User login
Study offers dozens of reasons to cut sugar
A new compilation of nearly all research to date on the health impacts of sugar offers dozens of reasons to cut back.
The studies accounted for decades of research on the topic, stretching back to the beginning of the largest electronic databases for scientific papers.
The result is a list that cites the world’s most common health problems like heart disease, diabetes, obesity, high blood pressure, heart attack, high cholesterol, cancer, and depression. The findings were published in the BMJ. Researchers looked at studies that evaluated the impacts of consuming free sugars, which means any food that contains processed or naturally occurring sugars like table sugar, honey, or maple syrup. Sugar found in whole fruits and vegetables and in milk is not free sugar.
U.S. dietary guidelines recommend getting no more than 10% of daily calories from added sugars. For a typical 2,000-calorie-per-day diet, that equals no more than 200 calories, or about 12 teaspoons. The CDC reports that the average person consumes 17 teaspoons per day, with the largest sources being sugar-sweetened beverages, desserts, and snacks. (For context: one 12-ounce can of soda contains the equivalent of 9 teaspoons of sugar, according to beverage maker Coca-Cola.)
The new analysis also found links between sugary beverage consumption and other diet and lifestyle characteristics that may contribute to health problems.
“People who consumed sugar-sweetened beverages more frequently were likely to ingest more total and saturated fat, carbohydrate, and sodium, and less fruit, fiber, dairy products, and whole grain foods,” the authors wrote. “This dietary pattern was also associated with more frequent smoking and drinking, lower physical activity levels, and more time spent watching television. Therefore, the role of these confounding factors should be taken into consideration when explaining the association between sugar consumption and burden of disease.”
Recommendations for limiting sugar consumption are in place worldwide, the authors noted. They concluded that more needs to be done given the known health dangers of sugar.
“To change sugar consumption patterns, especially for children and adolescents, a combination of widespread public health education and policies worldwide is urgently needed,” they said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
A new compilation of nearly all research to date on the health impacts of sugar offers dozens of reasons to cut back.
The studies accounted for decades of research on the topic, stretching back to the beginning of the largest electronic databases for scientific papers.
The result is a list that cites the world’s most common health problems like heart disease, diabetes, obesity, high blood pressure, heart attack, high cholesterol, cancer, and depression. The findings were published in the BMJ. Researchers looked at studies that evaluated the impacts of consuming free sugars, which means any food that contains processed or naturally occurring sugars like table sugar, honey, or maple syrup. Sugar found in whole fruits and vegetables and in milk is not free sugar.
U.S. dietary guidelines recommend getting no more than 10% of daily calories from added sugars. For a typical 2,000-calorie-per-day diet, that equals no more than 200 calories, or about 12 teaspoons. The CDC reports that the average person consumes 17 teaspoons per day, with the largest sources being sugar-sweetened beverages, desserts, and snacks. (For context: one 12-ounce can of soda contains the equivalent of 9 teaspoons of sugar, according to beverage maker Coca-Cola.)
The new analysis also found links between sugary beverage consumption and other diet and lifestyle characteristics that may contribute to health problems.
“People who consumed sugar-sweetened beverages more frequently were likely to ingest more total and saturated fat, carbohydrate, and sodium, and less fruit, fiber, dairy products, and whole grain foods,” the authors wrote. “This dietary pattern was also associated with more frequent smoking and drinking, lower physical activity levels, and more time spent watching television. Therefore, the role of these confounding factors should be taken into consideration when explaining the association between sugar consumption and burden of disease.”
Recommendations for limiting sugar consumption are in place worldwide, the authors noted. They concluded that more needs to be done given the known health dangers of sugar.
“To change sugar consumption patterns, especially for children and adolescents, a combination of widespread public health education and policies worldwide is urgently needed,” they said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
A new compilation of nearly all research to date on the health impacts of sugar offers dozens of reasons to cut back.
The studies accounted for decades of research on the topic, stretching back to the beginning of the largest electronic databases for scientific papers.
The result is a list that cites the world’s most common health problems like heart disease, diabetes, obesity, high blood pressure, heart attack, high cholesterol, cancer, and depression. The findings were published in the BMJ. Researchers looked at studies that evaluated the impacts of consuming free sugars, which means any food that contains processed or naturally occurring sugars like table sugar, honey, or maple syrup. Sugar found in whole fruits and vegetables and in milk is not free sugar.
U.S. dietary guidelines recommend getting no more than 10% of daily calories from added sugars. For a typical 2,000-calorie-per-day diet, that equals no more than 200 calories, or about 12 teaspoons. The CDC reports that the average person consumes 17 teaspoons per day, with the largest sources being sugar-sweetened beverages, desserts, and snacks. (For context: one 12-ounce can of soda contains the equivalent of 9 teaspoons of sugar, according to beverage maker Coca-Cola.)
The new analysis also found links between sugary beverage consumption and other diet and lifestyle characteristics that may contribute to health problems.
“People who consumed sugar-sweetened beverages more frequently were likely to ingest more total and saturated fat, carbohydrate, and sodium, and less fruit, fiber, dairy products, and whole grain foods,” the authors wrote. “This dietary pattern was also associated with more frequent smoking and drinking, lower physical activity levels, and more time spent watching television. Therefore, the role of these confounding factors should be taken into consideration when explaining the association between sugar consumption and burden of disease.”
Recommendations for limiting sugar consumption are in place worldwide, the authors noted. They concluded that more needs to be done given the known health dangers of sugar.
“To change sugar consumption patterns, especially for children and adolescents, a combination of widespread public health education and policies worldwide is urgently needed,” they said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM THE BMJ
High salt intake linked to atherosclerosis even with normal BP
A high salt intake is an important risk factor for atherosclerosis, even in the absence of hypertension, a large study from Sweden concludes.
The study, including more than 10,000 individuals between the ages of 50 and 64 years from the Swedish Cardiopulmonary bioImage Study, showed a significant link between dietary salt intake and the risk for atherosclerotic lesions in the coronary and carotid arteries, even in participants with normal blood pressure and without known cardiovascular disease.
The finding suggests that salt could be a damaging factor in its own right before the development of hypertension, the authors write. The results were published online in European Heart Journal Open.
It has been known for a long time that salt is linked to hypertension, but the role that salt plays in atherosclerosis has not been examined, first author Jonas Wuopio, MD, Karolinska Institutet, Huddinge, and Clinical Research Center, Falun, Uppsala University, both in Sweden, told this news organization.
“Hardly anyone looks at changes in the arteries’ calcification, the atherosclerotic plaques and the association with salt intake,” Dr. Wuopio said. “We had this exclusive data from our cohort, so we wanted to use it to close this knowledge gap.”
The analysis included 10,788 adults aged 50-64 years, (average age, 58 years; 52% women) who underwent a coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) scan. The estimated 24-hour sodium excretion was used to measure sodium intake.
CCTA was used to obtain 3-D images of the coronary arteries to measure the degree of coronary artery calcium as well as detect stenosis in the coronary arteries. Participants also had an ultrasound of the carotid arteries.
After adjusting for age, sex, and study site (the study was done at Uppsala and Malmö, Sweden), the researchers found that rising salt consumption was linked with increasing atherosclerosis in a linear fashion in both the coronary and carotid arteries.
Each 1,000 mg rise in sodium excretion was associated with a 9% increased occurrence of carotid plaque (odds ratio, 1.09; P < .001; confidence interval, 1.06-1.12), a higher coronary artery calcium score (OR, 1.16; P < .001; CI, 1.12-1.19), and a 17% increased occurrence of coronary artery stenosis (OR, 1.17; P < .001; CI, 1.13-1.20).
The association was abolished, though, after adjusting for blood pressure, they note. Their “interpretation is that the increase in blood pressure from sodium intake, even below the level that currently defines arterial hypertension, is an important factor that mediates the interplay between salt intake and the atherosclerotic process,” they write. “As we observed an association in individuals with normal blood pressure, one possible explanation for these findings is that the detrimental pathological processes begin already prior to the development of hypertension,” they note, although they caution that no causal relationships can be gleaned from this cross-sectional study.
They also reported no sign of a “J-curve”; participants with the lowest levels of sodium excretion had the lowest occurrence of both coronary and carotid atherosclerosis, which contradicts findings in some studies that found very low sodium linked to increased cardiovascular disease–related events.
“There have been some controversies among researchers regarding very low intake, where some say very low salt intake can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, but we could not find this in this study,” Dr. Wuopio said.
“Our study is confirming that excess salt is not a good thing, but the fact that it is linked to atherosclerosis, even in the absence of hypertension, was a bit of a surprise,” he said.
“I will be telling my patients to follow the advice given by the World Health Organization and other medical societies, to limit your intake of salt to approximately 1 teaspoon, even if your blood pressure is normal.”
Time to scrutinize salt’s role in atherosclerosis
In an accompanying editorial, Maciej Banach, MD, Medical University of Lodz, and Stanislaw Surma, MD, Faculty of Medical Sciences in Katowice, both in Poland, write that excessive dietary salt intake is a well-documented cardiovascular risk factor, and that the association is explained in most studies by increased blood pressure.
“We should look more extensively on the role of dietary salt, as it affects many pathological mechanisms, by which, especially with the coexistence of other risk factors, atherosclerosis may progress very fast,” they write.
“The results of the study shed new light on the direct relationship between excessive dietary salt intake and the risk of ASCVD [atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease], indicating that salt intake might be a risk factor for atherosclerosis even prior to the development of hypertension,” they conclude.
Confirmatory and novel
“Nobody questions the fact that high blood pressure is a powerful risk factor for atherosclerotic disease, but not all studies have suggested that, at least at significantly higher levels of sodium intake, that high salt intake tracks with risk for atherosclerotic disease,” Alon Gitig, MD, assistant professor and director of cardiology, Mount Sinai Doctors-Westchester, Yonkers, New York, told this news organization.
Most of the studies of salt intake in the diet are based on patient self-reports via food frequency questionnaires, which can give a general idea of salt intake, but are often not totally accurate, Dr. Gitig said.
“Here, they measured sodium in the urine and estimated the 24-hour salt intake from that, which is slightly novel,” he said.
Everybody knows that high blood pressure is associated with future cardiovascular disease risk, but what many don’t realize is that that risk starts to increase slightly but significantly above a blood pressure that is already in the range of 115 mm Hg/75 mm Hg, he said.
“The lower you can get your blood pressure down, to around 115-120, the lower your risk for cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Gitig said.
It is possible for most people to lower blood pressure through attention to diet, restricting sodium, performing cardio and weight training exercises, and maintaining a healthy weight, he said.
An example of a cardiovascular health diet is the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet.
“The DASH diet, consisting of 9 servings of fruits and vegetables a day with few refined carbs, flour and sugar, has been shown in a randomized trial to dramatically reduce blood pressure. There are two reasons for that. One is that the fruits and vegetables have many phytonutrients that are good for arteries. The other is that a large proportion of U.S. adults have insulin resistance, which leads to high blood pressure.
“The more fruits and vegetables and healthy animal products, and less sugar and flour, the more you are going to improve your insulin resistance, so you can bring your blood pressure down that way,” Dr. Gitig said.
The study was funded by the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation, the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, the Swedish Research Council and Vinnova (Sweden’s Innovation agency), the University of Gothenburg and Sahlgrenska University Hospital, the Karolinska Institutet and Stockholm County Council, the Linköping University and University Hospital, the Lund University and Skane University Hospital, the Umea University and University Hospital, and the Uppsala University and University Hospital. Dr. Wuopio and Dr. Gitig report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Banach reports financial relationships with Adamed, Amgen, Daichii Sankyo, Esperion, KrKa, NewAmsterdam, Polpharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, Teva, Viatris, and CMDO at Longevity Group (LU). Dr. Surma reports a financial relationship with Sanofi and Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A high salt intake is an important risk factor for atherosclerosis, even in the absence of hypertension, a large study from Sweden concludes.
The study, including more than 10,000 individuals between the ages of 50 and 64 years from the Swedish Cardiopulmonary bioImage Study, showed a significant link between dietary salt intake and the risk for atherosclerotic lesions in the coronary and carotid arteries, even in participants with normal blood pressure and without known cardiovascular disease.
The finding suggests that salt could be a damaging factor in its own right before the development of hypertension, the authors write. The results were published online in European Heart Journal Open.
It has been known for a long time that salt is linked to hypertension, but the role that salt plays in atherosclerosis has not been examined, first author Jonas Wuopio, MD, Karolinska Institutet, Huddinge, and Clinical Research Center, Falun, Uppsala University, both in Sweden, told this news organization.
“Hardly anyone looks at changes in the arteries’ calcification, the atherosclerotic plaques and the association with salt intake,” Dr. Wuopio said. “We had this exclusive data from our cohort, so we wanted to use it to close this knowledge gap.”
The analysis included 10,788 adults aged 50-64 years, (average age, 58 years; 52% women) who underwent a coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) scan. The estimated 24-hour sodium excretion was used to measure sodium intake.
CCTA was used to obtain 3-D images of the coronary arteries to measure the degree of coronary artery calcium as well as detect stenosis in the coronary arteries. Participants also had an ultrasound of the carotid arteries.
After adjusting for age, sex, and study site (the study was done at Uppsala and Malmö, Sweden), the researchers found that rising salt consumption was linked with increasing atherosclerosis in a linear fashion in both the coronary and carotid arteries.
Each 1,000 mg rise in sodium excretion was associated with a 9% increased occurrence of carotid plaque (odds ratio, 1.09; P < .001; confidence interval, 1.06-1.12), a higher coronary artery calcium score (OR, 1.16; P < .001; CI, 1.12-1.19), and a 17% increased occurrence of coronary artery stenosis (OR, 1.17; P < .001; CI, 1.13-1.20).
The association was abolished, though, after adjusting for blood pressure, they note. Their “interpretation is that the increase in blood pressure from sodium intake, even below the level that currently defines arterial hypertension, is an important factor that mediates the interplay between salt intake and the atherosclerotic process,” they write. “As we observed an association in individuals with normal blood pressure, one possible explanation for these findings is that the detrimental pathological processes begin already prior to the development of hypertension,” they note, although they caution that no causal relationships can be gleaned from this cross-sectional study.
They also reported no sign of a “J-curve”; participants with the lowest levels of sodium excretion had the lowest occurrence of both coronary and carotid atherosclerosis, which contradicts findings in some studies that found very low sodium linked to increased cardiovascular disease–related events.
“There have been some controversies among researchers regarding very low intake, where some say very low salt intake can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, but we could not find this in this study,” Dr. Wuopio said.
“Our study is confirming that excess salt is not a good thing, but the fact that it is linked to atherosclerosis, even in the absence of hypertension, was a bit of a surprise,” he said.
“I will be telling my patients to follow the advice given by the World Health Organization and other medical societies, to limit your intake of salt to approximately 1 teaspoon, even if your blood pressure is normal.”
Time to scrutinize salt’s role in atherosclerosis
In an accompanying editorial, Maciej Banach, MD, Medical University of Lodz, and Stanislaw Surma, MD, Faculty of Medical Sciences in Katowice, both in Poland, write that excessive dietary salt intake is a well-documented cardiovascular risk factor, and that the association is explained in most studies by increased blood pressure.
“We should look more extensively on the role of dietary salt, as it affects many pathological mechanisms, by which, especially with the coexistence of other risk factors, atherosclerosis may progress very fast,” they write.
“The results of the study shed new light on the direct relationship between excessive dietary salt intake and the risk of ASCVD [atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease], indicating that salt intake might be a risk factor for atherosclerosis even prior to the development of hypertension,” they conclude.
Confirmatory and novel
“Nobody questions the fact that high blood pressure is a powerful risk factor for atherosclerotic disease, but not all studies have suggested that, at least at significantly higher levels of sodium intake, that high salt intake tracks with risk for atherosclerotic disease,” Alon Gitig, MD, assistant professor and director of cardiology, Mount Sinai Doctors-Westchester, Yonkers, New York, told this news organization.
Most of the studies of salt intake in the diet are based on patient self-reports via food frequency questionnaires, which can give a general idea of salt intake, but are often not totally accurate, Dr. Gitig said.
“Here, they measured sodium in the urine and estimated the 24-hour salt intake from that, which is slightly novel,” he said.
Everybody knows that high blood pressure is associated with future cardiovascular disease risk, but what many don’t realize is that that risk starts to increase slightly but significantly above a blood pressure that is already in the range of 115 mm Hg/75 mm Hg, he said.
“The lower you can get your blood pressure down, to around 115-120, the lower your risk for cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Gitig said.
It is possible for most people to lower blood pressure through attention to diet, restricting sodium, performing cardio and weight training exercises, and maintaining a healthy weight, he said.
An example of a cardiovascular health diet is the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet.
“The DASH diet, consisting of 9 servings of fruits and vegetables a day with few refined carbs, flour and sugar, has been shown in a randomized trial to dramatically reduce blood pressure. There are two reasons for that. One is that the fruits and vegetables have many phytonutrients that are good for arteries. The other is that a large proportion of U.S. adults have insulin resistance, which leads to high blood pressure.
“The more fruits and vegetables and healthy animal products, and less sugar and flour, the more you are going to improve your insulin resistance, so you can bring your blood pressure down that way,” Dr. Gitig said.
The study was funded by the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation, the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, the Swedish Research Council and Vinnova (Sweden’s Innovation agency), the University of Gothenburg and Sahlgrenska University Hospital, the Karolinska Institutet and Stockholm County Council, the Linköping University and University Hospital, the Lund University and Skane University Hospital, the Umea University and University Hospital, and the Uppsala University and University Hospital. Dr. Wuopio and Dr. Gitig report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Banach reports financial relationships with Adamed, Amgen, Daichii Sankyo, Esperion, KrKa, NewAmsterdam, Polpharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, Teva, Viatris, and CMDO at Longevity Group (LU). Dr. Surma reports a financial relationship with Sanofi and Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A high salt intake is an important risk factor for atherosclerosis, even in the absence of hypertension, a large study from Sweden concludes.
The study, including more than 10,000 individuals between the ages of 50 and 64 years from the Swedish Cardiopulmonary bioImage Study, showed a significant link between dietary salt intake and the risk for atherosclerotic lesions in the coronary and carotid arteries, even in participants with normal blood pressure and without known cardiovascular disease.
The finding suggests that salt could be a damaging factor in its own right before the development of hypertension, the authors write. The results were published online in European Heart Journal Open.
It has been known for a long time that salt is linked to hypertension, but the role that salt plays in atherosclerosis has not been examined, first author Jonas Wuopio, MD, Karolinska Institutet, Huddinge, and Clinical Research Center, Falun, Uppsala University, both in Sweden, told this news organization.
“Hardly anyone looks at changes in the arteries’ calcification, the atherosclerotic plaques and the association with salt intake,” Dr. Wuopio said. “We had this exclusive data from our cohort, so we wanted to use it to close this knowledge gap.”
The analysis included 10,788 adults aged 50-64 years, (average age, 58 years; 52% women) who underwent a coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) scan. The estimated 24-hour sodium excretion was used to measure sodium intake.
CCTA was used to obtain 3-D images of the coronary arteries to measure the degree of coronary artery calcium as well as detect stenosis in the coronary arteries. Participants also had an ultrasound of the carotid arteries.
After adjusting for age, sex, and study site (the study was done at Uppsala and Malmö, Sweden), the researchers found that rising salt consumption was linked with increasing atherosclerosis in a linear fashion in both the coronary and carotid arteries.
Each 1,000 mg rise in sodium excretion was associated with a 9% increased occurrence of carotid plaque (odds ratio, 1.09; P < .001; confidence interval, 1.06-1.12), a higher coronary artery calcium score (OR, 1.16; P < .001; CI, 1.12-1.19), and a 17% increased occurrence of coronary artery stenosis (OR, 1.17; P < .001; CI, 1.13-1.20).
The association was abolished, though, after adjusting for blood pressure, they note. Their “interpretation is that the increase in blood pressure from sodium intake, even below the level that currently defines arterial hypertension, is an important factor that mediates the interplay between salt intake and the atherosclerotic process,” they write. “As we observed an association in individuals with normal blood pressure, one possible explanation for these findings is that the detrimental pathological processes begin already prior to the development of hypertension,” they note, although they caution that no causal relationships can be gleaned from this cross-sectional study.
They also reported no sign of a “J-curve”; participants with the lowest levels of sodium excretion had the lowest occurrence of both coronary and carotid atherosclerosis, which contradicts findings in some studies that found very low sodium linked to increased cardiovascular disease–related events.
“There have been some controversies among researchers regarding very low intake, where some say very low salt intake can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, but we could not find this in this study,” Dr. Wuopio said.
“Our study is confirming that excess salt is not a good thing, but the fact that it is linked to atherosclerosis, even in the absence of hypertension, was a bit of a surprise,” he said.
“I will be telling my patients to follow the advice given by the World Health Organization and other medical societies, to limit your intake of salt to approximately 1 teaspoon, even if your blood pressure is normal.”
Time to scrutinize salt’s role in atherosclerosis
In an accompanying editorial, Maciej Banach, MD, Medical University of Lodz, and Stanislaw Surma, MD, Faculty of Medical Sciences in Katowice, both in Poland, write that excessive dietary salt intake is a well-documented cardiovascular risk factor, and that the association is explained in most studies by increased blood pressure.
“We should look more extensively on the role of dietary salt, as it affects many pathological mechanisms, by which, especially with the coexistence of other risk factors, atherosclerosis may progress very fast,” they write.
“The results of the study shed new light on the direct relationship between excessive dietary salt intake and the risk of ASCVD [atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease], indicating that salt intake might be a risk factor for atherosclerosis even prior to the development of hypertension,” they conclude.
Confirmatory and novel
“Nobody questions the fact that high blood pressure is a powerful risk factor for atherosclerotic disease, but not all studies have suggested that, at least at significantly higher levels of sodium intake, that high salt intake tracks with risk for atherosclerotic disease,” Alon Gitig, MD, assistant professor and director of cardiology, Mount Sinai Doctors-Westchester, Yonkers, New York, told this news organization.
Most of the studies of salt intake in the diet are based on patient self-reports via food frequency questionnaires, which can give a general idea of salt intake, but are often not totally accurate, Dr. Gitig said.
“Here, they measured sodium in the urine and estimated the 24-hour salt intake from that, which is slightly novel,” he said.
Everybody knows that high blood pressure is associated with future cardiovascular disease risk, but what many don’t realize is that that risk starts to increase slightly but significantly above a blood pressure that is already in the range of 115 mm Hg/75 mm Hg, he said.
“The lower you can get your blood pressure down, to around 115-120, the lower your risk for cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Gitig said.
It is possible for most people to lower blood pressure through attention to diet, restricting sodium, performing cardio and weight training exercises, and maintaining a healthy weight, he said.
An example of a cardiovascular health diet is the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet.
“The DASH diet, consisting of 9 servings of fruits and vegetables a day with few refined carbs, flour and sugar, has been shown in a randomized trial to dramatically reduce blood pressure. There are two reasons for that. One is that the fruits and vegetables have many phytonutrients that are good for arteries. The other is that a large proportion of U.S. adults have insulin resistance, which leads to high blood pressure.
“The more fruits and vegetables and healthy animal products, and less sugar and flour, the more you are going to improve your insulin resistance, so you can bring your blood pressure down that way,” Dr. Gitig said.
The study was funded by the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation, the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, the Swedish Research Council and Vinnova (Sweden’s Innovation agency), the University of Gothenburg and Sahlgrenska University Hospital, the Karolinska Institutet and Stockholm County Council, the Linköping University and University Hospital, the Lund University and Skane University Hospital, the Umea University and University Hospital, and the Uppsala University and University Hospital. Dr. Wuopio and Dr. Gitig report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Banach reports financial relationships with Adamed, Amgen, Daichii Sankyo, Esperion, KrKa, NewAmsterdam, Polpharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, Teva, Viatris, and CMDO at Longevity Group (LU). Dr. Surma reports a financial relationship with Sanofi and Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New AHA statement on pediatric primary hypertension issued
the American Heart Association said in a new scientific statement.
“Children can have secondary hypertension that is caused by an underlying condition such as chronic kidney disease, endocrine disorders, cardiac anomalies, and some syndromes. However, primary hypertension is now recognized as the most common type of hypertension in childhood,” Bonita Falkner, MD, chair of the writing group and emeritus professor of medicine and pediatrics, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, said in an interview.
And hypertensive children are “highly likely” to become hypertensive adults and to have measurable target organ injury, particularly left ventricular hypertrophy and vascular stiffening, the writing group noted.
The AHA statement on primary pediatric hypertension was published online in Hypertension.
Primary or essential hypertension occurs in up to 5% of children and adolescents in the United States and other countries.
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), European Society of Hypertension and Hypertension Canada all define hypertension as repeated BP readings at or above the 95th percentile for children, but the thresholds differ by age.
The AAP adopts 130/80 mm Hg starting at age 13 years; the European Society of Hypertension adopts 140/90 mm Hg starting at age 16 years; and Hypertension Canada adopts 120/80 mm Hg for those aged 6-11 years and 130/85 mm Hg for those aged 12-17 years.
Adolescents entering adulthood with a BP < 120/80 mm Hg is an optimal goal, the writing group advised.
They recommend that health care professionals be trained on evidence-based methods to obtain accurate and reliable BP values with either auscultatory or oscillometric methods.
When the initial BP measurement is abnormal, repeat measurement by auscultation is recommended, within the same visit if possible, and then within weeks if the screening BP is hypertensive, or months if the screening BP is elevated.
Because BP levels are variable, even within a single visit, “best practice” is to obtain up to three BP measurements and to record the average of the latter two measurements unless the first measurement is normal, the writing group said. Further confirmation of diagnosis of hypertension can be obtained with 24-hour ambulatory BP monitoring (ABPM).
“Primary hypertension in youth is difficult to recognize in asymptomatic, otherwise healthy youth. There is now evidence that children and adolescents with primary hypertension may also have cardiac and vascular injury due to the hypertension,” Dr. Falkner told this news organization.
“If not identified and treated, the condition can progress to hypertension in young adulthood with heightened risk of premature cardiovascular events,” Dr. Falkner said.
The writing group said “primordial prevention” is an important public health goal because a population with lower BP will have fewer comorbidities related to hypertension and CVD.
Modifiable risk factors for primary hypertension in childhood include obesity, physical inactivity and poor diet/nutrition, disturbed sleep patterns, and environmental stress.
A healthy lifestyle in childhood – including eating healthy food, encouraging physical activity that leads to improved physical fitness and healthy sleep, and avoiding the development of obesity – may help mitigate the risk of hypertension in childhood, the writing group noted.
Looking ahead, they said efforts to improve recognition and diagnosis of high BP in children, as well as clinical trials to evaluate medical treatment and recommend public health initiatives, are all vital to combat rising rates of primary hypertension in children.
This scientific statement was prepared by the volunteer writing group on behalf of the American Heart Association’s Council on Hypertension, the Council on Lifelong Congenital Heart Disease and Heart Health in the Young, the Council on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health, and the Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
the American Heart Association said in a new scientific statement.
“Children can have secondary hypertension that is caused by an underlying condition such as chronic kidney disease, endocrine disorders, cardiac anomalies, and some syndromes. However, primary hypertension is now recognized as the most common type of hypertension in childhood,” Bonita Falkner, MD, chair of the writing group and emeritus professor of medicine and pediatrics, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, said in an interview.
And hypertensive children are “highly likely” to become hypertensive adults and to have measurable target organ injury, particularly left ventricular hypertrophy and vascular stiffening, the writing group noted.
The AHA statement on primary pediatric hypertension was published online in Hypertension.
Primary or essential hypertension occurs in up to 5% of children and adolescents in the United States and other countries.
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), European Society of Hypertension and Hypertension Canada all define hypertension as repeated BP readings at or above the 95th percentile for children, but the thresholds differ by age.
The AAP adopts 130/80 mm Hg starting at age 13 years; the European Society of Hypertension adopts 140/90 mm Hg starting at age 16 years; and Hypertension Canada adopts 120/80 mm Hg for those aged 6-11 years and 130/85 mm Hg for those aged 12-17 years.
Adolescents entering adulthood with a BP < 120/80 mm Hg is an optimal goal, the writing group advised.
They recommend that health care professionals be trained on evidence-based methods to obtain accurate and reliable BP values with either auscultatory or oscillometric methods.
When the initial BP measurement is abnormal, repeat measurement by auscultation is recommended, within the same visit if possible, and then within weeks if the screening BP is hypertensive, or months if the screening BP is elevated.
Because BP levels are variable, even within a single visit, “best practice” is to obtain up to three BP measurements and to record the average of the latter two measurements unless the first measurement is normal, the writing group said. Further confirmation of diagnosis of hypertension can be obtained with 24-hour ambulatory BP monitoring (ABPM).
“Primary hypertension in youth is difficult to recognize in asymptomatic, otherwise healthy youth. There is now evidence that children and adolescents with primary hypertension may also have cardiac and vascular injury due to the hypertension,” Dr. Falkner told this news organization.
“If not identified and treated, the condition can progress to hypertension in young adulthood with heightened risk of premature cardiovascular events,” Dr. Falkner said.
The writing group said “primordial prevention” is an important public health goal because a population with lower BP will have fewer comorbidities related to hypertension and CVD.
Modifiable risk factors for primary hypertension in childhood include obesity, physical inactivity and poor diet/nutrition, disturbed sleep patterns, and environmental stress.
A healthy lifestyle in childhood – including eating healthy food, encouraging physical activity that leads to improved physical fitness and healthy sleep, and avoiding the development of obesity – may help mitigate the risk of hypertension in childhood, the writing group noted.
Looking ahead, they said efforts to improve recognition and diagnosis of high BP in children, as well as clinical trials to evaluate medical treatment and recommend public health initiatives, are all vital to combat rising rates of primary hypertension in children.
This scientific statement was prepared by the volunteer writing group on behalf of the American Heart Association’s Council on Hypertension, the Council on Lifelong Congenital Heart Disease and Heart Health in the Young, the Council on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health, and the Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
the American Heart Association said in a new scientific statement.
“Children can have secondary hypertension that is caused by an underlying condition such as chronic kidney disease, endocrine disorders, cardiac anomalies, and some syndromes. However, primary hypertension is now recognized as the most common type of hypertension in childhood,” Bonita Falkner, MD, chair of the writing group and emeritus professor of medicine and pediatrics, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, said in an interview.
And hypertensive children are “highly likely” to become hypertensive adults and to have measurable target organ injury, particularly left ventricular hypertrophy and vascular stiffening, the writing group noted.
The AHA statement on primary pediatric hypertension was published online in Hypertension.
Primary or essential hypertension occurs in up to 5% of children and adolescents in the United States and other countries.
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), European Society of Hypertension and Hypertension Canada all define hypertension as repeated BP readings at or above the 95th percentile for children, but the thresholds differ by age.
The AAP adopts 130/80 mm Hg starting at age 13 years; the European Society of Hypertension adopts 140/90 mm Hg starting at age 16 years; and Hypertension Canada adopts 120/80 mm Hg for those aged 6-11 years and 130/85 mm Hg for those aged 12-17 years.
Adolescents entering adulthood with a BP < 120/80 mm Hg is an optimal goal, the writing group advised.
They recommend that health care professionals be trained on evidence-based methods to obtain accurate and reliable BP values with either auscultatory or oscillometric methods.
When the initial BP measurement is abnormal, repeat measurement by auscultation is recommended, within the same visit if possible, and then within weeks if the screening BP is hypertensive, or months if the screening BP is elevated.
Because BP levels are variable, even within a single visit, “best practice” is to obtain up to three BP measurements and to record the average of the latter two measurements unless the first measurement is normal, the writing group said. Further confirmation of diagnosis of hypertension can be obtained with 24-hour ambulatory BP monitoring (ABPM).
“Primary hypertension in youth is difficult to recognize in asymptomatic, otherwise healthy youth. There is now evidence that children and adolescents with primary hypertension may also have cardiac and vascular injury due to the hypertension,” Dr. Falkner told this news organization.
“If not identified and treated, the condition can progress to hypertension in young adulthood with heightened risk of premature cardiovascular events,” Dr. Falkner said.
The writing group said “primordial prevention” is an important public health goal because a population with lower BP will have fewer comorbidities related to hypertension and CVD.
Modifiable risk factors for primary hypertension in childhood include obesity, physical inactivity and poor diet/nutrition, disturbed sleep patterns, and environmental stress.
A healthy lifestyle in childhood – including eating healthy food, encouraging physical activity that leads to improved physical fitness and healthy sleep, and avoiding the development of obesity – may help mitigate the risk of hypertension in childhood, the writing group noted.
Looking ahead, they said efforts to improve recognition and diagnosis of high BP in children, as well as clinical trials to evaluate medical treatment and recommend public health initiatives, are all vital to combat rising rates of primary hypertension in children.
This scientific statement was prepared by the volunteer writing group on behalf of the American Heart Association’s Council on Hypertension, the Council on Lifelong Congenital Heart Disease and Heart Health in the Young, the Council on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health, and the Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM HYPERTENSION
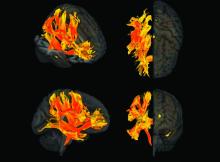
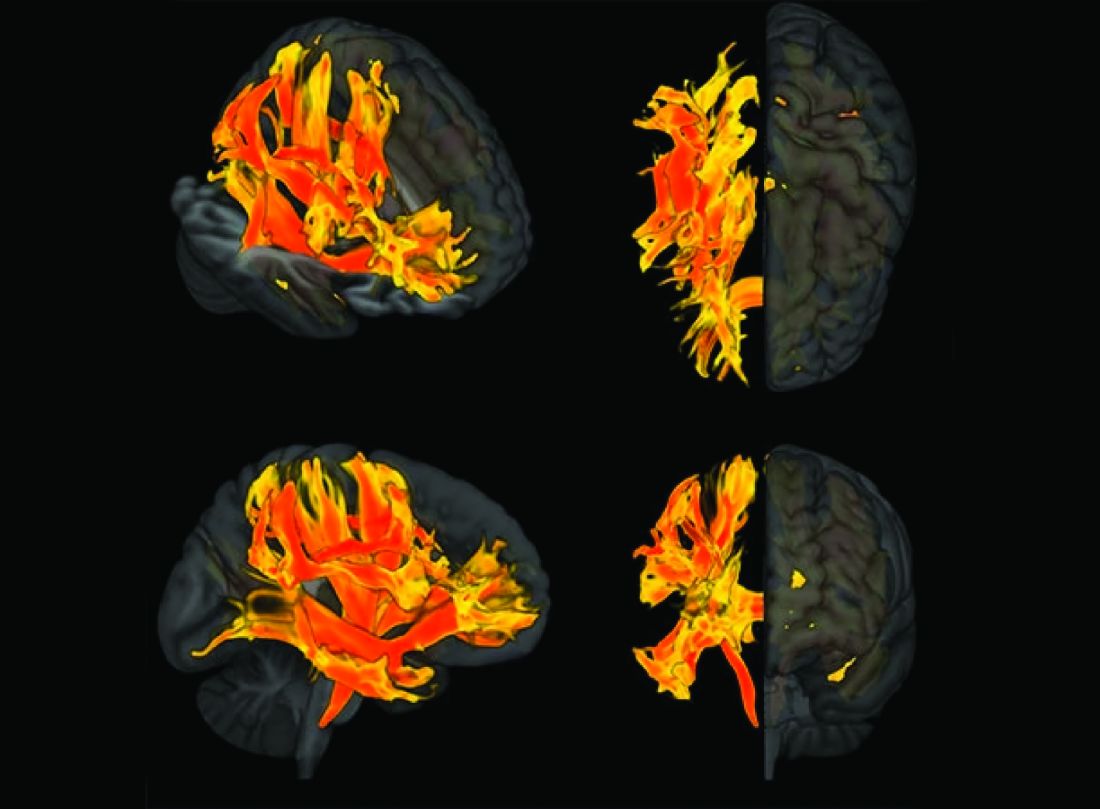
Specific brain damage links hypertension to cognitive impairment
Researchers have identified specific regions of the brain that appear to be damaged by high blood pressure. The finding may explain the link between hypertension and cognitive impairment.
They used genetic information from genome-wide association studies (GWASs) and MRI scans of the brain to study the relationship between hypertension, changes in brain structures, and cognitive impairment. Using Mendelian randomization techniques, they identified nine brain structures related to cognitive impairment that are affected by blood pressure.
“We knew before that raised blood pressure was related to changes in the brain, but our research has narrowed down the changes to those that appear to be potentially causally related to cognitive impairment,” senior author Tomasz Guzik, professor of cardiovascular medicine, at the University of Edinburgh and of the Jagiellonian University, Krakow, Poland, told this news organization.
“Our study confirms a potentially causal relationship between raised blood pressure and cognitive impairment, emphasizing the importance of preventing and treating hypertension,” Prof. Guzik noted.
“But it also identifies the brain culprits of this relationship,” he added.
In the future, it may be possible to assess these nine brain structures in people with high blood pressure to identify those at increased risk of developing cognitive impairment, he said. “These patients may need more intensive care for their blood pressure. We can also investigate these brain structures for potential signaling pathways and molecular changes to see if we can find new targets for treatment to prevent cognitive impairment.”
For this report, the investigators married together different research datasets to identify brain structures potentially responsible for the effects of blood pressure on cognitive function, using results from previous GWASs and observational data from 39,000 people in the UK Biobank registry for whom brain MRI data were available.
First, they mapped brain structures potentially influenced by blood pressure in midlife using MRI scans from people in the UK Biobank registry. Then they examined the relationship between blood pressure and cognitive function in the UK Biobank registry. Next, of the brain structures affected by blood pressure, they identified those that are causally linked to cognitive impairment.
This was possible thanks to genetic markers coding for increased blood pressure, brain structure imaging phenotypes, and those coding for cognitive impairment that could be used in Mendelian randomization studies.
“We looked at 3935 brain magnetic resonance imaging–derived phenotypes in the brain and cognitive function defined by fluid intelligence score to identify genetically predicted causal relationships,” Prof. Guzik said.
They identified 200 brain structures that were causally affected by systolic blood pressure. Of these, nine were also causally related to cognitive impairment. The results were validated in a second prospective cohort of patients with hypertension.
“Some of these structures, including putamen and the white matter regions spanning between the anterior corona radiata, anterior thalamic radiation, and anterior limb of the internal capsule, may represent the target brain regions at which systolic blood pressure acts on cognitive function,” the authors comment.
In an accompanying editorial, Ernesto Schiffrin, MD, and James Engert, PhD, McGill University, Montreal, say that further mechanistic studies of the effects of blood pressure on cognitive function are required to determine precise causal pathways and the roles of relevant brain regions.
“Eventually, biomarkers could be developed to inform antihypertensive trials. Whether clinical trials targeting the specific brain structures will be feasible or if specific antihypertensives could be found that target specific structures remains to be demonstrated,” they write.
“Thus, these new studies could lead to an understanding of the signaling pathways that explain how these structures relate vascular damage to cognitive impairment in hypertension, and contribute to the development of novel interventions to more successfully address the scourge of cognitive decline and dementia in the future,” the editorialists conclude.
The study was funded by the European Research Council, the British Heart Foundation, and the Italian Ministry of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Researchers have identified specific regions of the brain that appear to be damaged by high blood pressure. The finding may explain the link between hypertension and cognitive impairment.
They used genetic information from genome-wide association studies (GWASs) and MRI scans of the brain to study the relationship between hypertension, changes in brain structures, and cognitive impairment. Using Mendelian randomization techniques, they identified nine brain structures related to cognitive impairment that are affected by blood pressure.
“We knew before that raised blood pressure was related to changes in the brain, but our research has narrowed down the changes to those that appear to be potentially causally related to cognitive impairment,” senior author Tomasz Guzik, professor of cardiovascular medicine, at the University of Edinburgh and of the Jagiellonian University, Krakow, Poland, told this news organization.
“Our study confirms a potentially causal relationship between raised blood pressure and cognitive impairment, emphasizing the importance of preventing and treating hypertension,” Prof. Guzik noted.
“But it also identifies the brain culprits of this relationship,” he added.
In the future, it may be possible to assess these nine brain structures in people with high blood pressure to identify those at increased risk of developing cognitive impairment, he said. “These patients may need more intensive care for their blood pressure. We can also investigate these brain structures for potential signaling pathways and molecular changes to see if we can find new targets for treatment to prevent cognitive impairment.”
For this report, the investigators married together different research datasets to identify brain structures potentially responsible for the effects of blood pressure on cognitive function, using results from previous GWASs and observational data from 39,000 people in the UK Biobank registry for whom brain MRI data were available.
First, they mapped brain structures potentially influenced by blood pressure in midlife using MRI scans from people in the UK Biobank registry. Then they examined the relationship between blood pressure and cognitive function in the UK Biobank registry. Next, of the brain structures affected by blood pressure, they identified those that are causally linked to cognitive impairment.
This was possible thanks to genetic markers coding for increased blood pressure, brain structure imaging phenotypes, and those coding for cognitive impairment that could be used in Mendelian randomization studies.
“We looked at 3935 brain magnetic resonance imaging–derived phenotypes in the brain and cognitive function defined by fluid intelligence score to identify genetically predicted causal relationships,” Prof. Guzik said.
They identified 200 brain structures that were causally affected by systolic blood pressure. Of these, nine were also causally related to cognitive impairment. The results were validated in a second prospective cohort of patients with hypertension.
“Some of these structures, including putamen and the white matter regions spanning between the anterior corona radiata, anterior thalamic radiation, and anterior limb of the internal capsule, may represent the target brain regions at which systolic blood pressure acts on cognitive function,” the authors comment.
In an accompanying editorial, Ernesto Schiffrin, MD, and James Engert, PhD, McGill University, Montreal, say that further mechanistic studies of the effects of blood pressure on cognitive function are required to determine precise causal pathways and the roles of relevant brain regions.
“Eventually, biomarkers could be developed to inform antihypertensive trials. Whether clinical trials targeting the specific brain structures will be feasible or if specific antihypertensives could be found that target specific structures remains to be demonstrated,” they write.
“Thus, these new studies could lead to an understanding of the signaling pathways that explain how these structures relate vascular damage to cognitive impairment in hypertension, and contribute to the development of novel interventions to more successfully address the scourge of cognitive decline and dementia in the future,” the editorialists conclude.
The study was funded by the European Research Council, the British Heart Foundation, and the Italian Ministry of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Researchers have identified specific regions of the brain that appear to be damaged by high blood pressure. The finding may explain the link between hypertension and cognitive impairment.
They used genetic information from genome-wide association studies (GWASs) and MRI scans of the brain to study the relationship between hypertension, changes in brain structures, and cognitive impairment. Using Mendelian randomization techniques, they identified nine brain structures related to cognitive impairment that are affected by blood pressure.
“We knew before that raised blood pressure was related to changes in the brain, but our research has narrowed down the changes to those that appear to be potentially causally related to cognitive impairment,” senior author Tomasz Guzik, professor of cardiovascular medicine, at the University of Edinburgh and of the Jagiellonian University, Krakow, Poland, told this news organization.
“Our study confirms a potentially causal relationship between raised blood pressure and cognitive impairment, emphasizing the importance of preventing and treating hypertension,” Prof. Guzik noted.
“But it also identifies the brain culprits of this relationship,” he added.
In the future, it may be possible to assess these nine brain structures in people with high blood pressure to identify those at increased risk of developing cognitive impairment, he said. “These patients may need more intensive care for their blood pressure. We can also investigate these brain structures for potential signaling pathways and molecular changes to see if we can find new targets for treatment to prevent cognitive impairment.”
For this report, the investigators married together different research datasets to identify brain structures potentially responsible for the effects of blood pressure on cognitive function, using results from previous GWASs and observational data from 39,000 people in the UK Biobank registry for whom brain MRI data were available.
First, they mapped brain structures potentially influenced by blood pressure in midlife using MRI scans from people in the UK Biobank registry. Then they examined the relationship between blood pressure and cognitive function in the UK Biobank registry. Next, of the brain structures affected by blood pressure, they identified those that are causally linked to cognitive impairment.
This was possible thanks to genetic markers coding for increased blood pressure, brain structure imaging phenotypes, and those coding for cognitive impairment that could be used in Mendelian randomization studies.
“We looked at 3935 brain magnetic resonance imaging–derived phenotypes in the brain and cognitive function defined by fluid intelligence score to identify genetically predicted causal relationships,” Prof. Guzik said.
They identified 200 brain structures that were causally affected by systolic blood pressure. Of these, nine were also causally related to cognitive impairment. The results were validated in a second prospective cohort of patients with hypertension.
“Some of these structures, including putamen and the white matter regions spanning between the anterior corona radiata, anterior thalamic radiation, and anterior limb of the internal capsule, may represent the target brain regions at which systolic blood pressure acts on cognitive function,” the authors comment.
In an accompanying editorial, Ernesto Schiffrin, MD, and James Engert, PhD, McGill University, Montreal, say that further mechanistic studies of the effects of blood pressure on cognitive function are required to determine precise causal pathways and the roles of relevant brain regions.
“Eventually, biomarkers could be developed to inform antihypertensive trials. Whether clinical trials targeting the specific brain structures will be feasible or if specific antihypertensives could be found that target specific structures remains to be demonstrated,” they write.
“Thus, these new studies could lead to an understanding of the signaling pathways that explain how these structures relate vascular damage to cognitive impairment in hypertension, and contribute to the development of novel interventions to more successfully address the scourge of cognitive decline and dementia in the future,” the editorialists conclude.
The study was funded by the European Research Council, the British Heart Foundation, and the Italian Ministry of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Some diets better than others for heart protection
In an analysis of randomized trials, the Mediterranean diet and low-fat diets were linked to reduced risks of all-cause mortality and nonfatal MI over 3 years in adults at increased risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD), while the Mediterranean diet also showed lower risk of stroke.
Five other popular diets appeared to have little or no benefit with regard to these outcomes.
“These findings with data presentations are extremely important for patients who are skeptical about the desirability of diet change,” wrote the authors, led by Giorgio Karam, a medical student at the University of Manitoba, Winnipeg.
The results were published online in The BMJ.
Dietary guidelines recommend various diets along with physical activity or other cointerventions for adults at increased CVD risk, but they are often based on low-certainty evidence from nonrandomized studies and on surrogate outcomes.
Several meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials with mortality and major CV outcomes have reported benefits of some dietary programs, but those studies did not use network meta-analysis to give absolute estimates and certainty of estimates for adults at intermediate and high risk, the authors noted.
For this study, Mr. Karam and colleagues conducted a comprehensive systematic review and network meta-analysis in which they compared the effects of seven popular structured diets on mortality and CVD events for adults with CVD or CVD risk factors.
The seven diet plans were the Mediterranean, low fat, very low fat, modified fat, combined low fat and low sodium, Ornish, and Pritikin diets. Data for the analysis came from 40 randomized controlled trials that involved 35,548 participants who were followed for an average of 3 years.
There was evidence of “moderate” certainty that the Mediterranean diet was superior to minimal intervention for all-cause mortality (odds ratio [OR], 0.72), CV mortality (OR, 0.55), stroke (OR, 0.65), and nonfatal MI (OR, 0.48).
On an absolute basis (per 1,000 over 5 years), the Mediterranean diet let to 17 fewer deaths from any cause, 13 fewer CV deaths, seven fewer strokes, and 17 fewer nonfatal MIs.
There was evidence of moderate certainty that a low-fat diet was superior to minimal intervention for prevention of all-cause mortality (OR, 0.84; nine fewer deaths per 1,000) and nonfatal MI (OR, 0.77; seven fewer deaths per 1,000). The low-fat diet had little to no benefit with regard to stroke reduction.
The Mediterranean diet was not “convincingly” superior to a low-fat diet for mortality or nonfatal MI, the authors noted.
The absolute effects for the Mediterranean and low-fat diets were more pronounced in adults at high CVD risk. With the Mediterranean diet, there were 36 fewer all-cause deaths and 39 fewer CV deaths per 1,000 over 5 years.
The five other dietary programs generally had “little or no benefit” compared with minimal intervention. The evidence was of low to moderate certainty.
The studies did not provide enough data to gauge the impact of the diets on angina, heart failure, peripheral vascular events, and atrial fibrillation.
The researchers say that strengths of their analysis include a comprehensive review and thorough literature search and a rigorous assessment of study bias. In addition, the researchers adhered to recognized GRADE methods for assessing the certainty of estimates.
Limitations of their work include not being able to measure adherence to dietary programs and the possibility that some of the benefits may have been due to other factors, such as drug treatment and support for quitting smoking.
The study had no specific funding. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In an analysis of randomized trials, the Mediterranean diet and low-fat diets were linked to reduced risks of all-cause mortality and nonfatal MI over 3 years in adults at increased risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD), while the Mediterranean diet also showed lower risk of stroke.
Five other popular diets appeared to have little or no benefit with regard to these outcomes.
“These findings with data presentations are extremely important for patients who are skeptical about the desirability of diet change,” wrote the authors, led by Giorgio Karam, a medical student at the University of Manitoba, Winnipeg.
The results were published online in The BMJ.
Dietary guidelines recommend various diets along with physical activity or other cointerventions for adults at increased CVD risk, but they are often based on low-certainty evidence from nonrandomized studies and on surrogate outcomes.
Several meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials with mortality and major CV outcomes have reported benefits of some dietary programs, but those studies did not use network meta-analysis to give absolute estimates and certainty of estimates for adults at intermediate and high risk, the authors noted.
For this study, Mr. Karam and colleagues conducted a comprehensive systematic review and network meta-analysis in which they compared the effects of seven popular structured diets on mortality and CVD events for adults with CVD or CVD risk factors.
The seven diet plans were the Mediterranean, low fat, very low fat, modified fat, combined low fat and low sodium, Ornish, and Pritikin diets. Data for the analysis came from 40 randomized controlled trials that involved 35,548 participants who were followed for an average of 3 years.
There was evidence of “moderate” certainty that the Mediterranean diet was superior to minimal intervention for all-cause mortality (odds ratio [OR], 0.72), CV mortality (OR, 0.55), stroke (OR, 0.65), and nonfatal MI (OR, 0.48).
On an absolute basis (per 1,000 over 5 years), the Mediterranean diet let to 17 fewer deaths from any cause, 13 fewer CV deaths, seven fewer strokes, and 17 fewer nonfatal MIs.
There was evidence of moderate certainty that a low-fat diet was superior to minimal intervention for prevention of all-cause mortality (OR, 0.84; nine fewer deaths per 1,000) and nonfatal MI (OR, 0.77; seven fewer deaths per 1,000). The low-fat diet had little to no benefit with regard to stroke reduction.
The Mediterranean diet was not “convincingly” superior to a low-fat diet for mortality or nonfatal MI, the authors noted.
The absolute effects for the Mediterranean and low-fat diets were more pronounced in adults at high CVD risk. With the Mediterranean diet, there were 36 fewer all-cause deaths and 39 fewer CV deaths per 1,000 over 5 years.
The five other dietary programs generally had “little or no benefit” compared with minimal intervention. The evidence was of low to moderate certainty.
The studies did not provide enough data to gauge the impact of the diets on angina, heart failure, peripheral vascular events, and atrial fibrillation.
The researchers say that strengths of their analysis include a comprehensive review and thorough literature search and a rigorous assessment of study bias. In addition, the researchers adhered to recognized GRADE methods for assessing the certainty of estimates.
Limitations of their work include not being able to measure adherence to dietary programs and the possibility that some of the benefits may have been due to other factors, such as drug treatment and support for quitting smoking.
The study had no specific funding. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In an analysis of randomized trials, the Mediterranean diet and low-fat diets were linked to reduced risks of all-cause mortality and nonfatal MI over 3 years in adults at increased risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD), while the Mediterranean diet also showed lower risk of stroke.
Five other popular diets appeared to have little or no benefit with regard to these outcomes.
“These findings with data presentations are extremely important for patients who are skeptical about the desirability of diet change,” wrote the authors, led by Giorgio Karam, a medical student at the University of Manitoba, Winnipeg.
The results were published online in The BMJ.
Dietary guidelines recommend various diets along with physical activity or other cointerventions for adults at increased CVD risk, but they are often based on low-certainty evidence from nonrandomized studies and on surrogate outcomes.
Several meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials with mortality and major CV outcomes have reported benefits of some dietary programs, but those studies did not use network meta-analysis to give absolute estimates and certainty of estimates for adults at intermediate and high risk, the authors noted.
For this study, Mr. Karam and colleagues conducted a comprehensive systematic review and network meta-analysis in which they compared the effects of seven popular structured diets on mortality and CVD events for adults with CVD or CVD risk factors.
The seven diet plans were the Mediterranean, low fat, very low fat, modified fat, combined low fat and low sodium, Ornish, and Pritikin diets. Data for the analysis came from 40 randomized controlled trials that involved 35,548 participants who were followed for an average of 3 years.
There was evidence of “moderate” certainty that the Mediterranean diet was superior to minimal intervention for all-cause mortality (odds ratio [OR], 0.72), CV mortality (OR, 0.55), stroke (OR, 0.65), and nonfatal MI (OR, 0.48).
On an absolute basis (per 1,000 over 5 years), the Mediterranean diet let to 17 fewer deaths from any cause, 13 fewer CV deaths, seven fewer strokes, and 17 fewer nonfatal MIs.
There was evidence of moderate certainty that a low-fat diet was superior to minimal intervention for prevention of all-cause mortality (OR, 0.84; nine fewer deaths per 1,000) and nonfatal MI (OR, 0.77; seven fewer deaths per 1,000). The low-fat diet had little to no benefit with regard to stroke reduction.
The Mediterranean diet was not “convincingly” superior to a low-fat diet for mortality or nonfatal MI, the authors noted.
The absolute effects for the Mediterranean and low-fat diets were more pronounced in adults at high CVD risk. With the Mediterranean diet, there were 36 fewer all-cause deaths and 39 fewer CV deaths per 1,000 over 5 years.
The five other dietary programs generally had “little or no benefit” compared with minimal intervention. The evidence was of low to moderate certainty.
The studies did not provide enough data to gauge the impact of the diets on angina, heart failure, peripheral vascular events, and atrial fibrillation.
The researchers say that strengths of their analysis include a comprehensive review and thorough literature search and a rigorous assessment of study bias. In addition, the researchers adhered to recognized GRADE methods for assessing the certainty of estimates.
Limitations of their work include not being able to measure adherence to dietary programs and the possibility that some of the benefits may have been due to other factors, such as drug treatment and support for quitting smoking.
The study had no specific funding. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
One or two high-step days may reduce mortality risks
Taking 8,000 steps or more for just 1 or 2 days a week was linked to a significant reduction in all-cause and cardiovascular mortality, according to a study of about 3,000 adults.
Previous research has shown lower mortality rates among individuals who walk consistently, especially those who log at least 8,000 steps daily, but the benefit of intense walking just once or twice a week on long-term health outcomes has not been examined, wrote Kosuke Inoue, MD, of Kyoto University, Japan, and colleagues.
In a study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers reviewed 10-year follow-up data for 3,101 adults aged 20 years and older who were part of the 2005 and 2006 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES).
The participants were asked to wear accelerometers to track their steps for 7 consecutive days. The researchers assessed the dose-response relationship between days of taking 8,000 steps or more (about 4 miles) during 1 week, and the primary outcome of all-cause mortality risk after 10 years. Cardiovascular mortality risk after 10 years was a secondary outcome.
The mean age of the participants was 50.5 years and 51% were women. The breakdown by ethnicity was 51% White, 21% Black, 24% Hispanic, and 4% other races/ethnicities. A total of 632 individuals took 8,000 steps or more 0 days a week, 532 took at least 8,000 steps 1-2 days per week, and 1,937 took at least 8,000 steps 3-7 days a week.
During the 10-year follow-up period, overall all-cause mortality was 14.2% and cardiovascular mortality was 5.3% across all step groups.
In an adjusted analysis, individuals who took at least 8,000 steps 1-2 days a week had a 14.9% lower all-cause mortality risk compared with those who never reached 8,000 daily steps. This difference was similar to the 16.5% reduced mortality risk for those who took at least 8,000 steps 3-7 days a week.
Similarly, compared with the group with no days of at least 8,000 steps, cardiovascular mortality risk was 8.1% lower for those who took 8,000 steps 1-2 days per week and 8.4% lower for those who took at least 8,000 steps 3-7 days per week. The decreased mortality risk plateaued at 3-4 days.
These patterns in reduced all-cause mortality risk persisted in a stratified analysis by age (younger than 65 years and 65 years and older) and sex. Similar patterns in reduced mortality also emerged when the researchers used different thresholds of daily steps, such as a minimum of 10,000 steps instead of 8,000. The adjusted all-cause mortality for groups who took at least 10,000 steps 1-2 days a week, 3-7 days a week, and no days a week were 8.1%, 7.3%, and 16.7%, respectively, with corresponding cardiovascular mortality risks of 2.4%, 2.3%, and 7.0%, respectively.
“Given the simplicity and ease of counting daily steps, our findings indicate that the recommended number of steps taken on as few as 1 to 2 days per week may be a feasible option for individuals who are striving to achieve some health benefits through adhering to a recommended daily step count but are unable to accomplish this on a daily basis,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The findings were limited by several factors including the use daily step measures for 1 week only at baseline, with no data on how physical activity changes might impact mortality risk, the researchers noted. Other limitations included possible accelerometer error and misclassification of activity, possible selection bias, and lack of data on cause-specific mortality outside of cardiovascular death, they said.
However, the results were strengthened by the use of accelerometers as objective measures of activity and by the availability of 10-year follow-up data for nearly 100% of the participants, they said.
“Although our findings might suffer from residual confounding that should be addressed in future research, they suggest that people may receive substantial health benefits even if a sufficient number of steps are taken on only a couple days of the week,” they concluded.
Proceed with caution
The current study findings should be interpreted cautiously in light of the potential unmeasured confounding factors and selection bias that often occur in studies of physical activity, James Sawalla Guseh, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, and Jose F. Figueroa, MD, of Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
The results support previous studies showing some longevity benefits with “weekend warrior” patterns of intense physical activity for only a couple of days; however, “the body of evidence for sporadic activity is not as robust as the evidence for sustained and regular aerobic activity,” the authors emphasized.
The editorial authors also highlighted the limitations of the current study, including the observational design and significant differences in demographics and comorbidities between the 1- to 2-days of 8,000 steps exercise group and the 0-day group, as well as the reliance on only a week’s worth of data to infer 10 years’ mortality.
Although the data are consistent with previous observations that increased exercise volume reduces mortality, more research is needed, as the current study findings may not reflect other dimensions of health, including neurological health, they said.
Despite the need for cautious interpretation of the results, the current study “supports the emerging and popular idea that step counting, which does not require consideration of exercise duration or intensity, can offer guidance toward robust and favorable health outcomes,” and may inform step-based activity goals to improve public health, the editorialists wrote.
The study was supported by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, the Japan Endocrine Society, and the Meiji Yasuda Life Foundation of Health and Welfare. Dr. Inoue also was supported by the Program for the Development of Next-Generation Leading Scientists With Global Insight sponsored by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan. The other researchers had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose. The editorial authors had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Taking 8,000 steps or more for just 1 or 2 days a week was linked to a significant reduction in all-cause and cardiovascular mortality, according to a study of about 3,000 adults.
Previous research has shown lower mortality rates among individuals who walk consistently, especially those who log at least 8,000 steps daily, but the benefit of intense walking just once or twice a week on long-term health outcomes has not been examined, wrote Kosuke Inoue, MD, of Kyoto University, Japan, and colleagues.
In a study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers reviewed 10-year follow-up data for 3,101 adults aged 20 years and older who were part of the 2005 and 2006 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES).
The participants were asked to wear accelerometers to track their steps for 7 consecutive days. The researchers assessed the dose-response relationship between days of taking 8,000 steps or more (about 4 miles) during 1 week, and the primary outcome of all-cause mortality risk after 10 years. Cardiovascular mortality risk after 10 years was a secondary outcome.
The mean age of the participants was 50.5 years and 51% were women. The breakdown by ethnicity was 51% White, 21% Black, 24% Hispanic, and 4% other races/ethnicities. A total of 632 individuals took 8,000 steps or more 0 days a week, 532 took at least 8,000 steps 1-2 days per week, and 1,937 took at least 8,000 steps 3-7 days a week.
During the 10-year follow-up period, overall all-cause mortality was 14.2% and cardiovascular mortality was 5.3% across all step groups.
In an adjusted analysis, individuals who took at least 8,000 steps 1-2 days a week had a 14.9% lower all-cause mortality risk compared with those who never reached 8,000 daily steps. This difference was similar to the 16.5% reduced mortality risk for those who took at least 8,000 steps 3-7 days a week.
Similarly, compared with the group with no days of at least 8,000 steps, cardiovascular mortality risk was 8.1% lower for those who took 8,000 steps 1-2 days per week and 8.4% lower for those who took at least 8,000 steps 3-7 days per week. The decreased mortality risk plateaued at 3-4 days.
These patterns in reduced all-cause mortality risk persisted in a stratified analysis by age (younger than 65 years and 65 years and older) and sex. Similar patterns in reduced mortality also emerged when the researchers used different thresholds of daily steps, such as a minimum of 10,000 steps instead of 8,000. The adjusted all-cause mortality for groups who took at least 10,000 steps 1-2 days a week, 3-7 days a week, and no days a week were 8.1%, 7.3%, and 16.7%, respectively, with corresponding cardiovascular mortality risks of 2.4%, 2.3%, and 7.0%, respectively.
“Given the simplicity and ease of counting daily steps, our findings indicate that the recommended number of steps taken on as few as 1 to 2 days per week may be a feasible option for individuals who are striving to achieve some health benefits through adhering to a recommended daily step count but are unable to accomplish this on a daily basis,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The findings were limited by several factors including the use daily step measures for 1 week only at baseline, with no data on how physical activity changes might impact mortality risk, the researchers noted. Other limitations included possible accelerometer error and misclassification of activity, possible selection bias, and lack of data on cause-specific mortality outside of cardiovascular death, they said.
However, the results were strengthened by the use of accelerometers as objective measures of activity and by the availability of 10-year follow-up data for nearly 100% of the participants, they said.
“Although our findings might suffer from residual confounding that should be addressed in future research, they suggest that people may receive substantial health benefits even if a sufficient number of steps are taken on only a couple days of the week,” they concluded.
Proceed with caution
The current study findings should be interpreted cautiously in light of the potential unmeasured confounding factors and selection bias that often occur in studies of physical activity, James Sawalla Guseh, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, and Jose F. Figueroa, MD, of Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
The results support previous studies showing some longevity benefits with “weekend warrior” patterns of intense physical activity for only a couple of days; however, “the body of evidence for sporadic activity is not as robust as the evidence for sustained and regular aerobic activity,” the authors emphasized.
The editorial authors also highlighted the limitations of the current study, including the observational design and significant differences in demographics and comorbidities between the 1- to 2-days of 8,000 steps exercise group and the 0-day group, as well as the reliance on only a week’s worth of data to infer 10 years’ mortality.
Although the data are consistent with previous observations that increased exercise volume reduces mortality, more research is needed, as the current study findings may not reflect other dimensions of health, including neurological health, they said.
Despite the need for cautious interpretation of the results, the current study “supports the emerging and popular idea that step counting, which does not require consideration of exercise duration or intensity, can offer guidance toward robust and favorable health outcomes,” and may inform step-based activity goals to improve public health, the editorialists wrote.
The study was supported by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, the Japan Endocrine Society, and the Meiji Yasuda Life Foundation of Health and Welfare. Dr. Inoue also was supported by the Program for the Development of Next-Generation Leading Scientists With Global Insight sponsored by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan. The other researchers had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose. The editorial authors had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Taking 8,000 steps or more for just 1 or 2 days a week was linked to a significant reduction in all-cause and cardiovascular mortality, according to a study of about 3,000 adults.
Previous research has shown lower mortality rates among individuals who walk consistently, especially those who log at least 8,000 steps daily, but the benefit of intense walking just once or twice a week on long-term health outcomes has not been examined, wrote Kosuke Inoue, MD, of Kyoto University, Japan, and colleagues.
In a study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers reviewed 10-year follow-up data for 3,101 adults aged 20 years and older who were part of the 2005 and 2006 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES).
The participants were asked to wear accelerometers to track their steps for 7 consecutive days. The researchers assessed the dose-response relationship between days of taking 8,000 steps or more (about 4 miles) during 1 week, and the primary outcome of all-cause mortality risk after 10 years. Cardiovascular mortality risk after 10 years was a secondary outcome.
The mean age of the participants was 50.5 years and 51% were women. The breakdown by ethnicity was 51% White, 21% Black, 24% Hispanic, and 4% other races/ethnicities. A total of 632 individuals took 8,000 steps or more 0 days a week, 532 took at least 8,000 steps 1-2 days per week, and 1,937 took at least 8,000 steps 3-7 days a week.
During the 10-year follow-up period, overall all-cause mortality was 14.2% and cardiovascular mortality was 5.3% across all step groups.
In an adjusted analysis, individuals who took at least 8,000 steps 1-2 days a week had a 14.9% lower all-cause mortality risk compared with those who never reached 8,000 daily steps. This difference was similar to the 16.5% reduced mortality risk for those who took at least 8,000 steps 3-7 days a week.
Similarly, compared with the group with no days of at least 8,000 steps, cardiovascular mortality risk was 8.1% lower for those who took 8,000 steps 1-2 days per week and 8.4% lower for those who took at least 8,000 steps 3-7 days per week. The decreased mortality risk plateaued at 3-4 days.
These patterns in reduced all-cause mortality risk persisted in a stratified analysis by age (younger than 65 years and 65 years and older) and sex. Similar patterns in reduced mortality also emerged when the researchers used different thresholds of daily steps, such as a minimum of 10,000 steps instead of 8,000. The adjusted all-cause mortality for groups who took at least 10,000 steps 1-2 days a week, 3-7 days a week, and no days a week were 8.1%, 7.3%, and 16.7%, respectively, with corresponding cardiovascular mortality risks of 2.4%, 2.3%, and 7.0%, respectively.
“Given the simplicity and ease of counting daily steps, our findings indicate that the recommended number of steps taken on as few as 1 to 2 days per week may be a feasible option for individuals who are striving to achieve some health benefits through adhering to a recommended daily step count but are unable to accomplish this on a daily basis,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The findings were limited by several factors including the use daily step measures for 1 week only at baseline, with no data on how physical activity changes might impact mortality risk, the researchers noted. Other limitations included possible accelerometer error and misclassification of activity, possible selection bias, and lack of data on cause-specific mortality outside of cardiovascular death, they said.
However, the results were strengthened by the use of accelerometers as objective measures of activity and by the availability of 10-year follow-up data for nearly 100% of the participants, they said.
“Although our findings might suffer from residual confounding that should be addressed in future research, they suggest that people may receive substantial health benefits even if a sufficient number of steps are taken on only a couple days of the week,” they concluded.
Proceed with caution
The current study findings should be interpreted cautiously in light of the potential unmeasured confounding factors and selection bias that often occur in studies of physical activity, James Sawalla Guseh, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, and Jose F. Figueroa, MD, of Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
The results support previous studies showing some longevity benefits with “weekend warrior” patterns of intense physical activity for only a couple of days; however, “the body of evidence for sporadic activity is not as robust as the evidence for sustained and regular aerobic activity,” the authors emphasized.
The editorial authors also highlighted the limitations of the current study, including the observational design and significant differences in demographics and comorbidities between the 1- to 2-days of 8,000 steps exercise group and the 0-day group, as well as the reliance on only a week’s worth of data to infer 10 years’ mortality.
Although the data are consistent with previous observations that increased exercise volume reduces mortality, more research is needed, as the current study findings may not reflect other dimensions of health, including neurological health, they said.
Despite the need for cautious interpretation of the results, the current study “supports the emerging and popular idea that step counting, which does not require consideration of exercise duration or intensity, can offer guidance toward robust and favorable health outcomes,” and may inform step-based activity goals to improve public health, the editorialists wrote.
The study was supported by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, the Japan Endocrine Society, and the Meiji Yasuda Life Foundation of Health and Welfare. Dr. Inoue also was supported by the Program for the Development of Next-Generation Leading Scientists With Global Insight sponsored by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan. The other researchers had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose. The editorial authors had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Even small changes in fitness tied to lower mortality risk
Even relatively small changes in cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) are associated with “considerable” impact on clinical symptoms and mortality risk among individuals with and without cardiovascular disease, new observational data in United States veterans suggest.
“We had a few surprises,” Peter Kokkinos, PhD, Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N. J., and the VA Medical Center, Washington, told this news organization. “First, the mortality risk was greatly attenuated in those who were moderate- and high-fit at baseline, despite a decline in fitness over time. In fact, in those with no CVD, the risk was not significantly elevated even when CRF declined by at least one MET [metabolic equivalent of task] for the moderate-fit and two or more METs for the high-fit group.”
“Second,” he said, “Our findings suggest that the impact of CRF on human health is not ephemeral, but rather carries a certain protection over time. Third, the changes in CRF necessary to impact mortality risk are relatively small (> 1.0 METs). This has a substantial clinical and public health significance.”
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
CRF up, mortality risk down
Dr. Kokkinos and colleagues analyzed data from 93,060 U.S. veterans; of these, 95% were men (mean age, 61.4 years) and 5% were women (mean age, 57.1 years). Overall, 72% of participants were White; 19.8%, African American; 5.2%, Hispanic; 1.9%, Native American, Asian, or Hawaiian; and 1.2%, unknown.
Participants were assigned to age-specific fitness quartiles based on peak METs achieved on a baseline exercise treadmill test (ETT). Each CRF quartile was stratified based on CRF changes (increase, decrease, no change) on the final ETT, with at least two ETT assessments at least 1 year apart.
The mean follow-up was 5.8 years (663,522 person-years), during which 18,302 deaths (19.7%) occurred, for an average annual mortality rate of 27.6 events per 1,000 person-years.
CRF was unchanged in 25.1% of the cohort, increased in 29.3%, and decreased in 45.6%. The trend was similar for those with and without CVD.
Significant differences were seen in all variables across CRF categories. In general, body weight, body mass index, CVD risk factors, and overall disease burden were progressively more unfavorable for those in the lowest CRF categories.
Conversely, medication use was progressively higher among those in low CRF categories.
After adjustment, higher CRF was inversely related to mortality risk for the entire cohort, with and without CVD. Cumulative survival rates across CRF categories declined progressively with increased fitness.
For patients with CVD (hazard ratio, 1.11), other significant predictors of all-cause mortality for patients were age (HR, 1.07), body mass index (HR, 0.98), chronic kidney disease (HR, 1.85), smoking (HR, 1.57), type 2 diabetes (HR, 1.42), hypertension (HR, 1.39), and cancers (HR, 1.37).
Generally, changes in CRF of at least 1.0 MET were associated with inverse and proportionate changes in mortality risk, regardless of baseline CRF status. For example, they note, a CRF decline of > 2.0 METs was associated with a 74% increased mortality risk for low-fit individuals with CVD, and a 69% increase for those without CVD.
A second analysis was done after excluding patients whose CRF declined and who died within 2 years of their last ETT, to account for the possibility that higher mortality rates and CRF declines were consequences of underlying disease (reverse causality). The association between changes in CRF and mortality risk persisted and remained similar to that observed in the entire cohort.
The authors add, “It is noteworthy that CRF increased by at least 1 MET in approximately 29% of the participants in the current study and decreased in approximately 46% of participants. This finding underscores the need to promote physical activity to maintain or increase CRF levels in middle-aged and older individuals.”
“Our findings make a persuasive argument that CRF is a strong and independent determinant of all-cause mortality risk, independent of genetic factors,” Dr. Kokkinos said. “We know that CRF is determined to some degree by genetic factors. However, improvements in aerobic capacity or CRF over time are largely the outcomes of regular engagement in aerobic activities of adequate intensity and volume.”
“Conversely,” he said, “a decline in CRF is likely the result of sedentary behavior, the onset of a chronic condition, or aging.”
If genetics were the sole contributor to mortality risk, then changes in CRF would not influence mortality risk, he concluded.
CRF impact “woefully underestimated”
Barry A. Franklin, PhD, past chair of both the American Heart Association’s Council on Physical Activity and Metabolism and the National Advocacy Committee, said the study substantiates previous smaller studies and is a “seminal” work.
“CRF is woefully underestimated as an index of health outcomes and survival,” said Dr. Franklin, director of preventive cardiology and cardiac rehabilitation at Beaumont Health in Royal Oak, Mich. “Moderate to vigorous physical activity should be regularly promoted by the medical community.”
Dr. Franklin’s recent review, published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings, provides evidence for other exercise benefits that clinicians may not be aware of, he noted. These include:
- Each 1 MET increase in CRF is generally associated with approximately 16% reduction in mortality.
- At any given risk factor profile or coronary calcium score, unfit people have 2-3 times the mortality as their fit counterparts.
- Fitness is inversely related to annual health care costs (each 1 MET increase in CRF is associated with approximately 6% lower annual health care costs).
- Physically active people hospitalized with acute coronary syndromes have better short-term outcomes (likely because of a phenomenon called ‘exercise preconditioning’).
- Fit people who undergo elective or emergent surgical procedures have better outcomes.
- Regular physical activity is a common characteristic in population subsets who routinely live into their 90s and to 100+.
Dr. Franklin had this advice for clinicians seeking to promote CRF increases of 1 MET or more among patients: “Sedentary people who embark on a walking program, who over time increase their walking speed to 3 mph or faster, invariably show at least a 1 MET increase in CRF during subsequent peak or symptom-limited treadmill testing.”
“Another general rule is that if an exercise program decreases heart rate at a given or fixed workload by about 10 beats per minute [bpm], the same treadmill workload that initially was accomplished at a heart rate of 120 bpm is now being accomplished at a heart rate of 110 bpm,” likely resulting in about a 1 MET increase in fitness.
“Accordingly,” he added, “a 20-bpm decrease would suggest a 2 MET increase in fitness!”
In a related editorial, Leonard A. Kaminsky, Ball State University, Muncie, Ind. and colleagues, write, “We agree with and believe the conclusion, reached by Kokkinos et al., bears repeating. We (again) call on both clinicians and public health professionals to adopt CRF as a key health indicator.”
“This should be done by coupling routine assessments of CRF with continued advocacy for promoting physical activity as an essential healthy lifestyle behavior,” they write.
No funding or relevant financial relationships were disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Even relatively small changes in cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) are associated with “considerable” impact on clinical symptoms and mortality risk among individuals with and without cardiovascular disease, new observational data in United States veterans suggest.
“We had a few surprises,” Peter Kokkinos, PhD, Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N. J., and the VA Medical Center, Washington, told this news organization. “First, the mortality risk was greatly attenuated in those who were moderate- and high-fit at baseline, despite a decline in fitness over time. In fact, in those with no CVD, the risk was not significantly elevated even when CRF declined by at least one MET [metabolic equivalent of task] for the moderate-fit and two or more METs for the high-fit group.”
“Second,” he said, “Our findings suggest that the impact of CRF on human health is not ephemeral, but rather carries a certain protection over time. Third, the changes in CRF necessary to impact mortality risk are relatively small (> 1.0 METs). This has a substantial clinical and public health significance.”
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
CRF up, mortality risk down
Dr. Kokkinos and colleagues analyzed data from 93,060 U.S. veterans; of these, 95% were men (mean age, 61.4 years) and 5% were women (mean age, 57.1 years). Overall, 72% of participants were White; 19.8%, African American; 5.2%, Hispanic; 1.9%, Native American, Asian, or Hawaiian; and 1.2%, unknown.
Participants were assigned to age-specific fitness quartiles based on peak METs achieved on a baseline exercise treadmill test (ETT). Each CRF quartile was stratified based on CRF changes (increase, decrease, no change) on the final ETT, with at least two ETT assessments at least 1 year apart.
The mean follow-up was 5.8 years (663,522 person-years), during which 18,302 deaths (19.7%) occurred, for an average annual mortality rate of 27.6 events per 1,000 person-years.
CRF was unchanged in 25.1% of the cohort, increased in 29.3%, and decreased in 45.6%. The trend was similar for those with and without CVD.
Significant differences were seen in all variables across CRF categories. In general, body weight, body mass index, CVD risk factors, and overall disease burden were progressively more unfavorable for those in the lowest CRF categories.
Conversely, medication use was progressively higher among those in low CRF categories.
After adjustment, higher CRF was inversely related to mortality risk for the entire cohort, with and without CVD. Cumulative survival rates across CRF categories declined progressively with increased fitness.
For patients with CVD (hazard ratio, 1.11), other significant predictors of all-cause mortality for patients were age (HR, 1.07), body mass index (HR, 0.98), chronic kidney disease (HR, 1.85), smoking (HR, 1.57), type 2 diabetes (HR, 1.42), hypertension (HR, 1.39), and cancers (HR, 1.37).
Generally, changes in CRF of at least 1.0 MET were associated with inverse and proportionate changes in mortality risk, regardless of baseline CRF status. For example, they note, a CRF decline of > 2.0 METs was associated with a 74% increased mortality risk for low-fit individuals with CVD, and a 69% increase for those without CVD.
A second analysis was done after excluding patients whose CRF declined and who died within 2 years of their last ETT, to account for the possibility that higher mortality rates and CRF declines were consequences of underlying disease (reverse causality). The association between changes in CRF and mortality risk persisted and remained similar to that observed in the entire cohort.
The authors add, “It is noteworthy that CRF increased by at least 1 MET in approximately 29% of the participants in the current study and decreased in approximately 46% of participants. This finding underscores the need to promote physical activity to maintain or increase CRF levels in middle-aged and older individuals.”
“Our findings make a persuasive argument that CRF is a strong and independent determinant of all-cause mortality risk, independent of genetic factors,” Dr. Kokkinos said. “We know that CRF is determined to some degree by genetic factors. However, improvements in aerobic capacity or CRF over time are largely the outcomes of regular engagement in aerobic activities of adequate intensity and volume.”
“Conversely,” he said, “a decline in CRF is likely the result of sedentary behavior, the onset of a chronic condition, or aging.”
If genetics were the sole contributor to mortality risk, then changes in CRF would not influence mortality risk, he concluded.
CRF impact “woefully underestimated”
Barry A. Franklin, PhD, past chair of both the American Heart Association’s Council on Physical Activity and Metabolism and the National Advocacy Committee, said the study substantiates previous smaller studies and is a “seminal” work.
“CRF is woefully underestimated as an index of health outcomes and survival,” said Dr. Franklin, director of preventive cardiology and cardiac rehabilitation at Beaumont Health in Royal Oak, Mich. “Moderate to vigorous physical activity should be regularly promoted by the medical community.”
Dr. Franklin’s recent review, published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings, provides evidence for other exercise benefits that clinicians may not be aware of, he noted. These include:
- Each 1 MET increase in CRF is generally associated with approximately 16% reduction in mortality.
- At any given risk factor profile or coronary calcium score, unfit people have 2-3 times the mortality as their fit counterparts.
- Fitness is inversely related to annual health care costs (each 1 MET increase in CRF is associated with approximately 6% lower annual health care costs).
- Physically active people hospitalized with acute coronary syndromes have better short-term outcomes (likely because of a phenomenon called ‘exercise preconditioning’).
- Fit people who undergo elective or emergent surgical procedures have better outcomes.
- Regular physical activity is a common characteristic in population subsets who routinely live into their 90s and to 100+.
Dr. Franklin had this advice for clinicians seeking to promote CRF increases of 1 MET or more among patients: “Sedentary people who embark on a walking program, who over time increase their walking speed to 3 mph or faster, invariably show at least a 1 MET increase in CRF during subsequent peak or symptom-limited treadmill testing.”
“Another general rule is that if an exercise program decreases heart rate at a given or fixed workload by about 10 beats per minute [bpm], the same treadmill workload that initially was accomplished at a heart rate of 120 bpm is now being accomplished at a heart rate of 110 bpm,” likely resulting in about a 1 MET increase in fitness.
“Accordingly,” he added, “a 20-bpm decrease would suggest a 2 MET increase in fitness!”
In a related editorial, Leonard A. Kaminsky, Ball State University, Muncie, Ind. and colleagues, write, “We agree with and believe the conclusion, reached by Kokkinos et al., bears repeating. We (again) call on both clinicians and public health professionals to adopt CRF as a key health indicator.”
“This should be done by coupling routine assessments of CRF with continued advocacy for promoting physical activity as an essential healthy lifestyle behavior,” they write.
No funding or relevant financial relationships were disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Even relatively small changes in cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) are associated with “considerable” impact on clinical symptoms and mortality risk among individuals with and without cardiovascular disease, new observational data in United States veterans suggest.
“We had a few surprises,” Peter Kokkinos, PhD, Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N. J., and the VA Medical Center, Washington, told this news organization. “First, the mortality risk was greatly attenuated in those who were moderate- and high-fit at baseline, despite a decline in fitness over time. In fact, in those with no CVD, the risk was not significantly elevated even when CRF declined by at least one MET [metabolic equivalent of task] for the moderate-fit and two or more METs for the high-fit group.”
“Second,” he said, “Our findings suggest that the impact of CRF on human health is not ephemeral, but rather carries a certain protection over time. Third, the changes in CRF necessary to impact mortality risk are relatively small (> 1.0 METs). This has a substantial clinical and public health significance.”
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
CRF up, mortality risk down
Dr. Kokkinos and colleagues analyzed data from 93,060 U.S. veterans; of these, 95% were men (mean age, 61.4 years) and 5% were women (mean age, 57.1 years). Overall, 72% of participants were White; 19.8%, African American; 5.2%, Hispanic; 1.9%, Native American, Asian, or Hawaiian; and 1.2%, unknown.
Participants were assigned to age-specific fitness quartiles based on peak METs achieved on a baseline exercise treadmill test (ETT). Each CRF quartile was stratified based on CRF changes (increase, decrease, no change) on the final ETT, with at least two ETT assessments at least 1 year apart.
The mean follow-up was 5.8 years (663,522 person-years), during which 18,302 deaths (19.7%) occurred, for an average annual mortality rate of 27.6 events per 1,000 person-years.
CRF was unchanged in 25.1% of the cohort, increased in 29.3%, and decreased in 45.6%. The trend was similar for those with and without CVD.
Significant differences were seen in all variables across CRF categories. In general, body weight, body mass index, CVD risk factors, and overall disease burden were progressively more unfavorable for those in the lowest CRF categories.
Conversely, medication use was progressively higher among those in low CRF categories.
After adjustment, higher CRF was inversely related to mortality risk for the entire cohort, with and without CVD. Cumulative survival rates across CRF categories declined progressively with increased fitness.
For patients with CVD (hazard ratio, 1.11), other significant predictors of all-cause mortality for patients were age (HR, 1.07), body mass index (HR, 0.98), chronic kidney disease (HR, 1.85), smoking (HR, 1.57), type 2 diabetes (HR, 1.42), hypertension (HR, 1.39), and cancers (HR, 1.37).
Generally, changes in CRF of at least 1.0 MET were associated with inverse and proportionate changes in mortality risk, regardless of baseline CRF status. For example, they note, a CRF decline of > 2.0 METs was associated with a 74% increased mortality risk for low-fit individuals with CVD, and a 69% increase for those without CVD.
A second analysis was done after excluding patients whose CRF declined and who died within 2 years of their last ETT, to account for the possibility that higher mortality rates and CRF declines were consequences of underlying disease (reverse causality). The association between changes in CRF and mortality risk persisted and remained similar to that observed in the entire cohort.
The authors add, “It is noteworthy that CRF increased by at least 1 MET in approximately 29% of the participants in the current study and decreased in approximately 46% of participants. This finding underscores the need to promote physical activity to maintain or increase CRF levels in middle-aged and older individuals.”
“Our findings make a persuasive argument that CRF is a strong and independent determinant of all-cause mortality risk, independent of genetic factors,” Dr. Kokkinos said. “We know that CRF is determined to some degree by genetic factors. However, improvements in aerobic capacity or CRF over time are largely the outcomes of regular engagement in aerobic activities of adequate intensity and volume.”
“Conversely,” he said, “a decline in CRF is likely the result of sedentary behavior, the onset of a chronic condition, or aging.”
If genetics were the sole contributor to mortality risk, then changes in CRF would not influence mortality risk, he concluded.
CRF impact “woefully underestimated”
Barry A. Franklin, PhD, past chair of both the American Heart Association’s Council on Physical Activity and Metabolism and the National Advocacy Committee, said the study substantiates previous smaller studies and is a “seminal” work.
“CRF is woefully underestimated as an index of health outcomes and survival,” said Dr. Franklin, director of preventive cardiology and cardiac rehabilitation at Beaumont Health in Royal Oak, Mich. “Moderate to vigorous physical activity should be regularly promoted by the medical community.”
Dr. Franklin’s recent review, published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings, provides evidence for other exercise benefits that clinicians may not be aware of, he noted. These include:
- Each 1 MET increase in CRF is generally associated with approximately 16% reduction in mortality.
- At any given risk factor profile or coronary calcium score, unfit people have 2-3 times the mortality as their fit counterparts.
- Fitness is inversely related to annual health care costs (each 1 MET increase in CRF is associated with approximately 6% lower annual health care costs).
- Physically active people hospitalized with acute coronary syndromes have better short-term outcomes (likely because of a phenomenon called ‘exercise preconditioning’).
- Fit people who undergo elective or emergent surgical procedures have better outcomes.
- Regular physical activity is a common characteristic in population subsets who routinely live into their 90s and to 100+.
Dr. Franklin had this advice for clinicians seeking to promote CRF increases of 1 MET or more among patients: “Sedentary people who embark on a walking program, who over time increase their walking speed to 3 mph or faster, invariably show at least a 1 MET increase in CRF during subsequent peak or symptom-limited treadmill testing.”
“Another general rule is that if an exercise program decreases heart rate at a given or fixed workload by about 10 beats per minute [bpm], the same treadmill workload that initially was accomplished at a heart rate of 120 bpm is now being accomplished at a heart rate of 110 bpm,” likely resulting in about a 1 MET increase in fitness.
“Accordingly,” he added, “a 20-bpm decrease would suggest a 2 MET increase in fitness!”
In a related editorial, Leonard A. Kaminsky, Ball State University, Muncie, Ind. and colleagues, write, “We agree with and believe the conclusion, reached by Kokkinos et al., bears repeating. We (again) call on both clinicians and public health professionals to adopt CRF as a key health indicator.”
“This should be done by coupling routine assessments of CRF with continued advocacy for promoting physical activity as an essential healthy lifestyle behavior,” they write.
No funding or relevant financial relationships were disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
‘Unheard of’ PAH improvement with novel drug: STELLAR
NEW ORLEANS – An investigational, first-in class agent that delivers a completely new type of intervention to patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) scored a clear win in the STELLAR trial, the first to complete among three phase 3 trials that are testing this agent.
Sotatercept, administered subcutaneously every 3 weeks for 24 weeks, improved from baseline average 6-minute walk distance (6MWD) by a significant and clinically meaningful 40.8 meters, compared with placebo, for the trial’s primary efficacy endpoint (P < .001). The treatment also “delivered broad clinical benefit across multiple domains including hemodynamics, World Health Organization functional class, disease biomarkers, risk scores and patient-reported outcomes,” Marius M. Hoeper, MD, said at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
“These results establish the clinical utility of sotatercept, administered in combination with approved PAH therapies, as a new treatment for PAH,” added Dr. Hoeper, professor and deputy director of the department of respiratory medicine at Hannover (Germany) Medical School,
“The most important aspect was the hemodynamic improvement,” with sotatercept treatment, which led to an average 235 dyn/sec per cm−5 reduction in pulmonary vascular resistance from baseline and an average cut in pulmonary artery pressure of 13.9 mm Hg from baseline, compared with placebo, a result that’s “unheard of,” Dr. Hoeper said in a press conference during the meeting.
“With other tested agents we usually see very little improvement in pulmonary artery pressure. This is a signal that we achieved some reversing of the pathological changes in the pulmonary vessels that lead to” PAH, he added.
Simultaneously with his report the findings also appeared online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
‘A new hope’ for patients with PAH
Based on the reported findings, sotatercept is a “very exciting boutique molecule” that will “offer patients with PAH a very exciting new treatment,” commented Rhonda Cooper-DeHoff, PharmD, a designated discussant and a researcher at the University of Florida, Gainesville.
“This study is a new hope for patients with PAH. Until now, they’ve had really bad outcomes, but [in this study] we see significant differences in 6MWD, hemodynamics, and risk factors. Overall, I think the benefit is greater than the risk” it may pose to patients through potential adverse effects, commented Julia Grapsa, MD, PhD, a cardiologist at St. Thomas Hospital in London, and another discussant at the meeting.
“The results are impressive” and “encouraging,” and “suggest that sotatercept may represent a new and clinically consequential addition to current medications for PAH,” wrote three clinicians from Canyons Region Intermountain Medical Center in Murray, Utah, in an editorial that accompanied the published report.
But the authors of the editorial also raised several cautions and concerns. They questioned the generalizability of the findings, noting that the patients with PAH enrolled in the study were all adults who were clinically stable and an average of more than 8 years out from their initial PAH diagnosis, and more than 90% were on stable treatment for PAH with two or three agents specific for treating the disorder. The study cohort also had a disproportionately high enrollment of patients with idiopathic (59%) or heritable (18%) forms of PAH, and the 15% of patients in the trial with connective tissue disease represented a disproportionately low prevalence of this PAH subtype.
The editorialists also called for “ongoing vigilance” for adverse effects from sotatercept treatment, although they acknowledged that the adverse effects reported to date from sotatercept are “largely reassuring.”
Death or clinical worsening cut by 84%
STELLAR randomized 323 patients at 91 sites in 21 countries with WHO Group 1 PAH and with WHO functional class II or III disease to receive either sotatercept or placebo for 24 weeks, with an option for treatment to continue beyond that until the last patient in the study reached 24 weeks on treatment, resulting in an overall median treatment duration of nearly 33 weeks.
In addition to the significant result for the primary endpoint, the 163 patients who received sotatercept had significant improvements, compared with 160 placebo-treated patients, for eight of nine secondary endpoints. The only secondary endpoint with a neutral result was for a measure of cognitive and emotional wellbeing, a parameter that was already at a normal level at baseline in most enrolled patients, Dr. Hoeper explained.
The incidence of either death or an event indicative of clinical worsening during the overall median follow-up of almost 33 weeks was 26.3% among the control patients and 5.5% among those who received sotatercept. This translated into a significant reduction for this endpoint of 84% with sotatercept treatment, compared with placebo.
The rates of treatment-emergent adverse events leading to discontinuation were roughly the same in the control and sotatercept arms, and the incidence of severe or serious treatment-emergent adverse events was higher among the control patients.
The most common adverse event on sotatercept was bleeding events, which occurred in 32% of those on sotatercept and in 16% of the control patients, but the events in the sotatercept arm were “mostly mild,” said Dr. Hoeper. The next most frequent adverse event during sotatercept treatment was appearance of telangiectasias, which occurred in 14% of those on sotatercept and in 4% of control patients.
“It’s an uncommon adverse event profile, but not unexpected for a drug with its mechanism of action,” he said.
Drug binds activin, a pathologic driver of PAH
Sotatercept is an engineered molecule that combines a section of a human immunoglobulin G molecule with a portion of the receptor for activin. This structure allows sotatercept to bind free activin molecules in a patient’s blood, thereby removing a key driver of the pulmonary vascular wall remodeling that is at the pathologic root of PAH.
“Hyperproliferation of blood vessel–wall cells” caused by activin signaling “is perhaps the most important driver of PAH,” Dr. Hoeper said. “Sotatercept allows us for the first time to target the underlying mechanism behind PAH.”
Still ongoing are the HYPERION and ZENITH phase 3 trials of sotatercept. HYPERION is enrolling patients with newly diagnosed or high-risk PAH and is expected to complete in 2028. ZENITH is enrolling patients with more advanced PAH and a higher mortality risk, with results expected in 2026.
Sotatercept has received “Breakthrough Therapy” designation and “Orphan Drug” designation by the Food and Drug Administration, and “Priority Medicines” designation and “Orphan Drug” designation by the European Medicines Agency for the treatment of PAH. One recent review estimated a worldwide PAH prevalence of about 3-4 cases/100,000, which for the United States translates into a total prevalence of perhaps 10,000-15,000 affected people.
STELLAR was funded by Acceleron Pharma, a subsidiary of Merck. Dr. Hoeper is a consultant to Acceleron. Dr. Cooper-DeHoff, Dr. Grapsa, and the authors of the editorial on STELLAR have no relevant disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – An investigational, first-in class agent that delivers a completely new type of intervention to patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) scored a clear win in the STELLAR trial, the first to complete among three phase 3 trials that are testing this agent.
Sotatercept, administered subcutaneously every 3 weeks for 24 weeks, improved from baseline average 6-minute walk distance (6MWD) by a significant and clinically meaningful 40.8 meters, compared with placebo, for the trial’s primary efficacy endpoint (P < .001). The treatment also “delivered broad clinical benefit across multiple domains including hemodynamics, World Health Organization functional class, disease biomarkers, risk scores and patient-reported outcomes,” Marius M. Hoeper, MD, said at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
“These results establish the clinical utility of sotatercept, administered in combination with approved PAH therapies, as a new treatment for PAH,” added Dr. Hoeper, professor and deputy director of the department of respiratory medicine at Hannover (Germany) Medical School,
“The most important aspect was the hemodynamic improvement,” with sotatercept treatment, which led to an average 235 dyn/sec per cm−5 reduction in pulmonary vascular resistance from baseline and an average cut in pulmonary artery pressure of 13.9 mm Hg from baseline, compared with placebo, a result that’s “unheard of,” Dr. Hoeper said in a press conference during the meeting.
“With other tested agents we usually see very little improvement in pulmonary artery pressure. This is a signal that we achieved some reversing of the pathological changes in the pulmonary vessels that lead to” PAH, he added.
Simultaneously with his report the findings also appeared online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
‘A new hope’ for patients with PAH
Based on the reported findings, sotatercept is a “very exciting boutique molecule” that will “offer patients with PAH a very exciting new treatment,” commented Rhonda Cooper-DeHoff, PharmD, a designated discussant and a researcher at the University of Florida, Gainesville.
“This study is a new hope for patients with PAH. Until now, they’ve had really bad outcomes, but [in this study] we see significant differences in 6MWD, hemodynamics, and risk factors. Overall, I think the benefit is greater than the risk” it may pose to patients through potential adverse effects, commented Julia Grapsa, MD, PhD, a cardiologist at St. Thomas Hospital in London, and another discussant at the meeting.
“The results are impressive” and “encouraging,” and “suggest that sotatercept may represent a new and clinically consequential addition to current medications for PAH,” wrote three clinicians from Canyons Region Intermountain Medical Center in Murray, Utah, in an editorial that accompanied the published report.
But the authors of the editorial also raised several cautions and concerns. They questioned the generalizability of the findings, noting that the patients with PAH enrolled in the study were all adults who were clinically stable and an average of more than 8 years out from their initial PAH diagnosis, and more than 90% were on stable treatment for PAH with two or three agents specific for treating the disorder. The study cohort also had a disproportionately high enrollment of patients with idiopathic (59%) or heritable (18%) forms of PAH, and the 15% of patients in the trial with connective tissue disease represented a disproportionately low prevalence of this PAH subtype.
The editorialists also called for “ongoing vigilance” for adverse effects from sotatercept treatment, although they acknowledged that the adverse effects reported to date from sotatercept are “largely reassuring.”
Death or clinical worsening cut by 84%
STELLAR randomized 323 patients at 91 sites in 21 countries with WHO Group 1 PAH and with WHO functional class II or III disease to receive either sotatercept or placebo for 24 weeks, with an option for treatment to continue beyond that until the last patient in the study reached 24 weeks on treatment, resulting in an overall median treatment duration of nearly 33 weeks.
In addition to the significant result for the primary endpoint, the 163 patients who received sotatercept had significant improvements, compared with 160 placebo-treated patients, for eight of nine secondary endpoints. The only secondary endpoint with a neutral result was for a measure of cognitive and emotional wellbeing, a parameter that was already at a normal level at baseline in most enrolled patients, Dr. Hoeper explained.
The incidence of either death or an event indicative of clinical worsening during the overall median follow-up of almost 33 weeks was 26.3% among the control patients and 5.5% among those who received sotatercept. This translated into a significant reduction for this endpoint of 84% with sotatercept treatment, compared with placebo.
The rates of treatment-emergent adverse events leading to discontinuation were roughly the same in the control and sotatercept arms, and the incidence of severe or serious treatment-emergent adverse events was higher among the control patients.
The most common adverse event on sotatercept was bleeding events, which occurred in 32% of those on sotatercept and in 16% of the control patients, but the events in the sotatercept arm were “mostly mild,” said Dr. Hoeper. The next most frequent adverse event during sotatercept treatment was appearance of telangiectasias, which occurred in 14% of those on sotatercept and in 4% of control patients.
“It’s an uncommon adverse event profile, but not unexpected for a drug with its mechanism of action,” he said.
Drug binds activin, a pathologic driver of PAH
Sotatercept is an engineered molecule that combines a section of a human immunoglobulin G molecule with a portion of the receptor for activin. This structure allows sotatercept to bind free activin molecules in a patient’s blood, thereby removing a key driver of the pulmonary vascular wall remodeling that is at the pathologic root of PAH.
“Hyperproliferation of blood vessel–wall cells” caused by activin signaling “is perhaps the most important driver of PAH,” Dr. Hoeper said. “Sotatercept allows us for the first time to target the underlying mechanism behind PAH.”
Still ongoing are the HYPERION and ZENITH phase 3 trials of sotatercept. HYPERION is enrolling patients with newly diagnosed or high-risk PAH and is expected to complete in 2028. ZENITH is enrolling patients with more advanced PAH and a higher mortality risk, with results expected in 2026.
Sotatercept has received “Breakthrough Therapy” designation and “Orphan Drug” designation by the Food and Drug Administration, and “Priority Medicines” designation and “Orphan Drug” designation by the European Medicines Agency for the treatment of PAH. One recent review estimated a worldwide PAH prevalence of about 3-4 cases/100,000, which for the United States translates into a total prevalence of perhaps 10,000-15,000 affected people.
STELLAR was funded by Acceleron Pharma, a subsidiary of Merck. Dr. Hoeper is a consultant to Acceleron. Dr. Cooper-DeHoff, Dr. Grapsa, and the authors of the editorial on STELLAR have no relevant disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – An investigational, first-in class agent that delivers a completely new type of intervention to patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) scored a clear win in the STELLAR trial, the first to complete among three phase 3 trials that are testing this agent.
Sotatercept, administered subcutaneously every 3 weeks for 24 weeks, improved from baseline average 6-minute walk distance (6MWD) by a significant and clinically meaningful 40.8 meters, compared with placebo, for the trial’s primary efficacy endpoint (P < .001). The treatment also “delivered broad clinical benefit across multiple domains including hemodynamics, World Health Organization functional class, disease biomarkers, risk scores and patient-reported outcomes,” Marius M. Hoeper, MD, said at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
“These results establish the clinical utility of sotatercept, administered in combination with approved PAH therapies, as a new treatment for PAH,” added Dr. Hoeper, professor and deputy director of the department of respiratory medicine at Hannover (Germany) Medical School,
“The most important aspect was the hemodynamic improvement,” with sotatercept treatment, which led to an average 235 dyn/sec per cm−5 reduction in pulmonary vascular resistance from baseline and an average cut in pulmonary artery pressure of 13.9 mm Hg from baseline, compared with placebo, a result that’s “unheard of,” Dr. Hoeper said in a press conference during the meeting.
“With other tested agents we usually see very little improvement in pulmonary artery pressure. This is a signal that we achieved some reversing of the pathological changes in the pulmonary vessels that lead to” PAH, he added.
Simultaneously with his report the findings also appeared online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
‘A new hope’ for patients with PAH
Based on the reported findings, sotatercept is a “very exciting boutique molecule” that will “offer patients with PAH a very exciting new treatment,” commented Rhonda Cooper-DeHoff, PharmD, a designated discussant and a researcher at the University of Florida, Gainesville.
“This study is a new hope for patients with PAH. Until now, they’ve had really bad outcomes, but [in this study] we see significant differences in 6MWD, hemodynamics, and risk factors. Overall, I think the benefit is greater than the risk” it may pose to patients through potential adverse effects, commented Julia Grapsa, MD, PhD, a cardiologist at St. Thomas Hospital in London, and another discussant at the meeting.
“The results are impressive” and “encouraging,” and “suggest that sotatercept may represent a new and clinically consequential addition to current medications for PAH,” wrote three clinicians from Canyons Region Intermountain Medical Center in Murray, Utah, in an editorial that accompanied the published report.
But the authors of the editorial also raised several cautions and concerns. They questioned the generalizability of the findings, noting that the patients with PAH enrolled in the study were all adults who were clinically stable and an average of more than 8 years out from their initial PAH diagnosis, and more than 90% were on stable treatment for PAH with two or three agents specific for treating the disorder. The study cohort also had a disproportionately high enrollment of patients with idiopathic (59%) or heritable (18%) forms of PAH, and the 15% of patients in the trial with connective tissue disease represented a disproportionately low prevalence of this PAH subtype.
The editorialists also called for “ongoing vigilance” for adverse effects from sotatercept treatment, although they acknowledged that the adverse effects reported to date from sotatercept are “largely reassuring.”
Death or clinical worsening cut by 84%
STELLAR randomized 323 patients at 91 sites in 21 countries with WHO Group 1 PAH and with WHO functional class II or III disease to receive either sotatercept or placebo for 24 weeks, with an option for treatment to continue beyond that until the last patient in the study reached 24 weeks on treatment, resulting in an overall median treatment duration of nearly 33 weeks.
In addition to the significant result for the primary endpoint, the 163 patients who received sotatercept had significant improvements, compared with 160 placebo-treated patients, for eight of nine secondary endpoints. The only secondary endpoint with a neutral result was for a measure of cognitive and emotional wellbeing, a parameter that was already at a normal level at baseline in most enrolled patients, Dr. Hoeper explained.
The incidence of either death or an event indicative of clinical worsening during the overall median follow-up of almost 33 weeks was 26.3% among the control patients and 5.5% among those who received sotatercept. This translated into a significant reduction for this endpoint of 84% with sotatercept treatment, compared with placebo.
The rates of treatment-emergent adverse events leading to discontinuation were roughly the same in the control and sotatercept arms, and the incidence of severe or serious treatment-emergent adverse events was higher among the control patients.
The most common adverse event on sotatercept was bleeding events, which occurred in 32% of those on sotatercept and in 16% of the control patients, but the events in the sotatercept arm were “mostly mild,” said Dr. Hoeper. The next most frequent adverse event during sotatercept treatment was appearance of telangiectasias, which occurred in 14% of those on sotatercept and in 4% of control patients.
“It’s an uncommon adverse event profile, but not unexpected for a drug with its mechanism of action,” he said.
Drug binds activin, a pathologic driver of PAH
Sotatercept is an engineered molecule that combines a section of a human immunoglobulin G molecule with a portion of the receptor for activin. This structure allows sotatercept to bind free activin molecules in a patient’s blood, thereby removing a key driver of the pulmonary vascular wall remodeling that is at the pathologic root of PAH.
“Hyperproliferation of blood vessel–wall cells” caused by activin signaling “is perhaps the most important driver of PAH,” Dr. Hoeper said. “Sotatercept allows us for the first time to target the underlying mechanism behind PAH.”
Still ongoing are the HYPERION and ZENITH phase 3 trials of sotatercept. HYPERION is enrolling patients with newly diagnosed or high-risk PAH and is expected to complete in 2028. ZENITH is enrolling patients with more advanced PAH and a higher mortality risk, with results expected in 2026.
Sotatercept has received “Breakthrough Therapy” designation and “Orphan Drug” designation by the Food and Drug Administration, and “Priority Medicines” designation and “Orphan Drug” designation by the European Medicines Agency for the treatment of PAH. One recent review estimated a worldwide PAH prevalence of about 3-4 cases/100,000, which for the United States translates into a total prevalence of perhaps 10,000-15,000 affected people.
STELLAR was funded by Acceleron Pharma, a subsidiary of Merck. Dr. Hoeper is a consultant to Acceleron. Dr. Cooper-DeHoff, Dr. Grapsa, and the authors of the editorial on STELLAR have no relevant disclosures.
At ACC 2023
What’s it like to take Ozempic? A doctor’s own story
With the rising popularity of weight-loss drug injections, I’ve received many questions from patients about the pros, cons, and costs. While Ozempic (semaglutide) is perhaps the best known, it’s technically an agent approved only for type 2 diabetes that has been used off label for obesity. The same substance, semaglutide, is approved for use in obesity, but at a higher dose, under the brand name Wegovy. Alternatives are available, and results will vary depending on the specific agent used and the individual.
Ultimately, I decided to try these new injections for myself. I am not a paid representative for, nor an advocate of, any of these medications; I’m here only to share my personal experience.
In my discussions with patients about weight, I sometimes felt like an imposter. While I was overweight by medical standards, I fortunately had none of the underlying health problems. I wasn’t on medications for blood pressure nor did I have diabetes, but I was counseling people to lose weight and eat better while not always following my own advice.
Since having children and turning 40, my metabolism, like many other women’s, seems to have plummeted. I tried a number of older weight-loss medications, like phentermine and phendimetrazine, under the supervision of medical professionals.
Each time, the efforts worked for a short while, particularly when I followed good portion control and practiced moderate exercise. Once the side effects (that is, tachycardia, palpitations, mood changes, constipation) became intolerable, or I became tired or fearful of being on the medications too long, I’d stop and I would regain some of the weight.
When the newer subcutaneous injectable medications arrived on the scene and I started to talk to my patients about them, I was intrigued by their novel mode of action and seeming benefits.
These medications, glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, were first approved for type 2 diabetes, and it soon became apparent that patients were losing significant amounts of weight taking them, so manufacturers conducted further trials in obesity patients without type 2 diabetes.
The first of these, liraglutide, is injected daily and was first approved as Victoza for type 2 diabetes; it later received an additional approval for obesity, in December 2014, as Saxenda.
Semaglutide, another of the new GLP-1 agonists, was first approved for type 2 diabetes as Ozempic but again was found to lead to substantial weight loss, so a subsequent approval of the drug for obesity, as Wegovy, came in June 2021. Semaglutide is injected once a week.
Semaglutide was branded a “game changer” when it was licensed for obesity because the mean weight loss seen in trials was around 15%, more than for any other drug and approaching what could be achieved with bariatric surgery, some doctors said.
These medications work in a different way from the older weight loss drugs, which had focused on the use of amphetamines. The newer medications became very popular because treating obesity helps lower blood glucose, blood pressure, cholesterol, kidney disease risk, and other comorbidities that occur with diabetes. Plus, for most people, there were fewer side effects.
I first tried Saxenda when it arrived on the market, via some samples that our pharmaceutical representative brought, both out of curiosity and to see if it would help me lose the stubborn baby weight. I ended up stopping the daily injections after my second or third week because of nausea and vomiting. I took a break, got a prescription for antinausea medicine, and tried again because it did indeed decrease my appetite. However, when I took my prescription to the pharmacy, my insurance wouldn’t cover it. It happens to doctors, too.
Fast-forward to 2017-2018. The baby weight was still holding on despite lifestyle changes, diet, and exercising. The newer drug classes hit the market, and again we had samples from our reps.
When Ozempic was on backorder, I switched to a low dose of Mounjaro (tirzepatide), a new dual GLP-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide agonist, approved for type 2 diabetes in May 2022, again using it off label as a weekly injection, as it isn’t currently approved for weight loss. However, it does produce significant weight loss and is awaiting approval for obesity.
With these new medications, I noticed that both my patients and I didn’t complain as much about nausea and vomiting, but I did experience stomach upset, constipation, and acid reflux.
The appetite suppression is effective. It slows down the emptying of the gut so I feel full longer. I’ve lost 30 lb with these weekly injections and would like to lose another 20 lb. I follow a routine of reasonable, portion-controlled eating and moderate exercise (30 minutes of cardiovascular activity at least two to three times a week).
Discontinuing the medications may cause rebound weight gain, especially if I’m no longer following a routine of healthy eating and/or moderate exercise. I deal with minimal constipation by taking stool softeners, and I take antacids for acid reflux.
Here’s what I recommend applying when working with patients who have obesity: First, explain how these medications work. Then conduct a health history to make sure these injections are right for them. Patients with a family history of pancreatic cancer can’t take these medications. You also want to monitor use in patients with a history of hypoglycemia so their blood sugar doesn’t drop too low. It’s also important to make sure your patients are able to afford the medication. My husband takes Ozempic for diabetes, and recently we were told that a refill would cost about $1,500 a month, even with insurance. “Covered” doesn’t necessarily mean affordable.
Take a baseline hemoglobin A1c and repeat it after the patient has been on the medication for 2-3 weeks. Also remind them that they can’t rely solely on the medication but need to practice portion control and healthier eating and to exercise more.
For myself, I want to lose those remaining 20 lb or so by eating healthy and being physically active without having to rely on medication for the rest of my life. Research on these medications is still early so we don’t know the long-term effects yet.
As clinicians, I feel it’s okay to be honest with our patients about our own personal struggles to help them understand that they are not alone and that losing weight is a challenge for everyone.
Dr. Swiner is a family physician in Durham, N.C. She reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With the rising popularity of weight-loss drug injections, I’ve received many questions from patients about the pros, cons, and costs. While Ozempic (semaglutide) is perhaps the best known, it’s technically an agent approved only for type 2 diabetes that has been used off label for obesity. The same substance, semaglutide, is approved for use in obesity, but at a higher dose, under the brand name Wegovy. Alternatives are available, and results will vary depending on the specific agent used and the individual.
Ultimately, I decided to try these new injections for myself. I am not a paid representative for, nor an advocate of, any of these medications; I’m here only to share my personal experience.
In my discussions with patients about weight, I sometimes felt like an imposter. While I was overweight by medical standards, I fortunately had none of the underlying health problems. I wasn’t on medications for blood pressure nor did I have diabetes, but I was counseling people to lose weight and eat better while not always following my own advice.
Since having children and turning 40, my metabolism, like many other women’s, seems to have plummeted. I tried a number of older weight-loss medications, like phentermine and phendimetrazine, under the supervision of medical professionals.
Each time, the efforts worked for a short while, particularly when I followed good portion control and practiced moderate exercise. Once the side effects (that is, tachycardia, palpitations, mood changes, constipation) became intolerable, or I became tired or fearful of being on the medications too long, I’d stop and I would regain some of the weight.
When the newer subcutaneous injectable medications arrived on the scene and I started to talk to my patients about them, I was intrigued by their novel mode of action and seeming benefits.
These medications, glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, were first approved for type 2 diabetes, and it soon became apparent that patients were losing significant amounts of weight taking them, so manufacturers conducted further trials in obesity patients without type 2 diabetes.
The first of these, liraglutide, is injected daily and was first approved as Victoza for type 2 diabetes; it later received an additional approval for obesity, in December 2014, as Saxenda.
Semaglutide, another of the new GLP-1 agonists, was first approved for type 2 diabetes as Ozempic but again was found to lead to substantial weight loss, so a subsequent approval of the drug for obesity, as Wegovy, came in June 2021. Semaglutide is injected once a week.
Semaglutide was branded a “game changer” when it was licensed for obesity because the mean weight loss seen in trials was around 15%, more than for any other drug and approaching what could be achieved with bariatric surgery, some doctors said.
These medications work in a different way from the older weight loss drugs, which had focused on the use of amphetamines. The newer medications became very popular because treating obesity helps lower blood glucose, blood pressure, cholesterol, kidney disease risk, and other comorbidities that occur with diabetes. Plus, for most people, there were fewer side effects.
I first tried Saxenda when it arrived on the market, via some samples that our pharmaceutical representative brought, both out of curiosity and to see if it would help me lose the stubborn baby weight. I ended up stopping the daily injections after my second or third week because of nausea and vomiting. I took a break, got a prescription for antinausea medicine, and tried again because it did indeed decrease my appetite. However, when I took my prescription to the pharmacy, my insurance wouldn’t cover it. It happens to doctors, too.
Fast-forward to 2017-2018. The baby weight was still holding on despite lifestyle changes, diet, and exercising. The newer drug classes hit the market, and again we had samples from our reps.
When Ozempic was on backorder, I switched to a low dose of Mounjaro (tirzepatide), a new dual GLP-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide agonist, approved for type 2 diabetes in May 2022, again using it off label as a weekly injection, as it isn’t currently approved for weight loss. However, it does produce significant weight loss and is awaiting approval for obesity.
With these new medications, I noticed that both my patients and I didn’t complain as much about nausea and vomiting, but I did experience stomach upset, constipation, and acid reflux.
The appetite suppression is effective. It slows down the emptying of the gut so I feel full longer. I’ve lost 30 lb with these weekly injections and would like to lose another 20 lb. I follow a routine of reasonable, portion-controlled eating and moderate exercise (30 minutes of cardiovascular activity at least two to three times a week).
Discontinuing the medications may cause rebound weight gain, especially if I’m no longer following a routine of healthy eating and/or moderate exercise. I deal with minimal constipation by taking stool softeners, and I take antacids for acid reflux.
Here’s what I recommend applying when working with patients who have obesity: First, explain how these medications work. Then conduct a health history to make sure these injections are right for them. Patients with a family history of pancreatic cancer can’t take these medications. You also want to monitor use in patients with a history of hypoglycemia so their blood sugar doesn’t drop too low. It’s also important to make sure your patients are able to afford the medication. My husband takes Ozempic for diabetes, and recently we were told that a refill would cost about $1,500 a month, even with insurance. “Covered” doesn’t necessarily mean affordable.
Take a baseline hemoglobin A1c and repeat it after the patient has been on the medication for 2-3 weeks. Also remind them that they can’t rely solely on the medication but need to practice portion control and healthier eating and to exercise more.
For myself, I want to lose those remaining 20 lb or so by eating healthy and being physically active without having to rely on medication for the rest of my life. Research on these medications is still early so we don’t know the long-term effects yet.
As clinicians, I feel it’s okay to be honest with our patients about our own personal struggles to help them understand that they are not alone and that losing weight is a challenge for everyone.
Dr. Swiner is a family physician in Durham, N.C. She reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With the rising popularity of weight-loss drug injections, I’ve received many questions from patients about the pros, cons, and costs. While Ozempic (semaglutide) is perhaps the best known, it’s technically an agent approved only for type 2 diabetes that has been used off label for obesity. The same substance, semaglutide, is approved for use in obesity, but at a higher dose, under the brand name Wegovy. Alternatives are available, and results will vary depending on the specific agent used and the individual.
Ultimately, I decided to try these new injections for myself. I am not a paid representative for, nor an advocate of, any of these medications; I’m here only to share my personal experience.
In my discussions with patients about weight, I sometimes felt like an imposter. While I was overweight by medical standards, I fortunately had none of the underlying health problems. I wasn’t on medications for blood pressure nor did I have diabetes, but I was counseling people to lose weight and eat better while not always following my own advice.
Since having children and turning 40, my metabolism, like many other women’s, seems to have plummeted. I tried a number of older weight-loss medications, like phentermine and phendimetrazine, under the supervision of medical professionals.
Each time, the efforts worked for a short while, particularly when I followed good portion control and practiced moderate exercise. Once the side effects (that is, tachycardia, palpitations, mood changes, constipation) became intolerable, or I became tired or fearful of being on the medications too long, I’d stop and I would regain some of the weight.
When the newer subcutaneous injectable medications arrived on the scene and I started to talk to my patients about them, I was intrigued by their novel mode of action and seeming benefits.
These medications, glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, were first approved for type 2 diabetes, and it soon became apparent that patients were losing significant amounts of weight taking them, so manufacturers conducted further trials in obesity patients without type 2 diabetes.
The first of these, liraglutide, is injected daily and was first approved as Victoza for type 2 diabetes; it later received an additional approval for obesity, in December 2014, as Saxenda.
Semaglutide, another of the new GLP-1 agonists, was first approved for type 2 diabetes as Ozempic but again was found to lead to substantial weight loss, so a subsequent approval of the drug for obesity, as Wegovy, came in June 2021. Semaglutide is injected once a week.
Semaglutide was branded a “game changer” when it was licensed for obesity because the mean weight loss seen in trials was around 15%, more than for any other drug and approaching what could be achieved with bariatric surgery, some doctors said.
These medications work in a different way from the older weight loss drugs, which had focused on the use of amphetamines. The newer medications became very popular because treating obesity helps lower blood glucose, blood pressure, cholesterol, kidney disease risk, and other comorbidities that occur with diabetes. Plus, for most people, there were fewer side effects.
I first tried Saxenda when it arrived on the market, via some samples that our pharmaceutical representative brought, both out of curiosity and to see if it would help me lose the stubborn baby weight. I ended up stopping the daily injections after my second or third week because of nausea and vomiting. I took a break, got a prescription for antinausea medicine, and tried again because it did indeed decrease my appetite. However, when I took my prescription to the pharmacy, my insurance wouldn’t cover it. It happens to doctors, too.
Fast-forward to 2017-2018. The baby weight was still holding on despite lifestyle changes, diet, and exercising. The newer drug classes hit the market, and again we had samples from our reps.
When Ozempic was on backorder, I switched to a low dose of Mounjaro (tirzepatide), a new dual GLP-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide agonist, approved for type 2 diabetes in May 2022, again using it off label as a weekly injection, as it isn’t currently approved for weight loss. However, it does produce significant weight loss and is awaiting approval for obesity.
With these new medications, I noticed that both my patients and I didn’t complain as much about nausea and vomiting, but I did experience stomach upset, constipation, and acid reflux.
The appetite suppression is effective. It slows down the emptying of the gut so I feel full longer. I’ve lost 30 lb with these weekly injections and would like to lose another 20 lb. I follow a routine of reasonable, portion-controlled eating and moderate exercise (30 minutes of cardiovascular activity at least two to three times a week).
Discontinuing the medications may cause rebound weight gain, especially if I’m no longer following a routine of healthy eating and/or moderate exercise. I deal with minimal constipation by taking stool softeners, and I take antacids for acid reflux.
Here’s what I recommend applying when working with patients who have obesity: First, explain how these medications work. Then conduct a health history to make sure these injections are right for them. Patients with a family history of pancreatic cancer can’t take these medications. You also want to monitor use in patients with a history of hypoglycemia so their blood sugar doesn’t drop too low. It’s also important to make sure your patients are able to afford the medication. My husband takes Ozempic for diabetes, and recently we were told that a refill would cost about $1,500 a month, even with insurance. “Covered” doesn’t necessarily mean affordable.
Take a baseline hemoglobin A1c and repeat it after the patient has been on the medication for 2-3 weeks. Also remind them that they can’t rely solely on the medication but need to practice portion control and healthier eating and to exercise more.
For myself, I want to lose those remaining 20 lb or so by eating healthy and being physically active without having to rely on medication for the rest of my life. Research on these medications is still early so we don’t know the long-term effects yet.
As clinicians, I feel it’s okay to be honest with our patients about our own personal struggles to help them understand that they are not alone and that losing weight is a challenge for everyone.
Dr. Swiner is a family physician in Durham, N.C. She reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Keto-like’ diet linked to doubling of heart disease risk
Consumption of a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet, dubbed a “keto-like” diet, was associated with an increase in LDL levels and a twofold increase in the risk for future cardiovascular events, in a new observational study.
“To our knowledge this is the first study to demonstrate an association between a carbohydrate-restricted dietary platform and greater risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” said study investigator Iulia Iatan, MD, PhD, University of British Columbia, Vancouver.
“Hypercholesterolemia occurring during a low-carb, high-fat diet should not be assumed to be benign,” she concluded.
Dr. Iatan presented the study March 5 at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
The presentation received much media attention, with headlines implying a causal relationship with cardiac events based on these observational results. But lipid expert Steven Nissen, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic, warned against paying much attention to the headlines or to the study’s conclusions.
In an interview, Dr. Nissen pointed out that the LDL increase in the “keto-like” diet group was relatively small and “certainly not enough to produce a doubling in cardiovascular risk.
“The people who were on the ‘keto-like’ diet in this study were different than those who were on the standard diet,” he said. “Those on the ‘keto-like’ diet were on it for a reason – they were more overweight, they had a higher incidence of diabetes, so their risk profile was completely different. Even though the researchers tried to adjust for other cardiovascular risk factors, there will be unmeasured confounding in a study like this.”
He said he doesn’t think this study “answers any significant questions in a way that we want to have them answered. I’m not a big fan of this type of diet, but I don’t think it doubles the risk of adverse cardiovascular events, and I don’t think this study tells us one way or another.”
For the study, Dr. Iatan and colleagues defined a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet as consisting of no more than 25% of total daily energy from carbohydrates and more than 45% of total daily calories from fat. This is somewhat higher in carbohydrates and lower in fat than a strict ketogenic diet but could be thought of as a ‘keto-like’ diet.
They analyzed data from the UK Biobank, a large-scale prospective database with health information from over half a million people living in the United Kingdom who were followed for at least 10 years.
On enrollment in the Biobank, participants completed a one-time, self-reported 24-hour diet questionnaire and, at the same time, had blood drawn to check their levels of cholesterol. The researchers identified 305 participants whose questionnaire responses indicated that they followed a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet. These participants were matched by age and sex with 1,220 individuals who reported being on a standard diet.
Of the study population, 73% were women and the average age was 54 years. Those on a low carbohydrate/high fat diet had a higher average body mass index (27.7 vs. 26.7) and a higher incidence of diabetes (4.9% vs. 1.7%).
Results showed that compared with participants on a standard diet, those on the “keto-like” diet had significantly higher levels of both LDL cholesterol and apolipoprotein B (ApoB).
Levels of LDL were 3.80 mmol/L (147 mg/dL) in the keto-like group vs. 3.64 mmol/L (141 mg/dL) in the standard group (P = .004). Levels of ApoB were 1.09 g/L (109 mg/dL) in the keto-like group and 1.04 g/L (104 mg/dL) in the standard group (P < .001).
After an average of 11.8 years of follow-up, 9.8% of participants on the low-carbohydrate/high-fat diet vs. 4.3% in the standard diet group experienced one of the events included in the composite event endpoint: Angina, myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease, ischemic stroke, peripheral arterial disease, or coronary/carotid revascularization.
After adjustment for other risk factors for heart disease – diabetes, hypertension, obesity, and smoking – individuals on a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet were found to have a twofold risk of having a cardiovascular event (HR, 2.18; P < .001).
‘Closer monitoring needed’
“Our results have shown, I think for the first time, that there is an association between this increasingly popular dietary pattern and high LDL cholesterol and an increased future risk of cardiovascular events,” senior author Liam Brunham, MD, of the University of British Columbia, said in an interview. “This is concerning as there are many people out there following this type of diet, and I think it suggests there is a need for closer monitoring of these people.”
He explained that while it would be expected for cholesterol levels to rise on a high-fat diet, “there has been a perception by some that this is not worrisome as it is reflecting certain metabolic changes. What we’ve shown in this study is that if your cholesterol does increase significantly on this diet then you should not assume that this is not a problem.
“For some people with diabetes this diet can help lower blood sugar and some people can lose weight on it,” he noted, “but what our data show is that there is a subgroup of people who experience high levels of LDL and ApoB and that seems to be driving the risk.”
He pointed out that overall the mean level of LDL was only slightly increased in the individuals on the low-carb/high-fat diet but severe high cholesterol (more than 5 mmol/L or 190 mg/dL) was about doubled in that group (10% vs. 5%). And these patients had a sixfold increase in risk of cardiovascular disease (P < .001).
“This suggests that there is a subgroup of people who are susceptible to this exacerbation of hypercholesterolemia in response to a low-carb/high-fat diet.”
Dr. Brunham said his advice would be that if people choose to follow this diet, they should have their cholesterol monitored, and manage their cardiovascular risk factors.
“I wouldn’t say it is not appropriate to follow this diet based on this study,” he added. “This is just an observational study. It is not definitive. But if people do want to follow this dietary pattern because they feel there would be some benefits, then they should be aware of the potential risks and take steps to mitigate those risks.”
Jury still out
Dr. Nissen said in his view “the jury was still out” on this type of diet. “I’m open to the possibility that, particularly in the short run, a ‘keto-like’ diet may help some people lose weight and that’s a good thing. But I do not generally recommend this type of diet.”
Rather, he advises patients to follow a Mediterranean diet, which has been proven to reduce cardiovascular events in a randomized study, the PREDIMED trial.
“We can’t make decisions on what type of diet to recommend to patients based on observational studies like this where there is a lot of subtlety missing. But when studies like this are reported, the mass media seize on it. That’s not the way the public needs to be educated,” Dr. Nissen said.
“We refer to this type of study as hypothesis-generating. It raises a hypothesis. It doesn’t answer the question. It is worth looking at the question of whether a ketogenic-like diet is harmful. We don’t know at present, and I don’t think we know any more after this study,” he added.
The authors of the study reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Consumption of a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet, dubbed a “keto-like” diet, was associated with an increase in LDL levels and a twofold increase in the risk for future cardiovascular events, in a new observational study.
“To our knowledge this is the first study to demonstrate an association between a carbohydrate-restricted dietary platform and greater risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” said study investigator Iulia Iatan, MD, PhD, University of British Columbia, Vancouver.
“Hypercholesterolemia occurring during a low-carb, high-fat diet should not be assumed to be benign,” she concluded.
Dr. Iatan presented the study March 5 at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
The presentation received much media attention, with headlines implying a causal relationship with cardiac events based on these observational results. But lipid expert Steven Nissen, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic, warned against paying much attention to the headlines or to the study’s conclusions.
In an interview, Dr. Nissen pointed out that the LDL increase in the “keto-like” diet group was relatively small and “certainly not enough to produce a doubling in cardiovascular risk.
“The people who were on the ‘keto-like’ diet in this study were different than those who were on the standard diet,” he said. “Those on the ‘keto-like’ diet were on it for a reason – they were more overweight, they had a higher incidence of diabetes, so their risk profile was completely different. Even though the researchers tried to adjust for other cardiovascular risk factors, there will be unmeasured confounding in a study like this.”
He said he doesn’t think this study “answers any significant questions in a way that we want to have them answered. I’m not a big fan of this type of diet, but I don’t think it doubles the risk of adverse cardiovascular events, and I don’t think this study tells us one way or another.”
For the study, Dr. Iatan and colleagues defined a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet as consisting of no more than 25% of total daily energy from carbohydrates and more than 45% of total daily calories from fat. This is somewhat higher in carbohydrates and lower in fat than a strict ketogenic diet but could be thought of as a ‘keto-like’ diet.
They analyzed data from the UK Biobank, a large-scale prospective database with health information from over half a million people living in the United Kingdom who were followed for at least 10 years.
On enrollment in the Biobank, participants completed a one-time, self-reported 24-hour diet questionnaire and, at the same time, had blood drawn to check their levels of cholesterol. The researchers identified 305 participants whose questionnaire responses indicated that they followed a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet. These participants were matched by age and sex with 1,220 individuals who reported being on a standard diet.
Of the study population, 73% were women and the average age was 54 years. Those on a low carbohydrate/high fat diet had a higher average body mass index (27.7 vs. 26.7) and a higher incidence of diabetes (4.9% vs. 1.7%).
Results showed that compared with participants on a standard diet, those on the “keto-like” diet had significantly higher levels of both LDL cholesterol and apolipoprotein B (ApoB).
Levels of LDL were 3.80 mmol/L (147 mg/dL) in the keto-like group vs. 3.64 mmol/L (141 mg/dL) in the standard group (P = .004). Levels of ApoB were 1.09 g/L (109 mg/dL) in the keto-like group and 1.04 g/L (104 mg/dL) in the standard group (P < .001).
After an average of 11.8 years of follow-up, 9.8% of participants on the low-carbohydrate/high-fat diet vs. 4.3% in the standard diet group experienced one of the events included in the composite event endpoint: Angina, myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease, ischemic stroke, peripheral arterial disease, or coronary/carotid revascularization.
After adjustment for other risk factors for heart disease – diabetes, hypertension, obesity, and smoking – individuals on a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet were found to have a twofold risk of having a cardiovascular event (HR, 2.18; P < .001).
‘Closer monitoring needed’
“Our results have shown, I think for the first time, that there is an association between this increasingly popular dietary pattern and high LDL cholesterol and an increased future risk of cardiovascular events,” senior author Liam Brunham, MD, of the University of British Columbia, said in an interview. “This is concerning as there are many people out there following this type of diet, and I think it suggests there is a need for closer monitoring of these people.”
He explained that while it would be expected for cholesterol levels to rise on a high-fat diet, “there has been a perception by some that this is not worrisome as it is reflecting certain metabolic changes. What we’ve shown in this study is that if your cholesterol does increase significantly on this diet then you should not assume that this is not a problem.
“For some people with diabetes this diet can help lower blood sugar and some people can lose weight on it,” he noted, “but what our data show is that there is a subgroup of people who experience high levels of LDL and ApoB and that seems to be driving the risk.”
He pointed out that overall the mean level of LDL was only slightly increased in the individuals on the low-carb/high-fat diet but severe high cholesterol (more than 5 mmol/L or 190 mg/dL) was about doubled in that group (10% vs. 5%). And these patients had a sixfold increase in risk of cardiovascular disease (P < .001).
“This suggests that there is a subgroup of people who are susceptible to this exacerbation of hypercholesterolemia in response to a low-carb/high-fat diet.”
Dr. Brunham said his advice would be that if people choose to follow this diet, they should have their cholesterol monitored, and manage their cardiovascular risk factors.
“I wouldn’t say it is not appropriate to follow this diet based on this study,” he added. “This is just an observational study. It is not definitive. But if people do want to follow this dietary pattern because they feel there would be some benefits, then they should be aware of the potential risks and take steps to mitigate those risks.”
Jury still out
Dr. Nissen said in his view “the jury was still out” on this type of diet. “I’m open to the possibility that, particularly in the short run, a ‘keto-like’ diet may help some people lose weight and that’s a good thing. But I do not generally recommend this type of diet.”
Rather, he advises patients to follow a Mediterranean diet, which has been proven to reduce cardiovascular events in a randomized study, the PREDIMED trial.
“We can’t make decisions on what type of diet to recommend to patients based on observational studies like this where there is a lot of subtlety missing. But when studies like this are reported, the mass media seize on it. That’s not the way the public needs to be educated,” Dr. Nissen said.
“We refer to this type of study as hypothesis-generating. It raises a hypothesis. It doesn’t answer the question. It is worth looking at the question of whether a ketogenic-like diet is harmful. We don’t know at present, and I don’t think we know any more after this study,” he added.
The authors of the study reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Consumption of a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet, dubbed a “keto-like” diet, was associated with an increase in LDL levels and a twofold increase in the risk for future cardiovascular events, in a new observational study.
“To our knowledge this is the first study to demonstrate an association between a carbohydrate-restricted dietary platform and greater risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” said study investigator Iulia Iatan, MD, PhD, University of British Columbia, Vancouver.
“Hypercholesterolemia occurring during a low-carb, high-fat diet should not be assumed to be benign,” she concluded.
Dr. Iatan presented the study March 5 at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
The presentation received much media attention, with headlines implying a causal relationship with cardiac events based on these observational results. But lipid expert Steven Nissen, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic, warned against paying much attention to the headlines or to the study’s conclusions.
In an interview, Dr. Nissen pointed out that the LDL increase in the “keto-like” diet group was relatively small and “certainly not enough to produce a doubling in cardiovascular risk.
“The people who were on the ‘keto-like’ diet in this study were different than those who were on the standard diet,” he said. “Those on the ‘keto-like’ diet were on it for a reason – they were more overweight, they had a higher incidence of diabetes, so their risk profile was completely different. Even though the researchers tried to adjust for other cardiovascular risk factors, there will be unmeasured confounding in a study like this.”
He said he doesn’t think this study “answers any significant questions in a way that we want to have them answered. I’m not a big fan of this type of diet, but I don’t think it doubles the risk of adverse cardiovascular events, and I don’t think this study tells us one way or another.”
For the study, Dr. Iatan and colleagues defined a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet as consisting of no more than 25% of total daily energy from carbohydrates and more than 45% of total daily calories from fat. This is somewhat higher in carbohydrates and lower in fat than a strict ketogenic diet but could be thought of as a ‘keto-like’ diet.
They analyzed data from the UK Biobank, a large-scale prospective database with health information from over half a million people living in the United Kingdom who were followed for at least 10 years.
On enrollment in the Biobank, participants completed a one-time, self-reported 24-hour diet questionnaire and, at the same time, had blood drawn to check their levels of cholesterol. The researchers identified 305 participants whose questionnaire responses indicated that they followed a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet. These participants were matched by age and sex with 1,220 individuals who reported being on a standard diet.
Of the study population, 73% were women and the average age was 54 years. Those on a low carbohydrate/high fat diet had a higher average body mass index (27.7 vs. 26.7) and a higher incidence of diabetes (4.9% vs. 1.7%).
Results showed that compared with participants on a standard diet, those on the “keto-like” diet had significantly higher levels of both LDL cholesterol and apolipoprotein B (ApoB).
Levels of LDL were 3.80 mmol/L (147 mg/dL) in the keto-like group vs. 3.64 mmol/L (141 mg/dL) in the standard group (P = .004). Levels of ApoB were 1.09 g/L (109 mg/dL) in the keto-like group and 1.04 g/L (104 mg/dL) in the standard group (P < .001).
After an average of 11.8 years of follow-up, 9.8% of participants on the low-carbohydrate/high-fat diet vs. 4.3% in the standard diet group experienced one of the events included in the composite event endpoint: Angina, myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease, ischemic stroke, peripheral arterial disease, or coronary/carotid revascularization.
After adjustment for other risk factors for heart disease – diabetes, hypertension, obesity, and smoking – individuals on a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet were found to have a twofold risk of having a cardiovascular event (HR, 2.18; P < .001).
‘Closer monitoring needed’
“Our results have shown, I think for the first time, that there is an association between this increasingly popular dietary pattern and high LDL cholesterol and an increased future risk of cardiovascular events,” senior author Liam Brunham, MD, of the University of British Columbia, said in an interview. “This is concerning as there are many people out there following this type of diet, and I think it suggests there is a need for closer monitoring of these people.”
He explained that while it would be expected for cholesterol levels to rise on a high-fat diet, “there has been a perception by some that this is not worrisome as it is reflecting certain metabolic changes. What we’ve shown in this study is that if your cholesterol does increase significantly on this diet then you should not assume that this is not a problem.
“For some people with diabetes this diet can help lower blood sugar and some people can lose weight on it,” he noted, “but what our data show is that there is a subgroup of people who experience high levels of LDL and ApoB and that seems to be driving the risk.”
He pointed out that overall the mean level of LDL was only slightly increased in the individuals on the low-carb/high-fat diet but severe high cholesterol (more than 5 mmol/L or 190 mg/dL) was about doubled in that group (10% vs. 5%). And these patients had a sixfold increase in risk of cardiovascular disease (P < .001).
“This suggests that there is a subgroup of people who are susceptible to this exacerbation of hypercholesterolemia in response to a low-carb/high-fat diet.”
Dr. Brunham said his advice would be that if people choose to follow this diet, they should have their cholesterol monitored, and manage their cardiovascular risk factors.
“I wouldn’t say it is not appropriate to follow this diet based on this study,” he added. “This is just an observational study. It is not definitive. But if people do want to follow this dietary pattern because they feel there would be some benefits, then they should be aware of the potential risks and take steps to mitigate those risks.”
Jury still out
Dr. Nissen said in his view “the jury was still out” on this type of diet. “I’m open to the possibility that, particularly in the short run, a ‘keto-like’ diet may help some people lose weight and that’s a good thing. But I do not generally recommend this type of diet.”
Rather, he advises patients to follow a Mediterranean diet, which has been proven to reduce cardiovascular events in a randomized study, the PREDIMED trial.
“We can’t make decisions on what type of diet to recommend to patients based on observational studies like this where there is a lot of subtlety missing. But when studies like this are reported, the mass media seize on it. That’s not the way the public needs to be educated,” Dr. Nissen said.
“We refer to this type of study as hypothesis-generating. It raises a hypothesis. It doesn’t answer the question. It is worth looking at the question of whether a ketogenic-like diet is harmful. We don’t know at present, and I don’t think we know any more after this study,” he added.
The authors of the study reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACC 2023