on a rolling basis as data become available.
Fast track designation also provides the company with opportunities for more frequent meetings and written communications with the FDA.
Tazemetostat also has fast track designation from the FDA as a treatment for patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) with EZH2-activating mutations.
Tazemetostat is under investigation as monotherapy and in combination with other agents as a treatment for multiple cancers.
Results from a phase 1 study suggested tazemetostat can produce durable responses in patients with advanced non-Hodgkin lymphomas, including follicular lymphoma and DLBCL. The study was presented at the 2015 ASH Annual Meeting.
Tazemetostat is currently under investigation in a phase 2 trial of adults with relapsed or refractory DLBCL or follicular lymphoma.
Interim efficacy and safety data from this study are scheduled to be presented at the International Conference on Malignant Lymphoma (ICML) in Lugano, Switzerland, on June 14, 2017, at 2:00 pm CET.
Tazemetostat is being developed by Epizyme, Inc. ![]()
In mantle cell lymphoma, triple therapy proves too toxic
Combined idelalisib, lenalidomide, and rituximab proved excessively toxic for the treatment of relapsed and refractory mantle cell and follicular lymphoma in two phase I trials conducted by the Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology.
The unexpected outcome, which led to early study termination, underscores the need for caution as new treatment combinations are proposed, Sonali M. Smith, MD, of the University of Chicago and her colleagues said in The Lancet Haematology.
In four of the first eight patients enrolled in the mantle cell lymphoma (A051201) and follicular lymphoma (A051202) phase I trials between July 9, 2013, and Sept. 30, 2014, unexpected dose-limiting toxicities occurred, including grade 4 sepsis syndrome, grade 4 hypotension with grade 3 rash and fevers, grade 4 aspartate aminotransferase (AST) or alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevation with fevers, and grade 3 pulmonary infection with grade 3 maculopapular rash.
The adverse events occurred between 9 and 20 days after treatment initiation and coincided with rituximab infusions, the researchers said. No treatment-related deaths occurred (Lancet Haematol. 2017 Apr;4:e176-82).
Overall, 8 of 11 patients were removed from treatment because of an adverse event, and 3 of those required intensive care unit level of care.
Although rituximab was removed in both trials, two of the remaining three patients in the studies, including three with mantle cell lymphoma and eight with follicular lymphoma, experienced grade 3 rashes, and one had grade 3 AST elevations. In those with mantle cell lymphoma, the most common grade 3-4 adverse events were ALT elevations and rash. In those with follicular lymphoma, the most common grade 3-4 adverse events were neutropenia and rash.
“Given the inability to deliver treatment due to toxicity, both studies were permanently closed,” the researchers wrote, noting that the primary endpoint of safety and tolerability was not met.
The trials had the overall goal of developing targeted regimens to replace cytotoxic therapy.
“Both ... trials were designed to capitalize on the clinical synergy of lenalidomide and rituximab observed in previous trials by adding the highly specific PI3K delta inhibitor, idelalisib, for patients with relapsed mantle cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma,” they said.
Previously available data implied that lenalidomide plus rituximab would be a safe backbone for therapy, and there was clinical rationale for adding idelalisib to that combination, they explained.
“Overall, our brief experience underscores the limited knowledge regarding drug interactions and off-target effects and serves as a cautionary note in developing biological agents in combination and against ad-hoc combinations outside of carefully monitored clinical trials,” they said.
The researchers noted that the nature of the toxicities observed in these trials supports an immune-activated state characterized by excessive inflammation.
“A more detailed assessment of effect on cytokines, T-cell subsets, natural killer cells, and clinical features predictive of toxicity and response should be included in any further testing of these classes of agents, and they should never be combined outside of a carefully designed and diligently monitored clinical trial setting,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Smith received research funding and consulting fees from Gilead and Celgene.
The findings by Dr. Smith and her colleagues add to several other reported studies that involved unexpected toxicities with various combinations of targeted agents in lymphoid malignancies.
Combinations of B-cell receptor signaling inhibitors can lead to immune dysregulation, which can be acute and severe when combined with immunomodulatory agents.
While the study of rational targeted combinations continues to hold immense potential in both untreated and relapsed/refractory disease, the combination must be thoroughly studied in the context of carefully and conservatively designed clinical trials.
Given the unpredictable nature of adverse events, the use of novel combinations outside of a clinical trial should be strongly discouraged.
Patrick M. Reagan, MD , and Paul M. Barr, MD , are with the James P. Wilmot Cancer Institute, University of Rochester, New York. Dr. Reagan reported having no disclosures. Dr. Barr has consulted for Gilead, Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, and Celgene. They made their remarks in an editorial that accompanied the article.
