User login
Pretreatment Lab Testing for Chronic Skin Diseases Diverges From Guidelines
in a national commercial insurance claims database.
Because of concerns for the potential reactivation of tuberculosis or hepatitis B or C, or for an increased risk for infections, myelosuppression, and hepatoxicity in the wake of immunomodulator use, some medical societies recommend screening patients for hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and tuberculosis before starting these medications, wrote Maria C. Schneeweiss, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, and colleagues.
“Conducting this study was crucial because of the increasing use of systemic immunomodulatory agents for chronic inflammatory skin diseases and the recognized need for pretreatment testing to prevent complications,” coauthor Denys Shay, a PhD candidate in population health sciences at Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts, said in an interview.
“Despite recommendations from professional societies, there was a lack of clarity on how consistently these guidelines were being followed in the United States. This study aimed to fill that gap in knowledge, providing a comprehensive view of current practices and highlighting areas for improvement,” he said.
In the study, published online in JAMA Dermatology, he and his coauthors identified 122,308 adults in the United States with psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa, or atopic dermatitis who started an immunomodulatory agent, including methotrexate (28,684 patients), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha inhibitors (40,965), ustekinumab (12,841), interleukin (IL)-23 inhibitors (6116), IL-17A inhibitors (9799), dupilumab (7787), and apremilast (16,116). The data were from a commercial insurance claims database from December 31, 2002, to December 31, 2020.
The primary outcome was the proportion of patients who underwent recommended screening lab tests including tuberculosis, hepatitis, liver function, complete blood cell counts (CBCs), and lipid panels within 6 months before treatment initiation and during the first 2 years of treatment. The median age of the study population was 49 years, and 52.1% were male.
A CBC was the most common pretreatment test across treatments, performed in 41%-69% of patients before starting treatment. Tuberculosis screening occurred in 11%-59% of patients within 6 months of initiating treatment, and 3%-26% had updated tests after 1 year. Similarly, 13%-41% of patients underwent hepatitis screening prior to treatment.
The highest levels of pretreatment testing occurred for TNF-alpha inhibitors, ustekinumab, IL-17A inhibitors, and IL-23 inhibitors, with similar patterns, while the lowest levels of testing occurred with apremilast and dupilumab.
Testing prevalence before starting apremilast and after a year of treatment was 15%-45% and 9%-36%, respectively. Testing before initiation and a year into treatment with dupilumab was 11%-41% and 3%-25%, respectively.
The findings were limited by several factors including the descriptive design, which does not allow for evaluation of the testing practices, the researchers said.
However, the results show the extent of patients with chronic inflammatory skin diseases (CISDs) who do not undergo pretreatment testing, and research is needed to create testing practices on the basis of recommendations for each agent and incorporating each patient’s history and clinical profile, they concluded.
“The finding that less than 60% of patients received recommended pretreatment testing was initially somewhat surprising,” Shay said in the interview. “However, the context provided by higher rates of baseline testing within the 6-12 months before treatment initiation and the potential for additional testing not captured by the dataset — such as hospital stays — suggests that the gap may not be as large as this estimate,” he said.
“The key message for clinicians is that there are considerable variations in laboratory testing practices with regard to the initiation of systemic immunomodulatory agents in patients with CISDs,” Shay said. “This represents a divergence from existing testing guidelines.”
“Further research is needed to understand the reasons for the variations in pretreatment testing practices and whether this heterogeneity affects patient outcomes,” he added.
Resist Routine Testing
The study findings represent a call to action in the form of ongoing assessment of the safety, clinical utility, and cost-effectiveness of pretreatment testing, wrote Clinton W. Enos, MD, Ana Ormaza Vera, MD, and Abby S. Van Voorhees, MD, of the Department of Dermatology, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, Virginia, in an accompanying editorial.
The data in the current study suggesting less frequent laboratory testing compared with current guidelines could stem from a high comfort level with many of the therapies that have been available and in use for many years, they noted. Clinicians’ lack of knowledge of the laboratory screening and monitoring guidelines also may play a role, they said.
However, the authors cautioned against routine checking of laboratory results “without purpose” and without attention to their clinical utility and cost. “A thorough medical history is essential and can serve as a sensitive indicator of which patients are more at risk for diseases such as TB or hepatitis, thereby allowing for more meaningful laboratory screening use,” they said.
Evidence supporting prescreening labs for the spectrum of systemic agents used in dermatology varies considerably, “some trapped in time and carried forward for decades until finally questioned, others rooted in treatment mechanism and clinical data,” Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chief of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, said in an interview.
The study elucidated the current state of clinical practice, said Friedman, who was not involved with the study. This includes screening even if the label says it is not necessary and letting screening slide when guidelines say otherwise — even if the guidelines are outdated and insurance requires certain metrics prior to approval, he said.
Looking ahead, “we need better consensus and even better communication/education on said guidance,” Dr. Friedman said. “Clear, concise, evidenced-based, and expert-validated guidance to ensure we are meaningfully using medical resources” is what is needed, he added. “It will certainly take a village, and close collaboration between the industry and practitioners is key to success.”
The study was supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Shay had no financial conflicts to disclose. Lead author Dr. Schneeweiss disclosed grants from UCB Pharma and AbbVie to Brigham and Women’s Hospital outside the submitted work. Other authors disclosed receiving personal fees from Aetion and grants from UCB Pharma and Takeda outside the submitted work; grants from Amarin, Kowa, Novartis, and Pfizer outside the submitted work; and personal fees from Hims & Hers, AbbVie, Sun Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Digital Diagnostics, Lilly, Equillium, ASLAN, Boehringer Ingelheim, ACOM, Olaplex, and Legacy Healthcare during the study. No other disclosures were reported.
Editorial author Dr. Enos disclosed serving as an investigator for Amgen and Castle Biosciences and receiving grants from Arcutis Biotherapeutics outside the submitted work. Dr. Van Voorhees disclosed an honorarium outside the submitted work.
Dr. Friedman had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
in a national commercial insurance claims database.
Because of concerns for the potential reactivation of tuberculosis or hepatitis B or C, or for an increased risk for infections, myelosuppression, and hepatoxicity in the wake of immunomodulator use, some medical societies recommend screening patients for hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and tuberculosis before starting these medications, wrote Maria C. Schneeweiss, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, and colleagues.
“Conducting this study was crucial because of the increasing use of systemic immunomodulatory agents for chronic inflammatory skin diseases and the recognized need for pretreatment testing to prevent complications,” coauthor Denys Shay, a PhD candidate in population health sciences at Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts, said in an interview.
“Despite recommendations from professional societies, there was a lack of clarity on how consistently these guidelines were being followed in the United States. This study aimed to fill that gap in knowledge, providing a comprehensive view of current practices and highlighting areas for improvement,” he said.
In the study, published online in JAMA Dermatology, he and his coauthors identified 122,308 adults in the United States with psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa, or atopic dermatitis who started an immunomodulatory agent, including methotrexate (28,684 patients), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha inhibitors (40,965), ustekinumab (12,841), interleukin (IL)-23 inhibitors (6116), IL-17A inhibitors (9799), dupilumab (7787), and apremilast (16,116). The data were from a commercial insurance claims database from December 31, 2002, to December 31, 2020.
The primary outcome was the proportion of patients who underwent recommended screening lab tests including tuberculosis, hepatitis, liver function, complete blood cell counts (CBCs), and lipid panels within 6 months before treatment initiation and during the first 2 years of treatment. The median age of the study population was 49 years, and 52.1% were male.
A CBC was the most common pretreatment test across treatments, performed in 41%-69% of patients before starting treatment. Tuberculosis screening occurred in 11%-59% of patients within 6 months of initiating treatment, and 3%-26% had updated tests after 1 year. Similarly, 13%-41% of patients underwent hepatitis screening prior to treatment.
The highest levels of pretreatment testing occurred for TNF-alpha inhibitors, ustekinumab, IL-17A inhibitors, and IL-23 inhibitors, with similar patterns, while the lowest levels of testing occurred with apremilast and dupilumab.
Testing prevalence before starting apremilast and after a year of treatment was 15%-45% and 9%-36%, respectively. Testing before initiation and a year into treatment with dupilumab was 11%-41% and 3%-25%, respectively.
The findings were limited by several factors including the descriptive design, which does not allow for evaluation of the testing practices, the researchers said.
However, the results show the extent of patients with chronic inflammatory skin diseases (CISDs) who do not undergo pretreatment testing, and research is needed to create testing practices on the basis of recommendations for each agent and incorporating each patient’s history and clinical profile, they concluded.
“The finding that less than 60% of patients received recommended pretreatment testing was initially somewhat surprising,” Shay said in the interview. “However, the context provided by higher rates of baseline testing within the 6-12 months before treatment initiation and the potential for additional testing not captured by the dataset — such as hospital stays — suggests that the gap may not be as large as this estimate,” he said.
“The key message for clinicians is that there are considerable variations in laboratory testing practices with regard to the initiation of systemic immunomodulatory agents in patients with CISDs,” Shay said. “This represents a divergence from existing testing guidelines.”
“Further research is needed to understand the reasons for the variations in pretreatment testing practices and whether this heterogeneity affects patient outcomes,” he added.
Resist Routine Testing
The study findings represent a call to action in the form of ongoing assessment of the safety, clinical utility, and cost-effectiveness of pretreatment testing, wrote Clinton W. Enos, MD, Ana Ormaza Vera, MD, and Abby S. Van Voorhees, MD, of the Department of Dermatology, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, Virginia, in an accompanying editorial.
The data in the current study suggesting less frequent laboratory testing compared with current guidelines could stem from a high comfort level with many of the therapies that have been available and in use for many years, they noted. Clinicians’ lack of knowledge of the laboratory screening and monitoring guidelines also may play a role, they said.
However, the authors cautioned against routine checking of laboratory results “without purpose” and without attention to their clinical utility and cost. “A thorough medical history is essential and can serve as a sensitive indicator of which patients are more at risk for diseases such as TB or hepatitis, thereby allowing for more meaningful laboratory screening use,” they said.
Evidence supporting prescreening labs for the spectrum of systemic agents used in dermatology varies considerably, “some trapped in time and carried forward for decades until finally questioned, others rooted in treatment mechanism and clinical data,” Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chief of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, said in an interview.
The study elucidated the current state of clinical practice, said Friedman, who was not involved with the study. This includes screening even if the label says it is not necessary and letting screening slide when guidelines say otherwise — even if the guidelines are outdated and insurance requires certain metrics prior to approval, he said.
Looking ahead, “we need better consensus and even better communication/education on said guidance,” Dr. Friedman said. “Clear, concise, evidenced-based, and expert-validated guidance to ensure we are meaningfully using medical resources” is what is needed, he added. “It will certainly take a village, and close collaboration between the industry and practitioners is key to success.”
The study was supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Shay had no financial conflicts to disclose. Lead author Dr. Schneeweiss disclosed grants from UCB Pharma and AbbVie to Brigham and Women’s Hospital outside the submitted work. Other authors disclosed receiving personal fees from Aetion and grants from UCB Pharma and Takeda outside the submitted work; grants from Amarin, Kowa, Novartis, and Pfizer outside the submitted work; and personal fees from Hims & Hers, AbbVie, Sun Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Digital Diagnostics, Lilly, Equillium, ASLAN, Boehringer Ingelheim, ACOM, Olaplex, and Legacy Healthcare during the study. No other disclosures were reported.
Editorial author Dr. Enos disclosed serving as an investigator for Amgen and Castle Biosciences and receiving grants from Arcutis Biotherapeutics outside the submitted work. Dr. Van Voorhees disclosed an honorarium outside the submitted work.
Dr. Friedman had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
in a national commercial insurance claims database.
Because of concerns for the potential reactivation of tuberculosis or hepatitis B or C, or for an increased risk for infections, myelosuppression, and hepatoxicity in the wake of immunomodulator use, some medical societies recommend screening patients for hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and tuberculosis before starting these medications, wrote Maria C. Schneeweiss, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, and colleagues.
“Conducting this study was crucial because of the increasing use of systemic immunomodulatory agents for chronic inflammatory skin diseases and the recognized need for pretreatment testing to prevent complications,” coauthor Denys Shay, a PhD candidate in population health sciences at Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts, said in an interview.
“Despite recommendations from professional societies, there was a lack of clarity on how consistently these guidelines were being followed in the United States. This study aimed to fill that gap in knowledge, providing a comprehensive view of current practices and highlighting areas for improvement,” he said.
In the study, published online in JAMA Dermatology, he and his coauthors identified 122,308 adults in the United States with psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa, or atopic dermatitis who started an immunomodulatory agent, including methotrexate (28,684 patients), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha inhibitors (40,965), ustekinumab (12,841), interleukin (IL)-23 inhibitors (6116), IL-17A inhibitors (9799), dupilumab (7787), and apremilast (16,116). The data were from a commercial insurance claims database from December 31, 2002, to December 31, 2020.
The primary outcome was the proportion of patients who underwent recommended screening lab tests including tuberculosis, hepatitis, liver function, complete blood cell counts (CBCs), and lipid panels within 6 months before treatment initiation and during the first 2 years of treatment. The median age of the study population was 49 years, and 52.1% were male.
A CBC was the most common pretreatment test across treatments, performed in 41%-69% of patients before starting treatment. Tuberculosis screening occurred in 11%-59% of patients within 6 months of initiating treatment, and 3%-26% had updated tests after 1 year. Similarly, 13%-41% of patients underwent hepatitis screening prior to treatment.
The highest levels of pretreatment testing occurred for TNF-alpha inhibitors, ustekinumab, IL-17A inhibitors, and IL-23 inhibitors, with similar patterns, while the lowest levels of testing occurred with apremilast and dupilumab.
Testing prevalence before starting apremilast and after a year of treatment was 15%-45% and 9%-36%, respectively. Testing before initiation and a year into treatment with dupilumab was 11%-41% and 3%-25%, respectively.
The findings were limited by several factors including the descriptive design, which does not allow for evaluation of the testing practices, the researchers said.
However, the results show the extent of patients with chronic inflammatory skin diseases (CISDs) who do not undergo pretreatment testing, and research is needed to create testing practices on the basis of recommendations for each agent and incorporating each patient’s history and clinical profile, they concluded.
“The finding that less than 60% of patients received recommended pretreatment testing was initially somewhat surprising,” Shay said in the interview. “However, the context provided by higher rates of baseline testing within the 6-12 months before treatment initiation and the potential for additional testing not captured by the dataset — such as hospital stays — suggests that the gap may not be as large as this estimate,” he said.
“The key message for clinicians is that there are considerable variations in laboratory testing practices with regard to the initiation of systemic immunomodulatory agents in patients with CISDs,” Shay said. “This represents a divergence from existing testing guidelines.”
“Further research is needed to understand the reasons for the variations in pretreatment testing practices and whether this heterogeneity affects patient outcomes,” he added.
Resist Routine Testing
The study findings represent a call to action in the form of ongoing assessment of the safety, clinical utility, and cost-effectiveness of pretreatment testing, wrote Clinton W. Enos, MD, Ana Ormaza Vera, MD, and Abby S. Van Voorhees, MD, of the Department of Dermatology, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, Virginia, in an accompanying editorial.
The data in the current study suggesting less frequent laboratory testing compared with current guidelines could stem from a high comfort level with many of the therapies that have been available and in use for many years, they noted. Clinicians’ lack of knowledge of the laboratory screening and monitoring guidelines also may play a role, they said.
However, the authors cautioned against routine checking of laboratory results “without purpose” and without attention to their clinical utility and cost. “A thorough medical history is essential and can serve as a sensitive indicator of which patients are more at risk for diseases such as TB or hepatitis, thereby allowing for more meaningful laboratory screening use,” they said.
Evidence supporting prescreening labs for the spectrum of systemic agents used in dermatology varies considerably, “some trapped in time and carried forward for decades until finally questioned, others rooted in treatment mechanism and clinical data,” Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chief of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, said in an interview.
The study elucidated the current state of clinical practice, said Friedman, who was not involved with the study. This includes screening even if the label says it is not necessary and letting screening slide when guidelines say otherwise — even if the guidelines are outdated and insurance requires certain metrics prior to approval, he said.
Looking ahead, “we need better consensus and even better communication/education on said guidance,” Dr. Friedman said. “Clear, concise, evidenced-based, and expert-validated guidance to ensure we are meaningfully using medical resources” is what is needed, he added. “It will certainly take a village, and close collaboration between the industry and practitioners is key to success.”
The study was supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Shay had no financial conflicts to disclose. Lead author Dr. Schneeweiss disclosed grants from UCB Pharma and AbbVie to Brigham and Women’s Hospital outside the submitted work. Other authors disclosed receiving personal fees from Aetion and grants from UCB Pharma and Takeda outside the submitted work; grants from Amarin, Kowa, Novartis, and Pfizer outside the submitted work; and personal fees from Hims & Hers, AbbVie, Sun Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Digital Diagnostics, Lilly, Equillium, ASLAN, Boehringer Ingelheim, ACOM, Olaplex, and Legacy Healthcare during the study. No other disclosures were reported.
Editorial author Dr. Enos disclosed serving as an investigator for Amgen and Castle Biosciences and receiving grants from Arcutis Biotherapeutics outside the submitted work. Dr. Van Voorhees disclosed an honorarium outside the submitted work.
Dr. Friedman had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Oral IL-23 Inhibitor Calms Moderate to Severe Psoriasis
A novel oral drug for plaque psoriasis that targets the same inflammatory pathway as currently available parenteral therapies showed promise for treating moderate to severe disease in a phase 2 dose-finding trial.
Among 255 at week 16 of at least 75% (PASI 75) compared with 9% of patients assigned to placebo, reported Robert Bissonnette, MD, from Innovaderm Research in Montreal, Quebec, Canada, and colleagues.
“The level of reduction of psoriasis that was observed with higher doses of JNJ-77242113 at week 16 was similar in magnitude to the responses seen with several of the injectable biologics that are currently approved for psoriasis,” investigators in the FRONTIER 1 trial wrote in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The investigators noted that among patients assigned to the 100-mg dose of the active drug, 60% had a PASI 90 response, which compares favorably with that seen in phase 3 trials of two other orally available therapies for psoriasis, deucravacitinib (Sotyktu) and apremilast (Otezla). They cautioned, however, against drawing any further inferences from these data, because these agents have not been tested head-to-head against JNJ-77242113 in comparison trials.
Targets IL-23 and IL-17
The investigational agent is an oral IL-23 receptor antagonist peptide that selectively blocks IL-23 proximal signaling as well as the production of downstream inflammatory cytokines such as IL-17, according to the authors.
“Modulation of the interleukin-23 pathway with the use of monoclonal antibodies has shown efficacy in the treatment of psoriasis and is considered to be associated with a more favorable safety profile than older oral therapies (eg, cyclosporine, acitretin, methotrexate, and dimethyl fumarate),” the investigators wrote.
Currently available biologic agents targeting IL-23 include guselkumab (Tremfya), risankizumab (Skyrizi) and tildrakizumab (Ilumya). These agents require intravenous or subcutaneous administration, whereas JNJ-77242113 is taken orally, giving it a theoretical advantage in terms of patient preference.
The novel drug must be taken twice daily on an empty stomach at least 2 hours before food or drink, and those who take it must wait an additional 30 minutes to eat or drink after taking the drug. (This news organization has learned that in planned phase 3 studies, patients will be instructed to take a double daily dose on awakening and then wait 30 minutes for eating or drinking.)
‘Profoundly Effective’
The results of this study have convinced at least one former skeptic of the efficacy of the novel agent.
“They asked me to do the trial, and I turned it down, because I didn’t believe it would work,” said Mark G. Lebwohl, MD, dean for Clinical Therapeutics at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and professor and chairman emeritus of the Department of Dermatology at Mount Sinai Medicine in New York, NY.
In an interview with this news organization, Dr. Lebwohl said that he was initially dubious that a peptide, a short chain of amino acids directed against a receptor, could be effective because it would likely be digested in the intestinal tract.
“Indeed, more than 99% of it is digested, but the data show that the tiny amount that gets through is profoundly effective,” he said.
“I would never have believed that this was going to work – and it did,” Dr. Lebwohl added.
He has signed on as an investigator in the currently recruiting phase 3 ICONIC-LEAD trial, in which JNJ-77242113 will be tested against placebo in adolescents and adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
In an editorial accompanying the study in the NEJM, Joel M. Gelfand, MD, MSCE, vice chair of clinical research and medical director of the Dermatology Clinical Studies Unit at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, noted that if confirmed in larger studies, the PASI 90 rate at the highest dose “would be similar to the most effective injectable biologics,” with no evidence of increased adverse events at higher doses.
“However, two occurrences of infection (COVID-19 and an infected cyst) and a suicide attempt were reported as serious adverse events; larger trials will be needed to determine whether such events are attributable to chance, psoriasis itself, or inhibition of interleukin-23 signaling,” cautioned Dr. Gelfand, director of the psoriasis and phototherapy treatment center at the University of Pennsylvania.
In an interview, Dr. Lebwohl said that currently available IL-23 signaling inhibitors have an excellent safety profile and that the investigational oral agent also appears to be very safe. “It’s seeing a target whose effects are known, and the effects are all good and not bad,” he said.
FRONTIER-1 Details
The investigators enrolled eligible adults aged 18 years or older who had moderate to severe plaque psoriasis as defined by an Investigator’s Global Assessment score ≥ 3, a total body-surface area of psoriasis involvement of at least 10%, and a PASI score ≥ 12 who had received their diagnosis of plaque psoriasis at least 6 months before starting the trial. The participants had to be candidates for phototherapy or systemic psoriasis therapy.
Patients were randomly assigned to the active agent at doses of 25 mg once or twice daily, 50 mg once daily, or 100 mg once or twice daily for 16 weeks.
There was a clear dose response, with 37% of patients assigned to 25-mg once-daily dose meeting the primary endpoint of a PASI 75 response at week 16 compared with 51% of those assigned to the 25-mg twice-daily dose, 58% assigned to 50-mg once-daily dose, 65% assigned to 100-mg once-daily dose, and 79% assigned to 100-mg twice-daily dose (P for dose response < .001).
As noted previously, 9% of patients in the placebo group had a PASI 75 response at week 16.
After a mean duration of 15.9 weeks, adverse events after the first dose of JNJ-77242113 (all dose groups were pooled for the safety analysis) were reported in 47% of patients on the 25-mg once-daily dose, 49% on 25-mg twice-daily dose, 60% on 50-mg once-daily dose, 44% on 100-mg once-daily dose, and 62% on 100-mg twice-daily dose. Adverse events after the first dose occurred in 51% of patients assigned to placebo.
The incidence of adverse events did not increase significantly with successively higher dose levels.
As noted by Dr. Gelfand in his editorial, there were three serious adverse events, all occurring in patients on the active drug: a case of COVID-19 in one patient and a suicide attempt in one patient, both in the 100-mg once-daily dose group, and an infected cyst in the 50-mg once-daily group. All three events were determined by the principal investigator and the sponsor to be unrelated to JNJ-77242113.
There were no reports of deaths, major adverse cardiovascular events, or incident cancers during the trial.
The study was supported by Janssen Research and Development. Dr. Bissonnette disclosed institutional research funding and advisory board participation and honoraria with Janssen. Dr. Gelfand disclosed consulting for Janssen Biotech. Dr. Lebwohl disclosed institutional research funding from Janssen but no personal fees.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A novel oral drug for plaque psoriasis that targets the same inflammatory pathway as currently available parenteral therapies showed promise for treating moderate to severe disease in a phase 2 dose-finding trial.
Among 255 at week 16 of at least 75% (PASI 75) compared with 9% of patients assigned to placebo, reported Robert Bissonnette, MD, from Innovaderm Research in Montreal, Quebec, Canada, and colleagues.
“The level of reduction of psoriasis that was observed with higher doses of JNJ-77242113 at week 16 was similar in magnitude to the responses seen with several of the injectable biologics that are currently approved for psoriasis,” investigators in the FRONTIER 1 trial wrote in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The investigators noted that among patients assigned to the 100-mg dose of the active drug, 60% had a PASI 90 response, which compares favorably with that seen in phase 3 trials of two other orally available therapies for psoriasis, deucravacitinib (Sotyktu) and apremilast (Otezla). They cautioned, however, against drawing any further inferences from these data, because these agents have not been tested head-to-head against JNJ-77242113 in comparison trials.
Targets IL-23 and IL-17
The investigational agent is an oral IL-23 receptor antagonist peptide that selectively blocks IL-23 proximal signaling as well as the production of downstream inflammatory cytokines such as IL-17, according to the authors.
“Modulation of the interleukin-23 pathway with the use of monoclonal antibodies has shown efficacy in the treatment of psoriasis and is considered to be associated with a more favorable safety profile than older oral therapies (eg, cyclosporine, acitretin, methotrexate, and dimethyl fumarate),” the investigators wrote.
Currently available biologic agents targeting IL-23 include guselkumab (Tremfya), risankizumab (Skyrizi) and tildrakizumab (Ilumya). These agents require intravenous or subcutaneous administration, whereas JNJ-77242113 is taken orally, giving it a theoretical advantage in terms of patient preference.
The novel drug must be taken twice daily on an empty stomach at least 2 hours before food or drink, and those who take it must wait an additional 30 minutes to eat or drink after taking the drug. (This news organization has learned that in planned phase 3 studies, patients will be instructed to take a double daily dose on awakening and then wait 30 minutes for eating or drinking.)
‘Profoundly Effective’
The results of this study have convinced at least one former skeptic of the efficacy of the novel agent.
“They asked me to do the trial, and I turned it down, because I didn’t believe it would work,” said Mark G. Lebwohl, MD, dean for Clinical Therapeutics at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and professor and chairman emeritus of the Department of Dermatology at Mount Sinai Medicine in New York, NY.
In an interview with this news organization, Dr. Lebwohl said that he was initially dubious that a peptide, a short chain of amino acids directed against a receptor, could be effective because it would likely be digested in the intestinal tract.
“Indeed, more than 99% of it is digested, but the data show that the tiny amount that gets through is profoundly effective,” he said.
“I would never have believed that this was going to work – and it did,” Dr. Lebwohl added.
He has signed on as an investigator in the currently recruiting phase 3 ICONIC-LEAD trial, in which JNJ-77242113 will be tested against placebo in adolescents and adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
In an editorial accompanying the study in the NEJM, Joel M. Gelfand, MD, MSCE, vice chair of clinical research and medical director of the Dermatology Clinical Studies Unit at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, noted that if confirmed in larger studies, the PASI 90 rate at the highest dose “would be similar to the most effective injectable biologics,” with no evidence of increased adverse events at higher doses.
“However, two occurrences of infection (COVID-19 and an infected cyst) and a suicide attempt were reported as serious adverse events; larger trials will be needed to determine whether such events are attributable to chance, psoriasis itself, or inhibition of interleukin-23 signaling,” cautioned Dr. Gelfand, director of the psoriasis and phototherapy treatment center at the University of Pennsylvania.
In an interview, Dr. Lebwohl said that currently available IL-23 signaling inhibitors have an excellent safety profile and that the investigational oral agent also appears to be very safe. “It’s seeing a target whose effects are known, and the effects are all good and not bad,” he said.
FRONTIER-1 Details
The investigators enrolled eligible adults aged 18 years or older who had moderate to severe plaque psoriasis as defined by an Investigator’s Global Assessment score ≥ 3, a total body-surface area of psoriasis involvement of at least 10%, and a PASI score ≥ 12 who had received their diagnosis of plaque psoriasis at least 6 months before starting the trial. The participants had to be candidates for phototherapy or systemic psoriasis therapy.
Patients were randomly assigned to the active agent at doses of 25 mg once or twice daily, 50 mg once daily, or 100 mg once or twice daily for 16 weeks.
There was a clear dose response, with 37% of patients assigned to 25-mg once-daily dose meeting the primary endpoint of a PASI 75 response at week 16 compared with 51% of those assigned to the 25-mg twice-daily dose, 58% assigned to 50-mg once-daily dose, 65% assigned to 100-mg once-daily dose, and 79% assigned to 100-mg twice-daily dose (P for dose response < .001).
As noted previously, 9% of patients in the placebo group had a PASI 75 response at week 16.
After a mean duration of 15.9 weeks, adverse events after the first dose of JNJ-77242113 (all dose groups were pooled for the safety analysis) were reported in 47% of patients on the 25-mg once-daily dose, 49% on 25-mg twice-daily dose, 60% on 50-mg once-daily dose, 44% on 100-mg once-daily dose, and 62% on 100-mg twice-daily dose. Adverse events after the first dose occurred in 51% of patients assigned to placebo.
The incidence of adverse events did not increase significantly with successively higher dose levels.
As noted by Dr. Gelfand in his editorial, there were three serious adverse events, all occurring in patients on the active drug: a case of COVID-19 in one patient and a suicide attempt in one patient, both in the 100-mg once-daily dose group, and an infected cyst in the 50-mg once-daily group. All three events were determined by the principal investigator and the sponsor to be unrelated to JNJ-77242113.
There were no reports of deaths, major adverse cardiovascular events, or incident cancers during the trial.
The study was supported by Janssen Research and Development. Dr. Bissonnette disclosed institutional research funding and advisory board participation and honoraria with Janssen. Dr. Gelfand disclosed consulting for Janssen Biotech. Dr. Lebwohl disclosed institutional research funding from Janssen but no personal fees.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A novel oral drug for plaque psoriasis that targets the same inflammatory pathway as currently available parenteral therapies showed promise for treating moderate to severe disease in a phase 2 dose-finding trial.
Among 255 at week 16 of at least 75% (PASI 75) compared with 9% of patients assigned to placebo, reported Robert Bissonnette, MD, from Innovaderm Research in Montreal, Quebec, Canada, and colleagues.
“The level of reduction of psoriasis that was observed with higher doses of JNJ-77242113 at week 16 was similar in magnitude to the responses seen with several of the injectable biologics that are currently approved for psoriasis,” investigators in the FRONTIER 1 trial wrote in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The investigators noted that among patients assigned to the 100-mg dose of the active drug, 60% had a PASI 90 response, which compares favorably with that seen in phase 3 trials of two other orally available therapies for psoriasis, deucravacitinib (Sotyktu) and apremilast (Otezla). They cautioned, however, against drawing any further inferences from these data, because these agents have not been tested head-to-head against JNJ-77242113 in comparison trials.
Targets IL-23 and IL-17
The investigational agent is an oral IL-23 receptor antagonist peptide that selectively blocks IL-23 proximal signaling as well as the production of downstream inflammatory cytokines such as IL-17, according to the authors.
“Modulation of the interleukin-23 pathway with the use of monoclonal antibodies has shown efficacy in the treatment of psoriasis and is considered to be associated with a more favorable safety profile than older oral therapies (eg, cyclosporine, acitretin, methotrexate, and dimethyl fumarate),” the investigators wrote.
Currently available biologic agents targeting IL-23 include guselkumab (Tremfya), risankizumab (Skyrizi) and tildrakizumab (Ilumya). These agents require intravenous or subcutaneous administration, whereas JNJ-77242113 is taken orally, giving it a theoretical advantage in terms of patient preference.
The novel drug must be taken twice daily on an empty stomach at least 2 hours before food or drink, and those who take it must wait an additional 30 minutes to eat or drink after taking the drug. (This news organization has learned that in planned phase 3 studies, patients will be instructed to take a double daily dose on awakening and then wait 30 minutes for eating or drinking.)
‘Profoundly Effective’
The results of this study have convinced at least one former skeptic of the efficacy of the novel agent.
“They asked me to do the trial, and I turned it down, because I didn’t believe it would work,” said Mark G. Lebwohl, MD, dean for Clinical Therapeutics at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and professor and chairman emeritus of the Department of Dermatology at Mount Sinai Medicine in New York, NY.
In an interview with this news organization, Dr. Lebwohl said that he was initially dubious that a peptide, a short chain of amino acids directed against a receptor, could be effective because it would likely be digested in the intestinal tract.
“Indeed, more than 99% of it is digested, but the data show that the tiny amount that gets through is profoundly effective,” he said.
“I would never have believed that this was going to work – and it did,” Dr. Lebwohl added.
He has signed on as an investigator in the currently recruiting phase 3 ICONIC-LEAD trial, in which JNJ-77242113 will be tested against placebo in adolescents and adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
In an editorial accompanying the study in the NEJM, Joel M. Gelfand, MD, MSCE, vice chair of clinical research and medical director of the Dermatology Clinical Studies Unit at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, noted that if confirmed in larger studies, the PASI 90 rate at the highest dose “would be similar to the most effective injectable biologics,” with no evidence of increased adverse events at higher doses.
“However, two occurrences of infection (COVID-19 and an infected cyst) and a suicide attempt were reported as serious adverse events; larger trials will be needed to determine whether such events are attributable to chance, psoriasis itself, or inhibition of interleukin-23 signaling,” cautioned Dr. Gelfand, director of the psoriasis and phototherapy treatment center at the University of Pennsylvania.
In an interview, Dr. Lebwohl said that currently available IL-23 signaling inhibitors have an excellent safety profile and that the investigational oral agent also appears to be very safe. “It’s seeing a target whose effects are known, and the effects are all good and not bad,” he said.
FRONTIER-1 Details
The investigators enrolled eligible adults aged 18 years or older who had moderate to severe plaque psoriasis as defined by an Investigator’s Global Assessment score ≥ 3, a total body-surface area of psoriasis involvement of at least 10%, and a PASI score ≥ 12 who had received their diagnosis of plaque psoriasis at least 6 months before starting the trial. The participants had to be candidates for phototherapy or systemic psoriasis therapy.
Patients were randomly assigned to the active agent at doses of 25 mg once or twice daily, 50 mg once daily, or 100 mg once or twice daily for 16 weeks.
There was a clear dose response, with 37% of patients assigned to 25-mg once-daily dose meeting the primary endpoint of a PASI 75 response at week 16 compared with 51% of those assigned to the 25-mg twice-daily dose, 58% assigned to 50-mg once-daily dose, 65% assigned to 100-mg once-daily dose, and 79% assigned to 100-mg twice-daily dose (P for dose response < .001).
As noted previously, 9% of patients in the placebo group had a PASI 75 response at week 16.
After a mean duration of 15.9 weeks, adverse events after the first dose of JNJ-77242113 (all dose groups were pooled for the safety analysis) were reported in 47% of patients on the 25-mg once-daily dose, 49% on 25-mg twice-daily dose, 60% on 50-mg once-daily dose, 44% on 100-mg once-daily dose, and 62% on 100-mg twice-daily dose. Adverse events after the first dose occurred in 51% of patients assigned to placebo.
The incidence of adverse events did not increase significantly with successively higher dose levels.
As noted by Dr. Gelfand in his editorial, there were three serious adverse events, all occurring in patients on the active drug: a case of COVID-19 in one patient and a suicide attempt in one patient, both in the 100-mg once-daily dose group, and an infected cyst in the 50-mg once-daily group. All three events were determined by the principal investigator and the sponsor to be unrelated to JNJ-77242113.
There were no reports of deaths, major adverse cardiovascular events, or incident cancers during the trial.
The study was supported by Janssen Research and Development. Dr. Bissonnette disclosed institutional research funding and advisory board participation and honoraria with Janssen. Dr. Gelfand disclosed consulting for Janssen Biotech. Dr. Lebwohl disclosed institutional research funding from Janssen but no personal fees.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Comorbidities and Disease Type Weigh Heavily in Pregnancy Outcomes of Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases
Comorbidities may play a large role in driving poor pregnancy outcomes in pregnant people with certain immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs).
In a new study of 12 individual IMIDs, people with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) did not have signficantly increased risk for preterm birth (PTB) or low birth weight (LBW), compared with people who did not have an IMID, after adjusting for additional chronic conditions and other confounding factors.
The study was published online on February 1 in eClinicalMedicine.
While many studies have explored the relationships between pregnancy outcomes and IMIDs, “the impact of comorbidities on the relation between IMIDs and pregnancy course is insufficiently examined,” the authors wrote. These previous studies also tended to have a small sample size.
Pregnancy Outcome Risks Varied Between IMIDs
To remedy this, researchers used electronic health record data from Providence St Joseph Health — a multistate integrated healthcare system — to identify more than 365,000 pregnant people with live births between January 1, 2013, and December 31, 2022. The cohort included more than 5700 people with at least one of 12 IMIDs: Psoriasis, IBD, RA, spondyloarthritis (SpA), multiple sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), Sjögren syndrome (SjS), vasculitis, sarcoidosis, and systemic sclerosis. The study included only live births with a gestational age of 20 weeks or greater.
Researchers compared maternal-fetal health outcomes between the two groups, controlling for comorbidities including diabetes, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, obesity, and depression. They also accounted for confounding variables including race, age, smoking status, and socioeconomic status.
In total, 83% of people in the IMID group had no immunomodulatory medication prescriptions during their pregnancy. Of the 17% taking medication, 48%-70% continued taking their medication until delivery. Most patients were White, comprising 62.9% of the non-IMID group and 73.1% of the IMID group.
After adjusting for comorbidities, patients with any of the 12 IMIDs had a 10%-20% higher risk for PTB, LBW, small for gestation age (SGA), and cesarean section than did comparators.
But these risks varied between IMIDs. Patients with RA and IBD did not have an increased risk for PTB or LBW. However, when researchers did not control for comorbidities, pregnancy risks were higher and showed statistical significance in these two groups.
“This suggests that for RA and IBD, comorbidities may be a more important factor for adverse outcomes than the underlying autoimmune disease,” senior author Jennifer Hadlock, MD, an associate professor and director of medical data science at the Institute for Systems Biology in Seattle, Washington, said in a video accompanying a press release.
Overall, the analysis found that women with IMIDs were approximately two to three times more likely to have chronic comorbidities than the control group.
Like previous studies, there was a strong association between SLE and APS and poor pregnancy outcomes, even after controlling for confounding factors. Patients with SpA had a 50% increased risk for PTB, while those with SLE and APS had more than a twofold higher risk. Patients with SLE were 90% more likely than comparators to deliver babies with an SGA condition, while RA patients had a 30% higher risk. SLE was the only condition with an increased risk for LBW (relative risk, 3.5). IBD, RA, PsA, SpA, SLE, APS, and SjS were all associated with a higher likelihood of delivery via cesarean section.
“The findings of this study reveal that the associations between IMIDs and adverse pregnancy outcomes are influenced by the specific type of IMIDs and the presence of comorbidities,” the authors wrote.
A Large Study, But How Representative Is It?
Asked to comment on the study, Catherine Sims, MD, a rheumatologist at Duke University Medical Center in Durham, North Carolina, noted that the analysis was much larger than many reproductive rheumatology studies, and “their statistics were phenomenal.”
She agreed that “not all autoimmune diseases are created equal when it comes to pregnancy-associated risks.” However, she added that this study’s patient population may not be totally representative of pregnant people with IMIDs or autoimmune diseases.
“We’re making generalizations about autoimmune diseases based on this demographic of White women who are not taking immunosuppression,” she said.
“We know that race and ethnicity play a huge role in pregnancy outcomes, and Black women have higher maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality, which is likely related to systemic racism and biases in the medical system,” she added. “While the study did control for sociodemographic factors, the population studied is not diverse.”
Only 17% of people with IMID in the cohort were on immunosuppressive medication, which could suggest low disease activity in the study population, Dr. Sims said. If the population generally had well-controlled disease, that could have positioned them for better pregnancy outcomes.
The authors noted that their analysis did not have information on IMID disease activity or severity — one of the limitations of the study.
However, the authors argued that the observed low prescription rate during the study may have increased poor pregnancy outcomes.
“Although this reflects real-world care in the population studied, results from this study may show higher risk than might be achieved with recommended care guidelines,” they wrote.
Ultimately, the authors argued that these findings show how co-occurring health conditions can affect pregnancy outcomes in autoimmune diseases, particularly for RA and IBD.
“There is a need to take comorbidities into consideration for guidelines for patients with inflammatory bowel disease and rheumatoid arthritis and when designing future research to investigate maternal health in patients with IMIDs,” they wrote.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Sims declared no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Hadlock has received research funding (paid to the institute) from Pfizer, Novartis, Janssen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Gilead.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Comorbidities may play a large role in driving poor pregnancy outcomes in pregnant people with certain immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs).
In a new study of 12 individual IMIDs, people with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) did not have signficantly increased risk for preterm birth (PTB) or low birth weight (LBW), compared with people who did not have an IMID, after adjusting for additional chronic conditions and other confounding factors.
The study was published online on February 1 in eClinicalMedicine.
While many studies have explored the relationships between pregnancy outcomes and IMIDs, “the impact of comorbidities on the relation between IMIDs and pregnancy course is insufficiently examined,” the authors wrote. These previous studies also tended to have a small sample size.
Pregnancy Outcome Risks Varied Between IMIDs
To remedy this, researchers used electronic health record data from Providence St Joseph Health — a multistate integrated healthcare system — to identify more than 365,000 pregnant people with live births between January 1, 2013, and December 31, 2022. The cohort included more than 5700 people with at least one of 12 IMIDs: Psoriasis, IBD, RA, spondyloarthritis (SpA), multiple sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), Sjögren syndrome (SjS), vasculitis, sarcoidosis, and systemic sclerosis. The study included only live births with a gestational age of 20 weeks or greater.
Researchers compared maternal-fetal health outcomes between the two groups, controlling for comorbidities including diabetes, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, obesity, and depression. They also accounted for confounding variables including race, age, smoking status, and socioeconomic status.
In total, 83% of people in the IMID group had no immunomodulatory medication prescriptions during their pregnancy. Of the 17% taking medication, 48%-70% continued taking their medication until delivery. Most patients were White, comprising 62.9% of the non-IMID group and 73.1% of the IMID group.
After adjusting for comorbidities, patients with any of the 12 IMIDs had a 10%-20% higher risk for PTB, LBW, small for gestation age (SGA), and cesarean section than did comparators.
But these risks varied between IMIDs. Patients with RA and IBD did not have an increased risk for PTB or LBW. However, when researchers did not control for comorbidities, pregnancy risks were higher and showed statistical significance in these two groups.
“This suggests that for RA and IBD, comorbidities may be a more important factor for adverse outcomes than the underlying autoimmune disease,” senior author Jennifer Hadlock, MD, an associate professor and director of medical data science at the Institute for Systems Biology in Seattle, Washington, said in a video accompanying a press release.
Overall, the analysis found that women with IMIDs were approximately two to three times more likely to have chronic comorbidities than the control group.
Like previous studies, there was a strong association between SLE and APS and poor pregnancy outcomes, even after controlling for confounding factors. Patients with SpA had a 50% increased risk for PTB, while those with SLE and APS had more than a twofold higher risk. Patients with SLE were 90% more likely than comparators to deliver babies with an SGA condition, while RA patients had a 30% higher risk. SLE was the only condition with an increased risk for LBW (relative risk, 3.5). IBD, RA, PsA, SpA, SLE, APS, and SjS were all associated with a higher likelihood of delivery via cesarean section.
“The findings of this study reveal that the associations between IMIDs and adverse pregnancy outcomes are influenced by the specific type of IMIDs and the presence of comorbidities,” the authors wrote.
A Large Study, But How Representative Is It?
Asked to comment on the study, Catherine Sims, MD, a rheumatologist at Duke University Medical Center in Durham, North Carolina, noted that the analysis was much larger than many reproductive rheumatology studies, and “their statistics were phenomenal.”
She agreed that “not all autoimmune diseases are created equal when it comes to pregnancy-associated risks.” However, she added that this study’s patient population may not be totally representative of pregnant people with IMIDs or autoimmune diseases.
“We’re making generalizations about autoimmune diseases based on this demographic of White women who are not taking immunosuppression,” she said.
“We know that race and ethnicity play a huge role in pregnancy outcomes, and Black women have higher maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality, which is likely related to systemic racism and biases in the medical system,” she added. “While the study did control for sociodemographic factors, the population studied is not diverse.”
Only 17% of people with IMID in the cohort were on immunosuppressive medication, which could suggest low disease activity in the study population, Dr. Sims said. If the population generally had well-controlled disease, that could have positioned them for better pregnancy outcomes.
The authors noted that their analysis did not have information on IMID disease activity or severity — one of the limitations of the study.
However, the authors argued that the observed low prescription rate during the study may have increased poor pregnancy outcomes.
“Although this reflects real-world care in the population studied, results from this study may show higher risk than might be achieved with recommended care guidelines,” they wrote.
Ultimately, the authors argued that these findings show how co-occurring health conditions can affect pregnancy outcomes in autoimmune diseases, particularly for RA and IBD.
“There is a need to take comorbidities into consideration for guidelines for patients with inflammatory bowel disease and rheumatoid arthritis and when designing future research to investigate maternal health in patients with IMIDs,” they wrote.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Sims declared no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Hadlock has received research funding (paid to the institute) from Pfizer, Novartis, Janssen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Gilead.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Comorbidities may play a large role in driving poor pregnancy outcomes in pregnant people with certain immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs).
In a new study of 12 individual IMIDs, people with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) did not have signficantly increased risk for preterm birth (PTB) or low birth weight (LBW), compared with people who did not have an IMID, after adjusting for additional chronic conditions and other confounding factors.
The study was published online on February 1 in eClinicalMedicine.
While many studies have explored the relationships between pregnancy outcomes and IMIDs, “the impact of comorbidities on the relation between IMIDs and pregnancy course is insufficiently examined,” the authors wrote. These previous studies also tended to have a small sample size.
Pregnancy Outcome Risks Varied Between IMIDs
To remedy this, researchers used electronic health record data from Providence St Joseph Health — a multistate integrated healthcare system — to identify more than 365,000 pregnant people with live births between January 1, 2013, and December 31, 2022. The cohort included more than 5700 people with at least one of 12 IMIDs: Psoriasis, IBD, RA, spondyloarthritis (SpA), multiple sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), Sjögren syndrome (SjS), vasculitis, sarcoidosis, and systemic sclerosis. The study included only live births with a gestational age of 20 weeks or greater.
Researchers compared maternal-fetal health outcomes between the two groups, controlling for comorbidities including diabetes, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, obesity, and depression. They also accounted for confounding variables including race, age, smoking status, and socioeconomic status.
In total, 83% of people in the IMID group had no immunomodulatory medication prescriptions during their pregnancy. Of the 17% taking medication, 48%-70% continued taking their medication until delivery. Most patients were White, comprising 62.9% of the non-IMID group and 73.1% of the IMID group.
After adjusting for comorbidities, patients with any of the 12 IMIDs had a 10%-20% higher risk for PTB, LBW, small for gestation age (SGA), and cesarean section than did comparators.
But these risks varied between IMIDs. Patients with RA and IBD did not have an increased risk for PTB or LBW. However, when researchers did not control for comorbidities, pregnancy risks were higher and showed statistical significance in these two groups.
“This suggests that for RA and IBD, comorbidities may be a more important factor for adverse outcomes than the underlying autoimmune disease,” senior author Jennifer Hadlock, MD, an associate professor and director of medical data science at the Institute for Systems Biology in Seattle, Washington, said in a video accompanying a press release.
Overall, the analysis found that women with IMIDs were approximately two to three times more likely to have chronic comorbidities than the control group.
Like previous studies, there was a strong association between SLE and APS and poor pregnancy outcomes, even after controlling for confounding factors. Patients with SpA had a 50% increased risk for PTB, while those with SLE and APS had more than a twofold higher risk. Patients with SLE were 90% more likely than comparators to deliver babies with an SGA condition, while RA patients had a 30% higher risk. SLE was the only condition with an increased risk for LBW (relative risk, 3.5). IBD, RA, PsA, SpA, SLE, APS, and SjS were all associated with a higher likelihood of delivery via cesarean section.
“The findings of this study reveal that the associations between IMIDs and adverse pregnancy outcomes are influenced by the specific type of IMIDs and the presence of comorbidities,” the authors wrote.
A Large Study, But How Representative Is It?
Asked to comment on the study, Catherine Sims, MD, a rheumatologist at Duke University Medical Center in Durham, North Carolina, noted that the analysis was much larger than many reproductive rheumatology studies, and “their statistics were phenomenal.”
She agreed that “not all autoimmune diseases are created equal when it comes to pregnancy-associated risks.” However, she added that this study’s patient population may not be totally representative of pregnant people with IMIDs or autoimmune diseases.
“We’re making generalizations about autoimmune diseases based on this demographic of White women who are not taking immunosuppression,” she said.
“We know that race and ethnicity play a huge role in pregnancy outcomes, and Black women have higher maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality, which is likely related to systemic racism and biases in the medical system,” she added. “While the study did control for sociodemographic factors, the population studied is not diverse.”
Only 17% of people with IMID in the cohort were on immunosuppressive medication, which could suggest low disease activity in the study population, Dr. Sims said. If the population generally had well-controlled disease, that could have positioned them for better pregnancy outcomes.
The authors noted that their analysis did not have information on IMID disease activity or severity — one of the limitations of the study.
However, the authors argued that the observed low prescription rate during the study may have increased poor pregnancy outcomes.
“Although this reflects real-world care in the population studied, results from this study may show higher risk than might be achieved with recommended care guidelines,” they wrote.
Ultimately, the authors argued that these findings show how co-occurring health conditions can affect pregnancy outcomes in autoimmune diseases, particularly for RA and IBD.
“There is a need to take comorbidities into consideration for guidelines for patients with inflammatory bowel disease and rheumatoid arthritis and when designing future research to investigate maternal health in patients with IMIDs,” they wrote.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Sims declared no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Hadlock has received research funding (paid to the institute) from Pfizer, Novartis, Janssen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Gilead.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ECLINICALMEDICINE
A Cross-sectional Analysis of Regional Trends in Medicare Reimbursement for Phototherapy Services From 2010 to 2023
To the Editor:
Phototherapy regularly is utilized in the outpatient setting to address various skin pathologies, including atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, pruritus, vitiligo, and mycosis fungoides.1,2 Phototherapy is broadly defined by the measured administration of nonionizing radiation within the UV range including wavelengths within the UVA (eg, psoralen sensitizer plus UVA-1) and UVB (eg, broadband UVB, narrowband UVB) spectrums.1,3 Generally, the mechanism of action is derived from effects on inflammatory components of cutaneous disorders and the induction of apoptosis, both precipitating numerous downstream events.4
From 2015 to 2018, there were more than 1.3 million outpatient phototherapy visits in the United States, with the most common procedural indications being dermatitis not otherwise specified, atopic dermatitis, and pruritus.5 From 2000 to 2015, the quantity of phototherapy services billed to Medicare trended upwards by an average of 5% per year, increasing from 334,670 in the year 2000 to 692,093 in 2015.6 Therefore, an illustration of associated costs would be beneficial. Additionally, because total cost and physician reimbursement fluctuate from year to year, studies demonstrating overall trends can inform both US policymakers and physicians. There is a paucity of research on geographical trends for procedural reimbursements in dermatology for phototherapy. Understanding geographic trends of reimbursement could duly serve to optimize dermatologist practice patterns involving access to viable and quality care for patients seeking treatment as well as draw health policymakers’ attention to striking adjustments in physician fees. Therefore, in this study we aimed to illustrate the most recent regional payment trends in phototherapy procedures for Medicare B patients.
We queried the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (MPFS) database (https://www.cms.gov/medicare/payment/fee-schedules/physician/lookup-tool) for the years 2010 to 2023 for Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes common to phototherapy procedures: actinotherapy (96900); photochemotherapy by Goeckerman treatment or using petrolatum and UVB (96910); photochemotherapy using psoralen plus UVA (96912); and photochemotherapy of severe dermatoses requiring a minimum of 4 hours of care under direct physician supervision (96913). Nonfacility prices for these procedures were analyzed. For 2010, due to midyear alterations to Medicare reimbursement (owed to bills HR 3962 and HR 4872), the mean price data of MPFS files 2010A and 2010B were used. All dollar values were converted to January 2023 US dollars using corresponding consumer price index inflation data. The Medicare Administrative Contractors were used to group state pricing information by region in accordance with established US Census Bureau subdivisions (https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/economic-census/guidance-geographies/levels.html). Weighted percentage change in reimbursement rate was calculated using physician (MD or DO) utilization (procedure volume) data available in the 2020 Physician and Other Practitioners Public Use File (https://data.cms.gov/provider-summary-by-type-of-service/medicare-physician-other-practitioners/medicare-physician-other-practitioners-by-provider-and-service). All descriptive statistics and visualization were generated using R software (v4.2.2)(R Development Core Team).
Table 1 provides physician utilization data and the corresponding number of Part B beneficiaries for phototherapy procedures in 2020. There were 65,045 services of actinotherapy provided to a total of 6855 unique Part B beneficiaries, 173,979 services of photochemotherapy by Goeckerman treatment or using petrolatum and UVB provided to 13,122 unique Part B beneficiaries, 2524 services of photochemotherapy using psoralen plus UVA provided to a total of 357 unique Part B beneficiaries, and 37 services of photochemotherapy of severe dermatoses requiring a minimum of 4 hours of care under direct physician supervision provided to a total of 27 unique Part B beneficiaries.
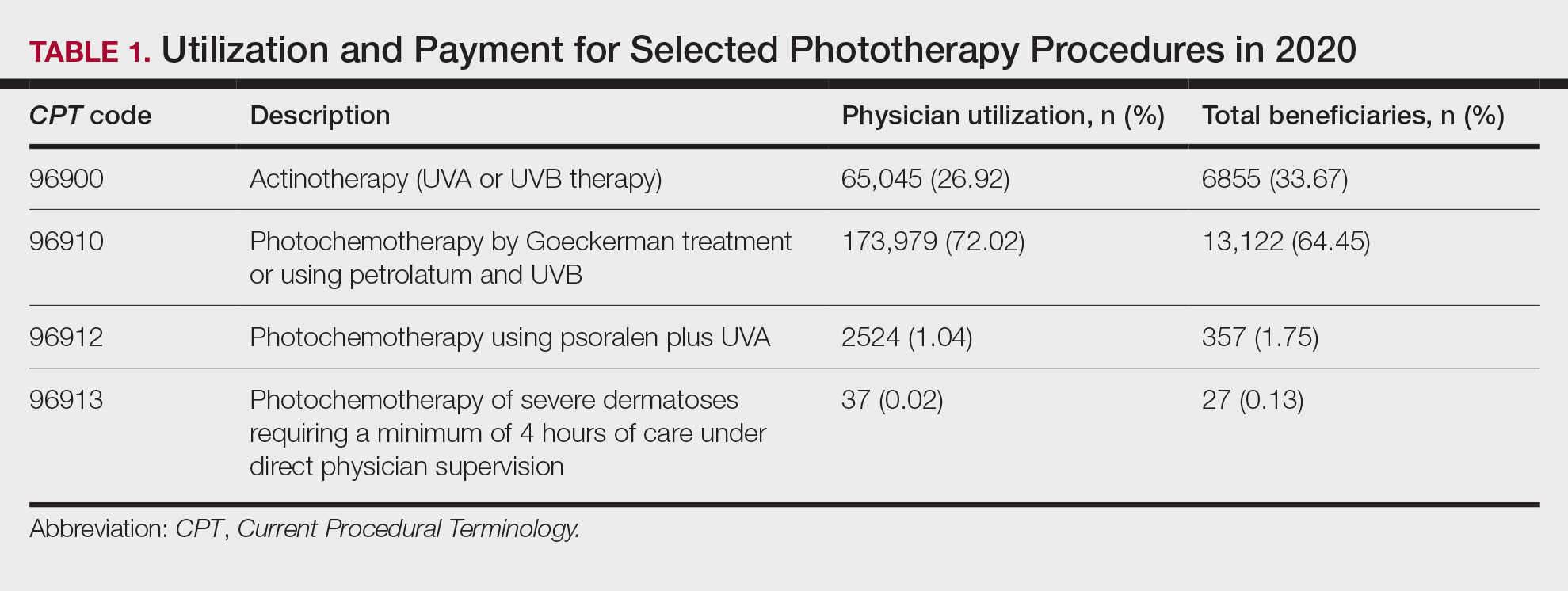
On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the North increased by 0.68% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 2). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +19.37%. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted increase in reimbursement (+31.45%)($98.12 to $128.98; compound annual growth rate [CAGR], +0.0213), and CPT code 96912 reported the greatest adjusted decrease in reimbursement (−12.76%)($126.09 to $109.97; CAGR, −0.0105). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −11.68% ($30.21 to $26.68; CAGR, −0.0095), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −4.27% ($174.03 to $166.60; CAGR, −0.0034).
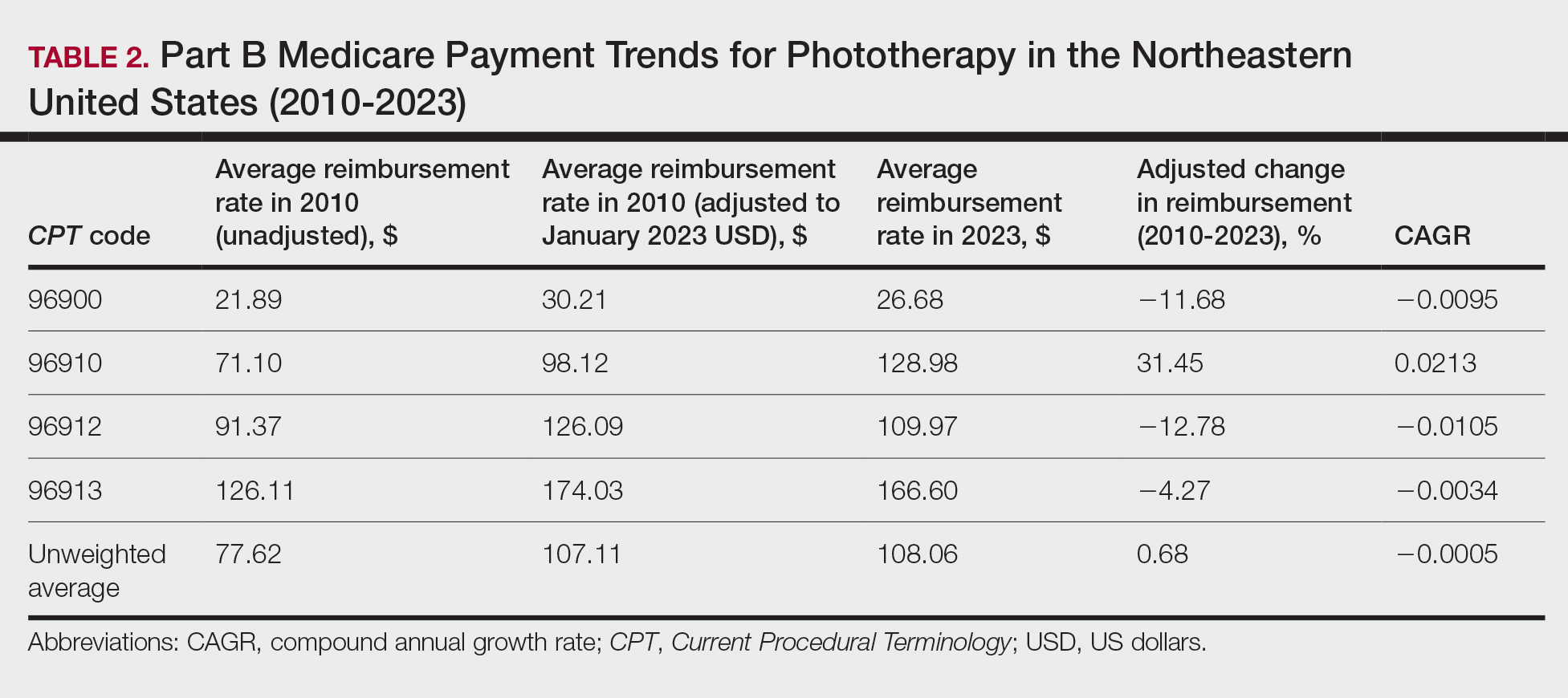
On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the Midwest increased by 8.40% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 3). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +28.53%. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted change in reimbursement (+41.48%)($80.42 to $113.78; CAGR, +0.0270), and CPT code 96912 reported the greatest adjusted decrease in reimbursement (−6.14%)($103.28 to $97.03; CAGR, −0.0049). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −4.73% ($24.69 to $23.52; CAGR, −0.0037), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted increase in reimbursement was +2.99% ($142.72 to $146.99; CAGR, +0.0023).
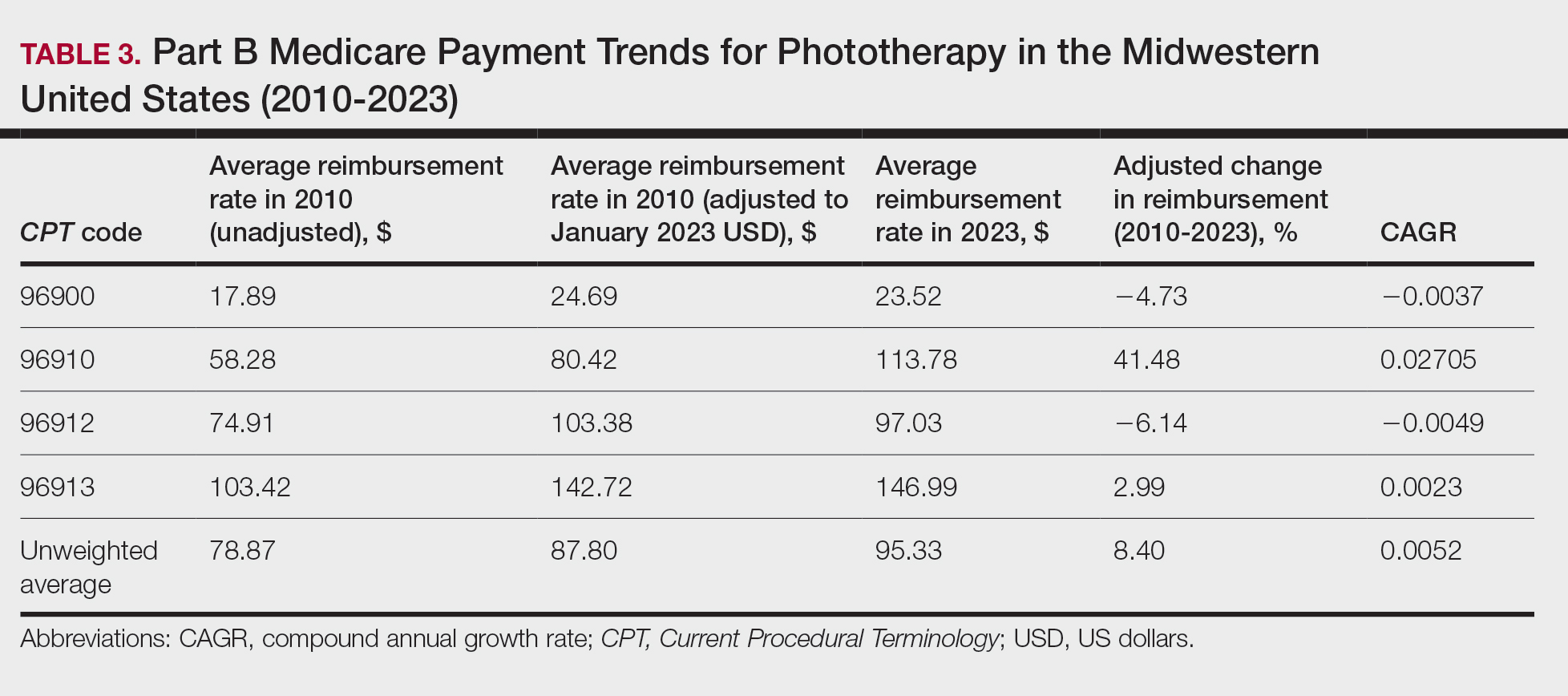
On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the South decreased by 2.62% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 4). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +15.41%. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted change in reimbursement (+27.26%)($90.40 to $115.04 USD; CAGR, +0.0187), and CPT code 96912 reported the greatest adjusted decrease in reimbursement (−15.50%)($116.08 to $98.09; CAGR, −0.0129). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −15.06% ($28.02 to $23.80; CAGR, −0.0125), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −7.19% ($160.11 to $148.61; CAGR, −0.0057).
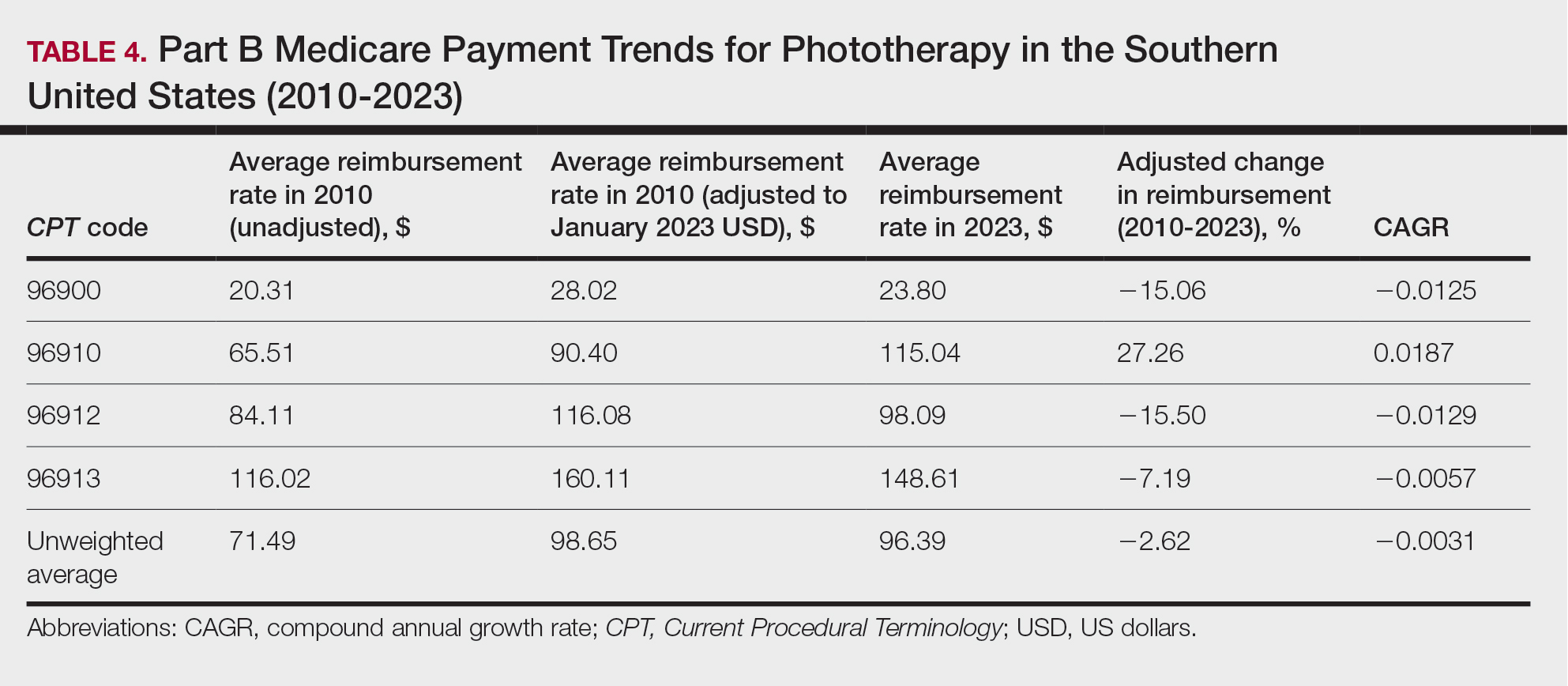
On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the West increased by 27.53% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 5). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +51.16%. Reimbursement for all analyzed procedures increased in the western United States. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted increase in reimbursement (+66.56%)($80.84 to $134.65; CAGR, +0.0400), and CPT code 96912 reported the lowest adjusted increase in reimbursement (+10.64%)($103.88 to $114.93; CAGR, +0.0078). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted increase in reimbursement was 11.54% ($24.88 to $27.75; CAGR, +0.0084), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted increase in reimbursement was 21.38% ($143.39 to $174.04; CAGR, +0.0150).
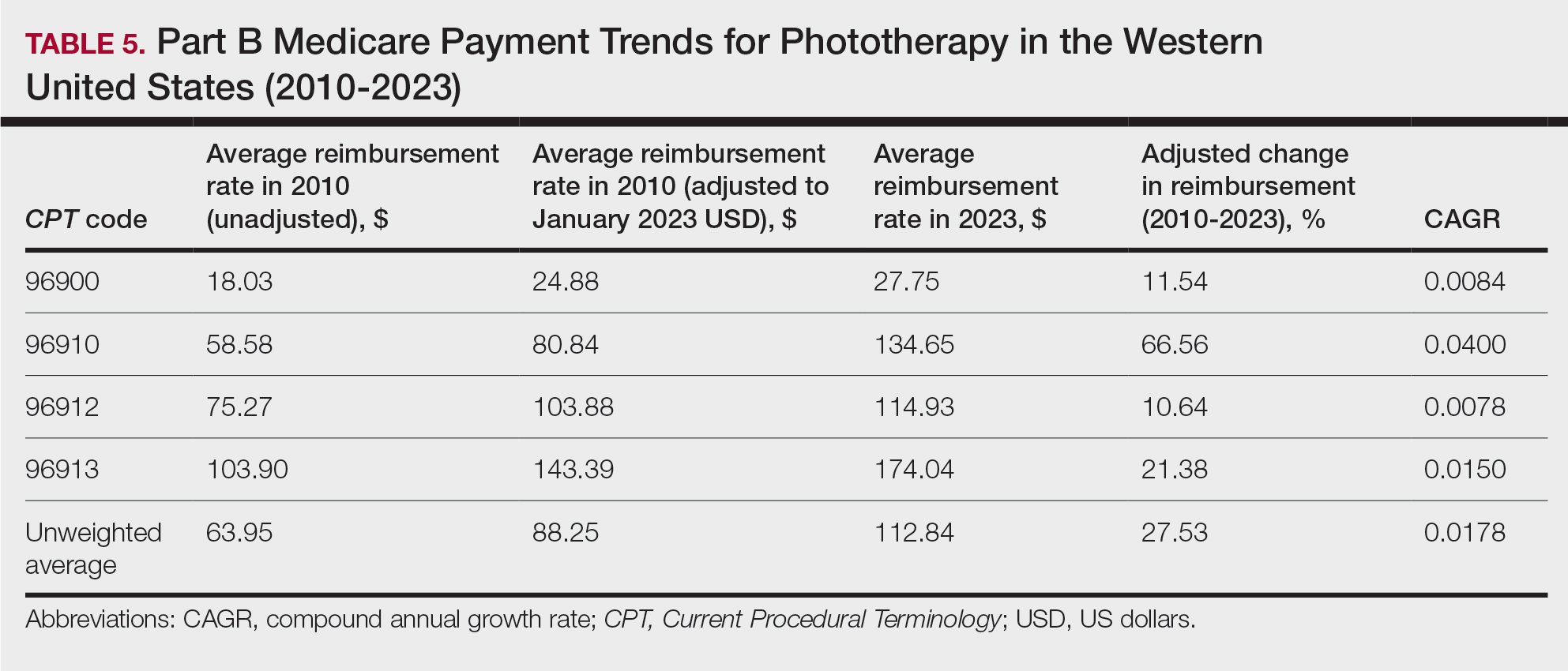
In this study evaluating geographical payment trends for phototherapy from 2010 to 2023, we demonstrated regional inconsistency in mean inflation-adjusted Medicare reimbursement rates. We found that all phototherapy procedures had increased reimbursement in the western United States, whereas all other regions reported cuts in reimbursement rates for at least half of the analyzed procedures. After adjusting for procedure utilization by physicians, weighted mean reimbursement for phototherapy increased in all US regions.
In a cross-sectional study that explored trends in the geographic distribution of dermatologists from 2012 to 2017, dermatologists in the northeastern and western United States were more likely to be located in higher-income zip codes, whereas dermatologists in the southern United States were more likely to be located in lower-income zip codes,7 suggesting that payment rate changes are not concordant with cost of living. Additionally, Lauck and colleagues8 observed that 75% of the top 20 most common procedures performed by dermatologists had decreased reimbursement (mean change, −10.8%) from 2011 to 2021. Other studies on Medicare reimbursement trends over the last 2 decades have reported major decreases within other specialties, suggesting that declining Medicare reimbursements are not unique to dermatology.9,10 It is critical to monitor these developments, as the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services emphasized health care policy changes aimed at increasing reimbursements for evaluation and management services with compensatory payment cuts in billing for procedural services.11
Mazmudar et al12 previously reported a mean reimbursement decrease of −6.6% for laser/phototherapy procedures between 2007 and 2021, but these data did not include the heavily utilized Goeckerman treatment. Changes in reimbursement pose major ramifications for dermatologists—for practice size, scope, and longevity—as rates influence changes in commercial insurance reimbursements.13 Medicare plays a major role in the US health care system as the second largest expenditure14; indeed, between 2000 and 2015, Part B billing volume for phototherapy procedures increased 5% annually. However, phototherapy remains inaccessible in many locations due to unequal regional distribution of phototherapy clinics.6 Moreover, home phototherapy units are not yet widely utilized because of safety and efficacy concerns, lack of physician oversight, and difficulty obtaining insurance coverage.15 Acknowledgment and consideration of these geographical trends may persuasively allow policymakers, hospitals, and physicians to facilitate cost-effective phototherapy reimbursements that ensure continued access to quality and sustainable dermatologic care in the United States that tailor to regional needs.
In sum, this analysis reveals regional trends in Part B physician reimbursement for phototherapy procedures, with all US regions reporting a mean increase in phototherapy reimbursement after adjusting for utilization, albeit to varying degrees. Mean reimbursement for photochemotherapy by Goeckerman treatment or using petrolatum and UVB increased most among phototherapy procedures. Mean reimbursement for both actinotherapy and photochemotherapy using psoralen plus UVA decreased in all regions except the western United States.
Limitations include the restriction to Part B MPFS and the reliance on single-year (2020) physician utilization data to compute weighted changes in average reimbursement across a multiyear range, effectively restricting sweeping conclusions. Still, this study puts forth actionable insights for dermatologists and policymakers alike to appreciate and consider.
- Rathod DG, Muneer H, Masood S. Phototherapy. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2002.
- Branisteanu DE, Dirzu DS, Toader MP, et al. Phototherapy in dermatological maladies (Review). Exp Ther Med. 2022;23:259. doi:10.3892/etm.2022.11184
- Barros NM, Sbroglio LL, Buffara MO, et al. Phototherapy. An Bras Dermatol. 2021;96:397-407. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2021.03.001
- Vieyra-Garcia PA, Wolf P. A deep dive into UV-based phototherapy: mechanisms of action and emerging molecular targets in inflammation and cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 2021;222:107784. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107784
- Oulee A, Javadi SS, Martin A, et al. Phototherapy trends in dermatology 2015-2018. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022;33:2545-2546. doi:10.1080/09546634.2021.2019660
- Tan SY, Buzney E, Mostaghimi A. Trends in phototherapy utilization among Medicare beneficiaries in the United States, 2000 to 2015. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:672-679. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.03.018
- Benlagha I, Nguyen BM. Changes in dermatology practice characteristics in the United States from 2012 to 2017. JAAD Int. 2021;3:92-101. doi:10.1016/j.jdin.2021.03.005
- Lauck K, Nguyen QB, Hebert A. Trends in Medicare reimbursement within dermatology: 2011-2021. Skin. 2022;6:122-131. doi:10.25251/skin.6.2.5
- Smith JF, Moore ML, Pollock JR, et al. National and geographic trends in Medicare reimbursement rates for orthopedic shoulder and upper extremity surgery from 2000 to 2020. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2022;31:860-867. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2021.09.001
- Haglin JM, Eltorai AEM, Richter KR, et al. Medicare reimbursement for general surgery procedures: 2000 to 2018. Ann Surg. 2020;271:17-22. doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000003289
- Fleishon HB. Evaluation and management coding initiative. J Am Coll Radiol. 2020;17:1539-1540. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2020.09.057
- Mazmudar RS, Sheth A, Tripathi R, et al. Inflation-adjusted trends in Medicare reimbursement for common dermatologic procedures, 2007-2021. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1355-1358. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.3453
- Clemens J, Gottlieb JD. In the shadow of a giant: Medicare’s influence on private physician payments. J Polit Econ. 2017;125:1-39. doi:10.1086/689772
- Ya J, Ezaldein HH, Scott JF. Trends in Medicare utilization by dermatologists, 2012-2015. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:471-474. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.4212
- Rajpara AN, O’Neill JL, Nolan BV, et al. Review of home phototherapy. Dermatol Online J. 2010;16:2.
To the Editor:
Phototherapy regularly is utilized in the outpatient setting to address various skin pathologies, including atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, pruritus, vitiligo, and mycosis fungoides.1,2 Phototherapy is broadly defined by the measured administration of nonionizing radiation within the UV range including wavelengths within the UVA (eg, psoralen sensitizer plus UVA-1) and UVB (eg, broadband UVB, narrowband UVB) spectrums.1,3 Generally, the mechanism of action is derived from effects on inflammatory components of cutaneous disorders and the induction of apoptosis, both precipitating numerous downstream events.4
From 2015 to 2018, there were more than 1.3 million outpatient phototherapy visits in the United States, with the most common procedural indications being dermatitis not otherwise specified, atopic dermatitis, and pruritus.5 From 2000 to 2015, the quantity of phototherapy services billed to Medicare trended upwards by an average of 5% per year, increasing from 334,670 in the year 2000 to 692,093 in 2015.6 Therefore, an illustration of associated costs would be beneficial. Additionally, because total cost and physician reimbursement fluctuate from year to year, studies demonstrating overall trends can inform both US policymakers and physicians. There is a paucity of research on geographical trends for procedural reimbursements in dermatology for phototherapy. Understanding geographic trends of reimbursement could duly serve to optimize dermatologist practice patterns involving access to viable and quality care for patients seeking treatment as well as draw health policymakers’ attention to striking adjustments in physician fees. Therefore, in this study we aimed to illustrate the most recent regional payment trends in phototherapy procedures for Medicare B patients.
We queried the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (MPFS) database (https://www.cms.gov/medicare/payment/fee-schedules/physician/lookup-tool) for the years 2010 to 2023 for Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes common to phototherapy procedures: actinotherapy (96900); photochemotherapy by Goeckerman treatment or using petrolatum and UVB (96910); photochemotherapy using psoralen plus UVA (96912); and photochemotherapy of severe dermatoses requiring a minimum of 4 hours of care under direct physician supervision (96913). Nonfacility prices for these procedures were analyzed. For 2010, due to midyear alterations to Medicare reimbursement (owed to bills HR 3962 and HR 4872), the mean price data of MPFS files 2010A and 2010B were used. All dollar values were converted to January 2023 US dollars using corresponding consumer price index inflation data. The Medicare Administrative Contractors were used to group state pricing information by region in accordance with established US Census Bureau subdivisions (https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/economic-census/guidance-geographies/levels.html). Weighted percentage change in reimbursement rate was calculated using physician (MD or DO) utilization (procedure volume) data available in the 2020 Physician and Other Practitioners Public Use File (https://data.cms.gov/provider-summary-by-type-of-service/medicare-physician-other-practitioners/medicare-physician-other-practitioners-by-provider-and-service). All descriptive statistics and visualization were generated using R software (v4.2.2)(R Development Core Team).
Table 1 provides physician utilization data and the corresponding number of Part B beneficiaries for phototherapy procedures in 2020. There were 65,045 services of actinotherapy provided to a total of 6855 unique Part B beneficiaries, 173,979 services of photochemotherapy by Goeckerman treatment or using petrolatum and UVB provided to 13,122 unique Part B beneficiaries, 2524 services of photochemotherapy using psoralen plus UVA provided to a total of 357 unique Part B beneficiaries, and 37 services of photochemotherapy of severe dermatoses requiring a minimum of 4 hours of care under direct physician supervision provided to a total of 27 unique Part B beneficiaries.

On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the North increased by 0.68% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 2). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +19.37%. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted increase in reimbursement (+31.45%)($98.12 to $128.98; compound annual growth rate [CAGR], +0.0213), and CPT code 96912 reported the greatest adjusted decrease in reimbursement (−12.76%)($126.09 to $109.97; CAGR, −0.0105). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −11.68% ($30.21 to $26.68; CAGR, −0.0095), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −4.27% ($174.03 to $166.60; CAGR, −0.0034).

On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the Midwest increased by 8.40% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 3). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +28.53%. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted change in reimbursement (+41.48%)($80.42 to $113.78; CAGR, +0.0270), and CPT code 96912 reported the greatest adjusted decrease in reimbursement (−6.14%)($103.28 to $97.03; CAGR, −0.0049). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −4.73% ($24.69 to $23.52; CAGR, −0.0037), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted increase in reimbursement was +2.99% ($142.72 to $146.99; CAGR, +0.0023).

On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the South decreased by 2.62% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 4). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +15.41%. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted change in reimbursement (+27.26%)($90.40 to $115.04 USD; CAGR, +0.0187), and CPT code 96912 reported the greatest adjusted decrease in reimbursement (−15.50%)($116.08 to $98.09; CAGR, −0.0129). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −15.06% ($28.02 to $23.80; CAGR, −0.0125), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −7.19% ($160.11 to $148.61; CAGR, −0.0057).

On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the West increased by 27.53% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 5). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +51.16%. Reimbursement for all analyzed procedures increased in the western United States. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted increase in reimbursement (+66.56%)($80.84 to $134.65; CAGR, +0.0400), and CPT code 96912 reported the lowest adjusted increase in reimbursement (+10.64%)($103.88 to $114.93; CAGR, +0.0078). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted increase in reimbursement was 11.54% ($24.88 to $27.75; CAGR, +0.0084), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted increase in reimbursement was 21.38% ($143.39 to $174.04; CAGR, +0.0150).

In this study evaluating geographical payment trends for phototherapy from 2010 to 2023, we demonstrated regional inconsistency in mean inflation-adjusted Medicare reimbursement rates. We found that all phototherapy procedures had increased reimbursement in the western United States, whereas all other regions reported cuts in reimbursement rates for at least half of the analyzed procedures. After adjusting for procedure utilization by physicians, weighted mean reimbursement for phototherapy increased in all US regions.
In a cross-sectional study that explored trends in the geographic distribution of dermatologists from 2012 to 2017, dermatologists in the northeastern and western United States were more likely to be located in higher-income zip codes, whereas dermatologists in the southern United States were more likely to be located in lower-income zip codes,7 suggesting that payment rate changes are not concordant with cost of living. Additionally, Lauck and colleagues8 observed that 75% of the top 20 most common procedures performed by dermatologists had decreased reimbursement (mean change, −10.8%) from 2011 to 2021. Other studies on Medicare reimbursement trends over the last 2 decades have reported major decreases within other specialties, suggesting that declining Medicare reimbursements are not unique to dermatology.9,10 It is critical to monitor these developments, as the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services emphasized health care policy changes aimed at increasing reimbursements for evaluation and management services with compensatory payment cuts in billing for procedural services.11
Mazmudar et al12 previously reported a mean reimbursement decrease of −6.6% for laser/phototherapy procedures between 2007 and 2021, but these data did not include the heavily utilized Goeckerman treatment. Changes in reimbursement pose major ramifications for dermatologists—for practice size, scope, and longevity—as rates influence changes in commercial insurance reimbursements.13 Medicare plays a major role in the US health care system as the second largest expenditure14; indeed, between 2000 and 2015, Part B billing volume for phototherapy procedures increased 5% annually. However, phototherapy remains inaccessible in many locations due to unequal regional distribution of phototherapy clinics.6 Moreover, home phototherapy units are not yet widely utilized because of safety and efficacy concerns, lack of physician oversight, and difficulty obtaining insurance coverage.15 Acknowledgment and consideration of these geographical trends may persuasively allow policymakers, hospitals, and physicians to facilitate cost-effective phototherapy reimbursements that ensure continued access to quality and sustainable dermatologic care in the United States that tailor to regional needs.
In sum, this analysis reveals regional trends in Part B physician reimbursement for phototherapy procedures, with all US regions reporting a mean increase in phototherapy reimbursement after adjusting for utilization, albeit to varying degrees. Mean reimbursement for photochemotherapy by Goeckerman treatment or using petrolatum and UVB increased most among phototherapy procedures. Mean reimbursement for both actinotherapy and photochemotherapy using psoralen plus UVA decreased in all regions except the western United States.
Limitations include the restriction to Part B MPFS and the reliance on single-year (2020) physician utilization data to compute weighted changes in average reimbursement across a multiyear range, effectively restricting sweeping conclusions. Still, this study puts forth actionable insights for dermatologists and policymakers alike to appreciate and consider.
To the Editor:
Phototherapy regularly is utilized in the outpatient setting to address various skin pathologies, including atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, pruritus, vitiligo, and mycosis fungoides.1,2 Phototherapy is broadly defined by the measured administration of nonionizing radiation within the UV range including wavelengths within the UVA (eg, psoralen sensitizer plus UVA-1) and UVB (eg, broadband UVB, narrowband UVB) spectrums.1,3 Generally, the mechanism of action is derived from effects on inflammatory components of cutaneous disorders and the induction of apoptosis, both precipitating numerous downstream events.4
From 2015 to 2018, there were more than 1.3 million outpatient phototherapy visits in the United States, with the most common procedural indications being dermatitis not otherwise specified, atopic dermatitis, and pruritus.5 From 2000 to 2015, the quantity of phototherapy services billed to Medicare trended upwards by an average of 5% per year, increasing from 334,670 in the year 2000 to 692,093 in 2015.6 Therefore, an illustration of associated costs would be beneficial. Additionally, because total cost and physician reimbursement fluctuate from year to year, studies demonstrating overall trends can inform both US policymakers and physicians. There is a paucity of research on geographical trends for procedural reimbursements in dermatology for phototherapy. Understanding geographic trends of reimbursement could duly serve to optimize dermatologist practice patterns involving access to viable and quality care for patients seeking treatment as well as draw health policymakers’ attention to striking adjustments in physician fees. Therefore, in this study we aimed to illustrate the most recent regional payment trends in phototherapy procedures for Medicare B patients.
We queried the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (MPFS) database (https://www.cms.gov/medicare/payment/fee-schedules/physician/lookup-tool) for the years 2010 to 2023 for Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes common to phototherapy procedures: actinotherapy (96900); photochemotherapy by Goeckerman treatment or using petrolatum and UVB (96910); photochemotherapy using psoralen plus UVA (96912); and photochemotherapy of severe dermatoses requiring a minimum of 4 hours of care under direct physician supervision (96913). Nonfacility prices for these procedures were analyzed. For 2010, due to midyear alterations to Medicare reimbursement (owed to bills HR 3962 and HR 4872), the mean price data of MPFS files 2010A and 2010B were used. All dollar values were converted to January 2023 US dollars using corresponding consumer price index inflation data. The Medicare Administrative Contractors were used to group state pricing information by region in accordance with established US Census Bureau subdivisions (https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/economic-census/guidance-geographies/levels.html). Weighted percentage change in reimbursement rate was calculated using physician (MD or DO) utilization (procedure volume) data available in the 2020 Physician and Other Practitioners Public Use File (https://data.cms.gov/provider-summary-by-type-of-service/medicare-physician-other-practitioners/medicare-physician-other-practitioners-by-provider-and-service). All descriptive statistics and visualization were generated using R software (v4.2.2)(R Development Core Team).
Table 1 provides physician utilization data and the corresponding number of Part B beneficiaries for phototherapy procedures in 2020. There were 65,045 services of actinotherapy provided to a total of 6855 unique Part B beneficiaries, 173,979 services of photochemotherapy by Goeckerman treatment or using petrolatum and UVB provided to 13,122 unique Part B beneficiaries, 2524 services of photochemotherapy using psoralen plus UVA provided to a total of 357 unique Part B beneficiaries, and 37 services of photochemotherapy of severe dermatoses requiring a minimum of 4 hours of care under direct physician supervision provided to a total of 27 unique Part B beneficiaries.

On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the North increased by 0.68% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 2). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +19.37%. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted increase in reimbursement (+31.45%)($98.12 to $128.98; compound annual growth rate [CAGR], +0.0213), and CPT code 96912 reported the greatest adjusted decrease in reimbursement (−12.76%)($126.09 to $109.97; CAGR, −0.0105). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −11.68% ($30.21 to $26.68; CAGR, −0.0095), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −4.27% ($174.03 to $166.60; CAGR, −0.0034).

On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the Midwest increased by 8.40% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 3). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +28.53%. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted change in reimbursement (+41.48%)($80.42 to $113.78; CAGR, +0.0270), and CPT code 96912 reported the greatest adjusted decrease in reimbursement (−6.14%)($103.28 to $97.03; CAGR, −0.0049). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −4.73% ($24.69 to $23.52; CAGR, −0.0037), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted increase in reimbursement was +2.99% ($142.72 to $146.99; CAGR, +0.0023).

On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the South decreased by 2.62% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 4). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +15.41%. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted change in reimbursement (+27.26%)($90.40 to $115.04 USD; CAGR, +0.0187), and CPT code 96912 reported the greatest adjusted decrease in reimbursement (−15.50%)($116.08 to $98.09; CAGR, −0.0129). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −15.06% ($28.02 to $23.80; CAGR, −0.0125), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −7.19% ($160.11 to $148.61; CAGR, −0.0057).

On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the West increased by 27.53% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 5). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +51.16%. Reimbursement for all analyzed procedures increased in the western United States. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted increase in reimbursement (+66.56%)($80.84 to $134.65; CAGR, +0.0400), and CPT code 96912 reported the lowest adjusted increase in reimbursement (+10.64%)($103.88 to $114.93; CAGR, +0.0078). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted increase in reimbursement was 11.54% ($24.88 to $27.75; CAGR, +0.0084), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted increase in reimbursement was 21.38% ($143.39 to $174.04; CAGR, +0.0150).

In this study evaluating geographical payment trends for phototherapy from 2010 to 2023, we demonstrated regional inconsistency in mean inflation-adjusted Medicare reimbursement rates. We found that all phototherapy procedures had increased reimbursement in the western United States, whereas all other regions reported cuts in reimbursement rates for at least half of the analyzed procedures. After adjusting for procedure utilization by physicians, weighted mean reimbursement for phototherapy increased in all US regions.
In a cross-sectional study that explored trends in the geographic distribution of dermatologists from 2012 to 2017, dermatologists in the northeastern and western United States were more likely to be located in higher-income zip codes, whereas dermatologists in the southern United States were more likely to be located in lower-income zip codes,7 suggesting that payment rate changes are not concordant with cost of living. Additionally, Lauck and colleagues8 observed that 75% of the top 20 most common procedures performed by dermatologists had decreased reimbursement (mean change, −10.8%) from 2011 to 2021. Other studies on Medicare reimbursement trends over the last 2 decades have reported major decreases within other specialties, suggesting that declining Medicare reimbursements are not unique to dermatology.9,10 It is critical to monitor these developments, as the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services emphasized health care policy changes aimed at increasing reimbursements for evaluation and management services with compensatory payment cuts in billing for procedural services.11
Mazmudar et al12 previously reported a mean reimbursement decrease of −6.6% for laser/phototherapy procedures between 2007 and 2021, but these data did not include the heavily utilized Goeckerman treatment. Changes in reimbursement pose major ramifications for dermatologists—for practice size, scope, and longevity—as rates influence changes in commercial insurance reimbursements.13 Medicare plays a major role in the US health care system as the second largest expenditure14; indeed, between 2000 and 2015, Part B billing volume for phototherapy procedures increased 5% annually. However, phototherapy remains inaccessible in many locations due to unequal regional distribution of phototherapy clinics.6 Moreover, home phototherapy units are not yet widely utilized because of safety and efficacy concerns, lack of physician oversight, and difficulty obtaining insurance coverage.15 Acknowledgment and consideration of these geographical trends may persuasively allow policymakers, hospitals, and physicians to facilitate cost-effective phototherapy reimbursements that ensure continued access to quality and sustainable dermatologic care in the United States that tailor to regional needs.
In sum, this analysis reveals regional trends in Part B physician reimbursement for phototherapy procedures, with all US regions reporting a mean increase in phototherapy reimbursement after adjusting for utilization, albeit to varying degrees. Mean reimbursement for photochemotherapy by Goeckerman treatment or using petrolatum and UVB increased most among phototherapy procedures. Mean reimbursement for both actinotherapy and photochemotherapy using psoralen plus UVA decreased in all regions except the western United States.
Limitations include the restriction to Part B MPFS and the reliance on single-year (2020) physician utilization data to compute weighted changes in average reimbursement across a multiyear range, effectively restricting sweeping conclusions. Still, this study puts forth actionable insights for dermatologists and policymakers alike to appreciate and consider.
- Rathod DG, Muneer H, Masood S. Phototherapy. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2002.
- Branisteanu DE, Dirzu DS, Toader MP, et al. Phototherapy in dermatological maladies (Review). Exp Ther Med. 2022;23:259. doi:10.3892/etm.2022.11184
- Barros NM, Sbroglio LL, Buffara MO, et al. Phototherapy. An Bras Dermatol. 2021;96:397-407. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2021.03.001
- Vieyra-Garcia PA, Wolf P. A deep dive into UV-based phototherapy: mechanisms of action and emerging molecular targets in inflammation and cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 2021;222:107784. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107784
- Oulee A, Javadi SS, Martin A, et al. Phototherapy trends in dermatology 2015-2018. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022;33:2545-2546. doi:10.1080/09546634.2021.2019660
- Tan SY, Buzney E, Mostaghimi A. Trends in phototherapy utilization among Medicare beneficiaries in the United States, 2000 to 2015. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:672-679. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.03.018
- Benlagha I, Nguyen BM. Changes in dermatology practice characteristics in the United States from 2012 to 2017. JAAD Int. 2021;3:92-101. doi:10.1016/j.jdin.2021.03.005
- Lauck K, Nguyen QB, Hebert A. Trends in Medicare reimbursement within dermatology: 2011-2021. Skin. 2022;6:122-131. doi:10.25251/skin.6.2.5
- Smith JF, Moore ML, Pollock JR, et al. National and geographic trends in Medicare reimbursement rates for orthopedic shoulder and upper extremity surgery from 2000 to 2020. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2022;31:860-867. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2021.09.001
- Haglin JM, Eltorai AEM, Richter KR, et al. Medicare reimbursement for general surgery procedures: 2000 to 2018. Ann Surg. 2020;271:17-22. doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000003289
- Fleishon HB. Evaluation and management coding initiative. J Am Coll Radiol. 2020;17:1539-1540. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2020.09.057
- Mazmudar RS, Sheth A, Tripathi R, et al. Inflation-adjusted trends in Medicare reimbursement for common dermatologic procedures, 2007-2021. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1355-1358. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.3453
- Clemens J, Gottlieb JD. In the shadow of a giant: Medicare’s influence on private physician payments. J Polit Econ. 2017;125:1-39. doi:10.1086/689772
- Ya J, Ezaldein HH, Scott JF. Trends in Medicare utilization by dermatologists, 2012-2015. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:471-474. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.4212
- Rajpara AN, O’Neill JL, Nolan BV, et al. Review of home phototherapy. Dermatol Online J. 2010;16:2.
- Rathod DG, Muneer H, Masood S. Phototherapy. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2002.
- Branisteanu DE, Dirzu DS, Toader MP, et al. Phototherapy in dermatological maladies (Review). Exp Ther Med. 2022;23:259. doi:10.3892/etm.2022.11184
- Barros NM, Sbroglio LL, Buffara MO, et al. Phototherapy. An Bras Dermatol. 2021;96:397-407. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2021.03.001
- Vieyra-Garcia PA, Wolf P. A deep dive into UV-based phototherapy: mechanisms of action and emerging molecular targets in inflammation and cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 2021;222:107784. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107784
- Oulee A, Javadi SS, Martin A, et al. Phototherapy trends in dermatology 2015-2018. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022;33:2545-2546. doi:10.1080/09546634.2021.2019660
- Tan SY, Buzney E, Mostaghimi A. Trends in phototherapy utilization among Medicare beneficiaries in the United States, 2000 to 2015. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:672-679. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.03.018
- Benlagha I, Nguyen BM. Changes in dermatology practice characteristics in the United States from 2012 to 2017. JAAD Int. 2021;3:92-101. doi:10.1016/j.jdin.2021.03.005
- Lauck K, Nguyen QB, Hebert A. Trends in Medicare reimbursement within dermatology: 2011-2021. Skin. 2022;6:122-131. doi:10.25251/skin.6.2.5
- Smith JF, Moore ML, Pollock JR, et al. National and geographic trends in Medicare reimbursement rates for orthopedic shoulder and upper extremity surgery from 2000 to 2020. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2022;31:860-867. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2021.09.001
- Haglin JM, Eltorai AEM, Richter KR, et al. Medicare reimbursement for general surgery procedures: 2000 to 2018. Ann Surg. 2020;271:17-22. doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000003289
- Fleishon HB. Evaluation and management coding initiative. J Am Coll Radiol. 2020;17:1539-1540. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2020.09.057
- Mazmudar RS, Sheth A, Tripathi R, et al. Inflation-adjusted trends in Medicare reimbursement for common dermatologic procedures, 2007-2021. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1355-1358. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.3453
- Clemens J, Gottlieb JD. In the shadow of a giant: Medicare’s influence on private physician payments. J Polit Econ. 2017;125:1-39. doi:10.1086/689772
- Ya J, Ezaldein HH, Scott JF. Trends in Medicare utilization by dermatologists, 2012-2015. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:471-474. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.4212
- Rajpara AN, O’Neill JL, Nolan BV, et al. Review of home phototherapy. Dermatol Online J. 2010;16:2.
Practice Points
- After weighting for procedure utilization, mean reimbursement for phototherapy increased across all US regions from 2010 to 2023 (mean change, +28.62%), yet with marked regional diversity.
- The southern United States reported the least growth in weighted mean reimbursement (+15.41%), and the western United States reported the greatest growth in weighted mean reimbursement (+51.16%).
- Region- and procedure-specific payment changes are especially valuable to dermatologists and policymakers alike, potentially reinvigorating payment reform discussions.
The Potential Benefits of Dietary Changes in Psoriasis Patients
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease for which several lifestyle factors—smoking, alcohol use, and psychological stress—are associated with higher incidence and more severe disease.1-3 Diet also has been implicated as a factor that can affect psoriasis,4 and many patients have shown interest in possible dietary interventions to help their disease.5
In 2018, the National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) presented dietary recommendations for patients based on results from a systematic review. From the available literature, only dietary weight reduction with hypocaloric diets in overweight or obese patients could be strongly recommended, and it has been proven that obesity is associated with worse psoriasis severity.6 Other more recent studies have shown that dietary modifications such as intermittent fasting and the ketogenic diet also led to weight loss and improved psoriasis severity in overweight patients; however, it is difficult to discern if the improvement was due to weight loss alone or if the dietary patterns themselves played a role.7,8 The paucity of well-designed studies evaluating the effects of other dietary changes has prevented further guidelines from being written. We propose that dietary patterns such as the Mediterranean diet (MeD) and vegan/vegetarian diets—even without strong data showing benefits in skin disease—may help to decrease systemic inflammation, improve gut dysbiosis, and help decrease the risk for cardiometabolic comorbidities that are associated with psoriasis.
Mediterranean Diet
The MeD is based on the dietary tendencies of inhabitants from the regions surrounding the Mediterranean Sea and is centered around nutrient-rich foods such as vegetables, olive oil, and legumes while limiting meat and dairy.9 The NPF recommended considering a trial of the MeD based on low-quality evidence.6 Observational studies have indicated that psoriasis patients are less likely to adhere to the MeD, but those who do have less severe disease.8 However, a search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms Mediterranean diet and psoriasis yielded no prospective interventional studies. Given the association of the MeD with less severe disease, it is important to understand which specific foods in the MeD could be beneficial. Intake of omega-3 fatty acids, such as those found in fatty fish, are important for modulation of systemic inflammation.7 High intake of polyphenols—found in fruits and vegetables, extra-virgin olive oil, and wine—also have been implicated in improving inflammatory diseases due to potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Individually, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and sea fish have been associated with lowering C-reactive protein levels, which also is indicative of the benefits of these foods on systemic inflammation.7
Vegan/Vegetarian Diets
Although fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains are a substantial component of the MeD, there are limited data on vegetarian or purely vegan plant-based diets. An observational study from the NPF found that only 48.4% (15/31) of patients on the MeD vs 69.0% (20/29) on a vegan diet reported a favorable skin response.5 Two case reports also have shown beneficial results of a strict vegan diet for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, where whole-food plant-based diets also improved joint symptoms.10-12 As with any diet, those who pursue a plant-based diet should strive to consume a variety of foods to avoid nutrient deficiencies. A recent systematic meta-analysis of 141 studies evaluated nutrient status of vegan and vegetarian diets compared to pescovegetarians and those who consume meat. All dietary patterns showed varying degrees of low levels of different nutrients.13 Of note, the researchers found that vitamin B12, vitamin D, iron, zinc, iodine, calcium, and docosahexaenoic acid were lower in plant-based diets. In contrast, folate; vitamins B1, B6, C, and E; polyunsaturated fatty acids; α-linolenic acid; and magnesium intake were higher. Those who consumed meat were at risk for inadequate intake of fiber, polyunsaturated fatty acids, α-linolenic acid, folate, vitamin E, calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D, though vitamin D intake was higher than in vegans/vegetarians.13 The results of this meta-analysis indicated the importance of educating patients on what constitutes a well-rounded, micronutrient-rich diet or appropriate supplementation for any diet.
Effects on Gut Microbiome
Any changes in diet can lead to alterations in the gut microbiome, which may impact skin disease, as evidence indicates a bidirectional relationship between gut and skin health.10 A metagenomic analysis of the gut microbiota in patients with untreated plaque psoriasis revealed a signature dysbiosis for which the researchers developed a psoriasis microbiota index, suggesting the gut microbiota may play a role in psoriasis pathophysiology.14 Research shows that both the MeD and vegan/vegetarian diets, which are relatively rich in fiber and omega-3 fatty acids and low in saturated fat and animal protein compared to many diets, cause increases in dietary fiber–metabolizing bacteria that produce short-chain fatty acids. These short-chain fatty acids improve gut epithelial integrity and alleviate both gut and systemic inflammation.10
The changes to the gut microbiome induced by a high-fat diet also are concerning. In contrast to the MeD or vegan/vegetarian diets, consumption of a high-fat diet induces alterations in the composition of the gut microbiota that in turn increase the release of proinflammatory cytokines and promote higher intestinal permeability.10 Similarly, high sugar consumption promotes increased intestinal permeability and shifts the gut microbiota to organisms that can rapidly utilize simple carbohydrates at the expense of other beneficial organisms, reducing bacterial diversity.15 The Western diet, which is notable for both high fat and high sugar content, is sometimes referred to as a proinflammatory diet and has been shown to worsen psoriasiformlike lesions in mice.16 Importantly, most research indicates that high fat and high sugar consumption appear to be more prevalent in psoriasis patients,8 but the type of fat consumed in the diet matters. The Western diet includes abundant saturated fat found in meat, dairy products, palm and coconut oils, and processed foods, as well as omega-6 fatty acids that are found in meat, poultry, and eggs. Saturated fat has been shown to promote helper T cell (TH17) accumulation in the skin, and omega-6 fatty acids serve as precursors to various inflammatory lipid mediators.4 This distinction of sources of fat between the Western diet and MeD is important in understanding the diets’ different effects on psoriasis and overall health. As previously discussed, the high intake of omega-3 acids in the MeD is one of the ways it may exert its anti-inflammatory benefits.7
Next Steps in Advising Psoriasis Patients
A major limitation of the data for MeD and vegan/vegetarian diets is limited randomized controlled trials evaluating the impact of these diets on psoriasis. Thus, dietary recommendations for psoriasis are not as strong as for other diseases for which more conclusive data exist.8 Although the data on diet and psoriasis are not definitive, perhaps dermatologists should shift the question from “Does this diet definitely improve psoriasis?” to “Does this diet definitely improve my patient’s health as a whole and maybe also their psoriasis?” For instance, the MeD has been shown to reduce the risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease as well as to slow cognitive decline.17 Vegan/vegetarian diets focusing on whole vs processed foods have been shown to be highly effective in combatting obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease including severe atherosclerosis, and hypertension.18 Psoriasis patients are at increased risk for many of the ailments that the MeD and plant-based diets protect against, making these diets potentially even more impactful than for someone without psoriasis.19 Dietary recommendations should still be made in conjunction with continuing traditional therapies for psoriasis and in consultation with the patient’s primary care physician and/or dietitian; however, rather than waiting for more randomized controlled trials before making health-promoting recommendations, what would be the downside of starting now? At worst, the dietary change decreases their risk for several metabolic conditions, and at best they may even see an improvement in their psoriasis.
- Naldi L, Chatenoud L, Linder D, et al. Cigarette smoking, body mass index, and stressful life events as risk factors for psoriasis: results from an Italian case–control study. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;125:61-67. doi:10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23681.x
- Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Dhillon JS, et al. Psoriasis and smoking: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:304-314. doi:10.1111/bjd.12670
- Zhu K, Zhu C, Fan Y. Alcohol consumption and psoriatic risk: a meta‐analysis of case–control studies. J Dermatol. 2012;39:770-773. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2012.01577.x
- Kanda N, Hoashi T, Saeki H. Nutrition and psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:5405. doi:10.3390/ijms21155405
- Afifi L, Danesh MJ, Lee KM, et al. Dietary behaviors in psoriasis: patient-reported outcomes from a U.S. national survey. Dermatol Ther. 2017;7:227-242. doi:10.1007/s13555-017-0183-4
- Ford AR, Siegel M, Bagel J, et al. Dietary recommendations for adults with psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis from the medical board of the National Psoriasis Foundation: a systematic review. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:934. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.1412
- Duchnik E, Kruk J, Tuchowska A, et al. The impact of diet and physical activity on psoriasis: a narrative review of the current evidence. Nutrients. 2023;15:840. doi:10.3390/nu15040840
- Chung M, Bartholomew E, Yeroushalmi S, et al. Dietary intervention and supplements in the management of psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis Targets Ther. 2022;12:151-176. doi:10.2147/PTT.S328581
- Mazza E, Ferro Y, Pujia R, et al. Mediterranean diet in healthy aging. J Nutr Health Aging. 2021;25:1076-1083. doi:10.1007/s12603-021-1675-6
- Flores-Balderas X, Peña-Peña M, Rada KM, et al. Beneficial effects of plant-based diets on skin health and inflammatory skin diseases. Nutrients. 2023;15:2842. doi:10.3390/nu15132842
- Bonjour M, Gabriel S, Valencia A, et al. Challenging case in clinical practice: prolonged water-only fasting followed by an exclusively whole-plant-food diet in the management of severe plaque psoriasis. Integr Complement Ther. 2022;28:85-87. doi:10.1089/ict.2022.29010.mbo
- Lewandowska M, Dunbar K, Kassam S. Managing psoriatic arthritis with a whole food plant-based diet: a case study. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2021;15:402-406. doi:10.1177/1559827621993435
- Neufingerl N, Eilander A. Nutrient intake and status in adults consuming plant-based diets compared to meat-eaters: a systematic review. Nutrients. 2021;14:29. doi:10.3390/nu14010029
- Dei-Cas I, Giliberto F, Luce L, et al. Metagenomic analysis of gut microbiota in non-treated plaque psoriasis patients stratified by disease severity: development of a new psoriasis-microbiome index. Sci Rep. 2020;10:12754. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-69537-3
- Satokari R. High intake of sugar and the balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory gut bacteria. Nutrients. 2020;12:1348. doi:10.3390/nu12051348
- Shi Z, Wu X, Santos Rocha C, et al. Short-term Western diet intake promotes IL-23–mediated skin and joint inflammation accompanied by changes to the gut microbiota in mice. J Invest Dermatol. 2021;141:1780-1791. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2020.11.032
- Romagnolo DF, Selmin OI. Mediterranean diet and prevention of chronic diseases. Nutr Today. 2017;52:208-222. doi:10.1097/NT.0000000000000228
- Tuso PJ, Ismail MH, Ha BP, et al. Nutritional update for physicians: plant-based diets. Perm J. 2013;17:61-66. doi:10.7812/TPP/12-085
- Parisi R, Symmons DPM, Griffiths CEM, et al. Global epidemiology of psoriasis: a systematic review of incidence and prevalence. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:377-385. doi:10.1038/jid.2012.339
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease for which several lifestyle factors—smoking, alcohol use, and psychological stress—are associated with higher incidence and more severe disease.1-3 Diet also has been implicated as a factor that can affect psoriasis,4 and many patients have shown interest in possible dietary interventions to help their disease.5
In 2018, the National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) presented dietary recommendations for patients based on results from a systematic review. From the available literature, only dietary weight reduction with hypocaloric diets in overweight or obese patients could be strongly recommended, and it has been proven that obesity is associated with worse psoriasis severity.6 Other more recent studies have shown that dietary modifications such as intermittent fasting and the ketogenic diet also led to weight loss and improved psoriasis severity in overweight patients; however, it is difficult to discern if the improvement was due to weight loss alone or if the dietary patterns themselves played a role.7,8 The paucity of well-designed studies evaluating the effects of other dietary changes has prevented further guidelines from being written. We propose that dietary patterns such as the Mediterranean diet (MeD) and vegan/vegetarian diets—even without strong data showing benefits in skin disease—may help to decrease systemic inflammation, improve gut dysbiosis, and help decrease the risk for cardiometabolic comorbidities that are associated with psoriasis.
Mediterranean Diet
The MeD is based on the dietary tendencies of inhabitants from the regions surrounding the Mediterranean Sea and is centered around nutrient-rich foods such as vegetables, olive oil, and legumes while limiting meat and dairy.9 The NPF recommended considering a trial of the MeD based on low-quality evidence.6 Observational studies have indicated that psoriasis patients are less likely to adhere to the MeD, but those who do have less severe disease.8 However, a search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms Mediterranean diet and psoriasis yielded no prospective interventional studies. Given the association of the MeD with less severe disease, it is important to understand which specific foods in the MeD could be beneficial. Intake of omega-3 fatty acids, such as those found in fatty fish, are important for modulation of systemic inflammation.7 High intake of polyphenols—found in fruits and vegetables, extra-virgin olive oil, and wine—also have been implicated in improving inflammatory diseases due to potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Individually, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and sea fish have been associated with lowering C-reactive protein levels, which also is indicative of the benefits of these foods on systemic inflammation.7
Vegan/Vegetarian Diets
Although fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains are a substantial component of the MeD, there are limited data on vegetarian or purely vegan plant-based diets. An observational study from the NPF found that only 48.4% (15/31) of patients on the MeD vs 69.0% (20/29) on a vegan diet reported a favorable skin response.5 Two case reports also have shown beneficial results of a strict vegan diet for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, where whole-food plant-based diets also improved joint symptoms.10-12 As with any diet, those who pursue a plant-based diet should strive to consume a variety of foods to avoid nutrient deficiencies. A recent systematic meta-analysis of 141 studies evaluated nutrient status of vegan and vegetarian diets compared to pescovegetarians and those who consume meat. All dietary patterns showed varying degrees of low levels of different nutrients.13 Of note, the researchers found that vitamin B12, vitamin D, iron, zinc, iodine, calcium, and docosahexaenoic acid were lower in plant-based diets. In contrast, folate; vitamins B1, B6, C, and E; polyunsaturated fatty acids; α-linolenic acid; and magnesium intake were higher. Those who consumed meat were at risk for inadequate intake of fiber, polyunsaturated fatty acids, α-linolenic acid, folate, vitamin E, calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D, though vitamin D intake was higher than in vegans/vegetarians.13 The results of this meta-analysis indicated the importance of educating patients on what constitutes a well-rounded, micronutrient-rich diet or appropriate supplementation for any diet.
Effects on Gut Microbiome
Any changes in diet can lead to alterations in the gut microbiome, which may impact skin disease, as evidence indicates a bidirectional relationship between gut and skin health.10 A metagenomic analysis of the gut microbiota in patients with untreated plaque psoriasis revealed a signature dysbiosis for which the researchers developed a psoriasis microbiota index, suggesting the gut microbiota may play a role in psoriasis pathophysiology.14 Research shows that both the MeD and vegan/vegetarian diets, which are relatively rich in fiber and omega-3 fatty acids and low in saturated fat and animal protein compared to many diets, cause increases in dietary fiber–metabolizing bacteria that produce short-chain fatty acids. These short-chain fatty acids improve gut epithelial integrity and alleviate both gut and systemic inflammation.10
The changes to the gut microbiome induced by a high-fat diet also are concerning. In contrast to the MeD or vegan/vegetarian diets, consumption of a high-fat diet induces alterations in the composition of the gut microbiota that in turn increase the release of proinflammatory cytokines and promote higher intestinal permeability.10 Similarly, high sugar consumption promotes increased intestinal permeability and shifts the gut microbiota to organisms that can rapidly utilize simple carbohydrates at the expense of other beneficial organisms, reducing bacterial diversity.15 The Western diet, which is notable for both high fat and high sugar content, is sometimes referred to as a proinflammatory diet and has been shown to worsen psoriasiformlike lesions in mice.16 Importantly, most research indicates that high fat and high sugar consumption appear to be more prevalent in psoriasis patients,8 but the type of fat consumed in the diet matters. The Western diet includes abundant saturated fat found in meat, dairy products, palm and coconut oils, and processed foods, as well as omega-6 fatty acids that are found in meat, poultry, and eggs. Saturated fat has been shown to promote helper T cell (TH17) accumulation in the skin, and omega-6 fatty acids serve as precursors to various inflammatory lipid mediators.4 This distinction of sources of fat between the Western diet and MeD is important in understanding the diets’ different effects on psoriasis and overall health. As previously discussed, the high intake of omega-3 acids in the MeD is one of the ways it may exert its anti-inflammatory benefits.7
Next Steps in Advising Psoriasis Patients
A major limitation of the data for MeD and vegan/vegetarian diets is limited randomized controlled trials evaluating the impact of these diets on psoriasis. Thus, dietary recommendations for psoriasis are not as strong as for other diseases for which more conclusive data exist.8 Although the data on diet and psoriasis are not definitive, perhaps dermatologists should shift the question from “Does this diet definitely improve psoriasis?” to “Does this diet definitely improve my patient’s health as a whole and maybe also their psoriasis?” For instance, the MeD has been shown to reduce the risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease as well as to slow cognitive decline.17 Vegan/vegetarian diets focusing on whole vs processed foods have been shown to be highly effective in combatting obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease including severe atherosclerosis, and hypertension.18 Psoriasis patients are at increased risk for many of the ailments that the MeD and plant-based diets protect against, making these diets potentially even more impactful than for someone without psoriasis.19 Dietary recommendations should still be made in conjunction with continuing traditional therapies for psoriasis and in consultation with the patient’s primary care physician and/or dietitian; however, rather than waiting for more randomized controlled trials before making health-promoting recommendations, what would be the downside of starting now? At worst, the dietary change decreases their risk for several metabolic conditions, and at best they may even see an improvement in their psoriasis.
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease for which several lifestyle factors—smoking, alcohol use, and psychological stress—are associated with higher incidence and more severe disease.1-3 Diet also has been implicated as a factor that can affect psoriasis,4 and many patients have shown interest in possible dietary interventions to help their disease.5
In 2018, the National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) presented dietary recommendations for patients based on results from a systematic review. From the available literature, only dietary weight reduction with hypocaloric diets in overweight or obese patients could be strongly recommended, and it has been proven that obesity is associated with worse psoriasis severity.6 Other more recent studies have shown that dietary modifications such as intermittent fasting and the ketogenic diet also led to weight loss and improved psoriasis severity in overweight patients; however, it is difficult to discern if the improvement was due to weight loss alone or if the dietary patterns themselves played a role.7,8 The paucity of well-designed studies evaluating the effects of other dietary changes has prevented further guidelines from being written. We propose that dietary patterns such as the Mediterranean diet (MeD) and vegan/vegetarian diets—even without strong data showing benefits in skin disease—may help to decrease systemic inflammation, improve gut dysbiosis, and help decrease the risk for cardiometabolic comorbidities that are associated with psoriasis.
Mediterranean Diet
The MeD is based on the dietary tendencies of inhabitants from the regions surrounding the Mediterranean Sea and is centered around nutrient-rich foods such as vegetables, olive oil, and legumes while limiting meat and dairy.9 The NPF recommended considering a trial of the MeD based on low-quality evidence.6 Observational studies have indicated that psoriasis patients are less likely to adhere to the MeD, but those who do have less severe disease.8 However, a search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms Mediterranean diet and psoriasis yielded no prospective interventional studies. Given the association of the MeD with less severe disease, it is important to understand which specific foods in the MeD could be beneficial. Intake of omega-3 fatty acids, such as those found in fatty fish, are important for modulation of systemic inflammation.7 High intake of polyphenols—found in fruits and vegetables, extra-virgin olive oil, and wine—also have been implicated in improving inflammatory diseases due to potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Individually, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and sea fish have been associated with lowering C-reactive protein levels, which also is indicative of the benefits of these foods on systemic inflammation.7
Vegan/Vegetarian Diets
Although fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains are a substantial component of the MeD, there are limited data on vegetarian or purely vegan plant-based diets. An observational study from the NPF found that only 48.4% (15/31) of patients on the MeD vs 69.0% (20/29) on a vegan diet reported a favorable skin response.5 Two case reports also have shown beneficial results of a strict vegan diet for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, where whole-food plant-based diets also improved joint symptoms.10-12 As with any diet, those who pursue a plant-based diet should strive to consume a variety of foods to avoid nutrient deficiencies. A recent systematic meta-analysis of 141 studies evaluated nutrient status of vegan and vegetarian diets compared to pescovegetarians and those who consume meat. All dietary patterns showed varying degrees of low levels of different nutrients.13 Of note, the researchers found that vitamin B12, vitamin D, iron, zinc, iodine, calcium, and docosahexaenoic acid were lower in plant-based diets. In contrast, folate; vitamins B1, B6, C, and E; polyunsaturated fatty acids; α-linolenic acid; and magnesium intake were higher. Those who consumed meat were at risk for inadequate intake of fiber, polyunsaturated fatty acids, α-linolenic acid, folate, vitamin E, calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D, though vitamin D intake was higher than in vegans/vegetarians.13 The results of this meta-analysis indicated the importance of educating patients on what constitutes a well-rounded, micronutrient-rich diet or appropriate supplementation for any diet.
Effects on Gut Microbiome
Any changes in diet can lead to alterations in the gut microbiome, which may impact skin disease, as evidence indicates a bidirectional relationship between gut and skin health.10 A metagenomic analysis of the gut microbiota in patients with untreated plaque psoriasis revealed a signature dysbiosis for which the researchers developed a psoriasis microbiota index, suggesting the gut microbiota may play a role in psoriasis pathophysiology.14 Research shows that both the MeD and vegan/vegetarian diets, which are relatively rich in fiber and omega-3 fatty acids and low in saturated fat and animal protein compared to many diets, cause increases in dietary fiber–metabolizing bacteria that produce short-chain fatty acids. These short-chain fatty acids improve gut epithelial integrity and alleviate both gut and systemic inflammation.10
The changes to the gut microbiome induced by a high-fat diet also are concerning. In contrast to the MeD or vegan/vegetarian diets, consumption of a high-fat diet induces alterations in the composition of the gut microbiota that in turn increase the release of proinflammatory cytokines and promote higher intestinal permeability.10 Similarly, high sugar consumption promotes increased intestinal permeability and shifts the gut microbiota to organisms that can rapidly utilize simple carbohydrates at the expense of other beneficial organisms, reducing bacterial diversity.15 The Western diet, which is notable for both high fat and high sugar content, is sometimes referred to as a proinflammatory diet and has been shown to worsen psoriasiformlike lesions in mice.16 Importantly, most research indicates that high fat and high sugar consumption appear to be more prevalent in psoriasis patients,8 but the type of fat consumed in the diet matters. The Western diet includes abundant saturated fat found in meat, dairy products, palm and coconut oils, and processed foods, as well as omega-6 fatty acids that are found in meat, poultry, and eggs. Saturated fat has been shown to promote helper T cell (TH17) accumulation in the skin, and omega-6 fatty acids serve as precursors to various inflammatory lipid mediators.4 This distinction of sources of fat between the Western diet and MeD is important in understanding the diets’ different effects on psoriasis and overall health. As previously discussed, the high intake of omega-3 acids in the MeD is one of the ways it may exert its anti-inflammatory benefits.7
Next Steps in Advising Psoriasis Patients
A major limitation of the data for MeD and vegan/vegetarian diets is limited randomized controlled trials evaluating the impact of these diets on psoriasis. Thus, dietary recommendations for psoriasis are not as strong as for other diseases for which more conclusive data exist.8 Although the data on diet and psoriasis are not definitive, perhaps dermatologists should shift the question from “Does this diet definitely improve psoriasis?” to “Does this diet definitely improve my patient’s health as a whole and maybe also their psoriasis?” For instance, the MeD has been shown to reduce the risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease as well as to slow cognitive decline.17 Vegan/vegetarian diets focusing on whole vs processed foods have been shown to be highly effective in combatting obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease including severe atherosclerosis, and hypertension.18 Psoriasis patients are at increased risk for many of the ailments that the MeD and plant-based diets protect against, making these diets potentially even more impactful than for someone without psoriasis.19 Dietary recommendations should still be made in conjunction with continuing traditional therapies for psoriasis and in consultation with the patient’s primary care physician and/or dietitian; however, rather than waiting for more randomized controlled trials before making health-promoting recommendations, what would be the downside of starting now? At worst, the dietary change decreases their risk for several metabolic conditions, and at best they may even see an improvement in their psoriasis.
- Naldi L, Chatenoud L, Linder D, et al. Cigarette smoking, body mass index, and stressful life events as risk factors for psoriasis: results from an Italian case–control study. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;125:61-67. doi:10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23681.x
- Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Dhillon JS, et al. Psoriasis and smoking: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:304-314. doi:10.1111/bjd.12670
- Zhu K, Zhu C, Fan Y. Alcohol consumption and psoriatic risk: a meta‐analysis of case–control studies. J Dermatol. 2012;39:770-773. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2012.01577.x
- Kanda N, Hoashi T, Saeki H. Nutrition and psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:5405. doi:10.3390/ijms21155405
- Afifi L, Danesh MJ, Lee KM, et al. Dietary behaviors in psoriasis: patient-reported outcomes from a U.S. national survey. Dermatol Ther. 2017;7:227-242. doi:10.1007/s13555-017-0183-4
- Ford AR, Siegel M, Bagel J, et al. Dietary recommendations for adults with psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis from the medical board of the National Psoriasis Foundation: a systematic review. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:934. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.1412
- Duchnik E, Kruk J, Tuchowska A, et al. The impact of diet and physical activity on psoriasis: a narrative review of the current evidence. Nutrients. 2023;15:840. doi:10.3390/nu15040840
- Chung M, Bartholomew E, Yeroushalmi S, et al. Dietary intervention and supplements in the management of psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis Targets Ther. 2022;12:151-176. doi:10.2147/PTT.S328581
- Mazza E, Ferro Y, Pujia R, et al. Mediterranean diet in healthy aging. J Nutr Health Aging. 2021;25:1076-1083. doi:10.1007/s12603-021-1675-6
- Flores-Balderas X, Peña-Peña M, Rada KM, et al. Beneficial effects of plant-based diets on skin health and inflammatory skin diseases. Nutrients. 2023;15:2842. doi:10.3390/nu15132842
- Bonjour M, Gabriel S, Valencia A, et al. Challenging case in clinical practice: prolonged water-only fasting followed by an exclusively whole-plant-food diet in the management of severe plaque psoriasis. Integr Complement Ther. 2022;28:85-87. doi:10.1089/ict.2022.29010.mbo
- Lewandowska M, Dunbar K, Kassam S. Managing psoriatic arthritis with a whole food plant-based diet: a case study. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2021;15:402-406. doi:10.1177/1559827621993435
- Neufingerl N, Eilander A. Nutrient intake and status in adults consuming plant-based diets compared to meat-eaters: a systematic review. Nutrients. 2021;14:29. doi:10.3390/nu14010029
- Dei-Cas I, Giliberto F, Luce L, et al. Metagenomic analysis of gut microbiota in non-treated plaque psoriasis patients stratified by disease severity: development of a new psoriasis-microbiome index. Sci Rep. 2020;10:12754. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-69537-3
- Satokari R. High intake of sugar and the balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory gut bacteria. Nutrients. 2020;12:1348. doi:10.3390/nu12051348
- Shi Z, Wu X, Santos Rocha C, et al. Short-term Western diet intake promotes IL-23–mediated skin and joint inflammation accompanied by changes to the gut microbiota in mice. J Invest Dermatol. 2021;141:1780-1791. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2020.11.032
- Romagnolo DF, Selmin OI. Mediterranean diet and prevention of chronic diseases. Nutr Today. 2017;52:208-222. doi:10.1097/NT.0000000000000228
- Tuso PJ, Ismail MH, Ha BP, et al. Nutritional update for physicians: plant-based diets. Perm J. 2013;17:61-66. doi:10.7812/TPP/12-085
- Parisi R, Symmons DPM, Griffiths CEM, et al. Global epidemiology of psoriasis: a systematic review of incidence and prevalence. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:377-385. doi:10.1038/jid.2012.339
- Naldi L, Chatenoud L, Linder D, et al. Cigarette smoking, body mass index, and stressful life events as risk factors for psoriasis: results from an Italian case–control study. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;125:61-67. doi:10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23681.x
- Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Dhillon JS, et al. Psoriasis and smoking: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:304-314. doi:10.1111/bjd.12670
- Zhu K, Zhu C, Fan Y. Alcohol consumption and psoriatic risk: a meta‐analysis of case–control studies. J Dermatol. 2012;39:770-773. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2012.01577.x
- Kanda N, Hoashi T, Saeki H. Nutrition and psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:5405. doi:10.3390/ijms21155405
- Afifi L, Danesh MJ, Lee KM, et al. Dietary behaviors in psoriasis: patient-reported outcomes from a U.S. national survey. Dermatol Ther. 2017;7:227-242. doi:10.1007/s13555-017-0183-4
- Ford AR, Siegel M, Bagel J, et al. Dietary recommendations for adults with psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis from the medical board of the National Psoriasis Foundation: a systematic review. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:934. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.1412
- Duchnik E, Kruk J, Tuchowska A, et al. The impact of diet and physical activity on psoriasis: a narrative review of the current evidence. Nutrients. 2023;15:840. doi:10.3390/nu15040840
- Chung M, Bartholomew E, Yeroushalmi S, et al. Dietary intervention and supplements in the management of psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis Targets Ther. 2022;12:151-176. doi:10.2147/PTT.S328581
- Mazza E, Ferro Y, Pujia R, et al. Mediterranean diet in healthy aging. J Nutr Health Aging. 2021;25:1076-1083. doi:10.1007/s12603-021-1675-6
- Flores-Balderas X, Peña-Peña M, Rada KM, et al. Beneficial effects of plant-based diets on skin health and inflammatory skin diseases. Nutrients. 2023;15:2842. doi:10.3390/nu15132842
- Bonjour M, Gabriel S, Valencia A, et al. Challenging case in clinical practice: prolonged water-only fasting followed by an exclusively whole-plant-food diet in the management of severe plaque psoriasis. Integr Complement Ther. 2022;28:85-87. doi:10.1089/ict.2022.29010.mbo
- Lewandowska M, Dunbar K, Kassam S. Managing psoriatic arthritis with a whole food plant-based diet: a case study. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2021;15:402-406. doi:10.1177/1559827621993435
- Neufingerl N, Eilander A. Nutrient intake and status in adults consuming plant-based diets compared to meat-eaters: a systematic review. Nutrients. 2021;14:29. doi:10.3390/nu14010029
- Dei-Cas I, Giliberto F, Luce L, et al. Metagenomic analysis of gut microbiota in non-treated plaque psoriasis patients stratified by disease severity: development of a new psoriasis-microbiome index. Sci Rep. 2020;10:12754. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-69537-3
- Satokari R. High intake of sugar and the balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory gut bacteria. Nutrients. 2020;12:1348. doi:10.3390/nu12051348
- Shi Z, Wu X, Santos Rocha C, et al. Short-term Western diet intake promotes IL-23–mediated skin and joint inflammation accompanied by changes to the gut microbiota in mice. J Invest Dermatol. 2021;141:1780-1791. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2020.11.032
- Romagnolo DF, Selmin OI. Mediterranean diet and prevention of chronic diseases. Nutr Today. 2017;52:208-222. doi:10.1097/NT.0000000000000228
- Tuso PJ, Ismail MH, Ha BP, et al. Nutritional update for physicians: plant-based diets. Perm J. 2013;17:61-66. doi:10.7812/TPP/12-085
- Parisi R, Symmons DPM, Griffiths CEM, et al. Global epidemiology of psoriasis: a systematic review of incidence and prevalence. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:377-385. doi:10.1038/jid.2012.339
Practice Points
- Psoriasis is affected by lifestyle factors such as diet, which is an area of interest for many patients.
- Low-calorie diets are strongly recommended for overweight/obese patients with psoriasis to improve their disease.
- Changes in dietary patterns, such as adopting a Mediterranean diet or a plant-based diet, also have shown promise.
Navigating Psoriasis Treatment Innovations
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that affects approximately 2% to 4% of the US population and notably impacts overall quality of life.1,2 There is no cure for this long-lasting condition. Fortunately, recent developments in research have led to more targeted therapies, paving the way for a more promising transformative landscape of psoriasis management. Herein, we explore the most up-to-date advancements and developments in the realm of psoriasis care.
Emerging Systemic Therapies
Biologics are cutting-edge treatments available for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, as IL-17A, IL-23, and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) have been recognized as key targets.3
IL-17—Bimekizumab is a unique monoclonal antibody that inhibits the activity of both IL-17A and IL-17F cytokines.3 This treatment was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in October 2023 for patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy.4
Bimekizumab outperformed ustekinumab in the BE VIVID phase 3 trial, with 273 of 321 patients (85%) receiving bimekizumab vs 81 of 163 patients (50%) receiving ustekinumab experiencing at least 90% improvement in psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) score at week 16.4 In a 2020 observational study (PSO-BIO-REAL), the efficacy rate of skin clearance after 6 months of treatment with biologics was only 25% (1/4).5 Aside from moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, bimekizumab demonstrated notable improvement in patients with psoriatic arthritis who had inadequate response or intolerance to TNF-α inhibitors compared to a placebo group in the BE COMPLETE phase 3 trial.6
IL-23—Guselkumab, risankizumab, and tildrakizumab are injectable therapies approved by the FDA in 2017 for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.3 They inhibit IL-23 signaling by targeting the p19 subunit in addition to sparing IL-12.3,7
A novel oral therapeutic peptide, JNJ-2113—the first oral IL-23 receptor antagonist peptide that blocks IL-23 signaling—has been developed, offering a new way to treat moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. Trial results from a phase 2 study (FRONTIER1) have supported JNJ-2113’s advancement into phase 3.7,8 Patients who received JNJ-2113 successfully achieved PASI75 in addition to surpassing PASI90 and PASI100 at greater proportions compared to placebo at week 16.7
The promising early results of JNJ-2113 provide patients with greater flexibility and convenience for treatment options to address the manifestations of psoriasis. Although a considerable number of patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis qualify for advanced therapies, a substantial proportion remain untreated. Introducing an oral route of medication administration may help overcome barriers to therapy access due to a greater preference for pills over injections.9
TNF-α Inhibitors—Adalimumab is a TNF-α inhibitor that is used to treat moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis in adults who are candidates for systemic phototherapy.1,10 However, one of the main barriers to initiating treatment has been cost. Biosimilars contribute to market competition, thus allowing the possibility of lower drug prices.10
There are 9 FDA-approved biosimilar products for adalimumab, with 2 having interchangeable designation. The first interchangeable biosimilar to enter the US market, adalimumab-adbm, became available in July 2023. In October 2023, adalimumab-afzb was granted interchangeable designation,11 which enables pharmacists to swiftly substitute brand products for lower-cost biosimilars, providing patients with equally safe and effective alternatives without the delay of involving the prescribing clinician.12 Pricing information indicates an initial 5% discount, which may later increase to 60%, from brand name adalimumab. Hopefully, reduced drug costs due to market competition will allow more patients to overcome barriers to therapy access.
IL-12/IL-23—Ustekinumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets IL-12 and IL-23. The FDA recently approved ustekinumab-auub as the first interchangeable ustekinumab biosimilar for the treatment of various inflammatory diseases, including moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.12,13 The approval of ustekinumab-auub expands therapeutic options for the treatment of diverse inflammatory diseases. As the first interchangeable biosimilar in its category, this development underscores the importance of biosimilars in providing effective and accessible treatment.12,14
Topical Innovations
In October 2023, the FDA approved an expanded indication for roflumilast cream 0.3% to treat children as young as 6 years for plaque psoriasis, even for use in intertriginous areas,15 which is a milestone given the lack of treatment options for the pediatric population because topical steroids, the most common treatment option for plaque psoriasis, can have safety concerns related to long-term use. With the advent of this steroid-free topical agent, pediatric patients have a safe and well-tolerated option for managing plaque psoriasis.16 This promising effort will now expand to trials in children as young as 2 years to test efficacy.16
Engel et al17 proposed a new algorithmic approach to the topical management of psoriasis with roflumilast cream and tapinarof cream as first-line treatments for mild disease due to their novelty in treating intertriginous areas, whereas traditional topical steroids in these areas would be inapt.17 The latest indication for roflumilast cream suggests that this proposed recommendation could be a promising and convenient enhancement to psoriasis management, potentially outperforming traditional topical corticosteroids.15,17
Final Thoughts
Innovative targeted therapies ranging from new biologic agents to broader applications of topical treatments hold the potential to transform conventional psoriasis management with greater efficacy and safety, which can help create a more effective and personalized approach with greater patient satisfaction, ultimately enhancing overall quality of life. The choice of treatment is dependent not only on the severity of the disease but also on accessibility considerations such as cost. Overall, these innovative therapies add substantial value to the treatment armamentarium for psoriasis.
- Li C, Sunhe Y, Zhou H, Dong W. Efficacy and safety evaluations of adalimumab biosimilars in the treatment of psoriasis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2023;34:2249145. doi:10.1080/09546634.2023.2249145
- Liu J, Thatiparthi A, Martin A, et al. Association between psoriasis and thyroid dysfunction among US adults in the 2009-2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey [published online Mary 17, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:897-899. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.03.030
- Lee EB, Amin M, Bhutani T, et al. Emerging therapies in psoriasis: a systematic review. Cutis. 2018;101(3S):5-9.
- Reich K, Papp KA, Blauvelt A, et al. Bimekizumab versus ustekinumab for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis (BE VIVID): efficacy and safety from a 52-week, multicentre, double-blind, active comparator and placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;397:487-498. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00125-2
- Seneschal J, Lacour JP, Bewley A, et al. A multinational, prospective, observational study to estimate complete skin clearance in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque PSOriasis treated with BIOlogics in a REAL world setting (PSO-BIO-REAL) [published online June 8, 2020]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:2566-2573. doi:10.1111/jdv.16568
- Merola JF, Landewé R, McInnes IB, et al. Bimekizumab in patients with active psoriatic arthritis and previous inadequate response or intolerance to tumour necrosis factor-α inhibitors: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial (BE COMPLETE)[published online December 6, 2022]. Lancet. 2023;401:38-48. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02303-0
- Janssen announces positive topline results for JNJ-2113—a novel, first and only oral IL-23 receptor antagonist peptide in development for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. News release. Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies; July 4, 2023.
- Bissonnette R, Pinter A, Ferris L, et al. A Phase 2, randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study of oral JNJ-77242113 for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: FRONTIER 1. Abstract presented at: World Congress of Dermatology, July 3-8, 2023; Singapore.
- Xu Y, Sudharshan L, Hsu MA, et al. Patient preferences associated with therapies for psoriatic arthritis: a conjoint analysis. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2018;11:408-417.
- Maurelli M, Girolomoni G, Gisondi P. Cost per responder of adalimumab biosimilars versus methotrexate in patients with psoriasis: a real-life experience. J Dermatolog Treat. 2023;34:2218504. doi:10.1080/09546634.2023.2218504
- Food and Drug Administration/Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Expiration of first interchangeable exclusivity (“FIE”) when section 351(l)(6) litigation ends prior to the submission of an application for interchangeability [memorandum]. Published October 3, 2023. Accessed January 18, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/media/173749/download
- US Food & Drug Administration. Biosimilar and interchangeable biologics: more treatment choices. Accessed January 18, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/biosimilar-and-interchangeable-biologics-more-treatment-choices
- Chow V, Mytych DT, Das S, et al. Pharmacokinetic similarity of ABP 654, an ustekinumab biosimilar candidate: results from a randomized, double-blind study in healthy subjects [published online July 7, 2023]. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2023;12:863-873. doi:10.1002/cpdd.1301
- Wezlana (ustekinumab-auub) [prescribing information]. Published October 2023. Accessed January 18, 2024. www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2023/761285s000,761331s000lbl.pdf
- ZORYVE (roflumilast) topical cream [prescribing information]. Westlake Village, CA: Arcutis Biotherapeutics. Revised October 2023. Accessed January 18, 2024. https://www.arcutis.com/wp-content/uploads/USPI-roflumilast-cream.pdf
- Lie E, Choi M, Wang SP, et al. Topical management of pediatric psoriasis: a review of new developments and existing therapies. Paediatr Drugs. 2024;26:9-18. doi:10.1007/s40272-023-00592-9
- Engel PV, Smith B, Javadi SS, et al. It is time to consider anew topical algorithm for psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023:S0190-9622(23)02906-7. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.07.1048
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that affects approximately 2% to 4% of the US population and notably impacts overall quality of life.1,2 There is no cure for this long-lasting condition. Fortunately, recent developments in research have led to more targeted therapies, paving the way for a more promising transformative landscape of psoriasis management. Herein, we explore the most up-to-date advancements and developments in the realm of psoriasis care.
Emerging Systemic Therapies
Biologics are cutting-edge treatments available for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, as IL-17A, IL-23, and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) have been recognized as key targets.3
IL-17—Bimekizumab is a unique monoclonal antibody that inhibits the activity of both IL-17A and IL-17F cytokines.3 This treatment was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in October 2023 for patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy.4
Bimekizumab outperformed ustekinumab in the BE VIVID phase 3 trial, with 273 of 321 patients (85%) receiving bimekizumab vs 81 of 163 patients (50%) receiving ustekinumab experiencing at least 90% improvement in psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) score at week 16.4 In a 2020 observational study (PSO-BIO-REAL), the efficacy rate of skin clearance after 6 months of treatment with biologics was only 25% (1/4).5 Aside from moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, bimekizumab demonstrated notable improvement in patients with psoriatic arthritis who had inadequate response or intolerance to TNF-α inhibitors compared to a placebo group in the BE COMPLETE phase 3 trial.6
IL-23—Guselkumab, risankizumab, and tildrakizumab are injectable therapies approved by the FDA in 2017 for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.3 They inhibit IL-23 signaling by targeting the p19 subunit in addition to sparing IL-12.3,7
A novel oral therapeutic peptide, JNJ-2113—the first oral IL-23 receptor antagonist peptide that blocks IL-23 signaling—has been developed, offering a new way to treat moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. Trial results from a phase 2 study (FRONTIER1) have supported JNJ-2113’s advancement into phase 3.7,8 Patients who received JNJ-2113 successfully achieved PASI75 in addition to surpassing PASI90 and PASI100 at greater proportions compared to placebo at week 16.7
The promising early results of JNJ-2113 provide patients with greater flexibility and convenience for treatment options to address the manifestations of psoriasis. Although a considerable number of patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis qualify for advanced therapies, a substantial proportion remain untreated. Introducing an oral route of medication administration may help overcome barriers to therapy access due to a greater preference for pills over injections.9
TNF-α Inhibitors—Adalimumab is a TNF-α inhibitor that is used to treat moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis in adults who are candidates for systemic phototherapy.1,10 However, one of the main barriers to initiating treatment has been cost. Biosimilars contribute to market competition, thus allowing the possibility of lower drug prices.10
There are 9 FDA-approved biosimilar products for adalimumab, with 2 having interchangeable designation. The first interchangeable biosimilar to enter the US market, adalimumab-adbm, became available in July 2023. In October 2023, adalimumab-afzb was granted interchangeable designation,11 which enables pharmacists to swiftly substitute brand products for lower-cost biosimilars, providing patients with equally safe and effective alternatives without the delay of involving the prescribing clinician.12 Pricing information indicates an initial 5% discount, which may later increase to 60%, from brand name adalimumab. Hopefully, reduced drug costs due to market competition will allow more patients to overcome barriers to therapy access.
IL-12/IL-23—Ustekinumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets IL-12 and IL-23. The FDA recently approved ustekinumab-auub as the first interchangeable ustekinumab biosimilar for the treatment of various inflammatory diseases, including moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.12,13 The approval of ustekinumab-auub expands therapeutic options for the treatment of diverse inflammatory diseases. As the first interchangeable biosimilar in its category, this development underscores the importance of biosimilars in providing effective and accessible treatment.12,14
Topical Innovations
In October 2023, the FDA approved an expanded indication for roflumilast cream 0.3% to treat children as young as 6 years for plaque psoriasis, even for use in intertriginous areas,15 which is a milestone given the lack of treatment options for the pediatric population because topical steroids, the most common treatment option for plaque psoriasis, can have safety concerns related to long-term use. With the advent of this steroid-free topical agent, pediatric patients have a safe and well-tolerated option for managing plaque psoriasis.16 This promising effort will now expand to trials in children as young as 2 years to test efficacy.16
Engel et al17 proposed a new algorithmic approach to the topical management of psoriasis with roflumilast cream and tapinarof cream as first-line treatments for mild disease due to their novelty in treating intertriginous areas, whereas traditional topical steroids in these areas would be inapt.17 The latest indication for roflumilast cream suggests that this proposed recommendation could be a promising and convenient enhancement to psoriasis management, potentially outperforming traditional topical corticosteroids.15,17
Final Thoughts
Innovative targeted therapies ranging from new biologic agents to broader applications of topical treatments hold the potential to transform conventional psoriasis management with greater efficacy and safety, which can help create a more effective and personalized approach with greater patient satisfaction, ultimately enhancing overall quality of life. The choice of treatment is dependent not only on the severity of the disease but also on accessibility considerations such as cost. Overall, these innovative therapies add substantial value to the treatment armamentarium for psoriasis.
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that affects approximately 2% to 4% of the US population and notably impacts overall quality of life.1,2 There is no cure for this long-lasting condition. Fortunately, recent developments in research have led to more targeted therapies, paving the way for a more promising transformative landscape of psoriasis management. Herein, we explore the most up-to-date advancements and developments in the realm of psoriasis care.
Emerging Systemic Therapies
Biologics are cutting-edge treatments available for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, as IL-17A, IL-23, and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) have been recognized as key targets.3
IL-17—Bimekizumab is a unique monoclonal antibody that inhibits the activity of both IL-17A and IL-17F cytokines.3 This treatment was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in October 2023 for patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy.4
Bimekizumab outperformed ustekinumab in the BE VIVID phase 3 trial, with 273 of 321 patients (85%) receiving bimekizumab vs 81 of 163 patients (50%) receiving ustekinumab experiencing at least 90% improvement in psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) score at week 16.4 In a 2020 observational study (PSO-BIO-REAL), the efficacy rate of skin clearance after 6 months of treatment with biologics was only 25% (1/4).5 Aside from moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, bimekizumab demonstrated notable improvement in patients with psoriatic arthritis who had inadequate response or intolerance to TNF-α inhibitors compared to a placebo group in the BE COMPLETE phase 3 trial.6
IL-23—Guselkumab, risankizumab, and tildrakizumab are injectable therapies approved by the FDA in 2017 for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.3 They inhibit IL-23 signaling by targeting the p19 subunit in addition to sparing IL-12.3,7
A novel oral therapeutic peptide, JNJ-2113—the first oral IL-23 receptor antagonist peptide that blocks IL-23 signaling—has been developed, offering a new way to treat moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. Trial results from a phase 2 study (FRONTIER1) have supported JNJ-2113’s advancement into phase 3.7,8 Patients who received JNJ-2113 successfully achieved PASI75 in addition to surpassing PASI90 and PASI100 at greater proportions compared to placebo at week 16.7
The promising early results of JNJ-2113 provide patients with greater flexibility and convenience for treatment options to address the manifestations of psoriasis. Although a considerable number of patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis qualify for advanced therapies, a substantial proportion remain untreated. Introducing an oral route of medication administration may help overcome barriers to therapy access due to a greater preference for pills over injections.9
TNF-α Inhibitors—Adalimumab is a TNF-α inhibitor that is used to treat moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis in adults who are candidates for systemic phototherapy.1,10 However, one of the main barriers to initiating treatment has been cost. Biosimilars contribute to market competition, thus allowing the possibility of lower drug prices.10
There are 9 FDA-approved biosimilar products for adalimumab, with 2 having interchangeable designation. The first interchangeable biosimilar to enter the US market, adalimumab-adbm, became available in July 2023. In October 2023, adalimumab-afzb was granted interchangeable designation,11 which enables pharmacists to swiftly substitute brand products for lower-cost biosimilars, providing patients with equally safe and effective alternatives without the delay of involving the prescribing clinician.12 Pricing information indicates an initial 5% discount, which may later increase to 60%, from brand name adalimumab. Hopefully, reduced drug costs due to market competition will allow more patients to overcome barriers to therapy access.
IL-12/IL-23—Ustekinumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets IL-12 and IL-23. The FDA recently approved ustekinumab-auub as the first interchangeable ustekinumab biosimilar for the treatment of various inflammatory diseases, including moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.12,13 The approval of ustekinumab-auub expands therapeutic options for the treatment of diverse inflammatory diseases. As the first interchangeable biosimilar in its category, this development underscores the importance of biosimilars in providing effective and accessible treatment.12,14
Topical Innovations
In October 2023, the FDA approved an expanded indication for roflumilast cream 0.3% to treat children as young as 6 years for plaque psoriasis, even for use in intertriginous areas,15 which is a milestone given the lack of treatment options for the pediatric population because topical steroids, the most common treatment option for plaque psoriasis, can have safety concerns related to long-term use. With the advent of this steroid-free topical agent, pediatric patients have a safe and well-tolerated option for managing plaque psoriasis.16 This promising effort will now expand to trials in children as young as 2 years to test efficacy.16
Engel et al17 proposed a new algorithmic approach to the topical management of psoriasis with roflumilast cream and tapinarof cream as first-line treatments for mild disease due to their novelty in treating intertriginous areas, whereas traditional topical steroids in these areas would be inapt.17 The latest indication for roflumilast cream suggests that this proposed recommendation could be a promising and convenient enhancement to psoriasis management, potentially outperforming traditional topical corticosteroids.15,17
Final Thoughts
Innovative targeted therapies ranging from new biologic agents to broader applications of topical treatments hold the potential to transform conventional psoriasis management with greater efficacy and safety, which can help create a more effective and personalized approach with greater patient satisfaction, ultimately enhancing overall quality of life. The choice of treatment is dependent not only on the severity of the disease but also on accessibility considerations such as cost. Overall, these innovative therapies add substantial value to the treatment armamentarium for psoriasis.
- Li C, Sunhe Y, Zhou H, Dong W. Efficacy and safety evaluations of adalimumab biosimilars in the treatment of psoriasis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2023;34:2249145. doi:10.1080/09546634.2023.2249145
- Liu J, Thatiparthi A, Martin A, et al. Association between psoriasis and thyroid dysfunction among US adults in the 2009-2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey [published online Mary 17, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:897-899. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.03.030
- Lee EB, Amin M, Bhutani T, et al. Emerging therapies in psoriasis: a systematic review. Cutis. 2018;101(3S):5-9.
- Reich K, Papp KA, Blauvelt A, et al. Bimekizumab versus ustekinumab for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis (BE VIVID): efficacy and safety from a 52-week, multicentre, double-blind, active comparator and placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;397:487-498. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00125-2
- Seneschal J, Lacour JP, Bewley A, et al. A multinational, prospective, observational study to estimate complete skin clearance in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque PSOriasis treated with BIOlogics in a REAL world setting (PSO-BIO-REAL) [published online June 8, 2020]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:2566-2573. doi:10.1111/jdv.16568
- Merola JF, Landewé R, McInnes IB, et al. Bimekizumab in patients with active psoriatic arthritis and previous inadequate response or intolerance to tumour necrosis factor-α inhibitors: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial (BE COMPLETE)[published online December 6, 2022]. Lancet. 2023;401:38-48. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02303-0
- Janssen announces positive topline results for JNJ-2113—a novel, first and only oral IL-23 receptor antagonist peptide in development for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. News release. Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies; July 4, 2023.
- Bissonnette R, Pinter A, Ferris L, et al. A Phase 2, randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study of oral JNJ-77242113 for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: FRONTIER 1. Abstract presented at: World Congress of Dermatology, July 3-8, 2023; Singapore.
- Xu Y, Sudharshan L, Hsu MA, et al. Patient preferences associated with therapies for psoriatic arthritis: a conjoint analysis. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2018;11:408-417.
- Maurelli M, Girolomoni G, Gisondi P. Cost per responder of adalimumab biosimilars versus methotrexate in patients with psoriasis: a real-life experience. J Dermatolog Treat. 2023;34:2218504. doi:10.1080/09546634.2023.2218504
- Food and Drug Administration/Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Expiration of first interchangeable exclusivity (“FIE”) when section 351(l)(6) litigation ends prior to the submission of an application for interchangeability [memorandum]. Published October 3, 2023. Accessed January 18, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/media/173749/download
- US Food & Drug Administration. Biosimilar and interchangeable biologics: more treatment choices. Accessed January 18, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/biosimilar-and-interchangeable-biologics-more-treatment-choices
- Chow V, Mytych DT, Das S, et al. Pharmacokinetic similarity of ABP 654, an ustekinumab biosimilar candidate: results from a randomized, double-blind study in healthy subjects [published online July 7, 2023]. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2023;12:863-873. doi:10.1002/cpdd.1301
- Wezlana (ustekinumab-auub) [prescribing information]. Published October 2023. Accessed January 18, 2024. www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2023/761285s000,761331s000lbl.pdf
- ZORYVE (roflumilast) topical cream [prescribing information]. Westlake Village, CA: Arcutis Biotherapeutics. Revised October 2023. Accessed January 18, 2024. https://www.arcutis.com/wp-content/uploads/USPI-roflumilast-cream.pdf
- Lie E, Choi M, Wang SP, et al. Topical management of pediatric psoriasis: a review of new developments and existing therapies. Paediatr Drugs. 2024;26:9-18. doi:10.1007/s40272-023-00592-9
- Engel PV, Smith B, Javadi SS, et al. It is time to consider anew topical algorithm for psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023:S0190-9622(23)02906-7. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.07.1048
- Li C, Sunhe Y, Zhou H, Dong W. Efficacy and safety evaluations of adalimumab biosimilars in the treatment of psoriasis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2023;34:2249145. doi:10.1080/09546634.2023.2249145
- Liu J, Thatiparthi A, Martin A, et al. Association between psoriasis and thyroid dysfunction among US adults in the 2009-2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey [published online Mary 17, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:897-899. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.03.030
- Lee EB, Amin M, Bhutani T, et al. Emerging therapies in psoriasis: a systematic review. Cutis. 2018;101(3S):5-9.
- Reich K, Papp KA, Blauvelt A, et al. Bimekizumab versus ustekinumab for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis (BE VIVID): efficacy and safety from a 52-week, multicentre, double-blind, active comparator and placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;397:487-498. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00125-2
- Seneschal J, Lacour JP, Bewley A, et al. A multinational, prospective, observational study to estimate complete skin clearance in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque PSOriasis treated with BIOlogics in a REAL world setting (PSO-BIO-REAL) [published online June 8, 2020]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:2566-2573. doi:10.1111/jdv.16568
- Merola JF, Landewé R, McInnes IB, et al. Bimekizumab in patients with active psoriatic arthritis and previous inadequate response or intolerance to tumour necrosis factor-α inhibitors: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial (BE COMPLETE)[published online December 6, 2022]. Lancet. 2023;401:38-48. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02303-0
- Janssen announces positive topline results for JNJ-2113—a novel, first and only oral IL-23 receptor antagonist peptide in development for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. News release. Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies; July 4, 2023.
- Bissonnette R, Pinter A, Ferris L, et al. A Phase 2, randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study of oral JNJ-77242113 for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: FRONTIER 1. Abstract presented at: World Congress of Dermatology, July 3-8, 2023; Singapore.
- Xu Y, Sudharshan L, Hsu MA, et al. Patient preferences associated with therapies for psoriatic arthritis: a conjoint analysis. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2018;11:408-417.
- Maurelli M, Girolomoni G, Gisondi P. Cost per responder of adalimumab biosimilars versus methotrexate in patients with psoriasis: a real-life experience. J Dermatolog Treat. 2023;34:2218504. doi:10.1080/09546634.2023.2218504
- Food and Drug Administration/Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Expiration of first interchangeable exclusivity (“FIE”) when section 351(l)(6) litigation ends prior to the submission of an application for interchangeability [memorandum]. Published October 3, 2023. Accessed January 18, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/media/173749/download
- US Food & Drug Administration. Biosimilar and interchangeable biologics: more treatment choices. Accessed January 18, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/biosimilar-and-interchangeable-biologics-more-treatment-choices
- Chow V, Mytych DT, Das S, et al. Pharmacokinetic similarity of ABP 654, an ustekinumab biosimilar candidate: results from a randomized, double-blind study in healthy subjects [published online July 7, 2023]. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2023;12:863-873. doi:10.1002/cpdd.1301
- Wezlana (ustekinumab-auub) [prescribing information]. Published October 2023. Accessed January 18, 2024. www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2023/761285s000,761331s000lbl.pdf
- ZORYVE (roflumilast) topical cream [prescribing information]. Westlake Village, CA: Arcutis Biotherapeutics. Revised October 2023. Accessed January 18, 2024. https://www.arcutis.com/wp-content/uploads/USPI-roflumilast-cream.pdf
- Lie E, Choi M, Wang SP, et al. Topical management of pediatric psoriasis: a review of new developments and existing therapies. Paediatr Drugs. 2024;26:9-18. doi:10.1007/s40272-023-00592-9
- Engel PV, Smith B, Javadi SS, et al. It is time to consider anew topical algorithm for psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023:S0190-9622(23)02906-7. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.07.1048
Impact of Ketogenic and Low-Glycemic Diets on Inflammatory Skin Conditions
Inflammatory skin conditions often have a relapsing and remitting course and represent a large proportion of chronic skin diseases. Common inflammatory skin disorders include acne, psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), atopic dermatitis (AD), and seborrheic dermatitis (SD).1 Although each of these conditions has a unique pathogenesis, they all are driven by a background of chronic inflammation. It has been reported that diets with high levels of refined carbohydrates and saturated or trans-fatty acids may exacerbate existing inflammation.2 Consequently, dietary interventions, such as the ketogenic and low-glycemic diets, have potential anti-inflammatory and metabolic effects that are being assessed as stand-alone or adjunctive therapies for dermatologic diseases.
Diet may partially influence systemic inflammation through its effect on weight. Higher body mass index and obesity are linked to a low-grade inflammatory state and higher levels of circulating inflammatory markers. Therefore, weight loss leads to decreases in inflammatory cytokines, including C-reactive protein, tumor necrosis factor α, and IL-6.3 These cytokines and metabolic effects overlap with inflammatory skin condition pathways. It also is posited that decreased insulin release associated with weight loss results in decreased sebaceous lipogenesis and androgens, which drive keratinocyte proliferation and acne development.4,5 For instance, in a 2015 meta-analysis of 5 randomized controlled trials on psoriasis, patients in the weight loss intervention group had more substantial reductions in psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) scores compared with controls receiving usual care (P=.004).6 However, in a systematic review of 35 studies on acne vulgaris, overweight and obese patients (defined by a body mass index of ≥23 kg/m2) had similar odds of having acne compared with normal-weight individuals (P=.671).7
Similar to weight loss, ketogenesis acts as a negative feedback mechanism to reduce insulin release, leading to decreased inflammation and androgens that often exacerbate inflammatory skin diseases.8 Ketogenesis ensues when daily carbohydrate intake is limited to less than 50 g, and long-term adherence to a ketogenic diet results in metabolic reliance on ketone bodies such as acetoacetate, β-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone.9 These metabolites may decrease free radical damage and consequently improve signs and symptoms of acne, psoriasis, and other inflammatory skin diseases.10-12 Similarly, increased ketones also may decrease activation of the NLRP3 (NOD-, LRR-, and Pyrin domain-containing protein 3) inflammasome and therefore reduce inflammatory markers such as IL-1β and IL-1.4,13 Several proposed mechanisms are outlined in the Table.

Collectively, low-glycemic and ketogenic diets have been proposed as potential interventions for reducing inflammatory skin conditions. These dietary approaches are hypothesized to exert their effects by facilitating weight loss, elevating ketone levels, and reducing systemic inflammation. The current review summarizes the existing evidence on ketogenic and low-glycemic diets as treatments for inflammatory skin conditions and evaluates the potential benefits of these dietary interventions in managing and improving outcomes for individuals with inflammatory skin conditions.
Methods
Using PubMed for articles indexed for MEDLINE and Google Scholar, a review of the literature was conducted with a combination of the following search terms: low-glycemic diet, inflammatory, dermatologic, ketogenic diet, inflammation, dermatology, acne, psoriasis, eczema, seborrheic dermatitis, and hidradenitis suppurativa. Reference citations in identified works also were reviewed. Interventional (experimental studies or clinical trials), survey-based, and observational studies that investigated the effects of low-glycemic or ketogenic diets for the treatment of inflammatory skin conditions were included. Inclusion criteria were studies assessing acne, psoriasis, SD, AD, and HS. Exclusion criteria were studies published before 1965; those written in languages other than English; and those analyzing other diets, such as the Mediterranean or low-fat diets. The search yielded a total of 11 observational studies and 4 controlled studies published between 1966 and January 2023. Because this analysis utilized publicly available data and did not qualify as human subject research, institutional review board approval was not required.
Results
Acne Vulgaris—Acne vulgaris is a disease of chronic pilosebaceous inflammation and follicular epithelial proliferation associated with Propionibacterium acnes. The association between acne and low-glycemic diets has been examined in several studies. Diet quality is measured and assessed using the glycemic index (GI), which is the effect of a single food on postprandial blood glucose, and the glycemic load, which is the GI adjusted for carbohydrates per serving.14 High levels of GI and glycemic load are associated with hyperinsulinemia and an increase in insulinlike growth factor 1 concentration that promotes
Six survey-based studies evaluated sugar intake in patients with acne compared to healthy matched controls (eTable). Among these studies, 5 reported higher glycemic loads or daily sugar intake in acne patients compared to individuals without acne.12,19,20,26,28 The remaining study was conducted in 1967 and enrolled 16 acne patients and 32 matched controls. It reported no significant difference in sugar intake between the groups (P>.05).17

Smith et al18 randomized 43 male patients aged 15 to 25 years with facial acne into 2 cohorts for 12 weeks, each consuming either a low-glycemic diet (25% protein, 45% low-glycemic food [fruits, whole grains], and 30% fat) or a carbohydrate-dense diet of foods with medium to high GI based on prior documentation of the original diet. Patients were instructed to use a noncomedogenic cleanser as their only acne treatment. At 12 weeks, patients consuming the low-glycemic diet had an average of 23.5 fewer inflammatory lesions, while those in the intervention group had 12.0 fewer lesions (P=.03).18
In another controlled study by Kwon et al,21 32 male and female acne patients were randomized to a low-glycemic diet (25% protein, 45% low-glycemic food, and 30% fat) or a standard diet for 10 weeks. Patients on the low-glycemic diet experienced a 70.9% reduction in inflammatory lesions (P<.05). Hematoxylin and eosin staining and image analysis were performed to measure sebaceous gland surface area in the low-glycemic diet group, which decreased from 0.32 to 0.24 mm2 (P=.03). The sebaceous gland surface area in the control group was not reported. Moreover, patients on the low-glycemic diet had reduced IL-8 immunohistochemical staining (decreasing from 2.9 to 1.7 [P=.03]) and sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 levels (decreasing from 2.6 to 1.3 [P=.03]), suggesting suppression of ongoing inflammation. Patients on the low-glycemic diet had no significant difference in transforming growth factor β1(P=.83). In the control group, there was no difference in IL-8, sterol regulatory element binding protein 1, or transforming growth factor β1 (P>.05) on immunohistochemical staining.21
Psoriasis—Psoriasis is a systemic inflammatory disease characterized by hyperproliferation and aberrant keratinocyte plaque formation. The innate immune response of keratinocytes in response to epidermal damage or infection begins with neutrophil recruitment and dendritic cell activation. Dendritic cell secretion of IL-23 promotes T-cell differentiation into helper T cells (TH1) that subsequently secrete IL-17 and IL-22, thereby stimulating keratinocyte proliferation and eventual plaque formation. The relationship between diet and psoriasis is poorly understood; however, hyperinsulinemia is associated with greater severity of psoriasis.31
Four observational studies examined sugar intake in psoriasis patients. Barrea et al23 conducted a survey-based study of 82 male participants (41 with psoriasis and 41 healthy controls), reporting that PASI score was correlated with intake of simple carbohydrates (percentage of total kilocalorie)(r=0.564, P<.001). Another study by Yamashita et al27 found higher sugar intake in psoriasis patients than controls (P=.003) based on surveys from 70 patients with psoriasis and 70 matched healthy controls.
These findings contrast with 2 survey-based studies by Johnson et al22 and Afifi et al25 of sugar intake in psoriasis patients using the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Johnson et al22 reported reduced sugar intake among 156 psoriasis patients compared with 6104 unmatched controls (odds ratio, 0.998; CI, 0.996-1 [P=.04]) from 2003 to 2006. Similarly, Afifi et al25 reported decreased sugar intake in 1206 psoriasis patients compared with sex- and age-matched controls (P<.0001) in 2009 and 2010. When patients were asked about dietary triggers, 13.8% of psoriasis patients reported sugar as the most common trigger, which was more frequent than alcohol (13.6%), gluten (7.2%), and dairy (6%).25
Castaldo et al29,30 published 2 nonrandomized clinical intervention studies in 2020 and 2021 evaluating the impact of the ketogenic diet on psoriasis. In the first study, 37 psoriasis patients followed a 10-week diet consisting of 4 weeks on a ketogenic diet (500 kcal/d) followed by 6 weeks on a low-caloric Mediterranean diet.29 At the end of the intervention, there was a 17.4% reduction in PASI score, a 33.2-point reduction in itch severity score, and a 13.4-point reduction in the dermatology life quality index score; however, this study did not include a control diet group for comparison.29 The second study included 30 psoriasis patients on a ketogenic diet and 30 control patients without psoriasis on a regular diet.30 The ketogenic diet consisted of 400 to 500 g of vegetables, 20 to 30 g of fat, and a proportion of protein based on body weight with at least 12 g of whey protein and various amino acids. Patients on the ketogenic diet had significant reduction in PASI scores (value relative to clinical features, 1.4916 [P=.007]). Furthermore, concentrations of cytokines IL-2 (P=.04) and IL-1β (P=.006) decreased following the ketogenic diet but were not measured in the control group.30
Seborrheic Dermatitis—Seborrheic dermatitis is associated with overcolonization of Malassezia species near lipid-rich sebaceous glands. Malassezia hydrolyzes free fatty acids, yielding oleic acids and leading to T-cell release of IL-8 and IL-17.32 Literature is sparse regarding how dietary modifications may play a role in disease severity. In a survey study, Bett et al17 compared 16 SD patients to 1:2 matched controls (N=29) to investigate the relationship between sugar consumption and presence of disease. Two control cohorts were selected, 1 from clinic patients diagnosed with verruca and 1 matched by age and sex from a survey-based study at a facility in London, England. Sugar intake was measured both in total grams per day and in “beverage sugar” per day, defined as sugar taken in tea and coffee. There was higher total sugar and higher beverage sugar intake among the SD group compared with both control groups (P<.05).17
Atopic Dermatitis—Atopic dermatitis is a disease of epidermal barrier dysfunction and IgE-mediated allergic sensitization.33 There are several mechanisms by which skin structure may be disrupted. It is well established that filaggrin mutations inhibit stratum corneum maturation and lamellar matrix deposition.34 Upregulation of IL-4–, IL-13–, and IL-17–secreting TH2 cells also is associated with disruption of tight junctions and reduction of filaggrin.35,36 Given that a T cell–mediated inflammatory response is involved in disease pathogenesis, glycemic control is hypothesized to have therapeutic potential.
Nosrati et al24 surveyed 169 AD patients about their perceived dietary triggers through a 61-question survey based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Respondents were queried about their perceptions and dietary changes, such as removal or addition of specific food groups and trial of specific diets. Overall, 16.5% of patients reported sugar being a trigger, making it the fourth most common among those surveyed and less common than dairy (24.8%), gluten (18.3%), and alcohol (17.1%).24
Hidradenitis Suppurativa—Hidradenitis suppurativa is driven by hyperkeratosis, dilatation, and occlusion of pilosebaceous follicular ducts, whose eventual rupture evokes a local acute inflammatory response.37 The inciting event for both acne and HS involves mTOR complex–mediated follicular hyperproliferation andinsulinlike growth factor 1 stimulation of androgen receptors in pilosebaceous glands. Given the similarities between the pathogenesis of acne and HS, it is hypothesized that lifestyle changes, including diet modification, may have a beneficial effect on HS.38-40
Comment
Acne—Overall, there is strong evidence supporting the efficacy of a low-glycemic diet in the treatment of acne. Notably, among the 6 observational studies identified, there was 1 conflicting study by Bett et al17 that did not find a statistically significant difference in glucose intake between acne and control patients. However, this study included only 16 acne patients, whereas the other 5 observational studies included 32 to 2255 patients.17 The strongest evidence supporting low-glycemic dietary interventions in acne treatment is from 2 rigorous randomized clinical trials by Kwon et al21 and Smith et al.18 These trials used intention-to-treat models and maintained consistency in gender, age, and acne treatment protocols across both control and treatment groups. To ensure compliance with dietary interventions, daily telephone calls, food logs, and 24-hour urea sampling were utilized. Acne outcomes were assessed by a dermatologist who remained blinded with well-defined outcome measures. An important limitation of these studies is the difficulty in attributing the observed results solely to reduced glucose intake, as low-glycemic diets often lead to other dietary changes, including reduced fat intake and increased nutrient consumption.18,21
A 2022 systematic review of acne by Meixiong et al41 further reinforced the beneficial effects of low-glycemic diets in the management of acne patients. The group reviewed 6 interventional studies and 28 observational studies to investigate the relationship among acne, dairy, and glycemic content and found an association between decreased glucose and dairy on reduction of acne.41
It is likely that the ketogenic diet, which limits glucose, would be beneficial for acne patients. There may be added benefit through elevated ketone bodies and substantially reduced insulin secretion. However, because there are no observational or interventional studies, further research is needed to draw firm conclusions regarding diet for acne treatment. A randomized clinical trial investigating the effects of the ketogenic diet compared to the low-glycemic diet compared to a regular diet would be valuable.
Psoriasis—Among psoriasis studies, there was a lack of consensus regarding glucose intake and correlation with disease. Among the 4 observational studies, 2 reported increased glucose intake among psoriasis patients and 2 reported decreased glucose intake. It is plausible that the variability in studies is due to differences in sample size and diet heterogeneity among study populations. More specifically, Johnson et al22 and Afifi et al25 analyzed large sample sizes of 6260 and 2412 US participants, respectively, and found decreased sugar intake among psoriasis patients compared to controls. In comparison, Barrea et al23 and Yamashita et al27 analyzed substantially smaller and more specific populations consisting of 82 Italian and 140 Japanese participants, respectively; both reported increased glucose intake among psoriasis patients compared to controls. These seemingly antithetical results may be explained by regional dietary differences, with varying proportions of meats, vegetables, antioxidants, and vitamins.
Moreover, the variation among studies may be further explained by the high prevalence of comorbidities among psoriasis patients. In the study by Barrea et al,23 psoriasis patients had higher fasting glucose (P=.004) and insulin (P=.022) levels than healthy patients. After adjusting for body mass index and metabolic syndrome, the correlation coefficient measuring the relationship between the PASI score and intake of simple carbohydrates changed from r=0.564 (P<.001) to r=0.352 (P=.028). The confounding impact of these comorbidities was further highlighted by Yamashita et al,27 who found statistically significant differences in glucose intake between psoriasis and healthy patients (P=.003). However, they reported diminished significance on additional subgroup analysis accounting for potential comorbidities (P=.994).27 Johnson et al22 and Afifi et al25 did not account for comorbidities; therefore, the 4 observational study results must be interpreted cautiously.
The 2 randomized clinical trials by Castaldo et al29,30 weakly suggest that a ketogenic diet may be beneficial for psoriasis patients. The studies have several notable limitations, including insufficient sample sizes and control groups. Thus, the decreased PASI scores reported in psoriasis patients on the ketogenic diets are challenging to interpret. Additionally, both studies placed patients on highly restrictive diets of 500 kcal/d for 4 weeks. The feasibility of recommending such a diet to patients in clinical practice is questionable. Diets of less than 500 kcal/d may be dangerous for patients with underlying comorbidities and are unlikely to serve as long-term solutions.23 To contextualize our findings, a 2022 review by Chung et al42 examined the impact of various diets—low-caloric, gluten-free, Mediterranean, Western, and ketogenic—on psoriasis and reported insufficient evidence to suggest a benefit to the ketogenic diet for psoriasis patients, though the Mediterranean diet may be well suited for psoriasis patients because of improved cardiovascular health and reduced mortality.
Seborrheic Dermatitis—Sanders et al43 found that patients with a high-fruit diet had lower odds of having SD, while those on a Western diet had higher odds of having SD. Although the study did not measure glycemic load, it is conceivable that the high glycemic load characteristic of the Western diet contributed to these findings.43 However, no studies have investigated the direct link between low-glycemic or ketogenic diets and SD, leaving this area open for further study.
Atopic Dermatitis—It has been hypothesized that mitigating T cell–mediated inflammation via glucose control may contribute to the improvement in AD.35,36 However, in one study, 16.5% of AD patients self-identified sugar as a dietary trigger, ranking fourth among other dietary triggers.24 Thus, the connection between glucose levels and AD warrants further exploration.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa—Given the role of metabolic and hormonal influence in HS as well as the overlapping pathophysiology with acne, it is possible that low-glycemic and ketogenic diets may have a role in improving HS.38-40 However, there is a gap in observation and controlled studies investigating the link between low-glycemic or ketogenic diets and HS.
Conclusion
Our analysis focused on interventional and observational research exploring the effects of low-glycemic and ketogenic diets on associations and treatment of inflammatory skin conditions. There is sufficient evidence to counsel acne patients on the benefits of a low-glycemic diet as an adjunctive treatment for acne. Currently, there is insufficient evidence to recommend a low-glycemic or ketogenic diet as a treatment for patients with any other inflammatory skin disease. Prospective and controlled clinical trials are needed to clarify the utility of dietary interventions for treating inflammatory skin conditions.
- Pickett K, Loveman E, Kalita N, et al. Educational interventions to improve quality of life in people with chronic inflammatory skin diseases: systematic reviews of clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness. Health Technol Assess. 2015;19:1-176, v-vi.
- Giugliano D, Ceriello A, Esposito K. The effects of diet on inflammation: emphasis on the metabolic syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48:677-685.
- Dowlatshahi EA, van der Voort EA, Arends LR, et al. Markers of systemic inflammation in psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:266-282.
- Youm YH, Nguyen KY, Grant RW, et al. The ketone metabolite beta-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease. Nat Med. 2015;21:263-269.
- Melnik BC. Acne vulgaris: the metabolic syndrome of the pilosebaceous follicle. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:29-40.
- Upala S, Sanguankeo A. Effect of lifestyle weight loss intervention on disease severity in patients with psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Obes (Lond). 2015;39:1197-1202.
- Heng AHS, Chew FT. Systematic review of the epidemiology of acne vulgaris. Sci Rep. 2020;10:5754.
- Paoli A, Grimaldi K, Toniolo L, et al. Nutrition and acne: therapeutic potential of ketogenic diets. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2012;25:111-117.
- Masood W, Annamaraju P, Khan Suheb MZ, et al. Ketogenic diet. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- Fomin DA, McDaniel B, Crane J. The promising potential role of ketones in inflammatory dermatologic disease: a new frontier in treatment research. J Dermatolog Treat. 2017;28:484-487.
- Zhang D, Jin W, Wu R, et al. High glucose intake exacerbates autoimmunity through reactive-oxygen-species-mediated TGF-β cytokine activation. Immunity. 2019;51:671-681.e5.
- Cerman AA, Aktas E, Altunay IK, et al. Dietary glycemic factors, insulin resistance, and adiponectin levels in acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:155-162.
- Ferrere G, Tidjani Alou M, Liu P, et al. Ketogenic diet and ketone bodies enhance the anticancer effects of PD-1 blockade. JCI Insight. 2021;6:e145207.
- Burris J, Shikany JM, Rietkerk W, et al. A Low glycemic index and glycemic load diet decreases insulin-like growth factor-1 among adults with moderate and severe acne: a short-duration, 2-week randomized controlled trial. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2018;118:1874-1885.
- Tan JKL, Stein Gold LF, Alexis AF, et al. Current concepts in acne pathogenesis: pathways to inflammation. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2018;37(3S):S60-S62.
- Kim J, Ochoa MT, Krutzik SR, et al. Activation of toll-like receptor 2 in acne triggers inflammatory cytokine responses. J Immunol. 2002;169:1535-1541.
- Bett DG, Morland J, Yudkin J. Sugar consumption in acne vulgaris and seborrhoeic dermatitis. Br Med J. 1967;3:153-155.
- Smith RN, Mann NJ, Braue A, et al. A low-glycemic-load diet improves symptoms in acne vulgaris patients: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86:107-115.
- Rouhani P, Berman B, Rouhani G. Acne improves with a popular, low glycemic diet from South Beach. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60(Suppl 1):AB14.
- Aksu AE, Metintas S, Saracoglu ZN, et al. Acne: prevalence and relationship with dietary habits in Eskisehir, Turkey. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26:1503-1509.
- Kwon HH, Yoon JY, Hong JS, et al. Clinical and histological effect of a low glycaemic load diet in treatment of acne vulgaris in Korean patients: a randomized, controlled trial. Acta Derm Venereol. 2012;92:241-246.
- Johnson JA, Ma C, Kanada KN, et al. Diet and nutrition in psoriasis: analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) in the United States. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:327-332.
- Barrea L, Macchia PE, Tarantino G, et al. Nutrition: a key environmental dietary factor in clinical severity and cardio-metabolic risk in psoriatic male patients evaluated by 7-day food-frequency questionnaire. J Transl Med. 2015;13:303.
- Nosrati A, Afifi L, Danesh MJ, et al. Dietary modifications in atopic dermatitis: patient-reported outcomes. J Dermatolog Treat. 2017;28:523-538.
- Afifi L, Danesh MJ, Lee KM, et al. Dietary behaviors in psoriasis: patient-reported outcomes from a U.S. national survey. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2017;7:227-242.
- Burris J, Rietkerk W, Shikany JM, et al. Differences in dietary glycemic load and hormones in New York City adults with no and moderate/severe acne. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2017;117:1375-1383.
- Yamashita H, Morita T, Ito M, et al. Dietary habits in Japanese patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: low intake of meat in psoriasis and high intake of vitamin A in psoriatic arthritis. J Dermatol. 2019;46:759-769.
- Marson J, Baldwin HE. 12761 Acne, twins, and glycemic index: a sweet pilot study of diet and dietary beliefs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83(Suppl):AB110.
- Castaldo G, Rastrelli L, Galdo G, et al. Aggressive weight-loss program with a ketogenic induction phase for the treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis: a proof-of-concept, single-arm, open-label clinical trial. Nutrition. 2020;74:110757.
- Castaldo G, Pagano I, Grimaldi M, et al. Effect of very-low-calorie ketogenic diet on psoriasis patients: a nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomic study. J Proteome Res. 2021;20:1509-1521.
- Ip W, Kirchhof MG. Glycemic control in the treatment of psoriasis. Dermatology. 2017;233:23-29.
- Vijaya Chandra SH, Srinivas R, Dawson TL Jr, et al. Cutaneous Malassezia: commensal, pathogen, or protector? Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020;10:614446.
- David Boothe W, Tarbox JA, Tarbox MB. Atopic dermatitis: pathophysiology. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1027:21-37.
- Guttman-Yassky E, Hanifin JM, Boguniewicz M, et al. The role of phosphodiesterase 4 in the pathophysiology of atopic dermatitis and the perspective for its inhibition. Exp Dermatol. 2019;28:3-10.
- Furue K, Ito T, Tsuji G, et al. The IL-13–OVOL1–FLG axis in atopic dermatitis. Immunology. 2019;158:281-286.
- Renert-Yuval Y, Guttman-Yassky E. New treatments for atopic dermatitis targeting beyond IL-4/IL-13 cytokines. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020;124:28-35.
- Sellheyer K, Krahl D. “Hidradenitis suppurativa” is acne inversa! An appeal to (finally) abandon a misnomer. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:535-540.
- Danby FW, Margesson LJ. Hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Clin. 2010;28:779-793.
- Fernandez JM, Marr KD, Hendricks AJ, et al. Alleviating and exacerbating foods in hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E14246.
- Yamanaka-Takaichi M, Revankar R, Shih T, et al. Expert consensus on priority research gaps in dietary and lifestyle factors in hidradenitis suppurativa: a Delphi consensus study. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:2129-2136.
- Meixiong J, Ricco C, Vasavda C, et al. Diet and acne: a systematic review. JAAD Int. 2022;7:95-112.
- Chung M, Bartholomew E, Yeroushalmi S, et al. Dietary intervention and supplements in the management of psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckland). 2022;12:151-176. doi:10.2147/PTT.S328581
- Sanders MGH, Pardo LM, Ginger RS, et al. Association between diet and seborrheic dermatitis: a cross-sectional study. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:108-114.
Inflammatory skin conditions often have a relapsing and remitting course and represent a large proportion of chronic skin diseases. Common inflammatory skin disorders include acne, psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), atopic dermatitis (AD), and seborrheic dermatitis (SD).1 Although each of these conditions has a unique pathogenesis, they all are driven by a background of chronic inflammation. It has been reported that diets with high levels of refined carbohydrates and saturated or trans-fatty acids may exacerbate existing inflammation.2 Consequently, dietary interventions, such as the ketogenic and low-glycemic diets, have potential anti-inflammatory and metabolic effects that are being assessed as stand-alone or adjunctive therapies for dermatologic diseases.
Diet may partially influence systemic inflammation through its effect on weight. Higher body mass index and obesity are linked to a low-grade inflammatory state and higher levels of circulating inflammatory markers. Therefore, weight loss leads to decreases in inflammatory cytokines, including C-reactive protein, tumor necrosis factor α, and IL-6.3 These cytokines and metabolic effects overlap with inflammatory skin condition pathways. It also is posited that decreased insulin release associated with weight loss results in decreased sebaceous lipogenesis and androgens, which drive keratinocyte proliferation and acne development.4,5 For instance, in a 2015 meta-analysis of 5 randomized controlled trials on psoriasis, patients in the weight loss intervention group had more substantial reductions in psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) scores compared with controls receiving usual care (P=.004).6 However, in a systematic review of 35 studies on acne vulgaris, overweight and obese patients (defined by a body mass index of ≥23 kg/m2) had similar odds of having acne compared with normal-weight individuals (P=.671).7
Similar to weight loss, ketogenesis acts as a negative feedback mechanism to reduce insulin release, leading to decreased inflammation and androgens that often exacerbate inflammatory skin diseases.8 Ketogenesis ensues when daily carbohydrate intake is limited to less than 50 g, and long-term adherence to a ketogenic diet results in metabolic reliance on ketone bodies such as acetoacetate, β-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone.9 These metabolites may decrease free radical damage and consequently improve signs and symptoms of acne, psoriasis, and other inflammatory skin diseases.10-12 Similarly, increased ketones also may decrease activation of the NLRP3 (NOD-, LRR-, and Pyrin domain-containing protein 3) inflammasome and therefore reduce inflammatory markers such as IL-1β and IL-1.4,13 Several proposed mechanisms are outlined in the Table.

Collectively, low-glycemic and ketogenic diets have been proposed as potential interventions for reducing inflammatory skin conditions. These dietary approaches are hypothesized to exert their effects by facilitating weight loss, elevating ketone levels, and reducing systemic inflammation. The current review summarizes the existing evidence on ketogenic and low-glycemic diets as treatments for inflammatory skin conditions and evaluates the potential benefits of these dietary interventions in managing and improving outcomes for individuals with inflammatory skin conditions.
Methods
Using PubMed for articles indexed for MEDLINE and Google Scholar, a review of the literature was conducted with a combination of the following search terms: low-glycemic diet, inflammatory, dermatologic, ketogenic diet, inflammation, dermatology, acne, psoriasis, eczema, seborrheic dermatitis, and hidradenitis suppurativa. Reference citations in identified works also were reviewed. Interventional (experimental studies or clinical trials), survey-based, and observational studies that investigated the effects of low-glycemic or ketogenic diets for the treatment of inflammatory skin conditions were included. Inclusion criteria were studies assessing acne, psoriasis, SD, AD, and HS. Exclusion criteria were studies published before 1965; those written in languages other than English; and those analyzing other diets, such as the Mediterranean or low-fat diets. The search yielded a total of 11 observational studies and 4 controlled studies published between 1966 and January 2023. Because this analysis utilized publicly available data and did not qualify as human subject research, institutional review board approval was not required.
Results
Acne Vulgaris—Acne vulgaris is a disease of chronic pilosebaceous inflammation and follicular epithelial proliferation associated with Propionibacterium acnes. The association between acne and low-glycemic diets has been examined in several studies. Diet quality is measured and assessed using the glycemic index (GI), which is the effect of a single food on postprandial blood glucose, and the glycemic load, which is the GI adjusted for carbohydrates per serving.14 High levels of GI and glycemic load are associated with hyperinsulinemia and an increase in insulinlike growth factor 1 concentration that promotes
Six survey-based studies evaluated sugar intake in patients with acne compared to healthy matched controls (eTable). Among these studies, 5 reported higher glycemic loads or daily sugar intake in acne patients compared to individuals without acne.12,19,20,26,28 The remaining study was conducted in 1967 and enrolled 16 acne patients and 32 matched controls. It reported no significant difference in sugar intake between the groups (P>.05).17


Smith et al18 randomized 43 male patients aged 15 to 25 years with facial acne into 2 cohorts for 12 weeks, each consuming either a low-glycemic diet (25% protein, 45% low-glycemic food [fruits, whole grains], and 30% fat) or a carbohydrate-dense diet of foods with medium to high GI based on prior documentation of the original diet. Patients were instructed to use a noncomedogenic cleanser as their only acne treatment. At 12 weeks, patients consuming the low-glycemic diet had an average of 23.5 fewer inflammatory lesions, while those in the intervention group had 12.0 fewer lesions (P=.03).18
In another controlled study by Kwon et al,21 32 male and female acne patients were randomized to a low-glycemic diet (25% protein, 45% low-glycemic food, and 30% fat) or a standard diet for 10 weeks. Patients on the low-glycemic diet experienced a 70.9% reduction in inflammatory lesions (P<.05). Hematoxylin and eosin staining and image analysis were performed to measure sebaceous gland surface area in the low-glycemic diet group, which decreased from 0.32 to 0.24 mm2 (P=.03). The sebaceous gland surface area in the control group was not reported. Moreover, patients on the low-glycemic diet had reduced IL-8 immunohistochemical staining (decreasing from 2.9 to 1.7 [P=.03]) and sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 levels (decreasing from 2.6 to 1.3 [P=.03]), suggesting suppression of ongoing inflammation. Patients on the low-glycemic diet had no significant difference in transforming growth factor β1(P=.83). In the control group, there was no difference in IL-8, sterol regulatory element binding protein 1, or transforming growth factor β1 (P>.05) on immunohistochemical staining.21
Psoriasis—Psoriasis is a systemic inflammatory disease characterized by hyperproliferation and aberrant keratinocyte plaque formation. The innate immune response of keratinocytes in response to epidermal damage or infection begins with neutrophil recruitment and dendritic cell activation. Dendritic cell secretion of IL-23 promotes T-cell differentiation into helper T cells (TH1) that subsequently secrete IL-17 and IL-22, thereby stimulating keratinocyte proliferation and eventual plaque formation. The relationship between diet and psoriasis is poorly understood; however, hyperinsulinemia is associated with greater severity of psoriasis.31
Four observational studies examined sugar intake in psoriasis patients. Barrea et al23 conducted a survey-based study of 82 male participants (41 with psoriasis and 41 healthy controls), reporting that PASI score was correlated with intake of simple carbohydrates (percentage of total kilocalorie)(r=0.564, P<.001). Another study by Yamashita et al27 found higher sugar intake in psoriasis patients than controls (P=.003) based on surveys from 70 patients with psoriasis and 70 matched healthy controls.
These findings contrast with 2 survey-based studies by Johnson et al22 and Afifi et al25 of sugar intake in psoriasis patients using the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Johnson et al22 reported reduced sugar intake among 156 psoriasis patients compared with 6104 unmatched controls (odds ratio, 0.998; CI, 0.996-1 [P=.04]) from 2003 to 2006. Similarly, Afifi et al25 reported decreased sugar intake in 1206 psoriasis patients compared with sex- and age-matched controls (P<.0001) in 2009 and 2010. When patients were asked about dietary triggers, 13.8% of psoriasis patients reported sugar as the most common trigger, which was more frequent than alcohol (13.6%), gluten (7.2%), and dairy (6%).25
Castaldo et al29,30 published 2 nonrandomized clinical intervention studies in 2020 and 2021 evaluating the impact of the ketogenic diet on psoriasis. In the first study, 37 psoriasis patients followed a 10-week diet consisting of 4 weeks on a ketogenic diet (500 kcal/d) followed by 6 weeks on a low-caloric Mediterranean diet.29 At the end of the intervention, there was a 17.4% reduction in PASI score, a 33.2-point reduction in itch severity score, and a 13.4-point reduction in the dermatology life quality index score; however, this study did not include a control diet group for comparison.29 The second study included 30 psoriasis patients on a ketogenic diet and 30 control patients without psoriasis on a regular diet.30 The ketogenic diet consisted of 400 to 500 g of vegetables, 20 to 30 g of fat, and a proportion of protein based on body weight with at least 12 g of whey protein and various amino acids. Patients on the ketogenic diet had significant reduction in PASI scores (value relative to clinical features, 1.4916 [P=.007]). Furthermore, concentrations of cytokines IL-2 (P=.04) and IL-1β (P=.006) decreased following the ketogenic diet but were not measured in the control group.30
Seborrheic Dermatitis—Seborrheic dermatitis is associated with overcolonization of Malassezia species near lipid-rich sebaceous glands. Malassezia hydrolyzes free fatty acids, yielding oleic acids and leading to T-cell release of IL-8 and IL-17.32 Literature is sparse regarding how dietary modifications may play a role in disease severity. In a survey study, Bett et al17 compared 16 SD patients to 1:2 matched controls (N=29) to investigate the relationship between sugar consumption and presence of disease. Two control cohorts were selected, 1 from clinic patients diagnosed with verruca and 1 matched by age and sex from a survey-based study at a facility in London, England. Sugar intake was measured both in total grams per day and in “beverage sugar” per day, defined as sugar taken in tea and coffee. There was higher total sugar and higher beverage sugar intake among the SD group compared with both control groups (P<.05).17
Atopic Dermatitis—Atopic dermatitis is a disease of epidermal barrier dysfunction and IgE-mediated allergic sensitization.33 There are several mechanisms by which skin structure may be disrupted. It is well established that filaggrin mutations inhibit stratum corneum maturation and lamellar matrix deposition.34 Upregulation of IL-4–, IL-13–, and IL-17–secreting TH2 cells also is associated with disruption of tight junctions and reduction of filaggrin.35,36 Given that a T cell–mediated inflammatory response is involved in disease pathogenesis, glycemic control is hypothesized to have therapeutic potential.
Nosrati et al24 surveyed 169 AD patients about their perceived dietary triggers through a 61-question survey based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Respondents were queried about their perceptions and dietary changes, such as removal or addition of specific food groups and trial of specific diets. Overall, 16.5% of patients reported sugar being a trigger, making it the fourth most common among those surveyed and less common than dairy (24.8%), gluten (18.3%), and alcohol (17.1%).24
Hidradenitis Suppurativa—Hidradenitis suppurativa is driven by hyperkeratosis, dilatation, and occlusion of pilosebaceous follicular ducts, whose eventual rupture evokes a local acute inflammatory response.37 The inciting event for both acne and HS involves mTOR complex–mediated follicular hyperproliferation andinsulinlike growth factor 1 stimulation of androgen receptors in pilosebaceous glands. Given the similarities between the pathogenesis of acne and HS, it is hypothesized that lifestyle changes, including diet modification, may have a beneficial effect on HS.38-40
Comment
Acne—Overall, there is strong evidence supporting the efficacy of a low-glycemic diet in the treatment of acne. Notably, among the 6 observational studies identified, there was 1 conflicting study by Bett et al17 that did not find a statistically significant difference in glucose intake between acne and control patients. However, this study included only 16 acne patients, whereas the other 5 observational studies included 32 to 2255 patients.17 The strongest evidence supporting low-glycemic dietary interventions in acne treatment is from 2 rigorous randomized clinical trials by Kwon et al21 and Smith et al.18 These trials used intention-to-treat models and maintained consistency in gender, age, and acne treatment protocols across both control and treatment groups. To ensure compliance with dietary interventions, daily telephone calls, food logs, and 24-hour urea sampling were utilized. Acne outcomes were assessed by a dermatologist who remained blinded with well-defined outcome measures. An important limitation of these studies is the difficulty in attributing the observed results solely to reduced glucose intake, as low-glycemic diets often lead to other dietary changes, including reduced fat intake and increased nutrient consumption.18,21
A 2022 systematic review of acne by Meixiong et al41 further reinforced the beneficial effects of low-glycemic diets in the management of acne patients. The group reviewed 6 interventional studies and 28 observational studies to investigate the relationship among acne, dairy, and glycemic content and found an association between decreased glucose and dairy on reduction of acne.41
It is likely that the ketogenic diet, which limits glucose, would be beneficial for acne patients. There may be added benefit through elevated ketone bodies and substantially reduced insulin secretion. However, because there are no observational or interventional studies, further research is needed to draw firm conclusions regarding diet for acne treatment. A randomized clinical trial investigating the effects of the ketogenic diet compared to the low-glycemic diet compared to a regular diet would be valuable.
Psoriasis—Among psoriasis studies, there was a lack of consensus regarding glucose intake and correlation with disease. Among the 4 observational studies, 2 reported increased glucose intake among psoriasis patients and 2 reported decreased glucose intake. It is plausible that the variability in studies is due to differences in sample size and diet heterogeneity among study populations. More specifically, Johnson et al22 and Afifi et al25 analyzed large sample sizes of 6260 and 2412 US participants, respectively, and found decreased sugar intake among psoriasis patients compared to controls. In comparison, Barrea et al23 and Yamashita et al27 analyzed substantially smaller and more specific populations consisting of 82 Italian and 140 Japanese participants, respectively; both reported increased glucose intake among psoriasis patients compared to controls. These seemingly antithetical results may be explained by regional dietary differences, with varying proportions of meats, vegetables, antioxidants, and vitamins.
Moreover, the variation among studies may be further explained by the high prevalence of comorbidities among psoriasis patients. In the study by Barrea et al,23 psoriasis patients had higher fasting glucose (P=.004) and insulin (P=.022) levels than healthy patients. After adjusting for body mass index and metabolic syndrome, the correlation coefficient measuring the relationship between the PASI score and intake of simple carbohydrates changed from r=0.564 (P<.001) to r=0.352 (P=.028). The confounding impact of these comorbidities was further highlighted by Yamashita et al,27 who found statistically significant differences in glucose intake between psoriasis and healthy patients (P=.003). However, they reported diminished significance on additional subgroup analysis accounting for potential comorbidities (P=.994).27 Johnson et al22 and Afifi et al25 did not account for comorbidities; therefore, the 4 observational study results must be interpreted cautiously.
The 2 randomized clinical trials by Castaldo et al29,30 weakly suggest that a ketogenic diet may be beneficial for psoriasis patients. The studies have several notable limitations, including insufficient sample sizes and control groups. Thus, the decreased PASI scores reported in psoriasis patients on the ketogenic diets are challenging to interpret. Additionally, both studies placed patients on highly restrictive diets of 500 kcal/d for 4 weeks. The feasibility of recommending such a diet to patients in clinical practice is questionable. Diets of less than 500 kcal/d may be dangerous for patients with underlying comorbidities and are unlikely to serve as long-term solutions.23 To contextualize our findings, a 2022 review by Chung et al42 examined the impact of various diets—low-caloric, gluten-free, Mediterranean, Western, and ketogenic—on psoriasis and reported insufficient evidence to suggest a benefit to the ketogenic diet for psoriasis patients, though the Mediterranean diet may be well suited for psoriasis patients because of improved cardiovascular health and reduced mortality.
Seborrheic Dermatitis—Sanders et al43 found that patients with a high-fruit diet had lower odds of having SD, while those on a Western diet had higher odds of having SD. Although the study did not measure glycemic load, it is conceivable that the high glycemic load characteristic of the Western diet contributed to these findings.43 However, no studies have investigated the direct link between low-glycemic or ketogenic diets and SD, leaving this area open for further study.
Atopic Dermatitis—It has been hypothesized that mitigating T cell–mediated inflammation via glucose control may contribute to the improvement in AD.35,36 However, in one study, 16.5% of AD patients self-identified sugar as a dietary trigger, ranking fourth among other dietary triggers.24 Thus, the connection between glucose levels and AD warrants further exploration.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa—Given the role of metabolic and hormonal influence in HS as well as the overlapping pathophysiology with acne, it is possible that low-glycemic and ketogenic diets may have a role in improving HS.38-40 However, there is a gap in observation and controlled studies investigating the link between low-glycemic or ketogenic diets and HS.
Conclusion
Our analysis focused on interventional and observational research exploring the effects of low-glycemic and ketogenic diets on associations and treatment of inflammatory skin conditions. There is sufficient evidence to counsel acne patients on the benefits of a low-glycemic diet as an adjunctive treatment for acne. Currently, there is insufficient evidence to recommend a low-glycemic or ketogenic diet as a treatment for patients with any other inflammatory skin disease. Prospective and controlled clinical trials are needed to clarify the utility of dietary interventions for treating inflammatory skin conditions.
Inflammatory skin conditions often have a relapsing and remitting course and represent a large proportion of chronic skin diseases. Common inflammatory skin disorders include acne, psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), atopic dermatitis (AD), and seborrheic dermatitis (SD).1 Although each of these conditions has a unique pathogenesis, they all are driven by a background of chronic inflammation. It has been reported that diets with high levels of refined carbohydrates and saturated or trans-fatty acids may exacerbate existing inflammation.2 Consequently, dietary interventions, such as the ketogenic and low-glycemic diets, have potential anti-inflammatory and metabolic effects that are being assessed as stand-alone or adjunctive therapies for dermatologic diseases.
Diet may partially influence systemic inflammation through its effect on weight. Higher body mass index and obesity are linked to a low-grade inflammatory state and higher levels of circulating inflammatory markers. Therefore, weight loss leads to decreases in inflammatory cytokines, including C-reactive protein, tumor necrosis factor α, and IL-6.3 These cytokines and metabolic effects overlap with inflammatory skin condition pathways. It also is posited that decreased insulin release associated with weight loss results in decreased sebaceous lipogenesis and androgens, which drive keratinocyte proliferation and acne development.4,5 For instance, in a 2015 meta-analysis of 5 randomized controlled trials on psoriasis, patients in the weight loss intervention group had more substantial reductions in psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) scores compared with controls receiving usual care (P=.004).6 However, in a systematic review of 35 studies on acne vulgaris, overweight and obese patients (defined by a body mass index of ≥23 kg/m2) had similar odds of having acne compared with normal-weight individuals (P=.671).7
Similar to weight loss, ketogenesis acts as a negative feedback mechanism to reduce insulin release, leading to decreased inflammation and androgens that often exacerbate inflammatory skin diseases.8 Ketogenesis ensues when daily carbohydrate intake is limited to less than 50 g, and long-term adherence to a ketogenic diet results in metabolic reliance on ketone bodies such as acetoacetate, β-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone.9 These metabolites may decrease free radical damage and consequently improve signs and symptoms of acne, psoriasis, and other inflammatory skin diseases.10-12 Similarly, increased ketones also may decrease activation of the NLRP3 (NOD-, LRR-, and Pyrin domain-containing protein 3) inflammasome and therefore reduce inflammatory markers such as IL-1β and IL-1.4,13 Several proposed mechanisms are outlined in the Table.

Collectively, low-glycemic and ketogenic diets have been proposed as potential interventions for reducing inflammatory skin conditions. These dietary approaches are hypothesized to exert their effects by facilitating weight loss, elevating ketone levels, and reducing systemic inflammation. The current review summarizes the existing evidence on ketogenic and low-glycemic diets as treatments for inflammatory skin conditions and evaluates the potential benefits of these dietary interventions in managing and improving outcomes for individuals with inflammatory skin conditions.
Methods
Using PubMed for articles indexed for MEDLINE and Google Scholar, a review of the literature was conducted with a combination of the following search terms: low-glycemic diet, inflammatory, dermatologic, ketogenic diet, inflammation, dermatology, acne, psoriasis, eczema, seborrheic dermatitis, and hidradenitis suppurativa. Reference citations in identified works also were reviewed. Interventional (experimental studies or clinical trials), survey-based, and observational studies that investigated the effects of low-glycemic or ketogenic diets for the treatment of inflammatory skin conditions were included. Inclusion criteria were studies assessing acne, psoriasis, SD, AD, and HS. Exclusion criteria were studies published before 1965; those written in languages other than English; and those analyzing other diets, such as the Mediterranean or low-fat diets. The search yielded a total of 11 observational studies and 4 controlled studies published between 1966 and January 2023. Because this analysis utilized publicly available data and did not qualify as human subject research, institutional review board approval was not required.
Results
Acne Vulgaris—Acne vulgaris is a disease of chronic pilosebaceous inflammation and follicular epithelial proliferation associated with Propionibacterium acnes. The association between acne and low-glycemic diets has been examined in several studies. Diet quality is measured and assessed using the glycemic index (GI), which is the effect of a single food on postprandial blood glucose, and the glycemic load, which is the GI adjusted for carbohydrates per serving.14 High levels of GI and glycemic load are associated with hyperinsulinemia and an increase in insulinlike growth factor 1 concentration that promotes
Six survey-based studies evaluated sugar intake in patients with acne compared to healthy matched controls (eTable). Among these studies, 5 reported higher glycemic loads or daily sugar intake in acne patients compared to individuals without acne.12,19,20,26,28 The remaining study was conducted in 1967 and enrolled 16 acne patients and 32 matched controls. It reported no significant difference in sugar intake between the groups (P>.05).17


Smith et al18 randomized 43 male patients aged 15 to 25 years with facial acne into 2 cohorts for 12 weeks, each consuming either a low-glycemic diet (25% protein, 45% low-glycemic food [fruits, whole grains], and 30% fat) or a carbohydrate-dense diet of foods with medium to high GI based on prior documentation of the original diet. Patients were instructed to use a noncomedogenic cleanser as their only acne treatment. At 12 weeks, patients consuming the low-glycemic diet had an average of 23.5 fewer inflammatory lesions, while those in the intervention group had 12.0 fewer lesions (P=.03).18
In another controlled study by Kwon et al,21 32 male and female acne patients were randomized to a low-glycemic diet (25% protein, 45% low-glycemic food, and 30% fat) or a standard diet for 10 weeks. Patients on the low-glycemic diet experienced a 70.9% reduction in inflammatory lesions (P<.05). Hematoxylin and eosin staining and image analysis were performed to measure sebaceous gland surface area in the low-glycemic diet group, which decreased from 0.32 to 0.24 mm2 (P=.03). The sebaceous gland surface area in the control group was not reported. Moreover, patients on the low-glycemic diet had reduced IL-8 immunohistochemical staining (decreasing from 2.9 to 1.7 [P=.03]) and sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 levels (decreasing from 2.6 to 1.3 [P=.03]), suggesting suppression of ongoing inflammation. Patients on the low-glycemic diet had no significant difference in transforming growth factor β1(P=.83). In the control group, there was no difference in IL-8, sterol regulatory element binding protein 1, or transforming growth factor β1 (P>.05) on immunohistochemical staining.21
Psoriasis—Psoriasis is a systemic inflammatory disease characterized by hyperproliferation and aberrant keratinocyte plaque formation. The innate immune response of keratinocytes in response to epidermal damage or infection begins with neutrophil recruitment and dendritic cell activation. Dendritic cell secretion of IL-23 promotes T-cell differentiation into helper T cells (TH1) that subsequently secrete IL-17 and IL-22, thereby stimulating keratinocyte proliferation and eventual plaque formation. The relationship between diet and psoriasis is poorly understood; however, hyperinsulinemia is associated with greater severity of psoriasis.31
Four observational studies examined sugar intake in psoriasis patients. Barrea et al23 conducted a survey-based study of 82 male participants (41 with psoriasis and 41 healthy controls), reporting that PASI score was correlated with intake of simple carbohydrates (percentage of total kilocalorie)(r=0.564, P<.001). Another study by Yamashita et al27 found higher sugar intake in psoriasis patients than controls (P=.003) based on surveys from 70 patients with psoriasis and 70 matched healthy controls.
These findings contrast with 2 survey-based studies by Johnson et al22 and Afifi et al25 of sugar intake in psoriasis patients using the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Johnson et al22 reported reduced sugar intake among 156 psoriasis patients compared with 6104 unmatched controls (odds ratio, 0.998; CI, 0.996-1 [P=.04]) from 2003 to 2006. Similarly, Afifi et al25 reported decreased sugar intake in 1206 psoriasis patients compared with sex- and age-matched controls (P<.0001) in 2009 and 2010. When patients were asked about dietary triggers, 13.8% of psoriasis patients reported sugar as the most common trigger, which was more frequent than alcohol (13.6%), gluten (7.2%), and dairy (6%).25
Castaldo et al29,30 published 2 nonrandomized clinical intervention studies in 2020 and 2021 evaluating the impact of the ketogenic diet on psoriasis. In the first study, 37 psoriasis patients followed a 10-week diet consisting of 4 weeks on a ketogenic diet (500 kcal/d) followed by 6 weeks on a low-caloric Mediterranean diet.29 At the end of the intervention, there was a 17.4% reduction in PASI score, a 33.2-point reduction in itch severity score, and a 13.4-point reduction in the dermatology life quality index score; however, this study did not include a control diet group for comparison.29 The second study included 30 psoriasis patients on a ketogenic diet and 30 control patients without psoriasis on a regular diet.30 The ketogenic diet consisted of 400 to 500 g of vegetables, 20 to 30 g of fat, and a proportion of protein based on body weight with at least 12 g of whey protein and various amino acids. Patients on the ketogenic diet had significant reduction in PASI scores (value relative to clinical features, 1.4916 [P=.007]). Furthermore, concentrations of cytokines IL-2 (P=.04) and IL-1β (P=.006) decreased following the ketogenic diet but were not measured in the control group.30
Seborrheic Dermatitis—Seborrheic dermatitis is associated with overcolonization of Malassezia species near lipid-rich sebaceous glands. Malassezia hydrolyzes free fatty acids, yielding oleic acids and leading to T-cell release of IL-8 and IL-17.32 Literature is sparse regarding how dietary modifications may play a role in disease severity. In a survey study, Bett et al17 compared 16 SD patients to 1:2 matched controls (N=29) to investigate the relationship between sugar consumption and presence of disease. Two control cohorts were selected, 1 from clinic patients diagnosed with verruca and 1 matched by age and sex from a survey-based study at a facility in London, England. Sugar intake was measured both in total grams per day and in “beverage sugar” per day, defined as sugar taken in tea and coffee. There was higher total sugar and higher beverage sugar intake among the SD group compared with both control groups (P<.05).17
Atopic Dermatitis—Atopic dermatitis is a disease of epidermal barrier dysfunction and IgE-mediated allergic sensitization.33 There are several mechanisms by which skin structure may be disrupted. It is well established that filaggrin mutations inhibit stratum corneum maturation and lamellar matrix deposition.34 Upregulation of IL-4–, IL-13–, and IL-17–secreting TH2 cells also is associated with disruption of tight junctions and reduction of filaggrin.35,36 Given that a T cell–mediated inflammatory response is involved in disease pathogenesis, glycemic control is hypothesized to have therapeutic potential.
Nosrati et al24 surveyed 169 AD patients about their perceived dietary triggers through a 61-question survey based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Respondents were queried about their perceptions and dietary changes, such as removal or addition of specific food groups and trial of specific diets. Overall, 16.5% of patients reported sugar being a trigger, making it the fourth most common among those surveyed and less common than dairy (24.8%), gluten (18.3%), and alcohol (17.1%).24
Hidradenitis Suppurativa—Hidradenitis suppurativa is driven by hyperkeratosis, dilatation, and occlusion of pilosebaceous follicular ducts, whose eventual rupture evokes a local acute inflammatory response.37 The inciting event for both acne and HS involves mTOR complex–mediated follicular hyperproliferation andinsulinlike growth factor 1 stimulation of androgen receptors in pilosebaceous glands. Given the similarities between the pathogenesis of acne and HS, it is hypothesized that lifestyle changes, including diet modification, may have a beneficial effect on HS.38-40
Comment
Acne—Overall, there is strong evidence supporting the efficacy of a low-glycemic diet in the treatment of acne. Notably, among the 6 observational studies identified, there was 1 conflicting study by Bett et al17 that did not find a statistically significant difference in glucose intake between acne and control patients. However, this study included only 16 acne patients, whereas the other 5 observational studies included 32 to 2255 patients.17 The strongest evidence supporting low-glycemic dietary interventions in acne treatment is from 2 rigorous randomized clinical trials by Kwon et al21 and Smith et al.18 These trials used intention-to-treat models and maintained consistency in gender, age, and acne treatment protocols across both control and treatment groups. To ensure compliance with dietary interventions, daily telephone calls, food logs, and 24-hour urea sampling were utilized. Acne outcomes were assessed by a dermatologist who remained blinded with well-defined outcome measures. An important limitation of these studies is the difficulty in attributing the observed results solely to reduced glucose intake, as low-glycemic diets often lead to other dietary changes, including reduced fat intake and increased nutrient consumption.18,21
A 2022 systematic review of acne by Meixiong et al41 further reinforced the beneficial effects of low-glycemic diets in the management of acne patients. The group reviewed 6 interventional studies and 28 observational studies to investigate the relationship among acne, dairy, and glycemic content and found an association between decreased glucose and dairy on reduction of acne.41
It is likely that the ketogenic diet, which limits glucose, would be beneficial for acne patients. There may be added benefit through elevated ketone bodies and substantially reduced insulin secretion. However, because there are no observational or interventional studies, further research is needed to draw firm conclusions regarding diet for acne treatment. A randomized clinical trial investigating the effects of the ketogenic diet compared to the low-glycemic diet compared to a regular diet would be valuable.
Psoriasis—Among psoriasis studies, there was a lack of consensus regarding glucose intake and correlation with disease. Among the 4 observational studies, 2 reported increased glucose intake among psoriasis patients and 2 reported decreased glucose intake. It is plausible that the variability in studies is due to differences in sample size and diet heterogeneity among study populations. More specifically, Johnson et al22 and Afifi et al25 analyzed large sample sizes of 6260 and 2412 US participants, respectively, and found decreased sugar intake among psoriasis patients compared to controls. In comparison, Barrea et al23 and Yamashita et al27 analyzed substantially smaller and more specific populations consisting of 82 Italian and 140 Japanese participants, respectively; both reported increased glucose intake among psoriasis patients compared to controls. These seemingly antithetical results may be explained by regional dietary differences, with varying proportions of meats, vegetables, antioxidants, and vitamins.
Moreover, the variation among studies may be further explained by the high prevalence of comorbidities among psoriasis patients. In the study by Barrea et al,23 psoriasis patients had higher fasting glucose (P=.004) and insulin (P=.022) levels than healthy patients. After adjusting for body mass index and metabolic syndrome, the correlation coefficient measuring the relationship between the PASI score and intake of simple carbohydrates changed from r=0.564 (P<.001) to r=0.352 (P=.028). The confounding impact of these comorbidities was further highlighted by Yamashita et al,27 who found statistically significant differences in glucose intake between psoriasis and healthy patients (P=.003). However, they reported diminished significance on additional subgroup analysis accounting for potential comorbidities (P=.994).27 Johnson et al22 and Afifi et al25 did not account for comorbidities; therefore, the 4 observational study results must be interpreted cautiously.
The 2 randomized clinical trials by Castaldo et al29,30 weakly suggest that a ketogenic diet may be beneficial for psoriasis patients. The studies have several notable limitations, including insufficient sample sizes and control groups. Thus, the decreased PASI scores reported in psoriasis patients on the ketogenic diets are challenging to interpret. Additionally, both studies placed patients on highly restrictive diets of 500 kcal/d for 4 weeks. The feasibility of recommending such a diet to patients in clinical practice is questionable. Diets of less than 500 kcal/d may be dangerous for patients with underlying comorbidities and are unlikely to serve as long-term solutions.23 To contextualize our findings, a 2022 review by Chung et al42 examined the impact of various diets—low-caloric, gluten-free, Mediterranean, Western, and ketogenic—on psoriasis and reported insufficient evidence to suggest a benefit to the ketogenic diet for psoriasis patients, though the Mediterranean diet may be well suited for psoriasis patients because of improved cardiovascular health and reduced mortality.
Seborrheic Dermatitis—Sanders et al43 found that patients with a high-fruit diet had lower odds of having SD, while those on a Western diet had higher odds of having SD. Although the study did not measure glycemic load, it is conceivable that the high glycemic load characteristic of the Western diet contributed to these findings.43 However, no studies have investigated the direct link between low-glycemic or ketogenic diets and SD, leaving this area open for further study.
Atopic Dermatitis—It has been hypothesized that mitigating T cell–mediated inflammation via glucose control may contribute to the improvement in AD.35,36 However, in one study, 16.5% of AD patients self-identified sugar as a dietary trigger, ranking fourth among other dietary triggers.24 Thus, the connection between glucose levels and AD warrants further exploration.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa—Given the role of metabolic and hormonal influence in HS as well as the overlapping pathophysiology with acne, it is possible that low-glycemic and ketogenic diets may have a role in improving HS.38-40 However, there is a gap in observation and controlled studies investigating the link between low-glycemic or ketogenic diets and HS.
Conclusion
Our analysis focused on interventional and observational research exploring the effects of low-glycemic and ketogenic diets on associations and treatment of inflammatory skin conditions. There is sufficient evidence to counsel acne patients on the benefits of a low-glycemic diet as an adjunctive treatment for acne. Currently, there is insufficient evidence to recommend a low-glycemic or ketogenic diet as a treatment for patients with any other inflammatory skin disease. Prospective and controlled clinical trials are needed to clarify the utility of dietary interventions for treating inflammatory skin conditions.
- Pickett K, Loveman E, Kalita N, et al. Educational interventions to improve quality of life in people with chronic inflammatory skin diseases: systematic reviews of clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness. Health Technol Assess. 2015;19:1-176, v-vi.
- Giugliano D, Ceriello A, Esposito K. The effects of diet on inflammation: emphasis on the metabolic syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48:677-685.
- Dowlatshahi EA, van der Voort EA, Arends LR, et al. Markers of systemic inflammation in psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:266-282.
- Youm YH, Nguyen KY, Grant RW, et al. The ketone metabolite beta-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease. Nat Med. 2015;21:263-269.
- Melnik BC. Acne vulgaris: the metabolic syndrome of the pilosebaceous follicle. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:29-40.
- Upala S, Sanguankeo A. Effect of lifestyle weight loss intervention on disease severity in patients with psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Obes (Lond). 2015;39:1197-1202.
- Heng AHS, Chew FT. Systematic review of the epidemiology of acne vulgaris. Sci Rep. 2020;10:5754.
- Paoli A, Grimaldi K, Toniolo L, et al. Nutrition and acne: therapeutic potential of ketogenic diets. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2012;25:111-117.
- Masood W, Annamaraju P, Khan Suheb MZ, et al. Ketogenic diet. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- Fomin DA, McDaniel B, Crane J. The promising potential role of ketones in inflammatory dermatologic disease: a new frontier in treatment research. J Dermatolog Treat. 2017;28:484-487.
- Zhang D, Jin W, Wu R, et al. High glucose intake exacerbates autoimmunity through reactive-oxygen-species-mediated TGF-β cytokine activation. Immunity. 2019;51:671-681.e5.
- Cerman AA, Aktas E, Altunay IK, et al. Dietary glycemic factors, insulin resistance, and adiponectin levels in acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:155-162.
- Ferrere G, Tidjani Alou M, Liu P, et al. Ketogenic diet and ketone bodies enhance the anticancer effects of PD-1 blockade. JCI Insight. 2021;6:e145207.
- Burris J, Shikany JM, Rietkerk W, et al. A Low glycemic index and glycemic load diet decreases insulin-like growth factor-1 among adults with moderate and severe acne: a short-duration, 2-week randomized controlled trial. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2018;118:1874-1885.
- Tan JKL, Stein Gold LF, Alexis AF, et al. Current concepts in acne pathogenesis: pathways to inflammation. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2018;37(3S):S60-S62.
- Kim J, Ochoa MT, Krutzik SR, et al. Activation of toll-like receptor 2 in acne triggers inflammatory cytokine responses. J Immunol. 2002;169:1535-1541.
- Bett DG, Morland J, Yudkin J. Sugar consumption in acne vulgaris and seborrhoeic dermatitis. Br Med J. 1967;3:153-155.
- Smith RN, Mann NJ, Braue A, et al. A low-glycemic-load diet improves symptoms in acne vulgaris patients: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86:107-115.
- Rouhani P, Berman B, Rouhani G. Acne improves with a popular, low glycemic diet from South Beach. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60(Suppl 1):AB14.
- Aksu AE, Metintas S, Saracoglu ZN, et al. Acne: prevalence and relationship with dietary habits in Eskisehir, Turkey. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26:1503-1509.
- Kwon HH, Yoon JY, Hong JS, et al. Clinical and histological effect of a low glycaemic load diet in treatment of acne vulgaris in Korean patients: a randomized, controlled trial. Acta Derm Venereol. 2012;92:241-246.
- Johnson JA, Ma C, Kanada KN, et al. Diet and nutrition in psoriasis: analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) in the United States. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:327-332.
- Barrea L, Macchia PE, Tarantino G, et al. Nutrition: a key environmental dietary factor in clinical severity and cardio-metabolic risk in psoriatic male patients evaluated by 7-day food-frequency questionnaire. J Transl Med. 2015;13:303.
- Nosrati A, Afifi L, Danesh MJ, et al. Dietary modifications in atopic dermatitis: patient-reported outcomes. J Dermatolog Treat. 2017;28:523-538.
- Afifi L, Danesh MJ, Lee KM, et al. Dietary behaviors in psoriasis: patient-reported outcomes from a U.S. national survey. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2017;7:227-242.
- Burris J, Rietkerk W, Shikany JM, et al. Differences in dietary glycemic load and hormones in New York City adults with no and moderate/severe acne. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2017;117:1375-1383.
- Yamashita H, Morita T, Ito M, et al. Dietary habits in Japanese patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: low intake of meat in psoriasis and high intake of vitamin A in psoriatic arthritis. J Dermatol. 2019;46:759-769.
- Marson J, Baldwin HE. 12761 Acne, twins, and glycemic index: a sweet pilot study of diet and dietary beliefs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83(Suppl):AB110.
- Castaldo G, Rastrelli L, Galdo G, et al. Aggressive weight-loss program with a ketogenic induction phase for the treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis: a proof-of-concept, single-arm, open-label clinical trial. Nutrition. 2020;74:110757.
- Castaldo G, Pagano I, Grimaldi M, et al. Effect of very-low-calorie ketogenic diet on psoriasis patients: a nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomic study. J Proteome Res. 2021;20:1509-1521.
- Ip W, Kirchhof MG. Glycemic control in the treatment of psoriasis. Dermatology. 2017;233:23-29.
- Vijaya Chandra SH, Srinivas R, Dawson TL Jr, et al. Cutaneous Malassezia: commensal, pathogen, or protector? Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020;10:614446.
- David Boothe W, Tarbox JA, Tarbox MB. Atopic dermatitis: pathophysiology. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1027:21-37.
- Guttman-Yassky E, Hanifin JM, Boguniewicz M, et al. The role of phosphodiesterase 4 in the pathophysiology of atopic dermatitis and the perspective for its inhibition. Exp Dermatol. 2019;28:3-10.
- Furue K, Ito T, Tsuji G, et al. The IL-13–OVOL1–FLG axis in atopic dermatitis. Immunology. 2019;158:281-286.
- Renert-Yuval Y, Guttman-Yassky E. New treatments for atopic dermatitis targeting beyond IL-4/IL-13 cytokines. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020;124:28-35.
- Sellheyer K, Krahl D. “Hidradenitis suppurativa” is acne inversa! An appeal to (finally) abandon a misnomer. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:535-540.
- Danby FW, Margesson LJ. Hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Clin. 2010;28:779-793.
- Fernandez JM, Marr KD, Hendricks AJ, et al. Alleviating and exacerbating foods in hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E14246.
- Yamanaka-Takaichi M, Revankar R, Shih T, et al. Expert consensus on priority research gaps in dietary and lifestyle factors in hidradenitis suppurativa: a Delphi consensus study. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:2129-2136.
- Meixiong J, Ricco C, Vasavda C, et al. Diet and acne: a systematic review. JAAD Int. 2022;7:95-112.
- Chung M, Bartholomew E, Yeroushalmi S, et al. Dietary intervention and supplements in the management of psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckland). 2022;12:151-176. doi:10.2147/PTT.S328581
- Sanders MGH, Pardo LM, Ginger RS, et al. Association between diet and seborrheic dermatitis: a cross-sectional study. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:108-114.
- Pickett K, Loveman E, Kalita N, et al. Educational interventions to improve quality of life in people with chronic inflammatory skin diseases: systematic reviews of clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness. Health Technol Assess. 2015;19:1-176, v-vi.
- Giugliano D, Ceriello A, Esposito K. The effects of diet on inflammation: emphasis on the metabolic syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48:677-685.
- Dowlatshahi EA, van der Voort EA, Arends LR, et al. Markers of systemic inflammation in psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:266-282.
- Youm YH, Nguyen KY, Grant RW, et al. The ketone metabolite beta-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease. Nat Med. 2015;21:263-269.
- Melnik BC. Acne vulgaris: the metabolic syndrome of the pilosebaceous follicle. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:29-40.
- Upala S, Sanguankeo A. Effect of lifestyle weight loss intervention on disease severity in patients with psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Obes (Lond). 2015;39:1197-1202.
- Heng AHS, Chew FT. Systematic review of the epidemiology of acne vulgaris. Sci Rep. 2020;10:5754.
- Paoli A, Grimaldi K, Toniolo L, et al. Nutrition and acne: therapeutic potential of ketogenic diets. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2012;25:111-117.
- Masood W, Annamaraju P, Khan Suheb MZ, et al. Ketogenic diet. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- Fomin DA, McDaniel B, Crane J. The promising potential role of ketones in inflammatory dermatologic disease: a new frontier in treatment research. J Dermatolog Treat. 2017;28:484-487.
- Zhang D, Jin W, Wu R, et al. High glucose intake exacerbates autoimmunity through reactive-oxygen-species-mediated TGF-β cytokine activation. Immunity. 2019;51:671-681.e5.
- Cerman AA, Aktas E, Altunay IK, et al. Dietary glycemic factors, insulin resistance, and adiponectin levels in acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:155-162.
- Ferrere G, Tidjani Alou M, Liu P, et al. Ketogenic diet and ketone bodies enhance the anticancer effects of PD-1 blockade. JCI Insight. 2021;6:e145207.
- Burris J, Shikany JM, Rietkerk W, et al. A Low glycemic index and glycemic load diet decreases insulin-like growth factor-1 among adults with moderate and severe acne: a short-duration, 2-week randomized controlled trial. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2018;118:1874-1885.
- Tan JKL, Stein Gold LF, Alexis AF, et al. Current concepts in acne pathogenesis: pathways to inflammation. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2018;37(3S):S60-S62.
- Kim J, Ochoa MT, Krutzik SR, et al. Activation of toll-like receptor 2 in acne triggers inflammatory cytokine responses. J Immunol. 2002;169:1535-1541.
- Bett DG, Morland J, Yudkin J. Sugar consumption in acne vulgaris and seborrhoeic dermatitis. Br Med J. 1967;3:153-155.
- Smith RN, Mann NJ, Braue A, et al. A low-glycemic-load diet improves symptoms in acne vulgaris patients: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86:107-115.
- Rouhani P, Berman B, Rouhani G. Acne improves with a popular, low glycemic diet from South Beach. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60(Suppl 1):AB14.
- Aksu AE, Metintas S, Saracoglu ZN, et al. Acne: prevalence and relationship with dietary habits in Eskisehir, Turkey. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26:1503-1509.
- Kwon HH, Yoon JY, Hong JS, et al. Clinical and histological effect of a low glycaemic load diet in treatment of acne vulgaris in Korean patients: a randomized, controlled trial. Acta Derm Venereol. 2012;92:241-246.
- Johnson JA, Ma C, Kanada KN, et al. Diet and nutrition in psoriasis: analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) in the United States. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:327-332.
- Barrea L, Macchia PE, Tarantino G, et al. Nutrition: a key environmental dietary factor in clinical severity and cardio-metabolic risk in psoriatic male patients evaluated by 7-day food-frequency questionnaire. J Transl Med. 2015;13:303.
- Nosrati A, Afifi L, Danesh MJ, et al. Dietary modifications in atopic dermatitis: patient-reported outcomes. J Dermatolog Treat. 2017;28:523-538.
- Afifi L, Danesh MJ, Lee KM, et al. Dietary behaviors in psoriasis: patient-reported outcomes from a U.S. national survey. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2017;7:227-242.
- Burris J, Rietkerk W, Shikany JM, et al. Differences in dietary glycemic load and hormones in New York City adults with no and moderate/severe acne. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2017;117:1375-1383.
- Yamashita H, Morita T, Ito M, et al. Dietary habits in Japanese patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: low intake of meat in psoriasis and high intake of vitamin A in psoriatic arthritis. J Dermatol. 2019;46:759-769.
- Marson J, Baldwin HE. 12761 Acne, twins, and glycemic index: a sweet pilot study of diet and dietary beliefs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83(Suppl):AB110.
- Castaldo G, Rastrelli L, Galdo G, et al. Aggressive weight-loss program with a ketogenic induction phase for the treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis: a proof-of-concept, single-arm, open-label clinical trial. Nutrition. 2020;74:110757.
- Castaldo G, Pagano I, Grimaldi M, et al. Effect of very-low-calorie ketogenic diet on psoriasis patients: a nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomic study. J Proteome Res. 2021;20:1509-1521.
- Ip W, Kirchhof MG. Glycemic control in the treatment of psoriasis. Dermatology. 2017;233:23-29.
- Vijaya Chandra SH, Srinivas R, Dawson TL Jr, et al. Cutaneous Malassezia: commensal, pathogen, or protector? Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020;10:614446.
- David Boothe W, Tarbox JA, Tarbox MB. Atopic dermatitis: pathophysiology. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1027:21-37.
- Guttman-Yassky E, Hanifin JM, Boguniewicz M, et al. The role of phosphodiesterase 4 in the pathophysiology of atopic dermatitis and the perspective for its inhibition. Exp Dermatol. 2019;28:3-10.
- Furue K, Ito T, Tsuji G, et al. The IL-13–OVOL1–FLG axis in atopic dermatitis. Immunology. 2019;158:281-286.
- Renert-Yuval Y, Guttman-Yassky E. New treatments for atopic dermatitis targeting beyond IL-4/IL-13 cytokines. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020;124:28-35.
- Sellheyer K, Krahl D. “Hidradenitis suppurativa” is acne inversa! An appeal to (finally) abandon a misnomer. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:535-540.
- Danby FW, Margesson LJ. Hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Clin. 2010;28:779-793.
- Fernandez JM, Marr KD, Hendricks AJ, et al. Alleviating and exacerbating foods in hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E14246.
- Yamanaka-Takaichi M, Revankar R, Shih T, et al. Expert consensus on priority research gaps in dietary and lifestyle factors in hidradenitis suppurativa: a Delphi consensus study. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:2129-2136.
- Meixiong J, Ricco C, Vasavda C, et al. Diet and acne: a systematic review. JAAD Int. 2022;7:95-112.
- Chung M, Bartholomew E, Yeroushalmi S, et al. Dietary intervention and supplements in the management of psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckland). 2022;12:151-176. doi:10.2147/PTT.S328581
- Sanders MGH, Pardo LM, Ginger RS, et al. Association between diet and seborrheic dermatitis: a cross-sectional study. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:108-114.
Practice Points
- As the ketogenic diet gains in popularity, dermatologists may inform patients that there is emerging evidence supporting the idea that low-glycemic diets may contribute to improvement in inflammatory skin conditions.
- Dermatologists may educate patients about the potential benefits of a low-glycemic diet as a supplementary treatment for acne based on existing evidence.
- Current evidence is insufficient to endorse a ketogenic diet as superior to other dietary approaches in treating inflammatory skin conditions.
Expanding the Psoriasis Framework: Immunopathogenesis and Treatment Updates
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects approximately 3% of the US population.1 Plaque psoriasis comprises 80% to 90% of cases, while pustular, erythrodermic, guttate, inverse, and palmoplantar disease are less common variants (Figure 1). Psoriatic skin manifestations range from localized to widespread or generalized disease with recurrent flares. Body surface area or psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) measurements primarily focus on skin manifestations and are important for evaluating disease activity and response to treatment, but they have inherent limitations: they do not capture extracutaneous disease activity, systemic inflammation, comorbid conditions, quality of life impact, or the economic burden of psoriasis.
A common manifestation of psoriasis is psoriatic arthritis (PsA), which can involve the nails, joints, ligaments, or tendons in 30% to 41% of affected individuals (Figure 2).2,3 A growing number of psoriasis-associated comorbidities also have been reported including metabolic syndrome4; hyperlipidemia5; cardiovascular disease6; stroke7; hypertension8; obesity9; sleep disorders10; malignancy11; infections12; inflammatory bowel disease13; and mental health disorders such as depression,14 anxiety,15 and suicidal ideation.15 Psoriatic disease also interferes with daily life activities and a patient’s overall quality of life, including interpersonal relationships, intimacy, employment, and work productivity.16 Finally, the total estimated cost of psoriasis-related health care is more than $35 billion annually,17 representing a substantial economic burden to our health care system and individual patients.
The overall burden of psoriatic disease has declined markedly in the last 2 decades due to revolutionary advances in our understanding of the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis and the subsequent development of improved therapies that predominantly interrupt IL-23/IL-17 cytokine signaling; however, critical knowledge and treatment gaps persist, underscoring the importance of ongoing clinical and research efforts in psoriatic disease. We review the working immune model of psoriasis, summarize related immune discoveries, and highlight recent therapeutic innovations that are shaping psoriatic disease management.
Current Immune Model of Psoriatic Disease
Psoriasis is an autoinflammatory T cell–mediated disease with negligible contributions from the humoral immune response. Early clinical observations reported increased inflammatory infiltrates in psoriatic skin lesions primarily consisting of both CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell populations.18,19 Additionally, patients treated with broad-acting, systemic immunosuppressive medications (eg, cyclosporine, oral corticosteroids) experienced improvement of psoriatic lesions and normalization of the immune infiltrates observed in skin biopsy specimens.20,21 These early clinical findings led to more sophisticated experimentation in xenotransplant models of psoriasis,22,23 which explored the clinical efficacy of several less immunosuppressive (eg, methotrexate, anti–tumor necrosis factor [TNF] biologics)24 or T cell–specific agents (eg, alefacept, abatacept, efalizumab).25-27 The results of these translational studies provided indisputable evidence for the role of the dysregulated immune response as the primary pathogenic process driving plaque formation; they also led to a paradigm shift in how the immunopathogenesis of psoriatic disease was viewed and paved the way for the identification and targeting of other specific proinflammatory signals produced by activated dendritic cell (DC) and T-lymphocyte populations. Among the psoriasis-associated cytokines subsequently identified and studied, elevated IL-23 and IL-17 cytokine levels in psoriatic skin were most closely associated with disease activity, and rapid normalization of IL-23/IL-17 signaling in response to effective oral or injectable antipsoriatic treatments was the hallmark of skin clearance.28 The predominant role of IL-23/IL-17 signaling in the development and maintenance of psoriatic disease is the central feature of all working immune models for this disease (Figure 3).
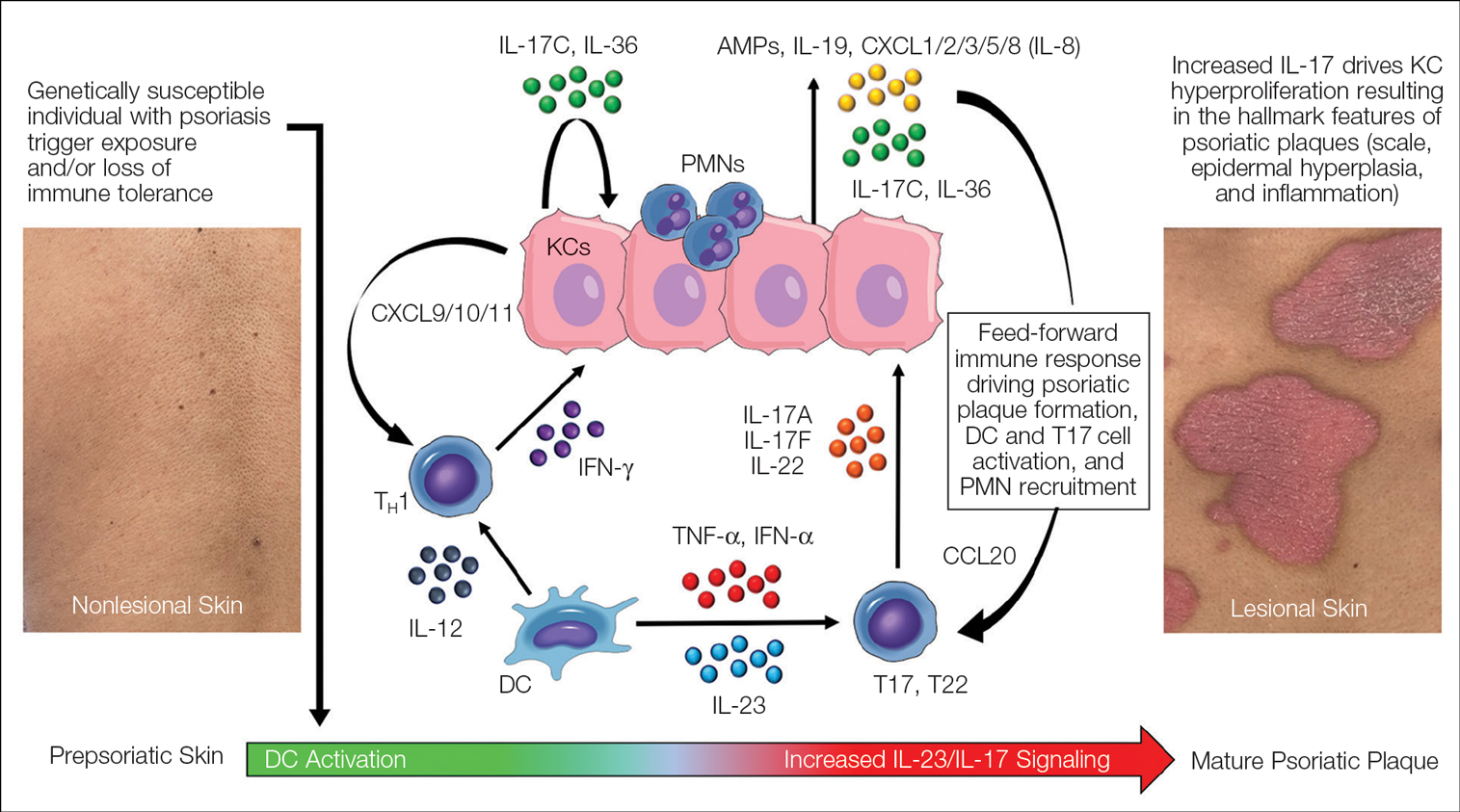
Psoriasis-Associated Genetic and Environmental Risk Factors
The exact sequence of events that lead to the initiation and formation of plaque psoriasis in susceptible individuals is still poorly understood; however, several important risk factors and key immune events have been identified. First, decades of genetic research have reported more than 80 known psoriasis-associated susceptibility loci,29 which explains approximately 50% of psoriasis heritability. The major genetic determinant of psoriasis, HLA-C*06:02 (formerly HLA-Cw6), resides in the major histocompatibility complex class I region on chromosome 6p21.3 (psoriasis susceptibility gene 1, PSORS1) and is most strongly associated with psoriatic disease.30 Less common psoriasis-associated susceptibility genes also are known to directly or indirectly impact innate and adaptive immune functions that contribute to the pathogenesis of psoriasis.
Second, several nongenetic environmental risk factors for psoriasis have been reported across diverse patient populations, including skin trauma/injury, infections, alcohol/tobacco use, obesity, medication exposure (eg, lithium, antimalarials, beta-blockers), and stress.31 These genetic and/or environmental risk factors can trigger the onset of psoriatic disease at any stage of life, though most patients develop disease in early adulthood or later (age range, 50–60 years). Some patients never develop psoriasis despite exposure to environmental risk factors and/or a genetic makeup that is similar to affected first-degree relatives, which requires further study.
Prepsoriatic Skin and Initiation of Plaque Development
In response to environmental stimuli and/or other triggers of the immune system, DC and resident IL-17–producing T-cell (T17) populations become activated in predisposed individuals. Dendritic cell activation leads to the upregulation and increase of several proinflammatory cytokines, including TNF, interferon (IFN) α, IFN-γ, IL-12, and IL-23. Tumor necrosis factor and IL-23 play a vital role in psoriasis by helping to regulate the polarization and expansion of T22 and T17 cells in the skin, whereas IL-12 promotes a corresponding type 1 inflammatory response.32 Increased IL-17 and IL-22 result in alteration of the terminal differentiation and proliferative potential of epidermal keratinocytes, leading to the early clinical hallmarks of psoriatic plaques. The potential contribution of overexpressed psoriasis-related autoantigens, such as LL-37/cathelicidin, ADAMTSL5, and PLA2G4D,33 in the initiation of psoriatic plaques has been suggested but is poorly characterized.34 Whether these specific autoantigens or others presented by HLA-C variants found on antigen-presenting cells are required for the breakdown of immune tolerance and psoriatic disease initiation is highly relevant but requires further investigation and validation.
Feed-Forward Inflammation, Mature Psoriatic Plaques, and Resident Memory T Cells
In response to the upstream production of IL-23 by dermal DCs, high levels of IL-17 cytokines can be found in mature psoriatic plaques. The IL-17 family consists of 6 dimeric cytokines (IL-17A through IL-17F) that provide innate cutaneous protection against bacterial, viral, and fungal infectious agents, such as Candida albicans. Unlike other IL-17 isoforms, IL-17A and IL-17F share the same receptor complex and have the highest structural homology of any pair (approximately 50% similar).35 The relative expression of IL-17F is higher than IL-17A in psoriasis,36 though IL-17A has been considered as the predominant IL-17 cytokine found in psoriatic skin lesions due to its higher potency.
Binding of IL-17A/F with the IL-17 receptor (IL-17R) on keratinocytes contributes to the development of psoriatic plaques by inducing epidermal hyperplasia via activation of CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins β and δ, nuclear factor κB, and signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 gene (STAT1).37,38 This also increases the expression of other keratinocyte-derived proteins (eg, human β-defensins, S-100 proteins, LL-37, other antimicrobial peptides, IL-19, IL-36, IL-17C) that act as reinforcing proinflammatory signals or chemotactic factors (eg, chemokine [C-C motif] ligand 20 [CCL20], chemokine [C-C motif] ligand 1/2/3/5 [CXCL1/2/3/5], CXCL8, IL-8) that facilitate the recruitment of additional immune cells to the skin including polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs), macrophages, and DCs.39-41 Routine immunohistochemical staining for these keratinocyte-derived proteins reveals a striking epidermal gene expression gradient wherein levels of IL-17–induced proteins are most highly expressed in the uppermost layers of keratinocytes and facilitate the recruitment of immune cells into the epidermis. Activated T17 cells also stimulate the production of keratinocyte-derived chemokines (eg, CXCL9/10/11), which recruit type 1 inflammatory T-cell populations into developing psoriatic plaques.42,43 Finally, TNF, IL-36, and IL-17C cytokines act synergistically with IL-17A/F to amplify the proinflammatory effects of IL-17 signaling and further stimulate their production from T17 cell populations.40 This inflammatory circuit in the skin creates and supports a self-amplifying or positive feedback loop between the skin and immune system that commonly is referred to as feed-forward inflammation (Figure 3).34 The feed-forward inflammatory loop in psoriasis—predominantly driven by increased IL-23/IL-17 signaling—best characterizes the mature psoriatic plaque.
Several findings suggest that the influx of persistent, long-lived resident memory T cells (Trms) may contribute to the mature psoriatic plaque. It is believed that CD8+CD103+CD49a− Trm cell populations may be responsible for the sharply demarcated borders of untreated psoriasis plaques or their recurrence at specific body sites such as the scalp, buttocks, extremity extensor surfaces, umbilicus, or acral skin following specific stimuli or trauma (Koebner phenomenon or isomorphic response).44,45 It is not known if repeated stimuli or trauma induce disease formation via the activation of Trm cell populations; further study in large patient cohorts is needed, but this remains an intriguing area of study for durable treatment responses and potential cures for psoriasis.
Recent Discoveries in Psoriatic Disease
Remarkable treatment outcomes for psoriasis have been achieved with multiple selective IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors (eTable). As demonstrated in several pivotal phase 3 clinical trials for members of these classes of medications, the majority of treated psoriasis patients achieved PASI90 clearance.46 Due to their more favorable dosing schedule (ie, fewer injections) and ability to induce a durable remissionlike treatment response, IL-23 inhibitors have become the preferred treatment class for cutaneous disease, while IL-17 inhibitors may be preferred when treating patients with both plaque psoriasis and PsA.47,48 Nevertheless, the complexity of this disease is punctuated by treated patients who do not adequately respond to selective IL-23/IL-17 blockade.49 Recent and emerging treatments may shed light on these recalcitrant cases and will add to the rapidly growing arsenal of available psoriasis therapies.
The Role of IL-17F in Psoriasis and Other Inflammatory Skin Diseases
Dysregulation of IL-17A and IL-17F is associated with several chronic inflammatory conditions, such as psoriasis and PsA.35,50 Both cytokines, either as homodimers or heterodimers, can selectively bind to the heterodimeric IL-17R formed by the IL-17RA and IL-17RC subunits.35 IL-17F and IL-17C also can synergize with TNF and other cytokines to promote and support the self-sustaining inflammatory circuits in mature psoriatic plaques, though their inflammatory effects in the skin are more limited than IL-17A.51,52 Therefore, incomplete blockade of IL-17 signaling (ie, unopposed IL-17F and IL-17C) represents a potential mechanism to explain the persistence of psoriasis in patients treated with selective IL-17A inhibitors. This hypothesis is supported by reports of psoriasis patients who have inadequate clinical responses to selective IL-17A inhibition but subsequently improve with IL-17R blockade, which results in disruption of IL-17A as well as IL-17C/E/F cytokine signaling. This formed the basis for further study into the specific role of IL-17F in psoriatic disease and any potential therapeutic benefits associated with its inhibition.
Recently approved in the European Union, Canada, Australia, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States for moderate to severe psoriasis, bimekizumab is a novel humanized IgG antibody that selectively inhibits both IL-17A and IL-17F cytokines.53 Specifically, bimekizumab simultaneously prevents binding of IL-17A/A, IL-17A/F, and IL-17F/F dimers with the IL-17R. Compared to other IL-17 and IL-23 biologic therapies, bimekizumab (320 mg) achieved relatively higher response rates for PASI75, PASI90, and PASI100.49 Neutralization of IL-17A and IL-17F by bimekizumab also resulted in more complete suppression of cytokine responses and PMN chemotaxis than either cytokine alone in treated PsA patients,54 which is notable because of the incremental benefits of recent IL-23 and IL-17 inhibitors on inflammatory arthritis symptoms in contrast to the substantial improvements observed for cutaneous disease with those same agents.
The primary disadvantage of bimekizumab and its more complete blockade of the IL-17 signaling pathway is that treated patients have a substantially increased risk for oral candidiasis (>10%).55 However, the precise link between candidiasis and IL-17 blockade is not yet fully understood because other targeted agents that also broadly suppress IL-17 signaling (ie, IL-17R, IL-23 inhibitors) are associated with much lower rates of candidiasis.56-58 Bimekizumab also is being investigated as a novel therapy for hidradenitis suppurativa and will provide important reference information regarding the role for bispecific biologic agents in the treatment of chronic inflammatory skin diseases.59
IL-36 Signaling and Generalized Pustular Psoriasis
Recent genetic and clinical studies have expanded our understanding of the role of IL-36 signaling in the immunopathogenesis of pustular psoriasis variants. Generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) is a rare distinct psoriasis subtype characterized by the recurrent development of widespread erythema, superficial sterile pustules, and desquamation. Systemic symptoms such as fever, malaise, itching, and skin pain accompany acute GPP flares.60 Generalized pustular psoriasis is more common in female patients (in contrast with plaque psoriasis), and acute flares may be caused by multiple stimuli including infections, hypocalcemia, initiation or discontinuation of medications (eg, oral corticosteroids), pregnancy, or stress.61,62 Flares of GPP often require emergency or in-patient care, as untreated symptoms increase the risk for severe health complications such as secondary infections, sepsis, or multisystem organ failure.63 The prevalence of GPP is estimated to be approximately 1 in 10,000 individuals in the United States,64-67 with mortality rates ranging from 0 to 3.3 deaths per 100 patient-years.67
In contrast to plaque psoriasis, aberrant IL-36 signaling is the predominant driver of GPP. IL-36 is a member of the IL-1 cytokine family that includes three IL-36 agonists (IL-36α, IL-36β, IL-36γ) and 1 endogenous antagonist (IL-36Ra, encoded by IL36RN).68 The immunopathogenesis of GPP involves dysregulation of the IL-36–chemokine–PMN axis, resulting in unopposed IL-36 signaling and the subsequent recruitment and influx of PMNs into the epidermis. IL36RN mutations are strongly associated with GPP and result in impaired function of the IL-36Ra protein, leading to unopposed IL-36 signaling.69 However, approximately two-thirds of GPP patients lack identifiable gene mutations, suggesting other immune mechanisms or triggers causing upregulated IL-36 signaling.70 In response to these triggers, increased IL-36 cytokines released by keratinocytes bind to the IL-36R, resulting in substantial keratinocyte hyperproliferation, increased IL-36 levels, and the expression of hundreds of additional inflammatory signals (eg, IL-17C, antimicrobial peptides, TNF, IL-6).71 Increased IL-36 levels also drive the production of PMN chemotactic proteins (eg, CXCL1/2/3/5/6/8 and CXCR1/2) and act synergistically with IL-17 cytokines to create an autoamplifying circuit that is analogous to the feed-forward inflammatory loop in plaque psoriasis.72 Biopsies of involved GPP skin reveal increased expression of IL-36 in the uppermost layers of the epidermis, which creates a gene expression gradient that acts as a strong attractant for PMNs and forms the basis for the hallmark pustular lesions observed in GPP patients.
Until recently, treatment strategies for GPP involved the off-label use of topical, oral, or biologic therapies approved for plaque psoriasis, which often was associated with variable or incomplete disease control. In September 2022, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved intravenous spesolimab as a first-in-class humanized monoclonal IgG1 antibody for the treatment of GPP flares in adults. Spesolimab binds to IL-36R and prevents its activation by its endogenous agonists. A phase 2, randomized, 12-week clinical trial (Effisayil-1) evaluated the efficacy and safety of a single 900-mg intravenous dose of spesolimab followed by an optional second dose 1 week later for inadequate treatment responses in 53 enrolled GPP patients (2:1 treatment to placebo randomization).73 Remarkably, more than half (19/35 [54%]) of GPP patients experienced complete resolution of pustules (GPP physician global assessment subscore of 0 [range, 0–4]) and showed sustained efficacy out to week 12 after just 1 or 2 doses of spesolimab. Overall, the safety profile of spesolimab was good; asthenia, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, headache, pruritus, infusion-related reaction and symptoms, and mild infections (eg, urinary tract infection) were the most common adverse events reported.73
Imsidolimab, a high-affinity humanized IgG4 monoclonal antibody that binds and blocks activation of IL-36R, also has completed phase 2 testing,74 with phase 3 study results expected in early 2024. The rapid onset of action and overall safety of imsidolimab was in line with and similar to spesolimab. Future approval of imsidolimab would add to the limited treatment options available for GPP and has the additional convenience of being administered to patients subcutaneously. Overall, the development of selective IL-36R inhibitors offers a much-needed therapeutic option for GPP and illustrates the importance of translational research.
Role of Tyrosine Kinase in Psoriatic Disease
The Janus kinase (JAK) enzyme family consists of 4 enzymes—tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2), JAK1, JAK2, and JAK3—that function as intracellular transduction signals that mediate the biologic response of most extracellular cytokines and growth factors.75 Critical psoriasis-related cytokines are dependent on intact JAK-STAT signaling, including IL-23, IL-12, and type I IFNs. In 2010, a genome-wide association identified TYK2 as a psoriasis susceptibility locus,76 and loss-of-function TYK2 mutations confer a reduced risk for psoriasis.77 Unlike other JAK isoforms, TYK2 mediates biologic functions that are highly restricted to the immune responses associated with IL-23, IL-12, and type I IFN signaling.78,79 For these reasons, blockade of TYK2 signaling is an attractive therapeutic target for the potential treatment of psoriatic disease.
In September 2022, the FDA approved deucravacitinib as a first-in-class, oral, selective TYK2 inhibitor for the treatment of adult patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. It was the first FDA approval of an oral small-molecule treatment for plaque psoriasis in nearly a decade. Deucravacitinib inhibits TYK2 signaling via selective binding of its unique regulatory domain, resulting in a conformational (allosteric) change that interferes with its active domain.80 This novel mechanism of action limits the unwanted blockade of other broad biologic processes mediated by JAK1/2/3. Of note, the FDA did not issue any boxed warnings for deucravacitinib as it did for other FDA-approved JAK inhibitors.
In a head-to-head, 52-week, double-blind, prospective, randomized, phase 3 study, deucravacitinib showed clear superiority over apremilast for PASI75 at week 16 (53.0% [271/511] vs 39.8% [101/254]) and week 24 (58.7% [296/504] vs 37.8% [96/254]).81 Clinical responses were sustained through week 52 and showed efficacy for difficult-to-treat areas such as the scalp, acral sites, and nails. Other advantages of deucravacitinib include once-daily dosing with no need for dose titration or adjustments for renal insufficiency as well as the absence of statistically significant differences in gastrointestinal tract symptoms compared to placebo. The most common adverse effects included nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infections, headache, diarrhea, and herpes infections.81 The potential benefit of deucravacitinib for PsA and psoriasis comorbidities remains to be seen, but it is promising due to its simultaneous disruption of multiple psoriasis-related cytokine networks. Several other TYK2 inhibitors are being developed for psoriatic disease and related inflammatory conditions, underscoring the promise of targeting this intracellular pathway.
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Agonism
Topical steroids are the mainstay treatment option for localized or limited plaque psoriasis due to their potent immunosuppressive effect on the skin and relatively low cost. Combined with vitamin D analogs, topical steroids result in marked improvements in disease severity and improved tolerability.82 However, chronic use of topical steroids is limited by the need for twice-daily application, resulting in poor treatment compliance; loss of efficacy over time; risk for steroid-induced skin atrophy on special body sites; and patient concerns of potential systemic effects. The discovery of novel drug targets amenable to topical inhibition is needed.
Dysregulated aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) levels have been reported in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.83 Aryl hydrocarbon receptors are ubiquitously expressed in many cell types and play an integral role in immune homeostasis within the skin, skin barrier function, protection against oxidative stressors, and regulation of proliferating melanocytes and keratinocytes.84,85 They are widely expressed in multiple immune cell types (eg, antigen-presenting cells, T lymphocytes, fibroblasts) and modulate the differentiation of T17 and T22 cells as well as their balance with regulatory T-cell populations.86 In keratinocytes, AHR helps to regulate terminal differentiation, enhance skin barrier integrity via AHR-dependent filaggrin (FLG) expression, and prevent transepidermal water loss.87,88 The mechanisms by which AHR ligands lead to the upregulation or downregulation of specific genes is intricate and highly context dependent, such as the specific ligand and cell type involved. In preclinical studies, AHR-deficient mice develop psoriasiform skin inflammation, increased IL-17 and IL-22 expression, and abnormal skin barrier function.89 Keratinocytes treated with AHR ligands in vitro modulated psoriasis-associated inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, IL-8, and type I and II IFNs.89,90 The use of coal tar, one of the earliest historical treatments for psoriasis, is thought to activate AHRs in the skin via organic compound mixtures containing polyaromatic hydrocarbons that help normalize the proinflammatory environment in psoriatic skin.91
In June 2022, the FDA approved tapinarof as a first-in-class, topical, nonsteroidal AHR agonist for the treatment of plaque psoriasis in adults. Although the exact mechanism of action for tapinarof has not been fully elucidated, early studies suggest that its primary function is the activation of AHR, leading to reduced T-cell expansion and T17 cell differentiation. In the imiquimod mouse model, cytokine expression of IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-19, IL-22, IL-23A, and IL-lβ in psoriasiform skin lesions were downregulated following tapinarof treatment.92 In humans, tapinarof treatment is associated with a remittive effect, in which the average time for tapinarof-treated psoriasis lesions to remain clear was approximately 4 months.93 Preliminary research investigating the mechanism by which tapinarof induces this remittive effect is ongoing and may involve the reduced activation and influx of T17 and Trm populations into the skin.94 However, these preclinical studies were performed on healthy dermatome-derived skin tissue cultured in T17-skewing conditions and needs to be replicated in larger samples sizes using human-derived psoriatic tissue. Alternatively, a strong inhibitory effect on IL-23 cytokine signaling may, in part, explain the remittive effect of tapinarof, as an analogous response is observed in patients who start and discontinue treatment with selective IL-23 antagonists. Regardless, the once-daily dosing of tapinarof and sustained treatment response is appealing to psoriasis patients. Tapinarof generally is well tolerated with mild folliculitis (>20% of patients) and contact dermatitis (5% of patients) reported as the most common skin-related adverse events.
New Roles for Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibition
Phosphodiesterases (PDEs) are enzymes that hydrolyze cyclic nucleotides (eg, cyclic adenosine monophosphate) to regulate intracellular secondary messengers involved in the inflammatory response. One of several enzymes in the PDE family, PDE4, has been shown to have greater activity in psoriatic skin compared to healthy skin.95 Phosphodiesterase inhibitors decrease the degradation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate, which triggers protein kinase A to downregulate proinflammatory (eg, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-17, IL-12, IL-23) cytokines and increased expression of anti-inflammatory signals such as IL-10.96,97 Apremilast, the first oral PDE4 inhibitor approved by the FDA for psoriasis, offered a safe alternative to traditional oral immunosuppressive agents that had extensive risks and potential end-organ adverse effects. Unfortunately, apremilast demonstrated modest efficacy for psoriatic disease (better efficacy in the skin vs joint manifestations) and was supplanted easily by next-generation targeted biologic agents that were more efficacious and lacked the troublesome gastrointestinal tract adverse effects of PDE4 inhibition.98
Crisaborole became the first topical PDE4 inhibitor approved in the United States in December 2016 for twice-daily treatment of atopic dermatitis. Although phase 2 trial results were reported in psoriasis, this indication was never pursued, presumably due to similar improvements in primary outcome measures at week 12, compared to placebo (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT01300052).
In July 2022, the first topical PDE4 inhibitor indicated for plaque psoriasis was approved by the FDA—roflumilast cream 0.3% for once-daily use in individuals 12 years and older. Roflumilast was found to be clinically efficacious as early as 2 weeks after its use in an early-phase clinical trial.99 In 2 phase 3 clinical trials (DERMIS-1 and DERMIS-2), roflumilast significantly increased the proportion of patients achieving PASI75 at week 8 compared to vehicle (39%–41.6% vs 5.3%–7.6%, respectively)(P<.001).100 Overall, this nonsteroidal topical therapy was found to be well tolerated, with infrequent reports of application site pain or irritation as adverse events. Similar to tapinarof, patients can apply roflumilast on all body surface areas including the face, external genitalia, and other intertriginous areas.100 Importantly, the broad immune impact of PDE4 inhibition suggests that topical roflumilast likely will be an effective treatment for several additional inflammatory conditions, including seborrheic dermatitis and atopic dermatitis, which would expand the clinical utility of this specific medication.
Conclusion
In the last 2 decades, we have witnessed a translational revolution in our understanding of the underlying genetics and immunology of psoriatic disease. Psoriasis is widely considered one of the best-managed inflammatory conditions in all of medicine due to the development and availability of highly targeted, effective topical and systemic therapies that predominantly disrupt IL-23/IL-17 cytokine signaling in affected tissues. However, future clinical studies and laboratory research are necessary to elucidate the precise cause of psoriasis as well as the underlying genetic and immune signaling pathways driving less common clinical variants and recalcitrant disease.
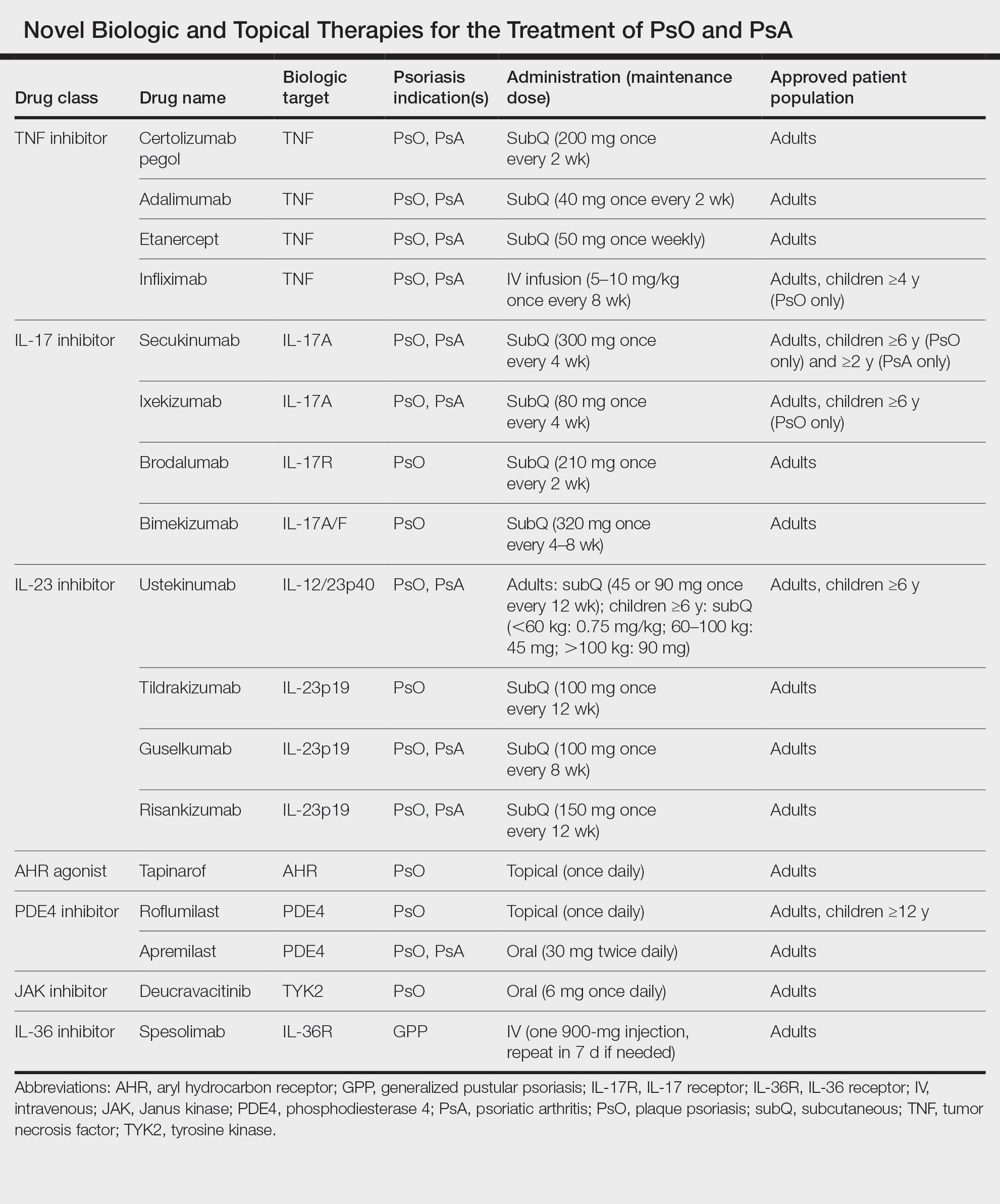
- Armstrong AW, Mehta MD, Schupp CW, et al. Psoriasis prevalence in adults in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:940-946. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.2007
- Ogdie A, Langan S, Love T, et al. Prevalence and treatment patterns of psoriatic arthritis in the UK. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013;52:568-575. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kes324
- Mease PJ, Gladman DD, Papp KA, et al. Prevalence of rheumatologistdiagnosed psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis in European/ North American dermatology clinics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:729- 735. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.07.023
- Langan SM, Seminara NM, Shin DB, et al. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in patients with psoriasis: a population-based study in the United Kingdom. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132(3 pt 1):556-562. doi:10.1038/jid.2011.365
- Wu S, Li WQ, Han J, et al. Hypercholesterolemia and risk of incident psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis in US women. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66:304-310. doi:10.1002/art.38227
- Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Armstrong EJ. The association between psoriasis and hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J Hypertens. 2013;31:433-442; discussion 442-443. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e32835bcce1
- Gelfand JM, Dommasch ED, Shin DB, et al. The risk of stroke in patients with psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:2411-2418. doi:10.1038 /jid.2009.112
- Armstrong AW, Lin SW, Chambers CJ, et al. Psoriasis and hypertension severity: results from a case-control study. PLoS One. 2011;6:E18227. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018227
- Naldi L, Chatenoud L, Linder D, et al. Cigarette smoking, body mass index, and stressful life events as risk factors for psoriasis: results from an Italian case-control study. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;125:61-67. doi:10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23681.x
- Yang YW, Kang JH, Lin HC. Increased risk of psoriasis following obstructive sleep apnea: a longitudinal population-based study. Sleep Med. 2012;13:285-289. doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2011.07.018
- Vaengebjerg S, Skov L, Egeberg A, et al. Prevalence, incidence, and risk of cancer in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:421-429. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.0024
- Loft N, Skov L, Richardson C, et al. A nationwide population-based cohort study of the incidence of severe and rare infections among adults with psoriasis in Denmark. Br J Dermatol. 2022;187:353-363. doi:10.1111/bjd.21595
- Fu Y, Lee CH, Chi CC. Association of psoriasis with inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1417-1423. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.3631
- Dowlatshahi EA, Wakkee M, Arends LR, et al. The prevalence and odds of depressive symptoms and clinical depression in psoriasis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:1542-1551. doi:10.1038/jid.2013.508
- Kurd SK, Troxel AB, Crits-Christoph P, et al. The risk of depression, anxiety, and suicidality in patients with psoriasis: a populationbased cohort study. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:891-895. doi:10.1001 /archdermatol.2010.186
- Elmets CA, Leonardi CL, Davis DMR, et al. Joint AAD-NPF guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with awareness and attention to comorbidities. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1073-1113. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.058
- Vanderpuye-Orgle J, Zhao Y, Lu J, et al. Evaluating the economic burden of psoriasis in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:961-967. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.02.1099
- Bos JD, Hagenaars C, Das PK, et al. Predominance of “memory” T cells (CD4+, CDw29+) over “naive” T cells (CD4+, CD45R+) in both normal and diseased human skin. Arch Dermatol Res. 1989;281:24-30. doi:10.1007/BF00424268
- Bos JD, Hulsebosch HJ, Krieg SR, et al. Immunocompetent cells in psoriasis. in situ immunophenotyping by monoclonal antibodies. Arch Dermatol Res. 1983;275:181-189. doi:10.1007/BF00510050
- Griffiths CE, Powles AV, Leonard JN, et al. Clearance of psoriasis with low dose cyclosporin. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1986;293:731-732. doi:10.1136/bmj.293.6549.731
- Ellis CN, Gorsulowsky DC, Hamilton TA, et al. Cyclosporine improves psoriasis in a double-blind study. JAMA. 1986;256:3110-3116.
- Langrish CL, Chen Y, Blumenschein WM, et al. IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med. 2005;201:233-240. doi:10.1084/jem.20041257
- Ferber IA, Brocke S, Taylor-Edwards C, et al. Mice with a disrupted IFN-gamma gene are susceptible to the induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). J Immunol. 1996;156:5-7.
- Bharadwaj R, Lusi CF, Mashayekh S, et al. Methotrexate suppresses psoriatic skin inflammation by inhibiting muropeptide transporter SLC46A2 activity. Immunity. 2023;56:998-1012. doi:10.1016/j. immuni.2023.04.001
- Jenneck C, Novak N. The safety and efficacy of alefacept in the treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2007;3:411-420.
- Pariser DM, Gordon KB, Papp KA, et al. Clinical efficacy of efalizumab in patients with chronic plaque psoriasis: results from three randomized placebo-controlled phase III trials: part I. J Cutan Med Surg. 2005; 9:303-312. doi:10.1007/s10227-005-0116-1
- Mease PJ, Gottlieb AB, van der Heijde D, et al. Efficacy and safety of abatacept, a T-cell modulator, in a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III study in psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:1550-1558. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210724
- Hawkes JE, Yan BY, Chan TC, et al. Discovery of the IL-23/IL-17 signaling pathway and the treatment of psoriasis. J Immunol. 2018;201:1605-1613. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1800013
- Ogawa K, Okada Y. The current landscape of psoriasis genetics in 2020. J Dermatol Sci. 2020;99:2-8. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2020.05.008
- Arakawa A, Siewert K, Stohr J, et al. Melanocyte antigen triggers autoimmunity in human psoriasis. J Exp Med. 2015;212:2203-2212. doi:10.1084/jem.20151093
- Griffiths CE, Barker JN. Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet. 2007;370:263-271. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61128-3
- Wang CQF, Akalu YT, Suarez-Farinas M, et al. IL-17 and TNF synergistically modulate cytokine expression while suppressing melanogenesis: potential relevance to psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:2741-2752. doi:10.1038/jid.2013.237
- Cheung KL, Jarrett R, Subramaniam S, et la. Psoriatic T cells recognize neolipid antigens generated by mast cell phospholipase delivered by exosomes and presented by CD1a. J Exp Med. 2016;213:2399-2412. doi:10.1084/jem.20160258
- Hawkes JE, Gonzalez JA, Krueger JG. Autoimmunity in psoriasis: evidence for specific autoantigens. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2017;6:104-112. doi:10.1007/s13671-017-0177-6
- Johansen C, Usher PA, Kjellerup RB, et al. Characterization of the interleukin-17 isoforms and receptors in lesional psoriatic skin. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160:319-324. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133 .2008.08902.x
- Kolbinger F, Loesche C, Valentin MA, et al. beta-Defensin 2 is a responsive biomarker of IL-17A-driven skin pathology in patients with psoriasis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139:923-932. doi:10.1016/j .jaci.2016.06.038
- Ruddy MJ, Wong GC, Liu XK, et al. Functional cooperation between interleukin-17 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha is mediated by CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein family members. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:2559-2567. doi:10.1074/jbc.M308809200
- Shen F, Hu Z, Goswami J, et al. Identification of common transcriptional regulatory elements in interleukin-17 target genes. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:24138-24148. doi:10.1074/jbc.M604597200
- Harper EG, Guo C, Rizzo H, et al. Th17 cytokines stimulate CCL20 expression in keratinocytes in vitro and in vivo: implications for psoriasis pathogenesis. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:2175-2183. doi:10.1038/jid.2009.65
- Chiricozzi A, Guttman-Yassky E, Suarez-Farinas M, et al. Integrative responses to IL-17 and TNF-alpha in human keratinocytes account for key inflammatory pathogenic circuits in psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 2011;131:677-687. doi:10.1038/jid.2010.340
- Homey B, Dieu-Nosjean MC, Wiesenborn A, et al. Up-regulation of macrophage inflammatory protein-3 alpha/CCL20 and CC chemokine receptor 6 in psoriasis. J Immunol. 2000;164:6621-6632. doi:10.4049 /jimmunol.164.12.6621
- Stephen-Victor E, Fickenscher H, Bayry J. IL-26: an emerging proinflammatory member of the IL-10 Cytokine family with multifaceted actions in antiviral, antimicrobial, and autoimmune responses. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12:E1005624. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1005624
- Wolk K, Witte K, Witte E, et al. IL-29 is produced by T(H)17 cells and mediates the cutaneous antiviral competence in psoriasis [published online September 25, 2013]. Sci Transl Med. doi:10.1126 /scitranslmed.3006245
- Kasprowicz-Furmanczyk M, Czerwinska J, Placek W, et al. Assessment of the tissue resident memory cells in lesional skin of patients with psoriasis and in healthy skin of healthy volunteers. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18:11251. doi:10.3390/ijerph182111251
- Cheuk S, Schlums H, Gallais Serezal I, et al. CD49a expression defines tissue-resident CD8(+) T cells poised for cytotoxic function in human skin. Immunity. 2017;46:287-300. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2017.01.009
- Sawyer LM, Malottki K, Sabry-Grant C, et al. Assessing the relative efficacy of interleukin-17 and interleukin-23 targeted treatments for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of PASI response. PLoS One. 2019;14:E0220868. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0220868
- Coates LC, Kavanaugh A, Mease PJ, et al. Group for research and assessment of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis 2015 treatment recommendations for psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68:1060-1071. doi:10.1002/art.39573
- Wang EA, Suzuki E, Maverakis E, et al. Targeting IL-17 in psoriatic arthritis. Eur J Rheumatol. 2017;4:272-277. doi:10.5152/eurjrheum.2017.17037
- Armstrong A, Fahrbach K, Leonardi C, et al. Efficacy of bimekizumab and other biologics in moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: a systematic literature review and a network meta-analysis. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:1777-1792. doi:10.1007/s13555-022-00760-8
- van Baarsen LG, Lebre MC, van der Coelen D, et al. Heterogeneous expression pattern of interleukin 17A (IL-17A), IL-17F and their receptors in synovium of rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and osteoarthritis: possible explanation for nonresponse to anti-IL-17 therapy? Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16:426. doi:10.1186/s13075-014-0426-z
- Hot A, Zrioual S, Toh ML, et al. IL-17A- versus IL-17F-induced intracellular signal transduction pathways and modulation by IL-17RA and IL-17RC RNA interference in rheumatoid synoviocytes. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:341-348. doi:10.1136/ard.2010.132233
- Adams R, Maroof A, Baker T, et al. Bimekizumab, a novel humanized IgG1 antibody that neutralizes both IL-17A and IL-17F. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1894. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01894
- Gordon KB, Foley P, Krueger JG, et al. Bimekizumab efficacy and safety in moderate to severe plaque psoriasis (BE READY): a multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised withdrawal phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;397:475-486. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00126-4
- Glatt S, Baeten D, Baker T, et al. Dual IL-17A and IL-17F neutralisation by bimekizumab in psoriatic arthritis: evidence from preclinical experiments and a randomised placebo-controlled clinical trial that IL-17F contributes to human chronic tissue inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:523-532. doi:10.1136 /annrheumdis-2017-212127
- Gordon KB, Langley RG, Warren RB, et al. Bimekizumab safety in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: pooled results from phase 2 and phase 3 randomized clinical trials. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:735-744. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.1185
- Reich K, Warren RB, Lebwohl M, et al. Bimekizumab versus secukinumab in plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:142-152. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2102383
- Reich K, Iversen L, Puig L, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of brodalumab in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: a post hoc pooled analysis of AMAGINE-2 and -3. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36:1275-1283. doi:10.1111/jdv.18068
- Papp KA, Blauvelt A, Puig L, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of risankizumab for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: interim analysis of the LIMMitless open-label extension trial up to 5 years of follow-up. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:1149-1158. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2023.07.1024
- Glatt S, Jemec GBE, Forman S, et al. Efficacy and safety of bimekizumab in moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa: a phase 2, doubleblind, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1279-1288. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.2905
- Choon SE, Lai NM, Mohammad NA, et al. Clinical profile, morbidity, and outcome of adult-onset generalized pustular psoriasis: analysis of 102 cases seen in a tertiary hospital in Johor, Malaysia. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:676-684. doi:10.1111/ijd.12070
- Zheng M, Jullien D, Eyerich K. The prevalence and disease characteristics of generalized pustular psoriasis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23 (suppl 1):5-12. doi:10.1007/s40257-021-00664-x
- Fujita H, Gooderham M, Romiti R. Diagnosis of generalized pustular psoriasis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23(suppl 1):31-38. doi:10.1007/s40257-021-00652-1
- Choon SE, Navarini AA, Pinter A. Clinical course and characteristics of generalized pustular psoriasis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23 (suppl 1):21-29. doi:10.1007/s40257-021-00654-z
- Augey F, Renaudier P, Nicolas JF. Generalized pustular psoriasis (Zumbusch): a French epidemiological survey. Eur J Dermatol. 2006;16:669-673.
- Ohkawara A, Yasuda H, Kobayashi H, et al. Generalized pustular psoriasis in Japan: two distinct groups formed by differences in symptoms and genetic background. Acta Derm Venereol. 1996;76:68-71. doi:10.2340/00015555766871
- Lee JY, Kang S, Park JS, et al. Prevalence of psoriasis in Korea: A population-based epidemiological study using the Korean National Health Insurance database. Ann Dermatol. 2017;29:761-767. doi:10.5021 /ad.2017.29.6.761
- Prinz JC, Choon SE, Griffiths CEM, et al. Prevalence, comorbidities and mortality of generalized pustular psoriasis: a literature review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37:256-273. doi:10.1111/jdv.18720
- Johnston A, Xing X, Wolterink L, et al. IL-1 and IL-36 are dominant cytokines in generalized pustular psoriasis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;140:109-120. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2016.08.056
- Rajan N, Sinclair N, Nakai H, et al. A tale of two sisters: identical IL36RN mutations and discordant phenotypes. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:417-420. doi:10.1111/bjd.14003
- Ly K, Beck KM, Smith MP, et al. Diagnosis and screening of patients with generalized pustular psoriasis. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2019;9:37-42. doi:10.2147/PTT.S181808
- Sugiura K. Role of interleukin 36 in generalised pustular psoriasis and beyond. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:315-328. doi:10.1007 /s13555-021-00677-8
- Akiyama M, Takeichi T, McGrath JA, et al. Autoinflammatory keratinization diseases: an emerging concept encompassing various inflammatory keratinization disorders of the skin. J Dermatol Sci. 2018;90:105-111. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2018.01.012
- Bachelez H, Choon SE, Marrakchi S, et al. Trial of spesolimab for generalized pustular psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2431-2440. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2111563
- Warren RB, Reich A, Kaszuba A, et al. Imsidolimab, an anti-IL-36 receptor monoclonal antibody for the treatment of generalised pustular psoriasis: results from the phase 2 GALLOP trial. Br J Dermatol. 2023;189:161-169. doi:10.1093/bjd/ljad083
- Villarino AV, Kanno Y, O’Shea JJ. Mechanisms and consequences of Jak-STAT signaling in the immune system. Nat Immunol. 2017; 18:374-384. doi:10.1038/ni.3691
- Genetic Analysis of Psoriasis Consortium & the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2; Strange A, Capon F, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies new psoriasis susceptibility loci and an interaction between HLA-C and ERAP1. Nat Genet. 2010;42:985-990. doi:10.1038/ng.694
- Enerback C, Sandin C, Lambert S, et al. The psoriasis-protective TYK2 I684S variant impairs IL-12 stimulated pSTAT4 response in skin-homing CD4+ and CD8+ memory T-cells. Sci Rep. 2018;8:7043. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-25282-2
- Shimoda K, Kato K, Aoki K, et al. Tyk2 plays a restricted role in IFN alpha signaling, although it is required for IL-12-mediated T cell function. Immunity. 2000;13:561-571. doi:10.1016/s1074-7613(00)00055-8
- Karaghiosoff M, Neubauer H, Lassnig C, et al. Partial impairment of cytokine responses in Tyk2-deficient mice. Immunity. 2000;13:549-560. doi:10.1016/s1074-7613(00)00054-6
- Burke JR, Cheng L, Gillooly KM, et al. Autoimmune pathways in mice and humans are blocked by pharmacological stabilization of the TYK2 pseudokinase domain [published online July 24, 2019]. Sci Transl Med. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aaw1736
- Strober B, Thaci D, Sofen H, et al. Deucravacitinib versus placebo and apremilast in moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: efficacy and safety results from the 52-week, randomized, double-blinded, phase 3 program for evaluation of TYK2 inhibitor psoriasis second trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;88:40-51. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.08.061
- Stein Gold L, Lebwohl M, Menter A, et al. Aerosol foam formulation of fixed combination calcipotriene plus betamethasone dipropionate is highly efficacious in patients with psoriasis vulgaris: pooled data from three randomized controlled studies. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15:951-957.
- Beranek M, Fiala Z, Kremlacek J, et al. Serum levels of aryl hydrocarbon receptor, cytochromes p450 1a1 and 1b1 in patients with exacerbated psoriasis vulgaris. Folia Biol (Praha). 2018;64:97-102.
- Esser C, Rannug A. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor in barrier organ physiology, immunology, and toxicology. Pharmacol Rev. 2015;67:259- 279. doi:10.1124/pr.114.009001
- Furue M, Uchi H, Mitoma C, et al. Antioxidants for healthy skin: the emerging role of aryl hydrocarbon receptors and nuclear factorerythroid 2-related factor-2. Nutrients. 2017;9:223. doi:10.3390/nu9030223
- Papp KA, Langley RG, Lebwohl M, et al. Efficacy and safety of ustekinumab, a human interleukin-12/23 monoclonal antibody, in patients with psoriasis: 52-week results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (PHOENIX 2). Lancet. 2008;371:1675-1684. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60726-6
- Sutter CH, Olesen KM, Bhuju J, et al. AHR regulates metabolic reprogramming to promote SIRT1-dependent keratinocyte differentiation. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:818-826. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2018.10.019
- Haas K, Weighardt H, Deenen R, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor in keratinocytes is essential for murine skin barrier integrity. J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136:2260-2269. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2016.06.627
- Di Meglio P, Duarte JH, Ahlfors H, et al. Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor dampens the severity of inflammatory skin conditions. Immunity. 2014;40:989-1001. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2014.04.019
- Kim HO, Kim JH, Chung BY, et al. Increased expression of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in patients with chronic inflammatory skin diseases. Exp Dermatol. 2014;23:278-281. doi:10.1111/exd.12350
- van den Bogaard EH, Bergboer JG, Vonk-Bergers M, et al. Coal tar induces AHR-dependent skin barrier repair in atopic dermatitis. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:917-927. doi:10.1172/JCI65642
- Smith SH, Jayawickreme C, Rickard DJ, et al. Tapinarof is a natural AHR agonist that resolves skin inflammation in mice and humans. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137:2110-2119. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2017.05.004
- Strober B, Stein Gold L, Bissonnette R, et al. One-year safety and efficacy of tapinarof cream for the treatment of plaque psoriasis: results from the PSOARING 3 trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:800-806. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.06.1171
- Mooney N, Teague JE, Gehad AE, et al. Tapinarof inhibits the formation, cytokine production, and persistence of resident memory T cells in vitro. SKIN J Cutan Med. 2023;7:S194. doi:10.25251/skin.7.supp.194
- Schafer PH, Truzzi F, Parton A, et al. Phosphodiesterase 4 in inflammatory diseases: effects of apremilast in psoriatic blood and in dermal myofibroblasts through the PDE4/CD271 complex. Cell Signal. 2016;28:753-763. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.01.007
- Li H, Zuo J, Tang W. Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1048. doi:10.3389/ fphar.2018.01048
- Schafer PH, Parton A, Gandhi AK, et al. Apremilast, a cAMP phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, demonstrates anti-inflammatory activity in vitro and in a model of psoriasis. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;159:842-855. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00559.x
- Papp K, Reich K, Leonardi CL, et al. Apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor, in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: results of a phase III, randomized, controlled trial (Efficacy and Safety Trial Evaluating the Effects of Apremilast in Psoriasis [ESTEEM] 1). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:37-49. doi:10.1016/j .jaad.2015.03.049
- Papp KA, Gooderham M, Droege M, et al. Roflumilast cream improves signs and symptoms of plaque psoriasis: results from a phase 1/2a randomized, controlled study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2020;19:734-740. doi:10.36849/JDD.2020.5370
- Lebwohl MG, Kircik LH, Moore AY, et al. Effect of roflumilast cream vs vehicle cream on chronic plaque psoriasis: the DERMIS-1 and DERMIS-2 randomized clinical trials. JAMA. 2022;328:1073-1084. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.15632
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects approximately 3% of the US population.1 Plaque psoriasis comprises 80% to 90% of cases, while pustular, erythrodermic, guttate, inverse, and palmoplantar disease are less common variants (Figure 1). Psoriatic skin manifestations range from localized to widespread or generalized disease with recurrent flares. Body surface area or psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) measurements primarily focus on skin manifestations and are important for evaluating disease activity and response to treatment, but they have inherent limitations: they do not capture extracutaneous disease activity, systemic inflammation, comorbid conditions, quality of life impact, or the economic burden of psoriasis.

A common manifestation of psoriasis is psoriatic arthritis (PsA), which can involve the nails, joints, ligaments, or tendons in 30% to 41% of affected individuals (Figure 2).2,3 A growing number of psoriasis-associated comorbidities also have been reported including metabolic syndrome4; hyperlipidemia5; cardiovascular disease6; stroke7; hypertension8; obesity9; sleep disorders10; malignancy11; infections12; inflammatory bowel disease13; and mental health disorders such as depression,14 anxiety,15 and suicidal ideation.15 Psoriatic disease also interferes with daily life activities and a patient’s overall quality of life, including interpersonal relationships, intimacy, employment, and work productivity.16 Finally, the total estimated cost of psoriasis-related health care is more than $35 billion annually,17 representing a substantial economic burden to our health care system and individual patients.

The overall burden of psoriatic disease has declined markedly in the last 2 decades due to revolutionary advances in our understanding of the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis and the subsequent development of improved therapies that predominantly interrupt IL-23/IL-17 cytokine signaling; however, critical knowledge and treatment gaps persist, underscoring the importance of ongoing clinical and research efforts in psoriatic disease. We review the working immune model of psoriasis, summarize related immune discoveries, and highlight recent therapeutic innovations that are shaping psoriatic disease management.
Current Immune Model of Psoriatic Disease
Psoriasis is an autoinflammatory T cell–mediated disease with negligible contributions from the humoral immune response. Early clinical observations reported increased inflammatory infiltrates in psoriatic skin lesions primarily consisting of both CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell populations.18,19 Additionally, patients treated with broad-acting, systemic immunosuppressive medications (eg, cyclosporine, oral corticosteroids) experienced improvement of psoriatic lesions and normalization of the immune infiltrates observed in skin biopsy specimens.20,21 These early clinical findings led to more sophisticated experimentation in xenotransplant models of psoriasis,22,23 which explored the clinical efficacy of several less immunosuppressive (eg, methotrexate, anti–tumor necrosis factor [TNF] biologics)24 or T cell–specific agents (eg, alefacept, abatacept, efalizumab).25-27 The results of these translational studies provided indisputable evidence for the role of the dysregulated immune response as the primary pathogenic process driving plaque formation; they also led to a paradigm shift in how the immunopathogenesis of psoriatic disease was viewed and paved the way for the identification and targeting of other specific proinflammatory signals produced by activated dendritic cell (DC) and T-lymphocyte populations. Among the psoriasis-associated cytokines subsequently identified and studied, elevated IL-23 and IL-17 cytokine levels in psoriatic skin were most closely associated with disease activity, and rapid normalization of IL-23/IL-17 signaling in response to effective oral or injectable antipsoriatic treatments was the hallmark of skin clearance.28 The predominant role of IL-23/IL-17 signaling in the development and maintenance of psoriatic disease is the central feature of all working immune models for this disease (Figure 3).

Psoriasis-Associated Genetic and Environmental Risk Factors
The exact sequence of events that lead to the initiation and formation of plaque psoriasis in susceptible individuals is still poorly understood; however, several important risk factors and key immune events have been identified. First, decades of genetic research have reported more than 80 known psoriasis-associated susceptibility loci,29 which explains approximately 50% of psoriasis heritability. The major genetic determinant of psoriasis, HLA-C*06:02 (formerly HLA-Cw6), resides in the major histocompatibility complex class I region on chromosome 6p21.3 (psoriasis susceptibility gene 1, PSORS1) and is most strongly associated with psoriatic disease.30 Less common psoriasis-associated susceptibility genes also are known to directly or indirectly impact innate and adaptive immune functions that contribute to the pathogenesis of psoriasis.
Second, several nongenetic environmental risk factors for psoriasis have been reported across diverse patient populations, including skin trauma/injury, infections, alcohol/tobacco use, obesity, medication exposure (eg, lithium, antimalarials, beta-blockers), and stress.31 These genetic and/or environmental risk factors can trigger the onset of psoriatic disease at any stage of life, though most patients develop disease in early adulthood or later (age range, 50–60 years). Some patients never develop psoriasis despite exposure to environmental risk factors and/or a genetic makeup that is similar to affected first-degree relatives, which requires further study.
Prepsoriatic Skin and Initiation of Plaque Development
In response to environmental stimuli and/or other triggers of the immune system, DC and resident IL-17–producing T-cell (T17) populations become activated in predisposed individuals. Dendritic cell activation leads to the upregulation and increase of several proinflammatory cytokines, including TNF, interferon (IFN) α, IFN-γ, IL-12, and IL-23. Tumor necrosis factor and IL-23 play a vital role in psoriasis by helping to regulate the polarization and expansion of T22 and T17 cells in the skin, whereas IL-12 promotes a corresponding type 1 inflammatory response.32 Increased IL-17 and IL-22 result in alteration of the terminal differentiation and proliferative potential of epidermal keratinocytes, leading to the early clinical hallmarks of psoriatic plaques. The potential contribution of overexpressed psoriasis-related autoantigens, such as LL-37/cathelicidin, ADAMTSL5, and PLA2G4D,33 in the initiation of psoriatic plaques has been suggested but is poorly characterized.34 Whether these specific autoantigens or others presented by HLA-C variants found on antigen-presenting cells are required for the breakdown of immune tolerance and psoriatic disease initiation is highly relevant but requires further investigation and validation.
Feed-Forward Inflammation, Mature Psoriatic Plaques, and Resident Memory T Cells
In response to the upstream production of IL-23 by dermal DCs, high levels of IL-17 cytokines can be found in mature psoriatic plaques. The IL-17 family consists of 6 dimeric cytokines (IL-17A through IL-17F) that provide innate cutaneous protection against bacterial, viral, and fungal infectious agents, such as Candida albicans. Unlike other IL-17 isoforms, IL-17A and IL-17F share the same receptor complex and have the highest structural homology of any pair (approximately 50% similar).35 The relative expression of IL-17F is higher than IL-17A in psoriasis,36 though IL-17A has been considered as the predominant IL-17 cytokine found in psoriatic skin lesions due to its higher potency.
Binding of IL-17A/F with the IL-17 receptor (IL-17R) on keratinocytes contributes to the development of psoriatic plaques by inducing epidermal hyperplasia via activation of CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins β and δ, nuclear factor κB, and signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 gene (STAT1).37,38 This also increases the expression of other keratinocyte-derived proteins (eg, human β-defensins, S-100 proteins, LL-37, other antimicrobial peptides, IL-19, IL-36, IL-17C) that act as reinforcing proinflammatory signals or chemotactic factors (eg, chemokine [C-C motif] ligand 20 [CCL20], chemokine [C-C motif] ligand 1/2/3/5 [CXCL1/2/3/5], CXCL8, IL-8) that facilitate the recruitment of additional immune cells to the skin including polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs), macrophages, and DCs.39-41 Routine immunohistochemical staining for these keratinocyte-derived proteins reveals a striking epidermal gene expression gradient wherein levels of IL-17–induced proteins are most highly expressed in the uppermost layers of keratinocytes and facilitate the recruitment of immune cells into the epidermis. Activated T17 cells also stimulate the production of keratinocyte-derived chemokines (eg, CXCL9/10/11), which recruit type 1 inflammatory T-cell populations into developing psoriatic plaques.42,43 Finally, TNF, IL-36, and IL-17C cytokines act synergistically with IL-17A/F to amplify the proinflammatory effects of IL-17 signaling and further stimulate their production from T17 cell populations.40 This inflammatory circuit in the skin creates and supports a self-amplifying or positive feedback loop between the skin and immune system that commonly is referred to as feed-forward inflammation (Figure 3).34 The feed-forward inflammatory loop in psoriasis—predominantly driven by increased IL-23/IL-17 signaling—best characterizes the mature psoriatic plaque.
Several findings suggest that the influx of persistent, long-lived resident memory T cells (Trms) may contribute to the mature psoriatic plaque. It is believed that CD8+CD103+CD49a− Trm cell populations may be responsible for the sharply demarcated borders of untreated psoriasis plaques or their recurrence at specific body sites such as the scalp, buttocks, extremity extensor surfaces, umbilicus, or acral skin following specific stimuli or trauma (Koebner phenomenon or isomorphic response).44,45 It is not known if repeated stimuli or trauma induce disease formation via the activation of Trm cell populations; further study in large patient cohorts is needed, but this remains an intriguing area of study for durable treatment responses and potential cures for psoriasis.
Recent Discoveries in Psoriatic Disease
Remarkable treatment outcomes for psoriasis have been achieved with multiple selective IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors (eTable). As demonstrated in several pivotal phase 3 clinical trials for members of these classes of medications, the majority of treated psoriasis patients achieved PASI90 clearance.46 Due to their more favorable dosing schedule (ie, fewer injections) and ability to induce a durable remissionlike treatment response, IL-23 inhibitors have become the preferred treatment class for cutaneous disease, while IL-17 inhibitors may be preferred when treating patients with both plaque psoriasis and PsA.47,48 Nevertheless, the complexity of this disease is punctuated by treated patients who do not adequately respond to selective IL-23/IL-17 blockade.49 Recent and emerging treatments may shed light on these recalcitrant cases and will add to the rapidly growing arsenal of available psoriasis therapies.
The Role of IL-17F in Psoriasis and Other Inflammatory Skin Diseases
Dysregulation of IL-17A and IL-17F is associated with several chronic inflammatory conditions, such as psoriasis and PsA.35,50 Both cytokines, either as homodimers or heterodimers, can selectively bind to the heterodimeric IL-17R formed by the IL-17RA and IL-17RC subunits.35 IL-17F and IL-17C also can synergize with TNF and other cytokines to promote and support the self-sustaining inflammatory circuits in mature psoriatic plaques, though their inflammatory effects in the skin are more limited than IL-17A.51,52 Therefore, incomplete blockade of IL-17 signaling (ie, unopposed IL-17F and IL-17C) represents a potential mechanism to explain the persistence of psoriasis in patients treated with selective IL-17A inhibitors. This hypothesis is supported by reports of psoriasis patients who have inadequate clinical responses to selective IL-17A inhibition but subsequently improve with IL-17R blockade, which results in disruption of IL-17A as well as IL-17C/E/F cytokine signaling. This formed the basis for further study into the specific role of IL-17F in psoriatic disease and any potential therapeutic benefits associated with its inhibition.
Recently approved in the European Union, Canada, Australia, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States for moderate to severe psoriasis, bimekizumab is a novel humanized IgG antibody that selectively inhibits both IL-17A and IL-17F cytokines.53 Specifically, bimekizumab simultaneously prevents binding of IL-17A/A, IL-17A/F, and IL-17F/F dimers with the IL-17R. Compared to other IL-17 and IL-23 biologic therapies, bimekizumab (320 mg) achieved relatively higher response rates for PASI75, PASI90, and PASI100.49 Neutralization of IL-17A and IL-17F by bimekizumab also resulted in more complete suppression of cytokine responses and PMN chemotaxis than either cytokine alone in treated PsA patients,54 which is notable because of the incremental benefits of recent IL-23 and IL-17 inhibitors on inflammatory arthritis symptoms in contrast to the substantial improvements observed for cutaneous disease with those same agents.
The primary disadvantage of bimekizumab and its more complete blockade of the IL-17 signaling pathway is that treated patients have a substantially increased risk for oral candidiasis (>10%).55 However, the precise link between candidiasis and IL-17 blockade is not yet fully understood because other targeted agents that also broadly suppress IL-17 signaling (ie, IL-17R, IL-23 inhibitors) are associated with much lower rates of candidiasis.56-58 Bimekizumab also is being investigated as a novel therapy for hidradenitis suppurativa and will provide important reference information regarding the role for bispecific biologic agents in the treatment of chronic inflammatory skin diseases.59
IL-36 Signaling and Generalized Pustular Psoriasis
Recent genetic and clinical studies have expanded our understanding of the role of IL-36 signaling in the immunopathogenesis of pustular psoriasis variants. Generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) is a rare distinct psoriasis subtype characterized by the recurrent development of widespread erythema, superficial sterile pustules, and desquamation. Systemic symptoms such as fever, malaise, itching, and skin pain accompany acute GPP flares.60 Generalized pustular psoriasis is more common in female patients (in contrast with plaque psoriasis), and acute flares may be caused by multiple stimuli including infections, hypocalcemia, initiation or discontinuation of medications (eg, oral corticosteroids), pregnancy, or stress.61,62 Flares of GPP often require emergency or in-patient care, as untreated symptoms increase the risk for severe health complications such as secondary infections, sepsis, or multisystem organ failure.63 The prevalence of GPP is estimated to be approximately 1 in 10,000 individuals in the United States,64-67 with mortality rates ranging from 0 to 3.3 deaths per 100 patient-years.67
In contrast to plaque psoriasis, aberrant IL-36 signaling is the predominant driver of GPP. IL-36 is a member of the IL-1 cytokine family that includes three IL-36 agonists (IL-36α, IL-36β, IL-36γ) and 1 endogenous antagonist (IL-36Ra, encoded by IL36RN).68 The immunopathogenesis of GPP involves dysregulation of the IL-36–chemokine–PMN axis, resulting in unopposed IL-36 signaling and the subsequent recruitment and influx of PMNs into the epidermis. IL36RN mutations are strongly associated with GPP and result in impaired function of the IL-36Ra protein, leading to unopposed IL-36 signaling.69 However, approximately two-thirds of GPP patients lack identifiable gene mutations, suggesting other immune mechanisms or triggers causing upregulated IL-36 signaling.70 In response to these triggers, increased IL-36 cytokines released by keratinocytes bind to the IL-36R, resulting in substantial keratinocyte hyperproliferation, increased IL-36 levels, and the expression of hundreds of additional inflammatory signals (eg, IL-17C, antimicrobial peptides, TNF, IL-6).71 Increased IL-36 levels also drive the production of PMN chemotactic proteins (eg, CXCL1/2/3/5/6/8 and CXCR1/2) and act synergistically with IL-17 cytokines to create an autoamplifying circuit that is analogous to the feed-forward inflammatory loop in plaque psoriasis.72 Biopsies of involved GPP skin reveal increased expression of IL-36 in the uppermost layers of the epidermis, which creates a gene expression gradient that acts as a strong attractant for PMNs and forms the basis for the hallmark pustular lesions observed in GPP patients.
Until recently, treatment strategies for GPP involved the off-label use of topical, oral, or biologic therapies approved for plaque psoriasis, which often was associated with variable or incomplete disease control. In September 2022, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved intravenous spesolimab as a first-in-class humanized monoclonal IgG1 antibody for the treatment of GPP flares in adults. Spesolimab binds to IL-36R and prevents its activation by its endogenous agonists. A phase 2, randomized, 12-week clinical trial (Effisayil-1) evaluated the efficacy and safety of a single 900-mg intravenous dose of spesolimab followed by an optional second dose 1 week later for inadequate treatment responses in 53 enrolled GPP patients (2:1 treatment to placebo randomization).73 Remarkably, more than half (19/35 [54%]) of GPP patients experienced complete resolution of pustules (GPP physician global assessment subscore of 0 [range, 0–4]) and showed sustained efficacy out to week 12 after just 1 or 2 doses of spesolimab. Overall, the safety profile of spesolimab was good; asthenia, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, headache, pruritus, infusion-related reaction and symptoms, and mild infections (eg, urinary tract infection) were the most common adverse events reported.73
Imsidolimab, a high-affinity humanized IgG4 monoclonal antibody that binds and blocks activation of IL-36R, also has completed phase 2 testing,74 with phase 3 study results expected in early 2024. The rapid onset of action and overall safety of imsidolimab was in line with and similar to spesolimab. Future approval of imsidolimab would add to the limited treatment options available for GPP and has the additional convenience of being administered to patients subcutaneously. Overall, the development of selective IL-36R inhibitors offers a much-needed therapeutic option for GPP and illustrates the importance of translational research.
Role of Tyrosine Kinase in Psoriatic Disease
The Janus kinase (JAK) enzyme family consists of 4 enzymes—tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2), JAK1, JAK2, and JAK3—that function as intracellular transduction signals that mediate the biologic response of most extracellular cytokines and growth factors.75 Critical psoriasis-related cytokines are dependent on intact JAK-STAT signaling, including IL-23, IL-12, and type I IFNs. In 2010, a genome-wide association identified TYK2 as a psoriasis susceptibility locus,76 and loss-of-function TYK2 mutations confer a reduced risk for psoriasis.77 Unlike other JAK isoforms, TYK2 mediates biologic functions that are highly restricted to the immune responses associated with IL-23, IL-12, and type I IFN signaling.78,79 For these reasons, blockade of TYK2 signaling is an attractive therapeutic target for the potential treatment of psoriatic disease.
In September 2022, the FDA approved deucravacitinib as a first-in-class, oral, selective TYK2 inhibitor for the treatment of adult patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. It was the first FDA approval of an oral small-molecule treatment for plaque psoriasis in nearly a decade. Deucravacitinib inhibits TYK2 signaling via selective binding of its unique regulatory domain, resulting in a conformational (allosteric) change that interferes with its active domain.80 This novel mechanism of action limits the unwanted blockade of other broad biologic processes mediated by JAK1/2/3. Of note, the FDA did not issue any boxed warnings for deucravacitinib as it did for other FDA-approved JAK inhibitors.
In a head-to-head, 52-week, double-blind, prospective, randomized, phase 3 study, deucravacitinib showed clear superiority over apremilast for PASI75 at week 16 (53.0% [271/511] vs 39.8% [101/254]) and week 24 (58.7% [296/504] vs 37.8% [96/254]).81 Clinical responses were sustained through week 52 and showed efficacy for difficult-to-treat areas such as the scalp, acral sites, and nails. Other advantages of deucravacitinib include once-daily dosing with no need for dose titration or adjustments for renal insufficiency as well as the absence of statistically significant differences in gastrointestinal tract symptoms compared to placebo. The most common adverse effects included nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infections, headache, diarrhea, and herpes infections.81 The potential benefit of deucravacitinib for PsA and psoriasis comorbidities remains to be seen, but it is promising due to its simultaneous disruption of multiple psoriasis-related cytokine networks. Several other TYK2 inhibitors are being developed for psoriatic disease and related inflammatory conditions, underscoring the promise of targeting this intracellular pathway.
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Agonism
Topical steroids are the mainstay treatment option for localized or limited plaque psoriasis due to their potent immunosuppressive effect on the skin and relatively low cost. Combined with vitamin D analogs, topical steroids result in marked improvements in disease severity and improved tolerability.82 However, chronic use of topical steroids is limited by the need for twice-daily application, resulting in poor treatment compliance; loss of efficacy over time; risk for steroid-induced skin atrophy on special body sites; and patient concerns of potential systemic effects. The discovery of novel drug targets amenable to topical inhibition is needed.
Dysregulated aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) levels have been reported in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.83 Aryl hydrocarbon receptors are ubiquitously expressed in many cell types and play an integral role in immune homeostasis within the skin, skin barrier function, protection against oxidative stressors, and regulation of proliferating melanocytes and keratinocytes.84,85 They are widely expressed in multiple immune cell types (eg, antigen-presenting cells, T lymphocytes, fibroblasts) and modulate the differentiation of T17 and T22 cells as well as their balance with regulatory T-cell populations.86 In keratinocytes, AHR helps to regulate terminal differentiation, enhance skin barrier integrity via AHR-dependent filaggrin (FLG) expression, and prevent transepidermal water loss.87,88 The mechanisms by which AHR ligands lead to the upregulation or downregulation of specific genes is intricate and highly context dependent, such as the specific ligand and cell type involved. In preclinical studies, AHR-deficient mice develop psoriasiform skin inflammation, increased IL-17 and IL-22 expression, and abnormal skin barrier function.89 Keratinocytes treated with AHR ligands in vitro modulated psoriasis-associated inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, IL-8, and type I and II IFNs.89,90 The use of coal tar, one of the earliest historical treatments for psoriasis, is thought to activate AHRs in the skin via organic compound mixtures containing polyaromatic hydrocarbons that help normalize the proinflammatory environment in psoriatic skin.91
In June 2022, the FDA approved tapinarof as a first-in-class, topical, nonsteroidal AHR agonist for the treatment of plaque psoriasis in adults. Although the exact mechanism of action for tapinarof has not been fully elucidated, early studies suggest that its primary function is the activation of AHR, leading to reduced T-cell expansion and T17 cell differentiation. In the imiquimod mouse model, cytokine expression of IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-19, IL-22, IL-23A, and IL-lβ in psoriasiform skin lesions were downregulated following tapinarof treatment.92 In humans, tapinarof treatment is associated with a remittive effect, in which the average time for tapinarof-treated psoriasis lesions to remain clear was approximately 4 months.93 Preliminary research investigating the mechanism by which tapinarof induces this remittive effect is ongoing and may involve the reduced activation and influx of T17 and Trm populations into the skin.94 However, these preclinical studies were performed on healthy dermatome-derived skin tissue cultured in T17-skewing conditions and needs to be replicated in larger samples sizes using human-derived psoriatic tissue. Alternatively, a strong inhibitory effect on IL-23 cytokine signaling may, in part, explain the remittive effect of tapinarof, as an analogous response is observed in patients who start and discontinue treatment with selective IL-23 antagonists. Regardless, the once-daily dosing of tapinarof and sustained treatment response is appealing to psoriasis patients. Tapinarof generally is well tolerated with mild folliculitis (>20% of patients) and contact dermatitis (5% of patients) reported as the most common skin-related adverse events.
New Roles for Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibition
Phosphodiesterases (PDEs) are enzymes that hydrolyze cyclic nucleotides (eg, cyclic adenosine monophosphate) to regulate intracellular secondary messengers involved in the inflammatory response. One of several enzymes in the PDE family, PDE4, has been shown to have greater activity in psoriatic skin compared to healthy skin.95 Phosphodiesterase inhibitors decrease the degradation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate, which triggers protein kinase A to downregulate proinflammatory (eg, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-17, IL-12, IL-23) cytokines and increased expression of anti-inflammatory signals such as IL-10.96,97 Apremilast, the first oral PDE4 inhibitor approved by the FDA for psoriasis, offered a safe alternative to traditional oral immunosuppressive agents that had extensive risks and potential end-organ adverse effects. Unfortunately, apremilast demonstrated modest efficacy for psoriatic disease (better efficacy in the skin vs joint manifestations) and was supplanted easily by next-generation targeted biologic agents that were more efficacious and lacked the troublesome gastrointestinal tract adverse effects of PDE4 inhibition.98
Crisaborole became the first topical PDE4 inhibitor approved in the United States in December 2016 for twice-daily treatment of atopic dermatitis. Although phase 2 trial results were reported in psoriasis, this indication was never pursued, presumably due to similar improvements in primary outcome measures at week 12, compared to placebo (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT01300052).
In July 2022, the first topical PDE4 inhibitor indicated for plaque psoriasis was approved by the FDA—roflumilast cream 0.3% for once-daily use in individuals 12 years and older. Roflumilast was found to be clinically efficacious as early as 2 weeks after its use in an early-phase clinical trial.99 In 2 phase 3 clinical trials (DERMIS-1 and DERMIS-2), roflumilast significantly increased the proportion of patients achieving PASI75 at week 8 compared to vehicle (39%–41.6% vs 5.3%–7.6%, respectively)(P<.001).100 Overall, this nonsteroidal topical therapy was found to be well tolerated, with infrequent reports of application site pain or irritation as adverse events. Similar to tapinarof, patients can apply roflumilast on all body surface areas including the face, external genitalia, and other intertriginous areas.100 Importantly, the broad immune impact of PDE4 inhibition suggests that topical roflumilast likely will be an effective treatment for several additional inflammatory conditions, including seborrheic dermatitis and atopic dermatitis, which would expand the clinical utility of this specific medication.
Conclusion
In the last 2 decades, we have witnessed a translational revolution in our understanding of the underlying genetics and immunology of psoriatic disease. Psoriasis is widely considered one of the best-managed inflammatory conditions in all of medicine due to the development and availability of highly targeted, effective topical and systemic therapies that predominantly disrupt IL-23/IL-17 cytokine signaling in affected tissues. However, future clinical studies and laboratory research are necessary to elucidate the precise cause of psoriasis as well as the underlying genetic and immune signaling pathways driving less common clinical variants and recalcitrant disease.

Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects approximately 3% of the US population.1 Plaque psoriasis comprises 80% to 90% of cases, while pustular, erythrodermic, guttate, inverse, and palmoplantar disease are less common variants (Figure 1). Psoriatic skin manifestations range from localized to widespread or generalized disease with recurrent flares. Body surface area or psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) measurements primarily focus on skin manifestations and are important for evaluating disease activity and response to treatment, but they have inherent limitations: they do not capture extracutaneous disease activity, systemic inflammation, comorbid conditions, quality of life impact, or the economic burden of psoriasis.

A common manifestation of psoriasis is psoriatic arthritis (PsA), which can involve the nails, joints, ligaments, or tendons in 30% to 41% of affected individuals (Figure 2).2,3 A growing number of psoriasis-associated comorbidities also have been reported including metabolic syndrome4; hyperlipidemia5; cardiovascular disease6; stroke7; hypertension8; obesity9; sleep disorders10; malignancy11; infections12; inflammatory bowel disease13; and mental health disorders such as depression,14 anxiety,15 and suicidal ideation.15 Psoriatic disease also interferes with daily life activities and a patient’s overall quality of life, including interpersonal relationships, intimacy, employment, and work productivity.16 Finally, the total estimated cost of psoriasis-related health care is more than $35 billion annually,17 representing a substantial economic burden to our health care system and individual patients.

The overall burden of psoriatic disease has declined markedly in the last 2 decades due to revolutionary advances in our understanding of the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis and the subsequent development of improved therapies that predominantly interrupt IL-23/IL-17 cytokine signaling; however, critical knowledge and treatment gaps persist, underscoring the importance of ongoing clinical and research efforts in psoriatic disease. We review the working immune model of psoriasis, summarize related immune discoveries, and highlight recent therapeutic innovations that are shaping psoriatic disease management.
Current Immune Model of Psoriatic Disease
Psoriasis is an autoinflammatory T cell–mediated disease with negligible contributions from the humoral immune response. Early clinical observations reported increased inflammatory infiltrates in psoriatic skin lesions primarily consisting of both CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell populations.18,19 Additionally, patients treated with broad-acting, systemic immunosuppressive medications (eg, cyclosporine, oral corticosteroids) experienced improvement of psoriatic lesions and normalization of the immune infiltrates observed in skin biopsy specimens.20,21 These early clinical findings led to more sophisticated experimentation in xenotransplant models of psoriasis,22,23 which explored the clinical efficacy of several less immunosuppressive (eg, methotrexate, anti–tumor necrosis factor [TNF] biologics)24 or T cell–specific agents (eg, alefacept, abatacept, efalizumab).25-27 The results of these translational studies provided indisputable evidence for the role of the dysregulated immune response as the primary pathogenic process driving plaque formation; they also led to a paradigm shift in how the immunopathogenesis of psoriatic disease was viewed and paved the way for the identification and targeting of other specific proinflammatory signals produced by activated dendritic cell (DC) and T-lymphocyte populations. Among the psoriasis-associated cytokines subsequently identified and studied, elevated IL-23 and IL-17 cytokine levels in psoriatic skin were most closely associated with disease activity, and rapid normalization of IL-23/IL-17 signaling in response to effective oral or injectable antipsoriatic treatments was the hallmark of skin clearance.28 The predominant role of IL-23/IL-17 signaling in the development and maintenance of psoriatic disease is the central feature of all working immune models for this disease (Figure 3).

Psoriasis-Associated Genetic and Environmental Risk Factors
The exact sequence of events that lead to the initiation and formation of plaque psoriasis in susceptible individuals is still poorly understood; however, several important risk factors and key immune events have been identified. First, decades of genetic research have reported more than 80 known psoriasis-associated susceptibility loci,29 which explains approximately 50% of psoriasis heritability. The major genetic determinant of psoriasis, HLA-C*06:02 (formerly HLA-Cw6), resides in the major histocompatibility complex class I region on chromosome 6p21.3 (psoriasis susceptibility gene 1, PSORS1) and is most strongly associated with psoriatic disease.30 Less common psoriasis-associated susceptibility genes also are known to directly or indirectly impact innate and adaptive immune functions that contribute to the pathogenesis of psoriasis.
Second, several nongenetic environmental risk factors for psoriasis have been reported across diverse patient populations, including skin trauma/injury, infections, alcohol/tobacco use, obesity, medication exposure (eg, lithium, antimalarials, beta-blockers), and stress.31 These genetic and/or environmental risk factors can trigger the onset of psoriatic disease at any stage of life, though most patients develop disease in early adulthood or later (age range, 50–60 years). Some patients never develop psoriasis despite exposure to environmental risk factors and/or a genetic makeup that is similar to affected first-degree relatives, which requires further study.
Prepsoriatic Skin and Initiation of Plaque Development
In response to environmental stimuli and/or other triggers of the immune system, DC and resident IL-17–producing T-cell (T17) populations become activated in predisposed individuals. Dendritic cell activation leads to the upregulation and increase of several proinflammatory cytokines, including TNF, interferon (IFN) α, IFN-γ, IL-12, and IL-23. Tumor necrosis factor and IL-23 play a vital role in psoriasis by helping to regulate the polarization and expansion of T22 and T17 cells in the skin, whereas IL-12 promotes a corresponding type 1 inflammatory response.32 Increased IL-17 and IL-22 result in alteration of the terminal differentiation and proliferative potential of epidermal keratinocytes, leading to the early clinical hallmarks of psoriatic plaques. The potential contribution of overexpressed psoriasis-related autoantigens, such as LL-37/cathelicidin, ADAMTSL5, and PLA2G4D,33 in the initiation of psoriatic plaques has been suggested but is poorly characterized.34 Whether these specific autoantigens or others presented by HLA-C variants found on antigen-presenting cells are required for the breakdown of immune tolerance and psoriatic disease initiation is highly relevant but requires further investigation and validation.
Feed-Forward Inflammation, Mature Psoriatic Plaques, and Resident Memory T Cells
In response to the upstream production of IL-23 by dermal DCs, high levels of IL-17 cytokines can be found in mature psoriatic plaques. The IL-17 family consists of 6 dimeric cytokines (IL-17A through IL-17F) that provide innate cutaneous protection against bacterial, viral, and fungal infectious agents, such as Candida albicans. Unlike other IL-17 isoforms, IL-17A and IL-17F share the same receptor complex and have the highest structural homology of any pair (approximately 50% similar).35 The relative expression of IL-17F is higher than IL-17A in psoriasis,36 though IL-17A has been considered as the predominant IL-17 cytokine found in psoriatic skin lesions due to its higher potency.
Binding of IL-17A/F with the IL-17 receptor (IL-17R) on keratinocytes contributes to the development of psoriatic plaques by inducing epidermal hyperplasia via activation of CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins β and δ, nuclear factor κB, and signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 gene (STAT1).37,38 This also increases the expression of other keratinocyte-derived proteins (eg, human β-defensins, S-100 proteins, LL-37, other antimicrobial peptides, IL-19, IL-36, IL-17C) that act as reinforcing proinflammatory signals or chemotactic factors (eg, chemokine [C-C motif] ligand 20 [CCL20], chemokine [C-C motif] ligand 1/2/3/5 [CXCL1/2/3/5], CXCL8, IL-8) that facilitate the recruitment of additional immune cells to the skin including polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs), macrophages, and DCs.39-41 Routine immunohistochemical staining for these keratinocyte-derived proteins reveals a striking epidermal gene expression gradient wherein levels of IL-17–induced proteins are most highly expressed in the uppermost layers of keratinocytes and facilitate the recruitment of immune cells into the epidermis. Activated T17 cells also stimulate the production of keratinocyte-derived chemokines (eg, CXCL9/10/11), which recruit type 1 inflammatory T-cell populations into developing psoriatic plaques.42,43 Finally, TNF, IL-36, and IL-17C cytokines act synergistically with IL-17A/F to amplify the proinflammatory effects of IL-17 signaling and further stimulate their production from T17 cell populations.40 This inflammatory circuit in the skin creates and supports a self-amplifying or positive feedback loop between the skin and immune system that commonly is referred to as feed-forward inflammation (Figure 3).34 The feed-forward inflammatory loop in psoriasis—predominantly driven by increased IL-23/IL-17 signaling—best characterizes the mature psoriatic plaque.
Several findings suggest that the influx of persistent, long-lived resident memory T cells (Trms) may contribute to the mature psoriatic plaque. It is believed that CD8+CD103+CD49a− Trm cell populations may be responsible for the sharply demarcated borders of untreated psoriasis plaques or their recurrence at specific body sites such as the scalp, buttocks, extremity extensor surfaces, umbilicus, or acral skin following specific stimuli or trauma (Koebner phenomenon or isomorphic response).44,45 It is not known if repeated stimuli or trauma induce disease formation via the activation of Trm cell populations; further study in large patient cohorts is needed, but this remains an intriguing area of study for durable treatment responses and potential cures for psoriasis.
Recent Discoveries in Psoriatic Disease
Remarkable treatment outcomes for psoriasis have been achieved with multiple selective IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors (eTable). As demonstrated in several pivotal phase 3 clinical trials for members of these classes of medications, the majority of treated psoriasis patients achieved PASI90 clearance.46 Due to their more favorable dosing schedule (ie, fewer injections) and ability to induce a durable remissionlike treatment response, IL-23 inhibitors have become the preferred treatment class for cutaneous disease, while IL-17 inhibitors may be preferred when treating patients with both plaque psoriasis and PsA.47,48 Nevertheless, the complexity of this disease is punctuated by treated patients who do not adequately respond to selective IL-23/IL-17 blockade.49 Recent and emerging treatments may shed light on these recalcitrant cases and will add to the rapidly growing arsenal of available psoriasis therapies.
The Role of IL-17F in Psoriasis and Other Inflammatory Skin Diseases
Dysregulation of IL-17A and IL-17F is associated with several chronic inflammatory conditions, such as psoriasis and PsA.35,50 Both cytokines, either as homodimers or heterodimers, can selectively bind to the heterodimeric IL-17R formed by the IL-17RA and IL-17RC subunits.35 IL-17F and IL-17C also can synergize with TNF and other cytokines to promote and support the self-sustaining inflammatory circuits in mature psoriatic plaques, though their inflammatory effects in the skin are more limited than IL-17A.51,52 Therefore, incomplete blockade of IL-17 signaling (ie, unopposed IL-17F and IL-17C) represents a potential mechanism to explain the persistence of psoriasis in patients treated with selective IL-17A inhibitors. This hypothesis is supported by reports of psoriasis patients who have inadequate clinical responses to selective IL-17A inhibition but subsequently improve with IL-17R blockade, which results in disruption of IL-17A as well as IL-17C/E/F cytokine signaling. This formed the basis for further study into the specific role of IL-17F in psoriatic disease and any potential therapeutic benefits associated with its inhibition.
Recently approved in the European Union, Canada, Australia, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States for moderate to severe psoriasis, bimekizumab is a novel humanized IgG antibody that selectively inhibits both IL-17A and IL-17F cytokines.53 Specifically, bimekizumab simultaneously prevents binding of IL-17A/A, IL-17A/F, and IL-17F/F dimers with the IL-17R. Compared to other IL-17 and IL-23 biologic therapies, bimekizumab (320 mg) achieved relatively higher response rates for PASI75, PASI90, and PASI100.49 Neutralization of IL-17A and IL-17F by bimekizumab also resulted in more complete suppression of cytokine responses and PMN chemotaxis than either cytokine alone in treated PsA patients,54 which is notable because of the incremental benefits of recent IL-23 and IL-17 inhibitors on inflammatory arthritis symptoms in contrast to the substantial improvements observed for cutaneous disease with those same agents.
The primary disadvantage of bimekizumab and its more complete blockade of the IL-17 signaling pathway is that treated patients have a substantially increased risk for oral candidiasis (>10%).55 However, the precise link between candidiasis and IL-17 blockade is not yet fully understood because other targeted agents that also broadly suppress IL-17 signaling (ie, IL-17R, IL-23 inhibitors) are associated with much lower rates of candidiasis.56-58 Bimekizumab also is being investigated as a novel therapy for hidradenitis suppurativa and will provide important reference information regarding the role for bispecific biologic agents in the treatment of chronic inflammatory skin diseases.59
IL-36 Signaling and Generalized Pustular Psoriasis
Recent genetic and clinical studies have expanded our understanding of the role of IL-36 signaling in the immunopathogenesis of pustular psoriasis variants. Generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) is a rare distinct psoriasis subtype characterized by the recurrent development of widespread erythema, superficial sterile pustules, and desquamation. Systemic symptoms such as fever, malaise, itching, and skin pain accompany acute GPP flares.60 Generalized pustular psoriasis is more common in female patients (in contrast with plaque psoriasis), and acute flares may be caused by multiple stimuli including infections, hypocalcemia, initiation or discontinuation of medications (eg, oral corticosteroids), pregnancy, or stress.61,62 Flares of GPP often require emergency or in-patient care, as untreated symptoms increase the risk for severe health complications such as secondary infections, sepsis, or multisystem organ failure.63 The prevalence of GPP is estimated to be approximately 1 in 10,000 individuals in the United States,64-67 with mortality rates ranging from 0 to 3.3 deaths per 100 patient-years.67
In contrast to plaque psoriasis, aberrant IL-36 signaling is the predominant driver of GPP. IL-36 is a member of the IL-1 cytokine family that includes three IL-36 agonists (IL-36α, IL-36β, IL-36γ) and 1 endogenous antagonist (IL-36Ra, encoded by IL36RN).68 The immunopathogenesis of GPP involves dysregulation of the IL-36–chemokine–PMN axis, resulting in unopposed IL-36 signaling and the subsequent recruitment and influx of PMNs into the epidermis. IL36RN mutations are strongly associated with GPP and result in impaired function of the IL-36Ra protein, leading to unopposed IL-36 signaling.69 However, approximately two-thirds of GPP patients lack identifiable gene mutations, suggesting other immune mechanisms or triggers causing upregulated IL-36 signaling.70 In response to these triggers, increased IL-36 cytokines released by keratinocytes bind to the IL-36R, resulting in substantial keratinocyte hyperproliferation, increased IL-36 levels, and the expression of hundreds of additional inflammatory signals (eg, IL-17C, antimicrobial peptides, TNF, IL-6).71 Increased IL-36 levels also drive the production of PMN chemotactic proteins (eg, CXCL1/2/3/5/6/8 and CXCR1/2) and act synergistically with IL-17 cytokines to create an autoamplifying circuit that is analogous to the feed-forward inflammatory loop in plaque psoriasis.72 Biopsies of involved GPP skin reveal increased expression of IL-36 in the uppermost layers of the epidermis, which creates a gene expression gradient that acts as a strong attractant for PMNs and forms the basis for the hallmark pustular lesions observed in GPP patients.
Until recently, treatment strategies for GPP involved the off-label use of topical, oral, or biologic therapies approved for plaque psoriasis, which often was associated with variable or incomplete disease control. In September 2022, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved intravenous spesolimab as a first-in-class humanized monoclonal IgG1 antibody for the treatment of GPP flares in adults. Spesolimab binds to IL-36R and prevents its activation by its endogenous agonists. A phase 2, randomized, 12-week clinical trial (Effisayil-1) evaluated the efficacy and safety of a single 900-mg intravenous dose of spesolimab followed by an optional second dose 1 week later for inadequate treatment responses in 53 enrolled GPP patients (2:1 treatment to placebo randomization).73 Remarkably, more than half (19/35 [54%]) of GPP patients experienced complete resolution of pustules (GPP physician global assessment subscore of 0 [range, 0–4]) and showed sustained efficacy out to week 12 after just 1 or 2 doses of spesolimab. Overall, the safety profile of spesolimab was good; asthenia, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, headache, pruritus, infusion-related reaction and symptoms, and mild infections (eg, urinary tract infection) were the most common adverse events reported.73
Imsidolimab, a high-affinity humanized IgG4 monoclonal antibody that binds and blocks activation of IL-36R, also has completed phase 2 testing,74 with phase 3 study results expected in early 2024. The rapid onset of action and overall safety of imsidolimab was in line with and similar to spesolimab. Future approval of imsidolimab would add to the limited treatment options available for GPP and has the additional convenience of being administered to patients subcutaneously. Overall, the development of selective IL-36R inhibitors offers a much-needed therapeutic option for GPP and illustrates the importance of translational research.
Role of Tyrosine Kinase in Psoriatic Disease
The Janus kinase (JAK) enzyme family consists of 4 enzymes—tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2), JAK1, JAK2, and JAK3—that function as intracellular transduction signals that mediate the biologic response of most extracellular cytokines and growth factors.75 Critical psoriasis-related cytokines are dependent on intact JAK-STAT signaling, including IL-23, IL-12, and type I IFNs. In 2010, a genome-wide association identified TYK2 as a psoriasis susceptibility locus,76 and loss-of-function TYK2 mutations confer a reduced risk for psoriasis.77 Unlike other JAK isoforms, TYK2 mediates biologic functions that are highly restricted to the immune responses associated with IL-23, IL-12, and type I IFN signaling.78,79 For these reasons, blockade of TYK2 signaling is an attractive therapeutic target for the potential treatment of psoriatic disease.
In September 2022, the FDA approved deucravacitinib as a first-in-class, oral, selective TYK2 inhibitor for the treatment of adult patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. It was the first FDA approval of an oral small-molecule treatment for plaque psoriasis in nearly a decade. Deucravacitinib inhibits TYK2 signaling via selective binding of its unique regulatory domain, resulting in a conformational (allosteric) change that interferes with its active domain.80 This novel mechanism of action limits the unwanted blockade of other broad biologic processes mediated by JAK1/2/3. Of note, the FDA did not issue any boxed warnings for deucravacitinib as it did for other FDA-approved JAK inhibitors.
In a head-to-head, 52-week, double-blind, prospective, randomized, phase 3 study, deucravacitinib showed clear superiority over apremilast for PASI75 at week 16 (53.0% [271/511] vs 39.8% [101/254]) and week 24 (58.7% [296/504] vs 37.8% [96/254]).81 Clinical responses were sustained through week 52 and showed efficacy for difficult-to-treat areas such as the scalp, acral sites, and nails. Other advantages of deucravacitinib include once-daily dosing with no need for dose titration or adjustments for renal insufficiency as well as the absence of statistically significant differences in gastrointestinal tract symptoms compared to placebo. The most common adverse effects included nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infections, headache, diarrhea, and herpes infections.81 The potential benefit of deucravacitinib for PsA and psoriasis comorbidities remains to be seen, but it is promising due to its simultaneous disruption of multiple psoriasis-related cytokine networks. Several other TYK2 inhibitors are being developed for psoriatic disease and related inflammatory conditions, underscoring the promise of targeting this intracellular pathway.
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Agonism
Topical steroids are the mainstay treatment option for localized or limited plaque psoriasis due to their potent immunosuppressive effect on the skin and relatively low cost. Combined with vitamin D analogs, topical steroids result in marked improvements in disease severity and improved tolerability.82 However, chronic use of topical steroids is limited by the need for twice-daily application, resulting in poor treatment compliance; loss of efficacy over time; risk for steroid-induced skin atrophy on special body sites; and patient concerns of potential systemic effects. The discovery of novel drug targets amenable to topical inhibition is needed.
Dysregulated aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) levels have been reported in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.83 Aryl hydrocarbon receptors are ubiquitously expressed in many cell types and play an integral role in immune homeostasis within the skin, skin barrier function, protection against oxidative stressors, and regulation of proliferating melanocytes and keratinocytes.84,85 They are widely expressed in multiple immune cell types (eg, antigen-presenting cells, T lymphocytes, fibroblasts) and modulate the differentiation of T17 and T22 cells as well as their balance with regulatory T-cell populations.86 In keratinocytes, AHR helps to regulate terminal differentiation, enhance skin barrier integrity via AHR-dependent filaggrin (FLG) expression, and prevent transepidermal water loss.87,88 The mechanisms by which AHR ligands lead to the upregulation or downregulation of specific genes is intricate and highly context dependent, such as the specific ligand and cell type involved. In preclinical studies, AHR-deficient mice develop psoriasiform skin inflammation, increased IL-17 and IL-22 expression, and abnormal skin barrier function.89 Keratinocytes treated with AHR ligands in vitro modulated psoriasis-associated inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, IL-8, and type I and II IFNs.89,90 The use of coal tar, one of the earliest historical treatments for psoriasis, is thought to activate AHRs in the skin via organic compound mixtures containing polyaromatic hydrocarbons that help normalize the proinflammatory environment in psoriatic skin.91
In June 2022, the FDA approved tapinarof as a first-in-class, topical, nonsteroidal AHR agonist for the treatment of plaque psoriasis in adults. Although the exact mechanism of action for tapinarof has not been fully elucidated, early studies suggest that its primary function is the activation of AHR, leading to reduced T-cell expansion and T17 cell differentiation. In the imiquimod mouse model, cytokine expression of IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-19, IL-22, IL-23A, and IL-lβ in psoriasiform skin lesions were downregulated following tapinarof treatment.92 In humans, tapinarof treatment is associated with a remittive effect, in which the average time for tapinarof-treated psoriasis lesions to remain clear was approximately 4 months.93 Preliminary research investigating the mechanism by which tapinarof induces this remittive effect is ongoing and may involve the reduced activation and influx of T17 and Trm populations into the skin.94 However, these preclinical studies were performed on healthy dermatome-derived skin tissue cultured in T17-skewing conditions and needs to be replicated in larger samples sizes using human-derived psoriatic tissue. Alternatively, a strong inhibitory effect on IL-23 cytokine signaling may, in part, explain the remittive effect of tapinarof, as an analogous response is observed in patients who start and discontinue treatment with selective IL-23 antagonists. Regardless, the once-daily dosing of tapinarof and sustained treatment response is appealing to psoriasis patients. Tapinarof generally is well tolerated with mild folliculitis (>20% of patients) and contact dermatitis (5% of patients) reported as the most common skin-related adverse events.
New Roles for Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibition
Phosphodiesterases (PDEs) are enzymes that hydrolyze cyclic nucleotides (eg, cyclic adenosine monophosphate) to regulate intracellular secondary messengers involved in the inflammatory response. One of several enzymes in the PDE family, PDE4, has been shown to have greater activity in psoriatic skin compared to healthy skin.95 Phosphodiesterase inhibitors decrease the degradation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate, which triggers protein kinase A to downregulate proinflammatory (eg, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-17, IL-12, IL-23) cytokines and increased expression of anti-inflammatory signals such as IL-10.96,97 Apremilast, the first oral PDE4 inhibitor approved by the FDA for psoriasis, offered a safe alternative to traditional oral immunosuppressive agents that had extensive risks and potential end-organ adverse effects. Unfortunately, apremilast demonstrated modest efficacy for psoriatic disease (better efficacy in the skin vs joint manifestations) and was supplanted easily by next-generation targeted biologic agents that were more efficacious and lacked the troublesome gastrointestinal tract adverse effects of PDE4 inhibition.98
Crisaborole became the first topical PDE4 inhibitor approved in the United States in December 2016 for twice-daily treatment of atopic dermatitis. Although phase 2 trial results were reported in psoriasis, this indication was never pursued, presumably due to similar improvements in primary outcome measures at week 12, compared to placebo (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT01300052).
In July 2022, the first topical PDE4 inhibitor indicated for plaque psoriasis was approved by the FDA—roflumilast cream 0.3% for once-daily use in individuals 12 years and older. Roflumilast was found to be clinically efficacious as early as 2 weeks after its use in an early-phase clinical trial.99 In 2 phase 3 clinical trials (DERMIS-1 and DERMIS-2), roflumilast significantly increased the proportion of patients achieving PASI75 at week 8 compared to vehicle (39%–41.6% vs 5.3%–7.6%, respectively)(P<.001).100 Overall, this nonsteroidal topical therapy was found to be well tolerated, with infrequent reports of application site pain or irritation as adverse events. Similar to tapinarof, patients can apply roflumilast on all body surface areas including the face, external genitalia, and other intertriginous areas.100 Importantly, the broad immune impact of PDE4 inhibition suggests that topical roflumilast likely will be an effective treatment for several additional inflammatory conditions, including seborrheic dermatitis and atopic dermatitis, which would expand the clinical utility of this specific medication.
Conclusion
In the last 2 decades, we have witnessed a translational revolution in our understanding of the underlying genetics and immunology of psoriatic disease. Psoriasis is widely considered one of the best-managed inflammatory conditions in all of medicine due to the development and availability of highly targeted, effective topical and systemic therapies that predominantly disrupt IL-23/IL-17 cytokine signaling in affected tissues. However, future clinical studies and laboratory research are necessary to elucidate the precise cause of psoriasis as well as the underlying genetic and immune signaling pathways driving less common clinical variants and recalcitrant disease.

- Armstrong AW, Mehta MD, Schupp CW, et al. Psoriasis prevalence in adults in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:940-946. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.2007
- Ogdie A, Langan S, Love T, et al. Prevalence and treatment patterns of psoriatic arthritis in the UK. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013;52:568-575. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kes324
- Mease PJ, Gladman DD, Papp KA, et al. Prevalence of rheumatologistdiagnosed psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis in European/ North American dermatology clinics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:729- 735. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.07.023
- Langan SM, Seminara NM, Shin DB, et al. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in patients with psoriasis: a population-based study in the United Kingdom. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132(3 pt 1):556-562. doi:10.1038/jid.2011.365
- Wu S, Li WQ, Han J, et al. Hypercholesterolemia and risk of incident psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis in US women. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66:304-310. doi:10.1002/art.38227
- Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Armstrong EJ. The association between psoriasis and hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J Hypertens. 2013;31:433-442; discussion 442-443. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e32835bcce1
- Gelfand JM, Dommasch ED, Shin DB, et al. The risk of stroke in patients with psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:2411-2418. doi:10.1038 /jid.2009.112
- Armstrong AW, Lin SW, Chambers CJ, et al. Psoriasis and hypertension severity: results from a case-control study. PLoS One. 2011;6:E18227. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018227
- Naldi L, Chatenoud L, Linder D, et al. Cigarette smoking, body mass index, and stressful life events as risk factors for psoriasis: results from an Italian case-control study. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;125:61-67. doi:10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23681.x
- Yang YW, Kang JH, Lin HC. Increased risk of psoriasis following obstructive sleep apnea: a longitudinal population-based study. Sleep Med. 2012;13:285-289. doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2011.07.018
- Vaengebjerg S, Skov L, Egeberg A, et al. Prevalence, incidence, and risk of cancer in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:421-429. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.0024
- Loft N, Skov L, Richardson C, et al. A nationwide population-based cohort study of the incidence of severe and rare infections among adults with psoriasis in Denmark. Br J Dermatol. 2022;187:353-363. doi:10.1111/bjd.21595
- Fu Y, Lee CH, Chi CC. Association of psoriasis with inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1417-1423. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.3631
- Dowlatshahi EA, Wakkee M, Arends LR, et al. The prevalence and odds of depressive symptoms and clinical depression in psoriasis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:1542-1551. doi:10.1038/jid.2013.508
- Kurd SK, Troxel AB, Crits-Christoph P, et al. The risk of depression, anxiety, and suicidality in patients with psoriasis: a populationbased cohort study. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:891-895. doi:10.1001 /archdermatol.2010.186
- Elmets CA, Leonardi CL, Davis DMR, et al. Joint AAD-NPF guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with awareness and attention to comorbidities. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1073-1113. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.058
- Vanderpuye-Orgle J, Zhao Y, Lu J, et al. Evaluating the economic burden of psoriasis in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:961-967. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.02.1099
- Bos JD, Hagenaars C, Das PK, et al. Predominance of “memory” T cells (CD4+, CDw29+) over “naive” T cells (CD4+, CD45R+) in both normal and diseased human skin. Arch Dermatol Res. 1989;281:24-30. doi:10.1007/BF00424268
- Bos JD, Hulsebosch HJ, Krieg SR, et al. Immunocompetent cells in psoriasis. in situ immunophenotyping by monoclonal antibodies. Arch Dermatol Res. 1983;275:181-189. doi:10.1007/BF00510050
- Griffiths CE, Powles AV, Leonard JN, et al. Clearance of psoriasis with low dose cyclosporin. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1986;293:731-732. doi:10.1136/bmj.293.6549.731
- Ellis CN, Gorsulowsky DC, Hamilton TA, et al. Cyclosporine improves psoriasis in a double-blind study. JAMA. 1986;256:3110-3116.
- Langrish CL, Chen Y, Blumenschein WM, et al. IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med. 2005;201:233-240. doi:10.1084/jem.20041257
- Ferber IA, Brocke S, Taylor-Edwards C, et al. Mice with a disrupted IFN-gamma gene are susceptible to the induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). J Immunol. 1996;156:5-7.
- Bharadwaj R, Lusi CF, Mashayekh S, et al. Methotrexate suppresses psoriatic skin inflammation by inhibiting muropeptide transporter SLC46A2 activity. Immunity. 2023;56:998-1012. doi:10.1016/j. immuni.2023.04.001
- Jenneck C, Novak N. The safety and efficacy of alefacept in the treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2007;3:411-420.
- Pariser DM, Gordon KB, Papp KA, et al. Clinical efficacy of efalizumab in patients with chronic plaque psoriasis: results from three randomized placebo-controlled phase III trials: part I. J Cutan Med Surg. 2005; 9:303-312. doi:10.1007/s10227-005-0116-1
- Mease PJ, Gottlieb AB, van der Heijde D, et al. Efficacy and safety of abatacept, a T-cell modulator, in a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III study in psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:1550-1558. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210724
- Hawkes JE, Yan BY, Chan TC, et al. Discovery of the IL-23/IL-17 signaling pathway and the treatment of psoriasis. J Immunol. 2018;201:1605-1613. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1800013
- Ogawa K, Okada Y. The current landscape of psoriasis genetics in 2020. J Dermatol Sci. 2020;99:2-8. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2020.05.008
- Arakawa A, Siewert K, Stohr J, et al. Melanocyte antigen triggers autoimmunity in human psoriasis. J Exp Med. 2015;212:2203-2212. doi:10.1084/jem.20151093
- Griffiths CE, Barker JN. Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet. 2007;370:263-271. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61128-3
- Wang CQF, Akalu YT, Suarez-Farinas M, et al. IL-17 and TNF synergistically modulate cytokine expression while suppressing melanogenesis: potential relevance to psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:2741-2752. doi:10.1038/jid.2013.237
- Cheung KL, Jarrett R, Subramaniam S, et la. Psoriatic T cells recognize neolipid antigens generated by mast cell phospholipase delivered by exosomes and presented by CD1a. J Exp Med. 2016;213:2399-2412. doi:10.1084/jem.20160258
- Hawkes JE, Gonzalez JA, Krueger JG. Autoimmunity in psoriasis: evidence for specific autoantigens. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2017;6:104-112. doi:10.1007/s13671-017-0177-6
- Johansen C, Usher PA, Kjellerup RB, et al. Characterization of the interleukin-17 isoforms and receptors in lesional psoriatic skin. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160:319-324. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133 .2008.08902.x
- Kolbinger F, Loesche C, Valentin MA, et al. beta-Defensin 2 is a responsive biomarker of IL-17A-driven skin pathology in patients with psoriasis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139:923-932. doi:10.1016/j .jaci.2016.06.038
- Ruddy MJ, Wong GC, Liu XK, et al. Functional cooperation between interleukin-17 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha is mediated by CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein family members. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:2559-2567. doi:10.1074/jbc.M308809200
- Shen F, Hu Z, Goswami J, et al. Identification of common transcriptional regulatory elements in interleukin-17 target genes. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:24138-24148. doi:10.1074/jbc.M604597200
- Harper EG, Guo C, Rizzo H, et al. Th17 cytokines stimulate CCL20 expression in keratinocytes in vitro and in vivo: implications for psoriasis pathogenesis. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:2175-2183. doi:10.1038/jid.2009.65
- Chiricozzi A, Guttman-Yassky E, Suarez-Farinas M, et al. Integrative responses to IL-17 and TNF-alpha in human keratinocytes account for key inflammatory pathogenic circuits in psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 2011;131:677-687. doi:10.1038/jid.2010.340
- Homey B, Dieu-Nosjean MC, Wiesenborn A, et al. Up-regulation of macrophage inflammatory protein-3 alpha/CCL20 and CC chemokine receptor 6 in psoriasis. J Immunol. 2000;164:6621-6632. doi:10.4049 /jimmunol.164.12.6621
- Stephen-Victor E, Fickenscher H, Bayry J. IL-26: an emerging proinflammatory member of the IL-10 Cytokine family with multifaceted actions in antiviral, antimicrobial, and autoimmune responses. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12:E1005624. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1005624
- Wolk K, Witte K, Witte E, et al. IL-29 is produced by T(H)17 cells and mediates the cutaneous antiviral competence in psoriasis [published online September 25, 2013]. Sci Transl Med. doi:10.1126 /scitranslmed.3006245
- Kasprowicz-Furmanczyk M, Czerwinska J, Placek W, et al. Assessment of the tissue resident memory cells in lesional skin of patients with psoriasis and in healthy skin of healthy volunteers. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18:11251. doi:10.3390/ijerph182111251
- Cheuk S, Schlums H, Gallais Serezal I, et al. CD49a expression defines tissue-resident CD8(+) T cells poised for cytotoxic function in human skin. Immunity. 2017;46:287-300. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2017.01.009
- Sawyer LM, Malottki K, Sabry-Grant C, et al. Assessing the relative efficacy of interleukin-17 and interleukin-23 targeted treatments for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of PASI response. PLoS One. 2019;14:E0220868. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0220868
- Coates LC, Kavanaugh A, Mease PJ, et al. Group for research and assessment of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis 2015 treatment recommendations for psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68:1060-1071. doi:10.1002/art.39573
- Wang EA, Suzuki E, Maverakis E, et al. Targeting IL-17 in psoriatic arthritis. Eur J Rheumatol. 2017;4:272-277. doi:10.5152/eurjrheum.2017.17037
- Armstrong A, Fahrbach K, Leonardi C, et al. Efficacy of bimekizumab and other biologics in moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: a systematic literature review and a network meta-analysis. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:1777-1792. doi:10.1007/s13555-022-00760-8
- van Baarsen LG, Lebre MC, van der Coelen D, et al. Heterogeneous expression pattern of interleukin 17A (IL-17A), IL-17F and their receptors in synovium of rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and osteoarthritis: possible explanation for nonresponse to anti-IL-17 therapy? Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16:426. doi:10.1186/s13075-014-0426-z
- Hot A, Zrioual S, Toh ML, et al. IL-17A- versus IL-17F-induced intracellular signal transduction pathways and modulation by IL-17RA and IL-17RC RNA interference in rheumatoid synoviocytes. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:341-348. doi:10.1136/ard.2010.132233
- Adams R, Maroof A, Baker T, et al. Bimekizumab, a novel humanized IgG1 antibody that neutralizes both IL-17A and IL-17F. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1894. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01894
- Gordon KB, Foley P, Krueger JG, et al. Bimekizumab efficacy and safety in moderate to severe plaque psoriasis (BE READY): a multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised withdrawal phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;397:475-486. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00126-4
- Glatt S, Baeten D, Baker T, et al. Dual IL-17A and IL-17F neutralisation by bimekizumab in psoriatic arthritis: evidence from preclinical experiments and a randomised placebo-controlled clinical trial that IL-17F contributes to human chronic tissue inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:523-532. doi:10.1136 /annrheumdis-2017-212127
- Gordon KB, Langley RG, Warren RB, et al. Bimekizumab safety in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: pooled results from phase 2 and phase 3 randomized clinical trials. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:735-744. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.1185
- Reich K, Warren RB, Lebwohl M, et al. Bimekizumab versus secukinumab in plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:142-152. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2102383
- Reich K, Iversen L, Puig L, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of brodalumab in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: a post hoc pooled analysis of AMAGINE-2 and -3. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36:1275-1283. doi:10.1111/jdv.18068
- Papp KA, Blauvelt A, Puig L, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of risankizumab for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: interim analysis of the LIMMitless open-label extension trial up to 5 years of follow-up. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:1149-1158. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2023.07.1024
- Glatt S, Jemec GBE, Forman S, et al. Efficacy and safety of bimekizumab in moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa: a phase 2, doubleblind, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1279-1288. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.2905
- Choon SE, Lai NM, Mohammad NA, et al. Clinical profile, morbidity, and outcome of adult-onset generalized pustular psoriasis: analysis of 102 cases seen in a tertiary hospital in Johor, Malaysia. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:676-684. doi:10.1111/ijd.12070
- Zheng M, Jullien D, Eyerich K. The prevalence and disease characteristics of generalized pustular psoriasis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23 (suppl 1):5-12. doi:10.1007/s40257-021-00664-x
- Fujita H, Gooderham M, Romiti R. Diagnosis of generalized pustular psoriasis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23(suppl 1):31-38. doi:10.1007/s40257-021-00652-1
- Choon SE, Navarini AA, Pinter A. Clinical course and characteristics of generalized pustular psoriasis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23 (suppl 1):21-29. doi:10.1007/s40257-021-00654-z
- Augey F, Renaudier P, Nicolas JF. Generalized pustular psoriasis (Zumbusch): a French epidemiological survey. Eur J Dermatol. 2006;16:669-673.
- Ohkawara A, Yasuda H, Kobayashi H, et al. Generalized pustular psoriasis in Japan: two distinct groups formed by differences in symptoms and genetic background. Acta Derm Venereol. 1996;76:68-71. doi:10.2340/00015555766871
- Lee JY, Kang S, Park JS, et al. Prevalence of psoriasis in Korea: A population-based epidemiological study using the Korean National Health Insurance database. Ann Dermatol. 2017;29:761-767. doi:10.5021 /ad.2017.29.6.761
- Prinz JC, Choon SE, Griffiths CEM, et al. Prevalence, comorbidities and mortality of generalized pustular psoriasis: a literature review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37:256-273. doi:10.1111/jdv.18720
- Johnston A, Xing X, Wolterink L, et al. IL-1 and IL-36 are dominant cytokines in generalized pustular psoriasis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;140:109-120. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2016.08.056
- Rajan N, Sinclair N, Nakai H, et al. A tale of two sisters: identical IL36RN mutations and discordant phenotypes. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:417-420. doi:10.1111/bjd.14003
- Ly K, Beck KM, Smith MP, et al. Diagnosis and screening of patients with generalized pustular psoriasis. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2019;9:37-42. doi:10.2147/PTT.S181808
- Sugiura K. Role of interleukin 36 in generalised pustular psoriasis and beyond. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:315-328. doi:10.1007 /s13555-021-00677-8
- Akiyama M, Takeichi T, McGrath JA, et al. Autoinflammatory keratinization diseases: an emerging concept encompassing various inflammatory keratinization disorders of the skin. J Dermatol Sci. 2018;90:105-111. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2018.01.012
- Bachelez H, Choon SE, Marrakchi S, et al. Trial of spesolimab for generalized pustular psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2431-2440. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2111563
- Warren RB, Reich A, Kaszuba A, et al. Imsidolimab, an anti-IL-36 receptor monoclonal antibody for the treatment of generalised pustular psoriasis: results from the phase 2 GALLOP trial. Br J Dermatol. 2023;189:161-169. doi:10.1093/bjd/ljad083
- Villarino AV, Kanno Y, O’Shea JJ. Mechanisms and consequences of Jak-STAT signaling in the immune system. Nat Immunol. 2017; 18:374-384. doi:10.1038/ni.3691
- Genetic Analysis of Psoriasis Consortium & the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2; Strange A, Capon F, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies new psoriasis susceptibility loci and an interaction between HLA-C and ERAP1. Nat Genet. 2010;42:985-990. doi:10.1038/ng.694
- Enerback C, Sandin C, Lambert S, et al. The psoriasis-protective TYK2 I684S variant impairs IL-12 stimulated pSTAT4 response in skin-homing CD4+ and CD8+ memory T-cells. Sci Rep. 2018;8:7043. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-25282-2
- Shimoda K, Kato K, Aoki K, et al. Tyk2 plays a restricted role in IFN alpha signaling, although it is required for IL-12-mediated T cell function. Immunity. 2000;13:561-571. doi:10.1016/s1074-7613(00)00055-8
- Karaghiosoff M, Neubauer H, Lassnig C, et al. Partial impairment of cytokine responses in Tyk2-deficient mice. Immunity. 2000;13:549-560. doi:10.1016/s1074-7613(00)00054-6
- Burke JR, Cheng L, Gillooly KM, et al. Autoimmune pathways in mice and humans are blocked by pharmacological stabilization of the TYK2 pseudokinase domain [published online July 24, 2019]. Sci Transl Med. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aaw1736
- Strober B, Thaci D, Sofen H, et al. Deucravacitinib versus placebo and apremilast in moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: efficacy and safety results from the 52-week, randomized, double-blinded, phase 3 program for evaluation of TYK2 inhibitor psoriasis second trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;88:40-51. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.08.061
- Stein Gold L, Lebwohl M, Menter A, et al. Aerosol foam formulation of fixed combination calcipotriene plus betamethasone dipropionate is highly efficacious in patients with psoriasis vulgaris: pooled data from three randomized controlled studies. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15:951-957.
- Beranek M, Fiala Z, Kremlacek J, et al. Serum levels of aryl hydrocarbon receptor, cytochromes p450 1a1 and 1b1 in patients with exacerbated psoriasis vulgaris. Folia Biol (Praha). 2018;64:97-102.
- Esser C, Rannug A. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor in barrier organ physiology, immunology, and toxicology. Pharmacol Rev. 2015;67:259- 279. doi:10.1124/pr.114.009001
- Furue M, Uchi H, Mitoma C, et al. Antioxidants for healthy skin: the emerging role of aryl hydrocarbon receptors and nuclear factorerythroid 2-related factor-2. Nutrients. 2017;9:223. doi:10.3390/nu9030223
- Papp KA, Langley RG, Lebwohl M, et al. Efficacy and safety of ustekinumab, a human interleukin-12/23 monoclonal antibody, in patients with psoriasis: 52-week results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (PHOENIX 2). Lancet. 2008;371:1675-1684. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60726-6
- Sutter CH, Olesen KM, Bhuju J, et al. AHR regulates metabolic reprogramming to promote SIRT1-dependent keratinocyte differentiation. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:818-826. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2018.10.019
- Haas K, Weighardt H, Deenen R, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor in keratinocytes is essential for murine skin barrier integrity. J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136:2260-2269. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2016.06.627
- Di Meglio P, Duarte JH, Ahlfors H, et al. Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor dampens the severity of inflammatory skin conditions. Immunity. 2014;40:989-1001. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2014.04.019
- Kim HO, Kim JH, Chung BY, et al. Increased expression of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in patients with chronic inflammatory skin diseases. Exp Dermatol. 2014;23:278-281. doi:10.1111/exd.12350
- van den Bogaard EH, Bergboer JG, Vonk-Bergers M, et al. Coal tar induces AHR-dependent skin barrier repair in atopic dermatitis. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:917-927. doi:10.1172/JCI65642
- Smith SH, Jayawickreme C, Rickard DJ, et al. Tapinarof is a natural AHR agonist that resolves skin inflammation in mice and humans. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137:2110-2119. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2017.05.004
- Strober B, Stein Gold L, Bissonnette R, et al. One-year safety and efficacy of tapinarof cream for the treatment of plaque psoriasis: results from the PSOARING 3 trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:800-806. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.06.1171
- Mooney N, Teague JE, Gehad AE, et al. Tapinarof inhibits the formation, cytokine production, and persistence of resident memory T cells in vitro. SKIN J Cutan Med. 2023;7:S194. doi:10.25251/skin.7.supp.194
- Schafer PH, Truzzi F, Parton A, et al. Phosphodiesterase 4 in inflammatory diseases: effects of apremilast in psoriatic blood and in dermal myofibroblasts through the PDE4/CD271 complex. Cell Signal. 2016;28:753-763. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.01.007
- Li H, Zuo J, Tang W. Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1048. doi:10.3389/ fphar.2018.01048
- Schafer PH, Parton A, Gandhi AK, et al. Apremilast, a cAMP phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, demonstrates anti-inflammatory activity in vitro and in a model of psoriasis. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;159:842-855. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00559.x
- Papp K, Reich K, Leonardi CL, et al. Apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor, in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: results of a phase III, randomized, controlled trial (Efficacy and Safety Trial Evaluating the Effects of Apremilast in Psoriasis [ESTEEM] 1). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:37-49. doi:10.1016/j .jaad.2015.03.049
- Papp KA, Gooderham M, Droege M, et al. Roflumilast cream improves signs and symptoms of plaque psoriasis: results from a phase 1/2a randomized, controlled study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2020;19:734-740. doi:10.36849/JDD.2020.5370
- Lebwohl MG, Kircik LH, Moore AY, et al. Effect of roflumilast cream vs vehicle cream on chronic plaque psoriasis: the DERMIS-1 and DERMIS-2 randomized clinical trials. JAMA. 2022;328:1073-1084. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.15632
- Armstrong AW, Mehta MD, Schupp CW, et al. Psoriasis prevalence in adults in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:940-946. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.2007
- Ogdie A, Langan S, Love T, et al. Prevalence and treatment patterns of psoriatic arthritis in the UK. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013;52:568-575. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kes324
- Mease PJ, Gladman DD, Papp KA, et al. Prevalence of rheumatologistdiagnosed psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis in European/ North American dermatology clinics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:729- 735. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.07.023
- Langan SM, Seminara NM, Shin DB, et al. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in patients with psoriasis: a population-based study in the United Kingdom. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132(3 pt 1):556-562. doi:10.1038/jid.2011.365
- Wu S, Li WQ, Han J, et al. Hypercholesterolemia and risk of incident psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis in US women. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66:304-310. doi:10.1002/art.38227
- Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Armstrong EJ. The association between psoriasis and hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J Hypertens. 2013;31:433-442; discussion 442-443. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e32835bcce1
- Gelfand JM, Dommasch ED, Shin DB, et al. The risk of stroke in patients with psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:2411-2418. doi:10.1038 /jid.2009.112
- Armstrong AW, Lin SW, Chambers CJ, et al. Psoriasis and hypertension severity: results from a case-control study. PLoS One. 2011;6:E18227. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018227
- Naldi L, Chatenoud L, Linder D, et al. Cigarette smoking, body mass index, and stressful life events as risk factors for psoriasis: results from an Italian case-control study. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;125:61-67. doi:10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23681.x
- Yang YW, Kang JH, Lin HC. Increased risk of psoriasis following obstructive sleep apnea: a longitudinal population-based study. Sleep Med. 2012;13:285-289. doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2011.07.018
- Vaengebjerg S, Skov L, Egeberg A, et al. Prevalence, incidence, and risk of cancer in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:421-429. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.0024
- Loft N, Skov L, Richardson C, et al. A nationwide population-based cohort study of the incidence of severe and rare infections among adults with psoriasis in Denmark. Br J Dermatol. 2022;187:353-363. doi:10.1111/bjd.21595
- Fu Y, Lee CH, Chi CC. Association of psoriasis with inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1417-1423. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.3631
- Dowlatshahi EA, Wakkee M, Arends LR, et al. The prevalence and odds of depressive symptoms and clinical depression in psoriasis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:1542-1551. doi:10.1038/jid.2013.508
- Kurd SK, Troxel AB, Crits-Christoph P, et al. The risk of depression, anxiety, and suicidality in patients with psoriasis: a populationbased cohort study. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:891-895. doi:10.1001 /archdermatol.2010.186
- Elmets CA, Leonardi CL, Davis DMR, et al. Joint AAD-NPF guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with awareness and attention to comorbidities. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1073-1113. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.058
- Vanderpuye-Orgle J, Zhao Y, Lu J, et al. Evaluating the economic burden of psoriasis in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:961-967. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.02.1099
- Bos JD, Hagenaars C, Das PK, et al. Predominance of “memory” T cells (CD4+, CDw29+) over “naive” T cells (CD4+, CD45R+) in both normal and diseased human skin. Arch Dermatol Res. 1989;281:24-30. doi:10.1007/BF00424268
- Bos JD, Hulsebosch HJ, Krieg SR, et al. Immunocompetent cells in psoriasis. in situ immunophenotyping by monoclonal antibodies. Arch Dermatol Res. 1983;275:181-189. doi:10.1007/BF00510050
- Griffiths CE, Powles AV, Leonard JN, et al. Clearance of psoriasis with low dose cyclosporin. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1986;293:731-732. doi:10.1136/bmj.293.6549.731
- Ellis CN, Gorsulowsky DC, Hamilton TA, et al. Cyclosporine improves psoriasis in a double-blind study. JAMA. 1986;256:3110-3116.
- Langrish CL, Chen Y, Blumenschein WM, et al. IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med. 2005;201:233-240. doi:10.1084/jem.20041257
- Ferber IA, Brocke S, Taylor-Edwards C, et al. Mice with a disrupted IFN-gamma gene are susceptible to the induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). J Immunol. 1996;156:5-7.
- Bharadwaj R, Lusi CF, Mashayekh S, et al. Methotrexate suppresses psoriatic skin inflammation by inhibiting muropeptide transporter SLC46A2 activity. Immunity. 2023;56:998-1012. doi:10.1016/j. immuni.2023.04.001
- Jenneck C, Novak N. The safety and efficacy of alefacept in the treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2007;3:411-420.
- Pariser DM, Gordon KB, Papp KA, et al. Clinical efficacy of efalizumab in patients with chronic plaque psoriasis: results from three randomized placebo-controlled phase III trials: part I. J Cutan Med Surg. 2005; 9:303-312. doi:10.1007/s10227-005-0116-1
- Mease PJ, Gottlieb AB, van der Heijde D, et al. Efficacy and safety of abatacept, a T-cell modulator, in a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III study in psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:1550-1558. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210724
- Hawkes JE, Yan BY, Chan TC, et al. Discovery of the IL-23/IL-17 signaling pathway and the treatment of psoriasis. J Immunol. 2018;201:1605-1613. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1800013
- Ogawa K, Okada Y. The current landscape of psoriasis genetics in 2020. J Dermatol Sci. 2020;99:2-8. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2020.05.008
- Arakawa A, Siewert K, Stohr J, et al. Melanocyte antigen triggers autoimmunity in human psoriasis. J Exp Med. 2015;212:2203-2212. doi:10.1084/jem.20151093
- Griffiths CE, Barker JN. Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet. 2007;370:263-271. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61128-3
- Wang CQF, Akalu YT, Suarez-Farinas M, et al. IL-17 and TNF synergistically modulate cytokine expression while suppressing melanogenesis: potential relevance to psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:2741-2752. doi:10.1038/jid.2013.237
- Cheung KL, Jarrett R, Subramaniam S, et la. Psoriatic T cells recognize neolipid antigens generated by mast cell phospholipase delivered by exosomes and presented by CD1a. J Exp Med. 2016;213:2399-2412. doi:10.1084/jem.20160258
- Hawkes JE, Gonzalez JA, Krueger JG. Autoimmunity in psoriasis: evidence for specific autoantigens. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2017;6:104-112. doi:10.1007/s13671-017-0177-6
- Johansen C, Usher PA, Kjellerup RB, et al. Characterization of the interleukin-17 isoforms and receptors in lesional psoriatic skin. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160:319-324. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133 .2008.08902.x
- Kolbinger F, Loesche C, Valentin MA, et al. beta-Defensin 2 is a responsive biomarker of IL-17A-driven skin pathology in patients with psoriasis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139:923-932. doi:10.1016/j .jaci.2016.06.038
- Ruddy MJ, Wong GC, Liu XK, et al. Functional cooperation between interleukin-17 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha is mediated by CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein family members. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:2559-2567. doi:10.1074/jbc.M308809200
- Shen F, Hu Z, Goswami J, et al. Identification of common transcriptional regulatory elements in interleukin-17 target genes. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:24138-24148. doi:10.1074/jbc.M604597200
- Harper EG, Guo C, Rizzo H, et al. Th17 cytokines stimulate CCL20 expression in keratinocytes in vitro and in vivo: implications for psoriasis pathogenesis. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:2175-2183. doi:10.1038/jid.2009.65
- Chiricozzi A, Guttman-Yassky E, Suarez-Farinas M, et al. Integrative responses to IL-17 and TNF-alpha in human keratinocytes account for key inflammatory pathogenic circuits in psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 2011;131:677-687. doi:10.1038/jid.2010.340
- Homey B, Dieu-Nosjean MC, Wiesenborn A, et al. Up-regulation of macrophage inflammatory protein-3 alpha/CCL20 and CC chemokine receptor 6 in psoriasis. J Immunol. 2000;164:6621-6632. doi:10.4049 /jimmunol.164.12.6621
- Stephen-Victor E, Fickenscher H, Bayry J. IL-26: an emerging proinflammatory member of the IL-10 Cytokine family with multifaceted actions in antiviral, antimicrobial, and autoimmune responses. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12:E1005624. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1005624
- Wolk K, Witte K, Witte E, et al. IL-29 is produced by T(H)17 cells and mediates the cutaneous antiviral competence in psoriasis [published online September 25, 2013]. Sci Transl Med. doi:10.1126 /scitranslmed.3006245
- Kasprowicz-Furmanczyk M, Czerwinska J, Placek W, et al. Assessment of the tissue resident memory cells in lesional skin of patients with psoriasis and in healthy skin of healthy volunteers. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18:11251. doi:10.3390/ijerph182111251
- Cheuk S, Schlums H, Gallais Serezal I, et al. CD49a expression defines tissue-resident CD8(+) T cells poised for cytotoxic function in human skin. Immunity. 2017;46:287-300. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2017.01.009
- Sawyer LM, Malottki K, Sabry-Grant C, et al. Assessing the relative efficacy of interleukin-17 and interleukin-23 targeted treatments for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of PASI response. PLoS One. 2019;14:E0220868. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0220868
- Coates LC, Kavanaugh A, Mease PJ, et al. Group for research and assessment of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis 2015 treatment recommendations for psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68:1060-1071. doi:10.1002/art.39573
- Wang EA, Suzuki E, Maverakis E, et al. Targeting IL-17 in psoriatic arthritis. Eur J Rheumatol. 2017;4:272-277. doi:10.5152/eurjrheum.2017.17037
- Armstrong A, Fahrbach K, Leonardi C, et al. Efficacy of bimekizumab and other biologics in moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: a systematic literature review and a network meta-analysis. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:1777-1792. doi:10.1007/s13555-022-00760-8
- van Baarsen LG, Lebre MC, van der Coelen D, et al. Heterogeneous expression pattern of interleukin 17A (IL-17A), IL-17F and their receptors in synovium of rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and osteoarthritis: possible explanation for nonresponse to anti-IL-17 therapy? Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16:426. doi:10.1186/s13075-014-0426-z
- Hot A, Zrioual S, Toh ML, et al. IL-17A- versus IL-17F-induced intracellular signal transduction pathways and modulation by IL-17RA and IL-17RC RNA interference in rheumatoid synoviocytes. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:341-348. doi:10.1136/ard.2010.132233
- Adams R, Maroof A, Baker T, et al. Bimekizumab, a novel humanized IgG1 antibody that neutralizes both IL-17A and IL-17F. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1894. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01894
- Gordon KB, Foley P, Krueger JG, et al. Bimekizumab efficacy and safety in moderate to severe plaque psoriasis (BE READY): a multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised withdrawal phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;397:475-486. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00126-4
- Glatt S, Baeten D, Baker T, et al. Dual IL-17A and IL-17F neutralisation by bimekizumab in psoriatic arthritis: evidence from preclinical experiments and a randomised placebo-controlled clinical trial that IL-17F contributes to human chronic tissue inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:523-532. doi:10.1136 /annrheumdis-2017-212127
- Gordon KB, Langley RG, Warren RB, et al. Bimekizumab safety in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: pooled results from phase 2 and phase 3 randomized clinical trials. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:735-744. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.1185
- Reich K, Warren RB, Lebwohl M, et al. Bimekizumab versus secukinumab in plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:142-152. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2102383
- Reich K, Iversen L, Puig L, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of brodalumab in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: a post hoc pooled analysis of AMAGINE-2 and -3. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36:1275-1283. doi:10.1111/jdv.18068
- Papp KA, Blauvelt A, Puig L, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of risankizumab for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: interim analysis of the LIMMitless open-label extension trial up to 5 years of follow-up. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:1149-1158. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2023.07.1024
- Glatt S, Jemec GBE, Forman S, et al. Efficacy and safety of bimekizumab in moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa: a phase 2, doubleblind, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1279-1288. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.2905
- Choon SE, Lai NM, Mohammad NA, et al. Clinical profile, morbidity, and outcome of adult-onset generalized pustular psoriasis: analysis of 102 cases seen in a tertiary hospital in Johor, Malaysia. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:676-684. doi:10.1111/ijd.12070
- Zheng M, Jullien D, Eyerich K. The prevalence and disease characteristics of generalized pustular psoriasis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23 (suppl 1):5-12. doi:10.1007/s40257-021-00664-x
- Fujita H, Gooderham M, Romiti R. Diagnosis of generalized pustular psoriasis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23(suppl 1):31-38. doi:10.1007/s40257-021-00652-1
- Choon SE, Navarini AA, Pinter A. Clinical course and characteristics of generalized pustular psoriasis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23 (suppl 1):21-29. doi:10.1007/s40257-021-00654-z
- Augey F, Renaudier P, Nicolas JF. Generalized pustular psoriasis (Zumbusch): a French epidemiological survey. Eur J Dermatol. 2006;16:669-673.
- Ohkawara A, Yasuda H, Kobayashi H, et al. Generalized pustular psoriasis in Japan: two distinct groups formed by differences in symptoms and genetic background. Acta Derm Venereol. 1996;76:68-71. doi:10.2340/00015555766871
- Lee JY, Kang S, Park JS, et al. Prevalence of psoriasis in Korea: A population-based epidemiological study using the Korean National Health Insurance database. Ann Dermatol. 2017;29:761-767. doi:10.5021 /ad.2017.29.6.761
- Prinz JC, Choon SE, Griffiths CEM, et al. Prevalence, comorbidities and mortality of generalized pustular psoriasis: a literature review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37:256-273. doi:10.1111/jdv.18720
- Johnston A, Xing X, Wolterink L, et al. IL-1 and IL-36 are dominant cytokines in generalized pustular psoriasis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;140:109-120. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2016.08.056
- Rajan N, Sinclair N, Nakai H, et al. A tale of two sisters: identical IL36RN mutations and discordant phenotypes. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:417-420. doi:10.1111/bjd.14003
- Ly K, Beck KM, Smith MP, et al. Diagnosis and screening of patients with generalized pustular psoriasis. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2019;9:37-42. doi:10.2147/PTT.S181808
- Sugiura K. Role of interleukin 36 in generalised pustular psoriasis and beyond. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:315-328. doi:10.1007 /s13555-021-00677-8
- Akiyama M, Takeichi T, McGrath JA, et al. Autoinflammatory keratinization diseases: an emerging concept encompassing various inflammatory keratinization disorders of the skin. J Dermatol Sci. 2018;90:105-111. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2018.01.012
- Bachelez H, Choon SE, Marrakchi S, et al. Trial of spesolimab for generalized pustular psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2431-2440. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2111563
- Warren RB, Reich A, Kaszuba A, et al. Imsidolimab, an anti-IL-36 receptor monoclonal antibody for the treatment of generalised pustular psoriasis: results from the phase 2 GALLOP trial. Br J Dermatol. 2023;189:161-169. doi:10.1093/bjd/ljad083
- Villarino AV, Kanno Y, O’Shea JJ. Mechanisms and consequences of Jak-STAT signaling in the immune system. Nat Immunol. 2017; 18:374-384. doi:10.1038/ni.3691
- Genetic Analysis of Psoriasis Consortium & the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2; Strange A, Capon F, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies new psoriasis susceptibility loci and an interaction between HLA-C and ERAP1. Nat Genet. 2010;42:985-990. doi:10.1038/ng.694
- Enerback C, Sandin C, Lambert S, et al. The psoriasis-protective TYK2 I684S variant impairs IL-12 stimulated pSTAT4 response in skin-homing CD4+ and CD8+ memory T-cells. Sci Rep. 2018;8:7043. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-25282-2
- Shimoda K, Kato K, Aoki K, et al. Tyk2 plays a restricted role in IFN alpha signaling, although it is required for IL-12-mediated T cell function. Immunity. 2000;13:561-571. doi:10.1016/s1074-7613(00)00055-8
- Karaghiosoff M, Neubauer H, Lassnig C, et al. Partial impairment of cytokine responses in Tyk2-deficient mice. Immunity. 2000;13:549-560. doi:10.1016/s1074-7613(00)00054-6
- Burke JR, Cheng L, Gillooly KM, et al. Autoimmune pathways in mice and humans are blocked by pharmacological stabilization of the TYK2 pseudokinase domain [published online July 24, 2019]. Sci Transl Med. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aaw1736
- Strober B, Thaci D, Sofen H, et al. Deucravacitinib versus placebo and apremilast in moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: efficacy and safety results from the 52-week, randomized, double-blinded, phase 3 program for evaluation of TYK2 inhibitor psoriasis second trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;88:40-51. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.08.061
- Stein Gold L, Lebwohl M, Menter A, et al. Aerosol foam formulation of fixed combination calcipotriene plus betamethasone dipropionate is highly efficacious in patients with psoriasis vulgaris: pooled data from three randomized controlled studies. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15:951-957.
- Beranek M, Fiala Z, Kremlacek J, et al. Serum levels of aryl hydrocarbon receptor, cytochromes p450 1a1 and 1b1 in patients with exacerbated psoriasis vulgaris. Folia Biol (Praha). 2018;64:97-102.
- Esser C, Rannug A. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor in barrier organ physiology, immunology, and toxicology. Pharmacol Rev. 2015;67:259- 279. doi:10.1124/pr.114.009001
- Furue M, Uchi H, Mitoma C, et al. Antioxidants for healthy skin: the emerging role of aryl hydrocarbon receptors and nuclear factorerythroid 2-related factor-2. Nutrients. 2017;9:223. doi:10.3390/nu9030223
- Papp KA, Langley RG, Lebwohl M, et al. Efficacy and safety of ustekinumab, a human interleukin-12/23 monoclonal antibody, in patients with psoriasis: 52-week results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (PHOENIX 2). Lancet. 2008;371:1675-1684. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60726-6
- Sutter CH, Olesen KM, Bhuju J, et al. AHR regulates metabolic reprogramming to promote SIRT1-dependent keratinocyte differentiation. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:818-826. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2018.10.019
- Haas K, Weighardt H, Deenen R, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor in keratinocytes is essential for murine skin barrier integrity. J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136:2260-2269. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2016.06.627
- Di Meglio P, Duarte JH, Ahlfors H, et al. Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor dampens the severity of inflammatory skin conditions. Immunity. 2014;40:989-1001. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2014.04.019
- Kim HO, Kim JH, Chung BY, et al. Increased expression of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in patients with chronic inflammatory skin diseases. Exp Dermatol. 2014;23:278-281. doi:10.1111/exd.12350
- van den Bogaard EH, Bergboer JG, Vonk-Bergers M, et al. Coal tar induces AHR-dependent skin barrier repair in atopic dermatitis. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:917-927. doi:10.1172/JCI65642
- Smith SH, Jayawickreme C, Rickard DJ, et al. Tapinarof is a natural AHR agonist that resolves skin inflammation in mice and humans. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137:2110-2119. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2017.05.004
- Strober B, Stein Gold L, Bissonnette R, et al. One-year safety and efficacy of tapinarof cream for the treatment of plaque psoriasis: results from the PSOARING 3 trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:800-806. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.06.1171
- Mooney N, Teague JE, Gehad AE, et al. Tapinarof inhibits the formation, cytokine production, and persistence of resident memory T cells in vitro. SKIN J Cutan Med. 2023;7:S194. doi:10.25251/skin.7.supp.194
- Schafer PH, Truzzi F, Parton A, et al. Phosphodiesterase 4 in inflammatory diseases: effects of apremilast in psoriatic blood and in dermal myofibroblasts through the PDE4/CD271 complex. Cell Signal. 2016;28:753-763. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.01.007
- Li H, Zuo J, Tang W. Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1048. doi:10.3389/ fphar.2018.01048
- Schafer PH, Parton A, Gandhi AK, et al. Apremilast, a cAMP phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, demonstrates anti-inflammatory activity in vitro and in a model of psoriasis. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;159:842-855. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00559.x
- Papp K, Reich K, Leonardi CL, et al. Apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor, in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: results of a phase III, randomized, controlled trial (Efficacy and Safety Trial Evaluating the Effects of Apremilast in Psoriasis [ESTEEM] 1). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:37-49. doi:10.1016/j .jaad.2015.03.049
- Papp KA, Gooderham M, Droege M, et al. Roflumilast cream improves signs and symptoms of plaque psoriasis: results from a phase 1/2a randomized, controlled study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2020;19:734-740. doi:10.36849/JDD.2020.5370
- Lebwohl MG, Kircik LH, Moore AY, et al. Effect of roflumilast cream vs vehicle cream on chronic plaque psoriasis: the DERMIS-1 and DERMIS-2 randomized clinical trials. JAMA. 2022;328:1073-1084. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.15632
Practice Points
- Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory condition characterized by systemic inflammation and dysregulated IL-23/IL-17 signaling.
- Modern discoveries highlight the role of additional immune signals in psoriatic disease such as IL-17C, IL-17F, IL-36, and tyrosine kinase 2, which also contribute to disease development.
- Novel systemic, oral, and topical therapies have become available and add to the rapidly growing armamentarium of safe and effective treatments for psoriatic disease.
A Look at the Evidence Linking Diet to Skin Conditions
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — Amid all the hype, claims, and confusion, there is evidence linking some foods and drinks to an increased risk for acne, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, rosacea, and other common skin conditions. So, what is the connection in each case? And how can people with any of these skin conditions potentially improve their health and quality of life with dietary changes?
What is clear is that there has been an explosion of interest in learning which foods can improve or worsen skin issues in recent years. It’s a good idea to familiarize yourself with the research and also to Google ‘diet’ and ‘skin’, said Vivian Shi, MD, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock. “As practitioners, we should be well prepared to talk about what patients want to talk about.”
Acne
One of the major areas of interest is diet and acne. “We’ve all heard sugar and dairy are bad, and the Western diet is high in sugar and dairy,” Dr. Shi said at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgical Conference.
Dairy, red meat, and carbohydrates can break down into leucine, an essential amino acid found in protein. Leucine and sugar together, in turn, can produce insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), which, through different pathways, can reach the androgen receptors throughout the body, including the skin. This results in sebogenesis, lipogenesis, and keratinization, which triggers follicular inflammation and results in more of the acne-causing bacteria Cutibacterium acnes.
Milk and other dairy products also can increase IGF-1 levels, which can alter hormonal mediators and increase acne.
Not all types of dairy milk are created equal, however, when it comes to acne. Dr. Shi wondered why 2% milk has overall color and nutritional content very similar to that of whole milk. “I looked into this.” She discovered that when milk manufacturers remove the fat, they often add whey proteins to restore some nutrients. Whey protein can increase acne, Dr. Shi added.
“So, if you’re going to choose any milk to drink, I think from an acne perspective, it’s better to use whole milk. If you can get it organic, even better.” Skim milk is the most acnegenic, she said.
Psoriasis
A systematic review of 55 studies evaluating diet and psoriasis found obesity can be an exacerbating factor. The strongest evidence for dietary weight reduction points to a hypocaloric diet in people with overweight or obesity, according to the review. Other evidence suggests alcohol can lower response to treatment and is linked with more severe psoriasis. Furthermore, a gluten-free diet or vitamin D supplements can help some subpopulations of people with psoriasis.
“An overwhelming majority of our psoriasis patients are vitamin D deficient,” Dr. Shi said.
The National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) publishes dietary modification guidelines, updated as recently as November 2023. The NPF states that “there is no diet that will cure psoriatic disease, but there are many ways in which eating healthful food may lessen the severity of symptoms and play a role in lowering the likelihood of developing comorbidities.”
Healthier choices include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fat-free or low-fat dairy products. Include lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, eggs, and nuts. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet has been linked to a lower severity of psoriasis.
Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is “one of the prototypical diseases related to diet,” Dr. Shi said. A different meta-analysis looked at randomized controlled trials of synbiotics (a combination of prebiotics and probiotics) for treatment of AD.
These researchers found that synbiotics do not prevent AD, but they can help treat it in adults and children older than 1 year. In addition, synbiotics are more beneficial than probiotics in treating the condition, although there are no head-to-head comparison studies. In addition, the meta-analysis found that prebiotics alone can lower AD severity.
However, Dr. Shi said, there are no recommendations from the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) on prebiotics or probiotics for AD, and the AAD does not recommend any supplement or essential oil for AD.
In a 2022 review, investigators ranked the efficacy of different supplements for AD based on available evidence. They found the greatest benefit associated with vitamin D supplementation, followed by vitamin E, probiotics, hemp seed oil, histidine, and oolong tea. They also noted the ‘Six Food Elimination Diet and Autoimmune Protocol’ featured the least amount of evidence to back it up.
Rosacea
Rosacea appears to be caused by “all the fun things in life” like sunlight, alcohol, chocolate, spicy foods, and caffeine, Dr. Shi said. In people with rosacea, they can cause facial flushing, edema, burning, and an inflammatory response.
Certain foods can activate skin receptors and sensory neurons, which can release neuropeptides that act on mast cells in blood that lead to flushing. The skin-gut axis may also be involved, evidence suggests. “And that is why food has a pretty profound impact on rosacea,” Dr. Shi said.
Dr. Shi reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — Amid all the hype, claims, and confusion, there is evidence linking some foods and drinks to an increased risk for acne, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, rosacea, and other common skin conditions. So, what is the connection in each case? And how can people with any of these skin conditions potentially improve their health and quality of life with dietary changes?
What is clear is that there has been an explosion of interest in learning which foods can improve or worsen skin issues in recent years. It’s a good idea to familiarize yourself with the research and also to Google ‘diet’ and ‘skin’, said Vivian Shi, MD, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock. “As practitioners, we should be well prepared to talk about what patients want to talk about.”
Acne
One of the major areas of interest is diet and acne. “We’ve all heard sugar and dairy are bad, and the Western diet is high in sugar and dairy,” Dr. Shi said at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgical Conference.
Dairy, red meat, and carbohydrates can break down into leucine, an essential amino acid found in protein. Leucine and sugar together, in turn, can produce insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), which, through different pathways, can reach the androgen receptors throughout the body, including the skin. This results in sebogenesis, lipogenesis, and keratinization, which triggers follicular inflammation and results in more of the acne-causing bacteria Cutibacterium acnes.
Milk and other dairy products also can increase IGF-1 levels, which can alter hormonal mediators and increase acne.
Not all types of dairy milk are created equal, however, when it comes to acne. Dr. Shi wondered why 2% milk has overall color and nutritional content very similar to that of whole milk. “I looked into this.” She discovered that when milk manufacturers remove the fat, they often add whey proteins to restore some nutrients. Whey protein can increase acne, Dr. Shi added.
“So, if you’re going to choose any milk to drink, I think from an acne perspective, it’s better to use whole milk. If you can get it organic, even better.” Skim milk is the most acnegenic, she said.
Psoriasis
A systematic review of 55 studies evaluating diet and psoriasis found obesity can be an exacerbating factor. The strongest evidence for dietary weight reduction points to a hypocaloric diet in people with overweight or obesity, according to the review. Other evidence suggests alcohol can lower response to treatment and is linked with more severe psoriasis. Furthermore, a gluten-free diet or vitamin D supplements can help some subpopulations of people with psoriasis.
“An overwhelming majority of our psoriasis patients are vitamin D deficient,” Dr. Shi said.
The National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) publishes dietary modification guidelines, updated as recently as November 2023. The NPF states that “there is no diet that will cure psoriatic disease, but there are many ways in which eating healthful food may lessen the severity of symptoms and play a role in lowering the likelihood of developing comorbidities.”
Healthier choices include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fat-free or low-fat dairy products. Include lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, eggs, and nuts. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet has been linked to a lower severity of psoriasis.
Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is “one of the prototypical diseases related to diet,” Dr. Shi said. A different meta-analysis looked at randomized controlled trials of synbiotics (a combination of prebiotics and probiotics) for treatment of AD.
These researchers found that synbiotics do not prevent AD, but they can help treat it in adults and children older than 1 year. In addition, synbiotics are more beneficial than probiotics in treating the condition, although there are no head-to-head comparison studies. In addition, the meta-analysis found that prebiotics alone can lower AD severity.
However, Dr. Shi said, there are no recommendations from the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) on prebiotics or probiotics for AD, and the AAD does not recommend any supplement or essential oil for AD.
In a 2022 review, investigators ranked the efficacy of different supplements for AD based on available evidence. They found the greatest benefit associated with vitamin D supplementation, followed by vitamin E, probiotics, hemp seed oil, histidine, and oolong tea. They also noted the ‘Six Food Elimination Diet and Autoimmune Protocol’ featured the least amount of evidence to back it up.
Rosacea
Rosacea appears to be caused by “all the fun things in life” like sunlight, alcohol, chocolate, spicy foods, and caffeine, Dr. Shi said. In people with rosacea, they can cause facial flushing, edema, burning, and an inflammatory response.
Certain foods can activate skin receptors and sensory neurons, which can release neuropeptides that act on mast cells in blood that lead to flushing. The skin-gut axis may also be involved, evidence suggests. “And that is why food has a pretty profound impact on rosacea,” Dr. Shi said.
Dr. Shi reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — Amid all the hype, claims, and confusion, there is evidence linking some foods and drinks to an increased risk for acne, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, rosacea, and other common skin conditions. So, what is the connection in each case? And how can people with any of these skin conditions potentially improve their health and quality of life with dietary changes?
What is clear is that there has been an explosion of interest in learning which foods can improve or worsen skin issues in recent years. It’s a good idea to familiarize yourself with the research and also to Google ‘diet’ and ‘skin’, said Vivian Shi, MD, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock. “As practitioners, we should be well prepared to talk about what patients want to talk about.”
Acne
One of the major areas of interest is diet and acne. “We’ve all heard sugar and dairy are bad, and the Western diet is high in sugar and dairy,” Dr. Shi said at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgical Conference.
Dairy, red meat, and carbohydrates can break down into leucine, an essential amino acid found in protein. Leucine and sugar together, in turn, can produce insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), which, through different pathways, can reach the androgen receptors throughout the body, including the skin. This results in sebogenesis, lipogenesis, and keratinization, which triggers follicular inflammation and results in more of the acne-causing bacteria Cutibacterium acnes.
Milk and other dairy products also can increase IGF-1 levels, which can alter hormonal mediators and increase acne.
Not all types of dairy milk are created equal, however, when it comes to acne. Dr. Shi wondered why 2% milk has overall color and nutritional content very similar to that of whole milk. “I looked into this.” She discovered that when milk manufacturers remove the fat, they often add whey proteins to restore some nutrients. Whey protein can increase acne, Dr. Shi added.
“So, if you’re going to choose any milk to drink, I think from an acne perspective, it’s better to use whole milk. If you can get it organic, even better.” Skim milk is the most acnegenic, she said.
Psoriasis
A systematic review of 55 studies evaluating diet and psoriasis found obesity can be an exacerbating factor. The strongest evidence for dietary weight reduction points to a hypocaloric diet in people with overweight or obesity, according to the review. Other evidence suggests alcohol can lower response to treatment and is linked with more severe psoriasis. Furthermore, a gluten-free diet or vitamin D supplements can help some subpopulations of people with psoriasis.
“An overwhelming majority of our psoriasis patients are vitamin D deficient,” Dr. Shi said.
The National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) publishes dietary modification guidelines, updated as recently as November 2023. The NPF states that “there is no diet that will cure psoriatic disease, but there are many ways in which eating healthful food may lessen the severity of symptoms and play a role in lowering the likelihood of developing comorbidities.”
Healthier choices include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fat-free or low-fat dairy products. Include lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, eggs, and nuts. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet has been linked to a lower severity of psoriasis.
Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is “one of the prototypical diseases related to diet,” Dr. Shi said. A different meta-analysis looked at randomized controlled trials of synbiotics (a combination of prebiotics and probiotics) for treatment of AD.
These researchers found that synbiotics do not prevent AD, but they can help treat it in adults and children older than 1 year. In addition, synbiotics are more beneficial than probiotics in treating the condition, although there are no head-to-head comparison studies. In addition, the meta-analysis found that prebiotics alone can lower AD severity.
However, Dr. Shi said, there are no recommendations from the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) on prebiotics or probiotics for AD, and the AAD does not recommend any supplement or essential oil for AD.
In a 2022 review, investigators ranked the efficacy of different supplements for AD based on available evidence. They found the greatest benefit associated with vitamin D supplementation, followed by vitamin E, probiotics, hemp seed oil, histidine, and oolong tea. They also noted the ‘Six Food Elimination Diet and Autoimmune Protocol’ featured the least amount of evidence to back it up.
Rosacea
Rosacea appears to be caused by “all the fun things in life” like sunlight, alcohol, chocolate, spicy foods, and caffeine, Dr. Shi said. In people with rosacea, they can cause facial flushing, edema, burning, and an inflammatory response.
Certain foods can activate skin receptors and sensory neurons, which can release neuropeptides that act on mast cells in blood that lead to flushing. The skin-gut axis may also be involved, evidence suggests. “And that is why food has a pretty profound impact on rosacea,” Dr. Shi said.
Dr. Shi reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
How much would you bet on a diagnosis?
“You have psoriasis,” I say all the time. I mean it when I say it, of course. But I don’t always to the same degree. Sometimes I’m trying to say, “You probably have psoriasis.” Other times I mean, “You most definitely have psoriasis.” I rarely use those terms though.
One 36-year-old man with a flaky scalp and scaly elbows wasn’t satisfied with my assessment. His dad has psoriasis. So does his older brother. He was in to see me to find out if he had psoriasis too. “Probably” was what I gave him. He pushed back, “What percent chance?” That’s a good question — must be an engineer. I’m unsure.
With the exception of the poker players, our species is notoriously bad at probabilities. We’re wired to notice the significance of events, but terrible at understanding their likelihood. This is salient in lottery ticket holders and some NFL offensive coordinators who persist despite very long odds of things working out. It’s also reflected in the language we use. Rarely do we say, there’s a sixty percent chance something will happen. Rather, we say, “it’s likely.” There are two problems here. One, we often misjudge the actual probability of something occurring and two, the terms we use are subjective and differences in interpretation can lead to misunderstandings.
Let’s take a look. A 55-year-old man with a chronic eczematous rash on his trunk and extremities is getting worse despite dupilumab. He recently had night sweats. Do you think he has atopic dermatitis or cutaneous T-cell lymphoma? If you had to place a $100 bet, would you change your answer? Immanuel Kant thinks you would. In his “Critique of Pure Reason,” the German philosopher proposes that betting helps clarify the mind, an antidote to brashness. The example Kant uses is of a physician who observes a patient and concludes he has phthisis (tuberculosis), but we really don’t know if the physician is confident. Kant proposes that if he had to bet on his conclusion, then we’d have insight into just how convinced he is of phthisis. So, what’s your bet?
If you’re a bad poker player, then you might bet he has cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. However, not having any additional information, the smart call is atopic dermatitis, which has a base rate 1000-fold higher than CTCL. It is therefore more probable to be eczema even in a case that worsens despite dupilumab or with recent night sweats, both of which could be a result of common variables such as weather and COVID. Failure to account for the base rate is a mistake we physicians sometimes make. Economists rarely do. Try to think like one before answering a likelihood question.
If you think about it, “probably” means something different even to me, depending on the situation. I might say I’ll probably go to Montana this summer and I’ll probably retire at 65. The actual likelihoods might be 95% and 70%. That’s a big difference. What about between probably and likely? Or possibly and maybe? Do they mean the same to you as to the person you’re speaking with? For much of the work we do, precise likelihoods aren’t critical. Yet, it can be important in decision making and in discussing probabilities, such as the risk of hepatitis on terbinafine or of melanoma recurrence after Mohs.
I told my patient “I say about a 70% chance you have psoriasis. I could do a biopsy today to confirm.” He thought for a second and asked, “What is the chance it’s psoriasis if the biopsy shows it?” “Eighty six percent,” I replied.
Seemed like a good bet to me.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on X. Write to him at [email protected].
“You have psoriasis,” I say all the time. I mean it when I say it, of course. But I don’t always to the same degree. Sometimes I’m trying to say, “You probably have psoriasis.” Other times I mean, “You most definitely have psoriasis.” I rarely use those terms though.
One 36-year-old man with a flaky scalp and scaly elbows wasn’t satisfied with my assessment. His dad has psoriasis. So does his older brother. He was in to see me to find out if he had psoriasis too. “Probably” was what I gave him. He pushed back, “What percent chance?” That’s a good question — must be an engineer. I’m unsure.
With the exception of the poker players, our species is notoriously bad at probabilities. We’re wired to notice the significance of events, but terrible at understanding their likelihood. This is salient in lottery ticket holders and some NFL offensive coordinators who persist despite very long odds of things working out. It’s also reflected in the language we use. Rarely do we say, there’s a sixty percent chance something will happen. Rather, we say, “it’s likely.” There are two problems here. One, we often misjudge the actual probability of something occurring and two, the terms we use are subjective and differences in interpretation can lead to misunderstandings.
Let’s take a look. A 55-year-old man with a chronic eczematous rash on his trunk and extremities is getting worse despite dupilumab. He recently had night sweats. Do you think he has atopic dermatitis or cutaneous T-cell lymphoma? If you had to place a $100 bet, would you change your answer? Immanuel Kant thinks you would. In his “Critique of Pure Reason,” the German philosopher proposes that betting helps clarify the mind, an antidote to brashness. The example Kant uses is of a physician who observes a patient and concludes he has phthisis (tuberculosis), but we really don’t know if the physician is confident. Kant proposes that if he had to bet on his conclusion, then we’d have insight into just how convinced he is of phthisis. So, what’s your bet?
If you’re a bad poker player, then you might bet he has cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. However, not having any additional information, the smart call is atopic dermatitis, which has a base rate 1000-fold higher than CTCL. It is therefore more probable to be eczema even in a case that worsens despite dupilumab or with recent night sweats, both of which could be a result of common variables such as weather and COVID. Failure to account for the base rate is a mistake we physicians sometimes make. Economists rarely do. Try to think like one before answering a likelihood question.
If you think about it, “probably” means something different even to me, depending on the situation. I might say I’ll probably go to Montana this summer and I’ll probably retire at 65. The actual likelihoods might be 95% and 70%. That’s a big difference. What about between probably and likely? Or possibly and maybe? Do they mean the same to you as to the person you’re speaking with? For much of the work we do, precise likelihoods aren’t critical. Yet, it can be important in decision making and in discussing probabilities, such as the risk of hepatitis on terbinafine or of melanoma recurrence after Mohs.
I told my patient “I say about a 70% chance you have psoriasis. I could do a biopsy today to confirm.” He thought for a second and asked, “What is the chance it’s psoriasis if the biopsy shows it?” “Eighty six percent,” I replied.
Seemed like a good bet to me.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on X. Write to him at [email protected].
“You have psoriasis,” I say all the time. I mean it when I say it, of course. But I don’t always to the same degree. Sometimes I’m trying to say, “You probably have psoriasis.” Other times I mean, “You most definitely have psoriasis.” I rarely use those terms though.
One 36-year-old man with a flaky scalp and scaly elbows wasn’t satisfied with my assessment. His dad has psoriasis. So does his older brother. He was in to see me to find out if he had psoriasis too. “Probably” was what I gave him. He pushed back, “What percent chance?” That’s a good question — must be an engineer. I’m unsure.
With the exception of the poker players, our species is notoriously bad at probabilities. We’re wired to notice the significance of events, but terrible at understanding their likelihood. This is salient in lottery ticket holders and some NFL offensive coordinators who persist despite very long odds of things working out. It’s also reflected in the language we use. Rarely do we say, there’s a sixty percent chance something will happen. Rather, we say, “it’s likely.” There are two problems here. One, we often misjudge the actual probability of something occurring and two, the terms we use are subjective and differences in interpretation can lead to misunderstandings.
Let’s take a look. A 55-year-old man with a chronic eczematous rash on his trunk and extremities is getting worse despite dupilumab. He recently had night sweats. Do you think he has atopic dermatitis or cutaneous T-cell lymphoma? If you had to place a $100 bet, would you change your answer? Immanuel Kant thinks you would. In his “Critique of Pure Reason,” the German philosopher proposes that betting helps clarify the mind, an antidote to brashness. The example Kant uses is of a physician who observes a patient and concludes he has phthisis (tuberculosis), but we really don’t know if the physician is confident. Kant proposes that if he had to bet on his conclusion, then we’d have insight into just how convinced he is of phthisis. So, what’s your bet?
If you’re a bad poker player, then you might bet he has cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. However, not having any additional information, the smart call is atopic dermatitis, which has a base rate 1000-fold higher than CTCL. It is therefore more probable to be eczema even in a case that worsens despite dupilumab or with recent night sweats, both of which could be a result of common variables such as weather and COVID. Failure to account for the base rate is a mistake we physicians sometimes make. Economists rarely do. Try to think like one before answering a likelihood question.
If you think about it, “probably” means something different even to me, depending on the situation. I might say I’ll probably go to Montana this summer and I’ll probably retire at 65. The actual likelihoods might be 95% and 70%. That’s a big difference. What about between probably and likely? Or possibly and maybe? Do they mean the same to you as to the person you’re speaking with? For much of the work we do, precise likelihoods aren’t critical. Yet, it can be important in decision making and in discussing probabilities, such as the risk of hepatitis on terbinafine or of melanoma recurrence after Mohs.
I told my patient “I say about a 70% chance you have psoriasis. I could do a biopsy today to confirm.” He thought for a second and asked, “What is the chance it’s psoriasis if the biopsy shows it?” “Eighty six percent,” I replied.
Seemed like a good bet to me.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on X. Write to him at [email protected].







