User login
Eyes on ESC ‘21: Hope for EMPEROR-Preserved, guidelines remade
There will be so much more to the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology, which begins Aug. 27 with an all-virtual format, than detailed primary results of EMPEROR-Preserved, a trial that could mark a turning point for heart failure (HF) medical therapy.
Also among the featured Hot Line and Late-Breaking Science sessions are – along with many other studies – explorations of arrhythmia management (ablation or guided by loop recorder); secondary prevention, including by vaccination; oral anticoagulation, notably after transcatheter valve procedures; and colchicine or thrombosis prophylaxis in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
There will even be a head-to-head comparison of two long-familiar left atrial appendage (LAA) occluders, and a population-based, randomized trial of sodium restriction through wide-scale use of a potassium-based salt substitute.
The congress will also introduce four guideline documents at sessions throughout the Congress, one on each day. They cover new and modified recommendations for heart failure; pacing, including cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT); cardiovascular (CV) disease prevention; and, with cosponsorship from the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, valvular heart disease.
The virtues of virtual
That next year’s Congress is slated for Aug. 27-30 in Barcelona should be welcome news for anyone whose “what if” curiosity about all-virtual conferences has already been satisfied. But with experience comes wisdom, as the medical societies have learned that online scientific meetings have some winning qualities that may be worth keeping, as least for a while.
“I think there is no doubt that the digital format will continue, for several reasons. One is that this pandemic is not over,” ESC Congress program committee chair Stephan Windecker, MD, Bern (Switzerland) University Hospital, , told this news organization. “As long as it is not over, the digital format is here to stay.”
But it also appears that people who haven’t been able to attend the congress in person are keen to log in and engage online, Dr. Windecker said. The 2020 all-virtual conference drew a much younger pool of registrants, on average, than did the live conferences before the pandemic.
“I think that’s an indication of people that may be in training, in early stages of their career, or they don’t have the support from departments or from their practice, or other financial means.” But they are able to participate via computer, tablet, or smartphone, he said.
“Another advantage is that the recorded content can be replayed at the convenience of whoever wants to consume it at a later point in time,” he added. “Those are just some examples why the digital format is likely to stay,” on its own or in a new age of hybrid meetings.
New and updated guidelines
Leading off the guideline series is the document on diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic HF, which leveraged the past few busy years of HF clinical trials to arrive at a number of new recommendations and strengthened level-of-evidence ratings. It covers both drug and device therapy of HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and acute decompensated HF, and tweaks and further enshrines the concept of HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF).
Several updated recommendations for both long-used and novel medications, notably the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, will be included because of the recently appreciated evidence-based impact in HFrEF, Dr. Windecker noted.
“I think it will be particularly interesting to look for the SGLT2 inhibitors as not a completely new class of drugs, but certainly one where there has been a lot of new evidence, to look at how those drugs will be integrated in the overall care pathway.”
A top-line preview of the new HF guideline limited to drug therapy, presented at July’s Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA), provided a simple answer to a common question in the new, bountiful age of HFrEF medications: Which meds, initiated in what order?
As it happens, the new recommendation for first-line HFrEF drug therapy is not a silver bullet, but a shotgun – prompt initiation of at least four meds, one from each of four drug classes: renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRA), and SGLT2 inhibitors. Each class, as described in the document, is to be started as soon as safely feasible, in a sequence deemed appropriate for each individual patient.
Spotlight on EMPEROR-Preserved
The world already knows that the trial, which tested the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin (Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly) on top of standard therapy, “met” its primary endpoint in almost 6,000 patients with HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), who included some with HFmrEF by more contemporary definitions.
That means patients in EMPEROR-Preserved assigned to take empagliflozin showed significantly fewer events that made up the study’s primary endpoint, a composite of CV death or HF hospitalization. It appears to be the first clearly significant overall medical therapy benefit for a clinical primary endpoint in a major randomized HFpEF drug trial.
And that, pending fuller presentation of trial results at the Congress on Aug. 27, could be a huge deal for the half of HF patients with left ventricular ejection fractions (LVEF) higher than the HFrEF range.
Those early top-line results weren’t a decisive bombshell for a field now filled with hope for a practice-changing empagliflozin outcome in EMPEROR-Preserved, which isn’t a certainty. They were more like the “boom” of a mortar launching a rocket of fireworks that may explode into a chrysanthemum or green comet or, sometimes, turn out to be no more than a dud. The promise of the early cursory results critically depends on further details.
“Provided there is a compelling benefit, this is what everyone has been waiting for in this condition for decades,” Mikhail N. Kosiborod, MD, director of cardiometabolic research at Saint Luke’s Mid-America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Mo., said.
“Already knowing that the trial met the primary endpoint is obviously very intriguing and encouraging,” he added. “But there are things we don’t know, such as: What is the magnitude of benefit? And whether that benefit, whatever the magnitude, is driven by reductions in both heart failure hospitalizations and cardiovascular death, or only one of the two.”
For example: “If we see an impressive benefit for reduction of hospitalizations, but not a significant reduction in death, that would still be a huge advance. That’s because, to date, we don’t have any drug for HFpEF that has convincingly demonstrated a compelling reduction in heart failure hospitalization or improvement in symptoms, function, or quality of life,” observed Dr. Kosiborod, who wasn’t part of EMPEROR-Preserved.
There have been “suggestions” from HFrEF trials that empagliflozin and dapagliflozin (Farxiga, AstraZeneca) “have very comparable effects on at least the endpoint of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure,” he said. “So, my expectation would be that whatever is observed in EMPEROR-Preserved is likely a class effect, as well.”
Following EMPEROR-Preserved on the agenda is EMPEROR-Pooled, a patient-level combined analysis of the EMPEROR series of trials that spans the range of HF, regardless of ejection fraction or diabetes status, primarily exploring the effects of empagliflozin on renal function.
Other offerings, Friday, Aug. 27
Scheduled immediately after EMPEROR-Preserved is a presentation on the SMART-MI trial, which should clarify whether management guided by continuous ambulatory monitoring is effective in patients considered at especially high arrhythmic risk. Entry called for recent myocardial infarction and an LVEF of 36%-50% with evidence of cardiac autonomic dysfunction.
The trial randomly assigned 400 such patients to be or not be implanted with a Reveal LINQ (Medtronic) loop recorder and followed them for up to 18 months, primarily for detection of potentially serious arrhythmic events. Endpoints that involved mortality, hospitalization or other clinical events were secondary.
In a time slot preceding both SMART-MI and EMPEROR-Preserved, the GUIDE-HF trial is following a projected 3,600 patients with HF implanted with a CardioMEMS HF System (Abbott) pulmonary artery (PA) pressure sensor to explore the its value for guiding management.
The trial’s three cohorts, followed for at least 12 months, include randomized sensor-monitored and control groups of patients with New York Heart Association class 2-4 symptoms, as well as a third observational set of patients in NYHA class 3. That’s the indication for which the CardioMEMS monitor gained approval in the United States in 2014 based on the 2011 CHAMPION trial, and which fared just as well in the 2017 CHAMPION Post-Approval Study.
The Friday Hot Lines also include Dal-GenE, which has entered about 6,000 patients with recent MI to test the once-abandoned cholesterol ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitor dalcetrapib (DalCor) for any secondary-prevention benefits when used selectively. The trial’s hook: All its patients are confirmed to have the AA genotype of the rs1967309 variant in the ADCY9 gene, which has been associated with a pronounced clinical response to CETP inhibition.
Saturday, Aug. 28
The direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) have largely replaced vitamin K antagonists in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (AFib). But whether DOACs are similarly preferable in the growing world population of people who have undergone transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR or TAVI), an issue explored with variable results in the ATLANTIS and GALILEO trials, is far from settled.
The ENVISAGE-TAVI AF trial explored the question for the factor X inhibitor edoxaban (Savaysa, Lixiana, Daiichi-Sankyo) in 1,400 patients with AFib and a transfemoral TAVR in the previous 5 days, who were randomly assigned to the DOAC or standard management along with discretionary antiplatelet therapy. They’ve been followed for up to 3 years for a composite endpoint of clinical events – including death, MI, and stroke – and for major bleeding.
The day will also feature MASTER DAPT, a comparison of two dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) regimens in an estimated 4,300 patients considered to be high-risk for bleeding who had received the sirolimus-eluting Ultimaster (Terumo) coronary stent, which has a bioresorbable polymer coating.
Investigators have randomly assigned patients to receive either very-short-duration DAPT, for about a month after stenting, followed by a P2Y12 inhibitor alone for up to a year after the procedure; or a more conventional regimen of a P2Y12 inhibitor for 6-12 months with aspirin maintained for a total of 12 months.
Later that day, investigators from the FIGARO-DKD trial will present their results based on 7,437 patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD), a much fuller version than the top-line findings announced by sponsor Bayer 3 months ago.
Those top-line results suggested that patients assigned to receive the nonsteroidal nonselective mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) finerenone (Kerendia) on top of standard care benefited with a drop in risk for the primary endpoint of CV death or nonfatal CV events.
Finerenone was recently approved in the United States for treating patients with both type 2 diabetes and CKD based on the published FIDELIO-DKD trial, which had seen less CKD progression and fewer CV events in such patients who took the novel MRA.
Although similar in design to FIGARO-DKD, FIDELIO-DKD had entered fewer patients with early-stage diabetic kidney disease (DKD). That led researchers to pool the two trials’ populations to create a cohort that spans the spectrum of DKD severity. An analysis of the pooled cohort, dubbed FIDELITY, is on the schedule after FIGARO-DKD.
After FIDELITY is the prospective APAF-CRT trial that is following a projected 1,830 patients with permanent, symptomatic AFib and a recent hospitalization for AFib or HF and who were not good candidates for standard ablation. They were assigned to receive either atrioventricular junctional ablation followed by CRT, with or without a defibrillation, on top of optimal meds – a so-called “ablate-and-pace” strategy – or an implantable cardioverter defibrillator with rate-control drug therapy.
The new analysis represents the trial’s second phase in which mortality was followed for 4 years as the primary endpoint, in contrast to the previously reported initial phase that followed the first 102 patients for 2 years for the composite primary endpoint of death, worsening HF, and HF hospitalization. The first phase had halted enrollment before reaching its planned target of 280 patients after an interim analysis showed a significant benefit for ablate and pace.
Next up: DECAAF 2, a randomized assessment of whether catheter ablation for AFib guided by delayed gadolinium enhancement on MRI, a proxy for scar tissue, can be more effective than standard AFib ablation by pulmonary vein isolation alone. An estimated 900 patients with persistent AFib who had never before undergone ablation for the arrhythmia were randomly assigned to one strategy or the other and followed for AFib recurrence over 18 months.
Sunday, Aug. 29
The TOMAHAWK trial aimed to clarify the optimal timing of invasive coronary angiography for resuscitated patients with non–ST-segment elevation out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, a broad population in a setting for which there is little randomized-trial guidance. Investigators randomly assigned 558 such patients to undergo immediate invasive angiography or to direct intensive care unit admission for initial standard care with discretionary delayed angiography. Patients were followed for all-cause mortality, with other clinical events and neurologic outcomes as secondary endpoints.
Next on the schedule, the RIPCORD-2 trial randomly assigned 1,100 patients with stable known or suspected coronary artery disease (CAD) to undergo conventional angiography alone or with added direct pressure-wire measurement of fractional flow reserve to guide management decisions. Primary outcomes include health care costs and patient-reported quality of life at 1 year.
Slated for later that day, the Asymptomatic Carotid Surgery Trial-2 (ACST-2) has entered an estimated 3600 patients with a substantial carotid artery narrowing not associated with symptoms but for which either carotid endarterectomy (CEA) or carotid artery stenting (CAS) was considered anatomically feasible. There also must have been “substantial uncertainty” regarding the optimal procedure choice.
The trial, conducted in 40 countries primarily in Europe and North America and launched in 2008, randomly assigned the patients to undergo either CEA or CAS, in both cases with appropriate medical therapy, and followed them for periprocedural events and up to 10 years for strokes and stroke-related events.
The LOOP study, which is to directly follow ACST-2, has explored whether screening for AFib using the Medtronic Reveal LINQ monitor in older patients with non-AFib stroke risk factors – with oral anticoagulation prescribed for those who test positive – can lower their risk for stroke or systemic embolism. It randomly assigned 6,000 such patients to care guided by the loop recorder or to standard care.
On a somewhat larger scale, the Salt Substitute and Stroke Study (SSaSS) randomly assigned a total of 20,996 people in about 600 villages across northern China and Tibet to sodium-restriction intervention and control groups by village. All participants had a history of stroke or were aged at least 60 years with uncontrolled hypertension.
As described by the trial’s online portal, participants in villages assigned to the intervention group were given a supply of a low-sodium, potassium-supplementing salt substitute to replace their own salt supplies, along with education on the health benefits of sodium restriction. Participants in control villages continued their normal diets and, at the trial’s beginning, received “advice to reduce their salt intake.” All were required to own a telephone.
Clinical events, including strokes and hospitalizations throughout a 5-year follow-up, were tracked by phone calls made to all participants every 6 months and were documented at follow-up home visits.
Sunday is also to feature a Late-Breaking Trials session with a focus on COVID-19, which leads off with COLCOVID, a test of colchicine in patients hospitalized for suspected SARS-CoV-2 infection and in acute respiratory distress.
The 1,279 participants in Argentina were randomly assigned to receive or not receive the potent anti-inflammatory agent on top of antivirals and other standard management and followed for death or new need for mechanical ventilation. A successful outcome would contrast with the RECOVERY trial, which terminated a colchicine group of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 because of a lack of efficacy earlier this year.
COLCOVID is to be followed by the MICHELLE trial of rivaroxaban (Xarelto, Bayer/Janssen) prophylaxis, compared with no preventive oral anticoagulant, in 320 patients who, when hospitalized with COVID-19, had been on parenteral anticoagulants because of an elevated risk for venous thromboembolism. The trial, conducted in Brazil, called for postdischarge rivaroxaban at a once-daily dosage of 10 mg for about 1 month.
The session also includes a presentation called “Insights into the Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Comprehensive Analysis from the GUIDE-HF Trial,” the primary outcomes of which will be reported on the first day of the Congress.
Following is a presentation on the PREPARE-IT study of icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin), given at high dosages intended to be anti-inflammatory, compared with placebo, in an estimated 4,000 adults. The trial has two groups: A prevention group of adults living and circulating in the community; and a treatment group of patients aged at least 40 years with confirmed symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection for whom the need for hospitalization isn’t clear.
Monday, Aug. 30
The final day of the Congress features a trial called Influenza Vaccination after Myocardial Infarction (IAMI), which has tested the secondary preventive effect of influenza vaccination by randomly assigning 2,571 patients to receive a standard vaccine or a saline placebo injection on one occasion.
Entry to the international trial called for a diagnosis of MI with or without ST-segment elevation, or stable CAD and age at least 75 years with other risk factors. The patients were followed for death, MI, stent thrombosis, and a slew of secondary endpoints over 12 months.
Monday offerings continue later in a time block leading off with the STEP trial, which has randomly assigned an estimated 8,000 patients at 40 centers in China who are 60 to 80 years of age with a systolic blood pressure of 140 to <190 mm Hg to be on standard guideline-based therapy or an intensive drug-management strategy.
The systolic BP goals are 130 to <150 mm Hg for standard care and 110 to <130 mm Hg for the intensive regimen. The composite primary endpoint includes death and clinical events related to acute coronary syndromes, HF, revascularization, and stroke.
Following on heels of STEP, the Amulet IDE trial – the first major randomized comparison of two transcatheter LAA closure devices – entered 1,878 patients with nonvalvular AFib who were considered high-risk for bleeding and stroke or systemic embolism.
They were randomly assigned in the noninferiority trial to receive either the AMPLATZER Amulet (Abbott Medical Devices) or the WATCHMAN (Boston Scientific) closure devices and were followed for safety and efficacy for up to 5 years.
Both LAA closure devices, intended to make patients with AFib less reliant on oral anticoagulation, are now available on both sides of the Atlantic – as well as many other countries – after the Amulet’s United States market approval on Aug. 16, based largely on the Amulet IDE trial.
Rounding out the final Hot Line set is one of the latest efforts to show the efficacy and safety of a very short DAPT period after coronary stenting in patients with acute coronary syndromes, the STOPDAPT-2 ACS trial.
The study assigned 3,008 patients in Japan to receive aspirin and clopidogrel for either 1 month or 1 year after implantation with an everolimus-eluting cobalt-chromium stent and followed them for up to 5 years for a composite of MI, CV death, stent thrombosis, stroke, and bleeding.
The trial follows the published STOPDAPT-2 trial that showed superiority for the 1-month DAPT regimen in a predominantly stable-CAD population treated with the same kind of stent.
Program structure and format
A total of 15 online channels are to be available in the morning, European time, their schedules running in parallel. Presentations often are prerecorded, but also include live sessions at 8:00 a.m. Central time and 12 p.m. CET (2:00 a.m. and 6:00 a.m. Eastern time) to liven up the channel offerings, Dr. Windecker observed, and to make them more immediate and potentially interactive.
Many of the parallel channels are devoted throughout the Congress to particular silos of cardiology; for example, arrhythmias and device therapy is on channel 3; CAD and acute care is on 5; HF is on 6; and preventive cardiology is on 9.
Other channels swing across different topics from day to day, such as channel 1, which covers COVID-19 topics on the first and third day of the meeting, “advances in science” on day 2, and “digital health, public health, health economics” on day 4.
The focus each day, starting at 2:00 p.m. CET (8:00 a.m. ET) and continuing into the evening in Europe, shifts over to the Prime Time live program, which features the Hot Line and guideline presentations and many of the live abstract presentations.
Dr. Kosiborod, not a researcher with the EMPEROR trials, is chair of the Dapagliflozin in Preserved Ejection Fraction Heart Failure ( PRESERVED-HF ) trial, which is scheduled for presentation at the September 2021 Heart Failure Society of American meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There will be so much more to the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology, which begins Aug. 27 with an all-virtual format, than detailed primary results of EMPEROR-Preserved, a trial that could mark a turning point for heart failure (HF) medical therapy.
Also among the featured Hot Line and Late-Breaking Science sessions are – along with many other studies – explorations of arrhythmia management (ablation or guided by loop recorder); secondary prevention, including by vaccination; oral anticoagulation, notably after transcatheter valve procedures; and colchicine or thrombosis prophylaxis in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
There will even be a head-to-head comparison of two long-familiar left atrial appendage (LAA) occluders, and a population-based, randomized trial of sodium restriction through wide-scale use of a potassium-based salt substitute.
The congress will also introduce four guideline documents at sessions throughout the Congress, one on each day. They cover new and modified recommendations for heart failure; pacing, including cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT); cardiovascular (CV) disease prevention; and, with cosponsorship from the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, valvular heart disease.
The virtues of virtual
That next year’s Congress is slated for Aug. 27-30 in Barcelona should be welcome news for anyone whose “what if” curiosity about all-virtual conferences has already been satisfied. But with experience comes wisdom, as the medical societies have learned that online scientific meetings have some winning qualities that may be worth keeping, as least for a while.
“I think there is no doubt that the digital format will continue, for several reasons. One is that this pandemic is not over,” ESC Congress program committee chair Stephan Windecker, MD, Bern (Switzerland) University Hospital, , told this news organization. “As long as it is not over, the digital format is here to stay.”
But it also appears that people who haven’t been able to attend the congress in person are keen to log in and engage online, Dr. Windecker said. The 2020 all-virtual conference drew a much younger pool of registrants, on average, than did the live conferences before the pandemic.
“I think that’s an indication of people that may be in training, in early stages of their career, or they don’t have the support from departments or from their practice, or other financial means.” But they are able to participate via computer, tablet, or smartphone, he said.
“Another advantage is that the recorded content can be replayed at the convenience of whoever wants to consume it at a later point in time,” he added. “Those are just some examples why the digital format is likely to stay,” on its own or in a new age of hybrid meetings.
New and updated guidelines
Leading off the guideline series is the document on diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic HF, which leveraged the past few busy years of HF clinical trials to arrive at a number of new recommendations and strengthened level-of-evidence ratings. It covers both drug and device therapy of HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and acute decompensated HF, and tweaks and further enshrines the concept of HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF).
Several updated recommendations for both long-used and novel medications, notably the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, will be included because of the recently appreciated evidence-based impact in HFrEF, Dr. Windecker noted.
“I think it will be particularly interesting to look for the SGLT2 inhibitors as not a completely new class of drugs, but certainly one where there has been a lot of new evidence, to look at how those drugs will be integrated in the overall care pathway.”
A top-line preview of the new HF guideline limited to drug therapy, presented at July’s Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA), provided a simple answer to a common question in the new, bountiful age of HFrEF medications: Which meds, initiated in what order?
As it happens, the new recommendation for first-line HFrEF drug therapy is not a silver bullet, but a shotgun – prompt initiation of at least four meds, one from each of four drug classes: renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRA), and SGLT2 inhibitors. Each class, as described in the document, is to be started as soon as safely feasible, in a sequence deemed appropriate for each individual patient.
Spotlight on EMPEROR-Preserved
The world already knows that the trial, which tested the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin (Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly) on top of standard therapy, “met” its primary endpoint in almost 6,000 patients with HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), who included some with HFmrEF by more contemporary definitions.
That means patients in EMPEROR-Preserved assigned to take empagliflozin showed significantly fewer events that made up the study’s primary endpoint, a composite of CV death or HF hospitalization. It appears to be the first clearly significant overall medical therapy benefit for a clinical primary endpoint in a major randomized HFpEF drug trial.
And that, pending fuller presentation of trial results at the Congress on Aug. 27, could be a huge deal for the half of HF patients with left ventricular ejection fractions (LVEF) higher than the HFrEF range.
Those early top-line results weren’t a decisive bombshell for a field now filled with hope for a practice-changing empagliflozin outcome in EMPEROR-Preserved, which isn’t a certainty. They were more like the “boom” of a mortar launching a rocket of fireworks that may explode into a chrysanthemum or green comet or, sometimes, turn out to be no more than a dud. The promise of the early cursory results critically depends on further details.
“Provided there is a compelling benefit, this is what everyone has been waiting for in this condition for decades,” Mikhail N. Kosiborod, MD, director of cardiometabolic research at Saint Luke’s Mid-America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Mo., said.
“Already knowing that the trial met the primary endpoint is obviously very intriguing and encouraging,” he added. “But there are things we don’t know, such as: What is the magnitude of benefit? And whether that benefit, whatever the magnitude, is driven by reductions in both heart failure hospitalizations and cardiovascular death, or only one of the two.”
For example: “If we see an impressive benefit for reduction of hospitalizations, but not a significant reduction in death, that would still be a huge advance. That’s because, to date, we don’t have any drug for HFpEF that has convincingly demonstrated a compelling reduction in heart failure hospitalization or improvement in symptoms, function, or quality of life,” observed Dr. Kosiborod, who wasn’t part of EMPEROR-Preserved.
There have been “suggestions” from HFrEF trials that empagliflozin and dapagliflozin (Farxiga, AstraZeneca) “have very comparable effects on at least the endpoint of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure,” he said. “So, my expectation would be that whatever is observed in EMPEROR-Preserved is likely a class effect, as well.”
Following EMPEROR-Preserved on the agenda is EMPEROR-Pooled, a patient-level combined analysis of the EMPEROR series of trials that spans the range of HF, regardless of ejection fraction or diabetes status, primarily exploring the effects of empagliflozin on renal function.
Other offerings, Friday, Aug. 27
Scheduled immediately after EMPEROR-Preserved is a presentation on the SMART-MI trial, which should clarify whether management guided by continuous ambulatory monitoring is effective in patients considered at especially high arrhythmic risk. Entry called for recent myocardial infarction and an LVEF of 36%-50% with evidence of cardiac autonomic dysfunction.
The trial randomly assigned 400 such patients to be or not be implanted with a Reveal LINQ (Medtronic) loop recorder and followed them for up to 18 months, primarily for detection of potentially serious arrhythmic events. Endpoints that involved mortality, hospitalization or other clinical events were secondary.
In a time slot preceding both SMART-MI and EMPEROR-Preserved, the GUIDE-HF trial is following a projected 3,600 patients with HF implanted with a CardioMEMS HF System (Abbott) pulmonary artery (PA) pressure sensor to explore the its value for guiding management.
The trial’s three cohorts, followed for at least 12 months, include randomized sensor-monitored and control groups of patients with New York Heart Association class 2-4 symptoms, as well as a third observational set of patients in NYHA class 3. That’s the indication for which the CardioMEMS monitor gained approval in the United States in 2014 based on the 2011 CHAMPION trial, and which fared just as well in the 2017 CHAMPION Post-Approval Study.
The Friday Hot Lines also include Dal-GenE, which has entered about 6,000 patients with recent MI to test the once-abandoned cholesterol ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitor dalcetrapib (DalCor) for any secondary-prevention benefits when used selectively. The trial’s hook: All its patients are confirmed to have the AA genotype of the rs1967309 variant in the ADCY9 gene, which has been associated with a pronounced clinical response to CETP inhibition.
Saturday, Aug. 28
The direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) have largely replaced vitamin K antagonists in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (AFib). But whether DOACs are similarly preferable in the growing world population of people who have undergone transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR or TAVI), an issue explored with variable results in the ATLANTIS and GALILEO trials, is far from settled.
The ENVISAGE-TAVI AF trial explored the question for the factor X inhibitor edoxaban (Savaysa, Lixiana, Daiichi-Sankyo) in 1,400 patients with AFib and a transfemoral TAVR in the previous 5 days, who were randomly assigned to the DOAC or standard management along with discretionary antiplatelet therapy. They’ve been followed for up to 3 years for a composite endpoint of clinical events – including death, MI, and stroke – and for major bleeding.
The day will also feature MASTER DAPT, a comparison of two dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) regimens in an estimated 4,300 patients considered to be high-risk for bleeding who had received the sirolimus-eluting Ultimaster (Terumo) coronary stent, which has a bioresorbable polymer coating.
Investigators have randomly assigned patients to receive either very-short-duration DAPT, for about a month after stenting, followed by a P2Y12 inhibitor alone for up to a year after the procedure; or a more conventional regimen of a P2Y12 inhibitor for 6-12 months with aspirin maintained for a total of 12 months.
Later that day, investigators from the FIGARO-DKD trial will present their results based on 7,437 patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD), a much fuller version than the top-line findings announced by sponsor Bayer 3 months ago.
Those top-line results suggested that patients assigned to receive the nonsteroidal nonselective mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) finerenone (Kerendia) on top of standard care benefited with a drop in risk for the primary endpoint of CV death or nonfatal CV events.
Finerenone was recently approved in the United States for treating patients with both type 2 diabetes and CKD based on the published FIDELIO-DKD trial, which had seen less CKD progression and fewer CV events in such patients who took the novel MRA.
Although similar in design to FIGARO-DKD, FIDELIO-DKD had entered fewer patients with early-stage diabetic kidney disease (DKD). That led researchers to pool the two trials’ populations to create a cohort that spans the spectrum of DKD severity. An analysis of the pooled cohort, dubbed FIDELITY, is on the schedule after FIGARO-DKD.
After FIDELITY is the prospective APAF-CRT trial that is following a projected 1,830 patients with permanent, symptomatic AFib and a recent hospitalization for AFib or HF and who were not good candidates for standard ablation. They were assigned to receive either atrioventricular junctional ablation followed by CRT, with or without a defibrillation, on top of optimal meds – a so-called “ablate-and-pace” strategy – or an implantable cardioverter defibrillator with rate-control drug therapy.
The new analysis represents the trial’s second phase in which mortality was followed for 4 years as the primary endpoint, in contrast to the previously reported initial phase that followed the first 102 patients for 2 years for the composite primary endpoint of death, worsening HF, and HF hospitalization. The first phase had halted enrollment before reaching its planned target of 280 patients after an interim analysis showed a significant benefit for ablate and pace.
Next up: DECAAF 2, a randomized assessment of whether catheter ablation for AFib guided by delayed gadolinium enhancement on MRI, a proxy for scar tissue, can be more effective than standard AFib ablation by pulmonary vein isolation alone. An estimated 900 patients with persistent AFib who had never before undergone ablation for the arrhythmia were randomly assigned to one strategy or the other and followed for AFib recurrence over 18 months.
Sunday, Aug. 29
The TOMAHAWK trial aimed to clarify the optimal timing of invasive coronary angiography for resuscitated patients with non–ST-segment elevation out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, a broad population in a setting for which there is little randomized-trial guidance. Investigators randomly assigned 558 such patients to undergo immediate invasive angiography or to direct intensive care unit admission for initial standard care with discretionary delayed angiography. Patients were followed for all-cause mortality, with other clinical events and neurologic outcomes as secondary endpoints.
Next on the schedule, the RIPCORD-2 trial randomly assigned 1,100 patients with stable known or suspected coronary artery disease (CAD) to undergo conventional angiography alone or with added direct pressure-wire measurement of fractional flow reserve to guide management decisions. Primary outcomes include health care costs and patient-reported quality of life at 1 year.
Slated for later that day, the Asymptomatic Carotid Surgery Trial-2 (ACST-2) has entered an estimated 3600 patients with a substantial carotid artery narrowing not associated with symptoms but for which either carotid endarterectomy (CEA) or carotid artery stenting (CAS) was considered anatomically feasible. There also must have been “substantial uncertainty” regarding the optimal procedure choice.
The trial, conducted in 40 countries primarily in Europe and North America and launched in 2008, randomly assigned the patients to undergo either CEA or CAS, in both cases with appropriate medical therapy, and followed them for periprocedural events and up to 10 years for strokes and stroke-related events.
The LOOP study, which is to directly follow ACST-2, has explored whether screening for AFib using the Medtronic Reveal LINQ monitor in older patients with non-AFib stroke risk factors – with oral anticoagulation prescribed for those who test positive – can lower their risk for stroke or systemic embolism. It randomly assigned 6,000 such patients to care guided by the loop recorder or to standard care.
On a somewhat larger scale, the Salt Substitute and Stroke Study (SSaSS) randomly assigned a total of 20,996 people in about 600 villages across northern China and Tibet to sodium-restriction intervention and control groups by village. All participants had a history of stroke or were aged at least 60 years with uncontrolled hypertension.
As described by the trial’s online portal, participants in villages assigned to the intervention group were given a supply of a low-sodium, potassium-supplementing salt substitute to replace their own salt supplies, along with education on the health benefits of sodium restriction. Participants in control villages continued their normal diets and, at the trial’s beginning, received “advice to reduce their salt intake.” All were required to own a telephone.
Clinical events, including strokes and hospitalizations throughout a 5-year follow-up, were tracked by phone calls made to all participants every 6 months and were documented at follow-up home visits.
Sunday is also to feature a Late-Breaking Trials session with a focus on COVID-19, which leads off with COLCOVID, a test of colchicine in patients hospitalized for suspected SARS-CoV-2 infection and in acute respiratory distress.
The 1,279 participants in Argentina were randomly assigned to receive or not receive the potent anti-inflammatory agent on top of antivirals and other standard management and followed for death or new need for mechanical ventilation. A successful outcome would contrast with the RECOVERY trial, which terminated a colchicine group of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 because of a lack of efficacy earlier this year.
COLCOVID is to be followed by the MICHELLE trial of rivaroxaban (Xarelto, Bayer/Janssen) prophylaxis, compared with no preventive oral anticoagulant, in 320 patients who, when hospitalized with COVID-19, had been on parenteral anticoagulants because of an elevated risk for venous thromboembolism. The trial, conducted in Brazil, called for postdischarge rivaroxaban at a once-daily dosage of 10 mg for about 1 month.
The session also includes a presentation called “Insights into the Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Comprehensive Analysis from the GUIDE-HF Trial,” the primary outcomes of which will be reported on the first day of the Congress.
Following is a presentation on the PREPARE-IT study of icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin), given at high dosages intended to be anti-inflammatory, compared with placebo, in an estimated 4,000 adults. The trial has two groups: A prevention group of adults living and circulating in the community; and a treatment group of patients aged at least 40 years with confirmed symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection for whom the need for hospitalization isn’t clear.
Monday, Aug. 30
The final day of the Congress features a trial called Influenza Vaccination after Myocardial Infarction (IAMI), which has tested the secondary preventive effect of influenza vaccination by randomly assigning 2,571 patients to receive a standard vaccine or a saline placebo injection on one occasion.
Entry to the international trial called for a diagnosis of MI with or without ST-segment elevation, or stable CAD and age at least 75 years with other risk factors. The patients were followed for death, MI, stent thrombosis, and a slew of secondary endpoints over 12 months.
Monday offerings continue later in a time block leading off with the STEP trial, which has randomly assigned an estimated 8,000 patients at 40 centers in China who are 60 to 80 years of age with a systolic blood pressure of 140 to <190 mm Hg to be on standard guideline-based therapy or an intensive drug-management strategy.
The systolic BP goals are 130 to <150 mm Hg for standard care and 110 to <130 mm Hg for the intensive regimen. The composite primary endpoint includes death and clinical events related to acute coronary syndromes, HF, revascularization, and stroke.
Following on heels of STEP, the Amulet IDE trial – the first major randomized comparison of two transcatheter LAA closure devices – entered 1,878 patients with nonvalvular AFib who were considered high-risk for bleeding and stroke or systemic embolism.
They were randomly assigned in the noninferiority trial to receive either the AMPLATZER Amulet (Abbott Medical Devices) or the WATCHMAN (Boston Scientific) closure devices and were followed for safety and efficacy for up to 5 years.
Both LAA closure devices, intended to make patients with AFib less reliant on oral anticoagulation, are now available on both sides of the Atlantic – as well as many other countries – after the Amulet’s United States market approval on Aug. 16, based largely on the Amulet IDE trial.
Rounding out the final Hot Line set is one of the latest efforts to show the efficacy and safety of a very short DAPT period after coronary stenting in patients with acute coronary syndromes, the STOPDAPT-2 ACS trial.
The study assigned 3,008 patients in Japan to receive aspirin and clopidogrel for either 1 month or 1 year after implantation with an everolimus-eluting cobalt-chromium stent and followed them for up to 5 years for a composite of MI, CV death, stent thrombosis, stroke, and bleeding.
The trial follows the published STOPDAPT-2 trial that showed superiority for the 1-month DAPT regimen in a predominantly stable-CAD population treated with the same kind of stent.
Program structure and format
A total of 15 online channels are to be available in the morning, European time, their schedules running in parallel. Presentations often are prerecorded, but also include live sessions at 8:00 a.m. Central time and 12 p.m. CET (2:00 a.m. and 6:00 a.m. Eastern time) to liven up the channel offerings, Dr. Windecker observed, and to make them more immediate and potentially interactive.
Many of the parallel channels are devoted throughout the Congress to particular silos of cardiology; for example, arrhythmias and device therapy is on channel 3; CAD and acute care is on 5; HF is on 6; and preventive cardiology is on 9.
Other channels swing across different topics from day to day, such as channel 1, which covers COVID-19 topics on the first and third day of the meeting, “advances in science” on day 2, and “digital health, public health, health economics” on day 4.
The focus each day, starting at 2:00 p.m. CET (8:00 a.m. ET) and continuing into the evening in Europe, shifts over to the Prime Time live program, which features the Hot Line and guideline presentations and many of the live abstract presentations.
Dr. Kosiborod, not a researcher with the EMPEROR trials, is chair of the Dapagliflozin in Preserved Ejection Fraction Heart Failure ( PRESERVED-HF ) trial, which is scheduled for presentation at the September 2021 Heart Failure Society of American meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There will be so much more to the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology, which begins Aug. 27 with an all-virtual format, than detailed primary results of EMPEROR-Preserved, a trial that could mark a turning point for heart failure (HF) medical therapy.
Also among the featured Hot Line and Late-Breaking Science sessions are – along with many other studies – explorations of arrhythmia management (ablation or guided by loop recorder); secondary prevention, including by vaccination; oral anticoagulation, notably after transcatheter valve procedures; and colchicine or thrombosis prophylaxis in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
There will even be a head-to-head comparison of two long-familiar left atrial appendage (LAA) occluders, and a population-based, randomized trial of sodium restriction through wide-scale use of a potassium-based salt substitute.
The congress will also introduce four guideline documents at sessions throughout the Congress, one on each day. They cover new and modified recommendations for heart failure; pacing, including cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT); cardiovascular (CV) disease prevention; and, with cosponsorship from the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, valvular heart disease.
The virtues of virtual
That next year’s Congress is slated for Aug. 27-30 in Barcelona should be welcome news for anyone whose “what if” curiosity about all-virtual conferences has already been satisfied. But with experience comes wisdom, as the medical societies have learned that online scientific meetings have some winning qualities that may be worth keeping, as least for a while.
“I think there is no doubt that the digital format will continue, for several reasons. One is that this pandemic is not over,” ESC Congress program committee chair Stephan Windecker, MD, Bern (Switzerland) University Hospital, , told this news organization. “As long as it is not over, the digital format is here to stay.”
But it also appears that people who haven’t been able to attend the congress in person are keen to log in and engage online, Dr. Windecker said. The 2020 all-virtual conference drew a much younger pool of registrants, on average, than did the live conferences before the pandemic.
“I think that’s an indication of people that may be in training, in early stages of their career, or they don’t have the support from departments or from their practice, or other financial means.” But they are able to participate via computer, tablet, or smartphone, he said.
“Another advantage is that the recorded content can be replayed at the convenience of whoever wants to consume it at a later point in time,” he added. “Those are just some examples why the digital format is likely to stay,” on its own or in a new age of hybrid meetings.
New and updated guidelines
Leading off the guideline series is the document on diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic HF, which leveraged the past few busy years of HF clinical trials to arrive at a number of new recommendations and strengthened level-of-evidence ratings. It covers both drug and device therapy of HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and acute decompensated HF, and tweaks and further enshrines the concept of HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF).
Several updated recommendations for both long-used and novel medications, notably the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, will be included because of the recently appreciated evidence-based impact in HFrEF, Dr. Windecker noted.
“I think it will be particularly interesting to look for the SGLT2 inhibitors as not a completely new class of drugs, but certainly one where there has been a lot of new evidence, to look at how those drugs will be integrated in the overall care pathway.”
A top-line preview of the new HF guideline limited to drug therapy, presented at July’s Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA), provided a simple answer to a common question in the new, bountiful age of HFrEF medications: Which meds, initiated in what order?
As it happens, the new recommendation for first-line HFrEF drug therapy is not a silver bullet, but a shotgun – prompt initiation of at least four meds, one from each of four drug classes: renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRA), and SGLT2 inhibitors. Each class, as described in the document, is to be started as soon as safely feasible, in a sequence deemed appropriate for each individual patient.
Spotlight on EMPEROR-Preserved
The world already knows that the trial, which tested the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin (Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly) on top of standard therapy, “met” its primary endpoint in almost 6,000 patients with HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), who included some with HFmrEF by more contemporary definitions.
That means patients in EMPEROR-Preserved assigned to take empagliflozin showed significantly fewer events that made up the study’s primary endpoint, a composite of CV death or HF hospitalization. It appears to be the first clearly significant overall medical therapy benefit for a clinical primary endpoint in a major randomized HFpEF drug trial.
And that, pending fuller presentation of trial results at the Congress on Aug. 27, could be a huge deal for the half of HF patients with left ventricular ejection fractions (LVEF) higher than the HFrEF range.
Those early top-line results weren’t a decisive bombshell for a field now filled with hope for a practice-changing empagliflozin outcome in EMPEROR-Preserved, which isn’t a certainty. They were more like the “boom” of a mortar launching a rocket of fireworks that may explode into a chrysanthemum or green comet or, sometimes, turn out to be no more than a dud. The promise of the early cursory results critically depends on further details.
“Provided there is a compelling benefit, this is what everyone has been waiting for in this condition for decades,” Mikhail N. Kosiborod, MD, director of cardiometabolic research at Saint Luke’s Mid-America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Mo., said.
“Already knowing that the trial met the primary endpoint is obviously very intriguing and encouraging,” he added. “But there are things we don’t know, such as: What is the magnitude of benefit? And whether that benefit, whatever the magnitude, is driven by reductions in both heart failure hospitalizations and cardiovascular death, or only one of the two.”
For example: “If we see an impressive benefit for reduction of hospitalizations, but not a significant reduction in death, that would still be a huge advance. That’s because, to date, we don’t have any drug for HFpEF that has convincingly demonstrated a compelling reduction in heart failure hospitalization or improvement in symptoms, function, or quality of life,” observed Dr. Kosiborod, who wasn’t part of EMPEROR-Preserved.
There have been “suggestions” from HFrEF trials that empagliflozin and dapagliflozin (Farxiga, AstraZeneca) “have very comparable effects on at least the endpoint of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure,” he said. “So, my expectation would be that whatever is observed in EMPEROR-Preserved is likely a class effect, as well.”
Following EMPEROR-Preserved on the agenda is EMPEROR-Pooled, a patient-level combined analysis of the EMPEROR series of trials that spans the range of HF, regardless of ejection fraction or diabetes status, primarily exploring the effects of empagliflozin on renal function.
Other offerings, Friday, Aug. 27
Scheduled immediately after EMPEROR-Preserved is a presentation on the SMART-MI trial, which should clarify whether management guided by continuous ambulatory monitoring is effective in patients considered at especially high arrhythmic risk. Entry called for recent myocardial infarction and an LVEF of 36%-50% with evidence of cardiac autonomic dysfunction.
The trial randomly assigned 400 such patients to be or not be implanted with a Reveal LINQ (Medtronic) loop recorder and followed them for up to 18 months, primarily for detection of potentially serious arrhythmic events. Endpoints that involved mortality, hospitalization or other clinical events were secondary.
In a time slot preceding both SMART-MI and EMPEROR-Preserved, the GUIDE-HF trial is following a projected 3,600 patients with HF implanted with a CardioMEMS HF System (Abbott) pulmonary artery (PA) pressure sensor to explore the its value for guiding management.
The trial’s three cohorts, followed for at least 12 months, include randomized sensor-monitored and control groups of patients with New York Heart Association class 2-4 symptoms, as well as a third observational set of patients in NYHA class 3. That’s the indication for which the CardioMEMS monitor gained approval in the United States in 2014 based on the 2011 CHAMPION trial, and which fared just as well in the 2017 CHAMPION Post-Approval Study.
The Friday Hot Lines also include Dal-GenE, which has entered about 6,000 patients with recent MI to test the once-abandoned cholesterol ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitor dalcetrapib (DalCor) for any secondary-prevention benefits when used selectively. The trial’s hook: All its patients are confirmed to have the AA genotype of the rs1967309 variant in the ADCY9 gene, which has been associated with a pronounced clinical response to CETP inhibition.
Saturday, Aug. 28
The direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) have largely replaced vitamin K antagonists in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (AFib). But whether DOACs are similarly preferable in the growing world population of people who have undergone transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR or TAVI), an issue explored with variable results in the ATLANTIS and GALILEO trials, is far from settled.
The ENVISAGE-TAVI AF trial explored the question for the factor X inhibitor edoxaban (Savaysa, Lixiana, Daiichi-Sankyo) in 1,400 patients with AFib and a transfemoral TAVR in the previous 5 days, who were randomly assigned to the DOAC or standard management along with discretionary antiplatelet therapy. They’ve been followed for up to 3 years for a composite endpoint of clinical events – including death, MI, and stroke – and for major bleeding.
The day will also feature MASTER DAPT, a comparison of two dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) regimens in an estimated 4,300 patients considered to be high-risk for bleeding who had received the sirolimus-eluting Ultimaster (Terumo) coronary stent, which has a bioresorbable polymer coating.
Investigators have randomly assigned patients to receive either very-short-duration DAPT, for about a month after stenting, followed by a P2Y12 inhibitor alone for up to a year after the procedure; or a more conventional regimen of a P2Y12 inhibitor for 6-12 months with aspirin maintained for a total of 12 months.
Later that day, investigators from the FIGARO-DKD trial will present their results based on 7,437 patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD), a much fuller version than the top-line findings announced by sponsor Bayer 3 months ago.
Those top-line results suggested that patients assigned to receive the nonsteroidal nonselective mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) finerenone (Kerendia) on top of standard care benefited with a drop in risk for the primary endpoint of CV death or nonfatal CV events.
Finerenone was recently approved in the United States for treating patients with both type 2 diabetes and CKD based on the published FIDELIO-DKD trial, which had seen less CKD progression and fewer CV events in such patients who took the novel MRA.
Although similar in design to FIGARO-DKD, FIDELIO-DKD had entered fewer patients with early-stage diabetic kidney disease (DKD). That led researchers to pool the two trials’ populations to create a cohort that spans the spectrum of DKD severity. An analysis of the pooled cohort, dubbed FIDELITY, is on the schedule after FIGARO-DKD.
After FIDELITY is the prospective APAF-CRT trial that is following a projected 1,830 patients with permanent, symptomatic AFib and a recent hospitalization for AFib or HF and who were not good candidates for standard ablation. They were assigned to receive either atrioventricular junctional ablation followed by CRT, with or without a defibrillation, on top of optimal meds – a so-called “ablate-and-pace” strategy – or an implantable cardioverter defibrillator with rate-control drug therapy.
The new analysis represents the trial’s second phase in which mortality was followed for 4 years as the primary endpoint, in contrast to the previously reported initial phase that followed the first 102 patients for 2 years for the composite primary endpoint of death, worsening HF, and HF hospitalization. The first phase had halted enrollment before reaching its planned target of 280 patients after an interim analysis showed a significant benefit for ablate and pace.
Next up: DECAAF 2, a randomized assessment of whether catheter ablation for AFib guided by delayed gadolinium enhancement on MRI, a proxy for scar tissue, can be more effective than standard AFib ablation by pulmonary vein isolation alone. An estimated 900 patients with persistent AFib who had never before undergone ablation for the arrhythmia were randomly assigned to one strategy or the other and followed for AFib recurrence over 18 months.
