User login
FDA targets flavored cartridge-based e-cigarettes, but says it is not a ‘ban’
but states it is not a “ban.”
On Jan. 2, the agency issued enforcement guidance alerting companies that manufacture, distribute, and sell unauthorized flavored cartridge-based e-cigarettes within the next 30 days will risk FDA enforcement action.
FDA has had the authority to require premarket authorization of all e-cigarettes and other electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS) since August 2016, but thus far has exercised enforcement discretion regarding the need for premarket authorization for these types of products.
“By prioritizing enforcement against the products that are most widely used by children, our action today seeks to strike the right public health balance by maintaining e-cigarettes as a potential off-ramp for adults using combustible tobacco while ensuring these products don’t provide an on-ramp to nicotine addiction for our youth,” Department of Health & Human Services Secretary Alex Azar said in a statement.
The action comes in the wake of more than 2,500 vaping-related injuries being reported, including more than 50 deaths associated with vaping reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (although many are related to the use of tetrahydrocannabinol [THC] within vaping products) and a continued rise in youth use of e-cigarettes noted in government surveys.
The agency noted in a Jan. 2 statement announcing the enforcement action that, to date, no ENDS products have received a premarket authorization, “meaning that all ENDS products currently on the market are considered illegally marketed and are subject to enforcement, at any time, in the FDA’s discretion.”
FDA said it is prioritizing enforcement in 30 days against:
- Any flavored, cartridge-based ENDS product, other than those with a tobacco or menthol flavoring.
- All other ENDS products for which manufacturers are failing to take adequate measures to prevent access by minors.
- Any ENDS product that is targeted to minors or is likely to promote use by minors.
In the last category, this might include labeling or advertising resembling “kid-friendly food and drinks such as juice boxes or kid-friendly cereal; products marketed directly to minors by promoting ease of concealing the product or disguising it as another product; and products marketed with characters designed to appeal to youth,” according to the FDA statement.
As of May 12, FDA also will prioritize enforcement against any ENDS product for which the manufacturer has not submitted a premarket application. The agency will continue to exercise enforcement discretion for up to 1 year on these products if an application has been submitted, pending the review of that application.
“By not prioritizing enforcement against other flavored ENDS products in the same way as flavored cartridge-based ENDS products, the FDA has attempted to balance the public health concerns related to youth use of ENDS products with consideration regarding addicted adult cigarette smokers who may try to use ENDS products to transition away from combustible tobacco products,” the agency stated, adding that cartridge-based ENDS products are most commonly used among youth.
The FDA statement noted that the enforcement priorities outlined in the guidance document were not a “ban” on flavored or cartridge-based ENDS, noting the agency “has already accepted and begun review of several premarket applications for flavored ENDS products through the pathway that Congress established in the Tobacco Control Act. ... If a company can demonstrate to the FDA that a specific product meets the applicable standard set forth by Congress, including considering how the marketing of the product may affect youth initiation and use, then the FDA could authorize that product for sale.”
“Coupled with the recently signed legislation increasing the minimum age of sale of tobacco to 21, we believe this policy balances the urgency with which we must address the public health threat of youth use of e-cigarette products with the potential role that e-cigarettes may play in helping adult smokers transition completely away from combustible tobacco to a potentially less risky form of nicotine delivery,” FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD, said in a statement. “While we expect that responsible members of industry will comply with premarket requirements, we’re ready to take action against any unauthorized e-cigarette products as outlined in our priorities. We’ll also closely monitor the use rates of all e-cigarette products and take additional steps to address youth use as necessary.”
The American Medical Association criticized the action as not going far enough, even though it was a step in the right direction.
“The AMA is disappointed that menthol flavors, one of the most popular, will still be allowed, and that flavored e-liquids will remain on the market, leaving young people with easy access to alternative flavored e-cigarette products,” AMA President Patrice A. Harris, MD, said in a statement. “If we are serious about tackling this epidemic and keeping these harmful products out of the hands of young people, a total ban on all flavored e-cigarettes, in all forms and at all locations, is prudent and urgently needed. We are pleased the administration committed today to closely monitoring the situation and trends in e-cigarette use among young people, and to taking further action if needed.”
but states it is not a “ban.”
On Jan. 2, the agency issued enforcement guidance alerting companies that manufacture, distribute, and sell unauthorized flavored cartridge-based e-cigarettes within the next 30 days will risk FDA enforcement action.
FDA has had the authority to require premarket authorization of all e-cigarettes and other electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS) since August 2016, but thus far has exercised enforcement discretion regarding the need for premarket authorization for these types of products.
“By prioritizing enforcement against the products that are most widely used by children, our action today seeks to strike the right public health balance by maintaining e-cigarettes as a potential off-ramp for adults using combustible tobacco while ensuring these products don’t provide an on-ramp to nicotine addiction for our youth,” Department of Health & Human Services Secretary Alex Azar said in a statement.
The action comes in the wake of more than 2,500 vaping-related injuries being reported, including more than 50 deaths associated with vaping reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (although many are related to the use of tetrahydrocannabinol [THC] within vaping products) and a continued rise in youth use of e-cigarettes noted in government surveys.
The agency noted in a Jan. 2 statement announcing the enforcement action that, to date, no ENDS products have received a premarket authorization, “meaning that all ENDS products currently on the market are considered illegally marketed and are subject to enforcement, at any time, in the FDA’s discretion.”
FDA said it is prioritizing enforcement in 30 days against:
- Any flavored, cartridge-based ENDS product, other than those with a tobacco or menthol flavoring.
- All other ENDS products for which manufacturers are failing to take adequate measures to prevent access by minors.
- Any ENDS product that is targeted to minors or is likely to promote use by minors.
In the last category, this might include labeling or advertising resembling “kid-friendly food and drinks such as juice boxes or kid-friendly cereal; products marketed directly to minors by promoting ease of concealing the product or disguising it as another product; and products marketed with characters designed to appeal to youth,” according to the FDA statement.
As of May 12, FDA also will prioritize enforcement against any ENDS product for which the manufacturer has not submitted a premarket application. The agency will continue to exercise enforcement discretion for up to 1 year on these products if an application has been submitted, pending the review of that application.
“By not prioritizing enforcement against other flavored ENDS products in the same way as flavored cartridge-based ENDS products, the FDA has attempted to balance the public health concerns related to youth use of ENDS products with consideration regarding addicted adult cigarette smokers who may try to use ENDS products to transition away from combustible tobacco products,” the agency stated, adding that cartridge-based ENDS products are most commonly used among youth.
The FDA statement noted that the enforcement priorities outlined in the guidance document were not a “ban” on flavored or cartridge-based ENDS, noting the agency “has already accepted and begun review of several premarket applications for flavored ENDS products through the pathway that Congress established in the Tobacco Control Act. ... If a company can demonstrate to the FDA that a specific product meets the applicable standard set forth by Congress, including considering how the marketing of the product may affect youth initiation and use, then the FDA could authorize that product for sale.”
“Coupled with the recently signed legislation increasing the minimum age of sale of tobacco to 21, we believe this policy balances the urgency with which we must address the public health threat of youth use of e-cigarette products with the potential role that e-cigarettes may play in helping adult smokers transition completely away from combustible tobacco to a potentially less risky form of nicotine delivery,” FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD, said in a statement. “While we expect that responsible members of industry will comply with premarket requirements, we’re ready to take action against any unauthorized e-cigarette products as outlined in our priorities. We’ll also closely monitor the use rates of all e-cigarette products and take additional steps to address youth use as necessary.”
The American Medical Association criticized the action as not going far enough, even though it was a step in the right direction.
“The AMA is disappointed that menthol flavors, one of the most popular, will still be allowed, and that flavored e-liquids will remain on the market, leaving young people with easy access to alternative flavored e-cigarette products,” AMA President Patrice A. Harris, MD, said in a statement. “If we are serious about tackling this epidemic and keeping these harmful products out of the hands of young people, a total ban on all flavored e-cigarettes, in all forms and at all locations, is prudent and urgently needed. We are pleased the administration committed today to closely monitoring the situation and trends in e-cigarette use among young people, and to taking further action if needed.”
but states it is not a “ban.”
On Jan. 2, the agency issued enforcement guidance alerting companies that manufacture, distribute, and sell unauthorized flavored cartridge-based e-cigarettes within the next 30 days will risk FDA enforcement action.
FDA has had the authority to require premarket authorization of all e-cigarettes and other electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS) since August 2016, but thus far has exercised enforcement discretion regarding the need for premarket authorization for these types of products.
“By prioritizing enforcement against the products that are most widely used by children, our action today seeks to strike the right public health balance by maintaining e-cigarettes as a potential off-ramp for adults using combustible tobacco while ensuring these products don’t provide an on-ramp to nicotine addiction for our youth,” Department of Health & Human Services Secretary Alex Azar said in a statement.
The action comes in the wake of more than 2,500 vaping-related injuries being reported, including more than 50 deaths associated with vaping reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (although many are related to the use of tetrahydrocannabinol [THC] within vaping products) and a continued rise in youth use of e-cigarettes noted in government surveys.
The agency noted in a Jan. 2 statement announcing the enforcement action that, to date, no ENDS products have received a premarket authorization, “meaning that all ENDS products currently on the market are considered illegally marketed and are subject to enforcement, at any time, in the FDA’s discretion.”
FDA said it is prioritizing enforcement in 30 days against:
- Any flavored, cartridge-based ENDS product, other than those with a tobacco or menthol flavoring.
- All other ENDS products for which manufacturers are failing to take adequate measures to prevent access by minors.
- Any ENDS product that is targeted to minors or is likely to promote use by minors.
In the last category, this might include labeling or advertising resembling “kid-friendly food and drinks such as juice boxes or kid-friendly cereal; products marketed directly to minors by promoting ease of concealing the product or disguising it as another product; and products marketed with characters designed to appeal to youth,” according to the FDA statement.
As of May 12, FDA also will prioritize enforcement against any ENDS product for which the manufacturer has not submitted a premarket application. The agency will continue to exercise enforcement discretion for up to 1 year on these products if an application has been submitted, pending the review of that application.
“By not prioritizing enforcement against other flavored ENDS products in the same way as flavored cartridge-based ENDS products, the FDA has attempted to balance the public health concerns related to youth use of ENDS products with consideration regarding addicted adult cigarette smokers who may try to use ENDS products to transition away from combustible tobacco products,” the agency stated, adding that cartridge-based ENDS products are most commonly used among youth.
The FDA statement noted that the enforcement priorities outlined in the guidance document were not a “ban” on flavored or cartridge-based ENDS, noting the agency “has already accepted and begun review of several premarket applications for flavored ENDS products through the pathway that Congress established in the Tobacco Control Act. ... If a company can demonstrate to the FDA that a specific product meets the applicable standard set forth by Congress, including considering how the marketing of the product may affect youth initiation and use, then the FDA could authorize that product for sale.”
“Coupled with the recently signed legislation increasing the minimum age of sale of tobacco to 21, we believe this policy balances the urgency with which we must address the public health threat of youth use of e-cigarette products with the potential role that e-cigarettes may play in helping adult smokers transition completely away from combustible tobacco to a potentially less risky form of nicotine delivery,” FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD, said in a statement. “While we expect that responsible members of industry will comply with premarket requirements, we’re ready to take action against any unauthorized e-cigarette products as outlined in our priorities. We’ll also closely monitor the use rates of all e-cigarette products and take additional steps to address youth use as necessary.”
The American Medical Association criticized the action as not going far enough, even though it was a step in the right direction.
“The AMA is disappointed that menthol flavors, one of the most popular, will still be allowed, and that flavored e-liquids will remain on the market, leaving young people with easy access to alternative flavored e-cigarette products,” AMA President Patrice A. Harris, MD, said in a statement. “If we are serious about tackling this epidemic and keeping these harmful products out of the hands of young people, a total ban on all flavored e-cigarettes, in all forms and at all locations, is prudent and urgently needed. We are pleased the administration committed today to closely monitoring the situation and trends in e-cigarette use among young people, and to taking further action if needed.”
Dual e-cigarette and combustible tobacco use compound respiratory disease risk
according to recent longitudinal analysis published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
E-cigarettes have been promoted as a safer alternative to combustible tobacco, and until recently, there has been little and conflicting evidence by which to test this hypothesis. This study conducted by Dharma N. Bhatta, PhD, and Stanton A. Glantz, PhD, of the Center for Tobacco Control Research and Education at the University of California, San Francisco, is one of the first longitudinal examinations of e-cigarette use and controlling for combustible tobacco use.
Dr. Bhatta and Dr. Glantz performed a multivariable, logistic regression analysis of adults enrolled in the nationally representative, population-based, longitudinal Population Assessment of Tobacco and Health study. The researchers analyzed the tobacco use of adults in the study in three waves, following them through wave 1 (September 2013 to December 2014), wave 2 (October 2014 to October 2015), and wave 3 (October 2015 to October 2016), analyzing the data between 2018 and 2019. Overall, wave 1 began with 32,320 participants, and 15.1% of adults reported respiratory disease at baseline.
Lung or respiratory disease was assessed by asking participants whether they had been told by a health professional that they had chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or asthma. The researchers defined e-cigarette and combustible tobacco use as participants who never, currently, or formerly used e-cigarettes or smoked combustible tobacco. Participants who indicated they used e-cigarettes or combustible tobacco frequently or infrequently were placed in the current-user group, while past users were those participants who said they used to, but no longer use e-cigarettes or combustible tobacco.
The results showed former e-cigarette use (adjusted odds ratio, 1.34; 95% confidence interval, 1.23-1.46) and current e-cigarette use (aOR, 1.32; 95% CI, 1.17-1.49) were associated with an increased risk of having incident respiratory disease.
The data showed a not unexpected statistically significant association between former combustible tobacco use (aOR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.14-1.47) as well as current combustible tobacco use (aOR, 1.61; 95% CI, 1.42-1.82) and incident respiratory disease risk.
There was a statistically significant association between respiratory disease and former or current e-cigarette use for adults who did not have respiratory disease at baseline, after adjusting for factors such as current combustible tobacco use, clinical variables, and demographic differences. Participants in wave 1 who reported former (aOR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.07-1.60) or current e-cigarette use (aOR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.03-1.61) had a significantly higher risk of developing incident respiratory disease in subsequent waves. There was also a statistically significant association between use of combustible tobacco and subsequent respiratory disease in later waves of the study (aOR, 2.56; 95% CI, 1.92-3.41), which the researchers noted was independent of the usual risks associated with combustible tobacco.
The investigators also looked at the link between dual use of e-cigarettes and combustible tobacco and respiratory disease risk. “The much more common pattern is dual use, in which an e-cigarette user continues to smoke combusted tobacco products at the same time (93.7% of e-cigarette users at wave 2 and 91.2% at wave 3 also used combustible tobacco; 73.3% of e-cigarette users at wave 2 and 64.9% at wave 3 also smoked cigarettes),” they wrote.
The odds of developing respiratory disease for participants who used both e-cigarettes and combustible tobacco were 3.30, compared with a participant who never used e-cigarettes, with similar results seen when comparing e-cigarettes and cigarettes.
“Although switching from combustible tobacco, including cigarettes, to e-cigarettes theoretically could reduce the risk of developing respiratory disease, current evidence indicates a high prevalence of dual use, which is associated with in-creased risk beyond combustible tobacco use,” the investigators wrote.
Harold J. Farber, MD, FCCP, professor of pediatrics in the pulmonary section at Baylor College of Medicine and Texas Children’s Hospital, both in Houston, said in an interview that the increased respiratory risk among dual users, who are likely using e-cigarettes and combustible tobacco together as a way to quit smoking, is particularly concerning.
“There is substantial reason to be concerned about efficacy of electronic cigarette products. Real-world observational studies have shown that, on average, tobacco smokers who use electronic cigarettes are less likely to stop smoking than those who do not use electronic cigarettes,” he said. “People who have stopped tobacco smoking but use electronic cigarettes are more likely to relapse to tobacco smoking than those who do not use electronic cigarettes.”
Dr. Farber noted that there are other Food and Drug Administration–approved medications for treating tobacco addiction. In addition, the World Health Organization, American Medical Association, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and FDA have all advised that e-cigarettes should not be used as smoking cessation aids, he said, especially in light of current outbreak of life-threatening e-cigarette and vaping lung injuries currently being investigated by the CDC and FDA.
“These study results suggest that the CDC reports of e-cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury are likely to be just the tip of the iceberg,” he said. “Although the CDC has identified vitamin E acetate–containing products as an important culprit, it is unlikely to be the only one. There are many substances in the emissions of e-cigarettes that have known irritant and/or toxic effects on the airways.”
Dr. Bhatta and Dr. Glantz acknowledged several limitations in their analysis, including the possibility of recall bias, not distinguishing between nondaily and daily e-cigarette or combustible tobacco use, and combining respiratory conditions together to achieve adequate power. The study shows an association, but the mechanism by which e-cigarettes may contribute to the development of lung disease remains under investigation.
This study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Drug Abuse; the National Cancer Institute; the FDA Center for Tobacco Products; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and the University of California, San Francisco Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center Global Cancer Program. Dr. Bhatta and Dr. Glantz reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Bhatta DN, Glantz SA. Am J Prev Med. 2019 Dec 16. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2019.07.028.
according to recent longitudinal analysis published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
E-cigarettes have been promoted as a safer alternative to combustible tobacco, and until recently, there has been little and conflicting evidence by which to test this hypothesis. This study conducted by Dharma N. Bhatta, PhD, and Stanton A. Glantz, PhD, of the Center for Tobacco Control Research and Education at the University of California, San Francisco, is one of the first longitudinal examinations of e-cigarette use and controlling for combustible tobacco use.
Dr. Bhatta and Dr. Glantz performed a multivariable, logistic regression analysis of adults enrolled in the nationally representative, population-based, longitudinal Population Assessment of Tobacco and Health study. The researchers analyzed the tobacco use of adults in the study in three waves, following them through wave 1 (September 2013 to December 2014), wave 2 (October 2014 to October 2015), and wave 3 (October 2015 to October 2016), analyzing the data between 2018 and 2019. Overall, wave 1 began with 32,320 participants, and 15.1% of adults reported respiratory disease at baseline.
Lung or respiratory disease was assessed by asking participants whether they had been told by a health professional that they had chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or asthma. The researchers defined e-cigarette and combustible tobacco use as participants who never, currently, or formerly used e-cigarettes or smoked combustible tobacco. Participants who indicated they used e-cigarettes or combustible tobacco frequently or infrequently were placed in the current-user group, while past users were those participants who said they used to, but no longer use e-cigarettes or combustible tobacco.
The results showed former e-cigarette use (adjusted odds ratio, 1.34; 95% confidence interval, 1.23-1.46) and current e-cigarette use (aOR, 1.32; 95% CI, 1.17-1.49) were associated with an increased risk of having incident respiratory disease.
The data showed a not unexpected statistically significant association between former combustible tobacco use (aOR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.14-1.47) as well as current combustible tobacco use (aOR, 1.61; 95% CI, 1.42-1.82) and incident respiratory disease risk.
There was a statistically significant association between respiratory disease and former or current e-cigarette use for adults who did not have respiratory disease at baseline, after adjusting for factors such as current combustible tobacco use, clinical variables, and demographic differences. Participants in wave 1 who reported former (aOR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.07-1.60) or current e-cigarette use (aOR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.03-1.61) had a significantly higher risk of developing incident respiratory disease in subsequent waves. There was also a statistically significant association between use of combustible tobacco and subsequent respiratory disease in later waves of the study (aOR, 2.56; 95% CI, 1.92-3.41), which the researchers noted was independent of the usual risks associated with combustible tobacco.
The investigators also looked at the link between dual use of e-cigarettes and combustible tobacco and respiratory disease risk. “The much more common pattern is dual use, in which an e-cigarette user continues to smoke combusted tobacco products at the same time (93.7% of e-cigarette users at wave 2 and 91.2% at wave 3 also used combustible tobacco; 73.3% of e-cigarette users at wave 2 and 64.9% at wave 3 also smoked cigarettes),” they wrote.
The odds of developing respiratory disease for participants who used both e-cigarettes and combustible tobacco were 3.30, compared with a participant who never used e-cigarettes, with similar results seen when comparing e-cigarettes and cigarettes.
“Although switching from combustible tobacco, including cigarettes, to e-cigarettes theoretically could reduce the risk of developing respiratory disease, current evidence indicates a high prevalence of dual use, which is associated with in-creased risk beyond combustible tobacco use,” the investigators wrote.
Harold J. Farber, MD, FCCP, professor of pediatrics in the pulmonary section at Baylor College of Medicine and Texas Children’s Hospital, both in Houston, said in an interview that the increased respiratory risk among dual users, who are likely using e-cigarettes and combustible tobacco together as a way to quit smoking, is particularly concerning.
“There is substantial reason to be concerned about efficacy of electronic cigarette products. Real-world observational studies have shown that, on average, tobacco smokers who use electronic cigarettes are less likely to stop smoking than those who do not use electronic cigarettes,” he said. “People who have stopped tobacco smoking but use electronic cigarettes are more likely to relapse to tobacco smoking than those who do not use electronic cigarettes.”
Dr. Farber noted that there are other Food and Drug Administration–approved medications for treating tobacco addiction. In addition, the World Health Organization, American Medical Association, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and FDA have all advised that e-cigarettes should not be used as smoking cessation aids, he said, especially in light of current outbreak of life-threatening e-cigarette and vaping lung injuries currently being investigated by the CDC and FDA.
“These study results suggest that the CDC reports of e-cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury are likely to be just the tip of the iceberg,” he said. “Although the CDC has identified vitamin E acetate–containing products as an important culprit, it is unlikely to be the only one. There are many substances in the emissions of e-cigarettes that have known irritant and/or toxic effects on the airways.”
Dr. Bhatta and Dr. Glantz acknowledged several limitations in their analysis, including the possibility of recall bias, not distinguishing between nondaily and daily e-cigarette or combustible tobacco use, and combining respiratory conditions together to achieve adequate power. The study shows an association, but the mechanism by which e-cigarettes may contribute to the development of lung disease remains under investigation.
This study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Drug Abuse; the National Cancer Institute; the FDA Center for Tobacco Products; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and the University of California, San Francisco Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center Global Cancer Program. Dr. Bhatta and Dr. Glantz reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Bhatta DN, Glantz SA. Am J Prev Med. 2019 Dec 16. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2019.07.028.
according to recent longitudinal analysis published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
E-cigarettes have been promoted as a safer alternative to combustible tobacco, and until recently, there has been little and conflicting evidence by which to test this hypothesis. This study conducted by Dharma N. Bhatta, PhD, and Stanton A. Glantz, PhD, of the Center for Tobacco Control Research and Education at the University of California, San Francisco, is one of the first longitudinal examinations of e-cigarette use and controlling for combustible tobacco use.
Dr. Bhatta and Dr. Glantz performed a multivariable, logistic regression analysis of adults enrolled in the nationally representative, population-based, longitudinal Population Assessment of Tobacco and Health study. The researchers analyzed the tobacco use of adults in the study in three waves, following them through wave 1 (September 2013 to December 2014), wave 2 (October 2014 to October 2015), and wave 3 (October 2015 to October 2016), analyzing the data between 2018 and 2019. Overall, wave 1 began with 32,320 participants, and 15.1% of adults reported respiratory disease at baseline.
Lung or respiratory disease was assessed by asking participants whether they had been told by a health professional that they had chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or asthma. The researchers defined e-cigarette and combustible tobacco use as participants who never, currently, or formerly used e-cigarettes or smoked combustible tobacco. Participants who indicated they used e-cigarettes or combustible tobacco frequently or infrequently were placed in the current-user group, while past users were those participants who said they used to, but no longer use e-cigarettes or combustible tobacco.
The results showed former e-cigarette use (adjusted odds ratio, 1.34; 95% confidence interval, 1.23-1.46) and current e-cigarette use (aOR, 1.32; 95% CI, 1.17-1.49) were associated with an increased risk of having incident respiratory disease.
The data showed a not unexpected statistically significant association between former combustible tobacco use (aOR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.14-1.47) as well as current combustible tobacco use (aOR, 1.61; 95% CI, 1.42-1.82) and incident respiratory disease risk.
There was a statistically significant association between respiratory disease and former or current e-cigarette use for adults who did not have respiratory disease at baseline, after adjusting for factors such as current combustible tobacco use, clinical variables, and demographic differences. Participants in wave 1 who reported former (aOR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.07-1.60) or current e-cigarette use (aOR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.03-1.61) had a significantly higher risk of developing incident respiratory disease in subsequent waves. There was also a statistically significant association between use of combustible tobacco and subsequent respiratory disease in later waves of the study (aOR, 2.56; 95% CI, 1.92-3.41), which the researchers noted was independent of the usual risks associated with combustible tobacco.
The investigators also looked at the link between dual use of e-cigarettes and combustible tobacco and respiratory disease risk. “The much more common pattern is dual use, in which an e-cigarette user continues to smoke combusted tobacco products at the same time (93.7% of e-cigarette users at wave 2 and 91.2% at wave 3 also used combustible tobacco; 73.3% of e-cigarette users at wave 2 and 64.9% at wave 3 also smoked cigarettes),” they wrote.
The odds of developing respiratory disease for participants who used both e-cigarettes and combustible tobacco were 3.30, compared with a participant who never used e-cigarettes, with similar results seen when comparing e-cigarettes and cigarettes.
“Although switching from combustible tobacco, including cigarettes, to e-cigarettes theoretically could reduce the risk of developing respiratory disease, current evidence indicates a high prevalence of dual use, which is associated with in-creased risk beyond combustible tobacco use,” the investigators wrote.
Harold J. Farber, MD, FCCP, professor of pediatrics in the pulmonary section at Baylor College of Medicine and Texas Children’s Hospital, both in Houston, said in an interview that the increased respiratory risk among dual users, who are likely using e-cigarettes and combustible tobacco together as a way to quit smoking, is particularly concerning.
“There is substantial reason to be concerned about efficacy of electronic cigarette products. Real-world observational studies have shown that, on average, tobacco smokers who use electronic cigarettes are less likely to stop smoking than those who do not use electronic cigarettes,” he said. “People who have stopped tobacco smoking but use electronic cigarettes are more likely to relapse to tobacco smoking than those who do not use electronic cigarettes.”
Dr. Farber noted that there are other Food and Drug Administration–approved medications for treating tobacco addiction. In addition, the World Health Organization, American Medical Association, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and FDA have all advised that e-cigarettes should not be used as smoking cessation aids, he said, especially in light of current outbreak of life-threatening e-cigarette and vaping lung injuries currently being investigated by the CDC and FDA.
“These study results suggest that the CDC reports of e-cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury are likely to be just the tip of the iceberg,” he said. “Although the CDC has identified vitamin E acetate–containing products as an important culprit, it is unlikely to be the only one. There are many substances in the emissions of e-cigarettes that have known irritant and/or toxic effects on the airways.”
Dr. Bhatta and Dr. Glantz acknowledged several limitations in their analysis, including the possibility of recall bias, not distinguishing between nondaily and daily e-cigarette or combustible tobacco use, and combining respiratory conditions together to achieve adequate power. The study shows an association, but the mechanism by which e-cigarettes may contribute to the development of lung disease remains under investigation.
This study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Drug Abuse; the National Cancer Institute; the FDA Center for Tobacco Products; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and the University of California, San Francisco Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center Global Cancer Program. Dr. Bhatta and Dr. Glantz reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Bhatta DN, Glantz SA. Am J Prev Med. 2019 Dec 16. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2019.07.028.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PREVENTIVE MEDICINE
Early increase in flu activity shows no signs of slowing
An important measure of U.S. flu activity for the 2019-2020 season has already surpassed last season’s high, and more than half the states are experiencing high levels of activity, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
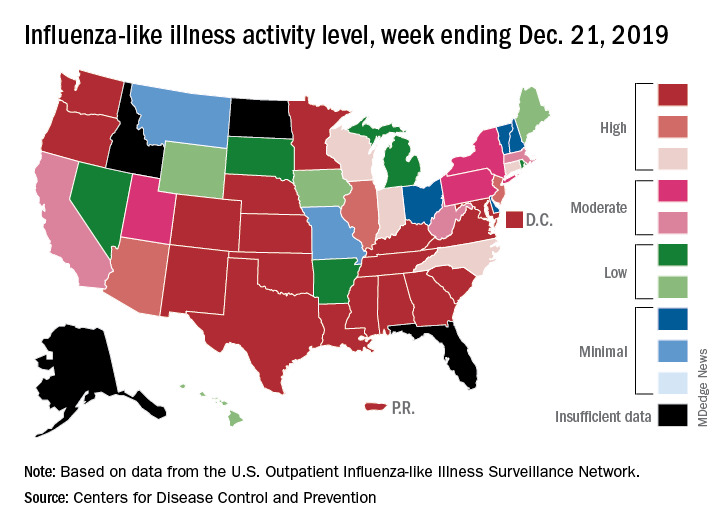
reported Dec. 27.
The last time the outpatient visit rate was higher than that was in February of the 2017-2018 season, when it peaked at 7.5%. The peak month of flu activity occurs most often – about once every 3 years – in February, and the odds of a December peak are about one in five, the CDC has said.
Outpatient illness activity also increased at the state level during the week ending Dec. 21. There were 20 jurisdictions – 18 states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico – at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale of activity, compared with 13 the previous week, and the number of jurisdictions in the “high” range (levels 8-10) jumped from 21 to 28, the CDC data show.
The influenza division estimated that there have been 4.6 million flu illnesses so far this season, nearly a million more than the total after last week, along with 39,000 hospitalizations. The overall hospitalization rate for the season is up to 6.6 per 100,000 population, which is about average at this point. The proportion of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza increased to 5.7%, which is below the epidemic threshold, the CDC said.
Three pediatric deaths related to influenza-like illness were reported during the week ending Dec. 21, two of which occurred in an earlier week. For the 2019-2020 season so far, a total of 22 pediatric deaths have been reported to the CDC.
An important measure of U.S. flu activity for the 2019-2020 season has already surpassed last season’s high, and more than half the states are experiencing high levels of activity, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

reported Dec. 27.
The last time the outpatient visit rate was higher than that was in February of the 2017-2018 season, when it peaked at 7.5%. The peak month of flu activity occurs most often – about once every 3 years – in February, and the odds of a December peak are about one in five, the CDC has said.
Outpatient illness activity also increased at the state level during the week ending Dec. 21. There were 20 jurisdictions – 18 states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico – at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale of activity, compared with 13 the previous week, and the number of jurisdictions in the “high” range (levels 8-10) jumped from 21 to 28, the CDC data show.
The influenza division estimated that there have been 4.6 million flu illnesses so far this season, nearly a million more than the total after last week, along with 39,000 hospitalizations. The overall hospitalization rate for the season is up to 6.6 per 100,000 population, which is about average at this point. The proportion of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza increased to 5.7%, which is below the epidemic threshold, the CDC said.
Three pediatric deaths related to influenza-like illness were reported during the week ending Dec. 21, two of which occurred in an earlier week. For the 2019-2020 season so far, a total of 22 pediatric deaths have been reported to the CDC.
An important measure of U.S. flu activity for the 2019-2020 season has already surpassed last season’s high, and more than half the states are experiencing high levels of activity, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

reported Dec. 27.
The last time the outpatient visit rate was higher than that was in February of the 2017-2018 season, when it peaked at 7.5%. The peak month of flu activity occurs most often – about once every 3 years – in February, and the odds of a December peak are about one in five, the CDC has said.
Outpatient illness activity also increased at the state level during the week ending Dec. 21. There were 20 jurisdictions – 18 states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico – at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale of activity, compared with 13 the previous week, and the number of jurisdictions in the “high” range (levels 8-10) jumped from 21 to 28, the CDC data show.
The influenza division estimated that there have been 4.6 million flu illnesses so far this season, nearly a million more than the total after last week, along with 39,000 hospitalizations. The overall hospitalization rate for the season is up to 6.6 per 100,000 population, which is about average at this point. The proportion of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza increased to 5.7%, which is below the epidemic threshold, the CDC said.
Three pediatric deaths related to influenza-like illness were reported during the week ending Dec. 21, two of which occurred in an earlier week. For the 2019-2020 season so far, a total of 22 pediatric deaths have been reported to the CDC.
New cystic fibrosis therapy raises hopes among specialists and patients
A newly approved triple-combination modulator to treat cystic fibrosis (CF) has raised expectations of a treatment turning point among patients and specialists. If the early results are sustained, elexacaftor/ivacaftor/tezacaftor (Trikafta) could prove to be the rare case of a much-touted new medicine that meets high expectations.
“CF even in infants causes inflammation, so we know that lung damage can start early and progress,” said Susan Millard, MD, FCCP, of Helen DeVos Children’s Hospital in Grand Rapids, Mich., and the local clinical research director for the pediatric pulmonary and sleep medicine section. “This oral drug therapy is actually treating the underlying problem, as opposed to many of the therapies we have that take hours to nebulize and only work locally in the airways.”
Dr. Millard is the recent past pediatric editor for Chest Physician and has been a local principal investigator at Helen DeVos Children’s Hospital for many Vertex-sponsored clinical studies.
The pivotal studies
The Food and Drug Administration approval of Trikafta rested on two pivotal phase 3, placebo-controlled studies, one in patients with two copies of the most common CF mutations, F508del, and the second in patients with one copy of F508del and a second mutation that was called a “minimal-function” mutation. The findings have ignited the hopes of many people with CF and their physicians. The drug was approved in October 2019 for patients aged 12 years and older who have at least one F508del mutation of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene. About 90% of patients in the United States have at least one copy of F508del. In the study looking at patients with one copy of F508del, the mean predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second increased 13.8% in patients taking the drug versus placebo (N Engl J Med. 2019 Oct 31. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1908639). The number of pulmonary exacerbations decreased by 63% in the Trikafta group, compared with placebo. Pulmonary exacerbations were described as a change in specific symptoms that required treatment with a new oral, intravenous, or inhaled antibiotic. Serious adverse drug reactions that occurred more frequently in patients receiving Trikafta, compared with placebo, were rash and influenza events.
In the study that included patients with two copies of F508del, on average, the lung function increased 10% versus patients on ivacaftor/tezacaftor at 4 weeks. In addition, there was a 45.1 mmol/L on average decrease in the sweat chloride level in the Trikafta group, compared with ivacaftor/tezacaftor.
A hopeful start
Robert Giusti, MD, a pediatric pulmonologist at New York University Langone Health, is also hopeful. “This could be the kind of treatment that will make a revolution in terms of [cystic fibrosis] care if it can be started very early in life shortly after diagnosis. We anticipate that patients will be disease free for a longer period of time.”
The Cystic Fibrosis Foundation’s (CFF) “venture philanthropy” initiative played an important role in the development of the drug by Vertex Pharmaceuticals. The CFF has invested many millions of dollars in research by drug companies since the 1980s and was an early backer of Vertex. According to a statement on the CFF website, the Foundation sold its royalty rights for treatments developed by Vertex for $3.3 billion in 2014. The drug has a list price of about $311,000 a year. Payment issues may arise in the future, but for now, Vertex has stated that insurers and some Medicaid programs have begun paying claims for Trikafta
Specialists who treat CF now are watching to see how well patients tolerate this highly anticipated drug – and how well it meets expectations. The Therapeutic Development Network, the clinical research division of the CFF, is enrolling patients taking Trikafta in an observational study to follow for long-term follow-up.
Meeting expectations
“[Long-term efficacy is] something that we’re always concerned about. When the drug comes to market, is it going to be as effective as we thought it might be?” said Ryan Thomas, MD, director of the Cystic Fibrosis Center at Michigan State University, East Lansing. The MSU Cystic Fibrosis Center receives funding from the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation.
Almost one in five patients could not tolerate treatment with Orkambi, most often because of adverse breathing events, according to a French study published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. The investigators wrote: “Among the 845 patients (292 adolescents, 553 adults) who initiated lumacaftor/ivacaftor, 18.2% (154 patients) discontinued treatment, often due to respiratory (48.1%, 74 patients) or nonrespiratory (27.9%, 43 patients) adverse events” and that the discontinuation rate was considerably higher than previously reported in clinical trials.
“We thought [Orkambi] was going to be something that could have a big effect,” Dr. Thomas said. “It turned out that it was harder for people to tolerate than we thought and the improvements weren’t as sustained as we thought they might be. I really don’t think this will end up being the case with Trikafta.”
Longer-term data are starting to emerge, which may ease some of the concerns inherent in working with a newer medicine. “These [data] suggest that this is going to be a game changer,” Dr. Thomas said. “If Trikafta is this efficacious, well, we’re talking about having people with CF who will live full lifespans without a lung transplant, and that is so rare.”
The decrease in hospitalizations, improved CT scans, and lower rates of lung function decline suggest it could be “the Holy Grail,” Dr. Thomas said.
A different disease
Trikafta is the latest in a series of improvements of CF treatment in recent decades, recalled Dr. Giusti, who has been in this field for about 3 decades. “It used to be that I attended many funerals for children with CF. Now with patients living longer and healthier lives I am invited to attend their weddings and even their children’s baptisms and bris ceremonies. It is a very different disease than it used to be.”
The promise of Trikafta leaves behind the minority of patients for whom the drug won’t work. This is for the 10% of patients that have rare mutations. That can lead to difficult conversations with parents about why this new option is not a choice for their child, Dr. Millard said. “It just crushes you, but the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation is committing a lot of new research in that direction. Their mantra is ‘until it is done.’ ”
Realistic expectations
William (Randy) Hunt, MD, FAAP, FACP, assistant professor of medicine in the Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, Critical Care and Sleep, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, agrees that Trikafta is an exciting development in CF treatment. He noted, “Starting this medication early in life may very well significantly attenuate the disease, but it is not a cure. For individuals who already have significant disease, we may not see the same level of improvements in lung function as what we saw in the studies. The studies generally excluded individuals with ppFEV1 < 40%. Nevertheless, I remain optimistic and have been prescribing it to nearly everyone that qualifies after a discussion.”
Dr. Hunt added, “Patients are asking if they can stop their current chronic CF therapies once they start Trikafta. The answer is “no, at least not right now.” While all the relatively short-term data around Trikafta are very promising, we do not yet know how sustained the long-term benefits will be. Still, safely removing therapeutic burden from our patient population is a real interest. There are plans underway by the CFF and other institutions to systematically research whether discontinuing chronic CF therapies is safe in the setting of Trikafta.”
He concluded that 10% of individuals with CF mutations still do not respond to the modulators currently available. “We will not leave that population behind, but treating these remaining mutations is going to take continued efforts and likely modulators that are therapeutically differently from the mechanism of actions of those that are currently available,” he said.
Therese Borden contributed to this article.
1/2/2020 - This story was updated.
A newly approved triple-combination modulator to treat cystic fibrosis (CF) has raised expectations of a treatment turning point among patients and specialists. If the early results are sustained, elexacaftor/ivacaftor/tezacaftor (Trikafta) could prove to be the rare case of a much-touted new medicine that meets high expectations.
“CF even in infants causes inflammation, so we know that lung damage can start early and progress,” said Susan Millard, MD, FCCP, of Helen DeVos Children’s Hospital in Grand Rapids, Mich., and the local clinical research director for the pediatric pulmonary and sleep medicine section. “This oral drug therapy is actually treating the underlying problem, as opposed to many of the therapies we have that take hours to nebulize and only work locally in the airways.”
Dr. Millard is the recent past pediatric editor for Chest Physician and has been a local principal investigator at Helen DeVos Children’s Hospital for many Vertex-sponsored clinical studies.
The pivotal studies
The Food and Drug Administration approval of Trikafta rested on two pivotal phase 3, placebo-controlled studies, one in patients with two copies of the most common CF mutations, F508del, and the second in patients with one copy of F508del and a second mutation that was called a “minimal-function” mutation. The findings have ignited the hopes of many people with CF and their physicians. The drug was approved in October 2019 for patients aged 12 years and older who have at least one F508del mutation of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene. About 90% of patients in the United States have at least one copy of F508del. In the study looking at patients with one copy of F508del, the mean predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second increased 13.8% in patients taking the drug versus placebo (N Engl J Med. 2019 Oct 31. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1908639). The number of pulmonary exacerbations decreased by 63% in the Trikafta group, compared with placebo. Pulmonary exacerbations were described as a change in specific symptoms that required treatment with a new oral, intravenous, or inhaled antibiotic. Serious adverse drug reactions that occurred more frequently in patients receiving Trikafta, compared with placebo, were rash and influenza events.
In the study that included patients with two copies of F508del, on average, the lung function increased 10% versus patients on ivacaftor/tezacaftor at 4 weeks. In addition, there was a 45.1 mmol/L on average decrease in the sweat chloride level in the Trikafta group, compared with ivacaftor/tezacaftor.
A hopeful start
Robert Giusti, MD, a pediatric pulmonologist at New York University Langone Health, is also hopeful. “This could be the kind of treatment that will make a revolution in terms of [cystic fibrosis] care if it can be started very early in life shortly after diagnosis. We anticipate that patients will be disease free for a longer period of time.”
The Cystic Fibrosis Foundation’s (CFF) “venture philanthropy” initiative played an important role in the development of the drug by Vertex Pharmaceuticals. The CFF has invested many millions of dollars in research by drug companies since the 1980s and was an early backer of Vertex. According to a statement on the CFF website, the Foundation sold its royalty rights for treatments developed by Vertex for $3.3 billion in 2014. The drug has a list price of about $311,000 a year. Payment issues may arise in the future, but for now, Vertex has stated that insurers and some Medicaid programs have begun paying claims for Trikafta
Specialists who treat CF now are watching to see how well patients tolerate this highly anticipated drug – and how well it meets expectations. The Therapeutic Development Network, the clinical research division of the CFF, is enrolling patients taking Trikafta in an observational study to follow for long-term follow-up.
Meeting expectations
“[Long-term efficacy is] something that we’re always concerned about. When the drug comes to market, is it going to be as effective as we thought it might be?” said Ryan Thomas, MD, director of the Cystic Fibrosis Center at Michigan State University, East Lansing. The MSU Cystic Fibrosis Center receives funding from the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation.
Almost one in five patients could not tolerate treatment with Orkambi, most often because of adverse breathing events, according to a French study published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. The investigators wrote: “Among the 845 patients (292 adolescents, 553 adults) who initiated lumacaftor/ivacaftor, 18.2% (154 patients) discontinued treatment, often due to respiratory (48.1%, 74 patients) or nonrespiratory (27.9%, 43 patients) adverse events” and that the discontinuation rate was considerably higher than previously reported in clinical trials.
“We thought [Orkambi] was going to be something that could have a big effect,” Dr. Thomas said. “It turned out that it was harder for people to tolerate than we thought and the improvements weren’t as sustained as we thought they might be. I really don’t think this will end up being the case with Trikafta.”
Longer-term data are starting to emerge, which may ease some of the concerns inherent in working with a newer medicine. “These [data] suggest that this is going to be a game changer,” Dr. Thomas said. “If Trikafta is this efficacious, well, we’re talking about having people with CF who will live full lifespans without a lung transplant, and that is so rare.”
The decrease in hospitalizations, improved CT scans, and lower rates of lung function decline suggest it could be “the Holy Grail,” Dr. Thomas said.
A different disease
Trikafta is the latest in a series of improvements of CF treatment in recent decades, recalled Dr. Giusti, who has been in this field for about 3 decades. “It used to be that I attended many funerals for children with CF. Now with patients living longer and healthier lives I am invited to attend their weddings and even their children’s baptisms and bris ceremonies. It is a very different disease than it used to be.”
The promise of Trikafta leaves behind the minority of patients for whom the drug won’t work. This is for the 10% of patients that have rare mutations. That can lead to difficult conversations with parents about why this new option is not a choice for their child, Dr. Millard said. “It just crushes you, but the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation is committing a lot of new research in that direction. Their mantra is ‘until it is done.’ ”
Realistic expectations
William (Randy) Hunt, MD, FAAP, FACP, assistant professor of medicine in the Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, Critical Care and Sleep, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, agrees that Trikafta is an exciting development in CF treatment. He noted, “Starting this medication early in life may very well significantly attenuate the disease, but it is not a cure. For individuals who already have significant disease, we may not see the same level of improvements in lung function as what we saw in the studies. The studies generally excluded individuals with ppFEV1 < 40%. Nevertheless, I remain optimistic and have been prescribing it to nearly everyone that qualifies after a discussion.”
Dr. Hunt added, “Patients are asking if they can stop their current chronic CF therapies once they start Trikafta. The answer is “no, at least not right now.” While all the relatively short-term data around Trikafta are very promising, we do not yet know how sustained the long-term benefits will be. Still, safely removing therapeutic burden from our patient population is a real interest. There are plans underway by the CFF and other institutions to systematically research whether discontinuing chronic CF therapies is safe in the setting of Trikafta.”
He concluded that 10% of individuals with CF mutations still do not respond to the modulators currently available. “We will not leave that population behind, but treating these remaining mutations is going to take continued efforts and likely modulators that are therapeutically differently from the mechanism of actions of those that are currently available,” he said.
Therese Borden contributed to this article.
1/2/2020 - This story was updated.
A newly approved triple-combination modulator to treat cystic fibrosis (CF) has raised expectations of a treatment turning point among patients and specialists. If the early results are sustained, elexacaftor/ivacaftor/tezacaftor (Trikafta) could prove to be the rare case of a much-touted new medicine that meets high expectations.
“CF even in infants causes inflammation, so we know that lung damage can start early and progress,” said Susan Millard, MD, FCCP, of Helen DeVos Children’s Hospital in Grand Rapids, Mich., and the local clinical research director for the pediatric pulmonary and sleep medicine section. “This oral drug therapy is actually treating the underlying problem, as opposed to many of the therapies we have that take hours to nebulize and only work locally in the airways.”
Dr. Millard is the recent past pediatric editor for Chest Physician and has been a local principal investigator at Helen DeVos Children’s Hospital for many Vertex-sponsored clinical studies.
The pivotal studies
The Food and Drug Administration approval of Trikafta rested on two pivotal phase 3, placebo-controlled studies, one in patients with two copies of the most common CF mutations, F508del, and the second in patients with one copy of F508del and a second mutation that was called a “minimal-function” mutation. The findings have ignited the hopes of many people with CF and their physicians. The drug was approved in October 2019 for patients aged 12 years and older who have at least one F508del mutation of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene. About 90% of patients in the United States have at least one copy of F508del. In the study looking at patients with one copy of F508del, the mean predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second increased 13.8% in patients taking the drug versus placebo (N Engl J Med. 2019 Oct 31. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1908639). The number of pulmonary exacerbations decreased by 63% in the Trikafta group, compared with placebo. Pulmonary exacerbations were described as a change in specific symptoms that required treatment with a new oral, intravenous, or inhaled antibiotic. Serious adverse drug reactions that occurred more frequently in patients receiving Trikafta, compared with placebo, were rash and influenza events.
In the study that included patients with two copies of F508del, on average, the lung function increased 10% versus patients on ivacaftor/tezacaftor at 4 weeks. In addition, there was a 45.1 mmol/L on average decrease in the sweat chloride level in the Trikafta group, compared with ivacaftor/tezacaftor.
A hopeful start
Robert Giusti, MD, a pediatric pulmonologist at New York University Langone Health, is also hopeful. “This could be the kind of treatment that will make a revolution in terms of [cystic fibrosis] care if it can be started very early in life shortly after diagnosis. We anticipate that patients will be disease free for a longer period of time.”
The Cystic Fibrosis Foundation’s (CFF) “venture philanthropy” initiative played an important role in the development of the drug by Vertex Pharmaceuticals. The CFF has invested many millions of dollars in research by drug companies since the 1980s and was an early backer of Vertex. According to a statement on the CFF website, the Foundation sold its royalty rights for treatments developed by Vertex for $3.3 billion in 2014. The drug has a list price of about $311,000 a year. Payment issues may arise in the future, but for now, Vertex has stated that insurers and some Medicaid programs have begun paying claims for Trikafta
Specialists who treat CF now are watching to see how well patients tolerate this highly anticipated drug – and how well it meets expectations. The Therapeutic Development Network, the clinical research division of the CFF, is enrolling patients taking Trikafta in an observational study to follow for long-term follow-up.
Meeting expectations
“[Long-term efficacy is] something that we’re always concerned about. When the drug comes to market, is it going to be as effective as we thought it might be?” said Ryan Thomas, MD, director of the Cystic Fibrosis Center at Michigan State University, East Lansing. The MSU Cystic Fibrosis Center receives funding from the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation.
Almost one in five patients could not tolerate treatment with Orkambi, most often because of adverse breathing events, according to a French study published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. The investigators wrote: “Among the 845 patients (292 adolescents, 553 adults) who initiated lumacaftor/ivacaftor, 18.2% (154 patients) discontinued treatment, often due to respiratory (48.1%, 74 patients) or nonrespiratory (27.9%, 43 patients) adverse events” and that the discontinuation rate was considerably higher than previously reported in clinical trials.
“We thought [Orkambi] was going to be something that could have a big effect,” Dr. Thomas said. “It turned out that it was harder for people to tolerate than we thought and the improvements weren’t as sustained as we thought they might be. I really don’t think this will end up being the case with Trikafta.”
Longer-term data are starting to emerge, which may ease some of the concerns inherent in working with a newer medicine. “These [data] suggest that this is going to be a game changer,” Dr. Thomas said. “If Trikafta is this efficacious, well, we’re talking about having people with CF who will live full lifespans without a lung transplant, and that is so rare.”
The decrease in hospitalizations, improved CT scans, and lower rates of lung function decline suggest it could be “the Holy Grail,” Dr. Thomas said.
A different disease
Trikafta is the latest in a series of improvements of CF treatment in recent decades, recalled Dr. Giusti, who has been in this field for about 3 decades. “It used to be that I attended many funerals for children with CF. Now with patients living longer and healthier lives I am invited to attend their weddings and even their children’s baptisms and bris ceremonies. It is a very different disease than it used to be.”
The promise of Trikafta leaves behind the minority of patients for whom the drug won’t work. This is for the 10% of patients that have rare mutations. That can lead to difficult conversations with parents about why this new option is not a choice for their child, Dr. Millard said. “It just crushes you, but the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation is committing a lot of new research in that direction. Their mantra is ‘until it is done.’ ”
Realistic expectations
William (Randy) Hunt, MD, FAAP, FACP, assistant professor of medicine in the Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, Critical Care and Sleep, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, agrees that Trikafta is an exciting development in CF treatment. He noted, “Starting this medication early in life may very well significantly attenuate the disease, but it is not a cure. For individuals who already have significant disease, we may not see the same level of improvements in lung function as what we saw in the studies. The studies generally excluded individuals with ppFEV1 < 40%. Nevertheless, I remain optimistic and have been prescribing it to nearly everyone that qualifies after a discussion.”
Dr. Hunt added, “Patients are asking if they can stop their current chronic CF therapies once they start Trikafta. The answer is “no, at least not right now.” While all the relatively short-term data around Trikafta are very promising, we do not yet know how sustained the long-term benefits will be. Still, safely removing therapeutic burden from our patient population is a real interest. There are plans underway by the CFF and other institutions to systematically research whether discontinuing chronic CF therapies is safe in the setting of Trikafta.”
He concluded that 10% of individuals with CF mutations still do not respond to the modulators currently available. “We will not leave that population behind, but treating these remaining mutations is going to take continued efforts and likely modulators that are therapeutically differently from the mechanism of actions of those that are currently available,” he said.
Therese Borden contributed to this article.
1/2/2020 - This story was updated.
The measles comeback of 2019
Measles made a comeback in 2019.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that, as of Dec. 5, 2019, 1,276 individual cases of measles of measles were confirmed in 31 states, the largest number since 1992. This number is a major uptick in cases, compared with previous years since 2000 when the CDC declared measles eliminated from the United States. No deaths have been reported for 2019.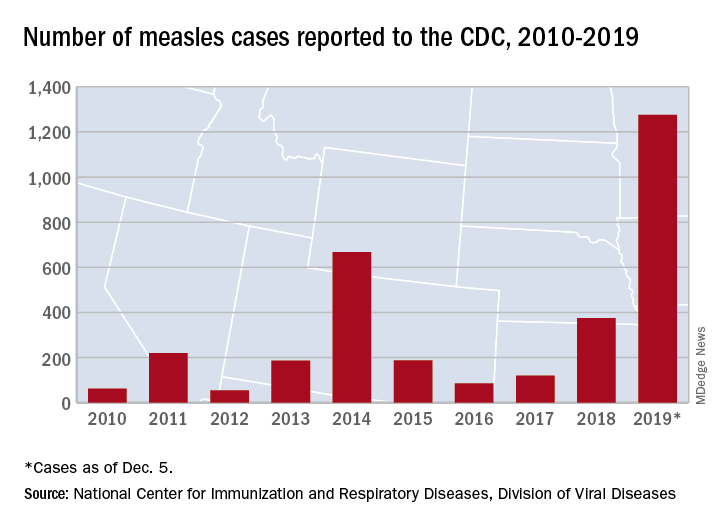
Three-quarters of these cases in 2019 were linked to recent outbreaks in New York and occurred in primarily in underimmunized, close-knit communities and in patients with links to international travel. A total of 124 of the people who got measles this year were hospitalized, and 61 reported having complications, including pneumonia and encephalitis. The overall median patient age was 6 years (31% aged 1-4 years, 27% aged 5-17 years, and 29% aged at least 18 years).
The good news is that most of these cases occurred in unvaccinated patients. The national vaccination rate for the almost 4 million kindergartners reported as enrolled in 2018-2019 was 94.7% for two doses of the MMR vaccine, falling just short of the CDC recommended 95% vaccination rate threshold. The CDC reported an approximate 2.5% rate of vaccination exemptions among school-age children.
The bad news is that, despite the high rate of MMR vaccination rates among U.S. children, there are gaps in measles protection in the U.S. population because of factors leaving patients immunocompromised and antivaccination sentiment that has led some parents to defer or refuse the MMR.
In addition, adults who were vaccinated prior to 1968 with either inactivated measles vaccine or measles vaccine of unknown type may have limited immunity. The inactivated measles vaccine, which was available in 1963-1967, did not achieve effective measles protection.
A global measles surge
While antivaccination sentiment contributed to the 2019 measles cases, a more significant factor may be the global surge of measles. More than 140,000 people worldwide died from measles in 2018, according to the World Health Organization and the CDC.
“[Recent data on measles] indicates that during the first 6 months of the year there have been more measles cases reported worldwide than in any year since 2006. From Jan. 1 to July 31, 2019, 182 countries reported 364,808 measles cases to the WHO. This surpasses the 129,239 reported during the same time period in 2018. WHO regions with the biggest increases in cases include the African region (900%), the Western Pacific region (230%), and the European region (150%),” according to a CDC report.