The findings by Dr. Smith and her colleagues add to several other reported studies that involved unexpected toxicities with various combinations of targeted agents in lymphoid malignancies.
Combinations of B-cell receptor signaling inhibitors can lead to immune dysregulation, which can be acute and severe when combined with immunomodulatory agents.
While the study of rational targeted combinations continues to hold immense potential in both untreated and relapsed/refractory disease, the combination must be thoroughly studied in the context of carefully and conservatively designed clinical trials.
Given the unpredictable nature of adverse events, the use of novel combinations outside of a clinical trial should be strongly discouraged.
Patrick M. Reagan, MD , and Paul M. Barr, MD , are with the James P. Wilmot Cancer Institute, University of Rochester, New York. Dr. Reagan reported having no disclosures. Dr. Barr has consulted for Gilead, Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, and Celgene. They made their remarks in an editorial that accompanied the article.
The findings by Dr. Smith and her colleagues add to several other reported studies that involved unexpected toxicities with various combinations of targeted agents in lymphoid malignancies.
Combinations of B-cell receptor signaling inhibitors can lead to immune dysregulation, which can be acute and severe when combined with immunomodulatory agents.
While the study of rational targeted combinations continues to hold immense potential in both untreated and relapsed/refractory disease, the combination must be thoroughly studied in the context of carefully and conservatively designed clinical trials.
Given the unpredictable nature of adverse events, the use of novel combinations outside of a clinical trial should be strongly discouraged.
Patrick M. Reagan, MD , and Paul M. Barr, MD , are with the James P. Wilmot Cancer Institute, University of Rochester, New York. Dr. Reagan reported having no disclosures. Dr. Barr has consulted for Gilead, Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, and Celgene. They made their remarks in an editorial that accompanied the article.
Combined idelalisib, lenalidomide, and rituximab proved excessively toxic for the treatment of relapsed and refractory mantle cell and follicular lymphoma in two phase I trials conducted by the Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology.
The unexpected outcome, which led to early study termination, underscores the need for caution as new treatment combinations are proposed, Sonali M. Smith, MD, of the University of Chicago and her colleagues said in The Lancet Haematology.
In four of the first eight patients enrolled in the mantle cell lymphoma (A051201) and follicular lymphoma (A051202) phase I trials between July 9, 2013, and Sept. 30, 2014, unexpected dose-limiting toxicities occurred, including grade 4 sepsis syndrome, grade 4 hypotension with grade 3 rash and fevers, grade 4 aspartate aminotransferase (AST) or alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevation with fevers, and grade 3 pulmonary infection with grade 3 maculopapular rash.
The adverse events occurred between 9 and 20 days after treatment initiation and coincided with rituximab infusions, the researchers said. No treatment-related deaths occurred (Lancet Haematol. 2017 Apr;4:e176-82).
Overall, 8 of 11 patients were removed from treatment because of an adverse event, and 3 of those required intensive care unit level of care.
Although rituximab was removed in both trials, two of the remaining three patients in the studies, including three with mantle cell lymphoma and eight with follicular lymphoma, experienced grade 3 rashes, and one had grade 3 AST elevations. In those with mantle cell lymphoma, the most common grade 3-4 adverse events were ALT elevations and rash. In those with follicular lymphoma, the most common grade 3-4 adverse events were neutropenia and rash.
“Given the inability to deliver treatment due to toxicity, both studies were permanently closed,” the researchers wrote, noting that the primary endpoint of safety and tolerability was not met.
The trials had the overall goal of developing targeted regimens to replace cytotoxic therapy.
“Both ... trials were designed to capitalize on the clinical synergy of lenalidomide and rituximab observed in previous trials by adding the highly specific PI3K delta inhibitor, idelalisib, for patients with relapsed mantle cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma,” they said.
Previously available data implied that lenalidomide plus rituximab would be a safe backbone for therapy, and there was clinical rationale for adding idelalisib to that combination, they explained.
“Overall, our brief experience underscores the limited knowledge regarding drug interactions and off-target effects and serves as a cautionary note in developing biological agents in combination and against ad-hoc combinations outside of carefully monitored clinical trials,” they said.
The researchers noted that the nature of the toxicities observed in these trials supports an immune-activated state characterized by excessive inflammation.
“A more detailed assessment of effect on cytokines, T-cell subsets, natural killer cells, and clinical features predictive of toxicity and response should be included in any further testing of these classes of agents, and they should never be combined outside of a carefully designed and diligently monitored clinical trial setting,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Smith received research funding and consulting fees from Gilead and Celgene.
Combined idelalisib, lenalidomide, and rituximab proved excessively toxic for the treatment of relapsed and refractory mantle cell and follicular lymphoma in two phase I trials conducted by the Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology.
The unexpected outcome, which led to early study termination, underscores the need for caution as new treatment combinations are proposed, Sonali M. Smith, MD, of the University of Chicago and her colleagues said in The Lancet Haematology.
In four of the first eight patients enrolled in the mantle cell lymphoma (A051201) and follicular lymphoma (A051202) phase I trials between July 9, 2013, and Sept. 30, 2014, unexpected dose-limiting toxicities occurred, including grade 4 sepsis syndrome, grade 4 hypotension with grade 3 rash and fevers, grade 4 aspartate aminotransferase (AST) or alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevation with fevers, and grade 3 pulmonary infection with grade 3 maculopapular rash.
The adverse events occurred between 9 and 20 days after treatment initiation and coincided with rituximab infusions, the researchers said. No treatment-related deaths occurred (Lancet Haematol. 2017 Apr;4:e176-82).
Overall, 8 of 11 patients were removed from treatment because of an adverse event, and 3 of those required intensive care unit level of care.
Although rituximab was removed in both trials, two of the remaining three patients in the studies, including three with mantle cell lymphoma and eight with follicular lymphoma, experienced grade 3 rashes, and one had grade 3 AST elevations. In those with mantle cell lymphoma, the most common grade 3-4 adverse events were ALT elevations and rash. In those with follicular lymphoma, the most common grade 3-4 adverse events were neutropenia and rash.
“Given the inability to deliver treatment due to toxicity, both studies were permanently closed,” the researchers wrote, noting that the primary endpoint of safety and tolerability was not met.
The trials had the overall goal of developing targeted regimens to replace cytotoxic therapy.
“Both ... trials were designed to capitalize on the clinical synergy of lenalidomide and rituximab observed in previous trials by adding the highly specific PI3K delta inhibitor, idelalisib, for patients with relapsed mantle cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma,” they said.
Previously available data implied that lenalidomide plus rituximab would be a safe backbone for therapy, and there was clinical rationale for adding idelalisib to that combination, they explained.
“Overall, our brief experience underscores the limited knowledge regarding drug interactions and off-target effects and serves as a cautionary note in developing biological agents in combination and against ad-hoc combinations outside of carefully monitored clinical trials,” they said.
The researchers noted that the nature of the toxicities observed in these trials supports an immune-activated state characterized by excessive inflammation.
“A more detailed assessment of effect on cytokines, T-cell subsets, natural killer cells, and clinical features predictive of toxicity and response should be included in any further testing of these classes of agents, and they should never be combined outside of a carefully designed and diligently monitored clinical trial setting,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Smith received research funding and consulting fees from Gilead and Celgene.
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Of 11 patients, 8 were removed from treatment because of an adverse event, and 3 of those required intensive care unit–level care.
Data source: Two phase I trials involving 11 patients.
Disclosures: The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Smith received research funding and consulting fees from Gilead and Celgene.
CHMP recommends approval for rituximab biosimilar
The European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended marketing authorization for a biosimilar rituximab product called Rixathon.
The recommended authorization for Rixathon encompasses all the same indications as the reference medicine, MabThera, which includes non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA).
The CHMP’s recommendation for Rixathon has been forwarded to the European Commission, which normally decides whether it will grant marketing authorization for a product within 67 days from the time the CHMP adopts its opinion.
The active substance of Rixathon is rituximab, a monoclonal antibody that binds specifically to the transmembrane protein CD20, which is found on both malignant and normal B cells.
In NHL and CLL, this promotes destruction of malignant B cells and controls tumor growth. In RA, GPA, and MPA, it reduces B cells involved in their pathogenesis.
The reference product for Rixathon is Mabthera, which was authorized for use in the European Union in June 1998.
The CHMP says studies have shown Rixathon to have comparable quality, safety, and efficacy to Mabthera.1, 2, 3
The applicant for Rixathon is Sandoz GmbH.
If authorized by the European Commission, Rixathon will be available for the following indications.
NHL
Rixathon is indicated for use in combination with chemotherapy to treat previously untreated patients with stage III-IV follicular lymphoma (FL).
Rixathon maintenance therapy is indicated for the treatment of FL patients responding to induction therapy.
Rixathon monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of patients with stage III-IV FL who are chemo-resistant or are in their second or subsequent relapse after chemotherapy.
Rixathon is indicated for use in combination with CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone) for the treatment of patients with CD20-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
CLL
Rixathon in combination with chemotherapy is indicated for the treatment of patients with previously untreated and relapsed/refractory CLL.
The CHMP noted that limited efficacy and safety data are available for patients previously treated with monoclonal antibodies, including rituximab, or patients who are refractory to previous rituximab plus chemotherapy.
RA, GPA, and MPA
Rixathon in combination with methotrexate is indicated for the treatment of adults with severe, active RA who have had an inadequate response to or cannot tolerate other disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs, including one or more tumor necrosis factor inhibitor therapies.
Rixathon in combination with glucocorticoids is indicated for the induction of remission in adults with severe, active GPA or MPA. ![]()
1. Visser J et al. Physicochemical and Functional Comparability Between the Proposed Biosimilar Rituximab GP2013 and Originator Rituximab. BioDrugs. 2013;27:495-507.
2. Da Silva A et al. Target-directed development and preclinical characterization of the proposed biosimilar rituximab GP2013. Leuk Lymphoma. 2014;55:1609-1617.
3. Jurczak W et al. A Phase III Efficacy and Safety Study of the Proposed Rituximab Biosimilar GP2013 Versus Rituximab in Patients with Previously Untreated Advanced Follicular Lymphoma. ASH Annual Meeting 2016.
The European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended marketing authorization for a biosimilar rituximab product called Rixathon.
The recommended authorization for Rixathon encompasses all the same indications as the reference medicine, MabThera, which includes non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA).
The CHMP’s recommendation for Rixathon has been forwarded to the European Commission, which normally decides whether it will grant marketing authorization for a product within 67 days from the time the CHMP adopts its opinion.
The active substance of Rixathon is rituximab, a monoclonal antibody that binds specifically to the transmembrane protein CD20, which is found on both malignant and normal B cells.
In NHL and CLL, this promotes destruction of malignant B cells and controls tumor growth. In RA, GPA, and MPA, it reduces B cells involved in their pathogenesis.
The reference product for Rixathon is Mabthera, which was authorized for use in the European Union in June 1998.
The CHMP says studies have shown Rixathon to have comparable quality, safety, and efficacy to Mabthera.1, 2, 3
The applicant for Rixathon is Sandoz GmbH.
If authorized by the European Commission, Rixathon will be available for the following indications.
NHL
Rixathon is indicated for use in combination with chemotherapy to treat previously untreated patients with stage III-IV follicular lymphoma (FL).
Rixathon maintenance therapy is indicated for the treatment of FL patients responding to induction therapy.
Rixathon monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of patients with stage III-IV FL who are chemo-resistant or are in their second or subsequent relapse after chemotherapy.
Rixathon is indicated for use in combination with CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone) for the treatment of patients with CD20-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
CLL
Rixathon in combination with chemotherapy is indicated for the treatment of patients with previously untreated and relapsed/refractory CLL.
The CHMP noted that limited efficacy and safety data are available for patients previously treated with monoclonal antibodies, including rituximab, or patients who are refractory to previous rituximab plus chemotherapy.
RA, GPA, and MPA
Rixathon in combination with methotrexate is indicated for the treatment of adults with severe, active RA who have had an inadequate response to or cannot tolerate other disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs, including one or more tumor necrosis factor inhibitor therapies.
Rixathon in combination with glucocorticoids is indicated for the induction of remission in adults with severe, active GPA or MPA. ![]()
1. Visser J et al. Physicochemical and Functional Comparability Between the Proposed Biosimilar Rituximab GP2013 and Originator Rituximab. BioDrugs. 2013;27:495-507.
2. Da Silva A et al. Target-directed development and preclinical characterization of the proposed biosimilar rituximab GP2013. Leuk Lymphoma. 2014;55:1609-1617.
3. Jurczak W et al. A Phase III Efficacy and Safety Study of the Proposed Rituximab Biosimilar GP2013 Versus Rituximab in Patients with Previously Untreated Advanced Follicular Lymphoma. ASH Annual Meeting 2016.
The European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended marketing authorization for a biosimilar rituximab product called Rixathon.
The recommended authorization for Rixathon encompasses all the same indications as the reference medicine, MabThera, which includes non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA).
The CHMP’s recommendation for Rixathon has been forwarded to the European Commission, which normally decides whether it will grant marketing authorization for a product within 67 days from the time the CHMP adopts its opinion.
The active substance of Rixathon is rituximab, a monoclonal antibody that binds specifically to the transmembrane protein CD20, which is found on both malignant and normal B cells.
In NHL and CLL, this promotes destruction of malignant B cells and controls tumor growth. In RA, GPA, and MPA, it reduces B cells involved in their pathogenesis.
The reference product for Rixathon is Mabthera, which was authorized for use in the European Union in June 1998.
The CHMP says studies have shown Rixathon to have comparable quality, safety, and efficacy to Mabthera.1, 2, 3
The applicant for Rixathon is Sandoz GmbH.
If authorized by the European Commission, Rixathon will be available for the following indications.
NHL
Rixathon is indicated for use in combination with chemotherapy to treat previously untreated patients with stage III-IV follicular lymphoma (FL).
Rixathon maintenance therapy is indicated for the treatment of FL patients responding to induction therapy.
Rixathon monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of patients with stage III-IV FL who are chemo-resistant or are in their second or subsequent relapse after chemotherapy.
Rixathon is indicated for use in combination with CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone) for the treatment of patients with CD20-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
CLL
Rixathon in combination with chemotherapy is indicated for the treatment of patients with previously untreated and relapsed/refractory CLL.
The CHMP noted that limited efficacy and safety data are available for patients previously treated with monoclonal antibodies, including rituximab, or patients who are refractory to previous rituximab plus chemotherapy.
RA, GPA, and MPA
Rixathon in combination with methotrexate is indicated for the treatment of adults with severe, active RA who have had an inadequate response to or cannot tolerate other disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs, including one or more tumor necrosis factor inhibitor therapies.
Rixathon in combination with glucocorticoids is indicated for the induction of remission in adults with severe, active GPA or MPA. ![]()
1. Visser J et al. Physicochemical and Functional Comparability Between the Proposed Biosimilar Rituximab GP2013 and Originator Rituximab. BioDrugs. 2013;27:495-507.
2. Da Silva A et al. Target-directed development and preclinical characterization of the proposed biosimilar rituximab GP2013. Leuk Lymphoma. 2014;55:1609-1617.
3. Jurczak W et al. A Phase III Efficacy and Safety Study of the Proposed Rituximab Biosimilar GP2013 Versus Rituximab in Patients with Previously Untreated Advanced Follicular Lymphoma. ASH Annual Meeting 2016.
Thousands expected to get CAR T-cells by 2018
NEW YORK – Should the first chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell treatment receive Food and Drug Administration approval for refractory, aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma, possibly before the end of 2017, several thousand U.S. patients will be potential candidates for the treatment, Jeremy S. Abramson, MD, predicted at a conference held by Imedex.
Dr. Abramson has led studies using a CAR T cell that differs from the one furthest along in development. He based his predicted timetable for an approved biologics license of the process, with which he can engineer patient-specific T cells that are under development by Kite Pharma, on the “remarkable” level of complete responses the intervention produced in a pivotal phase II study.
“Seeing a complete response rate of close to 40% that is sustained for more than 3 months and a complete response rate of close to a third at 6 months is light years beyond what is now available for patients” with these chemotherapy refractory B-cell lymphomas, said Dr. Abramson, clinical director of the Center for Lymphoma at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. “This is the first treatment to show a significant impact on large B-cell lymphoma, and that makes me optimistic” that the FDA will grant license approval later in 2017, he said in an interview.
Dr. Abramson acknowledged that some patients developed grade 3 or 4 cytokine-release syndrome and neurologic events, but the events were reversible and manageable if treated with the immunosuppressant tocilizumab (Actemra) or a corticosteroid.
At the end of March, Kite reported the completion of its FDA application, and, on April 2, the ZUMA-1 investigators presented an updated report on their results, with a 36% complete response rate across all enrolled patients at 6 month follow-up and a 39% complete response rate in all patients out to a median follow-up of 8.7 months.
Annually, in U.S. practice, perhaps 3,000 new patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma would meet the enrollment criteria for ZUMA-1, Dr. Abramson estimated. Once axicabtagene ciloleucel becomes commercially available in the United States, several thousand U.S. patients might initially seek the treatment.
Dr. Abramson has been a consultant to Kite Pharma and to AbbVie, Genentech, Gilead, and Seattle Genetics.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
NEW YORK – Should the first chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell treatment receive Food and Drug Administration approval for refractory, aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma, possibly before the end of 2017, several thousand U.S. patients will be potential candidates for the treatment, Jeremy S. Abramson, MD, predicted at a conference held by Imedex.
Dr. Abramson has led studies using a CAR T cell that differs from the one furthest along in development. He based his predicted timetable for an approved biologics license of the process, with which he can engineer patient-specific T cells that are under development by Kite Pharma, on the “remarkable” level of complete responses the intervention produced in a pivotal phase II study.
“Seeing a complete response rate of close to 40% that is sustained for more than 3 months and a complete response rate of close to a third at 6 months is light years beyond what is now available for patients” with these chemotherapy refractory B-cell lymphomas, said Dr. Abramson, clinical director of the Center for Lymphoma at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. “This is the first treatment to show a significant impact on large B-cell lymphoma, and that makes me optimistic” that the FDA will grant license approval later in 2017, he said in an interview.
Dr. Abramson acknowledged that some patients developed grade 3 or 4 cytokine-release syndrome and neurologic events, but the events were reversible and manageable if treated with the immunosuppressant tocilizumab (Actemra) or a corticosteroid.
At the end of March, Kite reported the completion of its FDA application, and, on April 2, the ZUMA-1 investigators presented an updated report on their results, with a 36% complete response rate across all enrolled patients at 6 month follow-up and a 39% complete response rate in all patients out to a median follow-up of 8.7 months.
Annually, in U.S. practice, perhaps 3,000 new patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma would meet the enrollment criteria for ZUMA-1, Dr. Abramson estimated. Once axicabtagene ciloleucel becomes commercially available in the United States, several thousand U.S. patients might initially seek the treatment.
Dr. Abramson has been a consultant to Kite Pharma and to AbbVie, Genentech, Gilead, and Seattle Genetics.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
NEW YORK – Should the first chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell treatment receive Food and Drug Administration approval for refractory, aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma, possibly before the end of 2017, several thousand U.S. patients will be potential candidates for the treatment, Jeremy S. Abramson, MD, predicted at a conference held by Imedex.
Dr. Abramson has led studies using a CAR T cell that differs from the one furthest along in development. He based his predicted timetable for an approved biologics license of the process, with which he can engineer patient-specific T cells that are under development by Kite Pharma, on the “remarkable” level of complete responses the intervention produced in a pivotal phase II study.
“Seeing a complete response rate of close to 40% that is sustained for more than 3 months and a complete response rate of close to a third at 6 months is light years beyond what is now available for patients” with these chemotherapy refractory B-cell lymphomas, said Dr. Abramson, clinical director of the Center for Lymphoma at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. “This is the first treatment to show a significant impact on large B-cell lymphoma, and that makes me optimistic” that the FDA will grant license approval later in 2017, he said in an interview.
Dr. Abramson acknowledged that some patients developed grade 3 or 4 cytokine-release syndrome and neurologic events, but the events were reversible and manageable if treated with the immunosuppressant tocilizumab (Actemra) or a corticosteroid.
At the end of March, Kite reported the completion of its FDA application, and, on April 2, the ZUMA-1 investigators presented an updated report on their results, with a 36% complete response rate across all enrolled patients at 6 month follow-up and a 39% complete response rate in all patients out to a median follow-up of 8.7 months.
Annually, in U.S. practice, perhaps 3,000 new patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma would meet the enrollment criteria for ZUMA-1, Dr. Abramson estimated. Once axicabtagene ciloleucel becomes commercially available in the United States, several thousand U.S. patients might initially seek the treatment.
Dr. Abramson has been a consultant to Kite Pharma and to AbbVie, Genentech, Gilead, and Seattle Genetics.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM A MEETING ON HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES
Obinutuzumab vs. rituximab weighed as follicular lymphoma therapy
NEW YORK – Does obinutuzumab have a leg up over rituximab for treating follicular lymphoma?
A strict reading of the efficacy records of the two anti-CD20 antibodies when they went head-to-head suggests that obinutuzumab (Gazyva) edged out rituximab (Rituxan), but a broader view leaves the door open for rituximab as a still viable option depending on a patient’s status and priorities, experts said at the conference held by Imedex.
While conceding that quality of life correlates with progression-free survival (PFS), he stressed that it also correlates with treatment toxicities, treatment duration, and disease-related side effects.
Trial results have indicated that patients with newly diagnosed follicular lymphoma are reasonably treated with rituximab alone, or with rituximab plus bendamustine, without need for maintenance therapy, Dr. Leonard said.
In contrast, GALLIUM, a phase III trial that compared rituximab against obinutuzumab, used a maintenance phase of monotherapy with each of these two drugs following an induction phase when each of the drugs was combined with chemotherapy.
“If you use this approach [tested in GALLIUM] you need to use maintenance therapy,” and it was in GALLIUM that the most dramatic efficacy advantage for obinutuzumab over rituximab appeared, in the form of longer PFS although, so far, without demonstrated advantage in overall survival. The GALLIUM results, reported in December 2016 at the American Society of Hematology meeting, showed a 3-year PFS rate of 80% among patients treated with obinutuzumab and 73% among those treated with rituximab, a hazard ratio of 0.66 in favor of obinutuzumab that was statistically significant (P = .001) for the study’s primary endpoint (Blood. 2016 Dec 4;abstract 6).
“If you follow this study, you commit the patient to maintenance. We need to talk with patients about the pros and cons of maintenance, the pros and cons of chemotherapy, and the pros and cons of single agent therapy” with one of these anti-CD20 antibodies, Dr. Leonard said. “Right now, I think it’s unclear which antibody is best,” he concluded
To further buttress the case for obinutuzumab, he also cited the higher response rate among relapsed patients when single-agent obinutuzumab went against single-agent rituximab (J Clin Oncol. 2015 Oct 20:33[30]:3467-74), and the overall survival advantage that obinutuzumab gave patients when combined with bendamustine in patients refractory to rituximab (Blood. 2016 Dec 5; abstract 615).
Agreeing that the design of GALLIUM focused on combining an anti-CD20 antibody with chemotherapy, Dr. Friedberg acknowledged that, as initial therapy, “using rituximab monotherapy is very reasonable for many patients. I divide [follicular lymphoma] patients into those who are very symptomatic” (for example, those with hydronephrosis) “and need chemotherapy, and those who are not that symptomatic for whom single-agent rituximab is very reasonable,” he said in an interview.
Tumor aggressiveness is another way to identify patients who need chemotherapy plus an antibody, he added. “If the patient is not symptomatic, I generally first observe them, and if the growth is slow, you can sometimes intervene with rituximab alone, but, if the growth is fast, you also need chemotherapy,” Dr. Friedberg said.
Cost may soon become another consideration now that the U.S. patent on rituximab has expired leading to the ongoing development of several biosimilar versions of the antibody. If biosimilar formulations of rituximab soon appear on the U.S. market and if they result in a significant drop in drug price, it would introduce yet another significant variable. “Presuming biosimilar rituximab lowers the cost, that would be another important treatment decision,” he said.
Dr. Friedberg has been a consultant to Bayer. Dr. Leonard has been a consultant to 13 drug companies. Neither disclosed a relationship with the companies that market obinutuzumab or rituximab.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
NEW YORK – Does obinutuzumab have a leg up over rituximab for treating follicular lymphoma?
A strict reading of the efficacy records of the two anti-CD20 antibodies when they went head-to-head suggests that obinutuzumab (Gazyva) edged out rituximab (Rituxan), but a broader view leaves the door open for rituximab as a still viable option depending on a patient’s status and priorities, experts said at the conference held by Imedex.
While conceding that quality of life correlates with progression-free survival (PFS), he stressed that it also correlates with treatment toxicities, treatment duration, and disease-related side effects.
Trial results have indicated that patients with newly diagnosed follicular lymphoma are reasonably treated with rituximab alone, or with rituximab plus bendamustine, without need for maintenance therapy, Dr. Leonard said.
In contrast, GALLIUM, a phase III trial that compared rituximab against obinutuzumab, used a maintenance phase of monotherapy with each of these two drugs following an induction phase when each of the drugs was combined with chemotherapy.
“If you use this approach [tested in GALLIUM] you need to use maintenance therapy,” and it was in GALLIUM that the most dramatic efficacy advantage for obinutuzumab over rituximab appeared, in the form of longer PFS although, so far, without demonstrated advantage in overall survival. The GALLIUM results, reported in December 2016 at the American Society of Hematology meeting, showed a 3-year PFS rate of 80% among patients treated with obinutuzumab and 73% among those treated with rituximab, a hazard ratio of 0.66 in favor of obinutuzumab that was statistically significant (P = .001) for the study’s primary endpoint (Blood. 2016 Dec 4;abstract 6).
“If you follow this study, you commit the patient to maintenance. We need to talk with patients about the pros and cons of maintenance, the pros and cons of chemotherapy, and the pros and cons of single agent therapy” with one of these anti-CD20 antibodies, Dr. Leonard said. “Right now, I think it’s unclear which antibody is best,” he concluded
To further buttress the case for obinutuzumab, he also cited the higher response rate among relapsed patients when single-agent obinutuzumab went against single-agent rituximab (J Clin Oncol. 2015 Oct 20:33[30]:3467-74), and the overall survival advantage that obinutuzumab gave patients when combined with bendamustine in patients refractory to rituximab (Blood. 2016 Dec 5; abstract 615).
Agreeing that the design of GALLIUM focused on combining an anti-CD20 antibody with chemotherapy, Dr. Friedberg acknowledged that, as initial therapy, “using rituximab monotherapy is very reasonable for many patients. I divide [follicular lymphoma] patients into those who are very symptomatic” (for example, those with hydronephrosis) “and need chemotherapy, and those who are not that symptomatic for whom single-agent rituximab is very reasonable,” he said in an interview.
Tumor aggressiveness is another way to identify patients who need chemotherapy plus an antibody, he added. “If the patient is not symptomatic, I generally first observe them, and if the growth is slow, you can sometimes intervene with rituximab alone, but, if the growth is fast, you also need chemotherapy,” Dr. Friedberg said.
Cost may soon become another consideration now that the U.S. patent on rituximab has expired leading to the ongoing development of several biosimilar versions of the antibody. If biosimilar formulations of rituximab soon appear on the U.S. market and if they result in a significant drop in drug price, it would introduce yet another significant variable. “Presuming biosimilar rituximab lowers the cost, that would be another important treatment decision,” he said.
Dr. Friedberg has been a consultant to Bayer. Dr. Leonard has been a consultant to 13 drug companies. Neither disclosed a relationship with the companies that market obinutuzumab or rituximab.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
NEW YORK – Does obinutuzumab have a leg up over rituximab for treating follicular lymphoma?
A strict reading of the efficacy records of the two anti-CD20 antibodies when they went head-to-head suggests that obinutuzumab (Gazyva) edged out rituximab (Rituxan), but a broader view leaves the door open for rituximab as a still viable option depending on a patient’s status and priorities, experts said at the conference held by Imedex.
While conceding that quality of life correlates with progression-free survival (PFS), he stressed that it also correlates with treatment toxicities, treatment duration, and disease-related side effects.
Trial results have indicated that patients with newly diagnosed follicular lymphoma are reasonably treated with rituximab alone, or with rituximab plus bendamustine, without need for maintenance therapy, Dr. Leonard said.
In contrast, GALLIUM, a phase III trial that compared rituximab against obinutuzumab, used a maintenance phase of monotherapy with each of these two drugs following an induction phase when each of the drugs was combined with chemotherapy.
“If you use this approach [tested in GALLIUM] you need to use maintenance therapy,” and it was in GALLIUM that the most dramatic efficacy advantage for obinutuzumab over rituximab appeared, in the form of longer PFS although, so far, without demonstrated advantage in overall survival. The GALLIUM results, reported in December 2016 at the American Society of Hematology meeting, showed a 3-year PFS rate of 80% among patients treated with obinutuzumab and 73% among those treated with rituximab, a hazard ratio of 0.66 in favor of obinutuzumab that was statistically significant (P = .001) for the study’s primary endpoint (Blood. 2016 Dec 4;abstract 6).
“If you follow this study, you commit the patient to maintenance. We need to talk with patients about the pros and cons of maintenance, the pros and cons of chemotherapy, and the pros and cons of single agent therapy” with one of these anti-CD20 antibodies, Dr. Leonard said. “Right now, I think it’s unclear which antibody is best,” he concluded
To further buttress the case for obinutuzumab, he also cited the higher response rate among relapsed patients when single-agent obinutuzumab went against single-agent rituximab (J Clin Oncol. 2015 Oct 20:33[30]:3467-74), and the overall survival advantage that obinutuzumab gave patients when combined with bendamustine in patients refractory to rituximab (Blood. 2016 Dec 5; abstract 615).
Agreeing that the design of GALLIUM focused on combining an anti-CD20 antibody with chemotherapy, Dr. Friedberg acknowledged that, as initial therapy, “using rituximab monotherapy is very reasonable for many patients. I divide [follicular lymphoma] patients into those who are very symptomatic” (for example, those with hydronephrosis) “and need chemotherapy, and those who are not that symptomatic for whom single-agent rituximab is very reasonable,” he said in an interview.
Tumor aggressiveness is another way to identify patients who need chemotherapy plus an antibody, he added. “If the patient is not symptomatic, I generally first observe them, and if the growth is slow, you can sometimes intervene with rituximab alone, but, if the growth is fast, you also need chemotherapy,” Dr. Friedberg said.
Cost may soon become another consideration now that the U.S. patent on rituximab has expired leading to the ongoing development of several biosimilar versions of the antibody. If biosimilar formulations of rituximab soon appear on the U.S. market and if they result in a significant drop in drug price, it would introduce yet another significant variable. “Presuming biosimilar rituximab lowers the cost, that would be another important treatment decision,” he said.
Dr. Friedberg has been a consultant to Bayer. Dr. Leonard has been a consultant to 13 drug companies. Neither disclosed a relationship with the companies that market obinutuzumab or rituximab.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM A MEETING ON HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES