User login
Decreased visual acuity and paresthesia
All of the above conditions can have ophthalmic manifestations, but the majority of optic neuritis cases seen in clinical practice are either sporadic or MS related. Optic neuritis is the first demyelinating event in approximately 20% of patients with MS. It develops in approximately 40% of MS patients during the course of their disease.
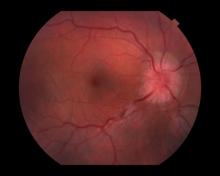
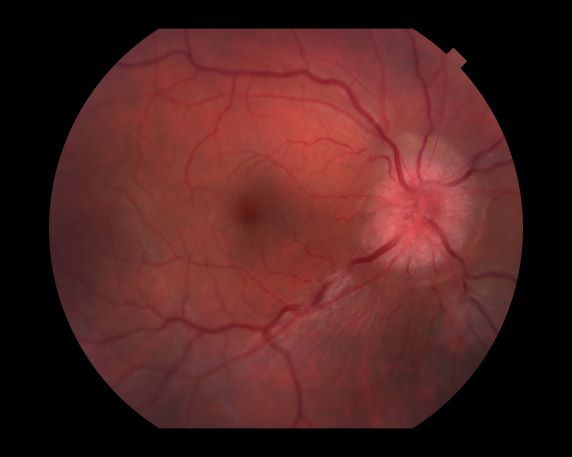
Optic neuritis is characterized by loss of vision (or loss of color vision) in the affected eye and pain on movement of the eye (painful ophthalmoplegia). Less often, patients with optic neuritis may describe phosphenes (transient flashes of light or black squares) lasting from hours to months. Phosphenes may occur before or during an optic neuritis event or even several months after recovery.
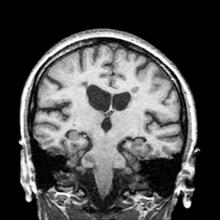
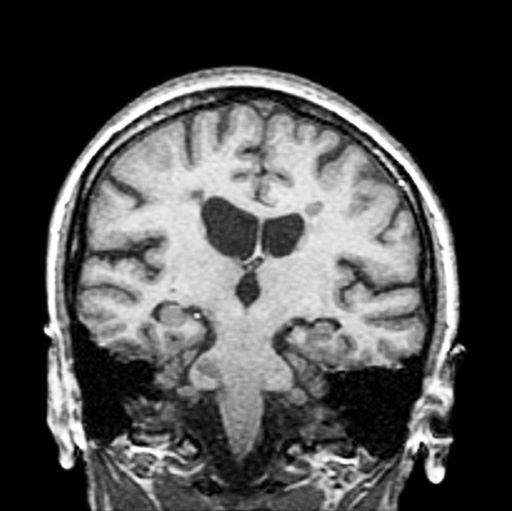
The diagnosis of optic neuritis is usually made clinically, with direct imaging of the optic nerves showing evidence of optic disc swelling with blurred margins. The real contribution of imaging in the setting of optic neuritis, however, is made by imaging of the brain, not of the optic nerves themselves. MRI of the brain provides information that can change the management of optic neuritis and yields prognostic information regarding the patient's future risk of developing MS. The most valuable predictor of the development of subsequent MS is the presence of white matter abnormalities. Between 27% and 70% of patients (in various studies) with isolated optic neuritis showed abnormal MRI brain findings, as defined by the presence of two or more white matter lesions on T2-weighted images. Patients with two or more lesions may have up to an 80% chance of meeting criteria for MS within the next 5 years.
A gradual recovery of visual acuity with time is characteristic of optic neuritis, although permanent residual deficits in color vision and contrast and brightness sensitivity are common. The symptoms of optic neuritis will usually resolve without medical treatment, although continuing to take regular MS disease-modulating medication is usually helpful. An intravenous steroid or oral prednisone is sometimes recommended to speed recovery. A 3- to 5-day course of high-dose (1 g) IV methylprednisolone, followed by a rapid oral taper of prednisone, has been shown to provide rapid recovery of symptoms in the acute phase. However, IV steroids do little to affect the ultimate visual acuity in patients with optic neuritis.
Typically, patients begin to recover 2-4 weeks after the onset of the vision loss. The optic nerve may take up to 6-12 months to heal completely, but most patients recover as much vision as they are going to within the first few months.
For patients with optic neuritis whose brain lesions on MRI indicate a high risk of developing clinically definite MS, treatment with immunomodulators may be considered. IV immunoglobulin treatment of acute optic neuritis has been shown to have no beneficial effect. In severe cases, plasma exchange may be considered.
Krupa Pandey, MD, Director, Multiple Sclerosis Center, Department of Neurology & Neuroscience Institute, Hackensack University Medical Center; Neurologist, Department of Neurology, Hackensack Meridian Health, Hackensack, NJ.
Krupa Pandey, MD, has serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: Bristol-Myers Squibb; Biogen; Alexion; Genentech; Sanofi-Genzyme.
All of the above conditions can have ophthalmic manifestations, but the majority of optic neuritis cases seen in clinical practice are either sporadic or MS related. Optic neuritis is the first demyelinating event in approximately 20% of patients with MS. It develops in approximately 40% of MS patients during the course of their disease.
Optic neuritis is characterized by loss of vision (or loss of color vision) in the affected eye and pain on movement of the eye (painful ophthalmoplegia). Less often, patients with optic neuritis may describe phosphenes (transient flashes of light or black squares) lasting from hours to months. Phosphenes may occur before or during an optic neuritis event or even several months after recovery.
The diagnosis of optic neuritis is usually made clinically, with direct imaging of the optic nerves showing evidence of optic disc swelling with blurred margins. The real contribution of imaging in the setting of optic neuritis, however, is made by imaging of the brain, not of the optic nerves themselves. MRI of the brain provides information that can change the management of optic neuritis and yields prognostic information regarding the patient's future risk of developing MS. The most valuable predictor of the development of subsequent MS is the presence of white matter abnormalities. Between 27% and 70% of patients (in various studies) with isolated optic neuritis showed abnormal MRI brain findings, as defined by the presence of two or more white matter lesions on T2-weighted images. Patients with two or more lesions may have up to an 80% chance of meeting criteria for MS within the next 5 years.
A gradual recovery of visual acuity with time is characteristic of optic neuritis, although permanent residual deficits in color vision and contrast and brightness sensitivity are common. The symptoms of optic neuritis will usually resolve without medical treatment, although continuing to take regular MS disease-modulating medication is usually helpful. An intravenous steroid or oral prednisone is sometimes recommended to speed recovery. A 3- to 5-day course of high-dose (1 g) IV methylprednisolone, followed by a rapid oral taper of prednisone, has been shown to provide rapid recovery of symptoms in the acute phase. However, IV steroids do little to affect the ultimate visual acuity in patients with optic neuritis.
Typically, patients begin to recover 2-4 weeks after the onset of the vision loss. The optic nerve may take up to 6-12 months to heal completely, but most patients recover as much vision as they are going to within the first few months.
For patients with optic neuritis whose brain lesions on MRI indicate a high risk of developing clinically definite MS, treatment with immunomodulators may be considered. IV immunoglobulin treatment of acute optic neuritis has been shown to have no beneficial effect. In severe cases, plasma exchange may be considered.
Krupa Pandey, MD, Director, Multiple Sclerosis Center, Department of Neurology & Neuroscience Institute, Hackensack University Medical Center; Neurologist, Department of Neurology, Hackensack Meridian Health, Hackensack, NJ.
Krupa Pandey, MD, has serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: Bristol-Myers Squibb; Biogen; Alexion; Genentech; Sanofi-Genzyme.
All of the above conditions can have ophthalmic manifestations, but the majority of optic neuritis cases seen in clinical practice are either sporadic or MS related. Optic neuritis is the first demyelinating event in approximately 20% of patients with MS. It develops in approximately 40% of MS patients during the course of their disease.
Optic neuritis is characterized by loss of vision (or loss of color vision) in the affected eye and pain on movement of the eye (painful ophthalmoplegia). Less often, patients with optic neuritis may describe phosphenes (transient flashes of light or black squares) lasting from hours to months. Phosphenes may occur before or during an optic neuritis event or even several months after recovery.
The diagnosis of optic neuritis is usually made clinically, with direct imaging of the optic nerves showing evidence of optic disc swelling with blurred margins. The real contribution of imaging in the setting of optic neuritis, however, is made by imaging of the brain, not of the optic nerves themselves. MRI of the brain provides information that can change the management of optic neuritis and yields prognostic information regarding the patient's future risk of developing MS. The most valuable predictor of the development of subsequent MS is the presence of white matter abnormalities. Between 27% and 70% of patients (in various studies) with isolated optic neuritis showed abnormal MRI brain findings, as defined by the presence of two or more white matter lesions on T2-weighted images. Patients with two or more lesions may have up to an 80% chance of meeting criteria for MS within the next 5 years.
A gradual recovery of visual acuity with time is characteristic of optic neuritis, although permanent residual deficits in color vision and contrast and brightness sensitivity are common. The symptoms of optic neuritis will usually resolve without medical treatment, although continuing to take regular MS disease-modulating medication is usually helpful. An intravenous steroid or oral prednisone is sometimes recommended to speed recovery. A 3- to 5-day course of high-dose (1 g) IV methylprednisolone, followed by a rapid oral taper of prednisone, has been shown to provide rapid recovery of symptoms in the acute phase. However, IV steroids do little to affect the ultimate visual acuity in patients with optic neuritis.
Typically, patients begin to recover 2-4 weeks after the onset of the vision loss. The optic nerve may take up to 6-12 months to heal completely, but most patients recover as much vision as they are going to within the first few months.
For patients with optic neuritis whose brain lesions on MRI indicate a high risk of developing clinically definite MS, treatment with immunomodulators may be considered. IV immunoglobulin treatment of acute optic neuritis has been shown to have no beneficial effect. In severe cases, plasma exchange may be considered.
Krupa Pandey, MD, Director, Multiple Sclerosis Center, Department of Neurology & Neuroscience Institute, Hackensack University Medical Center; Neurologist, Department of Neurology, Hackensack Meridian Health, Hackensack, NJ.
Krupa Pandey, MD, has serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: Bristol-Myers Squibb; Biogen; Alexion; Genentech; Sanofi-Genzyme.
A 44-year-old woman presents with decreased visual acuity, painful ophthalmoplegia, photophobia, and paresthesia of the left hand. The patient's ocular history was unremarkable. Her medical history was significant only for recurrent urinary tract infections. She did not have a history of neurologic problems and reported that she did not have dizziness, tingling, tremors, sensory changes, speech changes, or focal weaknesses. Besides current use of naproxen, she said she was not taking any other medications. Her family ocular history was significant for glaucoma in her father and paternal grandfather. Her maternal grandfather died at age 58 of multiple sclerosis (MS).
3-year-history of difficulty walking
The patient has probably transitioned to the secondary progressive form of multiple sclerosis (MS). Four phenotypes have been identified in MS, with relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) representing the most common and secondary progressive MS (SPMS) the second most common. RRMS is thought to begin as an inflammatory disease that over time becomes primarily neurodegenerative. The course of RRMS is marked by episodes of neurologic deficit followed by periods of remission which may be asymptomatic. When symptoms do not resolve — becoming fixed without remission — this is a sign of progression to SPMS. One in two RRMS patients will develop SPMS within 15 years of their diagnosis, leading to a progressive decrease of neurologic function and limitation of daily activities. Risk factors for developing SPMS include older age at onset of RRMS, longer duration of RRMS, and more cortical inflammatory lesions at baseline.