Studies on hospitalization and complications linked to measles in the United States are scarce, but two outbreaks in Minnesota (2011 and 2017) provided some data on what to expect if the measles surge continues into 2020. The investigators found that poor feeding was a primary reason for admission (97%); additional complications included otitis media (42%), pneumonia (30%), and tracheitis (6%). Three-quarters received antibiotics, 30% required oxygen, and 21% received vitamin A. Median length of stay was 3.7 days (range, 1.1-26.2 days) (Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2019 Jun;38[6]:547-52. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000002221).
‘Immunological amnesia’
Infection with the measles virus appears to reduce immunity to other pathogens, according to a paper published in Science (2019 Nov 1;366[6465]599-606).
The hypothesis that the measles virus could cause “immunological amnesia” by impairing immune memory is supported by early research showing children with measles had negative cutaneous tuberculin reactions after having previously tested positive.
“Subsequent studies have shown decreased interferon signaling, skewed cytokine responses, lymphopenia, and suppression of lymphocyte proliferation shortly after infection,” wrote Michael Mina, MD, from Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and coauthors.
“Given the variation in the degree of immune repertoire modulation we observed, we anticipate that future risk of morbidity and mortality after measles would not be homogeneous but would be skewed toward individuals with the most severe elimination of immunological memory,” they wrote. “These findings underscore the crucial need for continued widespread vaccination.”
In this study, researchers compared the levels of around 400 pathogen-specific antibodies in blood samples from 77 unvaccinated children, taken before and 2 months after natural measles infection, with 5 unvaccinated children who did not contract measles. A total of 34 children experienced mild measles, and 43 had severe measles.
They found that the samples taken after measles infection showed “substantial” reductions in the number of pathogen epitopes, compared with the samples from children who did not get infected with measles.
This amounted to approximately a 20% mean reduction in overall diversity or size of the antibody repertoire. However, in children who experienced severe measles, there was a median loss of 40% (range, 11%-62%) of antibody repertoire, compared with a median of 33% (range, 12%-73%) range in children who experienced mild infection. Meanwhile, the control subjects retained approximately 90% of their antibody repertoire over a similar or longer time period. Some children lost up to 70% of antibodies for specific pathogens.
Maternal-acquired immunity fades
In another study of measles immunity, maternal antibodies were found to be insufficient to provide immunity to infants after 6 months.
The study of 196 infants showed that maternal measles antibodies had dropped below the protective threshold by 3 months of age – well before the recommended age of 12-15 months for the first dose of MMR vaccine.
The odds of inadequate protection doubled for each additional month of age, Michelle Science, MD, of the University of Toronto and associates reported in Pediatrics (2019 Dec 1. doi 10.1542/peds.2019-0630).
“The widening gap between loss of maternal antibodies and measles vaccination described in our study leaves infants vulnerable to measles for much of their infancy and highlights the need for further research to support public health policy,” Dr. Science and colleagues wrote.
The researchers randomly selected 25 samples for each of eight different age groups: up to 30 days old; 1 month (31-60 days), 2 months (61-89 days), 3 months (90-119 days), 4 months, 5 months, 6-9 months, and 9-11 months.
Just over half the babies (56%) were male, and 35% had an underlying condition, but none had conditions that might affect antibody levels. The conditions were primarily a developmental delay or otherwise affecting the central nervous system, liver, or gastrointestinal function. Mean maternal age was 32 years.
To ensure high test sensitivity, the researchers used the plaque-reduction neutralization test to test for measles-neutralizing antibodies instead of using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, because “ELISA sensitivity decreases as antibody titers decrease,” Dr. Science and colleagues wrote. They used a neutralization titer of less than 192 mIU/mL as the threshold for protection against measles.
When the researchers calculated the predicted standardized mean antibody titer for infants with a mother aged 32 years, they determined their mean to be 541 mIU/mL at 1 month, 142 mIU/mL at 3 months (below the measles threshold of susceptibility of 192 mIU/mL), and 64 mIU/mL at 6 months. None of the infants had measles antibodies above the protective threshold at 6 months old, the authors noted.
Children’s odds of susceptibility to measles doubled for each additional month of age, after adjustment for infant sex and maternal age (odds ratio, 2.13). Children’s likelihood of susceptibility to measles modestly increased as maternal age increased in 5-year increments from 25 to 40 years.
Children with an underlying conditions had greater susceptibility to measles (83%), compared with those without a comorbidity (68%, P = .03). No difference in susceptibility existed between males and females or based on gestational age at birth (ranging from 37 to 41 weeks).
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices permits measles vaccination “as early as 6 months for infants who plan to travel internationally, infants with ongoing risk for exposure during measles outbreaks and as postexposure prophylaxis,” Huong Q. McLean, PhD, of Marshfield (Wisc.) Clinic Research Institute, and Walter A. Orenstein, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, noted in an editorial.
The research was funded by the Public Health Ontario Project Initiation Fund. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
Bianca Nogrady and Tara Haelle contributed to this story.
Measles made a comeback in 2019.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that, as of Dec. 5, 2019, 1,276 individual cases of measles of measles were confirmed in 31 states, the largest number since 1992. This number is a major uptick in cases, compared with previous years since 2000 when the CDC declared measles eliminated from the United States. No deaths have been reported for 2019.
Three-quarters of these cases in 2019 were linked to recent outbreaks in New York and occurred in primarily in underimmunized, close-knit communities and in patients with links to international travel. A total of 124 of the people who got measles this year were hospitalized, and 61 reported having complications, including pneumonia and encephalitis. The overall median patient age was 6 years (31% aged 1-4 years, 27% aged 5-17 years, and 29% aged at least 18 years).
The good news is that most of these cases occurred in unvaccinated patients. The national vaccination rate for the almost 4 million kindergartners reported as enrolled in 2018-2019 was 94.7% for two doses of the MMR vaccine, falling just short of the CDC recommended 95% vaccination rate threshold. The CDC reported an approximate 2.5% rate of vaccination exemptions among school-age children.
The bad news is that, despite the high rate of MMR vaccination rates among U.S. children, there are gaps in measles protection in the U.S. population because of factors leaving patients immunocompromised and antivaccination sentiment that has led some parents to defer or refuse the MMR.
In addition, adults who were vaccinated prior to 1968 with either inactivated measles vaccine or measles vaccine of unknown type may have limited immunity. The inactivated measles vaccine, which was available in 1963-1967, did not achieve effective measles protection.
A global measles surge
While antivaccination sentiment contributed to the 2019 measles cases, a more significant factor may be the global surge of measles. More than 140,000 people worldwide died from measles in 2018, according to the World Health Organization and the CDC.
“[Recent data on measles] indicates that during the first 6 months of the year there have been more measles cases reported worldwide than in any year since 2006. From Jan. 1 to July 31, 2019, 182 countries reported 364,808 measles cases to the WHO. This surpasses the 129,239 reported during the same time period in 2018. WHO regions with the biggest increases in cases include the African region (900%), the Western Pacific region (230%), and the European region (150%),” according to a CDC report.
Studies on hospitalization and complications linked to measles in the United States are scarce, but two outbreaks in Minnesota (2011 and 2017) provided some data on what to expect if the measles surge continues into 2020. The investigators found that poor feeding was a primary reason for admission (97%); additional complications included otitis media (42%), pneumonia (30%), and tracheitis (6%). Three-quarters received antibiotics, 30% required oxygen, and 21% received vitamin A. Median length of stay was 3.7 days (range, 1.1-26.2 days) (Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2019 Jun;38[6]:547-52. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000002221).
‘Immunological amnesia’
Infection with the measles virus appears to reduce immunity to other pathogens, according to a paper published in Science (2019 Nov 1;366[6465]599-606).
The hypothesis that the measles virus could cause “immunological amnesia” by impairing immune memory is supported by early research showing children with measles had negative cutaneous tuberculin reactions after having previously tested positive.
“Subsequent studies have shown decreased interferon signaling, skewed cytokine responses, lymphopenia, and suppression of lymphocyte proliferation shortly after infection,” wrote Michael Mina, MD, from Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and coauthors.
“Given the variation in the degree of immune repertoire modulation we observed, we anticipate that future risk of morbidity and mortality after measles would not be homogeneous but would be skewed toward individuals with the most severe elimination of immunological memory,” they wrote. “These findings underscore the crucial need for continued widespread vaccination.”
In this study, researchers compared the levels of around 400 pathogen-specific antibodies in blood samples from 77 unvaccinated children, taken before and 2 months after natural measles infection, with 5 unvaccinated children who did not contract measles. A total of 34 children experienced mild measles, and 43 had severe measles.
They found that the samples taken after measles infection showed “substantial” reductions in the number of pathogen epitopes, compared with the samples from children who did not get infected with measles.
This amounted to approximately a 20% mean reduction in overall diversity or size of the antibody repertoire. However, in children who experienced severe measles, there was a median loss of 40% (range, 11%-62%) of antibody repertoire, compared with a median of 33% (range, 12%-73%) range in children who experienced mild infection. Meanwhile, the control subjects retained approximately 90% of their antibody repertoire over a similar or longer time period. Some children lost up to 70% of antibodies for specific pathogens.
Maternal-acquired immunity fades
In another study of measles immunity, maternal antibodies were found to be insufficient to provide immunity to infants after 6 months.
The study of 196 infants showed that maternal measles antibodies had dropped below the protective threshold by 3 months of age – well before the recommended age of 12-15 months for the first dose of MMR vaccine.
The odds of inadequate protection doubled for each additional month of age, Michelle Science, MD, of the University of Toronto and associates reported in Pediatrics (2019 Dec 1. doi 10.1542/peds.2019-0630).
“The widening gap between loss of maternal antibodies and measles vaccination described in our study leaves infants vulnerable to measles for much of their infancy and highlights the need for further research to support public health policy,” Dr. Science and colleagues wrote.
The researchers randomly selected 25 samples for each of eight different age groups: up to 30 days old; 1 month (31-60 days), 2 months (61-89 days), 3 months (90-119 days), 4 months, 5 months, 6-9 months, and 9-11 months.
Just over half the babies (56%) were male, and 35% had an underlying condition, but none had conditions that might affect antibody levels. The conditions were primarily a developmental delay or otherwise affecting the central nervous system, liver, or gastrointestinal function. Mean maternal age was 32 years.
To ensure high test sensitivity, the researchers used the plaque-reduction neutralization test to test for measles-neutralizing antibodies instead of using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, because “ELISA sensitivity decreases as antibody titers decrease,” Dr. Science and colleagues wrote. They used a neutralization titer of less than 192 mIU/mL as the threshold for protection against measles.
When the researchers calculated the predicted standardized mean antibody titer for infants with a mother aged 32 years, they determined their mean to be 541 mIU/mL at 1 month, 142 mIU/mL at 3 months (below the measles threshold of susceptibility of 192 mIU/mL), and 64 mIU/mL at 6 months. None of the infants had measles antibodies above the protective threshold at 6 months old, the authors noted.
Children’s odds of susceptibility to measles doubled for each additional month of age, after adjustment for infant sex and maternal age (odds ratio, 2.13). Children’s likelihood of susceptibility to measles modestly increased as maternal age increased in 5-year increments from 25 to 40 years.
Children with an underlying conditions had greater susceptibility to measles (83%), compared with those without a comorbidity (68%, P = .03). No difference in susceptibility existed between males and females or based on gestational age at birth (ranging from 37 to 41 weeks).
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices permits measles vaccination “as early as 6 months for infants who plan to travel internationally, infants with ongoing risk for exposure during measles outbreaks and as postexposure prophylaxis,” Huong Q. McLean, PhD, of Marshfield (Wisc.) Clinic Research Institute, and Walter A. Orenstein, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, noted in an editorial.
The research was funded by the Public Health Ontario Project Initiation Fund. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
Bianca Nogrady and Tara Haelle contributed to this story.
Measles made a comeback in 2019.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that, as of Dec. 5, 2019, 1,276 individual cases of measles of measles were confirmed in 31 states, the largest number since 1992. This number is a major uptick in cases, compared with previous years since 2000 when the CDC declared measles eliminated from the United States. No deaths have been reported for 2019.
Three-quarters of these cases in 2019 were linked to recent outbreaks in New York and occurred in primarily in underimmunized, close-knit communities and in patients with links to international travel. A total of 124 of the people who got measles this year were hospitalized, and 61 reported having complications, including pneumonia and encephalitis. The overall median patient age was 6 years (31% aged 1-4 years, 27% aged 5-17 years, and 29% aged at least 18 years).
The good news is that most of these cases occurred in unvaccinated patients. The national vaccination rate for the almost 4 million kindergartners reported as enrolled in 2018-2019 was 94.7% for two doses of the MMR vaccine, falling just short of the CDC recommended 95% vaccination rate threshold. The CDC reported an approximate 2.5% rate of vaccination exemptions among school-age children.
The bad news is that, despite the high rate of MMR vaccination rates among U.S. children, there are gaps in measles protection in the U.S. population because of factors leaving patients immunocompromised and antivaccination sentiment that has led some parents to defer or refuse the MMR.
In addition, adults who were vaccinated prior to 1968 with either inactivated measles vaccine or measles vaccine of unknown type may have limited immunity. The inactivated measles vaccine, which was available in 1963-1967, did not achieve effective measles protection.
A global measles surge
While antivaccination sentiment contributed to the 2019 measles cases, a more significant factor may be the global surge of measles. More than 140,000 people worldwide died from measles in 2018, according to the World Health Organization and the CDC.
“[Recent data on measles] indicates that during the first 6 months of the year there have been more measles cases reported worldwide than in any year since 2006. From Jan. 1 to July 31, 2019, 182 countries reported 364,808 measles cases to the WHO. This surpasses the 129,239 reported during the same time period in 2018. WHO regions with the biggest increases in cases include the African region (900%), the Western Pacific region (230%), and the European region (150%),” according to a CDC report.
Studies on hospitalization and complications linked to measles in the United States are scarce, but two outbreaks in Minnesota (2011 and 2017) provided some data on what to expect if the measles surge continues into 2020. The investigators found that poor feeding was a primary reason for admission (97%); additional complications included otitis media (42%), pneumonia (30%), and tracheitis (6%). Three-quarters received antibiotics, 30% required oxygen, and 21% received vitamin A. Median length of stay was 3.7 days (range, 1.1-26.2 days) (Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2019 Jun;38[6]:547-52. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000002221).
‘Immunological amnesia’
Infection with the measles virus appears to reduce immunity to other pathogens, according to a paper published in Science (2019 Nov 1;366[6465]599-606).
The hypothesis that the measles virus could cause “immunological amnesia” by impairing immune memory is supported by early research showing children with measles had negative cutaneous tuberculin reactions after having previously tested positive.
“Subsequent studies have shown decreased interferon signaling, skewed cytokine responses, lymphopenia, and suppression of lymphocyte proliferation shortly after infection,” wrote Michael Mina, MD, from Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and coauthors.
“Given the variation in the degree of immune repertoire modulation we observed, we anticipate that future risk of morbidity and mortality after measles would not be homogeneous but would be skewed toward individuals with the most severe elimination of immunological memory,” they wrote. “These findings underscore the crucial need for continued widespread vaccination.”
In this study, researchers compared the levels of around 400 pathogen-specific antibodies in blood samples from 77 unvaccinated children, taken before and 2 months after natural measles infection, with 5 unvaccinated children who did not contract measles. A total of 34 children experienced mild measles, and 43 had severe measles.
They found that the samples taken after measles infection showed “substantial” reductions in the number of pathogen epitopes, compared with the samples from children who did not get infected with measles.
This amounted to approximately a 20% mean reduction in overall diversity or size of the antibody repertoire. However, in children who experienced severe measles, there was a median loss of 40% (range, 11%-62%) of antibody repertoire, compared with a median of 33% (range, 12%-73%) range in children who experienced mild infection. Meanwhile, the control subjects retained approximately 90% of their antibody repertoire over a similar or longer time period. Some children lost up to 70% of antibodies for specific pathogens.
Maternal-acquired immunity fades
In another study of measles immunity, maternal antibodies were found to be insufficient to provide immunity to infants after 6 months.
The study of 196 infants showed that maternal measles antibodies had dropped below the protective threshold by 3 months of age – well before the recommended age of 12-15 months for the first dose of MMR vaccine.
The odds of inadequate protection doubled for each additional month of age, Michelle Science, MD, of the University of Toronto and associates reported in Pediatrics (2019 Dec 1. doi 10.1542/peds.2019-0630).
“The widening gap between loss of maternal antibodies and measles vaccination described in our study leaves infants vulnerable to measles for much of their infancy and highlights the need for further research to support public health policy,” Dr. Science and colleagues wrote.
The researchers randomly selected 25 samples for each of eight different age groups: up to 30 days old; 1 month (31-60 days), 2 months (61-89 days), 3 months (90-119 days), 4 months, 5 months, 6-9 months, and 9-11 months.
Just over half the babies (56%) were male, and 35% had an underlying condition, but none had conditions that might affect antibody levels. The conditions were primarily a developmental delay or otherwise affecting the central nervous system, liver, or gastrointestinal function. Mean maternal age was 32 years.
To ensure high test sensitivity, the researchers used the plaque-reduction neutralization test to test for measles-neutralizing antibodies instead of using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, because “ELISA sensitivity decreases as antibody titers decrease,” Dr. Science and colleagues wrote. They used a neutralization titer of less than 192 mIU/mL as the threshold for protection against measles.
When the researchers calculated the predicted standardized mean antibody titer for infants with a mother aged 32 years, they determined their mean to be 541 mIU/mL at 1 month, 142 mIU/mL at 3 months (below the measles threshold of susceptibility of 192 mIU/mL), and 64 mIU/mL at 6 months. None of the infants had measles antibodies above the protective threshold at 6 months old, the authors noted.
Children’s odds of susceptibility to measles doubled for each additional month of age, after adjustment for infant sex and maternal age (odds ratio, 2.13). Children’s likelihood of susceptibility to measles modestly increased as maternal age increased in 5-year increments from 25 to 40 years.
Children with an underlying conditions had greater susceptibility to measles (83%), compared with those without a comorbidity (68%, P = .03). No difference in susceptibility existed between males and females or based on gestational age at birth (ranging from 37 to 41 weeks).
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices permits measles vaccination “as early as 6 months for infants who plan to travel internationally, infants with ongoing risk for exposure during measles outbreaks and as postexposure prophylaxis,” Huong Q. McLean, PhD, of Marshfield (Wisc.) Clinic Research Institute, and Walter A. Orenstein, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, noted in an editorial.
The research was funded by the Public Health Ontario Project Initiation Fund. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
Bianca Nogrady and Tara Haelle contributed to this story.
EVALI readmissions and deaths prompt guideline change
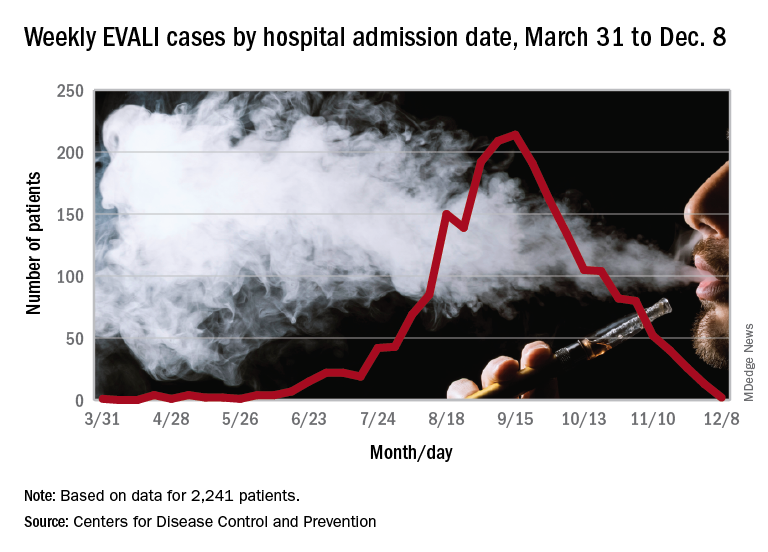
Those who required rehospitalization for e-cigarette or vaping product use–associated lung injury (EVALI) and those who died after discharge were more likely to have one or more chronic conditions than were other EVALI patients, and those “who died also were more likely to have been admitted to an intensive care unit, experienced respiratory failure necessitating intubation and mechanical ventilation, and were significantly older,” Christina A. Mikosz, MD, and associates wrote in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Their analysis included the 1,139 EVALI patients who were discharged on or after Oct. 31, 2019. Of that group, 31 (2.7%) patients were rehospitalized and subsequently discharged and another 7 died after the initial discharge. The median age was 54 years for those who died, 27 years for those who were rehospitalized, and 23 for those who survived without rehospitalization, said Dr. Mikosz of the CDC National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Atlanta, and associates.
Those findings, along with the rates of one or more comorbidities – 83% for those who died, 71% for those who were rehospitalized, and 26% for those who did not die or get readmitted – prompted the CDC to update its guidance for postdischarge follow-up of EVALI patients.
That update involves six specific recommendations to determine readiness for discharge, which include “confirming no clinically significant fluctuations in vital signs for at least 24-48 hours before discharge [and] preparation for hospital discharge and postdischarge care coordination to reduce risk of rehospitalization and death,” Mary E. Evans, MD, and associates said in a separate CDC communication (MMWR. 2019 Dec. 20. 68[early release]:1-6).
As of Dec. 17, the CDC reports that 2,506 patients have been hospitalized with EVALI since March 31, 2019, and 54 deaths have been confirmed in 27 states and the District of Columbia. The outbreak appears to have peaked in September, but cases are still being reported: 13 during the week of Dec. 1-7 and one case for the week of Dec. 8-14.
SOURCE: Mikosz CA et al. MMWR. 2019 Dec. 20. 68[early release]:1-7.

Those who required rehospitalization for e-cigarette or vaping product use–associated lung injury (EVALI) and those who died after discharge were more likely to have one or more chronic conditions than were other EVALI patients, and those “who died also were more likely to have been admitted to an intensive care unit, experienced respiratory failure necessitating intubation and mechanical ventilation, and were significantly older,” Christina A. Mikosz, MD, and associates wrote in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Their analysis included the 1,139 EVALI patients who were discharged on or after Oct. 31, 2019. Of that group, 31 (2.7%) patients were rehospitalized and subsequently discharged and another 7 died after the initial discharge. The median age was 54 years for those who died, 27 years for those who were rehospitalized, and 23 for those who survived without rehospitalization, said Dr. Mikosz of the CDC National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Atlanta, and associates.
Those findings, along with the rates of one or more comorbidities – 83% for those who died, 71% for those who were rehospitalized, and 26% for those who did not die or get readmitted – prompted the CDC to update its guidance for postdischarge follow-up of EVALI patients.
That update involves six specific recommendations to determine readiness for discharge, which include “confirming no clinically significant fluctuations in vital signs for at least 24-48 hours before discharge [and] preparation for hospital discharge and postdischarge care coordination to reduce risk of rehospitalization and death,” Mary E. Evans, MD, and associates said in a separate CDC communication (MMWR. 2019 Dec. 20. 68[early release]:1-6).
As of Dec. 17, the CDC reports that 2,506 patients have been hospitalized with EVALI since March 31, 2019, and 54 deaths have been confirmed in 27 states and the District of Columbia. The outbreak appears to have peaked in September, but cases are still being reported: 13 during the week of Dec. 1-7 and one case for the week of Dec. 8-14.
SOURCE: Mikosz CA et al. MMWR. 2019 Dec. 20. 68[early release]:1-7.

Those who required rehospitalization for e-cigarette or vaping product use–associated lung injury (EVALI) and those who died after discharge were more likely to have one or more chronic conditions than were other EVALI patients, and those “who died also were more likely to have been admitted to an intensive care unit, experienced respiratory failure necessitating intubation and mechanical ventilation, and were significantly older,” Christina A. Mikosz, MD, and associates wrote in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Their analysis included the 1,139 EVALI patients who were discharged on or after Oct. 31, 2019. Of that group, 31 (2.7%) patients were rehospitalized and subsequently discharged and another 7 died after the initial discharge. The median age was 54 years for those who died, 27 years for those who were rehospitalized, and 23 for those who survived without rehospitalization, said Dr. Mikosz of the CDC National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Atlanta, and associates.
Those findings, along with the rates of one or more comorbidities – 83% for those who died, 71% for those who were rehospitalized, and 26% for those who did not die or get readmitted – prompted the CDC to update its guidance for postdischarge follow-up of EVALI patients.
That update involves six specific recommendations to determine readiness for discharge, which include “confirming no clinically significant fluctuations in vital signs for at least 24-48 hours before discharge [and] preparation for hospital discharge and postdischarge care coordination to reduce risk of rehospitalization and death,” Mary E. Evans, MD, and associates said in a separate CDC communication (MMWR. 2019 Dec. 20. 68[early release]:1-6).
As of Dec. 17, the CDC reports that 2,506 patients have been hospitalized with EVALI since March 31, 2019, and 54 deaths have been confirmed in 27 states and the District of Columbia. The outbreak appears to have peaked in September, but cases are still being reported: 13 during the week of Dec. 1-7 and one case for the week of Dec. 8-14.
SOURCE: Mikosz CA et al. MMWR. 2019 Dec. 20. 68[early release]:1-7.
FROM MMWR
Vitamin E acetate confirmed as likely source of EVALI
Vitamin E acetate was found in fluid from the lungs of 94% of patients with electronic cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury, data from a convenience sample of 51 patients indicate. The findings were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Cases of electronic cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury (EVALI) were reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention starting in early 2019, and numbers rose throughout the year, “which suggests new or increased exposure to one or more toxicants from the use of e-cigarette products,” wrote Benjamin C. Blount, PhD, of the National Center for Environmental Health at the CDC, and colleagues.
To further investigate potential toxins in patients with EVALI, the researchers examined bronchoalveolar-lavage (BAL) fluid from 51 EVALI patients and 99 healthy controls.
After the researchers used isotope dilution mass spectrometry on the samples, 48 of the 51 patients (94%) showed vitamin E acetate in their BAL samples. No other potential toxins – including plant oils, medium-chain triglyceride oil, petroleum distillates, and diluent terpenes – were identified. The samples of one patient each showed coconut oil and limonene.
A total of 47 of 51 patients for whom complete laboratory data were available either reported vaping tetrahydrocannabinol products within 90 days of becoming ill, or showed tetrahydrocannabinol or its metabolites in their BAL fluid. In addition, 30 of 47 patients showed nicotine or nicotine metabolites in their BAL fluid.
The average age of the patients was 23 years, 69% were male. Overall, 25 were confirmed EVALI cases and 26 were probable cases, and probable cases included the three patients who showed no vitamin E acetate.
The safety of inhaling vitamin E acetate, which is a common ingredient in dietary supplements and skin care creams, has not been well studied. It could contribute to lung injury when heated in e-cigarette products by splitting the acetate to create the reactive compound and potential lung irritant ketene, the researchers said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the possibility that vitamin E acetate is a marker for exposure to other toxicants, a lack of data on the impact of heating vitamin e acetate, and the inability to assess the timing of the vitamin E acetate exposure compared to BAL sample collection, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that vitamin E acetate may play a role in EVALI because of the high detection rate in patients from across the United States, the biologically possible potential for lung injury from vitamin e acetate, and the timing of the rise of EVALI and the use of vitamin E acetate in vaping products, they concluded.
The research was supported by the National Cancer Institute, the FDA Center for Tobacco Products, and The Ohio State University Pelotonia intramural research program. The authors had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Blount BC et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Dec 20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1916433.
Vitamin E acetate was found in fluid from the lungs of 94% of patients with electronic cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury, data from a convenience sample of 51 patients indicate. The findings were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Cases of electronic cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury (EVALI) were reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention starting in early 2019, and numbers rose throughout the year, “which suggests new or increased exposure to one or more toxicants from the use of e-cigarette products,” wrote Benjamin C. Blount, PhD, of the National Center for Environmental Health at the CDC, and colleagues.
To further investigate potential toxins in patients with EVALI, the researchers examined bronchoalveolar-lavage (BAL) fluid from 51 EVALI patients and 99 healthy controls.
After the researchers used isotope dilution mass spectrometry on the samples, 48 of the 51 patients (94%) showed vitamin E acetate in their BAL samples. No other potential toxins – including plant oils, medium-chain triglyceride oil, petroleum distillates, and diluent terpenes – were identified. The samples of one patient each showed coconut oil and limonene.
A total of 47 of 51 patients for whom complete laboratory data were available either reported vaping tetrahydrocannabinol products within 90 days of becoming ill, or showed tetrahydrocannabinol or its metabolites in their BAL fluid. In addition, 30 of 47 patients showed nicotine or nicotine metabolites in their BAL fluid.
The average age of the patients was 23 years, 69% were male. Overall, 25 were confirmed EVALI cases and 26 were probable cases, and probable cases included the three patients who showed no vitamin E acetate.
The safety of inhaling vitamin E acetate, which is a common ingredient in dietary supplements and skin care creams, has not been well studied. It could contribute to lung injury when heated in e-cigarette products by splitting the acetate to create the reactive compound and potential lung irritant ketene, the researchers said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the possibility that vitamin E acetate is a marker for exposure to other toxicants, a lack of data on the impact of heating vitamin e acetate, and the inability to assess the timing of the vitamin E acetate exposure compared to BAL sample collection, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that vitamin E acetate may play a role in EVALI because of the high detection rate in patients from across the United States, the biologically possible potential for lung injury from vitamin e acetate, and the timing of the rise of EVALI and the use of vitamin E acetate in vaping products, they concluded.
The research was supported by the National Cancer Institute, the FDA Center for Tobacco Products, and The Ohio State University Pelotonia intramural research program. The authors had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Blount BC et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Dec 20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1916433.
Vitamin E acetate was found in fluid from the lungs of 94% of patients with electronic cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury, data from a convenience sample of 51 patients indicate. The findings were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Cases of electronic cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury (EVALI) were reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention starting in early 2019, and numbers rose throughout the year, “which suggests new or increased exposure to one or more toxicants from the use of e-cigarette products,” wrote Benjamin C. Blount, PhD, of the National Center for Environmental Health at the CDC, and colleagues.
To further investigate potential toxins in patients with EVALI, the researchers examined bronchoalveolar-lavage (BAL) fluid from 51 EVALI patients and 99 healthy controls.
After the researchers used isotope dilution mass spectrometry on the samples, 48 of the 51 patients (94%) showed vitamin E acetate in their BAL samples. No other potential toxins – including plant oils, medium-chain triglyceride oil, petroleum distillates, and diluent terpenes – were identified. The samples of one patient each showed coconut oil and limonene.
A total of 47 of 51 patients for whom complete laboratory data were available either reported vaping tetrahydrocannabinol products within 90 days of becoming ill, or showed tetrahydrocannabinol or its metabolites in their BAL fluid. In addition, 30 of 47 patients showed nicotine or nicotine metabolites in their BAL fluid.
The average age of the patients was 23 years, 69% were male. Overall, 25 were confirmed EVALI cases and 26 were probable cases, and probable cases included the three patients who showed no vitamin E acetate.
The safety of inhaling vitamin E acetate, which is a common ingredient in dietary supplements and skin care creams, has not been well studied. It could contribute to lung injury when heated in e-cigarette products by splitting the acetate to create the reactive compound and potential lung irritant ketene, the researchers said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the possibility that vitamin E acetate is a marker for exposure to other toxicants, a lack of data on the impact of heating vitamin e acetate, and the inability to assess the timing of the vitamin E acetate exposure compared to BAL sample collection, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that vitamin E acetate may play a role in EVALI because of the high detection rate in patients from across the United States, the biologically possible potential for lung injury from vitamin e acetate, and the timing of the rise of EVALI and the use of vitamin E acetate in vaping products, they concluded.
The research was supported by the National Cancer Institute, the FDA Center for Tobacco Products, and The Ohio State University Pelotonia intramural research program. The authors had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Blount BC et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Dec 20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1916433.
FROM NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Influenza activity continues to be unusually high
The 2019-2020 flu season continues its unusually early rise in activity, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimating that 3.7 million cases have occurred through Dec. 14.
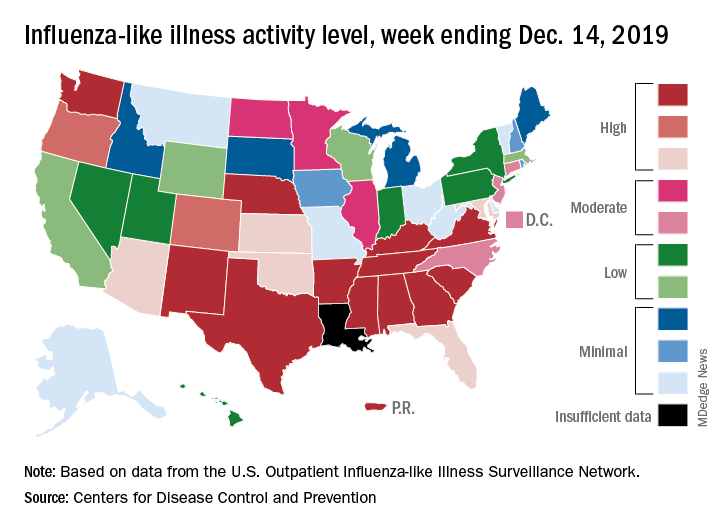
which is up from 3.2% the previous week and is the sixth consecutive week that the United States has been at or above the national baseline of 2.4%, the CDC reported Dec. 20. This year’s 3.9% is the highest mid-December rate recorded since 2003, when it reached almost 7.4%.
Most of the influenza activity so far this season is being driven by influenza B/Victoria viruses. Nationwide testing puts influenza B prevalence at 68.5% of all positive specimens, exactly the same as last week, but A(H1N1) viruses “are increasing in proportion relative to other influenza viruses in some regions,” the CDC’s influenza division said.
A look at this week’s activity map shows that 21 states, compared with 12 last week, were in the “high” range of activity – that’s levels 8-10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale. Twelve of those states, along with Puerto Rico, were at level 10, which was up from nine a week earlier, the CDC said.
The overall hospitalization rate through the week of Dec. 8-14 (5.5 per 100,000 population) “is similar to what has been seen at this time during recent seasons,” the CDC noted. The highest rates are occurring among adults over age 65 years (12.7 per 100,000) and children aged 0-4 years (10.9 per 100,000).
Three ILI-related deaths among children that occurred last week were reported, which brings the total for the 2019-2020 season to 19, the CDC said.
The 2019-2020 flu season continues its unusually early rise in activity, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimating that 3.7 million cases have occurred through Dec. 14.

which is up from 3.2% the previous week and is the sixth consecutive week that the United States has been at or above the national baseline of 2.4%, the CDC reported Dec. 20. This year’s 3.9% is the highest mid-December rate recorded since 2003, when it reached almost 7.4%.
Most of the influenza activity so far this season is being driven by influenza B/Victoria viruses. Nationwide testing puts influenza B prevalence at 68.5% of all positive specimens, exactly the same as last week, but A(H1N1) viruses “are increasing in proportion relative to other influenza viruses in some regions,” the CDC’s influenza division said.
A look at this week’s activity map shows that 21 states, compared with 12 last week, were in the “high” range of activity – that’s levels 8-10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale. Twelve of those states, along with Puerto Rico, were at level 10, which was up from nine a week earlier, the CDC said.
The overall hospitalization rate through the week of Dec. 8-14 (5.5 per 100,000 population) “is similar to what has been seen at this time during recent seasons,” the CDC noted. The highest rates are occurring among adults over age 65 years (12.7 per 100,000) and children aged 0-4 years (10.9 per 100,000).
Three ILI-related deaths among children that occurred last week were reported, which brings the total for the 2019-2020 season to 19, the CDC said.
The 2019-2020 flu season continues its unusually early rise in activity, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimating that 3.7 million cases have occurred through Dec. 14.

which is up from 3.2% the previous week and is the sixth consecutive week that the United States has been at or above the national baseline of 2.4%, the CDC reported Dec. 20. This year’s 3.9% is the highest mid-December rate recorded since 2003, when it reached almost 7.4%.
Most of the influenza activity so far this season is being driven by influenza B/Victoria viruses. Nationwide testing puts influenza B prevalence at 68.5% of all positive specimens, exactly the same as last week, but A(H1N1) viruses “are increasing in proportion relative to other influenza viruses in some regions,” the CDC’s influenza division said.
A look at this week’s activity map shows that 21 states, compared with 12 last week, were in the “high” range of activity – that’s levels 8-10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale. Twelve of those states, along with Puerto Rico, were at level 10, which was up from nine a week earlier, the CDC said.
The overall hospitalization rate through the week of Dec. 8-14 (5.5 per 100,000 population) “is similar to what has been seen at this time during recent seasons,” the CDC noted. The highest rates are occurring among adults over age 65 years (12.7 per 100,000) and children aged 0-4 years (10.9 per 100,000).
Three ILI-related deaths among children that occurred last week were reported, which brings the total for the 2019-2020 season to 19, the CDC said.
Vaping marijuana gaining traction among U.S. teens
Monitoring the Future survey asked about daily vaping this year for first time
Vaping has expanded as a popular method of drug delivery for U.S. teenagers, and one in five students in grades 10 and 12 reported vaping marijuana in the past year, according to results of the 2019 Monitoring the Future survey conducted by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA).
This year’s findings, announced Dec. 18, continue to illustrate “a clear shift in the pattern of drug taking among teenagers,” said NIDA Director Nora D. Volkow, MD, in a teleconference held to review the results.
Use of alcohol and drugs – including opioids and stimulants – continues to decline among teens, but vaping continues its significant rise, with a surge in marijuana vaping this year.
The increase in past-month marijuana vaping among 12th graders, from 7.5% in 2018 to 14% in 2019, represents the second-largest 1-year jump tracked for any substance in the survey’s history, Dr. Volkow said. The largest jump was the increase in past-month nicotine vaping among 12th-graders from 2017-2018.
“It is very unfortunate that we are seeing the steep rise in the use of vaping devices” because the devices deliver drugs in very high concentration, Dr. Volkow said. The growing popularity of vaping “threatens to undo years of progress protecting the health of adolescents in the U.S.,” Dr. Volkow said in a statement. The Monitoring the Future survey began including vaping questions in 2017.
Monitoring the Future is a national tool to assess drug and alcohol use and related attitudes among adolescent students across the United States. This year’s self-reported survey included 42,531 in grades 8, 10, and 12 from 396 public and private schools.
Nicotine vaping increased from 2018 to 2019 across all three grades; past-month nicotine use equated to 1 in 4, 1 in 5, and 1 in 10 (26%, 20%, and 10%) among 12th, 10th, and 8th graders, respectively, according to the survey. Daily nicotine vaping, measured for the first time this year because of public health concerns, was approximately 12% for 12th graders, 7% for 10th graders, and 2% for 8th graders. Daily marijuana vaping, also measured for the first time this year, was approximately 4%, 3%, and 1% among 12th, 10th, and 8th graders, respectively. Additional findings on the rise of vaping by U.S. teenagers were released Dec. 17 in a research letter published online in JAMA (doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.20185).
Meanwhile, positive trends in this year’s survey included a reduction in the misuse of prescription drugs, including OxyContin, Vicodin, and Adderall, and in the use of traditional cigarettes and other tobacco products, as well as alcohol, noted Richard A. Miech, PhD, MPH, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, principal investigator for Monitoring the Future. However, the challenge of preventing and reducing vaping in teens remains “a whole new uncharted territory,” in part because the design of the vaping devices facilitates discreet use at home and at school, he said.
Physicians and parents have important roles to play in screening for vaping among teens, Dr. Volkow said in a question and answer session. Health care clinicians, including pediatricians and family physicians, “are in a unique position to communicate with their young patients” by educating them about the dangers of vaping, encouraging them to stop if they have started using these devices, and referring them for further treatment if they are showing signs of addiction, she said.
Monitoring the Future was funded by NIDA. The researchers had no disclosures.
Monitoring the Future survey asked about daily vaping this year for first time
Monitoring the Future survey asked about daily vaping this year for first time
Vaping has expanded as a popular method of drug delivery for U.S. teenagers, and one in five students in grades 10 and 12 reported vaping marijuana in the past year, according to results of the 2019 Monitoring the Future survey conducted by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA).
This year’s findings, announced Dec. 18, continue to illustrate “a clear shift in the pattern of drug taking among teenagers,” said NIDA Director Nora D. Volkow, MD, in a teleconference held to review the results.
Use of alcohol and drugs – including opioids and stimulants – continues to decline among teens, but vaping continues its significant rise, with a surge in marijuana vaping this year.
The increase in past-month marijuana vaping among 12th graders, from 7.5% in 2018 to 14% in 2019, represents the second-largest 1-year jump tracked for any substance in the survey’s history, Dr. Volkow said. The largest jump was the increase in past-month nicotine vaping among 12th-graders from 2017-2018.
“It is very unfortunate that we are seeing the steep rise in the use of vaping devices” because the devices deliver drugs in very high concentration, Dr. Volkow said. The growing popularity of vaping “threatens to undo years of progress protecting the health of adolescents in the U.S.,” Dr. Volkow said in a statement. The Monitoring the Future survey began including vaping questions in 2017.
Monitoring the Future is a national tool to assess drug and alcohol use and related attitudes among adolescent students across the United States. This year’s self-reported survey included 42,531 in grades 8, 10, and 12 from 396 public and private schools.
Nicotine vaping increased from 2018 to 2019 across all three grades; past-month nicotine use equated to 1 in 4, 1 in 5, and 1 in 10 (26%, 20%, and 10%) among 12th, 10th, and 8th graders, respectively, according to the survey. Daily nicotine vaping, measured for the first time this year because of public health concerns, was approximately 12% for 12th graders, 7% for 10th graders, and 2% for 8th graders. Daily marijuana vaping, also measured for the first time this year, was approximately 4%, 3%, and 1% among 12th, 10th, and 8th graders, respectively. Additional findings on the rise of vaping by U.S. teenagers were released Dec. 17 in a research letter published online in JAMA (doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.20185).
Meanwhile, positive trends in this year’s survey included a reduction in the misuse of prescription drugs, including OxyContin, Vicodin, and Adderall, and in the use of traditional cigarettes and other tobacco products, as well as alcohol, noted Richard A. Miech, PhD, MPH, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, principal investigator for Monitoring the Future. However, the challenge of preventing and reducing vaping in teens remains “a whole new uncharted territory,” in part because the design of the vaping devices facilitates discreet use at home and at school, he said.
Physicians and parents have important roles to play in screening for vaping among teens, Dr. Volkow said in a question and answer session. Health care clinicians, including pediatricians and family physicians, “are in a unique position to communicate with their young patients” by educating them about the dangers of vaping, encouraging them to stop if they have started using these devices, and referring them for further treatment if they are showing signs of addiction, she said.
Monitoring the Future was funded by NIDA. The researchers had no disclosures.
Vaping has expanded as a popular method of drug delivery for U.S. teenagers, and one in five students in grades 10 and 12 reported vaping marijuana in the past year, according to results of the 2019 Monitoring the Future survey conducted by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA).
This year’s findings, announced Dec. 18, continue to illustrate “a clear shift in the pattern of drug taking among teenagers,” said NIDA Director Nora D. Volkow, MD, in a teleconference held to review the results.
Use of alcohol and drugs – including opioids and stimulants – continues to decline among teens, but vaping continues its significant rise, with a surge in marijuana vaping this year.
The increase in past-month marijuana vaping among 12th graders, from 7.5% in 2018 to 14% in 2019, represents the second-largest 1-year jump tracked for any substance in the survey’s history, Dr. Volkow said. The largest jump was the increase in past-month nicotine vaping among 12th-graders from 2017-2018.
“It is very unfortunate that we are seeing the steep rise in the use of vaping devices” because the devices deliver drugs in very high concentration, Dr. Volkow said. The growing popularity of vaping “threatens to undo years of progress protecting the health of adolescents in the U.S.,” Dr. Volkow said in a statement. The Monitoring the Future survey began including vaping questions in 2017.
Monitoring the Future is a national tool to assess drug and alcohol use and related attitudes among adolescent students across the United States. This year’s self-reported survey included 42,531 in grades 8, 10, and 12 from 396 public and private schools.
Nicotine vaping increased from 2018 to 2019 across all three grades; past-month nicotine use equated to 1 in 4, 1 in 5, and 1 in 10 (26%, 20%, and 10%) among 12th, 10th, and 8th graders, respectively, according to the survey. Daily nicotine vaping, measured for the first time this year because of public health concerns, was approximately 12% for 12th graders, 7% for 10th graders, and 2% for 8th graders. Daily marijuana vaping, also measured for the first time this year, was approximately 4%, 3%, and 1% among 12th, 10th, and 8th graders, respectively. Additional findings on the rise of vaping by U.S. teenagers were released Dec. 17 in a research letter published online in JAMA (doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.20185).
Meanwhile, positive trends in this year’s survey included a reduction in the misuse of prescription drugs, including OxyContin, Vicodin, and Adderall, and in the use of traditional cigarettes and other tobacco products, as well as alcohol, noted Richard A. Miech, PhD, MPH, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, principal investigator for Monitoring the Future. However, the challenge of preventing and reducing vaping in teens remains “a whole new uncharted territory,” in part because the design of the vaping devices facilitates discreet use at home and at school, he said.
Physicians and parents have important roles to play in screening for vaping among teens, Dr. Volkow said in a question and answer session. Health care clinicians, including pediatricians and family physicians, “are in a unique position to communicate with their young patients” by educating them about the dangers of vaping, encouraging them to stop if they have started using these devices, and referring them for further treatment if they are showing signs of addiction, she said.
Monitoring the Future was funded by NIDA. The researchers had no disclosures.
Signs of COPD detected among smokers under 50 years
A study using a new definition of meet the criteria.
The population-based cohort looked at individuals who had been exposed to at least 10 pack-years, and defined early COPD as the ratio of forced expiratory volume to forced vital capacity being less than the lower limit of normal (FEV1/FVC less than LLN). The definition of early COPD, published in 2018 (Am J Resp and Crit Care Med. 2018;197:1540-51), also included the presence of abnormalities on a CT scan or a decline in FEV1 (greater than 60 mL/year) that is accelerated relative to FVC, but the new population study did not include the latter two criteria.
The researchers, under corresponding author Peter Lange, MD, of the University of Copenhagen found that those with early COPD were more likely to have chronic respiratory symptoms, severe impairment of lung function, acute respirator hospitalization, and early mortality at baseline and at follow-up. The work was published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine.
“To dig through the smokers and try to figure out which smokers are more at risk than other smokers is probably the best way to summarize what they’ve done here,” said Robert Reed, MD, from the University of Maryland, Baltimore, in an interview. However, he added that he would like to see the research extended to an even younger population, as well as nonsmokers. “We don’t need all of this information to tell us that smoking is bad. I think nonsmokers would be really interesting – creating a definition of COPD that excludes patients that meet the usual definition for COPD would be of potential interest,” added Dr. Reed, who was not involved in the study.
Using a cohort of 105,630 randomly selected individuals from Danish nationwide health registries, the study identified 8,064 individuals aged under 50 years with 10 or more pack-years of tobacco exposure. In this group, 1,175 (15%) had early COPD, of whom 58% were current smokers. The cohort of smokers was followed for up to 14.4 years. Multivariate analyses found that those with early COPD, compared with smokers without COPD, were at substantially greater risk of acute obstructive lung disease hospitalization (hazard ratio, 6.42; 95% confidence interval, 3.39-12.2), acute pneumonia hospitalization (HR, 2.03; 95% CI, 1.43-2.88), and all-cause mortality (HR, 1.79; 95% CI, 1.28-2.52).
There is value in gaining a better understanding of which smokers are at greatest risk of COPD down the line, but data on younger people, even 30-year-olds, could guide therapeutic decisions when and if new drugs that can alter the state of the disease become available. Focusing more on younger, high-risk patients could also be used to create greater incentives to quit smoking, though Dr. Reed has mixed feelings even about that. “What if we identified 15% of smokers that are at risk of COPD, and the other 85% say, ‘I’ll keep smoking,’ and they fall over dead from a heart attack?” said Dr. Reed, noting that smoking has a wide range of known risks. “They should all stop,” he added.
The study also captures a wide range of patients, from some with early disease that will likely progress to COPD later in life along with some who already developed full-blown COPD in, for example, their early 40s. “Those are very different patients and to lump them together is potentially problematic,” said Dr. Reed. More granulated data could potentially inform more personalized medicine, and the discovery and verification of genetic risk factors.
Nevertheless, Dr. Reed expects the data to move the field forward. “They created a nice, rich database that I think will generate a lot more analysis and discussion.”
The study was funded by the Lundbeck Foundation. One of the authors has received support from the National Institute for Health Research Manchester (England) Biomedical Research Centre. Dr. Reed has no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Colak Y et al. Am J Resp Crit Care Med. 2019 Nov 26. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201908-1644OC
A study using a new definition of meet the criteria.
The population-based cohort looked at individuals who had been exposed to at least 10 pack-years, and defined early COPD as the ratio of forced expiratory volume to forced vital capacity being less than the lower limit of normal (FEV1/FVC less than LLN). The definition of early COPD, published in 2018 (Am J Resp and Crit Care Med. 2018;197:1540-51), also included the presence of abnormalities on a CT scan or a decline in FEV1 (greater than 60 mL/year) that is accelerated relative to FVC, but the new population study did not include the latter two criteria.
The researchers, under corresponding author Peter Lange, MD, of the University of Copenhagen found that those with early COPD were more likely to have chronic respiratory symptoms, severe impairment of lung function, acute respirator hospitalization, and early mortality at baseline and at follow-up. The work was published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine.
“To dig through the smokers and try to figure out which smokers are more at risk than other smokers is probably the best way to summarize what they’ve done here,” said Robert Reed, MD, from the University of Maryland, Baltimore, in an interview. However, he added that he would like to see the research extended to an even younger population, as well as nonsmokers. “We don’t need all of this information to tell us that smoking is bad. I think nonsmokers would be really interesting – creating a definition of COPD that excludes patients that meet the usual definition for COPD would be of potential interest,” added Dr. Reed, who was not involved in the study.
Using a cohort of 105,630 randomly selected individuals from Danish nationwide health registries, the study identified 8,064 individuals aged under 50 years with 10 or more pack-years of tobacco exposure. In this group, 1,175 (15%) had early COPD, of whom 58% were current smokers. The cohort of smokers was followed for up to 14.4 years. Multivariate analyses found that those with early COPD, compared with smokers without COPD, were at substantially greater risk of acute obstructive lung disease hospitalization (hazard ratio, 6.42; 95% confidence interval, 3.39-12.2), acute pneumonia hospitalization (HR, 2.03; 95% CI, 1.43-2.88), and all-cause mortality (HR, 1.79; 95% CI, 1.28-2.52).
There is value in gaining a better understanding of which smokers are at greatest risk of COPD down the line, but data on younger people, even 30-year-olds, could guide therapeutic decisions when and if new drugs that can alter the state of the disease become available. Focusing more on younger, high-risk patients could also be used to create greater incentives to quit smoking, though Dr. Reed has mixed feelings even about that. “What if we identified 15% of smokers that are at risk of COPD, and the other 85% say, ‘I’ll keep smoking,’ and they fall over dead from a heart attack?” said Dr. Reed, noting that smoking has a wide range of known risks. “They should all stop,” he added.
The study also captures a wide range of patients, from some with early disease that will likely progress to COPD later in life along with some who already developed full-blown COPD in, for example, their early 40s. “Those are very different patients and to lump them together is potentially problematic,” said Dr. Reed. More granulated data could potentially inform more personalized medicine, and the discovery and verification of genetic risk factors.
Nevertheless, Dr. Reed expects the data to move the field forward. “They created a nice, rich database that I think will generate a lot more analysis and discussion.”
The study was funded by the Lundbeck Foundation. One of the authors has received support from the National Institute for Health Research Manchester (England) Biomedical Research Centre. Dr. Reed has no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Colak Y et al. Am J Resp Crit Care Med. 2019 Nov 26. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201908-1644OC
A study using a new definition of meet the criteria.
The population-based cohort looked at individuals who had been exposed to at least 10 pack-years, and defined early COPD as the ratio of forced expiratory volume to forced vital capacity being less than the lower limit of normal (FEV1/FVC less than LLN). The definition of early COPD, published in 2018 (Am J Resp and Crit Care Med. 2018;197:1540-51), also included the presence of abnormalities on a CT scan or a decline in FEV1 (greater than 60 mL/year) that is accelerated relative to FVC, but the new population study did not include the latter two criteria.
The researchers, under corresponding author Peter Lange, MD, of the University of Copenhagen found that those with early COPD were more likely to have chronic respiratory symptoms, severe impairment of lung function, acute respirator hospitalization, and early mortality at baseline and at follow-up. The work was published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine.
“To dig through the smokers and try to figure out which smokers are more at risk than other smokers is probably the best way to summarize what they’ve done here,” said Robert Reed, MD, from the University of Maryland, Baltimore, in an interview. However, he added that he would like to see the research extended to an even younger population, as well as nonsmokers. “We don’t need all of this information to tell us that smoking is bad. I think nonsmokers would be really interesting – creating a definition of COPD that excludes patients that meet the usual definition for COPD would be of potential interest,” added Dr. Reed, who was not involved in the study.
Using a cohort of 105,630 randomly selected individuals from Danish nationwide health registries, the study identified 8,064 individuals aged under 50 years with 10 or more pack-years of tobacco exposure. In this group, 1,175 (15%) had early COPD, of whom 58% were current smokers. The cohort of smokers was followed for up to 14.4 years. Multivariate analyses found that those with early COPD, compared with smokers without COPD, were at substantially greater risk of acute obstructive lung disease hospitalization (hazard ratio, 6.42; 95% confidence interval, 3.39-12.2), acute pneumonia hospitalization (HR, 2.03; 95% CI, 1.43-2.88), and all-cause mortality (HR, 1.79; 95% CI, 1.28-2.52).
There is value in gaining a better understanding of which smokers are at greatest risk of COPD down the line, but data on younger people, even 30-year-olds, could guide therapeutic decisions when and if new drugs that can alter the state of the disease become available. Focusing more on younger, high-risk patients could also be used to create greater incentives to quit smoking, though Dr. Reed has mixed feelings even about that. “What if we identified 15% of smokers that are at risk of COPD, and the other 85% say, ‘I’ll keep smoking,’ and they fall over dead from a heart attack?” said Dr. Reed, noting that smoking has a wide range of known risks. “They should all stop,” he added.
The study also captures a wide range of patients, from some with early disease that will likely progress to COPD later in life along with some who already developed full-blown COPD in, for example, their early 40s. “Those are very different patients and to lump them together is potentially problematic,” said Dr. Reed. More granulated data could potentially inform more personalized medicine, and the discovery and verification of genetic risk factors.
Nevertheless, Dr. Reed expects the data to move the field forward. “They created a nice, rich database that I think will generate a lot more analysis and discussion.”
The study was funded by the Lundbeck Foundation. One of the authors has received support from the National Institute for Health Research Manchester (England) Biomedical Research Centre. Dr. Reed has no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Colak Y et al. Am J Resp Crit Care Med. 2019 Nov 26. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201908-1644OC
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF RESPIRATORY AND CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE