User login
Puzzling, unique ECG from pig-to-human transplanted heart
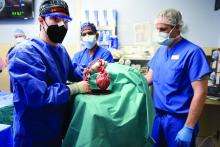
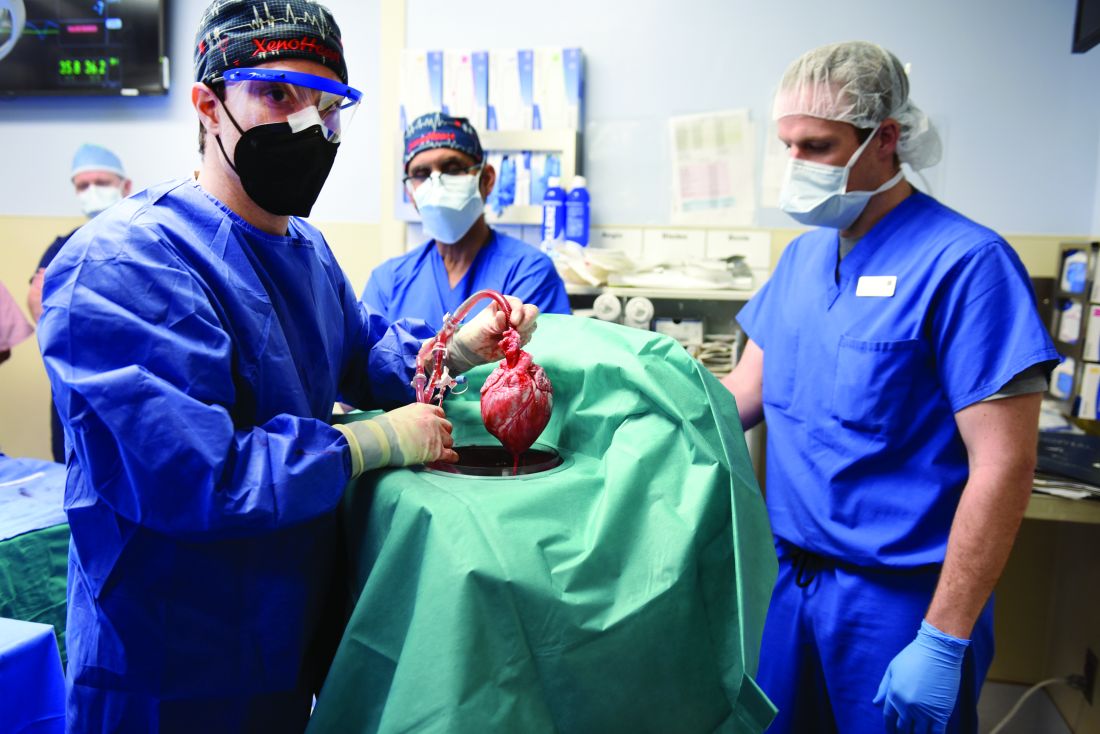
In the first transplant of a genetically altered pig heart into a human in January, initial unexpected, prolonged ECG readings apparently did not affect the heart’s function, although the organ suddenly began to fail at day 50.
A study of these ECG changes, scheduled for presentation by Calvin Kagan, MD, and colleagues at the American Heart Association scientific sessions, offers insight into this novel operation.
As widely reported, the patient, 57-year-old David Bennett of Maryland, had end-stage heart disease and was a poor candidate for a ventricular assist device and was ineligible for a human heart, when he consented to be the first human to be transplanted with a pig heart that had a number of genes added or subtracted with the goal, in part, to prevent rejection.
The heart initially performed well after it was transplanted in an operation at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) in Baltimore on Jan. 7, but failed in the second month, and Mr. Bennett died on March 9.
The Food and Drug Administration had granted emergency authorization for the surgery through its expanded access (compassionate use) program, coauthor Muhammad Mohiuddin, MD, said in an interview.
“We have learned a lot and hope we can do more,” said Dr. Mohiuddin, scientific and program director of the cardiac xenotransplantation program at UMSOM.
“Suddenly on day 50, the heart started to get thicker and was not relaxing enough,” explained senior author Timm-Michael Dickfeld, MD, PhD, director of electrophysiology research at UMSOM. A biopsy revealed substantial buildup of interstitial fluid that restricted movement. The fluid was replaced by fibrous tissue, leading to irreversible damage.
Persistent, prolonged ECG parameters
In the heart from a genetically modified pig, three genes associated with antibody-mediated rejection and a gene associated with pig heart tissue growth had been inactivated and six human genes associated with immune acceptance had been added. The donor pig was supplied by Revivicor (Blacksburg, Va.).
The patient’s immunosuppressant therapy included an experimental antirejection medication (Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals; Lexington, Mass.).
The patient had daily 12-lead ECGs after the transplant.
In prior research using a pig heart transplanted into a pig body, ECG readings showed a short PR interval (50-120 ms), short QRS duration (70-90 ms) and short QT intervals (260-380 ms).
However, in the transplanted xenograft heart, the initial ECG readings showed a longer PR interval of 190 ms, QRS duration of 138 ms, and QT of 538 ms.
Prolonged intrinsic PR intervals remained stable during the postoperative course (210 ms, range 142-246 ms).
QRS duration also remained prolonged (145 ms, range 116-192 ms), but shortened during the postoperative course (days 21-40 vs. 41-60: 148 ms vs. 132 ms; P < .001).
Increased QT persisted (509 ms, range 384-650 ms) with dynamic fluctuations. The shortest QT duration was observed on day 14 (P < .001).
“In a human heart, when those parameters get longer, this can indicate signs of electrical or myocardial disease,” Dr. Dickfeld explained in a press release from the AHA.
“The QRS duration may prolong when, for example, the muscle and the electrical system itself is diseased, and that is why it takes a long time for electricity to travel from cell to cell and travel from one side of the heart to the other,” he said.
“In the human heart, the QT duration is correlated with an increased risk of abnormal heart rhythms,” he noted. “In our patient, it was concerning that the QT measure was prolonged. While we saw some fluctuations, the QT measure remained prolonged during the whole 61 days.”
‘Interesting study’
Two experts who were not involved with this research weighed in on the findings for this news organization.
“This very interesting study reinforces the difficulties in xenotransplantation, and the need for more research to be able to safely monitor recipients, as baseline values are unknown,” said Edward Vigmond, PhD.
Dr. Vigmond, from the Electrophysiology and Heart Modeling Institute at the University of Bordeaux in France, published a related study about a model of translation of pig to human electrophysiology.
The ECG is sensitive to the electrical activation pattern of the heart, along with the cellular and tissue electrical properties, he noted.
“Although pigs and humans may be similar in size, there are many differences between them,” Dr. Vigmond observed, including “the extent of the rapid conduction system of the heart, the number of nuclei in the muscle cells, the proteins in the cell membrane which control electrical activity, the orientation of the heart and thorax, and the handling of calcium inside the cell.”
“On top of this,” he continued, “donor hearts are denervated, so they no longer respond to nervous modulation, and circulating compounds in the blood which affect heart function vary between species.
“With all these differences, it is not surprising that the ECG of a pig heart transplanted into a human resembles neither that of a human nor that of a pig,” Dr. Vigmond said.
“It is interesting to note that the humanized-gene-edited porcine heart exhibited abnormal electrical conduction parameters from the outset,” said Mandeep R. Mehra, MD.
“Whether these changes were due to the gene modifications (i.e., already inherent in the pig ECG prior to transplant) or a result of the transplant operation challenges (such as the ischemia reperfusion injury and early immunological interactions) is uncertain and should be clarified,” said Dr. Mehra, of Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Medicine in Boston.
“Knowledge of these changes is important to determine whether a simple ECG parameter may be useful to identify changes that could indicate developing pathology,” Dr. Mehra added.
“In the older days of human transplantation, we often used ECG parameters such as a change in voltage amplitude to identify signals for rejection,” he continued. “Whether such changes occurred in this case could be another interesting aspect to explore as changes occurred in cardiac performance in response to the physiological and pathological challenges that were encountered in this sentinel case.”
The study authors reported having no outside sources of funding.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the first transplant of a genetically altered pig heart into a human in January, initial unexpected, prolonged ECG readings apparently did not affect the heart’s function, although the organ suddenly began to fail at day 50.
A study of these ECG changes, scheduled for presentation by Calvin Kagan, MD, and colleagues at the American Heart Association scientific sessions, offers insight into this novel operation.
As widely reported, the patient, 57-year-old David Bennett of Maryland, had end-stage heart disease and was a poor candidate for a ventricular assist device and was ineligible for a human heart, when he consented to be the first human to be transplanted with a pig heart that had a number of genes added or subtracted with the goal, in part, to prevent rejection.
The heart initially performed well after it was transplanted in an operation at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) in Baltimore on Jan. 7, but failed in the second month, and Mr. Bennett died on March 9.
The Food and Drug Administration had granted emergency authorization for the surgery through its expanded access (compassionate use) program, coauthor Muhammad Mohiuddin, MD, said in an interview.
“We have learned a lot and hope we can do more,” said Dr. Mohiuddin, scientific and program director of the cardiac xenotransplantation program at UMSOM.
“Suddenly on day 50, the heart started to get thicker and was not relaxing enough,” explained senior author Timm-Michael Dickfeld, MD, PhD, director of electrophysiology research at UMSOM. A biopsy revealed substantial buildup of interstitial fluid that restricted movement. The fluid was replaced by fibrous tissue, leading to irreversible damage.
Persistent, prolonged ECG parameters
In the heart from a genetically modified pig, three genes associated with antibody-mediated rejection and a gene associated with pig heart tissue growth had been inactivated and six human genes associated with immune acceptance had been added. The donor pig was supplied by Revivicor (Blacksburg, Va.).
The patient’s immunosuppressant therapy included an experimental antirejection medication (Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals; Lexington, Mass.).
The patient had daily 12-lead ECGs after the transplant.
In prior research using a pig heart transplanted into a pig body, ECG readings showed a short PR interval (50-120 ms), short QRS duration (70-90 ms) and short QT intervals (260-380 ms).
However, in the transplanted xenograft heart, the initial ECG readings showed a longer PR interval of 190 ms, QRS duration of 138 ms, and QT of 538 ms.
Prolonged intrinsic PR intervals remained stable during the postoperative course (210 ms, range 142-246 ms).
QRS duration also remained prolonged (145 ms, range 116-192 ms), but shortened during the postoperative course (days 21-40 vs. 41-60: 148 ms vs. 132 ms; P < .001).
Increased QT persisted (509 ms, range 384-650 ms) with dynamic fluctuations. The shortest QT duration was observed on day 14 (P < .001).
“In a human heart, when those parameters get longer, this can indicate signs of electrical or myocardial disease,” Dr. Dickfeld explained in a press release from the AHA.
“The QRS duration may prolong when, for example, the muscle and the electrical system itself is diseased, and that is why it takes a long time for electricity to travel from cell to cell and travel from one side of the heart to the other,” he said.
“In the human heart, the QT duration is correlated with an increased risk of abnormal heart rhythms,” he noted. “In our patient, it was concerning that the QT measure was prolonged. While we saw some fluctuations, the QT measure remained prolonged during the whole 61 days.”
‘Interesting study’
Two experts who were not involved with this research weighed in on the findings for this news organization.
“This very interesting study reinforces the difficulties in xenotransplantation, and the need for more research to be able to safely monitor recipients, as baseline values are unknown,” said Edward Vigmond, PhD.
Dr. Vigmond, from the Electrophysiology and Heart Modeling Institute at the University of Bordeaux in France, published a related study about a model of translation of pig to human electrophysiology.
The ECG is sensitive to the electrical activation pattern of the heart, along with the cellular and tissue electrical properties, he noted.
“Although pigs and humans may be similar in size, there are many differences between them,” Dr. Vigmond observed, including “the extent of the rapid conduction system of the heart, the number of nuclei in the muscle cells, the proteins in the cell membrane which control electrical activity, the orientation of the heart and thorax, and the handling of calcium inside the cell.”
“On top of this,” he continued, “donor hearts are denervated, so they no longer respond to nervous modulation, and circulating compounds in the blood which affect heart function vary between species.
“With all these differences, it is not surprising that the ECG of a pig heart transplanted into a human resembles neither that of a human nor that of a pig,” Dr. Vigmond said.
“It is interesting to note that the humanized-gene-edited porcine heart exhibited abnormal electrical conduction parameters from the outset,” said Mandeep R. Mehra, MD.
“Whether these changes were due to the gene modifications (i.e., already inherent in the pig ECG prior to transplant) or a result of the transplant operation challenges (such as the ischemia reperfusion injury and early immunological interactions) is uncertain and should be clarified,” said Dr. Mehra, of Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Medicine in Boston.
“Knowledge of these changes is important to determine whether a simple ECG parameter may be useful to identify changes that could indicate developing pathology,” Dr. Mehra added.
“In the older days of human transplantation, we often used ECG parameters such as a change in voltage amplitude to identify signals for rejection,” he continued. “Whether such changes occurred in this case could be another interesting aspect to explore as changes occurred in cardiac performance in response to the physiological and pathological challenges that were encountered in this sentinel case.”
The study authors reported having no outside sources of funding.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the first transplant of a genetically altered pig heart into a human in January, initial unexpected, prolonged ECG readings apparently did not affect the heart’s function, although the organ suddenly began to fail at day 50.
A study of these ECG changes, scheduled for presentation by Calvin Kagan, MD, and colleagues at the American Heart Association scientific sessions, offers insight into this novel operation.
As widely reported, the patient, 57-year-old David Bennett of Maryland, had end-stage heart disease and was a poor candidate for a ventricular assist device and was ineligible for a human heart, when he consented to be the first human to be transplanted with a pig heart that had a number of genes added or subtracted with the goal, in part, to prevent rejection.
The heart initially performed well after it was transplanted in an operation at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) in Baltimore on Jan. 7, but failed in the second month, and Mr. Bennett died on March 9.
The Food and Drug Administration had granted emergency authorization for the surgery through its expanded access (compassionate use) program, coauthor Muhammad Mohiuddin, MD, said in an interview.
“We have learned a lot and hope we can do more,” said Dr. Mohiuddin, scientific and program director of the cardiac xenotransplantation program at UMSOM.
“Suddenly on day 50, the heart started to get thicker and was not relaxing enough,” explained senior author Timm-Michael Dickfeld, MD, PhD, director of electrophysiology research at UMSOM. A biopsy revealed substantial buildup of interstitial fluid that restricted movement. The fluid was replaced by fibrous tissue, leading to irreversible damage.
Persistent, prolonged ECG parameters
In the heart from a genetically modified pig, three genes associated with antibody-mediated rejection and a gene associated with pig heart tissue growth had been inactivated and six human genes associated with immune acceptance had been added. The donor pig was supplied by Revivicor (Blacksburg, Va.).
The patient’s immunosuppressant therapy included an experimental antirejection medication (Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals; Lexington, Mass.).
The patient had daily 12-lead ECGs after the transplant.
In prior research using a pig heart transplanted into a pig body, ECG readings showed a short PR interval (50-120 ms), short QRS duration (70-90 ms) and short QT intervals (260-380 ms).
However, in the transplanted xenograft heart, the initial ECG readings showed a longer PR interval of 190 ms, QRS duration of 138 ms, and QT of 538 ms.
Prolonged intrinsic PR intervals remained stable during the postoperative course (210 ms, range 142-246 ms).
QRS duration also remained prolonged (145 ms, range 116-192 ms), but shortened during the postoperative course (days 21-40 vs. 41-60: 148 ms vs. 132 ms; P < .001).
Increased QT persisted (509 ms, range 384-650 ms) with dynamic fluctuations. The shortest QT duration was observed on day 14 (P < .001).
“In a human heart, when those parameters get longer, this can indicate signs of electrical or myocardial disease,” Dr. Dickfeld explained in a press release from the AHA.
“The QRS duration may prolong when, for example, the muscle and the electrical system itself is diseased, and that is why it takes a long time for electricity to travel from cell to cell and travel from one side of the heart to the other,” he said.
“In the human heart, the QT duration is correlated with an increased risk of abnormal heart rhythms,” he noted. “In our patient, it was concerning that the QT measure was prolonged. While we saw some fluctuations, the QT measure remained prolonged during the whole 61 days.”
‘Interesting study’
Two experts who were not involved with this research weighed in on the findings for this news organization.
“This very interesting study reinforces the difficulties in xenotransplantation, and the need for more research to be able to safely monitor recipients, as baseline values are unknown,” said Edward Vigmond, PhD.
Dr. Vigmond, from the Electrophysiology and Heart Modeling Institute at the University of Bordeaux in France, published a related study about a model of translation of pig to human electrophysiology.
The ECG is sensitive to the electrical activation pattern of the heart, along with the cellular and tissue electrical properties, he noted.
“Although pigs and humans may be similar in size, there are many differences between them,” Dr. Vigmond observed, including “the extent of the rapid conduction system of the heart, the number of nuclei in the muscle cells, the proteins in the cell membrane which control electrical activity, the orientation of the heart and thorax, and the handling of calcium inside the cell.”
“On top of this,” he continued, “donor hearts are denervated, so they no longer respond to nervous modulation, and circulating compounds in the blood which affect heart function vary between species.
“With all these differences, it is not surprising that the ECG of a pig heart transplanted into a human resembles neither that of a human nor that of a pig,” Dr. Vigmond said.
“It is interesting to note that the humanized-gene-edited porcine heart exhibited abnormal electrical conduction parameters from the outset,” said Mandeep R. Mehra, MD.
“Whether these changes were due to the gene modifications (i.e., already inherent in the pig ECG prior to transplant) or a result of the transplant operation challenges (such as the ischemia reperfusion injury and early immunological interactions) is uncertain and should be clarified,” said Dr. Mehra, of Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Medicine in Boston.
“Knowledge of these changes is important to determine whether a simple ECG parameter may be useful to identify changes that could indicate developing pathology,” Dr. Mehra added.
“In the older days of human transplantation, we often used ECG parameters such as a change in voltage amplitude to identify signals for rejection,” he continued. “Whether such changes occurred in this case could be another interesting aspect to explore as changes occurred in cardiac performance in response to the physiological and pathological challenges that were encountered in this sentinel case.”
The study authors reported having no outside sources of funding.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2022
Diuretic agents equal to prevent CV events in hypertension: DCP
There was no difference in major cardiovascular outcomes with the use of two different diuretics – chlorthalidone or hydrochlorothiazide – in the treatment of hypertension in a new large randomized real-world study.
The Diuretic Comparison Project (DCP), which was conducted in more than 13,500 U.S. veterans age 65 years or over, showed almost identical rates of the primary composite endpoint, including myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, noncancer death, hospitalization for acute heart failure, or urgent revascularization, after a median of 2.4 years of follow-up.
There was no difference in any of the individual endpoints or other secondary cardiovascular outcomes.
However, in the subgroup of patients who had a history of MI or stroke (who made up about 10% of the study population), there was a significant reduction in the primary endpoint with chlorthalidone, whereas those without a history of MI or stroke appeared to have an increased risk for primary outcome events while receiving chlorthalidone compared with those receiving hydrochlorothiazide.
The DCP trial was presented at the American Heart Association scientific sessions by Areef Ishani, MD, director of the Minneapolis Primary Care and Specialty Care Integrated Care Community and director of the Veterans Affairs (VA) Midwest Health Care Network.
Asked how to interpret the result for clinical practice, Dr. Ishani said, “I think we can now say that either of these two drugs is appropriate to use for the treatment of hypertension.”
But he added that the decision on what to do with the subgroup of patients with previous MI or stroke was more “challenging.”
“We saw a highly significant benefit in this subgroup, but this was in the context of an overall negative trial,” he noted. “I think this is a discussion with the patients on how they want to hedge their bets. Because these two drugs are so similar, if they wanted to take one or the other because of this subgroup result I think that is a conversation to have, but I think we now need to conduct another trial specifically in this subgroup of patients to see if chlorthalidone really is of benefit in that group.”
Dr. Ishani explained that both chlorthalidone and hydrochlorothiazide have been around for more than 50 years and are considered first-line treatments for hypertension. Early studies suggested better cardiovascular outcomes and 24-hour blood pressure control with chlorthalidone, but recent observational studies have not shown more benefit with chlorthalidone. These studies have suggested that chlorthalidone may be associated with an increase in adverse events, such as hypokalemia, acute kidney injury, and chronic kidney disease.
Pragmatic study
The DCP trial was conducted to try to definitively answer this question of whether chlorthalidone is superior to hydrochlorothiazide. The pragmatic study had a “point-of-care” design that allowed participants and health care professionals to know which medication was being prescribed and to administer the medication in a real-world setting.
“Patients can continue with their normal care with their usual care team because we integrated this trial into primary care clinics,” Dr. Ishani said. “We followed participant results using their electronic health record. This study was nonintrusive, cost-effective, and inexpensive. Plus, we were able to recruit a large rural population, which is unusual for large, randomized trials, where we usually rely on big academic medical centers.”
Using VA electronic medical records, the investigators recruited primary care physicians who identified patients older than age 65 years who were receiving hydrochlorothiazide (25 mg or 50 mg) for hypertension. These patients (97% of whom were male) were then randomly assigned to continue receiving hydrochlorothiazide or to switch to an equivalent dose of chlorthalidone. Patients were followed through the electronic medical record as well as Medicare claims and the National Death Index.
Results after a median follow-up of 2.4 years showed no difference in blood pressure control between the two groups.
In terms of clinical events, the primary composite outcome of MI, stroke, noncancer death, hospitalization for acute heart failure, or urgent revascularization occurred in 10.4% of the chlorthalidone group and in 10.0% of the hydrochlorothiazide group (hazard ratio [HR], 1.04; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.94-1.16; P = .4).
There was no difference in any individual components of the primary endpoint or the secondary outcomes of all-cause mortality, any revascularization, or erectile dysfunction.
In terms of adverse events, chlorthalidone was associated with an increase in hypokalemia (6% vs. 4.4%; HR, 1.38), but there was no difference in hospitalization for acute kidney injury.
Benefit in MI, stroke subgroup?
In the subgroup analysis, patients with a history of MI or stroke who were receiving chlorthalidone had a significant 27% reduction in the primary endpoint (HR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.57-0.94). Conversely, patients without a history of MI or stroke appeared to do worse while taking chlorthalidone (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.00-1.26).
“We were surprised by these results,” Dr. Ishani said. “We expected chlorthalidone to be more effective overall. However, learning about these differences in patients who have a history of cardiovascular disease may affect patient care. It’s best for people to talk with their health care clinicians about which of these medications is better for their individual needs.”
He added: “More research is needed to explore these results further because we don’t know how they may fit into treating the general population.”
Dr. Ishani noted that a limitations of this study was that most patients were receiving the low dose of chlorthalidone, and previous studies that suggested benefits with chlorthalidone used the higher dose.
“But the world has voted – we had 4,000 clinicians involved in this study, and the vast majority are using the low dose of hydrochlorothiazide. And this is a definitively negative study,” he said. “The world has also voted in that 10 times more patients were on hydrochlorothiazide than on chlorthalidone.”
Commenting on the study at an AHA press conference, Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, pointed out that in all of the landmark National Institutes of Health hypertension trials, there was a signal for benefit with chlorthalidone compared with other antihypertensives.
“We’ve always had this concept that chlorthalidone is better,” she said. “But this study shows no difference in major cardiovascular endpoints. There was more hypokalemia with chlorthalidone, but that’s recognizable as chlorthalidone is a more potent diuretic.”
Other limitations of the DCP trial are its open-label design, which could interject some bias; the enduring effects of hydrochlorothiazide – most of these patients were receiving this agent as background therapy; and inability to look at the effectiveness of decongestion of the agents in such a pragmatic study, Dr. Bozkurt noted.
She said she would like to see more analysis in the subgroup of patients with previous MI or stroke. “Does this result mean that chlorthalidone is better for sicker patients or is this result just due to chance?” she asked.
“While this study demonstrates equal effectiveness of these two diuretics in the targeted population, the question of subgroups of patients for which we use a more potent diuretic I think remains unanswered,” she concluded.
Designated discussant of the DCP trial at the late-breaking trial session, Daniel Levy, MD, director of the Framingham Heart Study at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, reminded attendees that chlorthalidone had shown impressive results in previous important hypertension studies including SHEP and ALLHAT.
He said the current DCP was a pragmatic study addressing a knowledge gap that “would never have been performed by industry.”
Dr. Levy concluded that the results showing no difference in outcomes between the two diuretics were “compelling,” although a few questions remain.
These include a possible bias toward hydrochlorothiazide – patients were selected who were already taking that drug and so would have already had a favorable response to it. In addition, because the trial was conducted in an older male population, he questioned whether the results could be generalized to women and younger patients.
The DCP study was funded by the VA Cooperative Studies Program. Dr. Ishani reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There was no difference in major cardiovascular outcomes with the use of two different diuretics – chlorthalidone or hydrochlorothiazide – in the treatment of hypertension in a new large randomized real-world study.
The Diuretic Comparison Project (DCP), which was conducted in more than 13,500 U.S. veterans age 65 years or over, showed almost identical rates of the primary composite endpoint, including myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, noncancer death, hospitalization for acute heart failure, or urgent revascularization, after a median of 2.4 years of follow-up.
There was no difference in any of the individual endpoints or other secondary cardiovascular outcomes.
However, in the subgroup of patients who had a history of MI or stroke (who made up about 10% of the study population), there was a significant reduction in the primary endpoint with chlorthalidone, whereas those without a history of MI or stroke appeared to have an increased risk for primary outcome events while receiving chlorthalidone compared with those receiving hydrochlorothiazide.
The DCP trial was presented at the American Heart Association scientific sessions by Areef Ishani, MD, director of the Minneapolis Primary Care and Specialty Care Integrated Care Community and director of the Veterans Affairs (VA) Midwest Health Care Network.
Asked how to interpret the result for clinical practice, Dr. Ishani said, “I think we can now say that either of these two drugs is appropriate to use for the treatment of hypertension.”
But he added that the decision on what to do with the subgroup of patients with previous MI or stroke was more “challenging.”
“We saw a highly significant benefit in this subgroup, but this was in the context of an overall negative trial,” he noted. “I think this is a discussion with the patients on how they want to hedge their bets. Because these two drugs are so similar, if they wanted to take one or the other because of this subgroup result I think that is a conversation to have, but I think we now need to conduct another trial specifically in this subgroup of patients to see if chlorthalidone really is of benefit in that group.”
Dr. Ishani explained that both chlorthalidone and hydrochlorothiazide have been around for more than 50 years and are considered first-line treatments for hypertension. Early studies suggested better cardiovascular outcomes and 24-hour blood pressure control with chlorthalidone, but recent observational studies have not shown more benefit with chlorthalidone. These studies have suggested that chlorthalidone may be associated with an increase in adverse events, such as hypokalemia, acute kidney injury, and chronic kidney disease.
Pragmatic study
The DCP trial was conducted to try to definitively answer this question of whether chlorthalidone is superior to hydrochlorothiazide. The pragmatic study had a “point-of-care” design that allowed participants and health care professionals to know which medication was being prescribed and to administer the medication in a real-world setting.
“Patients can continue with their normal care with their usual care team because we integrated this trial into primary care clinics,” Dr. Ishani said. “We followed participant results using their electronic health record. This study was nonintrusive, cost-effective, and inexpensive. Plus, we were able to recruit a large rural population, which is unusual for large, randomized trials, where we usually rely on big academic medical centers.”
Using VA electronic medical records, the investigators recruited primary care physicians who identified patients older than age 65 years who were receiving hydrochlorothiazide (25 mg or 50 mg) for hypertension. These patients (97% of whom were male) were then randomly assigned to continue receiving hydrochlorothiazide or to switch to an equivalent dose of chlorthalidone. Patients were followed through the electronic medical record as well as Medicare claims and the National Death Index.
Results after a median follow-up of 2.4 years showed no difference in blood pressure control between the two groups.
In terms of clinical events, the primary composite outcome of MI, stroke, noncancer death, hospitalization for acute heart failure, or urgent revascularization occurred in 10.4% of the chlorthalidone group and in 10.0% of the hydrochlorothiazide group (hazard ratio [HR], 1.04; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.94-1.16; P = .4).
There was no difference in any individual components of the primary endpoint or the secondary outcomes of all-cause mortality, any revascularization, or erectile dysfunction.
In terms of adverse events, chlorthalidone was associated with an increase in hypokalemia (6% vs. 4.4%; HR, 1.38), but there was no difference in hospitalization for acute kidney injury.
Benefit in MI, stroke subgroup?
In the subgroup analysis, patients with a history of MI or stroke who were receiving chlorthalidone had a significant 27% reduction in the primary endpoint (HR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.57-0.94). Conversely, patients without a history of MI or stroke appeared to do worse while taking chlorthalidone (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.00-1.26).
“We were surprised by these results,” Dr. Ishani said. “We expected chlorthalidone to be more effective overall. However, learning about these differences in patients who have a history of cardiovascular disease may affect patient care. It’s best for people to talk with their health care clinicians about which of these medications is better for their individual needs.”
He added: “More research is needed to explore these results further because we don’t know how they may fit into treating the general population.”
Dr. Ishani noted that a limitations of this study was that most patients were receiving the low dose of chlorthalidone, and previous studies that suggested benefits with chlorthalidone used the higher dose.
“But the world has voted – we had 4,000 clinicians involved in this study, and the vast majority are using the low dose of hydrochlorothiazide. And this is a definitively negative study,” he said. “The world has also voted in that 10 times more patients were on hydrochlorothiazide than on chlorthalidone.”
Commenting on the study at an AHA press conference, Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, pointed out that in all of the landmark National Institutes of Health hypertension trials, there was a signal for benefit with chlorthalidone compared with other antihypertensives.
“We’ve always had this concept that chlorthalidone is better,” she said. “But this study shows no difference in major cardiovascular endpoints. There was more hypokalemia with chlorthalidone, but that’s recognizable as chlorthalidone is a more potent diuretic.”
Other limitations of the DCP trial are its open-label design, which could interject some bias; the enduring effects of hydrochlorothiazide – most of these patients were receiving this agent as background therapy; and inability to look at the effectiveness of decongestion of the agents in such a pragmatic study, Dr. Bozkurt noted.
She said she would like to see more analysis in the subgroup of patients with previous MI or stroke. “Does this result mean that chlorthalidone is better for sicker patients or is this result just due to chance?” she asked.
“While this study demonstrates equal effectiveness of these two diuretics in the targeted population, the question of subgroups of patients for which we use a more potent diuretic I think remains unanswered,” she concluded.
Designated discussant of the DCP trial at the late-breaking trial session, Daniel Levy, MD, director of the Framingham Heart Study at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, reminded attendees that chlorthalidone had shown impressive results in previous important hypertension studies including SHEP and ALLHAT.
He said the current DCP was a pragmatic study addressing a knowledge gap that “would never have been performed by industry.”
Dr. Levy concluded that the results showing no difference in outcomes between the two diuretics were “compelling,” although a few questions remain.
These include a possible bias toward hydrochlorothiazide – patients were selected who were already taking that drug and so would have already had a favorable response to it. In addition, because the trial was conducted in an older male population, he questioned whether the results could be generalized to women and younger patients.
The DCP study was funded by the VA Cooperative Studies Program. Dr. Ishani reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There was no difference in major cardiovascular outcomes with the use of two different diuretics – chlorthalidone or hydrochlorothiazide – in the treatment of hypertension in a new large randomized real-world study.
The Diuretic Comparison Project (DCP), which was conducted in more than 13,500 U.S. veterans age 65 years or over, showed almost identical rates of the primary composite endpoint, including myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, noncancer death, hospitalization for acute heart failure, or urgent revascularization, after a median of 2.4 years of follow-up.
There was no difference in any of the individual endpoints or other secondary cardiovascular outcomes.
However, in the subgroup of patients who had a history of MI or stroke (who made up about 10% of the study population), there was a significant reduction in the primary endpoint with chlorthalidone, whereas those without a history of MI or stroke appeared to have an increased risk for primary outcome events while receiving chlorthalidone compared with those receiving hydrochlorothiazide.
The DCP trial was presented at the American Heart Association scientific sessions by Areef Ishani, MD, director of the Minneapolis Primary Care and Specialty Care Integrated Care Community and director of the Veterans Affairs (VA) Midwest Health Care Network.
Asked how to interpret the result for clinical practice, Dr. Ishani said, “I think we can now say that either of these two drugs is appropriate to use for the treatment of hypertension.”
But he added that the decision on what to do with the subgroup of patients with previous MI or stroke was more “challenging.”
“We saw a highly significant benefit in this subgroup, but this was in the context of an overall negative trial,” he noted. “I think this is a discussion with the patients on how they want to hedge their bets. Because these two drugs are so similar, if they wanted to take one or the other because of this subgroup result I think that is a conversation to have, but I think we now need to conduct another trial specifically in this subgroup of patients to see if chlorthalidone really is of benefit in that group.”
Dr. Ishani explained that both chlorthalidone and hydrochlorothiazide have been around for more than 50 years and are considered first-line treatments for hypertension. Early studies suggested better cardiovascular outcomes and 24-hour blood pressure control with chlorthalidone, but recent observational studies have not shown more benefit with chlorthalidone. These studies have suggested that chlorthalidone may be associated with an increase in adverse events, such as hypokalemia, acute kidney injury, and chronic kidney disease.
Pragmatic study
The DCP trial was conducted to try to definitively answer this question of whether chlorthalidone is superior to hydrochlorothiazide. The pragmatic study had a “point-of-care” design that allowed participants and health care professionals to know which medication was being prescribed and to administer the medication in a real-world setting.
“Patients can continue with their normal care with their usual care team because we integrated this trial into primary care clinics,” Dr. Ishani said. “We followed participant results using their electronic health record. This study was nonintrusive, cost-effective, and inexpensive. Plus, we were able to recruit a large rural population, which is unusual for large, randomized trials, where we usually rely on big academic medical centers.”
Using VA electronic medical records, the investigators recruited primary care physicians who identified patients older than age 65 years who were receiving hydrochlorothiazide (25 mg or 50 mg) for hypertension. These patients (97% of whom were male) were then randomly assigned to continue receiving hydrochlorothiazide or to switch to an equivalent dose of chlorthalidone. Patients were followed through the electronic medical record as well as Medicare claims and the National Death Index.
Results after a median follow-up of 2.4 years showed no difference in blood pressure control between the two groups.
In terms of clinical events, the primary composite outcome of MI, stroke, noncancer death, hospitalization for acute heart failure, or urgent revascularization occurred in 10.4% of the chlorthalidone group and in 10.0% of the hydrochlorothiazide group (hazard ratio [HR], 1.04; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.94-1.16; P = .4).
There was no difference in any individual components of the primary endpoint or the secondary outcomes of all-cause mortality, any revascularization, or erectile dysfunction.
In terms of adverse events, chlorthalidone was associated with an increase in hypokalemia (6% vs. 4.4%; HR, 1.38), but there was no difference in hospitalization for acute kidney injury.
Benefit in MI, stroke subgroup?
In the subgroup analysis, patients with a history of MI or stroke who were receiving chlorthalidone had a significant 27% reduction in the primary endpoint (HR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.57-0.94). Conversely, patients without a history of MI or stroke appeared to do worse while taking chlorthalidone (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.00-1.26).
“We were surprised by these results,” Dr. Ishani said. “We expected chlorthalidone to be more effective overall. However, learning about these differences in patients who have a history of cardiovascular disease may affect patient care. It’s best for people to talk with their health care clinicians about which of these medications is better for their individual needs.”
He added: “More research is needed to explore these results further because we don’t know how they may fit into treating the general population.”
Dr. Ishani noted that a limitations of this study was that most patients were receiving the low dose of chlorthalidone, and previous studies that suggested benefits with chlorthalidone used the higher dose.
“But the world has voted – we had 4,000 clinicians involved in this study, and the vast majority are using the low dose of hydrochlorothiazide. And this is a definitively negative study,” he said. “The world has also voted in that 10 times more patients were on hydrochlorothiazide than on chlorthalidone.”
Commenting on the study at an AHA press conference, Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, pointed out that in all of the landmark National Institutes of Health hypertension trials, there was a signal for benefit with chlorthalidone compared with other antihypertensives.
“We’ve always had this concept that chlorthalidone is better,” she said. “But this study shows no difference in major cardiovascular endpoints. There was more hypokalemia with chlorthalidone, but that’s recognizable as chlorthalidone is a more potent diuretic.”
Other limitations of the DCP trial are its open-label design, which could interject some bias; the enduring effects of hydrochlorothiazide – most of these patients were receiving this agent as background therapy; and inability to look at the effectiveness of decongestion of the agents in such a pragmatic study, Dr. Bozkurt noted.
She said she would like to see more analysis in the subgroup of patients with previous MI or stroke. “Does this result mean that chlorthalidone is better for sicker patients or is this result just due to chance?” she asked.
“While this study demonstrates equal effectiveness of these two diuretics in the targeted population, the question of subgroups of patients for which we use a more potent diuretic I think remains unanswered,” she concluded.
Designated discussant of the DCP trial at the late-breaking trial session, Daniel Levy, MD, director of the Framingham Heart Study at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, reminded attendees that chlorthalidone had shown impressive results in previous important hypertension studies including SHEP and ALLHAT.
He said the current DCP was a pragmatic study addressing a knowledge gap that “would never have been performed by industry.”
Dr. Levy concluded that the results showing no difference in outcomes between the two diuretics were “compelling,” although a few questions remain.
These include a possible bias toward hydrochlorothiazide – patients were selected who were already taking that drug and so would have already had a favorable response to it. In addition, because the trial was conducted in an older male population, he questioned whether the results could be generalized to women and younger patients.
The DCP study was funded by the VA Cooperative Studies Program. Dr. Ishani reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2022
ACC/AHA issues updated guidance on aortic disease
focusing on surgical intervention considerations, consistent imaging practices, genetic and familial screenings, and the importance of multidisciplinary care.
“There has been a host of new evidence-based research available for clinicians in the past decade when it comes to aortic disease. It was time to reevaluate and update the previous, existing guidelines,” Eric M. Isselbacher, MD, MSc, chair of the writing committee, said in a statement.
“We hope this new guideline can inform clinical practices with up-to-date and synthesized recommendations, targeted toward a full multidisciplinary aortic team working to provide the best possible care for this vulnerable patient population,” added Dr. Isselbacher, codirector of the Thoracic Aortic Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
The 2022 ACC/AHA Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Aortic Disease was simultaneously published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation.
The new guideline replaces the 2010 ACCF/AHA Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Patients With Thoracic Aortic Disease and the 2015 Surgery for Aortic Dilation in Patients With Bicuspid Aortic Valves: A Statement of Clarification From the ACC/AHA Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines.
The new guideline is intended to be used with the 2020 ACC/AHA Guideline for the Management of Patients With Valvular Heart Disease.
It brings together guidelines for both the thoracic and abdominal aorta and is targeted to cardiovascular clinicians involved in the care of people with aortic disease, including general cardiovascular care clinicians and emergency medicine clinicians, the writing group says.
Among the key recommendations in the new guideline are the following:
- Screen first-degree relatives of individuals diagnosed with aneurysms of the aortic root or ascending thoracic aorta, or those with aortic dissection to identify individuals most at risk for aortic disease. Screening would include genetic testing and imaging.
- Be consistent in the way CT or MRI are obtained and reported; in the measurement of aortic size and features; and in how often images are used for monitoring before and after repair surgery or other intervention. Ideally, all surveillance imaging for an individual should be done using the same modality and in the same lab, the guideline notes.
- For individuals who require aortic intervention, know that outcomes are optimized when surgery is performed by an experienced surgeon working in a multidisciplinary aortic team. The new guideline recommends “a specialized hospital team with expertise in the evaluation and management of aortic disease, in which care is delivered in a comprehensive, multidisciplinary manner.”
- At centers with multidisciplinary aortic teams and experienced surgeons, the threshold for surgical intervention for sporadic aortic root and ascending aortic aneurysms has been lowered from 5.5 cm to 5.0 cm in select individuals, and even lower in specific scenarios among patients with heritable thoracic aortic aneurysms.
- In patients who are significantly smaller or taller than average, surgical thresholds may incorporate indexing of the aortic root or ascending aortic diameter to either patient body surface area or height, or aortic cross-sectional area to patient height.
- Rapid aortic growth is a risk factor for rupture and the definition for rapid aneurysm growth rate has been updated. Surgery is now recommended for patients with aneurysms of aortic root and ascending thoracic aorta with a confirmed growth rate of ≥ 0.3 cm per year across 2 consecutive years or ≥ 0.5 cm in 1 year.
- In patients undergoing aortic root replacement surgery, valve-sparing aortic root replacement is reasonable if the valve is suitable for repair and when performed by experienced surgeons in a multidisciplinary aortic team.
- Patients with acute type A aortic dissection, if clinically stable, should be considered for transfer to a high-volume aortic center to improve survival. The operative repair of type A aortic dissection should entail at least an open distal anastomosis rather than just a simple supracoronary interposition graft.
- For management of uncomplicated type B aortic dissection, there is an increasing role for . Clinical trials of repair of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms with endografts are reporting results that suggest endovascular repair is an option for patients with suitable anatomy.
- Shared decision-making between the patient and multidisciplinary aortic team is highly encouraged, especially when the patient is on the borderline of thresholds for repair or eligible for different types of surgical repair.
- Shared decision-making should also be used with individuals who are pregnant or may become pregnant to consider the risks of pregnancy in individuals with aortic disease.
The guideline was developed in collaboration with and endorsed by the American Association for Thoracic Surgery, the American College of Radiology, the Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists, the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, the Society of Thoracic Surgeons, and the Society for Vascular Medicine.
It has been endorsed by the Society of Interventional Radiology and the Society for Vascular Surgery.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
focusing on surgical intervention considerations, consistent imaging practices, genetic and familial screenings, and the importance of multidisciplinary care.
“There has been a host of new evidence-based research available for clinicians in the past decade when it comes to aortic disease. It was time to reevaluate and update the previous, existing guidelines,” Eric M. Isselbacher, MD, MSc, chair of the writing committee, said in a statement.
“We hope this new guideline can inform clinical practices with up-to-date and synthesized recommendations, targeted toward a full multidisciplinary aortic team working to provide the best possible care for this vulnerable patient population,” added Dr. Isselbacher, codirector of the Thoracic Aortic Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
The 2022 ACC/AHA Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Aortic Disease was simultaneously published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation.
The new guideline replaces the 2010 ACCF/AHA Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Patients With Thoracic Aortic Disease and the 2015 Surgery for Aortic Dilation in Patients With Bicuspid Aortic Valves: A Statement of Clarification From the ACC/AHA Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines.
The new guideline is intended to be used with the 2020 ACC/AHA Guideline for the Management of Patients With Valvular Heart Disease.
It brings together guidelines for both the thoracic and abdominal aorta and is targeted to cardiovascular clinicians involved in the care of people with aortic disease, including general cardiovascular care clinicians and emergency medicine clinicians, the writing group says.
Among the key recommendations in the new guideline are the following:
- Screen first-degree relatives of individuals diagnosed with aneurysms of the aortic root or ascending thoracic aorta, or those with aortic dissection to identify individuals most at risk for aortic disease. Screening would include genetic testing and imaging.
- Be consistent in the way CT or MRI are obtained and reported; in the measurement of aortic size and features; and in how often images are used for monitoring before and after repair surgery or other intervention. Ideally, all surveillance imaging for an individual should be done using the same modality and in the same lab, the guideline notes.
- For individuals who require aortic intervention, know that outcomes are optimized when surgery is performed by an experienced surgeon working in a multidisciplinary aortic team. The new guideline recommends “a specialized hospital team with expertise in the evaluation and management of aortic disease, in which care is delivered in a comprehensive, multidisciplinary manner.”
- At centers with multidisciplinary aortic teams and experienced surgeons, the threshold for surgical intervention for sporadic aortic root and ascending aortic aneurysms has been lowered from 5.5 cm to 5.0 cm in select individuals, and even lower in specific scenarios among patients with heritable thoracic aortic aneurysms.
- In patients who are significantly smaller or taller than average, surgical thresholds may incorporate indexing of the aortic root or ascending aortic diameter to either patient body surface area or height, or aortic cross-sectional area to patient height.
- Rapid aortic growth is a risk factor for rupture and the definition for rapid aneurysm growth rate has been updated. Surgery is now recommended for patients with aneurysms of aortic root and ascending thoracic aorta with a confirmed growth rate of ≥ 0.3 cm per year across 2 consecutive years or ≥ 0.5 cm in 1 year.
- In patients undergoing aortic root replacement surgery, valve-sparing aortic root replacement is reasonable if the valve is suitable for repair and when performed by experienced surgeons in a multidisciplinary aortic team.
- Patients with acute type A aortic dissection, if clinically stable, should be considered for transfer to a high-volume aortic center to improve survival. The operative repair of type A aortic dissection should entail at least an open distal anastomosis rather than just a simple supracoronary interposition graft.
- For management of uncomplicated type B aortic dissection, there is an increasing role for . Clinical trials of repair of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms with endografts are reporting results that suggest endovascular repair is an option for patients with suitable anatomy.
- Shared decision-making between the patient and multidisciplinary aortic team is highly encouraged, especially when the patient is on the borderline of thresholds for repair or eligible for different types of surgical repair.
- Shared decision-making should also be used with individuals who are pregnant or may become pregnant to consider the risks of pregnancy in individuals with aortic disease.
The guideline was developed in collaboration with and endorsed by the American Association for Thoracic Surgery, the American College of Radiology, the Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists, the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, the Society of Thoracic Surgeons, and the Society for Vascular Medicine.
It has been endorsed by the Society of Interventional Radiology and the Society for Vascular Surgery.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
focusing on surgical intervention considerations, consistent imaging practices, genetic and familial screenings, and the importance of multidisciplinary care.
“There has been a host of new evidence-based research available for clinicians in the past decade when it comes to aortic disease. It was time to reevaluate and update the previous, existing guidelines,” Eric M. Isselbacher, MD, MSc, chair of the writing committee, said in a statement.
“We hope this new guideline can inform clinical practices with up-to-date and synthesized recommendations, targeted toward a full multidisciplinary aortic team working to provide the best possible care for this vulnerable patient population,” added Dr. Isselbacher, codirector of the Thoracic Aortic Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
The 2022 ACC/AHA Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Aortic Disease was simultaneously published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation.
The new guideline replaces the 2010 ACCF/AHA Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Patients With Thoracic Aortic Disease and the 2015 Surgery for Aortic Dilation in Patients With Bicuspid Aortic Valves: A Statement of Clarification From the ACC/AHA Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines.
The new guideline is intended to be used with the 2020 ACC/AHA Guideline for the Management of Patients With Valvular Heart Disease.
It brings together guidelines for both the thoracic and abdominal aorta and is targeted to cardiovascular clinicians involved in the care of people with aortic disease, including general cardiovascular care clinicians and emergency medicine clinicians, the writing group says.
Among the key recommendations in the new guideline are the following:
- Screen first-degree relatives of individuals diagnosed with aneurysms of the aortic root or ascending thoracic aorta, or those with aortic dissection to identify individuals most at risk for aortic disease. Screening would include genetic testing and imaging.
- Be consistent in the way CT or MRI are obtained and reported; in the measurement of aortic size and features; and in how often images are used for monitoring before and after repair surgery or other intervention. Ideally, all surveillance imaging for an individual should be done using the same modality and in the same lab, the guideline notes.
- For individuals who require aortic intervention, know that outcomes are optimized when surgery is performed by an experienced surgeon working in a multidisciplinary aortic team. The new guideline recommends “a specialized hospital team with expertise in the evaluation and management of aortic disease, in which care is delivered in a comprehensive, multidisciplinary manner.”
- At centers with multidisciplinary aortic teams and experienced surgeons, the threshold for surgical intervention for sporadic aortic root and ascending aortic aneurysms has been lowered from 5.5 cm to 5.0 cm in select individuals, and even lower in specific scenarios among patients with heritable thoracic aortic aneurysms.
- In patients who are significantly smaller or taller than average, surgical thresholds may incorporate indexing of the aortic root or ascending aortic diameter to either patient body surface area or height, or aortic cross-sectional area to patient height.
- Rapid aortic growth is a risk factor for rupture and the definition for rapid aneurysm growth rate has been updated. Surgery is now recommended for patients with aneurysms of aortic root and ascending thoracic aorta with a confirmed growth rate of ≥ 0.3 cm per year across 2 consecutive years or ≥ 0.5 cm in 1 year.
- In patients undergoing aortic root replacement surgery, valve-sparing aortic root replacement is reasonable if the valve is suitable for repair and when performed by experienced surgeons in a multidisciplinary aortic team.
- Patients with acute type A aortic dissection, if clinically stable, should be considered for transfer to a high-volume aortic center to improve survival. The operative repair of type A aortic dissection should entail at least an open distal anastomosis rather than just a simple supracoronary interposition graft.
- For management of uncomplicated type B aortic dissection, there is an increasing role for . Clinical trials of repair of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms with endografts are reporting results that suggest endovascular repair is an option for patients with suitable anatomy.
- Shared decision-making between the patient and multidisciplinary aortic team is highly encouraged, especially when the patient is on the borderline of thresholds for repair or eligible for different types of surgical repair.
- Shared decision-making should also be used with individuals who are pregnant or may become pregnant to consider the risks of pregnancy in individuals with aortic disease.
The guideline was developed in collaboration with and endorsed by the American Association for Thoracic Surgery, the American College of Radiology, the Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists, the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, the Society of Thoracic Surgeons, and the Society for Vascular Medicine.
It has been endorsed by the Society of Interventional Radiology and the Society for Vascular Surgery.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CIRCULATION
Uptake of high-sensitivity troponin assays lags in U.S. hospitals
Most hospitals in the United States have yet to transition from conventional to high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) assays, despite their greater sensitivity for myocardial injury, a new National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR) registry study indicates.
hs-cTn assays have been used in routine clinical practice in Europe, Canada, and Australia since 2010, but the first such assay did not gain approval in the United States until 2017. Although single-center studies have examined their efficacy and potential downstream consequences, few data exist on hs-cTn implementation nationally, explained study author Cian McCarthy, MB, BCh, BAO, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
The results were published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and will be presented Nov. 5 at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
For the study, Dr. McCarthy and colleagues examined 550 hospitals participating in the NCDR Chest Pain-MI registry from January 2019 through September 2021.
Of the 251,000 patients included in the analysis (mean age, 64 years; 41.5% female), 155,049 had a non–ST-segment myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), 15,989 had unstable angina, and 79,962 had low-risk chest pain.
The hs-cTn assays included Roche Diagnostic’s Elecsys Gen5 STAT troponin T assay (23%); Abbott’s ARCHITECT STAT (17%); Beckman Coulter’s ACCESS (21%); and Siemens’ Atellica IM (18%), Dimension VISTA (14%), Dimension EXL (4%), and ADVIA Centaur (2%) troponin I assays.
During the study period, 11.5% of patients were evaluated with hs-cTn assays and the remainder were evaluated with conventional troponin assays. These patients were slightly older (65.0 vs. 64.0 years), more commonly White (83.1% vs. 79.9%), less likely to be of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity (8.9% vs. 10.0%), and less likely to be uninsured (6.8% vs. 8.3%; P for all < .001).
A slightly higher proportion of patients evaluated with hs-cTn assays were diagnosed with unstable angina (7.1% vs. 6.3%), a lower proportion with NSTEMI (61.1% vs. 61.9%), and a similar proportion with low-risk chest pain (31.8% vs. 31.9%) compared with those evaluated by conventional troponin assays.
Implementation, defined as at least 25% of patients evaluated by hs-cTn in each quarter, increased from 3.3% in the first quarter of 2019 to 32.6% in the third quarter of 2021 (P trend < .001).
Using higher implementation thresholds of at least 50% and 75% of patients evaluated by hs-cTn, the prevalence in 2021 was 28.9% and 24.7%, respectively.
“So still, the majority of the hospitals by the end of the third quarter 2021 were not using these assays,” Dr. McCarthy said.
Potential explanations for the slow uptake are that prospective comparative effectiveness trials of These assays have predominantly been in international populations and real-world data on U.S. implementation have been limited to integrated health networks at academic institutions.
Approval of several assays was also delayed and the study data cut off just before the October publication of the 2021 AHA/ACC Chest Pain guideline. “So, whether the chest pain guideline with the new class 1 recommendation for hs-cTn will lead to further uptake is something that will need to be looked at in the future,” he said.
Downstream testing
In adjusted analyses, hs-cTn use was associated with more echocardiography among patients with non-ST elevation–acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS) (82.4% vs. 75.0%; odds ratio [OR], 1.43; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.19-1.73), but not among those with low-risk chest pain (19.7% vs. 19.4%; OR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.71-1.22) compared with conventional cTn assays.
Importantly, hs-cTn was not associated with a difference in stress testing or CT coronary angiography utilization.
Use of hs-cTn was associated with lower use of invasive coronary angiography among patients with low-risk chest pain (3.7% vs. 4.5%; OR, 0.73, 95% CI, 0.58-0.92) but similar use for NSTE-ACS (96.3% vs. 95.8%; OR, 0.99, 95% CI, 0.82-1.19).
Among patients with NSTE-ACS, there also was no difference in revascularization with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) (52.7% vs. 52.3%; OR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.94-1.04) or coronary bypass graft surgery (9.4% vs. 9.1%; OR, 1.06; 95% CI, 0.94-1.18).
PCI (0.1% vs. 0.2%; P = .05) and bypass graft surgery (both 0.1%) were uncommon among patients with low-risk chest pain.
In-hospital mortality was similar among patients with low-risk chest pain evaluated using hs-cTn assays vs. conventional troponin assays (0% vs. 0.02%; P = .16) and among patients with NSTE-ACS (2.8% vs. 3.2%; OR, 0.98, 95% CI, 0.87-1.11).
Length of stay was slightly shorter with hs-cTn use for patients with low-risk chest pain (median, 5.8 vs. 6.2 hours; P < .001) and patients with NSTE-ACS (66.9 vs. 67.8 hours; P = .01).
“There was always a concern that maybe high-sensitivity cardiac troponin would dramatically increase testing and could even increase length of stay, but I think these data are reassuring, in that this study suggests high-sensitivity cardiac troponin is associated with a small reduction in length of stay and possibly more appropriate use of testing with echocardiography in STEMI and a reduction in invasive angiography in low-risk patients,” Dr. McCarthy said. “But the majority of hospitals haven’t implemented the assay.”
The authors pointed out that because registry entry of patients with low-risk chest pain and unstable angina is optional for participating sites, the percentage of patients with NSTEMI is higher than in typical chest pain analyses. This higher pretest probability for MI may thus affect post-test accuracy for a true positive result. “That stated, this is the exact scenario where higher sensitivity might be associated with favorable impact on utilization.”
Among other limitations: There was the potential for unmeasured confounders, the accuracy of diagnoses could not be confirmed, patients with type 2 MI were excluded from the registry, and post-discharge safety was not assessed.
“These data indicate further opportunities to more widely and effectively implement hs-cTn in the U.S. hospitals persist that could optimize care for patients with possible or definitive ACS,” Dr. McCarthy and colleagues concluded.
The study was funded by the American College of Cardiology’s National Cardiovascular Data Registry. Dr. McCarthy is supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and has received consulting income from Abbott Laboratories.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most hospitals in the United States have yet to transition from conventional to high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) assays, despite their greater sensitivity for myocardial injury, a new National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR) registry study indicates.
hs-cTn assays have been used in routine clinical practice in Europe, Canada, and Australia since 2010, but the first such assay did not gain approval in the United States until 2017. Although single-center studies have examined their efficacy and potential downstream consequences, few data exist on hs-cTn implementation nationally, explained study author Cian McCarthy, MB, BCh, BAO, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
The results were published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and will be presented Nov. 5 at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
For the study, Dr. McCarthy and colleagues examined 550 hospitals participating in the NCDR Chest Pain-MI registry from January 2019 through September 2021.
Of the 251,000 patients included in the analysis (mean age, 64 years; 41.5% female), 155,049 had a non–ST-segment myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), 15,989 had unstable angina, and 79,962 had low-risk chest pain.
The hs-cTn assays included Roche Diagnostic’s Elecsys Gen5 STAT troponin T assay (23%); Abbott’s ARCHITECT STAT (17%); Beckman Coulter’s ACCESS (21%); and Siemens’ Atellica IM (18%), Dimension VISTA (14%), Dimension EXL (4%), and ADVIA Centaur (2%) troponin I assays.
During the study period, 11.5% of patients were evaluated with hs-cTn assays and the remainder were evaluated with conventional troponin assays. These patients were slightly older (65.0 vs. 64.0 years), more commonly White (83.1% vs. 79.9%), less likely to be of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity (8.9% vs. 10.0%), and less likely to be uninsured (6.8% vs. 8.3%; P for all < .001).
A slightly higher proportion of patients evaluated with hs-cTn assays were diagnosed with unstable angina (7.1% vs. 6.3%), a lower proportion with NSTEMI (61.1% vs. 61.9%), and a similar proportion with low-risk chest pain (31.8% vs. 31.9%) compared with those evaluated by conventional troponin assays.
Implementation, defined as at least 25% of patients evaluated by hs-cTn in each quarter, increased from 3.3% in the first quarter of 2019 to 32.6% in the third quarter of 2021 (P trend < .001).
Using higher implementation thresholds of at least 50% and 75% of patients evaluated by hs-cTn, the prevalence in 2021 was 28.9% and 24.7%, respectively.
“So still, the majority of the hospitals by the end of the third quarter 2021 were not using these assays,” Dr. McCarthy said.
Potential explanations for the slow uptake are that prospective comparative effectiveness trials of These assays have predominantly been in international populations and real-world data on U.S. implementation have been limited to integrated health networks at academic institutions.
Approval of several assays was also delayed and the study data cut off just before the October publication of the 2021 AHA/ACC Chest Pain guideline. “So, whether the chest pain guideline with the new class 1 recommendation for hs-cTn will lead to further uptake is something that will need to be looked at in the future,” he said.
Downstream testing
In adjusted analyses, hs-cTn use was associated with more echocardiography among patients with non-ST elevation–acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS) (82.4% vs. 75.0%; odds ratio [OR], 1.43; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.19-1.73), but not among those with low-risk chest pain (19.7% vs. 19.4%; OR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.71-1.22) compared with conventional cTn assays.
Importantly, hs-cTn was not associated with a difference in stress testing or CT coronary angiography utilization.
Use of hs-cTn was associated with lower use of invasive coronary angiography among patients with low-risk chest pain (3.7% vs. 4.5%; OR, 0.73, 95% CI, 0.58-0.92) but similar use for NSTE-ACS (96.3% vs. 95.8%; OR, 0.99, 95% CI, 0.82-1.19).
Among patients with NSTE-ACS, there also was no difference in revascularization with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) (52.7% vs. 52.3%; OR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.94-1.04) or coronary bypass graft surgery (9.4% vs. 9.1%; OR, 1.06; 95% CI, 0.94-1.18).
PCI (0.1% vs. 0.2%; P = .05) and bypass graft surgery (both 0.1%) were uncommon among patients with low-risk chest pain.
In-hospital mortality was similar among patients with low-risk chest pain evaluated using hs-cTn assays vs. conventional troponin assays (0% vs. 0.02%; P = .16) and among patients with NSTE-ACS (2.8% vs. 3.2%; OR, 0.98, 95% CI, 0.87-1.11).
Length of stay was slightly shorter with hs-cTn use for patients with low-risk chest pain (median, 5.8 vs. 6.2 hours; P < .001) and patients with NSTE-ACS (66.9 vs. 67.8 hours; P = .01).
“There was always a concern that maybe high-sensitivity cardiac troponin would dramatically increase testing and could even increase length of stay, but I think these data are reassuring, in that this study suggests high-sensitivity cardiac troponin is associated with a small reduction in length of stay and possibly more appropriate use of testing with echocardiography in STEMI and a reduction in invasive angiography in low-risk patients,” Dr. McCarthy said. “But the majority of hospitals haven’t implemented the assay.”
The authors pointed out that because registry entry of patients with low-risk chest pain and unstable angina is optional for participating sites, the percentage of patients with NSTEMI is higher than in typical chest pain analyses. This higher pretest probability for MI may thus affect post-test accuracy for a true positive result. “That stated, this is the exact scenario where higher sensitivity might be associated with favorable impact on utilization.”
Among other limitations: There was the potential for unmeasured confounders, the accuracy of diagnoses could not be confirmed, patients with type 2 MI were excluded from the registry, and post-discharge safety was not assessed.
“These data indicate further opportunities to more widely and effectively implement hs-cTn in the U.S. hospitals persist that could optimize care for patients with possible or definitive ACS,” Dr. McCarthy and colleagues concluded.
The study was funded by the American College of Cardiology’s National Cardiovascular Data Registry. Dr. McCarthy is supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and has received consulting income from Abbott Laboratories.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most hospitals in the United States have yet to transition from conventional to high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) assays, despite their greater sensitivity for myocardial injury, a new National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR) registry study indicates.
hs-cTn assays have been used in routine clinical practice in Europe, Canada, and Australia since 2010, but the first such assay did not gain approval in the United States until 2017. Although single-center studies have examined their efficacy and potential downstream consequences, few data exist on hs-cTn implementation nationally, explained study author Cian McCarthy, MB, BCh, BAO, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
The results were published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and will be presented Nov. 5 at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
For the study, Dr. McCarthy and colleagues examined 550 hospitals participating in the NCDR Chest Pain-MI registry from January 2019 through September 2021.
Of the 251,000 patients included in the analysis (mean age, 64 years; 41.5% female), 155,049 had a non–ST-segment myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), 15,989 had unstable angina, and 79,962 had low-risk chest pain.
The hs-cTn assays included Roche Diagnostic’s Elecsys Gen5 STAT troponin T assay (23%); Abbott’s ARCHITECT STAT (17%); Beckman Coulter’s ACCESS (21%); and Siemens’ Atellica IM (18%), Dimension VISTA (14%), Dimension EXL (4%), and ADVIA Centaur (2%) troponin I assays.
During the study period, 11.5% of patients were evaluated with hs-cTn assays and the remainder were evaluated with conventional troponin assays. These patients were slightly older (65.0 vs. 64.0 years), more commonly White (83.1% vs. 79.9%), less likely to be of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity (8.9% vs. 10.0%), and less likely to be uninsured (6.8% vs. 8.3%; P for all < .001).
A slightly higher proportion of patients evaluated with hs-cTn assays were diagnosed with unstable angina (7.1% vs. 6.3%), a lower proportion with NSTEMI (61.1% vs. 61.9%), and a similar proportion with low-risk chest pain (31.8% vs. 31.9%) compared with those evaluated by conventional troponin assays.
Implementation, defined as at least 25% of patients evaluated by hs-cTn in each quarter, increased from 3.3% in the first quarter of 2019 to 32.6% in the third quarter of 2021 (P trend < .001).
Using higher implementation thresholds of at least 50% and 75% of patients evaluated by hs-cTn, the prevalence in 2021 was 28.9% and 24.7%, respectively.
“So still, the majority of the hospitals by the end of the third quarter 2021 were not using these assays,” Dr. McCarthy said.
Potential explanations for the slow uptake are that prospective comparative effectiveness trials of These assays have predominantly been in international populations and real-world data on U.S. implementation have been limited to integrated health networks at academic institutions.
Approval of several assays was also delayed and the study data cut off just before the October publication of the 2021 AHA/ACC Chest Pain guideline. “So, whether the chest pain guideline with the new class 1 recommendation for hs-cTn will lead to further uptake is something that will need to be looked at in the future,” he said.
Downstream testing
In adjusted analyses, hs-cTn use was associated with more echocardiography among patients with non-ST elevation–acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS) (82.4% vs. 75.0%; odds ratio [OR], 1.43; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.19-1.73), but not among those with low-risk chest pain (19.7% vs. 19.4%; OR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.71-1.22) compared with conventional cTn assays.
Importantly, hs-cTn was not associated with a difference in stress testing or CT coronary angiography utilization.
Use of hs-cTn was associated with lower use of invasive coronary angiography among patients with low-risk chest pain (3.7% vs. 4.5%; OR, 0.73, 95% CI, 0.58-0.92) but similar use for NSTE-ACS (96.3% vs. 95.8%; OR, 0.99, 95% CI, 0.82-1.19).
Among patients with NSTE-ACS, there also was no difference in revascularization with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) (52.7% vs. 52.3%; OR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.94-1.04) or coronary bypass graft surgery (9.4% vs. 9.1%; OR, 1.06; 95% CI, 0.94-1.18).
PCI (0.1% vs. 0.2%; P = .05) and bypass graft surgery (both 0.1%) were uncommon among patients with low-risk chest pain.
In-hospital mortality was similar among patients with low-risk chest pain evaluated using hs-cTn assays vs. conventional troponin assays (0% vs. 0.02%; P = .16) and among patients with NSTE-ACS (2.8% vs. 3.2%; OR, 0.98, 95% CI, 0.87-1.11).
Length of stay was slightly shorter with hs-cTn use for patients with low-risk chest pain (median, 5.8 vs. 6.2 hours; P < .001) and patients with NSTE-ACS (66.9 vs. 67.8 hours; P = .01).
“There was always a concern that maybe high-sensitivity cardiac troponin would dramatically increase testing and could even increase length of stay, but I think these data are reassuring, in that this study suggests high-sensitivity cardiac troponin is associated with a small reduction in length of stay and possibly more appropriate use of testing with echocardiography in STEMI and a reduction in invasive angiography in low-risk patients,” Dr. McCarthy said. “But the majority of hospitals haven’t implemented the assay.”
The authors pointed out that because registry entry of patients with low-risk chest pain and unstable angina is optional for participating sites, the percentage of patients with NSTEMI is higher than in typical chest pain analyses. This higher pretest probability for MI may thus affect post-test accuracy for a true positive result. “That stated, this is the exact scenario where higher sensitivity might be associated with favorable impact on utilization.”
Among other limitations: There was the potential for unmeasured confounders, the accuracy of diagnoses could not be confirmed, patients with type 2 MI were excluded from the registry, and post-discharge safety was not assessed.
“These data indicate further opportunities to more widely and effectively implement hs-cTn in the U.S. hospitals persist that could optimize care for patients with possible or definitive ACS,” Dr. McCarthy and colleagues concluded.
The study was funded by the American College of Cardiology’s National Cardiovascular Data Registry. Dr. McCarthy is supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and has received consulting income from Abbott Laboratories.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2022
AHA 2022 to recapture in-person vibe but preserve global reach
That a bustling medical conference can have global reach as it unfolds is one of the COVID pandemic’s many lessons for science. Hybrid meetings such as the American Heart Association scientific sessions, getting underway Nov. 5 in Chicago and cyberspace, are one of its legacies.
The conference is set to recapture the magic of the in-person Scientific Sessions last experienced in Philadelphia in 2019. But planners are mindful of a special responsibility to younger clinicians and scientists who entered the field knowing only the virtual format and who may not know “what it’s like in a room when major science is presented or to present posters and have people come by for conversations,” Manesh R. Patel, MD, chair of the AHA 2022 Scientific Sessions program committee, told this news organization.
Still, the pandemic has underlined the value of live streaming for the great many who can’t attend in person, Dr. Patel said. At AHA 2022, virtual access doesn’t mean only late breaking and featured presentations; more than 70 full sessions will be streamed from Friday through Monday.
Overall, the conference has more than 800 sessions on the schedule, about a third are panels or invited lectures and two-thirds are original reports on the latest research. At the core of the research offerings, 78 studies and analyses are slated across 18 Late-Breaking Science (LBS) and Featured Science (FS) sessions from Saturday through Monday. At least 30 presentations and abstracts will enter the peer-reviewed literature right away with their simultaneous online publication, Dr. Patel said.
More a meet-and-greet than a presentation, the Puppy Snuggles Booth will make a return appearance in Chicago after earning rave reviews at the 2019 Sessions in Philadelphia. All are invited to take a breather from their schedules to pet, cuddle, and play with a passel of pups, all in need of homes and available for adoption. The experience’s favorable effect on blood pressure is almost guaranteed.
LBS and FS highlights
“It’s an amazing year for Late Breaking Science and Featured Science at the Scientific Sessions,” Dr. Patel said of the presentations selected for special attention after a rigorous review process. “We have science that is as broad and as deep as we’ve seen in years.”
Saturday’s two LBS sessions kick off the series with studies looking at agents long available in heart failure and hypertension but lacking solid supporting evidence, “pretty large randomized trials that are, we think, going to affect clinical practice as soon as they are presented,” Dr. Patel said.
They include TRANSFORM-HF, a comparison of the loop diuretics furosemide and torsemide in patients hospitalized with heart failure. And the Diuretic Comparison Project (DCP), with more than 13,000 patients with hypertension assigned to the diuretics chlorthalidone or hydrochlorothiazide, “is going to immediately impact how people think about blood pressure management,” Dr. Patel said.
Other highlights in the hypertension arena include the CRHCP trial, the MB-BP study, the Rich Life Project, and the polypill efficacy and safety trial QUARTET-USA, all in Sunday’s LBS-4; and the FRESH, PRECISION, and BrigHTN trials, all in LBS-9 on Monday.
Other heart failure trials joining TRANSFORM-HF in the line-up include IRONMAN, which revisited IV iron therapy in iron-deficient patients, in LBS-2 on Saturday and, in FS-4 on Monday, BETA3LVH and STRONG-HF, the latter a timely randomized test of pre- and post-discharge biomarker-driven uptitration of guideline-directed heart failure meds.
STRONG-HF was halted early, the trial’s nonprofit sponsor announced only weeks ago, after patients following the intensive uptitration strategy versus usual care showed a reduced risk of death or heart failure readmission; few other details were given.
Several sessions will be devoted to a rare breed of randomized trial, one that tests the efficacy of traditional herbal meds or nonprescription supplements against proven medications. “These are going to get a lot of people’s interest, one can imagine, because they are on common questions that patients bring to the clinic every day,” Dr. Patel said.
Such studies include CTS-AMI, which explored the traditional Chinese herbal medicine tongxinluo in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, in LBS-3 on Sunday, and SPORT in Sunday’s LBS-5, a small randomized comparison of low-dose rosuvastatin, cinnamon, garlic, turmeric, an omega-3 fish-oil supplement, a plant sterol, red yeast rice, and placebo for any effects on LDL-C levels.
Other novel approaches to dyslipidemia management are to be covered in RESPECT-EPA and OCEAN(a)-DOSE, both in LBS-5 on Sunday, and all five presentations in Monday’s FS-9, including ARCHES-2, SHASTA-2, FOURIER-OLE, and ORION-3.
The interplay of antiplatelets and coronary interventions will be explored in presentations called OPTION, in LBS-6 on Sunday, and HOST-EXAM and TWILIGHT, in FS-6 on Monday.
Coronary and peripheral-vascular interventions are center stage in reports on RAPCO in LBS-3 and BRIGHT-4 in LBS-6, both on Sunday, and BEST-CLI in LBS-7 and the After-80 Study in FS-6, both on Monday.
Several Monday reports will cover comorbidities and complications associated with COVID-19, including PREVENT-HD in LBS-7, and PANAMO, FERMIN, COVID-NET, and a secondary analysis of the DELIVER trial in FS-5.
Rebroadcasts for the Pacific Rim
The sessions will also feature several evening rebroadcasts of earlier LBS sessions that meeting planners scored highly for scientific merit and potential clinical impact but also for their “regional pull,” primarily for our colleagues in Asia, Dr. Patel said.
The first two LBS sessions presented live during the day in Chicago will be rebroadcast that evening as, for example, Sunday morning and afternoon fare in Tokyo and Singapore. And LBS-5 live Sunday afternoon will rebroadcast that night as a Monday mid-morning session in, say, Hong Kong or Seoul.
This year’s AHA meeting spans the range of cardiovascular care, from precision therapies, such as gene editing or specific drugs, to broad strategies that consider, for example, social determinants of health, Dr. Patel said. “I think people, when they leave the Scientific Sessions, will feel very engaged in the larger conversation about how you impact very common conditions globally.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
That a bustling medical conference can have global reach as it unfolds is one of the COVID pandemic’s many lessons for science. Hybrid meetings such as the American Heart Association scientific sessions, getting underway Nov. 5 in Chicago and cyberspace, are one of its legacies.
The conference is set to recapture the magic of the in-person Scientific Sessions last experienced in Philadelphia in 2019. But planners are mindful of a special responsibility to younger clinicians and scientists who entered the field knowing only the virtual format and who may not know “what it’s like in a room when major science is presented or to present posters and have people come by for conversations,” Manesh R. Patel, MD, chair of the AHA 2022 Scientific Sessions program committee, told this news organization.
Still, the pandemic has underlined the value of live streaming for the great many who can’t attend in person, Dr. Patel said. At AHA 2022, virtual access doesn’t mean only late breaking and featured presentations; more than 70 full sessions will be streamed from Friday through Monday.
Overall, the conference has more than 800 sessions on the schedule, about a third are panels or invited lectures and two-thirds are original reports on the latest research. At the core of the research offerings, 78 studies and analyses are slated across 18 Late-Breaking Science (LBS) and Featured Science (FS) sessions from Saturday through Monday. At least 30 presentations and abstracts will enter the peer-reviewed literature right away with their simultaneous online publication, Dr. Patel said.
More a meet-and-greet than a presentation, the Puppy Snuggles Booth will make a return appearance in Chicago after earning rave reviews at the 2019 Sessions in Philadelphia. All are invited to take a breather from their schedules to pet, cuddle, and play with a passel of pups, all in need of homes and available for adoption. The experience’s favorable effect on blood pressure is almost guaranteed.
LBS and FS highlights
“It’s an amazing year for Late Breaking Science and Featured Science at the Scientific Sessions,” Dr. Patel said of the presentations selected for special attention after a rigorous review process. “We have science that is as broad and as deep as we’ve seen in years.”
Saturday’s two LBS sessions kick off the series with studies looking at agents long available in heart failure and hypertension but lacking solid supporting evidence, “pretty large randomized trials that are, we think, going to affect clinical practice as soon as they are presented,” Dr. Patel said.
They include TRANSFORM-HF, a comparison of the loop diuretics furosemide and torsemide in patients hospitalized with heart failure. And the Diuretic Comparison Project (DCP), with more than 13,000 patients with hypertension assigned to the diuretics chlorthalidone or hydrochlorothiazide, “is going to immediately impact how people think about blood pressure management,” Dr. Patel said.
Other highlights in the hypertension arena include the CRHCP trial, the MB-BP study, the Rich Life Project, and the polypill efficacy and safety trial QUARTET-USA, all in Sunday’s LBS-4; and the FRESH, PRECISION, and BrigHTN trials, all in LBS-9 on Monday.
Other heart failure trials joining TRANSFORM-HF in the line-up include IRONMAN, which revisited IV iron therapy in iron-deficient patients, in LBS-2 on Saturday and, in FS-4 on Monday, BETA3LVH and STRONG-HF, the latter a timely randomized test of pre- and post-discharge biomarker-driven uptitration of guideline-directed heart failure meds.
STRONG-HF was halted early, the trial’s nonprofit sponsor announced only weeks ago, after patients following the intensive uptitration strategy versus usual care showed a reduced risk of death or heart failure readmission; few other details were given.
Several sessions will be devoted to a rare breed of randomized trial, one that tests the efficacy of traditional herbal meds or nonprescription supplements against proven medications. “These are going to get a lot of people’s interest, one can imagine, because they are on common questions that patients bring to the clinic every day,” Dr. Patel said.
Such studies include CTS-AMI, which explored the traditional Chinese herbal medicine tongxinluo in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, in LBS-3 on Sunday, and SPORT in Sunday’s LBS-5, a small randomized comparison of low-dose rosuvastatin, cinnamon, garlic, turmeric, an omega-3 fish-oil supplement, a plant sterol, red yeast rice, and placebo for any effects on LDL-C levels.
Other novel approaches to dyslipidemia management are to be covered in RESPECT-EPA and OCEAN(a)-DOSE, both in LBS-5 on Sunday, and all five presentations in Monday’s FS-9, including ARCHES-2, SHASTA-2, FOURIER-OLE, and ORION-3.
The interplay of antiplatelets and coronary interventions will be explored in presentations called OPTION, in LBS-6 on Sunday, and HOST-EXAM and TWILIGHT, in FS-6 on Monday.
Coronary and peripheral-vascular interventions are center stage in reports on RAPCO in LBS-3 and BRIGHT-4 in LBS-6, both on Sunday, and BEST-CLI in LBS-7 and the After-80 Study in FS-6, both on Monday.
Several Monday reports will cover comorbidities and complications associated with COVID-19, including PREVENT-HD in LBS-7, and PANAMO, FERMIN, COVID-NET, and a secondary analysis of the DELIVER trial in FS-5.
Rebroadcasts for the Pacific Rim
The sessions will also feature several evening rebroadcasts of earlier LBS sessions that meeting planners scored highly for scientific merit and potential clinical impact but also for their “regional pull,” primarily for our colleagues in Asia, Dr. Patel said.
The first two LBS sessions presented live during the day in Chicago will be rebroadcast that evening as, for example, Sunday morning and afternoon fare in Tokyo and Singapore. And LBS-5 live Sunday afternoon will rebroadcast that night as a Monday mid-morning session in, say, Hong Kong or Seoul.
This year’s AHA meeting spans the range of cardiovascular care, from precision therapies, such as gene editing or specific drugs, to broad strategies that consider, for example, social determinants of health, Dr. Patel said. “I think people, when they leave the Scientific Sessions, will feel very engaged in the larger conversation about how you impact very common conditions globally.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
That a bustling medical conference can have global reach as it unfolds is one of the COVID pandemic’s many lessons for science. Hybrid meetings such as the American Heart Association scientific sessions, getting underway Nov. 5 in Chicago and cyberspace, are one of its legacies.
The conference is set to recapture the magic of the in-person Scientific Sessions last experienced in Philadelphia in 2019. But planners are mindful of a special responsibility to younger clinicians and scientists who entered the field knowing only the virtual format and who may not know “what it’s like in a room when major science is presented or to present posters and have people come by for conversations,” Manesh R. Patel, MD, chair of the AHA 2022 Scientific Sessions program committee, told this news organization.
Still, the pandemic has underlined the value of live streaming for the great many who can’t attend in person, Dr. Patel said. At AHA 2022, virtual access doesn’t mean only late breaking and featured presentations; more than 70 full sessions will be streamed from Friday through Monday.
Overall, the conference has more than 800 sessions on the schedule, about a third are panels or invited lectures and two-thirds are original reports on the latest research. At the core of the research offerings, 78 studies and analyses are slated across 18 Late-Breaking Science (LBS) and Featured Science (FS) sessions from Saturday through Monday. At least 30 presentations and abstracts will enter the peer-reviewed literature right away with their simultaneous online publication, Dr. Patel said.
More a meet-and-greet than a presentation, the Puppy Snuggles Booth will make a return appearance in Chicago after earning rave reviews at the 2019 Sessions in Philadelphia. All are invited to take a breather from their schedules to pet, cuddle, and play with a passel of pups, all in need of homes and available for adoption. The experience’s favorable effect on blood pressure is almost guaranteed.
LBS and FS highlights
“It’s an amazing year for Late Breaking Science and Featured Science at the Scientific Sessions,” Dr. Patel said of the presentations selected for special attention after a rigorous review process. “We have science that is as broad and as deep as we’ve seen in years.”
Saturday’s two LBS sessions kick off the series with studies looking at agents long available in heart failure and hypertension but lacking solid supporting evidence, “pretty large randomized trials that are, we think, going to affect clinical practice as soon as they are presented,” Dr. Patel said.
They include TRANSFORM-HF, a comparison of the loop diuretics furosemide and torsemide in patients hospitalized with heart failure. And the Diuretic Comparison Project (DCP), with more than 13,000 patients with hypertension assigned to the diuretics chlorthalidone or hydrochlorothiazide, “is going to immediately impact how people think about blood pressure management,” Dr. Patel said.
Other highlights in the hypertension arena include the CRHCP trial, the MB-BP study, the Rich Life Project, and the polypill efficacy and safety trial QUARTET-USA, all in Sunday’s LBS-4; and the FRESH, PRECISION, and BrigHTN trials, all in LBS-9 on Monday.
Other heart failure trials joining TRANSFORM-HF in the line-up include IRONMAN, which revisited IV iron therapy in iron-deficient patients, in LBS-2 on Saturday and, in FS-4 on Monday, BETA3LVH and STRONG-HF, the latter a timely randomized test of pre- and post-discharge biomarker-driven uptitration of guideline-directed heart failure meds.
STRONG-HF was halted early, the trial’s nonprofit sponsor announced only weeks ago, after patients following the intensive uptitration strategy versus usual care showed a reduced risk of death or heart failure readmission; few other details were given.
Several sessions will be devoted to a rare breed of randomized trial, one that tests the efficacy of traditional herbal meds or nonprescription supplements against proven medications. “These are going to get a lot of people’s interest, one can imagine, because they are on common questions that patients bring to the clinic every day,” Dr. Patel said.
Such studies include CTS-AMI, which explored the traditional Chinese herbal medicine tongxinluo in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, in LBS-3 on Sunday, and SPORT in Sunday’s LBS-5, a small randomized comparison of low-dose rosuvastatin, cinnamon, garlic, turmeric, an omega-3 fish-oil supplement, a plant sterol, red yeast rice, and placebo for any effects on LDL-C levels.
Other novel approaches to dyslipidemia management are to be covered in RESPECT-EPA and OCEAN(a)-DOSE, both in LBS-5 on Sunday, and all five presentations in Monday’s FS-9, including ARCHES-2, SHASTA-2, FOURIER-OLE, and ORION-3.
The interplay of antiplatelets and coronary interventions will be explored in presentations called OPTION, in LBS-6 on Sunday, and HOST-EXAM and TWILIGHT, in FS-6 on Monday.
Coronary and peripheral-vascular interventions are center stage in reports on RAPCO in LBS-3 and BRIGHT-4 in LBS-6, both on Sunday, and BEST-CLI in LBS-7 and the After-80 Study in FS-6, both on Monday.
Several Monday reports will cover comorbidities and complications associated with COVID-19, including PREVENT-HD in LBS-7, and PANAMO, FERMIN, COVID-NET, and a secondary analysis of the DELIVER trial in FS-5.
Rebroadcasts for the Pacific Rim
The sessions will also feature several evening rebroadcasts of earlier LBS sessions that meeting planners scored highly for scientific merit and potential clinical impact but also for their “regional pull,” primarily for our colleagues in Asia, Dr. Patel said.
The first two LBS sessions presented live during the day in Chicago will be rebroadcast that evening as, for example, Sunday morning and afternoon fare in Tokyo and Singapore. And LBS-5 live Sunday afternoon will rebroadcast that night as a Monday mid-morning session in, say, Hong Kong or Seoul.
This year’s AHA meeting spans the range of cardiovascular care, from precision therapies, such as gene editing or specific drugs, to broad strategies that consider, for example, social determinants of health, Dr. Patel said. “I think people, when they leave the Scientific Sessions, will feel very engaged in the larger conversation about how you impact very common conditions globally.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Poor control of serum urate linked to cardiovascular risk in patients with gout
A new study based on U.S. veterans’ medical records adds to the evidence for a link between gout – especially poorly controlled cases – and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk, Tate Johnson, MD, reported at the annual research symposium of the Gout, Hyperuricemia, and Crystal Associated Disease Network.
Gout was associated with a 68% increased risk of heart failure (HF) hospitalization, 25% increased risk of HF-related death, and a 22% increased risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), said Dr. Johnson, of the division of rheumatology at the University of Nebraska, Omaha.
Poorly controlled serum urate was associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular events, regardless of the use of urate-lowering therapy (ULT). He said more research is needed to see if there is a causal link between gout, hyperuricemia – or its treatment – and CVD risk.
Dr. Johnson and colleagues used records from the Veterans Health Administration for this study. They created a retrospective, matched cohort study that looked at records dating from January 1999 to September 2015. Patients with gout (≥ 2 ICD-9 codes) were matched 1:10 on age, sex, and year of VHA enrollment to patients without a gout ICD-9 code or a record of receiving ULT. They matched 559,243 people with gout to 5,407,379 people who did not have a diagnosis or a recorded treatment for this condition.
Over 43,331,604 person-years, Dr. Johnson and colleagues observed 137,162 CVD events in gout (incidence rate 33.96 per 1,000 person-years) vs. 879,903 in non-gout patients (IR 22.37 per 1,000 person-years). Gout was most strongly associated with HF hospitalization, with a nearly threefold higher risk (hazard ratio, 2.78; 95% confidence interval, 2.73-2.83), which attenuated but persisted after adjustment for additional CVD risk factors (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.68; 95% CI, 1.65-1.70) and excluding patients with prevalent HF (aHR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.57-1.64).
People with gout were also at higher risk of HF-related death (aHR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.21-1.29), MACE (aHR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.21-1.23), and coronary artery disease–related death (aHR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.20-1.22).
Among people with gout in the study, poor serum urate control was associated with a higher risk of all CVD events, with the highest CVD risk occurring in patients with inadequately controlled serum urate despite receipt of ULT, particularly related to HF hospitalization (aHR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.34-1.52) and HF-related death (aHR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.34-1.61).
Limits of the study include the generalizability of the study population. Reflecting the VHA’s patient population, 99% of the cohort were men, with 62% of the gout group and 59.4% of the control group identifying as White and non-Hispanic.
The study provides evidence that may be found only by studying medical records, Richard J. Johnson, MD, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, said in an interview.
Dr. Richard Johnson, who is not related to the author, said that only about one-third of people with gout are adequately treated, and about another one-third take urate-lowering therapy (ULT) but fail to get their serum urate level under control. But it would be unethical to design a clinical trial to study CVD risk and poorly controlled serum urate without ULT treatment.
“The only way you can figure out if uric acid lowering is going to help these guys is to actually do a study like this where you see the ones who don’t get adequate treatment versus adequate treatment and you show that there’s going to be a difference in outcome,” he said.
Dr. Richard Johnson contrasted this approach with the one used in the recently reported study that appeared to cast doubt on the link between serum uric acid levels and cardiovascular disease. The ALL-HEART trial found that allopurinol, a drug commonly used to treat gout, provided no benefit in terms of reducing cardiovascular events in patients with ischemic heart disease. But these patients did not have gout, and that was a critical difference, he said.
He noted that it was not surprising that the results of ALL-HEART were negative, given the study design.
“The ALL-HEART study treated people regardless of their uric acid level, and they also excluded subjects who had a history of gout,” he said. “Yet the risk associated with uric acid occurs primarily among those with elevated serum uric acid levels and those with gout.”
The study received funding from the Rheumatology Research Foundation and the VHA. Neither Dr. Tate Johnson nor Dr. Richard Johnson had any relevant disclosures.
A new study based on U.S. veterans’ medical records adds to the evidence for a link between gout – especially poorly controlled cases – and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk, Tate Johnson, MD, reported at the annual research symposium of the Gout, Hyperuricemia, and Crystal Associated Disease Network.
Gout was associated with a 68% increased risk of heart failure (HF) hospitalization, 25% increased risk of HF-related death, and a 22% increased risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), said Dr. Johnson, of the division of rheumatology at the University of Nebraska, Omaha.
Poorly controlled serum urate was associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular events, regardless of the use of urate-lowering therapy (ULT). He said more research is needed to see if there is a causal link between gout, hyperuricemia – or its treatment – and CVD risk.
Dr. Johnson and colleagues used records from the Veterans Health Administration for this study. They created a retrospective, matched cohort study that looked at records dating from January 1999 to September 2015. Patients with gout (≥ 2 ICD-9 codes) were matched 1:10 on age, sex, and year of VHA enrollment to patients without a gout ICD-9 code or a record of receiving ULT. They matched 559,243 people with gout to 5,407,379 people who did not have a diagnosis or a recorded treatment for this condition.
Over 43,331,604 person-years, Dr. Johnson and colleagues observed 137,162 CVD events in gout (incidence rate 33.96 per 1,000 person-years) vs. 879,903 in non-gout patients (IR 22.37 per 1,000 person-years). Gout was most strongly associated with HF hospitalization, with a nearly threefold higher risk (hazard ratio, 2.78; 95% confidence interval, 2.73-2.83), which attenuated but persisted after adjustment for additional CVD risk factors (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.68; 95% CI, 1.65-1.70) and excluding patients with prevalent HF (aHR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.57-1.64).
People with gout were also at higher risk of HF-related death (aHR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.21-1.29), MACE (aHR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.21-1.23), and coronary artery disease–related death (aHR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.20-1.22).
Among people with gout in the study, poor serum urate control was associated with a higher risk of all CVD events, with the highest CVD risk occurring in patients with inadequately controlled serum urate despite receipt of ULT, particularly related to HF hospitalization (aHR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.34-1.52) and HF-related death (aHR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.34-1.61).
Limits of the study include the generalizability of the study population. Reflecting the VHA’s patient population, 99% of the cohort were men, with 62% of the gout group and 59.4% of the control group identifying as White and non-Hispanic.
The study provides evidence that may be found only by studying medical records, Richard J. Johnson, MD, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, said in an interview.
Dr. Richard Johnson, who is not related to the author, said that only about one-third of people with gout are adequately treated, and about another one-third take urate-lowering therapy (ULT) but fail to get their serum urate level under control. But it would be unethical to design a clinical trial to study CVD risk and poorly controlled serum urate without ULT treatment.
“The only way you can figure out if uric acid lowering is going to help these guys is to actually do a study like this where you see the ones who don’t get adequate treatment versus adequate treatment and you show that there’s going to be a difference in outcome,” he said.
Dr. Richard Johnson contrasted this approach with the one used in the recently reported study that appeared to cast doubt on the link between serum uric acid levels and cardiovascular disease. The ALL-HEART trial found that allopurinol, a drug commonly used to treat gout, provided no benefit in terms of reducing cardiovascular events in patients with ischemic heart disease. But these patients did not have gout, and that was a critical difference, he said.
He noted that it was not surprising that the results of ALL-HEART were negative, given the study design.
“The ALL-HEART study treated people regardless of their uric acid level, and they also excluded subjects who had a history of gout,” he said. “Yet the risk associated with uric acid occurs primarily among those with elevated serum uric acid levels and those with gout.”
The study received funding from the Rheumatology Research Foundation and the VHA. Neither Dr. Tate Johnson nor Dr. Richard Johnson had any relevant disclosures.
A new study based on U.S. veterans’ medical records adds to the evidence for a link between gout – especially poorly controlled cases – and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk, Tate Johnson, MD, reported at the annual research symposium of the Gout, Hyperuricemia, and Crystal Associated Disease Network.
Gout was associated with a 68% increased risk of heart failure (HF) hospitalization, 25% increased risk of HF-related death, and a 22% increased risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), said Dr. Johnson, of the division of rheumatology at the University of Nebraska, Omaha.
Poorly controlled serum urate was associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular events, regardless of the use of urate-lowering therapy (ULT). He said more research is needed to see if there is a causal link between gout, hyperuricemia – or its treatment – and CVD risk.
Dr. Johnson and colleagues used records from the Veterans Health Administration for this study. They created a retrospective, matched cohort study that looked at records dating from January 1999 to September 2015. Patients with gout (≥ 2 ICD-9 codes) were matched 1:10 on age, sex, and year of VHA enrollment to patients without a gout ICD-9 code or a record of receiving ULT. They matched 559,243 people with gout to 5,407,379 people who did not have a diagnosis or a recorded treatment for this condition.
Over 43,331,604 person-years, Dr. Johnson and colleagues observed 137,162 CVD events in gout (incidence rate 33.96 per 1,000 person-years) vs. 879,903 in non-gout patients (IR 22.37 per 1,000 person-years). Gout was most strongly associated with HF hospitalization, with a nearly threefold higher risk (hazard ratio, 2.78; 95% confidence interval, 2.73-2.83), which attenuated but persisted after adjustment for additional CVD risk factors (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.68; 95% CI, 1.65-1.70) and excluding patients with prevalent HF (aHR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.57-1.64).
People with gout were also at higher risk of HF-related death (aHR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.21-1.29), MACE (aHR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.21-1.23), and coronary artery disease–related death (aHR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.20-1.22).
Among people with gout in the study, poor serum urate control was associated with a higher risk of all CVD events, with the highest CVD risk occurring in patients with inadequately controlled serum urate despite receipt of ULT, particularly related to HF hospitalization (aHR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.34-1.52) and HF-related death (aHR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.34-1.61).
Limits of the study include the generalizability of the study population. Reflecting the VHA’s patient population, 99% of the cohort were men, with 62% of the gout group and 59.4% of the control group identifying as White and non-Hispanic.
The study provides evidence that may be found only by studying medical records, Richard J. Johnson, MD, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, said in an interview.
Dr. Richard Johnson, who is not related to the author, said that only about one-third of people with gout are adequately treated, and about another one-third take urate-lowering therapy (ULT) but fail to get their serum urate level under control. But it would be unethical to design a clinical trial to study CVD risk and poorly controlled serum urate without ULT treatment.
“The only way you can figure out if uric acid lowering is going to help these guys is to actually do a study like this where you see the ones who don’t get adequate treatment versus adequate treatment and you show that there’s going to be a difference in outcome,” he said.
Dr. Richard Johnson contrasted this approach with the one used in the recently reported study that appeared to cast doubt on the link between serum uric acid levels and cardiovascular disease. The ALL-HEART trial found that allopurinol, a drug commonly used to treat gout, provided no benefit in terms of reducing cardiovascular events in patients with ischemic heart disease. But these patients did not have gout, and that was a critical difference, he said.
He noted that it was not surprising that the results of ALL-HEART were negative, given the study design.
“The ALL-HEART study treated people regardless of their uric acid level, and they also excluded subjects who had a history of gout,” he said. “Yet the risk associated with uric acid occurs primarily among those with elevated serum uric acid levels and those with gout.”
The study received funding from the Rheumatology Research Foundation and the VHA. Neither Dr. Tate Johnson nor Dr. Richard Johnson had any relevant disclosures.
FROM G-CAN 2022
Diet high in plant omega-3s tied to better HF prognosis
Heart failure (HF) patients with high serum levels of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) had a better prognosis than those with the lowest levels, in an observational study.
ALA is an omega-3 fatty acid that is found mainly in plants, including flaxseed, chia, walnuts, or canola oil.
“The most striking finding to us is the clear difference between patients at the bottom quartile compared to the other 75%, pointing to a threshold on the putative effect of ALA, reinforcing the notion that ‘one size does not fill all,’ ” Aleix Sala-Vila, PharmD, PhD, of the Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute, Barcelona, told this news organization.The analysis, which was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, showed statistically significant reductions in all-cause death, cardiovascular (CV) death, and first HF hospitalization among those in the three upper quartiles of serum ALA levels, compared with those in the lowest quartile.
The team’s earlier finding that higher levels of serum phosphatidylcholine eicosapentaenoic acid (PC EPA) and ALA were associated with a lower risk of adverse events in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction prompted the current study, Dr. Sala-Vila said.
Although their findings are hypothesis-generating at this point, he added, “inclusion of some ALA-rich foods, such as walnuts, in the diet of any individual, whether they have HF or not, might translate into CV benefits, besides the putative effect on HF. There is no evidence of any deleterious effect of one daily serving of walnuts, not even on weight gain.”
Plant power
Dr. Sala-Vila and colleagues analyzed data and samples from 905 patients (mean age, 67; 32% women) with HF of different etiologies. ALA was assessed by gas chromatography in serum phospholipids, which reflect long-term dietary ALA intake and metabolism.
The primary outcome was a composite of all-cause death or first HF hospitalization. The secondary outcome was the composite of CV death or HF hospitalization.
After a median follow-up of 2.4 years, 140 all-cause deaths, 85 CV deaths, and 141 first HF hospitalizations occurred (composite of all-cause death and first HF hospitalization, 238; composite of CV death and HF hospitalization, 184).
Compared with patients at the lowest quartile of ALA in serum phospholipids, those at the three upper quartiles showed a 39% reduction in the risk of the primary endpoint (hazard ratio, 0.61).
Statistically significant reductions also were observed for all-cause death (HR, 0.58), CV death (HR, 0.51), first HF hospitalization (HR, 0.58), and the composite of CV death and HF hospitalization (HR, 0.58).
By contrast, nonstatistically significant associations were seen for fish-derived EPA, DHA, and the sum of EPA + DHA.
Limitations of the study include its observational nature; a relatively young cohort with reduced or mid-range ejection fraction and stage 2 chronic kidney disease; and no dietary data except for those regarding fatty acids.
“Controversial results from landmark recent trials on omega-3 might have translated into confusion/negative impact on the reputation of these fatty acids,” Dr. Sala-Vila noted. “Many factors affect how each participant responds to a certain intervention (precision nutrition), such as genetics, the microbiome, and the environment. In this regard, nutritional status – omega-3 background – is emerging as a key determinant.”
Randomized trials needed
JoAnn E. Manson, MD, MPH, DrPH, chief of the Division of Preventive Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said the findings “are promising in the context of earlier research on omega-3s.”
Those studies include the landmark GISSI-HF trial, a randomized, controlled trial (RCT) that showed a small benefit of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids regarding hospital admissions and mortality among patients with chronic HF, and her team’s VITAL-HF study, which showed a significant reduction in recurrent HF hospitalization with marine omega-3 supplementation versus placebo.
“This may not be a causal association, and the authors acknowledge that they don’t have information on other dietary factors,” Dr. Manson said. “It may be that the foods that are leading to this higher blood level of ALA comprise the type of plant-based diet that’s been linked to lower risk of CVD, such as the Mediterranean diet. The findings also could be the result of other factors that aren’t fully controlled for in the analysis, or the participants could be more compliant with their medications.”
Nevertheless, she said, “it’s reasonable to recommend that people with a history of HF or who are at high risk of HF increase their intake of ALA-enriched foods, including canola oil, flaxseed oils, soybeans and soybean oils, and walnuts.”
“I think the evidence is promising enough that an RCT of ALA in people with heart failure also would be reasonable,” she added.
Similarly, Abdallah Al-Mohammad, MD, of Northern General Hospital, Sheffield, England, writes in a related editorial that while a potential role for ALA in improving morbidity and mortality in HF patients cannot be substantiated yet, the findings “open the field to more questions” for which “the judge and jury ... shall be prospective randomized controlled trials.”
No commercial funding or relevant conflicts of interest were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Heart failure (HF) patients with high serum levels of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) had a better prognosis than those with the lowest levels, in an observational study.
ALA is an omega-3 fatty acid that is found mainly in plants, including flaxseed, chia, walnuts, or canola oil.
“The most striking finding to us is the clear difference between patients at the bottom quartile compared to the other 75%, pointing to a threshold on the putative effect of ALA, reinforcing the notion that ‘one size does not fill all,’ ” Aleix Sala-Vila, PharmD, PhD, of the Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute, Barcelona, told this news organization.The analysis, which was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, showed statistically significant reductions in all-cause death, cardiovascular (CV) death, and first HF hospitalization among those in the three upper quartiles of serum ALA levels, compared with those in the lowest quartile.
The team’s earlier finding that higher levels of serum phosphatidylcholine eicosapentaenoic acid (PC EPA) and ALA were associated with a lower risk of adverse events in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction prompted the current study, Dr. Sala-Vila said.
Although their findings are hypothesis-generating at this point, he added, “inclusion of some ALA-rich foods, such as walnuts, in the diet of any individual, whether they have HF or not, might translate into CV benefits, besides the putative effect on HF. There is no evidence of any deleterious effect of one daily serving of walnuts, not even on weight gain.”
Plant power
Dr. Sala-Vila and colleagues analyzed data and samples from 905 patients (mean age, 67; 32% women) with HF of different etiologies. ALA was assessed by gas chromatography in serum phospholipids, which reflect long-term dietary ALA intake and metabolism.
The primary outcome was a composite of all-cause death or first HF hospitalization. The secondary outcome was the composite of CV death or HF hospitalization.
After a median follow-up of 2.4 years, 140 all-cause deaths, 85 CV deaths, and 141 first HF hospitalizations occurred (composite of all-cause death and first HF hospitalization, 238; composite of CV death and HF hospitalization, 184).
Compared with patients at the lowest quartile of ALA in serum phospholipids, those at the three upper quartiles showed a 39% reduction in the risk of the primary endpoint (hazard ratio, 0.61).
Statistically significant reductions also were observed for all-cause death (HR, 0.58), CV death (HR, 0.51), first HF hospitalization (HR, 0.58), and the composite of CV death and HF hospitalization (HR, 0.58).
By contrast, nonstatistically significant associations were seen for fish-derived EPA, DHA, and the sum of EPA + DHA.
Limitations of the study include its observational nature; a relatively young cohort with reduced or mid-range ejection fraction and stage 2 chronic kidney disease; and no dietary data except for those regarding fatty acids.
“Controversial results from landmark recent trials on omega-3 might have translated into confusion/negative impact on the reputation of these fatty acids,” Dr. Sala-Vila noted. “Many factors affect how each participant responds to a certain intervention (precision nutrition), such as genetics, the microbiome, and the environment. In this regard, nutritional status – omega-3 background – is emerging as a key determinant.”
Randomized trials needed
JoAnn E. Manson, MD, MPH, DrPH, chief of the Division of Preventive Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said the findings “are promising in the context of earlier research on omega-3s.”
Those studies include the landmark GISSI-HF trial, a randomized, controlled trial (RCT) that showed a small benefit of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids regarding hospital admissions and mortality among patients with chronic HF, and her team’s VITAL-HF study, which showed a significant reduction in recurrent HF hospitalization with marine omega-3 supplementation versus placebo.
“This may not be a causal association, and the authors acknowledge that they don’t have information on other dietary factors,” Dr. Manson said. “It may be that the foods that are leading to this higher blood level of ALA comprise the type of plant-based diet that’s been linked to lower risk of CVD, such as the Mediterranean diet. The findings also could be the result of other factors that aren’t fully controlled for in the analysis, or the participants could be more compliant with their medications.”
Nevertheless, she said, “it’s reasonable to recommend that people with a history of HF or who are at high risk of HF increase their intake of ALA-enriched foods, including canola oil, flaxseed oils, soybeans and soybean oils, and walnuts.”
“I think the evidence is promising enough that an RCT of ALA in people with heart failure also would be reasonable,” she added.
Similarly, Abdallah Al-Mohammad, MD, of Northern General Hospital, Sheffield, England, writes in a related editorial that while a potential role for ALA in improving morbidity and mortality in HF patients cannot be substantiated yet, the findings “open the field to more questions” for which “the judge and jury ... shall be prospective randomized controlled trials.”
No commercial funding or relevant conflicts of interest were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Heart failure (HF) patients with high serum levels of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) had a better prognosis than those with the lowest levels, in an observational study.
ALA is an omega-3 fatty acid that is found mainly in plants, including flaxseed, chia, walnuts, or canola oil.
“The most striking finding to us is the clear difference between patients at the bottom quartile compared to the other 75%, pointing to a threshold on the putative effect of ALA, reinforcing the notion that ‘one size does not fill all,’ ” Aleix Sala-Vila, PharmD, PhD, of the Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute, Barcelona, told this news organization.The analysis, which was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, showed statistically significant reductions in all-cause death, cardiovascular (CV) death, and first HF hospitalization among those in the three upper quartiles of serum ALA levels, compared with those in the lowest quartile.
The team’s earlier finding that higher levels of serum phosphatidylcholine eicosapentaenoic acid (PC EPA) and ALA were associated with a lower risk of adverse events in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction prompted the current study, Dr. Sala-Vila said.
Although their findings are hypothesis-generating at this point, he added, “inclusion of some ALA-rich foods, such as walnuts, in the diet of any individual, whether they have HF or not, might translate into CV benefits, besides the putative effect on HF. There is no evidence of any deleterious effect of one daily serving of walnuts, not even on weight gain.”
Plant power
Dr. Sala-Vila and colleagues analyzed data and samples from 905 patients (mean age, 67; 32% women) with HF of different etiologies. ALA was assessed by gas chromatography in serum phospholipids, which reflect long-term dietary ALA intake and metabolism.
The primary outcome was a composite of all-cause death or first HF hospitalization. The secondary outcome was the composite of CV death or HF hospitalization.
After a median follow-up of 2.4 years, 140 all-cause deaths, 85 CV deaths, and 141 first HF hospitalizations occurred (composite of all-cause death and first HF hospitalization, 238; composite of CV death and HF hospitalization, 184).
Compared with patients at the lowest quartile of ALA in serum phospholipids, those at the three upper quartiles showed a 39% reduction in the risk of the primary endpoint (hazard ratio, 0.61).
Statistically significant reductions also were observed for all-cause death (HR, 0.58), CV death (HR, 0.51), first HF hospitalization (HR, 0.58), and the composite of CV death and HF hospitalization (HR, 0.58).
By contrast, nonstatistically significant associations were seen for fish-derived EPA, DHA, and the sum of EPA + DHA.
Limitations of the study include its observational nature; a relatively young cohort with reduced or mid-range ejection fraction and stage 2 chronic kidney disease; and no dietary data except for those regarding fatty acids.
“Controversial results from landmark recent trials on omega-3 might have translated into confusion/negative impact on the reputation of these fatty acids,” Dr. Sala-Vila noted. “Many factors affect how each participant responds to a certain intervention (precision nutrition), such as genetics, the microbiome, and the environment. In this regard, nutritional status – omega-3 background – is emerging as a key determinant.”
Randomized trials needed
JoAnn E. Manson, MD, MPH, DrPH, chief of the Division of Preventive Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said the findings “are promising in the context of earlier research on omega-3s.”
Those studies include the landmark GISSI-HF trial, a randomized, controlled trial (RCT) that showed a small benefit of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids regarding hospital admissions and mortality among patients with chronic HF, and her team’s VITAL-HF study, which showed a significant reduction in recurrent HF hospitalization with marine omega-3 supplementation versus placebo.
“This may not be a causal association, and the authors acknowledge that they don’t have information on other dietary factors,” Dr. Manson said. “It may be that the foods that are leading to this higher blood level of ALA comprise the type of plant-based diet that’s been linked to lower risk of CVD, such as the Mediterranean diet. The findings also could be the result of other factors that aren’t fully controlled for in the analysis, or the participants could be more compliant with their medications.”
Nevertheless, she said, “it’s reasonable to recommend that people with a history of HF or who are at high risk of HF increase their intake of ALA-enriched foods, including canola oil, flaxseed oils, soybeans and soybean oils, and walnuts.”
“I think the evidence is promising enough that an RCT of ALA in people with heart failure also would be reasonable,” she added.
Similarly, Abdallah Al-Mohammad, MD, of Northern General Hospital, Sheffield, England, writes in a related editorial that while a potential role for ALA in improving morbidity and mortality in HF patients cannot be substantiated yet, the findings “open the field to more questions” for which “the judge and jury ... shall be prospective randomized controlled trials.”
No commercial funding or relevant conflicts of interest were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Finerenone: ‘Striking’ cut in pneumonia, COVID-19 risks
The nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist finerenone (Kerendia) unexpectedly showed that it might protect against incident infective pneumonia and COVID-19. The finding was based on secondary analyses run on more than 13,000 people enrolled in the two pivotal trials for finerenone.
Finerenone was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2021 for slowing progressive renal dysfunction and preventing cardiovascular events in adults with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD).
‘Striking reduction in the risk of pneumonia’
The “striking reduction in risk of pneumonia” in a new analysis suggests that “the propagation of pulmonary infection into lobar or bronchial consolidation may be reduced by finerenone,” write Bertram Pitt, MD, and coauthors in a report published on October 26 in JAMA Network Open.
They also suggest that if further studies confirm that finerenone treatment reduces complications from pneumonia and COVID-19, it would have “significant medical implications,” especially because of the limited treatment options now available for complications from COVID-19.
The new analyses used the FIDELITY dataset, a prespecified merging of results from the FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD trials, which together enrolled 13,026 people with type 2 diabetes and CKD, as determined on the basis of the patients’ having a urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio of at least 30 mg/g.
The primary outcomes of these trials showed that treatment with finerenone led to significant slowing of the progression of CKD and a significant reduction in the incidence of cardiovascular events, compared with placebo during median follow-up of 3 years.
The new, secondary analyses focused on the 6.0% of participants in whom there was evidence of pneumonia and the 1.6% in whom there was evidence of having COVID-19. Pneumonia was the most common serious adverse event in the two trials, a finding consistent with the documented risk for pneumonia faced by people with CKD.
Finerenone linked with a 29% relative reduction in pneumonia
When analyzed by treatment, the incidence of pneumonia was 4.7% among those who received finerenone and 6.7% among those who received placebo. This translated into a significant relative risk reduction of 29% associated with finerenone treatment.
Analysis of COVID-19 adverse events showed a 1.3% incidence among those who received finerenone and a 1.8% incidence among those in the placebo group, which translated into a significant 27% relative risk reduction linked with finerenone treatment.
In contrast, the data showed no reduced incidence of several other respiratory infections among the finerenone recipients, including nasopharyngitis, bronchitis, and influenza. The data also showed no signal that pneumonia or COVID-19 was more severe among the people who did not receive finerenone, nor did finerenone treatment appear to affect pneumonia recovery.
Analysis based on adverse events reports
These secondary analyses are far from definitive. The authors relied on pneumonia and COVID-19 being reported as adverse events. Each investigator diagnosed pneumonia at their discretion, and the trials did not specify diagnostic criteria. The authors also acknowledge that testing for COVID-19 was “not widespread” and that one of the two pivotal trials largely ran prior to the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic so that only 6 participants developed COVID-19 symptoms out of more than 5,700 enrolled.
The authors hypothesize that several actions of finerenone might potentially help mediate an effect on pneumonia and COVID-19: improvements in pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis, upregulation of expression of angiotensin converting enzyme 2, and amelioration of right heart pressure and pulmonary congestion. Also, antagonizing the mineralocorticoid receptor on monocytes and macrophages may block macrophage infiltration and accumulation of active macrophages, which can mediate the pulmonary tissue damage caused by COVID-19.
The FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD trials and the FIDELITY combined database were sponsored by Bayer, the company that markets finerenone (Kerendia). Dr. Pitt has received personal fees from Bayer and personal fees and stock options from numerous other companies. Several coauthors reported having a financial relationship with Bayer, as well as with other companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist finerenone (Kerendia) unexpectedly showed that it might protect against incident infective pneumonia and COVID-19. The finding was based on secondary analyses run on more than 13,000 people enrolled in the two pivotal trials for finerenone.
Finerenone was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2021 for slowing progressive renal dysfunction and preventing cardiovascular events in adults with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD).
‘Striking reduction in the risk of pneumonia’
The “striking reduction in risk of pneumonia” in a new analysis suggests that “the propagation of pulmonary infection into lobar or bronchial consolidation may be reduced by finerenone,” write Bertram Pitt, MD, and coauthors in a report published on October 26 in JAMA Network Open.
They also suggest that if further studies confirm that finerenone treatment reduces complications from pneumonia and COVID-19, it would have “significant medical implications,” especially because of the limited treatment options now available for complications from COVID-19.
The new analyses used the FIDELITY dataset, a prespecified merging of results from the FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD trials, which together enrolled 13,026 people with type 2 diabetes and CKD, as determined on the basis of the patients’ having a urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio of at least 30 mg/g.
The primary outcomes of these trials showed that treatment with finerenone led to significant slowing of the progression of CKD and a significant reduction in the incidence of cardiovascular events, compared with placebo during median follow-up of 3 years.
The new, secondary analyses focused on the 6.0% of participants in whom there was evidence of pneumonia and the 1.6% in whom there was evidence of having COVID-19. Pneumonia was the most common serious adverse event in the two trials, a finding consistent with the documented risk for pneumonia faced by people with CKD.
Finerenone linked with a 29% relative reduction in pneumonia
When analyzed by treatment, the incidence of pneumonia was 4.7% among those who received finerenone and 6.7% among those who received placebo. This translated into a significant relative risk reduction of 29% associated with finerenone treatment.
Analysis of COVID-19 adverse events showed a 1.3% incidence among those who received finerenone and a 1.8% incidence among those in the placebo group, which translated into a significant 27% relative risk reduction linked with finerenone treatment.
In contrast, the data showed no reduced incidence of several other respiratory infections among the finerenone recipients, including nasopharyngitis, bronchitis, and influenza. The data also showed no signal that pneumonia or COVID-19 was more severe among the people who did not receive finerenone, nor did finerenone treatment appear to affect pneumonia recovery.
Analysis based on adverse events reports
These secondary analyses are far from definitive. The authors relied on pneumonia and COVID-19 being reported as adverse events. Each investigator diagnosed pneumonia at their discretion, and the trials did not specify diagnostic criteria. The authors also acknowledge that testing for COVID-19 was “not widespread” and that one of the two pivotal trials largely ran prior to the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic so that only 6 participants developed COVID-19 symptoms out of more than 5,700 enrolled.
The authors hypothesize that several actions of finerenone might potentially help mediate an effect on pneumonia and COVID-19: improvements in pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis, upregulation of expression of angiotensin converting enzyme 2, and amelioration of right heart pressure and pulmonary congestion. Also, antagonizing the mineralocorticoid receptor on monocytes and macrophages may block macrophage infiltration and accumulation of active macrophages, which can mediate the pulmonary tissue damage caused by COVID-19.
The FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD trials and the FIDELITY combined database were sponsored by Bayer, the company that markets finerenone (Kerendia). Dr. Pitt has received personal fees from Bayer and personal fees and stock options from numerous other companies. Several coauthors reported having a financial relationship with Bayer, as well as with other companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist finerenone (Kerendia) unexpectedly showed that it might protect against incident infective pneumonia and COVID-19. The finding was based on secondary analyses run on more than 13,000 people enrolled in the two pivotal trials for finerenone.
Finerenone was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2021 for slowing progressive renal dysfunction and preventing cardiovascular events in adults with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD).
‘Striking reduction in the risk of pneumonia’
The “striking reduction in risk of pneumonia” in a new analysis suggests that “the propagation of pulmonary infection into lobar or bronchial consolidation may be reduced by finerenone,” write Bertram Pitt, MD, and coauthors in a report published on October 26 in JAMA Network Open.
They also suggest that if further studies confirm that finerenone treatment reduces complications from pneumonia and COVID-19, it would have “significant medical implications,” especially because of the limited treatment options now available for complications from COVID-19.
The new analyses used the FIDELITY dataset, a prespecified merging of results from the FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD trials, which together enrolled 13,026 people with type 2 diabetes and CKD, as determined on the basis of the patients’ having a urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio of at least 30 mg/g.
The primary outcomes of these trials showed that treatment with finerenone led to significant slowing of the progression of CKD and a significant reduction in the incidence of cardiovascular events, compared with placebo during median follow-up of 3 years.
The new, secondary analyses focused on the 6.0% of participants in whom there was evidence of pneumonia and the 1.6% in whom there was evidence of having COVID-19. Pneumonia was the most common serious adverse event in the two trials, a finding consistent with the documented risk for pneumonia faced by people with CKD.
Finerenone linked with a 29% relative reduction in pneumonia
When analyzed by treatment, the incidence of pneumonia was 4.7% among those who received finerenone and 6.7% among those who received placebo. This translated into a significant relative risk reduction of 29% associated with finerenone treatment.
Analysis of COVID-19 adverse events showed a 1.3% incidence among those who received finerenone and a 1.8% incidence among those in the placebo group, which translated into a significant 27% relative risk reduction linked with finerenone treatment.
In contrast, the data showed no reduced incidence of several other respiratory infections among the finerenone recipients, including nasopharyngitis, bronchitis, and influenza. The data also showed no signal that pneumonia or COVID-19 was more severe among the people who did not receive finerenone, nor did finerenone treatment appear to affect pneumonia recovery.
Analysis based on adverse events reports
These secondary analyses are far from definitive. The authors relied on pneumonia and COVID-19 being reported as adverse events. Each investigator diagnosed pneumonia at their discretion, and the trials did not specify diagnostic criteria. The authors also acknowledge that testing for COVID-19 was “not widespread” and that one of the two pivotal trials largely ran prior to the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic so that only 6 participants developed COVID-19 symptoms out of more than 5,700 enrolled.
The authors hypothesize that several actions of finerenone might potentially help mediate an effect on pneumonia and COVID-19: improvements in pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis, upregulation of expression of angiotensin converting enzyme 2, and amelioration of right heart pressure and pulmonary congestion. Also, antagonizing the mineralocorticoid receptor on monocytes and macrophages may block macrophage infiltration and accumulation of active macrophages, which can mediate the pulmonary tissue damage caused by COVID-19.
The FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD trials and the FIDELITY combined database were sponsored by Bayer, the company that markets finerenone (Kerendia). Dr. Pitt has received personal fees from Bayer and personal fees and stock options from numerous other companies. Several coauthors reported having a financial relationship with Bayer, as well as with other companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study reveals racial disparities in advanced HF therapies
A new study shows that Black Americans received ventricular assist devices (VADs) and heart transplants about half as often as White Americans, even when receiving care at an advanced heart failure (HF) center.
The analysis, drawn from 377 patients treated at one of 21 VAD centers in the United States as part of the RIVIVAL study, found that 22.3% of White adults received a heart transplant or VAD, compared with 11% of Black adults.
“That’s what is so concerning to us, that we’re seeing this pattern within this select population. I think it would be too reasonable to hypothesize that it very well could be worse in the general population,” study author Thomas Cascino, MD, MSc, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, commented.
The study was published online in Circulation: Heart Failure, and it builds on previous work by the researchers, showing that patient preference for early VAD therapy is associated with higher New York Heart Association (NYHA) class and lower income level but not race.
In the present analysis, the number of Black and White participants who said they “definitely or probably” wanted VAD therapy was similar (27% vs. 29%), as was the number wanting “any and all life-sustaining therapies” (74% vs. 65%).
Two-thirds of the cohort was NYHA class III, the average EuroQoL visual analog scale (EQ-VAS) score was 64.6 among the 100 participants who identified as Black and 62.1 in the 277 White participants, and the average age was 58 and 61 years, respectively.
Death rates were also similar during the 2-year follow-up: 18% of Black patients and 13% of White patients.
After controlling for multiple clinical and social determinants of health, including age, Interagency Registry for Mechanically Assisted Circulator Support (INTERMACS) patient profile, EQ-VAS score, and level of education, Black participants had a 55% lower rate of VAD or transplant, compared with White participants (hazard ratio, 0.45; 95% confidence interval, 0.23-0.85). Adding VAD preference to the model did not affect the association.
“Our study suggests that we as providers may be making decisions differently,” Dr. Cascino said. “We can’t say for sure what the reasons are but certainly structural racism, discrimination, and provider biases are the things I worry about.”
“There’s an absolute need for us to look inwards, reflect, and acknowledge that we are likely playing a role in this and then start to be part of the change,” he added.
“The lives disabled or lost are simply too many,” coauthor Wendy Taddei-Peters, PhD, a clinical trials project official at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, said in an NIH statement. “An immediate step could be to require implicit bias training, particularly for transplant and VAD team members.”
Other suggestions are better tracking of underserved patients and the reasons why they do not receive VAD or become listed for transplant; inclusion of psychosocial components into decision-making about advanced therapy candidacy; and having “disparity experts” join in heart team meetings to help identify biases in real time.
Commenting on the study, Khadijah Breathett, MD, HF/transplant cardiologist and tenured associate professor of medicine, Indiana University Bloomington, said, “I’m glad there’s more push for awareness, because there’s still a population of people that don’t believe this is a real problem.”
Dr. Breathett, who is also a racial equity researcher, noted that the findings are similar to those of multiple studies suggesting racial disparities in HF care. In her own 2019 study of 400 providers shown identical clinical vignettes except for race, survey results and think-aloud interviews showed that decisions about advanced HF therapies are hierarchal and not democratic, social history and adherence are the most influential factors, and Black men are seen as not trustworthy and adherent, despite identical social histories, which ultimately led to White men being offered transplantation and Black men VAD implantation. The bias was particularly evident among older providers.
“This problem is real,” Dr. Breathett said. “The process of allocating life-saving therapies is not fair, and there is some level of discrimination that’s taking place towards persons of color, particularly Black patients. It’s time that we consider how we fix these issues.”
To see whether centers can move the needle and put systemic level changes into practice, Dr. Breathett and colleagues are launching the Seeking Objectivity in Allocation of Advanced Heart Failure (SOCIAL HF) Therapies Trial at 14 sites in the United States. It will measure the number of minority and female patients receiving advanced HF therapies at centers randomized to usual care or HF training, including evidence-based bias reduction training, use of objective measures of social support, and changes to facilitate group dynamics. The trial is set to start in January and be completed in September 2026.
“The main takeaway from this study is that it highlights and re-highlights the fact that racial disparities do exist in access to advanced therapy care,” Jaimin Trivedi, MD, MPH, associate professor of cardiothoracic surgery and director of clinical research and bioinformatics, University of Louisville, Ky., said in an interview.
He also called for education and training for all professionals, not just during residency or fellowship, to specifically identify issues with Black patients and encourage Black patients and their family members to get more involved in their HF care.
Dr. Trivedi said that further studies should examine why death rates were similar in the study despite the observed disparities in VAD implantation and transplantation.
He also pointed out that while patients in the study were treated from July 2015 to June 2016, a recent analysis by his team of the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) database showed that 26% of transplants in 2019 were among Black patients, up from just 5% in 1987. “So, there are some encouraging signs as well.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Dr. Cascino reports having no relevant financial relationships. Four coauthors report financial relationships, including David Lanfear, who serves on the advisory board at Medscape. Dr. Breathett reported funding from multiple NHLBI grants.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study shows that Black Americans received ventricular assist devices (VADs) and heart transplants about half as often as White Americans, even when receiving care at an advanced heart failure (HF) center.
The analysis, drawn from 377 patients treated at one of 21 VAD centers in the United States as part of the RIVIVAL study, found that 22.3% of White adults received a heart transplant or VAD, compared with 11% of Black adults.
“That’s what is so concerning to us, that we’re seeing this pattern within this select population. I think it would be too reasonable to hypothesize that it very well could be worse in the general population,” study author Thomas Cascino, MD, MSc, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, commented.
The study was published online in Circulation: Heart Failure, and it builds on previous work by the researchers, showing that patient preference for early VAD therapy is associated with higher New York Heart Association (NYHA) class and lower income level but not race.
In the present analysis, the number of Black and White participants who said they “definitely or probably” wanted VAD therapy was similar (27% vs. 29%), as was the number wanting “any and all life-sustaining therapies” (74% vs. 65%).
Two-thirds of the cohort was NYHA class III, the average EuroQoL visual analog scale (EQ-VAS) score was 64.6 among the 100 participants who identified as Black and 62.1 in the 277 White participants, and the average age was 58 and 61 years, respectively.
Death rates were also similar during the 2-year follow-up: 18% of Black patients and 13% of White patients.
After controlling for multiple clinical and social determinants of health, including age, Interagency Registry for Mechanically Assisted Circulator Support (INTERMACS) patient profile, EQ-VAS score, and level of education, Black participants had a 55% lower rate of VAD or transplant, compared with White participants (hazard ratio, 0.45; 95% confidence interval, 0.23-0.85). Adding VAD preference to the model did not affect the association.
“Our study suggests that we as providers may be making decisions differently,” Dr. Cascino said. “We can’t say for sure what the reasons are but certainly structural racism, discrimination, and provider biases are the things I worry about.”
“There’s an absolute need for us to look inwards, reflect, and acknowledge that we are likely playing a role in this and then start to be part of the change,” he added.
“The lives disabled or lost are simply too many,” coauthor Wendy Taddei-Peters, PhD, a clinical trials project official at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, said in an NIH statement. “An immediate step could be to require implicit bias training, particularly for transplant and VAD team members.”
Other suggestions are better tracking of underserved patients and the reasons why they do not receive VAD or become listed for transplant; inclusion of psychosocial components into decision-making about advanced therapy candidacy; and having “disparity experts” join in heart team meetings to help identify biases in real time.
Commenting on the study, Khadijah Breathett, MD, HF/transplant cardiologist and tenured associate professor of medicine, Indiana University Bloomington, said, “I’m glad there’s more push for awareness, because there’s still a population of people that don’t believe this is a real problem.”
Dr. Breathett, who is also a racial equity researcher, noted that the findings are similar to those of multiple studies suggesting racial disparities in HF care. In her own 2019 study of 400 providers shown identical clinical vignettes except for race, survey results and think-aloud interviews showed that decisions about advanced HF therapies are hierarchal and not democratic, social history and adherence are the most influential factors, and Black men are seen as not trustworthy and adherent, despite identical social histories, which ultimately led to White men being offered transplantation and Black men VAD implantation. The bias was particularly evident among older providers.
“This problem is real,” Dr. Breathett said. “The process of allocating life-saving therapies is not fair, and there is some level of discrimination that’s taking place towards persons of color, particularly Black patients. It’s time that we consider how we fix these issues.”
To see whether centers can move the needle and put systemic level changes into practice, Dr. Breathett and colleagues are launching the Seeking Objectivity in Allocation of Advanced Heart Failure (SOCIAL HF) Therapies Trial at 14 sites in the United States. It will measure the number of minority and female patients receiving advanced HF therapies at centers randomized to usual care or HF training, including evidence-based bias reduction training, use of objective measures of social support, and changes to facilitate group dynamics. The trial is set to start in January and be completed in September 2026.
“The main takeaway from this study is that it highlights and re-highlights the fact that racial disparities do exist in access to advanced therapy care,” Jaimin Trivedi, MD, MPH, associate professor of cardiothoracic surgery and director of clinical research and bioinformatics, University of Louisville, Ky., said in an interview.
He also called for education and training for all professionals, not just during residency or fellowship, to specifically identify issues with Black patients and encourage Black patients and their family members to get more involved in their HF care.
Dr. Trivedi said that further studies should examine why death rates were similar in the study despite the observed disparities in VAD implantation and transplantation.
He also pointed out that while patients in the study were treated from July 2015 to June 2016, a recent analysis by his team of the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) database showed that 26% of transplants in 2019 were among Black patients, up from just 5% in 1987. “So, there are some encouraging signs as well.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Dr. Cascino reports having no relevant financial relationships. Four coauthors report financial relationships, including David Lanfear, who serves on the advisory board at Medscape. Dr. Breathett reported funding from multiple NHLBI grants.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study shows that Black Americans received ventricular assist devices (VADs) and heart transplants about half as often as White Americans, even when receiving care at an advanced heart failure (HF) center.
The analysis, drawn from 377 patients treated at one of 21 VAD centers in the United States as part of the RIVIVAL study, found that 22.3% of White adults received a heart transplant or VAD, compared with 11% of Black adults.
“That’s what is so concerning to us, that we’re seeing this pattern within this select population. I think it would be too reasonable to hypothesize that it very well could be worse in the general population,” study author Thomas Cascino, MD, MSc, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, commented.
The study was published online in Circulation: Heart Failure, and it builds on previous work by the researchers, showing that patient preference for early VAD therapy is associated with higher New York Heart Association (NYHA) class and lower income level but not race.
In the present analysis, the number of Black and White participants who said they “definitely or probably” wanted VAD therapy was similar (27% vs. 29%), as was the number wanting “any and all life-sustaining therapies” (74% vs. 65%).
Two-thirds of the cohort was NYHA class III, the average EuroQoL visual analog scale (EQ-VAS) score was 64.6 among the 100 participants who identified as Black and 62.1 in the 277 White participants, and the average age was 58 and 61 years, respectively.
Death rates were also similar during the 2-year follow-up: 18% of Black patients and 13% of White patients.
After controlling for multiple clinical and social determinants of health, including age, Interagency Registry for Mechanically Assisted Circulator Support (INTERMACS) patient profile, EQ-VAS score, and level of education, Black participants had a 55% lower rate of VAD or transplant, compared with White participants (hazard ratio, 0.45; 95% confidence interval, 0.23-0.85). Adding VAD preference to the model did not affect the association.
“Our study suggests that we as providers may be making decisions differently,” Dr. Cascino said. “We can’t say for sure what the reasons are but certainly structural racism, discrimination, and provider biases are the things I worry about.”
“There’s an absolute need for us to look inwards, reflect, and acknowledge that we are likely playing a role in this and then start to be part of the change,” he added.
“The lives disabled or lost are simply too many,” coauthor Wendy Taddei-Peters, PhD, a clinical trials project official at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, said in an NIH statement. “An immediate step could be to require implicit bias training, particularly for transplant and VAD team members.”
Other suggestions are better tracking of underserved patients and the reasons why they do not receive VAD or become listed for transplant; inclusion of psychosocial components into decision-making about advanced therapy candidacy; and having “disparity experts” join in heart team meetings to help identify biases in real time.
Commenting on the study, Khadijah Breathett, MD, HF/transplant cardiologist and tenured associate professor of medicine, Indiana University Bloomington, said, “I’m glad there’s more push for awareness, because there’s still a population of people that don’t believe this is a real problem.”
Dr. Breathett, who is also a racial equity researcher, noted that the findings are similar to those of multiple studies suggesting racial disparities in HF care. In her own 2019 study of 400 providers shown identical clinical vignettes except for race, survey results and think-aloud interviews showed that decisions about advanced HF therapies are hierarchal and not democratic, social history and adherence are the most influential factors, and Black men are seen as not trustworthy and adherent, despite identical social histories, which ultimately led to White men being offered transplantation and Black men VAD implantation. The bias was particularly evident among older providers.
“This problem is real,” Dr. Breathett said. “The process of allocating life-saving therapies is not fair, and there is some level of discrimination that’s taking place towards persons of color, particularly Black patients. It’s time that we consider how we fix these issues.”
To see whether centers can move the needle and put systemic level changes into practice, Dr. Breathett and colleagues are launching the Seeking Objectivity in Allocation of Advanced Heart Failure (SOCIAL HF) Therapies Trial at 14 sites in the United States. It will measure the number of minority and female patients receiving advanced HF therapies at centers randomized to usual care or HF training, including evidence-based bias reduction training, use of objective measures of social support, and changes to facilitate group dynamics. The trial is set to start in January and be completed in September 2026.
“The main takeaway from this study is that it highlights and re-highlights the fact that racial disparities do exist in access to advanced therapy care,” Jaimin Trivedi, MD, MPH, associate professor of cardiothoracic surgery and director of clinical research and bioinformatics, University of Louisville, Ky., said in an interview.
He also called for education and training for all professionals, not just during residency or fellowship, to specifically identify issues with Black patients and encourage Black patients and their family members to get more involved in their HF care.
Dr. Trivedi said that further studies should examine why death rates were similar in the study despite the observed disparities in VAD implantation and transplantation.
He also pointed out that while patients in the study were treated from July 2015 to June 2016, a recent analysis by his team of the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) database showed that 26% of transplants in 2019 were among Black patients, up from just 5% in 1987. “So, there are some encouraging signs as well.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Dr. Cascino reports having no relevant financial relationships. Four coauthors report financial relationships, including David Lanfear, who serves on the advisory board at Medscape. Dr. Breathett reported funding from multiple NHLBI grants.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Myocarditis after COVID vax rare and mild in teens
New data from Israel provide further evidence that myocarditis is a rare adverse event of vaccination with the Pfizer/BioNTech mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in adolescents – one that predominantly occurs in males and typically after the second dose.
The new data also indicate a “mild and benign” clinical course of myocarditis after vaccination, with “favorable” long-term prognosis based on cardiac imaging findings.
Guy Witberg, MD, MPH, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, and colleagues report their latest observations in correspondence in The New England Journal of Medicine, online.
The group previously reported in December 2021 that the incidence of myocarditis in Israel after receipt of the Pfizer/BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine was highest among males between the ages of 16 and 29 (10.7 cases per 100,000).
The vaccine has since been approved for adolescents aged 12-15. Initial evidence for this age group, reported by Dr. Witberg and colleagues in March 2022, suggests a similar low incidence and mild course of myocarditis, although follow-up was limited to 30 days.
In their latest report, with follow-up out to 6 months, Dr. Witberg and colleagues identified nine probable or definite cases of myocarditis among 182,605 Israeli adolescents aged 12-15 who received the Pfizer/BioNTech mRNA vaccine – an incidence of 4.8 cases per 100,000.
Eight cases occurred after the second vaccine dose. All nine cases were mild.
Cardiac and inflammatory markers were elevated in all adolescent patients and electrocardiographic results were abnormal in two-thirds.
Eight patients had a normal ejection fraction, and four had a pericardial effusion. The patients spent 2-4 days hospitalized, and the in-hospital course was uneventful.
Echocardiographic findings were available a median of 10 days after discharge for eight patients. All echocardiograms showed a normal ejection fraction and resolution of pericardial effusion.
Five patients underwent cardiac MRI, including three scans performed at a median of 104 days after discharge. The scans showed “minimal evidence” of myocardial scarring or fibrosis, with evidence of late gadolinium enhancement ranging from 0% to 2%.
At a median of 206 days following discharge, all of the patients were alive, and none had been readmitted to the hospital, Dr. Witberg and colleagues report.
This research had no specific funding. Five authors have received research grants from Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data from Israel provide further evidence that myocarditis is a rare adverse event of vaccination with the Pfizer/BioNTech mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in adolescents – one that predominantly occurs in males and typically after the second dose.
The new data also indicate a “mild and benign” clinical course of myocarditis after vaccination, with “favorable” long-term prognosis based on cardiac imaging findings.
Guy Witberg, MD, MPH, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, and colleagues report their latest observations in correspondence in The New England Journal of Medicine, online.
The group previously reported in December 2021 that the incidence of myocarditis in Israel after receipt of the Pfizer/BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine was highest among males between the ages of 16 and 29 (10.7 cases per 100,000).
The vaccine has since been approved for adolescents aged 12-15. Initial evidence for this age group, reported by Dr. Witberg and colleagues in March 2022, suggests a similar low incidence and mild course of myocarditis, although follow-up was limited to 30 days.
In their latest report, with follow-up out to 6 months, Dr. Witberg and colleagues identified nine probable or definite cases of myocarditis among 182,605 Israeli adolescents aged 12-15 who received the Pfizer/BioNTech mRNA vaccine – an incidence of 4.8 cases per 100,000.
Eight cases occurred after the second vaccine dose. All nine cases were mild.
Cardiac and inflammatory markers were elevated in all adolescent patients and electrocardiographic results were abnormal in two-thirds.
Eight patients had a normal ejection fraction, and four had a pericardial effusion. The patients spent 2-4 days hospitalized, and the in-hospital course was uneventful.
Echocardiographic findings were available a median of 10 days after discharge for eight patients. All echocardiograms showed a normal ejection fraction and resolution of pericardial effusion.
Five patients underwent cardiac MRI, including three scans performed at a median of 104 days after discharge. The scans showed “minimal evidence” of myocardial scarring or fibrosis, with evidence of late gadolinium enhancement ranging from 0% to 2%.
At a median of 206 days following discharge, all of the patients were alive, and none had been readmitted to the hospital, Dr. Witberg and colleagues report.
This research had no specific funding. Five authors have received research grants from Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data from Israel provide further evidence that myocarditis is a rare adverse event of vaccination with the Pfizer/BioNTech mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in adolescents – one that predominantly occurs in males and typically after the second dose.
The new data also indicate a “mild and benign” clinical course of myocarditis after vaccination, with “favorable” long-term prognosis based on cardiac imaging findings.
Guy Witberg, MD, MPH, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, and colleagues report their latest observations in correspondence in The New England Journal of Medicine, online.
The group previously reported in December 2021 that the incidence of myocarditis in Israel after receipt of the Pfizer/BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine was highest among males between the ages of 16 and 29 (10.7 cases per 100,000).
The vaccine has since been approved for adolescents aged 12-15. Initial evidence for this age group, reported by Dr. Witberg and colleagues in March 2022, suggests a similar low incidence and mild course of myocarditis, although follow-up was limited to 30 days.
In their latest report, with follow-up out to 6 months, Dr. Witberg and colleagues identified nine probable or definite cases of myocarditis among 182,605 Israeli adolescents aged 12-15 who received the Pfizer/BioNTech mRNA vaccine – an incidence of 4.8 cases per 100,000.
Eight cases occurred after the second vaccine dose. All nine cases were mild.
Cardiac and inflammatory markers were elevated in all adolescent patients and electrocardiographic results were abnormal in two-thirds.
Eight patients had a normal ejection fraction, and four had a pericardial effusion. The patients spent 2-4 days hospitalized, and the in-hospital course was uneventful.
Echocardiographic findings were available a median of 10 days after discharge for eight patients. All echocardiograms showed a normal ejection fraction and resolution of pericardial effusion.
Five patients underwent cardiac MRI, including three scans performed at a median of 104 days after discharge. The scans showed “minimal evidence” of myocardial scarring or fibrosis, with evidence of late gadolinium enhancement ranging from 0% to 2%.
At a median of 206 days following discharge, all of the patients were alive, and none had been readmitted to the hospital, Dr. Witberg and colleagues report.
This research had no specific funding. Five authors have received research grants from Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.