User login
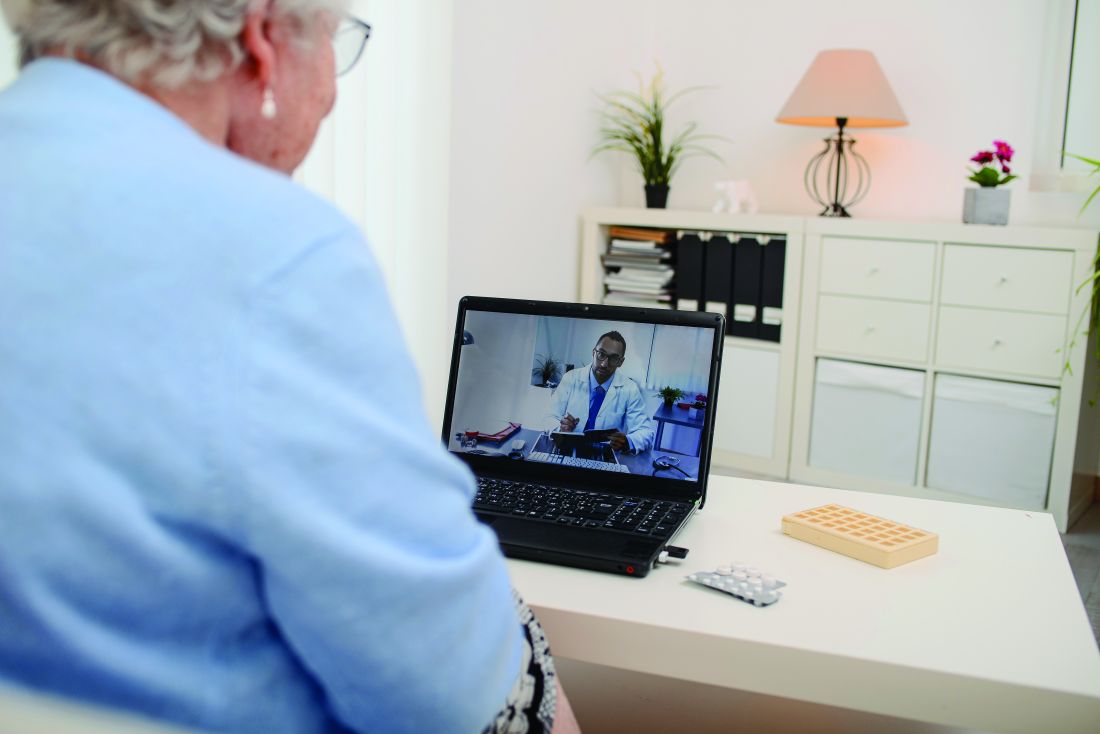
NPF provides guidance for virtual psoriasis visits
.
The success of telemedicine in managing chronic inflammatory skin conditions including psoriasis during the COVID-19 pandemic “highlighted that teledermatology can be used beyond the context of a global health crisis to provide continuity of care and improve access to health care more broadly,” the task force wrote in a paper published online in JAAD International.
Co–senior author George Han, MD, PhD, said in an interview that the impetus for the guidelines came from NPF patient advocates, who realized that the organization needed something to take to payers and governmental agencies to advocate for better access to dermatologic care. He is associate professor of dermatology and director of teledermatology at the Hofstra/Northwell department of dermatology, Hyde Park, New York.
“We realized that, in many places around the country, people don’t have access to dermatology.” In upstate New York, said Dr. Han, his anecdotal research has revealed wait times of 6 months or more.
As a guiding principle, the authors pronounce teledermatology “a reasonable alternative for providing long-term management of patients with psoriasis.” Research shows that nearly all dermatologists used teledermatology during the pandemic, the authors noted, and that well-run programs improve Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) scores and other measures on par with in-person care. Telemedicine may be especially useful for initial visits, they added, particularly when distance, patient incapacity, and circumstances prevent face-to-face evaluation.
Additional position statements emphasize that teledermatology should support rather than supplant in-person visits, and that this balance may be particularly important in cases involving psoriatic arthritis (PsA). “Even though we can’t do a physical exam and palpate some of those joints in person,” said Dr. Han, “tools have been developed that, through a series of questions the patient can answer, can guide you towards whether there is a high index of suspicion for psoriatic arthritis.” Such patients require in-person evaluation with urgency, he said, because delays in PsA diagnosis and treatment can lead to irreversible joint damage and significant functional impairment.
Another motivation for producing the guidelines, said Dr. Han, was that, even when underserved patients get a dermatology appointment, some providers may not have all the latest tools or medicines available for treating psoriasis. In such cases, telemedicine may allow dermatologists specializing in psoriasis care to extend their reach in comanaging patients with primary care physicians and community dermatologists.
Before the appointment, guidelines suggest determining what form of teledermatology will best suit each patient. Authors recommended gauging patients’ savviness with computers and cameras, and counseling patients regarding available virtual evaluation tools – such as live video visits, store-and-forward photo strategies, and assessment-tool training videos.
A subsequent guideline underscores the importance of continuously improving technology to support expeditious image capture and workflows that emulate in-person practice. Dr. Han explained, “we wanted to make sure that on the back end there’s adequate support such that – if through teledermatology, we determine that the patient should get, say, a systemic treatment – the patient is able to get the appropriate lab tests, get the medicine, and know how to inject it.”
Regarding reimbursement, Dr. Han said that policies varied prepandemic, but many commercial insurers covered telemedicine at a rate 20% lower than the in-person rate. During the pandemic, he said, insurers shifted to provide the higher rate for telemedicine, consistent with policies adopted by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
“There are differences in coverage and reimbursement from plan to plan,” Dr. Han added. “And even within the same plan, there are carve-outs so that some plans don’t allow certain services. The big picture is that for the most part these services are covered at a level comparable to an in-person visit at present.”
With the Department of Health & Human Services’ public health emergency declaration expiring in May, he said, physicians have worried that some of the allowances made by CMS – such as lifting requirements that Medicare patients in rural areas be seen at care sites – will expire. “It seems that some of those limitations have been addressed, and those allowances are going to be extended until Congress is able to pass something that gives us durable access to telemedicine care. We think that based on the current environment telemedicine is here to stay.”
The study was funded by the NPF. Dr. Han has been an investigator, adviser, speaker, or researcher for AbbVie, Amgen, Apogee Therapeutics, Arcutis, Athenex, Bausch Health, Beiersdorf, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bond Avillion, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, CeraVe, Dermavant, DermTech, Eli Lilly, EPI Health, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, LEO Pharma, L’Oreal, MC2 Therapeutics, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, PellePharm, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi Genzyme, SUN Pharmaceuticals, and UCB.
.
The success of telemedicine in managing chronic inflammatory skin conditions including psoriasis during the COVID-19 pandemic “highlighted that teledermatology can be used beyond the context of a global health crisis to provide continuity of care and improve access to health care more broadly,” the task force wrote in a paper published online in JAAD International.
Co–senior author George Han, MD, PhD, said in an interview that the impetus for the guidelines came from NPF patient advocates, who realized that the organization needed something to take to payers and governmental agencies to advocate for better access to dermatologic care. He is associate professor of dermatology and director of teledermatology at the Hofstra/Northwell department of dermatology, Hyde Park, New York.
“We realized that, in many places around the country, people don’t have access to dermatology.” In upstate New York, said Dr. Han, his anecdotal research has revealed wait times of 6 months or more.
As a guiding principle, the authors pronounce teledermatology “a reasonable alternative for providing long-term management of patients with psoriasis.” Research shows that nearly all dermatologists used teledermatology during the pandemic, the authors noted, and that well-run programs improve Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) scores and other measures on par with in-person care. Telemedicine may be especially useful for initial visits, they added, particularly when distance, patient incapacity, and circumstances prevent face-to-face evaluation.
Additional position statements emphasize that teledermatology should support rather than supplant in-person visits, and that this balance may be particularly important in cases involving psoriatic arthritis (PsA). “Even though we can’t do a physical exam and palpate some of those joints in person,” said Dr. Han, “tools have been developed that, through a series of questions the patient can answer, can guide you towards whether there is a high index of suspicion for psoriatic arthritis.” Such patients require in-person evaluation with urgency, he said, because delays in PsA diagnosis and treatment can lead to irreversible joint damage and significant functional impairment.
Another motivation for producing the guidelines, said Dr. Han, was that, even when underserved patients get a dermatology appointment, some providers may not have all the latest tools or medicines available for treating psoriasis. In such cases, telemedicine may allow dermatologists specializing in psoriasis care to extend their reach in comanaging patients with primary care physicians and community dermatologists.
Before the appointment, guidelines suggest determining what form of teledermatology will best suit each patient. Authors recommended gauging patients’ savviness with computers and cameras, and counseling patients regarding available virtual evaluation tools – such as live video visits, store-and-forward photo strategies, and assessment-tool training videos.
A subsequent guideline underscores the importance of continuously improving technology to support expeditious image capture and workflows that emulate in-person practice. Dr. Han explained, “we wanted to make sure that on the back end there’s adequate support such that – if through teledermatology, we determine that the patient should get, say, a systemic treatment – the patient is able to get the appropriate lab tests, get the medicine, and know how to inject it.”
Regarding reimbursement, Dr. Han said that policies varied prepandemic, but many commercial insurers covered telemedicine at a rate 20% lower than the in-person rate. During the pandemic, he said, insurers shifted to provide the higher rate for telemedicine, consistent with policies adopted by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
“There are differences in coverage and reimbursement from plan to plan,” Dr. Han added. “And even within the same plan, there are carve-outs so that some plans don’t allow certain services. The big picture is that for the most part these services are covered at a level comparable to an in-person visit at present.”
With the Department of Health & Human Services’ public health emergency declaration expiring in May, he said, physicians have worried that some of the allowances made by CMS – such as lifting requirements that Medicare patients in rural areas be seen at care sites – will expire. “It seems that some of those limitations have been addressed, and those allowances are going to be extended until Congress is able to pass something that gives us durable access to telemedicine care. We think that based on the current environment telemedicine is here to stay.”
The study was funded by the NPF. Dr. Han has been an investigator, adviser, speaker, or researcher for AbbVie, Amgen, Apogee Therapeutics, Arcutis, Athenex, Bausch Health, Beiersdorf, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bond Avillion, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, CeraVe, Dermavant, DermTech, Eli Lilly, EPI Health, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, LEO Pharma, L’Oreal, MC2 Therapeutics, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, PellePharm, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi Genzyme, SUN Pharmaceuticals, and UCB.
.
The success of telemedicine in managing chronic inflammatory skin conditions including psoriasis during the COVID-19 pandemic “highlighted that teledermatology can be used beyond the context of a global health crisis to provide continuity of care and improve access to health care more broadly,” the task force wrote in a paper published online in JAAD International.
Co–senior author George Han, MD, PhD, said in an interview that the impetus for the guidelines came from NPF patient advocates, who realized that the organization needed something to take to payers and governmental agencies to advocate for better access to dermatologic care. He is associate professor of dermatology and director of teledermatology at the Hofstra/Northwell department of dermatology, Hyde Park, New York.
“We realized that, in many places around the country, people don’t have access to dermatology.” In upstate New York, said Dr. Han, his anecdotal research has revealed wait times of 6 months or more.
As a guiding principle, the authors pronounce teledermatology “a reasonable alternative for providing long-term management of patients with psoriasis.” Research shows that nearly all dermatologists used teledermatology during the pandemic, the authors noted, and that well-run programs improve Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) scores and other measures on par with in-person care. Telemedicine may be especially useful for initial visits, they added, particularly when distance, patient incapacity, and circumstances prevent face-to-face evaluation.
Additional position statements emphasize that teledermatology should support rather than supplant in-person visits, and that this balance may be particularly important in cases involving psoriatic arthritis (PsA). “Even though we can’t do a physical exam and palpate some of those joints in person,” said Dr. Han, “tools have been developed that, through a series of questions the patient can answer, can guide you towards whether there is a high index of suspicion for psoriatic arthritis.” Such patients require in-person evaluation with urgency, he said, because delays in PsA diagnosis and treatment can lead to irreversible joint damage and significant functional impairment.
Another motivation for producing the guidelines, said Dr. Han, was that, even when underserved patients get a dermatology appointment, some providers may not have all the latest tools or medicines available for treating psoriasis. In such cases, telemedicine may allow dermatologists specializing in psoriasis care to extend their reach in comanaging patients with primary care physicians and community dermatologists.
Before the appointment, guidelines suggest determining what form of teledermatology will best suit each patient. Authors recommended gauging patients’ savviness with computers and cameras, and counseling patients regarding available virtual evaluation tools – such as live video visits, store-and-forward photo strategies, and assessment-tool training videos.
A subsequent guideline underscores the importance of continuously improving technology to support expeditious image capture and workflows that emulate in-person practice. Dr. Han explained, “we wanted to make sure that on the back end there’s adequate support such that – if through teledermatology, we determine that the patient should get, say, a systemic treatment – the patient is able to get the appropriate lab tests, get the medicine, and know how to inject it.”
Regarding reimbursement, Dr. Han said that policies varied prepandemic, but many commercial insurers covered telemedicine at a rate 20% lower than the in-person rate. During the pandemic, he said, insurers shifted to provide the higher rate for telemedicine, consistent with policies adopted by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
“There are differences in coverage and reimbursement from plan to plan,” Dr. Han added. “And even within the same plan, there are carve-outs so that some plans don’t allow certain services. The big picture is that for the most part these services are covered at a level comparable to an in-person visit at present.”
With the Department of Health & Human Services’ public health emergency declaration expiring in May, he said, physicians have worried that some of the allowances made by CMS – such as lifting requirements that Medicare patients in rural areas be seen at care sites – will expire. “It seems that some of those limitations have been addressed, and those allowances are going to be extended until Congress is able to pass something that gives us durable access to telemedicine care. We think that based on the current environment telemedicine is here to stay.”
The study was funded by the NPF. Dr. Han has been an investigator, adviser, speaker, or researcher for AbbVie, Amgen, Apogee Therapeutics, Arcutis, Athenex, Bausch Health, Beiersdorf, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bond Avillion, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, CeraVe, Dermavant, DermTech, Eli Lilly, EPI Health, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, LEO Pharma, L’Oreal, MC2 Therapeutics, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, PellePharm, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi Genzyme, SUN Pharmaceuticals, and UCB.
FROM JAAD INTERNATIONAL
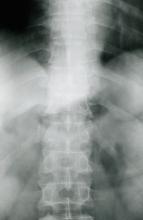
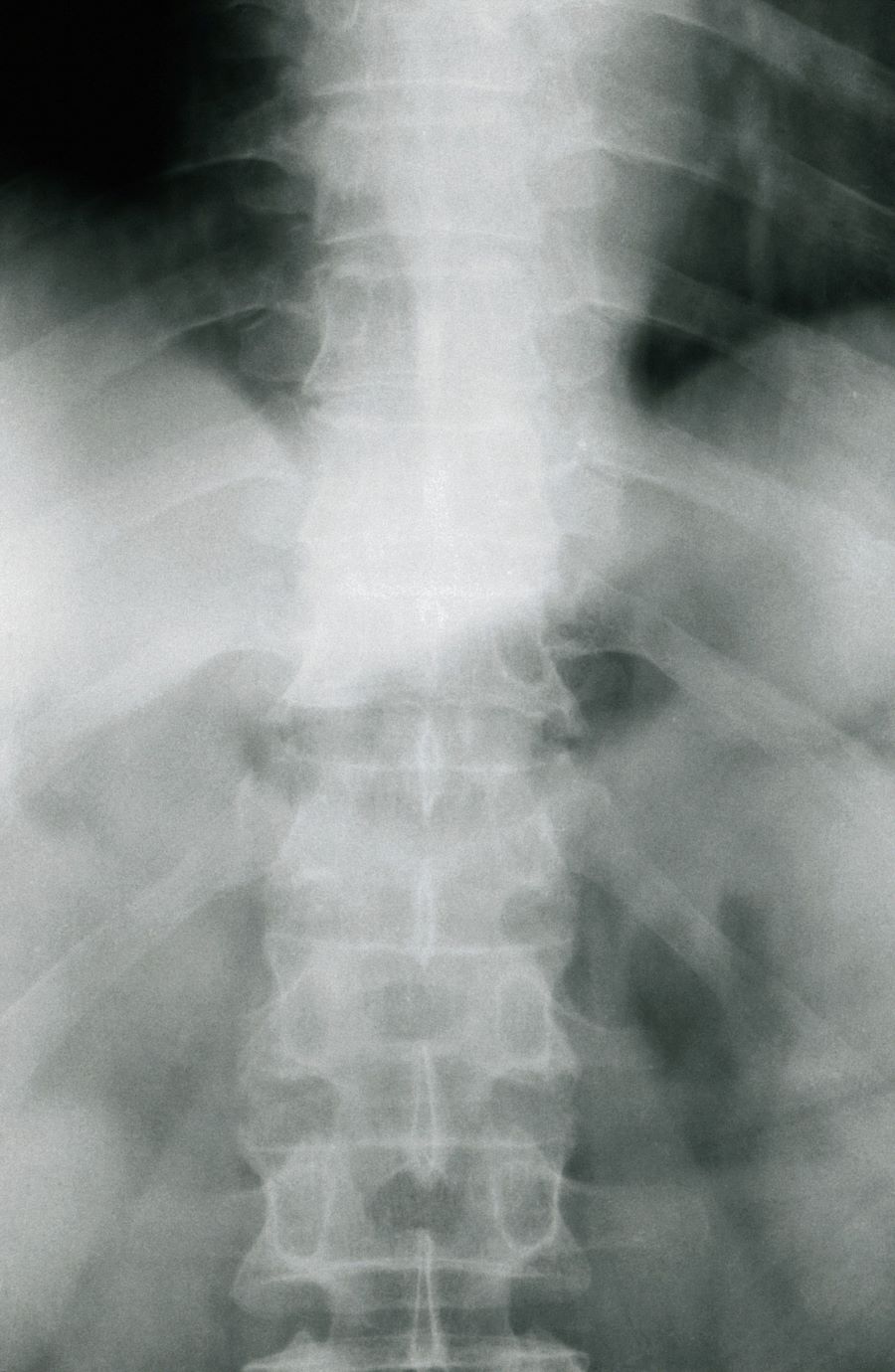
Moderate to severe back pain
The history and findings in this case are suggestive of axial psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Psoriasis is a complex, chronic, inflammatory, immune-mediated disease that is associated with significant morbidity, reduced quality of life, and increased mortality. Approximately 7.4 million adults in the United States have psoriasis; worldwide, approximately 2%-3% of the population is affected. Patients with psoriasis frequently have comorbidities; PsA, an inflammatory, seronegative musculoskeletal disease, is among the most common. It is estimated that 25%-30% of patients with psoriasis develop PsA.
PsA is a heterogeneous disease. Patients may present with nail and skin changes, peripheral arthritis, enthesitis, dactylitis, and axial spondyloarthritis (SpA), either alone or in combination. Men and women are equally affected by PsA, which typically develops when patients are age 30-50 years. Like psoriasis, PsA is associated with numerous comorbidities, including cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, obesity, diabetes, depression, uveitis, and anxiety.
PsA is a potentially erosive disease. Structural damage and functional impairment occurs within 2 years of initial assessment in approximately 50% of patients; as the disease progresses, patients may experience irreversible joint damage and disability. Axial involvement occurs in 25%-70% of patients with PsA; exclusive axial involvement is uncommon, occurring in 5% of patients. Common symptoms of axial PsA include inflammatory back pain (eg, pain that improves with activity but worsens with rest, morning stiffness lasting longer than 30 minutes). Some patients with axial involvement may be asymptomatic. If untreated, cervical spinal mobility and lateral flexion significantly decline within 5 years in patients with axial PsA. In addition, sacroiliitis worsens over time; 37% and 52% of patients develop grade 2 or higher sacroiliitis within 5 and 10 years, respectively. This highlights the importance of early identification and treatment of patients with axial PsA.
The diagnosis of axial PsA is confirmed by physical examination and imaging. Axial PsA characteristics, including sacroiliitis and spondylitis, are distinguished by the development of syndesmophytes (ie, ossification of the annulus fibrosis). PsA can be differentiated from ankylosing spondylitis by the asymmetric and frequently unilateral presentation of sacroiliitis and syndesmophytes, which frequently presents as nonmarginal, bulky, asymmetric, and discontinuous skipping vertebral levels.
Plain radiography, CT, ultrasound, and MRI are all useful tools for evaluating patients with PsA. MRI and ultrasound may be more sensitive than plain radiography is for detecting early joint inflammation and damage as well as axial changes, including sacroiliitis; however, they are not required for a diagnosis of PsA.
The treatment of axial PsA is based on international guidelines developed by the American College of Rheumatology/Spondylitis Association of America/Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network, the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis and the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society–European League Against Rheumatism. Treatment focuses on minimizing pain, stiffness, and fatigue; improving and preserving spinal flexibility and posture; enhancing functional capacity; and maintaining the ability to work, with a target of remission or minimal/low disease activity.
Medications for symptomatic relief include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), glucocorticoids, and sacroiliac joint injections with glucocorticoids for mild disease; however, long-term treatment with systemic glucocorticoids is not recommended. If patients remain symptomatic or if erosive disease or other indications of high disease activity is observed, guidelines recommend initiation of a TNF inhibitor. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, such as methotrexate, are not routinely prescribed for patients with axial disease because they have not been shown to be effective.
If symptoms of axial PsA are not controlled by NSAIDs, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors are recommended. However, interleukin 17A inhibitors may be used in preference to TNF inhibitors in patients with significant skin involvement. In the United States, adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, golimumab, and infliximab are recommended over etanercept for patients with axial SpA in the presence of concomitant inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or recurrent uveitis (although there is no evidence for golimumab) because etanercept has contradictory results for uveitis and has not been shown to have efficacy in IBD.
If patients fail to respond to a first trial of a TNF inhibitor, trying a second TNF inhibitor before switching to a different class of biologic is recommended by US guidelines. A Janus kinase inhibitor (tofacitinib) may be considered for patients who do not respond to TNF inhibitors.
Nonpharmacologic therapies (ie, exercise, physical therapy, massage therapy, occupational therapy, acupuncture) are recommended for all patients with active PsA.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, Professor of Medicine (retired), Temple University School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh; Chairman, Department of Medicine Emeritus, Western Pennsylvania Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
The history and findings in this case are suggestive of axial psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Psoriasis is a complex, chronic, inflammatory, immune-mediated disease that is associated with significant morbidity, reduced quality of life, and increased mortality. Approximately 7.4 million adults in the United States have psoriasis; worldwide, approximately 2%-3% of the population is affected. Patients with psoriasis frequently have comorbidities; PsA, an inflammatory, seronegative musculoskeletal disease, is among the most common. It is estimated that 25%-30% of patients with psoriasis develop PsA.
PsA is a heterogeneous disease. Patients may present with nail and skin changes, peripheral arthritis, enthesitis, dactylitis, and axial spondyloarthritis (SpA), either alone or in combination. Men and women are equally affected by PsA, which typically develops when patients are age 30-50 years. Like psoriasis, PsA is associated with numerous comorbidities, including cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, obesity, diabetes, depression, uveitis, and anxiety.
PsA is a potentially erosive disease. Structural damage and functional impairment occurs within 2 years of initial assessment in approximately 50% of patients; as the disease progresses, patients may experience irreversible joint damage and disability. Axial involvement occurs in 25%-70% of patients with PsA; exclusive axial involvement is uncommon, occurring in 5% of patients. Common symptoms of axial PsA include inflammatory back pain (eg, pain that improves with activity but worsens with rest, morning stiffness lasting longer than 30 minutes). Some patients with axial involvement may be asymptomatic. If untreated, cervical spinal mobility and lateral flexion significantly decline within 5 years in patients with axial PsA. In addition, sacroiliitis worsens over time; 37% and 52% of patients develop grade 2 or higher sacroiliitis within 5 and 10 years, respectively. This highlights the importance of early identification and treatment of patients with axial PsA.
The diagnosis of axial PsA is confirmed by physical examination and imaging. Axial PsA characteristics, including sacroiliitis and spondylitis, are distinguished by the development of syndesmophytes (ie, ossification of the annulus fibrosis). PsA can be differentiated from ankylosing spondylitis by the asymmetric and frequently unilateral presentation of sacroiliitis and syndesmophytes, which frequently presents as nonmarginal, bulky, asymmetric, and discontinuous skipping vertebral levels.
Plain radiography, CT, ultrasound, and MRI are all useful tools for evaluating patients with PsA. MRI and ultrasound may be more sensitive than plain radiography is for detecting early joint inflammation and damage as well as axial changes, including sacroiliitis; however, they are not required for a diagnosis of PsA.
The treatment of axial PsA is based on international guidelines developed by the American College of Rheumatology/Spondylitis Association of America/Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network, the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis and the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society–European League Against Rheumatism. Treatment focuses on minimizing pain, stiffness, and fatigue; improving and preserving spinal flexibility and posture; enhancing functional capacity; and maintaining the ability to work, with a target of remission or minimal/low disease activity.
Medications for symptomatic relief include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), glucocorticoids, and sacroiliac joint injections with glucocorticoids for mild disease; however, long-term treatment with systemic glucocorticoids is not recommended. If patients remain symptomatic or if erosive disease or other indications of high disease activity is observed, guidelines recommend initiation of a TNF inhibitor. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, such as methotrexate, are not routinely prescribed for patients with axial disease because they have not been shown to be effective.
If symptoms of axial PsA are not controlled by NSAIDs, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors are recommended. However, interleukin 17A inhibitors may be used in preference to TNF inhibitors in patients with significant skin involvement. In the United States, adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, golimumab, and infliximab are recommended over etanercept for patients with axial SpA in the presence of concomitant inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or recurrent uveitis (although there is no evidence for golimumab) because etanercept has contradictory results for uveitis and has not been shown to have efficacy in IBD.
If patients fail to respond to a first trial of a TNF inhibitor, trying a second TNF inhibitor before switching to a different class of biologic is recommended by US guidelines. A Janus kinase inhibitor (tofacitinib) may be considered for patients who do not respond to TNF inhibitors.
Nonpharmacologic therapies (ie, exercise, physical therapy, massage therapy, occupational therapy, acupuncture) are recommended for all patients with active PsA.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, Professor of Medicine (retired), Temple University School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh; Chairman, Department of Medicine Emeritus, Western Pennsylvania Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
The history and findings in this case are suggestive of axial psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Psoriasis is a complex, chronic, inflammatory, immune-mediated disease that is associated with significant morbidity, reduced quality of life, and increased mortality. Approximately 7.4 million adults in the United States have psoriasis; worldwide, approximately 2%-3% of the population is affected. Patients with psoriasis frequently have comorbidities; PsA, an inflammatory, seronegative musculoskeletal disease, is among the most common. It is estimated that 25%-30% of patients with psoriasis develop PsA.
PsA is a heterogeneous disease. Patients may present with nail and skin changes, peripheral arthritis, enthesitis, dactylitis, and axial spondyloarthritis (SpA), either alone or in combination. Men and women are equally affected by PsA, which typically develops when patients are age 30-50 years. Like psoriasis, PsA is associated with numerous comorbidities, including cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, obesity, diabetes, depression, uveitis, and anxiety.
PsA is a potentially erosive disease. Structural damage and functional impairment occurs within 2 years of initial assessment in approximately 50% of patients; as the disease progresses, patients may experience irreversible joint damage and disability. Axial involvement occurs in 25%-70% of patients with PsA; exclusive axial involvement is uncommon, occurring in 5% of patients. Common symptoms of axial PsA include inflammatory back pain (eg, pain that improves with activity but worsens with rest, morning stiffness lasting longer than 30 minutes). Some patients with axial involvement may be asymptomatic. If untreated, cervical spinal mobility and lateral flexion significantly decline within 5 years in patients with axial PsA. In addition, sacroiliitis worsens over time; 37% and 52% of patients develop grade 2 or higher sacroiliitis within 5 and 10 years, respectively. This highlights the importance of early identification and treatment of patients with axial PsA.
The diagnosis of axial PsA is confirmed by physical examination and imaging. Axial PsA characteristics, including sacroiliitis and spondylitis, are distinguished by the development of syndesmophytes (ie, ossification of the annulus fibrosis). PsA can be differentiated from ankylosing spondylitis by the asymmetric and frequently unilateral presentation of sacroiliitis and syndesmophytes, which frequently presents as nonmarginal, bulky, asymmetric, and discontinuous skipping vertebral levels.
Plain radiography, CT, ultrasound, and MRI are all useful tools for evaluating patients with PsA. MRI and ultrasound may be more sensitive than plain radiography is for detecting early joint inflammation and damage as well as axial changes, including sacroiliitis; however, they are not required for a diagnosis of PsA.
The treatment of axial PsA is based on international guidelines developed by the American College of Rheumatology/Spondylitis Association of America/Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network, the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis and the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society–European League Against Rheumatism. Treatment focuses on minimizing pain, stiffness, and fatigue; improving and preserving spinal flexibility and posture; enhancing functional capacity; and maintaining the ability to work, with a target of remission or minimal/low disease activity.
Medications for symptomatic relief include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), glucocorticoids, and sacroiliac joint injections with glucocorticoids for mild disease; however, long-term treatment with systemic glucocorticoids is not recommended. If patients remain symptomatic or if erosive disease or other indications of high disease activity is observed, guidelines recommend initiation of a TNF inhibitor. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, such as methotrexate, are not routinely prescribed for patients with axial disease because they have not been shown to be effective.
If symptoms of axial PsA are not controlled by NSAIDs, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors are recommended. However, interleukin 17A inhibitors may be used in preference to TNF inhibitors in patients with significant skin involvement. In the United States, adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, golimumab, and infliximab are recommended over etanercept for patients with axial SpA in the presence of concomitant inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or recurrent uveitis (although there is no evidence for golimumab) because etanercept has contradictory results for uveitis and has not been shown to have efficacy in IBD.
If patients fail to respond to a first trial of a TNF inhibitor, trying a second TNF inhibitor before switching to a different class of biologic is recommended by US guidelines. A Janus kinase inhibitor (tofacitinib) may be considered for patients who do not respond to TNF inhibitors.
Nonpharmacologic therapies (ie, exercise, physical therapy, massage therapy, occupational therapy, acupuncture) are recommended for all patients with active PsA.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, Professor of Medicine (retired), Temple University School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh; Chairman, Department of Medicine Emeritus, Western Pennsylvania Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 38-year-old nonsmoking woman presents with complaints of moderate to severe back pain of approximately 6 months' duration. She also reports morning back/neck stiffness that lasts for approximately 45 minutes and pain/stiffness in her wrists and fingers. The patient states that her back pain improves with exercise (walking and stretching) and worsens in the evening and during long periods of rest. On occasion, she is awakened during the early morning hours because of her back pain. The patient has a 15-year history of moderate to severe psoriasis and a history of irritable bowel disease (IBD). Current medications include cyclosporine 3 mg/d, topical roflumilast 0.3%/d, and loperamide 3 mg as needed. The patient is 5 ft 5 in and weighs 183 lb (BMI of 30.4).
Physical examination reveals psoriatic plaques on the hands, elbows, and knees and nail dystrophy (onycholysis and pitting). Vital signs are within normal ranges. Pertinent laboratory findings include white blood count of 12,000 mcL (> 50% polymorphonuclear leukocytes), erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 19 mm/h, and c-reactive protein of 3 mg/dL. Rheumatoid factor, antinuclear antibody, and anti-citrullinated protein antibody antibody were negative.
PsA Pathophysiology and Etiology
Study identifies risk factors associated with PsA occurrence in patients with psoriasis
Key clinical point: Age, body mass index (BMI), chronic-plaque psoriasis, hospitalization for psoriasis, use of systemic therapy, and genital and nail involvement in psoriasis were the risk factors for psoriatic arthritis (PsA) occurrence in patients with psoriasis.
Major finding: Overall, 226 patients were diagnosed with PsA, with an incidence of 1.9 cases per 100 patient-years. Age between 40-59 years (P < .001), BMI ≥25 (P = .015), genital psoriasis (P = .027), nail psoriasis (P = .038), classic chronic-plaque psoriasis (P = .014), previous hospitalization for psoriasis (P < .001), previous use of systemic therapy for psoriasis (P = .003), and use of conventional nonbiologic agents (P = .014) were significantly associated with PsA occurrence.
Study details: This cohort study included 8895 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of psoriasis from the PsoReal registry.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Bristol Myers Squibb. K Heidemeyer and L Naldi declared receiving honoraria from various sources, including AbbVie, Almirall, or Bristol Myers Squibb.
Source: Heidemeyer K et al. Variables associated with joint involvement and development of a prediction rule for arthritis in psoriasis patients. An analysis of the Italian PsoReal database. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023 (Mar 23). Doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2023.02.059
Key clinical point: Age, body mass index (BMI), chronic-plaque psoriasis, hospitalization for psoriasis, use of systemic therapy, and genital and nail involvement in psoriasis were the risk factors for psoriatic arthritis (PsA) occurrence in patients with psoriasis.
Major finding: Overall, 226 patients were diagnosed with PsA, with an incidence of 1.9 cases per 100 patient-years. Age between 40-59 years (P < .001), BMI ≥25 (P = .015), genital psoriasis (P = .027), nail psoriasis (P = .038), classic chronic-plaque psoriasis (P = .014), previous hospitalization for psoriasis (P < .001), previous use of systemic therapy for psoriasis (P = .003), and use of conventional nonbiologic agents (P = .014) were significantly associated with PsA occurrence.
Study details: This cohort study included 8895 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of psoriasis from the PsoReal registry.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Bristol Myers Squibb. K Heidemeyer and L Naldi declared receiving honoraria from various sources, including AbbVie, Almirall, or Bristol Myers Squibb.
Source: Heidemeyer K et al. Variables associated with joint involvement and development of a prediction rule for arthritis in psoriasis patients. An analysis of the Italian PsoReal database. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023 (Mar 23). Doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2023.02.059
Key clinical point: Age, body mass index (BMI), chronic-plaque psoriasis, hospitalization for psoriasis, use of systemic therapy, and genital and nail involvement in psoriasis were the risk factors for psoriatic arthritis (PsA) occurrence in patients with psoriasis.
Major finding: Overall, 226 patients were diagnosed with PsA, with an incidence of 1.9 cases per 100 patient-years. Age between 40-59 years (P < .001), BMI ≥25 (P = .015), genital psoriasis (P = .027), nail psoriasis (P = .038), classic chronic-plaque psoriasis (P = .014), previous hospitalization for psoriasis (P < .001), previous use of systemic therapy for psoriasis (P = .003), and use of conventional nonbiologic agents (P = .014) were significantly associated with PsA occurrence.
Study details: This cohort study included 8895 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of psoriasis from the PsoReal registry.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Bristol Myers Squibb. K Heidemeyer and L Naldi declared receiving honoraria from various sources, including AbbVie, Almirall, or Bristol Myers Squibb.
Source: Heidemeyer K et al. Variables associated with joint involvement and development of a prediction rule for arthritis in psoriasis patients. An analysis of the Italian PsoReal database. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023 (Mar 23). Doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2023.02.059
Patients with PsA have lower vitamin D levels than general population, says meta-analysis
Key clinical point: Patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) had lower serum vitamin D (25(OH)D3) levels and bone mineral density (BMD) compared with the general population; however, serum vitamin D levels were higher in patients with PsA vs psoriasis.
Major finding: The serum 25(OH)D3 levels in patients with PsA were lower than those in control individuals (mean difference [MD] −6.42; P < .01) but higher than those in patients with psoriasis (MD 2.37; P < .01). Lumbar spine BMD was significantly lower in patients with PsA vs control individuals (MD −0.08).
Study details: This was a meta-analysis of nine studies, of which four studies included patients with PsA (n = 264) and control individuals from the general population (n = 287) and five studies included patients with PsA (n = 225) and psoriasis (n = 391).
Disclosures: This study was supported by the project “Digitalization and improvement of nutritional care for patients with chronic diseases” cofinanced by the European Regional Development Fund. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Radić M et al. Vitamin D in psoriatic arthritis – A systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2023;60:152200 (Apr 1). Doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2023.152200
Key clinical point: Patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) had lower serum vitamin D (25(OH)D3) levels and bone mineral density (BMD) compared with the general population; however, serum vitamin D levels were higher in patients with PsA vs psoriasis.
Major finding: The serum 25(OH)D3 levels in patients with PsA were lower than those in control individuals (mean difference [MD] −6.42; P < .01) but higher than those in patients with psoriasis (MD 2.37; P < .01). Lumbar spine BMD was significantly lower in patients with PsA vs control individuals (MD −0.08).
Study details: This was a meta-analysis of nine studies, of which four studies included patients with PsA (n = 264) and control individuals from the general population (n = 287) and five studies included patients with PsA (n = 225) and psoriasis (n = 391).
Disclosures: This study was supported by the project “Digitalization and improvement of nutritional care for patients with chronic diseases” cofinanced by the European Regional Development Fund. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Radić M et al. Vitamin D in psoriatic arthritis – A systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2023;60:152200 (Apr 1). Doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2023.152200
Key clinical point: Patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) had lower serum vitamin D (25(OH)D3) levels and bone mineral density (BMD) compared with the general population; however, serum vitamin D levels were higher in patients with PsA vs psoriasis.
Major finding: The serum 25(OH)D3 levels in patients with PsA were lower than those in control individuals (mean difference [MD] −6.42; P < .01) but higher than those in patients with psoriasis (MD 2.37; P < .01). Lumbar spine BMD was significantly lower in patients with PsA vs control individuals (MD −0.08).
Study details: This was a meta-analysis of nine studies, of which four studies included patients with PsA (n = 264) and control individuals from the general population (n = 287) and five studies included patients with PsA (n = 225) and psoriasis (n = 391).
Disclosures: This study was supported by the project “Digitalization and improvement of nutritional care for patients with chronic diseases” cofinanced by the European Regional Development Fund. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Radić M et al. Vitamin D in psoriatic arthritis – A systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2023;60:152200 (Apr 1). Doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2023.152200
Are patients with PsA more prone to cancer?
Key clinical point: Patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) are at a higher risk for overall cancer compared with the general population, highlighting the importance of regular cancer screening among these patients.
Major finding: The risk for overall cancer was slightly higher among patients with PsA vs age- and sex-matched control individuals (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.20; 95% CI 1.02-1.41), with the risk being mainly driven by non-melanoma skin cancer (aHR 3.64; 95% CI 1.61-8.23), lymphoma (aHR 2.63, 95% CI 1.30-5.30), and thyroid cancer (aHR 1.83, 95% CI 1.18-2.85).
Study details: The data come from a population-based cohort study including 4688 patients with newly diagnosed PsA and 46,880 age- and sex-matched control individuals without a history of cancer and other coexisting autoimmune diseases from the general population.
Disclosures: This study did not report the source of funding. The authors did not declare conflicts of interest.
Source: Eun Y et al. Risk of cancer in Korean patients with psoriatic arthritis: A nationwide population-based cohort study. RMD Open. 2023;9(1):e002874 (Mar 23). Doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002874
Key clinical point: Patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) are at a higher risk for overall cancer compared with the general population, highlighting the importance of regular cancer screening among these patients.
Major finding: The risk for overall cancer was slightly higher among patients with PsA vs age- and sex-matched control individuals (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.20; 95% CI 1.02-1.41), with the risk being mainly driven by non-melanoma skin cancer (aHR 3.64; 95% CI 1.61-8.23), lymphoma (aHR 2.63, 95% CI 1.30-5.30), and thyroid cancer (aHR 1.83, 95% CI 1.18-2.85).
Study details: The data come from a population-based cohort study including 4688 patients with newly diagnosed PsA and 46,880 age- and sex-matched control individuals without a history of cancer and other coexisting autoimmune diseases from the general population.
Disclosures: This study did not report the source of funding. The authors did not declare conflicts of interest.
Source: Eun Y et al. Risk of cancer in Korean patients with psoriatic arthritis: A nationwide population-based cohort study. RMD Open. 2023;9(1):e002874 (Mar 23). Doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002874
Key clinical point: Patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) are at a higher risk for overall cancer compared with the general population, highlighting the importance of regular cancer screening among these patients.
Major finding: The risk for overall cancer was slightly higher among patients with PsA vs age- and sex-matched control individuals (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.20; 95% CI 1.02-1.41), with the risk being mainly driven by non-melanoma skin cancer (aHR 3.64; 95% CI 1.61-8.23), lymphoma (aHR 2.63, 95% CI 1.30-5.30), and thyroid cancer (aHR 1.83, 95% CI 1.18-2.85).
Study details: The data come from a population-based cohort study including 4688 patients with newly diagnosed PsA and 46,880 age- and sex-matched control individuals without a history of cancer and other coexisting autoimmune diseases from the general population.
Disclosures: This study did not report the source of funding. The authors did not declare conflicts of interest.
Source: Eun Y et al. Risk of cancer in Korean patients with psoriatic arthritis: A nationwide population-based cohort study. RMD Open. 2023;9(1):e002874 (Mar 23). Doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002874
Age at disease onset influences disease characteristics in PsA
Key clinical point: Age at onset of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) influences disease characteristics, with individuals developing PsA at older age having worse functionality and greater structural damage but a lower frequency of enthesitis and dactylitis.
Major finding: Patients with late vs early onset PsA showed greater structural damage (odds ratio [OR] 3.3; 95% CI 1.3-8.1), higher frequency of arthritis in upper limbs (OR 2.8; 95% CI 1.0-7.7), greater loss of functionality (OR 1.3; 95% CI 1.0-1.6), and lower frequency of enthesitis (OR 0.1; 95% CI 0-0.5) and sacroiliitis (OR 0.06; 95% CI 0-0.5).
Study details: This observational cross-sectional study included 231 patients with PsA with <10 years of disease duration from the REGISPONSER and RESPONDIA registries who were categorized into the early onset (≤40 years) or late onset (≥60 years) group depending on age at PsA symptom onset.
Disclosures: This study did not report the source of funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Puche-Larrubia MÁ et al. Differences between early vs late-onset of psoriatic arthritis: Data from the respondia and regisponser registries. Joint Bone Spine. 2023;105563 (Mar 17). Doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2023.105563
Key clinical point: Age at onset of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) influences disease characteristics, with individuals developing PsA at older age having worse functionality and greater structural damage but a lower frequency of enthesitis and dactylitis.
Major finding: Patients with late vs early onset PsA showed greater structural damage (odds ratio [OR] 3.3; 95% CI 1.3-8.1), higher frequency of arthritis in upper limbs (OR 2.8; 95% CI 1.0-7.7), greater loss of functionality (OR 1.3; 95% CI 1.0-1.6), and lower frequency of enthesitis (OR 0.1; 95% CI 0-0.5) and sacroiliitis (OR 0.06; 95% CI 0-0.5).
Study details: This observational cross-sectional study included 231 patients with PsA with <10 years of disease duration from the REGISPONSER and RESPONDIA registries who were categorized into the early onset (≤40 years) or late onset (≥60 years) group depending on age at PsA symptom onset.
Disclosures: This study did not report the source of funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Puche-Larrubia MÁ et al. Differences between early vs late-onset of psoriatic arthritis: Data from the respondia and regisponser registries. Joint Bone Spine. 2023;105563 (Mar 17). Doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2023.105563
Key clinical point: Age at onset of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) influences disease characteristics, with individuals developing PsA at older age having worse functionality and greater structural damage but a lower frequency of enthesitis and dactylitis.
Major finding: Patients with late vs early onset PsA showed greater structural damage (odds ratio [OR] 3.3; 95% CI 1.3-8.1), higher frequency of arthritis in upper limbs (OR 2.8; 95% CI 1.0-7.7), greater loss of functionality (OR 1.3; 95% CI 1.0-1.6), and lower frequency of enthesitis (OR 0.1; 95% CI 0-0.5) and sacroiliitis (OR 0.06; 95% CI 0-0.5).
Study details: This observational cross-sectional study included 231 patients with PsA with <10 years of disease duration from the REGISPONSER and RESPONDIA registries who were categorized into the early onset (≤40 years) or late onset (≥60 years) group depending on age at PsA symptom onset.
Disclosures: This study did not report the source of funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Puche-Larrubia MÁ et al. Differences between early vs late-onset of psoriatic arthritis: Data from the respondia and regisponser registries. Joint Bone Spine. 2023;105563 (Mar 17). Doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2023.105563
Vitamin D deficiency associated with lowest retention rates of first bDMARD in PsA
Key clinical point: Vitamin D deficiency in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) had worse impact on the retention rate of the first biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARD) and response to methotrexate and was associated with severe disease course in terms of sacroiliitis.
Major finding: The risk for discontinuation of the first bDMARD (hazard ratio [HR] 2.129; P = .011) and methotrexate discontinuation because of therapy failure (HR 2.168; P = .002) were significantly higher among patients with 25(OH)D level of ≤20 vs 20-30 and ≥30 ng/mL, with the prevalence of sacroiliitis being significantly higher in patients with 25(OH)D level of ≤20 vs ≥30 ng/mL (P = .0001).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study including 233 patients with PsA.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Rotondo C et al. Vitamin D status and psoriatic arthritis: Association with the risk for sacroiliitis and influence on the retention rate of methotrexate monotherapy and first biological drug survival—A retrospective study. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5368 (Mar 10). Doi: 10.3390/ijms24065368
Key clinical point: Vitamin D deficiency in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) had worse impact on the retention rate of the first biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARD) and response to methotrexate and was associated with severe disease course in terms of sacroiliitis.
Major finding: The risk for discontinuation of the first bDMARD (hazard ratio [HR] 2.129; P = .011) and methotrexate discontinuation because of therapy failure (HR 2.168; P = .002) were significantly higher among patients with 25(OH)D level of ≤20 vs 20-30 and ≥30 ng/mL, with the prevalence of sacroiliitis being significantly higher in patients with 25(OH)D level of ≤20 vs ≥30 ng/mL (P = .0001).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study including 233 patients with PsA.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Rotondo C et al. Vitamin D status and psoriatic arthritis: Association with the risk for sacroiliitis and influence on the retention rate of methotrexate monotherapy and first biological drug survival—A retrospective study. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5368 (Mar 10). Doi: 10.3390/ijms24065368
Key clinical point: Vitamin D deficiency in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) had worse impact on the retention rate of the first biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARD) and response to methotrexate and was associated with severe disease course in terms of sacroiliitis.
Major finding: The risk for discontinuation of the first bDMARD (hazard ratio [HR] 2.129; P = .011) and methotrexate discontinuation because of therapy failure (HR 2.168; P = .002) were significantly higher among patients with 25(OH)D level of ≤20 vs 20-30 and ≥30 ng/mL, with the prevalence of sacroiliitis being significantly higher in patients with 25(OH)D level of ≤20 vs ≥30 ng/mL (P = .0001).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study including 233 patients with PsA.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Rotondo C et al. Vitamin D status and psoriatic arthritis: Association with the risk for sacroiliitis and influence on the retention rate of methotrexate monotherapy and first biological drug survival—A retrospective study. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5368 (Mar 10). Doi: 10.3390/ijms24065368
Vitamin D deficiency associated with lowest retention rates of first bDMARD in PsA
Key clinical point: Vitamin D deficiency in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) had worse impact on the retention rate of the first biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARD) and response to methotrexate and was associated with severe disease course in terms of sacroiliitis.
Major finding: The risk for discontinuation of the first bDMARD (hazard ratio [HR] 2.129; P = .011) and methotrexate discontinuation because of therapy failure (HR 2.168; P = .002) were significantly higher among patients with 25(OH)D level of ≤20 vs 20-30 and ≥30 ng/mL, with the prevalence of sacroiliitis being significantly higher in patients with 25(OH)D level of ≤20 vs ≥30 ng/mL (P = .0001).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study including 233 patients with PsA.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Rotondo C et al. Vitamin D status and psoriatic arthritis: Association with the risk for sacroiliitis and influence on the retention rate of methotrexate monotherapy and first biological drug survival—A retrospective study. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5368 (Mar 10). Doi: 10.3390/ijms24065368
Key clinical point: Vitamin D deficiency in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) had worse impact on the retention rate of the first biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARD) and response to methotrexate and was associated with severe disease course in terms of sacroiliitis.
Major finding: The risk for discontinuation of the first bDMARD (hazard ratio [HR] 2.129; P = .011) and methotrexate discontinuation because of therapy failure (HR 2.168; P = .002) were significantly higher among patients with 25(OH)D level of ≤20 vs 20-30 and ≥30 ng/mL, with the prevalence of sacroiliitis being significantly higher in patients with 25(OH)D level of ≤20 vs ≥30 ng/mL (P = .0001).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study including 233 patients with PsA.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Rotondo C et al. Vitamin D status and psoriatic arthritis: Association with the risk for sacroiliitis and influence on the retention rate of methotrexate monotherapy and first biological drug survival—A retrospective study. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5368 (Mar 10). Doi: 10.3390/ijms24065368
Key clinical point: Vitamin D deficiency in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) had worse impact on the retention rate of the first biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARD) and response to methotrexate and was associated with severe disease course in terms of sacroiliitis.
Major finding: The risk for discontinuation of the first bDMARD (hazard ratio [HR] 2.129; P = .011) and methotrexate discontinuation because of therapy failure (HR 2.168; P = .002) were significantly higher among patients with 25(OH)D level of ≤20 vs 20-30 and ≥30 ng/mL, with the prevalence of sacroiliitis being significantly higher in patients with 25(OH)D level of ≤20 vs ≥30 ng/mL (P = .0001).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study including 233 patients with PsA.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Rotondo C et al. Vitamin D status and psoriatic arthritis: Association with the risk for sacroiliitis and influence on the retention rate of methotrexate monotherapy and first biological drug survival—A retrospective study. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5368 (Mar 10). Doi: 10.3390/ijms24065368
Distinct clinical manifestations of PsA with axial involvement and axial spondyloarthritis with psoriasis
Key clinical point: Psoriatic arthritis with axial involvement (axPsA), defined either clinically or by imaging, showed distinct disease manifestations compared with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) plus psoriasis, indicating that axPsA and axSpA were distinct entities.
Major finding: Regardless of clinical or imaging definition used, patients with axPsA vs axSpA+psoriasis were significantly more often women and older individuals and less often human leucocyte antigen-B27 positive (all P < .05), as well as had more frequent peripheral manifestations (P < .001) but less frequent uveitis (P < .001).
Study details: Findings are from the RABBIT-SpA, a prospective longitudinal observational study, including 1395 patients with PsA (359 patients had axial involvement) and 1428 patients with axSpA (181 patients had psoriasis).
Disclosures: The study was supported by AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen, Celltrion, Hexal, Janssen-Cilag, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, and Viatris. The authors did not report conflicts of interest.
Source: Regierer AC et al. Comparison of patients with axial PsA and patients with axSpA and concomitant psoriasis: An analysis of the German register RABBIT-SpA. RMD Open. 2023;9(1):e002837 (Mar 10). Doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002837.
Key clinical point: Psoriatic arthritis with axial involvement (axPsA), defined either clinically or by imaging, showed distinct disease manifestations compared with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) plus psoriasis, indicating that axPsA and axSpA were distinct entities.
Major finding: Regardless of clinical or imaging definition used, patients with axPsA vs axSpA+psoriasis were significantly more often women and older individuals and less often human leucocyte antigen-B27 positive (all P < .05), as well as had more frequent peripheral manifestations (P < .001) but less frequent uveitis (P < .001).
Study details: Findings are from the RABBIT-SpA, a prospective longitudinal observational study, including 1395 patients with PsA (359 patients had axial involvement) and 1428 patients with axSpA (181 patients had psoriasis).
Disclosures: The study was supported by AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen, Celltrion, Hexal, Janssen-Cilag, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, and Viatris. The authors did not report conflicts of interest.
Source: Regierer AC et al. Comparison of patients with axial PsA and patients with axSpA and concomitant psoriasis: An analysis of the German register RABBIT-SpA. RMD Open. 2023;9(1):e002837 (Mar 10). Doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002837.
Key clinical point: Psoriatic arthritis with axial involvement (axPsA), defined either clinically or by imaging, showed distinct disease manifestations compared with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) plus psoriasis, indicating that axPsA and axSpA were distinct entities.
Major finding: Regardless of clinical or imaging definition used, patients with axPsA vs axSpA+psoriasis were significantly more often women and older individuals and less often human leucocyte antigen-B27 positive (all P < .05), as well as had more frequent peripheral manifestations (P < .001) but less frequent uveitis (P < .001).
Study details: Findings are from the RABBIT-SpA, a prospective longitudinal observational study, including 1395 patients with PsA (359 patients had axial involvement) and 1428 patients with axSpA (181 patients had psoriasis).
Disclosures: The study was supported by AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen, Celltrion, Hexal, Janssen-Cilag, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, and Viatris. The authors did not report conflicts of interest.
Source: Regierer AC et al. Comparison of patients with axial PsA and patients with axSpA and concomitant psoriasis: An analysis of the German register RABBIT-SpA. RMD Open. 2023;9(1):e002837 (Mar 10). Doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002837.