User login
New year brings reduced flu activity
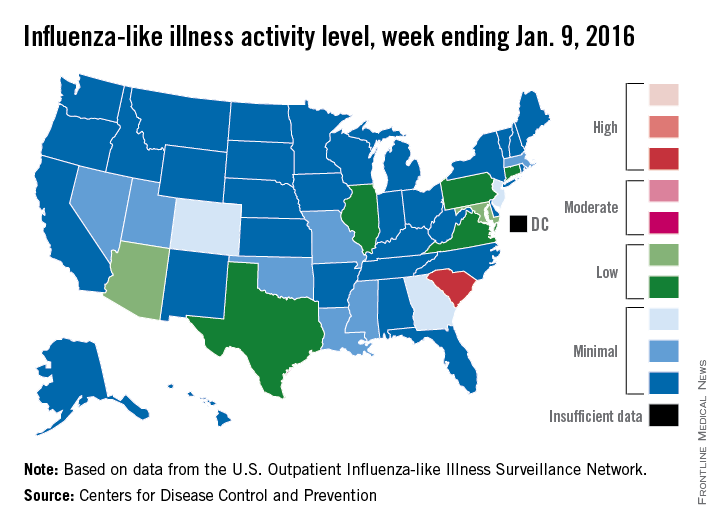
Influenza-like illness (ILI) activity was down during the first full week in January – a not-so-unlucky week 13 of the 2015-2016 flu season, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
South Carolina was at level 8, making it the only state in the “high” range of activity for the week ending Jan. 9. Puerto Rico was also at level 8, but there was no state in the “moderate” range and only seven states in the “low” range: Arizona and Maryland at level 5 and Connecticut, Illinois, Pennsylvania, Texas, and Virginia at level 4. There were 18 states at level 2 or higher, compared with 24 the previous week, according to data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network.
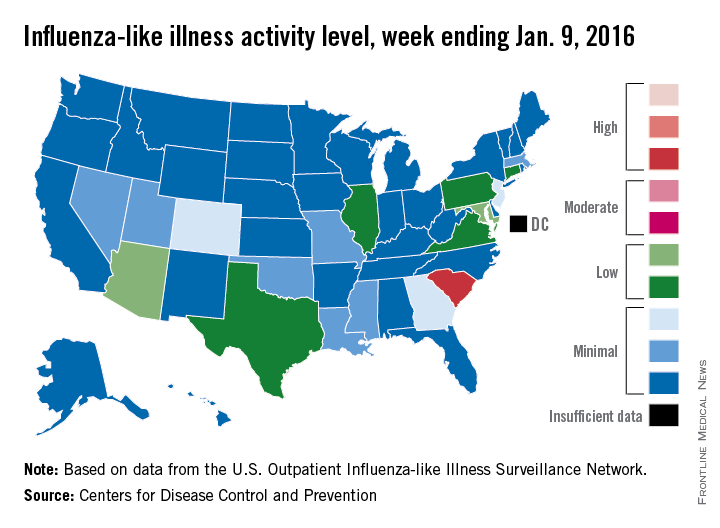
The proportion of outpatient visits for ILI was 2% for week 13, which was down from 2.8% in week 12 and below the national baseline of 2.1%, the CDC said. ILI is defined as fever (temperature of 100°F [37.8°C] or greater) and cough and/or sore throat.
One ILI-related pediatric death was reported during week 13, although it actually occurred in December. So far, there have been seven pediatric deaths reported during the 2015-2016 flu season, the CDC report noted.
Since Oct. 1, 2015, there have been 423 laboratory-confirmed influenza-associated hospitalizations reported in the 13 states – including California, New York, and Ohio – of the CDC’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network, for an overall hospitalization rate of 1.5 per 100,000 population. That rate, however, is “likely to be an underestimate as influenza-related hospitalizations can be missed, either because testing is not performed, or because cases may be attributed to other causes of pneumonia or other common influenza-related complications,” the CDC said.
Influenza-like illness (ILI) activity was down during the first full week in January – a not-so-unlucky week 13 of the 2015-2016 flu season, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
South Carolina was at level 8, making it the only state in the “high” range of activity for the week ending Jan. 9. Puerto Rico was also at level 8, but there was no state in the “moderate” range and only seven states in the “low” range: Arizona and Maryland at level 5 and Connecticut, Illinois, Pennsylvania, Texas, and Virginia at level 4. There were 18 states at level 2 or higher, compared with 24 the previous week, according to data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network.

The proportion of outpatient visits for ILI was 2% for week 13, which was down from 2.8% in week 12 and below the national baseline of 2.1%, the CDC said. ILI is defined as fever (temperature of 100°F [37.8°C] or greater) and cough and/or sore throat.
One ILI-related pediatric death was reported during week 13, although it actually occurred in December. So far, there have been seven pediatric deaths reported during the 2015-2016 flu season, the CDC report noted.
Since Oct. 1, 2015, there have been 423 laboratory-confirmed influenza-associated hospitalizations reported in the 13 states – including California, New York, and Ohio – of the CDC’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network, for an overall hospitalization rate of 1.5 per 100,000 population. That rate, however, is “likely to be an underestimate as influenza-related hospitalizations can be missed, either because testing is not performed, or because cases may be attributed to other causes of pneumonia or other common influenza-related complications,” the CDC said.
Influenza-like illness (ILI) activity was down during the first full week in January – a not-so-unlucky week 13 of the 2015-2016 flu season, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
South Carolina was at level 8, making it the only state in the “high” range of activity for the week ending Jan. 9. Puerto Rico was also at level 8, but there was no state in the “moderate” range and only seven states in the “low” range: Arizona and Maryland at level 5 and Connecticut, Illinois, Pennsylvania, Texas, and Virginia at level 4. There were 18 states at level 2 or higher, compared with 24 the previous week, according to data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network.

The proportion of outpatient visits for ILI was 2% for week 13, which was down from 2.8% in week 12 and below the national baseline of 2.1%, the CDC said. ILI is defined as fever (temperature of 100°F [37.8°C] or greater) and cough and/or sore throat.
One ILI-related pediatric death was reported during week 13, although it actually occurred in December. So far, there have been seven pediatric deaths reported during the 2015-2016 flu season, the CDC report noted.
Since Oct. 1, 2015, there have been 423 laboratory-confirmed influenza-associated hospitalizations reported in the 13 states – including California, New York, and Ohio – of the CDC’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network, for an overall hospitalization rate of 1.5 per 100,000 population. That rate, however, is “likely to be an underestimate as influenza-related hospitalizations can be missed, either because testing is not performed, or because cases may be attributed to other causes of pneumonia or other common influenza-related complications,” the CDC said.
Flu activity high in New Jersey, South Carolina
Week 12 of the 2015-2016 U.S. flu season saw two states in the “high” range of the influenza-like illness (ILI) activity scale, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
New Jersey was at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale for the week ending Jan. 2, 2016, and South Carolina was at level 9. The next-most-active state, Texas, was at level 7, putting it in the “moderate” range along with Maryland, which was at level 6, the CDC said.
States in the “low” range were Arizona, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, and Virginia at level 5 and California, Colorado, and Georgia at level 4. Altogether, there were 24 states at level 2 or higher, according to data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network.
Puerto Rico also moved up to level 10 for the week ending Jan. 2 and, in a case of geographic concentration, New York City was at level 6 even though New York State was still at level 1.
The proportion of outpatient visits for ILI nationally was 2.8% at the end of week 12, which is above the national baseline of 2.1%. For comparison, at this point in the 2014-2015 flu season, the proportion of visits for ILI was about 6%, and in 2013-2014 it was around 4.5%.
There were two flu-related pediatric deaths reported during the week, bringing the total to six for the 2015-2016 season. One death was associated with an influenza A (H3) virus and the other was associated with
an influenza A (H1N1)pdm09 virus. Looking again at previous years, there had been single weeks with at least six pediatric deaths by week 12 in each of the last three seasons, the CDC report showed.
Week 12 of the 2015-2016 U.S. flu season saw two states in the “high” range of the influenza-like illness (ILI) activity scale, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
New Jersey was at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale for the week ending Jan. 2, 2016, and South Carolina was at level 9. The next-most-active state, Texas, was at level 7, putting it in the “moderate” range along with Maryland, which was at level 6, the CDC said.
States in the “low” range were Arizona, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, and Virginia at level 5 and California, Colorado, and Georgia at level 4. Altogether, there were 24 states at level 2 or higher, according to data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network.
Puerto Rico also moved up to level 10 for the week ending Jan. 2 and, in a case of geographic concentration, New York City was at level 6 even though New York State was still at level 1.
The proportion of outpatient visits for ILI nationally was 2.8% at the end of week 12, which is above the national baseline of 2.1%. For comparison, at this point in the 2014-2015 flu season, the proportion of visits for ILI was about 6%, and in 2013-2014 it was around 4.5%.
There were two flu-related pediatric deaths reported during the week, bringing the total to six for the 2015-2016 season. One death was associated with an influenza A (H3) virus and the other was associated with
an influenza A (H1N1)pdm09 virus. Looking again at previous years, there had been single weeks with at least six pediatric deaths by week 12 in each of the last three seasons, the CDC report showed.
Week 12 of the 2015-2016 U.S. flu season saw two states in the “high” range of the influenza-like illness (ILI) activity scale, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
New Jersey was at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale for the week ending Jan. 2, 2016, and South Carolina was at level 9. The next-most-active state, Texas, was at level 7, putting it in the “moderate” range along with Maryland, which was at level 6, the CDC said.
States in the “low” range were Arizona, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, and Virginia at level 5 and California, Colorado, and Georgia at level 4. Altogether, there were 24 states at level 2 or higher, according to data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network.
Puerto Rico also moved up to level 10 for the week ending Jan. 2 and, in a case of geographic concentration, New York City was at level 6 even though New York State was still at level 1.
The proportion of outpatient visits for ILI nationally was 2.8% at the end of week 12, which is above the national baseline of 2.1%. For comparison, at this point in the 2014-2015 flu season, the proportion of visits for ILI was about 6%, and in 2013-2014 it was around 4.5%.
There were two flu-related pediatric deaths reported during the week, bringing the total to six for the 2015-2016 season. One death was associated with an influenza A (H3) virus and the other was associated with
an influenza A (H1N1)pdm09 virus. Looking again at previous years, there had been single weeks with at least six pediatric deaths by week 12 in each of the last three seasons, the CDC report showed.
Infectious disease in elderly a significant burden for EDs
More U.S. adults over the age of 65 visited an emergency department because of an infectious disease than for myocardial infarction and congestive heart failure combined, according to a new study.
Based on a nationwide ED sample, adults over 65 visited the ED just over 3.1 million times in 2012 due to infectious diseases (ID), more than three times the estimated amount for myocardial infarction and congestive heart failure. The most common diagnoses were lower respiratory infections (26.2%), urinary tract infections (25.3%), and septicemia (18.9%).
Of the 3.1 million cases brought to the ED, nearly 1.8 million cases were hospitalized, with septicemia the most common cause for hospitalization, accounting for 32.2% of ID-related hospitalizations, followed by lower respiratory infections. Septicemia was also the most common cause of mortality, accounting for 74.7% of the nearly 124,000 deaths.
“These observations underscore the importance of integrated strategies aimed at reducing ID-related morbidity and health care use of elderly adults as a national priority for research, health policy, and community action,” Dr. Tadahiro Goto of the University of Fukui (Japan) Hospital and his associates concluded.
Find the full study in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society (2015 Dec 23. doi: 101111/jgs.13836).
More U.S. adults over the age of 65 visited an emergency department because of an infectious disease than for myocardial infarction and congestive heart failure combined, according to a new study.
Based on a nationwide ED sample, adults over 65 visited the ED just over 3.1 million times in 2012 due to infectious diseases (ID), more than three times the estimated amount for myocardial infarction and congestive heart failure. The most common diagnoses were lower respiratory infections (26.2%), urinary tract infections (25.3%), and septicemia (18.9%).
Of the 3.1 million cases brought to the ED, nearly 1.8 million cases were hospitalized, with septicemia the most common cause for hospitalization, accounting for 32.2% of ID-related hospitalizations, followed by lower respiratory infections. Septicemia was also the most common cause of mortality, accounting for 74.7% of the nearly 124,000 deaths.
“These observations underscore the importance of integrated strategies aimed at reducing ID-related morbidity and health care use of elderly adults as a national priority for research, health policy, and community action,” Dr. Tadahiro Goto of the University of Fukui (Japan) Hospital and his associates concluded.
Find the full study in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society (2015 Dec 23. doi: 101111/jgs.13836).
More U.S. adults over the age of 65 visited an emergency department because of an infectious disease than for myocardial infarction and congestive heart failure combined, according to a new study.
Based on a nationwide ED sample, adults over 65 visited the ED just over 3.1 million times in 2012 due to infectious diseases (ID), more than three times the estimated amount for myocardial infarction and congestive heart failure. The most common diagnoses were lower respiratory infections (26.2%), urinary tract infections (25.3%), and septicemia (18.9%).
Of the 3.1 million cases brought to the ED, nearly 1.8 million cases were hospitalized, with septicemia the most common cause for hospitalization, accounting for 32.2% of ID-related hospitalizations, followed by lower respiratory infections. Septicemia was also the most common cause of mortality, accounting for 74.7% of the nearly 124,000 deaths.
“These observations underscore the importance of integrated strategies aimed at reducing ID-related morbidity and health care use of elderly adults as a national priority for research, health policy, and community action,” Dr. Tadahiro Goto of the University of Fukui (Japan) Hospital and his associates concluded.
Find the full study in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society (2015 Dec 23. doi: 101111/jgs.13836).
FROM JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN GERIATRICS SOCIETY
LAIV, IIV almost equally effective against influenza
When vaccinating children against influenza, inactivated and live attenuated influenza vaccines show little significant difference in effectiveness against nearly all strains of the virus, according to a new study in Pediatrics.
However, the study – which examined the effectiveness of IIV and LAIV across four consecutive influenza seasons between 2010 and 2014 – cautions that the 2013-2014 season’s A/(H1N1)pdm09 showed an uncharacteristically large gap in effectiveness favoring IIV, a discrepancy likely due to a problem with a vaccine component in LAIV. (Pediatrics. 2016;137(2):e20153279)
“We found that lower LAIV effectiveness in 2013-2014 was specific to the A/(H1N1)pdm09 vaccine component and was consistent with a previously unexamined effect during the 2010-2011 influenza season,” Jessie R. Chung of the influenza division at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and associates wrote, adding that the impetus for the study was the lack of available data “from observational studies after the 2009 pandemic on relative effectiveness of LAIV and IIV in children and adolescents.”
Ms. Chung* and coinvestigators enrolled children aged 2-17 years from clinics and hospitals in Michigan, New York, Pennsylvania, Tennessee, Texas, Washington, and Wisconsin during the 2010-2011, 2011-2012, 2012-2013, and 2013-2014 influenza seasons. Children brought in with symptoms of acute respiratory illness – cough, fever, or feverishness – had nasal and throat swabs collected to test for presence and type of influenza.
In total, 7,718 subjects were evaluated across the four influenza seasons, but after excluding subjects for various reasons – unknown vaccine type, indeterminate vaccine status, and inconclusive reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction results, among others – 6,819 subjects were included for vaccine effectiveness analysis, of which 2,703 were ultimately matched age appropriately and placed into IIV and LAIV cohorts for comparison. The IIV cohort consisted of 2,066 individuals (76.4%), while the LAIV cohort had 637 (23.6%).
During the 2010-2011 season, 66 of the 477 IIV subjects contracted influenza, versus 21 of 116 who received LAIV (14% vs. 18%, respectively). In the 2011-2012 season, 51 of the 499 IIV subjects (10%) contracted influenza, compared with 12 of the 152 LAIV subjects (8%). In the 2012-2013 season, 198 of the 622 IIV subjects (32%) contracted influenza, versus 61 of the 205 LAIV subjects (30%). But, in the 2013-2014 season, 36 of the 468 IIV subjects (8%) contracted influenza, versus 34 of the 164 LAIV subjects (21%).
After adjustment for age and season, the odds ratio for the 2013-2014 season was significantly higher than those of the other seasons across the entire age spectrum of 2-17 years: 2.88, compared with 1.49 (2010-2011), 0.67 (2011-2012), and 0.92 (2012-2013).
When comparing influenza type/subtype, adjusted odds ratio was 5.53 for those with A/(H1N1)pdm09 in the 2010-2011 season, compared with 2.65 for those with the same in the 2013-2014 season. Those with A/H3N2 did not show as significant a difference across seasons (2010-2013), nor did those with influenza type B (2010-2011, 2012-2013).
“We found no statistically significant difference in LAIV effectiveness compared with IIV against medically attended, laboratory-confirmed influenza illness due to A/H3N2 or B viruses,” Ms. Chung and colleagues concluded. “We found significantly higher odds of influenza A/(H1N1)pdm09 among participants vaccinated with LAIV, compared with IIV, [but] reasons for lower effectiveness of LAIV against the A/(H1N1)pdm09 virus, compared with IIV are not fully understood.”
The investigators added that “the finding appears to be specific to the A/(H1N1)pdm09 vaccine component; we did not detect any statistically significant differences in effectiveness for the other components.” Three previous randomized controlled trials indicated that trivalent LAIV was just as effective, if not more so, than IIV, making the findings of this study surprising and “unexpected,” the authors noted.
This study was supported by the CDC through cooperative agreements with a variety of universities and foundations, and funded by the National Institutes of Health. Ms. Chung and associates reported no relevant financial disclosures.
*A previous version of this story misstated Jessie Chung’s academic title. Ms. Chung holds a Master’s in public health.
Influenza vaccination has been recommended for everyone for the past few years. Acceptance of this recommendation has been variable, and vaccine failures do not help the cause of convincing our patients to accept vaccination. In the paper by Chung et al. from the CDC and other coinvestigators who are prominent in influenza research, we learn that the live attenuated intranasally administered flu vaccine was significantly inferior to the killed injection administered flu vaccine for one of the type A flu strains. As a consequence, more kids vaccinated with the live attenuated vaccine got the flu. So parents who claim “the flu shot does not work” were partially correct more often since the 2009 flu season, if their child got the intranasal flu vaccine. However, neither the intranasal nor the injectable flu vaccine have an exceptionally high efficacy because the calculations by the authors for the study described and by citation of prior studies we are reminded that vaccine efficacy varies by strain and yearly by the season between 45% and 71%. We need to have better flu vaccines.

|
Dr. Michael E. Pichichero |
At Legacy Pediatrics, where I am in part-time private practice, we have seen increasing requests for the intranasal flu vaccine each year because parents and kids who can voice their wishes don’t want the shot. Our nurses like it, too, because the crying, wailing, and fighting to hold the kid down is avoided. There had been some reports before 2009 that the intranasal flu vaccine was more effective than the shot. But those of us who have been around long enough practicing medicine have learned about the pendulum of data and opinion sometimes swings back and forth. The article by Chung et al. reminds us once again of this reality.
Dr. Michael E. Pichichero is at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center. He has received investigator-initiated grants from Sanofi Pasteur to study novel pneumococcal protein vaccines over the past 3 years and currently but has received no funding from Sanofi regarding injectable influenza vaccine. He also has conducted research with study coauthor Dr. John J. Treanor that was supported by MedImmune, who makes the intranasal flu vaccine.
Influenza vaccination has been recommended for everyone for the past few years. Acceptance of this recommendation has been variable, and vaccine failures do not help the cause of convincing our patients to accept vaccination. In the paper by Chung et al. from the CDC and other coinvestigators who are prominent in influenza research, we learn that the live attenuated intranasally administered flu vaccine was significantly inferior to the killed injection administered flu vaccine for one of the type A flu strains. As a consequence, more kids vaccinated with the live attenuated vaccine got the flu. So parents who claim “the flu shot does not work” were partially correct more often since the 2009 flu season, if their child got the intranasal flu vaccine. However, neither the intranasal nor the injectable flu vaccine have an exceptionally high efficacy because the calculations by the authors for the study described and by citation of prior studies we are reminded that vaccine efficacy varies by strain and yearly by the season between 45% and 71%. We need to have better flu vaccines.

|
Dr. Michael E. Pichichero |
At Legacy Pediatrics, where I am in part-time private practice, we have seen increasing requests for the intranasal flu vaccine each year because parents and kids who can voice their wishes don’t want the shot. Our nurses like it, too, because the crying, wailing, and fighting to hold the kid down is avoided. There had been some reports before 2009 that the intranasal flu vaccine was more effective than the shot. But those of us who have been around long enough practicing medicine have learned about the pendulum of data and opinion sometimes swings back and forth. The article by Chung et al. reminds us once again of this reality.
Dr. Michael E. Pichichero is at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center. He has received investigator-initiated grants from Sanofi Pasteur to study novel pneumococcal protein vaccines over the past 3 years and currently but has received no funding from Sanofi regarding injectable influenza vaccine. He also has conducted research with study coauthor Dr. John J. Treanor that was supported by MedImmune, who makes the intranasal flu vaccine.
Influenza vaccination has been recommended for everyone for the past few years. Acceptance of this recommendation has been variable, and vaccine failures do not help the cause of convincing our patients to accept vaccination. In the paper by Chung et al. from the CDC and other coinvestigators who are prominent in influenza research, we learn that the live attenuated intranasally administered flu vaccine was significantly inferior to the killed injection administered flu vaccine for one of the type A flu strains. As a consequence, more kids vaccinated with the live attenuated vaccine got the flu. So parents who claim “the flu shot does not work” were partially correct more often since the 2009 flu season, if their child got the intranasal flu vaccine. However, neither the intranasal nor the injectable flu vaccine have an exceptionally high efficacy because the calculations by the authors for the study described and by citation of prior studies we are reminded that vaccine efficacy varies by strain and yearly by the season between 45% and 71%. We need to have better flu vaccines.

|
Dr. Michael E. Pichichero |
At Legacy Pediatrics, where I am in part-time private practice, we have seen increasing requests for the intranasal flu vaccine each year because parents and kids who can voice their wishes don’t want the shot. Our nurses like it, too, because the crying, wailing, and fighting to hold the kid down is avoided. There had been some reports before 2009 that the intranasal flu vaccine was more effective than the shot. But those of us who have been around long enough practicing medicine have learned about the pendulum of data and opinion sometimes swings back and forth. The article by Chung et al. reminds us once again of this reality.
Dr. Michael E. Pichichero is at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center. He has received investigator-initiated grants from Sanofi Pasteur to study novel pneumococcal protein vaccines over the past 3 years and currently but has received no funding from Sanofi regarding injectable influenza vaccine. He also has conducted research with study coauthor Dr. John J. Treanor that was supported by MedImmune, who makes the intranasal flu vaccine.
When vaccinating children against influenza, inactivated and live attenuated influenza vaccines show little significant difference in effectiveness against nearly all strains of the virus, according to a new study in Pediatrics.
However, the study – which examined the effectiveness of IIV and LAIV across four consecutive influenza seasons between 2010 and 2014 – cautions that the 2013-2014 season’s A/(H1N1)pdm09 showed an uncharacteristically large gap in effectiveness favoring IIV, a discrepancy likely due to a problem with a vaccine component in LAIV. (Pediatrics. 2016;137(2):e20153279)
“We found that lower LAIV effectiveness in 2013-2014 was specific to the A/(H1N1)pdm09 vaccine component and was consistent with a previously unexamined effect during the 2010-2011 influenza season,” Jessie R. Chung of the influenza division at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and associates wrote, adding that the impetus for the study was the lack of available data “from observational studies after the 2009 pandemic on relative effectiveness of LAIV and IIV in children and adolescents.”
Ms. Chung* and coinvestigators enrolled children aged 2-17 years from clinics and hospitals in Michigan, New York, Pennsylvania, Tennessee, Texas, Washington, and Wisconsin during the 2010-2011, 2011-2012, 2012-2013, and 2013-2014 influenza seasons. Children brought in with symptoms of acute respiratory illness – cough, fever, or feverishness – had nasal and throat swabs collected to test for presence and type of influenza.
In total, 7,718 subjects were evaluated across the four influenza seasons, but after excluding subjects for various reasons – unknown vaccine type, indeterminate vaccine status, and inconclusive reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction results, among others – 6,819 subjects were included for vaccine effectiveness analysis, of which 2,703 were ultimately matched age appropriately and placed into IIV and LAIV cohorts for comparison. The IIV cohort consisted of 2,066 individuals (76.4%), while the LAIV cohort had 637 (23.6%).
During the 2010-2011 season, 66 of the 477 IIV subjects contracted influenza, versus 21 of 116 who received LAIV (14% vs. 18%, respectively). In the 2011-2012 season, 51 of the 499 IIV subjects (10%) contracted influenza, compared with 12 of the 152 LAIV subjects (8%). In the 2012-2013 season, 198 of the 622 IIV subjects (32%) contracted influenza, versus 61 of the 205 LAIV subjects (30%). But, in the 2013-2014 season, 36 of the 468 IIV subjects (8%) contracted influenza, versus 34 of the 164 LAIV subjects (21%).
After adjustment for age and season, the odds ratio for the 2013-2014 season was significantly higher than those of the other seasons across the entire age spectrum of 2-17 years: 2.88, compared with 1.49 (2010-2011), 0.67 (2011-2012), and 0.92 (2012-2013).
When comparing influenza type/subtype, adjusted odds ratio was 5.53 for those with A/(H1N1)pdm09 in the 2010-2011 season, compared with 2.65 for those with the same in the 2013-2014 season. Those with A/H3N2 did not show as significant a difference across seasons (2010-2013), nor did those with influenza type B (2010-2011, 2012-2013).
“We found no statistically significant difference in LAIV effectiveness compared with IIV against medically attended, laboratory-confirmed influenza illness due to A/H3N2 or B viruses,” Ms. Chung and colleagues concluded. “We found significantly higher odds of influenza A/(H1N1)pdm09 among participants vaccinated with LAIV, compared with IIV, [but] reasons for lower effectiveness of LAIV against the A/(H1N1)pdm09 virus, compared with IIV are not fully understood.”
The investigators added that “the finding appears to be specific to the A/(H1N1)pdm09 vaccine component; we did not detect any statistically significant differences in effectiveness for the other components.” Three previous randomized controlled trials indicated that trivalent LAIV was just as effective, if not more so, than IIV, making the findings of this study surprising and “unexpected,” the authors noted.
This study was supported by the CDC through cooperative agreements with a variety of universities and foundations, and funded by the National Institutes of Health. Ms. Chung and associates reported no relevant financial disclosures.
*A previous version of this story misstated Jessie Chung’s academic title. Ms. Chung holds a Master’s in public health.
When vaccinating children against influenza, inactivated and live attenuated influenza vaccines show little significant difference in effectiveness against nearly all strains of the virus, according to a new study in Pediatrics.
However, the study – which examined the effectiveness of IIV and LAIV across four consecutive influenza seasons between 2010 and 2014 – cautions that the 2013-2014 season’s A/(H1N1)pdm09 showed an uncharacteristically large gap in effectiveness favoring IIV, a discrepancy likely due to a problem with a vaccine component in LAIV. (Pediatrics. 2016;137(2):e20153279)
“We found that lower LAIV effectiveness in 2013-2014 was specific to the A/(H1N1)pdm09 vaccine component and was consistent with a previously unexamined effect during the 2010-2011 influenza season,” Jessie R. Chung of the influenza division at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and associates wrote, adding that the impetus for the study was the lack of available data “from observational studies after the 2009 pandemic on relative effectiveness of LAIV and IIV in children and adolescents.”
Ms. Chung* and coinvestigators enrolled children aged 2-17 years from clinics and hospitals in Michigan, New York, Pennsylvania, Tennessee, Texas, Washington, and Wisconsin during the 2010-2011, 2011-2012, 2012-2013, and 2013-2014 influenza seasons. Children brought in with symptoms of acute respiratory illness – cough, fever, or feverishness – had nasal and throat swabs collected to test for presence and type of influenza.
In total, 7,718 subjects were evaluated across the four influenza seasons, but after excluding subjects for various reasons – unknown vaccine type, indeterminate vaccine status, and inconclusive reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction results, among others – 6,819 subjects were included for vaccine effectiveness analysis, of which 2,703 were ultimately matched age appropriately and placed into IIV and LAIV cohorts for comparison. The IIV cohort consisted of 2,066 individuals (76.4%), while the LAIV cohort had 637 (23.6%).
During the 2010-2011 season, 66 of the 477 IIV subjects contracted influenza, versus 21 of 116 who received LAIV (14% vs. 18%, respectively). In the 2011-2012 season, 51 of the 499 IIV subjects (10%) contracted influenza, compared with 12 of the 152 LAIV subjects (8%). In the 2012-2013 season, 198 of the 622 IIV subjects (32%) contracted influenza, versus 61 of the 205 LAIV subjects (30%). But, in the 2013-2014 season, 36 of the 468 IIV subjects (8%) contracted influenza, versus 34 of the 164 LAIV subjects (21%).
After adjustment for age and season, the odds ratio for the 2013-2014 season was significantly higher than those of the other seasons across the entire age spectrum of 2-17 years: 2.88, compared with 1.49 (2010-2011), 0.67 (2011-2012), and 0.92 (2012-2013).
When comparing influenza type/subtype, adjusted odds ratio was 5.53 for those with A/(H1N1)pdm09 in the 2010-2011 season, compared with 2.65 for those with the same in the 2013-2014 season. Those with A/H3N2 did not show as significant a difference across seasons (2010-2013), nor did those with influenza type B (2010-2011, 2012-2013).
“We found no statistically significant difference in LAIV effectiveness compared with IIV against medically attended, laboratory-confirmed influenza illness due to A/H3N2 or B viruses,” Ms. Chung and colleagues concluded. “We found significantly higher odds of influenza A/(H1N1)pdm09 among participants vaccinated with LAIV, compared with IIV, [but] reasons for lower effectiveness of LAIV against the A/(H1N1)pdm09 virus, compared with IIV are not fully understood.”
The investigators added that “the finding appears to be specific to the A/(H1N1)pdm09 vaccine component; we did not detect any statistically significant differences in effectiveness for the other components.” Three previous randomized controlled trials indicated that trivalent LAIV was just as effective, if not more so, than IIV, making the findings of this study surprising and “unexpected,” the authors noted.
This study was supported by the CDC through cooperative agreements with a variety of universities and foundations, and funded by the National Institutes of Health. Ms. Chung and associates reported no relevant financial disclosures.
*A previous version of this story misstated Jessie Chung’s academic title. Ms. Chung holds a Master’s in public health.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Key clinical point: Inactivated influenza vaccine was significantly more effective against at least one strain of influenza than live attenuated influenza vaccine in 2013-2014.
Major finding: While no significant differences were seen in influenza rates between the IIV and LAIV cohorts for three consecutive seasons (2010-2013), the A/(H1N1)pdm09 strain of 2013-2014 affected subjects with LAIV at a significantly higher rate than did those with IIV.
Data source: Prospective cohort study of 2,703 children aged 2-17 years vaccinated between 2010 and 2014 with either IIV or LAIV.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the CDC through cooperative agreements with a variety of universities and foundations, and funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Chung and his associates reported no relevant financial disclosures.
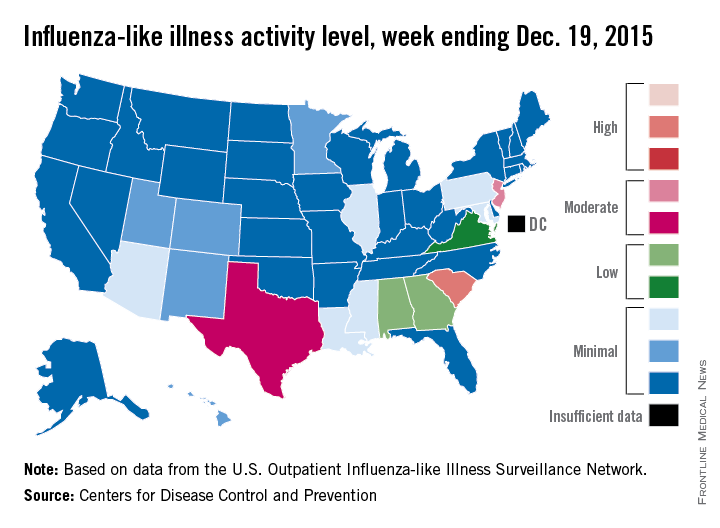
U.S. influenza cases rise above baseline level
For the first time this flu season, the proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was higher than the national baseline level of 2.1%, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
According to data from the U.S. Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network, for the week ending Dec. 19 (week 10 of the 2015-2016 season), 2.2% of outpatient visits nationwide involved ILI, the CDC said.
South Carolina remained the only state in the “high” range of activity. New Jersey went up to level 7 – the high end of the “moderate” range – to remain the second most affected state, and Texas jumped from level 2 last week to level 6 this week to move into “moderate” territory. Alabama and Georgia both moved up to “low” status for the first time with ILI activity at level 5, and Virginia stayed at level 4 – the only other state in the “low” range, according to the CDC.
A total of 17 states were at level 2 or higher during week 10, up from 15 states the week before. Arizona, Illinois, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Pennsylvania were at level 3, and Colorado, Hawaii, Minnesota, New Mexico, and Utah were at level 2, data from the Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network revealed.
One influenza-related pediatric death was reported during week 10, bringing the total for the season to four.
For the first time this flu season, the proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was higher than the national baseline level of 2.1%, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
According to data from the U.S. Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network, for the week ending Dec. 19 (week 10 of the 2015-2016 season), 2.2% of outpatient visits nationwide involved ILI, the CDC said.
South Carolina remained the only state in the “high” range of activity. New Jersey went up to level 7 – the high end of the “moderate” range – to remain the second most affected state, and Texas jumped from level 2 last week to level 6 this week to move into “moderate” territory. Alabama and Georgia both moved up to “low” status for the first time with ILI activity at level 5, and Virginia stayed at level 4 – the only other state in the “low” range, according to the CDC.
A total of 17 states were at level 2 or higher during week 10, up from 15 states the week before. Arizona, Illinois, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Pennsylvania were at level 3, and Colorado, Hawaii, Minnesota, New Mexico, and Utah were at level 2, data from the Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network revealed.
One influenza-related pediatric death was reported during week 10, bringing the total for the season to four.
For the first time this flu season, the proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was higher than the national baseline level of 2.1%, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
According to data from the U.S. Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network, for the week ending Dec. 19 (week 10 of the 2015-2016 season), 2.2% of outpatient visits nationwide involved ILI, the CDC said.
South Carolina remained the only state in the “high” range of activity. New Jersey went up to level 7 – the high end of the “moderate” range – to remain the second most affected state, and Texas jumped from level 2 last week to level 6 this week to move into “moderate” territory. Alabama and Georgia both moved up to “low” status for the first time with ILI activity at level 5, and Virginia stayed at level 4 – the only other state in the “low” range, according to the CDC.
A total of 17 states were at level 2 or higher during week 10, up from 15 states the week before. Arizona, Illinois, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Pennsylvania were at level 3, and Colorado, Hawaii, Minnesota, New Mexico, and Utah were at level 2, data from the Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network revealed.
One influenza-related pediatric death was reported during week 10, bringing the total for the season to four.
Flu activity increases slightly across U.S.
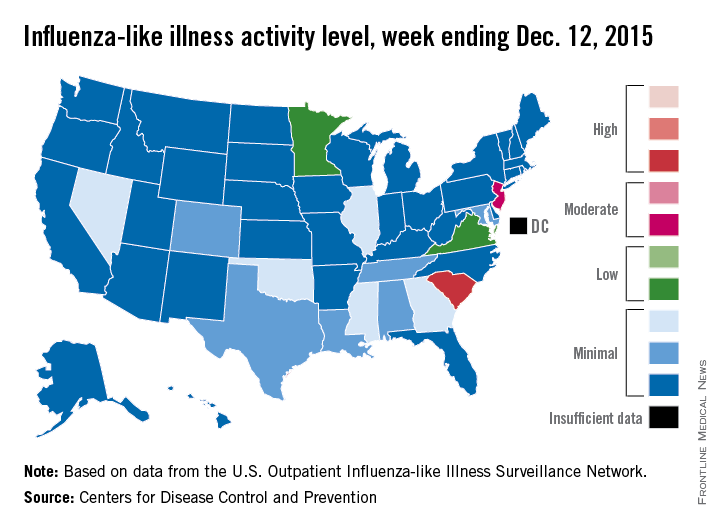
Influenza activity dropped slightly in South Carolina, but remained high enough to make it the nation’s hot spot during week 9 of the 2015-2016 U.S. flu season, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported Dec. 18.
The activity of influenza-like illness (ILI) in South Carolina went from level 9 down to level 8 for the week ending Dec. 12 (week 9), but that kept it in the “high” range, according to the CDC report.
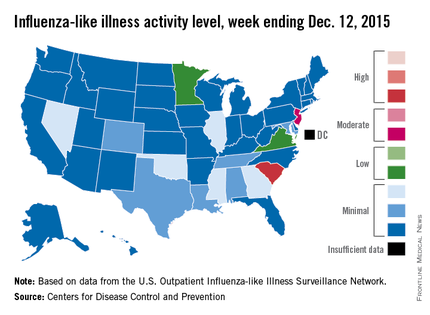
The rest of the United States saw a slight increase in activity, with 15 states at level 2 or higher, compared with 13 the week before. New Jersey had the next-highest level of activity after South Carolina, rising from level 5 last week to level 6, which moved it into the “moderate” range.
Minnesota had the largest increase in ILI activity from the previous week, going from level 1 to level 4, and other states with increased activity were Alabama, Colorado, Georgia, Illinois, Nevada, Tennessee, and Virginia. States besides South Carolina with decreased activity were Arizona, Hawaii, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Texas, the CDC data show.
The proportion of outpatient visits nationwide for ILI – defined as a temperature of 100° F or greater and cough and/or sore throat – was 1.9%, continuing to stay below the national baseline of 2.1%, the CDC said.
Outside of the fifty states, Guam reported widespread activity, Puerto Rico reported “moderate” (level 7) activity, and the District of Columbia and the U.S. Virgin Islands reported sporadic activity, the CDC noted.
Influenza activity dropped slightly in South Carolina, but remained high enough to make it the nation’s hot spot during week 9 of the 2015-2016 U.S. flu season, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported Dec. 18.
The activity of influenza-like illness (ILI) in South Carolina went from level 9 down to level 8 for the week ending Dec. 12 (week 9), but that kept it in the “high” range, according to the CDC report.

The rest of the United States saw a slight increase in activity, with 15 states at level 2 or higher, compared with 13 the week before. New Jersey had the next-highest level of activity after South Carolina, rising from level 5 last week to level 6, which moved it into the “moderate” range.
Minnesota had the largest increase in ILI activity from the previous week, going from level 1 to level 4, and other states with increased activity were Alabama, Colorado, Georgia, Illinois, Nevada, Tennessee, and Virginia. States besides South Carolina with decreased activity were Arizona, Hawaii, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Texas, the CDC data show.
The proportion of outpatient visits nationwide for ILI – defined as a temperature of 100° F or greater and cough and/or sore throat – was 1.9%, continuing to stay below the national baseline of 2.1%, the CDC said.
Outside of the fifty states, Guam reported widespread activity, Puerto Rico reported “moderate” (level 7) activity, and the District of Columbia and the U.S. Virgin Islands reported sporadic activity, the CDC noted.
Influenza activity dropped slightly in South Carolina, but remained high enough to make it the nation’s hot spot during week 9 of the 2015-2016 U.S. flu season, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported Dec. 18.
The activity of influenza-like illness (ILI) in South Carolina went from level 9 down to level 8 for the week ending Dec. 12 (week 9), but that kept it in the “high” range, according to the CDC report.

The rest of the United States saw a slight increase in activity, with 15 states at level 2 or higher, compared with 13 the week before. New Jersey had the next-highest level of activity after South Carolina, rising from level 5 last week to level 6, which moved it into the “moderate” range.
Minnesota had the largest increase in ILI activity from the previous week, going from level 1 to level 4, and other states with increased activity were Alabama, Colorado, Georgia, Illinois, Nevada, Tennessee, and Virginia. States besides South Carolina with decreased activity were Arizona, Hawaii, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Texas, the CDC data show.
The proportion of outpatient visits nationwide for ILI – defined as a temperature of 100° F or greater and cough and/or sore throat – was 1.9%, continuing to stay below the national baseline of 2.1%, the CDC said.
Outside of the fifty states, Guam reported widespread activity, Puerto Rico reported “moderate” (level 7) activity, and the District of Columbia and the U.S. Virgin Islands reported sporadic activity, the CDC noted.
Early infection-related hospitalization portends poor breast cancer prognosis
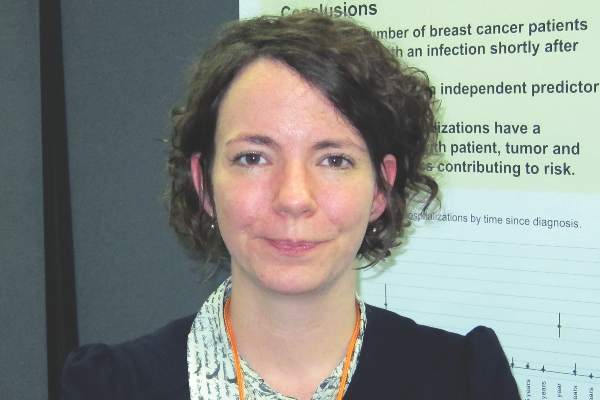
SAN ANTONIO – Hospitalization for an infection within the first year following diagnosis of primary nonmetastatic breast cancer is a red flag for increased risk of subsequent development of distant metastases or breast cancer–related death, Judith S. Brand, Ph.D., reported at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
This increased risk for future adverse breast cancer outcomes was statistically significant and clinically meaningful for women hospitalized for respiratory tract or skin infections or sepsis. Those are the patients for whom particularly close monitoring for recurrence of breast cancer is warranted in the next 5 years, said Dr. Brand of the Karolinska Institute, Stockholm.
In contrast, hospitalization for a gastrointestinal or urinary tract infection didn’t achieve significance as an independent predictor of increased risk of adverse breast cancer outcomes.
Dr. Brand presented a prospective population-based study of 8,338 women diagnosed with stage I-III breast cancer in the Stockholm area during 2001-2008. During a median 4.9 years of follow-up after diagnosis, 720 women had an infection-related hospitalization, with the great majority of these events occurring during the first year.
The incidence of hospitalization for sepsis among breast cancer patients in their first year post diagnosis was 14-fold greater than in the general Swedish female population matched for age and year. Respiratory infections resulting in hospitalization were fourfold more frequent than in the general population, skin infections were eightfold more common, and GI infections were twice as common.
Infection-related hospitalizations had a strong and independent association with breast cancer mortality during follow-up, as seen in a multivariate analysis adjusted for age at diagnosis, comorbid conditions, infectious disease history, type of breast cancer therapy, and tumor characteristics including size, grade, hormone receptor status, and lymph node involvement.
Moreover, the risk of developing distant metastases was 50%-78% greater in breast cancer patients hospitalized for respiratory infection, sepsis, or skin infection, compared with breast cancer patients who didn’t have an infection-related hospitalization.
“We think the sepsis results are the most interesting findings,” Dr. Brand said in an interview. “Sepsis could be an expression of an immunosuppressed state. And sepsis itself can induce immunosuppression for a long time, which could trigger tumor growth. Animal studies have shown that in postseptic mice, tumor grows faster.”
Infection-related hospitalizations didn’t increase the future risk of locoregional recurrences.
Independent predictors of infection-related hospitalization included older age, comorbidities, markers indicative of greater tumor aggressiveness, and treatment with chemotherapy or axillary radiotherapy.
“This shows that the risk of infection-related hospitalizations is not only due to immunosuppression caused by chemotherapy, but that the characteristics of the tumor itself play a role, as do patient characteristics. This is the first epidemiologic study to show with very extensive data that all three elements contribute to the risk,” Dr. Brand said.
SAN ANTONIO – Hospitalization for an infection within the first year following diagnosis of primary nonmetastatic breast cancer is a red flag for increased risk of subsequent development of distant metastases or breast cancer–related death, Judith S. Brand, Ph.D., reported at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
This increased risk for future adverse breast cancer outcomes was statistically significant and clinically meaningful for women hospitalized for respiratory tract or skin infections or sepsis. Those are the patients for whom particularly close monitoring for recurrence of breast cancer is warranted in the next 5 years, said Dr. Brand of the Karolinska Institute, Stockholm.
In contrast, hospitalization for a gastrointestinal or urinary tract infection didn’t achieve significance as an independent predictor of increased risk of adverse breast cancer outcomes.
Dr. Brand presented a prospective population-based study of 8,338 women diagnosed with stage I-III breast cancer in the Stockholm area during 2001-2008. During a median 4.9 years of follow-up after diagnosis, 720 women had an infection-related hospitalization, with the great majority of these events occurring during the first year.
The incidence of hospitalization for sepsis among breast cancer patients in their first year post diagnosis was 14-fold greater than in the general Swedish female population matched for age and year. Respiratory infections resulting in hospitalization were fourfold more frequent than in the general population, skin infections were eightfold more common, and GI infections were twice as common.
Infection-related hospitalizations had a strong and independent association with breast cancer mortality during follow-up, as seen in a multivariate analysis adjusted for age at diagnosis, comorbid conditions, infectious disease history, type of breast cancer therapy, and tumor characteristics including size, grade, hormone receptor status, and lymph node involvement.
Moreover, the risk of developing distant metastases was 50%-78% greater in breast cancer patients hospitalized for respiratory infection, sepsis, or skin infection, compared with breast cancer patients who didn’t have an infection-related hospitalization.
“We think the sepsis results are the most interesting findings,” Dr. Brand said in an interview. “Sepsis could be an expression of an immunosuppressed state. And sepsis itself can induce immunosuppression for a long time, which could trigger tumor growth. Animal studies have shown that in postseptic mice, tumor grows faster.”
Infection-related hospitalizations didn’t increase the future risk of locoregional recurrences.
Independent predictors of infection-related hospitalization included older age, comorbidities, markers indicative of greater tumor aggressiveness, and treatment with chemotherapy or axillary radiotherapy.
“This shows that the risk of infection-related hospitalizations is not only due to immunosuppression caused by chemotherapy, but that the characteristics of the tumor itself play a role, as do patient characteristics. This is the first epidemiologic study to show with very extensive data that all three elements contribute to the risk,” Dr. Brand said.
SAN ANTONIO – Hospitalization for an infection within the first year following diagnosis of primary nonmetastatic breast cancer is a red flag for increased risk of subsequent development of distant metastases or breast cancer–related death, Judith S. Brand, Ph.D., reported at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
This increased risk for future adverse breast cancer outcomes was statistically significant and clinically meaningful for women hospitalized for respiratory tract or skin infections or sepsis. Those are the patients for whom particularly close monitoring for recurrence of breast cancer is warranted in the next 5 years, said Dr. Brand of the Karolinska Institute, Stockholm.
In contrast, hospitalization for a gastrointestinal or urinary tract infection didn’t achieve significance as an independent predictor of increased risk of adverse breast cancer outcomes.
Dr. Brand presented a prospective population-based study of 8,338 women diagnosed with stage I-III breast cancer in the Stockholm area during 2001-2008. During a median 4.9 years of follow-up after diagnosis, 720 women had an infection-related hospitalization, with the great majority of these events occurring during the first year.
The incidence of hospitalization for sepsis among breast cancer patients in their first year post diagnosis was 14-fold greater than in the general Swedish female population matched for age and year. Respiratory infections resulting in hospitalization were fourfold more frequent than in the general population, skin infections were eightfold more common, and GI infections were twice as common.
Infection-related hospitalizations had a strong and independent association with breast cancer mortality during follow-up, as seen in a multivariate analysis adjusted for age at diagnosis, comorbid conditions, infectious disease history, type of breast cancer therapy, and tumor characteristics including size, grade, hormone receptor status, and lymph node involvement.
Moreover, the risk of developing distant metastases was 50%-78% greater in breast cancer patients hospitalized for respiratory infection, sepsis, or skin infection, compared with breast cancer patients who didn’t have an infection-related hospitalization.
“We think the sepsis results are the most interesting findings,” Dr. Brand said in an interview. “Sepsis could be an expression of an immunosuppressed state. And sepsis itself can induce immunosuppression for a long time, which could trigger tumor growth. Animal studies have shown that in postseptic mice, tumor grows faster.”
Infection-related hospitalizations didn’t increase the future risk of locoregional recurrences.
Independent predictors of infection-related hospitalization included older age, comorbidities, markers indicative of greater tumor aggressiveness, and treatment with chemotherapy or axillary radiotherapy.
“This shows that the risk of infection-related hospitalizations is not only due to immunosuppression caused by chemotherapy, but that the characteristics of the tumor itself play a role, as do patient characteristics. This is the first epidemiologic study to show with very extensive data that all three elements contribute to the risk,” Dr. Brand said.
AT SABCS 2015
Key clinical point: Particularly close monitoring for adverse breast cancer outcomes is warranted for women with an infection-related hospitalization during the first year after breast cancer diagnosis.
Major finding: Women hospitalized for sepsis or a respiratory or skin infection during the first year after being diagnosed with stage I-III breast cancer were up to 4.8 times more likely to subsequently die of breast cancer than those without an infection-related hospitalization.
Data source: This was a prospective observational study of 8,338 Stockholm-area breast cancer patients followed for a median of 4.9 years post diagnosis.
Disclosures: The study presenter reported having no financial conflicts regarding this university-funded study.
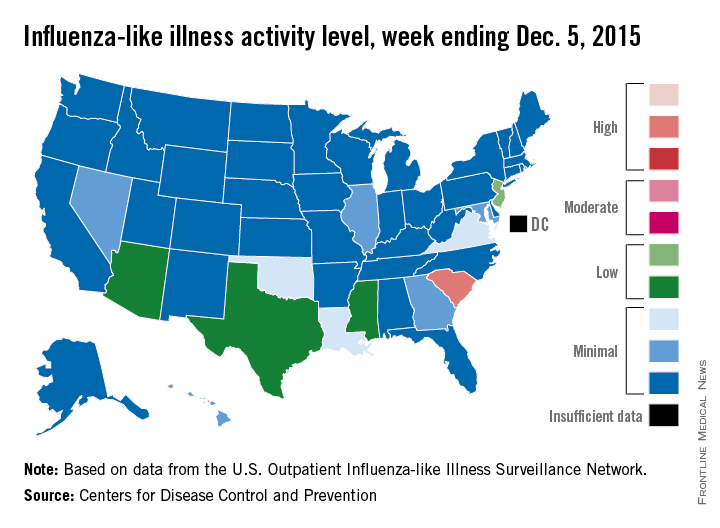
Flu activity at ‘high’ level in South Carolina
South Carolina officially became the first state to reach a “high” level of influenza activity during the 2015-2016 flu season, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported Dec. 11.
Activity of influenza-like illness (ILI) in the state was at level 9 on a scale of 1-10 for the week ending Dec. 5, 2015. For the country as a whole, however, activity was down a bit, with 13 states at level 2 or higher, compared with 20 states the week before. Among those with reduced ILI activity was Oklahoma, which went from level 6 for the week ending Nov. 28 to level 3 for the week ending Dec. 5, according to the CDC report.
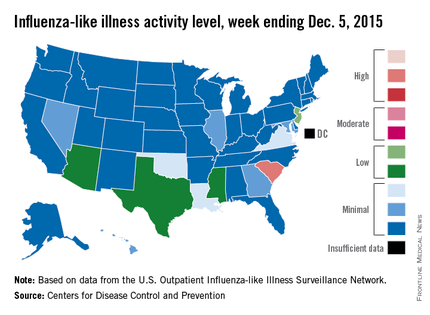
For the week, 1.8% of patient visits reported to the U.S. Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network were for ILI, which is below the national baseline of 2.1%. This measure peaked at almost 6% during last year’s flu season, with that high coming at the end of Dec. 2014. The pattern was similar for the 2013-2014 season, with a peak of about 4.5% during the same week at the end of December, the report showed.
There was one influenza-related pediatric death for the week ending Dec. 5, bringing the total to three that have been reported for the season, the CDC said.
South Carolina officially became the first state to reach a “high” level of influenza activity during the 2015-2016 flu season, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported Dec. 11.
Activity of influenza-like illness (ILI) in the state was at level 9 on a scale of 1-10 for the week ending Dec. 5, 2015. For the country as a whole, however, activity was down a bit, with 13 states at level 2 or higher, compared with 20 states the week before. Among those with reduced ILI activity was Oklahoma, which went from level 6 for the week ending Nov. 28 to level 3 for the week ending Dec. 5, according to the CDC report.

For the week, 1.8% of patient visits reported to the U.S. Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network were for ILI, which is below the national baseline of 2.1%. This measure peaked at almost 6% during last year’s flu season, with that high coming at the end of Dec. 2014. The pattern was similar for the 2013-2014 season, with a peak of about 4.5% during the same week at the end of December, the report showed.
There was one influenza-related pediatric death for the week ending Dec. 5, bringing the total to three that have been reported for the season, the CDC said.
South Carolina officially became the first state to reach a “high” level of influenza activity during the 2015-2016 flu season, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported Dec. 11.
Activity of influenza-like illness (ILI) in the state was at level 9 on a scale of 1-10 for the week ending Dec. 5, 2015. For the country as a whole, however, activity was down a bit, with 13 states at level 2 or higher, compared with 20 states the week before. Among those with reduced ILI activity was Oklahoma, which went from level 6 for the week ending Nov. 28 to level 3 for the week ending Dec. 5, according to the CDC report.

For the week, 1.8% of patient visits reported to the U.S. Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network were for ILI, which is below the national baseline of 2.1%. This measure peaked at almost 6% during last year’s flu season, with that high coming at the end of Dec. 2014. The pattern was similar for the 2013-2014 season, with a peak of about 4.5% during the same week at the end of December, the report showed.
There was one influenza-related pediatric death for the week ending Dec. 5, bringing the total to three that have been reported for the season, the CDC said.
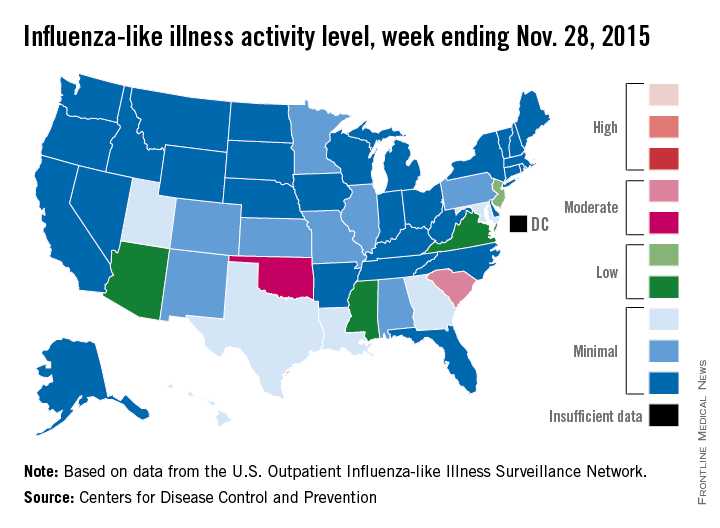
‘Moderate’ flu activity seen in two U.S. states
Two U.S. states experienced “moderate” activity of influenza-like illness for the week ending Nov. 28, 2015 – week 7 of the 2015-2016 flu season – the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported Dec. 4.
South Carolina had the highest (level 7) activity for the week, with Oklahoma joined by Puerto Rico at level 6. New Jersey was at the highest level (level 5) of “low” activity, while Arizona, Mississippi, and Virginia were a notch lower (level 4) but still in the “low” zone. All told, 20 states had flu activity of level 2 or higher, according to the CDC.
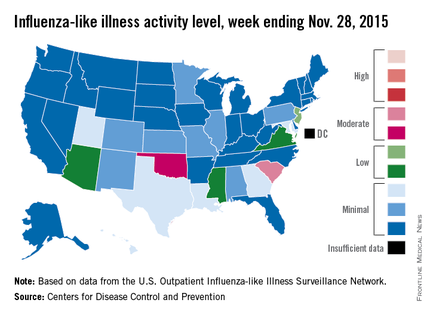
There were no influenza-associated pediatric deaths reported during the week, with two such deaths reported for the 2015-2016 season so far. For week 7 nationwide, 1.9% of patient visits reported through the U.S. Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network were the result of influenza-like illness – defined as a temperature of 100° F or greater and cough and/or sore throat – which is below the national baseline of 2.1%, the CDC said.
During week 7, 1.5% of the 11,288 specimens tested were positive for influenza, with 60% positive for influenza A and 40% positive for influenza B. For the season overall, 1.2% of the 102,675 specimens tested have been positive, with a 61/39 split for influenza A and B, the CDC noted.
Two U.S. states experienced “moderate” activity of influenza-like illness for the week ending Nov. 28, 2015 – week 7 of the 2015-2016 flu season – the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported Dec. 4.
South Carolina had the highest (level 7) activity for the week, with Oklahoma joined by Puerto Rico at level 6. New Jersey was at the highest level (level 5) of “low” activity, while Arizona, Mississippi, and Virginia were a notch lower (level 4) but still in the “low” zone. All told, 20 states had flu activity of level 2 or higher, according to the CDC.

There were no influenza-associated pediatric deaths reported during the week, with two such deaths reported for the 2015-2016 season so far. For week 7 nationwide, 1.9% of patient visits reported through the U.S. Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network were the result of influenza-like illness – defined as a temperature of 100° F or greater and cough and/or sore throat – which is below the national baseline of 2.1%, the CDC said.
During week 7, 1.5% of the 11,288 specimens tested were positive for influenza, with 60% positive for influenza A and 40% positive for influenza B. For the season overall, 1.2% of the 102,675 specimens tested have been positive, with a 61/39 split for influenza A and B, the CDC noted.
Two U.S. states experienced “moderate” activity of influenza-like illness for the week ending Nov. 28, 2015 – week 7 of the 2015-2016 flu season – the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported Dec. 4.
South Carolina had the highest (level 7) activity for the week, with Oklahoma joined by Puerto Rico at level 6. New Jersey was at the highest level (level 5) of “low” activity, while Arizona, Mississippi, and Virginia were a notch lower (level 4) but still in the “low” zone. All told, 20 states had flu activity of level 2 or higher, according to the CDC.

There were no influenza-associated pediatric deaths reported during the week, with two such deaths reported for the 2015-2016 season so far. For week 7 nationwide, 1.9% of patient visits reported through the U.S. Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network were the result of influenza-like illness – defined as a temperature of 100° F or greater and cough and/or sore throat – which is below the national baseline of 2.1%, the CDC said.
During week 7, 1.5% of the 11,288 specimens tested were positive for influenza, with 60% positive for influenza A and 40% positive for influenza B. For the season overall, 1.2% of the 102,675 specimens tested have been positive, with a 61/39 split for influenza A and B, the CDC noted.
Study: Exposure history critical to design of universal flu vaccine
In a study with implications for the development of new influenza vaccine strategies, researchers discovered that – among patients who received the 2009 H1N1 influenza vaccine – individuals with low levels of H1N1-specific antibodies prior to vaccination produced a more broadly protective immune response against the influenza virus than patients with high levels of H1N1-specific antibodies prior to vaccination.
A research team led by Patrick C. Wilson, Ph.D., of the Knapp Center for Lupus and Immunology Research at the University of Chicago, studied the B cell response in patients who received the pandemic 2009 H1N1 vaccine 2 years in a row and had varied histories of influenza exposure. All patients were 18 years or older, healthy, and had not received the yearly influenza vaccine prior to participating in the study. The researchers compared the patients’ “vaccine-induced plasmablast response upon first vaccination with the pandemic H1N1 strain in 2009-2010” with the patients’ plasmablast response upon revaccination with this same strain in 2010-2011 or 2011-2012. Each of the 21 study participants provided the researchers with at least four H1N1-specific plasmablasts.
The researchers “analyzed the immunoglobulin regions, strain specificity, and functional properties of the antibodies produced by this plasmablast population at the single-cell level across multiple years,” which allowed them to directly evaluate the effect of immune memory on the specificity of the current response to the virus.
Among the study’s findings was that “only individuals with low preexisting serological levels of pandemic H1N1 specific antibodies generated a broadly neutralizing plasmablast response directed toward the [hemagglutinin] stalk,” which is part of the hemagglutinin protein located on the surface of the influenza virus.
“[W]e demonstrate that the immune subdominance of the [hemagglutinin] stalk is a function of both the poor accessibility to the broadly protective epitopes and the inherent polyreactivity of the antibodies that can bind. We conclude that immunological memory profoundly shapes the viral epitopes targeted upon exposure with divergent influenza strains and determines the likelihood of generating a broadly protective response,” said Dr. Wilson and his coauthors. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
Read the full study in Science Translational Medicine (doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aad0522).
In a study with implications for the development of new influenza vaccine strategies, researchers discovered that – among patients who received the 2009 H1N1 influenza vaccine – individuals with low levels of H1N1-specific antibodies prior to vaccination produced a more broadly protective immune response against the influenza virus than patients with high levels of H1N1-specific antibodies prior to vaccination.
A research team led by Patrick C. Wilson, Ph.D., of the Knapp Center for Lupus and Immunology Research at the University of Chicago, studied the B cell response in patients who received the pandemic 2009 H1N1 vaccine 2 years in a row and had varied histories of influenza exposure. All patients were 18 years or older, healthy, and had not received the yearly influenza vaccine prior to participating in the study. The researchers compared the patients’ “vaccine-induced plasmablast response upon first vaccination with the pandemic H1N1 strain in 2009-2010” with the patients’ plasmablast response upon revaccination with this same strain in 2010-2011 or 2011-2012. Each of the 21 study participants provided the researchers with at least four H1N1-specific plasmablasts.
The researchers “analyzed the immunoglobulin regions, strain specificity, and functional properties of the antibodies produced by this plasmablast population at the single-cell level across multiple years,” which allowed them to directly evaluate the effect of immune memory on the specificity of the current response to the virus.
Among the study’s findings was that “only individuals with low preexisting serological levels of pandemic H1N1 specific antibodies generated a broadly neutralizing plasmablast response directed toward the [hemagglutinin] stalk,” which is part of the hemagglutinin protein located on the surface of the influenza virus.
“[W]e demonstrate that the immune subdominance of the [hemagglutinin] stalk is a function of both the poor accessibility to the broadly protective epitopes and the inherent polyreactivity of the antibodies that can bind. We conclude that immunological memory profoundly shapes the viral epitopes targeted upon exposure with divergent influenza strains and determines the likelihood of generating a broadly protective response,” said Dr. Wilson and his coauthors. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
Read the full study in Science Translational Medicine (doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aad0522).
In a study with implications for the development of new influenza vaccine strategies, researchers discovered that – among patients who received the 2009 H1N1 influenza vaccine – individuals with low levels of H1N1-specific antibodies prior to vaccination produced a more broadly protective immune response against the influenza virus than patients with high levels of H1N1-specific antibodies prior to vaccination.
A research team led by Patrick C. Wilson, Ph.D., of the Knapp Center for Lupus and Immunology Research at the University of Chicago, studied the B cell response in patients who received the pandemic 2009 H1N1 vaccine 2 years in a row and had varied histories of influenza exposure. All patients were 18 years or older, healthy, and had not received the yearly influenza vaccine prior to participating in the study. The researchers compared the patients’ “vaccine-induced plasmablast response upon first vaccination with the pandemic H1N1 strain in 2009-2010” with the patients’ plasmablast response upon revaccination with this same strain in 2010-2011 or 2011-2012. Each of the 21 study participants provided the researchers with at least four H1N1-specific plasmablasts.
The researchers “analyzed the immunoglobulin regions, strain specificity, and functional properties of the antibodies produced by this plasmablast population at the single-cell level across multiple years,” which allowed them to directly evaluate the effect of immune memory on the specificity of the current response to the virus.
Among the study’s findings was that “only individuals with low preexisting serological levels of pandemic H1N1 specific antibodies generated a broadly neutralizing plasmablast response directed toward the [hemagglutinin] stalk,” which is part of the hemagglutinin protein located on the surface of the influenza virus.
“[W]e demonstrate that the immune subdominance of the [hemagglutinin] stalk is a function of both the poor accessibility to the broadly protective epitopes and the inherent polyreactivity of the antibodies that can bind. We conclude that immunological memory profoundly shapes the viral epitopes targeted upon exposure with divergent influenza strains and determines the likelihood of generating a broadly protective response,” said Dr. Wilson and his coauthors. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
Read the full study in Science Translational Medicine (doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aad0522).
FROM SCIENCE TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE