User login
2020 Update on Menopause
The term genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) refers to the bothersome symptoms and physical findings associated with estrogen deficiency that involve the labia, vestibular tissue, clitoris, vagina, urethra, and bladder.1 GSM is associated with genital irritation, dryness, and burning; urinary symptoms including urgency, dysuria, and recurrent urinary tract infections; and sexual symptoms including vaginal dryness and pain. Vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA) represents a component of GSM.
GSM is highly prevalent, affecting more than three-quarters of menopausal women. In contrast to menopausal vasomotor symptoms, which often are most severe and frequent in recently menopausal women, GSM commonly presents years following menopause. Unfortunately, VVA symptoms may have a substantial negative impact on women’s quality of life.
In this 2020 Menopause Update, I review a large observational study that provides reassurance to clinicians and patients regarding the safety of the best-studied prescription treatment for GSM—vaginal estrogen. Because some women should not use vaginal estrogen and others choose not to use it, nonhormonal management of GSM is important. Dr. JoAnn Pinkerton provides details on a randomized clinical trial that compared the use of fractionated CO2 laser therapy with vaginal estrogen for the treatment of GSM. In addition, Dr. JoAnn Manson discusses recent studies that found lower health risks with vaginal estrogen use compared with systemic estrogen therapy.
Diagnosing GSM
GSM can be diagnosed presumptively based on a characteristic history in a menopausal patient. Performing a pelvic examination, however, allows clinicians to exclude other conditions that may present with similar symptoms, such as lichen sclerosus, Candida infection, and malignancy.
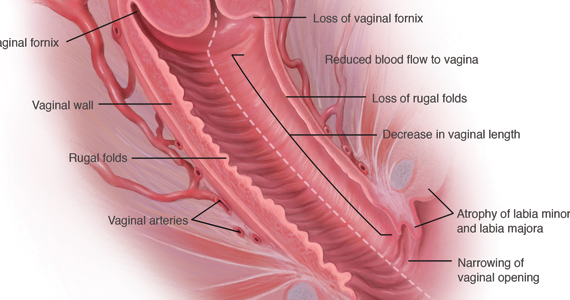
During inspection of the external genitalia, the clinician may note loss of the fat pad in the labia majora and mons as well as a reduction in labia minora pigmentation and tissue. The urethral meatus often becomes erythematous and prominent. If vaginal or introital narrowing is present, use of a pediatric (ultrathin) speculum reduces patient discomfort. The vaginal mucosa may appear smooth due to loss of rugation; it also may appear shiny and dry. Bleeding (friability) on contact with a spatula or cotton-tipped swab may occur. In addition, the vaginal fornices may become attenuated, leaving the cervix flush with the vaginal apex.
GSM can be diagnosed without laboratory assessment. However, vaginal pH, if measured, is characteristically higher than 5.0; microscopic wet prep often reveals many white blood cells, immature epithelial cells (large nuclei), and reduced or absent lactobacilli.2
Nonhormonal management of GSM
Water, silicone-based, and oil-based lubricants reduce the friction and discomfort associated with sexual activity. By contrast, vaginal moisturizers act longer than lubricants and can be applied several times weekly or daily. Natural oils, including olive and coconut oil, may be useful both as lubricants and as moisturizers. Aqueous lidocaine 4%, applied to vestibular tissue with cotton balls prior to penetration, reduces dyspareunia in women with GSM.3
Vaginal estrogen therapy
When nonhormonal management does not sufficiently reduce GSM symptoms, use of low-dose vaginal estrogen enhances thickness and elasticity of genital tissue and improves vaginal blood flow. Vaginal estrogen creams, tablets, an insert, and a ring are marketed in the United States. Although clinical improvement may be apparent within several weeks of initiating vaginal estrogen, the full benefit of treatment becomes apparent after 2 to 3 months.3
Despite the availability and effectiveness of low-dose vaginal estrogen, fears regarding the safety of menopausal hormone therapy have resulted in the underutilization of vaginal estrogen.4,5 Unfortunately, the package labeling for low-dose vaginal estrogen can exacerbate these fears.
Continue to: Nurses’ Health Study report...
Nurses’ Health Study report provides reassurance on long-term safety of vaginal estrogen
Bhupathiraju SN, Grodstein F, Stampfer MJ, et al. Vaginal estrogen use and chronic disease risk in the Nurses’ Health Study. Menopause. 2018;26:603-610
Bhupathiraju and colleagues published a report from the long-running Nurses’ Health prospective cohort study on the health outcomes associated with the use of vaginal estrogen.
Recap of the study
Starting in 1982, participants in the Nurses’Health Study were asked to report their use of vaginal estrogen via a validated questionnaire. For the years 1982 to 2012, investigators analyzed data from 896 and 52,901 women who had and had not used vaginal estrogen, respectively. The mean duration of vaginal estrogen use was 36 months.
In an analysis adjusted for numerous factors, the investigators observed no statistically significant differences in risk for cardiovascular outcomes (myocardial infarction, stroke, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism) or invasive cancers (colorectal, endometrial, ovarian, or breast).
Findings uphold safety of vaginal estrogen
This landmark study provides reassurance that 3 years of use of vaginal estrogen does not increase the risk of cardiovascular events or invasive breast cancer, findings that hopefully will allow clinicians and women to feel comfortable regarding the safety of vaginal estrogen. A study of vaginal estrogen from the Women’s Health Initiative provided similar reassurance. Recent research supports guidance from The North American Menopause Society and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists that vaginal estrogen can be used indefinitely, if indicated, and that use of concomitant progestin is not recommended in women who use vaginal estrogen and have an intact uterus.6,7
I agree with the authors, who point out that since treatment of GSM may need to be continued long term (even indefinitely), it would be helpful to have data that assessed the safety of longer-duration use of vaginal estrogen.
Results from Bhupathiraju and colleagues’ analysis of data from the Nurses’ Health Study on the 3-year safety of vaginal estrogen use encourage clinicians to recommend and women to use this safe and effective treatment for GSM.
How CO2 fractionated vaginal laser therapy compares with vaginal estrogen for relief of GSM symptoms
Paraiso MF, Ferrando CA, Sokol ER, et al. A randomized clinical trial comparing vaginal laser therapy to vaginal estrogen therapy in women with genitourinary syndrome of menopause: the VeLVET trial. Menopause. 2020;27:50-56.
Up to 50% to 60% of postmenopausal women experience GSM symptoms. However, many fewer receive treatment, either because they do not understand that the symptoms are related to menopause or they are not aware that safe and effective treatment is available. Sadly, many women are not asked about their symptoms or are embarrassed to tell providers.
GSM affects relationships and quality of life. Vaginal lubricants or moisturizers may provide relief. US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved therapies include low-dose vaginal estrogen, available as a vaginal tablet, cream, suppository, and ring; intravaginal dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA); and oral ospemifene, a selective estrogen replacement modulator. If women have an estrogen-sensitive breast or uterine cancer, an oncologist should be involved in decisions about vaginal hormonal therapy.
Energy-based devices such as vaginal lasers appear to induce wound healing; stimulate collagen and elastin fiber formation through increased storage of glycogen; and activate fibroblasts, which leads to increased extracellular matrix and restoration of vaginal pH.
These lasers are FDA approved for use in gynecology but not specifically for the treatment of GSM. In July 2016, the FDA issued a safety alert that energy-based devices, while approved for use in gynecology, have not been approved or adequately tested for menopausal vaginal conditions, and safety concerns include reports of vaginal burns.8 Lacking are publications of adequately powered randomized, sham-con-trolled trials to determine if laser therapy works better for women with GSM than placebos, moisturizers, or vaginal hormone therapies.
Recently, investigators conducted a multicenter, randomized, single-blinded trial of vaginal laser therapy and estrogen cream for treatment of GSM.
Continue to: Details of the study...
Details of the study
Paraiso and colleagues aimed to compare the 6-month efficacy and safety of fractionated CO2 vaginal laser therapy with that of estrogen vaginal cream for the treatment of vaginal dryness/GSM.
Participants randomly assigned to the estrogen therapy arm applied conjugated estrogen cream 0.5 g vaginally daily for 14 days, followed by twice weekly application for 24 weeks (a low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy). Participants randomly assigned to laser therapy underwent 3 vaginal treatments at a minimum of 6 weeks apart.
Sixty-nine women were enrolled in the trial before enrollment was closed because the FDA required that the sponsor obtain and maintain an investigational device exemption. Of 62 women who completed 6 months’ treatment, 30 received 3 laser treatments and 32 received estrogen cream.
The primary outcome compared subjective improvement in vaginal dryness using the visual analog scale (VAS) between the 2 groups at 6 months. Secondary outcomes included comparisons of the vaginal health index (VHI) and vaginal maturation index (VMI), the effect of GSM on quality of life, the effect of treatment on sexual function and urinary symptoms, and patient satisfaction.
Study findings
Efficacy. Laser therapy and estrogen therapy were found to be similarly effective except on the VMI, which favored estrogen. On patient global impression, 85.8% of laser-treated women rated their improvement as ‘‘better or much better’’ and 78.5% reported being either ‘‘satisfied or very satisfied,’’ compared with 70% and 73.3%, respectively, in the estrogen group, a statistically nonsignificant difference.
On linear regression, the investigators found a nonsignificant mean difference in female sexual function index scores. While VMI scores remained higher in the estrogen-treated group (adjusted P = .02), baseline and 6-month follow-up VMI data were available for only 34 participants (16 laser treated, 18 estrogen treated).
Regarding long-term effectiveness, 20% to 25% of the women in the laser-treated group needed further treatment after 1 year while the estrogen cream continued to work as long as it was used as prescribed.
Adverse effects. The incidence of vaginal bleeding was similar in the 2 groups: 6.7% in the laser group and 6.3% in the estrogen group. In the laser therapy group, 3% expe-rienced vaginal pain, discharge, and bladder infections, while in the estrogen cream group, 3% reported breast tenderness, migraine headaches, and abdominal cramping.
Takeaways. This small randomized, open-label (not blinded) trial provides pilot data on the effectiveness of vaginal CO2 laser compared with vaginal estrogen in treating vaginal atrophy, quality-of-life symptoms, sexual function, and urinary symptoms. Adverse events were minimal. Patient global impression of improvement and satisfaction improved for both vaginal laser and vaginal estrogen therapy.
Continue to: Study strengths and limitations...
Study strengths and limitations
To show noninferiority of vaginal laser therapy to vaginal estrogen, 196 study participants were needed. However, after 38% had been enrolled, the FDA sent a warning letter to the Foundation for Female Health Awareness, which required obtainment of an investigational device exemption for the laser and addition of a sham treatment arm.9 Instead of redesigning the trial and reconsenting the participants, the investigators closed the study, and analysis was performed only on the 62 participants who completed the study; vaginal maturation was assessed only in 34 participants.
The study lacked a placebo or sham control, which increases the risk of bias, while small numbers limit the strength of the findings. Longer-term evaluation of the effects of laser therapy beyond 6 months is needed to allow assessment of the effects of scarring on vaginal health, sexual function, and urinary issues.
Discussing therapy with patients
Despite this study’s preliminary findings, and until more robust data are available, providers should discuss the benefits and risks of all available treatment options for vaginal symptoms, including over-the-counter lubricants, vaginal moisturizers, FDA-approved vaginal hormone therapies (such as vaginal estrogen and intravaginal dehydroepiandrosterone), and systemic therapies, such as hormone therapy and ospemifene, to determine the best treatment for the individual woman with GSM.
In a healthy postmenopausal woman with bothersome GSM symptoms not responsive to lubricants and moisturizers, I recommend FDA-approved vaginal therapies as first-line treatment if there are no contraindications. For women with breast cancer, I involve their oncologist. If a patient asks about vaginal laser treatment, I share that vaginal energy-based therapies, such as the vaginal laser, have not been approved for menopausal vaginal concerns. In addition to the possibility of adverse events or unsuccessful treatment, there are significant out-of-pocket costs and the potential need for ongoing therapy after the initial 3 laser treatments.
For GSM that does not respond to lubricants and moisturizers, many FDA-approved vaginal and systemic therapies are available to treat vaginal symptoms. Vaginal laser treatment is a promising therapy for vaginal symptoms of GSM that needs further testing to determine its efficacy, safety, and long-term effects. If discussing vaginal energy-based therapies with patients, include the current lack of FDA approval for specific vaginal indications, potential adverse effects, the need for ongoing retreatment, and out-of-pocket costs.
JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, NCMP
Having more appropriate, evidence-based labeling of low-dose vaginal estrogen continues to be a high priority for The North American Menopause Society (NAMS), the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health (ISSWSH), and other professional societies.
NAMS and the Working Group on Women’s Health and Well-Being in Menopause had submitted a citizen’s petition to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2016 requesting modification of the label—including removal of the “black box warning”—for low-dose vaginal estrogen products. The petition was, disappointingly, denied in 2018.1
Currently, the class labeling, which was based on the results of randomized trials with systemic hormone therapy, is not applicable to low-dose vaginal estrogen, and the inclusion of the black box warning has led to serious underutilization of an effective and safe treatment for a very common and life-altering condition, the genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM). This condition affects nearly half of postmenopausal women. It tends to be chronic and progressive and, unlike hot flashes and vasomotor symptoms, it does not remit or decline over time, and it affects women’s health and quality of life.
While removal of the black box warning would be appropriate, labeling should include emphatic reminders for women that if they have any bleeding or spotting they should seek medical attention immediately, and if they have a history of breast cancer or other estrogen-sensitive cancers they should talk with their oncologist prior to starting treatment with low-dose vaginal estrogen. Although the text would still inform women of research results on systemic hormone therapy, it would explain the differences between low-dose vaginal estrogen and systemic therapy.
Studies show vaginal estrogen has good safety profile
In the last several years, large, observational studies of low-dose vaginal estrogen have suggested that this treatment is not associated with an increase in cardiovascular disease, pulmonary embolism, venous thrombosis, cancer, or dementia—conditions listed in the black box warning that were linked to systemic estrogen therapy plus synthetic progestin. Recent data from the Nurses’ Health Study, for example, demonstrated that 3 years of vaginal estrogen use did not increase the risk of cardiovascular events or invasive breast cancer.
Women’s Health Initiative. In a prospective observational cohort study, Crandall and colleagues used data from participants in the Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study to determine the association between use of vaginal estrogen and risk of a global index event (GIE), defined as time to first occurrence of coronary heart disease, invasive breast cancer, stroke, pulmonary embolism, hip fracture, colorectal cancer, endometrial cancer, or death from any cause.2
Women were recruited from multiple clinical centers, were aged 50 to 79 years at baseline, and did not use systemic estrogen therapy during follow-up. The study included 45,663 women and median follow-up was 7.2 years. The investigators collected data on women’s self-reported use of vaginal estrogen as well as the development of the conditions defined above.
In women with a uterus, there was no significant difference between vaginal estrogen users and nonusers in the risk of stroke, invasive breast cancer, colorectal cancer, endometrial cancer, pulmonary embolism, or deep vein thrombosis. The risks of coronary heart disease, fracture, all-cause mortality, and GIE were lower in vaginal estrogen users than in nonusers (GIE adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 0.68; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.55–0.86).
In women who had undergone hysterectomy, the risks of the individual GIE components and the overall GIE were not significantly different in users of vaginal estrogen compared with nonusers (GIE adjusted HR, 0.94; 95% CI, 0.70–1.26).
The investigators concluded that the risks of cardiovascular disease and cancer were not increased in postmenopausal women who used vaginal estrogen. Thus, this study offers reassurance on the treatment’s safety.2
Meta-analysis on menopausal hormone therapy and breast cancer risk. Further evidence now indicates that low-dose vaginal estrogen is not linked to chronic health conditions. In a large meta-analysis published in 2019, investigators looked at different types of hormone therapies—oral estrogen plus progestin, transdermal estrogen and progestin, estrogen alone, low-dose vaginal estrogen—and their relationship to breast cancer risk.3
Information on individual participants was obtained from 58 studies, 24 prospective and 34 retrospective. Breast cancer relative risks (RR) during years 5 to 14 of current hormone use were assessed according to the main hormonal contituents, doses, and modes of delivery of the last-used menopausal hormone therapy. For all systemic estrogen-only preparations, the RR was 1.33 (95% CI, 1.28–1.38), while for all estrogen-progestogen preparations, the RR was 2.08 (95% CI, 2.02–2.15). For transdermal estrogen, the RR was 1.35 (95% CI, 1.25–1.46). In contrast, for vaginal estrogen, the RR was 1.09 (95% CI, 0.97–1.23).3
Thus, the analysis found that in all the studies that had been done to date, there was no evidence of increased risk of breast cancer with vaginal estrogen therapy.
The evidence is growing that low-dose vaginal estrogen is different from systemic estrogen in terms of its safety profile and benefit-risk pattern. It is important for the FDA to consider these data and revise the vaginal estrogen label.
On the horizon: New estradiol reference ranges
It would be useful if we could accurately compare estradiol levels in women treated with vaginal estrogen against those of women treated with systemic estrogen therapy. In September 2019, NAMS held a workshop with the goal of establishing reference ranges for estradiol in postmenopausal women.4 It is very important to have good, reliable laboratory assays for estradiol and estrone, and to have a clear understanding of what is a reference range, that is, the range of estradiol levels in postmenopausal women who are not treated with estrogen. That way, you can observe what the estradiol blood levels are in women treated with low-dose vaginal estrogen or those treated with systemic estrogen versus the levels observed among postmenopausal women not receiving any estrogen product.
With the reference range information, we could look at data on the blood levels of estradiol with low-dose vaginal estrogen from the various studies available, as well as the increasing evidence from observational studies of the safety of low-dose vaginal estrogen to better understand its relationship with health. If these studies demonstrate that, with certain doses and formulations of low-dose vaginal estrogen, blood estradiol levels stay within the reference range of postmenopausal estradiol levels, it would inform the labeling modifications of these products. We need this information for future discussions with the FDA.
The laboratory assay technology used for such an investigation is primarily liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry, the so-called LC-MS/MS assay. With use of this technology, the reference range for estradiol may be less than 10 picograms per milliliter. Previously, a very wide and inconsistent range—about 5 to 30 picograms per milliliter—was considered a “normal” range.
NAMS is championing the efforts to define a true evidence-based reference range that would represent the range of levels seen in postmenopausal women.5 This effort has been spearheaded by Dr. Richard Santen and colleagues. Using the more sensitive and specific LC-MS/MS assay will enable researchers and clinicians to better understand how levels on low-dose vaginal estrogen relate to the reference range for postmenopausal women. We are hoping to work together with researchers to establish these reference ranges, and to use that information to look at how low-dose vaginal estrogen compares to levels in untreated postmenopausal women, as well as to levels in women on systemic estrogen.
Hopefully, establishing the reference range can be done in an expeditious and timely way, with discussions with the FDA resuming shortly thereafter.
References
1.NAMS Citizen’s Petition and FDA Response, June 7, 2018. http://www.menopause.org/docs/
2. Crandall CJ, Hovey KM, Andrews CA, et al. Breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and cardiovascular events in participants who used vaginal estrogen in the Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study. Menopause. 2018;25:11-20.
3. Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer. Type and timing of menopausal hormone therapy and breast cancer risk: individual participant meta-analysis of the worldwide epidemiological evidence. Lancet. 2019;394:1159-1168.
4. Santen RJ, Pinkerton JV, Liu JH, et al. Workshop on normal reference ranges for estradiol in postmenopausal women, September 2019, Chicago, Illinois. Menopause. May 4, 2020. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000001556.
5. Pinkerton JV, Liu JH, Santoro NF, et al. Workshop on normal reference ranges for estradiol in postmenopausal women: commentary from The North American Menopause Society on low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy. Menopause. 2020;27:611-613.
- Portman DJ, Gass ML. Genitourinary syndrome of menopause: new terminology for vulvovaginal atrophy from the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health and The North American Menopause Society. Maturitas. 2014;79:349-354.
- Kaunitz AM, Manson JE. Management of menopausal symptoms. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126:859-876.
- Shifren JL. Genitourinary syndrome of menopause. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2018;61:508-516.
- Manson JE, Kaunitz AM. Menopause management—getting clinical care back on track. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:803-806.
- Kingsberg SA, Krychman M, Graham S, et al. The women’s EMPOWER survey: identifying women’s perceptions on vulvar and vaginal atrophy and its treatment. J Sex Med. 2017;14:413-424.
- The NAMS 2017 Hormone Therapy Position Statement Advisory Panel. The 2017 Hormone therapy position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2017;24:728-753.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG practice bulletin No. 141: Management of menopausal symptoms. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123:202-216.
- US Food and Drug Administration website. FDA warns against the use of energy-based devices to perform vaginal ‘rejuvenation’ or vaginal cosmetic procedures: FDA safety communication. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/safety-communications/fda-warns-against-use-energy-based-devices-perform-vaginal-rejuvenation-or-vaginal-cosmetic. Updated November 20, 2018. Accessed May 21, 2020.
- US Food and Drug Administration website. Letters to industry. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/industry-medical-devices/letters-industry. July 24, 2018. Accessed May 21, 2020
The term genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) refers to the bothersome symptoms and physical findings associated with estrogen deficiency that involve the labia, vestibular tissue, clitoris, vagina, urethra, and bladder.1 GSM is associated with genital irritation, dryness, and burning; urinary symptoms including urgency, dysuria, and recurrent urinary tract infections; and sexual symptoms including vaginal dryness and pain. Vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA) represents a component of GSM.
GSM is highly prevalent, affecting more than three-quarters of menopausal women. In contrast to menopausal vasomotor symptoms, which often are most severe and frequent in recently menopausal women, GSM commonly presents years following menopause. Unfortunately, VVA symptoms may have a substantial negative impact on women’s quality of life.
In this 2020 Menopause Update, I review a large observational study that provides reassurance to clinicians and patients regarding the safety of the best-studied prescription treatment for GSM—vaginal estrogen. Because some women should not use vaginal estrogen and others choose not to use it, nonhormonal management of GSM is important. Dr. JoAnn Pinkerton provides details on a randomized clinical trial that compared the use of fractionated CO2 laser therapy with vaginal estrogen for the treatment of GSM. In addition, Dr. JoAnn Manson discusses recent studies that found lower health risks with vaginal estrogen use compared with systemic estrogen therapy.
Diagnosing GSM
GSM can be diagnosed presumptively based on a characteristic history in a menopausal patient. Performing a pelvic examination, however, allows clinicians to exclude other conditions that may present with similar symptoms, such as lichen sclerosus, Candida infection, and malignancy.
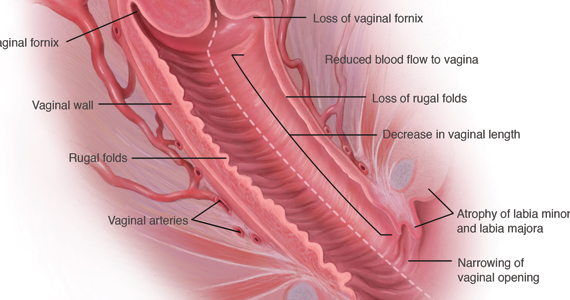
During inspection of the external genitalia, the clinician may note loss of the fat pad in the labia majora and mons as well as a reduction in labia minora pigmentation and tissue. The urethral meatus often becomes erythematous and prominent. If vaginal or introital narrowing is present, use of a pediatric (ultrathin) speculum reduces patient discomfort. The vaginal mucosa may appear smooth due to loss of rugation; it also may appear shiny and dry. Bleeding (friability) on contact with a spatula or cotton-tipped swab may occur. In addition, the vaginal fornices may become attenuated, leaving the cervix flush with the vaginal apex.
GSM can be diagnosed without laboratory assessment. However, vaginal pH, if measured, is characteristically higher than 5.0; microscopic wet prep often reveals many white blood cells, immature epithelial cells (large nuclei), and reduced or absent lactobacilli.2

Nonhormonal management of GSM
Water, silicone-based, and oil-based lubricants reduce the friction and discomfort associated with sexual activity. By contrast, vaginal moisturizers act longer than lubricants and can be applied several times weekly or daily. Natural oils, including olive and coconut oil, may be useful both as lubricants and as moisturizers. Aqueous lidocaine 4%, applied to vestibular tissue with cotton balls prior to penetration, reduces dyspareunia in women with GSM.3
Vaginal estrogen therapy
When nonhormonal management does not sufficiently reduce GSM symptoms, use of low-dose vaginal estrogen enhances thickness and elasticity of genital tissue and improves vaginal blood flow. Vaginal estrogen creams, tablets, an insert, and a ring are marketed in the United States. Although clinical improvement may be apparent within several weeks of initiating vaginal estrogen, the full benefit of treatment becomes apparent after 2 to 3 months.3
Despite the availability and effectiveness of low-dose vaginal estrogen, fears regarding the safety of menopausal hormone therapy have resulted in the underutilization of vaginal estrogen.4,5 Unfortunately, the package labeling for low-dose vaginal estrogen can exacerbate these fears.
Continue to: Nurses’ Health Study report...
Nurses’ Health Study report provides reassurance on long-term safety of vaginal estrogen
Bhupathiraju SN, Grodstein F, Stampfer MJ, et al. Vaginal estrogen use and chronic disease risk in the Nurses’ Health Study. Menopause. 2018;26:603-610
Bhupathiraju and colleagues published a report from the long-running Nurses’ Health prospective cohort study on the health outcomes associated with the use of vaginal estrogen.
Recap of the study
Starting in 1982, participants in the Nurses’Health Study were asked to report their use of vaginal estrogen via a validated questionnaire. For the years 1982 to 2012, investigators analyzed data from 896 and 52,901 women who had and had not used vaginal estrogen, respectively. The mean duration of vaginal estrogen use was 36 months.
In an analysis adjusted for numerous factors, the investigators observed no statistically significant differences in risk for cardiovascular outcomes (myocardial infarction, stroke, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism) or invasive cancers (colorectal, endometrial, ovarian, or breast).
Findings uphold safety of vaginal estrogen
This landmark study provides reassurance that 3 years of use of vaginal estrogen does not increase the risk of cardiovascular events or invasive breast cancer, findings that hopefully will allow clinicians and women to feel comfortable regarding the safety of vaginal estrogen. A study of vaginal estrogen from the Women’s Health Initiative provided similar reassurance. Recent research supports guidance from The North American Menopause Society and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists that vaginal estrogen can be used indefinitely, if indicated, and that use of concomitant progestin is not recommended in women who use vaginal estrogen and have an intact uterus.6,7
I agree with the authors, who point out that since treatment of GSM may need to be continued long term (even indefinitely), it would be helpful to have data that assessed the safety of longer-duration use of vaginal estrogen.
Results from Bhupathiraju and colleagues’ analysis of data from the Nurses’ Health Study on the 3-year safety of vaginal estrogen use encourage clinicians to recommend and women to use this safe and effective treatment for GSM.
How CO2 fractionated vaginal laser therapy compares with vaginal estrogen for relief of GSM symptoms
Paraiso MF, Ferrando CA, Sokol ER, et al. A randomized clinical trial comparing vaginal laser therapy to vaginal estrogen therapy in women with genitourinary syndrome of menopause: the VeLVET trial. Menopause. 2020;27:50-56.
Up to 50% to 60% of postmenopausal women experience GSM symptoms. However, many fewer receive treatment, either because they do not understand that the symptoms are related to menopause or they are not aware that safe and effective treatment is available. Sadly, many women are not asked about their symptoms or are embarrassed to tell providers.
GSM affects relationships and quality of life. Vaginal lubricants or moisturizers may provide relief. US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved therapies include low-dose vaginal estrogen, available as a vaginal tablet, cream, suppository, and ring; intravaginal dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA); and oral ospemifene, a selective estrogen replacement modulator. If women have an estrogen-sensitive breast or uterine cancer, an oncologist should be involved in decisions about vaginal hormonal therapy.
Energy-based devices such as vaginal lasers appear to induce wound healing; stimulate collagen and elastin fiber formation through increased storage of glycogen; and activate fibroblasts, which leads to increased extracellular matrix and restoration of vaginal pH.
These lasers are FDA approved for use in gynecology but not specifically for the treatment of GSM. In July 2016, the FDA issued a safety alert that energy-based devices, while approved for use in gynecology, have not been approved or adequately tested for menopausal vaginal conditions, and safety concerns include reports of vaginal burns.8 Lacking are publications of adequately powered randomized, sham-con-trolled trials to determine if laser therapy works better for women with GSM than placebos, moisturizers, or vaginal hormone therapies.
Recently, investigators conducted a multicenter, randomized, single-blinded trial of vaginal laser therapy and estrogen cream for treatment of GSM.
Continue to: Details of the study...
Details of the study
Paraiso and colleagues aimed to compare the 6-month efficacy and safety of fractionated CO2 vaginal laser therapy with that of estrogen vaginal cream for the treatment of vaginal dryness/GSM.
Participants randomly assigned to the estrogen therapy arm applied conjugated estrogen cream 0.5 g vaginally daily for 14 days, followed by twice weekly application for 24 weeks (a low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy). Participants randomly assigned to laser therapy underwent 3 vaginal treatments at a minimum of 6 weeks apart.
Sixty-nine women were enrolled in the trial before enrollment was closed because the FDA required that the sponsor obtain and maintain an investigational device exemption. Of 62 women who completed 6 months’ treatment, 30 received 3 laser treatments and 32 received estrogen cream.
The primary outcome compared subjective improvement in vaginal dryness using the visual analog scale (VAS) between the 2 groups at 6 months. Secondary outcomes included comparisons of the vaginal health index (VHI) and vaginal maturation index (VMI), the effect of GSM on quality of life, the effect of treatment on sexual function and urinary symptoms, and patient satisfaction.
Study findings
Efficacy. Laser therapy and estrogen therapy were found to be similarly effective except on the VMI, which favored estrogen. On patient global impression, 85.8% of laser-treated women rated their improvement as ‘‘better or much better’’ and 78.5% reported being either ‘‘satisfied or very satisfied,’’ compared with 70% and 73.3%, respectively, in the estrogen group, a statistically nonsignificant difference.
On linear regression, the investigators found a nonsignificant mean difference in female sexual function index scores. While VMI scores remained higher in the estrogen-treated group (adjusted P = .02), baseline and 6-month follow-up VMI data were available for only 34 participants (16 laser treated, 18 estrogen treated).
Regarding long-term effectiveness, 20% to 25% of the women in the laser-treated group needed further treatment after 1 year while the estrogen cream continued to work as long as it was used as prescribed.
Adverse effects. The incidence of vaginal bleeding was similar in the 2 groups: 6.7% in the laser group and 6.3% in the estrogen group. In the laser therapy group, 3% expe-rienced vaginal pain, discharge, and bladder infections, while in the estrogen cream group, 3% reported breast tenderness, migraine headaches, and abdominal cramping.
Takeaways. This small randomized, open-label (not blinded) trial provides pilot data on the effectiveness of vaginal CO2 laser compared with vaginal estrogen in treating vaginal atrophy, quality-of-life symptoms, sexual function, and urinary symptoms. Adverse events were minimal. Patient global impression of improvement and satisfaction improved for both vaginal laser and vaginal estrogen therapy.
Continue to: Study strengths and limitations...
Study strengths and limitations
To show noninferiority of vaginal laser therapy to vaginal estrogen, 196 study participants were needed. However, after 38% had been enrolled, the FDA sent a warning letter to the Foundation for Female Health Awareness, which required obtainment of an investigational device exemption for the laser and addition of a sham treatment arm.9 Instead of redesigning the trial and reconsenting the participants, the investigators closed the study, and analysis was performed only on the 62 participants who completed the study; vaginal maturation was assessed only in 34 participants.
The study lacked a placebo or sham control, which increases the risk of bias, while small numbers limit the strength of the findings. Longer-term evaluation of the effects of laser therapy beyond 6 months is needed to allow assessment of the effects of scarring on vaginal health, sexual function, and urinary issues.
Discussing therapy with patients
Despite this study’s preliminary findings, and until more robust data are available, providers should discuss the benefits and risks of all available treatment options for vaginal symptoms, including over-the-counter lubricants, vaginal moisturizers, FDA-approved vaginal hormone therapies (such as vaginal estrogen and intravaginal dehydroepiandrosterone), and systemic therapies, such as hormone therapy and ospemifene, to determine the best treatment for the individual woman with GSM.
In a healthy postmenopausal woman with bothersome GSM symptoms not responsive to lubricants and moisturizers, I recommend FDA-approved vaginal therapies as first-line treatment if there are no contraindications. For women with breast cancer, I involve their oncologist. If a patient asks about vaginal laser treatment, I share that vaginal energy-based therapies, such as the vaginal laser, have not been approved for menopausal vaginal concerns. In addition to the possibility of adverse events or unsuccessful treatment, there are significant out-of-pocket costs and the potential need for ongoing therapy after the initial 3 laser treatments.
For GSM that does not respond to lubricants and moisturizers, many FDA-approved vaginal and systemic therapies are available to treat vaginal symptoms. Vaginal laser treatment is a promising therapy for vaginal symptoms of GSM that needs further testing to determine its efficacy, safety, and long-term effects. If discussing vaginal energy-based therapies with patients, include the current lack of FDA approval for specific vaginal indications, potential adverse effects, the need for ongoing retreatment, and out-of-pocket costs.
JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, NCMP
Having more appropriate, evidence-based labeling of low-dose vaginal estrogen continues to be a high priority for The North American Menopause Society (NAMS), the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health (ISSWSH), and other professional societies.
NAMS and the Working Group on Women’s Health and Well-Being in Menopause had submitted a citizen’s petition to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2016 requesting modification of the label—including removal of the “black box warning”—for low-dose vaginal estrogen products. The petition was, disappointingly, denied in 2018.1
Currently, the class labeling, which was based on the results of randomized trials with systemic hormone therapy, is not applicable to low-dose vaginal estrogen, and the inclusion of the black box warning has led to serious underutilization of an effective and safe treatment for a very common and life-altering condition, the genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM). This condition affects nearly half of postmenopausal women. It tends to be chronic and progressive and, unlike hot flashes and vasomotor symptoms, it does not remit or decline over time, and it affects women’s health and quality of life.
While removal of the black box warning would be appropriate, labeling should include emphatic reminders for women that if they have any bleeding or spotting they should seek medical attention immediately, and if they have a history of breast cancer or other estrogen-sensitive cancers they should talk with their oncologist prior to starting treatment with low-dose vaginal estrogen. Although the text would still inform women of research results on systemic hormone therapy, it would explain the differences between low-dose vaginal estrogen and systemic therapy.
Studies show vaginal estrogen has good safety profile
In the last several years, large, observational studies of low-dose vaginal estrogen have suggested that this treatment is not associated with an increase in cardiovascular disease, pulmonary embolism, venous thrombosis, cancer, or dementia—conditions listed in the black box warning that were linked to systemic estrogen therapy plus synthetic progestin. Recent data from the Nurses’ Health Study, for example, demonstrated that 3 years of vaginal estrogen use did not increase the risk of cardiovascular events or invasive breast cancer.
Women’s Health Initiative. In a prospective observational cohort study, Crandall and colleagues used data from participants in the Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study to determine the association between use of vaginal estrogen and risk of a global index event (GIE), defined as time to first occurrence of coronary heart disease, invasive breast cancer, stroke, pulmonary embolism, hip fracture, colorectal cancer, endometrial cancer, or death from any cause.2
Women were recruited from multiple clinical centers, were aged 50 to 79 years at baseline, and did not use systemic estrogen therapy during follow-up. The study included 45,663 women and median follow-up was 7.2 years. The investigators collected data on women’s self-reported use of vaginal estrogen as well as the development of the conditions defined above.
In women with a uterus, there was no significant difference between vaginal estrogen users and nonusers in the risk of stroke, invasive breast cancer, colorectal cancer, endometrial cancer, pulmonary embolism, or deep vein thrombosis. The risks of coronary heart disease, fracture, all-cause mortality, and GIE were lower in vaginal estrogen users than in nonusers (GIE adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 0.68; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.55–0.86).
In women who had undergone hysterectomy, the risks of the individual GIE components and the overall GIE were not significantly different in users of vaginal estrogen compared with nonusers (GIE adjusted HR, 0.94; 95% CI, 0.70–1.26).
The investigators concluded that the risks of cardiovascular disease and cancer were not increased in postmenopausal women who used vaginal estrogen. Thus, this study offers reassurance on the treatment’s safety.2
Meta-analysis on menopausal hormone therapy and breast cancer risk. Further evidence now indicates that low-dose vaginal estrogen is not linked to chronic health conditions. In a large meta-analysis published in 2019, investigators looked at different types of hormone therapies—oral estrogen plus progestin, transdermal estrogen and progestin, estrogen alone, low-dose vaginal estrogen—and their relationship to breast cancer risk.3
Information on individual participants was obtained from 58 studies, 24 prospective and 34 retrospective. Breast cancer relative risks (RR) during years 5 to 14 of current hormone use were assessed according to the main hormonal contituents, doses, and modes of delivery of the last-used menopausal hormone therapy. For all systemic estrogen-only preparations, the RR was 1.33 (95% CI, 1.28–1.38), while for all estrogen-progestogen preparations, the RR was 2.08 (95% CI, 2.02–2.15). For transdermal estrogen, the RR was 1.35 (95% CI, 1.25–1.46). In contrast, for vaginal estrogen, the RR was 1.09 (95% CI, 0.97–1.23).3
Thus, the analysis found that in all the studies that had been done to date, there was no evidence of increased risk of breast cancer with vaginal estrogen therapy.
The evidence is growing that low-dose vaginal estrogen is different from systemic estrogen in terms of its safety profile and benefit-risk pattern. It is important for the FDA to consider these data and revise the vaginal estrogen label.
On the horizon: New estradiol reference ranges
It would be useful if we could accurately compare estradiol levels in women treated with vaginal estrogen against those of women treated with systemic estrogen therapy. In September 2019, NAMS held a workshop with the goal of establishing reference ranges for estradiol in postmenopausal women.4 It is very important to have good, reliable laboratory assays for estradiol and estrone, and to have a clear understanding of what is a reference range, that is, the range of estradiol levels in postmenopausal women who are not treated with estrogen. That way, you can observe what the estradiol blood levels are in women treated with low-dose vaginal estrogen or those treated with systemic estrogen versus the levels observed among postmenopausal women not receiving any estrogen product.
With the reference range information, we could look at data on the blood levels of estradiol with low-dose vaginal estrogen from the various studies available, as well as the increasing evidence from observational studies of the safety of low-dose vaginal estrogen to better understand its relationship with health. If these studies demonstrate that, with certain doses and formulations of low-dose vaginal estrogen, blood estradiol levels stay within the reference range of postmenopausal estradiol levels, it would inform the labeling modifications of these products. We need this information for future discussions with the FDA.
The laboratory assay technology used for such an investigation is primarily liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry, the so-called LC-MS/MS assay. With use of this technology, the reference range for estradiol may be less than 10 picograms per milliliter. Previously, a very wide and inconsistent range—about 5 to 30 picograms per milliliter—was considered a “normal” range.
NAMS is championing the efforts to define a true evidence-based reference range that would represent the range of levels seen in postmenopausal women.5 This effort has been spearheaded by Dr. Richard Santen and colleagues. Using the more sensitive and specific LC-MS/MS assay will enable researchers and clinicians to better understand how levels on low-dose vaginal estrogen relate to the reference range for postmenopausal women. We are hoping to work together with researchers to establish these reference ranges, and to use that information to look at how low-dose vaginal estrogen compares to levels in untreated postmenopausal women, as well as to levels in women on systemic estrogen.
Hopefully, establishing the reference range can be done in an expeditious and timely way, with discussions with the FDA resuming shortly thereafter.
References
1.NAMS Citizen’s Petition and FDA Response, June 7, 2018. http://www.menopause.org/docs/
2. Crandall CJ, Hovey KM, Andrews CA, et al. Breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and cardiovascular events in participants who used vaginal estrogen in the Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study. Menopause. 2018;25:11-20.
3. Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer. Type and timing of menopausal hormone therapy and breast cancer risk: individual participant meta-analysis of the worldwide epidemiological evidence. Lancet. 2019;394:1159-1168.
4. Santen RJ, Pinkerton JV, Liu JH, et al. Workshop on normal reference ranges for estradiol in postmenopausal women, September 2019, Chicago, Illinois. Menopause. May 4, 2020. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000001556.
5. Pinkerton JV, Liu JH, Santoro NF, et al. Workshop on normal reference ranges for estradiol in postmenopausal women: commentary from The North American Menopause Society on low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy. Menopause. 2020;27:611-613.
The term genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) refers to the bothersome symptoms and physical findings associated with estrogen deficiency that involve the labia, vestibular tissue, clitoris, vagina, urethra, and bladder.1 GSM is associated with genital irritation, dryness, and burning; urinary symptoms including urgency, dysuria, and recurrent urinary tract infections; and sexual symptoms including vaginal dryness and pain. Vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA) represents a component of GSM.
GSM is highly prevalent, affecting more than three-quarters of menopausal women. In contrast to menopausal vasomotor symptoms, which often are most severe and frequent in recently menopausal women, GSM commonly presents years following menopause. Unfortunately, VVA symptoms may have a substantial negative impact on women’s quality of life.
In this 2020 Menopause Update, I review a large observational study that provides reassurance to clinicians and patients regarding the safety of the best-studied prescription treatment for GSM—vaginal estrogen. Because some women should not use vaginal estrogen and others choose not to use it, nonhormonal management of GSM is important. Dr. JoAnn Pinkerton provides details on a randomized clinical trial that compared the use of fractionated CO2 laser therapy with vaginal estrogen for the treatment of GSM. In addition, Dr. JoAnn Manson discusses recent studies that found lower health risks with vaginal estrogen use compared with systemic estrogen therapy.
Diagnosing GSM
GSM can be diagnosed presumptively based on a characteristic history in a menopausal patient. Performing a pelvic examination, however, allows clinicians to exclude other conditions that may present with similar symptoms, such as lichen sclerosus, Candida infection, and malignancy.
During inspection of the external genitalia, the clinician may note loss of the fat pad in the labia majora and mons as well as a reduction in labia minora pigmentation and tissue. The urethral meatus often becomes erythematous and prominent. If vaginal or introital narrowing is present, use of a pediatric (ultrathin) speculum reduces patient discomfort. The vaginal mucosa may appear smooth due to loss of rugation; it also may appear shiny and dry. Bleeding (friability) on contact with a spatula or cotton-tipped swab may occur. In addition, the vaginal fornices may become attenuated, leaving the cervix flush with the vaginal apex.
GSM can be diagnosed without laboratory assessment. However, vaginal pH, if measured, is characteristically higher than 5.0; microscopic wet prep often reveals many white blood cells, immature epithelial cells (large nuclei), and reduced or absent lactobacilli.2

Nonhormonal management of GSM
Water, silicone-based, and oil-based lubricants reduce the friction and discomfort associated with sexual activity. By contrast, vaginal moisturizers act longer than lubricants and can be applied several times weekly or daily. Natural oils, including olive and coconut oil, may be useful both as lubricants and as moisturizers. Aqueous lidocaine 4%, applied to vestibular tissue with cotton balls prior to penetration, reduces dyspareunia in women with GSM.3
Vaginal estrogen therapy
When nonhormonal management does not sufficiently reduce GSM symptoms, use of low-dose vaginal estrogen enhances thickness and elasticity of genital tissue and improves vaginal blood flow. Vaginal estrogen creams, tablets, an insert, and a ring are marketed in the United States. Although clinical improvement may be apparent within several weeks of initiating vaginal estrogen, the full benefit of treatment becomes apparent after 2 to 3 months.3
Despite the availability and effectiveness of low-dose vaginal estrogen, fears regarding the safety of menopausal hormone therapy have resulted in the underutilization of vaginal estrogen.4,5 Unfortunately, the package labeling for low-dose vaginal estrogen can exacerbate these fears.
Continue to: Nurses’ Health Study report...
Nurses’ Health Study report provides reassurance on long-term safety of vaginal estrogen
Bhupathiraju SN, Grodstein F, Stampfer MJ, et al. Vaginal estrogen use and chronic disease risk in the Nurses’ Health Study. Menopause. 2018;26:603-610
Bhupathiraju and colleagues published a report from the long-running Nurses’ Health prospective cohort study on the health outcomes associated with the use of vaginal estrogen.
Recap of the study
Starting in 1982, participants in the Nurses’Health Study were asked to report their use of vaginal estrogen via a validated questionnaire. For the years 1982 to 2012, investigators analyzed data from 896 and 52,901 women who had and had not used vaginal estrogen, respectively. The mean duration of vaginal estrogen use was 36 months.
In an analysis adjusted for numerous factors, the investigators observed no statistically significant differences in risk for cardiovascular outcomes (myocardial infarction, stroke, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism) or invasive cancers (colorectal, endometrial, ovarian, or breast).
Findings uphold safety of vaginal estrogen
This landmark study provides reassurance that 3 years of use of vaginal estrogen does not increase the risk of cardiovascular events or invasive breast cancer, findings that hopefully will allow clinicians and women to feel comfortable regarding the safety of vaginal estrogen. A study of vaginal estrogen from the Women’s Health Initiative provided similar reassurance. Recent research supports guidance from The North American Menopause Society and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists that vaginal estrogen can be used indefinitely, if indicated, and that use of concomitant progestin is not recommended in women who use vaginal estrogen and have an intact uterus.6,7
I agree with the authors, who point out that since treatment of GSM may need to be continued long term (even indefinitely), it would be helpful to have data that assessed the safety of longer-duration use of vaginal estrogen.
Results from Bhupathiraju and colleagues’ analysis of data from the Nurses’ Health Study on the 3-year safety of vaginal estrogen use encourage clinicians to recommend and women to use this safe and effective treatment for GSM.
How CO2 fractionated vaginal laser therapy compares with vaginal estrogen for relief of GSM symptoms
Paraiso MF, Ferrando CA, Sokol ER, et al. A randomized clinical trial comparing vaginal laser therapy to vaginal estrogen therapy in women with genitourinary syndrome of menopause: the VeLVET trial. Menopause. 2020;27:50-56.
Up to 50% to 60% of postmenopausal women experience GSM symptoms. However, many fewer receive treatment, either because they do not understand that the symptoms are related to menopause or they are not aware that safe and effective treatment is available. Sadly, many women are not asked about their symptoms or are embarrassed to tell providers.
GSM affects relationships and quality of life. Vaginal lubricants or moisturizers may provide relief. US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved therapies include low-dose vaginal estrogen, available as a vaginal tablet, cream, suppository, and ring; intravaginal dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA); and oral ospemifene, a selective estrogen replacement modulator. If women have an estrogen-sensitive breast or uterine cancer, an oncologist should be involved in decisions about vaginal hormonal therapy.
Energy-based devices such as vaginal lasers appear to induce wound healing; stimulate collagen and elastin fiber formation through increased storage of glycogen; and activate fibroblasts, which leads to increased extracellular matrix and restoration of vaginal pH.
These lasers are FDA approved for use in gynecology but not specifically for the treatment of GSM. In July 2016, the FDA issued a safety alert that energy-based devices, while approved for use in gynecology, have not been approved or adequately tested for menopausal vaginal conditions, and safety concerns include reports of vaginal burns.8 Lacking are publications of adequately powered randomized, sham-con-trolled trials to determine if laser therapy works better for women with GSM than placebos, moisturizers, or vaginal hormone therapies.
Recently, investigators conducted a multicenter, randomized, single-blinded trial of vaginal laser therapy and estrogen cream for treatment of GSM.
Continue to: Details of the study...
Details of the study
Paraiso and colleagues aimed to compare the 6-month efficacy and safety of fractionated CO2 vaginal laser therapy with that of estrogen vaginal cream for the treatment of vaginal dryness/GSM.
Participants randomly assigned to the estrogen therapy arm applied conjugated estrogen cream 0.5 g vaginally daily for 14 days, followed by twice weekly application for 24 weeks (a low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy). Participants randomly assigned to laser therapy underwent 3 vaginal treatments at a minimum of 6 weeks apart.
Sixty-nine women were enrolled in the trial before enrollment was closed because the FDA required that the sponsor obtain and maintain an investigational device exemption. Of 62 women who completed 6 months’ treatment, 30 received 3 laser treatments and 32 received estrogen cream.
The primary outcome compared subjective improvement in vaginal dryness using the visual analog scale (VAS) between the 2 groups at 6 months. Secondary outcomes included comparisons of the vaginal health index (VHI) and vaginal maturation index (VMI), the effect of GSM on quality of life, the effect of treatment on sexual function and urinary symptoms, and patient satisfaction.
Study findings
Efficacy. Laser therapy and estrogen therapy were found to be similarly effective except on the VMI, which favored estrogen. On patient global impression, 85.8% of laser-treated women rated their improvement as ‘‘better or much better’’ and 78.5% reported being either ‘‘satisfied or very satisfied,’’ compared with 70% and 73.3%, respectively, in the estrogen group, a statistically nonsignificant difference.
On linear regression, the investigators found a nonsignificant mean difference in female sexual function index scores. While VMI scores remained higher in the estrogen-treated group (adjusted P = .02), baseline and 6-month follow-up VMI data were available for only 34 participants (16 laser treated, 18 estrogen treated).
Regarding long-term effectiveness, 20% to 25% of the women in the laser-treated group needed further treatment after 1 year while the estrogen cream continued to work as long as it was used as prescribed.
Adverse effects. The incidence of vaginal bleeding was similar in the 2 groups: 6.7% in the laser group and 6.3% in the estrogen group. In the laser therapy group, 3% expe-rienced vaginal pain, discharge, and bladder infections, while in the estrogen cream group, 3% reported breast tenderness, migraine headaches, and abdominal cramping.
Takeaways. This small randomized, open-label (not blinded) trial provides pilot data on the effectiveness of vaginal CO2 laser compared with vaginal estrogen in treating vaginal atrophy, quality-of-life symptoms, sexual function, and urinary symptoms. Adverse events were minimal. Patient global impression of improvement and satisfaction improved for both vaginal laser and vaginal estrogen therapy.
Continue to: Study strengths and limitations...
Study strengths and limitations
To show noninferiority of vaginal laser therapy to vaginal estrogen, 196 study participants were needed. However, after 38% had been enrolled, the FDA sent a warning letter to the Foundation for Female Health Awareness, which required obtainment of an investigational device exemption for the laser and addition of a sham treatment arm.9 Instead of redesigning the trial and reconsenting the participants, the investigators closed the study, and analysis was performed only on the 62 participants who completed the study; vaginal maturation was assessed only in 34 participants.
The study lacked a placebo or sham control, which increases the risk of bias, while small numbers limit the strength of the findings. Longer-term evaluation of the effects of laser therapy beyond 6 months is needed to allow assessment of the effects of scarring on vaginal health, sexual function, and urinary issues.
Discussing therapy with patients
Despite this study’s preliminary findings, and until more robust data are available, providers should discuss the benefits and risks of all available treatment options for vaginal symptoms, including over-the-counter lubricants, vaginal moisturizers, FDA-approved vaginal hormone therapies (such as vaginal estrogen and intravaginal dehydroepiandrosterone), and systemic therapies, such as hormone therapy and ospemifene, to determine the best treatment for the individual woman with GSM.
In a healthy postmenopausal woman with bothersome GSM symptoms not responsive to lubricants and moisturizers, I recommend FDA-approved vaginal therapies as first-line treatment if there are no contraindications. For women with breast cancer, I involve their oncologist. If a patient asks about vaginal laser treatment, I share that vaginal energy-based therapies, such as the vaginal laser, have not been approved for menopausal vaginal concerns. In addition to the possibility of adverse events or unsuccessful treatment, there are significant out-of-pocket costs and the potential need for ongoing therapy after the initial 3 laser treatments.
For GSM that does not respond to lubricants and moisturizers, many FDA-approved vaginal and systemic therapies are available to treat vaginal symptoms. Vaginal laser treatment is a promising therapy for vaginal symptoms of GSM that needs further testing to determine its efficacy, safety, and long-term effects. If discussing vaginal energy-based therapies with patients, include the current lack of FDA approval for specific vaginal indications, potential adverse effects, the need for ongoing retreatment, and out-of-pocket costs.
JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, NCMP
Having more appropriate, evidence-based labeling of low-dose vaginal estrogen continues to be a high priority for The North American Menopause Society (NAMS), the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health (ISSWSH), and other professional societies.
NAMS and the Working Group on Women’s Health and Well-Being in Menopause had submitted a citizen’s petition to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2016 requesting modification of the label—including removal of the “black box warning”—for low-dose vaginal estrogen products. The petition was, disappointingly, denied in 2018.1
Currently, the class labeling, which was based on the results of randomized trials with systemic hormone therapy, is not applicable to low-dose vaginal estrogen, and the inclusion of the black box warning has led to serious underutilization of an effective and safe treatment for a very common and life-altering condition, the genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM). This condition affects nearly half of postmenopausal women. It tends to be chronic and progressive and, unlike hot flashes and vasomotor symptoms, it does not remit or decline over time, and it affects women’s health and quality of life.
While removal of the black box warning would be appropriate, labeling should include emphatic reminders for women that if they have any bleeding or spotting they should seek medical attention immediately, and if they have a history of breast cancer or other estrogen-sensitive cancers they should talk with their oncologist prior to starting treatment with low-dose vaginal estrogen. Although the text would still inform women of research results on systemic hormone therapy, it would explain the differences between low-dose vaginal estrogen and systemic therapy.
Studies show vaginal estrogen has good safety profile
In the last several years, large, observational studies of low-dose vaginal estrogen have suggested that this treatment is not associated with an increase in cardiovascular disease, pulmonary embolism, venous thrombosis, cancer, or dementia—conditions listed in the black box warning that were linked to systemic estrogen therapy plus synthetic progestin. Recent data from the Nurses’ Health Study, for example, demonstrated that 3 years of vaginal estrogen use did not increase the risk of cardiovascular events or invasive breast cancer.
Women’s Health Initiative. In a prospective observational cohort study, Crandall and colleagues used data from participants in the Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study to determine the association between use of vaginal estrogen and risk of a global index event (GIE), defined as time to first occurrence of coronary heart disease, invasive breast cancer, stroke, pulmonary embolism, hip fracture, colorectal cancer, endometrial cancer, or death from any cause.2
Women were recruited from multiple clinical centers, were aged 50 to 79 years at baseline, and did not use systemic estrogen therapy during follow-up. The study included 45,663 women and median follow-up was 7.2 years. The investigators collected data on women’s self-reported use of vaginal estrogen as well as the development of the conditions defined above.
In women with a uterus, there was no significant difference between vaginal estrogen users and nonusers in the risk of stroke, invasive breast cancer, colorectal cancer, endometrial cancer, pulmonary embolism, or deep vein thrombosis. The risks of coronary heart disease, fracture, all-cause mortality, and GIE were lower in vaginal estrogen users than in nonusers (GIE adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 0.68; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.55–0.86).
In women who had undergone hysterectomy, the risks of the individual GIE components and the overall GIE were not significantly different in users of vaginal estrogen compared with nonusers (GIE adjusted HR, 0.94; 95% CI, 0.70–1.26).
The investigators concluded that the risks of cardiovascular disease and cancer were not increased in postmenopausal women who used vaginal estrogen. Thus, this study offers reassurance on the treatment’s safety.2
Meta-analysis on menopausal hormone therapy and breast cancer risk. Further evidence now indicates that low-dose vaginal estrogen is not linked to chronic health conditions. In a large meta-analysis published in 2019, investigators looked at different types of hormone therapies—oral estrogen plus progestin, transdermal estrogen and progestin, estrogen alone, low-dose vaginal estrogen—and their relationship to breast cancer risk.3
Information on individual participants was obtained from 58 studies, 24 prospective and 34 retrospective. Breast cancer relative risks (RR) during years 5 to 14 of current hormone use were assessed according to the main hormonal contituents, doses, and modes of delivery of the last-used menopausal hormone therapy. For all systemic estrogen-only preparations, the RR was 1.33 (95% CI, 1.28–1.38), while for all estrogen-progestogen preparations, the RR was 2.08 (95% CI, 2.02–2.15). For transdermal estrogen, the RR was 1.35 (95% CI, 1.25–1.46). In contrast, for vaginal estrogen, the RR was 1.09 (95% CI, 0.97–1.23).3
Thus, the analysis found that in all the studies that had been done to date, there was no evidence of increased risk of breast cancer with vaginal estrogen therapy.
The evidence is growing that low-dose vaginal estrogen is different from systemic estrogen in terms of its safety profile and benefit-risk pattern. It is important for the FDA to consider these data and revise the vaginal estrogen label.
On the horizon: New estradiol reference ranges
It would be useful if we could accurately compare estradiol levels in women treated with vaginal estrogen against those of women treated with systemic estrogen therapy. In September 2019, NAMS held a workshop with the goal of establishing reference ranges for estradiol in postmenopausal women.4 It is very important to have good, reliable laboratory assays for estradiol and estrone, and to have a clear understanding of what is a reference range, that is, the range of estradiol levels in postmenopausal women who are not treated with estrogen. That way, you can observe what the estradiol blood levels are in women treated with low-dose vaginal estrogen or those treated with systemic estrogen versus the levels observed among postmenopausal women not receiving any estrogen product.
With the reference range information, we could look at data on the blood levels of estradiol with low-dose vaginal estrogen from the various studies available, as well as the increasing evidence from observational studies of the safety of low-dose vaginal estrogen to better understand its relationship with health. If these studies demonstrate that, with certain doses and formulations of low-dose vaginal estrogen, blood estradiol levels stay within the reference range of postmenopausal estradiol levels, it would inform the labeling modifications of these products. We need this information for future discussions with the FDA.
The laboratory assay technology used for such an investigation is primarily liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry, the so-called LC-MS/MS assay. With use of this technology, the reference range for estradiol may be less than 10 picograms per milliliter. Previously, a very wide and inconsistent range—about 5 to 30 picograms per milliliter—was considered a “normal” range.
NAMS is championing the efforts to define a true evidence-based reference range that would represent the range of levels seen in postmenopausal women.5 This effort has been spearheaded by Dr. Richard Santen and colleagues. Using the more sensitive and specific LC-MS/MS assay will enable researchers and clinicians to better understand how levels on low-dose vaginal estrogen relate to the reference range for postmenopausal women. We are hoping to work together with researchers to establish these reference ranges, and to use that information to look at how low-dose vaginal estrogen compares to levels in untreated postmenopausal women, as well as to levels in women on systemic estrogen.
Hopefully, establishing the reference range can be done in an expeditious and timely way, with discussions with the FDA resuming shortly thereafter.
References
1.NAMS Citizen’s Petition and FDA Response, June 7, 2018. http://www.menopause.org/docs/
2. Crandall CJ, Hovey KM, Andrews CA, et al. Breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and cardiovascular events in participants who used vaginal estrogen in the Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study. Menopause. 2018;25:11-20.
3. Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer. Type and timing of menopausal hormone therapy and breast cancer risk: individual participant meta-analysis of the worldwide epidemiological evidence. Lancet. 2019;394:1159-1168.
4. Santen RJ, Pinkerton JV, Liu JH, et al. Workshop on normal reference ranges for estradiol in postmenopausal women, September 2019, Chicago, Illinois. Menopause. May 4, 2020. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000001556.
5. Pinkerton JV, Liu JH, Santoro NF, et al. Workshop on normal reference ranges for estradiol in postmenopausal women: commentary from The North American Menopause Society on low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy. Menopause. 2020;27:611-613.
- Portman DJ, Gass ML. Genitourinary syndrome of menopause: new terminology for vulvovaginal atrophy from the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health and The North American Menopause Society. Maturitas. 2014;79:349-354.
- Kaunitz AM, Manson JE. Management of menopausal symptoms. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126:859-876.
- Shifren JL. Genitourinary syndrome of menopause. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2018;61:508-516.
- Manson JE, Kaunitz AM. Menopause management—getting clinical care back on track. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:803-806.
- Kingsberg SA, Krychman M, Graham S, et al. The women’s EMPOWER survey: identifying women’s perceptions on vulvar and vaginal atrophy and its treatment. J Sex Med. 2017;14:413-424.
- The NAMS 2017 Hormone Therapy Position Statement Advisory Panel. The 2017 Hormone therapy position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2017;24:728-753.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG practice bulletin No. 141: Management of menopausal symptoms. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123:202-216.
- US Food and Drug Administration website. FDA warns against the use of energy-based devices to perform vaginal ‘rejuvenation’ or vaginal cosmetic procedures: FDA safety communication. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/safety-communications/fda-warns-against-use-energy-based-devices-perform-vaginal-rejuvenation-or-vaginal-cosmetic. Updated November 20, 2018. Accessed May 21, 2020.
- US Food and Drug Administration website. Letters to industry. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/industry-medical-devices/letters-industry. July 24, 2018. Accessed May 21, 2020
- Portman DJ, Gass ML. Genitourinary syndrome of menopause: new terminology for vulvovaginal atrophy from the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health and The North American Menopause Society. Maturitas. 2014;79:349-354.
- Kaunitz AM, Manson JE. Management of menopausal symptoms. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126:859-876.
- Shifren JL. Genitourinary syndrome of menopause. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2018;61:508-516.
- Manson JE, Kaunitz AM. Menopause management—getting clinical care back on track. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:803-806.
- Kingsberg SA, Krychman M, Graham S, et al. The women’s EMPOWER survey: identifying women’s perceptions on vulvar and vaginal atrophy and its treatment. J Sex Med. 2017;14:413-424.
- The NAMS 2017 Hormone Therapy Position Statement Advisory Panel. The 2017 Hormone therapy position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2017;24:728-753.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG practice bulletin No. 141: Management of menopausal symptoms. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123:202-216.
- US Food and Drug Administration website. FDA warns against the use of energy-based devices to perform vaginal ‘rejuvenation’ or vaginal cosmetic procedures: FDA safety communication. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/safety-communications/fda-warns-against-use-energy-based-devices-perform-vaginal-rejuvenation-or-vaginal-cosmetic. Updated November 20, 2018. Accessed May 21, 2020.
- US Food and Drug Administration website. Letters to industry. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/industry-medical-devices/letters-industry. July 24, 2018. Accessed May 21, 2020
REPLENISH: Oral estradiol/progesterone slowed bone turnover as it cut VMS
Menopausal women with an intact uterus treated for a year with a daily, oral, single-pill formulation of estradiol and progesterone for the primary goal of reducing moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms showed evidence of reduced bone turnover in a post hoc, subgroup analysis of 157 women enrolled in the REPLENISH trial.
These findings “provide support for a potential skeletal benefit” when menopausal women with an intact uterus regularly used the tested estradiol plus progesterone formulation to treat moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms (VMS), Risa Kagan, MD, and associates wrote in an abstract released ahead of the study’s scheduled presentation at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG canceled the meeting, and released abstracts for press coverage.
The reductions reported for three different markers of bone turnover compared with placebo control after 6 and 12 months on treatment with a U.S.-marketed estradiol plus progesterone formulation were ”reassuring and in line with expectations” said Lubna Pal, MBBS, professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who was not involved with the study. But the findings fell short of addressing the more clinically relevant issue of whether the tested regimen reduces the rate of bone fractures.
“Only longer-term data can tell us whether this magnitude of effect is sustainable,” which would need to happen to cut fracture incidence, said Dr. Pal, who directs the menopause program at her center. “The reduction in bone-turnover markers is adequate, but magnitude alone doesn’t entirely explain a reduction in fractures.”
The bone-marker findings came from a post hoc analysis of data collected in REPLENISH (Safety and Efficacy Study of the Combination Estradiol and Progesterone to Treat Vasomotor Symptoms in Postmenopausal Women With an Intact Uterus), a phase 3 randomized trial run at 119 U.S. sites that during 2013-2015 enrolled 1,845 menopausal women aged 65 years with an intact uterus and with moderate to severe VMS. The researchers randomized women to alternative daily treatment regimens with a single, oral pill that combined a bioidentical form of 17 beta-estradiol at dosages of 1.0 mg/day, 0.50 mg/day, or 0.25 mg/day, and dosages of bioidentical progesterone at dosages of 100 mg/day or 50 mg/day, or to a placebo control arm; not every possible dosage combination underwent testing.
The original study’s primary safety endpoint was the incidence of endometrial hyperplasia after 12 months on treatment, and the results showed no such events in any dosage arm. The primary efficacy endpoints assessed the frequency and severity of VMS after 4 and 12 weeks on treatment, and the results showed that all four tested formulations of estradiol plus progesterone had similar, statistically significant effects on decreasing VMS frequency, and the four formulations reduced severity in a dose-dependent way (Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Jul;132[1]:161-70). Based in part on results from this pivotal trial, the 1-mg estradiol/100 mg progesterone formulation (Bijuva) received Food and Drug Administration marketing approval in late 2018.
The new analysis of bone-turnover markers focused on a subgroup of women selected from two of the drug-treated arms and control patients who had at least 50 moderate to severe VMS events per week at baseline, were at least 5 years out from their last menstrual period, and had data recorded for three markers of bone turnover at baseline, and after 6 and 12 months on treatment, according to the abstract published in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
The analysis included 56 women treated with 1.0 mg estradiol and 100 mg progesterone daily, 56 who received 0.5 mg estradiol and 100 mg progesterone daily, and 45 women in the placebo arm. It assessed changes from baseline in the on-treatment compared with placebo groups using immunoassays for bone-specific alkaline phosphatase (BSAP), C-terminal telopeptide of type 1 collagen (CTX-1), and N-terminal propeptide of type 1 procollagen (PINP). For this analysis, the researchers combined the two active-treatment arms, and found that all three markers showed statistically significant drops from baseline with treatment, compared with placebo at both 6- and 12-month follow-up. For all three markers, the declines on active treatment grew larger with time, and after 12 months the mean drops from baseline compared with placebo were an 18% relative reduction in BSAP, a 41% relative reduction in CTX-1, and a 29% relative reduction in PINP, reported Dr. Kagan, a gynecologist based in Berkeley, Calif., who is affiliated with the University of California San Francisco.
In addition to not yet providing more clinically meaningful results on bone fracture rates, Dr. Pal cited additional issues that limit interpretation of both these findings and the broader REPLENISH results. First, the new analysis of bone-turnover markers as reported in the abstract does not allow assessment of a possible dose-dependent effect on bone turnover. More importantly, while the full REPLENISH trial provided reassuring data on endometrial protection, it has not yet reported data on the other major safety concern of hormone replacement: the effects of treatment on breast cancer rates. “They need to show no harm” in breast tissue, Dr. Pal said in an interview. In addition, the positive effect reported on markers of bone turnover is not unique to this formulation. Other formulations with estrogen at similar dosages would have similar effects, she said.
Other considerations when using an oral formulation include the reduced risk for prothrombotic effects from estradiol when delivered transdermally instead of orally, although some women have trouble getting insurance coverage for transdermal formulations, Dr. Pal said. Oral estrogen is appropriate only for women without an elevated clotting risk. Daily progesterone treatment also is more problematic than a cyclical dosage regimen, but noncontinuous progesterone results in monthly bleeding, something that some women prefer to avoid. “I’m not convinced that continuous progesterone is a physiologic approach,” said Dr. Pal, a member of the Ob.Gyn. News editorial advisory board. In addition, some women may find the formulation attractive because both the estradiol and progesterone are bioidentical and not synthetic molecules.
In short, the oral estradiol plus progesterone formulation tested in REPLENISH “is another tool” that’s an option for selected menopausal women with a uterus. “The bone findings are in line with expectations and are reassuring. Long-term data are keenly awaited to understand whether the bone marker changes lead to fewer fractures. The impact of the treatment on breast safety will be especially important.” For women who want a bioidentical, oral option and to not have bleeding, the tested formulation can be an effective option providing both symptom benefit and endometrial protection, Dr. Pal said.
REPLENISH was funded by TherapeuticsMD, the company that markets the tested estradiol plus progesterone formulation (Bijuva). Dr. Kagan has been a consultant and adviser to and speaker on behalf of Therapeutics MD, and she has also been a consultant or adviser to or has spoken on behalf of AMAG, Amgen, Astellas, Lupin, Radius, and Warner Chilcott/Allergan, and she has received research funding from Endoceutics. Dr. Pal has been a consultant to Flow Health.
SOURCE: Kagan R et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May;135:62S. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000665076.20231.a8.
Menopausal women with an intact uterus treated for a year with a daily, oral, single-pill formulation of estradiol and progesterone for the primary goal of reducing moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms showed evidence of reduced bone turnover in a post hoc, subgroup analysis of 157 women enrolled in the REPLENISH trial.
These findings “provide support for a potential skeletal benefit” when menopausal women with an intact uterus regularly used the tested estradiol plus progesterone formulation to treat moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms (VMS), Risa Kagan, MD, and associates wrote in an abstract released ahead of the study’s scheduled presentation at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG canceled the meeting, and released abstracts for press coverage.
The reductions reported for three different markers of bone turnover compared with placebo control after 6 and 12 months on treatment with a U.S.-marketed estradiol plus progesterone formulation were ”reassuring and in line with expectations” said Lubna Pal, MBBS, professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who was not involved with the study. But the findings fell short of addressing the more clinically relevant issue of whether the tested regimen reduces the rate of bone fractures.
“Only longer-term data can tell us whether this magnitude of effect is sustainable,” which would need to happen to cut fracture incidence, said Dr. Pal, who directs the menopause program at her center. “The reduction in bone-turnover markers is adequate, but magnitude alone doesn’t entirely explain a reduction in fractures.”
The bone-marker findings came from a post hoc analysis of data collected in REPLENISH (Safety and Efficacy Study of the Combination Estradiol and Progesterone to Treat Vasomotor Symptoms in Postmenopausal Women With an Intact Uterus), a phase 3 randomized trial run at 119 U.S. sites that during 2013-2015 enrolled 1,845 menopausal women aged 65 years with an intact uterus and with moderate to severe VMS. The researchers randomized women to alternative daily treatment regimens with a single, oral pill that combined a bioidentical form of 17 beta-estradiol at dosages of 1.0 mg/day, 0.50 mg/day, or 0.25 mg/day, and dosages of bioidentical progesterone at dosages of 100 mg/day or 50 mg/day, or to a placebo control arm; not every possible dosage combination underwent testing.
The original study’s primary safety endpoint was the incidence of endometrial hyperplasia after 12 months on treatment, and the results showed no such events in any dosage arm. The primary efficacy endpoints assessed the frequency and severity of VMS after 4 and 12 weeks on treatment, and the results showed that all four tested formulations of estradiol plus progesterone had similar, statistically significant effects on decreasing VMS frequency, and the four formulations reduced severity in a dose-dependent way (Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Jul;132[1]:161-70). Based in part on results from this pivotal trial, the 1-mg estradiol/100 mg progesterone formulation (Bijuva) received Food and Drug Administration marketing approval in late 2018.
The new analysis of bone-turnover markers focused on a subgroup of women selected from two of the drug-treated arms and control patients who had at least 50 moderate to severe VMS events per week at baseline, were at least 5 years out from their last menstrual period, and had data recorded for three markers of bone turnover at baseline, and after 6 and 12 months on treatment, according to the abstract published in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
The analysis included 56 women treated with 1.0 mg estradiol and 100 mg progesterone daily, 56 who received 0.5 mg estradiol and 100 mg progesterone daily, and 45 women in the placebo arm. It assessed changes from baseline in the on-treatment compared with placebo groups using immunoassays for bone-specific alkaline phosphatase (BSAP), C-terminal telopeptide of type 1 collagen (CTX-1), and N-terminal propeptide of type 1 procollagen (PINP). For this analysis, the researchers combined the two active-treatment arms, and found that all three markers showed statistically significant drops from baseline with treatment, compared with placebo at both 6- and 12-month follow-up. For all three markers, the declines on active treatment grew larger with time, and after 12 months the mean drops from baseline compared with placebo were an 18% relative reduction in BSAP, a 41% relative reduction in CTX-1, and a 29% relative reduction in PINP, reported Dr. Kagan, a gynecologist based in Berkeley, Calif., who is affiliated with the University of California San Francisco.
In addition to not yet providing more clinically meaningful results on bone fracture rates, Dr. Pal cited additional issues that limit interpretation of both these findings and the broader REPLENISH results. First, the new analysis of bone-turnover markers as reported in the abstract does not allow assessment of a possible dose-dependent effect on bone turnover. More importantly, while the full REPLENISH trial provided reassuring data on endometrial protection, it has not yet reported data on the other major safety concern of hormone replacement: the effects of treatment on breast cancer rates. “They need to show no harm” in breast tissue, Dr. Pal said in an interview. In addition, the positive effect reported on markers of bone turnover is not unique to this formulation. Other formulations with estrogen at similar dosages would have similar effects, she said.
Other considerations when using an oral formulation include the reduced risk for prothrombotic effects from estradiol when delivered transdermally instead of orally, although some women have trouble getting insurance coverage for transdermal formulations, Dr. Pal said. Oral estrogen is appropriate only for women without an elevated clotting risk. Daily progesterone treatment also is more problematic than a cyclical dosage regimen, but noncontinuous progesterone results in monthly bleeding, something that some women prefer to avoid. “I’m not convinced that continuous progesterone is a physiologic approach,” said Dr. Pal, a member of the Ob.Gyn. News editorial advisory board. In addition, some women may find the formulation attractive because both the estradiol and progesterone are bioidentical and not synthetic molecules.
In short, the oral estradiol plus progesterone formulation tested in REPLENISH “is another tool” that’s an option for selected menopausal women with a uterus. “The bone findings are in line with expectations and are reassuring. Long-term data are keenly awaited to understand whether the bone marker changes lead to fewer fractures. The impact of the treatment on breast safety will be especially important.” For women who want a bioidentical, oral option and to not have bleeding, the tested formulation can be an effective option providing both symptom benefit and endometrial protection, Dr. Pal said.
REPLENISH was funded by TherapeuticsMD, the company that markets the tested estradiol plus progesterone formulation (Bijuva). Dr. Kagan has been a consultant and adviser to and speaker on behalf of Therapeutics MD, and she has also been a consultant or adviser to or has spoken on behalf of AMAG, Amgen, Astellas, Lupin, Radius, and Warner Chilcott/Allergan, and she has received research funding from Endoceutics. Dr. Pal has been a consultant to Flow Health.
SOURCE: Kagan R et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May;135:62S. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000665076.20231.a8.
Menopausal women with an intact uterus treated for a year with a daily, oral, single-pill formulation of estradiol and progesterone for the primary goal of reducing moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms showed evidence of reduced bone turnover in a post hoc, subgroup analysis of 157 women enrolled in the REPLENISH trial.
These findings “provide support for a potential skeletal benefit” when menopausal women with an intact uterus regularly used the tested estradiol plus progesterone formulation to treat moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms (VMS), Risa Kagan, MD, and associates wrote in an abstract released ahead of the study’s scheduled presentation at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG canceled the meeting, and released abstracts for press coverage.
The reductions reported for three different markers of bone turnover compared with placebo control after 6 and 12 months on treatment with a U.S.-marketed estradiol plus progesterone formulation were ”reassuring and in line with expectations” said Lubna Pal, MBBS, professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who was not involved with the study. But the findings fell short of addressing the more clinically relevant issue of whether the tested regimen reduces the rate of bone fractures.
“Only longer-term data can tell us whether this magnitude of effect is sustainable,” which would need to happen to cut fracture incidence, said Dr. Pal, who directs the menopause program at her center. “The reduction in bone-turnover markers is adequate, but magnitude alone doesn’t entirely explain a reduction in fractures.”
The bone-marker findings came from a post hoc analysis of data collected in REPLENISH (Safety and Efficacy Study of the Combination Estradiol and Progesterone to Treat Vasomotor Symptoms in Postmenopausal Women With an Intact Uterus), a phase 3 randomized trial run at 119 U.S. sites that during 2013-2015 enrolled 1,845 menopausal women aged 65 years with an intact uterus and with moderate to severe VMS. The researchers randomized women to alternative daily treatment regimens with a single, oral pill that combined a bioidentical form of 17 beta-estradiol at dosages of 1.0 mg/day, 0.50 mg/day, or 0.25 mg/day, and dosages of bioidentical progesterone at dosages of 100 mg/day or 50 mg/day, or to a placebo control arm; not every possible dosage combination underwent testing.
The original study’s primary safety endpoint was the incidence of endometrial hyperplasia after 12 months on treatment, and the results showed no such events in any dosage arm. The primary efficacy endpoints assessed the frequency and severity of VMS after 4 and 12 weeks on treatment, and the results showed that all four tested formulations of estradiol plus progesterone had similar, statistically significant effects on decreasing VMS frequency, and the four formulations reduced severity in a dose-dependent way (Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Jul;132[1]:161-70). Based in part on results from this pivotal trial, the 1-mg estradiol/100 mg progesterone formulation (Bijuva) received Food and Drug Administration marketing approval in late 2018.
The new analysis of bone-turnover markers focused on a subgroup of women selected from two of the drug-treated arms and control patients who had at least 50 moderate to severe VMS events per week at baseline, were at least 5 years out from their last menstrual period, and had data recorded for three markers of bone turnover at baseline, and after 6 and 12 months on treatment, according to the abstract published in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
The analysis included 56 women treated with 1.0 mg estradiol and 100 mg progesterone daily, 56 who received 0.5 mg estradiol and 100 mg progesterone daily, and 45 women in the placebo arm. It assessed changes from baseline in the on-treatment compared with placebo groups using immunoassays for bone-specific alkaline phosphatase (BSAP), C-terminal telopeptide of type 1 collagen (CTX-1), and N-terminal propeptide of type 1 procollagen (PINP). For this analysis, the researchers combined the two active-treatment arms, and found that all three markers showed statistically significant drops from baseline with treatment, compared with placebo at both 6- and 12-month follow-up. For all three markers, the declines on active treatment grew larger with time, and after 12 months the mean drops from baseline compared with placebo were an 18% relative reduction in BSAP, a 41% relative reduction in CTX-1, and a 29% relative reduction in PINP, reported Dr. Kagan, a gynecologist based in Berkeley, Calif., who is affiliated with the University of California San Francisco.
In addition to not yet providing more clinically meaningful results on bone fracture rates, Dr. Pal cited additional issues that limit interpretation of both these findings and the broader REPLENISH results. First, the new analysis of bone-turnover markers as reported in the abstract does not allow assessment of a possible dose-dependent effect on bone turnover. More importantly, while the full REPLENISH trial provided reassuring data on endometrial protection, it has not yet reported data on the other major safety concern of hormone replacement: the effects of treatment on breast cancer rates. “They need to show no harm” in breast tissue, Dr. Pal said in an interview. In addition, the positive effect reported on markers of bone turnover is not unique to this formulation. Other formulations with estrogen at similar dosages would have similar effects, she said.
Other considerations when using an oral formulation include the reduced risk for prothrombotic effects from estradiol when delivered transdermally instead of orally, although some women have trouble getting insurance coverage for transdermal formulations, Dr. Pal said. Oral estrogen is appropriate only for women without an elevated clotting risk. Daily progesterone treatment also is more problematic than a cyclical dosage regimen, but noncontinuous progesterone results in monthly bleeding, something that some women prefer to avoid. “I’m not convinced that continuous progesterone is a physiologic approach,” said Dr. Pal, a member of the Ob.Gyn. News editorial advisory board. In addition, some women may find the formulation attractive because both the estradiol and progesterone are bioidentical and not synthetic molecules.
In short, the oral estradiol plus progesterone formulation tested in REPLENISH “is another tool” that’s an option for selected menopausal women with a uterus. “The bone findings are in line with expectations and are reassuring. Long-term data are keenly awaited to understand whether the bone marker changes lead to fewer fractures. The impact of the treatment on breast safety will be especially important.” For women who want a bioidentical, oral option and to not have bleeding, the tested formulation can be an effective option providing both symptom benefit and endometrial protection, Dr. Pal said.
REPLENISH was funded by TherapeuticsMD, the company that markets the tested estradiol plus progesterone formulation (Bijuva). Dr. Kagan has been a consultant and adviser to and speaker on behalf of Therapeutics MD, and she has also been a consultant or adviser to or has spoken on behalf of AMAG, Amgen, Astellas, Lupin, Radius, and Warner Chilcott/Allergan, and she has received research funding from Endoceutics. Dr. Pal has been a consultant to Flow Health.
SOURCE: Kagan R et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May;135:62S. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000665076.20231.a8.
FROM ACOG 2020
Fezolinetant safe, effective for menopausal vasomotor symptoms
The selective neurokinin 3 receptor antagonist Graeme L. Fraser, PhD, of Ogeda, a subsidiary of Astellas Pharma, and associates reported in Menopause.
The investigators conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging, parallel-group study between July 19, 2017, and Sept. 19, 2018, in 287 women who completed the full 12-week trial. The women were aged between 41 and 65 years, were menopausal, and had moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms (VMS) with an incidence of at least 50 episodes per week. The majority of the women were white, 25% were black, 1% were Asian, and 1% were “other.”
The reduction in VMS episodes in patients who received fezolinetant ranged from 1.9 to 3.5 episodes per day at week 4 and from 1.8 to 2.6 per day at week 12. The mean difference from placebo in VMS severity score was –0.4 to –1 at week 4 and was –0.2 to –0.6 at week 12. At least a 50% reduction in VMS frequency at week 12 was achieved by 81%-95% of patients who received fezolinetant, compared with 59% of those who received placebo.
Treatment-emergent adverse events were generally mild to moderate, with the most common events including nausea, diarrhea, fatigue, urinary tract infection, upper respiratory tract infections, sinusitis, headache, and cough. Of the five severe adverse events reported, only two were considered related to treatment – cholelithiasis and drug-induced liver injury. A total of 21 patients discontinued because of adverse events.
“Further evaluation of fezolinetant in larger and longer phase 3 trials of women with VMS associated with menopause is warranted to more fully characterize its efficacy and safety profile,” Dr. Fraser and colleagues concluded.
The study was funded by Astellas Pharma. The investigators reported numerous conflicts of interest with pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Fraser GL et al. Menopause. 2020 Feb 24. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000001510.
The selective neurokinin 3 receptor antagonist Graeme L. Fraser, PhD, of Ogeda, a subsidiary of Astellas Pharma, and associates reported in Menopause.
The investigators conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging, parallel-group study between July 19, 2017, and Sept. 19, 2018, in 287 women who completed the full 12-week trial. The women were aged between 41 and 65 years, were menopausal, and had moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms (VMS) with an incidence of at least 50 episodes per week. The majority of the women were white, 25% were black, 1% were Asian, and 1% were “other.”
The reduction in VMS episodes in patients who received fezolinetant ranged from 1.9 to 3.5 episodes per day at week 4 and from 1.8 to 2.6 per day at week 12. The mean difference from placebo in VMS severity score was –0.4 to –1 at week 4 and was –0.2 to –0.6 at week 12. At least a 50% reduction in VMS frequency at week 12 was achieved by 81%-95% of patients who received fezolinetant, compared with 59% of those who received placebo.
Treatment-emergent adverse events were generally mild to moderate, with the most common events including nausea, diarrhea, fatigue, urinary tract infection, upper respiratory tract infections, sinusitis, headache, and cough. Of the five severe adverse events reported, only two were considered related to treatment – cholelithiasis and drug-induced liver injury. A total of 21 patients discontinued because of adverse events.
“Further evaluation of fezolinetant in larger and longer phase 3 trials of women with VMS associated with menopause is warranted to more fully characterize its efficacy and safety profile,” Dr. Fraser and colleagues concluded.
The study was funded by Astellas Pharma. The investigators reported numerous conflicts of interest with pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Fraser GL et al. Menopause. 2020 Feb 24. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000001510.
The selective neurokinin 3 receptor antagonist Graeme L. Fraser, PhD, of Ogeda, a subsidiary of Astellas Pharma, and associates reported in Menopause.
The investigators conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging, parallel-group study between July 19, 2017, and Sept. 19, 2018, in 287 women who completed the full 12-week trial. The women were aged between 41 and 65 years, were menopausal, and had moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms (VMS) with an incidence of at least 50 episodes per week. The majority of the women were white, 25% were black, 1% were Asian, and 1% were “other.”
The reduction in VMS episodes in patients who received fezolinetant ranged from 1.9 to 3.5 episodes per day at week 4 and from 1.8 to 2.6 per day at week 12. The mean difference from placebo in VMS severity score was –0.4 to –1 at week 4 and was –0.2 to –0.6 at week 12. At least a 50% reduction in VMS frequency at week 12 was achieved by 81%-95% of patients who received fezolinetant, compared with 59% of those who received placebo.
Treatment-emergent adverse events were generally mild to moderate, with the most common events including nausea, diarrhea, fatigue, urinary tract infection, upper respiratory tract infections, sinusitis, headache, and cough. Of the five severe adverse events reported, only two were considered related to treatment – cholelithiasis and drug-induced liver injury. A total of 21 patients discontinued because of adverse events.
“Further evaluation of fezolinetant in larger and longer phase 3 trials of women with VMS associated with menopause is warranted to more fully characterize its efficacy and safety profile,” Dr. Fraser and colleagues concluded.
The study was funded by Astellas Pharma. The investigators reported numerous conflicts of interest with pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Fraser GL et al. Menopause. 2020 Feb 24. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000001510.
FROM MENOPAUSE
Beginning estrogen soon after menopause slows atherosclerosis progression
PHOENIX – Oral estrogen therapy taken within 6 years after the onset of menopause significantly reduced progression of lipid deposition in the carotid arterial wall, compared with placebo. However, starting oral estrogen 10 years after menopause did not confer a similar benefit.
“The clinical practice of estradiol therapy has been nothing short of a roller coaster ride,” lead study author Roksana Karim, PhD, MBBS, said in an interview at the Epidemiology and Prevention/Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health meeting sponsored by the American Heart Association. “Clinicians have been sort of conservative in terms of prescribing estradiol therapy. But over the last 2 decades things have changed, and eventually the timing hypothesis evolved based on the final analysis of the Women’s Health Initiative results as well.”
The findings come from a secondary analysis of the Early Versus Late Intervention Trial With Estradiol (ELITE), which examined the effects of oral 17-beta-estradiol (estrogen) on the progression of early atherosclerosis and cognitive decline in healthy postmenopausal women.
In the original trial, 643 healthy postmenopausal women were randomized to receive 1 mg/day of estradiol or a placebo pill either within 6 years after the onset of menopause or more than a decade after menopause (N Engl J Med 2016;374[13]:1221-31). All study participants took estradiol or placebo daily for an average of 5 years. The study’s initial findings showed that the mean carotid intima-media thickness progression rate was decreased by 0.0034 mm per year with estradiol, compared with placebo, but only in women who initiated hormone therapy within 6 years of menopause onset.
For the current analysis, researchers led by Dr. Karim looked further into estradiol’s impact on heart health by using echogenicity to analyze lipids in the arterial wall among the ELITE participants. The main outcome of interest was gray-scale median (GSM, unitless), a qualitative measure of atherosclerosis based on echogenicity obtained by high-resolution ultrasonography of the common carotid arterial wall. Whereas higher GSM values result with plaques rich in calcium and fibrous tissue, lower GSM values indicate more lipid deposition.
Dr. Karim, an associate professor of clinical preventive medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and colleagues assessed GSM and serum concentrations of estradiol every 6 months over a median 5-year trial period, and used linear mixed effects regression models to compare the rate of GSM progression between the randomized groups within time-since-menopause strata.
The researchers found that effect of estradiol on the annual rate of GSM progression significantly differed between women in the early and late postmenopause groups (P for interaction = .006). Specifically, the annual GSM progression rate among women in early postmenopause fell by 0.30 per year in women taking estradiol, compared with 1.41 per year in those in the placebo group (P less than .0001), indicating significantly more atherosclerosis in the placebo group. On the other hand, the annual GSM progression rate was not significantly different between the estradiol and placebo groups among the late postmenopausal women (P = .37).
“I think this should comfort clinicians in terms of prescribing estradiol therapy to women who don’t have any contraindications and who are within 6 years of menopause,” Dr. Karim said. “Accumulation of lipids is the key event for atherosclerosis progression.” She and her colleagues also observed that the positive association between mean on-trial serum estradiol levels and GSM progression rate was stronger and significant among early postmenopausal women (P = .008), compared with women in the late postmenopausal group (P = .003). However, this differential association between estradiol level and GSM progression rate was not statistically significant (P for interaction = .33).
“This study is important and raises a critical question: Is there a time period where getting hormone therapy would be most beneficial for the heart?” Nieca Goldberg, MD, medical director of the New York University women’s heart program and senior advisor for women’s health strategy at NYU Langone Health, said in an interview. “I think more studies and more analyses are needed, but we haven’t changed the indications for estradiol. We’re not giving estradiol to prevent progression of heart disease. We use estradiol hormone therapy as indicated for women who are having menopausal symptoms.”
Dr. Karim and colleagues plan to conduct a follow-up analysis from the same cohort of ELITE study participants to validate the findings by assessing lipid particles and markers of inflammation.
She reported having no financial disclosures. The study was funded by the National Institute on Aging.
SOURCE: Karim R et al. Epi/Lifestyle 2020, Abstract MP09.
PHOENIX – Oral estrogen therapy taken within 6 years after the onset of menopause significantly reduced progression of lipid deposition in the carotid arterial wall, compared with placebo. However, starting oral estrogen 10 years after menopause did not confer a similar benefit.
“The clinical practice of estradiol therapy has been nothing short of a roller coaster ride,” lead study author Roksana Karim, PhD, MBBS, said in an interview at the Epidemiology and Prevention/Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health meeting sponsored by the American Heart Association. “Clinicians have been sort of conservative in terms of prescribing estradiol therapy. But over the last 2 decades things have changed, and eventually the timing hypothesis evolved based on the final analysis of the Women’s Health Initiative results as well.”
The findings come from a secondary analysis of the Early Versus Late Intervention Trial With Estradiol (ELITE), which examined the effects of oral 17-beta-estradiol (estrogen) on the progression of early atherosclerosis and cognitive decline in healthy postmenopausal women.
In the original trial, 643 healthy postmenopausal women were randomized to receive 1 mg/day of estradiol or a placebo pill either within 6 years after the onset of menopause or more than a decade after menopause (N Engl J Med 2016;374[13]:1221-31). All study participants took estradiol or placebo daily for an average of 5 years. The study’s initial findings showed that the mean carotid intima-media thickness progression rate was decreased by 0.0034 mm per year with estradiol, compared with placebo, but only in women who initiated hormone therapy within 6 years of menopause onset.
For the current analysis, researchers led by Dr. Karim looked further into estradiol’s impact on heart health by using echogenicity to analyze lipids in the arterial wall among the ELITE participants. The main outcome of interest was gray-scale median (GSM, unitless), a qualitative measure of atherosclerosis based on echogenicity obtained by high-resolution ultrasonography of the common carotid arterial wall. Whereas higher GSM values result with plaques rich in calcium and fibrous tissue, lower GSM values indicate more lipid deposition.
Dr. Karim, an associate professor of clinical preventive medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and colleagues assessed GSM and serum concentrations of estradiol every 6 months over a median 5-year trial period, and used linear mixed effects regression models to compare the rate of GSM progression between the randomized groups within time-since-menopause strata.
The researchers found that effect of estradiol on the annual rate of GSM progression significantly differed between women in the early and late postmenopause groups (P for interaction = .006). Specifically, the annual GSM progression rate among women in early postmenopause fell by 0.30 per year in women taking estradiol, compared with 1.41 per year in those in the placebo group (P less than .0001), indicating significantly more atherosclerosis in the placebo group. On the other hand, the annual GSM progression rate was not significantly different between the estradiol and placebo groups among the late postmenopausal women (P = .37).
“I think this should comfort clinicians in terms of prescribing estradiol therapy to women who don’t have any contraindications and who are within 6 years of menopause,” Dr. Karim said. “Accumulation of lipids is the key event for atherosclerosis progression.” She and her colleagues also observed that the positive association between mean on-trial serum estradiol levels and GSM progression rate was stronger and significant among early postmenopausal women (P = .008), compared with women in the late postmenopausal group (P = .003). However, this differential association between estradiol level and GSM progression rate was not statistically significant (P for interaction = .33).
“This study is important and raises a critical question: Is there a time period where getting hormone therapy would be most beneficial for the heart?” Nieca Goldberg, MD, medical director of the New York University women’s heart program and senior advisor for women’s health strategy at NYU Langone Health, said in an interview. “I think more studies and more analyses are needed, but we haven’t changed the indications for estradiol. We’re not giving estradiol to prevent progression of heart disease. We use estradiol hormone therapy as indicated for women who are having menopausal symptoms.”
Dr. Karim and colleagues plan to conduct a follow-up analysis from the same cohort of ELITE study participants to validate the findings by assessing lipid particles and markers of inflammation.
She reported having no financial disclosures. The study was funded by the National Institute on Aging.
SOURCE: Karim R et al. Epi/Lifestyle 2020, Abstract MP09.
PHOENIX – Oral estrogen therapy taken within 6 years after the onset of menopause significantly reduced progression of lipid deposition in the carotid arterial wall, compared with placebo. However, starting oral estrogen 10 years after menopause did not confer a similar benefit.
“The clinical practice of estradiol therapy has been nothing short of a roller coaster ride,” lead study author Roksana Karim, PhD, MBBS, said in an interview at the Epidemiology and Prevention/Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health meeting sponsored by the American Heart Association. “Clinicians have been sort of conservative in terms of prescribing estradiol therapy. But over the last 2 decades things have changed, and eventually the timing hypothesis evolved based on the final analysis of the Women’s Health Initiative results as well.”
The findings come from a secondary analysis of the Early Versus Late Intervention Trial With Estradiol (ELITE), which examined the effects of oral 17-beta-estradiol (estrogen) on the progression of early atherosclerosis and cognitive decline in healthy postmenopausal women.
In the original trial, 643 healthy postmenopausal women were randomized to receive 1 mg/day of estradiol or a placebo pill either within 6 years after the onset of menopause or more than a decade after menopause (N Engl J Med 2016;374[13]:1221-31). All study participants took estradiol or placebo daily for an average of 5 years. The study’s initial findings showed that the mean carotid intima-media thickness progression rate was decreased by 0.0034 mm per year with estradiol, compared with placebo, but only in women who initiated hormone therapy within 6 years of menopause onset.
For the current analysis, researchers led by Dr. Karim looked further into estradiol’s impact on heart health by using echogenicity to analyze lipids in the arterial wall among the ELITE participants. The main outcome of interest was gray-scale median (GSM, unitless), a qualitative measure of atherosclerosis based on echogenicity obtained by high-resolution ultrasonography of the common carotid arterial wall. Whereas higher GSM values result with plaques rich in calcium and fibrous tissue, lower GSM values indicate more lipid deposition.
Dr. Karim, an associate professor of clinical preventive medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and colleagues assessed GSM and serum concentrations of estradiol every 6 months over a median 5-year trial period, and used linear mixed effects regression models to compare the rate of GSM progression between the randomized groups within time-since-menopause strata.
The researchers found that effect of estradiol on the annual rate of GSM progression significantly differed between women in the early and late postmenopause groups (P for interaction = .006). Specifically, the annual GSM progression rate among women in early postmenopause fell by 0.30 per year in women taking estradiol, compared with 1.41 per year in those in the placebo group (P less than .0001), indicating significantly more atherosclerosis in the placebo group. On the other hand, the annual GSM progression rate was not significantly different between the estradiol and placebo groups among the late postmenopausal women (P = .37).
“I think this should comfort clinicians in terms of prescribing estradiol therapy to women who don’t have any contraindications and who are within 6 years of menopause,” Dr. Karim said. “Accumulation of lipids is the key event for atherosclerosis progression.” She and her colleagues also observed that the positive association between mean on-trial serum estradiol levels and GSM progression rate was stronger and significant among early postmenopausal women (P = .008), compared with women in the late postmenopausal group (P = .003). However, this differential association between estradiol level and GSM progression rate was not statistically significant (P for interaction = .33).
“This study is important and raises a critical question: Is there a time period where getting hormone therapy would be most beneficial for the heart?” Nieca Goldberg, MD, medical director of the New York University women’s heart program and senior advisor for women’s health strategy at NYU Langone Health, said in an interview. “I think more studies and more analyses are needed, but we haven’t changed the indications for estradiol. We’re not giving estradiol to prevent progression of heart disease. We use estradiol hormone therapy as indicated for women who are having menopausal symptoms.”
Dr. Karim and colleagues plan to conduct a follow-up analysis from the same cohort of ELITE study participants to validate the findings by assessing lipid particles and markers of inflammation.
She reported having no financial disclosures. The study was funded by the National Institute on Aging.
SOURCE: Karim R et al. Epi/Lifestyle 2020, Abstract MP09.
REPORTING FROM EPI/LIFESTYLE 2020
Family history of MI may increase CVD mortality after bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy
Family history of premature MI (FHPMI) in women with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (BSO) modifies the increased mortality associated with heart disease and cardiovascular disease in those women, according to an analysis published in Menopause.
Duke Appiah, PhD, of the department of public health at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Lubbock, and colleagues drew data for 4,066 postmenopausal women aged 40 years and older from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III (1988-1994). Women were excluded if they had partial or unilateral oophorectomy; unknown or missing age at menopause; or prevalent MI, stroke, or heart failure, which left a sample of 2,763 women for the analysis.
Women with BSO were considered postmenopausal if they had not experienced a menstrual period within the previous 12 months. Women were asked whether any blood relatives, and especially any first-degree relatives, had a heart attack before age 50 years, which was considered premature MI. The average age at baseline was 62 years. Of those 2,763 women, 610 women had BSO, 338 had FHPMI, and 95 had both, which yields weighted proportions of 24%, 15%, and 5%, respectively.
When compared with having neither factor, presence of any FHPMI was modestly associated with increased risk of mortality from heart disease (HD), cardiovascular disease (CVD), and all causes in the multivariable adjusted analysis, and having undergone BSO was not significantly associated with any of those on its own. However, the combination of those two factors yielded much higher multivariable adjusted hazard ratios – HD mortality, 2.88; CVD mortality, 2.05; and all-cause mortality, 1.58.
These multivariable adjusted HRs were even more dramatic with first-degree FHPMI and BSO: 3.51 for HD mortality, 2.55 for CVD mortality, and 1.63 for all-cause mortality.
In the women who had the combination of FHPMI and BSO, the elevated risks of HD, CVD, and all-cause mortality “were stronger in women who underwent BSO before the age of 45 years than among those who had this procedure at or after the age of 45 years,” reported Dr. Appiah and colleagues. A significantly elevated risk of HD, CVD, or all-cause mortality was not evident in women with BSO alone “regardless of age at surgery.”
“This study provides additional evidence that removal of the ovaries before the natural age of menopause is associated with multiple adverse long-term health outcomes, including cardiovascular disease and early mortality and should be strongly discouraged in women who are not at increased genetic risk for ovarian cancer,” Stephanie Faubion, MD, medical director of North American of Menopause Science, commented in a press release. She was not involved in the study.
Limitations of the study include how FHPMI was self-reported; however, the investigators suggested that, given findings of other research regarding reporting family history (Genet Epidemiol. 1999;17:141-50), the true rate may actually have been underreported. The investigators cited the large, population-based sample size as one of the study’s strengths, suggesting it helps make the findings generalizable.
The investigators disclosed no external funding or conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Appiah D et al. Menopause. 2020 Feb. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000001522.
Family history of premature MI (FHPMI) in women with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (BSO) modifies the increased mortality associated with heart disease and cardiovascular disease in those women, according to an analysis published in Menopause.
Duke Appiah, PhD, of the department of public health at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Lubbock, and colleagues drew data for 4,066 postmenopausal women aged 40 years and older from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III (1988-1994). Women were excluded if they had partial or unilateral oophorectomy; unknown or missing age at menopause; or prevalent MI, stroke, or heart failure, which left a sample of 2,763 women for the analysis.
Women with BSO were considered postmenopausal if they had not experienced a menstrual period within the previous 12 months. Women were asked whether any blood relatives, and especially any first-degree relatives, had a heart attack before age 50 years, which was considered premature MI. The average age at baseline was 62 years. Of those 2,763 women, 610 women had BSO, 338 had FHPMI, and 95 had both, which yields weighted proportions of 24%, 15%, and 5%, respectively.
When compared with having neither factor, presence of any FHPMI was modestly associated with increased risk of mortality from heart disease (HD), cardiovascular disease (CVD), and all causes in the multivariable adjusted analysis, and having undergone BSO was not significantly associated with any of those on its own. However, the combination of those two factors yielded much higher multivariable adjusted hazard ratios – HD mortality, 2.88; CVD mortality, 2.05; and all-cause mortality, 1.58.
These multivariable adjusted HRs were even more dramatic with first-degree FHPMI and BSO: 3.51 for HD mortality, 2.55 for CVD mortality, and 1.63 for all-cause mortality.
In the women who had the combination of FHPMI and BSO, the elevated risks of HD, CVD, and all-cause mortality “were stronger in women who underwent BSO before the age of 45 years than among those who had this procedure at or after the age of 45 years,” reported Dr. Appiah and colleagues. A significantly elevated risk of HD, CVD, or all-cause mortality was not evident in women with BSO alone “regardless of age at surgery.”
“This study provides additional evidence that removal of the ovaries before the natural age of menopause is associated with multiple adverse long-term health outcomes, including cardiovascular disease and early mortality and should be strongly discouraged in women who are not at increased genetic risk for ovarian cancer,” Stephanie Faubion, MD, medical director of North American of Menopause Science, commented in a press release. She was not involved in the study.
Limitations of the study include how FHPMI was self-reported; however, the investigators suggested that, given findings of other research regarding reporting family history (Genet Epidemiol. 1999;17:141-50), the true rate may actually have been underreported. The investigators cited the large, population-based sample size as one of the study’s strengths, suggesting it helps make the findings generalizable.
The investigators disclosed no external funding or conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Appiah D et al. Menopause. 2020 Feb. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000001522.
Family history of premature MI (FHPMI) in women with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (BSO) modifies the increased mortality associated with heart disease and cardiovascular disease in those women, according to an analysis published in Menopause.
Duke Appiah, PhD, of the department of public health at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Lubbock, and colleagues drew data for 4,066 postmenopausal women aged 40 years and older from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III (1988-1994). Women were excluded if they had partial or unilateral oophorectomy; unknown or missing age at menopause; or prevalent MI, stroke, or heart failure, which left a sample of 2,763 women for the analysis.
Women with BSO were considered postmenopausal if they had not experienced a menstrual period within the previous 12 months. Women were asked whether any blood relatives, and especially any first-degree relatives, had a heart attack before age 50 years, which was considered premature MI. The average age at baseline was 62 years. Of those 2,763 women, 610 women had BSO, 338 had FHPMI, and 95 had both, which yields weighted proportions of 24%, 15%, and 5%, respectively.
When compared with having neither factor, presence of any FHPMI was modestly associated with increased risk of mortality from heart disease (HD), cardiovascular disease (CVD), and all causes in the multivariable adjusted analysis, and having undergone BSO was not significantly associated with any of those on its own. However, the combination of those two factors yielded much higher multivariable adjusted hazard ratios – HD mortality, 2.88; CVD mortality, 2.05; and all-cause mortality, 1.58.
These multivariable adjusted HRs were even more dramatic with first-degree FHPMI and BSO: 3.51 for HD mortality, 2.55 for CVD mortality, and 1.63 for all-cause mortality.
In the women who had the combination of FHPMI and BSO, the elevated risks of HD, CVD, and all-cause mortality “were stronger in women who underwent BSO before the age of 45 years than among those who had this procedure at or after the age of 45 years,” reported Dr. Appiah and colleagues. A significantly elevated risk of HD, CVD, or all-cause mortality was not evident in women with BSO alone “regardless of age at surgery.”
“This study provides additional evidence that removal of the ovaries before the natural age of menopause is associated with multiple adverse long-term health outcomes, including cardiovascular disease and early mortality and should be strongly discouraged in women who are not at increased genetic risk for ovarian cancer,” Stephanie Faubion, MD, medical director of North American of Menopause Science, commented in a press release. She was not involved in the study.
Limitations of the study include how FHPMI was self-reported; however, the investigators suggested that, given findings of other research regarding reporting family history (Genet Epidemiol. 1999;17:141-50), the true rate may actually have been underreported. The investigators cited the large, population-based sample size as one of the study’s strengths, suggesting it helps make the findings generalizable.
The investigators disclosed no external funding or conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Appiah D et al. Menopause. 2020 Feb. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000001522.
FROM MENOPAUSE
New guideline offers recommendations for reproductive health in patients with rheumatic diseases
A new guideline from the American College of Rheumatology offers the organization’s first clinical recommendations on how to manage reproductive health issues in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs).
“With the development of this guideline, the ACR recognizes the key role of clinical rheumatologists not only in managing disease activity but also in understanding the interactions of RMDs and their therapies in the context of reproductive health,” wrote Lisa R. Sammaritano, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine and the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, and coauthors. The guideline was published in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
To develop an evidence-based guideline on reproductive health in RMD patients, the researchers embarked on a systematic review of studies in areas like contraception, pregnancy and lactation, assisted reproductive technology (ART), fertility preservation, and hormone therapy. The guideline contains 12 ungraded good practice statements and 131 graded recommendations, all developed through the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation methodology.
In counseling patients about these areas of care, the guideline says that rheumatologists and other clinicians “must collaborate with specialists in the fields of obstetrics-gynecology, maternal-fetal medicine, and reproductive endocrinology and infertility.”
“One thing this guideline does well is highlight the importance of involving maternal-fetal medicine colleagues,” Alison Cahill, MD, a professor in the department of women’s health at the University of Texas at Austin and a maternal-fetal medicine specialist within UT Health Austin’s Women’s Health Institute, said when asked for comment on the guideline. “We’re always very happy to see patients ahead of time who are planning pregnancy to be able to discuss what the care plan would look like. And specifically, to address medications, if required, for their rheumatologic care.
“As we learn more and more,” she added, “we’ve come to understand that most treatments and medications are actually safe or relatively safe to take in pregnancy. Certainly, the benefit of taking them outweighs any small or theoretic risks. On the flip side, the guideline does a nice job of highlighting the importance of good disease control, both at the time of conception and during pregnancy.”
Contraception
In regard to contraception, the guideline strongly recommends the use of effective contraceptives – with a conditional recommendation of IUDs or a subdermal progestin implant – in fertile women with a RMD who have neither systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) nor positive antiphospholipid antibody (aPL). They also strongly recommend discussing the use of emergency contraception with all RMD patients.
For SLE patients, the guideline strongly recommends the use of effective contraceptives in those with stable or low disease activity who are not positive for aPL. They also strongly recommend progestin‐only or IUD contraceptives over combined estrogen‐progestin contraception. For aPL-positive patients, the guideline strongly recommends against combined estrogen‐progestin contraceptives and for levonorgestrel or copper IUDs or the progestin‐only pill.
Assisted reproductive technology
In regard to ART, the guideline strongly recommends proceeding as needed in aPL-negative women with uncomplicated, stable RMD who are on pregnancy‐compatible medications. They also strongly recommend deferring ART in any RMD patients with moderately or severely active disease.
For aPL-positive patients undergoing ART procedures, they strongly recommend prophylactic anticoagulation with heparin or low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) in women with obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and therapeutic anticoagulation in women with thrombotic APS. In patients undergoing embryo and oocyte cryopreservation, they strongly recommend continuing immunosuppressive and biologic therapies – the exception being cyclophosphamide (CYC) – for anyone in stable condition.
Fertility preservation
In regard to fertility preservation in patients taking CYC, the guideline strongly suggests sperm cryopreservation as good practice prior to treatment. They also conditionally recommend monthly gonadotropin‐releasing hormone agonist cotherapy in premenopausal women with RMD.
Hormone therapy
In regard to menopause and hormone therapy, the guideline strongly suggests hormone therapy as good practice in postmenopausal women with RMD, without SLE or positive aPL, and who have severe vasomotor symptoms. Hormone therapy is conditionally recommended in patients with SLE, without positive aPL, and with no contraindications. For aPL-positive patients, they strongly recommend against hormone therapy in women with obstetric and/or thrombotic APS.
Pregnancy assessment and management
Among the many recommendations regarding pregnancy assessment and management, the guideline strongly suggests counseling women with RMD who are considering pregnancy to take into account the improved outcomes for pregnant women with low disease activity. They strongly recommend that women considering pregnancy should switch to pregnancy‐compatible medication and pause to assess its efficacy and tolerability before moving forward, along with strongly recommending that pregnant women with active disease initiate or continue a pregnancy‐compatible steroid‐sparing medication. They also recommend testing for anti‐Ro/SS-A and anti‐La/SS-B in women with SLE, Sjögren’s syndrome, systemic sclerosis, or rheumatoid arthritis, but only once and only before or early in the pregnancy.
For women with systemic sclerosis who develop scleroderma renal crisis during pregnancy, the authors strongly advise using ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers “because the risk of maternal or fetal death with untreated disease is higher than the risk associated with use of these medications during pregnancy.”
Among women with SLE, the recommendations strongly call for testing either before or early in pregnancy for anticardiolipin antibody, anti–beta2-glycoprotein I, or positive lupus anticoagulant, as well as initiating or continuing hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) if possible. Starting in the first trimester, the authors also conditionally recommend that SLE patients take low-dose aspirin daily
For pregnant women who test positive for aPL but do not meet criteria for obstetric or thrombotic APS, the guideline conditionally recommends prophylactic treatment with low-dose aspirin daily to protect against preeclampsia. When obstetric APS criteria are met, the guideline strongly advises combined treatment with daily low-dose aspirin and prophylactic-dose heparin (or LMWH), as well as prophylactic-dose anticoagulation for 6-12 weeks post partum. When patients have thrombotic APS, this combination treatment should contain heparin dose at a therapeutic level throughout pregnancy and postpartum. However, the authors conditionally recommend against giving low-dose aspirin plus prophylactic-dose heparin to women without obstetric APS. For refractory obstetric APS, the guideline also contains recommendations that are conditionally against treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin or an increased LMWH dose and strongly against adding prednisone to prophylactic-dose heparin or LMWH and low-dose aspirin. In pregnant patients with primary APS, the authors conditionally advise adding HCQ to prophylactic-dose heparin or LMWH and low-dose aspirin therapy. However, women with aPL who do not meet APS criteria or have another indication for HCQ are conditionally advised against prophylactic treatment with the antimalarial.
For women with Anti-Ro/SS-A and/or anti-La/SS-B antibodies in pregnancy, there is conditional advice to use HCQ. When there is no history of an infant with complete heart block or neonatal lupus erythematosus among women with these antibodies, the guideline conditionally advises serial fetal echocardiography (less often than weekly) starting between 16 and 18 weeks and continuing through 26 weeks, but this should be weekly when there is a prior history. Treatment with oral dexamethasone 4 mg daily is conditionally advised when there is echocardiographic evidence of fetal first- or second-degree heart block, but dexamethasone is not recommended when complete heart block is present.
Finally, in regard to medication use, the authors strongly recommend that men who are planning to be fathers continue on HCQ, azathioprine, 6‐mercaptopurine, colchicine, or tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. Conditional treatment recommendations for men planning for pregnancy include methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil/mycophenolic acid (MMF), leflunomide, sulfasalazine, calcineurin inhibitors, and NSAIDs. They also strongly recommend that this group of men discontinue CYC and thalidomide.
Pregnant women are strongly recommended to discontinue methotrexate, leflunomide (with cholestyramine washout if there are detectable serum levels of its metabolite prior to pregnancy or as soon as it is confirmed), MMF, CYC, and thalidomide within 3 months prior to conception, and they strongly recommend HCQ (in women with SLE), azathioprine/6‐mercaptopurine, colchicine, or sulfasalazine for use throughout pregnancy. They strongly recommend a combination of low‐dose aspirin and prophylactic‐dose heparin for pregnant women with obstetric APS, along with low‐dose aspirin and therapeutic‐dose heparin for women with thrombotic APS throughout pregnancy and postpartum. However, for women with SLE and those who test positive for aPL but do not meet criteria for obstetric or thrombotic APS, the authors conditionally recommend low-dose aspirin starting in the first trimester.
The guideline suggests that women with RMD should be encouraged to breastfeed if they are willing and able; they also suggest that disease control be maintained through lactation‐compatible medications and that the risks and benefits be reviewed on a patient-by-patient basis. Treatment with HCQ, colchicine, sulfasalazine, rituximab, and all tumor necrosis factor inhibitors are strongly recommended as being compatible with breastfeeding, and they strongly recommend against using CYC, leflunomide, MMF, and thalidomide while breastfeeding.
The authors acknowledged the limitations of their guideline, including the literature review being conducted on studies involving adults and an “inability to include recommendations for uncommon but important clinical situations,” including those involving transgender patients and hormonal therapies.
The authors reported numerous potential conflicts of interest, including receiving research support, consulting fees, speaking fees, and honoraria from various pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Sammaritano LR et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Feb 23. doi: 10.1002/art.41191.
A new guideline from the American College of Rheumatology offers the organization’s first clinical recommendations on how to manage reproductive health issues in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs).
“With the development of this guideline, the ACR recognizes the key role of clinical rheumatologists not only in managing disease activity but also in understanding the interactions of RMDs and their therapies in the context of reproductive health,” wrote Lisa R. Sammaritano, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine and the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, and coauthors. The guideline was published in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
To develop an evidence-based guideline on reproductive health in RMD patients, the researchers embarked on a systematic review of studies in areas like contraception, pregnancy and lactation, assisted reproductive technology (ART), fertility preservation, and hormone therapy. The guideline contains 12 ungraded good practice statements and 131 graded recommendations, all developed through the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation methodology.
In counseling patients about these areas of care, the guideline says that rheumatologists and other clinicians “must collaborate with specialists in the fields of obstetrics-gynecology, maternal-fetal medicine, and reproductive endocrinology and infertility.”
“One thing this guideline does well is highlight the importance of involving maternal-fetal medicine colleagues,” Alison Cahill, MD, a professor in the department of women’s health at the University of Texas at Austin and a maternal-fetal medicine specialist within UT Health Austin’s Women’s Health Institute, said when asked for comment on the guideline. “We’re always very happy to see patients ahead of time who are planning pregnancy to be able to discuss what the care plan would look like. And specifically, to address medications, if required, for their rheumatologic care.
“As we learn more and more,” she added, “we’ve come to understand that most treatments and medications are actually safe or relatively safe to take in pregnancy. Certainly, the benefit of taking them outweighs any small or theoretic risks. On the flip side, the guideline does a nice job of highlighting the importance of good disease control, both at the time of conception and during pregnancy.”
Contraception
In regard to contraception, the guideline strongly recommends the use of effective contraceptives – with a conditional recommendation of IUDs or a subdermal progestin implant – in fertile women with a RMD who have neither systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) nor positive antiphospholipid antibody (aPL). They also strongly recommend discussing the use of emergency contraception with all RMD patients.
For SLE patients, the guideline strongly recommends the use of effective contraceptives in those with stable or low disease activity who are not positive for aPL. They also strongly recommend progestin‐only or IUD contraceptives over combined estrogen‐progestin contraception. For aPL-positive patients, the guideline strongly recommends against combined estrogen‐progestin contraceptives and for levonorgestrel or copper IUDs or the progestin‐only pill.
Assisted reproductive technology
In regard to ART, the guideline strongly recommends proceeding as needed in aPL-negative women with uncomplicated, stable RMD who are on pregnancy‐compatible medications. They also strongly recommend deferring ART in any RMD patients with moderately or severely active disease.
For aPL-positive patients undergoing ART procedures, they strongly recommend prophylactic anticoagulation with heparin or low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) in women with obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and therapeutic anticoagulation in women with thrombotic APS. In patients undergoing embryo and oocyte cryopreservation, they strongly recommend continuing immunosuppressive and biologic therapies – the exception being cyclophosphamide (CYC) – for anyone in stable condition.
Fertility preservation
In regard to fertility preservation in patients taking CYC, the guideline strongly suggests sperm cryopreservation as good practice prior to treatment. They also conditionally recommend monthly gonadotropin‐releasing hormone agonist cotherapy in premenopausal women with RMD.
Hormone therapy
In regard to menopause and hormone therapy, the guideline strongly suggests hormone therapy as good practice in postmenopausal women with RMD, without SLE or positive aPL, and who have severe vasomotor symptoms. Hormone therapy is conditionally recommended in patients with SLE, without positive aPL, and with no contraindications. For aPL-positive patients, they strongly recommend against hormone therapy in women with obstetric and/or thrombotic APS.
Pregnancy assessment and management
Among the many recommendations regarding pregnancy assessment and management, the guideline strongly suggests counseling women with RMD who are considering pregnancy to take into account the improved outcomes for pregnant women with low disease activity. They strongly recommend that women considering pregnancy should switch to pregnancy‐compatible medication and pause to assess its efficacy and tolerability before moving forward, along with strongly recommending that pregnant women with active disease initiate or continue a pregnancy‐compatible steroid‐sparing medication. They also recommend testing for anti‐Ro/SS-A and anti‐La/SS-B in women with SLE, Sjögren’s syndrome, systemic sclerosis, or rheumatoid arthritis, but only once and only before or early in the pregnancy.
For women with systemic sclerosis who develop scleroderma renal crisis during pregnancy, the authors strongly advise using ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers “because the risk of maternal or fetal death with untreated disease is higher than the risk associated with use of these medications during pregnancy.”
Among women with SLE, the recommendations strongly call for testing either before or early in pregnancy for anticardiolipin antibody, anti–beta2-glycoprotein I, or positive lupus anticoagulant, as well as initiating or continuing hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) if possible. Starting in the first trimester, the authors also conditionally recommend that SLE patients take low-dose aspirin daily
For pregnant women who test positive for aPL but do not meet criteria for obstetric or thrombotic APS, the guideline conditionally recommends prophylactic treatment with low-dose aspirin daily to protect against preeclampsia. When obstetric APS criteria are met, the guideline strongly advises combined treatment with daily low-dose aspirin and prophylactic-dose heparin (or LMWH), as well as prophylactic-dose anticoagulation for 6-12 weeks post partum. When patients have thrombotic APS, this combination treatment should contain heparin dose at a therapeutic level throughout pregnancy and postpartum. However, the authors conditionally recommend against giving low-dose aspirin plus prophylactic-dose heparin to women without obstetric APS. For refractory obstetric APS, the guideline also contains recommendations that are conditionally against treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin or an increased LMWH dose and strongly against adding prednisone to prophylactic-dose heparin or LMWH and low-dose aspirin. In pregnant patients with primary APS, the authors conditionally advise adding HCQ to prophylactic-dose heparin or LMWH and low-dose aspirin therapy. However, women with aPL who do not meet APS criteria or have another indication for HCQ are conditionally advised against prophylactic treatment with the antimalarial.
For women with Anti-Ro/SS-A and/or anti-La/SS-B antibodies in pregnancy, there is conditional advice to use HCQ. When there is no history of an infant with complete heart block or neonatal lupus erythematosus among women with these antibodies, the guideline conditionally advises serial fetal echocardiography (less often than weekly) starting between 16 and 18 weeks and continuing through 26 weeks, but this should be weekly when there is a prior history. Treatment with oral dexamethasone 4 mg daily is conditionally advised when there is echocardiographic evidence of fetal first- or second-degree heart block, but dexamethasone is not recommended when complete heart block is present.
Finally, in regard to medication use, the authors strongly recommend that men who are planning to be fathers continue on HCQ, azathioprine, 6‐mercaptopurine, colchicine, or tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. Conditional treatment recommendations for men planning for pregnancy include methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil/mycophenolic acid (MMF), leflunomide, sulfasalazine, calcineurin inhibitors, and NSAIDs. They also strongly recommend that this group of men discontinue CYC and thalidomide.
Pregnant women are strongly recommended to discontinue methotrexate, leflunomide (with cholestyramine washout if there are detectable serum levels of its metabolite prior to pregnancy or as soon as it is confirmed), MMF, CYC, and thalidomide within 3 months prior to conception, and they strongly recommend HCQ (in women with SLE), azathioprine/6‐mercaptopurine, colchicine, or sulfasalazine for use throughout pregnancy. They strongly recommend a combination of low‐dose aspirin and prophylactic‐dose heparin for pregnant women with obstetric APS, along with low‐dose aspirin and therapeutic‐dose heparin for women with thrombotic APS throughout pregnancy and postpartum. However, for women with SLE and those who test positive for aPL but do not meet criteria for obstetric or thrombotic APS, the authors conditionally recommend low-dose aspirin starting in the first trimester.
The guideline suggests that women with RMD should be encouraged to breastfeed if they are willing and able; they also suggest that disease control be maintained through lactation‐compatible medications and that the risks and benefits be reviewed on a patient-by-patient basis. Treatment with HCQ, colchicine, sulfasalazine, rituximab, and all tumor necrosis factor inhibitors are strongly recommended as being compatible with breastfeeding, and they strongly recommend against using CYC, leflunomide, MMF, and thalidomide while breastfeeding.
The authors acknowledged the limitations of their guideline, including the literature review being conducted on studies involving adults and an “inability to include recommendations for uncommon but important clinical situations,” including those involving transgender patients and hormonal therapies.
The authors reported numerous potential conflicts of interest, including receiving research support, consulting fees, speaking fees, and honoraria from various pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Sammaritano LR et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Feb 23. doi: 10.1002/art.41191.
A new guideline from the American College of Rheumatology offers the organization’s first clinical recommendations on how to manage reproductive health issues in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs).
“With the development of this guideline, the ACR recognizes the key role of clinical rheumatologists not only in managing disease activity but also in understanding the interactions of RMDs and their therapies in the context of reproductive health,” wrote Lisa R. Sammaritano, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine and the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, and coauthors. The guideline was published in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
To develop an evidence-based guideline on reproductive health in RMD patients, the researchers embarked on a systematic review of studies in areas like contraception, pregnancy and lactation, assisted reproductive technology (ART), fertility preservation, and hormone therapy. The guideline contains 12 ungraded good practice statements and 131 graded recommendations, all developed through the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation methodology.
In counseling patients about these areas of care, the guideline says that rheumatologists and other clinicians “must collaborate with specialists in the fields of obstetrics-gynecology, maternal-fetal medicine, and reproductive endocrinology and infertility.”
“One thing this guideline does well is highlight the importance of involving maternal-fetal medicine colleagues,” Alison Cahill, MD, a professor in the department of women’s health at the University of Texas at Austin and a maternal-fetal medicine specialist within UT Health Austin’s Women’s Health Institute, said when asked for comment on the guideline. “We’re always very happy to see patients ahead of time who are planning pregnancy to be able to discuss what the care plan would look like. And specifically, to address medications, if required, for their rheumatologic care.
“As we learn more and more,” she added, “we’ve come to understand that most treatments and medications are actually safe or relatively safe to take in pregnancy. Certainly, the benefit of taking them outweighs any small or theoretic risks. On the flip side, the guideline does a nice job of highlighting the importance of good disease control, both at the time of conception and during pregnancy.”
Contraception
In regard to contraception, the guideline strongly recommends the use of effective contraceptives – with a conditional recommendation of IUDs or a subdermal progestin implant – in fertile women with a RMD who have neither systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) nor positive antiphospholipid antibody (aPL). They also strongly recommend discussing the use of emergency contraception with all RMD patients.
For SLE patients, the guideline strongly recommends the use of effective contraceptives in those with stable or low disease activity who are not positive for aPL. They also strongly recommend progestin‐only or IUD contraceptives over combined estrogen‐progestin contraception. For aPL-positive patients, the guideline strongly recommends against combined estrogen‐progestin contraceptives and for levonorgestrel or copper IUDs or the progestin‐only pill.
Assisted reproductive technology
In regard to ART, the guideline strongly recommends proceeding as needed in aPL-negative women with uncomplicated, stable RMD who are on pregnancy‐compatible medications. They also strongly recommend deferring ART in any RMD patients with moderately or severely active disease.
For aPL-positive patients undergoing ART procedures, they strongly recommend prophylactic anticoagulation with heparin or low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) in women with obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and therapeutic anticoagulation in women with thrombotic APS. In patients undergoing embryo and oocyte cryopreservation, they strongly recommend continuing immunosuppressive and biologic therapies – the exception being cyclophosphamide (CYC) – for anyone in stable condition.
Fertility preservation
In regard to fertility preservation in patients taking CYC, the guideline strongly suggests sperm cryopreservation as good practice prior to treatment. They also conditionally recommend monthly gonadotropin‐releasing hormone agonist cotherapy in premenopausal women with RMD.
Hormone therapy
In regard to menopause and hormone therapy, the guideline strongly suggests hormone therapy as good practice in postmenopausal women with RMD, without SLE or positive aPL, and who have severe vasomotor symptoms. Hormone therapy is conditionally recommended in patients with SLE, without positive aPL, and with no contraindications. For aPL-positive patients, they strongly recommend against hormone therapy in women with obstetric and/or thrombotic APS.
Pregnancy assessment and management
Among the many recommendations regarding pregnancy assessment and management, the guideline strongly suggests counseling women with RMD who are considering pregnancy to take into account the improved outcomes for pregnant women with low disease activity. They strongly recommend that women considering pregnancy should switch to pregnancy‐compatible medication and pause to assess its efficacy and tolerability before moving forward, along with strongly recommending that pregnant women with active disease initiate or continue a pregnancy‐compatible steroid‐sparing medication. They also recommend testing for anti‐Ro/SS-A and anti‐La/SS-B in women with SLE, Sjögren’s syndrome, systemic sclerosis, or rheumatoid arthritis, but only once and only before or early in the pregnancy.
For women with systemic sclerosis who develop scleroderma renal crisis during pregnancy, the authors strongly advise using ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers “because the risk of maternal or fetal death with untreated disease is higher than the risk associated with use of these medications during pregnancy.”
Among women with SLE, the recommendations strongly call for testing either before or early in pregnancy for anticardiolipin antibody, anti–beta2-glycoprotein I, or positive lupus anticoagulant, as well as initiating or continuing hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) if possible. Starting in the first trimester, the authors also conditionally recommend that SLE patients take low-dose aspirin daily
For pregnant women who test positive for aPL but do not meet criteria for obstetric or thrombotic APS, the guideline conditionally recommends prophylactic treatment with low-dose aspirin daily to protect against preeclampsia. When obstetric APS criteria are met, the guideline strongly advises combined treatment with daily low-dose aspirin and prophylactic-dose heparin (or LMWH), as well as prophylactic-dose anticoagulation for 6-12 weeks post partum. When patients have thrombotic APS, this combination treatment should contain heparin dose at a therapeutic level throughout pregnancy and postpartum. However, the authors conditionally recommend against giving low-dose aspirin plus prophylactic-dose heparin to women without obstetric APS. For refractory obstetric APS, the guideline also contains recommendations that are conditionally against treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin or an increased LMWH dose and strongly against adding prednisone to prophylactic-dose heparin or LMWH and low-dose aspirin. In pregnant patients with primary APS, the authors conditionally advise adding HCQ to prophylactic-dose heparin or LMWH and low-dose aspirin therapy. However, women with aPL who do not meet APS criteria or have another indication for HCQ are conditionally advised against prophylactic treatment with the antimalarial.
For women with Anti-Ro/SS-A and/or anti-La/SS-B antibodies in pregnancy, there is conditional advice to use HCQ. When there is no history of an infant with complete heart block or neonatal lupus erythematosus among women with these antibodies, the guideline conditionally advises serial fetal echocardiography (less often than weekly) starting between 16 and 18 weeks and continuing through 26 weeks, but this should be weekly when there is a prior history. Treatment with oral dexamethasone 4 mg daily is conditionally advised when there is echocardiographic evidence of fetal first- or second-degree heart block, but dexamethasone is not recommended when complete heart block is present.
Finally, in regard to medication use, the authors strongly recommend that men who are planning to be fathers continue on HCQ, azathioprine, 6‐mercaptopurine, colchicine, or tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. Conditional treatment recommendations for men planning for pregnancy include methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil/mycophenolic acid (MMF), leflunomide, sulfasalazine, calcineurin inhibitors, and NSAIDs. They also strongly recommend that this group of men discontinue CYC and thalidomide.
Pregnant women are strongly recommended to discontinue methotrexate, leflunomide (with cholestyramine washout if there are detectable serum levels of its metabolite prior to pregnancy or as soon as it is confirmed), MMF, CYC, and thalidomide within 3 months prior to conception, and they strongly recommend HCQ (in women with SLE), azathioprine/6‐mercaptopurine, colchicine, or sulfasalazine for use throughout pregnancy. They strongly recommend a combination of low‐dose aspirin and prophylactic‐dose heparin for pregnant women with obstetric APS, along with low‐dose aspirin and therapeutic‐dose heparin for women with thrombotic APS throughout pregnancy and postpartum. However, for women with SLE and those who test positive for aPL but do not meet criteria for obstetric or thrombotic APS, the authors conditionally recommend low-dose aspirin starting in the first trimester.
The guideline suggests that women with RMD should be encouraged to breastfeed if they are willing and able; they also suggest that disease control be maintained through lactation‐compatible medications and that the risks and benefits be reviewed on a patient-by-patient basis. Treatment with HCQ, colchicine, sulfasalazine, rituximab, and all tumor necrosis factor inhibitors are strongly recommended as being compatible with breastfeeding, and they strongly recommend against using CYC, leflunomide, MMF, and thalidomide while breastfeeding.
The authors acknowledged the limitations of their guideline, including the literature review being conducted on studies involving adults and an “inability to include recommendations for uncommon but important clinical situations,” including those involving transgender patients and hormonal therapies.
The authors reported numerous potential conflicts of interest, including receiving research support, consulting fees, speaking fees, and honoraria from various pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Sammaritano LR et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Feb 23. doi: 10.1002/art.41191.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY
Progestin-only systemic hormone therapy for menopausal hot flashes
The field of menopause medicine is dominated by studies documenting the effectiveness of systemic estrogen or estrogen-progestin hormone therapy for the treatment of hot flashes caused by hypoestrogenism. The effectiveness of progestin-only systemic hormone therapy for the treatment of hot flashes is much less studied and seldom is utilized in clinical practice. A small number of studies have reported that progestins, including micronized progesterone, medroxyprogesterone acetate, and norethindrone acetate, are effective treatment for hot flashes. Progestin-only systemic hormone therapy might be especially helpful for postmenopausal women with moderate to severe hot flashes who have a contraindication to estrogen treatment.
Micronized progesterone
Micronized progesterone (Prometrium) 300 mg daily taken at bedtime has been reported to effectively treat hot flashes in postmenopausal women. In one study, 133 postmenopausal women with an average age of 55 years and approximately 3 years from their last menstrual period were randomly assigned to 12 weeks of treatment with placebo or micronized progesterone 300 mg daily taken at bedtime.1 Mean serum progesterone levels were 0.28 ng/mL (0.89 nM) and 27 ng/mL (86 nM) in the women taking placebo and micronized progesterone, respectively. Compared with placebo, micronized progesterone reduced daytime and nighttime hot flash frequency and severity. In addition, compared with placebo, micronized progesterone improved the quality of sleep.1
Most reviews conclude that micronized progesterone has minimal cardiovascular risk.2 Micronized progesterone therapy might be especially helpful for postmenopausal women with moderate to severe hot flashes who have a contraindication to estrogen treatment such as those at increased risk for cardiovascular disease or women with a thrombophilia. Many experts believe that systemic estrogen therapy is contraindicated in postmenopausal women with an American Heart Association risk score greater than 10% over 10 years.3 Additional contraindications to systemic estrogen include women with cardiac disease who have a thrombophilia, such as the Factor V Leiden mutation.4
For women who are at high risk for estrogen-induced cardiovascular events, micronized progesterone may be a better option than systemic estrogen for treating hot flashes. Alternatively, in these women at risk of cardiovascular disease a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, such as escitalopram, 10 mg to 20 mg daily, may be a good option for treating postmenopausal hot flashes.5
Medroxyprogesterone acetate
Medroxyprogesterone acetate, at a dosage of 20 mg daily, is an effective treatment for hot flashes. In a randomized clinical trial 27 postmenopausal women with hot flashes were randomly assigned to treatment with placebo or medroxyprogesterone acetate 20 mg daily for 4 weeks. Vasomotor flushes were decreased by 26% and 74% in the placebo and medroxyprogesterone groups, respectively.6
Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate injections at dosages from 150 mg to 400 mg also have been reported to effectively treat hot flashes.7,8 In a trial comparing the effectiveness of estrogen monotherapy (conjugated equine estrogen 0.6 mg daily) with progestin monotherapy (medroxyprogesterone acetate 10 mg daily), both treatments were equally effective in reducing hot flashes.9
Continue to: Micronized progesterone vs medroxyprogesterone acetate...
Micronized progesterone vs medroxyprogesterone acetate
Experts in menopause medicine have suggested that in postmenopausal women micronized progesterone has a better pattern of benefits and fewer risks than medroxyprogesterone acetate.10,11 For example, in the E3N observational study of hormones and breast cancer risk, among 80,377 French postmenopausal women followed for a mean of 8 years, the combination of transdermal estradiol plus oral micronized progesterone was associated with no significantly increased risk of breast cancer (relative risk [RR], 1.08, 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.89–1.31) compared with never users of postmenopausal hormone therapy.12 By contrast, the combination of oral estrogen plus medroxyprogesterone acetate was associated with an increased risk of breast cancer (RR, 1.48; 95% CI, 1.02–2.16) compared with never users of postmenopausal hormone therapy. The E3N study indicates that micronized progesterone may have a more favorable breast health profile than medroxyprogesterone acetate.12

Norethindrone acetate
Norethindrone acetate monotherapy is not commonly prescribed for the treatment of menopausal hot flashes. However, a large clinical trial has demonstrated that norethindrone acetate effectively suppresses hot flashes in women with endometriosis treated with depot leuprolide acetate (LA). In one trial 201 women with endometriosis were randomly assigned to 12 months of treatment with13:
- LA plus placebo pills
- LA plus norethindrone acetate (NEA) 5 mg daily
- LA plus NEA 5 mg daily plus conjugated equine estrogen (CEE) 0.625 mg daily, or
- LA plus NEA 5 mg daily plus CEE 1.25 mg daily.
The median number of hot flashes in 24 hours was 6 in the LA plus placebo group and 0 in both the LA plus NEA 5 mg daily group and the LA plus NEA 5 mg plus CEE 1.25 mg daily group. This study demonstrates that NEA 5 mg daily is an effective treatment for hot flashes.
In the same study, LA plus placebo was associated with a significant decrease in lumbar spine bone mineral density. No significant decrease in bone mineral density was observed in the women who received LA plus NEA 5 mg daily. This finding indicates that NEA 5 mg reduces bone absorption caused by hypoestrogenism. In humans, norethindrone is a substrate for the aromatase enzyme system.14 Small quantities of ethinyl estradiol may be formed by aromatization of norethindrone in vivo,15,16 contributing to the effectiveness of NEA in suppressing hot flashes and preserving bone density.
Progestin: The estrogen alternative to hot flashes
For postmenopausal women with moderate to severe hot flashes, estrogen treatment reliably suppresses hot flashes and often improves sleep quality and mood. For postmenopausal women with a contraindication to estrogen treatment, progestin-only treatment with micronized progesterone or norethindrone acetate may be an effective option.
- Hitchcock CL, Prior JC. Oral micronized progesterone for vasomotor symptoms—a placebo-controlled randomized trial in healthy postmenopausal women. Menopause. 2012;19:886-893.
- Spark MJ, Willis J. Systematic review of progesterone use by midlife menopausal women. Maturitas 2012; 72: 192-202.
- Manson JE, Ames JM, Shapiro M, et al. Algorithm and mobile app for menopausal symptom management and hormonal/nonhormonal therapy decision making: a clinical decision-suport tool from The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2015;22:247-253.
- Herrington DM, Vittinghoff E, Howard TD, et al. Factor V Leiden, hormone replacement therapy, and risk of venous thromboembolic events in women with coronary disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002;22:1012-1017.
- Ensrud KE, Joffe H, Guthrie KA, et al. Effect of escitalopram on insomnia symptoms and subjective sleep quality in healthy perimenopausal and postmenopausal women with hot flashes: a randomized controlled trial. Menopause. 2012;19:848-855.
- Schiff I, Tulchinsky D, Cramer D, et al. Oral medroxyprogesterone in the treatment of postmenopausal symptoms. JAMA. 1980;244:1443-1445.
- Bullock JL, Massey FM, Gambrell RD Jr. Use of medroxyprogesterone acetate to prevent menopausal symptoms. Obstet Gynecol. 1975;46:165-168.
- Loprinzi CL, Levitt R, Barton D, et al. Phase III comparison of depot medroxyprogesterone acetate to venlafaxine for managing hot flashes: North Central Cancer Treatment Group Trial N99C7. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:1409-1414.
- Prior JC, Nielsen JD, Hitchcock CL, et al. Medroxyprogesterone and conjugated oestrogen are equivalent for hot flushes: 1-year randomized double-blind trial following premenopausal ovariectomy. Clin Sci (Lond). 2007;112:517-525.
- L’hermite M, Simoncini T, Fuller S, et al. Could transdermal estradiol + progesterone be a safer postmenopausal HRT? A review. Maturitas. 2008;60:185-201.
- Simon JA. What if the Women’s Health Initiative had used transdermal estradiol and oral progesterone instead? Menopause. 2014;21:769-783.
- Fournier A, Berrino F, Clavel-Chapelon F. Unequal risks for breast cancer associated with different hormone replacement therapies: results from the E3N cohort study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008;107:103-111.
- Hornstein MD, Surrey ES, Weisberg GW, et al. Leuprolide acetate depot and hormonal add-back in endometriosis: a 12-month study. Lupron Add-Back Study Group. Obstet Gynecol. 1998;91:16-24.
- Barbieri RL, Canick JA, Ryan KJ. High-affinity steroid binding to rat testis 17 alpha-hydroxylase and human placental aromatase. J Steroid Biochem. 1981;14:387-393.
- Chu MC, Zhang X, Gentzschein E, et al. Formation of ethinyl estradiol in women during treatment with norethindrone acetate. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:2205-2207.
- Chwalisz K, Surrey E, Stanczyk FZ. The hormonal profile of norethindrone acetate: rationale for add-back therapy with gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists in women with endometriosis. Reprod Sci. 2012;19:563-571.
The field of menopause medicine is dominated by studies documenting the effectiveness of systemic estrogen or estrogen-progestin hormone therapy for the treatment of hot flashes caused by hypoestrogenism. The effectiveness of progestin-only systemic hormone therapy for the treatment of hot flashes is much less studied and seldom is utilized in clinical practice. A small number of studies have reported that progestins, including micronized progesterone, medroxyprogesterone acetate, and norethindrone acetate, are effective treatment for hot flashes. Progestin-only systemic hormone therapy might be especially helpful for postmenopausal women with moderate to severe hot flashes who have a contraindication to estrogen treatment.
Micronized progesterone
Micronized progesterone (Prometrium) 300 mg daily taken at bedtime has been reported to effectively treat hot flashes in postmenopausal women. In one study, 133 postmenopausal women with an average age of 55 years and approximately 3 years from their last menstrual period were randomly assigned to 12 weeks of treatment with placebo or micronized progesterone 300 mg daily taken at bedtime.1 Mean serum progesterone levels were 0.28 ng/mL (0.89 nM) and 27 ng/mL (86 nM) in the women taking placebo and micronized progesterone, respectively. Compared with placebo, micronized progesterone reduced daytime and nighttime hot flash frequency and severity. In addition, compared with placebo, micronized progesterone improved the quality of sleep.1
Most reviews conclude that micronized progesterone has minimal cardiovascular risk.2 Micronized progesterone therapy might be especially helpful for postmenopausal women with moderate to severe hot flashes who have a contraindication to estrogen treatment such as those at increased risk for cardiovascular disease or women with a thrombophilia. Many experts believe that systemic estrogen therapy is contraindicated in postmenopausal women with an American Heart Association risk score greater than 10% over 10 years.3 Additional contraindications to systemic estrogen include women with cardiac disease who have a thrombophilia, such as the Factor V Leiden mutation.4
For women who are at high risk for estrogen-induced cardiovascular events, micronized progesterone may be a better option than systemic estrogen for treating hot flashes. Alternatively, in these women at risk of cardiovascular disease a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, such as escitalopram, 10 mg to 20 mg daily, may be a good option for treating postmenopausal hot flashes.5
Medroxyprogesterone acetate
Medroxyprogesterone acetate, at a dosage of 20 mg daily, is an effective treatment for hot flashes. In a randomized clinical trial 27 postmenopausal women with hot flashes were randomly assigned to treatment with placebo or medroxyprogesterone acetate 20 mg daily for 4 weeks. Vasomotor flushes were decreased by 26% and 74% in the placebo and medroxyprogesterone groups, respectively.6
Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate injections at dosages from 150 mg to 400 mg also have been reported to effectively treat hot flashes.7,8 In a trial comparing the effectiveness of estrogen monotherapy (conjugated equine estrogen 0.6 mg daily) with progestin monotherapy (medroxyprogesterone acetate 10 mg daily), both treatments were equally effective in reducing hot flashes.9
Continue to: Micronized progesterone vs medroxyprogesterone acetate...
Micronized progesterone vs medroxyprogesterone acetate
Experts in menopause medicine have suggested that in postmenopausal women micronized progesterone has a better pattern of benefits and fewer risks than medroxyprogesterone acetate.10,11 For example, in the E3N observational study of hormones and breast cancer risk, among 80,377 French postmenopausal women followed for a mean of 8 years, the combination of transdermal estradiol plus oral micronized progesterone was associated with no significantly increased risk of breast cancer (relative risk [RR], 1.08, 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.89–1.31) compared with never users of postmenopausal hormone therapy.12 By contrast, the combination of oral estrogen plus medroxyprogesterone acetate was associated with an increased risk of breast cancer (RR, 1.48; 95% CI, 1.02–2.16) compared with never users of postmenopausal hormone therapy. The E3N study indicates that micronized progesterone may have a more favorable breast health profile than medroxyprogesterone acetate.12

Norethindrone acetate
Norethindrone acetate monotherapy is not commonly prescribed for the treatment of menopausal hot flashes. However, a large clinical trial has demonstrated that norethindrone acetate effectively suppresses hot flashes in women with endometriosis treated with depot leuprolide acetate (LA). In one trial 201 women with endometriosis were randomly assigned to 12 months of treatment with13:
- LA plus placebo pills
- LA plus norethindrone acetate (NEA) 5 mg daily
- LA plus NEA 5 mg daily plus conjugated equine estrogen (CEE) 0.625 mg daily, or
- LA plus NEA 5 mg daily plus CEE 1.25 mg daily.
The median number of hot flashes in 24 hours was 6 in the LA plus placebo group and 0 in both the LA plus NEA 5 mg daily group and the LA plus NEA 5 mg plus CEE 1.25 mg daily group. This study demonstrates that NEA 5 mg daily is an effective treatment for hot flashes.
In the same study, LA plus placebo was associated with a significant decrease in lumbar spine bone mineral density. No significant decrease in bone mineral density was observed in the women who received LA plus NEA 5 mg daily. This finding indicates that NEA 5 mg reduces bone absorption caused by hypoestrogenism. In humans, norethindrone is a substrate for the aromatase enzyme system.14 Small quantities of ethinyl estradiol may be formed by aromatization of norethindrone in vivo,15,16 contributing to the effectiveness of NEA in suppressing hot flashes and preserving bone density.
Progestin: The estrogen alternative to hot flashes
For postmenopausal women with moderate to severe hot flashes, estrogen treatment reliably suppresses hot flashes and often improves sleep quality and mood. For postmenopausal women with a contraindication to estrogen treatment, progestin-only treatment with micronized progesterone or norethindrone acetate may be an effective option.
The field of menopause medicine is dominated by studies documenting the effectiveness of systemic estrogen or estrogen-progestin hormone therapy for the treatment of hot flashes caused by hypoestrogenism. The effectiveness of progestin-only systemic hormone therapy for the treatment of hot flashes is much less studied and seldom is utilized in clinical practice. A small number of studies have reported that progestins, including micronized progesterone, medroxyprogesterone acetate, and norethindrone acetate, are effective treatment for hot flashes. Progestin-only systemic hormone therapy might be especially helpful for postmenopausal women with moderate to severe hot flashes who have a contraindication to estrogen treatment.
Micronized progesterone
Micronized progesterone (Prometrium) 300 mg daily taken at bedtime has been reported to effectively treat hot flashes in postmenopausal women. In one study, 133 postmenopausal women with an average age of 55 years and approximately 3 years from their last menstrual period were randomly assigned to 12 weeks of treatment with placebo or micronized progesterone 300 mg daily taken at bedtime.1 Mean serum progesterone levels were 0.28 ng/mL (0.89 nM) and 27 ng/mL (86 nM) in the women taking placebo and micronized progesterone, respectively. Compared with placebo, micronized progesterone reduced daytime and nighttime hot flash frequency and severity. In addition, compared with placebo, micronized progesterone improved the quality of sleep.1
Most reviews conclude that micronized progesterone has minimal cardiovascular risk.2 Micronized progesterone therapy might be especially helpful for postmenopausal women with moderate to severe hot flashes who have a contraindication to estrogen treatment such as those at increased risk for cardiovascular disease or women with a thrombophilia. Many experts believe that systemic estrogen therapy is contraindicated in postmenopausal women with an American Heart Association risk score greater than 10% over 10 years.3 Additional contraindications to systemic estrogen include women with cardiac disease who have a thrombophilia, such as the Factor V Leiden mutation.4
For women who are at high risk for estrogen-induced cardiovascular events, micronized progesterone may be a better option than systemic estrogen for treating hot flashes. Alternatively, in these women at risk of cardiovascular disease a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, such as escitalopram, 10 mg to 20 mg daily, may be a good option for treating postmenopausal hot flashes.5
Medroxyprogesterone acetate
Medroxyprogesterone acetate, at a dosage of 20 mg daily, is an effective treatment for hot flashes. In a randomized clinical trial 27 postmenopausal women with hot flashes were randomly assigned to treatment with placebo or medroxyprogesterone acetate 20 mg daily for 4 weeks. Vasomotor flushes were decreased by 26% and 74% in the placebo and medroxyprogesterone groups, respectively.6
Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate injections at dosages from 150 mg to 400 mg also have been reported to effectively treat hot flashes.7,8 In a trial comparing the effectiveness of estrogen monotherapy (conjugated equine estrogen 0.6 mg daily) with progestin monotherapy (medroxyprogesterone acetate 10 mg daily), both treatments were equally effective in reducing hot flashes.9
Continue to: Micronized progesterone vs medroxyprogesterone acetate...
Micronized progesterone vs medroxyprogesterone acetate
Experts in menopause medicine have suggested that in postmenopausal women micronized progesterone has a better pattern of benefits and fewer risks than medroxyprogesterone acetate.10,11 For example, in the E3N observational study of hormones and breast cancer risk, among 80,377 French postmenopausal women followed for a mean of 8 years, the combination of transdermal estradiol plus oral micronized progesterone was associated with no significantly increased risk of breast cancer (relative risk [RR], 1.08, 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.89–1.31) compared with never users of postmenopausal hormone therapy.12 By contrast, the combination of oral estrogen plus medroxyprogesterone acetate was associated with an increased risk of breast cancer (RR, 1.48; 95% CI, 1.02–2.16) compared with never users of postmenopausal hormone therapy. The E3N study indicates that micronized progesterone may have a more favorable breast health profile than medroxyprogesterone acetate.12

Norethindrone acetate
Norethindrone acetate monotherapy is not commonly prescribed for the treatment of menopausal hot flashes. However, a large clinical trial has demonstrated that norethindrone acetate effectively suppresses hot flashes in women with endometriosis treated with depot leuprolide acetate (LA). In one trial 201 women with endometriosis were randomly assigned to 12 months of treatment with13:
- LA plus placebo pills
- LA plus norethindrone acetate (NEA) 5 mg daily
- LA plus NEA 5 mg daily plus conjugated equine estrogen (CEE) 0.625 mg daily, or
- LA plus NEA 5 mg daily plus CEE 1.25 mg daily.
The median number of hot flashes in 24 hours was 6 in the LA plus placebo group and 0 in both the LA plus NEA 5 mg daily group and the LA plus NEA 5 mg plus CEE 1.25 mg daily group. This study demonstrates that NEA 5 mg daily is an effective treatment for hot flashes.
In the same study, LA plus placebo was associated with a significant decrease in lumbar spine bone mineral density. No significant decrease in bone mineral density was observed in the women who received LA plus NEA 5 mg daily. This finding indicates that NEA 5 mg reduces bone absorption caused by hypoestrogenism. In humans, norethindrone is a substrate for the aromatase enzyme system.14 Small quantities of ethinyl estradiol may be formed by aromatization of norethindrone in vivo,15,16 contributing to the effectiveness of NEA in suppressing hot flashes and preserving bone density.
Progestin: The estrogen alternative to hot flashes
For postmenopausal women with moderate to severe hot flashes, estrogen treatment reliably suppresses hot flashes and often improves sleep quality and mood. For postmenopausal women with a contraindication to estrogen treatment, progestin-only treatment with micronized progesterone or norethindrone acetate may be an effective option.
- Hitchcock CL, Prior JC. Oral micronized progesterone for vasomotor symptoms—a placebo-controlled randomized trial in healthy postmenopausal women. Menopause. 2012;19:886-893.
- Spark MJ, Willis J. Systematic review of progesterone use by midlife menopausal women. Maturitas 2012; 72: 192-202.
- Manson JE, Ames JM, Shapiro M, et al. Algorithm and mobile app for menopausal symptom management and hormonal/nonhormonal therapy decision making: a clinical decision-suport tool from The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2015;22:247-253.
- Herrington DM, Vittinghoff E, Howard TD, et al. Factor V Leiden, hormone replacement therapy, and risk of venous thromboembolic events in women with coronary disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002;22:1012-1017.
- Ensrud KE, Joffe H, Guthrie KA, et al. Effect of escitalopram on insomnia symptoms and subjective sleep quality in healthy perimenopausal and postmenopausal women with hot flashes: a randomized controlled trial. Menopause. 2012;19:848-855.
- Schiff I, Tulchinsky D, Cramer D, et al. Oral medroxyprogesterone in the treatment of postmenopausal symptoms. JAMA. 1980;244:1443-1445.
- Bullock JL, Massey FM, Gambrell RD Jr. Use of medroxyprogesterone acetate to prevent menopausal symptoms. Obstet Gynecol. 1975;46:165-168.
- Loprinzi CL, Levitt R, Barton D, et al. Phase III comparison of depot medroxyprogesterone acetate to venlafaxine for managing hot flashes: North Central Cancer Treatment Group Trial N99C7. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:1409-1414.
- Prior JC, Nielsen JD, Hitchcock CL, et al. Medroxyprogesterone and conjugated oestrogen are equivalent for hot flushes: 1-year randomized double-blind trial following premenopausal ovariectomy. Clin Sci (Lond). 2007;112:517-525.
- L’hermite M, Simoncini T, Fuller S, et al. Could transdermal estradiol + progesterone be a safer postmenopausal HRT? A review. Maturitas. 2008;60:185-201.
- Simon JA. What if the Women’s Health Initiative had used transdermal estradiol and oral progesterone instead? Menopause. 2014;21:769-783.
- Fournier A, Berrino F, Clavel-Chapelon F. Unequal risks for breast cancer associated with different hormone replacement therapies: results from the E3N cohort study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008;107:103-111.
- Hornstein MD, Surrey ES, Weisberg GW, et al. Leuprolide acetate depot and hormonal add-back in endometriosis: a 12-month study. Lupron Add-Back Study Group. Obstet Gynecol. 1998;91:16-24.
- Barbieri RL, Canick JA, Ryan KJ. High-affinity steroid binding to rat testis 17 alpha-hydroxylase and human placental aromatase. J Steroid Biochem. 1981;14:387-393.
- Chu MC, Zhang X, Gentzschein E, et al. Formation of ethinyl estradiol in women during treatment with norethindrone acetate. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:2205-2207.
- Chwalisz K, Surrey E, Stanczyk FZ. The hormonal profile of norethindrone acetate: rationale for add-back therapy with gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists in women with endometriosis. Reprod Sci. 2012;19:563-571.
- Hitchcock CL, Prior JC. Oral micronized progesterone for vasomotor symptoms—a placebo-controlled randomized trial in healthy postmenopausal women. Menopause. 2012;19:886-893.
- Spark MJ, Willis J. Systematic review of progesterone use by midlife menopausal women. Maturitas 2012; 72: 192-202.
- Manson JE, Ames JM, Shapiro M, et al. Algorithm and mobile app for menopausal symptom management and hormonal/nonhormonal therapy decision making: a clinical decision-suport tool from The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2015;22:247-253.
- Herrington DM, Vittinghoff E, Howard TD, et al. Factor V Leiden, hormone replacement therapy, and risk of venous thromboembolic events in women with coronary disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002;22:1012-1017.
- Ensrud KE, Joffe H, Guthrie KA, et al. Effect of escitalopram on insomnia symptoms and subjective sleep quality in healthy perimenopausal and postmenopausal women with hot flashes: a randomized controlled trial. Menopause. 2012;19:848-855.
- Schiff I, Tulchinsky D, Cramer D, et al. Oral medroxyprogesterone in the treatment of postmenopausal symptoms. JAMA. 1980;244:1443-1445.
- Bullock JL, Massey FM, Gambrell RD Jr. Use of medroxyprogesterone acetate to prevent menopausal symptoms. Obstet Gynecol. 1975;46:165-168.
- Loprinzi CL, Levitt R, Barton D, et al. Phase III comparison of depot medroxyprogesterone acetate to venlafaxine for managing hot flashes: North Central Cancer Treatment Group Trial N99C7. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:1409-1414.
- Prior JC, Nielsen JD, Hitchcock CL, et al. Medroxyprogesterone and conjugated oestrogen are equivalent for hot flushes: 1-year randomized double-blind trial following premenopausal ovariectomy. Clin Sci (Lond). 2007;112:517-525.
- L’hermite M, Simoncini T, Fuller S, et al. Could transdermal estradiol + progesterone be a safer postmenopausal HRT? A review. Maturitas. 2008;60:185-201.
- Simon JA. What if the Women’s Health Initiative had used transdermal estradiol and oral progesterone instead? Menopause. 2014;21:769-783.
- Fournier A, Berrino F, Clavel-Chapelon F. Unequal risks for breast cancer associated with different hormone replacement therapies: results from the E3N cohort study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008;107:103-111.
- Hornstein MD, Surrey ES, Weisberg GW, et al. Leuprolide acetate depot and hormonal add-back in endometriosis: a 12-month study. Lupron Add-Back Study Group. Obstet Gynecol. 1998;91:16-24.
- Barbieri RL, Canick JA, Ryan KJ. High-affinity steroid binding to rat testis 17 alpha-hydroxylase and human placental aromatase. J Steroid Biochem. 1981;14:387-393.
- Chu MC, Zhang X, Gentzschein E, et al. Formation of ethinyl estradiol in women during treatment with norethindrone acetate. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:2205-2207.
- Chwalisz K, Surrey E, Stanczyk FZ. The hormonal profile of norethindrone acetate: rationale for add-back therapy with gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists in women with endometriosis. Reprod Sci. 2012;19:563-571.
Menopause hormone therapy found to delay type 2 diabetes
LOS ANGELES – Although menopausal hormone therapy is not approved for the prevention of type 2 diabetes because of its complex balance of risks and benefits, it should not be withheld from women with increased risk of type 2 diabetes who seek treatment for menopausal symptoms, according to Franck Mauvais-Jarvis, MD.
“During the menopause transition, women accumulate metabolic disturbances, including visceral obesity, systemic inflammation, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and hypertension,” Dr. Mauvais-Jarvis, director of the Tulane Diabetes Research Program at Tulane University Health Sciences Center, New Orleans, said at the Annual World Congress on Insulin Resistance, Diabetes & Cardiovascular Disease. “They also lose muscle mass. Some of these abnormalities are partially explained by chronological aging, but they are also caused by estrogen deficiency. There’s a synergism between aging and estrogen deficiency.”
The best evidence of this synergy comes from older trials. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers examined the association between postmenopausal hormone use and the subsequent incidence of non–insulin dependent diabetes in a prospective cohort of 21,028 postmenopausal U.S. women aged 30-55 years, who were enrolled in the Nurse’s Health Study and followed for 12 years (Ann Epidemiol. 1992;2[5]:665-73). They found that study participants on hormone therapy experienced a 20% reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes. In a more recent trial, researchers examined the association between use of hormone therapy and new-onset diabetes in 63,624 postmenopausal women who were enrolled in the prospective French cohort of the Etude Epidemiologique de Femmes de la Mutuelle Générale de l’Education Nationale (E3N) and followed for 15 years (Diabetologia. 2009;52[10]:2092-100). It found that study participants on hormone therapy experienced a 20% reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes.
In the Heart and Estrogen/Progestin Replacement Study, researchers evaluated the effect of hormone therapy on fasting glucose level and incident diabetes in 2,763 postmenopausal women with coronary heart disease (Ann Intern Med. 2003;138[1]:1-9). At 20 U.S. centers, the study participants received 0.625 mg of conjugated estrogen plus 2.5 mg of medroxyprogesterone, or placebo, and were followed for 4 years. The researchers found that the use of hormone therapy reduced the incidence of diabetes by 35%.
According to Dr. Mauvais-Jarvis, the strongest data come from the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI), a randomized, double-blind trial that compared the effect of daily 0.625 mg conjugated estrogen plus 2.5 mg medroxyprogesterone acetate with that of placebo during 5.6 years of follow-up (Diabetologia. 2004; 47[7]:1175-87). It showed a 20% decrease in the incidence of diabetes at 5 years. More recently, researchers found that, whether WHI participants took estrogen plus medroxyprogesterone or estrogen alone, the protection from diabetes was present (N Engl J Med. 2016;374:803-6).
In 2006, researchers published results from a meta-analysis of 107 trials in an effort to quantify the effects of hormone therapy on components of metabolic syndrome in postmenopausal women (Diabetes Obes Metab. 2006;8[5]:538-54). In women without diabetes, hormone therapy reduced the HOMA-IR (Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance) score by 13% and incidence of type 2 diabetes by 30%. In women with diabetes, hormone therapy reduced fasting glucose by 11% and HOMA-IR by 36%.
The mechanisms by which estrogens improve glucose homeostasis are yet to be fully understood. “One of the most important [mechanisms] is a decrease in abdominal fat, which improves insulin resistance and systemic inflammation,” Dr. Mauvais-Jarvis said. “However, in the WHI, it was clear that the improvement in HOMA-IR was independent from the body weight and fat. Estrogen has also been found to increase insulin clearance and sensitivity, increase glucose disposal and effectiveness and decrease sarcopenia. There are fewer than 20 studies looking at beta-cell function. Half of them have shown that estrogen improves insulin secretion.”
Route of estrogen administration also comes into play. For example, oral estrogens increase liver exposure to estrogen, increase triglycerides, and increase clotting factors. “That is why oral estrogens are not indicated in women with risk of deep venous thrombosis,” Dr. Mauvais-Jarvis said. “They also increase inflammatory factors like C-reactive protein. Advantages are that they decrease LDL cholesterol levels and increase HDL cholesterol levels more than transdermal estrogen does.”
The main advantage with transdermal delivery of estrogen, he continued, is that it does not raise triglycerides, clotting factors, or inflammatory factors, and it confers less exposure to the liver. “That’s why it’s the preferred way of administration in women who are obese, who have a risk of DVT, or who have cardiovascular risk factors,” he said. “It has a lower suppression of hepatic glucose production, it increases circulating estradiol, and the delivery to nonhepatic tissue is increased. The oral form of estrogen is cheaper, compared with the transdermal form, though. This is a factor that is always taken into account.”
Dr. Mauvais-Jarvis and colleagues were first to evaluate the effect of conjugated estrogens plus bazedoxifene in mice (Mol Metab. 2014;3[2]:177-90). “The idea was that by combining estrogen and bazedoxifene, you have the beneficial effect of estrogen in the tissues but you block estrogen in the breast and in the uterus, and therefore, you prevent the risk of cancer,” he said. “We found that tissue-selective estrogen complexes with bazedoxifene prevent metabolic dysfunction in female mice. It increased energy expenditure and decreased fatty liver.”
In a subsequent pilot study, he and his colleagues assessed the effect of 12 weeks’ treatment with bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens, compared with placebo, on glucose homeostasis and body composition in 12 postmenopausal women (NCT02237079). “We did not find any significant alterations in the IVGTT [Intravenous Glucose Tolerance Test] but we observed improved fasting beta-cell function and serum glucose in menopausal women with obesity,” Dr. Mauvais-Jarvis said (J Endocr Soc. 2019;3[8]:1583-94).
In a separate, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial that he and his colleagues performed in eight postmenopausal women with obesity, the primary endpoint was insulin action as measured by a two-step hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp. Secondary endpoints were body composition, basal metabolic rate, ectopic fat, and metabolome. “We did not find any difference in systemic insulin action, ectopic fat, or energy expenditure,” he said. “But we found something very interesting. We did a metabolic analysis and found that oral estrogens increase hepatic de novo lipogenesis and liver triacylglycerol production. In other words, the oral estrogens were increasing [triacylglycerol] synthesis from glucose, but it does not accumulate in the liver.”
Dr. Mauvais-Jarvis disclosed that he has received research support from the National Institutes of Health, the American Diabetes Association, the Department of Veterans Affairs, and Pfizer.
LOS ANGELES – Although menopausal hormone therapy is not approved for the prevention of type 2 diabetes because of its complex balance of risks and benefits, it should not be withheld from women with increased risk of type 2 diabetes who seek treatment for menopausal symptoms, according to Franck Mauvais-Jarvis, MD.
“During the menopause transition, women accumulate metabolic disturbances, including visceral obesity, systemic inflammation, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and hypertension,” Dr. Mauvais-Jarvis, director of the Tulane Diabetes Research Program at Tulane University Health Sciences Center, New Orleans, said at the Annual World Congress on Insulin Resistance, Diabetes & Cardiovascular Disease. “They also lose muscle mass. Some of these abnormalities are partially explained by chronological aging, but they are also caused by estrogen deficiency. There’s a synergism between aging and estrogen deficiency.”
The best evidence of this synergy comes from older trials. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers examined the association between postmenopausal hormone use and the subsequent incidence of non–insulin dependent diabetes in a prospective cohort of 21,028 postmenopausal U.S. women aged 30-55 years, who were enrolled in the Nurse’s Health Study and followed for 12 years (Ann Epidemiol. 1992;2[5]:665-73). They found that study participants on hormone therapy experienced a 20% reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes. In a more recent trial, researchers examined the association between use of hormone therapy and new-onset diabetes in 63,624 postmenopausal women who were enrolled in the prospective French cohort of the Etude Epidemiologique de Femmes de la Mutuelle Générale de l’Education Nationale (E3N) and followed for 15 years (Diabetologia. 2009;52[10]:2092-100). It found that study participants on hormone therapy experienced a 20% reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes.
In the Heart and Estrogen/Progestin Replacement Study, researchers evaluated the effect of hormone therapy on fasting glucose level and incident diabetes in 2,763 postmenopausal women with coronary heart disease (Ann Intern Med. 2003;138[1]:1-9). At 20 U.S. centers, the study participants received 0.625 mg of conjugated estrogen plus 2.5 mg of medroxyprogesterone, or placebo, and were followed for 4 years. The researchers found that the use of hormone therapy reduced the incidence of diabetes by 35%.
According to Dr. Mauvais-Jarvis, the strongest data come from the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI), a randomized, double-blind trial that compared the effect of daily 0.625 mg conjugated estrogen plus 2.5 mg medroxyprogesterone acetate with that of placebo during 5.6 years of follow-up (Diabetologia. 2004; 47[7]:1175-87). It showed a 20% decrease in the incidence of diabetes at 5 years. More recently, researchers found that, whether WHI participants took estrogen plus medroxyprogesterone or estrogen alone, the protection from diabetes was present (N Engl J Med. 2016;374:803-6).
In 2006, researchers published results from a meta-analysis of 107 trials in an effort to quantify the effects of hormone therapy on components of metabolic syndrome in postmenopausal women (Diabetes Obes Metab. 2006;8[5]:538-54). In women without diabetes, hormone therapy reduced the HOMA-IR (Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance) score by 13% and incidence of type 2 diabetes by 30%. In women with diabetes, hormone therapy reduced fasting glucose by 11% and HOMA-IR by 36%.
The mechanisms by which estrogens improve glucose homeostasis are yet to be fully understood. “One of the most important [mechanisms] is a decrease in abdominal fat, which improves insulin resistance and systemic inflammation,” Dr. Mauvais-Jarvis said. “However, in the WHI, it was clear that the improvement in HOMA-IR was independent from the body weight and fat. Estrogen has also been found to increase insulin clearance and sensitivity, increase glucose disposal and effectiveness and decrease sarcopenia. There are fewer than 20 studies looking at beta-cell function. Half of them have shown that estrogen improves insulin secretion.”
Route of estrogen administration also comes into play. For example, oral estrogens increase liver exposure to estrogen, increase triglycerides, and increase clotting factors. “That is why oral estrogens are not indicated in women with risk of deep venous thrombosis,” Dr. Mauvais-Jarvis said. “They also increase inflammatory factors like C-reactive protein. Advantages are that they decrease LDL cholesterol levels and increase HDL cholesterol levels more than transdermal estrogen does.”
The main advantage with transdermal delivery of estrogen, he continued, is that it does not raise triglycerides, clotting factors, or inflammatory factors, and it confers less exposure to the liver. “That’s why it’s the preferred way of administration in women who are obese, who have a risk of DVT, or who have cardiovascular risk factors,” he said. “It has a lower suppression of hepatic glucose production, it increases circulating estradiol, and the delivery to nonhepatic tissue is increased. The oral form of estrogen is cheaper, compared with the transdermal form, though. This is a factor that is always taken into account.”
Dr. Mauvais-Jarvis and colleagues were first to evaluate the effect of conjugated estrogens plus bazedoxifene in mice (Mol Metab. 2014;3[2]:177-90). “The idea was that by combining estrogen and bazedoxifene, you have the beneficial effect of estrogen in the tissues but you block estrogen in the breast and in the uterus, and therefore, you prevent the risk of cancer,” he said. “We found that tissue-selective estrogen complexes with bazedoxifene prevent metabolic dysfunction in female mice. It increased energy expenditure and decreased fatty liver.”
In a subsequent pilot study, he and his colleagues assessed the effect of 12 weeks’ treatment with bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens, compared with placebo, on glucose homeostasis and body composition in 12 postmenopausal women (NCT02237079). “We did not find any significant alterations in the IVGTT [Intravenous Glucose Tolerance Test] but we observed improved fasting beta-cell function and serum glucose in menopausal women with obesity,” Dr. Mauvais-Jarvis said (J Endocr Soc. 2019;3[8]:1583-94).
In a separate, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial that he and his colleagues performed in eight postmenopausal women with obesity, the primary endpoint was insulin action as measured by a two-step hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp. Secondary endpoints were body composition, basal metabolic rate, ectopic fat, and metabolome. “We did not find any difference in systemic insulin action, ectopic fat, or energy expenditure,” he said. “But we found something very interesting. We did a metabolic analysis and found that oral estrogens increase hepatic de novo lipogenesis and liver triacylglycerol production. In other words, the oral estrogens were increasing [triacylglycerol] synthesis from glucose, but it does not accumulate in the liver.”
Dr. Mauvais-Jarvis disclosed that he has received research support from the National Institutes of Health, the American Diabetes Association, the Department of Veterans Affairs, and Pfizer.
LOS ANGELES – Although menopausal hormone therapy is not approved for the prevention of type 2 diabetes because of its complex balance of risks and benefits, it should not be withheld from women with increased risk of type 2 diabetes who seek treatment for menopausal symptoms, according to Franck Mauvais-Jarvis, MD.
“During the menopause transition, women accumulate metabolic disturbances, including visceral obesity, systemic inflammation, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and hypertension,” Dr. Mauvais-Jarvis, director of the Tulane Diabetes Research Program at Tulane University Health Sciences Center, New Orleans, said at the Annual World Congress on Insulin Resistance, Diabetes & Cardiovascular Disease. “They also lose muscle mass. Some of these abnormalities are partially explained by chronological aging, but they are also caused by estrogen deficiency. There’s a synergism between aging and estrogen deficiency.”
The best evidence of this synergy comes from older trials. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers examined the association between postmenopausal hormone use and the subsequent incidence of non–insulin dependent diabetes in a prospective cohort of 21,028 postmenopausal U.S. women aged 30-55 years, who were enrolled in the Nurse’s Health Study and followed for 12 years (Ann Epidemiol. 1992;2[5]:665-73). They found that study participants on hormone therapy experienced a 20% reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes. In a more recent trial, researchers examined the association between use of hormone therapy and new-onset diabetes in 63,624 postmenopausal women who were enrolled in the prospective French cohort of the Etude Epidemiologique de Femmes de la Mutuelle Générale de l’Education Nationale (E3N) and followed for 15 years (Diabetologia. 2009;52[10]:2092-100). It found that study participants on hormone therapy experienced a 20% reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes.
In the Heart and Estrogen/Progestin Replacement Study, researchers evaluated the effect of hormone therapy on fasting glucose level and incident diabetes in 2,763 postmenopausal women with coronary heart disease (Ann Intern Med. 2003;138[1]:1-9). At 20 U.S. centers, the study participants received 0.625 mg of conjugated estrogen plus 2.5 mg of medroxyprogesterone, or placebo, and were followed for 4 years. The researchers found that the use of hormone therapy reduced the incidence of diabetes by 35%.
According to Dr. Mauvais-Jarvis, the strongest data come from the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI), a randomized, double-blind trial that compared the effect of daily 0.625 mg conjugated estrogen plus 2.5 mg medroxyprogesterone acetate with that of placebo during 5.6 years of follow-up (Diabetologia. 2004; 47[7]:1175-87). It showed a 20% decrease in the incidence of diabetes at 5 years. More recently, researchers found that, whether WHI participants took estrogen plus medroxyprogesterone or estrogen alone, the protection from diabetes was present (N Engl J Med. 2016;374:803-6).
In 2006, researchers published results from a meta-analysis of 107 trials in an effort to quantify the effects of hormone therapy on components of metabolic syndrome in postmenopausal women (Diabetes Obes Metab. 2006;8[5]:538-54). In women without diabetes, hormone therapy reduced the HOMA-IR (Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance) score by 13% and incidence of type 2 diabetes by 30%. In women with diabetes, hormone therapy reduced fasting glucose by 11% and HOMA-IR by 36%.
The mechanisms by which estrogens improve glucose homeostasis are yet to be fully understood. “One of the most important [mechanisms] is a decrease in abdominal fat, which improves insulin resistance and systemic inflammation,” Dr. Mauvais-Jarvis said. “However, in the WHI, it was clear that the improvement in HOMA-IR was independent from the body weight and fat. Estrogen has also been found to increase insulin clearance and sensitivity, increase glucose disposal and effectiveness and decrease sarcopenia. There are fewer than 20 studies looking at beta-cell function. Half of them have shown that estrogen improves insulin secretion.”
Route of estrogen administration also comes into play. For example, oral estrogens increase liver exposure to estrogen, increase triglycerides, and increase clotting factors. “That is why oral estrogens are not indicated in women with risk of deep venous thrombosis,” Dr. Mauvais-Jarvis said. “They also increase inflammatory factors like C-reactive protein. Advantages are that they decrease LDL cholesterol levels and increase HDL cholesterol levels more than transdermal estrogen does.”
The main advantage with transdermal delivery of estrogen, he continued, is that it does not raise triglycerides, clotting factors, or inflammatory factors, and it confers less exposure to the liver. “That’s why it’s the preferred way of administration in women who are obese, who have a risk of DVT, or who have cardiovascular risk factors,” he said. “It has a lower suppression of hepatic glucose production, it increases circulating estradiol, and the delivery to nonhepatic tissue is increased. The oral form of estrogen is cheaper, compared with the transdermal form, though. This is a factor that is always taken into account.”
Dr. Mauvais-Jarvis and colleagues were first to evaluate the effect of conjugated estrogens plus bazedoxifene in mice (Mol Metab. 2014;3[2]:177-90). “The idea was that by combining estrogen and bazedoxifene, you have the beneficial effect of estrogen in the tissues but you block estrogen in the breast and in the uterus, and therefore, you prevent the risk of cancer,” he said. “We found that tissue-selective estrogen complexes with bazedoxifene prevent metabolic dysfunction in female mice. It increased energy expenditure and decreased fatty liver.”
In a subsequent pilot study, he and his colleagues assessed the effect of 12 weeks’ treatment with bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens, compared with placebo, on glucose homeostasis and body composition in 12 postmenopausal women (NCT02237079). “We did not find any significant alterations in the IVGTT [Intravenous Glucose Tolerance Test] but we observed improved fasting beta-cell function and serum glucose in menopausal women with obesity,” Dr. Mauvais-Jarvis said (J Endocr Soc. 2019;3[8]:1583-94).
In a separate, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial that he and his colleagues performed in eight postmenopausal women with obesity, the primary endpoint was insulin action as measured by a two-step hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp. Secondary endpoints were body composition, basal metabolic rate, ectopic fat, and metabolome. “We did not find any difference in systemic insulin action, ectopic fat, or energy expenditure,” he said. “But we found something very interesting. We did a metabolic analysis and found that oral estrogens increase hepatic de novo lipogenesis and liver triacylglycerol production. In other words, the oral estrogens were increasing [triacylglycerol] synthesis from glucose, but it does not accumulate in the liver.”
Dr. Mauvais-Jarvis disclosed that he has received research support from the National Institutes of Health, the American Diabetes Association, the Department of Veterans Affairs, and Pfizer.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM THE WCIRDC 2019
Early postmenopausal risk management leads to ‘optimum health’ for women
PHILADELPHIA – Postmenopausal women are at risk of numerous medical conditions after the onset of menopause, but many ob.gyns feel uncomfortable treating those patients, according to a keynote speaker at the annual meeting of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine.
The population of women entering menopause continues to rise, and they are at risk for developing chronic diseases about a decade after the onset of menopause, said Rogerio A. Lobo, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Columbia University, New York.
“For me, from a primary care perspective, there’s a major opportunity for all of us providers at the onset of menopause to identify risks and initiate preventive strategies,” he said.
These newly menopausal women are at risk for diseases across multiple specialty areas, which include obesity, metabolic syndrome, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, chronic arthritis, dementia, cognitive decline, depression, and cancer. “My focus along these lines is really longevity, reduction in mortality as well as quality of life,” said Dr. Lobo.
Understanding of the benefits of estrogen therapy for postmenopausal women began with work in two studies in the 1990s. One paper by Meir J. Stampfer, MD, and associates on 15 studies examining the effects of hormone therapy on coronary heart disease (CHD) found that the relative risk of estrogen therapy on the disease was 0.50 (95% confidence interval, 0.43-0.56) after adjusting for only prospective and angiographic studies (Prev Med. 1991;20[1]:47-63).
A second paper by Deborah Grady, MD, MPH, and associates found that hormone therapy with estrogen plus progestin decreased the risk of CHD and hip fracture in women but increased the risk of endometrial and breast cancer, and carried a recommendation for using estrogen plus progestin for women who have received a hysterectomy or who are at high risk for CHD (Ann Intern Med. 1992 Dec 15;117[12]:1016-37).
In the early 2000s, data from the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) began to show a different story: Therapy with estrogen plus progestin was shown to carry risks of early harm in postmenopausal women, and one study by JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, and associates had a hazard ratio of 1.24 (nominal 95% confidence interval, 1.00-1.54) for CHD in postmenopausal women aged 50-79 years receiving the combined therapy (N Engl J Med. 2003;349:523-34).
The confidence intervals were later adjusted so the association was not significant, but the results led to conclusions that hormone therapy was harmful to women and increased risk of breast cancer, declining cognition, and dementia, as well as cardiovascular diseases such as coronary disease, stroke and thrombosis.
“That was the dogma for many people to this day, but it was clearly a rush to judgment,” said Dr. Lobo. “More harm than good was done for the field.”
The contradictory findings from the WHI and other studies may be explained by the timing of hormone therapy, Dr. Lobo explained. In the ELITE trial, 643 postmenopausal women, stratified into early-postmenopausal (less than 6 years) and late-postmenopausal (equal to or greater than 10 years) groups, received 1 mg of daily oral 17-beta-estradiol with 45 mg of progesterone vaginal gel or placebo. Researchers found that it was beneficial for preventing the progression of subclinical atherosclerosis when therapy was initiated in early but not in late menopause (N Eng J Med. 2016; 374:1221-31).
Estrogen also has benefits for the brain, and might help improve rates of cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease in postmenopausal women, Dr. Lobo said. Of the 1,768 women in the Cache County Study who described their use of hormone therapy after menopause, 176 women developed Alzheimer’s; however, use of hormone therapy within 5 years of menopause was associated with a 30% reduced risk of Alzheimer’s (95% confidence interval, 0.49-0.99) and had better benefits for long-term use up to 10 years. But this effect was not present in women who started hormone therapy 5 years or more after onset of menopause (Neurology. 2012 Oct 30. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318271f823).
Clinicians also should look at the risk of hormone therapy in terms of absolute real risk rather than relative risk. “In WHI, even though many of these events were not statistically significant, even if they assumed they were, the absolute numbers were 7-8 events per 10,000 women per year,” he said. “Those, according to WHI, are rare events if they’re even true.”
“For breast cancer, which is a big concern a lot of women have, endogenous risk factors are much higher than what hormones do,” he added.
Yet clinicians continue to act on data from the WHI, Dr. Lobo noted. In fact, many ob.gyns. report that they are uncomfortable treating women with symptoms associated with menopause.
“Three out of four women who seek help for symptoms don’t receive it. The practice of menopause has largely disappeared from for many, many practices.”
The American Society for Reproductive Medicine used to have a “menopause day,” but the society no longer offers a track for menopause, Dr. Lobo said. One solution aimed at addressing the absence of training might be a menopause curriculum for ob.gyn. residents to help them initiate prevention strategies for postmenopausal women and have the confidence to manage this patient population. Dr. Lobo cited one study from Johns Hopkins where ob.gyn. residents underwent a 2-year menopause medicine curriculum and scored significantly higher on posttest scores after completing the program (78.7% vs. 57.3%; P less than .05). After the curriculum, 85.7% also reported they were more comfortable treating patients with menopause (Menopause. 2016 Mar. 23[3]:275-9).
Work also needs to be done on the front of understanding which hormone therapies are most effective for postmenopausal women. While there is currently no one hormone therapy to specifically recommend, in the future, pharmacogenetics and genetic or molecular risk analyses will play a role in knowing which products to prescribe. “It can be done, to be able to have a clear path for longevity and improved quality of life,” Dr. Lobo said.
Dr. Lobo reported serving as a consultant to Amgen, Mithra, Sojournix, and TherapeuticsMD. In addition, his institution is receiving support from Bayer and the National Institutes of Health for a clinical trial.
PHILADELPHIA – Postmenopausal women are at risk of numerous medical conditions after the onset of menopause, but many ob.gyns feel uncomfortable treating those patients, according to a keynote speaker at the annual meeting of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine.
The population of women entering menopause continues to rise, and they are at risk for developing chronic diseases about a decade after the onset of menopause, said Rogerio A. Lobo, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Columbia University, New York.
“For me, from a primary care perspective, there’s a major opportunity for all of us providers at the onset of menopause to identify risks and initiate preventive strategies,” he said.
These newly menopausal women are at risk for diseases across multiple specialty areas, which include obesity, metabolic syndrome, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, chronic arthritis, dementia, cognitive decline, depression, and cancer. “My focus along these lines is really longevity, reduction in mortality as well as quality of life,” said Dr. Lobo.
Understanding of the benefits of estrogen therapy for postmenopausal women began with work in two studies in the 1990s. One paper by Meir J. Stampfer, MD, and associates on 15 studies examining the effects of hormone therapy on coronary heart disease (CHD) found that the relative risk of estrogen therapy on the disease was 0.50 (95% confidence interval, 0.43-0.56) after adjusting for only prospective and angiographic studies (Prev Med. 1991;20[1]:47-63).
A second paper by Deborah Grady, MD, MPH, and associates found that hormone therapy with estrogen plus progestin decreased the risk of CHD and hip fracture in women but increased the risk of endometrial and breast cancer, and carried a recommendation for using estrogen plus progestin for women who have received a hysterectomy or who are at high risk for CHD (Ann Intern Med. 1992 Dec 15;117[12]:1016-37).
In the early 2000s, data from the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) began to show a different story: Therapy with estrogen plus progestin was shown to carry risks of early harm in postmenopausal women, and one study by JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, and associates had a hazard ratio of 1.24 (nominal 95% confidence interval, 1.00-1.54) for CHD in postmenopausal women aged 50-79 years receiving the combined therapy (N Engl J Med. 2003;349:523-34).
The confidence intervals were later adjusted so the association was not significant, but the results led to conclusions that hormone therapy was harmful to women and increased risk of breast cancer, declining cognition, and dementia, as well as cardiovascular diseases such as coronary disease, stroke and thrombosis.
“That was the dogma for many people to this day, but it was clearly a rush to judgment,” said Dr. Lobo. “More harm than good was done for the field.”
The contradictory findings from the WHI and other studies may be explained by the timing of hormone therapy, Dr. Lobo explained. In the ELITE trial, 643 postmenopausal women, stratified into early-postmenopausal (less than 6 years) and late-postmenopausal (equal to or greater than 10 years) groups, received 1 mg of daily oral 17-beta-estradiol with 45 mg of progesterone vaginal gel or placebo. Researchers found that it was beneficial for preventing the progression of subclinical atherosclerosis when therapy was initiated in early but not in late menopause (N Eng J Med. 2016; 374:1221-31).
Estrogen also has benefits for the brain, and might help improve rates of cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease in postmenopausal women, Dr. Lobo said. Of the 1,768 women in the Cache County Study who described their use of hormone therapy after menopause, 176 women developed Alzheimer’s; however, use of hormone therapy within 5 years of menopause was associated with a 30% reduced risk of Alzheimer’s (95% confidence interval, 0.49-0.99) and had better benefits for long-term use up to 10 years. But this effect was not present in women who started hormone therapy 5 years or more after onset of menopause (Neurology. 2012 Oct 30. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318271f823).
Clinicians also should look at the risk of hormone therapy in terms of absolute real risk rather than relative risk. “In WHI, even though many of these events were not statistically significant, even if they assumed they were, the absolute numbers were 7-8 events per 10,000 women per year,” he said. “Those, according to WHI, are rare events if they’re even true.”
“For breast cancer, which is a big concern a lot of women have, endogenous risk factors are much higher than what hormones do,” he added.
Yet clinicians continue to act on data from the WHI, Dr. Lobo noted. In fact, many ob.gyns. report that they are uncomfortable treating women with symptoms associated with menopause.
“Three out of four women who seek help for symptoms don’t receive it. The practice of menopause has largely disappeared from for many, many practices.”
The American Society for Reproductive Medicine used to have a “menopause day,” but the society no longer offers a track for menopause, Dr. Lobo said. One solution aimed at addressing the absence of training might be a menopause curriculum for ob.gyn. residents to help them initiate prevention strategies for postmenopausal women and have the confidence to manage this patient population. Dr. Lobo cited one study from Johns Hopkins where ob.gyn. residents underwent a 2-year menopause medicine curriculum and scored significantly higher on posttest scores after completing the program (78.7% vs. 57.3%; P less than .05). After the curriculum, 85.7% also reported they were more comfortable treating patients with menopause (Menopause. 2016 Mar. 23[3]:275-9).
Work also needs to be done on the front of understanding which hormone therapies are most effective for postmenopausal women. While there is currently no one hormone therapy to specifically recommend, in the future, pharmacogenetics and genetic or molecular risk analyses will play a role in knowing which products to prescribe. “It can be done, to be able to have a clear path for longevity and improved quality of life,” Dr. Lobo said.
Dr. Lobo reported serving as a consultant to Amgen, Mithra, Sojournix, and TherapeuticsMD. In addition, his institution is receiving support from Bayer and the National Institutes of Health for a clinical trial.
PHILADELPHIA – Postmenopausal women are at risk of numerous medical conditions after the onset of menopause, but many ob.gyns feel uncomfortable treating those patients, according to a keynote speaker at the annual meeting of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine.
The population of women entering menopause continues to rise, and they are at risk for developing chronic diseases about a decade after the onset of menopause, said Rogerio A. Lobo, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Columbia University, New York.
“For me, from a primary care perspective, there’s a major opportunity for all of us providers at the onset of menopause to identify risks and initiate preventive strategies,” he said.
These newly menopausal women are at risk for diseases across multiple specialty areas, which include obesity, metabolic syndrome, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, chronic arthritis, dementia, cognitive decline, depression, and cancer. “My focus along these lines is really longevity, reduction in mortality as well as quality of life,” said Dr. Lobo.
Understanding of the benefits of estrogen therapy for postmenopausal women began with work in two studies in the 1990s. One paper by Meir J. Stampfer, MD, and associates on 15 studies examining the effects of hormone therapy on coronary heart disease (CHD) found that the relative risk of estrogen therapy on the disease was 0.50 (95% confidence interval, 0.43-0.56) after adjusting for only prospective and angiographic studies (Prev Med. 1991;20[1]:47-63).
A second paper by Deborah Grady, MD, MPH, and associates found that hormone therapy with estrogen plus progestin decreased the risk of CHD and hip fracture in women but increased the risk of endometrial and breast cancer, and carried a recommendation for using estrogen plus progestin for women who have received a hysterectomy or who are at high risk for CHD (Ann Intern Med. 1992 Dec 15;117[12]:1016-37).
In the early 2000s, data from the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) began to show a different story: Therapy with estrogen plus progestin was shown to carry risks of early harm in postmenopausal women, and one study by JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, and associates had a hazard ratio of 1.24 (nominal 95% confidence interval, 1.00-1.54) for CHD in postmenopausal women aged 50-79 years receiving the combined therapy (N Engl J Med. 2003;349:523-34).
The confidence intervals were later adjusted so the association was not significant, but the results led to conclusions that hormone therapy was harmful to women and increased risk of breast cancer, declining cognition, and dementia, as well as cardiovascular diseases such as coronary disease, stroke and thrombosis.
“That was the dogma for many people to this day, but it was clearly a rush to judgment,” said Dr. Lobo. “More harm than good was done for the field.”
The contradictory findings from the WHI and other studies may be explained by the timing of hormone therapy, Dr. Lobo explained. In the ELITE trial, 643 postmenopausal women, stratified into early-postmenopausal (less than 6 years) and late-postmenopausal (equal to or greater than 10 years) groups, received 1 mg of daily oral 17-beta-estradiol with 45 mg of progesterone vaginal gel or placebo. Researchers found that it was beneficial for preventing the progression of subclinical atherosclerosis when therapy was initiated in early but not in late menopause (N Eng J Med. 2016; 374:1221-31).
Estrogen also has benefits for the brain, and might help improve rates of cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease in postmenopausal women, Dr. Lobo said. Of the 1,768 women in the Cache County Study who described their use of hormone therapy after menopause, 176 women developed Alzheimer’s; however, use of hormone therapy within 5 years of menopause was associated with a 30% reduced risk of Alzheimer’s (95% confidence interval, 0.49-0.99) and had better benefits for long-term use up to 10 years. But this effect was not present in women who started hormone therapy 5 years or more after onset of menopause (Neurology. 2012 Oct 30. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318271f823).
Clinicians also should look at the risk of hormone therapy in terms of absolute real risk rather than relative risk. “In WHI, even though many of these events were not statistically significant, even if they assumed they were, the absolute numbers were 7-8 events per 10,000 women per year,” he said. “Those, according to WHI, are rare events if they’re even true.”
“For breast cancer, which is a big concern a lot of women have, endogenous risk factors are much higher than what hormones do,” he added.
Yet clinicians continue to act on data from the WHI, Dr. Lobo noted. In fact, many ob.gyns. report that they are uncomfortable treating women with symptoms associated with menopause.
“Three out of four women who seek help for symptoms don’t receive it. The practice of menopause has largely disappeared from for many, many practices.”
The American Society for Reproductive Medicine used to have a “menopause day,” but the society no longer offers a track for menopause, Dr. Lobo said. One solution aimed at addressing the absence of training might be a menopause curriculum for ob.gyn. residents to help them initiate prevention strategies for postmenopausal women and have the confidence to manage this patient population. Dr. Lobo cited one study from Johns Hopkins where ob.gyn. residents underwent a 2-year menopause medicine curriculum and scored significantly higher on posttest scores after completing the program (78.7% vs. 57.3%; P less than .05). After the curriculum, 85.7% also reported they were more comfortable treating patients with menopause (Menopause. 2016 Mar. 23[3]:275-9).
Work also needs to be done on the front of understanding which hormone therapies are most effective for postmenopausal women. While there is currently no one hormone therapy to specifically recommend, in the future, pharmacogenetics and genetic or molecular risk analyses will play a role in knowing which products to prescribe. “It can be done, to be able to have a clear path for longevity and improved quality of life,” Dr. Lobo said.
Dr. Lobo reported serving as a consultant to Amgen, Mithra, Sojournix, and TherapeuticsMD. In addition, his institution is receiving support from Bayer and the National Institutes of Health for a clinical trial.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ASRM 2019
Bisphosphonates turn 50
ORLANDO – Cumulative evidence over the years has shown that bisphosphonates reduce distant metastases in postmenopausal women with early-stage breast cancer but that effect does not seem to extend to younger, premenopausal women who may experience adverse effects with bisphosphonates, nor has it been replicated in other types of cancer, such as lung or prostate, Robert Coleman MBBS, MD, said in a presentation marking the 50th anniversary of the publication of the first papers describing the then-new class of drugs.
“We have some science – at least in postmenopausal breast cancer – [showing] that we’re really making a difference, but we don’t understand why it’s not working in the other patients or in the other diseases,” said Dr. Coleman of the University of Sheffield (England) at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Mixed findings in early studies
Early studies showing the metastases-prevention effects of bisphosphonates were with clodronate. In one study, Dr. Coleman said, researchers found that oral clodronate at a dose of 1,600 mg/day as a supplementary treatment to standard treatment for primary, operable breast cancer reduced the risk of bone metastases in a cohort of 1,069 patients with stage 1-3 breast cancer (hazard ratio, 0.692; P = .043) over 5 years (Breast Cancer Res. 2006 Mar 15. doi: 10.1186/bcr1384). Another trial, of 302 patients with breast cancer who received oral clodronate at 1,600 mg/day for 2 years, found that 20.4% of patients who received oral clodronate had died by 8.5 years of follow-up, compared with 40.7% of those who did not receive the intervention (Ann Oncol. 2008;19[12]:2007-11).
However, those results were in conflict with findings from an earlier study in which researchers followed patients with breast cancer who received 1,600 mg/day of oral clodronate or placebo for 3 years. They found a similar number of bone metastases in the clodronate and placebo groups (32% and 29%, respectively), as well as a lower overall disease-free survival rate at 10 years for the clodronate group, compared with the placebo group (45% vs. 58%; Acta Oncol. 2004;43[7]:650-6).“For various other reasons, clodronate did not gain traction as a therapeutic strategy in early-stage breast cancer,” said Dr. Coleman, although emerging evidence showed that other bisphosphonate agents were effective in some patients with breast cancer.
In a 2009 article, Gnant et al. reported that premenopausal patients, who underwent primary surgery for stage 1 or stage 2 breast cancer and received standard goserelin therapy for induced menopause and endocrine therapy (either tamoxifen or anastrozole) in addition to treatment with zoledronic acid, had a disease-free survival rate of 94.0% at a median 47.8 months of follow-up (N Eng J Med. 2009;360:679-91). After a median 94.4 months of follow-up, the investigators reported a lower risk of disease progression (HR, 0.77; 95% confidence interval, 0.60-0.99; P = .042) and death (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.43-1.02; P = .064; Ann Oncol. 2015;26[2]:313-20).
In his own group, Dr. Coleman and colleagues recruited patients with early-stage breast cancer in the AZURE trial, a phase 3 study of 3,360 patients who received standard therapy with or without zoledronic acid 4 mg every 3-4 weeks for 6 doses, followed by 8 doses every 3 months then 5 doses every 6 months (N Eng J Med. 2011;365:1396-405). “We saw no effect,” said Dr. Coleman. “[That was] very different from what was shown by [Dr.] Gnant.”
For a subgroup of postmenopausal patients, Dr. Coleman and colleagues found that the adjusted HR for disease-free survival was 0.82 for women who were more than 5 years postmenopausal (95% CI, 0.67-1.00) at the time of breast cancer and bisphosphonate treatment, but women younger than 40 years had worse survival outcomes at 10 years (HR, 1.56; 95% CI, 1.09-2.22) and had a significantly higher risk of death from breast cancer (HR, 1.67; 95% CI, 1.16-2.40; J Bone Oncol. 2018 Sep 27. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2018.09.008).
Trying to reconcile disparate findings
Those findings left his group with a dilemma, said Dr. Coleman. “Do we start again and run trials, and wait another 10 years, or is there a shortcut to [understanding] what’s going on?” he asked.
In a meta-analysis of all trials from the Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group in 2015 examining adjuvant bisphosphonate treatment and placebo in patients with early-stage breast cancer, intent-to-treat analyses did not show significant benefit after therapy, but postmenopausal women (11,767 women in 36 trials) saw a clear benefit in all recurrence (rate ratio, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.78-0.94), bone recurrence (RR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.60-0.86), and breast cancer–related mortality (RR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.73-0.93; Lancet. 2015 Jul 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[15]60908-4). The effect seemed to be similar, regardless of bisphosphonate type, with other results seen across trials that used clodronate, zoledronic acid, pamidronate, or ibandronate.
“Although those outcome differences might look quite small for a common disease, that’s a really big effect. Reducing one-sixth of breast cancer deaths at 10 years is the equivalent of saving 10,000 lives across the [European Union], and about half that in the United States,” said Dr. Coleman, noting that guidelines in North America from the American Society of Clinical Oncology and the European Society for Medical Oncology now support adjuvant bisphosphonates in postmenopausal patients with breast cancer.
However, bisphosphonates’ effect on breast cancer does not extend to other cancers, such as non–small cell lung cancer or prostate cancer. In other absorption inhibitors such as denosumab, there also seems to be no benefit for patients with breast cancer, including in postmenopausal patient subgroups, said Dr. Coleman. “In my view, osteoclast inhibition is only part of the story,” he noted.
In the AZURE trial, secondary outcomes examined how the transcription factor MAF interacted with menopausal status and treatment with zoledronic acid. The 79% of patients with tumors that were negative for MAF fluorescence in situ hybridization had improved overall survival (0.69; 95% CI, 0.50-0.94), regardless of menopause status (J Bone Oncol. 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2018.09.008). “There’s probably a need to merge the treatment: in this case, the bisphosphonate, the biology of the cancer, and the environment the cancer finds itself in,” noted Dr. Coleman.
“From the cancer perspective, he concluded.
Dr. Coleman reports being a paid employee of prIME Oncology (until March 2019); is a consultant for Amgen, Astellas, Boehringer Ingelheim, Scandell, and Biocon; is on the speakers bureau for Amgen and Eisai; holds intellectual property rights for a biomarker being developed by Inbiomotion; and is on the scientific advisory board for Inbiomotion.
ORLANDO – Cumulative evidence over the years has shown that bisphosphonates reduce distant metastases in postmenopausal women with early-stage breast cancer but that effect does not seem to extend to younger, premenopausal women who may experience adverse effects with bisphosphonates, nor has it been replicated in other types of cancer, such as lung or prostate, Robert Coleman MBBS, MD, said in a presentation marking the 50th anniversary of the publication of the first papers describing the then-new class of drugs.
“We have some science – at least in postmenopausal breast cancer – [showing] that we’re really making a difference, but we don’t understand why it’s not working in the other patients or in the other diseases,” said Dr. Coleman of the University of Sheffield (England) at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Mixed findings in early studies
Early studies showing the metastases-prevention effects of bisphosphonates were with clodronate. In one study, Dr. Coleman said, researchers found that oral clodronate at a dose of 1,600 mg/day as a supplementary treatment to standard treatment for primary, operable breast cancer reduced the risk of bone metastases in a cohort of 1,069 patients with stage 1-3 breast cancer (hazard ratio, 0.692; P = .043) over 5 years (Breast Cancer Res. 2006 Mar 15. doi: 10.1186/bcr1384). Another trial, of 302 patients with breast cancer who received oral clodronate at 1,600 mg/day for 2 years, found that 20.4% of patients who received oral clodronate had died by 8.5 years of follow-up, compared with 40.7% of those who did not receive the intervention (Ann Oncol. 2008;19[12]:2007-11).
However, those results were in conflict with findings from an earlier study in which researchers followed patients with breast cancer who received 1,600 mg/day of oral clodronate or placebo for 3 years. They found a similar number of bone metastases in the clodronate and placebo groups (32% and 29%, respectively), as well as a lower overall disease-free survival rate at 10 years for the clodronate group, compared with the placebo group (45% vs. 58%; Acta Oncol. 2004;43[7]:650-6).“For various other reasons, clodronate did not gain traction as a therapeutic strategy in early-stage breast cancer,” said Dr. Coleman, although emerging evidence showed that other bisphosphonate agents were effective in some patients with breast cancer.
In a 2009 article, Gnant et al. reported that premenopausal patients, who underwent primary surgery for stage 1 or stage 2 breast cancer and received standard goserelin therapy for induced menopause and endocrine therapy (either tamoxifen or anastrozole) in addition to treatment with zoledronic acid, had a disease-free survival rate of 94.0% at a median 47.8 months of follow-up (N Eng J Med. 2009;360:679-91). After a median 94.4 months of follow-up, the investigators reported a lower risk of disease progression (HR, 0.77; 95% confidence interval, 0.60-0.99; P = .042) and death (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.43-1.02; P = .064; Ann Oncol. 2015;26[2]:313-20).
In his own group, Dr. Coleman and colleagues recruited patients with early-stage breast cancer in the AZURE trial, a phase 3 study of 3,360 patients who received standard therapy with or without zoledronic acid 4 mg every 3-4 weeks for 6 doses, followed by 8 doses every 3 months then 5 doses every 6 months (N Eng J Med. 2011;365:1396-405). “We saw no effect,” said Dr. Coleman. “[That was] very different from what was shown by [Dr.] Gnant.”
For a subgroup of postmenopausal patients, Dr. Coleman and colleagues found that the adjusted HR for disease-free survival was 0.82 for women who were more than 5 years postmenopausal (95% CI, 0.67-1.00) at the time of breast cancer and bisphosphonate treatment, but women younger than 40 years had worse survival outcomes at 10 years (HR, 1.56; 95% CI, 1.09-2.22) and had a significantly higher risk of death from breast cancer (HR, 1.67; 95% CI, 1.16-2.40; J Bone Oncol. 2018 Sep 27. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2018.09.008).
Trying to reconcile disparate findings
Those findings left his group with a dilemma, said Dr. Coleman. “Do we start again and run trials, and wait another 10 years, or is there a shortcut to [understanding] what’s going on?” he asked.
In a meta-analysis of all trials from the Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group in 2015 examining adjuvant bisphosphonate treatment and placebo in patients with early-stage breast cancer, intent-to-treat analyses did not show significant benefit after therapy, but postmenopausal women (11,767 women in 36 trials) saw a clear benefit in all recurrence (rate ratio, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.78-0.94), bone recurrence (RR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.60-0.86), and breast cancer–related mortality (RR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.73-0.93; Lancet. 2015 Jul 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[15]60908-4). The effect seemed to be similar, regardless of bisphosphonate type, with other results seen across trials that used clodronate, zoledronic acid, pamidronate, or ibandronate.
“Although those outcome differences might look quite small for a common disease, that’s a really big effect. Reducing one-sixth of breast cancer deaths at 10 years is the equivalent of saving 10,000 lives across the [European Union], and about half that in the United States,” said Dr. Coleman, noting that guidelines in North America from the American Society of Clinical Oncology and the European Society for Medical Oncology now support adjuvant bisphosphonates in postmenopausal patients with breast cancer.
However, bisphosphonates’ effect on breast cancer does not extend to other cancers, such as non–small cell lung cancer or prostate cancer. In other absorption inhibitors such as denosumab, there also seems to be no benefit for patients with breast cancer, including in postmenopausal patient subgroups, said Dr. Coleman. “In my view, osteoclast inhibition is only part of the story,” he noted.
In the AZURE trial, secondary outcomes examined how the transcription factor MAF interacted with menopausal status and treatment with zoledronic acid. The 79% of patients with tumors that were negative for MAF fluorescence in situ hybridization had improved overall survival (0.69; 95% CI, 0.50-0.94), regardless of menopause status (J Bone Oncol. 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2018.09.008). “There’s probably a need to merge the treatment: in this case, the bisphosphonate, the biology of the cancer, and the environment the cancer finds itself in,” noted Dr. Coleman.
“From the cancer perspective, he concluded.
Dr. Coleman reports being a paid employee of prIME Oncology (until March 2019); is a consultant for Amgen, Astellas, Boehringer Ingelheim, Scandell, and Biocon; is on the speakers bureau for Amgen and Eisai; holds intellectual property rights for a biomarker being developed by Inbiomotion; and is on the scientific advisory board for Inbiomotion.
ORLANDO – Cumulative evidence over the years has shown that bisphosphonates reduce distant metastases in postmenopausal women with early-stage breast cancer but that effect does not seem to extend to younger, premenopausal women who may experience adverse effects with bisphosphonates, nor has it been replicated in other types of cancer, such as lung or prostate, Robert Coleman MBBS, MD, said in a presentation marking the 50th anniversary of the publication of the first papers describing the then-new class of drugs.
“We have some science – at least in postmenopausal breast cancer – [showing] that we’re really making a difference, but we don’t understand why it’s not working in the other patients or in the other diseases,” said Dr. Coleman of the University of Sheffield (England) at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Mixed findings in early studies
Early studies showing the metastases-prevention effects of bisphosphonates were with clodronate. In one study, Dr. Coleman said, researchers found that oral clodronate at a dose of 1,600 mg/day as a supplementary treatment to standard treatment for primary, operable breast cancer reduced the risk of bone metastases in a cohort of 1,069 patients with stage 1-3 breast cancer (hazard ratio, 0.692; P = .043) over 5 years (Breast Cancer Res. 2006 Mar 15. doi: 10.1186/bcr1384). Another trial, of 302 patients with breast cancer who received oral clodronate at 1,600 mg/day for 2 years, found that 20.4% of patients who received oral clodronate had died by 8.5 years of follow-up, compared with 40.7% of those who did not receive the intervention (Ann Oncol. 2008;19[12]:2007-11).
However, those results were in conflict with findings from an earlier study in which researchers followed patients with breast cancer who received 1,600 mg/day of oral clodronate or placebo for 3 years. They found a similar number of bone metastases in the clodronate and placebo groups (32% and 29%, respectively), as well as a lower overall disease-free survival rate at 10 years for the clodronate group, compared with the placebo group (45% vs. 58%; Acta Oncol. 2004;43[7]:650-6).“For various other reasons, clodronate did not gain traction as a therapeutic strategy in early-stage breast cancer,” said Dr. Coleman, although emerging evidence showed that other bisphosphonate agents were effective in some patients with breast cancer.
In a 2009 article, Gnant et al. reported that premenopausal patients, who underwent primary surgery for stage 1 or stage 2 breast cancer and received standard goserelin therapy for induced menopause and endocrine therapy (either tamoxifen or anastrozole) in addition to treatment with zoledronic acid, had a disease-free survival rate of 94.0% at a median 47.8 months of follow-up (N Eng J Med. 2009;360:679-91). After a median 94.4 months of follow-up, the investigators reported a lower risk of disease progression (HR, 0.77; 95% confidence interval, 0.60-0.99; P = .042) and death (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.43-1.02; P = .064; Ann Oncol. 2015;26[2]:313-20).
In his own group, Dr. Coleman and colleagues recruited patients with early-stage breast cancer in the AZURE trial, a phase 3 study of 3,360 patients who received standard therapy with or without zoledronic acid 4 mg every 3-4 weeks for 6 doses, followed by 8 doses every 3 months then 5 doses every 6 months (N Eng J Med. 2011;365:1396-405). “We saw no effect,” said Dr. Coleman. “[That was] very different from what was shown by [Dr.] Gnant.”
For a subgroup of postmenopausal patients, Dr. Coleman and colleagues found that the adjusted HR for disease-free survival was 0.82 for women who were more than 5 years postmenopausal (95% CI, 0.67-1.00) at the time of breast cancer and bisphosphonate treatment, but women younger than 40 years had worse survival outcomes at 10 years (HR, 1.56; 95% CI, 1.09-2.22) and had a significantly higher risk of death from breast cancer (HR, 1.67; 95% CI, 1.16-2.40; J Bone Oncol. 2018 Sep 27. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2018.09.008).
Trying to reconcile disparate findings
Those findings left his group with a dilemma, said Dr. Coleman. “Do we start again and run trials, and wait another 10 years, or is there a shortcut to [understanding] what’s going on?” he asked.
In a meta-analysis of all trials from the Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group in 2015 examining adjuvant bisphosphonate treatment and placebo in patients with early-stage breast cancer, intent-to-treat analyses did not show significant benefit after therapy, but postmenopausal women (11,767 women in 36 trials) saw a clear benefit in all recurrence (rate ratio, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.78-0.94), bone recurrence (RR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.60-0.86), and breast cancer–related mortality (RR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.73-0.93; Lancet. 2015 Jul 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[15]60908-4). The effect seemed to be similar, regardless of bisphosphonate type, with other results seen across trials that used clodronate, zoledronic acid, pamidronate, or ibandronate.
“Although those outcome differences might look quite small for a common disease, that’s a really big effect. Reducing one-sixth of breast cancer deaths at 10 years is the equivalent of saving 10,000 lives across the [European Union], and about half that in the United States,” said Dr. Coleman, noting that guidelines in North America from the American Society of Clinical Oncology and the European Society for Medical Oncology now support adjuvant bisphosphonates in postmenopausal patients with breast cancer.
However, bisphosphonates’ effect on breast cancer does not extend to other cancers, such as non–small cell lung cancer or prostate cancer. In other absorption inhibitors such as denosumab, there also seems to be no benefit for patients with breast cancer, including in postmenopausal patient subgroups, said Dr. Coleman. “In my view, osteoclast inhibition is only part of the story,” he noted.
In the AZURE trial, secondary outcomes examined how the transcription factor MAF interacted with menopausal status and treatment with zoledronic acid. The 79% of patients with tumors that were negative for MAF fluorescence in situ hybridization had improved overall survival (0.69; 95% CI, 0.50-0.94), regardless of menopause status (J Bone Oncol. 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2018.09.008). “There’s probably a need to merge the treatment: in this case, the bisphosphonate, the biology of the cancer, and the environment the cancer finds itself in,” noted Dr. Coleman.
“From the cancer perspective, he concluded.
Dr. Coleman reports being a paid employee of prIME Oncology (until March 2019); is a consultant for Amgen, Astellas, Boehringer Ingelheim, Scandell, and Biocon; is on the speakers bureau for Amgen and Eisai; holds intellectual property rights for a biomarker being developed by Inbiomotion; and is on the scientific advisory board for Inbiomotion.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ASBMR 2019