User login
Autoimmune Diseases and Perinatal Depression May Share Two-Way Link
Women with autoimmune disease are more likely to have perinatal depression (PND), according to findings from a new study that also suggested the reverse relationship is true: Women with a history of PND have a higher risk of developing autoimmune disease.
The research, published online on January 9, 2024, in Molecular Psychiatry, was led by Emma Bränn, PhD, Institute of Environmental Medicine, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden.
The researchers used data from the Swedish Medical Birth Register and identified all women who had given birth in Sweden between 2001 and 2013. Out of the group of approximately 815,000 women and 1.3 million pregnancies, just more than 55,000 women had been diagnosed with depression during their pregnancy or within a year after delivery.
The researchers then compared the incidence of 41 autoimmune diseases in women who had and did not have PND. They controlled for factors including genetic makeup and childhood environment.
Results indicated that women with autoimmune disease were 30% more likely to have PND (odds ratio, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.25-1.35). Conversely, women with PND were 30% more likely than women with no PND to develop an autoimmune disease (hazard ratio, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.25-1.36).
A sibling comparison helped confirm the results by controlling for some shared genetic and early life environmental factors related to the household in which sisters grew up.
Potential Shared Biological Mechanisms
The association was independent of psychiatric comorbidities, suggesting there may be shared biological mechanisms.
Dr. Bränn told this news organization that the research team wanted to do the study because previous research has shown involvement of the immune system in depression, with similarities in both the symptoms of immune system–activated diseases and depression and the molecular pathways activated by the immune system.
“Adding on top of the tremendous changes in the immune system that we see in the body of the woman during the perinatal period, we hypothesized that autoimmune diseases could be associated to perinatal depression,” she said. “This had also been shown in some previous literature but not to the extent as what we have investigated in this paper.”
She said their results help make a case for counseling women at several points in healthcare interactions — before and after conception and childbirth — and in rheumatology visits to inform women with autoimmune diseases who are contemplating motherhood of the association with developing PND. The results may also demonstrate a need for monitoring women in these groups for depression or autoimmune disease.
Fred Miller, MD, PhD, retired Scientist Emeritus of the Environmental Autoimmunity Group at the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, who was not part of the study, said the results seem plausible as they build on early work that demonstrated selected associations between autoimmune conditions and mental illness.
“These associations may be the result of shared genetic and environmental risk factors, including stress, hormonal changes, medications, and the proinflammatory states that can lead to both,” he said.
The novelty, he said, is in the relatively strong associations of PND with autoimmune disease overall and with specific autoimmune diseases.
Strong Link Found With Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
According to the paper, a significant positive bidirectional link was found for autoimmune thyroid disease, psoriasis, MS, ulcerative colitis, and celiac disease.
Researchers found a particularly strong association — double the risk in both directions — between PND and MS.
Dr. Miller said though it is unclear from this study why the association of PND with MS was stronger than with other autoimmune diseases, people with MS are known to be at a high risk for depression in general. That may come from greater shared genetic and environmental risk factors, he added.
Additionally, MS is one of the more common autoimmune diseases, he noted, so the population is larger for study.
He said he was surprised the researchers didn’t investigate medication use because medications used in depression have immunologic effects and medications used in autoimmune diseases could have effects on mental conditions.
The study has implications for clinicians in a wide variety of specialties, Dr. Miller noted.
“It suggests that caregivers be more alert to the signs of developing autoimmune disease in women with perinatal depression and to the signs of developing perinatal depression in those with autoimmune disease,” Dr. Miller said, “so that appropriate screening, diagnostics, and interventions may be undertaken.”
The researchers say they will continue to examine the long-term effects of depression during pregnancy and in the year after childbirth.
“Depression during this sensitive period can have serious consequences for both the mother and the baby,” Dr. Bränn said. “We hope that our results will help decision-makers to steer funding toward maternal healthcare so that more women can get help and support in time.”
The study was financed by Karolinska Institute, Forte (the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare), the Swedish Research Council, and the Icelandic Research Fund.
The researchers and Dr. Miller reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Women with autoimmune disease are more likely to have perinatal depression (PND), according to findings from a new study that also suggested the reverse relationship is true: Women with a history of PND have a higher risk of developing autoimmune disease.
The research, published online on January 9, 2024, in Molecular Psychiatry, was led by Emma Bränn, PhD, Institute of Environmental Medicine, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden.
The researchers used data from the Swedish Medical Birth Register and identified all women who had given birth in Sweden between 2001 and 2013. Out of the group of approximately 815,000 women and 1.3 million pregnancies, just more than 55,000 women had been diagnosed with depression during their pregnancy or within a year after delivery.
The researchers then compared the incidence of 41 autoimmune diseases in women who had and did not have PND. They controlled for factors including genetic makeup and childhood environment.
Results indicated that women with autoimmune disease were 30% more likely to have PND (odds ratio, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.25-1.35). Conversely, women with PND were 30% more likely than women with no PND to develop an autoimmune disease (hazard ratio, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.25-1.36).
A sibling comparison helped confirm the results by controlling for some shared genetic and early life environmental factors related to the household in which sisters grew up.
Potential Shared Biological Mechanisms
The association was independent of psychiatric comorbidities, suggesting there may be shared biological mechanisms.
Dr. Bränn told this news organization that the research team wanted to do the study because previous research has shown involvement of the immune system in depression, with similarities in both the symptoms of immune system–activated diseases and depression and the molecular pathways activated by the immune system.
“Adding on top of the tremendous changes in the immune system that we see in the body of the woman during the perinatal period, we hypothesized that autoimmune diseases could be associated to perinatal depression,” she said. “This had also been shown in some previous literature but not to the extent as what we have investigated in this paper.”
She said their results help make a case for counseling women at several points in healthcare interactions — before and after conception and childbirth — and in rheumatology visits to inform women with autoimmune diseases who are contemplating motherhood of the association with developing PND. The results may also demonstrate a need for monitoring women in these groups for depression or autoimmune disease.
Fred Miller, MD, PhD, retired Scientist Emeritus of the Environmental Autoimmunity Group at the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, who was not part of the study, said the results seem plausible as they build on early work that demonstrated selected associations between autoimmune conditions and mental illness.
“These associations may be the result of shared genetic and environmental risk factors, including stress, hormonal changes, medications, and the proinflammatory states that can lead to both,” he said.
The novelty, he said, is in the relatively strong associations of PND with autoimmune disease overall and with specific autoimmune diseases.
Strong Link Found With Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
According to the paper, a significant positive bidirectional link was found for autoimmune thyroid disease, psoriasis, MS, ulcerative colitis, and celiac disease.
Researchers found a particularly strong association — double the risk in both directions — between PND and MS.
Dr. Miller said though it is unclear from this study why the association of PND with MS was stronger than with other autoimmune diseases, people with MS are known to be at a high risk for depression in general. That may come from greater shared genetic and environmental risk factors, he added.
Additionally, MS is one of the more common autoimmune diseases, he noted, so the population is larger for study.
He said he was surprised the researchers didn’t investigate medication use because medications used in depression have immunologic effects and medications used in autoimmune diseases could have effects on mental conditions.
The study has implications for clinicians in a wide variety of specialties, Dr. Miller noted.
“It suggests that caregivers be more alert to the signs of developing autoimmune disease in women with perinatal depression and to the signs of developing perinatal depression in those with autoimmune disease,” Dr. Miller said, “so that appropriate screening, diagnostics, and interventions may be undertaken.”
The researchers say they will continue to examine the long-term effects of depression during pregnancy and in the year after childbirth.
“Depression during this sensitive period can have serious consequences for both the mother and the baby,” Dr. Bränn said. “We hope that our results will help decision-makers to steer funding toward maternal healthcare so that more women can get help and support in time.”
The study was financed by Karolinska Institute, Forte (the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare), the Swedish Research Council, and the Icelandic Research Fund.
The researchers and Dr. Miller reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Women with autoimmune disease are more likely to have perinatal depression (PND), according to findings from a new study that also suggested the reverse relationship is true: Women with a history of PND have a higher risk of developing autoimmune disease.
The research, published online on January 9, 2024, in Molecular Psychiatry, was led by Emma Bränn, PhD, Institute of Environmental Medicine, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden.
The researchers used data from the Swedish Medical Birth Register and identified all women who had given birth in Sweden between 2001 and 2013. Out of the group of approximately 815,000 women and 1.3 million pregnancies, just more than 55,000 women had been diagnosed with depression during their pregnancy or within a year after delivery.
The researchers then compared the incidence of 41 autoimmune diseases in women who had and did not have PND. They controlled for factors including genetic makeup and childhood environment.
Results indicated that women with autoimmune disease were 30% more likely to have PND (odds ratio, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.25-1.35). Conversely, women with PND were 30% more likely than women with no PND to develop an autoimmune disease (hazard ratio, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.25-1.36).
A sibling comparison helped confirm the results by controlling for some shared genetic and early life environmental factors related to the household in which sisters grew up.
Potential Shared Biological Mechanisms
The association was independent of psychiatric comorbidities, suggesting there may be shared biological mechanisms.
Dr. Bränn told this news organization that the research team wanted to do the study because previous research has shown involvement of the immune system in depression, with similarities in both the symptoms of immune system–activated diseases and depression and the molecular pathways activated by the immune system.
“Adding on top of the tremendous changes in the immune system that we see in the body of the woman during the perinatal period, we hypothesized that autoimmune diseases could be associated to perinatal depression,” she said. “This had also been shown in some previous literature but not to the extent as what we have investigated in this paper.”
She said their results help make a case for counseling women at several points in healthcare interactions — before and after conception and childbirth — and in rheumatology visits to inform women with autoimmune diseases who are contemplating motherhood of the association with developing PND. The results may also demonstrate a need for monitoring women in these groups for depression or autoimmune disease.
Fred Miller, MD, PhD, retired Scientist Emeritus of the Environmental Autoimmunity Group at the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, who was not part of the study, said the results seem plausible as they build on early work that demonstrated selected associations between autoimmune conditions and mental illness.
“These associations may be the result of shared genetic and environmental risk factors, including stress, hormonal changes, medications, and the proinflammatory states that can lead to both,” he said.
The novelty, he said, is in the relatively strong associations of PND with autoimmune disease overall and with specific autoimmune diseases.
Strong Link Found With Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
According to the paper, a significant positive bidirectional link was found for autoimmune thyroid disease, psoriasis, MS, ulcerative colitis, and celiac disease.
Researchers found a particularly strong association — double the risk in both directions — between PND and MS.
Dr. Miller said though it is unclear from this study why the association of PND with MS was stronger than with other autoimmune diseases, people with MS are known to be at a high risk for depression in general. That may come from greater shared genetic and environmental risk factors, he added.
Additionally, MS is one of the more common autoimmune diseases, he noted, so the population is larger for study.
He said he was surprised the researchers didn’t investigate medication use because medications used in depression have immunologic effects and medications used in autoimmune diseases could have effects on mental conditions.
The study has implications for clinicians in a wide variety of specialties, Dr. Miller noted.
“It suggests that caregivers be more alert to the signs of developing autoimmune disease in women with perinatal depression and to the signs of developing perinatal depression in those with autoimmune disease,” Dr. Miller said, “so that appropriate screening, diagnostics, and interventions may be undertaken.”
The researchers say they will continue to examine the long-term effects of depression during pregnancy and in the year after childbirth.
“Depression during this sensitive period can have serious consequences for both the mother and the baby,” Dr. Bränn said. “We hope that our results will help decision-makers to steer funding toward maternal healthcare so that more women can get help and support in time.”
The study was financed by Karolinska Institute, Forte (the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare), the Swedish Research Council, and the Icelandic Research Fund.
The researchers and Dr. Miller reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM MOLECULAR PSYCHIATRY
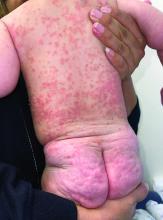
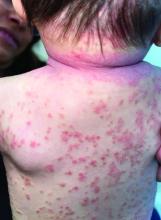
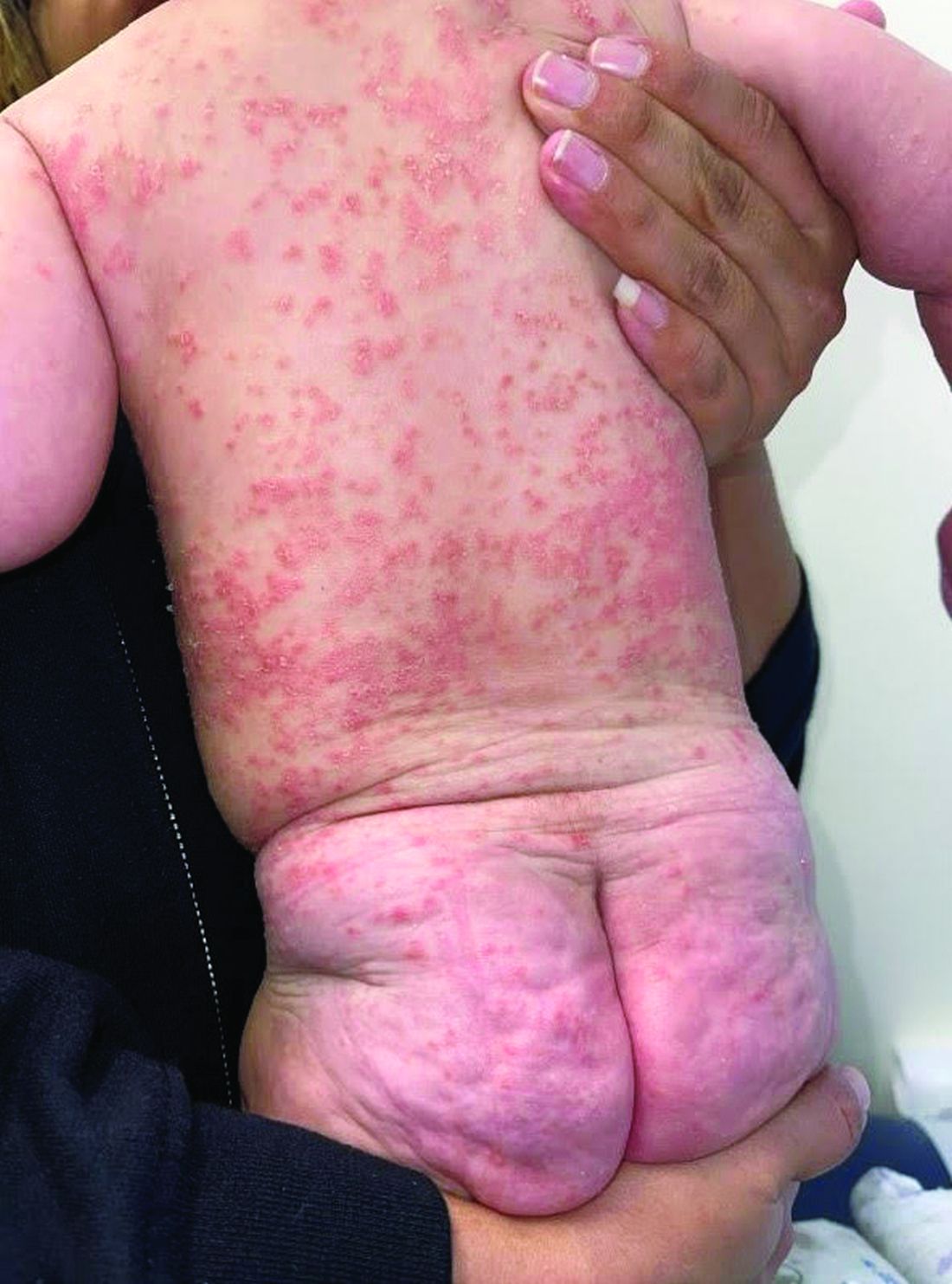
A 4-month-old male was referred for a 3-week history of an itchy generalized rash that started on the neck
Diagnosis: Infection-induced psoriasis (guttate-type, induced by streptococcal intertrigo)
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by well-defined, scaly, erythematous plaques. Guttate psoriasis is a distinct variant of psoriasis that is more common in children and adolescents. Guttate psoriasis usually presents with multiple, scattered, small, drop-like (“guttate”), scaly, erythematous papules and plaques.
The pathophysiology of psoriasis involves an interplay between genetic and environmental factors. Guttate psoriasis is a chronic T-cell–mediated inflammatory disease in which there is an altered balance between T-helper-1 (TH1) and TH2 cells, transcription factor genes, and their products. HLA B-13, B-17, and Cw6 are human leukocyte antigen alleles implicated in genetic susceptibility. It is hypothesized that streptococcal infection precipitates guttate psoriasis by streptococcal superantigen–driven activation of cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen (CLA)–positive lymphocytes. It has been shown that streptococcal exotoxins and streptococcal M proteins act as superantigens.
Diagnosis is often made clinically based on characteristic physical findings and a possible preceding history of streptococcal infection. In patients with streptococcal infection, culture from an appropriate site and measurement of serum antistreptococcal antibody titers (for example, anti-DNase, antihyaluronidase and antistreptolysin-O) can help. A skin biopsy is usually not necessary but may be considered.
This patient presented with intertrigo of the neck and axillae at the time of presentation with the papulosquamous rash. Culture of the intertrigo yielded 4+ Group A beta streptococcus.
Treatment
Although there is currently no cure for guttate psoriasis, various treatment options can relieve symptoms and clear skin lesions, and infection-triggered lesions may remit, usually within several months. However, guttate psoriasis may persist and progress to chronic plaque psoriasis. Many treatment options are based mainly on clinical trials targeted for plaque psoriasis treatment.
For mild psoriasis, topical corticosteroids are first-line treatment. Other topical steroids include vitamin D analogs (calcipotriene), topical retinoids (tazarotene), topical calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus and pimecrolimus), and newer non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents (roflumilast or tapinarof), neither approved yet in this young age group. In more severe cases, phototherapy with UVB light, traditional systemic immunosuppressive agents (methotrexate, cyclosporine) or targeted biologic therapies may be considered.
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis may include generalized intertrigo, pityriasis rubra pilaris, tinea corporis, atopic dermatitis, and staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome. Guttate psoriasis can be distinguished by history and physical exam. Further studies such as potassium hydroxide (KOH) scrapings may be helpful in ruling out the other disorders.
Intertrigo is an inflammatory condition of the flexural surfaces irritated by warm temperatures, friction, moisture, and poor ventilation that is commonly associated with Candida infection and/or streptococcal infection. Candidal intertrigo can present with erythematous patches or plaques in an intertriginous area that may develop erosions, macerations, fissures, crust, and weeping. Satellite papules and pustules are pathognomonic for Candida species. Streptococcal intertrigo usually presents with bright red color and may be painful or pruritic. Perianal streptococcal infection is reported as a trigger of guttate psoriasis in pediatric patients.
Pityriasis rubra pilaris is a rare inflammatory papulosquamous disorder with an unknown etiology. Red-orange papules and plaques, hyperkeratotic follicular papules, and palmoplantar hyperkeratosis are primary features. Diagnosis is based on clinical and histopathology. Pityriasis rubra pilaris is self-limited and asymptomatic in many cases. Treatment may not be required, but combination therapy with topical agents includes emollients, keratolytic agents (for example, urea, salicylic acid, alpha-hydroxy acids), topical corticosteroids, tazarotene, and topical calcineurin inhibitors. Systemic agents include oral retinoids and methotrexate.
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that involves genetic and environmental factors, leading to abnormalities in the epidermis and the immune system presenting with its typical morphology and distribution. The morphology of eczematous lesions is distinct from papulosquamous lesions of psoriasis.
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome is a toxin-mediated skin disorder which presents with denuded, peeling skin due to epidermolytic exotoxin producing Staphylococcus species. Fever, erythematous rash, malaise, skin pain, and irritability presents initially. Progressive desquamation with accentuation in folds is typical, with progression usually within 1-2 days. Systemic antibiotics covering Staphylococcus should be administered early. Emollients and nonadherent dressings should be applied to affected areas to promote healing. Supportive care includes dehydration management, temperature regulation, and nutrition. Skin desquamation usually occurs within 5 days with resolution within 2 weeks.
This infant displayed streptococcal intertrigo which triggered an early presentation of guttate psoriasis. The patient was managed with completion of a course of oral cephalexin, midstrength topical corticosteroids to the truncal lesions, and mild topical corticosteroids to the face and diaper area with good clinical response.
Danny Lee and Samuel Le serve as research fellows in the Pediatric Dermatology Division of the Department of Dermatology at the University of California San Diego and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is Distinguished Professor of Dermatology and Pediatrics and Vice-Chair of the Department of Dermatology at the University of California San Diego and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. The authors have no relevant financial disclosures.
Suggested Reading
Leung AK et al. Childhood guttate psoriasis: An updated review. Drugs Context. 2023 Oct 23:12:2023-8-2. doi: 10.7573/dic.2023-8-2.
Galili E et al. New-onset guttate psoriasis: A long-term follow-up study. Dermatology. 2023;239(2):188-194. doi: 10.1159/000527737.
Duffin KC et al. Advances and controversies in our understanding of guttate and plaque psoriasis. J Rheumatol. 2023 Nov;50(Suppl 2):4-7. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.2023-0500.
Saleh D, Tanner LS. Guttate Psoriasis. [Updated 2023 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482498/
Dupire G et al. Antistreptococcal interventions for guttate and chronic plaque psoriasis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Mar 5;3(3):CD011571. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011571.pub2.
Diagnosis: Infection-induced psoriasis (guttate-type, induced by streptococcal intertrigo)
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by well-defined, scaly, erythematous plaques. Guttate psoriasis is a distinct variant of psoriasis that is more common in children and adolescents. Guttate psoriasis usually presents with multiple, scattered, small, drop-like (“guttate”), scaly, erythematous papules and plaques.
The pathophysiology of psoriasis involves an interplay between genetic and environmental factors. Guttate psoriasis is a chronic T-cell–mediated inflammatory disease in which there is an altered balance between T-helper-1 (TH1) and TH2 cells, transcription factor genes, and their products. HLA B-13, B-17, and Cw6 are human leukocyte antigen alleles implicated in genetic susceptibility. It is hypothesized that streptococcal infection precipitates guttate psoriasis by streptococcal superantigen–driven activation of cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen (CLA)–positive lymphocytes. It has been shown that streptococcal exotoxins and streptococcal M proteins act as superantigens.
Diagnosis is often made clinically based on characteristic physical findings and a possible preceding history of streptococcal infection. In patients with streptococcal infection, culture from an appropriate site and measurement of serum antistreptococcal antibody titers (for example, anti-DNase, antihyaluronidase and antistreptolysin-O) can help. A skin biopsy is usually not necessary but may be considered.
This patient presented with intertrigo of the neck and axillae at the time of presentation with the papulosquamous rash. Culture of the intertrigo yielded 4+ Group A beta streptococcus.
Treatment
Although there is currently no cure for guttate psoriasis, various treatment options can relieve symptoms and clear skin lesions, and infection-triggered lesions may remit, usually within several months. However, guttate psoriasis may persist and progress to chronic plaque psoriasis. Many treatment options are based mainly on clinical trials targeted for plaque psoriasis treatment.
For mild psoriasis, topical corticosteroids are first-line treatment. Other topical steroids include vitamin D analogs (calcipotriene), topical retinoids (tazarotene), topical calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus and pimecrolimus), and newer non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents (roflumilast or tapinarof), neither approved yet in this young age group. In more severe cases, phototherapy with UVB light, traditional systemic immunosuppressive agents (methotrexate, cyclosporine) or targeted biologic therapies may be considered.
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis may include generalized intertrigo, pityriasis rubra pilaris, tinea corporis, atopic dermatitis, and staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome. Guttate psoriasis can be distinguished by history and physical exam. Further studies such as potassium hydroxide (KOH) scrapings may be helpful in ruling out the other disorders.
Intertrigo is an inflammatory condition of the flexural surfaces irritated by warm temperatures, friction, moisture, and poor ventilation that is commonly associated with Candida infection and/or streptococcal infection. Candidal intertrigo can present with erythematous patches or plaques in an intertriginous area that may develop erosions, macerations, fissures, crust, and weeping. Satellite papules and pustules are pathognomonic for Candida species. Streptococcal intertrigo usually presents with bright red color and may be painful or pruritic. Perianal streptococcal infection is reported as a trigger of guttate psoriasis in pediatric patients.
Pityriasis rubra pilaris is a rare inflammatory papulosquamous disorder with an unknown etiology. Red-orange papules and plaques, hyperkeratotic follicular papules, and palmoplantar hyperkeratosis are primary features. Diagnosis is based on clinical and histopathology. Pityriasis rubra pilaris is self-limited and asymptomatic in many cases. Treatment may not be required, but combination therapy with topical agents includes emollients, keratolytic agents (for example, urea, salicylic acid, alpha-hydroxy acids), topical corticosteroids, tazarotene, and topical calcineurin inhibitors. Systemic agents include oral retinoids and methotrexate.
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that involves genetic and environmental factors, leading to abnormalities in the epidermis and the immune system presenting with its typical morphology and distribution. The morphology of eczematous lesions is distinct from papulosquamous lesions of psoriasis.
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome is a toxin-mediated skin disorder which presents with denuded, peeling skin due to epidermolytic exotoxin producing Staphylococcus species. Fever, erythematous rash, malaise, skin pain, and irritability presents initially. Progressive desquamation with accentuation in folds is typical, with progression usually within 1-2 days. Systemic antibiotics covering Staphylococcus should be administered early. Emollients and nonadherent dressings should be applied to affected areas to promote healing. Supportive care includes dehydration management, temperature regulation, and nutrition. Skin desquamation usually occurs within 5 days with resolution within 2 weeks.
This infant displayed streptococcal intertrigo which triggered an early presentation of guttate psoriasis. The patient was managed with completion of a course of oral cephalexin, midstrength topical corticosteroids to the truncal lesions, and mild topical corticosteroids to the face and diaper area with good clinical response.
Danny Lee and Samuel Le serve as research fellows in the Pediatric Dermatology Division of the Department of Dermatology at the University of California San Diego and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is Distinguished Professor of Dermatology and Pediatrics and Vice-Chair of the Department of Dermatology at the University of California San Diego and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. The authors have no relevant financial disclosures.
Suggested Reading
Leung AK et al. Childhood guttate psoriasis: An updated review. Drugs Context. 2023 Oct 23:12:2023-8-2. doi: 10.7573/dic.2023-8-2.
Galili E et al. New-onset guttate psoriasis: A long-term follow-up study. Dermatology. 2023;239(2):188-194. doi: 10.1159/000527737.
Duffin KC et al. Advances and controversies in our understanding of guttate and plaque psoriasis. J Rheumatol. 2023 Nov;50(Suppl 2):4-7. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.2023-0500.
Saleh D, Tanner LS. Guttate Psoriasis. [Updated 2023 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482498/
Dupire G et al. Antistreptococcal interventions for guttate and chronic plaque psoriasis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Mar 5;3(3):CD011571. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011571.pub2.
Diagnosis: Infection-induced psoriasis (guttate-type, induced by streptococcal intertrigo)
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by well-defined, scaly, erythematous plaques. Guttate psoriasis is a distinct variant of psoriasis that is more common in children and adolescents. Guttate psoriasis usually presents with multiple, scattered, small, drop-like (“guttate”), scaly, erythematous papules and plaques.
The pathophysiology of psoriasis involves an interplay between genetic and environmental factors. Guttate psoriasis is a chronic T-cell–mediated inflammatory disease in which there is an altered balance between T-helper-1 (TH1) and TH2 cells, transcription factor genes, and their products. HLA B-13, B-17, and Cw6 are human leukocyte antigen alleles implicated in genetic susceptibility. It is hypothesized that streptococcal infection precipitates guttate psoriasis by streptococcal superantigen–driven activation of cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen (CLA)–positive lymphocytes. It has been shown that streptococcal exotoxins and streptococcal M proteins act as superantigens.
Diagnosis is often made clinically based on characteristic physical findings and a possible preceding history of streptococcal infection. In patients with streptococcal infection, culture from an appropriate site and measurement of serum antistreptococcal antibody titers (for example, anti-DNase, antihyaluronidase and antistreptolysin-O) can help. A skin biopsy is usually not necessary but may be considered.
This patient presented with intertrigo of the neck and axillae at the time of presentation with the papulosquamous rash. Culture of the intertrigo yielded 4+ Group A beta streptococcus.
Treatment
Although there is currently no cure for guttate psoriasis, various treatment options can relieve symptoms and clear skin lesions, and infection-triggered lesions may remit, usually within several months. However, guttate psoriasis may persist and progress to chronic plaque psoriasis. Many treatment options are based mainly on clinical trials targeted for plaque psoriasis treatment.
For mild psoriasis, topical corticosteroids are first-line treatment. Other topical steroids include vitamin D analogs (calcipotriene), topical retinoids (tazarotene), topical calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus and pimecrolimus), and newer non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents (roflumilast or tapinarof), neither approved yet in this young age group. In more severe cases, phototherapy with UVB light, traditional systemic immunosuppressive agents (methotrexate, cyclosporine) or targeted biologic therapies may be considered.
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis may include generalized intertrigo, pityriasis rubra pilaris, tinea corporis, atopic dermatitis, and staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome. Guttate psoriasis can be distinguished by history and physical exam. Further studies such as potassium hydroxide (KOH) scrapings may be helpful in ruling out the other disorders.
Intertrigo is an inflammatory condition of the flexural surfaces irritated by warm temperatures, friction, moisture, and poor ventilation that is commonly associated with Candida infection and/or streptococcal infection. Candidal intertrigo can present with erythematous patches or plaques in an intertriginous area that may develop erosions, macerations, fissures, crust, and weeping. Satellite papules and pustules are pathognomonic for Candida species. Streptococcal intertrigo usually presents with bright red color and may be painful or pruritic. Perianal streptococcal infection is reported as a trigger of guttate psoriasis in pediatric patients.
Pityriasis rubra pilaris is a rare inflammatory papulosquamous disorder with an unknown etiology. Red-orange papules and plaques, hyperkeratotic follicular papules, and palmoplantar hyperkeratosis are primary features. Diagnosis is based on clinical and histopathology. Pityriasis rubra pilaris is self-limited and asymptomatic in many cases. Treatment may not be required, but combination therapy with topical agents includes emollients, keratolytic agents (for example, urea, salicylic acid, alpha-hydroxy acids), topical corticosteroids, tazarotene, and topical calcineurin inhibitors. Systemic agents include oral retinoids and methotrexate.
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that involves genetic and environmental factors, leading to abnormalities in the epidermis and the immune system presenting with its typical morphology and distribution. The morphology of eczematous lesions is distinct from papulosquamous lesions of psoriasis.
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome is a toxin-mediated skin disorder which presents with denuded, peeling skin due to epidermolytic exotoxin producing Staphylococcus species. Fever, erythematous rash, malaise, skin pain, and irritability presents initially. Progressive desquamation with accentuation in folds is typical, with progression usually within 1-2 days. Systemic antibiotics covering Staphylococcus should be administered early. Emollients and nonadherent dressings should be applied to affected areas to promote healing. Supportive care includes dehydration management, temperature regulation, and nutrition. Skin desquamation usually occurs within 5 days with resolution within 2 weeks.
This infant displayed streptococcal intertrigo which triggered an early presentation of guttate psoriasis. The patient was managed with completion of a course of oral cephalexin, midstrength topical corticosteroids to the truncal lesions, and mild topical corticosteroids to the face and diaper area with good clinical response.
Danny Lee and Samuel Le serve as research fellows in the Pediatric Dermatology Division of the Department of Dermatology at the University of California San Diego and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is Distinguished Professor of Dermatology and Pediatrics and Vice-Chair of the Department of Dermatology at the University of California San Diego and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. The authors have no relevant financial disclosures.
Suggested Reading
Leung AK et al. Childhood guttate psoriasis: An updated review. Drugs Context. 2023 Oct 23:12:2023-8-2. doi: 10.7573/dic.2023-8-2.
Galili E et al. New-onset guttate psoriasis: A long-term follow-up study. Dermatology. 2023;239(2):188-194. doi: 10.1159/000527737.
Duffin KC et al. Advances and controversies in our understanding of guttate and plaque psoriasis. J Rheumatol. 2023 Nov;50(Suppl 2):4-7. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.2023-0500.
Saleh D, Tanner LS. Guttate Psoriasis. [Updated 2023 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482498/
Dupire G et al. Antistreptococcal interventions for guttate and chronic plaque psoriasis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Mar 5;3(3):CD011571. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011571.pub2.
On physical exam, there was an erythematous patch with overlying areas of macerations on the neck and axilla. The trunk, extremities, and diaper area had multiple psoriasiform erythematous thin plaques with overlying scales.
US Dermatologic Drug Approvals Rose Between 2012 and 2022
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Only five new drugs for diseases treated mostly by dermatologists were approved by the FDA between 1999 and 2009.
- In a cross-sectional analysis to characterize the frequency and degree of innovation of dermatologic drugs approved more recently, researchers identified new and supplemental dermatologic drugs approved between January 1, 2012, and December 31, 2022, from FDA lists, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services CenterWatch, and peer-reviewed articles.
- They used five proxy measures to estimate each drug’s degree of innovation: FDA designation (first in class, advance in class, or addition to class), independent clinical usefulness ratings, and benefit ratings by health technology assessment organizations.
TAKEAWAY:
- The study authors identified 52 new drug applications and 26 supplemental new indications approved by the FDA for dermatologic indications between 2012 and 2022.
- Of the 52 new drugs, the researchers categorized 11 (21%) as first in class and 13 (25%) as first in indication.
- An analysis of benefit ratings available for 38 of the drugs showed that 15 (39%) were rated as being clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
- Of the 10 supplemental new indications with ratings by any organization, 3 (30%) were rated as clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
IN PRACTICE:
While innovative drug development in dermatology may have increased, “these findings also highlight opportunities to develop more truly innovative dermatologic agents, particularly for diseases with unmet therapeutic need,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Samir Kamat, MD, of the Medical Education Department at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, and corresponding author Ravi Gupta, MD, MSHP, of the Internal Medicine Division at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, led the research. The study was published online as a research letter on December 20, 2023, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
They include the use of individual indications to assess clinical usefulness and benefit ratings. Many drugs, particularly supplemental indications, lacked such ratings. Reformulations of already marketed drugs or indications were not included.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Kamat and Dr. Gupta had no relevant disclosures. Three coauthors reported having received financial support outside of the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Only five new drugs for diseases treated mostly by dermatologists were approved by the FDA between 1999 and 2009.
- In a cross-sectional analysis to characterize the frequency and degree of innovation of dermatologic drugs approved more recently, researchers identified new and supplemental dermatologic drugs approved between January 1, 2012, and December 31, 2022, from FDA lists, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services CenterWatch, and peer-reviewed articles.
- They used five proxy measures to estimate each drug’s degree of innovation: FDA designation (first in class, advance in class, or addition to class), independent clinical usefulness ratings, and benefit ratings by health technology assessment organizations.
TAKEAWAY:
- The study authors identified 52 new drug applications and 26 supplemental new indications approved by the FDA for dermatologic indications between 2012 and 2022.
- Of the 52 new drugs, the researchers categorized 11 (21%) as first in class and 13 (25%) as first in indication.
- An analysis of benefit ratings available for 38 of the drugs showed that 15 (39%) were rated as being clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
- Of the 10 supplemental new indications with ratings by any organization, 3 (30%) were rated as clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
IN PRACTICE:
While innovative drug development in dermatology may have increased, “these findings also highlight opportunities to develop more truly innovative dermatologic agents, particularly for diseases with unmet therapeutic need,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Samir Kamat, MD, of the Medical Education Department at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, and corresponding author Ravi Gupta, MD, MSHP, of the Internal Medicine Division at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, led the research. The study was published online as a research letter on December 20, 2023, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
They include the use of individual indications to assess clinical usefulness and benefit ratings. Many drugs, particularly supplemental indications, lacked such ratings. Reformulations of already marketed drugs or indications were not included.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Kamat and Dr. Gupta had no relevant disclosures. Three coauthors reported having received financial support outside of the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Only five new drugs for diseases treated mostly by dermatologists were approved by the FDA between 1999 and 2009.
- In a cross-sectional analysis to characterize the frequency and degree of innovation of dermatologic drugs approved more recently, researchers identified new and supplemental dermatologic drugs approved between January 1, 2012, and December 31, 2022, from FDA lists, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services CenterWatch, and peer-reviewed articles.
- They used five proxy measures to estimate each drug’s degree of innovation: FDA designation (first in class, advance in class, or addition to class), independent clinical usefulness ratings, and benefit ratings by health technology assessment organizations.
TAKEAWAY:
- The study authors identified 52 new drug applications and 26 supplemental new indications approved by the FDA for dermatologic indications between 2012 and 2022.
- Of the 52 new drugs, the researchers categorized 11 (21%) as first in class and 13 (25%) as first in indication.
- An analysis of benefit ratings available for 38 of the drugs showed that 15 (39%) were rated as being clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
- Of the 10 supplemental new indications with ratings by any organization, 3 (30%) were rated as clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
IN PRACTICE:
While innovative drug development in dermatology may have increased, “these findings also highlight opportunities to develop more truly innovative dermatologic agents, particularly for diseases with unmet therapeutic need,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Samir Kamat, MD, of the Medical Education Department at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, and corresponding author Ravi Gupta, MD, MSHP, of the Internal Medicine Division at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, led the research. The study was published online as a research letter on December 20, 2023, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
They include the use of individual indications to assess clinical usefulness and benefit ratings. Many drugs, particularly supplemental indications, lacked such ratings. Reformulations of already marketed drugs or indications were not included.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Kamat and Dr. Gupta had no relevant disclosures. Three coauthors reported having received financial support outside of the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Experimental Topical Drug Shows Promise for Atopic Dermatitis and Plaque Psoriasis
, results from a phase 2a study showed.
PDE4 inhibitors are a promising therapeutic target for inflammatory diseases because “they can increase cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels and subsequently reduce the production of proinflammatory cytokines,” lead study author Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, of the dermatology department at the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues wrote. The paper was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
Currently Available Treatments
For plaque psoriasis, the FDA approved the topical PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast in 2022. The oral PDE4 inhibitor apremilast has shown to be effective for plaque psoriasis and is well tolerated, and “it has been associated with gastrointestinal adverse events (AEs) such as nausea and diarrhea,” the researchers wrote.
For AD, crisaborole is the only approved topical PDE4 treatment, and it is associated with application site burning and stinging, they wrote.
An Experimental Alternative
The new study tested a topical PDE4 inhibitor known as PF-07038124, which is being developed by Pfizer. It is designed to be “a potent, oxaborole-based PDE4 inhibitor [that shows] immunomodulatory activity in T-cell–based assays, contributing to inhibition of [interleukin]-4 and IL-13; thus, it could provide therapeutic benefit in the treatment of AD and plaque psoriasis,” the authors wrote.
The phase 2a study was conducted from December 21, 2020, to August 18, 2021. Researchers at 34 sites in four countries randomized 104 patients with mild to moderate AD (70) or plaque psoriasis (34) to receive PF-07038124 as a 0.001% topical ointment or a vehicle only once daily for 6 weeks.
The primary end point was the percent change from baseline in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) total score among patients with AD and in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score among patients with plaque psoriasis at week 6. Safety measures of interest included treatment-emergent adverse events.
Overall, the mean age of the 104 patients was 43 years, 52.9%, were women, 3.8% were Asian, 12.5% were Black, and 83.7% were White. Most had moderate disease.
At week 6 in patients with AD, the PF-07038124 group showed statistically significantly greater improvement in the EASI total score, compared with vehicle group (−74.9% vs −35.5% respectively; least squares mean [LSM] difference, −39.4%; 90% CI, −58.8% to−20.1%]; P < .001).
Similarly, at week 6 in patients with plaque psoriasis, the PF-07038124 group demonstrated a significantly greater improvement in the PASI total score, compared with the vehicle group (LSM, −4.8; 90% CI, −6.2 to −3.4] vs 0.1; 90% CI, −1.5 to 1.7), for a difference of −4.9; 90% CI, −7.0 to −2.8; P < .001.
In safety outcomes, treatment-emergent adverse events were reported in 16 people receiving PF-07038124 and 26 people receiving a vehicle. The treatment-related adverse events were reported only in the vehicle groups across all indications, while no patients in the PF-07038124 groups experienced pain or skin reactions at the application sites.
The researchers acknowledged certain limitations of the trial, including its small size and the 6-week treatment period. “Unlike crisaborole, topical PF-07038124 was not associated with application site burning and stinging,” they noted. “To confirm persistence of efficacy and the safety profile of PF-07038124, long-term data should be collected in larger studies.”
Pfizer supported the study. Dr. Eichenfield reported receiving personal fees from Pfizer during the conduct of the study. He also has received grant support from, is consultant to, and/or is a member of the advisory board for many other pharmaceutical companies. Several other study authors reported similar disclosures.
, results from a phase 2a study showed.
PDE4 inhibitors are a promising therapeutic target for inflammatory diseases because “they can increase cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels and subsequently reduce the production of proinflammatory cytokines,” lead study author Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, of the dermatology department at the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues wrote. The paper was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
Currently Available Treatments
For plaque psoriasis, the FDA approved the topical PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast in 2022. The oral PDE4 inhibitor apremilast has shown to be effective for plaque psoriasis and is well tolerated, and “it has been associated with gastrointestinal adverse events (AEs) such as nausea and diarrhea,” the researchers wrote.
For AD, crisaborole is the only approved topical PDE4 treatment, and it is associated with application site burning and stinging, they wrote.
An Experimental Alternative
The new study tested a topical PDE4 inhibitor known as PF-07038124, which is being developed by Pfizer. It is designed to be “a potent, oxaborole-based PDE4 inhibitor [that shows] immunomodulatory activity in T-cell–based assays, contributing to inhibition of [interleukin]-4 and IL-13; thus, it could provide therapeutic benefit in the treatment of AD and plaque psoriasis,” the authors wrote.
The phase 2a study was conducted from December 21, 2020, to August 18, 2021. Researchers at 34 sites in four countries randomized 104 patients with mild to moderate AD (70) or plaque psoriasis (34) to receive PF-07038124 as a 0.001% topical ointment or a vehicle only once daily for 6 weeks.
The primary end point was the percent change from baseline in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) total score among patients with AD and in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score among patients with plaque psoriasis at week 6. Safety measures of interest included treatment-emergent adverse events.
Overall, the mean age of the 104 patients was 43 years, 52.9%, were women, 3.8% were Asian, 12.5% were Black, and 83.7% were White. Most had moderate disease.
At week 6 in patients with AD, the PF-07038124 group showed statistically significantly greater improvement in the EASI total score, compared with vehicle group (−74.9% vs −35.5% respectively; least squares mean [LSM] difference, −39.4%; 90% CI, −58.8% to−20.1%]; P < .001).
Similarly, at week 6 in patients with plaque psoriasis, the PF-07038124 group demonstrated a significantly greater improvement in the PASI total score, compared with the vehicle group (LSM, −4.8; 90% CI, −6.2 to −3.4] vs 0.1; 90% CI, −1.5 to 1.7), for a difference of −4.9; 90% CI, −7.0 to −2.8; P < .001.
In safety outcomes, treatment-emergent adverse events were reported in 16 people receiving PF-07038124 and 26 people receiving a vehicle. The treatment-related adverse events were reported only in the vehicle groups across all indications, while no patients in the PF-07038124 groups experienced pain or skin reactions at the application sites.
The researchers acknowledged certain limitations of the trial, including its small size and the 6-week treatment period. “Unlike crisaborole, topical PF-07038124 was not associated with application site burning and stinging,” they noted. “To confirm persistence of efficacy and the safety profile of PF-07038124, long-term data should be collected in larger studies.”
Pfizer supported the study. Dr. Eichenfield reported receiving personal fees from Pfizer during the conduct of the study. He also has received grant support from, is consultant to, and/or is a member of the advisory board for many other pharmaceutical companies. Several other study authors reported similar disclosures.
, results from a phase 2a study showed.
PDE4 inhibitors are a promising therapeutic target for inflammatory diseases because “they can increase cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels and subsequently reduce the production of proinflammatory cytokines,” lead study author Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, of the dermatology department at the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues wrote. The paper was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
Currently Available Treatments
For plaque psoriasis, the FDA approved the topical PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast in 2022. The oral PDE4 inhibitor apremilast has shown to be effective for plaque psoriasis and is well tolerated, and “it has been associated with gastrointestinal adverse events (AEs) such as nausea and diarrhea,” the researchers wrote.
For AD, crisaborole is the only approved topical PDE4 treatment, and it is associated with application site burning and stinging, they wrote.
An Experimental Alternative
The new study tested a topical PDE4 inhibitor known as PF-07038124, which is being developed by Pfizer. It is designed to be “a potent, oxaborole-based PDE4 inhibitor [that shows] immunomodulatory activity in T-cell–based assays, contributing to inhibition of [interleukin]-4 and IL-13; thus, it could provide therapeutic benefit in the treatment of AD and plaque psoriasis,” the authors wrote.
The phase 2a study was conducted from December 21, 2020, to August 18, 2021. Researchers at 34 sites in four countries randomized 104 patients with mild to moderate AD (70) or plaque psoriasis (34) to receive PF-07038124 as a 0.001% topical ointment or a vehicle only once daily for 6 weeks.
The primary end point was the percent change from baseline in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) total score among patients with AD and in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score among patients with plaque psoriasis at week 6. Safety measures of interest included treatment-emergent adverse events.
Overall, the mean age of the 104 patients was 43 years, 52.9%, were women, 3.8% were Asian, 12.5% were Black, and 83.7% were White. Most had moderate disease.
At week 6 in patients with AD, the PF-07038124 group showed statistically significantly greater improvement in the EASI total score, compared with vehicle group (−74.9% vs −35.5% respectively; least squares mean [LSM] difference, −39.4%; 90% CI, −58.8% to−20.1%]; P < .001).
Similarly, at week 6 in patients with plaque psoriasis, the PF-07038124 group demonstrated a significantly greater improvement in the PASI total score, compared with the vehicle group (LSM, −4.8; 90% CI, −6.2 to −3.4] vs 0.1; 90% CI, −1.5 to 1.7), for a difference of −4.9; 90% CI, −7.0 to −2.8; P < .001.
In safety outcomes, treatment-emergent adverse events were reported in 16 people receiving PF-07038124 and 26 people receiving a vehicle. The treatment-related adverse events were reported only in the vehicle groups across all indications, while no patients in the PF-07038124 groups experienced pain or skin reactions at the application sites.
The researchers acknowledged certain limitations of the trial, including its small size and the 6-week treatment period. “Unlike crisaborole, topical PF-07038124 was not associated with application site burning and stinging,” they noted. “To confirm persistence of efficacy and the safety profile of PF-07038124, long-term data should be collected in larger studies.”
Pfizer supported the study. Dr. Eichenfield reported receiving personal fees from Pfizer during the conduct of the study. He also has received grant support from, is consultant to, and/or is a member of the advisory board for many other pharmaceutical companies. Several other study authors reported similar disclosures.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Paradoxical Eczema Risk Low With Biologic Psoriasis Treatments
examined in a large observational analysis.
Using data from the British Association of Dermatologists Biologics and Immunomodulators Register (BADBIR) database, Ali Al-Janabi, MA, from the University of Manchester (England) and associates found that 273 (1%) of approximately 25,000 drug exposures in 13,699 biologic-treated patients with psoriasis were associated with paradoxical eczema.
The incidence of paradoxical eczema was found to vary by class. The highest rate was seen for IL-17 inhibitors, at 1.22 per 100,000 person-years, and the lowest rate was seen with IL-23 inhibitors, at 0.56 per 100,000 person-years. The respective incidence rates for tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors and IL-12/IL-23 inhibitors were a respective 0.94 and 0.80 per 100,000 person-years.
“Compared with TNF inhibitors, IL-23 inhibitor exposure was associated with significantly lower risk of paradoxical eczema,” the BADBIR Study Group reported in JAMA Dermatology. Indeed, patients treated with IL-23 inhibitors were 61% less likely than were those taking TNF-inhibitors to experience a paradoxical eczema event.
“These findings remained when restricting the analysis to first-line biologic exposures and were specific to this eczema phenotype” the group said.
Cautious Interpretation
As the corresponding author for the work, Mr. Al-Janabi observed in an email that the research needs to be replicated, and the findings need to be interpreted with caution.
“As well as usual clinical variables influencing biologic selection, clinicians could consider IL-23 inhibitors in patients with previous atopic dermatitis, hay fever, or paradoxical eczema episodes, as this class was associated with the lowest risk of paradoxical eczema,” he suggested.
A prior history of atopic dermatitis (AD) and hay fever appears to be particularly relevant, as both substantially upped the chances that paradoxical eczema would occur, with hazard ratios of 12.40 and 3.78, respectively. Increasing age also increased the risk, albeit slightly (hazard ratio [HR], 1.02 per year), and there was an apparent lower risk (HR, 0.60) comparing men and women.
The BADBIR Study Group authors believe that, to the best of their knowledge, this is the first study to compare paradoxical eczema risk by biologic class. “Based on clinical experience and prevalence of eczematous reactions reported in some IL-17 inhibitor clinical trials, we suspected an association between IL-17 inhibitor exposure and paradoxical eczema,” they wrote.
“While the incidence of paradoxical eczema was numerically highest among IL-17 inhibitor exposures, it was not significantly different from the incidence among TNF inhibitor exposures.” The low overall incidence of paradoxical eczema “may be reassuring for patients and clinicians,” they added, “but it is possible that the incidence was underestimated due to underreporting or exclusion of adverse events with insufficient detail.”
Details of the Analysis, Other Findings
To explore the risk of paradoxical eczema by biologic class and identify possible risk factors, the BADBIR Study Group performed a prospective cohort study using data held within the BADBIR database between September 2007 and December 2022.
Adults over the age of 18 year or older with plaque psoriasis and who had been treated with at least one of the following biologics were eligible for inclusion: the TNF inhibitors adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, etanercept, and infliximab; the IL-17 inhibitors bimekizumab, brodalumab, ixekizumab, and secukinumab; the IL-12/23 inhibitor ustekinumab; and the IL-23 inhibitors guselkumab, risankizumab, and tildrakizumab.
Patient records and adverse event data were reviewed to determine the incidence of paradoxical eczema events, using terms such as eczema, eczematized, eczematous, atopy, atopic, and dermatitis.
Of 24,952 drug exposures analyzed, the majority (11,819) were for TNF inhibitors, followed by IL-17 inhibitors (4,776), IL-12/23 inhibitors (6,423), and finally, IL-23 inhibitors (1,934).
Mr. Al-Janabi and coauthors reported that the median time to onset of paradoxical eczema events was 294 days — approximately 9.8 months. The earliest that these events were recorded was at 120 days (4 months), and the latest at 699 days (almost 2 years).
The face and neck were the most common sites affected (26% of exposures), with other sites including the limbs (23%), the trunk (13%), and hands or feet (12%). Itching (18%), redness (7%), and dryness (4%) were the most commonly reported symptoms.
The researchers noted that 21 patients had skin biopsies taken and “all showed spongiosis or a feature of eczema, with 1 having overlapping features of psoriasis.”
In the majority (92 %) of cases, patients experienced only one eczema event. Of the 20 patients who had more than one event, just over one-fifth of repeat events occurred after receiving the same biologic as for the index event. A quarter of events occurred after a different biologic of the same class had been used, and just over half of events occurred after a different class of biologic had been given.
Strengths and Limitations
The “large sample size and inclusion of multiple lines of exposure per participant” are strengths of the study, said the researchers. “We included data for all currently available biologics, originating from more than 160 dermatology centers in the UK and Ireland.”
They added, however, that the “main limitation is the small numbers of observations within certain subgroups, such as specific biologic exposures or participants in ethnic minority groups, restricting generalizability of our findings and the interpretation of some subgroup analyses.”
Moreover, the small number of paradoxical eczema events seen may have resulted in imprecise effect estimates, they observe, noting that the number of exposures to IL-23 inhibitors was low compared with other classes.
“Future studies with more exposures and paradoxical eczema events would enable a more robust analysis of individual drugs and patient subgroups,” the authors concluded.
The study was funded by the Medical Research Council. BADBIR is coordinated by The University of Manchester, and funded by the British Association of Dermatologists (BAD). The BAD receives income from AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Celgene, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Lilly, Novartis, Samsung Bioepis, Sandoz Hexal AG, and UCB Pharma for providing pharmacovigilance services. This income finances a separate contract between the BAD and The University of Manchester, which coordinates BADBIR. Mr. Al-Janabi reported receiving grants from the Medical Research Council during the conduct of the study; nonfinancial support from UCB, Almirall, and Janssen; and personal fees from UCB outside the submitted work.
examined in a large observational analysis.
Using data from the British Association of Dermatologists Biologics and Immunomodulators Register (BADBIR) database, Ali Al-Janabi, MA, from the University of Manchester (England) and associates found that 273 (1%) of approximately 25,000 drug exposures in 13,699 biologic-treated patients with psoriasis were associated with paradoxical eczema.
The incidence of paradoxical eczema was found to vary by class. The highest rate was seen for IL-17 inhibitors, at 1.22 per 100,000 person-years, and the lowest rate was seen with IL-23 inhibitors, at 0.56 per 100,000 person-years. The respective incidence rates for tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors and IL-12/IL-23 inhibitors were a respective 0.94 and 0.80 per 100,000 person-years.
“Compared with TNF inhibitors, IL-23 inhibitor exposure was associated with significantly lower risk of paradoxical eczema,” the BADBIR Study Group reported in JAMA Dermatology. Indeed, patients treated with IL-23 inhibitors were 61% less likely than were those taking TNF-inhibitors to experience a paradoxical eczema event.
“These findings remained when restricting the analysis to first-line biologic exposures and were specific to this eczema phenotype” the group said.
Cautious Interpretation
As the corresponding author for the work, Mr. Al-Janabi observed in an email that the research needs to be replicated, and the findings need to be interpreted with caution.
“As well as usual clinical variables influencing biologic selection, clinicians could consider IL-23 inhibitors in patients with previous atopic dermatitis, hay fever, or paradoxical eczema episodes, as this class was associated with the lowest risk of paradoxical eczema,” he suggested.
A prior history of atopic dermatitis (AD) and hay fever appears to be particularly relevant, as both substantially upped the chances that paradoxical eczema would occur, with hazard ratios of 12.40 and 3.78, respectively. Increasing age also increased the risk, albeit slightly (hazard ratio [HR], 1.02 per year), and there was an apparent lower risk (HR, 0.60) comparing men and women.
The BADBIR Study Group authors believe that, to the best of their knowledge, this is the first study to compare paradoxical eczema risk by biologic class. “Based on clinical experience and prevalence of eczematous reactions reported in some IL-17 inhibitor clinical trials, we suspected an association between IL-17 inhibitor exposure and paradoxical eczema,” they wrote.
“While the incidence of paradoxical eczema was numerically highest among IL-17 inhibitor exposures, it was not significantly different from the incidence among TNF inhibitor exposures.” The low overall incidence of paradoxical eczema “may be reassuring for patients and clinicians,” they added, “but it is possible that the incidence was underestimated due to underreporting or exclusion of adverse events with insufficient detail.”
Details of the Analysis, Other Findings
To explore the risk of paradoxical eczema by biologic class and identify possible risk factors, the BADBIR Study Group performed a prospective cohort study using data held within the BADBIR database between September 2007 and December 2022.
Adults over the age of 18 year or older with plaque psoriasis and who had been treated with at least one of the following biologics were eligible for inclusion: the TNF inhibitors adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, etanercept, and infliximab; the IL-17 inhibitors bimekizumab, brodalumab, ixekizumab, and secukinumab; the IL-12/23 inhibitor ustekinumab; and the IL-23 inhibitors guselkumab, risankizumab, and tildrakizumab.
Patient records and adverse event data were reviewed to determine the incidence of paradoxical eczema events, using terms such as eczema, eczematized, eczematous, atopy, atopic, and dermatitis.
Of 24,952 drug exposures analyzed, the majority (11,819) were for TNF inhibitors, followed by IL-17 inhibitors (4,776), IL-12/23 inhibitors (6,423), and finally, IL-23 inhibitors (1,934).
Mr. Al-Janabi and coauthors reported that the median time to onset of paradoxical eczema events was 294 days — approximately 9.8 months. The earliest that these events were recorded was at 120 days (4 months), and the latest at 699 days (almost 2 years).
The face and neck were the most common sites affected (26% of exposures), with other sites including the limbs (23%), the trunk (13%), and hands or feet (12%). Itching (18%), redness (7%), and dryness (4%) were the most commonly reported symptoms.
The researchers noted that 21 patients had skin biopsies taken and “all showed spongiosis or a feature of eczema, with 1 having overlapping features of psoriasis.”
In the majority (92 %) of cases, patients experienced only one eczema event. Of the 20 patients who had more than one event, just over one-fifth of repeat events occurred after receiving the same biologic as for the index event. A quarter of events occurred after a different biologic of the same class had been used, and just over half of events occurred after a different class of biologic had been given.
Strengths and Limitations
The “large sample size and inclusion of multiple lines of exposure per participant” are strengths of the study, said the researchers. “We included data for all currently available biologics, originating from more than 160 dermatology centers in the UK and Ireland.”
They added, however, that the “main limitation is the small numbers of observations within certain subgroups, such as specific biologic exposures or participants in ethnic minority groups, restricting generalizability of our findings and the interpretation of some subgroup analyses.”
Moreover, the small number of paradoxical eczema events seen may have resulted in imprecise effect estimates, they observe, noting that the number of exposures to IL-23 inhibitors was low compared with other classes.
“Future studies with more exposures and paradoxical eczema events would enable a more robust analysis of individual drugs and patient subgroups,” the authors concluded.
The study was funded by the Medical Research Council. BADBIR is coordinated by The University of Manchester, and funded by the British Association of Dermatologists (BAD). The BAD receives income from AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Celgene, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Lilly, Novartis, Samsung Bioepis, Sandoz Hexal AG, and UCB Pharma for providing pharmacovigilance services. This income finances a separate contract between the BAD and The University of Manchester, which coordinates BADBIR. Mr. Al-Janabi reported receiving grants from the Medical Research Council during the conduct of the study; nonfinancial support from UCB, Almirall, and Janssen; and personal fees from UCB outside the submitted work.
examined in a large observational analysis.
Using data from the British Association of Dermatologists Biologics and Immunomodulators Register (BADBIR) database, Ali Al-Janabi, MA, from the University of Manchester (England) and associates found that 273 (1%) of approximately 25,000 drug exposures in 13,699 biologic-treated patients with psoriasis were associated with paradoxical eczema.
The incidence of paradoxical eczema was found to vary by class. The highest rate was seen for IL-17 inhibitors, at 1.22 per 100,000 person-years, and the lowest rate was seen with IL-23 inhibitors, at 0.56 per 100,000 person-years. The respective incidence rates for tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors and IL-12/IL-23 inhibitors were a respective 0.94 and 0.80 per 100,000 person-years.
“Compared with TNF inhibitors, IL-23 inhibitor exposure was associated with significantly lower risk of paradoxical eczema,” the BADBIR Study Group reported in JAMA Dermatology. Indeed, patients treated with IL-23 inhibitors were 61% less likely than were those taking TNF-inhibitors to experience a paradoxical eczema event.
“These findings remained when restricting the analysis to first-line biologic exposures and were specific to this eczema phenotype” the group said.
Cautious Interpretation
As the corresponding author for the work, Mr. Al-Janabi observed in an email that the research needs to be replicated, and the findings need to be interpreted with caution.
“As well as usual clinical variables influencing biologic selection, clinicians could consider IL-23 inhibitors in patients with previous atopic dermatitis, hay fever, or paradoxical eczema episodes, as this class was associated with the lowest risk of paradoxical eczema,” he suggested.
A prior history of atopic dermatitis (AD) and hay fever appears to be particularly relevant, as both substantially upped the chances that paradoxical eczema would occur, with hazard ratios of 12.40 and 3.78, respectively. Increasing age also increased the risk, albeit slightly (hazard ratio [HR], 1.02 per year), and there was an apparent lower risk (HR, 0.60) comparing men and women.
The BADBIR Study Group authors believe that, to the best of their knowledge, this is the first study to compare paradoxical eczema risk by biologic class. “Based on clinical experience and prevalence of eczematous reactions reported in some IL-17 inhibitor clinical trials, we suspected an association between IL-17 inhibitor exposure and paradoxical eczema,” they wrote.
“While the incidence of paradoxical eczema was numerically highest among IL-17 inhibitor exposures, it was not significantly different from the incidence among TNF inhibitor exposures.” The low overall incidence of paradoxical eczema “may be reassuring for patients and clinicians,” they added, “but it is possible that the incidence was underestimated due to underreporting or exclusion of adverse events with insufficient detail.”
Details of the Analysis, Other Findings
To explore the risk of paradoxical eczema by biologic class and identify possible risk factors, the BADBIR Study Group performed a prospective cohort study using data held within the BADBIR database between September 2007 and December 2022.
Adults over the age of 18 year or older with plaque psoriasis and who had been treated with at least one of the following biologics were eligible for inclusion: the TNF inhibitors adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, etanercept, and infliximab; the IL-17 inhibitors bimekizumab, brodalumab, ixekizumab, and secukinumab; the IL-12/23 inhibitor ustekinumab; and the IL-23 inhibitors guselkumab, risankizumab, and tildrakizumab.
Patient records and adverse event data were reviewed to determine the incidence of paradoxical eczema events, using terms such as eczema, eczematized, eczematous, atopy, atopic, and dermatitis.
Of 24,952 drug exposures analyzed, the majority (11,819) were for TNF inhibitors, followed by IL-17 inhibitors (4,776), IL-12/23 inhibitors (6,423), and finally, IL-23 inhibitors (1,934).
Mr. Al-Janabi and coauthors reported that the median time to onset of paradoxical eczema events was 294 days — approximately 9.8 months. The earliest that these events were recorded was at 120 days (4 months), and the latest at 699 days (almost 2 years).
The face and neck were the most common sites affected (26% of exposures), with other sites including the limbs (23%), the trunk (13%), and hands or feet (12%). Itching (18%), redness (7%), and dryness (4%) were the most commonly reported symptoms.
The researchers noted that 21 patients had skin biopsies taken and “all showed spongiosis or a feature of eczema, with 1 having overlapping features of psoriasis.”
In the majority (92 %) of cases, patients experienced only one eczema event. Of the 20 patients who had more than one event, just over one-fifth of repeat events occurred after receiving the same biologic as for the index event. A quarter of events occurred after a different biologic of the same class had been used, and just over half of events occurred after a different class of biologic had been given.
Strengths and Limitations
The “large sample size and inclusion of multiple lines of exposure per participant” are strengths of the study, said the researchers. “We included data for all currently available biologics, originating from more than 160 dermatology centers in the UK and Ireland.”
They added, however, that the “main limitation is the small numbers of observations within certain subgroups, such as specific biologic exposures or participants in ethnic minority groups, restricting generalizability of our findings and the interpretation of some subgroup analyses.”
Moreover, the small number of paradoxical eczema events seen may have resulted in imprecise effect estimates, they observe, noting that the number of exposures to IL-23 inhibitors was low compared with other classes.
“Future studies with more exposures and paradoxical eczema events would enable a more robust analysis of individual drugs and patient subgroups,” the authors concluded.
The study was funded by the Medical Research Council. BADBIR is coordinated by The University of Manchester, and funded by the British Association of Dermatologists (BAD). The BAD receives income from AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Celgene, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Lilly, Novartis, Samsung Bioepis, Sandoz Hexal AG, and UCB Pharma for providing pharmacovigilance services. This income finances a separate contract between the BAD and The University of Manchester, which coordinates BADBIR. Mr. Al-Janabi reported receiving grants from the Medical Research Council during the conduct of the study; nonfinancial support from UCB, Almirall, and Janssen; and personal fees from UCB outside the submitted work.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
How to Reduce Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality in Psoriasis and PsA
Patients with psoriatic disease have significantly higher risks of myocardial infarction, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality than does the general population, yet research consistently paints what dermatologist Joel M. Gelfand, MD, calls an “abysmal” picture: Only a minority of patients with psoriatic disease know about their increased risks, only a minority of dermatologists and rheumatologists screen for cardiovascular risk factors like lipid levels and blood pressure, and only a minority of patients diagnosed with hyperlipidemia are adequately treated with statin therapy.
In the literature and at medical meetings, Dr. Gelfand and others who have studied cardiovascular disease (CVD) comorbidity and physician practices have been urging dermatologists and rheumatologists to play a more consistent and active role in primary cardiovascular prevention for patients with psoriatic disease, who are up to 50% more likely than patients without it to develop CVD and who tend to have atherosclerosis at earlier ages.
According to the 2019 joint American Academy of Dermatology (AAD)–National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) guidelines for managing psoriasis “with awareness and attention to comorbidities,” this means not only ensuring that all patients with psoriasis receive standard CV risk assessment (screening for hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia), but also recognizing that patients who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy — or who have psoriasis involving > 10% of body surface area — may benefit from earlier and more frequent screening.
CV risk and premature mortality rises with the severity of skin disease, and patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) are believed to have risk levels similar to patients with moderate-severe psoriasis, cardiologist Michael S. Garshick, MD, director of the cardio-rheumatology program at New York University Langone Health, said in an interview.
In a recent survey study of 100 patients seen at NYU Langone Health’s psoriasis specialty clinic, only one-third indicated they had been advised by their physicians to be screened for CV risk factors, and only one-third reported having been told of the connection between psoriasis and CVD risk. Dr. Garshick shared the unpublished findings at the annual research symposium of the NPF in October.
Similarly, data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey shows that just 16% of psoriasis-related visits to dermatology providers from 2007 to 2016 involved screening for CV risk factors. Screening rates were 11% for body mass index, 7.4% for blood pressure, 2.9% for cholesterol, and 1.7% for glucose, Dr. Gelfand and coauthors reported in 2023. .
Such findings are concerning because research shows that fewer than a quarter of patients with psoriasis have a primary care visit within a year of establishing care with their physicians, and that, overall, fewer than half of commercially insured adults under age 65 visit a primary care physician each year, according to John S. Barbieri, MD, of the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. He included these findings when reporting in 2022 on a survey study on CVD screening.
In many cases, dermatologists and rheumatologists may be the primary providers for patients with psoriatic disease. So, “the question is, how can the dermatologist or rheumatologist use their interactions as a touchpoint to improve the patient’s well-being?” Dr. Barbieri said in an interview.
For the dermatologist, educating patients about the higher CVD risk fits well into conversations about “how there may be inflammation inside the body as well as in the skin,” he said. “Talk about cardiovascular risk just as you talk about PsA risk.” Both specialists, he added, can incorporate blood pressure readings and look for opportunities to measure lipid levels and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c). These labs can easily be integrated into a biologic work-up.
“The hard part — and this needs to be individualized — is how do you want to handle [abnormal readings]? Do you want to take on a lot of the ownership and calculate [10-year CVD] risk scores and then counsel patients accordingly?” Dr. Barbieri said. “Or do you want to try to refer, and encourage them to work with their PCP? There a high-touch version and a low-touch version of how you can turn screening into action, into a care plan.”
Beyond traditional risk elevation, the primary care hand-off
Rheumatologists “in general may be more apt to screen for cardiovascular disease” as a result of their internal medicine residency training, and “we’re generally more comfortable prescribing ... if we need to,” said Alexis R. Ogdie, MD, a rheumatologist at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and director of the Penn Psoriatic Arthritis Clinic.
Referral to a preventive cardiologist for management of abnormal lab results or ongoing monitoring and prevention is ideal, but when hand-offs to primary care physicians are made — the more common scenario — education is important. “A common problem is that there is underrecognition of the cardiovascular risk being elevated in our patients,” she said, above and beyond risk posed by traditional risk factors such as dyslipidemia, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, and obesity, all of which have been shown to occur more frequently in patients with psoriatic disease than in the general population.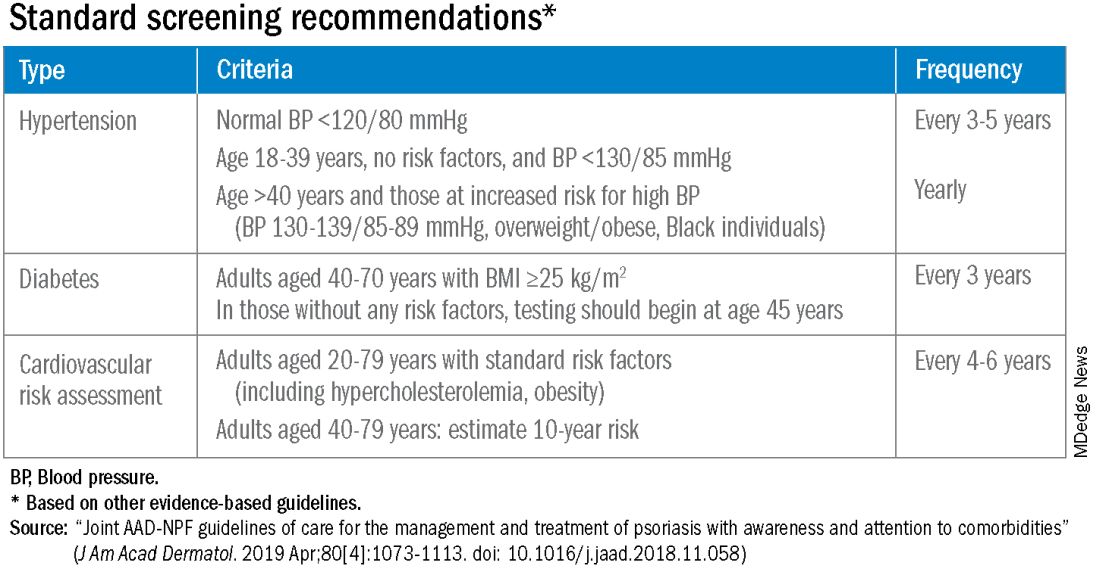
Risk stratification guides CVD prevention in the general population, and “if you use typical scores for cardiovascular risk, they may underestimate risk for our patients with PsA,” said Dr. Ogdie, who has reported on CV risk in patients with PsA. “Relative to what the patient’s perceived risk is, they may be treated similarly (to the general population). But relative to their actual risk, they’re undertreated.”
The 2019 AAD-NPF psoriasis guidelines recommend utilizing a 1.5 multiplication factor in risk score models, such as the American College of Cardiology’s Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD) Risk Estimator, when the patient has a body surface area >10% or is a candidate for systemic therapy or phototherapy.
Similarly, the 2018 American Heart Association (AHA)-ACC Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol defines psoriasis, along with RA, metabolic syndrome, HIV, and other diseases, as a “cardiovascular risk enhancer” that should be factored into assessments of ASCVD risk. (The guideline does not specify a psoriasis severity threshold.)
“It’s the first time the specialty [of cardiology] has said, ‘pay attention to a skin disease,’ ” Dr. Gelfand said at the NPF meeting.
Using the 1.5 multiplication factor, a patient who otherwise would be classified in the AHA/ACC guideline as “borderline risk,” with a 10-year ASCVD risk of 5% to <7.5%, would instead have an “intermediate” 10-year ASCVD risk of ≥7.5% to <20%. Application of the AHA-ACC “risk enhancer” would have a similar effect.
For management, the main impact of psoriasis being considered a risk enhancer is that “it lowers the threshold for treatment with standard cardiovascular prevention medications such as statins.”
In general, “we should be taking a more aggressive approach to the management of traditional cardiovascular risk factors” in patients with psoriatic disease, he said. Instead of telling a patient with mildly elevated blood pressure, ‘I’ll see you in a year or two,’ or a patient entering a prediabetic stage to “watch what you eat, and I’ll see you in a couple of years,” clinicians need to be more vigilant.
“It’s about recognizing that these traditional cardiometabolic risk factors, synergistically with psoriasis, can start enhancing CV risk at an earlier age than we might expect,” said Dr. Garshick, whose 2021 review of CV risk in psoriasis describes how the inflammatory milieu in psoriasis is linked to atherosclerosis development.
Cardiologists are aware of this, but “many primary care physicians are not. It takes time for medical knowledge to diffuse,” Dr. Gelfand said. “Tell the PCP, in notes or in a form letter, that there is a higher risk of CV disease, and reference the AHA/ACC guidelines,” he advised. “You don’t want your patient to go to their doctor and the doctor to [be uninformed].”
‘Patients trust us’
Dr. Gelfand has been at the forefront of research on psoriasis and heart disease. A study he coauthored in 2006, for instance, documented an independent risk of MI, with adjusted relative risks of 1.29 and 3.10 for a 30-year-old patient with mild or severe disease, respectively, and higher risks for a 60-year-old. In 2010, he and coinvestigators found that severe psoriasis was an independent risk factor for CV mortality (HR, 1.57) after adjusting for age, sex, smoking, diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia.
Today, along with Dr. Barbieri, Dr. Ogdie, and others, he is studying the feasibility and efficacy of a proposed national, “centralized care coordinator” model of care whereby dermatologists and rheumatologists would educate the patient, order lipid and HbA1c measurements as medically appropriate, and then refer patients as needed to a care coordinator. The care coordinator would calculate a 10-year CVD risk score and counsel the patient on possible next steps.
In a pilot study of 85 patients at four sites, 92% of patients followed through on their physician’s recommendations to have labs drawn, and 86% indicated the model was acceptable and feasible. A total of 27% of patients had “newly identified, previously undiagnosed, elevated cardiovascular disease risk,” and exploratory effectiveness results indicated a successful reduction in predicted CVD risk in patients who started statins, Dr. Gelfand reported at the NPF meeting.
With funding from the NPF, a larger, single-arm, pragmatic “CP3” trial (NCT05908240) is enrolling 525 patients with psoriasis at 10-20 academic and nonacademic dermatology sites across the United States to further test the model. The primary endpoint will be the change in LDL cholesterol measured at 6 months among people with a 10-year risk ≥5%. Secondary endpoints will cover improvement in disease severity and quality of life, behavior modification, patient experience, and other issues.
“We have only 10-15 minutes [with patients] ... a care coordinator who is empathetic and understanding and [informed] could make a big difference,” Dr. Gelfand said at the NPF meeting. If findings are positive, the model would be tested in rheumatology sites as well. The hope, he said, is that the NPF would be able to fund an in-house care coordinator(s) for the long-term.
Notably, a patient survey conducted as part of exploratory research leading up to the care coordinator project showed that patients trust their dermatologist or rheumatologist for CVD education and screening. Among 160 patients with psoriasis and 162 patients with PsA, 76% and 90% agreed that “I would like it if my dermatologist/rheumatologist educated me about my risk of heart disease,” and 60% and 75%, respectively, agree that “it would be convenient for me to have my cholesterol checked by my dermatologist/rheumatologist.”
“Patients trust us,” Dr. Gelfand said at the NPF meeting. “And the pilot study shows us that patients are motivated.”
Taking an individualized, holistic, longitudinal approach
“Sometimes you do have to triage bit,” Dr. Gelfand said in an interview. “For a young person with normal body weight who doesn’t smoke and has mild psoriasis, one could just educate and advise that they see their primary care physician” for monitoring.
“But for the same patient who is obese, maybe smokes, and doesn’t have a primary care physician, I’d order labs,” he said. “You don’t want a patient walking out the door with an [undiagnosed] LDL of 160 or hypertension.”
Age is also an important consideration, as excess CVD risk associated with autoimmune diseases like psoriasis rises with age, Dr. Gelfand said during a seminar on psoriasis and PsA held at NYU Langone in December. For a young person, typically, “I need to focus on education and lifestyle … setting them on a healthy lifestyle trajectory,” he said. “Once they get to 40, from 40 to 75 or so, that’s a sweet spot for medical intervention to lower cardiovascular risk.”
Even at older ages, however, lipid management is not the be-all and end-all, he said in the interview. “We have to be holistic.”
One advantage of having highly successful therapies for psoriasis, and to a lesser extent PsA, is the time that becomes available during follow-up visits — once disease is under control — to “focus on other things,” he said. Waiting until disease is under control to discuss diet, exercise, or smoking, for instance, makes sense anyway, he said. “You don’t want to overwhelm patients with too much to do at once.”
Indeed, said dermatologist Robert E. Kalb, MD, of the Buffalo Medical Group in Buffalo, NY, “patients have an open mind [about discussing cardiovascular disease risk], but it is not high on their radar. Most of them just want to get their skin clear.” (Dr. Kalb participated in the care coordinator pilot study, and said in an interview that since its completion, he has been more routinely ordering relevant labs.)
Rheumatologists are less fortunate with highly successful therapies, but “over the continuum of care, we do have time in office visits” to discuss issues like smoking, exercise, and lifestyle, Dr. Ogdie said. “I think of each of those pieces as part of our job.”
In the future, as researchers learn more about the impact of psoriasis and PsA treatments on CVD risk, it may be possible to tailor treatments or to prescribe treatments knowing that the therapies could reduce risk. Observational and epidemiologic data suggest that tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitor therapy over 3 years reduces the risk of MI, and that patients whose psoriasis is treated have reduced aortic inflammation, improved myocardial strain, and reduced coronary plaque burden, Dr. Garshick said at the NPF meeting.
“But when we look at the randomized controlled trials, they’re actually inconclusive that targeting inflammation in psoriatic disease reduces surrogates of cardiovascular disease,” he said. Dr. Garshick’s own research focuses on platelet and endothelial biology in psoriasis.
Dr. Barbieri reported he had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Garshick reported consulting fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Kiniksa, Horizon Therapeutics, and Agepha. Dr. Ogdie reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Takeda, and UCB. Dr. Gelfand reported serving as a consultant for AbbVie, Artax, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and other companies.
Patients with psoriatic disease have significantly higher risks of myocardial infarction, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality than does the general population, yet research consistently paints what dermatologist Joel M. Gelfand, MD, calls an “abysmal” picture: Only a minority of patients with psoriatic disease know about their increased risks, only a minority of dermatologists and rheumatologists screen for cardiovascular risk factors like lipid levels and blood pressure, and only a minority of patients diagnosed with hyperlipidemia are adequately treated with statin therapy.
In the literature and at medical meetings, Dr. Gelfand and others who have studied cardiovascular disease (CVD) comorbidity and physician practices have been urging dermatologists and rheumatologists to play a more consistent and active role in primary cardiovascular prevention for patients with psoriatic disease, who are up to 50% more likely than patients without it to develop CVD and who tend to have atherosclerosis at earlier ages.
According to the 2019 joint American Academy of Dermatology (AAD)–National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) guidelines for managing psoriasis “with awareness and attention to comorbidities,” this means not only ensuring that all patients with psoriasis receive standard CV risk assessment (screening for hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia), but also recognizing that patients who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy — or who have psoriasis involving > 10% of body surface area — may benefit from earlier and more frequent screening.
CV risk and premature mortality rises with the severity of skin disease, and patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) are believed to have risk levels similar to patients with moderate-severe psoriasis, cardiologist Michael S. Garshick, MD, director of the cardio-rheumatology program at New York University Langone Health, said in an interview.
In a recent survey study of 100 patients seen at NYU Langone Health’s psoriasis specialty clinic, only one-third indicated they had been advised by their physicians to be screened for CV risk factors, and only one-third reported having been told of the connection between psoriasis and CVD risk. Dr. Garshick shared the unpublished findings at the annual research symposium of the NPF in October.
Similarly, data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey shows that just 16% of psoriasis-related visits to dermatology providers from 2007 to 2016 involved screening for CV risk factors. Screening rates were 11% for body mass index, 7.4% for blood pressure, 2.9% for cholesterol, and 1.7% for glucose, Dr. Gelfand and coauthors reported in 2023. .
Such findings are concerning because research shows that fewer than a quarter of patients with psoriasis have a primary care visit within a year of establishing care with their physicians, and that, overall, fewer than half of commercially insured adults under age 65 visit a primary care physician each year, according to John S. Barbieri, MD, of the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. He included these findings when reporting in 2022 on a survey study on CVD screening.
In many cases, dermatologists and rheumatologists may be the primary providers for patients with psoriatic disease. So, “the question is, how can the dermatologist or rheumatologist use their interactions as a touchpoint to improve the patient’s well-being?” Dr. Barbieri said in an interview.
For the dermatologist, educating patients about the higher CVD risk fits well into conversations about “how there may be inflammation inside the body as well as in the skin,” he said. “Talk about cardiovascular risk just as you talk about PsA risk.” Both specialists, he added, can incorporate blood pressure readings and look for opportunities to measure lipid levels and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c). These labs can easily be integrated into a biologic work-up.
“The hard part — and this needs to be individualized — is how do you want to handle [abnormal readings]? Do you want to take on a lot of the ownership and calculate [10-year CVD] risk scores and then counsel patients accordingly?” Dr. Barbieri said. “Or do you want to try to refer, and encourage them to work with their PCP? There a high-touch version and a low-touch version of how you can turn screening into action, into a care plan.”
Beyond traditional risk elevation, the primary care hand-off
Rheumatologists “in general may be more apt to screen for cardiovascular disease” as a result of their internal medicine residency training, and “we’re generally more comfortable prescribing ... if we need to,” said Alexis R. Ogdie, MD, a rheumatologist at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and director of the Penn Psoriatic Arthritis Clinic.
Referral to a preventive cardiologist for management of abnormal lab results or ongoing monitoring and prevention is ideal, but when hand-offs to primary care physicians are made — the more common scenario — education is important. “A common problem is that there is underrecognition of the cardiovascular risk being elevated in our patients,” she said, above and beyond risk posed by traditional risk factors such as dyslipidemia, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, and obesity, all of which have been shown to occur more frequently in patients with psoriatic disease than in the general population.
Risk stratification guides CVD prevention in the general population, and “if you use typical scores for cardiovascular risk, they may underestimate risk for our patients with PsA,” said Dr. Ogdie, who has reported on CV risk in patients with PsA. “Relative to what the patient’s perceived risk is, they may be treated similarly (to the general population). But relative to their actual risk, they’re undertreated.”
The 2019 AAD-NPF psoriasis guidelines recommend utilizing a 1.5 multiplication factor in risk score models, such as the American College of Cardiology’s Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD) Risk Estimator, when the patient has a body surface area >10% or is a candidate for systemic therapy or phototherapy.
Similarly, the 2018 American Heart Association (AHA)-ACC Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol defines psoriasis, along with RA, metabolic syndrome, HIV, and other diseases, as a “cardiovascular risk enhancer” that should be factored into assessments of ASCVD risk. (The guideline does not specify a psoriasis severity threshold.)
“It’s the first time the specialty [of cardiology] has said, ‘pay attention to a skin disease,’ ” Dr. Gelfand said at the NPF meeting.
Using the 1.5 multiplication factor, a patient who otherwise would be classified in the AHA/ACC guideline as “borderline risk,” with a 10-year ASCVD risk of 5% to <7.5%, would instead have an “intermediate” 10-year ASCVD risk of ≥7.5% to <20%. Application of the AHA-ACC “risk enhancer” would have a similar effect.
For management, the main impact of psoriasis being considered a risk enhancer is that “it lowers the threshold for treatment with standard cardiovascular prevention medications such as statins.”
In general, “we should be taking a more aggressive approach to the management of traditional cardiovascular risk factors” in patients with psoriatic disease, he said. Instead of telling a patient with mildly elevated blood pressure, ‘I’ll see you in a year or two,’ or a patient entering a prediabetic stage to “watch what you eat, and I’ll see you in a couple of years,” clinicians need to be more vigilant.
“It’s about recognizing that these traditional cardiometabolic risk factors, synergistically with psoriasis, can start enhancing CV risk at an earlier age than we might expect,” said Dr. Garshick, whose 2021 review of CV risk in psoriasis describes how the inflammatory milieu in psoriasis is linked to atherosclerosis development.
Cardiologists are aware of this, but “many primary care physicians are not. It takes time for medical knowledge to diffuse,” Dr. Gelfand said. “Tell the PCP, in notes or in a form letter, that there is a higher risk of CV disease, and reference the AHA/ACC guidelines,” he advised. “You don’t want your patient to go to their doctor and the doctor to [be uninformed].”
‘Patients trust us’
Dr. Gelfand has been at the forefront of research on psoriasis and heart disease. A study he coauthored in 2006, for instance, documented an independent risk of MI, with adjusted relative risks of 1.29 and 3.10 for a 30-year-old patient with mild or severe disease, respectively, and higher risks for a 60-year-old. In 2010, he and coinvestigators found that severe psoriasis was an independent risk factor for CV mortality (HR, 1.57) after adjusting for age, sex, smoking, diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia.
Today, along with Dr. Barbieri, Dr. Ogdie, and others, he is studying the feasibility and efficacy of a proposed national, “centralized care coordinator” model of care whereby dermatologists and rheumatologists would educate the patient, order lipid and HbA1c measurements as medically appropriate, and then refer patients as needed to a care coordinator. The care coordinator would calculate a 10-year CVD risk score and counsel the patient on possible next steps.
In a pilot study of 85 patients at four sites, 92% of patients followed through on their physician’s recommendations to have labs drawn, and 86% indicated the model was acceptable and feasible. A total of 27% of patients had “newly identified, previously undiagnosed, elevated cardiovascular disease risk,” and exploratory effectiveness results indicated a successful reduction in predicted CVD risk in patients who started statins, Dr. Gelfand reported at the NPF meeting.
With funding from the NPF, a larger, single-arm, pragmatic “CP3” trial (NCT05908240) is enrolling 525 patients with psoriasis at 10-20 academic and nonacademic dermatology sites across the United States to further test the model. The primary endpoint will be the change in LDL cholesterol measured at 6 months among people with a 10-year risk ≥5%. Secondary endpoints will cover improvement in disease severity and quality of life, behavior modification, patient experience, and other issues.
“We have only 10-15 minutes [with patients] ... a care coordinator who is empathetic and understanding and [informed] could make a big difference,” Dr. Gelfand said at the NPF meeting. If findings are positive, the model would be tested in rheumatology sites as well. The hope, he said, is that the NPF would be able to fund an in-house care coordinator(s) for the long-term.
Notably, a patient survey conducted as part of exploratory research leading up to the care coordinator project showed that patients trust their dermatologist or rheumatologist for CVD education and screening. Among 160 patients with psoriasis and 162 patients with PsA, 76% and 90% agreed that “I would like it if my dermatologist/rheumatologist educated me about my risk of heart disease,” and 60% and 75%, respectively, agree that “it would be convenient for me to have my cholesterol checked by my dermatologist/rheumatologist.”
“Patients trust us,” Dr. Gelfand said at the NPF meeting. “And the pilot study shows us that patients are motivated.”
Taking an individualized, holistic, longitudinal approach
“Sometimes you do have to triage bit,” Dr. Gelfand said in an interview. “For a young person with normal body weight who doesn’t smoke and has mild psoriasis, one could just educate and advise that they see their primary care physician” for monitoring.
“But for the same patient who is obese, maybe smokes, and doesn’t have a primary care physician, I’d order labs,” he said. “You don’t want a patient walking out the door with an [undiagnosed] LDL of 160 or hypertension.”
Age is also an important consideration, as excess CVD risk associated with autoimmune diseases like psoriasis rises with age, Dr. Gelfand said during a seminar on psoriasis and PsA held at NYU Langone in December. For a young person, typically, “I need to focus on education and lifestyle … setting them on a healthy lifestyle trajectory,” he said. “Once they get to 40, from 40 to 75 or so, that’s a sweet spot for medical intervention to lower cardiovascular risk.”
Even at older ages, however, lipid management is not the be-all and end-all, he said in the interview. “We have to be holistic.”
One advantage of having highly successful therapies for psoriasis, and to a lesser extent PsA, is the time that becomes available during follow-up visits — once disease is under control — to “focus on other things,” he said. Waiting until disease is under control to discuss diet, exercise, or smoking, for instance, makes sense anyway, he said. “You don’t want to overwhelm patients with too much to do at once.”
Indeed, said dermatologist Robert E. Kalb, MD, of the Buffalo Medical Group in Buffalo, NY, “patients have an open mind [about discussing cardiovascular disease risk], but it is not high on their radar. Most of them just want to get their skin clear.” (Dr. Kalb participated in the care coordinator pilot study, and said in an interview that since its completion, he has been more routinely ordering relevant labs.)
Rheumatologists are less fortunate with highly successful therapies, but “over the continuum of care, we do have time in office visits” to discuss issues like smoking, exercise, and lifestyle, Dr. Ogdie said. “I think of each of those pieces as part of our job.”
In the future, as researchers learn more about the impact of psoriasis and PsA treatments on CVD risk, it may be possible to tailor treatments or to prescribe treatments knowing that the therapies could reduce risk. Observational and epidemiologic data suggest that tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitor therapy over 3 years reduces the risk of MI, and that patients whose psoriasis is treated have reduced aortic inflammation, improved myocardial strain, and reduced coronary plaque burden, Dr. Garshick said at the NPF meeting.
“But when we look at the randomized controlled trials, they’re actually inconclusive that targeting inflammation in psoriatic disease reduces surrogates of cardiovascular disease,” he said. Dr. Garshick’s own research focuses on platelet and endothelial biology in psoriasis.
Dr. Barbieri reported he had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Garshick reported consulting fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Kiniksa, Horizon Therapeutics, and Agepha. Dr. Ogdie reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Takeda, and UCB. Dr. Gelfand reported serving as a consultant for AbbVie, Artax, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and other companies.
Patients with psoriatic disease have significantly higher risks of myocardial infarction, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality than does the general population, yet research consistently paints what dermatologist Joel M. Gelfand, MD, calls an “abysmal” picture: Only a minority of patients with psoriatic disease know about their increased risks, only a minority of dermatologists and rheumatologists screen for cardiovascular risk factors like lipid levels and blood pressure, and only a minority of patients diagnosed with hyperlipidemia are adequately treated with statin therapy.
In the literature and at medical meetings, Dr. Gelfand and others who have studied cardiovascular disease (CVD) comorbidity and physician practices have been urging dermatologists and rheumatologists to play a more consistent and active role in primary cardiovascular prevention for patients with psoriatic disease, who are up to 50% more likely than patients without it to develop CVD and who tend to have atherosclerosis at earlier ages.
According to the 2019 joint American Academy of Dermatology (AAD)–National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) guidelines for managing psoriasis “with awareness and attention to comorbidities,” this means not only ensuring that all patients with psoriasis receive standard CV risk assessment (screening for hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia), but also recognizing that patients who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy — or who have psoriasis involving > 10% of body surface area — may benefit from earlier and more frequent screening.
CV risk and premature mortality rises with the severity of skin disease, and patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) are believed to have risk levels similar to patients with moderate-severe psoriasis, cardiologist Michael S. Garshick, MD, director of the cardio-rheumatology program at New York University Langone Health, said in an interview.
In a recent survey study of 100 patients seen at NYU Langone Health’s psoriasis specialty clinic, only one-third indicated they had been advised by their physicians to be screened for CV risk factors, and only one-third reported having been told of the connection between psoriasis and CVD risk. Dr. Garshick shared the unpublished findings at the annual research symposium of the NPF in October.
Similarly, data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey shows that just 16% of psoriasis-related visits to dermatology providers from 2007 to 2016 involved screening for CV risk factors. Screening rates were 11% for body mass index, 7.4% for blood pressure, 2.9% for cholesterol, and 1.7% for glucose, Dr. Gelfand and coauthors reported in 2023. .
Such findings are concerning because research shows that fewer than a quarter of patients with psoriasis have a primary care visit within a year of establishing care with their physicians, and that, overall, fewer than half of commercially insured adults under age 65 visit a primary care physician each year, according to John S. Barbieri, MD, of the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. He included these findings when reporting in 2022 on a survey study on CVD screening.
In many cases, dermatologists and rheumatologists may be the primary providers for patients with psoriatic disease. So, “the question is, how can the dermatologist or rheumatologist use their interactions as a touchpoint to improve the patient’s well-being?” Dr. Barbieri said in an interview.
For the dermatologist, educating patients about the higher CVD risk fits well into conversations about “how there may be inflammation inside the body as well as in the skin,” he said. “Talk about cardiovascular risk just as you talk about PsA risk.” Both specialists, he added, can incorporate blood pressure readings and look for opportunities to measure lipid levels and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c). These labs can easily be integrated into a biologic work-up.
“The hard part — and this needs to be individualized — is how do you want to handle [abnormal readings]? Do you want to take on a lot of the ownership and calculate [10-year CVD] risk scores and then counsel patients accordingly?” Dr. Barbieri said. “Or do you want to try to refer, and encourage them to work with their PCP? There a high-touch version and a low-touch version of how you can turn screening into action, into a care plan.”
Beyond traditional risk elevation, the primary care hand-off
Rheumatologists “in general may be more apt to screen for cardiovascular disease” as a result of their internal medicine residency training, and “we’re generally more comfortable prescribing ... if we need to,” said Alexis R. Ogdie, MD, a rheumatologist at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and director of the Penn Psoriatic Arthritis Clinic.
Referral to a preventive cardiologist for management of abnormal lab results or ongoing monitoring and prevention is ideal, but when hand-offs to primary care physicians are made — the more common scenario — education is important. “A common problem is that there is underrecognition of the cardiovascular risk being elevated in our patients,” she said, above and beyond risk posed by traditional risk factors such as dyslipidemia, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, and obesity, all of which have been shown to occur more frequently in patients with psoriatic disease than in the general population.
Risk stratification guides CVD prevention in the general population, and “if you use typical scores for cardiovascular risk, they may underestimate risk for our patients with PsA,” said Dr. Ogdie, who has reported on CV risk in patients with PsA. “Relative to what the patient’s perceived risk is, they may be treated similarly (to the general population). But relative to their actual risk, they’re undertreated.”
The 2019 AAD-NPF psoriasis guidelines recommend utilizing a 1.5 multiplication factor in risk score models, such as the American College of Cardiology’s Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD) Risk Estimator, when the patient has a body surface area >10% or is a candidate for systemic therapy or phototherapy.
Similarly, the 2018 American Heart Association (AHA)-ACC Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol defines psoriasis, along with RA, metabolic syndrome, HIV, and other diseases, as a “cardiovascular risk enhancer” that should be factored into assessments of ASCVD risk. (The guideline does not specify a psoriasis severity threshold.)
“It’s the first time the specialty [of cardiology] has said, ‘pay attention to a skin disease,’ ” Dr. Gelfand said at the NPF meeting.
Using the 1.5 multiplication factor, a patient who otherwise would be classified in the AHA/ACC guideline as “borderline risk,” with a 10-year ASCVD risk of 5% to <7.5%, would instead have an “intermediate” 10-year ASCVD risk of ≥7.5% to <20%. Application of the AHA-ACC “risk enhancer” would have a similar effect.
For management, the main impact of psoriasis being considered a risk enhancer is that “it lowers the threshold for treatment with standard cardiovascular prevention medications such as statins.”
In general, “we should be taking a more aggressive approach to the management of traditional cardiovascular risk factors” in patients with psoriatic disease, he said. Instead of telling a patient with mildly elevated blood pressure, ‘I’ll see you in a year or two,’ or a patient entering a prediabetic stage to “watch what you eat, and I’ll see you in a couple of years,” clinicians need to be more vigilant.
“It’s about recognizing that these traditional cardiometabolic risk factors, synergistically with psoriasis, can start enhancing CV risk at an earlier age than we might expect,” said Dr. Garshick, whose 2021 review of CV risk in psoriasis describes how the inflammatory milieu in psoriasis is linked to atherosclerosis development.
Cardiologists are aware of this, but “many primary care physicians are not. It takes time for medical knowledge to diffuse,” Dr. Gelfand said. “Tell the PCP, in notes or in a form letter, that there is a higher risk of CV disease, and reference the AHA/ACC guidelines,” he advised. “You don’t want your patient to go to their doctor and the doctor to [be uninformed].”
‘Patients trust us’
Dr. Gelfand has been at the forefront of research on psoriasis and heart disease. A study he coauthored in 2006, for instance, documented an independent risk of MI, with adjusted relative risks of 1.29 and 3.10 for a 30-year-old patient with mild or severe disease, respectively, and higher risks for a 60-year-old. In 2010, he and coinvestigators found that severe psoriasis was an independent risk factor for CV mortality (HR, 1.57) after adjusting for age, sex, smoking, diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia.
Today, along with Dr. Barbieri, Dr. Ogdie, and others, he is studying the feasibility and efficacy of a proposed national, “centralized care coordinator” model of care whereby dermatologists and rheumatologists would educate the patient, order lipid and HbA1c measurements as medically appropriate, and then refer patients as needed to a care coordinator. The care coordinator would calculate a 10-year CVD risk score and counsel the patient on possible next steps.
In a pilot study of 85 patients at four sites, 92% of patients followed through on their physician’s recommendations to have labs drawn, and 86% indicated the model was acceptable and feasible. A total of 27% of patients had “newly identified, previously undiagnosed, elevated cardiovascular disease risk,” and exploratory effectiveness results indicated a successful reduction in predicted CVD risk in patients who started statins, Dr. Gelfand reported at the NPF meeting.
With funding from the NPF, a larger, single-arm, pragmatic “CP3” trial (NCT05908240) is enrolling 525 patients with psoriasis at 10-20 academic and nonacademic dermatology sites across the United States to further test the model. The primary endpoint will be the change in LDL cholesterol measured at 6 months among people with a 10-year risk ≥5%. Secondary endpoints will cover improvement in disease severity and quality of life, behavior modification, patient experience, and other issues.
“We have only 10-15 minutes [with patients] ... a care coordinator who is empathetic and understanding and [informed] could make a big difference,” Dr. Gelfand said at the NPF meeting. If findings are positive, the model would be tested in rheumatology sites as well. The hope, he said, is that the NPF would be able to fund an in-house care coordinator(s) for the long-term.
Notably, a patient survey conducted as part of exploratory research leading up to the care coordinator project showed that patients trust their dermatologist or rheumatologist for CVD education and screening. Among 160 patients with psoriasis and 162 patients with PsA, 76% and 90% agreed that “I would like it if my dermatologist/rheumatologist educated me about my risk of heart disease,” and 60% and 75%, respectively, agree that “it would be convenient for me to have my cholesterol checked by my dermatologist/rheumatologist.”
“Patients trust us,” Dr. Gelfand said at the NPF meeting. “And the pilot study shows us that patients are motivated.”
Taking an individualized, holistic, longitudinal approach
“Sometimes you do have to triage bit,” Dr. Gelfand said in an interview. “For a young person with normal body weight who doesn’t smoke and has mild psoriasis, one could just educate and advise that they see their primary care physician” for monitoring.
“But for the same patient who is obese, maybe smokes, and doesn’t have a primary care physician, I’d order labs,” he said. “You don’t want a patient walking out the door with an [undiagnosed] LDL of 160 or hypertension.”
Age is also an important consideration, as excess CVD risk associated with autoimmune diseases like psoriasis rises with age, Dr. Gelfand said during a seminar on psoriasis and PsA held at NYU Langone in December. For a young person, typically, “I need to focus on education and lifestyle … setting them on a healthy lifestyle trajectory,” he said. “Once they get to 40, from 40 to 75 or so, that’s a sweet spot for medical intervention to lower cardiovascular risk.”
Even at older ages, however, lipid management is not the be-all and end-all, he said in the interview. “We have to be holistic.”
One advantage of having highly successful therapies for psoriasis, and to a lesser extent PsA, is the time that becomes available during follow-up visits — once disease is under control — to “focus on other things,” he said. Waiting until disease is under control to discuss diet, exercise, or smoking, for instance, makes sense anyway, he said. “You don’t want to overwhelm patients with too much to do at once.”
Indeed, said dermatologist Robert E. Kalb, MD, of the Buffalo Medical Group in Buffalo, NY, “patients have an open mind [about discussing cardiovascular disease risk], but it is not high on their radar. Most of them just want to get their skin clear.” (Dr. Kalb participated in the care coordinator pilot study, and said in an interview that since its completion, he has been more routinely ordering relevant labs.)
Rheumatologists are less fortunate with highly successful therapies, but “over the continuum of care, we do have time in office visits” to discuss issues like smoking, exercise, and lifestyle, Dr. Ogdie said. “I think of each of those pieces as part of our job.”
In the future, as researchers learn more about the impact of psoriasis and PsA treatments on CVD risk, it may be possible to tailor treatments or to prescribe treatments knowing that the therapies could reduce risk. Observational and epidemiologic data suggest that tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitor therapy over 3 years reduces the risk of MI, and that patients whose psoriasis is treated have reduced aortic inflammation, improved myocardial strain, and reduced coronary plaque burden, Dr. Garshick said at the NPF meeting.
“But when we look at the randomized controlled trials, they’re actually inconclusive that targeting inflammation in psoriatic disease reduces surrogates of cardiovascular disease,” he said. Dr. Garshick’s own research focuses on platelet and endothelial biology in psoriasis.
Dr. Barbieri reported he had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Garshick reported consulting fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Kiniksa, Horizon Therapeutics, and Agepha. Dr. Ogdie reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Takeda, and UCB. Dr. Gelfand reported serving as a consultant for AbbVie, Artax, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and other companies.
Bimekizumab shows promise for palmoplantar pustular psoriasis
.
PPP is a type of pustular psoriasis that remains a treatment challenge, and available treatments for palmoplantar plaque psoriasis with pustules also “remain unsatisfactory,” according to Thierry Passeron, MD, PhD, of the dermatology service at Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Nice (France), and colleagues. Bimekizumab, an anti-interleukin (IL)-17A and anti-IL-17F antibody therapy, has been used for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis (PsA), but its effectiveness for PPP has not been studied, they said. In the United States, bimekizumab (Bimzelx), administered subcutaneously, was recently approved for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adults; in the European Union, it is approved for treating psoriasis, in addition to psoriatic arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis.
In the case series published in JAMA Dermatology, Dr. Passeron and coinvestigators identified 11 adults with PPP and 10 with palmoplantar plaque psoriasis with pustules who were treated at one of seven tertiary dermatology centers in France from September 2022 through June 2023. PPP also has been associated with bone and joint inflammation in SAPHO (synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, osteitis) syndrome.
All patients received bimekizumab for at least 3 months. The patients — 19 women and 2 men — ranged in age from 24 to 68 years (mean age, 46 years). The primary outcome was complete clearance, defined as an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0.
A total of 17 patients achieved an IGA score of zero in 1-4 months. Over 3-6 months, three patients achieved an IGA score of 1 (almost clear), and one patient achieved an IGA score of 2 (mild).
Three patients with PPP also had acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau; in these patients, nail involvement improved by 50%-70% after 4-6 months of bimekizumab use. Two patients with SAPHO experienced complete clearance of skin lesions associated with improvement in joint pain.
Four patients developed oral and genital candidiasis during treatment, but all were treated successfully with antifungals. None of the patients discontinued bimekizumab because of adverse events. “All patients are still receiving treatment, and their psoriatic lesions remain controlled,” the authors wrote.
“The rapid and consistent improvement observed in the present case series supports the effectiveness of bimekizumab therapy in managing PPP, palmoplantar plaque psoriasis with pustules, and SAPHO syndrome,” they said in their discussion.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the small sample size and short follow-up period, and by the inclusion of only patients with severe disease; and prospective, placebo-controlled studies are needed to confirm the results, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that bimekizumab could be a treatment approach for PPP, palmoplantar plaque psoriasis with pustules, and SAPHO syndrome, and warrant a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial to confirm the findings, they concluded.
Dr. Passeron disclosed fees from AbbVie, ACM Pharma, Almirall, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Calypso, Celgene, Galderma, Genzyme/Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline, Incyte, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Roivant Sciences, Sun Pharmaceuticals, and VYNE Therapeutics outside the current study; he is a cofounder of Yukin Therapeutics. Three authors disclosed receiving personal fees from UCB, manufacturer of bimekizumab, outside of the submitted work, another author disclosed receiving personal fees from UCB during the conduct of the study, and another reported receiving grants from UCB and several other companies, outside the submitted work.
The study findings were also presented at a meeting, Les Journées Dermatologiques de Paris 2023, on December 6, in Paris.
.
PPP is a type of pustular psoriasis that remains a treatment challenge, and available treatments for palmoplantar plaque psoriasis with pustules also “remain unsatisfactory,” according to Thierry Passeron, MD, PhD, of the dermatology service at Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Nice (France), and colleagues. Bimekizumab, an anti-interleukin (IL)-17A and anti-IL-17F antibody therapy, has been used for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis (PsA), but its effectiveness for PPP has not been studied, they said. In the United States, bimekizumab (Bimzelx), administered subcutaneously, was recently approved for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adults; in the European Union, it is approved for treating psoriasis, in addition to psoriatic arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis.
In the case series published in JAMA Dermatology, Dr. Passeron and coinvestigators identified 11 adults with PPP and 10 with palmoplantar plaque psoriasis with pustules who were treated at one of seven tertiary dermatology centers in France from September 2022 through June 2023. PPP also has been associated with bone and joint inflammation in SAPHO (synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, osteitis) syndrome.
All patients received bimekizumab for at least 3 months. The patients — 19 women and 2 men — ranged in age from 24 to 68 years (mean age, 46 years). The primary outcome was complete clearance, defined as an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0.
A total of 17 patients achieved an IGA score of zero in 1-4 months. Over 3-6 months, three patients achieved an IGA score of 1 (almost clear), and one patient achieved an IGA score of 2 (mild).
Three patients with PPP also had acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau; in these patients, nail involvement improved by 50%-70% after 4-6 months of bimekizumab use. Two patients with SAPHO experienced complete clearance of skin lesions associated with improvement in joint pain.
Four patients developed oral and genital candidiasis during treatment, but all were treated successfully with antifungals. None of the patients discontinued bimekizumab because of adverse events. “All patients are still receiving treatment, and their psoriatic lesions remain controlled,” the authors wrote.
“The rapid and consistent improvement observed in the present case series supports the effectiveness of bimekizumab therapy in managing PPP, palmoplantar plaque psoriasis with pustules, and SAPHO syndrome,” they said in their discussion.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the small sample size and short follow-up period, and by the inclusion of only patients with severe disease; and prospective, placebo-controlled studies are needed to confirm the results, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that bimekizumab could be a treatment approach for PPP, palmoplantar plaque psoriasis with pustules, and SAPHO syndrome, and warrant a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial to confirm the findings, they concluded.
Dr. Passeron disclosed fees from AbbVie, ACM Pharma, Almirall, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Calypso, Celgene, Galderma, Genzyme/Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline, Incyte, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Roivant Sciences, Sun Pharmaceuticals, and VYNE Therapeutics outside the current study; he is a cofounder of Yukin Therapeutics. Three authors disclosed receiving personal fees from UCB, manufacturer of bimekizumab, outside of the submitted work, another author disclosed receiving personal fees from UCB during the conduct of the study, and another reported receiving grants from UCB and several other companies, outside the submitted work.
The study findings were also presented at a meeting, Les Journées Dermatologiques de Paris 2023, on December 6, in Paris.
.
PPP is a type of pustular psoriasis that remains a treatment challenge, and available treatments for palmoplantar plaque psoriasis with pustules also “remain unsatisfactory,” according to Thierry Passeron, MD, PhD, of the dermatology service at Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Nice (France), and colleagues. Bimekizumab, an anti-interleukin (IL)-17A and anti-IL-17F antibody therapy, has been used for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis (PsA), but its effectiveness for PPP has not been studied, they said. In the United States, bimekizumab (Bimzelx), administered subcutaneously, was recently approved for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adults; in the European Union, it is approved for treating psoriasis, in addition to psoriatic arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis.
In the case series published in JAMA Dermatology, Dr. Passeron and coinvestigators identified 11 adults with PPP and 10 with palmoplantar plaque psoriasis with pustules who were treated at one of seven tertiary dermatology centers in France from September 2022 through June 2023. PPP also has been associated with bone and joint inflammation in SAPHO (synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, osteitis) syndrome.
All patients received bimekizumab for at least 3 months. The patients — 19 women and 2 men — ranged in age from 24 to 68 years (mean age, 46 years). The primary outcome was complete clearance, defined as an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0.
A total of 17 patients achieved an IGA score of zero in 1-4 months. Over 3-6 months, three patients achieved an IGA score of 1 (almost clear), and one patient achieved an IGA score of 2 (mild).
Three patients with PPP also had acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau; in these patients, nail involvement improved by 50%-70% after 4-6 months of bimekizumab use. Two patients with SAPHO experienced complete clearance of skin lesions associated with improvement in joint pain.
Four patients developed oral and genital candidiasis during treatment, but all were treated successfully with antifungals. None of the patients discontinued bimekizumab because of adverse events. “All patients are still receiving treatment, and their psoriatic lesions remain controlled,” the authors wrote.
“The rapid and consistent improvement observed in the present case series supports the effectiveness of bimekizumab therapy in managing PPP, palmoplantar plaque psoriasis with pustules, and SAPHO syndrome,” they said in their discussion.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the small sample size and short follow-up period, and by the inclusion of only patients with severe disease; and prospective, placebo-controlled studies are needed to confirm the results, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that bimekizumab could be a treatment approach for PPP, palmoplantar plaque psoriasis with pustules, and SAPHO syndrome, and warrant a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial to confirm the findings, they concluded.
Dr. Passeron disclosed fees from AbbVie, ACM Pharma, Almirall, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Calypso, Celgene, Galderma, Genzyme/Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline, Incyte, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Roivant Sciences, Sun Pharmaceuticals, and VYNE Therapeutics outside the current study; he is a cofounder of Yukin Therapeutics. Three authors disclosed receiving personal fees from UCB, manufacturer of bimekizumab, outside of the submitted work, another author disclosed receiving personal fees from UCB during the conduct of the study, and another reported receiving grants from UCB and several other companies, outside the submitted work.
The study findings were also presented at a meeting, Les Journées Dermatologiques de Paris 2023, on December 6, in Paris.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Tape strips detect hidradenitis suppurativa biomarkers, novel study shows
, results from a novel study showed.
“Tape strips can provide important clues to when and which drugs to use in HS in patients with both early and late disease, which can change clinical practice,” corresponding study author Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, professor and chair of dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, said in an interview. “It is noninvasive and nonscarring,” she added.
Tape stripping has been validated in atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and other dermatologic conditions in recent years. For the current study, which was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, and is believed to be the first of its kind, Dr. Guttman-Yassky and colleagues performed RNA sequencing from large D-Squame tape strips collected from lesional and nonlesional skin of 22 patients with HS and from 21 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. They correlated the expression of skin biomarkers between tape strips and a previously published gene-signature of HS biopsies. The mean age of patients with HS was 43 years, while the mean age of healthy controls was 35. The average International Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity Score System (IHS4) score of the HS cohort was 36.
Consistent with published studies, the researchers found that tape strips identified an overall higher inflammatory burden in HS. Specifically, they observed an upregulation of known cytokines within the following pathways: Th1 (such as IFNG, CXCL9/10/11, and CCR5); Th17 (such as interleukin [IL]-17A/F, IL12B, IL23A, CAMP, and CCL20); Th2 (such as IL4R, IL13/IL31/IL10, CCR4, CCL7/CCL13/CCL24, TNFSF4/OX40L, and TNFRSF4/OX40); and Th22 (such as IL22 and IL32).
The researchers also found that the expression of Th17 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha pathways were highly correlated between tape strips and biopsies and that HS clinical severity was significantly associated with expression of biomarkers, such as TNF-alpha, IL17A/F, OX40, JAK1-3, and IL4R in HS lesional and/or nonlesional skin.
“It was quite unexpected that we are able to identify, using a minimally invasive approach that samples only the upper layers of the epidermis, products and processes that are considered to be deeper-situated, such as IL-17, and other immune markers,” Dr. Guttman-Yassky said in the interview. “We were also surprised to see how well the tape-stripped–derived skin molecular profile correlated with that of biopsies, as well as how well it correlated with the clinical disease severity of HS.”
Also surprising, she added, was that the biomarkers in nonlesional tape-stripped skin, such as IL-17 and TNF alpha, “show high correlations with disease severity and provide clues to early disease.”
If using tape strips in HS is validated in larger cohort studies, the potential cost implications of using this approach in practice remain unclear, Dr. Guttman-Yassky said. “It is currently not cheap, but we are hoping that one day, we can provide a means to diagnose the disease and treat it early, and appropriately, utilizing this approach,” she commented. “We are excited about the applicability of this study to the early treatment and longitudinal follow up of HS with drugs that are targeting specific immune molecules and pathways,” she said, adding that it will also be useful for helping determine which drug should be used for which patient.
She and her co-authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its small sample size and the fact that tape stripping is limited to the epidermis.
Asked to comment on the study, Jennifer L. Hsiao, MD, a dermatologist who directs the HS clinic at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, said the findings “have important potential implications for our ability to one day personalize treatments for a patient with early HS in a minimally invasive way.”
As the study authors point out, she added, “tape strips only allow sampling of the epidermis, which is limiting in a disease like HS where much of the disruption is in the dermis with deep nodules and dermal tunnels. However, our overall goal should be to catch patients in the early stages of their disease before the occurrence of irreversible tissue damage such as dermal tunnels. Thus, the ongoing campaign for early diagnosis and early intervention by various stakeholders in the field of HS can help mitigate the impact of this inherent limitation of tape strips. It will be exciting to see larger studies that investigate tape strip results in relation to clinical phenotypes, disease progression, and therapeutic responses.”
The study was funded by an International Dermatology Outcome Measures Hidradenitis Suppurativa Grant. Dr. Guttman-Yassky disclosed that she has been a consultant to, an adviser for, and has received research grants from many pharmaceutical companies. Of the remaining authors, 2 also had multiple disclosures and 11 had no disclosures. Dr. Hsiao disclosed that she is a member of the board of directors for the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation. She has also served as a consultant for AbbVie, Aclaris, Boehringer Ingelheim, Incyte, Novartis, and UCB; as a speaker for AbbVie; and as an investigator for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Incyte.
, results from a novel study showed.
“Tape strips can provide important clues to when and which drugs to use in HS in patients with both early and late disease, which can change clinical practice,” corresponding study author Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, professor and chair of dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, said in an interview. “It is noninvasive and nonscarring,” she added.
Tape stripping has been validated in atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and other dermatologic conditions in recent years. For the current study, which was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, and is believed to be the first of its kind, Dr. Guttman-Yassky and colleagues performed RNA sequencing from large D-Squame tape strips collected from lesional and nonlesional skin of 22 patients with HS and from 21 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. They correlated the expression of skin biomarkers between tape strips and a previously published gene-signature of HS biopsies. The mean age of patients with HS was 43 years, while the mean age of healthy controls was 35. The average International Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity Score System (IHS4) score of the HS cohort was 36.
Consistent with published studies, the researchers found that tape strips identified an overall higher inflammatory burden in HS. Specifically, they observed an upregulation of known cytokines within the following pathways: Th1 (such as IFNG, CXCL9/10/11, and CCR5); Th17 (such as interleukin [IL]-17A/F, IL12B, IL23A, CAMP, and CCL20); Th2 (such as IL4R, IL13/IL31/IL10, CCR4, CCL7/CCL13/CCL24, TNFSF4/OX40L, and TNFRSF4/OX40); and Th22 (such as IL22 and IL32).
The researchers also found that the expression of Th17 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha pathways were highly correlated between tape strips and biopsies and that HS clinical severity was significantly associated with expression of biomarkers, such as TNF-alpha, IL17A/F, OX40, JAK1-3, and IL4R in HS lesional and/or nonlesional skin.
“It was quite unexpected that we are able to identify, using a minimally invasive approach that samples only the upper layers of the epidermis, products and processes that are considered to be deeper-situated, such as IL-17, and other immune markers,” Dr. Guttman-Yassky said in the interview. “We were also surprised to see how well the tape-stripped–derived skin molecular profile correlated with that of biopsies, as well as how well it correlated with the clinical disease severity of HS.”
Also surprising, she added, was that the biomarkers in nonlesional tape-stripped skin, such as IL-17 and TNF alpha, “show high correlations with disease severity and provide clues to early disease.”
If using tape strips in HS is validated in larger cohort studies, the potential cost implications of using this approach in practice remain unclear, Dr. Guttman-Yassky said. “It is currently not cheap, but we are hoping that one day, we can provide a means to diagnose the disease and treat it early, and appropriately, utilizing this approach,” she commented. “We are excited about the applicability of this study to the early treatment and longitudinal follow up of HS with drugs that are targeting specific immune molecules and pathways,” she said, adding that it will also be useful for helping determine which drug should be used for which patient.
She and her co-authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its small sample size and the fact that tape stripping is limited to the epidermis.
Asked to comment on the study, Jennifer L. Hsiao, MD, a dermatologist who directs the HS clinic at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, said the findings “have important potential implications for our ability to one day personalize treatments for a patient with early HS in a minimally invasive way.”
As the study authors point out, she added, “tape strips only allow sampling of the epidermis, which is limiting in a disease like HS where much of the disruption is in the dermis with deep nodules and dermal tunnels. However, our overall goal should be to catch patients in the early stages of their disease before the occurrence of irreversible tissue damage such as dermal tunnels. Thus, the ongoing campaign for early diagnosis and early intervention by various stakeholders in the field of HS can help mitigate the impact of this inherent limitation of tape strips. It will be exciting to see larger studies that investigate tape strip results in relation to clinical phenotypes, disease progression, and therapeutic responses.”
The study was funded by an International Dermatology Outcome Measures Hidradenitis Suppurativa Grant. Dr. Guttman-Yassky disclosed that she has been a consultant to, an adviser for, and has received research grants from many pharmaceutical companies. Of the remaining authors, 2 also had multiple disclosures and 11 had no disclosures. Dr. Hsiao disclosed that she is a member of the board of directors for the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation. She has also served as a consultant for AbbVie, Aclaris, Boehringer Ingelheim, Incyte, Novartis, and UCB; as a speaker for AbbVie; and as an investigator for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Incyte.
, results from a novel study showed.
“Tape strips can provide important clues to when and which drugs to use in HS in patients with both early and late disease, which can change clinical practice,” corresponding study author Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, professor and chair of dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, said in an interview. “It is noninvasive and nonscarring,” she added.
Tape stripping has been validated in atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and other dermatologic conditions in recent years. For the current study, which was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, and is believed to be the first of its kind, Dr. Guttman-Yassky and colleagues performed RNA sequencing from large D-Squame tape strips collected from lesional and nonlesional skin of 22 patients with HS and from 21 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. They correlated the expression of skin biomarkers between tape strips and a previously published gene-signature of HS biopsies. The mean age of patients with HS was 43 years, while the mean age of healthy controls was 35. The average International Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity Score System (IHS4) score of the HS cohort was 36.
Consistent with published studies, the researchers found that tape strips identified an overall higher inflammatory burden in HS. Specifically, they observed an upregulation of known cytokines within the following pathways: Th1 (such as IFNG, CXCL9/10/11, and CCR5); Th17 (such as interleukin [IL]-17A/F, IL12B, IL23A, CAMP, and CCL20); Th2 (such as IL4R, IL13/IL31/IL10, CCR4, CCL7/CCL13/CCL24, TNFSF4/OX40L, and TNFRSF4/OX40); and Th22 (such as IL22 and IL32).
The researchers also found that the expression of Th17 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha pathways were highly correlated between tape strips and biopsies and that HS clinical severity was significantly associated with expression of biomarkers, such as TNF-alpha, IL17A/F, OX40, JAK1-3, and IL4R in HS lesional and/or nonlesional skin.
“It was quite unexpected that we are able to identify, using a minimally invasive approach that samples only the upper layers of the epidermis, products and processes that are considered to be deeper-situated, such as IL-17, and other immune markers,” Dr. Guttman-Yassky said in the interview. “We were also surprised to see how well the tape-stripped–derived skin molecular profile correlated with that of biopsies, as well as how well it correlated with the clinical disease severity of HS.”
Also surprising, she added, was that the biomarkers in nonlesional tape-stripped skin, such as IL-17 and TNF alpha, “show high correlations with disease severity and provide clues to early disease.”
If using tape strips in HS is validated in larger cohort studies, the potential cost implications of using this approach in practice remain unclear, Dr. Guttman-Yassky said. “It is currently not cheap, but we are hoping that one day, we can provide a means to diagnose the disease and treat it early, and appropriately, utilizing this approach,” she commented. “We are excited about the applicability of this study to the early treatment and longitudinal follow up of HS with drugs that are targeting specific immune molecules and pathways,” she said, adding that it will also be useful for helping determine which drug should be used for which patient.
She and her co-authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its small sample size and the fact that tape stripping is limited to the epidermis.
Asked to comment on the study, Jennifer L. Hsiao, MD, a dermatologist who directs the HS clinic at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, said the findings “have important potential implications for our ability to one day personalize treatments for a patient with early HS in a minimally invasive way.”
As the study authors point out, she added, “tape strips only allow sampling of the epidermis, which is limiting in a disease like HS where much of the disruption is in the dermis with deep nodules and dermal tunnels. However, our overall goal should be to catch patients in the early stages of their disease before the occurrence of irreversible tissue damage such as dermal tunnels. Thus, the ongoing campaign for early diagnosis and early intervention by various stakeholders in the field of HS can help mitigate the impact of this inherent limitation of tape strips. It will be exciting to see larger studies that investigate tape strip results in relation to clinical phenotypes, disease progression, and therapeutic responses.”
The study was funded by an International Dermatology Outcome Measures Hidradenitis Suppurativa Grant. Dr. Guttman-Yassky disclosed that she has been a consultant to, an adviser for, and has received research grants from many pharmaceutical companies. Of the remaining authors, 2 also had multiple disclosures and 11 had no disclosures. Dr. Hsiao disclosed that she is a member of the board of directors for the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation. She has also served as a consultant for AbbVie, Aclaris, Boehringer Ingelheim, Incyte, Novartis, and UCB; as a speaker for AbbVie; and as an investigator for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Incyte.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Analysis supports link between psoriasis and obstructive sleep apnea
TOPLINE:
Patients with psoriasis had a 1.77-fold increased risk of having obstructive sleep apnea, in a study comparing patients with psoriasis with controls.
METHODOLOGY:
- Prior studies have established a link between psoriasis and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), but some have suggested that confounders may drive the association.
- Using a case-control design, researchers analyzed data from 156,707 participants in the National Institutes of Health’s : 5140 with psoriasis and 151,567 controls.
- They used Pearson’s x 2 test to compare the prevalence of OSA among cases and controls, logistic regression to calculate odds ratios (ORs) in multivariable analysis, and two-sided t-tests to evaluate the significance between continuous variables.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with controls, patients with psoriasis were older (a mean of 62.4 vs 57.3 years, respectively), more likely to be White (86.1% vs 70.6%), reported higher annual household incomes (59.9% vs 52.6%), and were more likely to smoke (48.2% vs 43.4%).
- The rate of OSA was significantly higher among patients with psoriasis compared with controls (29.3% vs 17.1%; P < .001).
- On unadjusted multivariable logistic regression controlling for age, gender, and race, psoriasis was significantly associated with OSA (OR, 1.77, 95% CI, 1.66 - 1.89; P < .001).
- Psoriasis was also significantly associated with OSA in the adjusted model controlling for age, gender, race, BMI, and smoking status (OR, 1.66, 95% CI, 1.55 - 1.77; P < .001) and in the adjusted model controlling for age, gender, race, BMI, smoking status, type 2 diabetes, congestive heart failure, hypertension, history of myocardial infarction, angina, and peripheral artery disease (OR, 1.45, 95% CI, 1.35 - 1.55; P <.001).
IN PRACTICE:
“This study further substantiates the association between psoriasis and OSA, reinforcing the importance of evaluation for OSA when clinically appropriate given that both psoriasis and OSA contribute to adverse health outcomes,” the authors conclude.
SOURCE:
Corresponding author Jeffrey M. Cohen, MD, of the Department of Dermatology at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, led the research. The study was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Study limitations included the use of electronic health record data, a potential lack of generalizability to the US population, and reliance on survey data for certain variables such as income and smoking status.
DISCLOSURES:
The All of Us Research Program is supported by the National Institutes of Health. Cohen disclosed that he serves on a data safety and monitoring board for Advarra.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients with psoriasis had a 1.77-fold increased risk of having obstructive sleep apnea, in a study comparing patients with psoriasis with controls.
METHODOLOGY:
- Prior studies have established a link between psoriasis and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), but some have suggested that confounders may drive the association.
- Using a case-control design, researchers analyzed data from 156,707 participants in the National Institutes of Health’s : 5140 with psoriasis and 151,567 controls.
- They used Pearson’s x 2 test to compare the prevalence of OSA among cases and controls, logistic regression to calculate odds ratios (ORs) in multivariable analysis, and two-sided t-tests to evaluate the significance between continuous variables.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with controls, patients with psoriasis were older (a mean of 62.4 vs 57.3 years, respectively), more likely to be White (86.1% vs 70.6%), reported higher annual household incomes (59.9% vs 52.6%), and were more likely to smoke (48.2% vs 43.4%).
- The rate of OSA was significantly higher among patients with psoriasis compared with controls (29.3% vs 17.1%; P < .001).
- On unadjusted multivariable logistic regression controlling for age, gender, and race, psoriasis was significantly associated with OSA (OR, 1.77, 95% CI, 1.66 - 1.89; P < .001).
- Psoriasis was also significantly associated with OSA in the adjusted model controlling for age, gender, race, BMI, and smoking status (OR, 1.66, 95% CI, 1.55 - 1.77; P < .001) and in the adjusted model controlling for age, gender, race, BMI, smoking status, type 2 diabetes, congestive heart failure, hypertension, history of myocardial infarction, angina, and peripheral artery disease (OR, 1.45, 95% CI, 1.35 - 1.55; P <.001).
IN PRACTICE:
“This study further substantiates the association between psoriasis and OSA, reinforcing the importance of evaluation for OSA when clinically appropriate given that both psoriasis and OSA contribute to adverse health outcomes,” the authors conclude.
SOURCE:
Corresponding author Jeffrey M. Cohen, MD, of the Department of Dermatology at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, led the research. The study was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Study limitations included the use of electronic health record data, a potential lack of generalizability to the US population, and reliance on survey data for certain variables such as income and smoking status.
DISCLOSURES:
The All of Us Research Program is supported by the National Institutes of Health. Cohen disclosed that he serves on a data safety and monitoring board for Advarra.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients with psoriasis had a 1.77-fold increased risk of having obstructive sleep apnea, in a study comparing patients with psoriasis with controls.
METHODOLOGY:
- Prior studies have established a link between psoriasis and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), but some have suggested that confounders may drive the association.
- Using a case-control design, researchers analyzed data from 156,707 participants in the National Institutes of Health’s : 5140 with psoriasis and 151,567 controls.
- They used Pearson’s x 2 test to compare the prevalence of OSA among cases and controls, logistic regression to calculate odds ratios (ORs) in multivariable analysis, and two-sided t-tests to evaluate the significance between continuous variables.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with controls, patients with psoriasis were older (a mean of 62.4 vs 57.3 years, respectively), more likely to be White (86.1% vs 70.6%), reported higher annual household incomes (59.9% vs 52.6%), and were more likely to smoke (48.2% vs 43.4%).
- The rate of OSA was significantly higher among patients with psoriasis compared with controls (29.3% vs 17.1%; P < .001).
- On unadjusted multivariable logistic regression controlling for age, gender, and race, psoriasis was significantly associated with OSA (OR, 1.77, 95% CI, 1.66 - 1.89; P < .001).
- Psoriasis was also significantly associated with OSA in the adjusted model controlling for age, gender, race, BMI, and smoking status (OR, 1.66, 95% CI, 1.55 - 1.77; P < .001) and in the adjusted model controlling for age, gender, race, BMI, smoking status, type 2 diabetes, congestive heart failure, hypertension, history of myocardial infarction, angina, and peripheral artery disease (OR, 1.45, 95% CI, 1.35 - 1.55; P <.001).
IN PRACTICE:
“This study further substantiates the association between psoriasis and OSA, reinforcing the importance of evaluation for OSA when clinically appropriate given that both psoriasis and OSA contribute to adverse health outcomes,” the authors conclude.
SOURCE:
Corresponding author Jeffrey M. Cohen, MD, of the Department of Dermatology at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, led the research. The study was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Study limitations included the use of electronic health record data, a potential lack of generalizability to the US population, and reliance on survey data for certain variables such as income and smoking status.
DISCLOSURES:
The All of Us Research Program is supported by the National Institutes of Health. Cohen disclosed that he serves on a data safety and monitoring board for Advarra.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Low-dose methotrexate carries higher risk for older patients with CKD
TOPLINE:
The use of low-dose methotrexate among older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD) was associated with a significantly increased risk at 90 days for serious adverse events requiring a hospital visit, compared with starting treatment with hydroxychloroquine.
METHODOLOGY:
- In a retrospective, population-based cohort study conducted in Ontario, researchers used linked administrative healthcare data to identify adults aged 66 years and older with CKD who were not undergoing dialysis and were new to medication; CKD was defined as an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of less than 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
- The study population included 2,309 individuals who began treatment with low-dose methotrexate (5-35 mg/week); they were matched with 2,309 individuals who began treatment with hydroxychloroquine (200-400 mg/day). The median age was 76 years, 69% were women, and rheumatoid arthritis was the most common diagnosis (56%).
- The primary outcome was the risk of a hospital visit at 90 days for a composite of serious adverse events that included myelosuppression, sepsis, pneumotoxic effects, or hepatoxic effects.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 3.55% of methotrexate patients and 1.73% of hydroxychloroquine patients met the primary outcome (risk ratio, 2.05); these events occurred at a median of 49 days and 43 days after starting the medications for the two groups, respectively.
- In an analysis by eGFR category, the risk of serious adverse events at 90 days increased among patients with eGFR levels less than 45 mL/min per 1.73 m2 (RR, 2.79).
- In a secondary comparison, the 90-day risk of serious adverse events was higher among methotrexate patients who began treatment with doses of 15-35 mg/week in comparison with those whose initial doses were 5 to less than 15 mg/week.
IN PRACTICE:
“Patients with CKD starting low-dose methotrexate should have active surveillance, including blood tests and chest radiographs performed regularly to monitor for signs of myelosuppression, infection, hepatotoxic effects, and pneumotoxic effects,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The lead author on the study was Flory T. Muanda, MD, of Western University, London, Ont. The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The observational design and lack of data on patients’ adherence to medications were among the limiting factors, as were the focus on older adults with CKD and the lack of assessment of the risk-benefit ratio of low-dose methotrexate.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences. Dr. Muanda had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The use of low-dose methotrexate among older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD) was associated with a significantly increased risk at 90 days for serious adverse events requiring a hospital visit, compared with starting treatment with hydroxychloroquine.
METHODOLOGY:
- In a retrospective, population-based cohort study conducted in Ontario, researchers used linked administrative healthcare data to identify adults aged 66 years and older with CKD who were not undergoing dialysis and were new to medication; CKD was defined as an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of less than 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
- The study population included 2,309 individuals who began treatment with low-dose methotrexate (5-35 mg/week); they were matched with 2,309 individuals who began treatment with hydroxychloroquine (200-400 mg/day). The median age was 76 years, 69% were women, and rheumatoid arthritis was the most common diagnosis (56%).
- The primary outcome was the risk of a hospital visit at 90 days for a composite of serious adverse events that included myelosuppression, sepsis, pneumotoxic effects, or hepatoxic effects.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 3.55% of methotrexate patients and 1.73% of hydroxychloroquine patients met the primary outcome (risk ratio, 2.05); these events occurred at a median of 49 days and 43 days after starting the medications for the two groups, respectively.
- In an analysis by eGFR category, the risk of serious adverse events at 90 days increased among patients with eGFR levels less than 45 mL/min per 1.73 m2 (RR, 2.79).
- In a secondary comparison, the 90-day risk of serious adverse events was higher among methotrexate patients who began treatment with doses of 15-35 mg/week in comparison with those whose initial doses were 5 to less than 15 mg/week.
IN PRACTICE:
“Patients with CKD starting low-dose methotrexate should have active surveillance, including blood tests and chest radiographs performed regularly to monitor for signs of myelosuppression, infection, hepatotoxic effects, and pneumotoxic effects,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The lead author on the study was Flory T. Muanda, MD, of Western University, London, Ont. The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The observational design and lack of data on patients’ adherence to medications were among the limiting factors, as were the focus on older adults with CKD and the lack of assessment of the risk-benefit ratio of low-dose methotrexate.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences. Dr. Muanda had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The use of low-dose methotrexate among older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD) was associated with a significantly increased risk at 90 days for serious adverse events requiring a hospital visit, compared with starting treatment with hydroxychloroquine.
METHODOLOGY:
- In a retrospective, population-based cohort study conducted in Ontario, researchers used linked administrative healthcare data to identify adults aged 66 years and older with CKD who were not undergoing dialysis and were new to medication; CKD was defined as an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of less than 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
- The study population included 2,309 individuals who began treatment with low-dose methotrexate (5-35 mg/week); they were matched with 2,309 individuals who began treatment with hydroxychloroquine (200-400 mg/day). The median age was 76 years, 69% were women, and rheumatoid arthritis was the most common diagnosis (56%).
- The primary outcome was the risk of a hospital visit at 90 days for a composite of serious adverse events that included myelosuppression, sepsis, pneumotoxic effects, or hepatoxic effects.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 3.55% of methotrexate patients and 1.73% of hydroxychloroquine patients met the primary outcome (risk ratio, 2.05); these events occurred at a median of 49 days and 43 days after starting the medications for the two groups, respectively.
- In an analysis by eGFR category, the risk of serious adverse events at 90 days increased among patients with eGFR levels less than 45 mL/min per 1.73 m2 (RR, 2.79).
- In a secondary comparison, the 90-day risk of serious adverse events was higher among methotrexate patients who began treatment with doses of 15-35 mg/week in comparison with those whose initial doses were 5 to less than 15 mg/week.
IN PRACTICE:
“Patients with CKD starting low-dose methotrexate should have active surveillance, including blood tests and chest radiographs performed regularly to monitor for signs of myelosuppression, infection, hepatotoxic effects, and pneumotoxic effects,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The lead author on the study was Flory T. Muanda, MD, of Western University, London, Ont. The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The observational design and lack of data on patients’ adherence to medications were among the limiting factors, as were the focus on older adults with CKD and the lack of assessment of the risk-benefit ratio of low-dose methotrexate.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences. Dr. Muanda had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.