RRMS is diagnosed through clinical findings and laboratory results, the main approaches being MRI of the brain and spinal cord, and examination of cerebrospinal fluid. Neurologic symptoms must be consistent with those typically seen in MS, with deficit lasting for days to weeks. MRI is useful in monitoring disease progression (ie, new lesions that develop during relapses in RRMS). There are no universally accepted diagnostic criteria for SPMS, however. A patient usually can be diagnosed upon meeting these criteria: The patient was previously diagnosed with RRMS; the patient's symptoms are gradually worsening; this worsening is not tied to a relapse; and this worsening has been observed for 6 months or longer. Of note, SPMS' symptom-worsening characteristics can be subtle and difficult for patients to detect, and delays in diagnosis of up to several years are common.
Recognizing the onset of transition to SPMS is critical, as early initiation of therapy is thought to slow disease progression, the primary goal of treatment. In patients with SPMS, adhering to a holistic health program and managing comorbidities, especially vascular risk factors, can help preserve the health and functions of both the central nervous system and brain. Patients with SPMS who experience relapses or demonstrate new lesion formation as captured on MRI are thought to have active SPMS (aSPMS) and generally benefit from disease-modifying therapy (DMT). There is generally a transition period of about 5 years during which SPMS patients will still have a relapsing form of the disease, meaning that DMTs have proven to be effective in managing progressive MS should theoretically be beneficial for SPMS during this period. There are FDA-approved treatments for aSPMS, but off-label use is acceptable of those medications indicated for relapsing MS in those patients with evidence of relapses or new MRI activity.
Krupa Pandey, MD, Director, Multiple Sclerosis Center, Department of Neurology & Neuroscience Institute, Hackensack University Medical Center; Neurologist, Department of Neurology, Hackensack Meridian Health, Hackensack, NJ
Krupa Pandey, MD, has serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: Bristol-Myers Squibb; Biogen; Alexion; Genentech; Sanofi-Genzyme
The patient has probably transitioned to the secondary progressive form of multiple sclerosis (MS). Four phenotypes have been identified in MS, with relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) representing the most common and secondary progressive MS (SPMS) the second most common. RRMS is thought to begin as an inflammatory disease that over time becomes primarily neurodegenerative. The course of RRMS is marked by episodes of neurologic deficit followed by periods of remission which may be asymptomatic. When symptoms do not resolve — becoming fixed without remission — this is a sign of progression to SPMS. One in two RRMS patients will develop SPMS within 15 years of their diagnosis, leading to a progressive decrease of neurologic function and limitation of daily activities. Risk factors for developing SPMS include older age at onset of RRMS, longer duration of RRMS, and more cortical inflammatory lesions at baseline.
RRMS is diagnosed through clinical findings and laboratory results, the main approaches being MRI of the brain and spinal cord, and examination of cerebrospinal fluid. Neurologic symptoms must be consistent with those typically seen in MS, with deficit lasting for days to weeks. MRI is useful in monitoring disease progression (ie, new lesions that develop during relapses in RRMS). There are no universally accepted diagnostic criteria for SPMS, however. A patient usually can be diagnosed upon meeting these criteria: The patient was previously diagnosed with RRMS; the patient's symptoms are gradually worsening; this worsening is not tied to a relapse; and this worsening has been observed for 6 months or longer. Of note, SPMS' symptom-worsening characteristics can be subtle and difficult for patients to detect, and delays in diagnosis of up to several years are common.
Recognizing the onset of transition to SPMS is critical, as early initiation of therapy is thought to slow disease progression, the primary goal of treatment. In patients with SPMS, adhering to a holistic health program and managing comorbidities, especially vascular risk factors, can help preserve the health and functions of both the central nervous system and brain. Patients with SPMS who experience relapses or demonstrate new lesion formation as captured on MRI are thought to have active SPMS (aSPMS) and generally benefit from disease-modifying therapy (DMT). There is generally a transition period of about 5 years during which SPMS patients will still have a relapsing form of the disease, meaning that DMTs have proven to be effective in managing progressive MS should theoretically be beneficial for SPMS during this period. There are FDA-approved treatments for aSPMS, but off-label use is acceptable of those medications indicated for relapsing MS in those patients with evidence of relapses or new MRI activity.
Krupa Pandey, MD, Director, Multiple Sclerosis Center, Department of Neurology & Neuroscience Institute, Hackensack University Medical Center; Neurologist, Department of Neurology, Hackensack Meridian Health, Hackensack, NJ
Krupa Pandey, MD, has serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: Bristol-Myers Squibb; Biogen; Alexion; Genentech; Sanofi-Genzyme
The patient has probably transitioned to the secondary progressive form of multiple sclerosis (MS). Four phenotypes have been identified in MS, with relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) representing the most common and secondary progressive MS (SPMS) the second most common. RRMS is thought to begin as an inflammatory disease that over time becomes primarily neurodegenerative. The course of RRMS is marked by episodes of neurologic deficit followed by periods of remission which may be asymptomatic. When symptoms do not resolve — becoming fixed without remission — this is a sign of progression to SPMS. One in two RRMS patients will develop SPMS within 15 years of their diagnosis, leading to a progressive decrease of neurologic function and limitation of daily activities. Risk factors for developing SPMS include older age at onset of RRMS, longer duration of RRMS, and more cortical inflammatory lesions at baseline.
RRMS is diagnosed through clinical findings and laboratory results, the main approaches being MRI of the brain and spinal cord, and examination of cerebrospinal fluid. Neurologic symptoms must be consistent with those typically seen in MS, with deficit lasting for days to weeks. MRI is useful in monitoring disease progression (ie, new lesions that develop during relapses in RRMS). There are no universally accepted diagnostic criteria for SPMS, however. A patient usually can be diagnosed upon meeting these criteria: The patient was previously diagnosed with RRMS; the patient's symptoms are gradually worsening; this worsening is not tied to a relapse; and this worsening has been observed for 6 months or longer. Of note, SPMS' symptom-worsening characteristics can be subtle and difficult for patients to detect, and delays in diagnosis of up to several years are common.
Recognizing the onset of transition to SPMS is critical, as early initiation of therapy is thought to slow disease progression, the primary goal of treatment. In patients with SPMS, adhering to a holistic health program and managing comorbidities, especially vascular risk factors, can help preserve the health and functions of both the central nervous system and brain. Patients with SPMS who experience relapses or demonstrate new lesion formation as captured on MRI are thought to have active SPMS (aSPMS) and generally benefit from disease-modifying therapy (DMT). There is generally a transition period of about 5 years during which SPMS patients will still have a relapsing form of the disease, meaning that DMTs have proven to be effective in managing progressive MS should theoretically be beneficial for SPMS during this period. There are FDA-approved treatments for aSPMS, but off-label use is acceptable of those medications indicated for relapsing MS in those patients with evidence of relapses or new MRI activity.
Krupa Pandey, MD, Director, Multiple Sclerosis Center, Department of Neurology & Neuroscience Institute, Hackensack University Medical Center; Neurologist, Department of Neurology, Hackensack Meridian Health, Hackensack, NJ
Krupa Pandey, MD, has serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: Bristol-Myers Squibb; Biogen; Alexion; Genentech; Sanofi-Genzyme
A 51-year-old woman presents with a 3-year history of difficulty walking. She says that it is difficult to pinpoint when her walking problems began but reports that it has been gradual. She recalls about 10 years back a history of numbness and tingling in her hands that improved over the course of a few weeks without any further workup. She also recalls blurry vision and loss of color perception in her left eye 5 years ago while traveling for work. Because the symptoms resolved on their own over 6-8 weeks, she never sought care. MRI shows plaques of demyelination.
Best of MS
Good data is lacking on best first-line MS drug strategies
Personalized medicine is just about the biggest buzzword in health. But neurologist Ellen M. Mowry, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, steers patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) away from the concept when she first starts talking to them about initial therapy options and possible ways to forestall disability down the line.
Good data is lacking on best first-line MS drug strategies
Personalized medicine is just about the biggest buzzword in health. But neurologist Ellen M. Mowry, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, steers patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) away from the concept when she first starts talking to them about initial therapy options and possible ways to forestall disability down the line.
Good data is lacking on best first-line MS drug strategies
Personalized medicine is just about the biggest buzzword in health. But neurologist Ellen M. Mowry, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, steers patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) away from the concept when she first starts talking to them about initial therapy options and possible ways to forestall disability down the line.
Multiple Sclerosis: Treatment & Management
Highlights on DMT Use in Progressive MS From CMSC 2021
Dr Mitzi Joi Williams, medical director of the Joi Life Wellness Group in Atlanta, Georgia, shares updates from the 2021 CMSC Annual Meeting on the use of disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) in progressive multiple sclerosis (MS).
Dr Williams begins with a review of findings from ACAPELLA, a prospective real-world study of ocrelizumab-associated adverse events. The various subanalyses found no higher rates of adverse events on the basis of age or EDSS scores, no downward trend in IgG levels, and mild B-cell repletion that had no significant correlation between disease activity or adverse events.
Next, she turns to several subanalyses from the EXPAND trial that looked at efficacy and safety of siponimod in patients with secondary progressive MS. Siponimod provided similar clinical benefits in all age groups and was well-tolerated at 3 and 6 months. Several MRI measures were found to be prognostic of disease worsening or improvement.
Dr Williams concludes with a first look at a new agent, ATA188, which is being studied in adults with progressive forms of MS. This phase 1/2 double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-expansion trial aims to evaluate the effect of ATA188 on clinical disability, characterize the agent's safety and tolerability, and evaluate the impact of treatment on biological markers in progressive MS.
--
Mitzi Joi Williams, MD, Assistant Professor, Department of Neurology, Emory University; Medical Director, Joi Life Wellness Group, Atlanta, Georgia
Mitzi Joi Williams, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: AbbVie; Alexion; Genentech; EMD Serono; Novartis; Biogen Idec
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AbbVie; Genentech; Novartis; Biogen; EMD Serono
Received research grant from: Novartis; Genentech
Dr Mitzi Joi Williams, medical director of the Joi Life Wellness Group in Atlanta, Georgia, shares updates from the 2021 CMSC Annual Meeting on the use of disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) in progressive multiple sclerosis (MS).
Dr Williams begins with a review of findings from ACAPELLA, a prospective real-world study of ocrelizumab-associated adverse events. The various subanalyses found no higher rates of adverse events on the basis of age or EDSS scores, no downward trend in IgG levels, and mild B-cell repletion that had no significant correlation between disease activity or adverse events.
Next, she turns to several subanalyses from the EXPAND trial that looked at efficacy and safety of siponimod in patients with secondary progressive MS. Siponimod provided similar clinical benefits in all age groups and was well-tolerated at 3 and 6 months. Several MRI measures were found to be prognostic of disease worsening or improvement.
Dr Williams concludes with a first look at a new agent, ATA188, which is being studied in adults with progressive forms of MS. This phase 1/2 double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-expansion trial aims to evaluate the effect of ATA188 on clinical disability, characterize the agent's safety and tolerability, and evaluate the impact of treatment on biological markers in progressive MS.
--
Mitzi Joi Williams, MD, Assistant Professor, Department of Neurology, Emory University; Medical Director, Joi Life Wellness Group, Atlanta, Georgia
Mitzi Joi Williams, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: AbbVie; Alexion; Genentech; EMD Serono; Novartis; Biogen Idec
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AbbVie; Genentech; Novartis; Biogen; EMD Serono
Received research grant from: Novartis; Genentech
Dr Mitzi Joi Williams, medical director of the Joi Life Wellness Group in Atlanta, Georgia, shares updates from the 2021 CMSC Annual Meeting on the use of disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) in progressive multiple sclerosis (MS).
Dr Williams begins with a review of findings from ACAPELLA, a prospective real-world study of ocrelizumab-associated adverse events. The various subanalyses found no higher rates of adverse events on the basis of age or EDSS scores, no downward trend in IgG levels, and mild B-cell repletion that had no significant correlation between disease activity or adverse events.
Next, she turns to several subanalyses from the EXPAND trial that looked at efficacy and safety of siponimod in patients with secondary progressive MS. Siponimod provided similar clinical benefits in all age groups and was well-tolerated at 3 and 6 months. Several MRI measures were found to be prognostic of disease worsening or improvement.
Dr Williams concludes with a first look at a new agent, ATA188, which is being studied in adults with progressive forms of MS. This phase 1/2 double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-expansion trial aims to evaluate the effect of ATA188 on clinical disability, characterize the agent's safety and tolerability, and evaluate the impact of treatment on biological markers in progressive MS.
--
Mitzi Joi Williams, MD, Assistant Professor, Department of Neurology, Emory University; Medical Director, Joi Life Wellness Group, Atlanta, Georgia
Mitzi Joi Williams, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: AbbVie; Alexion; Genentech; EMD Serono; Novartis; Biogen Idec
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AbbVie; Genentech; Novartis; Biogen; EMD Serono
Received research grant from: Novartis; Genentech

Update on Multiple Sclerosis Comorbidities From CMSC 2021
Dr Mitzi Joi Williams, medical director of Joi Life Wellness Group in Atlanta, Georgia, reviews updates from the 2021 CMSC Annual Meeting focusing on important considerations for patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) who have comorbid physical and mental health conditions.
She begins with a longitudinal mediation analysis that assessed how differences in socioeconomic status, lifestyle, and comorbidities may affect Black vs White patients with MS. Overall, Black patients had longer timed 25-foot walks than White patients, and it was concluded that elevated BMIs, higher rates of hypertension, and living in lower income neighborhoods all played partial roles in this disparity.
Dr Williams next discusses a study that examined the prevalence of depression and anxiety in patients with primary-progressive MS (PPMS), secondary-progressive MS (SPMS), and relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS). Rates of both conditions were lower in patients with PPMS than in those with SPMS and RRMS, but overall they were higher in patients with MS compared with the general population.
The final study she reports on looked at the relationships between cognitive, emotional, and physical factors and weekly engagement in physical activity among patients with MS. Unsurprisingly, meeting weekly physical exercise recommendations was associated with improvement in leg functioning, whereas decreased exercise was associated with increased symptoms of depression and with underweight and obese BMIs.
--
Mitzi Joi Williams, MD, Assistant Professor, Department of Neurology, Emory University; Medical Director, Joi Life Wellness Group, Atlanta, Georgia
Mitzi Joi Williams, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Abbvie; Alexion; Genentech; EMD Serono; Novartis; Biogen Idec
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: Abbvie; Genentech; Novartis; Biogen; EMD Serono
Received research grant from: Novartis; Genentech
Dr Mitzi Joi Williams, medical director of Joi Life Wellness Group in Atlanta, Georgia, reviews updates from the 2021 CMSC Annual Meeting focusing on important considerations for patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) who have comorbid physical and mental health conditions.
She begins with a longitudinal mediation analysis that assessed how differences in socioeconomic status, lifestyle, and comorbidities may affect Black vs White patients with MS. Overall, Black patients had longer timed 25-foot walks than White patients, and it was concluded that elevated BMIs, higher rates of hypertension, and living in lower income neighborhoods all played partial roles in this disparity.
Dr Williams next discusses a study that examined the prevalence of depression and anxiety in patients with primary-progressive MS (PPMS), secondary-progressive MS (SPMS), and relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS). Rates of both conditions were lower in patients with PPMS than in those with SPMS and RRMS, but overall they were higher in patients with MS compared with the general population.
The final study she reports on looked at the relationships between cognitive, emotional, and physical factors and weekly engagement in physical activity among patients with MS. Unsurprisingly, meeting weekly physical exercise recommendations was associated with improvement in leg functioning, whereas decreased exercise was associated with increased symptoms of depression and with underweight and obese BMIs.
--
Mitzi Joi Williams, MD, Assistant Professor, Department of Neurology, Emory University; Medical Director, Joi Life Wellness Group, Atlanta, Georgia
Mitzi Joi Williams, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Abbvie; Alexion; Genentech; EMD Serono; Novartis; Biogen Idec
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: Abbvie; Genentech; Novartis; Biogen; EMD Serono
Received research grant from: Novartis; Genentech
Dr Mitzi Joi Williams, medical director of Joi Life Wellness Group in Atlanta, Georgia, reviews updates from the 2021 CMSC Annual Meeting focusing on important considerations for patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) who have comorbid physical and mental health conditions.
She begins with a longitudinal mediation analysis that assessed how differences in socioeconomic status, lifestyle, and comorbidities may affect Black vs White patients with MS. Overall, Black patients had longer timed 25-foot walks than White patients, and it was concluded that elevated BMIs, higher rates of hypertension, and living in lower income neighborhoods all played partial roles in this disparity.
Dr Williams next discusses a study that examined the prevalence of depression and anxiety in patients with primary-progressive MS (PPMS), secondary-progressive MS (SPMS), and relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS). Rates of both conditions were lower in patients with PPMS than in those with SPMS and RRMS, but overall they were higher in patients with MS compared with the general population.
The final study she reports on looked at the relationships between cognitive, emotional, and physical factors and weekly engagement in physical activity among patients with MS. Unsurprisingly, meeting weekly physical exercise recommendations was associated with improvement in leg functioning, whereas decreased exercise was associated with increased symptoms of depression and with underweight and obese BMIs.
--
Mitzi Joi Williams, MD, Assistant Professor, Department of Neurology, Emory University; Medical Director, Joi Life Wellness Group, Atlanta, Georgia
Mitzi Joi Williams, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Abbvie; Alexion; Genentech; EMD Serono; Novartis; Biogen Idec
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: Abbvie; Genentech; Novartis; Biogen; EMD Serono
Received research grant from: Novartis; Genentech

B-cell repletion is common with MS drug, but no symptom worsening
. However, there are no corresponding worsening of symptoms or signs of a “wearing off” effect, new research shows.
“Most people expect that since this is a B-cell depleting drug, that if you are not depleting B cells, then that should be reflected clinically and there should be some breakthrough activity,” said study investigator Joshua D. Katz, MD, codirector of the Elliot Lewis Center for Multiple Sclerosis Care in Wellesley, Massachusetts.
“So [these results] were a surprise, but I would not conclude from our data that B-cell repletion does not put someone at risk. We can only say that we didn’t observe anybody having a breakthrough,” he added.
The research was presented at the 2021 Annual Meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (CMSC).
Real-world study
Preapproval clinical trials of ocrelizumab suggest about 5% of patients experience a repletion of B cells. However, the timing and association with breakthrough symptoms were unclear.
To investigate, Dr. Katz and colleagues conducted two studies. The first is a substudy of the prospective ACAPELLA trial to assess ocrelizumab-associated adverse events in a real-world population. The study included 294 patients with relapsing and progressive forms of MS treated with at least two cycles of ocrelizumab, given as infusion once every 6 months.
The results showed that overall, 91 (31%) of the 294 patients had some degree of repletion at one or more timepoints.
In categorizing patients according to their highest CD19 measure after two cycles, 108 patients (64.7%) had no significant repletion of B-cells after infusion, defined as an increase of less than 10 cells/μL, while 45 (26.9%) were considered mild repleters, defined as having increases of 10-49 cells/μL.
Seven patients (4.2%) were moderate repleters, with an increase of 50-79 cells/μL, and 7 (4.2%) were categorized as marked repleters, with increases of 80 or more cells/μL.
Eight patients in the study fully repleted, with values from 114-319 cells/μL, occurring between 23 and 34 weeks of the last infusion.
However, there was no relationship between repletion of the B-cells and clinical or MRI evidence of relapse.
Of note, the proportion of patients who did not have B-cell repletion increased with greater numbers of infusions. Whereas 64.7% were non-repleters at cycle 2, that number increased to 88.8% by cycle 6, with a slight drop to 85.6% being non-repleters by cycle 7 (36 months).
“Mild B-cell repletion was fairly common after two cycles of ocrelizumab, but with repeated dosing, a greater proportion of patients were non-repleters, suggesting that cumulative exposure to ocrelizumab results in greater depletion,” the researchers noted.
However, “while the number of moderate or marked repleters in our study was small, they had a tendency to remain repleters over time with subsequent infusions,” they added.
In looking at patient characteristics, moderate and marketed repleters had higher mean BMI (34.1 and 32.6, respectively) compared with the non- and mild repleters (27.0 and 29.4, respectively; P < .0001).
Dr. Katz noted that the increased risk of B-cell repletion with higher BMI was not a surprise. This association, he said, “makes sense” because patients’ relative exposure to ocrelizumab decreases with higher BMI. Similar patterns with BMI were observed in the clinical trial for ocrelizumab approval, in which patients with lower BMI tended to have greater improvement.
No symptom worsening
In the second study, the investigators further examined changes in symptom burden related to the amount of time from ocrelizumab infusion. They evaluated 110 patients, aged 18-80 (mean age 44.8) who had Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) scores between 0-7. Study participants were either initiating ocrelizumab or had been on the drug for at least 1 year.
Symptom burden was evaluated with the Neurological Disorders (Neuro-Qol) questionnaire and SymptoMScreen patient-reported outcomes at the beginning of the study at week 4, and near the end of the ocrelizumab infusion cycle, at week 22.
The researchers found that among 69 participants who completed the questionnaires, there were no significant differences at week 22 versus week 4 across a wide range of symptoms, including walking, spasticity, pain, fatigue, cognitive function, dizziness, and depression between the two timepoints.
The only change on the Neuro-QoL score was in the sleep disturbance domain, which improved marginally at the end of the cycle (P = .052). This study did not evaluate changes in B-cells.
Dr. Katz noted that the inclusion of patients over age of 55 in the study offered important insights.
“Our hypothesis was that we were going to start seeing a higher rate of complications, especially infections, in people who are older and may be at a higher risk of infection and disability,” Dr. Katz noted. “But so far, we haven’t seen any higher risk in older patients or those with more disability than anyone else, which is good news.”
Amplification of baseline symptoms not uncommon
Commenting on the research, Scott D. Newsome, DO, current president of the CMSC, noted that although no association was observed between the B-cell repletion and symptoms, amplification of flare-up symptoms that are linked to B-cell depleting therapy infusion timing are not uncommon.
“The ‘wearing-off’ phenomenon is not unique to the B-cell therapies,” said Dr. Newsome, who is also director of Johns Hopkins University’s Neurosciences Consultation and Infusion Center and an associate professor of neurology at the JHU med school. “With natalizumab (Tysabri), patients can have an amplification of baseline symptoms as they come closer to their next infusion, and it has been speculated that maybe it was something biologically happening, such as inflammatory cytokines ramping back up or some other mechanisms.”
“Now that we have the B-cell depleting therapies, we tend see the same kind of pattern, where a few weeks leading up to the next infusion, people will develop these amplified symptoms,” he said.
The possibility of a cumulative effect, appearing to address the B-cell repletion associated with early infusions, could have implications over time, Dr. Newsome noted.
“This is important because if people are going on these therapies long-term, the question we may need to ask is whether they actually need to continue to get an infusion every 6 months,” he said.
As these questions around the safety of long-term immunosuppressant drug use continue, different dosing regimens may need to be considered in order to mitigate potential infection risk, he added.
Dr. Katz reports consulting and/or speakers’ bureau relationships with Alexion, Biogen, EMD Serono, Genentech, Novartis, and Sanofi. Dr. Newsome reports relationships with Autobahn, BioIncept, Biogen, Genentech, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, EMD Serono, Greenwich Biosciences, and MedDay Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
. However, there are no corresponding worsening of symptoms or signs of a “wearing off” effect, new research shows.
“Most people expect that since this is a B-cell depleting drug, that if you are not depleting B cells, then that should be reflected clinically and there should be some breakthrough activity,” said study investigator Joshua D. Katz, MD, codirector of the Elliot Lewis Center for Multiple Sclerosis Care in Wellesley, Massachusetts.
“So [these results] were a surprise, but I would not conclude from our data that B-cell repletion does not put someone at risk. We can only say that we didn’t observe anybody having a breakthrough,” he added.
The research was presented at the 2021 Annual Meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (CMSC).
Real-world study
Preapproval clinical trials of ocrelizumab suggest about 5% of patients experience a repletion of B cells. However, the timing and association with breakthrough symptoms were unclear.
To investigate, Dr. Katz and colleagues conducted two studies. The first is a substudy of the prospective ACAPELLA trial to assess ocrelizumab-associated adverse events in a real-world population. The study included 294 patients with relapsing and progressive forms of MS treated with at least two cycles of ocrelizumab, given as infusion once every 6 months.
The results showed that overall, 91 (31%) of the 294 patients had some degree of repletion at one or more timepoints.
In categorizing patients according to their highest CD19 measure after two cycles, 108 patients (64.7%) had no significant repletion of B-cells after infusion, defined as an increase of less than 10 cells/μL, while 45 (26.9%) were considered mild repleters, defined as having increases of 10-49 cells/μL.
Seven patients (4.2%) were moderate repleters, with an increase of 50-79 cells/μL, and 7 (4.2%) were categorized as marked repleters, with increases of 80 or more cells/μL.
Eight patients in the study fully repleted, with values from 114-319 cells/μL, occurring between 23 and 34 weeks of the last infusion.
However, there was no relationship between repletion of the B-cells and clinical or MRI evidence of relapse.
Of note, the proportion of patients who did not have B-cell repletion increased with greater numbers of infusions. Whereas 64.7% were non-repleters at cycle 2, that number increased to 88.8% by cycle 6, with a slight drop to 85.6% being non-repleters by cycle 7 (36 months).
“Mild B-cell repletion was fairly common after two cycles of ocrelizumab, but with repeated dosing, a greater proportion of patients were non-repleters, suggesting that cumulative exposure to ocrelizumab results in greater depletion,” the researchers noted.
However, “while the number of moderate or marked repleters in our study was small, they had a tendency to remain repleters over time with subsequent infusions,” they added.
In looking at patient characteristics, moderate and marketed repleters had higher mean BMI (34.1 and 32.6, respectively) compared with the non- and mild repleters (27.0 and 29.4, respectively; P < .0001).
Dr. Katz noted that the increased risk of B-cell repletion with higher BMI was not a surprise. This association, he said, “makes sense” because patients’ relative exposure to ocrelizumab decreases with higher BMI. Similar patterns with BMI were observed in the clinical trial for ocrelizumab approval, in which patients with lower BMI tended to have greater improvement.
No symptom worsening
In the second study, the investigators further examined changes in symptom burden related to the amount of time from ocrelizumab infusion. They evaluated 110 patients, aged 18-80 (mean age 44.8) who had Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) scores between 0-7. Study participants were either initiating ocrelizumab or had been on the drug for at least 1 year.
Symptom burden was evaluated with the Neurological Disorders (Neuro-Qol) questionnaire and SymptoMScreen patient-reported outcomes at the beginning of the study at week 4, and near the end of the ocrelizumab infusion cycle, at week 22.
The researchers found that among 69 participants who completed the questionnaires, there were no significant differences at week 22 versus week 4 across a wide range of symptoms, including walking, spasticity, pain, fatigue, cognitive function, dizziness, and depression between the two timepoints.
The only change on the Neuro-QoL score was in the sleep disturbance domain, which improved marginally at the end of the cycle (P = .052). This study did not evaluate changes in B-cells.
Dr. Katz noted that the inclusion of patients over age of 55 in the study offered important insights.
“Our hypothesis was that we were going to start seeing a higher rate of complications, especially infections, in people who are older and may be at a higher risk of infection and disability,” Dr. Katz noted. “But so far, we haven’t seen any higher risk in older patients or those with more disability than anyone else, which is good news.”
Amplification of baseline symptoms not uncommon
Commenting on the research, Scott D. Newsome, DO, current president of the CMSC, noted that although no association was observed between the B-cell repletion and symptoms, amplification of flare-up symptoms that are linked to B-cell depleting therapy infusion timing are not uncommon.
“The ‘wearing-off’ phenomenon is not unique to the B-cell therapies,” said Dr. Newsome, who is also director of Johns Hopkins University’s Neurosciences Consultation and Infusion Center and an associate professor of neurology at the JHU med school. “With natalizumab (Tysabri), patients can have an amplification of baseline symptoms as they come closer to their next infusion, and it has been speculated that maybe it was something biologically happening, such as inflammatory cytokines ramping back up or some other mechanisms.”
“Now that we have the B-cell depleting therapies, we tend see the same kind of pattern, where a few weeks leading up to the next infusion, people will develop these amplified symptoms,” he said.
The possibility of a cumulative effect, appearing to address the B-cell repletion associated with early infusions, could have implications over time, Dr. Newsome noted.
“This is important because if people are going on these therapies long-term, the question we may need to ask is whether they actually need to continue to get an infusion every 6 months,” he said.
As these questions around the safety of long-term immunosuppressant drug use continue, different dosing regimens may need to be considered in order to mitigate potential infection risk, he added.
Dr. Katz reports consulting and/or speakers’ bureau relationships with Alexion, Biogen, EMD Serono, Genentech, Novartis, and Sanofi. Dr. Newsome reports relationships with Autobahn, BioIncept, Biogen, Genentech, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, EMD Serono, Greenwich Biosciences, and MedDay Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
. However, there are no corresponding worsening of symptoms or signs of a “wearing off” effect, new research shows.
“Most people expect that since this is a B-cell depleting drug, that if you are not depleting B cells, then that should be reflected clinically and there should be some breakthrough activity,” said study investigator Joshua D. Katz, MD, codirector of the Elliot Lewis Center for Multiple Sclerosis Care in Wellesley, Massachusetts.
“So [these results] were a surprise, but I would not conclude from our data that B-cell repletion does not put someone at risk. We can only say that we didn’t observe anybody having a breakthrough,” he added.
The research was presented at the 2021 Annual Meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (CMSC).
Real-world study
Preapproval clinical trials of ocrelizumab suggest about 5% of patients experience a repletion of B cells. However, the timing and association with breakthrough symptoms were unclear.
To investigate, Dr. Katz and colleagues conducted two studies. The first is a substudy of the prospective ACAPELLA trial to assess ocrelizumab-associated adverse events in a real-world population. The study included 294 patients with relapsing and progressive forms of MS treated with at least two cycles of ocrelizumab, given as infusion once every 6 months.
The results showed that overall, 91 (31%) of the 294 patients had some degree of repletion at one or more timepoints.
In categorizing patients according to their highest CD19 measure after two cycles, 108 patients (64.7%) had no significant repletion of B-cells after infusion, defined as an increase of less than 10 cells/μL, while 45 (26.9%) were considered mild repleters, defined as having increases of 10-49 cells/μL.
Seven patients (4.2%) were moderate repleters, with an increase of 50-79 cells/μL, and 7 (4.2%) were categorized as marked repleters, with increases of 80 or more cells/μL.
Eight patients in the study fully repleted, with values from 114-319 cells/μL, occurring between 23 and 34 weeks of the last infusion.
However, there was no relationship between repletion of the B-cells and clinical or MRI evidence of relapse.
Of note, the proportion of patients who did not have B-cell repletion increased with greater numbers of infusions. Whereas 64.7% were non-repleters at cycle 2, that number increased to 88.8% by cycle 6, with a slight drop to 85.6% being non-repleters by cycle 7 (36 months).
“Mild B-cell repletion was fairly common after two cycles of ocrelizumab, but with repeated dosing, a greater proportion of patients were non-repleters, suggesting that cumulative exposure to ocrelizumab results in greater depletion,” the researchers noted.
However, “while the number of moderate or marked repleters in our study was small, they had a tendency to remain repleters over time with subsequent infusions,” they added.
In looking at patient characteristics, moderate and marketed repleters had higher mean BMI (34.1 and 32.6, respectively) compared with the non- and mild repleters (27.0 and 29.4, respectively; P < .0001).
Dr. Katz noted that the increased risk of B-cell repletion with higher BMI was not a surprise. This association, he said, “makes sense” because patients’ relative exposure to ocrelizumab decreases with higher BMI. Similar patterns with BMI were observed in the clinical trial for ocrelizumab approval, in which patients with lower BMI tended to have greater improvement.
No symptom worsening
In the second study, the investigators further examined changes in symptom burden related to the amount of time from ocrelizumab infusion. They evaluated 110 patients, aged 18-80 (mean age 44.8) who had Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) scores between 0-7. Study participants were either initiating ocrelizumab or had been on the drug for at least 1 year.
Symptom burden was evaluated with the Neurological Disorders (Neuro-Qol) questionnaire and SymptoMScreen patient-reported outcomes at the beginning of the study at week 4, and near the end of the ocrelizumab infusion cycle, at week 22.
The researchers found that among 69 participants who completed the questionnaires, there were no significant differences at week 22 versus week 4 across a wide range of symptoms, including walking, spasticity, pain, fatigue, cognitive function, dizziness, and depression between the two timepoints.
The only change on the Neuro-QoL score was in the sleep disturbance domain, which improved marginally at the end of the cycle (P = .052). This study did not evaluate changes in B-cells.
Dr. Katz noted that the inclusion of patients over age of 55 in the study offered important insights.
“Our hypothesis was that we were going to start seeing a higher rate of complications, especially infections, in people who are older and may be at a higher risk of infection and disability,” Dr. Katz noted. “But so far, we haven’t seen any higher risk in older patients or those with more disability than anyone else, which is good news.”
Amplification of baseline symptoms not uncommon
Commenting on the research, Scott D. Newsome, DO, current president of the CMSC, noted that although no association was observed between the B-cell repletion and symptoms, amplification of flare-up symptoms that are linked to B-cell depleting therapy infusion timing are not uncommon.
“The ‘wearing-off’ phenomenon is not unique to the B-cell therapies,” said Dr. Newsome, who is also director of Johns Hopkins University’s Neurosciences Consultation and Infusion Center and an associate professor of neurology at the JHU med school. “With natalizumab (Tysabri), patients can have an amplification of baseline symptoms as they come closer to their next infusion, and it has been speculated that maybe it was something biologically happening, such as inflammatory cytokines ramping back up or some other mechanisms.”
“Now that we have the B-cell depleting therapies, we tend see the same kind of pattern, where a few weeks leading up to the next infusion, people will develop these amplified symptoms,” he said.
The possibility of a cumulative effect, appearing to address the B-cell repletion associated with early infusions, could have implications over time, Dr. Newsome noted.
“This is important because if people are going on these therapies long-term, the question we may need to ask is whether they actually need to continue to get an infusion every 6 months,” he said.
As these questions around the safety of long-term immunosuppressant drug use continue, different dosing regimens may need to be considered in order to mitigate potential infection risk, he added.
Dr. Katz reports consulting and/or speakers’ bureau relationships with Alexion, Biogen, EMD Serono, Genentech, Novartis, and Sanofi. Dr. Newsome reports relationships with Autobahn, BioIncept, Biogen, Genentech, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, EMD Serono, Greenwich Biosciences, and MedDay Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CMSC 2021
Brief, automated cognitive test may offer key advantages in MS
(RRMS), new research shows.
“To our knowledge this is the first psychometric evaluation of the NIH Toolbox Cognition Battery in MS,” said study investigator Heena R. Manglani, MA, a clinical psychology fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
“[The findings] suggest that the NIH Toolbox Cognition Battery may be used as an alternative to other gold-standard measures which may cover limited domains or require manual scoring,” added Ms. Manglani, who is working toward her PhD in clinical psychology.
The study was presented at the 2021 Annual Meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (CMSC).
An indicator of disease activity?
Cognitive deficits affecting a range of functions – including memory, attention and communication – are common in MS and affect 34% to 65% of patients with the disease, and the ability to detect and monitor such deficits has important implications.
Cognitive changes can provide a unique opportunity to identify acute disease activity in patients with MS that might be already occurring before physical manifestations become apparent, said Ms. Manglani. “If we can detect subtle changes in cognition that might foreshadow other symptoms of disease worsening, we can then allocate interventions that might stave off cognitive decline,” she explained.
While there is an array of well-established neuropsychological tests for the assessment of cognitive deficits, each has limitations, so a shorter, computerized, convenient, and reliable test could prove beneficial.
The NIHTB-CB has been validated in a large, nationally representative sample of individuals aged 8 to 85 and represents a potentially attractive option, yielding composite measures and scores corrected for age, gender, education, race, and ethnicity.
Comparative testing
To compare the test with other leading cognition tools used in MS, the investigators recruited 87 patients with RRMS (79% female, mean age 47.3 years). Participants were recruited to perform the full NIHTB-CB (about 30 minutes) and the full Minimal Assessment of Cognitive Function in Multiple Sclerosis (MACFIMS), which takes about 90 minutes, as well as some subsets from the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-IV (WAIS-IV) covering processing speed and working memory. All patients had an EDSS of 5.0 or below and, on average, had been living with MS for about a decade.
The results showed the normative scores for NIHTB-CB had significant concordance with the other measures in terms of processing speed (concordance correlation coefficient [CCC] range = 0.28-0.48), working memory (CCC range = 0.27-0.37), and episodic memory (CCC range = 0.21-0.32). However, agreement was not shown for executive function (CCC range = 0.096-0.11).
Ms. Manglani noted executive function included various submeasures such as planning and inhibitory control. “Perhaps our gold standard measures tapped into a different facet of executive function than measured by the NIHTB,” she said.
The investigators found the proportion of participants classified as cognitively impaired was similar between the MACFIMS and the NIHTB tests.
Further assessment of fluid cognition on the NIHTB-CB – a composite of processing speed, working memory, episodic memory, and executive function that is automatically generated by the toolbox – showed the measure was negatively associated with disease severity, as measured by the EDSS (P = .006). However, the measure was not associated with a difference in depression (P = .39) or fatigue (P = .69).
Of note, a similar association with lower disease severity on the EDSS was not observed with MACFIMS.
“Interestingly, we found that only the NIHTB-CB fluid cognition was associated with disease severity, such that it was associated with nearly 11% of the variance in EDSS scores, and we were surprised that we didn’t see this with MACFIMS,” Ms. Manglani said.
Key advantages
The NIHTB-CB was developed as part of the NIH Blueprint for Neuroscience Research initiative and commissioned by 16 NIH Institutes to provide brief, efficient assessment measures of cognitive function.
The battery has been validated in healthy individuals and tested in other populations with neurologic disorders, including patients who have suffered stroke and traumatic brain injury.
Ms. Manglani noted that the NIHTB-CB had key advantages over other tests. “First, it is a 30-minute iPad-based battery, which is shorter than most cognitive batteries available, and one of the few that is completely computerized. In addition, it automatically scores performance and yields a report with both composite scores and scores for each subtest,” she said.
In addition, said Ms. Manglani, “the NIH toolbox has a large validation sample of individuals between 8-85 years of age and provides normative scores that account for age, gender, education, and race/ethnicity, which allows individuals’ performances to be compared with their peers.”
The findings underscore that with further validation, the battery could have an important role in MS, she added.
“The NIH Toolbox needs to be tested in all subtypes of MS, with a full range of disease severity, and in MS clinics to gauge the clinical feasibility. Larger samples and repeated assessments are also needed to assess the test-retest reliability,” she said.
The study had no specific funding. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
(RRMS), new research shows.
“To our knowledge this is the first psychometric evaluation of the NIH Toolbox Cognition Battery in MS,” said study investigator Heena R. Manglani, MA, a clinical psychology fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
“[The findings] suggest that the NIH Toolbox Cognition Battery may be used as an alternative to other gold-standard measures which may cover limited domains or require manual scoring,” added Ms. Manglani, who is working toward her PhD in clinical psychology.
The study was presented at the 2021 Annual Meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (CMSC).
An indicator of disease activity?
Cognitive deficits affecting a range of functions – including memory, attention and communication – are common in MS and affect 34% to 65% of patients with the disease, and the ability to detect and monitor such deficits has important implications.
Cognitive changes can provide a unique opportunity to identify acute disease activity in patients with MS that might be already occurring before physical manifestations become apparent, said Ms. Manglani. “If we can detect subtle changes in cognition that might foreshadow other symptoms of disease worsening, we can then allocate interventions that might stave off cognitive decline,” she explained.
While there is an array of well-established neuropsychological tests for the assessment of cognitive deficits, each has limitations, so a shorter, computerized, convenient, and reliable test could prove beneficial.
The NIHTB-CB has been validated in a large, nationally representative sample of individuals aged 8 to 85 and represents a potentially attractive option, yielding composite measures and scores corrected for age, gender, education, race, and ethnicity.
Comparative testing
To compare the test with other leading cognition tools used in MS, the investigators recruited 87 patients with RRMS (79% female, mean age 47.3 years). Participants were recruited to perform the full NIHTB-CB (about 30 minutes) and the full Minimal Assessment of Cognitive Function in Multiple Sclerosis (MACFIMS), which takes about 90 minutes, as well as some subsets from the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-IV (WAIS-IV) covering processing speed and working memory. All patients had an EDSS of 5.0 or below and, on average, had been living with MS for about a decade.
The results showed the normative scores for NIHTB-CB had significant concordance with the other measures in terms of processing speed (concordance correlation coefficient [CCC] range = 0.28-0.48), working memory (CCC range = 0.27-0.37), and episodic memory (CCC range = 0.21-0.32). However, agreement was not shown for executive function (CCC range = 0.096-0.11).
Ms. Manglani noted executive function included various submeasures such as planning and inhibitory control. “Perhaps our gold standard measures tapped into a different facet of executive function than measured by the NIHTB,” she said.
The investigators found the proportion of participants classified as cognitively impaired was similar between the MACFIMS and the NIHTB tests.
Further assessment of fluid cognition on the NIHTB-CB – a composite of processing speed, working memory, episodic memory, and executive function that is automatically generated by the toolbox – showed the measure was negatively associated with disease severity, as measured by the EDSS (P = .006). However, the measure was not associated with a difference in depression (P = .39) or fatigue (P = .69).
Of note, a similar association with lower disease severity on the EDSS was not observed with MACFIMS.
“Interestingly, we found that only the NIHTB-CB fluid cognition was associated with disease severity, such that it was associated with nearly 11% of the variance in EDSS scores, and we were surprised that we didn’t see this with MACFIMS,” Ms. Manglani said.
Key advantages
The NIHTB-CB was developed as part of the NIH Blueprint for Neuroscience Research initiative and commissioned by 16 NIH Institutes to provide brief, efficient assessment measures of cognitive function.
The battery has been validated in healthy individuals and tested in other populations with neurologic disorders, including patients who have suffered stroke and traumatic brain injury.
Ms. Manglani noted that the NIHTB-CB had key advantages over other tests. “First, it is a 30-minute iPad-based battery, which is shorter than most cognitive batteries available, and one of the few that is completely computerized. In addition, it automatically scores performance and yields a report with both composite scores and scores for each subtest,” she said.
In addition, said Ms. Manglani, “the NIH toolbox has a large validation sample of individuals between 8-85 years of age and provides normative scores that account for age, gender, education, and race/ethnicity, which allows individuals’ performances to be compared with their peers.”
The findings underscore that with further validation, the battery could have an important role in MS, she added.
“The NIH Toolbox needs to be tested in all subtypes of MS, with a full range of disease severity, and in MS clinics to gauge the clinical feasibility. Larger samples and repeated assessments are also needed to assess the test-retest reliability,” she said.
The study had no specific funding. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
(RRMS), new research shows.
“To our knowledge this is the first psychometric evaluation of the NIH Toolbox Cognition Battery in MS,” said study investigator Heena R. Manglani, MA, a clinical psychology fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
“[The findings] suggest that the NIH Toolbox Cognition Battery may be used as an alternative to other gold-standard measures which may cover limited domains or require manual scoring,” added Ms. Manglani, who is working toward her PhD in clinical psychology.
The study was presented at the 2021 Annual Meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (CMSC).
An indicator of disease activity?
Cognitive deficits affecting a range of functions – including memory, attention and communication – are common in MS and affect 34% to 65% of patients with the disease, and the ability to detect and monitor such deficits has important implications.
Cognitive changes can provide a unique opportunity to identify acute disease activity in patients with MS that might be already occurring before physical manifestations become apparent, said Ms. Manglani. “If we can detect subtle changes in cognition that might foreshadow other symptoms of disease worsening, we can then allocate interventions that might stave off cognitive decline,” she explained.
While there is an array of well-established neuropsychological tests for the assessment of cognitive deficits, each has limitations, so a shorter, computerized, convenient, and reliable test could prove beneficial.
The NIHTB-CB has been validated in a large, nationally representative sample of individuals aged 8 to 85 and represents a potentially attractive option, yielding composite measures and scores corrected for age, gender, education, race, and ethnicity.
Comparative testing
To compare the test with other leading cognition tools used in MS, the investigators recruited 87 patients with RRMS (79% female, mean age 47.3 years). Participants were recruited to perform the full NIHTB-CB (about 30 minutes) and the full Minimal Assessment of Cognitive Function in Multiple Sclerosis (MACFIMS), which takes about 90 minutes, as well as some subsets from the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-IV (WAIS-IV) covering processing speed and working memory. All patients had an EDSS of 5.0 or below and, on average, had been living with MS for about a decade.
The results showed the normative scores for NIHTB-CB had significant concordance with the other measures in terms of processing speed (concordance correlation coefficient [CCC] range = 0.28-0.48), working memory (CCC range = 0.27-0.37), and episodic memory (CCC range = 0.21-0.32). However, agreement was not shown for executive function (CCC range = 0.096-0.11).
Ms. Manglani noted executive function included various submeasures such as planning and inhibitory control. “Perhaps our gold standard measures tapped into a different facet of executive function than measured by the NIHTB,” she said.
The investigators found the proportion of participants classified as cognitively impaired was similar between the MACFIMS and the NIHTB tests.
Further assessment of fluid cognition on the NIHTB-CB – a composite of processing speed, working memory, episodic memory, and executive function that is automatically generated by the toolbox – showed the measure was negatively associated with disease severity, as measured by the EDSS (P = .006). However, the measure was not associated with a difference in depression (P = .39) or fatigue (P = .69).
Of note, a similar association with lower disease severity on the EDSS was not observed with MACFIMS.
“Interestingly, we found that only the NIHTB-CB fluid cognition was associated with disease severity, such that it was associated with nearly 11% of the variance in EDSS scores, and we were surprised that we didn’t see this with MACFIMS,” Ms. Manglani said.
Key advantages
The NIHTB-CB was developed as part of the NIH Blueprint for Neuroscience Research initiative and commissioned by 16 NIH Institutes to provide brief, efficient assessment measures of cognitive function.
The battery has been validated in healthy individuals and tested in other populations with neurologic disorders, including patients who have suffered stroke and traumatic brain injury.
Ms. Manglani noted that the NIHTB-CB had key advantages over other tests. “First, it is a 30-minute iPad-based battery, which is shorter than most cognitive batteries available, and one of the few that is completely computerized. In addition, it automatically scores performance and yields a report with both composite scores and scores for each subtest,” she said.
In addition, said Ms. Manglani, “the NIH toolbox has a large validation sample of individuals between 8-85 years of age and provides normative scores that account for age, gender, education, and race/ethnicity, which allows individuals’ performances to be compared with their peers.”
The findings underscore that with further validation, the battery could have an important role in MS, she added.
“The NIH Toolbox needs to be tested in all subtypes of MS, with a full range of disease severity, and in MS clinics to gauge the clinical feasibility. Larger samples and repeated assessments are also needed to assess the test-retest reliability,” she said.
The study had no specific funding. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CMSC 2021
Specialty pharmacists may speed time to MS treatment
, new data suggest.
“As DMT management and treatment options for MS symptoms become more complex, clinical pharmacists can be utilized for medication education and management,” Jenelle Hall Montgomery, PharmD, a clinical pharmacist practitioner at the Multiple Sclerosis and Neuroimmunology Division, department of neurology, Duke University Hospital, Durham, N.C., told delegates attending the 2021 Annual Meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (CMSC).
Since 2018, more than half a dozen DMTs have been approved for MS by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. However, there is currently no established DMT selection algorithm, and because of this, there is a need for specialty pharmacists, she added.
“DMT approvals by the FDA have outpaced MS guideline recommendations. This can be overwhelming for patients, especially now that they have so many options to choose from,” she said.
Key services provided by specialty pharmacists include coordinating pretreatment requirements, as well as help with dosing, side effects, safety monitoring, and treatment adherence. In addition, pharmacists help with switching therapies, dispensing, and cost and authorization problems.
In reporting on improvements associated with specialty pharmacists, researchers from prominent MS centers around the country described specific outcomes.
Aids early intervention
A report on the Kaiser Permanente Washington (KPWA) MS Pharmacy Program detailed significant reductions in the time to address patients’ needs through the use of specialty pharmacists. In an assessment of 391 referrals to the program from 2019 to 2020, the average total time spent per patient per year dropped from 145 minutes in 2019 to 109 minutes in 2020.
Services included assessment of medication adherence, adverse drug reaction consultation, lab monitoring, patient counseling on initiation of a DMT, shared decision making, and follow-up visits.
“The KPWA MS Pharmacy Program plays an integral role in the care of patients with MS. The MS clinical pharmacists ensure patients are well informed about their DMT options and are fully educated about selected treatment,” the investigators noted.
A report on an outpatient MS clinic at Emory Healthcare, Atlanta, described how use of specialty pharmacist services resulted in a 49% reduction in time to treatment initiation with fingolimod. The time decreased from 83.9 days to 42.9 days following the introduction of specialty pharmacist services.
“Integration of a clinical pharmacy specialist in the therapeutic management of MS patients is crucial to early intervention with disease-modifying therapy,” the investigators noted.
A report on the specialty pharmacy services provided at Johns Hopkins MS Precision Medicine Center of Excellence, Baltimore, described an evaluation of 708 assessments between July 2019 and June 2020. Results showed that the vast majority (98%) of patients reported no missed days from work or school due to MS-related symptoms and that 99.3% reported no hospitalizations due to MS relapses, which are both key measures of MS treatment adherence.
High patient satisfaction
Patients reported high satisfaction with the in-house pharmacy on the National Association of Specialty Pharmacy’s patient satisfaction survey. In the survey, the average score was 82, compared with 79 for external specialty pharmacies.
“Moreover, patients were highly satisfied with the services provided at the pharmacy and were likely to continue receiving their comprehensive pharmacy care at our institution,” the researchers reported.
The study “highlights the value of pharmacists’ involvement in patient care and supports the need for continuation of integrated clinical services in health system specialty pharmacy,” the investigators noted.
CMSC President Scott D. Newsome, DO, director of the Neurosciences Consultation and Infusion Center at Green Spring Station, Lutherville, Maryland, and associate professor of neurology at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, said that as a clinician, he is highly satisfied with the specialty pharmacy services for MS at Johns Hopkins.
“Our pharmacists are fantastic in communicating with the prescriber if something comes up related to medication safety or they are concerned that the patient isn’t adhering to the medication,” Dr. Newsome said.
He noted that in addition to helping to alleviate the burden of a myriad of tasks associated with prescribing for patients with MS, specialty pharmacists may have an important impact on outcomes, although more data are needed.
“Having a specialty pharmacy involved in the care of our patients can help navigate the challenges associated with the process of obtaining approval for DMTs,” he said. “We know how important it is to expedite and shorten the time frame from writing the prescription to getting the person on their DMT.”
Telemedicine, other models
Although integrated specialty pharmacist services may seem out of reach for smaller MS clinics, the use of telemedicine and other models may help achieve similar results.
“A model I have seen is having pharmacists split their time between a specialty pharmacy and the MS clinic,” said Dr. Montgomery.
“A telemedicine model can also be utilized, in which a pharmacist can reach out to patients by telephone or through video visits. This would allow a pharmacist to be utilized for multiple clinics or as an MS specialist within a specialty pharmacy,” she added.
Whether provided in house or through telemedicine, a key benefit for clinicians is in freeing up valuable time, which has a domino effect in improving quality all around.
“In addition to improving safety outcomes, specialty pharmacists help with the allocation of clinic staff to other clinic responsibilities, and the utilization of services by patients results in more resources allocated for their care,” Dr. Montgomery said.
Dr. Montgomery is a nonpromotional speaker for Novartis and is on its advisory board.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new data suggest.
“As DMT management and treatment options for MS symptoms become more complex, clinical pharmacists can be utilized for medication education and management,” Jenelle Hall Montgomery, PharmD, a clinical pharmacist practitioner at the Multiple Sclerosis and Neuroimmunology Division, department of neurology, Duke University Hospital, Durham, N.C., told delegates attending the 2021 Annual Meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (CMSC).
Since 2018, more than half a dozen DMTs have been approved for MS by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. However, there is currently no established DMT selection algorithm, and because of this, there is a need for specialty pharmacists, she added.
“DMT approvals by the FDA have outpaced MS guideline recommendations. This can be overwhelming for patients, especially now that they have so many options to choose from,” she said.
Key services provided by specialty pharmacists include coordinating pretreatment requirements, as well as help with dosing, side effects, safety monitoring, and treatment adherence. In addition, pharmacists help with switching therapies, dispensing, and cost and authorization problems.
In reporting on improvements associated with specialty pharmacists, researchers from prominent MS centers around the country described specific outcomes.
Aids early intervention
A report on the Kaiser Permanente Washington (KPWA) MS Pharmacy Program detailed significant reductions in the time to address patients’ needs through the use of specialty pharmacists. In an assessment of 391 referrals to the program from 2019 to 2020, the average total time spent per patient per year dropped from 145 minutes in 2019 to 109 minutes in 2020.
Services included assessment of medication adherence, adverse drug reaction consultation, lab monitoring, patient counseling on initiation of a DMT, shared decision making, and follow-up visits.
“The KPWA MS Pharmacy Program plays an integral role in the care of patients with MS. The MS clinical pharmacists ensure patients are well informed about their DMT options and are fully educated about selected treatment,” the investigators noted.
A report on an outpatient MS clinic at Emory Healthcare, Atlanta, described how use of specialty pharmacist services resulted in a 49% reduction in time to treatment initiation with fingolimod. The time decreased from 83.9 days to 42.9 days following the introduction of specialty pharmacist services.
“Integration of a clinical pharmacy specialist in the therapeutic management of MS patients is crucial to early intervention with disease-modifying therapy,” the investigators noted.
A report on the specialty pharmacy services provided at Johns Hopkins MS Precision Medicine Center of Excellence, Baltimore, described an evaluation of 708 assessments between July 2019 and June 2020. Results showed that the vast majority (98%) of patients reported no missed days from work or school due to MS-related symptoms and that 99.3% reported no hospitalizations due to MS relapses, which are both key measures of MS treatment adherence.
High patient satisfaction
Patients reported high satisfaction with the in-house pharmacy on the National Association of Specialty Pharmacy’s patient satisfaction survey. In the survey, the average score was 82, compared with 79 for external specialty pharmacies.
“Moreover, patients were highly satisfied with the services provided at the pharmacy and were likely to continue receiving their comprehensive pharmacy care at our institution,” the researchers reported.
The study “highlights the value of pharmacists’ involvement in patient care and supports the need for continuation of integrated clinical services in health system specialty pharmacy,” the investigators noted.
CMSC President Scott D. Newsome, DO, director of the Neurosciences Consultation and Infusion Center at Green Spring Station, Lutherville, Maryland, and associate professor of neurology at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, said that as a clinician, he is highly satisfied with the specialty pharmacy services for MS at Johns Hopkins.
“Our pharmacists are fantastic in communicating with the prescriber if something comes up related to medication safety or they are concerned that the patient isn’t adhering to the medication,” Dr. Newsome said.
He noted that in addition to helping to alleviate the burden of a myriad of tasks associated with prescribing for patients with MS, specialty pharmacists may have an important impact on outcomes, although more data are needed.
“Having a specialty pharmacy involved in the care of our patients can help navigate the challenges associated with the process of obtaining approval for DMTs,” he said. “We know how important it is to expedite and shorten the time frame from writing the prescription to getting the person on their DMT.”
Telemedicine, other models
Although integrated specialty pharmacist services may seem out of reach for smaller MS clinics, the use of telemedicine and other models may help achieve similar results.
“A model I have seen is having pharmacists split their time between a specialty pharmacy and the MS clinic,” said Dr. Montgomery.
“A telemedicine model can also be utilized, in which a pharmacist can reach out to patients by telephone or through video visits. This would allow a pharmacist to be utilized for multiple clinics or as an MS specialist within a specialty pharmacy,” she added.
Whether provided in house or through telemedicine, a key benefit for clinicians is in freeing up valuable time, which has a domino effect in improving quality all around.
“In addition to improving safety outcomes, specialty pharmacists help with the allocation of clinic staff to other clinic responsibilities, and the utilization of services by patients results in more resources allocated for their care,” Dr. Montgomery said.
Dr. Montgomery is a nonpromotional speaker for Novartis and is on its advisory board.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new data suggest.
“As DMT management and treatment options for MS symptoms become more complex, clinical pharmacists can be utilized for medication education and management,” Jenelle Hall Montgomery, PharmD, a clinical pharmacist practitioner at the Multiple Sclerosis and Neuroimmunology Division, department of neurology, Duke University Hospital, Durham, N.C., told delegates attending the 2021 Annual Meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (CMSC).
Since 2018, more than half a dozen DMTs have been approved for MS by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. However, there is currently no established DMT selection algorithm, and because of this, there is a need for specialty pharmacists, she added.
“DMT approvals by the FDA have outpaced MS guideline recommendations. This can be overwhelming for patients, especially now that they have so many options to choose from,” she said.
Key services provided by specialty pharmacists include coordinating pretreatment requirements, as well as help with dosing, side effects, safety monitoring, and treatment adherence. In addition, pharmacists help with switching therapies, dispensing, and cost and authorization problems.
In reporting on improvements associated with specialty pharmacists, researchers from prominent MS centers around the country described specific outcomes.
Aids early intervention
A report on the Kaiser Permanente Washington (KPWA) MS Pharmacy Program detailed significant reductions in the time to address patients’ needs through the use of specialty pharmacists. In an assessment of 391 referrals to the program from 2019 to 2020, the average total time spent per patient per year dropped from 145 minutes in 2019 to 109 minutes in 2020.
Services included assessment of medication adherence, adverse drug reaction consultation, lab monitoring, patient counseling on initiation of a DMT, shared decision making, and follow-up visits.
“The KPWA MS Pharmacy Program plays an integral role in the care of patients with MS. The MS clinical pharmacists ensure patients are well informed about their DMT options and are fully educated about selected treatment,” the investigators noted.
A report on an outpatient MS clinic at Emory Healthcare, Atlanta, described how use of specialty pharmacist services resulted in a 49% reduction in time to treatment initiation with fingolimod. The time decreased from 83.9 days to 42.9 days following the introduction of specialty pharmacist services.
“Integration of a clinical pharmacy specialist in the therapeutic management of MS patients is crucial to early intervention with disease-modifying therapy,” the investigators noted.
A report on the specialty pharmacy services provided at Johns Hopkins MS Precision Medicine Center of Excellence, Baltimore, described an evaluation of 708 assessments between July 2019 and June 2020. Results showed that the vast majority (98%) of patients reported no missed days from work or school due to MS-related symptoms and that 99.3% reported no hospitalizations due to MS relapses, which are both key measures of MS treatment adherence.
High patient satisfaction
Patients reported high satisfaction with the in-house pharmacy on the National Association of Specialty Pharmacy’s patient satisfaction survey. In the survey, the average score was 82, compared with 79 for external specialty pharmacies.
“Moreover, patients were highly satisfied with the services provided at the pharmacy and were likely to continue receiving their comprehensive pharmacy care at our institution,” the researchers reported.
The study “highlights the value of pharmacists’ involvement in patient care and supports the need for continuation of integrated clinical services in health system specialty pharmacy,” the investigators noted.
CMSC President Scott D. Newsome, DO, director of the Neurosciences Consultation and Infusion Center at Green Spring Station, Lutherville, Maryland, and associate professor of neurology at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, said that as a clinician, he is highly satisfied with the specialty pharmacy services for MS at Johns Hopkins.
“Our pharmacists are fantastic in communicating with the prescriber if something comes up related to medication safety or they are concerned that the patient isn’t adhering to the medication,” Dr. Newsome said.
He noted that in addition to helping to alleviate the burden of a myriad of tasks associated with prescribing for patients with MS, specialty pharmacists may have an important impact on outcomes, although more data are needed.
“Having a specialty pharmacy involved in the care of our patients can help navigate the challenges associated with the process of obtaining approval for DMTs,” he said. “We know how important it is to expedite and shorten the time frame from writing the prescription to getting the person on their DMT.”
Telemedicine, other models
Although integrated specialty pharmacist services may seem out of reach for smaller MS clinics, the use of telemedicine and other models may help achieve similar results.
“A model I have seen is having pharmacists split their time between a specialty pharmacy and the MS clinic,” said Dr. Montgomery.
“A telemedicine model can also be utilized, in which a pharmacist can reach out to patients by telephone or through video visits. This would allow a pharmacist to be utilized for multiple clinics or as an MS specialist within a specialty pharmacy,” she added.
Whether provided in house or through telemedicine, a key benefit for clinicians is in freeing up valuable time, which has a domino effect in improving quality all around.
“In addition to improving safety outcomes, specialty pharmacists help with the allocation of clinic staff to other clinic responsibilities, and the utilization of services by patients results in more resources allocated for their care,” Dr. Montgomery said.
Dr. Montgomery is a nonpromotional speaker for Novartis and is on its advisory board.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CMSC 2021
Radiologically Isolated Syndrome: A condition that often precedes an MS diagnosis in children
Naila Makhani, MD completed medical school training at the University of British Columbia (Vancouver, Canada). This was followed by a residency in child neurology and fellowship in MS and other demyelinating diseases at the University of Toronto and The Hospital for Sick Children (Toronto, Canada). Concurrent with fellowship training, Dr. Makhani obtained a Masters’ degree in public health from Harvard University. Dr. Makhani is the Director of the Pediatric MS Program at Yale and the lead investigator of a multi-center international study examining outcomes following the radiologically isolated syndrome in children.
Q1. Could you please provide an overview of Radiologically Isolated Syndrome ?
A1. Radiologically Isolated Syndrome (RIS) was first described in adults in 2009. Since then it has also been increasingly recognized and diagnosed in children. RIS is diagnosed after an MRI of the brain that the patient has sought for reasons other than suspected multiple sclerosis-- for instance, for evaluation of head trauma or headache. However, unexpectedly or incidentally, the patient’s MRI shows the typical findings that we see in multiple sclerosis, even in the absence of any typical clinical symptoms. RIS is generally considered a rare syndrome.
Q2. You created Yale Medicine’s Pediatric Multiple Sclerosis program which advocates for the eradication of MS. What criteria defines a rare disease? Does RIS meet these criteria? And if so, how?
A2. The criteria for a rare disease vary, depending on the reference. In the US, a rare disease is defined as a condition that affects fewer than 200,000 people, in total, across the country. By contrast, in Europe, a disease is considered rare if it affects fewer than one in every 2,000 people within the country’s population.
In the case of RIS, especially in children, we suspect that this is a rare condition, but we don't know for sure, as there have been very few population-based studies. There is one large study that was conducted in Europe that found one case of RIS among approximately 5,000 otherwise healthy children, who were between 7 and 14 years of age. I think that's our best estimate of the overall prevalence of RIS in children. Using that finding, it likely would qualify as a rare condition, although, as I said, we really don't know for sure, as the prevalence may vary among different populations or age groups.
Q3. How do you investigate and manage RIS in children? What are some of the challenges?
A3. For children with radiologically isolated syndrome, we usually undertake a comprehensive workup. This includes a detailed clinical neurological exam to ensure that there are no abnormalities that would, for instance, suggest a misdiagnosis of multiple sclerosis or an alternative diagnosis. In addition to the brain MRI, we usually obtain an MRI of the spinal cord to determine whether there is any spinal cord involvement. We also obtain blood tests. We often analyze spinal fluid as well, primarily to exclude other alternative processes that may explain the MRI findings. A key challenge in this field is that there are currently no formal guidelines for the investigation and management of children with RIS. Collaborations within the pediatric MS community are needed to develop such consensus approaches to standardize care.
Q4. What are the most significant risk factors that indicate children with RIS could one day develop multiple sclerosis?
A4.This is an area of active research within our group. So far, we've found that approximately 42% of children with RIS develop multiple sclerosis in the future; on average, two years following their first abnormal MRI. Therefore, this is a high-risk group for developing multiple sclerosis in the future. Thus far, we've determined that in children with RIS, it is the presence of abnormal spinal cord imaging and an abnormality in spinal fluid – namely, the presence of oligoclonal bands – that are likely the predictors of whether these children could develop MS in the future. a child’s possible development
Q5. Based on your recent studies, are there data in children highlighting the potential for higher prevalence in one population over another?
A5. Thus far, population-based studies assessing RIS, especially in children, have been rare and thus far have not identified particular subgroups with increased prevalence. We do know that the prevalence of multiple sclerosis varies across different age groups and across gender. Whether such associations are also present for RIS is an area of active research.
de Mol CL, Bruijstens AL, Jansen PR, Dremmen M, Wong Y, van der Lugt A, White T, Neuteboom RF.Mult Scler. 2021 Oct;27(11):1790-1793. doi: 10.1177/1352458521989220. Epub 2021 Jan 22.PMID: 33480814
2. Radiologically isolated syndrome in children: Clinical and radiologic outcomes.
Makhani N, Lebrun C, Siva A, Brassat D, Carra Dallière C, de Seze J, Du W, Durand Dubief F, Kantarci O, Langille M, Narula S, Pelletier J, Rojas JI, Shapiro ED, Stone RT, Tintoré M, Uygunoglu U, Vermersch P, Wassmer E, Okuda DT, Pelletier D.Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2017 Sep 25;4(6):e395. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000395. eCollection 2017 Nov.PMID: 28959703
Makhani N, Lebrun C, Siva A, Narula S, Wassmer E, Brassat D, Brenton JN, Cabre P, Carra Dallière C, de Seze J, Durand Dubief F, Inglese M, Langille M, Mathey G, Neuteboom RF, Pelletier J, Pohl D, Reich DS, Ignacio Rojas J, Shabanova V, Shapiro ED, Stone RT, Tenembaum S, Tintoré M, Uygunoglu U, Vargas W, Venkateswaren S, Vermersch P, Kantarci O, Okuda DT, Pelletier D; Observatoire Francophone de la Sclérose en Plaques (OFSEP), Société Francophone de la Sclérose en Plaques (SFSEP), the Radiologically Isolated Syndrome Consortium (RISC) and the Pediatric Radiologically Isolated Syndrome Consortium (PARIS).Mult Scler J Exp Transl Clin. 2019 Mar 20;5(1):2055217319836664. doi: 10.1177/2055217319836664. eCollection 2019 Jan-Mar.PMID: 30915227
Naila Makhani, MD completed medical school training at the University of British Columbia (Vancouver, Canada). This was followed by a residency in child neurology and fellowship in MS and other demyelinating diseases at the University of Toronto and The Hospital for Sick Children (Toronto, Canada). Concurrent with fellowship training, Dr. Makhani obtained a Masters’ degree in public health from Harvard University. Dr. Makhani is the Director of the Pediatric MS Program at Yale and the lead investigator of a multi-center international study examining outcomes following the radiologically isolated syndrome in children.
Q1. Could you please provide an overview of Radiologically Isolated Syndrome ?
A1. Radiologically Isolated Syndrome (RIS) was first described in adults in 2009. Since then it has also been increasingly recognized and diagnosed in children. RIS is diagnosed after an MRI of the brain that the patient has sought for reasons other than suspected multiple sclerosis-- for instance, for evaluation of head trauma or headache. However, unexpectedly or incidentally, the patient’s MRI shows the typical findings that we see in multiple sclerosis, even in the absence of any typical clinical symptoms. RIS is generally considered a rare syndrome.
Q2. You created Yale Medicine’s Pediatric Multiple Sclerosis program which advocates for the eradication of MS. What criteria defines a rare disease? Does RIS meet these criteria? And if so, how?
A2. The criteria for a rare disease vary, depending on the reference. In the US, a rare disease is defined as a condition that affects fewer than 200,000 people, in total, across the country. By contrast, in Europe, a disease is considered rare if it affects fewer than one in every 2,000 people within the country’s population.
In the case of RIS, especially in children, we suspect that this is a rare condition, but we don't know for sure, as there have been very few population-based studies. There is one large study that was conducted in Europe that found one case of RIS among approximately 5,000 otherwise healthy children, who were between 7 and 14 years of age. I think that's our best estimate of the overall prevalence of RIS in children. Using that finding, it likely would qualify as a rare condition, although, as I said, we really don't know for sure, as the prevalence may vary among different populations or age groups.
Q3. How do you investigate and manage RIS in children? What are some of the challenges?
A3. For children with radiologically isolated syndrome, we usually undertake a comprehensive workup. This includes a detailed clinical neurological exam to ensure that there are no abnormalities that would, for instance, suggest a misdiagnosis of multiple sclerosis or an alternative diagnosis. In addition to the brain MRI, we usually obtain an MRI of the spinal cord to determine whether there is any spinal cord involvement. We also obtain blood tests. We often analyze spinal fluid as well, primarily to exclude other alternative processes that may explain the MRI findings. A key challenge in this field is that there are currently no formal guidelines for the investigation and management of children with RIS. Collaborations within the pediatric MS community are needed to develop such consensus approaches to standardize care.
Q4. What are the most significant risk factors that indicate children with RIS could one day develop multiple sclerosis?
A4.This is an area of active research within our group. So far, we've found that approximately 42% of children with RIS develop multiple sclerosis in the future; on average, two years following their first abnormal MRI. Therefore, this is a high-risk group for developing multiple sclerosis in the future. Thus far, we've determined that in children with RIS, it is the presence of abnormal spinal cord imaging and an abnormality in spinal fluid – namely, the presence of oligoclonal bands – that are likely the predictors of whether these children could develop MS in the future. a child’s possible development
Q5. Based on your recent studies, are there data in children highlighting the potential for higher prevalence in one population over another?
A5. Thus far, population-based studies assessing RIS, especially in children, have been rare and thus far have not identified particular subgroups with increased prevalence. We do know that the prevalence of multiple sclerosis varies across different age groups and across gender. Whether such associations are also present for RIS is an area of active research.
Naila Makhani, MD completed medical school training at the University of British Columbia (Vancouver, Canada). This was followed by a residency in child neurology and fellowship in MS and other demyelinating diseases at the University of Toronto and The Hospital for Sick Children (Toronto, Canada). Concurrent with fellowship training, Dr. Makhani obtained a Masters’ degree in public health from Harvard University. Dr. Makhani is the Director of the Pediatric MS Program at Yale and the lead investigator of a multi-center international study examining outcomes following the radiologically isolated syndrome in children.
Q1. Could you please provide an overview of Radiologically Isolated Syndrome ?
A1. Radiologically Isolated Syndrome (RIS) was first described in adults in 2009. Since then it has also been increasingly recognized and diagnosed in children. RIS is diagnosed after an MRI of the brain that the patient has sought for reasons other than suspected multiple sclerosis-- for instance, for evaluation of head trauma or headache. However, unexpectedly or incidentally, the patient’s MRI shows the typical findings that we see in multiple sclerosis, even in the absence of any typical clinical symptoms. RIS is generally considered a rare syndrome.
Q2. You created Yale Medicine’s Pediatric Multiple Sclerosis program which advocates for the eradication of MS. What criteria defines a rare disease? Does RIS meet these criteria? And if so, how?
A2. The criteria for a rare disease vary, depending on the reference. In the US, a rare disease is defined as a condition that affects fewer than 200,000 people, in total, across the country. By contrast, in Europe, a disease is considered rare if it affects fewer than one in every 2,000 people within the country’s population.
In the case of RIS, especially in children, we suspect that this is a rare condition, but we don't know for sure, as there have been very few population-based studies. There is one large study that was conducted in Europe that found one case of RIS among approximately 5,000 otherwise healthy children, who were between 7 and 14 years of age. I think that's our best estimate of the overall prevalence of RIS in children. Using that finding, it likely would qualify as a rare condition, although, as I said, we really don't know for sure, as the prevalence may vary among different populations or age groups.
Q3. How do you investigate and manage RIS in children? What are some of the challenges?
A3. For children with radiologically isolated syndrome, we usually undertake a comprehensive workup. This includes a detailed clinical neurological exam to ensure that there are no abnormalities that would, for instance, suggest a misdiagnosis of multiple sclerosis or an alternative diagnosis. In addition to the brain MRI, we usually obtain an MRI of the spinal cord to determine whether there is any spinal cord involvement. We also obtain blood tests. We often analyze spinal fluid as well, primarily to exclude other alternative processes that may explain the MRI findings. A key challenge in this field is that there are currently no formal guidelines for the investigation and management of children with RIS. Collaborations within the pediatric MS community are needed to develop such consensus approaches to standardize care.
Q4. What are the most significant risk factors that indicate children with RIS could one day develop multiple sclerosis?
A4.This is an area of active research within our group. So far, we've found that approximately 42% of children with RIS develop multiple sclerosis in the future; on average, two years following their first abnormal MRI. Therefore, this is a high-risk group for developing multiple sclerosis in the future. Thus far, we've determined that in children with RIS, it is the presence of abnormal spinal cord imaging and an abnormality in spinal fluid – namely, the presence of oligoclonal bands – that are likely the predictors of whether these children could develop MS in the future. a child’s possible development
Q5. Based on your recent studies, are there data in children highlighting the potential for higher prevalence in one population over another?
A5. Thus far, population-based studies assessing RIS, especially in children, have been rare and thus far have not identified particular subgroups with increased prevalence. We do know that the prevalence of multiple sclerosis varies across different age groups and across gender. Whether such associations are also present for RIS is an area of active research.
de Mol CL, Bruijstens AL, Jansen PR, Dremmen M, Wong Y, van der Lugt A, White T, Neuteboom RF.Mult Scler. 2021 Oct;27(11):1790-1793. doi: 10.1177/1352458521989220. Epub 2021 Jan 22.PMID: 33480814
2. Radiologically isolated syndrome in children: Clinical and radiologic outcomes.
Makhani N, Lebrun C, Siva A, Brassat D, Carra Dallière C, de Seze J, Du W, Durand Dubief F, Kantarci O, Langille M, Narula S, Pelletier J, Rojas JI, Shapiro ED, Stone RT, Tintoré M, Uygunoglu U, Vermersch P, Wassmer E, Okuda DT, Pelletier D.Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2017 Sep 25;4(6):e395. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000395. eCollection 2017 Nov.PMID: 28959703
Makhani N, Lebrun C, Siva A, Narula S, Wassmer E, Brassat D, Brenton JN, Cabre P, Carra Dallière C, de Seze J, Durand Dubief F, Inglese M, Langille M, Mathey G, Neuteboom RF, Pelletier J, Pohl D, Reich DS, Ignacio Rojas J, Shabanova V, Shapiro ED, Stone RT, Tenembaum S, Tintoré M, Uygunoglu U, Vargas W, Venkateswaren S, Vermersch P, Kantarci O, Okuda DT, Pelletier D; Observatoire Francophone de la Sclérose en Plaques (OFSEP), Société Francophone de la Sclérose en Plaques (SFSEP), the Radiologically Isolated Syndrome Consortium (RISC) and the Pediatric Radiologically Isolated Syndrome Consortium (PARIS).Mult Scler J Exp Transl Clin. 2019 Mar 20;5(1):2055217319836664. doi: 10.1177/2055217319836664. eCollection 2019 Jan-Mar.PMID: 30915227
de Mol CL, Bruijstens AL, Jansen PR, Dremmen M, Wong Y, van der Lugt A, White T, Neuteboom RF.Mult Scler. 2021 Oct;27(11):1790-1793. doi: 10.1177/1352458521989220. Epub 2021 Jan 22.PMID: 33480814
2. Radiologically isolated syndrome in children: Clinical and radiologic outcomes.
Makhani N, Lebrun C, Siva A, Brassat D, Carra Dallière C, de Seze J, Du W, Durand Dubief F, Kantarci O, Langille M, Narula S, Pelletier J, Rojas JI, Shapiro ED, Stone RT, Tintoré M, Uygunoglu U, Vermersch P, Wassmer E, Okuda DT, Pelletier D.Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2017 Sep 25;4(6):e395. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000395. eCollection 2017 Nov.PMID: 28959703
Makhani N, Lebrun C, Siva A, Narula S, Wassmer E, Brassat D, Brenton JN, Cabre P, Carra Dallière C, de Seze J, Durand Dubief F, Inglese M, Langille M, Mathey G, Neuteboom RF, Pelletier J, Pohl D, Reich DS, Ignacio Rojas J, Shabanova V, Shapiro ED, Stone RT, Tenembaum S, Tintoré M, Uygunoglu U, Vargas W, Venkateswaren S, Vermersch P, Kantarci O, Okuda DT, Pelletier D; Observatoire Francophone de la Sclérose en Plaques (OFSEP), Société Francophone de la Sclérose en Plaques (SFSEP), the Radiologically Isolated Syndrome Consortium (RISC) and the Pediatric Radiologically Isolated Syndrome Consortium (PARIS).Mult Scler J Exp Transl Clin. 2019 Mar 20;5(1):2055217319836664. doi: 10.1177/2055217319836664. eCollection 2019 Jan-Mar.PMID: 30915227