User login
Clinician responsibilities during times of geopolitical conflict
In the realm of clinical psychology and psychiatry, our primary duty and commitment is (and should be) to the well-being of our patients. Yet, as we find ourselves in an era marked by escalating geopolitical conflict, such as the Israel-Hamas war, probably more aptly titled the Israeli-Hamas-Hezbollah-Houthi war (a clarification that elucidates a later point), clinicians are increasingly confronted with ethical dilemmas that extend far beyond what is outlined in our code of ethics.
These challenges are not only impacting us on a personal level but are also spilling over into our professional lives, creating a divisive and non-collegial environment within the healthcare community. We commit to “do no harm” when delivering care and yet we are doing harm to one another as colleagues.
We are no strangers to the complexities of human behavior and the intricate tapestry of emotions that are involved with our professional work. However, the current geopolitical landscape has added an extra layer of difficulty to our already taxing professional lives. We are, after all, human first with unconscious drives that govern how we negotiate cognitive dissonance and our need for the illusion of absolute justice as Yuval Noah Harari explains in a recent podcast.
Humans are notoriously bad at holding the multiplicity of experience in mind and various (often competing narratives) that impede the capacity for nuanced thinking. We would like to believe we are better and more capable than the average person in doing so, but divisiveness in our profession has become disturbingly pronounced, making it essential for us to carve out reflective space, more than ever.
The personal and professional divide
Geopolitical conflicts like the current war have a unique capacity to ignite strong emotions and deeply held convictions. It’s not hard to quickly become embroiled in passionate and engaged debate.
While discussion and discourse are healthy, these are bleeding into professional spheres, creating rifts within our clinical communities and contributing to a culture where not everyone feels safe. Look at any professional listserv in medicine or psychology and you will find the evidence. It should be an immediate call to action that we need to be fostering a different type of environment.
The impact of divisiveness is profound, hindering opportunities for collaboration, mentorship, and the free exchange of ideas among clinicians. It may lead to misunderstandings, mistrust, and an erosion of the support systems we rely on, ultimately diverting energy away from the pursuit of providing quality patient-care.
Balancing obligations and limits
Because of the inherent power differential that accompanies being in a provider role (physician and psychologist alike), we have a social and moral responsibility to be mindful of what we share – for the sake of humanity. There is an implicit assumption that a provider’s guidance should be adhered to and respected. In other words, words carry tremendous weight and deeply matter, and people in the general public ascribe significant meaning to messages put out by professionals.
When providers steer from their lanes of professional expertise to provide the general public with opinions or recommendations on nonmedical topics, problematic precedents can be set. We may be doing people a disservice.
Unfortunately, I have heard several anecdotes about clinicians who spend their patient’s time in session pushing their own ideological agendas. The patient-provider relationship is founded on principles of trust, empathy, and collaboration, with the primary goal of improving overall well-being and addressing a specific presenting problem. Of course, issues emerge that need to be addressed outside of the initial scope of treatment, an inherent part of the process. However, a grave concern emerges when clinicians initiate dialogue that is not meaningful to a patient, disclose and discuss their personal ideologies, or put pressure on patients to explain their beliefs in an attempt to change the patients’ minds.
Clinicians pushing their own agenda during patient sessions is antithetical to the objectives of psychotherapy and compromises the therapeutic alliance by diverting the focus of care in a way that serves the clinician rather than the client. It is quite the opposite of the patient-centered care that we strive for in training and practice.
Even within one’s theoretical professional scope of competence, I have seen the impact of emotions running high during this conflict, and have witnessed trained professionals making light of, or even mocking, hostages and their behavior upon release. These are care providers who could elucidate the complexities of captor-captive dynamics and the impact of trauma for the general public, yet they are contributing to dangerous perceptions and divisiveness.
I have also seen providers justify sexual violence, diminishing survivor and witness testimony due to ideological differences and strong personal beliefs. This is harmful to those impacted and does a disservice to our profession at large. In a helping profession we should strive to support and advocate for anyone who has been maltreated or experienced any form of victimization, violence, or abuse. This should be a professional standard.
As clinicians, we have an ethical obligation to uphold the well-being, autonomy, and dignity of our patients — and humanity. It is crucial to recognize the limits of our expertise and the ethical concerns that can arise in light of geopolitical conflict. How can we balance our duty to provide psychological support while also being cautious about delving into the realms of political analysis, foreign policy, or international relations?
The pitfalls of well-intentioned speaking out
In the age of social media and instant communication, a critical aspect to consider is the role of speaking out. The point I made above, in naming all partaking in the current conflict, speaks to this issue.
As providers and programs, we must be mindful of the inadvertent harm that can arise from making brief, underdeveloped, uninformed, or emotionally charged statements. Expressing opinions without a solid understanding of the historical, cultural, and political nuances of a conflict can contribute to misinformation and further polarization.
Anecdotally, there appears to be some significant degree of bias emerging within professional fields (e.g., psychology, medicine) and an innate calling for providers to “weigh in” as the war continues. Obviously, physicians and psychologists are trained to provide care and to be humanistic and empathic, but the majority do not have expertise in geopolitics or a nuanced awareness of the complexities of the conflict in the Middle East.
While hearts may be in the right place, issuing statements on complicated humanitarian/political situations can inadvertently have unintended and harmful consequences (in terms of antisemitism and islamophobia, increased incidence of hate crimes, and colleagues not feeling safe within professional societies or member organizations).
Unsophisticated, overly simplistic, and reductionistic statements that do not adequately convey nuance will not reflect the range of experience reflected by providers in the field (or the patients we treat). It is essential for clinicians and institutions putting out public statements to engage in deep reflection and utilize discernment. We must recognize that our words carry weight, given our position of influence as treatment providers. To minimize harm, we should seek to provide information that is fair, vetted, and balanced, and encourage open, respectful dialogue rather than asserting definitive positions.
Ultimately, as providers we must strive to seek unity and inclusivity amidst the current challenges. It is important for us to embody a spirit of collaboration during a time demarcated by deep fragmentation.
By acknowledging our limitations, promoting informed discussion, and avoiding the pitfalls of uninformed advocacy, we can contribute to a more compassionate and understanding world, even in the face of the most divisive geopolitical conflicts. We have an obligation to uphold when it comes to ourselves as professionals, and we need to foster healthy, respectful dialogue while maintaining an awareness of our blind spots.
Dr. Feldman is a licensed clinical psychologist in private practice in Miami. She is an adjunct professor in the College of Psychology at Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., where she teaches clinical psychology doctoral students. She is an affiliate of Baptist West Kendall Hospital/FIU Family Medicine Residency Program and serves as president on the board of directors of The Southeast Florida Association for Psychoanalytic Psychology. The opinions expressed by Dr. Feldman are her own and do not represent the institutions with which she is affiliated. She has no disclosures.
In the realm of clinical psychology and psychiatry, our primary duty and commitment is (and should be) to the well-being of our patients. Yet, as we find ourselves in an era marked by escalating geopolitical conflict, such as the Israel-Hamas war, probably more aptly titled the Israeli-Hamas-Hezbollah-Houthi war (a clarification that elucidates a later point), clinicians are increasingly confronted with ethical dilemmas that extend far beyond what is outlined in our code of ethics.
These challenges are not only impacting us on a personal level but are also spilling over into our professional lives, creating a divisive and non-collegial environment within the healthcare community. We commit to “do no harm” when delivering care and yet we are doing harm to one another as colleagues.
We are no strangers to the complexities of human behavior and the intricate tapestry of emotions that are involved with our professional work. However, the current geopolitical landscape has added an extra layer of difficulty to our already taxing professional lives. We are, after all, human first with unconscious drives that govern how we negotiate cognitive dissonance and our need for the illusion of absolute justice as Yuval Noah Harari explains in a recent podcast.
Humans are notoriously bad at holding the multiplicity of experience in mind and various (often competing narratives) that impede the capacity for nuanced thinking. We would like to believe we are better and more capable than the average person in doing so, but divisiveness in our profession has become disturbingly pronounced, making it essential for us to carve out reflective space, more than ever.
The personal and professional divide
Geopolitical conflicts like the current war have a unique capacity to ignite strong emotions and deeply held convictions. It’s not hard to quickly become embroiled in passionate and engaged debate.
While discussion and discourse are healthy, these are bleeding into professional spheres, creating rifts within our clinical communities and contributing to a culture where not everyone feels safe. Look at any professional listserv in medicine or psychology and you will find the evidence. It should be an immediate call to action that we need to be fostering a different type of environment.
The impact of divisiveness is profound, hindering opportunities for collaboration, mentorship, and the free exchange of ideas among clinicians. It may lead to misunderstandings, mistrust, and an erosion of the support systems we rely on, ultimately diverting energy away from the pursuit of providing quality patient-care.
Balancing obligations and limits
Because of the inherent power differential that accompanies being in a provider role (physician and psychologist alike), we have a social and moral responsibility to be mindful of what we share – for the sake of humanity. There is an implicit assumption that a provider’s guidance should be adhered to and respected. In other words, words carry tremendous weight and deeply matter, and people in the general public ascribe significant meaning to messages put out by professionals.
When providers steer from their lanes of professional expertise to provide the general public with opinions or recommendations on nonmedical topics, problematic precedents can be set. We may be doing people a disservice.
Unfortunately, I have heard several anecdotes about clinicians who spend their patient’s time in session pushing their own ideological agendas. The patient-provider relationship is founded on principles of trust, empathy, and collaboration, with the primary goal of improving overall well-being and addressing a specific presenting problem. Of course, issues emerge that need to be addressed outside of the initial scope of treatment, an inherent part of the process. However, a grave concern emerges when clinicians initiate dialogue that is not meaningful to a patient, disclose and discuss their personal ideologies, or put pressure on patients to explain their beliefs in an attempt to change the patients’ minds.
Clinicians pushing their own agenda during patient sessions is antithetical to the objectives of psychotherapy and compromises the therapeutic alliance by diverting the focus of care in a way that serves the clinician rather than the client. It is quite the opposite of the patient-centered care that we strive for in training and practice.
Even within one’s theoretical professional scope of competence, I have seen the impact of emotions running high during this conflict, and have witnessed trained professionals making light of, or even mocking, hostages and their behavior upon release. These are care providers who could elucidate the complexities of captor-captive dynamics and the impact of trauma for the general public, yet they are contributing to dangerous perceptions and divisiveness.
I have also seen providers justify sexual violence, diminishing survivor and witness testimony due to ideological differences and strong personal beliefs. This is harmful to those impacted and does a disservice to our profession at large. In a helping profession we should strive to support and advocate for anyone who has been maltreated or experienced any form of victimization, violence, or abuse. This should be a professional standard.
As clinicians, we have an ethical obligation to uphold the well-being, autonomy, and dignity of our patients — and humanity. It is crucial to recognize the limits of our expertise and the ethical concerns that can arise in light of geopolitical conflict. How can we balance our duty to provide psychological support while also being cautious about delving into the realms of political analysis, foreign policy, or international relations?
The pitfalls of well-intentioned speaking out
In the age of social media and instant communication, a critical aspect to consider is the role of speaking out. The point I made above, in naming all partaking in the current conflict, speaks to this issue.
As providers and programs, we must be mindful of the inadvertent harm that can arise from making brief, underdeveloped, uninformed, or emotionally charged statements. Expressing opinions without a solid understanding of the historical, cultural, and political nuances of a conflict can contribute to misinformation and further polarization.
Anecdotally, there appears to be some significant degree of bias emerging within professional fields (e.g., psychology, medicine) and an innate calling for providers to “weigh in” as the war continues. Obviously, physicians and psychologists are trained to provide care and to be humanistic and empathic, but the majority do not have expertise in geopolitics or a nuanced awareness of the complexities of the conflict in the Middle East.
While hearts may be in the right place, issuing statements on complicated humanitarian/political situations can inadvertently have unintended and harmful consequences (in terms of antisemitism and islamophobia, increased incidence of hate crimes, and colleagues not feeling safe within professional societies or member organizations).
Unsophisticated, overly simplistic, and reductionistic statements that do not adequately convey nuance will not reflect the range of experience reflected by providers in the field (or the patients we treat). It is essential for clinicians and institutions putting out public statements to engage in deep reflection and utilize discernment. We must recognize that our words carry weight, given our position of influence as treatment providers. To minimize harm, we should seek to provide information that is fair, vetted, and balanced, and encourage open, respectful dialogue rather than asserting definitive positions.
Ultimately, as providers we must strive to seek unity and inclusivity amidst the current challenges. It is important for us to embody a spirit of collaboration during a time demarcated by deep fragmentation.
By acknowledging our limitations, promoting informed discussion, and avoiding the pitfalls of uninformed advocacy, we can contribute to a more compassionate and understanding world, even in the face of the most divisive geopolitical conflicts. We have an obligation to uphold when it comes to ourselves as professionals, and we need to foster healthy, respectful dialogue while maintaining an awareness of our blind spots.
Dr. Feldman is a licensed clinical psychologist in private practice in Miami. She is an adjunct professor in the College of Psychology at Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., where she teaches clinical psychology doctoral students. She is an affiliate of Baptist West Kendall Hospital/FIU Family Medicine Residency Program and serves as president on the board of directors of The Southeast Florida Association for Psychoanalytic Psychology. The opinions expressed by Dr. Feldman are her own and do not represent the institutions with which she is affiliated. She has no disclosures.
In the realm of clinical psychology and psychiatry, our primary duty and commitment is (and should be) to the well-being of our patients. Yet, as we find ourselves in an era marked by escalating geopolitical conflict, such as the Israel-Hamas war, probably more aptly titled the Israeli-Hamas-Hezbollah-Houthi war (a clarification that elucidates a later point), clinicians are increasingly confronted with ethical dilemmas that extend far beyond what is outlined in our code of ethics.
These challenges are not only impacting us on a personal level but are also spilling over into our professional lives, creating a divisive and non-collegial environment within the healthcare community. We commit to “do no harm” when delivering care and yet we are doing harm to one another as colleagues.
We are no strangers to the complexities of human behavior and the intricate tapestry of emotions that are involved with our professional work. However, the current geopolitical landscape has added an extra layer of difficulty to our already taxing professional lives. We are, after all, human first with unconscious drives that govern how we negotiate cognitive dissonance and our need for the illusion of absolute justice as Yuval Noah Harari explains in a recent podcast.
Humans are notoriously bad at holding the multiplicity of experience in mind and various (often competing narratives) that impede the capacity for nuanced thinking. We would like to believe we are better and more capable than the average person in doing so, but divisiveness in our profession has become disturbingly pronounced, making it essential for us to carve out reflective space, more than ever.
The personal and professional divide
Geopolitical conflicts like the current war have a unique capacity to ignite strong emotions and deeply held convictions. It’s not hard to quickly become embroiled in passionate and engaged debate.
While discussion and discourse are healthy, these are bleeding into professional spheres, creating rifts within our clinical communities and contributing to a culture where not everyone feels safe. Look at any professional listserv in medicine or psychology and you will find the evidence. It should be an immediate call to action that we need to be fostering a different type of environment.
The impact of divisiveness is profound, hindering opportunities for collaboration, mentorship, and the free exchange of ideas among clinicians. It may lead to misunderstandings, mistrust, and an erosion of the support systems we rely on, ultimately diverting energy away from the pursuit of providing quality patient-care.
Balancing obligations and limits
Because of the inherent power differential that accompanies being in a provider role (physician and psychologist alike), we have a social and moral responsibility to be mindful of what we share – for the sake of humanity. There is an implicit assumption that a provider’s guidance should be adhered to and respected. In other words, words carry tremendous weight and deeply matter, and people in the general public ascribe significant meaning to messages put out by professionals.
When providers steer from their lanes of professional expertise to provide the general public with opinions or recommendations on nonmedical topics, problematic precedents can be set. We may be doing people a disservice.
Unfortunately, I have heard several anecdotes about clinicians who spend their patient’s time in session pushing their own ideological agendas. The patient-provider relationship is founded on principles of trust, empathy, and collaboration, with the primary goal of improving overall well-being and addressing a specific presenting problem. Of course, issues emerge that need to be addressed outside of the initial scope of treatment, an inherent part of the process. However, a grave concern emerges when clinicians initiate dialogue that is not meaningful to a patient, disclose and discuss their personal ideologies, or put pressure on patients to explain their beliefs in an attempt to change the patients’ minds.
Clinicians pushing their own agenda during patient sessions is antithetical to the objectives of psychotherapy and compromises the therapeutic alliance by diverting the focus of care in a way that serves the clinician rather than the client. It is quite the opposite of the patient-centered care that we strive for in training and practice.
Even within one’s theoretical professional scope of competence, I have seen the impact of emotions running high during this conflict, and have witnessed trained professionals making light of, or even mocking, hostages and their behavior upon release. These are care providers who could elucidate the complexities of captor-captive dynamics and the impact of trauma for the general public, yet they are contributing to dangerous perceptions and divisiveness.
I have also seen providers justify sexual violence, diminishing survivor and witness testimony due to ideological differences and strong personal beliefs. This is harmful to those impacted and does a disservice to our profession at large. In a helping profession we should strive to support and advocate for anyone who has been maltreated or experienced any form of victimization, violence, or abuse. This should be a professional standard.
As clinicians, we have an ethical obligation to uphold the well-being, autonomy, and dignity of our patients — and humanity. It is crucial to recognize the limits of our expertise and the ethical concerns that can arise in light of geopolitical conflict. How can we balance our duty to provide psychological support while also being cautious about delving into the realms of political analysis, foreign policy, or international relations?
The pitfalls of well-intentioned speaking out
In the age of social media and instant communication, a critical aspect to consider is the role of speaking out. The point I made above, in naming all partaking in the current conflict, speaks to this issue.
As providers and programs, we must be mindful of the inadvertent harm that can arise from making brief, underdeveloped, uninformed, or emotionally charged statements. Expressing opinions without a solid understanding of the historical, cultural, and political nuances of a conflict can contribute to misinformation and further polarization.
Anecdotally, there appears to be some significant degree of bias emerging within professional fields (e.g., psychology, medicine) and an innate calling for providers to “weigh in” as the war continues. Obviously, physicians and psychologists are trained to provide care and to be humanistic and empathic, but the majority do not have expertise in geopolitics or a nuanced awareness of the complexities of the conflict in the Middle East.
While hearts may be in the right place, issuing statements on complicated humanitarian/political situations can inadvertently have unintended and harmful consequences (in terms of antisemitism and islamophobia, increased incidence of hate crimes, and colleagues not feeling safe within professional societies or member organizations).
Unsophisticated, overly simplistic, and reductionistic statements that do not adequately convey nuance will not reflect the range of experience reflected by providers in the field (or the patients we treat). It is essential for clinicians and institutions putting out public statements to engage in deep reflection and utilize discernment. We must recognize that our words carry weight, given our position of influence as treatment providers. To minimize harm, we should seek to provide information that is fair, vetted, and balanced, and encourage open, respectful dialogue rather than asserting definitive positions.
Ultimately, as providers we must strive to seek unity and inclusivity amidst the current challenges. It is important for us to embody a spirit of collaboration during a time demarcated by deep fragmentation.
By acknowledging our limitations, promoting informed discussion, and avoiding the pitfalls of uninformed advocacy, we can contribute to a more compassionate and understanding world, even in the face of the most divisive geopolitical conflicts. We have an obligation to uphold when it comes to ourselves as professionals, and we need to foster healthy, respectful dialogue while maintaining an awareness of our blind spots.
Dr. Feldman is a licensed clinical psychologist in private practice in Miami. She is an adjunct professor in the College of Psychology at Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., where she teaches clinical psychology doctoral students. She is an affiliate of Baptist West Kendall Hospital/FIU Family Medicine Residency Program and serves as president on the board of directors of The Southeast Florida Association for Psychoanalytic Psychology. The opinions expressed by Dr. Feldman are her own and do not represent the institutions with which she is affiliated. She has no disclosures.
MDMA therapy for loneliness? Researchers say it could work
Some call the drug “ecstasy” or “molly.” Researchers are calling it a potential tool to help treat loneliness.
As public health experts sound the alarm on a rising loneliness epidemic in the United States and across the globe,
In the latest study, MDMA “led to a robust increase in feelings of connection” among people socializing in a controlled setting. Participants were dosed with either MDMA or a placebo and asked to chat with a stranger. Afterward, those who took MDMA said their companion was more responsive and attentive, and that they had plenty in common. The drug also “increased participants’ ratings of liking their partners, feeling connected and finding the conversation enjoyable and meaningful.”
The study was small — just 18 participants — but its results “have implications for MDMA-assisted therapy,” the authors wrote. “This feeling of connectedness could help patients feel safe and trusting, thereby facilitating deeper emotional exploration.”
MDMA “really does seem to make people want to interact more with other people,” says Harriet de Wit, PhD, a neuropharmacologist at the University of Chicago and one of the study’s authors. The results echo those of earlier research using psychedelics like LSD or psilocybin.
It’s important to note that any intervention involving MDMA or psychedelics would be a drug-assisted therapy — that is, used in conjunction with the appropriate therapy and in a therapeutic setting. MDMA-assisted therapy has already drawn popular and scientific attention, as it recently cleared clinical trials for treating posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and may be nearing approval by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
According to Friederike Holze, PhD, psychopharmacologist at the University of Basel, in Switzerland, “there could be a place” for MDMA and psychedelics in treating chronic loneliness, but only under professional supervision.
There would have to be clear guidelines too, says Joshua Woolley, MD, PhD, a psychiatrist at the University of California, San Francisco.
MDMA and psychedelics “induce this plastic state, a state where people can change. They feel open, they feel like things are possible,” Dr. Woolley says. Then, with therapy, “you can help them change.”
Loneliness Can Impact Our Health
On top of the mental health ramifications, the physiologic effects of loneliness could have grave consequences over time. In observational studies, loneliness has been linked to higher risks for cancer and heart disease, and shorter lifespan. One third of Americans over 45 say they are chronically lonely.
Chronic loneliness changes how we think and behave, research shows. It makes us fear contact with others and see them in a more negative light, as more threatening and less trustworthy. Lonely people prefer to stand farther apart from strangers and avoid touch.
This is where MDMA-assisted therapies could potentially help, by easing these defensive tendencies, according to Dr. Woolley.
MDMA, Psychedelics, and Social Behavior
MDMA, or 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine, is a hybrid between a stimulant and a psychedelic. In Dr. de Wit’s earlier experiments, volunteers given MDMA engaged more in communal activities, chatting, and playing games. They used more positive words during social encounters than those who had received a placebo. And after MDMA, people felt less rejected if they were slighted in Cyberball — a virtual ball-tossing game commonly used to measure the effects of social exclusion.
MDMA has been shown to reduce people’s response to other’s negative emotions, diminishing activation of the amygdala (the brain’s fear center) while looking at pictures of angry faces.
This could be helpful. “If you perceive a person’s natural expression as being a little bit angry, if that disappears, then you might be more inclined to interact,” de Wit says.
However, there may be downsides, too. If a drug makes people more trusting and willing to connect, they could be taken advantage of. This is why, Dr. Woolley says, “psychedelics have been used in cults.”
MDMA may also make the experience of touch more pleasant. In a series of experiments in 2019, researchers gently stroked volunteers ’ arms with a goat-hair brush, mimicking the comforting gestures one may receive from a loved one. At the same time, the scientists monitored the volunteers’ facial muscles. People on MDMA perceived gentle touch as more pleasant than those on placebo, and their smile muscles activated more.
MDMA and psychedelics boost social behaviors in animals, too — suggesting that their effects on relationships have a biological basis. Rats on MDMA are more likely to lie next to each other, and mice become more resilient to social stress. Even octopuses become more outgoing after a dose of MDMA, choosing to spend more time with other octopuses instead of a new toy. Classic psychedelics show similar effects — LSD, for example, makes mice more social.
Psychedelics can induce a sense of a “dissolution of the self-other boundary,” Dr. Woolley says. People who take them often say it’s “helped them feel more connected to themselves and other people.” LSD, first synthesized in 1938, may help increase empathy in some people.
Psilocybin, a compound found in over 200 species of mushrooms and used for centuries in Mesoamerican rituals, also seems to boost empathy, with effects persisting for at least seven days. In Cyberball, the online ball-throwing game, people who took psilocybin felt less socially rejected, an outcome reflected in their brain activation patterns in one study — the areas responsible for social-pain processing appeared to dim after a dose.
Making It Legal and Putting It to Use
In 2020, Oregon became the first state to establish a regulatory framework for psilocybin for therapeutic use, and Colorado followed suit in 2022. Such therapeutic applications of psilocybin could help fight loneliness as well, Dr. Woolley believes, because a “ common symptom of depression is that people feel socially withdrawn and lack motivation, ” he says. As mentioned above, MDMA-assisted therapy is also nearing FDA approval for PTSD.
What remain unclear are the exact mechanisms at play.
“MDMA releases oxytocin, and it does that through serotonin receptors,” Dr. de Wit says. Serotonin activates 5-HT1A receptors in the hypothalamus, releasing oxytocin into the bloodstream. In Dr. de Wit’s recent experiments, the more people felt connected after taking MDMA, the more oxytocin was found circulating in their bodies. (Another drug, methamphetamine, also upped the levels of oxytocin but did not increase feelings of connectedness.)
“It’s likely that both something in the serotonin system independent of oxytocin, and oxytocin itself, contribute,” Dr. de Wit says. Dopamine, a neurotransmitter responsible for motivation, appears to increase as well.
The empathy-boosting effects of LSD also seem to be at least partly driven by oxytocin, experiments published in 2021 revealed. Studies in mice, meanwhile, suggest that glutamate, a chemical messenger in the brain, may be behind some of LSD’s prosocial effects.
Scientists are fairly certain which receptors these drugs bind to and which neurotransmitters they affect. “How that gets translated into these higher-order things like empathy and feeling connected to the world, we don’t totally understand,” Dr. Woolley says.
Challenges and the Future
Although MDMA and psychedelics are largely considered safe when taken in a legal, medically controlled setting, there is reason to be cautious.
“They have relatively low impact on the body, like heart rate increase or blood pressure increase. But they might leave some disturbing psychological effects,” says Dr. Holze. Scientists routinely screen experiment volunteers for their risk for psychiatric disorders.
Although risk for addiction is low with both MDMA and psychedelics, there is always some risk for misuse. MDMA “ can produce feelings of well-being, and then people might use it repeatedly, ” Dr. de Wit says. “ That doesn ’ t seem to be a problem for really a lot of people, but it could easily happen. ”
Still, possibilities remain for MDMA in the fight against loneliness.
“[People] feel open, they feel like things are possible, they feel like they’re unstuck,” Dr. Woolley says. “You can harness that in psychotherapy.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Some call the drug “ecstasy” or “molly.” Researchers are calling it a potential tool to help treat loneliness.
As public health experts sound the alarm on a rising loneliness epidemic in the United States and across the globe,
In the latest study, MDMA “led to a robust increase in feelings of connection” among people socializing in a controlled setting. Participants were dosed with either MDMA or a placebo and asked to chat with a stranger. Afterward, those who took MDMA said their companion was more responsive and attentive, and that they had plenty in common. The drug also “increased participants’ ratings of liking their partners, feeling connected and finding the conversation enjoyable and meaningful.”
The study was small — just 18 participants — but its results “have implications for MDMA-assisted therapy,” the authors wrote. “This feeling of connectedness could help patients feel safe and trusting, thereby facilitating deeper emotional exploration.”
MDMA “really does seem to make people want to interact more with other people,” says Harriet de Wit, PhD, a neuropharmacologist at the University of Chicago and one of the study’s authors. The results echo those of earlier research using psychedelics like LSD or psilocybin.
It’s important to note that any intervention involving MDMA or psychedelics would be a drug-assisted therapy — that is, used in conjunction with the appropriate therapy and in a therapeutic setting. MDMA-assisted therapy has already drawn popular and scientific attention, as it recently cleared clinical trials for treating posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and may be nearing approval by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
According to Friederike Holze, PhD, psychopharmacologist at the University of Basel, in Switzerland, “there could be a place” for MDMA and psychedelics in treating chronic loneliness, but only under professional supervision.
There would have to be clear guidelines too, says Joshua Woolley, MD, PhD, a psychiatrist at the University of California, San Francisco.
MDMA and psychedelics “induce this plastic state, a state where people can change. They feel open, they feel like things are possible,” Dr. Woolley says. Then, with therapy, “you can help them change.”
Loneliness Can Impact Our Health
On top of the mental health ramifications, the physiologic effects of loneliness could have grave consequences over time. In observational studies, loneliness has been linked to higher risks for cancer and heart disease, and shorter lifespan. One third of Americans over 45 say they are chronically lonely.
Chronic loneliness changes how we think and behave, research shows. It makes us fear contact with others and see them in a more negative light, as more threatening and less trustworthy. Lonely people prefer to stand farther apart from strangers and avoid touch.
This is where MDMA-assisted therapies could potentially help, by easing these defensive tendencies, according to Dr. Woolley.
MDMA, Psychedelics, and Social Behavior
MDMA, or 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine, is a hybrid between a stimulant and a psychedelic. In Dr. de Wit’s earlier experiments, volunteers given MDMA engaged more in communal activities, chatting, and playing games. They used more positive words during social encounters than those who had received a placebo. And after MDMA, people felt less rejected if they were slighted in Cyberball — a virtual ball-tossing game commonly used to measure the effects of social exclusion.
MDMA has been shown to reduce people’s response to other’s negative emotions, diminishing activation of the amygdala (the brain’s fear center) while looking at pictures of angry faces.
This could be helpful. “If you perceive a person’s natural expression as being a little bit angry, if that disappears, then you might be more inclined to interact,” de Wit says.
However, there may be downsides, too. If a drug makes people more trusting and willing to connect, they could be taken advantage of. This is why, Dr. Woolley says, “psychedelics have been used in cults.”
MDMA may also make the experience of touch more pleasant. In a series of experiments in 2019, researchers gently stroked volunteers ’ arms with a goat-hair brush, mimicking the comforting gestures one may receive from a loved one. At the same time, the scientists monitored the volunteers’ facial muscles. People on MDMA perceived gentle touch as more pleasant than those on placebo, and their smile muscles activated more.
MDMA and psychedelics boost social behaviors in animals, too — suggesting that their effects on relationships have a biological basis. Rats on MDMA are more likely to lie next to each other, and mice become more resilient to social stress. Even octopuses become more outgoing after a dose of MDMA, choosing to spend more time with other octopuses instead of a new toy. Classic psychedelics show similar effects — LSD, for example, makes mice more social.
Psychedelics can induce a sense of a “dissolution of the self-other boundary,” Dr. Woolley says. People who take them often say it’s “helped them feel more connected to themselves and other people.” LSD, first synthesized in 1938, may help increase empathy in some people.
Psilocybin, a compound found in over 200 species of mushrooms and used for centuries in Mesoamerican rituals, also seems to boost empathy, with effects persisting for at least seven days. In Cyberball, the online ball-throwing game, people who took psilocybin felt less socially rejected, an outcome reflected in their brain activation patterns in one study — the areas responsible for social-pain processing appeared to dim after a dose.
Making It Legal and Putting It to Use
In 2020, Oregon became the first state to establish a regulatory framework for psilocybin for therapeutic use, and Colorado followed suit in 2022. Such therapeutic applications of psilocybin could help fight loneliness as well, Dr. Woolley believes, because a “ common symptom of depression is that people feel socially withdrawn and lack motivation, ” he says. As mentioned above, MDMA-assisted therapy is also nearing FDA approval for PTSD.
What remain unclear are the exact mechanisms at play.
“MDMA releases oxytocin, and it does that through serotonin receptors,” Dr. de Wit says. Serotonin activates 5-HT1A receptors in the hypothalamus, releasing oxytocin into the bloodstream. In Dr. de Wit’s recent experiments, the more people felt connected after taking MDMA, the more oxytocin was found circulating in their bodies. (Another drug, methamphetamine, also upped the levels of oxytocin but did not increase feelings of connectedness.)
“It’s likely that both something in the serotonin system independent of oxytocin, and oxytocin itself, contribute,” Dr. de Wit says. Dopamine, a neurotransmitter responsible for motivation, appears to increase as well.
The empathy-boosting effects of LSD also seem to be at least partly driven by oxytocin, experiments published in 2021 revealed. Studies in mice, meanwhile, suggest that glutamate, a chemical messenger in the brain, may be behind some of LSD’s prosocial effects.
Scientists are fairly certain which receptors these drugs bind to and which neurotransmitters they affect. “How that gets translated into these higher-order things like empathy and feeling connected to the world, we don’t totally understand,” Dr. Woolley says.
Challenges and the Future
Although MDMA and psychedelics are largely considered safe when taken in a legal, medically controlled setting, there is reason to be cautious.
“They have relatively low impact on the body, like heart rate increase or blood pressure increase. But they might leave some disturbing psychological effects,” says Dr. Holze. Scientists routinely screen experiment volunteers for their risk for psychiatric disorders.
Although risk for addiction is low with both MDMA and psychedelics, there is always some risk for misuse. MDMA “ can produce feelings of well-being, and then people might use it repeatedly, ” Dr. de Wit says. “ That doesn ’ t seem to be a problem for really a lot of people, but it could easily happen. ”
Still, possibilities remain for MDMA in the fight against loneliness.
“[People] feel open, they feel like things are possible, they feel like they’re unstuck,” Dr. Woolley says. “You can harness that in psychotherapy.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Some call the drug “ecstasy” or “molly.” Researchers are calling it a potential tool to help treat loneliness.
As public health experts sound the alarm on a rising loneliness epidemic in the United States and across the globe,
In the latest study, MDMA “led to a robust increase in feelings of connection” among people socializing in a controlled setting. Participants were dosed with either MDMA or a placebo and asked to chat with a stranger. Afterward, those who took MDMA said their companion was more responsive and attentive, and that they had plenty in common. The drug also “increased participants’ ratings of liking their partners, feeling connected and finding the conversation enjoyable and meaningful.”
The study was small — just 18 participants — but its results “have implications for MDMA-assisted therapy,” the authors wrote. “This feeling of connectedness could help patients feel safe and trusting, thereby facilitating deeper emotional exploration.”
MDMA “really does seem to make people want to interact more with other people,” says Harriet de Wit, PhD, a neuropharmacologist at the University of Chicago and one of the study’s authors. The results echo those of earlier research using psychedelics like LSD or psilocybin.
It’s important to note that any intervention involving MDMA or psychedelics would be a drug-assisted therapy — that is, used in conjunction with the appropriate therapy and in a therapeutic setting. MDMA-assisted therapy has already drawn popular and scientific attention, as it recently cleared clinical trials for treating posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and may be nearing approval by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
According to Friederike Holze, PhD, psychopharmacologist at the University of Basel, in Switzerland, “there could be a place” for MDMA and psychedelics in treating chronic loneliness, but only under professional supervision.
There would have to be clear guidelines too, says Joshua Woolley, MD, PhD, a psychiatrist at the University of California, San Francisco.
MDMA and psychedelics “induce this plastic state, a state where people can change. They feel open, they feel like things are possible,” Dr. Woolley says. Then, with therapy, “you can help them change.”
Loneliness Can Impact Our Health
On top of the mental health ramifications, the physiologic effects of loneliness could have grave consequences over time. In observational studies, loneliness has been linked to higher risks for cancer and heart disease, and shorter lifespan. One third of Americans over 45 say they are chronically lonely.
Chronic loneliness changes how we think and behave, research shows. It makes us fear contact with others and see them in a more negative light, as more threatening and less trustworthy. Lonely people prefer to stand farther apart from strangers and avoid touch.
This is where MDMA-assisted therapies could potentially help, by easing these defensive tendencies, according to Dr. Woolley.
MDMA, Psychedelics, and Social Behavior
MDMA, or 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine, is a hybrid between a stimulant and a psychedelic. In Dr. de Wit’s earlier experiments, volunteers given MDMA engaged more in communal activities, chatting, and playing games. They used more positive words during social encounters than those who had received a placebo. And after MDMA, people felt less rejected if they were slighted in Cyberball — a virtual ball-tossing game commonly used to measure the effects of social exclusion.
MDMA has been shown to reduce people’s response to other’s negative emotions, diminishing activation of the amygdala (the brain’s fear center) while looking at pictures of angry faces.
This could be helpful. “If you perceive a person’s natural expression as being a little bit angry, if that disappears, then you might be more inclined to interact,” de Wit says.
However, there may be downsides, too. If a drug makes people more trusting and willing to connect, they could be taken advantage of. This is why, Dr. Woolley says, “psychedelics have been used in cults.”
MDMA may also make the experience of touch more pleasant. In a series of experiments in 2019, researchers gently stroked volunteers ’ arms with a goat-hair brush, mimicking the comforting gestures one may receive from a loved one. At the same time, the scientists monitored the volunteers’ facial muscles. People on MDMA perceived gentle touch as more pleasant than those on placebo, and their smile muscles activated more.
MDMA and psychedelics boost social behaviors in animals, too — suggesting that their effects on relationships have a biological basis. Rats on MDMA are more likely to lie next to each other, and mice become more resilient to social stress. Even octopuses become more outgoing after a dose of MDMA, choosing to spend more time with other octopuses instead of a new toy. Classic psychedelics show similar effects — LSD, for example, makes mice more social.
Psychedelics can induce a sense of a “dissolution of the self-other boundary,” Dr. Woolley says. People who take them often say it’s “helped them feel more connected to themselves and other people.” LSD, first synthesized in 1938, may help increase empathy in some people.
Psilocybin, a compound found in over 200 species of mushrooms and used for centuries in Mesoamerican rituals, also seems to boost empathy, with effects persisting for at least seven days. In Cyberball, the online ball-throwing game, people who took psilocybin felt less socially rejected, an outcome reflected in their brain activation patterns in one study — the areas responsible for social-pain processing appeared to dim after a dose.
Making It Legal and Putting It to Use
In 2020, Oregon became the first state to establish a regulatory framework for psilocybin for therapeutic use, and Colorado followed suit in 2022. Such therapeutic applications of psilocybin could help fight loneliness as well, Dr. Woolley believes, because a “ common symptom of depression is that people feel socially withdrawn and lack motivation, ” he says. As mentioned above, MDMA-assisted therapy is also nearing FDA approval for PTSD.
What remain unclear are the exact mechanisms at play.
“MDMA releases oxytocin, and it does that through serotonin receptors,” Dr. de Wit says. Serotonin activates 5-HT1A receptors in the hypothalamus, releasing oxytocin into the bloodstream. In Dr. de Wit’s recent experiments, the more people felt connected after taking MDMA, the more oxytocin was found circulating in their bodies. (Another drug, methamphetamine, also upped the levels of oxytocin but did not increase feelings of connectedness.)
“It’s likely that both something in the serotonin system independent of oxytocin, and oxytocin itself, contribute,” Dr. de Wit says. Dopamine, a neurotransmitter responsible for motivation, appears to increase as well.
The empathy-boosting effects of LSD also seem to be at least partly driven by oxytocin, experiments published in 2021 revealed. Studies in mice, meanwhile, suggest that glutamate, a chemical messenger in the brain, may be behind some of LSD’s prosocial effects.
Scientists are fairly certain which receptors these drugs bind to and which neurotransmitters they affect. “How that gets translated into these higher-order things like empathy and feeling connected to the world, we don’t totally understand,” Dr. Woolley says.
Challenges and the Future
Although MDMA and psychedelics are largely considered safe when taken in a legal, medically controlled setting, there is reason to be cautious.
“They have relatively low impact on the body, like heart rate increase or blood pressure increase. But they might leave some disturbing psychological effects,” says Dr. Holze. Scientists routinely screen experiment volunteers for their risk for psychiatric disorders.
Although risk for addiction is low with both MDMA and psychedelics, there is always some risk for misuse. MDMA “ can produce feelings of well-being, and then people might use it repeatedly, ” Dr. de Wit says. “ That doesn ’ t seem to be a problem for really a lot of people, but it could easily happen. ”
Still, possibilities remain for MDMA in the fight against loneliness.
“[People] feel open, they feel like things are possible, they feel like they’re unstuck,” Dr. Woolley says. “You can harness that in psychotherapy.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Mass shooters and mental illness: Reexamining the connection
Our psychiatric research, which found a high incidence of undiagnosed mental illness in mass shooters, was recently awarded the esteemed Psychodynamic Psychiatry Journal Prize for best paper published in the last 2 years (2022-2023). The editors noted our integrity in using quantitative data to argue against the common, careless assumption that mass shooters are not mentally ill.
Some of the mass shooters we studied were motivated by religious or political ideologies that were considered forms of terrorism. Given the current tragically violent landscape both at home and in Israel/Palestine, the “desire for destruction” is vital to understand.
Although there have been a limited number of psychiatric studies of perpetrators of mass shootings, our team took the first step to lay the groundwork by conducting a systematic, quantitative study. Our psychiatric research team’s research findings were published in the Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology and then in greater detail in Psychodynamic Psychiatry,1,2 which provided important context to the complicated backgrounds of these mass shooters who suffer from abuse, marginalization, and severe undiagnosed brain illness.3
The Mother Jones database of 115 mass shootings from 1982 to 2019 was used to study retrospectively 55 shooters in the United States. We developed a uniform, comprehensive, 62-item questionnaire to compile the data collection from multiple sources and record our psychiatric assessments of the assailants, using DSM-5 criteria. After developing this detailed psychiatric assessment questionnaire, psychiatric researchers evaluated the weight and quality of clinical evidence by (1) interviewing forensic psychiatrists who had assessed the assailant following the crime, and/or (2) reviewing court records of psychiatric evaluations conducted during the postcrime judicial proceedings to determine the prevalence of psychiatric illness. Rather than accepting diagnoses from forensic psychiatrists and/or court records, our team independently reviewed the clinical data gathered from multiple sources to apply the DSM-5 criteria to diagnose mental illness.
In most incidents in the database, the perpetrator died either during or shortly after the crime. We examined every case (n=35) in which the assailant survived, and criminal proceedings were instituted.
Of the 35 cases in which the assailant survived and criminal proceedings were instituted, there was insufficient information to make a diagnosis in 3 cases. Of the remaining 32 cases in which we had sufficient information, we determined that 87.5% had the following psychiatric diagnosis: 18 assailants (56%) had schizophrenia, while 10 assailants (31%) had other psychiatric diagnoses: 3 had bipolar I disorder, 2 had delusional disorders (persecutory), 2 had personality disorders (1 paranoid, 1 borderline), 2 had substance-related disorders without other psychiatric diagnosis, and 1 had post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Out of the 32 surviving assailants for whom we have sufficient evidence, 87.5% of perpetrators of mass shootings were diagnosed with major psychiatric illness, and none were treated appropriately with medication at the time of the crime. Four assailants (12.5%) had no psychiatric diagnosis that we could discern. Of the 18 surviving assailants with schizophrenia, no assailant was on antipsychotic medication for the treatment of schizophrenia prior to the crime. Of the 10 surviving assailants with other psychiatric illnesses, no assailant was on antipsychotic and/or appropriate medication.
In addition, we found that the clinical misdiagnosis of early-onset schizophrenia was associated with the worsening of many of these assailants’ psychotic symptoms. Many of our adolescent shooters prior to the massacre had been misdiagnosed with attention-deficit disorder (ADD), major depression disorder (MDD), or autism spectrum disorder.
Though the vast majority of those suffering from psychiatric illnesses who are appropriately treated are not violent, .4,5,6 This research demonstrates that such untreated illness combined with access to firearms poses a lethal threat to society.
Most of the assailants also experienced profound estrangement, not only from families and friends, but most importantly from themselves. Being marginalized rendered them more vulnerable to their untreated psychiatric illness and to radicalization online, which fostered their violence. While there are complex reasons that a person is not diagnosed, there remains a vital need to decrease the stigma of mental illness to enable those with psychiatric illness to be more respected, less marginalized, and encouraged to receive effective psychiatric treatments.
Dr. Cerfolio is author of “Psychoanalytic and Spiritual Perspectives on Terrorism: Desire for Destruction.” She is clinical assistant professor at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Dr. Glick is Professor Emeritus, Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences at Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, Calif.
References
1. Glick ID, et al. Domestic Mass Shooters: The Association With Unmedicated and Untreated Psychiatric Illness. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2021 Jul-Aug;41(4):366-369. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0000000000001417.
2. Cerfolio NE, et al. A Retrospective Observational Study of Psychosocial Determinants and Psychiatric Diagnoses of Mass Shooters in the United States. Psychodyn Psychiatry. 2022 Fall;50(3):1-16. doi: 10.1521/pdps.2022.50.5.001.
3. Cerfolio NE. The Parkland gunman, a horrific crime, and mental illness. The New York Times. 2022 Oct 14. www.nytimes.com/2022/10/14/opinion/letters/jan-6-panel-trump.html#link-5e2ccc1.
4. Corner E, et al. Mental Health Disorders and the Terrorist: A Research Note Probing Selection Effects and Disorder Prevalence. Stud Confl Terror. 2016 Jan;39(6):560–568. doi: 10.1080/1057610X.2015.1120099.
5. Gruenewald J, et al. Distinguishing “Loner” Attacks from Other Domestic Extremist Violence. Criminol Public Policy. 2013 Feb;12(1):65–91. doi: 10.1111/1745-9133.12008.
6. Lankford A. Detecting mental health problems and suicidal motives among terrorists and mass shooters. Crim Behav Ment Health. 2016 Dec;26(5):315-321. doi: 10.1002/cbm.2020.
Our psychiatric research, which found a high incidence of undiagnosed mental illness in mass shooters, was recently awarded the esteemed Psychodynamic Psychiatry Journal Prize for best paper published in the last 2 years (2022-2023). The editors noted our integrity in using quantitative data to argue against the common, careless assumption that mass shooters are not mentally ill.
Some of the mass shooters we studied were motivated by religious or political ideologies that were considered forms of terrorism. Given the current tragically violent landscape both at home and in Israel/Palestine, the “desire for destruction” is vital to understand.
Although there have been a limited number of psychiatric studies of perpetrators of mass shootings, our team took the first step to lay the groundwork by conducting a systematic, quantitative study. Our psychiatric research team’s research findings were published in the Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology and then in greater detail in Psychodynamic Psychiatry,1,2 which provided important context to the complicated backgrounds of these mass shooters who suffer from abuse, marginalization, and severe undiagnosed brain illness.3
The Mother Jones database of 115 mass shootings from 1982 to 2019 was used to study retrospectively 55 shooters in the United States. We developed a uniform, comprehensive, 62-item questionnaire to compile the data collection from multiple sources and record our psychiatric assessments of the assailants, using DSM-5 criteria. After developing this detailed psychiatric assessment questionnaire, psychiatric researchers evaluated the weight and quality of clinical evidence by (1) interviewing forensic psychiatrists who had assessed the assailant following the crime, and/or (2) reviewing court records of psychiatric evaluations conducted during the postcrime judicial proceedings to determine the prevalence of psychiatric illness. Rather than accepting diagnoses from forensic psychiatrists and/or court records, our team independently reviewed the clinical data gathered from multiple sources to apply the DSM-5 criteria to diagnose mental illness.
In most incidents in the database, the perpetrator died either during or shortly after the crime. We examined every case (n=35) in which the assailant survived, and criminal proceedings were instituted.
Of the 35 cases in which the assailant survived and criminal proceedings were instituted, there was insufficient information to make a diagnosis in 3 cases. Of the remaining 32 cases in which we had sufficient information, we determined that 87.5% had the following psychiatric diagnosis: 18 assailants (56%) had schizophrenia, while 10 assailants (31%) had other psychiatric diagnoses: 3 had bipolar I disorder, 2 had delusional disorders (persecutory), 2 had personality disorders (1 paranoid, 1 borderline), 2 had substance-related disorders without other psychiatric diagnosis, and 1 had post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Out of the 32 surviving assailants for whom we have sufficient evidence, 87.5% of perpetrators of mass shootings were diagnosed with major psychiatric illness, and none were treated appropriately with medication at the time of the crime. Four assailants (12.5%) had no psychiatric diagnosis that we could discern. Of the 18 surviving assailants with schizophrenia, no assailant was on antipsychotic medication for the treatment of schizophrenia prior to the crime. Of the 10 surviving assailants with other psychiatric illnesses, no assailant was on antipsychotic and/or appropriate medication.
In addition, we found that the clinical misdiagnosis of early-onset schizophrenia was associated with the worsening of many of these assailants’ psychotic symptoms. Many of our adolescent shooters prior to the massacre had been misdiagnosed with attention-deficit disorder (ADD), major depression disorder (MDD), or autism spectrum disorder.
Though the vast majority of those suffering from psychiatric illnesses who are appropriately treated are not violent, .4,5,6 This research demonstrates that such untreated illness combined with access to firearms poses a lethal threat to society.
Most of the assailants also experienced profound estrangement, not only from families and friends, but most importantly from themselves. Being marginalized rendered them more vulnerable to their untreated psychiatric illness and to radicalization online, which fostered their violence. While there are complex reasons that a person is not diagnosed, there remains a vital need to decrease the stigma of mental illness to enable those with psychiatric illness to be more respected, less marginalized, and encouraged to receive effective psychiatric treatments.
Dr. Cerfolio is author of “Psychoanalytic and Spiritual Perspectives on Terrorism: Desire for Destruction.” She is clinical assistant professor at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Dr. Glick is Professor Emeritus, Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences at Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, Calif.
References
1. Glick ID, et al. Domestic Mass Shooters: The Association With Unmedicated and Untreated Psychiatric Illness. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2021 Jul-Aug;41(4):366-369. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0000000000001417.
2. Cerfolio NE, et al. A Retrospective Observational Study of Psychosocial Determinants and Psychiatric Diagnoses of Mass Shooters in the United States. Psychodyn Psychiatry. 2022 Fall;50(3):1-16. doi: 10.1521/pdps.2022.50.5.001.
3. Cerfolio NE. The Parkland gunman, a horrific crime, and mental illness. The New York Times. 2022 Oct 14. www.nytimes.com/2022/10/14/opinion/letters/jan-6-panel-trump.html#link-5e2ccc1.
4. Corner E, et al. Mental Health Disorders and the Terrorist: A Research Note Probing Selection Effects and Disorder Prevalence. Stud Confl Terror. 2016 Jan;39(6):560–568. doi: 10.1080/1057610X.2015.1120099.
5. Gruenewald J, et al. Distinguishing “Loner” Attacks from Other Domestic Extremist Violence. Criminol Public Policy. 2013 Feb;12(1):65–91. doi: 10.1111/1745-9133.12008.
6. Lankford A. Detecting mental health problems and suicidal motives among terrorists and mass shooters. Crim Behav Ment Health. 2016 Dec;26(5):315-321. doi: 10.1002/cbm.2020.
Our psychiatric research, which found a high incidence of undiagnosed mental illness in mass shooters, was recently awarded the esteemed Psychodynamic Psychiatry Journal Prize for best paper published in the last 2 years (2022-2023). The editors noted our integrity in using quantitative data to argue against the common, careless assumption that mass shooters are not mentally ill.
Some of the mass shooters we studied were motivated by religious or political ideologies that were considered forms of terrorism. Given the current tragically violent landscape both at home and in Israel/Palestine, the “desire for destruction” is vital to understand.
Although there have been a limited number of psychiatric studies of perpetrators of mass shootings, our team took the first step to lay the groundwork by conducting a systematic, quantitative study. Our psychiatric research team’s research findings were published in the Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology and then in greater detail in Psychodynamic Psychiatry,1,2 which provided important context to the complicated backgrounds of these mass shooters who suffer from abuse, marginalization, and severe undiagnosed brain illness.3
The Mother Jones database of 115 mass shootings from 1982 to 2019 was used to study retrospectively 55 shooters in the United States. We developed a uniform, comprehensive, 62-item questionnaire to compile the data collection from multiple sources and record our psychiatric assessments of the assailants, using DSM-5 criteria. After developing this detailed psychiatric assessment questionnaire, psychiatric researchers evaluated the weight and quality of clinical evidence by (1) interviewing forensic psychiatrists who had assessed the assailant following the crime, and/or (2) reviewing court records of psychiatric evaluations conducted during the postcrime judicial proceedings to determine the prevalence of psychiatric illness. Rather than accepting diagnoses from forensic psychiatrists and/or court records, our team independently reviewed the clinical data gathered from multiple sources to apply the DSM-5 criteria to diagnose mental illness.
In most incidents in the database, the perpetrator died either during or shortly after the crime. We examined every case (n=35) in which the assailant survived, and criminal proceedings were instituted.
Of the 35 cases in which the assailant survived and criminal proceedings were instituted, there was insufficient information to make a diagnosis in 3 cases. Of the remaining 32 cases in which we had sufficient information, we determined that 87.5% had the following psychiatric diagnosis: 18 assailants (56%) had schizophrenia, while 10 assailants (31%) had other psychiatric diagnoses: 3 had bipolar I disorder, 2 had delusional disorders (persecutory), 2 had personality disorders (1 paranoid, 1 borderline), 2 had substance-related disorders without other psychiatric diagnosis, and 1 had post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Out of the 32 surviving assailants for whom we have sufficient evidence, 87.5% of perpetrators of mass shootings were diagnosed with major psychiatric illness, and none were treated appropriately with medication at the time of the crime. Four assailants (12.5%) had no psychiatric diagnosis that we could discern. Of the 18 surviving assailants with schizophrenia, no assailant was on antipsychotic medication for the treatment of schizophrenia prior to the crime. Of the 10 surviving assailants with other psychiatric illnesses, no assailant was on antipsychotic and/or appropriate medication.
In addition, we found that the clinical misdiagnosis of early-onset schizophrenia was associated with the worsening of many of these assailants’ psychotic symptoms. Many of our adolescent shooters prior to the massacre had been misdiagnosed with attention-deficit disorder (ADD), major depression disorder (MDD), or autism spectrum disorder.
Though the vast majority of those suffering from psychiatric illnesses who are appropriately treated are not violent, .4,5,6 This research demonstrates that such untreated illness combined with access to firearms poses a lethal threat to society.
Most of the assailants also experienced profound estrangement, not only from families and friends, but most importantly from themselves. Being marginalized rendered them more vulnerable to their untreated psychiatric illness and to radicalization online, which fostered their violence. While there are complex reasons that a person is not diagnosed, there remains a vital need to decrease the stigma of mental illness to enable those with psychiatric illness to be more respected, less marginalized, and encouraged to receive effective psychiatric treatments.
Dr. Cerfolio is author of “Psychoanalytic and Spiritual Perspectives on Terrorism: Desire for Destruction.” She is clinical assistant professor at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Dr. Glick is Professor Emeritus, Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences at Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, Calif.
References
1. Glick ID, et al. Domestic Mass Shooters: The Association With Unmedicated and Untreated Psychiatric Illness. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2021 Jul-Aug;41(4):366-369. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0000000000001417.
2. Cerfolio NE, et al. A Retrospective Observational Study of Psychosocial Determinants and Psychiatric Diagnoses of Mass Shooters in the United States. Psychodyn Psychiatry. 2022 Fall;50(3):1-16. doi: 10.1521/pdps.2022.50.5.001.
3. Cerfolio NE. The Parkland gunman, a horrific crime, and mental illness. The New York Times. 2022 Oct 14. www.nytimes.com/2022/10/14/opinion/letters/jan-6-panel-trump.html#link-5e2ccc1.
4. Corner E, et al. Mental Health Disorders and the Terrorist: A Research Note Probing Selection Effects and Disorder Prevalence. Stud Confl Terror. 2016 Jan;39(6):560–568. doi: 10.1080/1057610X.2015.1120099.
5. Gruenewald J, et al. Distinguishing “Loner” Attacks from Other Domestic Extremist Violence. Criminol Public Policy. 2013 Feb;12(1):65–91. doi: 10.1111/1745-9133.12008.
6. Lankford A. Detecting mental health problems and suicidal motives among terrorists and mass shooters. Crim Behav Ment Health. 2016 Dec;26(5):315-321. doi: 10.1002/cbm.2020.
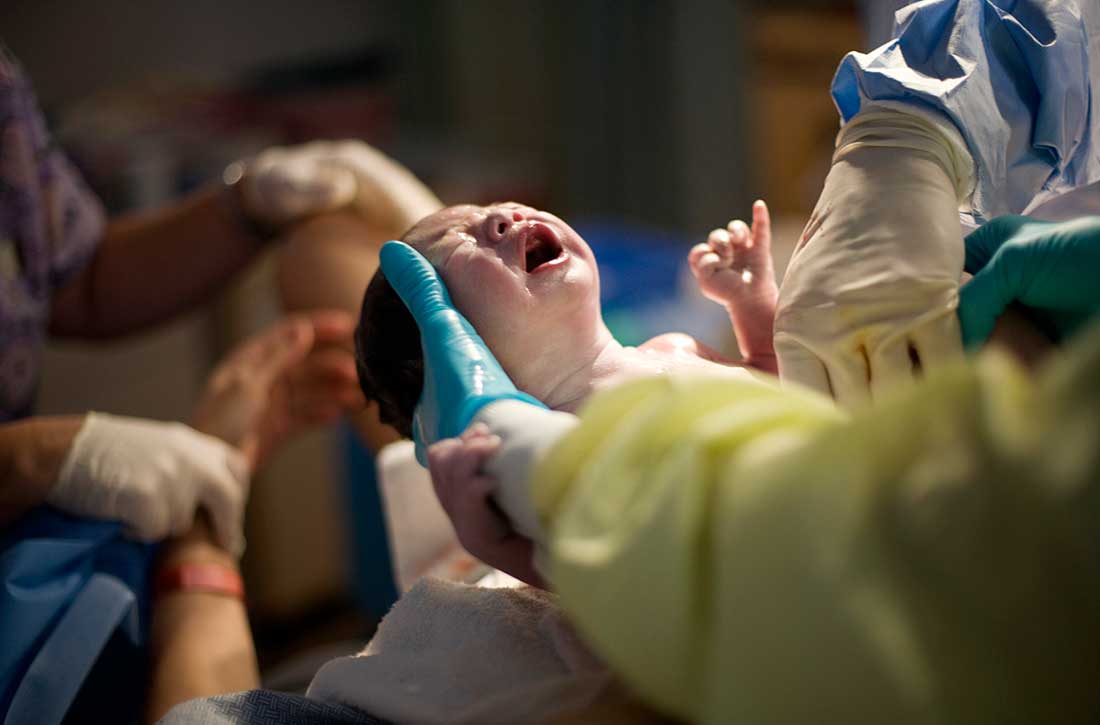
Childbirth-related PTSD: How it differs and who’s at risk
Childbirth-related posttraumatic stress disorder (CB-PTSD) is a form of PTSD that can develop related to trauma surrounding the events of giving birth. It affects approximately 5% of women after any birth, which is similar to the rate of PTSD after experiencing a natural disaster.1 Up to 17% of women may have posttraumatic symptoms in the postpartum period.1 Despite the high prevalence of CB-PTSD, many psychiatric clinicians have not incorporated screening for and management of CB-PTSD into their practice.
This is partly because childbirth has been conceptualized as a “stressful but positive life event.”2 Historically, childbirth was not recognized as a traumatic event; for example, in DSM-III-R, the criteria for trauma in PTSD required an event outside the range of usual human experience, and childbirth was implicitly excluded as being too common to be traumatic. In the past decade, this clinical phenomenon has been more formally recognized and studied.2

CB-PTSD presents with symptoms similar to those of other forms of PTSD, with some nuances, as outlined in Table 1.3 Avoidance can be the predominant symptom; this can affect mothers’ engagement in postnatal care and is a major risk factor for postpartum depression.3
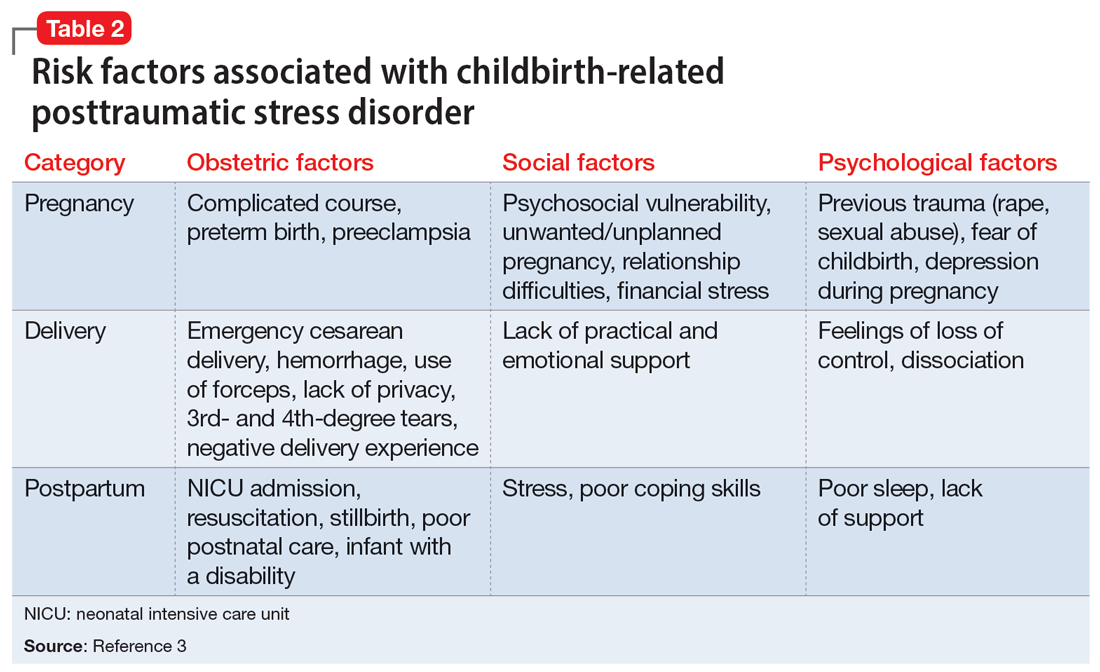
Many risk factors in the peripartum period can impact the development of CB-PTSD (Table 23). The most significant risk factor is whether the patient views the delivery of their baby as a subjectively negative experience, regardless of the presence or lack of peripartum complications.1 However, parents of infants who require treatment in a neonatal intensive care unit and women who require emergency medical treatment following delivery are at higher risk.
Screening and treatment
Ideally, every woman should be screened for CB-PTSD by their psychiatrist or obstetrician during a postpartum visit at least 1 month after delivery. In particular, high-risk populations and women with subjectively negative birth experiences should be screened, as well as women with postpartum depression that may have been precipitated or perpetuated by a traumatic experience. The City Birth Trauma Scale is a free 31-item self-report scale that can be used for such screening. It addresses both general and birth-related symptoms and is validated in multiple languages.4
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and prazosin may be helpful for symptomatic treatment of CB-PTSD. Ongoing research studying the efficacy of cognitive-behavioral therapy and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing for CB-PTSD has yielded promising results but is limited in its generalizability.
Many women who develop CB-PTSD choose to get pregnant again. Psychiatrists can apply the principles of trauma-informed care and collaborate with obstetric and pediatric physicians to reduce the risk of retraumatization. It is critical to identify at-risk women and educate and prepare them for their next delivery experience. By focusing on communication, informed consent, and emotional support, we can do our best to prevent the recurrence of CB-PTSD.
1. Dekel S, Stuebe C, Dishy G. Childbirth induced posttraumatic stress syndrome: a systematic review of prevalence and risk factors. Front Psych. 2017;8:560. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00560
2. Horesh D, Garthus-Niegel S, Horsch A. Childbirth-related PTSD: is it a unique post-traumatic disorder? J Reprod Infant Psych. 2021;39(3):221-224. doi:10.1080/02646838.2021.1930739
3. Kranenburg L, Lambregtse-van den Berg M, Stramrood C. Traumatic childbirth experience and childbirth-related post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): a contemporary overview. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(4):2775. doi:10.3390/ijerph20042775
4. Ayers S, Wright DB, Thornton A. Development of a measure of postpartum PTSD: The City Birth Trauma Scale. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9:409. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00409
Childbirth-related posttraumatic stress disorder (CB-PTSD) is a form of PTSD that can develop related to trauma surrounding the events of giving birth. It affects approximately 5% of women after any birth, which is similar to the rate of PTSD after experiencing a natural disaster.1 Up to 17% of women may have posttraumatic symptoms in the postpartum period.1 Despite the high prevalence of CB-PTSD, many psychiatric clinicians have not incorporated screening for and management of CB-PTSD into their practice.
This is partly because childbirth has been conceptualized as a “stressful but positive life event.”2 Historically, childbirth was not recognized as a traumatic event; for example, in DSM-III-R, the criteria for trauma in PTSD required an event outside the range of usual human experience, and childbirth was implicitly excluded as being too common to be traumatic. In the past decade, this clinical phenomenon has been more formally recognized and studied.2

CB-PTSD presents with symptoms similar to those of other forms of PTSD, with some nuances, as outlined in Table 1.3 Avoidance can be the predominant symptom; this can affect mothers’ engagement in postnatal care and is a major risk factor for postpartum depression.3
Many risk factors in the peripartum period can impact the development of CB-PTSD (Table 23). The most significant risk factor is whether the patient views the delivery of their baby as a subjectively negative experience, regardless of the presence or lack of peripartum complications.1 However, parents of infants who require treatment in a neonatal intensive care unit and women who require emergency medical treatment following delivery are at higher risk.

Screening and treatment
Ideally, every woman should be screened for CB-PTSD by their psychiatrist or obstetrician during a postpartum visit at least 1 month after delivery. In particular, high-risk populations and women with subjectively negative birth experiences should be screened, as well as women with postpartum depression that may have been precipitated or perpetuated by a traumatic experience. The City Birth Trauma Scale is a free 31-item self-report scale that can be used for such screening. It addresses both general and birth-related symptoms and is validated in multiple languages.4
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and prazosin may be helpful for symptomatic treatment of CB-PTSD. Ongoing research studying the efficacy of cognitive-behavioral therapy and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing for CB-PTSD has yielded promising results but is limited in its generalizability.
Many women who develop CB-PTSD choose to get pregnant again. Psychiatrists can apply the principles of trauma-informed care and collaborate with obstetric and pediatric physicians to reduce the risk of retraumatization. It is critical to identify at-risk women and educate and prepare them for their next delivery experience. By focusing on communication, informed consent, and emotional support, we can do our best to prevent the recurrence of CB-PTSD.
Childbirth-related posttraumatic stress disorder (CB-PTSD) is a form of PTSD that can develop related to trauma surrounding the events of giving birth. It affects approximately 5% of women after any birth, which is similar to the rate of PTSD after experiencing a natural disaster.1 Up to 17% of women may have posttraumatic symptoms in the postpartum period.1 Despite the high prevalence of CB-PTSD, many psychiatric clinicians have not incorporated screening for and management of CB-PTSD into their practice.
This is partly because childbirth has been conceptualized as a “stressful but positive life event.”2 Historically, childbirth was not recognized as a traumatic event; for example, in DSM-III-R, the criteria for trauma in PTSD required an event outside the range of usual human experience, and childbirth was implicitly excluded as being too common to be traumatic. In the past decade, this clinical phenomenon has been more formally recognized and studied.2

CB-PTSD presents with symptoms similar to those of other forms of PTSD, with some nuances, as outlined in Table 1.3 Avoidance can be the predominant symptom; this can affect mothers’ engagement in postnatal care and is a major risk factor for postpartum depression.3
Many risk factors in the peripartum period can impact the development of CB-PTSD (Table 23). The most significant risk factor is whether the patient views the delivery of their baby as a subjectively negative experience, regardless of the presence or lack of peripartum complications.1 However, parents of infants who require treatment in a neonatal intensive care unit and women who require emergency medical treatment following delivery are at higher risk.

Screening and treatment
Ideally, every woman should be screened for CB-PTSD by their psychiatrist or obstetrician during a postpartum visit at least 1 month after delivery. In particular, high-risk populations and women with subjectively negative birth experiences should be screened, as well as women with postpartum depression that may have been precipitated or perpetuated by a traumatic experience. The City Birth Trauma Scale is a free 31-item self-report scale that can be used for such screening. It addresses both general and birth-related symptoms and is validated in multiple languages.4
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and prazosin may be helpful for symptomatic treatment of CB-PTSD. Ongoing research studying the efficacy of cognitive-behavioral therapy and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing for CB-PTSD has yielded promising results but is limited in its generalizability.
Many women who develop CB-PTSD choose to get pregnant again. Psychiatrists can apply the principles of trauma-informed care and collaborate with obstetric and pediatric physicians to reduce the risk of retraumatization. It is critical to identify at-risk women and educate and prepare them for their next delivery experience. By focusing on communication, informed consent, and emotional support, we can do our best to prevent the recurrence of CB-PTSD.
1. Dekel S, Stuebe C, Dishy G. Childbirth induced posttraumatic stress syndrome: a systematic review of prevalence and risk factors. Front Psych. 2017;8:560. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00560
2. Horesh D, Garthus-Niegel S, Horsch A. Childbirth-related PTSD: is it a unique post-traumatic disorder? J Reprod Infant Psych. 2021;39(3):221-224. doi:10.1080/02646838.2021.1930739
3. Kranenburg L, Lambregtse-van den Berg M, Stramrood C. Traumatic childbirth experience and childbirth-related post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): a contemporary overview. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(4):2775. doi:10.3390/ijerph20042775
4. Ayers S, Wright DB, Thornton A. Development of a measure of postpartum PTSD: The City Birth Trauma Scale. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9:409. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00409
1. Dekel S, Stuebe C, Dishy G. Childbirth induced posttraumatic stress syndrome: a systematic review of prevalence and risk factors. Front Psych. 2017;8:560. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00560
2. Horesh D, Garthus-Niegel S, Horsch A. Childbirth-related PTSD: is it a unique post-traumatic disorder? J Reprod Infant Psych. 2021;39(3):221-224. doi:10.1080/02646838.2021.1930739
3. Kranenburg L, Lambregtse-van den Berg M, Stramrood C. Traumatic childbirth experience and childbirth-related post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): a contemporary overview. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(4):2775. doi:10.3390/ijerph20042775
4. Ayers S, Wright DB, Thornton A. Development of a measure of postpartum PTSD: The City Birth Trauma Scale. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9:409. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00409
PTSD symptoms in women tied to worse heart, brain health
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a cross-sectional study of 274 women (mean age, 59 years) participating in the MsBrain study of menopause and brain health.
- As part of the study, the women completed the PTSD Checklist–Civilian Version and underwent physical and neuropsychological testing, as well as carotid artery ultrasonography and brain MRI.
- Outcomes of interest were associations of PTSD symptoms with carotid intima media thickness (IMT), brain white matter hyperintensity volume (WMHV), and cognition, assessed in linear regression models.
- Interactions by APOEε4 were assessed; covariates included age, race/ethnicity, education, and CVD risk factors.
TAKEAWAY:
- Higher PTSD symptoms were associated with greater carotid IMT (P = .03); associations of PTSD symptoms with neurocognitive outcomes varied significantly by APOEε4 status.
- Among APOEε4 carriers, PTSD symptoms were associated with greater whole-brain WMHV (P = .009), periventricular WMHV (P = .02), deep WMHV (P = .01), and frontal WMHV (P = .04) in multivariable models.
- APOEε4 carriers with PTSD symptoms also had poorer cognition, specifically attention and working memory (P = .02), semantic fluency (P = .01), perceptual speed (P = .002) and processing speed (P = .002), in multivariable models.
IN PRACTICE:
“This study sheds important insight on the implications of PTSD symptoms to women’s cardiovascular and neurocognitive health. Our findings indicate that the APOEε4 genotype may identify a group of women with PTSD symptoms at particular risk for poor neurocognitive health,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Rebecca Thurston, PhD, of the department of psychiatry, University of Pittsburgh, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
No diagnostic clinical interviews were conducted, and PTSD treatment was not assessed. All participants identified as cisgender, and most were non-Hispanic Black or White. The study was observational and cross-sectional, precluding assertions about directionality or causality.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the University of Pittsburgh Clinical and Translational Science Institute, and the University of Pittsburgh Small Molecule Biomarker Core. Dr. Thurston reported receiving personal fees from Astellas Pharma, Bayer, Hello Therapeutics, Vira Health, and Happify Health outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a cross-sectional study of 274 women (mean age, 59 years) participating in the MsBrain study of menopause and brain health.
- As part of the study, the women completed the PTSD Checklist–Civilian Version and underwent physical and neuropsychological testing, as well as carotid artery ultrasonography and brain MRI.
- Outcomes of interest were associations of PTSD symptoms with carotid intima media thickness (IMT), brain white matter hyperintensity volume (WMHV), and cognition, assessed in linear regression models.
- Interactions by APOEε4 were assessed; covariates included age, race/ethnicity, education, and CVD risk factors.
TAKEAWAY:
- Higher PTSD symptoms were associated with greater carotid IMT (P = .03); associations of PTSD symptoms with neurocognitive outcomes varied significantly by APOEε4 status.
- Among APOEε4 carriers, PTSD symptoms were associated with greater whole-brain WMHV (P = .009), periventricular WMHV (P = .02), deep WMHV (P = .01), and frontal WMHV (P = .04) in multivariable models.
- APOEε4 carriers with PTSD symptoms also had poorer cognition, specifically attention and working memory (P = .02), semantic fluency (P = .01), perceptual speed (P = .002) and processing speed (P = .002), in multivariable models.
IN PRACTICE:
“This study sheds important insight on the implications of PTSD symptoms to women’s cardiovascular and neurocognitive health. Our findings indicate that the APOEε4 genotype may identify a group of women with PTSD symptoms at particular risk for poor neurocognitive health,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Rebecca Thurston, PhD, of the department of psychiatry, University of Pittsburgh, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
No diagnostic clinical interviews were conducted, and PTSD treatment was not assessed. All participants identified as cisgender, and most were non-Hispanic Black or White. The study was observational and cross-sectional, precluding assertions about directionality or causality.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the University of Pittsburgh Clinical and Translational Science Institute, and the University of Pittsburgh Small Molecule Biomarker Core. Dr. Thurston reported receiving personal fees from Astellas Pharma, Bayer, Hello Therapeutics, Vira Health, and Happify Health outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a cross-sectional study of 274 women (mean age, 59 years) participating in the MsBrain study of menopause and brain health.
- As part of the study, the women completed the PTSD Checklist–Civilian Version and underwent physical and neuropsychological testing, as well as carotid artery ultrasonography and brain MRI.
- Outcomes of interest were associations of PTSD symptoms with carotid intima media thickness (IMT), brain white matter hyperintensity volume (WMHV), and cognition, assessed in linear regression models.
- Interactions by APOEε4 were assessed; covariates included age, race/ethnicity, education, and CVD risk factors.
TAKEAWAY:
- Higher PTSD symptoms were associated with greater carotid IMT (P = .03); associations of PTSD symptoms with neurocognitive outcomes varied significantly by APOEε4 status.
- Among APOEε4 carriers, PTSD symptoms were associated with greater whole-brain WMHV (P = .009), periventricular WMHV (P = .02), deep WMHV (P = .01), and frontal WMHV (P = .04) in multivariable models.
- APOEε4 carriers with PTSD symptoms also had poorer cognition, specifically attention and working memory (P = .02), semantic fluency (P = .01), perceptual speed (P = .002) and processing speed (P = .002), in multivariable models.
IN PRACTICE:
“This study sheds important insight on the implications of PTSD symptoms to women’s cardiovascular and neurocognitive health. Our findings indicate that the APOEε4 genotype may identify a group of women with PTSD symptoms at particular risk for poor neurocognitive health,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Rebecca Thurston, PhD, of the department of psychiatry, University of Pittsburgh, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
No diagnostic clinical interviews were conducted, and PTSD treatment was not assessed. All participants identified as cisgender, and most were non-Hispanic Black or White. The study was observational and cross-sectional, precluding assertions about directionality or causality.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the University of Pittsburgh Clinical and Translational Science Institute, and the University of Pittsburgh Small Molecule Biomarker Core. Dr. Thurston reported receiving personal fees from Astellas Pharma, Bayer, Hello Therapeutics, Vira Health, and Happify Health outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mental health characteristics of refugee children
Since 1983, when I was a child and fled as a boat refugee from Vietnam with my mother, the international plight of displaced people has only worsened. From 1997 to 2022, the number of forcibly displaced people has more than tripled, growing from 34 million to more than 108 million.1
Displaced people are designated as refugees only when they cross international borders and meet the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees’ (UNHCR) definition as “persons outside their countries of origin who are in need of international protection because of a serious threat to their life, physical integrity, or freedom in their country of origin as a result of persecution, armed conflict, violence, or serious public disorder.”2 There is a separate mandate by the United Nations for the aid of Palestinian refugees under the United Nations General Assembly’s United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestinian Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA).3 Of the displaced in 2022, more than 36 million were recognized as refugees under UNHCR and UNRWA mandates.1 Of these, almost 50% were children, at 17.5 million.4 To make matters worse, worldwide children represent less than one-third of the population.4 Since 2022, the increase in refugeeism is mostly driven by Ukraine and Syria, though also significantly Afghanistan, Venezuela, Sudan, Myanmar, Congo, Somalia, and Central African Republic.4 Refugeeism is a growing problem that disproportionately impacts children through sheer number, and one suspects, given their greater overall vulnerabilities compared with adults, physical and mental health consequences.
Traumas of refugees compared with non-refugee immigrants
In terms of mental health, refugees are distinct from non-refugee immigrants in that they likely experience more severe psychosocial adversities from greater poverty, greater risk of family separation, and uncertainty of the asylum process.5-8
From my own experience, this stems from the urgent nature of the refugee’s displacement, where they are often fleeing an immediate danger. My family had fled persecution from Communist forces and the social economic collapse that rendered Vietnam, for a time, one of the poorest in the world.9 Or, as my mother observed, “We had to leave because even doctors were starving.”
Refugees often have little preparation, have little legal protection since they are often criminalized, and are forced to endure dangerous conditions where they are vulnerable to smugglers and criminals who exploit their unprotected status. Once they arrive in their new country, they often do not have other family as social supports or resources. They themselves become the anchor for future legal and orderly immigration of their remaining family, given that they can extend their refugee status to those left behind.10 These non-refugee immigrants, unlike their refugee counterparts, are often flown to their new homes with more preparation, protecting them from dangerous conditions, and have the benefit of family who provide them with resources. As such, refugees tend to experience more traumatic life events than non-refugee immigrants. This was true in my family where those of us who initially escaped became the anchors to legally, and more safely, immigrate most of our family in Vietnam. We became their resources, likely making their acclimation smoother.
The mental health of refugee children and their caregivers
It is important to understand the stressors affecting the caregivers of children, since effective treatment of their mental health conditions can also benefit the children as well.11 In fact, among the greatest protective factors for refugee children is the presence of an adult caregiver, suggesting that the child’s mental health is dependent on the caregivers.
Those children who are separated show much worse mental health sequalae.12 As such, an understanding of the caregiver’s stressors is important. For example, when we were escaping Vietnam, my mom would protect me from our hardships by talking about our goals in America, minimizing our dangers by saying that we would be rewarded with things like a hamburger with its seemingly impossible amount of meat. Physically, my mother would always sleep with her arms around me and a knife hidden in order to ward off any attackers at night. When I was starving in the hull of a boat, having not eaten for days, my mother begged for food and gave me what she could get. And post-escape, my family focused on work and applied for aid for shelter and food, while encouraging us to invest in education, likely preventing involvement in criminal activities or gangs. Though overall, my family shielded me from the worst consequences, they also passed on their fears. One of my uncles had been killed by the police when he tried to escape, and so my family passed down a deep suspicion of authorities, whether they were the police or school principals. My mother had vivid memories of Communist re-education camps, which likely gave her a lasting fear that a Communist would find out our identities in America and re-capture us.
The mental health risk of refugees
Given that refugees tend to experience greater amounts of traumatic life events and a vast array of stressors sustained across years and even decades before, during, and after migration, it is no wonder they have much higher rates of mental health conditions, most predominantly PTSD and affective disorders.13,14 They are at particular risk of developing psychoses because they are more likely to experience a range of physical, psychological, and psychosocial problems associated with adversities such as violence, discrimination, economic stress, and social isolation.13 For example, the period leading up to my escape consisted of decades of prolonged war: the French-Indochina from 1945 to 1954, then the Vietnam War from 1955 to 1975) as well as the persecution and re-education camps afterward. What my family had to endure created a period of fear and loss into which I was born into in 1976. That year, my family had lost its fortune due to the Communist government seizing of our home and business, plunging us from a comfortable middle- to upper-class life to poverty. There was also widespread fear of systematic rape by the Communist victors. So my family endured great stress and the loss of a way of life leading up to our escape.
For the refugees, the escape itself is often a dangerous journey where, given its emergent nature, they are often exposed to the elements. We know about the current situation in Ukraine and Gaza, where children are fleeing from bombs and bullets. In my situation, we endured weeks of starvation crammed in the hull of boat as we forged through the Indian Ocean to the Philippines. One of my aunts, on a separate trip, perished because her boat had capsized, like so many others. Though impossible to verify, it has been estimated that up to 70% of Vietnamese refugees died during their escape.15 After the boat, my mother and I still had to brave Malaysian jungles and prisons, and then refugee camps for a year before we reached safety at an American Embassy in the Philippines. After we gained sponsorship to America, the traumas did not abate, but were only replaced by those of culture shock, poverty, and alienation. Taken by themselves, significant traumas exist in each phase of a refugee child’s escape, whether before, during, or after. These traumas are likely compounded since they are continuously layered and sustained across years, even decades. They affect not only the children, but their parents, and sometimes even a whole nation of people.
Summary
Refugee children and their families experience a variety of traumas, often sustained across years and even decades, because of armed conflict, persecution, or social upheavals. It is known that refugees are at greater risk for PTSD and affective and psychotic disorders, presumably due to increased traumatic life events before, during, and after their migration. The writer uses his own experience as a child refugee from Vietnam to elucidate the stressors evident in various phases of forced displacement.
Dr. Nguyen is a second year resident at UCSF Fresno Psychiatry Residency. He was a public high school English teacher for 15 years previously.
References
1. UNHCR. Global Trends. Forced displacement in 2016. Geneva, Switzerland: The UN Refugee Agency, 2022. https://www.unhcr.org/global-trends.
2. Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. The refugee concept under international law. Global compact for safe, orderly and regular migration. https://www.unhcr.org/sites/
3. United Nations. (2023, November 11). The Question of Palestine. Un.org. https://www.un.org/unispal/document/un-general-assembly-renews-unrwa-mandate-press-release/
4. UNICEF. (2023, November 11). Child displacement. Data.unicef.org. https://data.unicef.org/topic/child-migration-and-displacement/displacement
5. Kinzie JD. Immigrants and refugees: The psychiatric perspective. Transcult Psychiatry. 2006 Dec;43(4):577-91. doi: 10.1177/1363461506070782.
6. Eaton W and Harrison G. Ethnic disadvantage and schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 2000:(407):38-43. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0447.2000.00007.x.
7. Gilliver SC et al. Recent research on the mental health of immigrants to Sweden: a literature review. Eur J Public Health. 2014 Aug:24 Suppl 1:72-9. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/cku101.
8. Rapp MA et al. When local poverty is more important than your income: Mental health in minorities in inner cities. World Psychiatry. 2015 Jun;14(2):249-50. doi: 10.1002/wps.20221.
9. Cima, Ronald, ed. Vietnam: A Country Study. Washington: GPO for the Library of Congress, 1987.
10. United States Citizenship & Immigration Services (2023, November 12). Refugees. Uscis.gov. https://www.uscis.gov/humanitarian/refugees-and-asylum/refugees
11. Fazel M and Betancourt TS. (2018). Preventive mental health interventions for refugee children and adolescents in high-income settings. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2018 Feb;2(2):121-32. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(17)30147-5.
12. Fazel M et al. Mental health of displaced and refugee children resettled in high-income countries: risk and protective factors. Lancet. 2012 Jan 21;379(9812):266-82. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60051-2.
13. Dapunt J et al. Refugees and psychosis: A review of the literature. Transl Psychiatry. 2017 Jun 13;7(6):e1149. doi: 10.1038/tp.2017.119.
14. Fazel M et al. Prevalence of serious mental disorder in 7,000 refugees resettled in western countries: a systematic review. Lancet. 2005 Apr;365(9467):1309-14. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)61027-6.
15. Rummel R. Statistics of Vietnamese Democide, in his Statistics of Democide. 1997. Table 6.1B,lines 730, 749-51.
Since 1983, when I was a child and fled as a boat refugee from Vietnam with my mother, the international plight of displaced people has only worsened. From 1997 to 2022, the number of forcibly displaced people has more than tripled, growing from 34 million to more than 108 million.1
Displaced people are designated as refugees only when they cross international borders and meet the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees’ (UNHCR) definition as “persons outside their countries of origin who are in need of international protection because of a serious threat to their life, physical integrity, or freedom in their country of origin as a result of persecution, armed conflict, violence, or serious public disorder.”2 There is a separate mandate by the United Nations for the aid of Palestinian refugees under the United Nations General Assembly’s United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestinian Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA).3 Of the displaced in 2022, more than 36 million were recognized as refugees under UNHCR and UNRWA mandates.1 Of these, almost 50% were children, at 17.5 million.4 To make matters worse, worldwide children represent less than one-third of the population.4 Since 2022, the increase in refugeeism is mostly driven by Ukraine and Syria, though also significantly Afghanistan, Venezuela, Sudan, Myanmar, Congo, Somalia, and Central African Republic.4 Refugeeism is a growing problem that disproportionately impacts children through sheer number, and one suspects, given their greater overall vulnerabilities compared with adults, physical and mental health consequences.
Traumas of refugees compared with non-refugee immigrants
In terms of mental health, refugees are distinct from non-refugee immigrants in that they likely experience more severe psychosocial adversities from greater poverty, greater risk of family separation, and uncertainty of the asylum process.5-8
From my own experience, this stems from the urgent nature of the refugee’s displacement, where they are often fleeing an immediate danger. My family had fled persecution from Communist forces and the social economic collapse that rendered Vietnam, for a time, one of the poorest in the world.9 Or, as my mother observed, “We had to leave because even doctors were starving.”
Refugees often have little preparation, have little legal protection since they are often criminalized, and are forced to endure dangerous conditions where they are vulnerable to smugglers and criminals who exploit their unprotected status. Once they arrive in their new country, they often do not have other family as social supports or resources. They themselves become the anchor for future legal and orderly immigration of their remaining family, given that they can extend their refugee status to those left behind.10 These non-refugee immigrants, unlike their refugee counterparts, are often flown to their new homes with more preparation, protecting them from dangerous conditions, and have the benefit of family who provide them with resources. As such, refugees tend to experience more traumatic life events than non-refugee immigrants. This was true in my family where those of us who initially escaped became the anchors to legally, and more safely, immigrate most of our family in Vietnam. We became their resources, likely making their acclimation smoother.
The mental health of refugee children and their caregivers
It is important to understand the stressors affecting the caregivers of children, since effective treatment of their mental health conditions can also benefit the children as well.11 In fact, among the greatest protective factors for refugee children is the presence of an adult caregiver, suggesting that the child’s mental health is dependent on the caregivers.
Those children who are separated show much worse mental health sequalae.12 As such, an understanding of the caregiver’s stressors is important. For example, when we were escaping Vietnam, my mom would protect me from our hardships by talking about our goals in America, minimizing our dangers by saying that we would be rewarded with things like a hamburger with its seemingly impossible amount of meat. Physically, my mother would always sleep with her arms around me and a knife hidden in order to ward off any attackers at night. When I was starving in the hull of a boat, having not eaten for days, my mother begged for food and gave me what she could get. And post-escape, my family focused on work and applied for aid for shelter and food, while encouraging us to invest in education, likely preventing involvement in criminal activities or gangs. Though overall, my family shielded me from the worst consequences, they also passed on their fears. One of my uncles had been killed by the police when he tried to escape, and so my family passed down a deep suspicion of authorities, whether they were the police or school principals. My mother had vivid memories of Communist re-education camps, which likely gave her a lasting fear that a Communist would find out our identities in America and re-capture us.
The mental health risk of refugees
Given that refugees tend to experience greater amounts of traumatic life events and a vast array of stressors sustained across years and even decades before, during, and after migration, it is no wonder they have much higher rates of mental health conditions, most predominantly PTSD and affective disorders.13,14 They are at particular risk of developing psychoses because they are more likely to experience a range of physical, psychological, and psychosocial problems associated with adversities such as violence, discrimination, economic stress, and social isolation.13 For example, the period leading up to my escape consisted of decades of prolonged war: the French-Indochina from 1945 to 1954, then the Vietnam War from 1955 to 1975) as well as the persecution and re-education camps afterward. What my family had to endure created a period of fear and loss into which I was born into in 1976. That year, my family had lost its fortune due to the Communist government seizing of our home and business, plunging us from a comfortable middle- to upper-class life to poverty. There was also widespread fear of systematic rape by the Communist victors. So my family endured great stress and the loss of a way of life leading up to our escape.
For the refugees, the escape itself is often a dangerous journey where, given its emergent nature, they are often exposed to the elements. We know about the current situation in Ukraine and Gaza, where children are fleeing from bombs and bullets. In my situation, we endured weeks of starvation crammed in the hull of boat as we forged through the Indian Ocean to the Philippines. One of my aunts, on a separate trip, perished because her boat had capsized, like so many others. Though impossible to verify, it has been estimated that up to 70% of Vietnamese refugees died during their escape.15 After the boat, my mother and I still had to brave Malaysian jungles and prisons, and then refugee camps for a year before we reached safety at an American Embassy in the Philippines. After we gained sponsorship to America, the traumas did not abate, but were only replaced by those of culture shock, poverty, and alienation. Taken by themselves, significant traumas exist in each phase of a refugee child’s escape, whether before, during, or after. These traumas are likely compounded since they are continuously layered and sustained across years, even decades. They affect not only the children, but their parents, and sometimes even a whole nation of people.
Summary
Refugee children and their families experience a variety of traumas, often sustained across years and even decades, because of armed conflict, persecution, or social upheavals. It is known that refugees are at greater risk for PTSD and affective and psychotic disorders, presumably due to increased traumatic life events before, during, and after their migration. The writer uses his own experience as a child refugee from Vietnam to elucidate the stressors evident in various phases of forced displacement.
Dr. Nguyen is a second year resident at UCSF Fresno Psychiatry Residency. He was a public high school English teacher for 15 years previously.
References
1. UNHCR. Global Trends. Forced displacement in 2016. Geneva, Switzerland: The UN Refugee Agency, 2022. https://www.unhcr.org/global-trends.
2. Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. The refugee concept under international law. Global compact for safe, orderly and regular migration. https://www.unhcr.org/sites/
3. United Nations. (2023, November 11). The Question of Palestine. Un.org. https://www.un.org/unispal/document/un-general-assembly-renews-unrwa-mandate-press-release/
4. UNICEF. (2023, November 11). Child displacement. Data.unicef.org. https://data.unicef.org/topic/child-migration-and-displacement/displacement
5. Kinzie JD. Immigrants and refugees: The psychiatric perspective. Transcult Psychiatry. 2006 Dec;43(4):577-91. doi: 10.1177/1363461506070782.
6. Eaton W and Harrison G. Ethnic disadvantage and schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 2000:(407):38-43. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0447.2000.00007.x.
7. Gilliver SC et al. Recent research on the mental health of immigrants to Sweden: a literature review. Eur J Public Health. 2014 Aug:24 Suppl 1:72-9. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/cku101.
8. Rapp MA et al. When local poverty is more important than your income: Mental health in minorities in inner cities. World Psychiatry. 2015 Jun;14(2):249-50. doi: 10.1002/wps.20221.
9. Cima, Ronald, ed. Vietnam: A Country Study. Washington: GPO for the Library of Congress, 1987.
10. United States Citizenship & Immigration Services (2023, November 12). Refugees. Uscis.gov. https://www.uscis.gov/humanitarian/refugees-and-asylum/refugees
11. Fazel M and Betancourt TS. (2018). Preventive mental health interventions for refugee children and adolescents in high-income settings. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2018 Feb;2(2):121-32. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(17)30147-5.
12. Fazel M et al. Mental health of displaced and refugee children resettled in high-income countries: risk and protective factors. Lancet. 2012 Jan 21;379(9812):266-82. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60051-2.
13. Dapunt J et al. Refugees and psychosis: A review of the literature. Transl Psychiatry. 2017 Jun 13;7(6):e1149. doi: 10.1038/tp.2017.119.
14. Fazel M et al. Prevalence of serious mental disorder in 7,000 refugees resettled in western countries: a systematic review. Lancet. 2005 Apr;365(9467):1309-14. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)61027-6.
15. Rummel R. Statistics of Vietnamese Democide, in his Statistics of Democide. 1997. Table 6.1B,lines 730, 749-51.
Since 1983, when I was a child and fled as a boat refugee from Vietnam with my mother, the international plight of displaced people has only worsened. From 1997 to 2022, the number of forcibly displaced people has more than tripled, growing from 34 million to more than 108 million.1
Displaced people are designated as refugees only when they cross international borders and meet the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees’ (UNHCR) definition as “persons outside their countries of origin who are in need of international protection because of a serious threat to their life, physical integrity, or freedom in their country of origin as a result of persecution, armed conflict, violence, or serious public disorder.”2 There is a separate mandate by the United Nations for the aid of Palestinian refugees under the United Nations General Assembly’s United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestinian Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA).3 Of the displaced in 2022, more than 36 million were recognized as refugees under UNHCR and UNRWA mandates.1 Of these, almost 50% were children, at 17.5 million.4 To make matters worse, worldwide children represent less than one-third of the population.4 Since 2022, the increase in refugeeism is mostly driven by Ukraine and Syria, though also significantly Afghanistan, Venezuela, Sudan, Myanmar, Congo, Somalia, and Central African Republic.4 Refugeeism is a growing problem that disproportionately impacts children through sheer number, and one suspects, given their greater overall vulnerabilities compared with adults, physical and mental health consequences.
Traumas of refugees compared with non-refugee immigrants
In terms of mental health, refugees are distinct from non-refugee immigrants in that they likely experience more severe psychosocial adversities from greater poverty, greater risk of family separation, and uncertainty of the asylum process.5-8
From my own experience, this stems from the urgent nature of the refugee’s displacement, where they are often fleeing an immediate danger. My family had fled persecution from Communist forces and the social economic collapse that rendered Vietnam, for a time, one of the poorest in the world.9 Or, as my mother observed, “We had to leave because even doctors were starving.”
Refugees often have little preparation, have little legal protection since they are often criminalized, and are forced to endure dangerous conditions where they are vulnerable to smugglers and criminals who exploit their unprotected status. Once they arrive in their new country, they often do not have other family as social supports or resources. They themselves become the anchor for future legal and orderly immigration of their remaining family, given that they can extend their refugee status to those left behind.10 These non-refugee immigrants, unlike their refugee counterparts, are often flown to their new homes with more preparation, protecting them from dangerous conditions, and have the benefit of family who provide them with resources. As such, refugees tend to experience more traumatic life events than non-refugee immigrants. This was true in my family where those of us who initially escaped became the anchors to legally, and more safely, immigrate most of our family in Vietnam. We became their resources, likely making their acclimation smoother.
The mental health of refugee children and their caregivers
It is important to understand the stressors affecting the caregivers of children, since effective treatment of their mental health conditions can also benefit the children as well.11 In fact, among the greatest protective factors for refugee children is the presence of an adult caregiver, suggesting that the child’s mental health is dependent on the caregivers.
Those children who are separated show much worse mental health sequalae.12 As such, an understanding of the caregiver’s stressors is important. For example, when we were escaping Vietnam, my mom would protect me from our hardships by talking about our goals in America, minimizing our dangers by saying that we would be rewarded with things like a hamburger with its seemingly impossible amount of meat. Physically, my mother would always sleep with her arms around me and a knife hidden in order to ward off any attackers at night. When I was starving in the hull of a boat, having not eaten for days, my mother begged for food and gave me what she could get. And post-escape, my family focused on work and applied for aid for shelter and food, while encouraging us to invest in education, likely preventing involvement in criminal activities or gangs. Though overall, my family shielded me from the worst consequences, they also passed on their fears. One of my uncles had been killed by the police when he tried to escape, and so my family passed down a deep suspicion of authorities, whether they were the police or school principals. My mother had vivid memories of Communist re-education camps, which likely gave her a lasting fear that a Communist would find out our identities in America and re-capture us.
The mental health risk of refugees
Given that refugees tend to experience greater amounts of traumatic life events and a vast array of stressors sustained across years and even decades before, during, and after migration, it is no wonder they have much higher rates of mental health conditions, most predominantly PTSD and affective disorders.13,14 They are at particular risk of developing psychoses because they are more likely to experience a range of physical, psychological, and psychosocial problems associated with adversities such as violence, discrimination, economic stress, and social isolation.13 For example, the period leading up to my escape consisted of decades of prolonged war: the French-Indochina from 1945 to 1954, then the Vietnam War from 1955 to 1975) as well as the persecution and re-education camps afterward. What my family had to endure created a period of fear and loss into which I was born into in 1976. That year, my family had lost its fortune due to the Communist government seizing of our home and business, plunging us from a comfortable middle- to upper-class life to poverty. There was also widespread fear of systematic rape by the Communist victors. So my family endured great stress and the loss of a way of life leading up to our escape.
For the refugees, the escape itself is often a dangerous journey where, given its emergent nature, they are often exposed to the elements. We know about the current situation in Ukraine and Gaza, where children are fleeing from bombs and bullets. In my situation, we endured weeks of starvation crammed in the hull of boat as we forged through the Indian Ocean to the Philippines. One of my aunts, on a separate trip, perished because her boat had capsized, like so many others. Though impossible to verify, it has been estimated that up to 70% of Vietnamese refugees died during their escape.15 After the boat, my mother and I still had to brave Malaysian jungles and prisons, and then refugee camps for a year before we reached safety at an American Embassy in the Philippines. After we gained sponsorship to America, the traumas did not abate, but were only replaced by those of culture shock, poverty, and alienation. Taken by themselves, significant traumas exist in each phase of a refugee child’s escape, whether before, during, or after. These traumas are likely compounded since they are continuously layered and sustained across years, even decades. They affect not only the children, but their parents, and sometimes even a whole nation of people.
Summary
Refugee children and their families experience a variety of traumas, often sustained across years and even decades, because of armed conflict, persecution, or social upheavals. It is known that refugees are at greater risk for PTSD and affective and psychotic disorders, presumably due to increased traumatic life events before, during, and after their migration. The writer uses his own experience as a child refugee from Vietnam to elucidate the stressors evident in various phases of forced displacement.
Dr. Nguyen is a second year resident at UCSF Fresno Psychiatry Residency. He was a public high school English teacher for 15 years previously.
References
1. UNHCR. Global Trends. Forced displacement in 2016. Geneva, Switzerland: The UN Refugee Agency, 2022. https://www.unhcr.org/global-trends.
2. Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. The refugee concept under international law. Global compact for safe, orderly and regular migration. https://www.unhcr.org/sites/
3. United Nations. (2023, November 11). The Question of Palestine. Un.org. https://www.un.org/unispal/document/un-general-assembly-renews-unrwa-mandate-press-release/
4. UNICEF. (2023, November 11). Child displacement. Data.unicef.org. https://data.unicef.org/topic/child-migration-and-displacement/displacement
5. Kinzie JD. Immigrants and refugees: The psychiatric perspective. Transcult Psychiatry. 2006 Dec;43(4):577-91. doi: 10.1177/1363461506070782.
6. Eaton W and Harrison G. Ethnic disadvantage and schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 2000:(407):38-43. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0447.2000.00007.x.
7. Gilliver SC et al. Recent research on the mental health of immigrants to Sweden: a literature review. Eur J Public Health. 2014 Aug:24 Suppl 1:72-9. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/cku101.
8. Rapp MA et al. When local poverty is more important than your income: Mental health in minorities in inner cities. World Psychiatry. 2015 Jun;14(2):249-50. doi: 10.1002/wps.20221.
9. Cima, Ronald, ed. Vietnam: A Country Study. Washington: GPO for the Library of Congress, 1987.
10. United States Citizenship & Immigration Services (2023, November 12). Refugees. Uscis.gov. https://www.uscis.gov/humanitarian/refugees-and-asylum/refugees
11. Fazel M and Betancourt TS. (2018). Preventive mental health interventions for refugee children and adolescents in high-income settings. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2018 Feb;2(2):121-32. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(17)30147-5.
12. Fazel M et al. Mental health of displaced and refugee children resettled in high-income countries: risk and protective factors. Lancet. 2012 Jan 21;379(9812):266-82. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60051-2.
13. Dapunt J et al. Refugees and psychosis: A review of the literature. Transl Psychiatry. 2017 Jun 13;7(6):e1149. doi: 10.1038/tp.2017.119.
14. Fazel M et al. Prevalence of serious mental disorder in 7,000 refugees resettled in western countries: a systematic review. Lancet. 2005 Apr;365(9467):1309-14. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)61027-6.
15. Rummel R. Statistics of Vietnamese Democide, in his Statistics of Democide. 1997. Table 6.1B,lines 730, 749-51.
Missing Table and a Clarification
Correction
In: Barbeito A, Raghunathan K, Connolly S, et al. Barriers to implementation of telehealth pre-anesthesia evaluation visits in the Department of Veterans Affairs. Fed Pract. 2023;40(7):210-217a. doi:10.12788/fp.0387. Federal Practitioner inadvertently excluded Table 2. It has been updated online and in PubMed Central.
Clarification
In: Weaver M, Geppert CMA. Salute to service dogs. Fed Pract . 2023;40(9):278-280. doi:10.12788/fp.0414, The PAWS Act was noted and the authors want to provide the following
Correction
In: Barbeito A, Raghunathan K, Connolly S, et al. Barriers to implementation of telehealth pre-anesthesia evaluation visits in the Department of Veterans Affairs. Fed Pract. 2023;40(7):210-217a. doi:10.12788/fp.0387. Federal Practitioner inadvertently excluded Table 2. It has been updated online and in PubMed Central.
Clarification
In: Weaver M, Geppert CMA. Salute to service dogs. Fed Pract . 2023;40(9):278-280. doi:10.12788/fp.0414, The PAWS Act was noted and the authors want to provide the following
Correction
In: Barbeito A, Raghunathan K, Connolly S, et al. Barriers to implementation of telehealth pre-anesthesia evaluation visits in the Department of Veterans Affairs. Fed Pract. 2023;40(7):210-217a. doi:10.12788/fp.0387. Federal Practitioner inadvertently excluded Table 2. It has been updated online and in PubMed Central.
Clarification
In: Weaver M, Geppert CMA. Salute to service dogs. Fed Pract . 2023;40(9):278-280. doi:10.12788/fp.0414, The PAWS Act was noted and the authors want to provide the following
Perinatal depression rarely stands alone
Mental health conditions are the leading cause of pregnancy-related death in Illinois (40%) and across the United States (21%).1,2 Funding bodies, such as the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality3 and the Health Resources and Service Administration,4 have spotlights on improving screening and access to care for depression and substance use disorders (SUDs). However, the needs of individuals with multiple mental health conditions still often go unrecognized and unaddressed in perinatal health settings.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all adults be screened for depression, alcohol use, and drug use, and will be recommending screening for anxiety.5,6 The American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology recommends screening for perinatal mental health conditions including depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, acute postpartum psychosis, and suicidality; however, despite these recommendations, screening and treatment for comorbid mental health disorders during pregnancy and the postpartum is not standard practice.7
Addressing perinatal mental health is critical because untreated mental health conditions during the perinatal period can cause long-term adverse psychiatric and medical outcomes for the birthing person, the baby, and the family.8 This commentary highlights the importance of recognizing and screening for perinatal mental health comorbidities, improving referral rates for mental health treatment, and raising awareness of the importance of addressing rural perinatal mental health.
Perinatal mental health comorbidities
Major depressive disorder is the most common mental health condition during the perinatal period9 and is often comorbid.10-12 In “Perinatal mental health in low-income urban and rural patients: The importance of screening for comorbidities,” Craemer et al.13 reported that nearly half of the perinatal patients who screened positive for MDD also screened positive for at least one other mental health condition, among them general anxiety disorder (GAD), SUD, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and suicidality.
Many (9%) of the perinatal patients with MDD had a severe comorbidity profile characterized by four diagnoses – MDD, GAD, SUD, and PTSD. In routine medical care these comorbidities often go undetected even though the risk to mothers and babies increases with more severe mental health symptoms.8
The high frequency of perinatal mental health comorbidities Craemer et al.13 found demonstrates a compelling need for comorbid mental health screening during the perinatal period, particularly for low-income Black, Hispanic, and rural birthing persons. Positive screens for perinatal mental health disorders may reflect the onset of these disorders in pregnancy or the postpartum, or preexisting disorders that have gone undetected or untreated before pregnancy.
For many patients, the perinatal period is the first time they are screened for any mental health disorder; typically, they are screened solely for depression. Screening alone can have a positive impact on perinatal mental health. In fact, the USPSTF found that programs to screen perinatal patients, with or without treatment-related support, resulted in a 2%-9% absolute reduction in depression prevalence.14 However, screening for MDD is too infrequent for many reasons, including the logistics of integrating screening into the clinic workflow and limited provider availability, time, and training in mental health.
We recommend screening perinatal patients for mental health comorbidities. This recommendation may seem impractical given the lack of screening tools for comorbid mental health conditions; however, the Computerized Adaptive Test for Mental Health (CAT-MH), the validated tool15-17 used in this study, is an ideal option. CAT-MH is uniquely capable of screening for MDD, GAD, PTSD, SUD, and suicidality in one platform and is routinely used in diverse settings including the Veterans Administration,18 foster care,19 and universities.20 The main limitation of this more comprehensive screening is that it takes about 10 minutes per patient. However, CAT-MH is self-administered and can be done in the waiting room or on a mobile device prior to a clinic visit.
CAT-MH can also be easily integrated into clinical workflow when added to the Electronic Medical Record21, and is a more comprehensive tool than existing perinatal depression tools such as the Perinatal Health Questionaire-9 (PHQ-9) and Edinburgh Perinatal Depression Scale (EPDS).22 Another limitation is cost – currently $5.00 per assessment – however, this is less than routine blood work.23 If CAT-MH is not an option, we recommend a stepped approach of screening for GAD when perinatal patients screen positive for MDD, as this is the most common comorbidity profile. The GAD-7 is a free and widely available tool.24
Barriers to care
In Craemer et al,13 nearly two-thirds (64.9%) of perinatal patients with a positive screen did not receive a referral to follow-up care or a medication prescription. These low referral rates may reflect a variety of widely recognized barriers to care, including lack of referral options, provider and/or patient reluctance to pursue referrals, barriers to insurance coverage, or inadequate behavioral health infrastructure to ensure referral and diagnostic follow-up.
Further, rural residing perinatal patients are an underserved population that need more resources and screening. Despite an on-site behavioral specialist at the rural clinic, Craemer et al13 found a stark disparity in referral rates: referrals to treatment for a positive diagnosis was over two times less at the rural clinic (23.9%), compared with the urban clinics (51.6%). The most common treatment offered at the rural clinic was a prescription for medication (17.4%), while referral to follow-up care was the most common at the urban clinics (35.5%). Rural areas not only have a shortage of health care providers, but community members seeking mental health care often encounter greater stigma, compared with urban residents.25,26
These data highlight an unmet need for referrals to treatment for patients in rural communities, particularly in Illinois where the pregnancy-related mortality ratio attributable to mental health conditions is three times greater in rural areas, compared with those residing in urban Cook County (Chicago).2 Increasing access and availability to mental health treatment and prevention resources in Illinois, especially in rural areas, is an opportunity to prevent pregnancy-related mortality attributable to mental health conditions.
Overall, there is a critical need for screening for perinatal mental health comorbidities, increased attention to low rates of referral to mental health treatment, and investing in rural perinatal mental health. Addressing perinatal mental health disorders is key to decreasing the burden of maternal mortality, particularly in Illinois.
Ms. Craemer and Ms. Sayah are senior research specialists at the Center for Research on Women & Gender, University of Illinois at Chicago. Dr. Duffecy is a professor of clinical psychiatry at the University of Illinois at Chicago. Dr. Geller is a professor of obstetrics & gynecology and director of the Center for Research on Women & Gender, University of Illinois at Chicago. Dr. Maki is a professor of psychiatry, psychology, and obstetrics & gynecology at the University of Illinois at Chicago.
References
1. Trost S et al. Pregnancy-related deaths: Data from maternal mortality review committees in 36 states, 2017-2019. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, 2022.
2. Illinois Department of Public Health. Illinois maternal morbidity and mortality report 2016-2017. 2021.
3. AHRQ. Funding opportunities to address opioid and other substance use disorders. Updated 2023.
4. HRSA. Screening and treatment for maternal mental health and substance use disorders.
5. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Recommendations for primary care practice. Accessed May 26, 2023.
6. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Draft recommendation statement: Anxiety in adults: Screening. 2022.
7. ACOG. Screening and diagnosis of mental health conditions during pregnancy and postpartum. Clinical Practice Guideline. Number 4. 2023 June.
8. Meltzer-Brody S and Stuebe A. The long-term psychiatric and medical prognosis of perinatal mental illness. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2014 Jan. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2013.08.009.
9. Van Niel MS and Payne JL. Perinatal depression: A review. Cleve Clin J Med. 2020 May. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.87a.19054.
10. Wisner KL et al. Onset timing, thoughts of self-harm, and diagnoses in postpartum women with screen-positive depression findings. 2013 May. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.87.
11. Falah-Hassani K et al. The prevalence of antenatal and postnatal co-morbid anxiety and depression: A meta-analysis. Psychol Med. 2017 Sep. doi: 10.1017/S0033291717000617.
12. Pentecost R et al. Scoping review of the associations between perinatal substance use and perinatal depression and anxiety. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. 2021 Jul. doi: 10.1016/j.jogn.2021.02.008.
13. Craemer KA et al. Perinatal mental health in low-income urban and rural patients: The importance of screening for comorbidities. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2023 Jul-Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2023.05.007.
14. O’Connor E et al. Primary care screening for and treatment of depression in pregnant and postpartum women: Evidence report and systematic review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016 Jan 26. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.18948.
15. Kozhimannil KB et al. Racial and ethnic disparities in postpartum depression care among low-income women. Psychiatr Serv. 2011 Jun. doi: 10.1176/ps.62.6.pss6206_0619.
16. Wenzel ES et al. Depression and anxiety symptoms across pregnancy and the postpartum in low-income Black and Latina women. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2021 Dec. doi: 10.1007/s00737-021-01139-y.
17. Gibbons RD et al. Development of a computerized adaptive substance use disorder scale for screening and measurement: The CAT‐SUD. Addiction. 2020 Jul. doi: 10.1111/add.14938.
18. Brenner LA et al. Validation of a computerized adaptive test suicide scale (CAT-SS) among united states military veterans. PloS One. 2022 Jan 21. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261920.
19. The Center for State Child Welfare Data. Using technology to diagnose and report on behavioral health challenges facing foster youth. 2018.
20. Kim JJ et al. The experience of depression, anxiety, and mania among perinatal women. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2016 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s00737-016-0632-6.
21. Tepper MC et al. Toward population health: Using a learning behavioral health system and measurement-based care to improve access, care, outcomes, and disparities. Community Ment Health J. 2022 Nov. doi: 10.1007/s10597-022-00957-3.
22. Wenzel E et al. Using computerised adaptive tests to screen for perinatal depression in underserved women of colour. Evid Based Ment Health. 2022 Feb. doi: 10.1136/ebmental-2021-300262.
23. Sanger-Katz M. They want it to be secret: How a common blood test can cost $11 or almost $1,000. New York Times. 2019 Apr 19.
24. Spitzer RL et al. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: The GAD-7. Arch Intern Med. 2006 May 22. doi: 10.1001/archinte.166.10.1092.
25. Mollard E et al. An integrative review of postpartum depression in rural US communities. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 2016 Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.apnu.2015.12.003.
26. Anglim AJ and Radke SM. Rural maternal health care outcomes, drivers, and patient perspectives. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Dec 1. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0000000000000753.
Mental health conditions are the leading cause of pregnancy-related death in Illinois (40%) and across the United States (21%).1,2 Funding bodies, such as the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality3 and the Health Resources and Service Administration,4 have spotlights on improving screening and access to care for depression and substance use disorders (SUDs). However, the needs of individuals with multiple mental health conditions still often go unrecognized and unaddressed in perinatal health settings.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all adults be screened for depression, alcohol use, and drug use, and will be recommending screening for anxiety.5,6 The American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology recommends screening for perinatal mental health conditions including depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, acute postpartum psychosis, and suicidality; however, despite these recommendations, screening and treatment for comorbid mental health disorders during pregnancy and the postpartum is not standard practice.7
Addressing perinatal mental health is critical because untreated mental health conditions during the perinatal period can cause long-term adverse psychiatric and medical outcomes for the birthing person, the baby, and the family.8 This commentary highlights the importance of recognizing and screening for perinatal mental health comorbidities, improving referral rates for mental health treatment, and raising awareness of the importance of addressing rural perinatal mental health.
Perinatal mental health comorbidities
Major depressive disorder is the most common mental health condition during the perinatal period9 and is often comorbid.10-12 In “Perinatal mental health in low-income urban and rural patients: The importance of screening for comorbidities,” Craemer et al.13 reported that nearly half of the perinatal patients who screened positive for MDD also screened positive for at least one other mental health condition, among them general anxiety disorder (GAD), SUD, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and suicidality.
Many (9%) of the perinatal patients with MDD had a severe comorbidity profile characterized by four diagnoses – MDD, GAD, SUD, and PTSD. In routine medical care these comorbidities often go undetected even though the risk to mothers and babies increases with more severe mental health symptoms.8
The high frequency of perinatal mental health comorbidities Craemer et al.13 found demonstrates a compelling need for comorbid mental health screening during the perinatal period, particularly for low-income Black, Hispanic, and rural birthing persons. Positive screens for perinatal mental health disorders may reflect the onset of these disorders in pregnancy or the postpartum, or preexisting disorders that have gone undetected or untreated before pregnancy.
For many patients, the perinatal period is the first time they are screened for any mental health disorder; typically, they are screened solely for depression. Screening alone can have a positive impact on perinatal mental health. In fact, the USPSTF found that programs to screen perinatal patients, with or without treatment-related support, resulted in a 2%-9% absolute reduction in depression prevalence.14 However, screening for MDD is too infrequent for many reasons, including the logistics of integrating screening into the clinic workflow and limited provider availability, time, and training in mental health.
We recommend screening perinatal patients for mental health comorbidities. This recommendation may seem impractical given the lack of screening tools for comorbid mental health conditions; however, the Computerized Adaptive Test for Mental Health (CAT-MH), the validated tool15-17 used in this study, is an ideal option. CAT-MH is uniquely capable of screening for MDD, GAD, PTSD, SUD, and suicidality in one platform and is routinely used in diverse settings including the Veterans Administration,18 foster care,19 and universities.20 The main limitation of this more comprehensive screening is that it takes about 10 minutes per patient. However, CAT-MH is self-administered and can be done in the waiting room or on a mobile device prior to a clinic visit.
CAT-MH can also be easily integrated into clinical workflow when added to the Electronic Medical Record21, and is a more comprehensive tool than existing perinatal depression tools such as the Perinatal Health Questionaire-9 (PHQ-9) and Edinburgh Perinatal Depression Scale (EPDS).22 Another limitation is cost – currently $5.00 per assessment – however, this is less than routine blood work.23 If CAT-MH is not an option, we recommend a stepped approach of screening for GAD when perinatal patients screen positive for MDD, as this is the most common comorbidity profile. The GAD-7 is a free and widely available tool.24
Barriers to care
In Craemer et al,13 nearly two-thirds (64.9%) of perinatal patients with a positive screen did not receive a referral to follow-up care or a medication prescription. These low referral rates may reflect a variety of widely recognized barriers to care, including lack of referral options, provider and/or patient reluctance to pursue referrals, barriers to insurance coverage, or inadequate behavioral health infrastructure to ensure referral and diagnostic follow-up.
Further, rural residing perinatal patients are an underserved population that need more resources and screening. Despite an on-site behavioral specialist at the rural clinic, Craemer et al13 found a stark disparity in referral rates: referrals to treatment for a positive diagnosis was over two times less at the rural clinic (23.9%), compared with the urban clinics (51.6%). The most common treatment offered at the rural clinic was a prescription for medication (17.4%), while referral to follow-up care was the most common at the urban clinics (35.5%). Rural areas not only have a shortage of health care providers, but community members seeking mental health care often encounter greater stigma, compared with urban residents.25,26
These data highlight an unmet need for referrals to treatment for patients in rural communities, particularly in Illinois where the pregnancy-related mortality ratio attributable to mental health conditions is three times greater in rural areas, compared with those residing in urban Cook County (Chicago).2 Increasing access and availability to mental health treatment and prevention resources in Illinois, especially in rural areas, is an opportunity to prevent pregnancy-related mortality attributable to mental health conditions.
Overall, there is a critical need for screening for perinatal mental health comorbidities, increased attention to low rates of referral to mental health treatment, and investing in rural perinatal mental health. Addressing perinatal mental health disorders is key to decreasing the burden of maternal mortality, particularly in Illinois.
Ms. Craemer and Ms. Sayah are senior research specialists at the Center for Research on Women & Gender, University of Illinois at Chicago. Dr. Duffecy is a professor of clinical psychiatry at the University of Illinois at Chicago. Dr. Geller is a professor of obstetrics & gynecology and director of the Center for Research on Women & Gender, University of Illinois at Chicago. Dr. Maki is a professor of psychiatry, psychology, and obstetrics & gynecology at the University of Illinois at Chicago.
References
1. Trost S et al. Pregnancy-related deaths: Data from maternal mortality review committees in 36 states, 2017-2019. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, 2022.
2. Illinois Department of Public Health. Illinois maternal morbidity and mortality report 2016-2017. 2021.
3. AHRQ. Funding opportunities to address opioid and other substance use disorders. Updated 2023.
4. HRSA. Screening and treatment for maternal mental health and substance use disorders.
5. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Recommendations for primary care practice. Accessed May 26, 2023.
6. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Draft recommendation statement: Anxiety in adults: Screening. 2022.
7. ACOG. Screening and diagnosis of mental health conditions during pregnancy and postpartum. Clinical Practice Guideline. Number 4. 2023 June.
8. Meltzer-Brody S and Stuebe A. The long-term psychiatric and medical prognosis of perinatal mental illness. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2014 Jan. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2013.08.009.
9. Van Niel MS and Payne JL. Perinatal depression: A review. Cleve Clin J Med. 2020 May. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.87a.19054.
10. Wisner KL et al. Onset timing, thoughts of self-harm, and diagnoses in postpartum women with screen-positive depression findings. 2013 May. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.87.
11. Falah-Hassani K et al. The prevalence of antenatal and postnatal co-morbid anxiety and depression: A meta-analysis. Psychol Med. 2017 Sep. doi: 10.1017/S0033291717000617.
12. Pentecost R et al. Scoping review of the associations between perinatal substance use and perinatal depression and anxiety. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. 2021 Jul. doi: 10.1016/j.jogn.2021.02.008.
13. Craemer KA et al. Perinatal mental health in low-income urban and rural patients: The importance of screening for comorbidities. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2023 Jul-Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2023.05.007.
14. O’Connor E et al. Primary care screening for and treatment of depression in pregnant and postpartum women: Evidence report and systematic review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016 Jan 26. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.18948.
15. Kozhimannil KB et al. Racial and ethnic disparities in postpartum depression care among low-income women. Psychiatr Serv. 2011 Jun. doi: 10.1176/ps.62.6.pss6206_0619.
16. Wenzel ES et al. Depression and anxiety symptoms across pregnancy and the postpartum in low-income Black and Latina women. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2021 Dec. doi: 10.1007/s00737-021-01139-y.
17. Gibbons RD et al. Development of a computerized adaptive substance use disorder scale for screening and measurement: The CAT‐SUD. Addiction. 2020 Jul. doi: 10.1111/add.14938.
18. Brenner LA et al. Validation of a computerized adaptive test suicide scale (CAT-SS) among united states military veterans. PloS One. 2022 Jan 21. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261920.
19. The Center for State Child Welfare Data. Using technology to diagnose and report on behavioral health challenges facing foster youth. 2018.
20. Kim JJ et al. The experience of depression, anxiety, and mania among perinatal women. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2016 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s00737-016-0632-6.
21. Tepper MC et al. Toward population health: Using a learning behavioral health system and measurement-based care to improve access, care, outcomes, and disparities. Community Ment Health J. 2022 Nov. doi: 10.1007/s10597-022-00957-3.
22. Wenzel E et al. Using computerised adaptive tests to screen for perinatal depression in underserved women of colour. Evid Based Ment Health. 2022 Feb. doi: 10.1136/ebmental-2021-300262.
23. Sanger-Katz M. They want it to be secret: How a common blood test can cost $11 or almost $1,000. New York Times. 2019 Apr 19.
24. Spitzer RL et al. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: The GAD-7. Arch Intern Med. 2006 May 22. doi: 10.1001/archinte.166.10.1092.
25. Mollard E et al. An integrative review of postpartum depression in rural US communities. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 2016 Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.apnu.2015.12.003.
26. Anglim AJ and Radke SM. Rural maternal health care outcomes, drivers, and patient perspectives. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Dec 1. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0000000000000753.
Mental health conditions are the leading cause of pregnancy-related death in Illinois (40%) and across the United States (21%).1,2 Funding bodies, such as the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality3 and the Health Resources and Service Administration,4 have spotlights on improving screening and access to care for depression and substance use disorders (SUDs). However, the needs of individuals with multiple mental health conditions still often go unrecognized and unaddressed in perinatal health settings.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all adults be screened for depression, alcohol use, and drug use, and will be recommending screening for anxiety.5,6 The American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology recommends screening for perinatal mental health conditions including depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, acute postpartum psychosis, and suicidality; however, despite these recommendations, screening and treatment for comorbid mental health disorders during pregnancy and the postpartum is not standard practice.7
Addressing perinatal mental health is critical because untreated mental health conditions during the perinatal period can cause long-term adverse psychiatric and medical outcomes for the birthing person, the baby, and the family.8 This commentary highlights the importance of recognizing and screening for perinatal mental health comorbidities, improving referral rates for mental health treatment, and raising awareness of the importance of addressing rural perinatal mental health.
Perinatal mental health comorbidities
Major depressive disorder is the most common mental health condition during the perinatal period9 and is often comorbid.10-12 In “Perinatal mental health in low-income urban and rural patients: The importance of screening for comorbidities,” Craemer et al.13 reported that nearly half of the perinatal patients who screened positive for MDD also screened positive for at least one other mental health condition, among them general anxiety disorder (GAD), SUD, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and suicidality.
Many (9%) of the perinatal patients with MDD had a severe comorbidity profile characterized by four diagnoses – MDD, GAD, SUD, and PTSD. In routine medical care these comorbidities often go undetected even though the risk to mothers and babies increases with more severe mental health symptoms.8
The high frequency of perinatal mental health comorbidities Craemer et al.13 found demonstrates a compelling need for comorbid mental health screening during the perinatal period, particularly for low-income Black, Hispanic, and rural birthing persons. Positive screens for perinatal mental health disorders may reflect the onset of these disorders in pregnancy or the postpartum, or preexisting disorders that have gone undetected or untreated before pregnancy.
For many patients, the perinatal period is the first time they are screened for any mental health disorder; typically, they are screened solely for depression. Screening alone can have a positive impact on perinatal mental health. In fact, the USPSTF found that programs to screen perinatal patients, with or without treatment-related support, resulted in a 2%-9% absolute reduction in depression prevalence.14 However, screening for MDD is too infrequent for many reasons, including the logistics of integrating screening into the clinic workflow and limited provider availability, time, and training in mental health.
We recommend screening perinatal patients for mental health comorbidities. This recommendation may seem impractical given the lack of screening tools for comorbid mental health conditions; however, the Computerized Adaptive Test for Mental Health (CAT-MH), the validated tool15-17 used in this study, is an ideal option. CAT-MH is uniquely capable of screening for MDD, GAD, PTSD, SUD, and suicidality in one platform and is routinely used in diverse settings including the Veterans Administration,18 foster care,19 and universities.20 The main limitation of this more comprehensive screening is that it takes about 10 minutes per patient. However, CAT-MH is self-administered and can be done in the waiting room or on a mobile device prior to a clinic visit.
CAT-MH can also be easily integrated into clinical workflow when added to the Electronic Medical Record21, and is a more comprehensive tool than existing perinatal depression tools such as the Perinatal Health Questionaire-9 (PHQ-9) and Edinburgh Perinatal Depression Scale (EPDS).22 Another limitation is cost – currently $5.00 per assessment – however, this is less than routine blood work.23 If CAT-MH is not an option, we recommend a stepped approach of screening for GAD when perinatal patients screen positive for MDD, as this is the most common comorbidity profile. The GAD-7 is a free and widely available tool.24
Barriers to care
In Craemer et al,13 nearly two-thirds (64.9%) of perinatal patients with a positive screen did not receive a referral to follow-up care or a medication prescription. These low referral rates may reflect a variety of widely recognized barriers to care, including lack of referral options, provider and/or patient reluctance to pursue referrals, barriers to insurance coverage, or inadequate behavioral health infrastructure to ensure referral and diagnostic follow-up.
Further, rural residing perinatal patients are an underserved population that need more resources and screening. Despite an on-site behavioral specialist at the rural clinic, Craemer et al13 found a stark disparity in referral rates: referrals to treatment for a positive diagnosis was over two times less at the rural clinic (23.9%), compared with the urban clinics (51.6%). The most common treatment offered at the rural clinic was a prescription for medication (17.4%), while referral to follow-up care was the most common at the urban clinics (35.5%). Rural areas not only have a shortage of health care providers, but community members seeking mental health care often encounter greater stigma, compared with urban residents.25,26
These data highlight an unmet need for referrals to treatment for patients in rural communities, particularly in Illinois where the pregnancy-related mortality ratio attributable to mental health conditions is three times greater in rural areas, compared with those residing in urban Cook County (Chicago).2 Increasing access and availability to mental health treatment and prevention resources in Illinois, especially in rural areas, is an opportunity to prevent pregnancy-related mortality attributable to mental health conditions.
Overall, there is a critical need for screening for perinatal mental health comorbidities, increased attention to low rates of referral to mental health treatment, and investing in rural perinatal mental health. Addressing perinatal mental health disorders is key to decreasing the burden of maternal mortality, particularly in Illinois.
Ms. Craemer and Ms. Sayah are senior research specialists at the Center for Research on Women & Gender, University of Illinois at Chicago. Dr. Duffecy is a professor of clinical psychiatry at the University of Illinois at Chicago. Dr. Geller is a professor of obstetrics & gynecology and director of the Center for Research on Women & Gender, University of Illinois at Chicago. Dr. Maki is a professor of psychiatry, psychology, and obstetrics & gynecology at the University of Illinois at Chicago.
References
1. Trost S et al. Pregnancy-related deaths: Data from maternal mortality review committees in 36 states, 2017-2019. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, 2022.
2. Illinois Department of Public Health. Illinois maternal morbidity and mortality report 2016-2017. 2021.
3. AHRQ. Funding opportunities to address opioid and other substance use disorders. Updated 2023.
4. HRSA. Screening and treatment for maternal mental health and substance use disorders.
5. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Recommendations for primary care practice. Accessed May 26, 2023.
6. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Draft recommendation statement: Anxiety in adults: Screening. 2022.
7. ACOG. Screening and diagnosis of mental health conditions during pregnancy and postpartum. Clinical Practice Guideline. Number 4. 2023 June.
8. Meltzer-Brody S and Stuebe A. The long-term psychiatric and medical prognosis of perinatal mental illness. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2014 Jan. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2013.08.009.
9. Van Niel MS and Payne JL. Perinatal depression: A review. Cleve Clin J Med. 2020 May. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.87a.19054.
10. Wisner KL et al. Onset timing, thoughts of self-harm, and diagnoses in postpartum women with screen-positive depression findings. 2013 May. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.87.
11. Falah-Hassani K et al. The prevalence of antenatal and postnatal co-morbid anxiety and depression: A meta-analysis. Psychol Med. 2017 Sep. doi: 10.1017/S0033291717000617.
12. Pentecost R et al. Scoping review of the associations between perinatal substance use and perinatal depression and anxiety. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. 2021 Jul. doi: 10.1016/j.jogn.2021.02.008.
13. Craemer KA et al. Perinatal mental health in low-income urban and rural patients: The importance of screening for comorbidities. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2023 Jul-Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2023.05.007.
14. O’Connor E et al. Primary care screening for and treatment of depression in pregnant and postpartum women: Evidence report and systematic review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016 Jan 26. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.18948.
15. Kozhimannil KB et al. Racial and ethnic disparities in postpartum depression care among low-income women. Psychiatr Serv. 2011 Jun. doi: 10.1176/ps.62.6.pss6206_0619.
16. Wenzel ES et al. Depression and anxiety symptoms across pregnancy and the postpartum in low-income Black and Latina women. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2021 Dec. doi: 10.1007/s00737-021-01139-y.
17. Gibbons RD et al. Development of a computerized adaptive substance use disorder scale for screening and measurement: The CAT‐SUD. Addiction. 2020 Jul. doi: 10.1111/add.14938.
18. Brenner LA et al. Validation of a computerized adaptive test suicide scale (CAT-SS) among united states military veterans. PloS One. 2022 Jan 21. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261920.
19. The Center for State Child Welfare Data. Using technology to diagnose and report on behavioral health challenges facing foster youth. 2018.
20. Kim JJ et al. The experience of depression, anxiety, and mania among perinatal women. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2016 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s00737-016-0632-6.
21. Tepper MC et al. Toward population health: Using a learning behavioral health system and measurement-based care to improve access, care, outcomes, and disparities. Community Ment Health J. 2022 Nov. doi: 10.1007/s10597-022-00957-3.
22. Wenzel E et al. Using computerised adaptive tests to screen for perinatal depression in underserved women of colour. Evid Based Ment Health. 2022 Feb. doi: 10.1136/ebmental-2021-300262.
23. Sanger-Katz M. They want it to be secret: How a common blood test can cost $11 or almost $1,000. New York Times. 2019 Apr 19.
24. Spitzer RL et al. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: The GAD-7. Arch Intern Med. 2006 May 22. doi: 10.1001/archinte.166.10.1092.
25. Mollard E et al. An integrative review of postpartum depression in rural US communities. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 2016 Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.apnu.2015.12.003.
26. Anglim AJ and Radke SM. Rural maternal health care outcomes, drivers, and patient perspectives. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Dec 1. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0000000000000753.
Psychedelic therapy tied to reduced depression, anxiety
TOPLINE:
Perhaps most surprising to investigators, however, was that treatment was also associated with improved cognitive scores in the veterans, many of whom had traumatic brain injuries.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators reviewed clinical charts of 86 SOFVs who received psychedelic-assisted treatment at a therapeutic program in Mexico, 86% of whom sustained head injuries during deployment.
- On the first day of the study, participants received a single oral dose (10 mg/kg) of ibogaine hydrochloride in a group setting with two to five other attendees and spent the next day reflecting on their experience with program staff.
- On the third day, participants inhaled 5-MeO-DMT in three incremental doses for a total of 50 mg and were then invited to reflect on their experience both individually and with the group of peers who shared the experience.
- Follow-up surveys at 1, 3, and 6 months posttreatment between September 2019 to March 2021 measured symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, cognitive functioning, generalized anxiety disorder, depression, and quality of life.
TAKEAWAY:
- There were significant improvements in self-reported PTSD symptoms, depression, anxiety, insomnia severity, anger, and a large improvement in self-reported satisfaction with life (P < .001 for all).
- Participants reported significant increases in psychological flexibility (P < .001), cognitive functioning (P < .001), and postconcussive symptoms (P < .001).
- Treatment was also associated with a significant reduction in suicidal ideation from pretreatment to 1-month follow-up (P < .01).
IN PRACTICE:
“If consistently replicated, this could have major implications for the landscape of mental health care if people are able to experience significant and sustained healing with 3 days of intensive treatment, relative to our traditionally available interventions that require 8-12 weeks of weekly therapy (for example, gold standard talk therapies such as [prolonged exposure] or [cognitive processing therapy]), or daily use of a pharmacotherapy such as [a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor] for months to years,” study authors write.
SOURCE:
Alan Kooi Davis, PhD, of the Center for Psychedelic Drug Research and Education at Ohio State University, led the study, which was published online in the American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse.
LIMITATIONS:
Study assessments are based solely on self-report measures. Future research should implement carefully designed batteries that include both self-report and gold-standard clinician-administered measures to better capture symptom improvement and other information. The sample also lacked diversity with regard to race, religion, and socioeconomic status.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by Veterans Exploring Treatment Solutions. Dr. Davis is a board member at Source Resource Foundation and a lead trainer at Fluence. Full disclosures are included in the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Perhaps most surprising to investigators, however, was that treatment was also associated with improved cognitive scores in the veterans, many of whom had traumatic brain injuries.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators reviewed clinical charts of 86 SOFVs who received psychedelic-assisted treatment at a therapeutic program in Mexico, 86% of whom sustained head injuries during deployment.
- On the first day of the study, participants received a single oral dose (10 mg/kg) of ibogaine hydrochloride in a group setting with two to five other attendees and spent the next day reflecting on their experience with program staff.
- On the third day, participants inhaled 5-MeO-DMT in three incremental doses for a total of 50 mg and were then invited to reflect on their experience both individually and with the group of peers who shared the experience.
- Follow-up surveys at 1, 3, and 6 months posttreatment between September 2019 to March 2021 measured symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, cognitive functioning, generalized anxiety disorder, depression, and quality of life.
TAKEAWAY:
- There were significant improvements in self-reported PTSD symptoms, depression, anxiety, insomnia severity, anger, and a large improvement in self-reported satisfaction with life (P < .001 for all).
- Participants reported significant increases in psychological flexibility (P < .001), cognitive functioning (P < .001), and postconcussive symptoms (P < .001).
- Treatment was also associated with a significant reduction in suicidal ideation from pretreatment to 1-month follow-up (P < .01).
IN PRACTICE:
“If consistently replicated, this could have major implications for the landscape of mental health care if people are able to experience significant and sustained healing with 3 days of intensive treatment, relative to our traditionally available interventions that require 8-12 weeks of weekly therapy (for example, gold standard talk therapies such as [prolonged exposure] or [cognitive processing therapy]), or daily use of a pharmacotherapy such as [a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor] for months to years,” study authors write.
SOURCE:
Alan Kooi Davis, PhD, of the Center for Psychedelic Drug Research and Education at Ohio State University, led the study, which was published online in the American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse.
LIMITATIONS:
Study assessments are based solely on self-report measures. Future research should implement carefully designed batteries that include both self-report and gold-standard clinician-administered measures to better capture symptom improvement and other information. The sample also lacked diversity with regard to race, religion, and socioeconomic status.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by Veterans Exploring Treatment Solutions. Dr. Davis is a board member at Source Resource Foundation and a lead trainer at Fluence. Full disclosures are included in the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Perhaps most surprising to investigators, however, was that treatment was also associated with improved cognitive scores in the veterans, many of whom had traumatic brain injuries.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators reviewed clinical charts of 86 SOFVs who received psychedelic-assisted treatment at a therapeutic program in Mexico, 86% of whom sustained head injuries during deployment.
- On the first day of the study, participants received a single oral dose (10 mg/kg) of ibogaine hydrochloride in a group setting with two to five other attendees and spent the next day reflecting on their experience with program staff.
- On the third day, participants inhaled 5-MeO-DMT in three incremental doses for a total of 50 mg and were then invited to reflect on their experience both individually and with the group of peers who shared the experience.
- Follow-up surveys at 1, 3, and 6 months posttreatment between September 2019 to March 2021 measured symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, cognitive functioning, generalized anxiety disorder, depression, and quality of life.
TAKEAWAY:
- There were significant improvements in self-reported PTSD symptoms, depression, anxiety, insomnia severity, anger, and a large improvement in self-reported satisfaction with life (P < .001 for all).
- Participants reported significant increases in psychological flexibility (P < .001), cognitive functioning (P < .001), and postconcussive symptoms (P < .001).
- Treatment was also associated with a significant reduction in suicidal ideation from pretreatment to 1-month follow-up (P < .01).
IN PRACTICE:
“If consistently replicated, this could have major implications for the landscape of mental health care if people are able to experience significant and sustained healing with 3 days of intensive treatment, relative to our traditionally available interventions that require 8-12 weeks of weekly therapy (for example, gold standard talk therapies such as [prolonged exposure] or [cognitive processing therapy]), or daily use of a pharmacotherapy such as [a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor] for months to years,” study authors write.
SOURCE:
Alan Kooi Davis, PhD, of the Center for Psychedelic Drug Research and Education at Ohio State University, led the study, which was published online in the American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse.
LIMITATIONS:
Study assessments are based solely on self-report measures. Future research should implement carefully designed batteries that include both self-report and gold-standard clinician-administered measures to better capture symptom improvement and other information. The sample also lacked diversity with regard to race, religion, and socioeconomic status.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by Veterans Exploring Treatment Solutions. Dr. Davis is a board member at Source Resource Foundation and a lead trainer at Fluence. Full disclosures are included in the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF DRUG AND ALCOHOL ABUSE
Antidepressants ‘don’t blunt’ semaglutide and weight loss
in a post hoc analysis of the Semaglutide Treatment Effect in People with Obesity (STEP) program.
Adverse events, including psychiatric events, were slightly more usual in the patients on antidepressants, Robert Kushner, MD, noted, in an oral session at the annual meeting of the Obesity Society.
“It is very common that patients who present for weight management are taking antidepressants for various reasons, including depression, anxiety, insomnia, or chronic pain,”Dr. Kushner, from Northwestern University in Chicago, said in an email. “We wanted to see if these participants responded differently to semaglutide, compared to those not on antidepressants.”
“We found that antidepressants do not blunt the effect of semaglutide for weight loss,” he said. “However, there is a slight increase in reported adverse effects.”
“Semaglutide 2.4 mg provides an effective treatment option for weight management, regardless of antidepressant use at baseline,” Dr. Kushner summarized. “Clinicians should be assured that we can use semaglutide in this population of patients.”
Jack Yanovski, MD, PhD, said this was a “great presentation,” noting that “it’s really important that we understand what goes on in patients with depression.”
“Of course, all these trials still had rules that prevent the folks with the most severe depressive symptoms or past suicidality to participate,” added Dr. Yanovski, chief of the Growth and Obesity Section, Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, Rockville, Md. “We need specific trials to know exactly how well we do.”
Dr. Kushner agreed, but also noted that, ever since some earlier antidepressants were associated with risk for suicidal ideation and death, strict guidelines were put in place that exclude certain patients from participating in clinical trials.
Dr. Yanovski suggested that now that the drugs are approved, it would be possible to study this, and the information would be important for clinicians.
Dr. Kushner said he hopes that such studies are forthcoming. In the meantime, “data like this will add some support and understanding,” he suggested.
36,000 Patients with obesity, 500 on antidepressants
Many people living with obesity report taking antidepressants for depression, anxiety, chronic pain, obsessive-compulsive disorder, sleep disturbance, neuropathy, panic disorder, or posttraumatic stress disorder, Dr. Kushner noted.
However, some of these medications can cause weight gain, and little is known about treatment outcomes for people with obesity who are on antidepressants, since most weight-loss studies exclude people with active major depressive disorder.
The researchers analyzed data from 1,961 patients in STEP 1 and 807 patients in STEP 2 as well as 611 patients in STEP 3 and 304 patients in STEP 5 – 3,683 participants in total, of which 539 were on antidepressants at baseline.
The patients were randomly assigned to 2.4 mg semaglutide vs. placebo plus a lifestyle intervention (STEP 1, 2, and 5) or intensive behavioral therapy (STEP 3 only), for 68 weeks, except STEP 5, which was 104 weeks.
Patients were included if they were aged 18 or older with a body mass index ≥30 kg/m2, or ≥27 kg/m2 with more than one weight-related complication (STEP 1, 3, and 5) or BMI ≥27 kg/m2 with type 2 diabetes (STEP 2 only), and at least one self-reported unsuccessful effort to lose weight by diet.
They were excluded if they had active major depressive disorder within 2 years prior to screening (or other severe psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder) or a Patient Health Questionnaire-9 score of 15 or higher (indicating moderately severe or severe depression), or suicide ideation (type 4 or 5 on the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale) or suicide behavior, within 30 days of screening.
From baseline to week 68, patients on semaglutide (with/without baseline antidepressant use) had a significantly greater change in weight vs. patients on placebo (with/without baseline antidepressant use), respectively:
- STEP 1: –15.7% / –14.7% vs. –0.2% / –2.8%
- STEP 2: –10.7% / –9.5% vs. –3.3% / –3.4%
- STEP 3: –16.2% / –15.9% vs. –5.0% / –5.9%
- STEP 5: –19.0% / –14.1% vs. +1.6% / – 4.0%.
The proportion of reported adverse events was generally slightly greater in patients receiving semaglutide (with/without baseline antidepressant use) than those on placebo (with/without baseline antidepressant use), respectively:
- STEP 1: 97.7% vs 88.6% and 92.9% vs. 86%
- STEP 2: 97.6% vs 86.5% and 88.6% vs. 77.2%
- STEP 3: 97.6% vs 95.3% and 100% vs. 95.8%
- STEP 5: 100% vs 94.8% and 95.5% vs. 89.2%.
Gastrointestinal adverse events were more frequently reported in the semaglutide group and in patients on antidepressants at baseline. The proportion of patients with psychiatric adverse events was greater in participants on antidepressants at baseline. There were no differences in suicidal ideation/behavior in patients with/without antidepressant use at baseline.
The STEP trials were funded by Novo Nordisk. Dr. Kushner discloses that he served as a consultant for Novo Nordisk, WeightWatchers, Eli Lilly, and Pfizer, and received a research grant from Epitomee.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
in a post hoc analysis of the Semaglutide Treatment Effect in People with Obesity (STEP) program.
Adverse events, including psychiatric events, were slightly more usual in the patients on antidepressants, Robert Kushner, MD, noted, in an oral session at the annual meeting of the Obesity Society.
“It is very common that patients who present for weight management are taking antidepressants for various reasons, including depression, anxiety, insomnia, or chronic pain,”Dr. Kushner, from Northwestern University in Chicago, said in an email. “We wanted to see if these participants responded differently to semaglutide, compared to those not on antidepressants.”
“We found that antidepressants do not blunt the effect of semaglutide for weight loss,” he said. “However, there is a slight increase in reported adverse effects.”
“Semaglutide 2.4 mg provides an effective treatment option for weight management, regardless of antidepressant use at baseline,” Dr. Kushner summarized. “Clinicians should be assured that we can use semaglutide in this population of patients.”
Jack Yanovski, MD, PhD, said this was a “great presentation,” noting that “it’s really important that we understand what goes on in patients with depression.”
“Of course, all these trials still had rules that prevent the folks with the most severe depressive symptoms or past suicidality to participate,” added Dr. Yanovski, chief of the Growth and Obesity Section, Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, Rockville, Md. “We need specific trials to know exactly how well we do.”
Dr. Kushner agreed, but also noted that, ever since some earlier antidepressants were associated with risk for suicidal ideation and death, strict guidelines were put in place that exclude certain patients from participating in clinical trials.
Dr. Yanovski suggested that now that the drugs are approved, it would be possible to study this, and the information would be important for clinicians.
Dr. Kushner said he hopes that such studies are forthcoming. In the meantime, “data like this will add some support and understanding,” he suggested.
36,000 Patients with obesity, 500 on antidepressants
Many people living with obesity report taking antidepressants for depression, anxiety, chronic pain, obsessive-compulsive disorder, sleep disturbance, neuropathy, panic disorder, or posttraumatic stress disorder, Dr. Kushner noted.
However, some of these medications can cause weight gain, and little is known about treatment outcomes for people with obesity who are on antidepressants, since most weight-loss studies exclude people with active major depressive disorder.
The researchers analyzed data from 1,961 patients in STEP 1 and 807 patients in STEP 2 as well as 611 patients in STEP 3 and 304 patients in STEP 5 – 3,683 participants in total, of which 539 were on antidepressants at baseline.
The patients were randomly assigned to 2.4 mg semaglutide vs. placebo plus a lifestyle intervention (STEP 1, 2, and 5) or intensive behavioral therapy (STEP 3 only), for 68 weeks, except STEP 5, which was 104 weeks.
Patients were included if they were aged 18 or older with a body mass index ≥30 kg/m2, or ≥27 kg/m2 with more than one weight-related complication (STEP 1, 3, and 5) or BMI ≥27 kg/m2 with type 2 diabetes (STEP 2 only), and at least one self-reported unsuccessful effort to lose weight by diet.
They were excluded if they had active major depressive disorder within 2 years prior to screening (or other severe psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder) or a Patient Health Questionnaire-9 score of 15 or higher (indicating moderately severe or severe depression), or suicide ideation (type 4 or 5 on the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale) or suicide behavior, within 30 days of screening.
From baseline to week 68, patients on semaglutide (with/without baseline antidepressant use) had a significantly greater change in weight vs. patients on placebo (with/without baseline antidepressant use), respectively:
- STEP 1: –15.7% / –14.7% vs. –0.2% / –2.8%
- STEP 2: –10.7% / –9.5% vs. –3.3% / –3.4%
- STEP 3: –16.2% / –15.9% vs. –5.0% / –5.9%
- STEP 5: –19.0% / –14.1% vs. +1.6% / – 4.0%.
The proportion of reported adverse events was generally slightly greater in patients receiving semaglutide (with/without baseline antidepressant use) than those on placebo (with/without baseline antidepressant use), respectively:
- STEP 1: 97.7% vs 88.6% and 92.9% vs. 86%
- STEP 2: 97.6% vs 86.5% and 88.6% vs. 77.2%
- STEP 3: 97.6% vs 95.3% and 100% vs. 95.8%
- STEP 5: 100% vs 94.8% and 95.5% vs. 89.2%.
Gastrointestinal adverse events were more frequently reported in the semaglutide group and in patients on antidepressants at baseline. The proportion of patients with psychiatric adverse events was greater in participants on antidepressants at baseline. There were no differences in suicidal ideation/behavior in patients with/without antidepressant use at baseline.
The STEP trials were funded by Novo Nordisk. Dr. Kushner discloses that he served as a consultant for Novo Nordisk, WeightWatchers, Eli Lilly, and Pfizer, and received a research grant from Epitomee.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
in a post hoc analysis of the Semaglutide Treatment Effect in People with Obesity (STEP) program.
Adverse events, including psychiatric events, were slightly more usual in the patients on antidepressants, Robert Kushner, MD, noted, in an oral session at the annual meeting of the Obesity Society.
“It is very common that patients who present for weight management are taking antidepressants for various reasons, including depression, anxiety, insomnia, or chronic pain,”Dr. Kushner, from Northwestern University in Chicago, said in an email. “We wanted to see if these participants responded differently to semaglutide, compared to those not on antidepressants.”
“We found that antidepressants do not blunt the effect of semaglutide for weight loss,” he said. “However, there is a slight increase in reported adverse effects.”
“Semaglutide 2.4 mg provides an effective treatment option for weight management, regardless of antidepressant use at baseline,” Dr. Kushner summarized. “Clinicians should be assured that we can use semaglutide in this population of patients.”
Jack Yanovski, MD, PhD, said this was a “great presentation,” noting that “it’s really important that we understand what goes on in patients with depression.”
“Of course, all these trials still had rules that prevent the folks with the most severe depressive symptoms or past suicidality to participate,” added Dr. Yanovski, chief of the Growth and Obesity Section, Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, Rockville, Md. “We need specific trials to know exactly how well we do.”
Dr. Kushner agreed, but also noted that, ever since some earlier antidepressants were associated with risk for suicidal ideation and death, strict guidelines were put in place that exclude certain patients from participating in clinical trials.
Dr. Yanovski suggested that now that the drugs are approved, it would be possible to study this, and the information would be important for clinicians.
Dr. Kushner said he hopes that such studies are forthcoming. In the meantime, “data like this will add some support and understanding,” he suggested.
36,000 Patients with obesity, 500 on antidepressants
Many people living with obesity report taking antidepressants for depression, anxiety, chronic pain, obsessive-compulsive disorder, sleep disturbance, neuropathy, panic disorder, or posttraumatic stress disorder, Dr. Kushner noted.
However, some of these medications can cause weight gain, and little is known about treatment outcomes for people with obesity who are on antidepressants, since most weight-loss studies exclude people with active major depressive disorder.
The researchers analyzed data from 1,961 patients in STEP 1 and 807 patients in STEP 2 as well as 611 patients in STEP 3 and 304 patients in STEP 5 – 3,683 participants in total, of which 539 were on antidepressants at baseline.
The patients were randomly assigned to 2.4 mg semaglutide vs. placebo plus a lifestyle intervention (STEP 1, 2, and 5) or intensive behavioral therapy (STEP 3 only), for 68 weeks, except STEP 5, which was 104 weeks.
Patients were included if they were aged 18 or older with a body mass index ≥30 kg/m2, or ≥27 kg/m2 with more than one weight-related complication (STEP 1, 3, and 5) or BMI ≥27 kg/m2 with type 2 diabetes (STEP 2 only), and at least one self-reported unsuccessful effort to lose weight by diet.
They were excluded if they had active major depressive disorder within 2 years prior to screening (or other severe psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder) or a Patient Health Questionnaire-9 score of 15 or higher (indicating moderately severe or severe depression), or suicide ideation (type 4 or 5 on the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale) or suicide behavior, within 30 days of screening.
From baseline to week 68, patients on semaglutide (with/without baseline antidepressant use) had a significantly greater change in weight vs. patients on placebo (with/without baseline antidepressant use), respectively:
- STEP 1: –15.7% / –14.7% vs. –0.2% / –2.8%
- STEP 2: –10.7% / –9.5% vs. –3.3% / –3.4%
- STEP 3: –16.2% / –15.9% vs. –5.0% / –5.9%
- STEP 5: –19.0% / –14.1% vs. +1.6% / – 4.0%.
The proportion of reported adverse events was generally slightly greater in patients receiving semaglutide (with/without baseline antidepressant use) than those on placebo (with/without baseline antidepressant use), respectively:
- STEP 1: 97.7% vs 88.6% and 92.9% vs. 86%
- STEP 2: 97.6% vs 86.5% and 88.6% vs. 77.2%
- STEP 3: 97.6% vs 95.3% and 100% vs. 95.8%
- STEP 5: 100% vs 94.8% and 95.5% vs. 89.2%.
Gastrointestinal adverse events were more frequently reported in the semaglutide group and in patients on antidepressants at baseline. The proportion of patients with psychiatric adverse events was greater in participants on antidepressants at baseline. There were no differences in suicidal ideation/behavior in patients with/without antidepressant use at baseline.
The STEP trials were funded by Novo Nordisk. Dr. Kushner discloses that he served as a consultant for Novo Nordisk, WeightWatchers, Eli Lilly, and Pfizer, and received a research grant from Epitomee.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM OBESITYWEEK® 2023