Sunday, Aug. 29
The TOMAHAWK trial aimed to clarify the optimal timing of invasive coronary angiography for resuscitated patients with non–ST-segment elevation out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, a broad population in a setting for which there is little randomized-trial guidance. Investigators randomly assigned 558 such patients to undergo immediate invasive angiography or to direct intensive care unit admission for initial standard care with discretionary delayed angiography. Patients were followed for all-cause mortality, with other clinical events and neurologic outcomes as secondary endpoints.
Next on the schedule, the RIPCORD-2 trial randomly assigned 1,100 patients with stable known or suspected coronary artery disease (CAD) to undergo conventional angiography alone or with added direct pressure-wire measurement of fractional flow reserve to guide management decisions. Primary outcomes include health care costs and patient-reported quality of life at 1 year.
Slated for later that day, the Asymptomatic Carotid Surgery Trial-2 (ACST-2) has entered an estimated 3600 patients with a substantial carotid artery narrowing not associated with symptoms but for which either carotid endarterectomy (CEA) or carotid artery stenting (CAS) was considered anatomically feasible. There also must have been “substantial uncertainty” regarding the optimal procedure choice.
The trial, conducted in 40 countries primarily in Europe and North America and launched in 2008, randomly assigned the patients to undergo either CEA or CAS, in both cases with appropriate medical therapy, and followed them for periprocedural events and up to 10 years for strokes and stroke-related events.
The LOOP study, which is to directly follow ACST-2, has explored whether screening for AFib using the Medtronic Reveal LINQ monitor in older patients with non-AFib stroke risk factors – with oral anticoagulation prescribed for those who test positive – can lower their risk for stroke or systemic embolism. It randomly assigned 6,000 such patients to care guided by the loop recorder or to standard care.
On a somewhat larger scale, the Salt Substitute and Stroke Study (SSaSS) randomly assigned a total of 20,996 people in about 600 villages across northern China and Tibet to sodium-restriction intervention and control groups by village. All participants had a history of stroke or were aged at least 60 years with uncontrolled hypertension.
As described by the trial’s online portal, participants in villages assigned to the intervention group were given a supply of a low-sodium, potassium-supplementing salt substitute to replace their own salt supplies, along with education on the health benefits of sodium restriction. Participants in control villages continued their normal diets and, at the trial’s beginning, received “advice to reduce their salt intake.” All were required to own a telephone.
Clinical events, including strokes and hospitalizations throughout a 5-year follow-up, were tracked by phone calls made to all participants every 6 months and were documented at follow-up home visits.
Sunday is also to feature a Late-Breaking Trials session with a focus on COVID-19, which leads off with COLCOVID, a test of colchicine in patients hospitalized for suspected SARS-CoV-2 infection and in acute respiratory distress.
The 1,279 participants in Argentina were randomly assigned to receive or not receive the potent anti-inflammatory agent on top of antivirals and other standard management and followed for death or new need for mechanical ventilation. A successful outcome would contrast with the RECOVERY trial, which terminated a colchicine group of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 because of a lack of efficacy earlier this year.
COLCOVID is to be followed by the MICHELLE trial of rivaroxaban (Xarelto, Bayer/Janssen) prophylaxis, compared with no preventive oral anticoagulant, in 320 patients who, when hospitalized with COVID-19, had been on parenteral anticoagulants because of an elevated risk for venous thromboembolism. The trial, conducted in Brazil, called for postdischarge rivaroxaban at a once-daily dosage of 10 mg for about 1 month.
The session also includes a presentation called “Insights into the Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Comprehensive Analysis from the GUIDE-HF Trial,” the primary outcomes of which will be reported on the first day of the Congress.
Following is a presentation on the PREPARE-IT study of icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin), given at high dosages intended to be anti-inflammatory, compared with placebo, in an estimated 4,000 adults. The trial has two groups: A prevention group of adults living and circulating in the community; and a treatment group of patients aged at least 40 years with confirmed symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection for whom the need for hospitalization isn’t clear.
Monday, Aug. 30
The final day of the Congress features a trial called Influenza Vaccination after Myocardial Infarction (IAMI), which has tested the secondary preventive effect of influenza vaccination by randomly assigning 2,571 patients to receive a standard vaccine or a saline placebo injection on one occasion.
Entry to the international trial called for a diagnosis of MI with or without ST-segment elevation, or stable CAD and age at least 75 years with other risk factors. The patients were followed for death, MI, stent thrombosis, and a slew of secondary endpoints over 12 months.
Monday offerings continue later in a time block leading off with the STEP trial, which has randomly assigned an estimated 8,000 patients at 40 centers in China who are 60 to 80 years of age with a systolic blood pressure of 140 to <190 mm Hg to be on standard guideline-based therapy or an intensive drug-management strategy.
The systolic BP goals are 130 to <150 mm Hg for standard care and 110 to <130 mm Hg for the intensive regimen. The composite primary endpoint includes death and clinical events related to acute coronary syndromes, HF, revascularization, and stroke.
Following on heels of STEP, the Amulet IDE trial – the first major randomized comparison of two transcatheter LAA closure devices – entered 1,878 patients with nonvalvular AFib who were considered high-risk for bleeding and stroke or systemic embolism.
They were randomly assigned in the noninferiority trial to receive either the AMPLATZER Amulet (Abbott Medical Devices) or the WATCHMAN (Boston Scientific) closure devices and were followed for safety and efficacy for up to 5 years.
Both LAA closure devices, intended to make patients with AFib less reliant on oral anticoagulation, are now available on both sides of the Atlantic – as well as many other countries – after the Amulet’s United States market approval on Aug. 16, based largely on the Amulet IDE trial.
Rounding out the final Hot Line set is one of the latest efforts to show the efficacy and safety of a very short DAPT period after coronary stenting in patients with acute coronary syndromes, the STOPDAPT-2 ACS trial.
The study assigned 3,008 patients in Japan to receive aspirin and clopidogrel for either 1 month or 1 year after implantation with an everolimus-eluting cobalt-chromium stent and followed them for up to 5 years for a composite of MI, CV death, stent thrombosis, stroke, and bleeding.
The trial follows the published STOPDAPT-2 trial that showed superiority for the 1-month DAPT regimen in a predominantly stable-CAD population treated with the same kind of stent.
Program structure and format
A total of 15 online channels are to be available in the morning, European time, their schedules running in parallel. Presentations often are prerecorded, but also include live sessions at 8:00 a.m. Central time and 12 p.m. CET (2:00 a.m. and 6:00 a.m. Eastern time) to liven up the channel offerings, Dr. Windecker observed, and to make them more immediate and potentially interactive.
Many of the parallel channels are devoted throughout the Congress to particular silos of cardiology; for example, arrhythmias and device therapy is on channel 3; CAD and acute care is on 5; HF is on 6; and preventive cardiology is on 9.
Other channels swing across different topics from day to day, such as channel 1, which covers COVID-19 topics on the first and third day of the meeting, “advances in science” on day 2, and “digital health, public health, health economics” on day 4.
The focus each day, starting at 2:00 p.m. CET (8:00 a.m. ET) and continuing into the evening in Europe, shifts over to the Prime Time live program, which features the Hot Line and guideline presentations and many of the live abstract presentations.
Dr. Kosiborod, not a researcher with the EMPEROR trials, is chair of the Dapagliflozin in Preserved Ejection Fraction Heart Failure ( PRESERVED-HF ) trial, which is scheduled for presentation at the September 2021 Heart Failure Society of American meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Flavonoid-rich foods, aided by gut bacteria, tied to lower BP
, an association that is partially explained by bacteria in an individual’s gut microbiome, new research suggests.
In a population-based study of more than 900 individuals, those with the highest intake of flavonoid-containing foods had significantly lower systolic blood pressure and pulse pressure, as well as greater gut microbial diversity, compared with those with the lowest intakes.
Up to 15% of this observed association was explained by the gut microbiome, suggesting that these microbes play a key role in metabolizing flavonoids to enhance their cardioprotective effects, according to the researchers.
The study was published online in the journal Hypertension.
“We know what we eat plays a critical role in shaping our gut microbiome, but little is known about the relative importance of plant foods and specific constituents called flavonoids,” lead researcher Aedin Cassidy, PhD, chair and professor of nutrition and medicine at the Institute for Global Food Security, Queen’s University, Belfast, Northern Ireland, said in an interview.
“Unlike many other food constituents, flavonoids are predominantly metabolized in the gut, suggesting that the gut microbiome may be more important in enhancing their biological activity than for other things we eat,” Dr. Cassidy said.
“There is mounting evidence from population-based studies and clinical trials that a higher intake of flavonoids and flavonoid-rich foods can improve heart health, but for the first time, we provide data highlighting the key role of the gut microbiome in explaining the association between such foods and blood pressure,” she noted. “This is one of the first studies to address this.”
For this analysis, Dr. Cassidy and her group sought to assess to what extent the composition of the gut microbiome might explain the association of habitual flavonoid and flavonoid-rich food intake with systolic and diastolic blood pressure in a community-based sample of 904 individuals aged 25-82 years from Germany’s PopGen biobank.
The researchers evaluated participants’ food intake, gut microbiome, and blood pressure levels together with other clinical and molecular phenotyping at regular follow-up examinations.
Participants’ intake of flavonoid-rich foods during the previous year was calculated from a self-reported food questionnaire detailing the frequency and quantity eaten of 112 foods, and flavonoid values were assigned to foods according to United States Department of Agriculture data on flavonoid content in food.
Participants’ gut microbiome was assessed by fecal bacterial DNA extracted from stool samples.
After an overnight fast, participants’ blood pressure levels were measured three times in 3-minute intervals after an initial 5-minute rest period. Researchers also collected participants’ diet and lifestyle information.
Analysis of the data showed the following:
- Eating 1.5 servings of berries per day (about 1 cup) was associated with a 4.1–mm Hg reduction in systolic BP; 12% of this association was explained by gut microbiome factors.
- Drinking three glasses of red wine per week was associated with a 3.7–mm Hg reduction in systolic BP; 15% of this association was explained by the gut microbiome.
“These blood pressure–lowering effects are achievable with simple changes to the daily diet,” Dr. Cassidy said.
“Incorporating flavonoid-rich foods into the diet can have clinically relevant reductions in systolic blood pressure and pulse pressure, and a healthy gut microbiome is important to break down flavonoids to a more cardioprotective form,” she said.
“Our findings indicate future trials should look at participants according to metabolic profile in order to more accurately study the roles of metabolism and the gut microbiome in regulating the effects of flavonoids on blood pressure,” said Dr. Cassidy.
“A better understanding of the highly individual variability of flavonoid metabolism could very well explain why some people have greater cardiovascular protection benefits from flavonoid-rich foods than others.”
‘Interesting’ data
“The data are interesting,” David Jenkins, MD, PhD, DSc, professor of medicine and nutrition at the University of Toronto, said in an interview.
“Berries and red wine appear to be associated with lower systolic blood pressures. Lower blood pressures have been found in general in people who consume more plant-based diets, especially those high in fruits and vegetables,” noted Dr. Jenkins, who was not involved with this study.
“Berries and grapes high in polyphenols may have many health benefits as antioxidants, and in a recent study have been shown to reduce cardiovascular mortality. The change in chronic microflora is also of interest as this will change with increased fruit and vegetable consumption,” he said.
Perhaps one word of caveat, Dr. Jenkins added: “Alcohol has been found to increase blood pressure and the risk of stroke. Presumably the beneficial effects as seen here were when wine is consumed in moderation.”
Supports recommendations
The study by Cassidy and colleagues supports the dietary recommendations from the American Heart Association (AHA) for heart health, Penny M. Kris-Etherton, PhD, RDN, professor of nutritional sciences, Penn State University, University Park, Pa., and chair, AHA Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health, said in an interview.
“The AHA recommends a healthy dietary pattern that emphasizes a variety of plant foods including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds and is low in sodium, saturated fat, and added sugars. Lean protein foods, including plant protein foods, are recommended, and red meat should be limited. If alcohol is consumed it should be done in moderation,” Dr. Kris-Etherton said.
“Based on these AHA dietary recommendations, a wide variety of plant foods will promote consumption of many flavonoids that have demonstrated CVD benefits, such as lowering systolic blood pressure as reported by the authors, as well as promoting healthy endothelial function and having antithrombotic, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects,” she said in email.
“This recommended dietary pattern will have other cardiovascular health benefits, such as decreasing LDL cholesterol, due to its very healthy nutrient profile. The exciting new finding reported by Cassidy et al. is that the effects of dietary flavonoids on lowering systolic blood pressure are modulated by the gut microbiome,” Dr. Kris-Etherton said.
“Further research needs to be done to confirm these findings and to identify how different foods affect specific gut bacteria that benefit cardiovascular health.”
The research was funded by grants from the German Research Foundation and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. Dr. Cassidy and Dr. Jenkins have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kris-Etherton is a spokesperson for the AHA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, an association that is partially explained by bacteria in an individual’s gut microbiome, new research suggests.
In a population-based study of more than 900 individuals, those with the highest intake of flavonoid-containing foods had significantly lower systolic blood pressure and pulse pressure, as well as greater gut microbial diversity, compared with those with the lowest intakes.
Up to 15% of this observed association was explained by the gut microbiome, suggesting that these microbes play a key role in metabolizing flavonoids to enhance their cardioprotective effects, according to the researchers.
The study was published online in the journal Hypertension.
“We know what we eat plays a critical role in shaping our gut microbiome, but little is known about the relative importance of plant foods and specific constituents called flavonoids,” lead researcher Aedin Cassidy, PhD, chair and professor of nutrition and medicine at the Institute for Global Food Security, Queen’s University, Belfast, Northern Ireland, said in an interview.
“Unlike many other food constituents, flavonoids are predominantly metabolized in the gut, suggesting that the gut microbiome may be more important in enhancing their biological activity than for other things we eat,” Dr. Cassidy said.
“There is mounting evidence from population-based studies and clinical trials that a higher intake of flavonoids and flavonoid-rich foods can improve heart health, but for the first time, we provide data highlighting the key role of the gut microbiome in explaining the association between such foods and blood pressure,” she noted. “This is one of the first studies to address this.”
For this analysis, Dr. Cassidy and her group sought to assess to what extent the composition of the gut microbiome might explain the association of habitual flavonoid and flavonoid-rich food intake with systolic and diastolic blood pressure in a community-based sample of 904 individuals aged 25-82 years from Germany’s PopGen biobank.
The researchers evaluated participants’ food intake, gut microbiome, and blood pressure levels together with other clinical and molecular phenotyping at regular follow-up examinations.
Participants’ intake of flavonoid-rich foods during the previous year was calculated from a self-reported food questionnaire detailing the frequency and quantity eaten of 112 foods, and flavonoid values were assigned to foods according to United States Department of Agriculture data on flavonoid content in food.
Participants’ gut microbiome was assessed by fecal bacterial DNA extracted from stool samples.
After an overnight fast, participants’ blood pressure levels were measured three times in 3-minute intervals after an initial 5-minute rest period. Researchers also collected participants’ diet and lifestyle information.
Analysis of the data showed the following:
- Eating 1.5 servings of berries per day (about 1 cup) was associated with a 4.1–mm Hg reduction in systolic BP; 12% of this association was explained by gut microbiome factors.
- Drinking three glasses of red wine per week was associated with a 3.7–mm Hg reduction in systolic BP; 15% of this association was explained by the gut microbiome.
“These blood pressure–lowering effects are achievable with simple changes to the daily diet,” Dr. Cassidy said.
“Incorporating flavonoid-rich foods into the diet can have clinically relevant reductions in systolic blood pressure and pulse pressure, and a healthy gut microbiome is important to break down flavonoids to a more cardioprotective form,” she said.
“Our findings indicate future trials should look at participants according to metabolic profile in order to more accurately study the roles of metabolism and the gut microbiome in regulating the effects of flavonoids on blood pressure,” said Dr. Cassidy.
“A better understanding of the highly individual variability of flavonoid metabolism could very well explain why some people have greater cardiovascular protection benefits from flavonoid-rich foods than others.”
‘Interesting’ data
“The data are interesting,” David Jenkins, MD, PhD, DSc, professor of medicine and nutrition at the University of Toronto, said in an interview.
“Berries and red wine appear to be associated with lower systolic blood pressures. Lower blood pressures have been found in general in people who consume more plant-based diets, especially those high in fruits and vegetables,” noted Dr. Jenkins, who was not involved with this study.
“Berries and grapes high in polyphenols may have many health benefits as antioxidants, and in a recent study have been shown to reduce cardiovascular mortality. The change in chronic microflora is also of interest as this will change with increased fruit and vegetable consumption,” he said.
Perhaps one word of caveat, Dr. Jenkins added: “Alcohol has been found to increase blood pressure and the risk of stroke. Presumably the beneficial effects as seen here were when wine is consumed in moderation.”
Supports recommendations
The study by Cassidy and colleagues supports the dietary recommendations from the American Heart Association (AHA) for heart health, Penny M. Kris-Etherton, PhD, RDN, professor of nutritional sciences, Penn State University, University Park, Pa., and chair, AHA Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health, said in an interview.
“The AHA recommends a healthy dietary pattern that emphasizes a variety of plant foods including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds and is low in sodium, saturated fat, and added sugars. Lean protein foods, including plant protein foods, are recommended, and red meat should be limited. If alcohol is consumed it should be done in moderation,” Dr. Kris-Etherton said.
“Based on these AHA dietary recommendations, a wide variety of plant foods will promote consumption of many flavonoids that have demonstrated CVD benefits, such as lowering systolic blood pressure as reported by the authors, as well as promoting healthy endothelial function and having antithrombotic, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects,” she said in email.
“This recommended dietary pattern will have other cardiovascular health benefits, such as decreasing LDL cholesterol, due to its very healthy nutrient profile. The exciting new finding reported by Cassidy et al. is that the effects of dietary flavonoids on lowering systolic blood pressure are modulated by the gut microbiome,” Dr. Kris-Etherton said.
“Further research needs to be done to confirm these findings and to identify how different foods affect specific gut bacteria that benefit cardiovascular health.”
The research was funded by grants from the German Research Foundation and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. Dr. Cassidy and Dr. Jenkins have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kris-Etherton is a spokesperson for the AHA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, an association that is partially explained by bacteria in an individual’s gut microbiome, new research suggests.
In a population-based study of more than 900 individuals, those with the highest intake of flavonoid-containing foods had significantly lower systolic blood pressure and pulse pressure, as well as greater gut microbial diversity, compared with those with the lowest intakes.
Up to 15% of this observed association was explained by the gut microbiome, suggesting that these microbes play a key role in metabolizing flavonoids to enhance their cardioprotective effects, according to the researchers.
The study was published online in the journal Hypertension.
“We know what we eat plays a critical role in shaping our gut microbiome, but little is known about the relative importance of plant foods and specific constituents called flavonoids,” lead researcher Aedin Cassidy, PhD, chair and professor of nutrition and medicine at the Institute for Global Food Security, Queen’s University, Belfast, Northern Ireland, said in an interview.
“Unlike many other food constituents, flavonoids are predominantly metabolized in the gut, suggesting that the gut microbiome may be more important in enhancing their biological activity than for other things we eat,” Dr. Cassidy said.
“There is mounting evidence from population-based studies and clinical trials that a higher intake of flavonoids and flavonoid-rich foods can improve heart health, but for the first time, we provide data highlighting the key role of the gut microbiome in explaining the association between such foods and blood pressure,” she noted. “This is one of the first studies to address this.”
For this analysis, Dr. Cassidy and her group sought to assess to what extent the composition of the gut microbiome might explain the association of habitual flavonoid and flavonoid-rich food intake with systolic and diastolic blood pressure in a community-based sample of 904 individuals aged 25-82 years from Germany’s PopGen biobank.
The researchers evaluated participants’ food intake, gut microbiome, and blood pressure levels together with other clinical and molecular phenotyping at regular follow-up examinations.
Participants’ intake of flavonoid-rich foods during the previous year was calculated from a self-reported food questionnaire detailing the frequency and quantity eaten of 112 foods, and flavonoid values were assigned to foods according to United States Department of Agriculture data on flavonoid content in food.
Participants’ gut microbiome was assessed by fecal bacterial DNA extracted from stool samples.
After an overnight fast, participants’ blood pressure levels were measured three times in 3-minute intervals after an initial 5-minute rest period. Researchers also collected participants’ diet and lifestyle information.
Analysis of the data showed the following:
- Eating 1.5 servings of berries per day (about 1 cup) was associated with a 4.1–mm Hg reduction in systolic BP; 12% of this association was explained by gut microbiome factors.
- Drinking three glasses of red wine per week was associated with a 3.7–mm Hg reduction in systolic BP; 15% of this association was explained by the gut microbiome.
“These blood pressure–lowering effects are achievable with simple changes to the daily diet,” Dr. Cassidy said.
“Incorporating flavonoid-rich foods into the diet can have clinically relevant reductions in systolic blood pressure and pulse pressure, and a healthy gut microbiome is important to break down flavonoids to a more cardioprotective form,” she said.
“Our findings indicate future trials should look at participants according to metabolic profile in order to more accurately study the roles of metabolism and the gut microbiome in regulating the effects of flavonoids on blood pressure,” said Dr. Cassidy.
“A better understanding of the highly individual variability of flavonoid metabolism could very well explain why some people have greater cardiovascular protection benefits from flavonoid-rich foods than others.”
‘Interesting’ data
“The data are interesting,” David Jenkins, MD, PhD, DSc, professor of medicine and nutrition at the University of Toronto, said in an interview.
“Berries and red wine appear to be associated with lower systolic blood pressures. Lower blood pressures have been found in general in people who consume more plant-based diets, especially those high in fruits and vegetables,” noted Dr. Jenkins, who was not involved with this study.
“Berries and grapes high in polyphenols may have many health benefits as antioxidants, and in a recent study have been shown to reduce cardiovascular mortality. The change in chronic microflora is also of interest as this will change with increased fruit and vegetable consumption,” he said.
Perhaps one word of caveat, Dr. Jenkins added: “Alcohol has been found to increase blood pressure and the risk of stroke. Presumably the beneficial effects as seen here were when wine is consumed in moderation.”
Supports recommendations
The study by Cassidy and colleagues supports the dietary recommendations from the American Heart Association (AHA) for heart health, Penny M. Kris-Etherton, PhD, RDN, professor of nutritional sciences, Penn State University, University Park, Pa., and chair, AHA Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health, said in an interview.
“The AHA recommends a healthy dietary pattern that emphasizes a variety of plant foods including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds and is low in sodium, saturated fat, and added sugars. Lean protein foods, including plant protein foods, are recommended, and red meat should be limited. If alcohol is consumed it should be done in moderation,” Dr. Kris-Etherton said.
“Based on these AHA dietary recommendations, a wide variety of plant foods will promote consumption of many flavonoids that have demonstrated CVD benefits, such as lowering systolic blood pressure as reported by the authors, as well as promoting healthy endothelial function and having antithrombotic, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects,” she said in email.
“This recommended dietary pattern will have other cardiovascular health benefits, such as decreasing LDL cholesterol, due to its very healthy nutrient profile. The exciting new finding reported by Cassidy et al. is that the effects of dietary flavonoids on lowering systolic blood pressure are modulated by the gut microbiome,” Dr. Kris-Etherton said.
“Further research needs to be done to confirm these findings and to identify how different foods affect specific gut bacteria that benefit cardiovascular health.”
The research was funded by grants from the German Research Foundation and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. Dr. Cassidy and Dr. Jenkins have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kris-Etherton is a spokesperson for the AHA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Some patients with more severe PH in COPD may respond to treatment
Patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH) as a complication of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) have worse functional impairment and higher mortality, compared with patients who have idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH).
Despite these factors, some patients with more severe PH in COPD may respond to treatment and show clinical improvement after treatment, according to recent research published in the journal CHEST®.
Carmine Dario Vizza, MD, of the pulmonary hypertension unit, department of cardiovascular and respiratory diseases at Sapienza University of Rome, and colleagues evaluated patients in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) database, enrolled up to August 2020, identifying 68 patients with moderate PH and COPD and 307 patients with severe PH and COPD. The researchers compared the PH and COPD groups with 307 patients who had idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Overall, mostly older men made up the group of patients with moderate (50%; mean, 68.5 years) and severe PH in COPD (61%; mean 68.4 years), compared with those who had IPAH (37%; mean 61.7 years. Oral monotherapy for patients with PH and COPD was the main treatment, consisting of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors, while most patients with IPAH received endothelin receptor antagonists.
On functional tests, patients in the PH and COPD group tended to perform poorer on the 6-minute walking distance (6MWD) and World Health Organization functional class (WHO FC) than patients with IPAH. Specifically, among 42.7% of patients in both group for whom follow-up data were available, there was a similar frequency of improvement for 6MWD of 30 meters or more from baseline for both PH and COPD and IPAH groups (46.9% vs. 52.6%; P = .294), but there were significant differences between 6MWD between patients with moderate and severe PH and COPD (51.6% vs. 31.6%; P = .04). There was a nonsignificant improvement in WHO FC improvement of one or more classes for 65.6% of patients with PH and COPD and 58.3% of patients with IPAH with follow-up data available, with 28.5% of patients with PH in COPD improving compared with 35.8% of patients with IPAH (P = .078) and nonsignificant differences between moderate and severe PH and COPD (19.0% vs. 30.4%; P = .188).
Comparing outcomes
Follow-up data were available for 84% of patients with IPAH and 94% of patients with PH and COPD. Dr. Dario Vizza and colleagues found 45.7% of patients in the PH and COPD group and 24.9% of patients in the IPAH group died during follow-up, while 1.1% in the PH and COPD group and 1.5% of patients in the IPAH group underwent lung transplantations. For patients with moderate PH and COPD, 31.3% died and none underwent lung transplantation, while 49.0% of patients in the severe PH and COPD group died and 1.4% underwent lung transplantations.
Patients in the moderate PH and COPD group were more likely to discontinue treatment (10.9%), compared with patients with IPAH (6.6%) and patients with severe PH and COPD (5.2%). The most common reasons for discontinuations were tolerability and efficacy failure; the IPAH group had 63% of patients discontinue because of tolerability and 7% for efficacy failure, 47% of patients in the severe PH and COPD group discontinued because of tolerability and efficacy, and 29% discontinued treatment for tolerability and 57% for efficacy failure in the moderate and COPD group.
The researchers said male sex, low 6MWD, and high pulmonary vascular resistance at baseline were predictive of poorer outcomes for PH and COPD, but patients with more severe PH and COPD had better outcomes if they improved by 30 meters or more in 6MWD, or improved in WHO FC after receiving medical therapy. For patients with IPAH response to therapy was better among patients who were younger, had higher WHO FC, had high diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide, had high mean pulmonary artery pressure, and had low PCO2.
“Our data suggest that PH-targeted drug therapy in patients with COPD and severe PH may improve exercise tolerance and WHO FC in a subgroup of patients and that patients with COPD and PH who respond to therapy may have a better prognosis than patients who do not show clinical improvement. These findings need to be explored further in prospective, randomized controlled clinical studies,” the authors concluded.
More research needed
In a related editorial, James R. Klinger, MD, a pulmonologist with Brown University, Providence, R.I., and the director of the Rhode Island Hospital Pulmonary Hypertension Center in East Providence, said there is a “keen interest” in treating PH in COPD despite a lack of consistency on whether treatment is effective in this patient population. About 80% of PH centers in the United States treat PH in COPD when they treat conditions like lung disease with PAH medication, he pointed out. However, he questioned whether current medications designed for PAH could improve pulmonary hemodynamics for PH in COPD.
“Reasons that the pathobiologic condition of PH-COPD may differ from PAH include the likely exposure of the pulmonary circulation to greater degrees of hypoxia and hypercapnia and the greater loss of alveolar capillaries associated with emphysema,” he said.
The study by Dr. Dario Vizza and colleagues is an attempt to evaluate treatment response for patients with PH and COPD “in a way that allows comparison with patients who have been treated with similar drugs for PAH,” Dr. Klinger said. He noted the study’s retrospective nature, lack of control group, and lack of information on lung disease severity could limit the findings.
“These limitations preclude recommendations for the routine treatment of patients with PH-COPD, but the findings suggest that, despite greater morbidity at baseline, patients with PH-COPD may be nearly as likely to benefit from PAH medications as patients with IPAH,” he said.
“What is needed now is well-designed randomized controlled studies to determine whether improved outcomes can be achieved in this population and which patients are most likely to benefit,” he concluded. “Simply put: How bad does PH need to be in patients with COPD before treatment is helpful, and how severe does COPD need to be before PH treatment is futile?”
The authors reported personal and institutional relationships in the form of grants, consultancies, advisory board memberships, speakers bureau appointments, honoraria, patents, grant and research funding, lectures, travel compensation, and steering committee positions for a variety of pharmaceutical companies, agencies, societies, journals, medical publishing companies, and other organizations. Dr. Klinger reported his institution receives grant support from Acceleron and United Therapeutics in the area of PH, and he has been an unpaid consultant for Bayer.
Patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH) as a complication of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) have worse functional impairment and higher mortality, compared with patients who have idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH).
Despite these factors, some patients with more severe PH in COPD may respond to treatment and show clinical improvement after treatment, according to recent research published in the journal CHEST®.
Carmine Dario Vizza, MD, of the pulmonary hypertension unit, department of cardiovascular and respiratory diseases at Sapienza University of Rome, and colleagues evaluated patients in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) database, enrolled up to August 2020, identifying 68 patients with moderate PH and COPD and 307 patients with severe PH and COPD. The researchers compared the PH and COPD groups with 307 patients who had idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Overall, mostly older men made up the group of patients with moderate (50%; mean, 68.5 years) and severe PH in COPD (61%; mean 68.4 years), compared with those who had IPAH (37%; mean 61.7 years. Oral monotherapy for patients with PH and COPD was the main treatment, consisting of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors, while most patients with IPAH received endothelin receptor antagonists.
On functional tests, patients in the PH and COPD group tended to perform poorer on the 6-minute walking distance (6MWD) and World Health Organization functional class (WHO FC) than patients with IPAH. Specifically, among 42.7% of patients in both group for whom follow-up data were available, there was a similar frequency of improvement for 6MWD of 30 meters or more from baseline for both PH and COPD and IPAH groups (46.9% vs. 52.6%; P = .294), but there were significant differences between 6MWD between patients with moderate and severe PH and COPD (51.6% vs. 31.6%; P = .04). There was a nonsignificant improvement in WHO FC improvement of one or more classes for 65.6% of patients with PH and COPD and 58.3% of patients with IPAH with follow-up data available, with 28.5% of patients with PH in COPD improving compared with 35.8% of patients with IPAH (P = .078) and nonsignificant differences between moderate and severe PH and COPD (19.0% vs. 30.4%; P = .188).
Comparing outcomes
Follow-up data were available for 84% of patients with IPAH and 94% of patients with PH and COPD. Dr. Dario Vizza and colleagues found 45.7% of patients in the PH and COPD group and 24.9% of patients in the IPAH group died during follow-up, while 1.1% in the PH and COPD group and 1.5% of patients in the IPAH group underwent lung transplantations. For patients with moderate PH and COPD, 31.3% died and none underwent lung transplantation, while 49.0% of patients in the severe PH and COPD group died and 1.4% underwent lung transplantations.
Patients in the moderate PH and COPD group were more likely to discontinue treatment (10.9%), compared with patients with IPAH (6.6%) and patients with severe PH and COPD (5.2%). The most common reasons for discontinuations were tolerability and efficacy failure; the IPAH group had 63% of patients discontinue because of tolerability and 7% for efficacy failure, 47% of patients in the severe PH and COPD group discontinued because of tolerability and efficacy, and 29% discontinued treatment for tolerability and 57% for efficacy failure in the moderate and COPD group.
The researchers said male sex, low 6MWD, and high pulmonary vascular resistance at baseline were predictive of poorer outcomes for PH and COPD, but patients with more severe PH and COPD had better outcomes if they improved by 30 meters or more in 6MWD, or improved in WHO FC after receiving medical therapy. For patients with IPAH response to therapy was better among patients who were younger, had higher WHO FC, had high diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide, had high mean pulmonary artery pressure, and had low PCO2.
“Our data suggest that PH-targeted drug therapy in patients with COPD and severe PH may improve exercise tolerance and WHO FC in a subgroup of patients and that patients with COPD and PH who respond to therapy may have a better prognosis than patients who do not show clinical improvement. These findings need to be explored further in prospective, randomized controlled clinical studies,” the authors concluded.
More research needed
In a related editorial, James R. Klinger, MD, a pulmonologist with Brown University, Providence, R.I., and the director of the Rhode Island Hospital Pulmonary Hypertension Center in East Providence, said there is a “keen interest” in treating PH in COPD despite a lack of consistency on whether treatment is effective in this patient population. About 80% of PH centers in the United States treat PH in COPD when they treat conditions like lung disease with PAH medication, he pointed out. However, he questioned whether current medications designed for PAH could improve pulmonary hemodynamics for PH in COPD.
“Reasons that the pathobiologic condition of PH-COPD may differ from PAH include the likely exposure of the pulmonary circulation to greater degrees of hypoxia and hypercapnia and the greater loss of alveolar capillaries associated with emphysema,” he said.
The study by Dr. Dario Vizza and colleagues is an attempt to evaluate treatment response for patients with PH and COPD “in a way that allows comparison with patients who have been treated with similar drugs for PAH,” Dr. Klinger said. He noted the study’s retrospective nature, lack of control group, and lack of information on lung disease severity could limit the findings.
“These limitations preclude recommendations for the routine treatment of patients with PH-COPD, but the findings suggest that, despite greater morbidity at baseline, patients with PH-COPD may be nearly as likely to benefit from PAH medications as patients with IPAH,” he said.
“What is needed now is well-designed randomized controlled studies to determine whether improved outcomes can be achieved in this population and which patients are most likely to benefit,” he concluded. “Simply put: How bad does PH need to be in patients with COPD before treatment is helpful, and how severe does COPD need to be before PH treatment is futile?”
The authors reported personal and institutional relationships in the form of grants, consultancies, advisory board memberships, speakers bureau appointments, honoraria, patents, grant and research funding, lectures, travel compensation, and steering committee positions for a variety of pharmaceutical companies, agencies, societies, journals, medical publishing companies, and other organizations. Dr. Klinger reported his institution receives grant support from Acceleron and United Therapeutics in the area of PH, and he has been an unpaid consultant for Bayer.
Patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH) as a complication of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) have worse functional impairment and higher mortality, compared with patients who have idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH).
Despite these factors, some patients with more severe PH in COPD may respond to treatment and show clinical improvement after treatment, according to recent research published in the journal CHEST®.
Carmine Dario Vizza, MD, of the pulmonary hypertension unit, department of cardiovascular and respiratory diseases at Sapienza University of Rome, and colleagues evaluated patients in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) database, enrolled up to August 2020, identifying 68 patients with moderate PH and COPD and 307 patients with severe PH and COPD. The researchers compared the PH and COPD groups with 307 patients who had idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Overall, mostly older men made up the group of patients with moderate (50%; mean, 68.5 years) and severe PH in COPD (61%; mean 68.4 years), compared with those who had IPAH (37%; mean 61.7 years. Oral monotherapy for patients with PH and COPD was the main treatment, consisting of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors, while most patients with IPAH received endothelin receptor antagonists.
On functional tests, patients in the PH and COPD group tended to perform poorer on the 6-minute walking distance (6MWD) and World Health Organization functional class (WHO FC) than patients with IPAH. Specifically, among 42.7% of patients in both group for whom follow-up data were available, there was a similar frequency of improvement for 6MWD of 30 meters or more from baseline for both PH and COPD and IPAH groups (46.9% vs. 52.6%; P = .294), but there were significant differences between 6MWD between patients with moderate and severe PH and COPD (51.6% vs. 31.6%; P = .04). There was a nonsignificant improvement in WHO FC improvement of one or more classes for 65.6% of patients with PH and COPD and 58.3% of patients with IPAH with follow-up data available, with 28.5% of patients with PH in COPD improving compared with 35.8% of patients with IPAH (P = .078) and nonsignificant differences between moderate and severe PH and COPD (19.0% vs. 30.4%; P = .188).
Comparing outcomes
Follow-up data were available for 84% of patients with IPAH and 94% of patients with PH and COPD. Dr. Dario Vizza and colleagues found 45.7% of patients in the PH and COPD group and 24.9% of patients in the IPAH group died during follow-up, while 1.1% in the PH and COPD group and 1.5% of patients in the IPAH group underwent lung transplantations. For patients with moderate PH and COPD, 31.3% died and none underwent lung transplantation, while 49.0% of patients in the severe PH and COPD group died and 1.4% underwent lung transplantations.
Patients in the moderate PH and COPD group were more likely to discontinue treatment (10.9%), compared with patients with IPAH (6.6%) and patients with severe PH and COPD (5.2%). The most common reasons for discontinuations were tolerability and efficacy failure; the IPAH group had 63% of patients discontinue because of tolerability and 7% for efficacy failure, 47% of patients in the severe PH and COPD group discontinued because of tolerability and efficacy, and 29% discontinued treatment for tolerability and 57% for efficacy failure in the moderate and COPD group.
The researchers said male sex, low 6MWD, and high pulmonary vascular resistance at baseline were predictive of poorer outcomes for PH and COPD, but patients with more severe PH and COPD had better outcomes if they improved by 30 meters or more in 6MWD, or improved in WHO FC after receiving medical therapy. For patients with IPAH response to therapy was better among patients who were younger, had higher WHO FC, had high diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide, had high mean pulmonary artery pressure, and had low PCO2.
“Our data suggest that PH-targeted drug therapy in patients with COPD and severe PH may improve exercise tolerance and WHO FC in a subgroup of patients and that patients with COPD and PH who respond to therapy may have a better prognosis than patients who do not show clinical improvement. These findings need to be explored further in prospective, randomized controlled clinical studies,” the authors concluded.
More research needed
In a related editorial, James R. Klinger, MD, a pulmonologist with Brown University, Providence, R.I., and the director of the Rhode Island Hospital Pulmonary Hypertension Center in East Providence, said there is a “keen interest” in treating PH in COPD despite a lack of consistency on whether treatment is effective in this patient population. About 80% of PH centers in the United States treat PH in COPD when they treat conditions like lung disease with PAH medication, he pointed out. However, he questioned whether current medications designed for PAH could improve pulmonary hemodynamics for PH in COPD.
“Reasons that the pathobiologic condition of PH-COPD may differ from PAH include the likely exposure of the pulmonary circulation to greater degrees of hypoxia and hypercapnia and the greater loss of alveolar capillaries associated with emphysema,” he said.
The study by Dr. Dario Vizza and colleagues is an attempt to evaluate treatment response for patients with PH and COPD “in a way that allows comparison with patients who have been treated with similar drugs for PAH,” Dr. Klinger said. He noted the study’s retrospective nature, lack of control group, and lack of information on lung disease severity could limit the findings.
“These limitations preclude recommendations for the routine treatment of patients with PH-COPD, but the findings suggest that, despite greater morbidity at baseline, patients with PH-COPD may be nearly as likely to benefit from PAH medications as patients with IPAH,” he said.
“What is needed now is well-designed randomized controlled studies to determine whether improved outcomes can be achieved in this population and which patients are most likely to benefit,” he concluded. “Simply put: How bad does PH need to be in patients with COPD before treatment is helpful, and how severe does COPD need to be before PH treatment is futile?”
The authors reported personal and institutional relationships in the form of grants, consultancies, advisory board memberships, speakers bureau appointments, honoraria, patents, grant and research funding, lectures, travel compensation, and steering committee positions for a variety of pharmaceutical companies, agencies, societies, journals, medical publishing companies, and other organizations. Dr. Klinger reported his institution receives grant support from Acceleron and United Therapeutics in the area of PH, and he has been an unpaid consultant for Bayer.
FROM THE JOURNAL CHEST®
Obesity leads to depression via social and metabolic factors
New research provides further evidence that a high body mass index (BMI) leads to depressed mood and poor well-being via social and physical factors.
Obesity and depression are “major global health challenges; our findings suggest that reducing obesity will lower depression and improve well-being,” co–lead author Jessica O’Loughlin, PhD student, University of Exeter Medical School, United Kingdom, told this news organization.
“Doctors should consider both the biological consequences of having a higher BMI as well as the social implications when treating patients with obesity in order to help reduce the odds of them developing depression,” Ms. O’Loughlin added.
The study was published online July 16 in Human Molecular Genetics.
Large body of evidence
A large body of evidence indicates that higher BMI leads to depression.
Ms. O’Loughlin and colleagues leveraged genetic data from more than 145,000 individuals in the UK Biobank and Mendelian randomization to determine whether the causal link between high BMI and depression is the result of psychosocial pathways, physical pathways, or both.
The analysis showed that a genetically determined 1 standard deviation higher BMI (4.6 kg/m2) was associated with higher likelihood of depression (odds ratio, 1.50; 95% confidence interval, 1.15-1.95) and lower well-being (beta, -0.15; 95% CI, -0.26 to -0.04).
Using genetics to distinguish metabolic and psychosocial effects, the results also indicate that, even in the absence of adverse metabolic effects, “higher adiposity remains causal to depression and lowers wellbeing,” the researchers report.
“ and when using genetic variants that make you fatter but metabolically healthier (favorable adiposity genetic variants),” said Ms. O’Loughlin.
“Although we can’t tell which factor plays a bigger role in the adiposity-depression relationship, our analysis suggests that both physical and social factors (e.g., social stigma) play a role in the relationship between higher BMI and higher odds of depression,” she added.
In contrast, there was little evidence that higher BMI in the presence or absence of adverse metabolic consequences causes generalized anxiety disorder.
“Finding ways to support people to lose weight could benefit their mental health as well as their physical health,” co–lead author Francesco Casanova, PhD, with the University of Exeter, said in a statement.
Unexpected finding
Reached for comment, Samoon Ahmad, MD, professor, department of psychiatry, New York University, said that “multiple studies have shown a correlation between stress, obesity, inflammation, overall well-being, and psychiatric disorders, particularly depressive and anxiety disorders.”
He said this new study is important for three reasons.
“The first is the cohort size. There were over 145,000 participants involved in the study, which is significant and serves to make its conclusions stronger,” Dr. Ahmad noted.
“The second point is that the authors found that the correlation between higher adiposity and depression and lower well-being scores occurred even in patients without adverse metabolic effects,” he said in an interview.
“Of note, obesity significantly increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and a host of other illnesses as well as inflammatory conditions, which can all have a negative impact on quality of life. Consequently, these can contribute to depression as well as anxiety,” Dr. Ahmad added.
“Interestingly, what this study suggests is that even people without these additional stressors are reporting higher rates of depression and lower scores of well-being, while higher adiposity is the common denominator,” he noted.
“Third, the paper found little to no correlation between higher adiposity and generalized anxiety disorder. This comes as a complete surprise because anxiety and depression are very common comorbidities,” Dr. Ahmad said.
“Moreover, numerous studies as well as clinical data suggest that obesity leads to chronic inflammation, which in turn is associated with less favorable metabolic profiles, and that anxiety and depressive disorders may in some way be psychiatric manifestations of inflammation. To see one but not the other was quite an unexpected finding,” Dr. Ahmad said.
The study was funded by the Academy of Medical Sciences. Ms. O’Loughlin, Dr. Casanova, and Dr. Ahmad have disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research provides further evidence that a high body mass index (BMI) leads to depressed mood and poor well-being via social and physical factors.
Obesity and depression are “major global health challenges; our findings suggest that reducing obesity will lower depression and improve well-being,” co–lead author Jessica O’Loughlin, PhD student, University of Exeter Medical School, United Kingdom, told this news organization.
“Doctors should consider both the biological consequences of having a higher BMI as well as the social implications when treating patients with obesity in order to help reduce the odds of them developing depression,” Ms. O’Loughlin added.
The study was published online July 16 in Human Molecular Genetics.
Large body of evidence
A large body of evidence indicates that higher BMI leads to depression.
Ms. O’Loughlin and colleagues leveraged genetic data from more than 145,000 individuals in the UK Biobank and Mendelian randomization to determine whether the causal link between high BMI and depression is the result of psychosocial pathways, physical pathways, or both.
The analysis showed that a genetically determined 1 standard deviation higher BMI (4.6 kg/m2) was associated with higher likelihood of depression (odds ratio, 1.50; 95% confidence interval, 1.15-1.95) and lower well-being (beta, -0.15; 95% CI, -0.26 to -0.04).
Using genetics to distinguish metabolic and psychosocial effects, the results also indicate that, even in the absence of adverse metabolic effects, “higher adiposity remains causal to depression and lowers wellbeing,” the researchers report.
“ and when using genetic variants that make you fatter but metabolically healthier (favorable adiposity genetic variants),” said Ms. O’Loughlin.
“Although we can’t tell which factor plays a bigger role in the adiposity-depression relationship, our analysis suggests that both physical and social factors (e.g., social stigma) play a role in the relationship between higher BMI and higher odds of depression,” she added.
In contrast, there was little evidence that higher BMI in the presence or absence of adverse metabolic consequences causes generalized anxiety disorder.
“Finding ways to support people to lose weight could benefit their mental health as well as their physical health,” co–lead author Francesco Casanova, PhD, with the University of Exeter, said in a statement.
Unexpected finding
Reached for comment, Samoon Ahmad, MD, professor, department of psychiatry, New York University, said that “multiple studies have shown a correlation between stress, obesity, inflammation, overall well-being, and psychiatric disorders, particularly depressive and anxiety disorders.”
He said this new study is important for three reasons.
“The first is the cohort size. There were over 145,000 participants involved in the study, which is significant and serves to make its conclusions stronger,” Dr. Ahmad noted.
“The second point is that the authors found that the correlation between higher adiposity and depression and lower well-being scores occurred even in patients without adverse metabolic effects,” he said in an interview.
“Of note, obesity significantly increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and a host of other illnesses as well as inflammatory conditions, which can all have a negative impact on quality of life. Consequently, these can contribute to depression as well as anxiety,” Dr. Ahmad added.
“Interestingly, what this study suggests is that even people without these additional stressors are reporting higher rates of depression and lower scores of well-being, while higher adiposity is the common denominator,” he noted.
“Third, the paper found little to no correlation between higher adiposity and generalized anxiety disorder. This comes as a complete surprise because anxiety and depression are very common comorbidities,” Dr. Ahmad said.
“Moreover, numerous studies as well as clinical data suggest that obesity leads to chronic inflammation, which in turn is associated with less favorable metabolic profiles, and that anxiety and depressive disorders may in some way be psychiatric manifestations of inflammation. To see one but not the other was quite an unexpected finding,” Dr. Ahmad said.
The study was funded by the Academy of Medical Sciences. Ms. O’Loughlin, Dr. Casanova, and Dr. Ahmad have disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research provides further evidence that a high body mass index (BMI) leads to depressed mood and poor well-being via social and physical factors.
Obesity and depression are “major global health challenges; our findings suggest that reducing obesity will lower depression and improve well-being,” co–lead author Jessica O’Loughlin, PhD student, University of Exeter Medical School, United Kingdom, told this news organization.
“Doctors should consider both the biological consequences of having a higher BMI as well as the social implications when treating patients with obesity in order to help reduce the odds of them developing depression,” Ms. O’Loughlin added.
The study was published online July 16 in Human Molecular Genetics.
Large body of evidence
A large body of evidence indicates that higher BMI leads to depression.
Ms. O’Loughlin and colleagues leveraged genetic data from more than 145,000 individuals in the UK Biobank and Mendelian randomization to determine whether the causal link between high BMI and depression is the result of psychosocial pathways, physical pathways, or both.
The analysis showed that a genetically determined 1 standard deviation higher BMI (4.6 kg/m2) was associated with higher likelihood of depression (odds ratio, 1.50; 95% confidence interval, 1.15-1.95) and lower well-being (beta, -0.15; 95% CI, -0.26 to -0.04).
Using genetics to distinguish metabolic and psychosocial effects, the results also indicate that, even in the absence of adverse metabolic effects, “higher adiposity remains causal to depression and lowers wellbeing,” the researchers report.
“ and when using genetic variants that make you fatter but metabolically healthier (favorable adiposity genetic variants),” said Ms. O’Loughlin.
“Although we can’t tell which factor plays a bigger role in the adiposity-depression relationship, our analysis suggests that both physical and social factors (e.g., social stigma) play a role in the relationship between higher BMI and higher odds of depression,” she added.
In contrast, there was little evidence that higher BMI in the presence or absence of adverse metabolic consequences causes generalized anxiety disorder.
“Finding ways to support people to lose weight could benefit their mental health as well as their physical health,” co–lead author Francesco Casanova, PhD, with the University of Exeter, said in a statement.
Unexpected finding
Reached for comment, Samoon Ahmad, MD, professor, department of psychiatry, New York University, said that “multiple studies have shown a correlation between stress, obesity, inflammation, overall well-being, and psychiatric disorders, particularly depressive and anxiety disorders.”
He said this new study is important for three reasons.
“The first is the cohort size. There were over 145,000 participants involved in the study, which is significant and serves to make its conclusions stronger,” Dr. Ahmad noted.
“The second point is that the authors found that the correlation between higher adiposity and depression and lower well-being scores occurred even in patients without adverse metabolic effects,” he said in an interview.
“Of note, obesity significantly increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and a host of other illnesses as well as inflammatory conditions, which can all have a negative impact on quality of life. Consequently, these can contribute to depression as well as anxiety,” Dr. Ahmad added.
“Interestingly, what this study suggests is that even people without these additional stressors are reporting higher rates of depression and lower scores of well-being, while higher adiposity is the common denominator,” he noted.
“Third, the paper found little to no correlation between higher adiposity and generalized anxiety disorder. This comes as a complete surprise because anxiety and depression are very common comorbidities,” Dr. Ahmad said.
“Moreover, numerous studies as well as clinical data suggest that obesity leads to chronic inflammation, which in turn is associated with less favorable metabolic profiles, and that anxiety and depressive disorders may in some way be psychiatric manifestations of inflammation. To see one but not the other was quite an unexpected finding,” Dr. Ahmad said.
The study was funded by the Academy of Medical Sciences. Ms. O’Loughlin, Dr. Casanova, and Dr. Ahmad have disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Aerobic exercise reduces BP in resistant hypertension
Aerobic exercise may help reduce blood pressure in patients whose hypertension responds poorly to medications, a new study suggests.
A randomized controlled clinical trial showed that patients with resistant hypertension assigned to a moderate-intensity aerobic exercise training program had lower blood pressure compared with patients who received usual care.
“Resistant hypertension persists as a big clinical challenge because the available treatment options to lower blood pressure in this clinical population, namely drugs and renal denervation, show limited success,” Fernando Ribeiro, PhD, University of Aveiro, Portugal, told this news organization. “Aerobic exercise was safe and associated with a significant and clinically relevant reduction in 24-hour, daytime ambulatory, and office blood pressure.”
The findings were published online August 4 in JAMA Cardiology.
The researchers enrolled 53 patients aged 40-75 years with a diagnosis of resistant hypertension in this prospective, single-blinded trial. Nearly half (24) were women.
Resistant hypertension was defined as having a “mean systolic BP of 130 mm Hg or greater on 24-hour ambulatory BP monitoring and/or 135 mm Hg or greater during daytime hours while taking maximally tolerated doses of at least 3 antihypertensive agents, including a diuretic, or to have a controlled BP while taking 4 or more antihypertensive agents.”
From March 2017 to December 2019 at two sites in Portugal, 26 patients were randomly assigned to a 12-week aerobic exercise training program involving three 40-minute supervised sessions per week in addition to usual care. Another 27 patients in the control group were allocated to receive usual care only.
24-hour ambulatory systolic blood pressure was reduced by 7.1 mm Hg (95% confidence interval, -12.8 to -1.4; P = .02) in patients in the exercise group compared with the control group. In the exercise group, there were additional reductions of:
- -5.1 mm Hg of 24-hour ambulatory diastolic blood pressure (95% CI, -7.9 to -2.3; P = .001)
- -8.4 mm Hg of daytime systolic blood pressure (95% CI, -14.3 to -2.5, P = .006)
- -5.7 mm Hg of daytime diastolic blood pressure (95% CI, -9.0 to -2.4; P = .001)
- -10.0 mm Hg of office systolic blood pressure (95% CI, -17.6 to -2.5; P = .01)
Additionally, a significant improvement in cardiorespiratory fitness (5.05 mL/kg per minute of oxygen consumption; 95% CI, 3.5-6.6; P < .001) was observed in the exercise group compared with the control group.
Although prior research has suggested that exercise may lower blood pressure, this study is particularly useful because it “outlines very specifically what types of exercise you can recommend,” said Daniel Lackland, DrPH, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
Although important, exercise is “one part of the overall management of high blood pressure. If people are being prescribed medication, they should continue taking it and work on lifestyle changes like reducing salt intake and drinking in moderation,” added Dr. Lackland, who was not involved in the research.
Also commenting on the findings, Wanpen Vongpatanasin, MD, UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, pointed out that there are many potential benefits from exercise training. “It might improve endothelial function, decrease vascular stiffness and nervous system reactivity to stress, and improve quality of life for patients,” she said.
The study has several limitations, including a small sample size and a patient population that mostly has “relatively mild hypertension,” Dr. Vongpatanasin said, adding, “We don’t know whether these findings will apply to patients with more severe hypertension.”
It would also have been helpful if investigators monitored patient adherence to prescribed medications through urine or blood samples rather than a questionnaire, and to measure nighttime blood pressure, which is a more important predictor of cardiovascular outcomes, said Dr. Vongpatanasin, who was not associated with the research.
Moving forward, it will be important to “investigate why some patients are nonresponders to the exercise intervention and why some are super-responders,” study author Dr. Ribeiro said.
Dr. Ribeiro, Dr. Lackland, and Dr. Vongpatanasin have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. This study was funded by the European Union through the European Regional Development Fund Operational Competitiveness Factors Program (COMPETE) and by the Portuguese government through the Foundation for Science and Technology. The funders had no role in the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Aerobic exercise may help reduce blood pressure in patients whose hypertension responds poorly to medications, a new study suggests.
A randomized controlled clinical trial showed that patients with resistant hypertension assigned to a moderate-intensity aerobic exercise training program had lower blood pressure compared with patients who received usual care.
“Resistant hypertension persists as a big clinical challenge because the available treatment options to lower blood pressure in this clinical population, namely drugs and renal denervation, show limited success,” Fernando Ribeiro, PhD, University of Aveiro, Portugal, told this news organization. “Aerobic exercise was safe and associated with a significant and clinically relevant reduction in 24-hour, daytime ambulatory, and office blood pressure.”
The findings were published online August 4 in JAMA Cardiology.
The researchers enrolled 53 patients aged 40-75 years with a diagnosis of resistant hypertension in this prospective, single-blinded trial. Nearly half (24) were women.
Resistant hypertension was defined as having a “mean systolic BP of 130 mm Hg or greater on 24-hour ambulatory BP monitoring and/or 135 mm Hg or greater during daytime hours while taking maximally tolerated doses of at least 3 antihypertensive agents, including a diuretic, or to have a controlled BP while taking 4 or more antihypertensive agents.”
From March 2017 to December 2019 at two sites in Portugal, 26 patients were randomly assigned to a 12-week aerobic exercise training program involving three 40-minute supervised sessions per week in addition to usual care. Another 27 patients in the control group were allocated to receive usual care only.
24-hour ambulatory systolic blood pressure was reduced by 7.1 mm Hg (95% confidence interval, -12.8 to -1.4; P = .02) in patients in the exercise group compared with the control group. In the exercise group, there were additional reductions of:
- -5.1 mm Hg of 24-hour ambulatory diastolic blood pressure (95% CI, -7.9 to -2.3; P = .001)
- -8.4 mm Hg of daytime systolic blood pressure (95% CI, -14.3 to -2.5, P = .006)
- -5.7 mm Hg of daytime diastolic blood pressure (95% CI, -9.0 to -2.4; P = .001)
- -10.0 mm Hg of office systolic blood pressure (95% CI, -17.6 to -2.5; P = .01)
Additionally, a significant improvement in cardiorespiratory fitness (5.05 mL/kg per minute of oxygen consumption; 95% CI, 3.5-6.6; P < .001) was observed in the exercise group compared with the control group.
Although prior research has suggested that exercise may lower blood pressure, this study is particularly useful because it “outlines very specifically what types of exercise you can recommend,” said Daniel Lackland, DrPH, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
Although important, exercise is “one part of the overall management of high blood pressure. If people are being prescribed medication, they should continue taking it and work on lifestyle changes like reducing salt intake and drinking in moderation,” added Dr. Lackland, who was not involved in the research.
Also commenting on the findings, Wanpen Vongpatanasin, MD, UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, pointed out that there are many potential benefits from exercise training. “It might improve endothelial function, decrease vascular stiffness and nervous system reactivity to stress, and improve quality of life for patients,” she said.
The study has several limitations, including a small sample size and a patient population that mostly has “relatively mild hypertension,” Dr. Vongpatanasin said, adding, “We don’t know whether these findings will apply to patients with more severe hypertension.”
It would also have been helpful if investigators monitored patient adherence to prescribed medications through urine or blood samples rather than a questionnaire, and to measure nighttime blood pressure, which is a more important predictor of cardiovascular outcomes, said Dr. Vongpatanasin, who was not associated with the research.
Moving forward, it will be important to “investigate why some patients are nonresponders to the exercise intervention and why some are super-responders,” study author Dr. Ribeiro said.
Dr. Ribeiro, Dr. Lackland, and Dr. Vongpatanasin have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. This study was funded by the European Union through the European Regional Development Fund Operational Competitiveness Factors Program (COMPETE) and by the Portuguese government through the Foundation for Science and Technology. The funders had no role in the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Aerobic exercise may help reduce blood pressure in patients whose hypertension responds poorly to medications, a new study suggests.
A randomized controlled clinical trial showed that patients with resistant hypertension assigned to a moderate-intensity aerobic exercise training program had lower blood pressure compared with patients who received usual care.
“Resistant hypertension persists as a big clinical challenge because the available treatment options to lower blood pressure in this clinical population, namely drugs and renal denervation, show limited success,” Fernando Ribeiro, PhD, University of Aveiro, Portugal, told this news organization. “Aerobic exercise was safe and associated with a significant and clinically relevant reduction in 24-hour, daytime ambulatory, and office blood pressure.”
The findings were published online August 4 in JAMA Cardiology.
The researchers enrolled 53 patients aged 40-75 years with a diagnosis of resistant hypertension in this prospective, single-blinded trial. Nearly half (24) were women.
Resistant hypertension was defined as having a “mean systolic BP of 130 mm Hg or greater on 24-hour ambulatory BP monitoring and/or 135 mm Hg or greater during daytime hours while taking maximally tolerated doses of at least 3 antihypertensive agents, including a diuretic, or to have a controlled BP while taking 4 or more antihypertensive agents.”
From March 2017 to December 2019 at two sites in Portugal, 26 patients were randomly assigned to a 12-week aerobic exercise training program involving three 40-minute supervised sessions per week in addition to usual care. Another 27 patients in the control group were allocated to receive usual care only.
24-hour ambulatory systolic blood pressure was reduced by 7.1 mm Hg (95% confidence interval, -12.8 to -1.4; P = .02) in patients in the exercise group compared with the control group. In the exercise group, there were additional reductions of:
- -5.1 mm Hg of 24-hour ambulatory diastolic blood pressure (95% CI, -7.9 to -2.3; P = .001)
- -8.4 mm Hg of daytime systolic blood pressure (95% CI, -14.3 to -2.5, P = .006)
- -5.7 mm Hg of daytime diastolic blood pressure (95% CI, -9.0 to -2.4; P = .001)
- -10.0 mm Hg of office systolic blood pressure (95% CI, -17.6 to -2.5; P = .01)
Additionally, a significant improvement in cardiorespiratory fitness (5.05 mL/kg per minute of oxygen consumption; 95% CI, 3.5-6.6; P < .001) was observed in the exercise group compared with the control group.
Although prior research has suggested that exercise may lower blood pressure, this study is particularly useful because it “outlines very specifically what types of exercise you can recommend,” said Daniel Lackland, DrPH, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
Although important, exercise is “one part of the overall management of high blood pressure. If people are being prescribed medication, they should continue taking it and work on lifestyle changes like reducing salt intake and drinking in moderation,” added Dr. Lackland, who was not involved in the research.
Also commenting on the findings, Wanpen Vongpatanasin, MD, UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, pointed out that there are many potential benefits from exercise training. “It might improve endothelial function, decrease vascular stiffness and nervous system reactivity to stress, and improve quality of life for patients,” she said.
The study has several limitations, including a small sample size and a patient population that mostly has “relatively mild hypertension,” Dr. Vongpatanasin said, adding, “We don’t know whether these findings will apply to patients with more severe hypertension.”
It would also have been helpful if investigators monitored patient adherence to prescribed medications through urine or blood samples rather than a questionnaire, and to measure nighttime blood pressure, which is a more important predictor of cardiovascular outcomes, said Dr. Vongpatanasin, who was not associated with the research.
Moving forward, it will be important to “investigate why some patients are nonresponders to the exercise intervention and why some are super-responders,” study author Dr. Ribeiro said.
Dr. Ribeiro, Dr. Lackland, and Dr. Vongpatanasin have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. This study was funded by the European Union through the European Regional Development Fund Operational Competitiveness Factors Program (COMPETE) and by the Portuguese government through the Foundation for Science and Technology. The funders had no role in the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Despite retraction, study using fraudulent Surgisphere data still cited
A retracted study on the safety of blood pressure medications in patients with COVID-19 continues to be cited nearly a year later, new research shows.
The study in question, published on May 1, 2020, in the New England Journal of Medicine, showed no increased risk for in-hospital death with the use of ACE inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
Concerns about the veracity of the Surgisphere database used for the study, however, led to a June 4 retraction and to the June 13 retraction of a second study, published in the Lancet, that focused on hydroxychloroquine as a COVID-19 treatment.
Although the Surgisphere scandal caused a global reckoning of COVID-19 scientific studies, the new analysis identified 652 citations of the NEJM article as of May 31.
More than a third of the citations occurred in the first 2 months after the retraction, 54% were at least 3 months later, and 2.8% at least 6 months later. In May, 11 months after the article was retracted, it was cited 21 times, senior author Emily G. McDonald, MD, MSc, McGill University, Montreal, and colleagues reported in a research letter in JAMA Internal Medicine.
“In early May and June there were already more than 200 citations in one of the world’s leading scientific journals, so I do believe it was a highly influential article early on and had an impact on different types of studies or research taking place,” she said in an interview.
Dr. McDonald said she’s also “certain that it impacted patient care,” observing that when there are no guidelines available on how to manage patients, physicians will turn to the most recent evidence in the most reputable journals.
“In the case of ACE [inhibitors] and ARBs, although the study was based on fraudulent data, we were lucky that the overall message was in the end probably correct, but that might not have been the case for another study or dataset,” she said.
Early in the pandemic, concerns existed that ACE inhibitors and ARBs could be harmful, increasing the expression of ACE2 receptors, which the SARS-CoV-2 virus uses to gain entry into cells. The first randomized trial to examine the issue, BRACE CORONA, showed no clinical benefit to interrupting use of the agents in hospitalized patients. An observational study suggested ACE inhibitors may even be protective.
Of two high-profile retractions, McDonald said they chose to bypass the hydroxychloroquine study, which had an eye-popping Altmetric attention score of 23,084, compared with 3,727 for the NEJM paper, because it may have been cited for “other” reasons. “We wanted to focus less on the politics and more on the problem of retracted work.”
The team found that researchers across the globe were citing the retracted ACE/ARB paper (18.7% in the United States, 8.1% in Italy, and 44% other countries). Most citations were used to support a statement in the main text of a study, but in nearly 3% of cases, the data were incorporated into new analyses.
Just 17.6% of the studies cited or noted the retraction. “For sure, that was surprising to us. We suspected it, but our study confirmed it,” Dr. McDonald said.
Although retracted articles can be identified by a watermark or line of text, in some cases that can be easily missed, she noted. What’s more, not all citation software points out when a study has been retracted, a fate shared by the copyediting process.
“There are a lot of mechanisms in place and, in general, what’s happening is rare but there isn’t a perfect automated system solution to absolutely prevent this from happening,” she said. “It’s still subject to human error.”
The findings also have to be taken in the context of a rapidly emerging pandemic and the unprecedented torrent of scientific papers released over the past year.
“That might have contributed to why this happened, but the takeaway message is that this can happen despite our best efforts, and we need to challenge ourselves to come up with a system solution to prevent this from happening in the future,” Dr. McDonald said. “Current mechanisms are probably capturing 95% of it, but we need to do better.”
Limitations of the present analysis are that it was limited to the single retracted study; used only a single search engine, Google Scholar, to identify the citing works; and that additional citations may have been missed, the authors noted.
McDonald and coauthor Todd C. Lee, MD, report being signatories on a public letter calling for the retraction of the Surgisphere papers. Dr. Lee also reported receiving research support from Fonds De Recherche du Quebec-Sante during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A retracted study on the safety of blood pressure medications in patients with COVID-19 continues to be cited nearly a year later, new research shows.
The study in question, published on May 1, 2020, in the New England Journal of Medicine, showed no increased risk for in-hospital death with the use of ACE inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
Concerns about the veracity of the Surgisphere database used for the study, however, led to a June 4 retraction and to the June 13 retraction of a second study, published in the Lancet, that focused on hydroxychloroquine as a COVID-19 treatment.
Although the Surgisphere scandal caused a global reckoning of COVID-19 scientific studies, the new analysis identified 652 citations of the NEJM article as of May 31.
More than a third of the citations occurred in the first 2 months after the retraction, 54% were at least 3 months later, and 2.8% at least 6 months later. In May, 11 months after the article was retracted, it was cited 21 times, senior author Emily G. McDonald, MD, MSc, McGill University, Montreal, and colleagues reported in a research letter in JAMA Internal Medicine.
“In early May and June there were already more than 200 citations in one of the world’s leading scientific journals, so I do believe it was a highly influential article early on and had an impact on different types of studies or research taking place,” she said in an interview.
Dr. McDonald said she’s also “certain that it impacted patient care,” observing that when there are no guidelines available on how to manage patients, physicians will turn to the most recent evidence in the most reputable journals.
“In the case of ACE [inhibitors] and ARBs, although the study was based on fraudulent data, we were lucky that the overall message was in the end probably correct, but that might not have been the case for another study or dataset,” she said.
Early in the pandemic, concerns existed that ACE inhibitors and ARBs could be harmful, increasing the expression of ACE2 receptors, which the SARS-CoV-2 virus uses to gain entry into cells. The first randomized trial to examine the issue, BRACE CORONA, showed no clinical benefit to interrupting use of the agents in hospitalized patients. An observational study suggested ACE inhibitors may even be protective.
Of two high-profile retractions, McDonald said they chose to bypass the hydroxychloroquine study, which had an eye-popping Altmetric attention score of 23,084, compared with 3,727 for the NEJM paper, because it may have been cited for “other” reasons. “We wanted to focus less on the politics and more on the problem of retracted work.”
The team found that researchers across the globe were citing the retracted ACE/ARB paper (18.7% in the United States, 8.1% in Italy, and 44% other countries). Most citations were used to support a statement in the main text of a study, but in nearly 3% of cases, the data were incorporated into new analyses.
Just 17.6% of the studies cited or noted the retraction. “For sure, that was surprising to us. We suspected it, but our study confirmed it,” Dr. McDonald said.
Although retracted articles can be identified by a watermark or line of text, in some cases that can be easily missed, she noted. What’s more, not all citation software points out when a study has been retracted, a fate shared by the copyediting process.
“There are a lot of mechanisms in place and, in general, what’s happening is rare but there isn’t a perfect automated system solution to absolutely prevent this from happening,” she said. “It’s still subject to human error.”
The findings also have to be taken in the context of a rapidly emerging pandemic and the unprecedented torrent of scientific papers released over the past year.
“That might have contributed to why this happened, but the takeaway message is that this can happen despite our best efforts, and we need to challenge ourselves to come up with a system solution to prevent this from happening in the future,” Dr. McDonald said. “Current mechanisms are probably capturing 95% of it, but we need to do better.”
Limitations of the present analysis are that it was limited to the single retracted study; used only a single search engine, Google Scholar, to identify the citing works; and that additional citations may have been missed, the authors noted.
McDonald and coauthor Todd C. Lee, MD, report being signatories on a public letter calling for the retraction of the Surgisphere papers. Dr. Lee also reported receiving research support from Fonds De Recherche du Quebec-Sante during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A retracted study on the safety of blood pressure medications in patients with COVID-19 continues to be cited nearly a year later, new research shows.
The study in question, published on May 1, 2020, in the New England Journal of Medicine, showed no increased risk for in-hospital death with the use of ACE inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
Concerns about the veracity of the Surgisphere database used for the study, however, led to a June 4 retraction and to the June 13 retraction of a second study, published in the Lancet, that focused on hydroxychloroquine as a COVID-19 treatment.
Although the Surgisphere scandal caused a global reckoning of COVID-19 scientific studies, the new analysis identified 652 citations of the NEJM article as of May 31.
More than a third of the citations occurred in the first 2 months after the retraction, 54% were at least 3 months later, and 2.8% at least 6 months later. In May, 11 months after the article was retracted, it was cited 21 times, senior author Emily G. McDonald, MD, MSc, McGill University, Montreal, and colleagues reported in a research letter in JAMA Internal Medicine.
“In early May and June there were already more than 200 citations in one of the world’s leading scientific journals, so I do believe it was a highly influential article early on and had an impact on different types of studies or research taking place,” she said in an interview.
Dr. McDonald said she’s also “certain that it impacted patient care,” observing that when there are no guidelines available on how to manage patients, physicians will turn to the most recent evidence in the most reputable journals.
“In the case of ACE [inhibitors] and ARBs, although the study was based on fraudulent data, we were lucky that the overall message was in the end probably correct, but that might not have been the case for another study or dataset,” she said.
Early in the pandemic, concerns existed that ACE inhibitors and ARBs could be harmful, increasing the expression of ACE2 receptors, which the SARS-CoV-2 virus uses to gain entry into cells. The first randomized trial to examine the issue, BRACE CORONA, showed no clinical benefit to interrupting use of the agents in hospitalized patients. An observational study suggested ACE inhibitors may even be protective.
Of two high-profile retractions, McDonald said they chose to bypass the hydroxychloroquine study, which had an eye-popping Altmetric attention score of 23,084, compared with 3,727 for the NEJM paper, because it may have been cited for “other” reasons. “We wanted to focus less on the politics and more on the problem of retracted work.”
The team found that researchers across the globe were citing the retracted ACE/ARB paper (18.7% in the United States, 8.1% in Italy, and 44% other countries). Most citations were used to support a statement in the main text of a study, but in nearly 3% of cases, the data were incorporated into new analyses.
Just 17.6% of the studies cited or noted the retraction. “For sure, that was surprising to us. We suspected it, but our study confirmed it,” Dr. McDonald said.
Although retracted articles can be identified by a watermark or line of text, in some cases that can be easily missed, she noted. What’s more, not all citation software points out when a study has been retracted, a fate shared by the copyediting process.
“There are a lot of mechanisms in place and, in general, what’s happening is rare but there isn’t a perfect automated system solution to absolutely prevent this from happening,” she said. “It’s still subject to human error.”
The findings also have to be taken in the context of a rapidly emerging pandemic and the unprecedented torrent of scientific papers released over the past year.
“That might have contributed to why this happened, but the takeaway message is that this can happen despite our best efforts, and we need to challenge ourselves to come up with a system solution to prevent this from happening in the future,” Dr. McDonald said. “Current mechanisms are probably capturing 95% of it, but we need to do better.”
Limitations of the present analysis are that it was limited to the single retracted study; used only a single search engine, Google Scholar, to identify the citing works; and that additional citations may have been missed, the authors noted.
McDonald and coauthor Todd C. Lee, MD, report being signatories on a public letter calling for the retraction of the Surgisphere papers. Dr. Lee also reported receiving research support from Fonds De Recherche du Quebec-Sante during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Midodrine reduces fainting in young patients
.
Vasovagal syncope is the most common cause of fainting and is often triggered by dehydration and upright posture, according to Johns Hopkins Medicine. But it can also be caused by stimuli like the sight of blood or sudden emotional distress. The stimulus causes the heart rate and blood pressure to drop rapidly, according to the Mayo Clinic.
The randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial included 133 patients with recurrent vasovagal syncope and was published in Annals of Internal Medicine. Those that received midodrine were less likely to have one syncope episode (28 of 66 [42%]), compared with those that took the placebo (41 of 67 [61%]). The absolute risk reduction for vasovagal syncope was 19 percentage points (95% confidence interval, 2-36 percentage points).
The study included patients from 25 university hospitals in Canada, the United States, Mexico, and the United Kingdom, who were followed for 12 months. The trial participants were highly symptomatic for vasovagal syncope, having experienced a median of 23 episodes in their lifetime and 5 syncope episodes in the last year, and they had no comorbid conditions.
“We don’t have many arrows in our quiver,” said Robert Sheldon, MD, PhD, a cardiologist at University of Calgary (Alta.) and lead author of the study, referring to the lack of evidence-based treatments for syncope.
For 20 years Dr. Sheldon’s lab has been testing drugs that showed some potential. While a previous study of fludrocortisone (Florinef ) showed some benefit, “[midodrine] was the first to be unequivocally, slam-dunk positive,” he said in an interview.
Earlier trials of midodrine
Other studies have shown midodrine to prevent syncope on tilt tests. There have been two randomized trials where midodrine significantly reduced vasovagal syncope, but one of these was short and in children, and the other one was open label with no placebo control.
“Risk reduction was very high in previous studies,” Dr. Sheldon said in an interview. But, because they were open label, there was a huge placebo effect, he noted.
“There were no adequately done, adequately powered [studies] that have been positive,” Dr. Sheldon added.
New study methods and outcomes
The study published in Annals of Internal Medicine this week included patients over 18 years of age with a Calgary Syncope Symptom Score of at least 2. All were educated on lifestyle measures that can prevent syncopes before beginning to take 5 mg of study drug or placebo three times daily, 4 hours apart.
In these cases, the study authors wrote, “taking medication three times a day seems worth the effort.” But in patients with a lower frequency of episodes, midodrine might not have an adequate payoff.
These results are “impressive,” said Roopinder K. Sandhu, MD, MPH, clinical electrophysiologist at Cedar-Sinai in Los Angeles. “This study demonstrated that midodrine is the first medical therapy, in addition to education and lifestyle measures, to unequivocally pass the scrutiny of an international, placebo-controlled, RCT to show a significant reduction in syncope recurrence in a younger population with frequent syncope events.”
“[Taking midodrine] doesn’t carry the long-term consequence of pacemakers,” she added.
Study limitations
Limitations of the new study include its small size and short observation period, the authors wrote. Additionally, a large proportion of patients enrolled were also from a single center in Calgary that specializes in syncope care. Twenty-seven patients in the trial stopped taking their assigned medication during the year observation period, but the authors concluded these participants “likely would bias the results against midodrine.”
For doctors considering midodrine for their patients, it’s critical to confirm the diagnosis and to try patient education first, Dr. Sheldon advised.
Lifestyle factors like hydration, adequate sodium intake, and squatting or lying down when the syncope is coming on can sufficiently suppress syncopes in two-thirds of patients, he noted.
This is a treatment for young people, Dr. Sandhu said. The median age in the trial was 35, so patients taking midodrine should be younger than 50. Midodrine is also not effective in patients with high blood pressure or heart failure, she said.
“[Midodrine] is easy to use but kind of a pain at first,” Dr. Sheldon noted. Every patient should start out taking 5 mg doses, three times a day – during waking hours. But then you have to adjust the dosage, “and it’s tricky,” he said.
If a patient experiences goosebumps or the sensation of worms crawling in the hair, the dose might be too much, Dr. Sheldon noted.
If the patient is still fainting, first consider when they are fainting, he said. If it’s around the time they should take another dose, it might be trough effect.
Dr. Sandhu was not involved in the study, but Cedar Sinai was a participating center, and she considers Dr. Sheldon to be a mentor. Dr. Sandhu also noted that she has published papers with Dr. Sheldon, who reported no conflicts.
.
Vasovagal syncope is the most common cause of fainting and is often triggered by dehydration and upright posture, according to Johns Hopkins Medicine. But it can also be caused by stimuli like the sight of blood or sudden emotional distress. The stimulus causes the heart rate and blood pressure to drop rapidly, according to the Mayo Clinic.
The randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial included 133 patients with recurrent vasovagal syncope and was published in Annals of Internal Medicine. Those that received midodrine were less likely to have one syncope episode (28 of 66 [42%]), compared with those that took the placebo (41 of 67 [61%]). The absolute risk reduction for vasovagal syncope was 19 percentage points (95% confidence interval, 2-36 percentage points).
The study included patients from 25 university hospitals in Canada, the United States, Mexico, and the United Kingdom, who were followed for 12 months. The trial participants were highly symptomatic for vasovagal syncope, having experienced a median of 23 episodes in their lifetime and 5 syncope episodes in the last year, and they had no comorbid conditions.
“We don’t have many arrows in our quiver,” said Robert Sheldon, MD, PhD, a cardiologist at University of Calgary (Alta.) and lead author of the study, referring to the lack of evidence-based treatments for syncope.
For 20 years Dr. Sheldon’s lab has been testing drugs that showed some potential. While a previous study of fludrocortisone (Florinef ) showed some benefit, “[midodrine] was the first to be unequivocally, slam-dunk positive,” he said in an interview.
Earlier trials of midodrine
Other studies have shown midodrine to prevent syncope on tilt tests. There have been two randomized trials where midodrine significantly reduced vasovagal syncope, but one of these was short and in children, and the other one was open label with no placebo control.
“Risk reduction was very high in previous studies,” Dr. Sheldon said in an interview. But, because they were open label, there was a huge placebo effect, he noted.
“There were no adequately done, adequately powered [studies] that have been positive,” Dr. Sheldon added.
New study methods and outcomes
The study published in Annals of Internal Medicine this week included patients over 18 years of age with a Calgary Syncope Symptom Score of at least 2. All were educated on lifestyle measures that can prevent syncopes before beginning to take 5 mg of study drug or placebo three times daily, 4 hours apart.
In these cases, the study authors wrote, “taking medication three times a day seems worth the effort.” But in patients with a lower frequency of episodes, midodrine might not have an adequate payoff.
These results are “impressive,” said Roopinder K. Sandhu, MD, MPH, clinical electrophysiologist at Cedar-Sinai in Los Angeles. “This study demonstrated that midodrine is the first medical therapy, in addition to education and lifestyle measures, to unequivocally pass the scrutiny of an international, placebo-controlled, RCT to show a significant reduction in syncope recurrence in a younger population with frequent syncope events.”
“[Taking midodrine] doesn’t carry the long-term consequence of pacemakers,” she added.
Study limitations
Limitations of the new study include its small size and short observation period, the authors wrote. Additionally, a large proportion of patients enrolled were also from a single center in Calgary that specializes in syncope care. Twenty-seven patients in the trial stopped taking their assigned medication during the year observation period, but the authors concluded these participants “likely would bias the results against midodrine.”
For doctors considering midodrine for their patients, it’s critical to confirm the diagnosis and to try patient education first, Dr. Sheldon advised.
Lifestyle factors like hydration, adequate sodium intake, and squatting or lying down when the syncope is coming on can sufficiently suppress syncopes in two-thirds of patients, he noted.
This is a treatment for young people, Dr. Sandhu said. The median age in the trial was 35, so patients taking midodrine should be younger than 50. Midodrine is also not effective in patients with high blood pressure or heart failure, she said.
“[Midodrine] is easy to use but kind of a pain at first,” Dr. Sheldon noted. Every patient should start out taking 5 mg doses, three times a day – during waking hours. But then you have to adjust the dosage, “and it’s tricky,” he said.
If a patient experiences goosebumps or the sensation of worms crawling in the hair, the dose might be too much, Dr. Sheldon noted.
If the patient is still fainting, first consider when they are fainting, he said. If it’s around the time they should take another dose, it might be trough effect.
Dr. Sandhu was not involved in the study, but Cedar Sinai was a participating center, and she considers Dr. Sheldon to be a mentor. Dr. Sandhu also noted that she has published papers with Dr. Sheldon, who reported no conflicts.
.
Vasovagal syncope is the most common cause of fainting and is often triggered by dehydration and upright posture, according to Johns Hopkins Medicine. But it can also be caused by stimuli like the sight of blood or sudden emotional distress. The stimulus causes the heart rate and blood pressure to drop rapidly, according to the Mayo Clinic.
The randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial included 133 patients with recurrent vasovagal syncope and was published in Annals of Internal Medicine. Those that received midodrine were less likely to have one syncope episode (28 of 66 [42%]), compared with those that took the placebo (41 of 67 [61%]). The absolute risk reduction for vasovagal syncope was 19 percentage points (95% confidence interval, 2-36 percentage points).
The study included patients from 25 university hospitals in Canada, the United States, Mexico, and the United Kingdom, who were followed for 12 months. The trial participants were highly symptomatic for vasovagal syncope, having experienced a median of 23 episodes in their lifetime and 5 syncope episodes in the last year, and they had no comorbid conditions.
“We don’t have many arrows in our quiver,” said Robert Sheldon, MD, PhD, a cardiologist at University of Calgary (Alta.) and lead author of the study, referring to the lack of evidence-based treatments for syncope.
For 20 years Dr. Sheldon’s lab has been testing drugs that showed some potential. While a previous study of fludrocortisone (Florinef ) showed some benefit, “[midodrine] was the first to be unequivocally, slam-dunk positive,” he said in an interview.
Earlier trials of midodrine
Other studies have shown midodrine to prevent syncope on tilt tests. There have been two randomized trials where midodrine significantly reduced vasovagal syncope, but one of these was short and in children, and the other one was open label with no placebo control.
“Risk reduction was very high in previous studies,” Dr. Sheldon said in an interview. But, because they were open label, there was a huge placebo effect, he noted.
“There were no adequately done, adequately powered [studies] that have been positive,” Dr. Sheldon added.
New study methods and outcomes
The study published in Annals of Internal Medicine this week included patients over 18 years of age with a Calgary Syncope Symptom Score of at least 2. All were educated on lifestyle measures that can prevent syncopes before beginning to take 5 mg of study drug or placebo three times daily, 4 hours apart.
In these cases, the study authors wrote, “taking medication three times a day seems worth the effort.” But in patients with a lower frequency of episodes, midodrine might not have an adequate payoff.
These results are “impressive,” said Roopinder K. Sandhu, MD, MPH, clinical electrophysiologist at Cedar-Sinai in Los Angeles. “This study demonstrated that midodrine is the first medical therapy, in addition to education and lifestyle measures, to unequivocally pass the scrutiny of an international, placebo-controlled, RCT to show a significant reduction in syncope recurrence in a younger population with frequent syncope events.”
“[Taking midodrine] doesn’t carry the long-term consequence of pacemakers,” she added.
Study limitations
Limitations of the new study include its small size and short observation period, the authors wrote. Additionally, a large proportion of patients enrolled were also from a single center in Calgary that specializes in syncope care. Twenty-seven patients in the trial stopped taking their assigned medication during the year observation period, but the authors concluded these participants “likely would bias the results against midodrine.”
For doctors considering midodrine for their patients, it’s critical to confirm the diagnosis and to try patient education first, Dr. Sheldon advised.
Lifestyle factors like hydration, adequate sodium intake, and squatting or lying down when the syncope is coming on can sufficiently suppress syncopes in two-thirds of patients, he noted.
This is a treatment for young people, Dr. Sandhu said. The median age in the trial was 35, so patients taking midodrine should be younger than 50. Midodrine is also not effective in patients with high blood pressure or heart failure, she said.
“[Midodrine] is easy to use but kind of a pain at first,” Dr. Sheldon noted. Every patient should start out taking 5 mg doses, three times a day – during waking hours. But then you have to adjust the dosage, “and it’s tricky,” he said.
If a patient experiences goosebumps or the sensation of worms crawling in the hair, the dose might be too much, Dr. Sheldon noted.
If the patient is still fainting, first consider when they are fainting, he said. If it’s around the time they should take another dose, it might be trough effect.
Dr. Sandhu was not involved in the study, but Cedar Sinai was a participating center, and she considers Dr. Sheldon to be a mentor. Dr. Sandhu also noted that she has published papers with Dr. Sheldon, who reported no conflicts.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
ESC heart failure guideline to integrate bounty of new meds
Today there are so many evidence-based drug therapies for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) that physicians treating HF patients almost don’t know what to do them.
It’s an exciting new age that way, but to many vexingly unclear how best to merge the shiny new options with mainstay regimens based on time-honored renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors and beta-blockers.
To impart some clarity, the authors of a new HF guideline document recently took center stage at the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA) annual meeting to preview their updated recommendations, with novel twists based on recent major trials, for the new age of HF pharmacotherapeutics.
The guideline committee considered the evidence base that existed “up until the end of March of this year,” Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College London, said during the presentation. The document “is now finalized, it’s with the publishers, and it will be presented in full with simultaneous publication at the ESC meeting” that starts August 27.
It describes a game plan, already followed by some clinicians in practice without official guidance, for initiating drugs from each of four classes in virtually all patients with HFrEF.
New indicated drugs, new perspective for HFrEF
Three of the drug categories are old acquaintances. Among them are the RAS inhibitors, which include angiotensin-receptor/neprilysin inhibitors, beta-blockers, and the mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists. The latter drugs are gaining new respect after having been underplayed in HF prescribing despite longstanding evidence of efficacy.
Completing the quartet of first-line HFrEF drug classes is a recent arrival to the HF arena, the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors.
“We now have new data and a simplified treatment algorithm for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction based on the early administration of the four major classes of drugs,” said Marco Metra, MD, University of Brescia (Italy), previewing the medical-therapy portions of the new guideline at the ESC-HFA sessions, which launched virtually and live in Florence, Italy, on July 29.
The new game plan offers a simple answer to a once-common but complex question: How and in what order are the different drug classes initiated in patients with HFrEF? In the new document, the stated goal is to get them all on board expeditiously and safely, by any means possible.
The guideline writers did not specify a sequence, preferring to leave that decision to physicians, said Dr. Metra, who stated only two guiding principles. The first is to consider the patient’s unique circumstances. The order in which the drugs are introduced might vary, depending on, for example, whether the patient has low or high blood pressure or renal dysfunction.
Second, “it is very important that we try to give all four classes of drugs to the patient in the shortest time possible, because this saves lives,” he said.
That there is no recommendation on sequencing the drugs has led some to the wrong interpretation that all should be started at once, observed coauthor Javed Butler, MD, MPH, University of Mississippi, Jackson, as a panelist during the presentation. Far from it, he said. “The doctor with the patient in front of you can make the best decision. The idea here is to get all the therapies on as soon as possible, as safely as possible.”
“The order in which they are introduced is not really important,” agreed Vijay Chopra, MD, Max Super Specialty Hospital Saket, New Delhi, another coauthor on the panel. “The important thing is that at least some dose of all the four drugs needs to be introduced in the first 4-6 weeks, and then up-titrated.”
Other medical therapy can be more tailored, Dr. Metra noted, such as loop diuretics for patients with congestion, iron for those with iron deficiency, and other drugs depending on whether there is, for example, atrial fibrillation or coronary disease.
Adoption of emerging definitions
The document adopts the emerging characterization of HFrEF by a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) up to 40%.
And it will leverage an expanding evidence base for medication in a segment of patients once said to have HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), who had therefore lacked specific, guideline-directed medical therapies. Now, patients with an LVEF of 41%-49% will be said to have HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF), a tweak to the recently introduced HF with “mid-range” LVEF that is designed to assert its nature as something to treat. The new document’s HFmrEF recommendations come with various class and level-of-evidence ratings.
That leaves HFpEF to be characterized by an LVEF of 50% in combination with structural or functional abnormalities associated with LV diastolic dysfunction or raised LV filling pressures, including raised natriuretic peptide levels.
The definitions are consistent with those proposed internationally by the ESC-HFA, the Heart Failure Society of America, and other groups in a statement published in March.
Expanded HFrEF med landscape
Since the 2016 ESC guideline on HF therapy, Dr. McDonagh said, “there’s been no substantial change in the evidence for many of the classical drugs that we use in heart failure. However, we had a lot of new and exciting evidence to consider,” especially in support of the SGLT2 inhibitors as one of the core medications in HFrEF.
The new data came from two controlled trials in particular. In DAPA-HF, patients with HFrEF who were initially without diabetes and who went on dapagliflozin (Farxiga, AstraZeneca) showed a 27% drop in cardiovascular (CV) death or worsening-HF events over a median of 18 months.
“That was followed up with very concordant results with empagliflozin [Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly] in HFrEF in the EMPEROR-Reduced trial,” Dr. McDonagh said. In that trial, comparable patients who took empagliflozin showed a 25% drop in a primary endpoint similar to that in DAPA-HF over the median 16-month follow-up.
Other HFrEF recommendations are for selected patients. They include ivabradine, already in the guidelines, for patients in sinus rhythm with an elevated resting heart rate who can’t take beta-blockers for whatever reason. But, Dr. McDonagh noted, “we had some new classes of drugs to consider as well.”
In particular, the oral soluble guanylate-cyclase receptor stimulator vericiguat (Verquvo) emerged about a year ago from the VICTORIA trial as a modest success for patients with HFrEF and a previous HF hospitalization. In the trial with more than 5,000 patients, treatment with vericiguat atop standard drug and device therapy was followed by a significant 10% drop in risk for CV death or HF hospitalization.
Available now or likely to be available in the United States, the European Union, Japan, and other countries, vericiguat is recommended in the new guideline for VICTORIA-like patients who don’t adequately respond to other indicated medications.
Little for HFpEF as newly defined
“Almost nothing is new” in the guidelines for HFpEF, Dr. Metra said. The document recommends screening for and treatment of any underlying disorder and comorbidities, plus diuretics for any congestion. “That’s what we have to date.”
But that evidence base might soon change. The new HFpEF recommendations could possibly be up-staged at the ESC sessions by the August 27 scheduled presentation of EMPEROR-Preserved, a randomized test of empagliflozin in HFpEF and – it could be said – HFmrEF. The trial entered patients with chronic HF and an LVEF greater than 40%.
Eli Lilly and Boehringer Ingelheim offered the world a peek at the results, which suggest the SGLT2 inhibitor had a positive impact on the primary endpoint of CV death or HF hospitalization. They announced the cursory top-line outcomes in early July as part of its regulatory obligations, noting that the trial had “met” its primary endpoint.
But many unknowns remain, including the degree of benefit and whether it varied among subgroups, and especially whether outcomes were different for HFmrEF than for HFpEF.
Upgrades for familiar agents
Still, HFmrEF gets noteworthy attention in the document. “For the first time, we have recommendations for these patients,” Dr. Metra said. “We already knew that diuretics are indicated for the treatment of congestion. But now, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid antagonists, as well as sacubitril/valsartan, may be considered to improve outcomes in these patients.” Their upgrades in the new guidelines were based on review of trials in the CHARM program and of TOPCAT and PARAGON-HF, among others, he said.
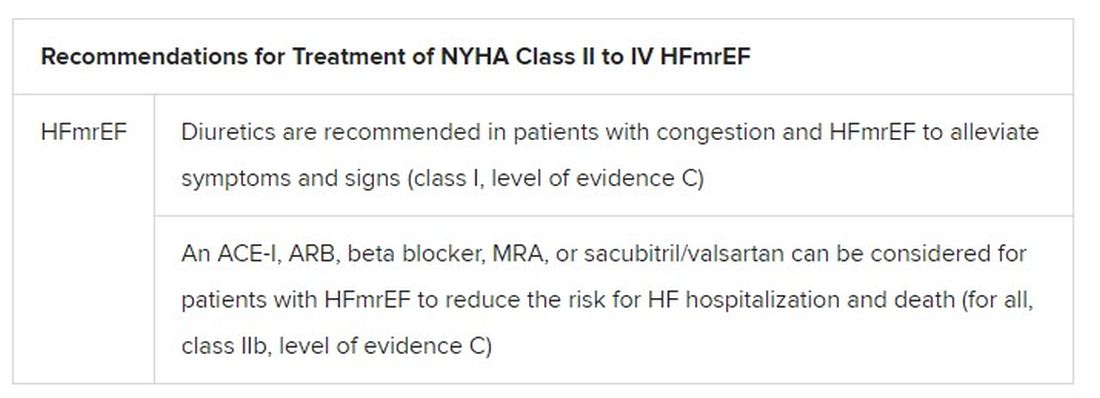
The new document also includes “treatment algorithms based on phenotypes”; that is, comorbidities and less common HF precipitants. For example, “assessment of iron status is now mandated in all patients with heart failure,” Dr. Metra said.
AFFIRM-HF is the key trial in this arena, with its more than 1,100 iron-deficient patients with LVEF less than 50% who had been recently hospitalized for HF. A year of treatment with ferric carboxymaltose (Ferinject/Injectafer, Vifor) led to a 26% drop in risk for HF hospitalization, but without affecting mortality.
For those who are iron deficient, Dr. Metra said, “ferric carboxymaltose intravenously should be considered not only in patients with low ejection fraction and outpatients, but also in patients recently hospitalized for acute heart failure.”
The SGLT2 inhibitors are recommended in HFrEF patients with type 2 diabetes. And treatment with tafamidis (Vyndaqel, Pfizer) in patients with genetic or wild-type transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis gets a class I recommendation based on survival gains seen in the ATTR-ACT trial.
Also recommended is a full CV assessment for patients with cancer who are on cardiotoxic agents or otherwise might be at risk for chemotherapy cardiotoxicity. “Beta-blockers and ACE inhibitors should be considered in those who develop left ventricular systolic dysfunction after anticancer therapy,” Dr. Metra said.
The ongoing pandemic made its mark on the document’s genesis, as it has with most everything else. “For better or worse, we were a ‘COVID guideline,’ ” Dr. McDonagh said. The writing committee consisted of “a large task force of 31 individuals, including two patients,” and there were “only two face-to-face meetings prior to the first wave of COVID hitting Europe.”
The committee voted on each of the recommendations, “and we had to have agreement of more than 75% of the task force to assign a class of recommendation or level of evidence,” she said. “I think we did the best we could in the circumstances. We had the benefit of many discussions over Zoom, and I think at the end of the day we have achieved a consensus.”
With such a large body of participants and the 75% threshold for agreement, “you end up with perhaps a conservative guideline. But that’s not a bad thing for clinical practice, for guidelines to be conservative,” Dr. McDonagh said. “They’re mainly concerned with looking at evidence and safety.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Today there are so many evidence-based drug therapies for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) that physicians treating HF patients almost don’t know what to do them.
It’s an exciting new age that way, but to many vexingly unclear how best to merge the shiny new options with mainstay regimens based on time-honored renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors and beta-blockers.
To impart some clarity, the authors of a new HF guideline document recently took center stage at the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA) annual meeting to preview their updated recommendations, with novel twists based on recent major trials, for the new age of HF pharmacotherapeutics.
The guideline committee considered the evidence base that existed “up until the end of March of this year,” Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College London, said during the presentation. The document “is now finalized, it’s with the publishers, and it will be presented in full with simultaneous publication at the ESC meeting” that starts August 27.
It describes a game plan, already followed by some clinicians in practice without official guidance, for initiating drugs from each of four classes in virtually all patients with HFrEF.
New indicated drugs, new perspective for HFrEF
Three of the drug categories are old acquaintances. Among them are the RAS inhibitors, which include angiotensin-receptor/neprilysin inhibitors, beta-blockers, and the mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists. The latter drugs are gaining new respect after having been underplayed in HF prescribing despite longstanding evidence of efficacy.
Completing the quartet of first-line HFrEF drug classes is a recent arrival to the HF arena, the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors.
“We now have new data and a simplified treatment algorithm for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction based on the early administration of the four major classes of drugs,” said Marco Metra, MD, University of Brescia (Italy), previewing the medical-therapy portions of the new guideline at the ESC-HFA sessions, which launched virtually and live in Florence, Italy, on July 29.
The new game plan offers a simple answer to a once-common but complex question: How and in what order are the different drug classes initiated in patients with HFrEF? In the new document, the stated goal is to get them all on board expeditiously and safely, by any means possible.
The guideline writers did not specify a sequence, preferring to leave that decision to physicians, said Dr. Metra, who stated only two guiding principles. The first is to consider the patient’s unique circumstances. The order in which the drugs are introduced might vary, depending on, for example, whether the patient has low or high blood pressure or renal dysfunction.
Second, “it is very important that we try to give all four classes of drugs to the patient in the shortest time possible, because this saves lives,” he said.
That there is no recommendation on sequencing the drugs has led some to the wrong interpretation that all should be started at once, observed coauthor Javed Butler, MD, MPH, University of Mississippi, Jackson, as a panelist during the presentation. Far from it, he said. “The doctor with the patient in front of you can make the best decision. The idea here is to get all the therapies on as soon as possible, as safely as possible.”
“The order in which they are introduced is not really important,” agreed Vijay Chopra, MD, Max Super Specialty Hospital Saket, New Delhi, another coauthor on the panel. “The important thing is that at least some dose of all the four drugs needs to be introduced in the first 4-6 weeks, and then up-titrated.”
Other medical therapy can be more tailored, Dr. Metra noted, such as loop diuretics for patients with congestion, iron for those with iron deficiency, and other drugs depending on whether there is, for example, atrial fibrillation or coronary disease.
Adoption of emerging definitions
The document adopts the emerging characterization of HFrEF by a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) up to 40%.
And it will leverage an expanding evidence base for medication in a segment of patients once said to have HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), who had therefore lacked specific, guideline-directed medical therapies. Now, patients with an LVEF of 41%-49% will be said to have HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF), a tweak to the recently introduced HF with “mid-range” LVEF that is designed to assert its nature as something to treat. The new document’s HFmrEF recommendations come with various class and level-of-evidence ratings.
That leaves HFpEF to be characterized by an LVEF of 50% in combination with structural or functional abnormalities associated with LV diastolic dysfunction or raised LV filling pressures, including raised natriuretic peptide levels.
The definitions are consistent with those proposed internationally by the ESC-HFA, the Heart Failure Society of America, and other groups in a statement published in March.
Expanded HFrEF med landscape
Since the 2016 ESC guideline on HF therapy, Dr. McDonagh said, “there’s been no substantial change in the evidence for many of the classical drugs that we use in heart failure. However, we had a lot of new and exciting evidence to consider,” especially in support of the SGLT2 inhibitors as one of the core medications in HFrEF.
The new data came from two controlled trials in particular. In DAPA-HF, patients with HFrEF who were initially without diabetes and who went on dapagliflozin (Farxiga, AstraZeneca) showed a 27% drop in cardiovascular (CV) death or worsening-HF events over a median of 18 months.
“That was followed up with very concordant results with empagliflozin [Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly] in HFrEF in the EMPEROR-Reduced trial,” Dr. McDonagh said. In that trial, comparable patients who took empagliflozin showed a 25% drop in a primary endpoint similar to that in DAPA-HF over the median 16-month follow-up.
Other HFrEF recommendations are for selected patients. They include ivabradine, already in the guidelines, for patients in sinus rhythm with an elevated resting heart rate who can’t take beta-blockers for whatever reason. But, Dr. McDonagh noted, “we had some new classes of drugs to consider as well.”
In particular, the oral soluble guanylate-cyclase receptor stimulator vericiguat (Verquvo) emerged about a year ago from the VICTORIA trial as a modest success for patients with HFrEF and a previous HF hospitalization. In the trial with more than 5,000 patients, treatment with vericiguat atop standard drug and device therapy was followed by a significant 10% drop in risk for CV death or HF hospitalization.
Available now or likely to be available in the United States, the European Union, Japan, and other countries, vericiguat is recommended in the new guideline for VICTORIA-like patients who don’t adequately respond to other indicated medications.
Little for HFpEF as newly defined
“Almost nothing is new” in the guidelines for HFpEF, Dr. Metra said. The document recommends screening for and treatment of any underlying disorder and comorbidities, plus diuretics for any congestion. “That’s what we have to date.”
But that evidence base might soon change. The new HFpEF recommendations could possibly be up-staged at the ESC sessions by the August 27 scheduled presentation of EMPEROR-Preserved, a randomized test of empagliflozin in HFpEF and – it could be said – HFmrEF. The trial entered patients with chronic HF and an LVEF greater than 40%.
Eli Lilly and Boehringer Ingelheim offered the world a peek at the results, which suggest the SGLT2 inhibitor had a positive impact on the primary endpoint of CV death or HF hospitalization. They announced the cursory top-line outcomes in early July as part of its regulatory obligations, noting that the trial had “met” its primary endpoint.
But many unknowns remain, including the degree of benefit and whether it varied among subgroups, and especially whether outcomes were different for HFmrEF than for HFpEF.
Upgrades for familiar agents
Still, HFmrEF gets noteworthy attention in the document. “For the first time, we have recommendations for these patients,” Dr. Metra said. “We already knew that diuretics are indicated for the treatment of congestion. But now, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid antagonists, as well as sacubitril/valsartan, may be considered to improve outcomes in these patients.” Their upgrades in the new guidelines were based on review of trials in the CHARM program and of TOPCAT and PARAGON-HF, among others, he said.

The new document also includes “treatment algorithms based on phenotypes”; that is, comorbidities and less common HF precipitants. For example, “assessment of iron status is now mandated in all patients with heart failure,” Dr. Metra said.
AFFIRM-HF is the key trial in this arena, with its more than 1,100 iron-deficient patients with LVEF less than 50% who had been recently hospitalized for HF. A year of treatment with ferric carboxymaltose (Ferinject/Injectafer, Vifor) led to a 26% drop in risk for HF hospitalization, but without affecting mortality.
For those who are iron deficient, Dr. Metra said, “ferric carboxymaltose intravenously should be considered not only in patients with low ejection fraction and outpatients, but also in patients recently hospitalized for acute heart failure.”
The SGLT2 inhibitors are recommended in HFrEF patients with type 2 diabetes. And treatment with tafamidis (Vyndaqel, Pfizer) in patients with genetic or wild-type transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis gets a class I recommendation based on survival gains seen in the ATTR-ACT trial.
Also recommended is a full CV assessment for patients with cancer who are on cardiotoxic agents or otherwise might be at risk for chemotherapy cardiotoxicity. “Beta-blockers and ACE inhibitors should be considered in those who develop left ventricular systolic dysfunction after anticancer therapy,” Dr. Metra said.
The ongoing pandemic made its mark on the document’s genesis, as it has with most everything else. “For better or worse, we were a ‘COVID guideline,’ ” Dr. McDonagh said. The writing committee consisted of “a large task force of 31 individuals, including two patients,” and there were “only two face-to-face meetings prior to the first wave of COVID hitting Europe.”
The committee voted on each of the recommendations, “and we had to have agreement of more than 75% of the task force to assign a class of recommendation or level of evidence,” she said. “I think we did the best we could in the circumstances. We had the benefit of many discussions over Zoom, and I think at the end of the day we have achieved a consensus.”
With such a large body of participants and the 75% threshold for agreement, “you end up with perhaps a conservative guideline. But that’s not a bad thing for clinical practice, for guidelines to be conservative,” Dr. McDonagh said. “They’re mainly concerned with looking at evidence and safety.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Today there are so many evidence-based drug therapies for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) that physicians treating HF patients almost don’t know what to do them.
It’s an exciting new age that way, but to many vexingly unclear how best to merge the shiny new options with mainstay regimens based on time-honored renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors and beta-blockers.
To impart some clarity, the authors of a new HF guideline document recently took center stage at the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA) annual meeting to preview their updated recommendations, with novel twists based on recent major trials, for the new age of HF pharmacotherapeutics.
The guideline committee considered the evidence base that existed “up until the end of March of this year,” Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College London, said during the presentation. The document “is now finalized, it’s with the publishers, and it will be presented in full with simultaneous publication at the ESC meeting” that starts August 27.
It describes a game plan, already followed by some clinicians in practice without official guidance, for initiating drugs from each of four classes in virtually all patients with HFrEF.
New indicated drugs, new perspective for HFrEF
Three of the drug categories are old acquaintances. Among them are the RAS inhibitors, which include angiotensin-receptor/neprilysin inhibitors, beta-blockers, and the mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists. The latter drugs are gaining new respect after having been underplayed in HF prescribing despite longstanding evidence of efficacy.
Completing the quartet of first-line HFrEF drug classes is a recent arrival to the HF arena, the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors.
“We now have new data and a simplified treatment algorithm for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction based on the early administration of the four major classes of drugs,” said Marco Metra, MD, University of Brescia (Italy), previewing the medical-therapy portions of the new guideline at the ESC-HFA sessions, which launched virtually and live in Florence, Italy, on July 29.
The new game plan offers a simple answer to a once-common but complex question: How and in what order are the different drug classes initiated in patients with HFrEF? In the new document, the stated goal is to get them all on board expeditiously and safely, by any means possible.
The guideline writers did not specify a sequence, preferring to leave that decision to physicians, said Dr. Metra, who stated only two guiding principles. The first is to consider the patient’s unique circumstances. The order in which the drugs are introduced might vary, depending on, for example, whether the patient has low or high blood pressure or renal dysfunction.
Second, “it is very important that we try to give all four classes of drugs to the patient in the shortest time possible, because this saves lives,” he said.
That there is no recommendation on sequencing the drugs has led some to the wrong interpretation that all should be started at once, observed coauthor Javed Butler, MD, MPH, University of Mississippi, Jackson, as a panelist during the presentation. Far from it, he said. “The doctor with the patient in front of you can make the best decision. The idea here is to get all the therapies on as soon as possible, as safely as possible.”
“The order in which they are introduced is not really important,” agreed Vijay Chopra, MD, Max Super Specialty Hospital Saket, New Delhi, another coauthor on the panel. “The important thing is that at least some dose of all the four drugs needs to be introduced in the first 4-6 weeks, and then up-titrated.”
Other medical therapy can be more tailored, Dr. Metra noted, such as loop diuretics for patients with congestion, iron for those with iron deficiency, and other drugs depending on whether there is, for example, atrial fibrillation or coronary disease.
Adoption of emerging definitions
The document adopts the emerging characterization of HFrEF by a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) up to 40%.
And it will leverage an expanding evidence base for medication in a segment of patients once said to have HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), who had therefore lacked specific, guideline-directed medical therapies. Now, patients with an LVEF of 41%-49% will be said to have HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF), a tweak to the recently introduced HF with “mid-range” LVEF that is designed to assert its nature as something to treat. The new document’s HFmrEF recommendations come with various class and level-of-evidence ratings.
That leaves HFpEF to be characterized by an LVEF of 50% in combination with structural or functional abnormalities associated with LV diastolic dysfunction or raised LV filling pressures, including raised natriuretic peptide levels.
The definitions are consistent with those proposed internationally by the ESC-HFA, the Heart Failure Society of America, and other groups in a statement published in March.
Expanded HFrEF med landscape
Since the 2016 ESC guideline on HF therapy, Dr. McDonagh said, “there’s been no substantial change in the evidence for many of the classical drugs that we use in heart failure. However, we had a lot of new and exciting evidence to consider,” especially in support of the SGLT2 inhibitors as one of the core medications in HFrEF.
The new data came from two controlled trials in particular. In DAPA-HF, patients with HFrEF who were initially without diabetes and who went on dapagliflozin (Farxiga, AstraZeneca) showed a 27% drop in cardiovascular (CV) death or worsening-HF events over a median of 18 months.
“That was followed up with very concordant results with empagliflozin [Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly] in HFrEF in the EMPEROR-Reduced trial,” Dr. McDonagh said. In that trial, comparable patients who took empagliflozin showed a 25% drop in a primary endpoint similar to that in DAPA-HF over the median 16-month follow-up.
Other HFrEF recommendations are for selected patients. They include ivabradine, already in the guidelines, for patients in sinus rhythm with an elevated resting heart rate who can’t take beta-blockers for whatever reason. But, Dr. McDonagh noted, “we had some new classes of drugs to consider as well.”
In particular, the oral soluble guanylate-cyclase receptor stimulator vericiguat (Verquvo) emerged about a year ago from the VICTORIA trial as a modest success for patients with HFrEF and a previous HF hospitalization. In the trial with more than 5,000 patients, treatment with vericiguat atop standard drug and device therapy was followed by a significant 10% drop in risk for CV death or HF hospitalization.
Available now or likely to be available in the United States, the European Union, Japan, and other countries, vericiguat is recommended in the new guideline for VICTORIA-like patients who don’t adequately respond to other indicated medications.
Little for HFpEF as newly defined
“Almost nothing is new” in the guidelines for HFpEF, Dr. Metra said. The document recommends screening for and treatment of any underlying disorder and comorbidities, plus diuretics for any congestion. “That’s what we have to date.”
But that evidence base might soon change. The new HFpEF recommendations could possibly be up-staged at the ESC sessions by the August 27 scheduled presentation of EMPEROR-Preserved, a randomized test of empagliflozin in HFpEF and – it could be said – HFmrEF. The trial entered patients with chronic HF and an LVEF greater than 40%.
Eli Lilly and Boehringer Ingelheim offered the world a peek at the results, which suggest the SGLT2 inhibitor had a positive impact on the primary endpoint of CV death or HF hospitalization. They announced the cursory top-line outcomes in early July as part of its regulatory obligations, noting that the trial had “met” its primary endpoint.
But many unknowns remain, including the degree of benefit and whether it varied among subgroups, and especially whether outcomes were different for HFmrEF than for HFpEF.
Upgrades for familiar agents
Still, HFmrEF gets noteworthy attention in the document. “For the first time, we have recommendations for these patients,” Dr. Metra said. “We already knew that diuretics are indicated for the treatment of congestion. But now, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid antagonists, as well as sacubitril/valsartan, may be considered to improve outcomes in these patients.” Their upgrades in the new guidelines were based on review of trials in the CHARM program and of TOPCAT and PARAGON-HF, among others, he said.

The new document also includes “treatment algorithms based on phenotypes”; that is, comorbidities and less common HF precipitants. For example, “assessment of iron status is now mandated in all patients with heart failure,” Dr. Metra said.
AFFIRM-HF is the key trial in this arena, with its more than 1,100 iron-deficient patients with LVEF less than 50% who had been recently hospitalized for HF. A year of treatment with ferric carboxymaltose (Ferinject/Injectafer, Vifor) led to a 26% drop in risk for HF hospitalization, but without affecting mortality.
For those who are iron deficient, Dr. Metra said, “ferric carboxymaltose intravenously should be considered not only in patients with low ejection fraction and outpatients, but also in patients recently hospitalized for acute heart failure.”
The SGLT2 inhibitors are recommended in HFrEF patients with type 2 diabetes. And treatment with tafamidis (Vyndaqel, Pfizer) in patients with genetic or wild-type transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis gets a class I recommendation based on survival gains seen in the ATTR-ACT trial.
Also recommended is a full CV assessment for patients with cancer who are on cardiotoxic agents or otherwise might be at risk for chemotherapy cardiotoxicity. “Beta-blockers and ACE inhibitors should be considered in those who develop left ventricular systolic dysfunction after anticancer therapy,” Dr. Metra said.
The ongoing pandemic made its mark on the document’s genesis, as it has with most everything else. “For better or worse, we were a ‘COVID guideline,’ ” Dr. McDonagh said. The writing committee consisted of “a large task force of 31 individuals, including two patients,” and there were “only two face-to-face meetings prior to the first wave of COVID hitting Europe.”
The committee voted on each of the recommendations, “and we had to have agreement of more than 75% of the task force to assign a class of recommendation or level of evidence,” she said. “I think we did the best we could in the circumstances. We had the benefit of many discussions over Zoom, and I think at the end of the day we have achieved a consensus.”
With such a large body of participants and the 75% threshold for agreement, “you end up with perhaps a conservative guideline. But that’s not a bad thing for clinical practice, for guidelines to be conservative,” Dr. McDonagh said. “They’re mainly concerned with looking at evidence and safety.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ARBs equal ACE inhibitors for hypertension, and better tolerated
In the largest comparison of angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) and ACE inhibitors to date, a study of nearly 2.3 million patients starting the drugs as monotherapy shows no significant differences between the two in the long-term prevention of hypertension-related cardiovascular events.
However, side effects were notably lower with ARBs.
“This is a very large, well-executed observational study that confirms that ARBs appear to have fewer side effects than ACE inhibitors, and no unexpected ARB side effects were detected,” senior author George Hripcsak, MD, professor and chair of biomedical informatics at Columbia University, New York, told this news organization.
“Despite being equally guideline-recommended first-line therapies for hypertension, these results support preferentially starting ARBs rather than ACE inhibitors when initiating treatment for hypertension for physicians and patients considering renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibition,” the authors added in the study, published online July 26, 2021, in the journal Hypertension.
They noted that both drug classes have been on the market a long time, with proven efficacy in hypertension and “a wide availability of inexpensive generic forms.”
They also stressed that their findings only apply to patients with hypertension for whom a RAS inhibitor would be the best choice of therapy.
Commenting on the research, George Bakris, MD, of the American Heart Association’s Comprehensive Hypertension Center at the University of Chicago, said the findings were consistent with his experience in prescribing as well as researching the two drug classes.
“I have been in practice for over 30 years and studied both classes, including head-to-head prospective trials to assess blood pressure, and found in many cases better blood pressure lowering by some ARBs and always better tolerability,” he told this news organization. “I think this study confirms and extends my thoughts between the two classes of blood pressure–lowering agents.”
Head-to-head comparisons of ACE inhibitors and ARBs limited to date
ACE inhibitors and ARBs each have extensive evidence supporting their roles as first-line medications in the treatment of hypertension, and each have the strongest recommendations in international guidelines.
However, ACE inhibitors are prescribed more commonly than ARBs as the first-line drug for lowering blood pressure, and head-to-head comparisons of the two are limited, with conflicting results.
For the study, Dr. Hripcsak and colleagues evaluated data on almost 3 million patients starting monotherapy with an ACE inhibitor or ARB for the first time between 1996 and 2018 in the United States, Germany, and South Korea, who had no history of heart disease or stroke.
They identified a total of 2,297,881 patients initiating ACE inhibitors and 673,938 starting ARBs. Among new users of ACE inhibitors, most received lisinopril (80%), followed by ramipril and enalapril, while most patients prescribed ARBs received losartan (45%), followed by valsartan and olmesartan.
With follow-up times ranging from about 4 months to more than 18 months, the data show no statistically significant differences between ACE inhibitors versus ARBs in the primary outcomes of acute myocardial infarction (hazard ratio, 1.11), heart failure (HR, 1.03), stroke (HR, 1.07), or composite cardiovascular events (HR, 1.06).
For secondary and safety outcomes, including an analysis of 51 possible side effects, ACE inhibitors, compared with ARBs, were associated with a significantly higher risk of angioedema (HR, 3.31; P < .01), cough (HR, 1.32; P < .01), acute pancreatitis (HR, 1.32; P = .02), gastrointestinal bleeding (HR, 1.18; P = .04), and abnormal weight loss (HR, 1.18; P = .04).
While the link between ACE inhibitors and pancreatitis has been previously reported, the association with GI bleeding may be a novel finding, with no prior studies comparing those effects in the two drug classes, the authors noted.
Despite most patients taking just a couple of drugs in either class, Dr. Hripcsak said, “we don’t expect that other drugs from those classes will have fewer differences. It is possible, of course, but that is not our expectation.”
Results only applicable to those starting therapy with RAS inhibitors
First author RuiJun Chen, MD, added that, importantly, the results may not apply to patients switching therapies or adding on therapy, “such as for the patient whose hypertension is not effectively controlled with one drug and requires the addition of a second medication,” he said in an interview.
“Also, the suggestion of preferentially prescribing ARBs only applies to those patients and providers intending to control blood pressure through RAS inhibition,” said Dr. Chen, an assistant professor in translational data science and informatics at Geisinger Medical Center in Danville, Pa., who was a National Library of Medicine postdoctoral fellow at Columbia University at the time of the study.
Hence, he stressed the results do not extend to other classes of recommended first-line blood pressure medications.
“Essentially, since this is an ACE inhibitor versus ARB study, we would not claim that ARBs are preferred over all other types of hypertension medications which were not studied here,” the researchers emphasize.
In addition to ARBs and ACE inhibitors, other medications recommended by the AHA/American College of Cardiology in the 2017 “Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults” for the primary treatment of hypertension include thiazide diuretics and calcium channel blockers.
The study received support from the National Library of Medicine and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases of the National Institutes of Health; the National Science Foundation; and the Ministries of Health & Welfare and of Trade, Industry & Energy of the Republic of Korea. Dr. Hripcsak reported receiving grants from the National Library of Medicine during the study and grants from Janssen Research outside the submitted work. Dr. Bakris reported being a consultant for Merck, KBP Biosciences, and Ionis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the largest comparison of angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) and ACE inhibitors to date, a study of nearly 2.3 million patients starting the drugs as monotherapy shows no significant differences between the two in the long-term prevention of hypertension-related cardiovascular events.
However, side effects were notably lower with ARBs.
“This is a very large, well-executed observational study that confirms that ARBs appear to have fewer side effects than ACE inhibitors, and no unexpected ARB side effects were detected,” senior author George Hripcsak, MD, professor and chair of biomedical informatics at Columbia University, New York, told this news organization.
“Despite being equally guideline-recommended first-line therapies for hypertension, these results support preferentially starting ARBs rather than ACE inhibitors when initiating treatment for hypertension for physicians and patients considering renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibition,” the authors added in the study, published online July 26, 2021, in the journal Hypertension.
They noted that both drug classes have been on the market a long time, with proven efficacy in hypertension and “a wide availability of inexpensive generic forms.”
They also stressed that their findings only apply to patients with hypertension for whom a RAS inhibitor would be the best choice of therapy.
Commenting on the research, George Bakris, MD, of the American Heart Association’s Comprehensive Hypertension Center at the University of Chicago, said the findings were consistent with his experience in prescribing as well as researching the two drug classes.
“I have been in practice for over 30 years and studied both classes, including head-to-head prospective trials to assess blood pressure, and found in many cases better blood pressure lowering by some ARBs and always better tolerability,” he told this news organization. “I think this study confirms and extends my thoughts between the two classes of blood pressure–lowering agents.”
Head-to-head comparisons of ACE inhibitors and ARBs limited to date
ACE inhibitors and ARBs each have extensive evidence supporting their roles as first-line medications in the treatment of hypertension, and each have the strongest recommendations in international guidelines.
However, ACE inhibitors are prescribed more commonly than ARBs as the first-line drug for lowering blood pressure, and head-to-head comparisons of the two are limited, with conflicting results.
For the study, Dr. Hripcsak and colleagues evaluated data on almost 3 million patients starting monotherapy with an ACE inhibitor or ARB for the first time between 1996 and 2018 in the United States, Germany, and South Korea, who had no history of heart disease or stroke.
They identified a total of 2,297,881 patients initiating ACE inhibitors and 673,938 starting ARBs. Among new users of ACE inhibitors, most received lisinopril (80%), followed by ramipril and enalapril, while most patients prescribed ARBs received losartan (45%), followed by valsartan and olmesartan.
With follow-up times ranging from about 4 months to more than 18 months, the data show no statistically significant differences between ACE inhibitors versus ARBs in the primary outcomes of acute myocardial infarction (hazard ratio, 1.11), heart failure (HR, 1.03), stroke (HR, 1.07), or composite cardiovascular events (HR, 1.06).
For secondary and safety outcomes, including an analysis of 51 possible side effects, ACE inhibitors, compared with ARBs, were associated with a significantly higher risk of angioedema (HR, 3.31; P < .01), cough (HR, 1.32; P < .01), acute pancreatitis (HR, 1.32; P = .02), gastrointestinal bleeding (HR, 1.18; P = .04), and abnormal weight loss (HR, 1.18; P = .04).
While the link between ACE inhibitors and pancreatitis has been previously reported, the association with GI bleeding may be a novel finding, with no prior studies comparing those effects in the two drug classes, the authors noted.
Despite most patients taking just a couple of drugs in either class, Dr. Hripcsak said, “we don’t expect that other drugs from those classes will have fewer differences. It is possible, of course, but that is not our expectation.”
Results only applicable to those starting therapy with RAS inhibitors
First author RuiJun Chen, MD, added that, importantly, the results may not apply to patients switching therapies or adding on therapy, “such as for the patient whose hypertension is not effectively controlled with one drug and requires the addition of a second medication,” he said in an interview.
“Also, the suggestion of preferentially prescribing ARBs only applies to those patients and providers intending to control blood pressure through RAS inhibition,” said Dr. Chen, an assistant professor in translational data science and informatics at Geisinger Medical Center in Danville, Pa., who was a National Library of Medicine postdoctoral fellow at Columbia University at the time of the study.
Hence, he stressed the results do not extend to other classes of recommended first-line blood pressure medications.
“Essentially, since this is an ACE inhibitor versus ARB study, we would not claim that ARBs are preferred over all other types of hypertension medications which were not studied here,” the researchers emphasize.
In addition to ARBs and ACE inhibitors, other medications recommended by the AHA/American College of Cardiology in the 2017 “Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults” for the primary treatment of hypertension include thiazide diuretics and calcium channel blockers.
The study received support from the National Library of Medicine and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases of the National Institutes of Health; the National Science Foundation; and the Ministries of Health & Welfare and of Trade, Industry & Energy of the Republic of Korea. Dr. Hripcsak reported receiving grants from the National Library of Medicine during the study and grants from Janssen Research outside the submitted work. Dr. Bakris reported being a consultant for Merck, KBP Biosciences, and Ionis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the largest comparison of angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) and ACE inhibitors to date, a study of nearly 2.3 million patients starting the drugs as monotherapy shows no significant differences between the two in the long-term prevention of hypertension-related cardiovascular events.
However, side effects were notably lower with ARBs.
“This is a very large, well-executed observational study that confirms that ARBs appear to have fewer side effects than ACE inhibitors, and no unexpected ARB side effects were detected,” senior author George Hripcsak, MD, professor and chair of biomedical informatics at Columbia University, New York, told this news organization.
“Despite being equally guideline-recommended first-line therapies for hypertension, these results support preferentially starting ARBs rather than ACE inhibitors when initiating treatment for hypertension for physicians and patients considering renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibition,” the authors added in the study, published online July 26, 2021, in the journal Hypertension.
They noted that both drug classes have been on the market a long time, with proven efficacy in hypertension and “a wide availability of inexpensive generic forms.”
They also stressed that their findings only apply to patients with hypertension for whom a RAS inhibitor would be the best choice of therapy.
Commenting on the research, George Bakris, MD, of the American Heart Association’s Comprehensive Hypertension Center at the University of Chicago, said the findings were consistent with his experience in prescribing as well as researching the two drug classes.
“I have been in practice for over 30 years and studied both classes, including head-to-head prospective trials to assess blood pressure, and found in many cases better blood pressure lowering by some ARBs and always better tolerability,” he told this news organization. “I think this study confirms and extends my thoughts between the two classes of blood pressure–lowering agents.”
Head-to-head comparisons of ACE inhibitors and ARBs limited to date
ACE inhibitors and ARBs each have extensive evidence supporting their roles as first-line medications in the treatment of hypertension, and each have the strongest recommendations in international guidelines.
However, ACE inhibitors are prescribed more commonly than ARBs as the first-line drug for lowering blood pressure, and head-to-head comparisons of the two are limited, with conflicting results.
For the study, Dr. Hripcsak and colleagues evaluated data on almost 3 million patients starting monotherapy with an ACE inhibitor or ARB for the first time between 1996 and 2018 in the United States, Germany, and South Korea, who had no history of heart disease or stroke.
They identified a total of 2,297,881 patients initiating ACE inhibitors and 673,938 starting ARBs. Among new users of ACE inhibitors, most received lisinopril (80%), followed by ramipril and enalapril, while most patients prescribed ARBs received losartan (45%), followed by valsartan and olmesartan.
With follow-up times ranging from about 4 months to more than 18 months, the data show no statistically significant differences between ACE inhibitors versus ARBs in the primary outcomes of acute myocardial infarction (hazard ratio, 1.11), heart failure (HR, 1.03), stroke (HR, 1.07), or composite cardiovascular events (HR, 1.06).
For secondary and safety outcomes, including an analysis of 51 possible side effects, ACE inhibitors, compared with ARBs, were associated with a significantly higher risk of angioedema (HR, 3.31; P < .01), cough (HR, 1.32; P < .01), acute pancreatitis (HR, 1.32; P = .02), gastrointestinal bleeding (HR, 1.18; P = .04), and abnormal weight loss (HR, 1.18; P = .04).
While the link between ACE inhibitors and pancreatitis has been previously reported, the association with GI bleeding may be a novel finding, with no prior studies comparing those effects in the two drug classes, the authors noted.
Despite most patients taking just a couple of drugs in either class, Dr. Hripcsak said, “we don’t expect that other drugs from those classes will have fewer differences. It is possible, of course, but that is not our expectation.”
Results only applicable to those starting therapy with RAS inhibitors
First author RuiJun Chen, MD, added that, importantly, the results may not apply to patients switching therapies or adding on therapy, “such as for the patient whose hypertension is not effectively controlled with one drug and requires the addition of a second medication,” he said in an interview.
“Also, the suggestion of preferentially prescribing ARBs only applies to those patients and providers intending to control blood pressure through RAS inhibition,” said Dr. Chen, an assistant professor in translational data science and informatics at Geisinger Medical Center in Danville, Pa., who was a National Library of Medicine postdoctoral fellow at Columbia University at the time of the study.
Hence, he stressed the results do not extend to other classes of recommended first-line blood pressure medications.
“Essentially, since this is an ACE inhibitor versus ARB study, we would not claim that ARBs are preferred over all other types of hypertension medications which were not studied here,” the researchers emphasize.
In addition to ARBs and ACE inhibitors, other medications recommended by the AHA/American College of Cardiology in the 2017 “Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults” for the primary treatment of hypertension include thiazide diuretics and calcium channel blockers.
The study received support from the National Library of Medicine and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases of the National Institutes of Health; the National Science Foundation; and the Ministries of Health & Welfare and of Trade, Industry & Energy of the Republic of Korea. Dr. Hripcsak reported receiving grants from the National Library of Medicine during the study and grants from Janssen Research outside the submitted work. Dr. Bakris reported being a consultant for Merck, KBP Biosciences, and Ionis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In sickness and in health: Spouses can share risk for cardiac events
A study from Japan suggests that a history of cardiovascular events in a spouse may elevate risk for future CV events in the other partner, with one caveat: Men in the cohort study were at increased risk if their wives had such a history, but the association was only one way. The risk of events didn’t go up for women with husbands who had previously experienced a CV event.
The results highlight the need for clinicians to screen and possibly intervene with a primary CV prevention strategy “not only first-degree relatives but also spouses with a history of cardiovascular disease,” which is not currently part of the primary prevention guidelines, Hiroyuki Ohbe, MD, University of Tokyo, told this news organization.
In their study published online July 9 in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes, Dr. Ohbe and Hideo Yasunaga, MD, PhD, of the same institution, assessed the risk of subsequent CV events in adults with a spouse who had experienced a stroke of any kind or had clinical ischemic heart disease such as angina or myocardial infarction.
Johanna Contreras, MD, director of heart failure at Mount Sinai Health System in New York, is not surprised by the finding that a wife’s CV history is linked to the CV risk in the husband.
“I see this often in my practice. When you live with someone, you also behave in a similar way as the other person,” Dr. Contreras told this news organization. “For example, couples who live together are likely to both exercise and have a healthy diet and not smoke.”
And most notably, she said, “the women are usually the ones who drive the healthy behaviors in the family; they watch what the family eats, where they eat, when they eat, and the men tend to allow the women to guide this behavior.”
Dr. Ohbe and Dr. Yasunaga agree, proposing that different results for men and women in the analysis may be because of the dependence of working-aged men on their wives for major aspects of lifestyle, such as diet and exercise. Moreover, they write, increased psychological and physical stress from taking care of a spouse with CV disease may also play a role, as caregivers often neglect their own health.
The team identified 13,759 adults in a large administrative database with no history of CV disease whose spouse had such a history at their first health checkup; they were the exposure group. The team matched each of them with up to four individuals (n = 55,027) who had no CV disease history and spouses without CV disease at their first health checkup; they were the nonexposure group.
The mean observation period was 7.9 years from the first health checkup, at which the subjects’ mean age was 56 years. During the follow-up, more people in the exposure group than the nonexposure group had a history of CV events, 0.6% versus 0.4%.
In the overall cohort, the hazard ratio for future severe CV events – heart failure hospitalization or MI – in those with spouses with a history of CV disease was 1.48 (95% confidence interval, 1.15-1.90).
When stratified by sex, men whose wives had CV disease showed a significantly increased risk of a future severe CV event (HR, 1.68; 95% CI, 1.22-2.32). But women with husbands with CV disease did not (HR, 1.22; 95% CI, 0.82-1.83).
The results of all four sensitivity analyses were similar to those of the primary analysis, both in the overall cohort and in the cohorts stratified by sex. The investigators performed multivariate survival analyses: one that excluded people whose partners had died, one that included death by any cause as an outcome, and one with propensity score matching.
Further studies are needed to confirm their observations and test whether a primary prevention strategy targeted at married couples could reduce CV events, note Dr. Ohbe and Dr. Yasunaga.
The findings have implications for everyday clinical practice, Dr. Contreras said. “When I see a patient who is married and has had a heart attack, I will insist on seeing the partner as well, and I will counsel them on working together to change their lifestyle,” she said in an interview.
“Often when you have that discussion with the couple after one has a heart attack, they quit smoking together, they go the gym together, and they get healthier together,” she said. “That’s now a very important conversation we have before they leave the hospital.”
The study was supported by grants from the Japan Ministry of Health, Ministry of Labour and Welfare, and the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. Dr. Ohbe, Dr. Yasunaga, and Dr. Contreras have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A study from Japan suggests that a history of cardiovascular events in a spouse may elevate risk for future CV events in the other partner, with one caveat: Men in the cohort study were at increased risk if their wives had such a history, but the association was only one way. The risk of events didn’t go up for women with husbands who had previously experienced a CV event.
The results highlight the need for clinicians to screen and possibly intervene with a primary CV prevention strategy “not only first-degree relatives but also spouses with a history of cardiovascular disease,” which is not currently part of the primary prevention guidelines, Hiroyuki Ohbe, MD, University of Tokyo, told this news organization.
In their study published online July 9 in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes, Dr. Ohbe and Hideo Yasunaga, MD, PhD, of the same institution, assessed the risk of subsequent CV events in adults with a spouse who had experienced a stroke of any kind or had clinical ischemic heart disease such as angina or myocardial infarction.
Johanna Contreras, MD, director of heart failure at Mount Sinai Health System in New York, is not surprised by the finding that a wife’s CV history is linked to the CV risk in the husband.
“I see this often in my practice. When you live with someone, you also behave in a similar way as the other person,” Dr. Contreras told this news organization. “For example, couples who live together are likely to both exercise and have a healthy diet and not smoke.”
And most notably, she said, “the women are usually the ones who drive the healthy behaviors in the family; they watch what the family eats, where they eat, when they eat, and the men tend to allow the women to guide this behavior.”
Dr. Ohbe and Dr. Yasunaga agree, proposing that different results for men and women in the analysis may be because of the dependence of working-aged men on their wives for major aspects of lifestyle, such as diet and exercise. Moreover, they write, increased psychological and physical stress from taking care of a spouse with CV disease may also play a role, as caregivers often neglect their own health.
The team identified 13,759 adults in a large administrative database with no history of CV disease whose spouse had such a history at their first health checkup; they were the exposure group. The team matched each of them with up to four individuals (n = 55,027) who had no CV disease history and spouses without CV disease at their first health checkup; they were the nonexposure group.
The mean observation period was 7.9 years from the first health checkup, at which the subjects’ mean age was 56 years. During the follow-up, more people in the exposure group than the nonexposure group had a history of CV events, 0.6% versus 0.4%.
In the overall cohort, the hazard ratio for future severe CV events – heart failure hospitalization or MI – in those with spouses with a history of CV disease was 1.48 (95% confidence interval, 1.15-1.90).
When stratified by sex, men whose wives had CV disease showed a significantly increased risk of a future severe CV event (HR, 1.68; 95% CI, 1.22-2.32). But women with husbands with CV disease did not (HR, 1.22; 95% CI, 0.82-1.83).
The results of all four sensitivity analyses were similar to those of the primary analysis, both in the overall cohort and in the cohorts stratified by sex. The investigators performed multivariate survival analyses: one that excluded people whose partners had died, one that included death by any cause as an outcome, and one with propensity score matching.
Further studies are needed to confirm their observations and test whether a primary prevention strategy targeted at married couples could reduce CV events, note Dr. Ohbe and Dr. Yasunaga.
The findings have implications for everyday clinical practice, Dr. Contreras said. “When I see a patient who is married and has had a heart attack, I will insist on seeing the partner as well, and I will counsel them on working together to change their lifestyle,” she said in an interview.
“Often when you have that discussion with the couple after one has a heart attack, they quit smoking together, they go the gym together, and they get healthier together,” she said. “That’s now a very important conversation we have before they leave the hospital.”
The study was supported by grants from the Japan Ministry of Health, Ministry of Labour and Welfare, and the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. Dr. Ohbe, Dr. Yasunaga, and Dr. Contreras have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A study from Japan suggests that a history of cardiovascular events in a spouse may elevate risk for future CV events in the other partner, with one caveat: Men in the cohort study were at increased risk if their wives had such a history, but the association was only one way. The risk of events didn’t go up for women with husbands who had previously experienced a CV event.
The results highlight the need for clinicians to screen and possibly intervene with a primary CV prevention strategy “not only first-degree relatives but also spouses with a history of cardiovascular disease,” which is not currently part of the primary prevention guidelines, Hiroyuki Ohbe, MD, University of Tokyo, told this news organization.
In their study published online July 9 in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes, Dr. Ohbe and Hideo Yasunaga, MD, PhD, of the same institution, assessed the risk of subsequent CV events in adults with a spouse who had experienced a stroke of any kind or had clinical ischemic heart disease such as angina or myocardial infarction.
Johanna Contreras, MD, director of heart failure at Mount Sinai Health System in New York, is not surprised by the finding that a wife’s CV history is linked to the CV risk in the husband.
“I see this often in my practice. When you live with someone, you also behave in a similar way as the other person,” Dr. Contreras told this news organization. “For example, couples who live together are likely to both exercise and have a healthy diet and not smoke.”
And most notably, she said, “the women are usually the ones who drive the healthy behaviors in the family; they watch what the family eats, where they eat, when they eat, and the men tend to allow the women to guide this behavior.”
Dr. Ohbe and Dr. Yasunaga agree, proposing that different results for men and women in the analysis may be because of the dependence of working-aged men on their wives for major aspects of lifestyle, such as diet and exercise. Moreover, they write, increased psychological and physical stress from taking care of a spouse with CV disease may also play a role, as caregivers often neglect their own health.
The team identified 13,759 adults in a large administrative database with no history of CV disease whose spouse had such a history at their first health checkup; they were the exposure group. The team matched each of them with up to four individuals (n = 55,027) who had no CV disease history and spouses without CV disease at their first health checkup; they were the nonexposure group.
The mean observation period was 7.9 years from the first health checkup, at which the subjects’ mean age was 56 years. During the follow-up, more people in the exposure group than the nonexposure group had a history of CV events, 0.6% versus 0.4%.
In the overall cohort, the hazard ratio for future severe CV events – heart failure hospitalization or MI – in those with spouses with a history of CV disease was 1.48 (95% confidence interval, 1.15-1.90).
When stratified by sex, men whose wives had CV disease showed a significantly increased risk of a future severe CV event (HR, 1.68; 95% CI, 1.22-2.32). But women with husbands with CV disease did not (HR, 1.22; 95% CI, 0.82-1.83).
The results of all four sensitivity analyses were similar to those of the primary analysis, both in the overall cohort and in the cohorts stratified by sex. The investigators performed multivariate survival analyses: one that excluded people whose partners had died, one that included death by any cause as an outcome, and one with propensity score matching.
Further studies are needed to confirm their observations and test whether a primary prevention strategy targeted at married couples could reduce CV events, note Dr. Ohbe and Dr. Yasunaga.
The findings have implications for everyday clinical practice, Dr. Contreras said. “When I see a patient who is married and has had a heart attack, I will insist on seeing the partner as well, and I will counsel them on working together to change their lifestyle,” she said in an interview.
“Often when you have that discussion with the couple after one has a heart attack, they quit smoking together, they go the gym together, and they get healthier together,” she said. “That’s now a very important conversation we have before they leave the hospital.”
The study was supported by grants from the Japan Ministry of Health, Ministry of Labour and Welfare, and the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. Dr. Ohbe, Dr. Yasunaga, and Dr. Contreras have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.