User login
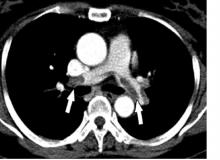
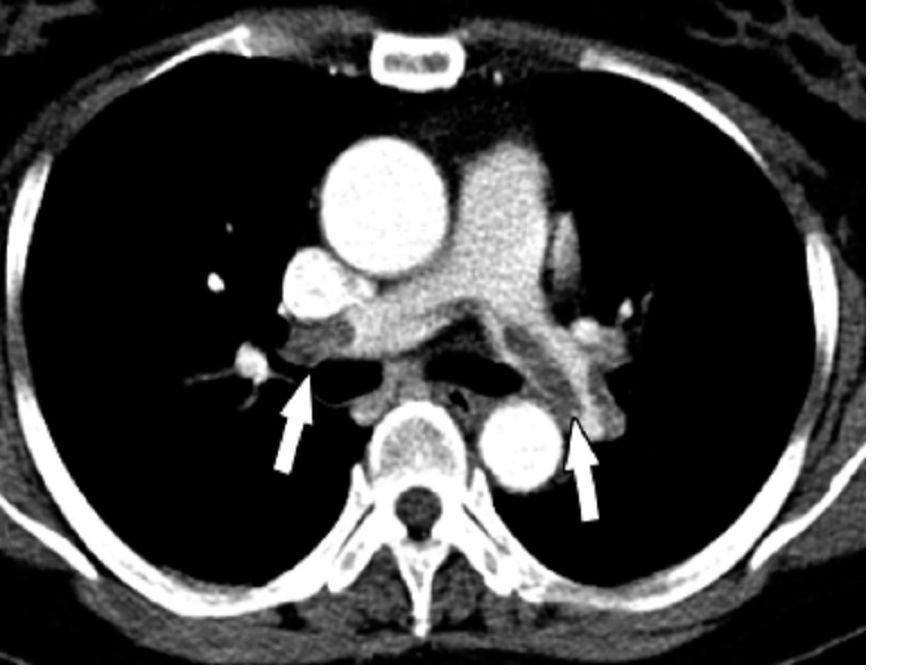
Risk of atrial fibrillation 900% higher with cancer
MELBOURNE – The overall prevalence of atrial fibrillation in people who have or have had cancer is 10 times that of individuals without cancer, according to a study presented at the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis congress.
Cihan Ay, MD, of the division of hematology and hemostaseology at the Medical University of Vienna reported on a nationwide cohort study using health insurance data from more than 8.3 million people in Austria, including roughly 159,000 with a diagnosis of cancer and 113,000 with a diagnosis of atrial fibrillation.
The analysis found that, in individuals whose records showed a diagnosis of cancer, there was a 950% higher relative risk of also having a diagnosis of atrial fibrillation, compared with those with no cancer diagnosis.
The overall prevalence of atrial fibrillation among individuals with a cancer diagnosis was 9.8%, compared with 1.2% in those without cancer.
There was significant variation in relative risk according to age. Although the prevalence of atrial fibrillation increased with age, the highest relative risks were seen in the youngest age groups.
In those aged 12 years or under with a cancer diagnosis, the relative risk of atrial fibrillation was 150 times greater than in those without cancer, and in those aged 13-18 years, it was 200 times higher. At the other end of the age spectrum, individuals aged 70-79 years with a recorded cancer diagnosis, the relative risk of atrial fibrillation was still 130% higher than the noncancer population, and in those aged 80-90 years it was a significant 54% higher.
However, the analysis did not find any effect of gender on the risk of atrial fibrillation associated with cancer, regardless of the age group.
Researchers also examined the influence of different cancer types. They found the highest relative risk of atrial fibrillation was in persons with hematologic malignancies – at nine times the risk in the noncancer population – and the lowest was in the endocrine cancer patients, who had three times the risk.
Dr. Ay told the conference that the association between cancer and atrial fibrillation had been suggested in the literature, but it was still an unexplored field. “The exact magnitude of this association between cancer and atrial fibrillation is still unclear.”
There was also the question of what mechanisms might underlie the association. Dr. Ay pointed out that the health insurance database did not allow researchers to explore the temporal relationship between the two diagnoses, and therefore could not tell which came first.
One audience member queried whether the fact that cancer patients were likely to be visiting a clinician more frequently might mean that the atrial fibrillation would be more likely to be diagnosed.
To that, Dr. Ay suggested the significantly higher relative risk in children was supportive of the notion that cancer itself, or treatment effects, were influencing atrial fibrillation risk.
“There is evidence suggesting that cancer treatments are triggering atrial fibrillation,” he said in an interview. “Also, patients with cancer have situations of in which they are sick – they have neutropenia or sepsis and so on – which can also trigger atrial fibrillation.”
Given the limitations of the retrospective cohort study, Dr. Ay said he was hoping to do a prospective study that would enable baseline measurements of cancer patients to determine how much of the atrial fibrillation was preexisting.
“We have also more and more cancer survivors, and over the years they’re living longer and the likelihood of getting atrial fibrillation increases,” he added.
Commenting on the data, Gerald Soff, MD, chief of hematology at the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, said it was very important to quantify the association between cancer and atrial fibrillation.
“What’s striking to me is how many people with cancer come in with preexisting atrial fibrillation,” he said. “It could be that they have cancer and they’re already messed up, but we have, on a given day, several people coming in with newly diagnosed cancers, already on warfarin or apixaban or rivaroxaban because they have atrial fibrillation.”
Dr. Ay reported advisory board positions and speaking engagements for the pharmaceutical sector.
MELBOURNE – The overall prevalence of atrial fibrillation in people who have or have had cancer is 10 times that of individuals without cancer, according to a study presented at the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis congress.
Cihan Ay, MD, of the division of hematology and hemostaseology at the Medical University of Vienna reported on a nationwide cohort study using health insurance data from more than 8.3 million people in Austria, including roughly 159,000 with a diagnosis of cancer and 113,000 with a diagnosis of atrial fibrillation.
The analysis found that, in individuals whose records showed a diagnosis of cancer, there was a 950% higher relative risk of also having a diagnosis of atrial fibrillation, compared with those with no cancer diagnosis.
The overall prevalence of atrial fibrillation among individuals with a cancer diagnosis was 9.8%, compared with 1.2% in those without cancer.
There was significant variation in relative risk according to age. Although the prevalence of atrial fibrillation increased with age, the highest relative risks were seen in the youngest age groups.
In those aged 12 years or under with a cancer diagnosis, the relative risk of atrial fibrillation was 150 times greater than in those without cancer, and in those aged 13-18 years, it was 200 times higher. At the other end of the age spectrum, individuals aged 70-79 years with a recorded cancer diagnosis, the relative risk of atrial fibrillation was still 130% higher than the noncancer population, and in those aged 80-90 years it was a significant 54% higher.
However, the analysis did not find any effect of gender on the risk of atrial fibrillation associated with cancer, regardless of the age group.
Researchers also examined the influence of different cancer types. They found the highest relative risk of atrial fibrillation was in persons with hematologic malignancies – at nine times the risk in the noncancer population – and the lowest was in the endocrine cancer patients, who had three times the risk.
Dr. Ay told the conference that the association between cancer and atrial fibrillation had been suggested in the literature, but it was still an unexplored field. “The exact magnitude of this association between cancer and atrial fibrillation is still unclear.”
There was also the question of what mechanisms might underlie the association. Dr. Ay pointed out that the health insurance database did not allow researchers to explore the temporal relationship between the two diagnoses, and therefore could not tell which came first.
One audience member queried whether the fact that cancer patients were likely to be visiting a clinician more frequently might mean that the atrial fibrillation would be more likely to be diagnosed.
To that, Dr. Ay suggested the significantly higher relative risk in children was supportive of the notion that cancer itself, or treatment effects, were influencing atrial fibrillation risk.
“There is evidence suggesting that cancer treatments are triggering atrial fibrillation,” he said in an interview. “Also, patients with cancer have situations of in which they are sick – they have neutropenia or sepsis and so on – which can also trigger atrial fibrillation.”
Given the limitations of the retrospective cohort study, Dr. Ay said he was hoping to do a prospective study that would enable baseline measurements of cancer patients to determine how much of the atrial fibrillation was preexisting.
“We have also more and more cancer survivors, and over the years they’re living longer and the likelihood of getting atrial fibrillation increases,” he added.
Commenting on the data, Gerald Soff, MD, chief of hematology at the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, said it was very important to quantify the association between cancer and atrial fibrillation.
“What’s striking to me is how many people with cancer come in with preexisting atrial fibrillation,” he said. “It could be that they have cancer and they’re already messed up, but we have, on a given day, several people coming in with newly diagnosed cancers, already on warfarin or apixaban or rivaroxaban because they have atrial fibrillation.”
Dr. Ay reported advisory board positions and speaking engagements for the pharmaceutical sector.
MELBOURNE – The overall prevalence of atrial fibrillation in people who have or have had cancer is 10 times that of individuals without cancer, according to a study presented at the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis congress.
Cihan Ay, MD, of the division of hematology and hemostaseology at the Medical University of Vienna reported on a nationwide cohort study using health insurance data from more than 8.3 million people in Austria, including roughly 159,000 with a diagnosis of cancer and 113,000 with a diagnosis of atrial fibrillation.
The analysis found that, in individuals whose records showed a diagnosis of cancer, there was a 950% higher relative risk of also having a diagnosis of atrial fibrillation, compared with those with no cancer diagnosis.
The overall prevalence of atrial fibrillation among individuals with a cancer diagnosis was 9.8%, compared with 1.2% in those without cancer.
There was significant variation in relative risk according to age. Although the prevalence of atrial fibrillation increased with age, the highest relative risks were seen in the youngest age groups.
In those aged 12 years or under with a cancer diagnosis, the relative risk of atrial fibrillation was 150 times greater than in those without cancer, and in those aged 13-18 years, it was 200 times higher. At the other end of the age spectrum, individuals aged 70-79 years with a recorded cancer diagnosis, the relative risk of atrial fibrillation was still 130% higher than the noncancer population, and in those aged 80-90 years it was a significant 54% higher.
However, the analysis did not find any effect of gender on the risk of atrial fibrillation associated with cancer, regardless of the age group.
Researchers also examined the influence of different cancer types. They found the highest relative risk of atrial fibrillation was in persons with hematologic malignancies – at nine times the risk in the noncancer population – and the lowest was in the endocrine cancer patients, who had three times the risk.
Dr. Ay told the conference that the association between cancer and atrial fibrillation had been suggested in the literature, but it was still an unexplored field. “The exact magnitude of this association between cancer and atrial fibrillation is still unclear.”
There was also the question of what mechanisms might underlie the association. Dr. Ay pointed out that the health insurance database did not allow researchers to explore the temporal relationship between the two diagnoses, and therefore could not tell which came first.
One audience member queried whether the fact that cancer patients were likely to be visiting a clinician more frequently might mean that the atrial fibrillation would be more likely to be diagnosed.
To that, Dr. Ay suggested the significantly higher relative risk in children was supportive of the notion that cancer itself, or treatment effects, were influencing atrial fibrillation risk.
“There is evidence suggesting that cancer treatments are triggering atrial fibrillation,” he said in an interview. “Also, patients with cancer have situations of in which they are sick – they have neutropenia or sepsis and so on – which can also trigger atrial fibrillation.”
Given the limitations of the retrospective cohort study, Dr. Ay said he was hoping to do a prospective study that would enable baseline measurements of cancer patients to determine how much of the atrial fibrillation was preexisting.
“We have also more and more cancer survivors, and over the years they’re living longer and the likelihood of getting atrial fibrillation increases,” he added.
Commenting on the data, Gerald Soff, MD, chief of hematology at the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, said it was very important to quantify the association between cancer and atrial fibrillation.
“What’s striking to me is how many people with cancer come in with preexisting atrial fibrillation,” he said. “It could be that they have cancer and they’re already messed up, but we have, on a given day, several people coming in with newly diagnosed cancers, already on warfarin or apixaban or rivaroxaban because they have atrial fibrillation.”
Dr. Ay reported advisory board positions and speaking engagements for the pharmaceutical sector.
REPORTING FROM 2019 ISTH CONGRESS
No reduction in PE risk with vena cava filters after severe injury
MELBOURNE – Use of a prophylactic vena cava filter to trap blood clots in severely injured patients does not appear to reduce the risk of pulmonary embolism or death, according to data presented at the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis congress.
The researchers reported the outcomes of a multicenter, controlled trial in which 240 severely injured patients with a contraindication to anticoagulants were randomized to receive a vena cava filter within 72 hours of admission, or no filter. The findings were published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The study showed no significant differences between the filter and no-filter groups in the primary outcome of a composite of symptomatic pulmonary embolism or death from any cause at 90 days after enrollment (13.9% vs. 14.4% respectively, P = .98).
In a prespecified subgroup analysis, researchers examined patients who survived 7 days after injury and did not receive prophylactic anticoagulation in those 7 days. Among this group of patients, none of those who received the vena cava filter experienced a symptomatic pulmonary embolism between day 8 and day 90, but five patients (14.7%) in the no-filter group did.
Filters were left in place for a median duration of 27 days (11-90 days). Among the 122 patients who received a filter – which included two patients in the control group – researchers found trapped thrombi in the filter in six patients.
Transfusion requirements, and the incidence of major and nonmajor bleeding and leg deep vein thrombosis, were similar between the filter and no-filter groups. Seven patients in the filter group (5.7%) required more than one attempt to remove the filter, and in one patient the filter had to be removed surgically.
Kwok M. Ho, PhD, of the department of intensive care medicine at Royal Perth Hospital, Australia, and coauthors wrote that while vena cava filters are widely used in trauma centers to prevent pulmonary embolism in patients at high risk of bleeding, there are conflicting recommendations regarding their use, and most studies so far have been observational.
“Given the cost and risks associated with a vena cava filter, our data suggest that there is no urgency to insert the filter in patients who can be treated with prophylactic anticoagulation within 7 days after injury,” they wrote. “Unnecessary insertion of a vena cava filter has the potential to cause harm.”
However, they noted that patients with multiple, large intracranial hematomas were particularly at risk from bleeding with anticoagulant therapy, and therefore may benefit from the use of a vena cava filter.
The Medical Research Foundation of Royal Perth Hospital and the Western Australian Department of Health funded the study. Dr. Ho reported funding from the Western Australian Department of Health and the Raine Medical Research Foundation to conduct the study, as well as serving as an adviser to Medtronic and Cardinal Health.
SOURCE: Ho KM et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Jul 7. doi: 10.156/NEJMoa1806515.
MELBOURNE – Use of a prophylactic vena cava filter to trap blood clots in severely injured patients does not appear to reduce the risk of pulmonary embolism or death, according to data presented at the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis congress.
The researchers reported the outcomes of a multicenter, controlled trial in which 240 severely injured patients with a contraindication to anticoagulants were randomized to receive a vena cava filter within 72 hours of admission, or no filter. The findings were published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The study showed no significant differences between the filter and no-filter groups in the primary outcome of a composite of symptomatic pulmonary embolism or death from any cause at 90 days after enrollment (13.9% vs. 14.4% respectively, P = .98).
In a prespecified subgroup analysis, researchers examined patients who survived 7 days after injury and did not receive prophylactic anticoagulation in those 7 days. Among this group of patients, none of those who received the vena cava filter experienced a symptomatic pulmonary embolism between day 8 and day 90, but five patients (14.7%) in the no-filter group did.
Filters were left in place for a median duration of 27 days (11-90 days). Among the 122 patients who received a filter – which included two patients in the control group – researchers found trapped thrombi in the filter in six patients.
Transfusion requirements, and the incidence of major and nonmajor bleeding and leg deep vein thrombosis, were similar between the filter and no-filter groups. Seven patients in the filter group (5.7%) required more than one attempt to remove the filter, and in one patient the filter had to be removed surgically.
Kwok M. Ho, PhD, of the department of intensive care medicine at Royal Perth Hospital, Australia, and coauthors wrote that while vena cava filters are widely used in trauma centers to prevent pulmonary embolism in patients at high risk of bleeding, there are conflicting recommendations regarding their use, and most studies so far have been observational.
“Given the cost and risks associated with a vena cava filter, our data suggest that there is no urgency to insert the filter in patients who can be treated with prophylactic anticoagulation within 7 days after injury,” they wrote. “Unnecessary insertion of a vena cava filter has the potential to cause harm.”
However, they noted that patients with multiple, large intracranial hematomas were particularly at risk from bleeding with anticoagulant therapy, and therefore may benefit from the use of a vena cava filter.
The Medical Research Foundation of Royal Perth Hospital and the Western Australian Department of Health funded the study. Dr. Ho reported funding from the Western Australian Department of Health and the Raine Medical Research Foundation to conduct the study, as well as serving as an adviser to Medtronic and Cardinal Health.
SOURCE: Ho KM et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Jul 7. doi: 10.156/NEJMoa1806515.
MELBOURNE – Use of a prophylactic vena cava filter to trap blood clots in severely injured patients does not appear to reduce the risk of pulmonary embolism or death, according to data presented at the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis congress.
The researchers reported the outcomes of a multicenter, controlled trial in which 240 severely injured patients with a contraindication to anticoagulants were randomized to receive a vena cava filter within 72 hours of admission, or no filter. The findings were published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The study showed no significant differences between the filter and no-filter groups in the primary outcome of a composite of symptomatic pulmonary embolism or death from any cause at 90 days after enrollment (13.9% vs. 14.4% respectively, P = .98).
In a prespecified subgroup analysis, researchers examined patients who survived 7 days after injury and did not receive prophylactic anticoagulation in those 7 days. Among this group of patients, none of those who received the vena cava filter experienced a symptomatic pulmonary embolism between day 8 and day 90, but five patients (14.7%) in the no-filter group did.
Filters were left in place for a median duration of 27 days (11-90 days). Among the 122 patients who received a filter – which included two patients in the control group – researchers found trapped thrombi in the filter in six patients.
Transfusion requirements, and the incidence of major and nonmajor bleeding and leg deep vein thrombosis, were similar between the filter and no-filter groups. Seven patients in the filter group (5.7%) required more than one attempt to remove the filter, and in one patient the filter had to be removed surgically.
Kwok M. Ho, PhD, of the department of intensive care medicine at Royal Perth Hospital, Australia, and coauthors wrote that while vena cava filters are widely used in trauma centers to prevent pulmonary embolism in patients at high risk of bleeding, there are conflicting recommendations regarding their use, and most studies so far have been observational.
“Given the cost and risks associated with a vena cava filter, our data suggest that there is no urgency to insert the filter in patients who can be treated with prophylactic anticoagulation within 7 days after injury,” they wrote. “Unnecessary insertion of a vena cava filter has the potential to cause harm.”
However, they noted that patients with multiple, large intracranial hematomas were particularly at risk from bleeding with anticoagulant therapy, and therefore may benefit from the use of a vena cava filter.
The Medical Research Foundation of Royal Perth Hospital and the Western Australian Department of Health funded the study. Dr. Ho reported funding from the Western Australian Department of Health and the Raine Medical Research Foundation to conduct the study, as well as serving as an adviser to Medtronic and Cardinal Health.
SOURCE: Ho KM et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Jul 7. doi: 10.156/NEJMoa1806515.
REPORTING FROM 2019 ISTH CONGRESS
Consider bleeding risk with oral anticoagulants in patients with GI cancer
MELBOURNE – The treatment of cancer-associated thrombosis may be complicated by increased bleeding risk in patients with gastrointestinal cancer, in whom direct oral anticoagulants may not be the ideal first choice, one expert reported at the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis congress.
Agnes Y.Y. Lee, MD, medical director of the Thrombosis Program at Vancouver General Hospital and the University of British Columbia, spoke about the challenges and necessity of treating cancer-associated thrombosis, pointing out that about 20% of all cases of venous thromboembolism (VTE) are associated with cancer.
“In those with cancer, thrombosis can also interfere with cancer treatment, increases health care costs, and is extraordinarily burdensome to patients and their families,” she said. “Fortunately the most effective way to reduce this burden is to use anticoagulant therapy for prevention and treatment.”
While direct oral anticoagulants have been shown in several studies to be comparable to warfarin in treating most patients with thrombosis, Dr. Lee said there has been a question of how they compare in safety and efficacy to low-molecular-weight heparin in individuals with cancer.
Data from the Hokusai VTE Cancer trial, which compared oral edoxaban with subcutaneous dalteparin in patients with cancer, showed that the two treatments were comparable in time to first occurrence of thrombosis. However, the study did show a fourfold higher risk of bleeding with edoxaban, compared with that of dalteparin, among individuals with gastrointestinal cancers, a difference in bleeding rate that was not seen in patients with nongastrointestinal cancers, Dr. Lee said.
Dr. Lee pointed out that this study also showed a higher bleeding risk in patients with other bleeding risk factors, including those with primary or metastatic brain cancer.
“This study also showed that, when patients developed major bleeding, 60%-80% of them required hospitalization or an ICU stay, so major bleeding is a serious complication and certainly will increase the cost of therapy for these patients,” she said.
In the SELECT-D pilot study, which compared rivaroxaban with dalteparin in patients with cancer, there was a higher risk of bleeding for patients with esophageal or gastroesophageal cancers.
Bleeding risk is generally not well addressed in current guidelines on managing hemostasis in patients with malignancies, partly because it is difficult to quantify bleeding in these patients whose hemoglobin levels would be affected by their disease and their chemotherapy, Dr. Lee said in an interview.
“The bleeding events in cancer patients do get more complicated because there’s all this other noise in the background,” she said.
Commenting on her personal approach to treatment, Dr. Lee said she favors starting patients on low-molecular-weight heparin because it gives her time to understand patients, their disease, and their needs.
“A lot of patients arrive, and they can’t really tell me what their cancer is doing, they can’t really tell me what cancer therapy they’re going through,” she says. “And if they’re on a long list of drugs, then I have to talk to my pharmacist about whether there are drug-drug interactions.”
If patients were well managed on low-molecular-weight heparin without any bleeding, then Dr. Lee said she would consider switching them to direct oral anticoagulants.
Cochair of the session, Ingrid Pabinger, MD, from the Medical University of Vienna commented that vitamin K antagonists should not be forgotten because some patients are unable to afford low-molecular-weight heparin.
However Dr. Lee said these were last on the list for her because of the risk of drug-drug interactions, drug-food interactions, and the issues faced by patients experiencing vomiting or diarrhea with their chemotherapy.
Dr. Lee reported research funding, consultancies, and honoraria from the pharmaceutical sector.
MELBOURNE – The treatment of cancer-associated thrombosis may be complicated by increased bleeding risk in patients with gastrointestinal cancer, in whom direct oral anticoagulants may not be the ideal first choice, one expert reported at the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis congress.
Agnes Y.Y. Lee, MD, medical director of the Thrombosis Program at Vancouver General Hospital and the University of British Columbia, spoke about the challenges and necessity of treating cancer-associated thrombosis, pointing out that about 20% of all cases of venous thromboembolism (VTE) are associated with cancer.
“In those with cancer, thrombosis can also interfere with cancer treatment, increases health care costs, and is extraordinarily burdensome to patients and their families,” she said. “Fortunately the most effective way to reduce this burden is to use anticoagulant therapy for prevention and treatment.”
While direct oral anticoagulants have been shown in several studies to be comparable to warfarin in treating most patients with thrombosis, Dr. Lee said there has been a question of how they compare in safety and efficacy to low-molecular-weight heparin in individuals with cancer.
Data from the Hokusai VTE Cancer trial, which compared oral edoxaban with subcutaneous dalteparin in patients with cancer, showed that the two treatments were comparable in time to first occurrence of thrombosis. However, the study did show a fourfold higher risk of bleeding with edoxaban, compared with that of dalteparin, among individuals with gastrointestinal cancers, a difference in bleeding rate that was not seen in patients with nongastrointestinal cancers, Dr. Lee said.
Dr. Lee pointed out that this study also showed a higher bleeding risk in patients with other bleeding risk factors, including those with primary or metastatic brain cancer.
“This study also showed that, when patients developed major bleeding, 60%-80% of them required hospitalization or an ICU stay, so major bleeding is a serious complication and certainly will increase the cost of therapy for these patients,” she said.
In the SELECT-D pilot study, which compared rivaroxaban with dalteparin in patients with cancer, there was a higher risk of bleeding for patients with esophageal or gastroesophageal cancers.
Bleeding risk is generally not well addressed in current guidelines on managing hemostasis in patients with malignancies, partly because it is difficult to quantify bleeding in these patients whose hemoglobin levels would be affected by their disease and their chemotherapy, Dr. Lee said in an interview.
“The bleeding events in cancer patients do get more complicated because there’s all this other noise in the background,” she said.
Commenting on her personal approach to treatment, Dr. Lee said she favors starting patients on low-molecular-weight heparin because it gives her time to understand patients, their disease, and their needs.
“A lot of patients arrive, and they can’t really tell me what their cancer is doing, they can’t really tell me what cancer therapy they’re going through,” she says. “And if they’re on a long list of drugs, then I have to talk to my pharmacist about whether there are drug-drug interactions.”
If patients were well managed on low-molecular-weight heparin without any bleeding, then Dr. Lee said she would consider switching them to direct oral anticoagulants.
Cochair of the session, Ingrid Pabinger, MD, from the Medical University of Vienna commented that vitamin K antagonists should not be forgotten because some patients are unable to afford low-molecular-weight heparin.
However Dr. Lee said these were last on the list for her because of the risk of drug-drug interactions, drug-food interactions, and the issues faced by patients experiencing vomiting or diarrhea with their chemotherapy.
Dr. Lee reported research funding, consultancies, and honoraria from the pharmaceutical sector.
MELBOURNE – The treatment of cancer-associated thrombosis may be complicated by increased bleeding risk in patients with gastrointestinal cancer, in whom direct oral anticoagulants may not be the ideal first choice, one expert reported at the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis congress.
Agnes Y.Y. Lee, MD, medical director of the Thrombosis Program at Vancouver General Hospital and the University of British Columbia, spoke about the challenges and necessity of treating cancer-associated thrombosis, pointing out that about 20% of all cases of venous thromboembolism (VTE) are associated with cancer.
“In those with cancer, thrombosis can also interfere with cancer treatment, increases health care costs, and is extraordinarily burdensome to patients and their families,” she said. “Fortunately the most effective way to reduce this burden is to use anticoagulant therapy for prevention and treatment.”
While direct oral anticoagulants have been shown in several studies to be comparable to warfarin in treating most patients with thrombosis, Dr. Lee said there has been a question of how they compare in safety and efficacy to low-molecular-weight heparin in individuals with cancer.
Data from the Hokusai VTE Cancer trial, which compared oral edoxaban with subcutaneous dalteparin in patients with cancer, showed that the two treatments were comparable in time to first occurrence of thrombosis. However, the study did show a fourfold higher risk of bleeding with edoxaban, compared with that of dalteparin, among individuals with gastrointestinal cancers, a difference in bleeding rate that was not seen in patients with nongastrointestinal cancers, Dr. Lee said.
Dr. Lee pointed out that this study also showed a higher bleeding risk in patients with other bleeding risk factors, including those with primary or metastatic brain cancer.
“This study also showed that, when patients developed major bleeding, 60%-80% of them required hospitalization or an ICU stay, so major bleeding is a serious complication and certainly will increase the cost of therapy for these patients,” she said.
In the SELECT-D pilot study, which compared rivaroxaban with dalteparin in patients with cancer, there was a higher risk of bleeding for patients with esophageal or gastroesophageal cancers.
Bleeding risk is generally not well addressed in current guidelines on managing hemostasis in patients with malignancies, partly because it is difficult to quantify bleeding in these patients whose hemoglobin levels would be affected by their disease and their chemotherapy, Dr. Lee said in an interview.
“The bleeding events in cancer patients do get more complicated because there’s all this other noise in the background,” she said.
Commenting on her personal approach to treatment, Dr. Lee said she favors starting patients on low-molecular-weight heparin because it gives her time to understand patients, their disease, and their needs.
“A lot of patients arrive, and they can’t really tell me what their cancer is doing, they can’t really tell me what cancer therapy they’re going through,” she says. “And if they’re on a long list of drugs, then I have to talk to my pharmacist about whether there are drug-drug interactions.”
If patients were well managed on low-molecular-weight heparin without any bleeding, then Dr. Lee said she would consider switching them to direct oral anticoagulants.
Cochair of the session, Ingrid Pabinger, MD, from the Medical University of Vienna commented that vitamin K antagonists should not be forgotten because some patients are unable to afford low-molecular-weight heparin.
However Dr. Lee said these were last on the list for her because of the risk of drug-drug interactions, drug-food interactions, and the issues faced by patients experiencing vomiting or diarrhea with their chemotherapy.
Dr. Lee reported research funding, consultancies, and honoraria from the pharmaceutical sector.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM 2019 ISTH CONGRESS
FDA expands Doptelet approval to ITP patients with thrombocytopenia
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a supplemental New Drug Application expanding the indication of avatrombopag (Doptelet) to include treatment of thrombocytopenia in adults with chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) with insufficient response to previous therapy, according to Dova Pharmaceuticals.
FDA approval was based on results of a phase 3 trial in which a majority of patients who received avatrombopag achieved a platelet count of at least 50,000 per mcg after 8 days of therapy. In addition, efficacy was superior to patients in the placebo group in the maintenance of platelet counts during the 6-month treatment period.
Avatrombopag – an oral, thrombopoietin receptor agonist administered with food – was previously indicated for the treatment of chronic liver disease in adult patients who are scheduled to undergo a procedure. The most common adverse reactions in patients with ITP include headache, fatigue, contusion, epistaxis, upper respiratory tract infection, arthralgia, gingival bleeding, petechiae, and nasopharyngitis.
Find the full press release on the Dova Pharmaceuticals website.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a supplemental New Drug Application expanding the indication of avatrombopag (Doptelet) to include treatment of thrombocytopenia in adults with chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) with insufficient response to previous therapy, according to Dova Pharmaceuticals.
FDA approval was based on results of a phase 3 trial in which a majority of patients who received avatrombopag achieved a platelet count of at least 50,000 per mcg after 8 days of therapy. In addition, efficacy was superior to patients in the placebo group in the maintenance of platelet counts during the 6-month treatment period.
Avatrombopag – an oral, thrombopoietin receptor agonist administered with food – was previously indicated for the treatment of chronic liver disease in adult patients who are scheduled to undergo a procedure. The most common adverse reactions in patients with ITP include headache, fatigue, contusion, epistaxis, upper respiratory tract infection, arthralgia, gingival bleeding, petechiae, and nasopharyngitis.
Find the full press release on the Dova Pharmaceuticals website.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a supplemental New Drug Application expanding the indication of avatrombopag (Doptelet) to include treatment of thrombocytopenia in adults with chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) with insufficient response to previous therapy, according to Dova Pharmaceuticals.
FDA approval was based on results of a phase 3 trial in which a majority of patients who received avatrombopag achieved a platelet count of at least 50,000 per mcg after 8 days of therapy. In addition, efficacy was superior to patients in the placebo group in the maintenance of platelet counts during the 6-month treatment period.
Avatrombopag – an oral, thrombopoietin receptor agonist administered with food – was previously indicated for the treatment of chronic liver disease in adult patients who are scheduled to undergo a procedure. The most common adverse reactions in patients with ITP include headache, fatigue, contusion, epistaxis, upper respiratory tract infection, arthralgia, gingival bleeding, petechiae, and nasopharyngitis.
Find the full press release on the Dova Pharmaceuticals website.
Risk model could help predict VTE in acute leukemia
AMSTERDAM – A new clinical prediction model can determine the risk of venous thromboembolism in patients with leukemia, according to investigators.
The scoring system, which incorporates historical, morphological, and cytologic factors, was internally validated at multiple time points over the course of a year, reported lead author, Alejandro Lazo-Langner, MD, of the University of Western Ontario, London.
“It is important that we can predict or anticipate which patients [with acute leukemia] will develop venous thrombosis so that we can develop preventions and aim for better surveillance strategies,” Dr. Lazo-Langner said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association. Venous thromboembolism (VTE) risk modeling is available for patients with solid tumors, but a similar prognostic tool for leukemia patients has been missing.
To fill this practice gap, Dr. Lazo-Langner and colleagues conducted a retrospective cohort study involving 501 patients with acute leukemia who were diagnosed between 2006 and 2017. Of these patients, 427 (85.2%) had myeloid lineage and 74 (14.8%) had lymphoblastic disease. VTE outcomes of interest included proximal lower- and upper-extremity deep vein thrombosis; pulmonary embolism; and thrombosis of unusual sites, such as splanchnic and cerebral. Patients were followed until last follow-up, VTE, or death. Single variable and multiple variable logistic regression were used sequentially to evaluate and confirm potential predictive factors, with nonparametric bootstrapping for internal validation.
After last follow-up, 77 patients (15.3%) had developed VTE; specifically, 44 patients had upper-extremity deep vein thrombosis, 28 had lower-extremity deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, and 5 had cerebral vein thrombosis. The median time from leukemia diagnosis to VTE was approximately 2 months (64 days). Out of 20 possible predictive factors, 7 were included in the multivariable model, and 3 constitute the final model. These three factors are platelet count greater than 50 x 109/L at time of diagnosis (1 point), lymphoblastic leukemia (2 points), and previous history of venous thromboembolism (3 points).
Dr. Lazo-Langner explained that leukemia patients at high risk of VTE are those with a score of 3 or more points. Using this risk threshold, the investigators found that the overall cumulative incidence of VTE in the high-risk group was 44.0%, compared with 10.5% in the low-risk group. Temporal analysis showed a widening disparity between the two groups, from 3 months (28.8% vs. 6.3%), to 6 months (41.1% vs. 7.9%), and 12 months (42.5% vs. 9.3%).
When asked if treatment type was evaluated, Dr. Lazo-Langner said that treatment type was evaluated but proved unfruitful for the model, which is designed for universal use in leukemia.
“We did include a number of different chemotherapy regimens,” he said. “The problem is, because we included both AML [acute myeloid leukemia] and ALL [acute lymphoblastic leukemia] lineage, and the cornerstone of treatment is different for both lineages. It’s difficult to actually include what kind of chemotherapy [patients had]. For instance, it is known that anthracyclines increase risk of thrombosis, but in both lineages, you use anthracyclines, so you really cannot use that as a predictor.”
Looking to the future, the next step will be validation in other cohorts. If this is successful, then Dr. Lazo-Langner speculated that clinicians could use the scoring system to direct monitoring and treatment. For example, patients with high scores and low platelet counts could receive earlier transfusional support, while all high-risk patients could be placed under more intensive surveillance and given additional education about thrombosis.
“I think recognizing symptoms early is important,” Dr. Lazo-Langner said, “and that would be training not only clinicians, but also nursing personnel and the patients themselves to be aware of the symptoms, so they can actually recognize them sooner.”
The study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Lazo-Langner is an investigator with the Canadian Venous Thromboembolism Clinical Trials and Outcomes Research (CanVECTOR) Network.
SOURCE: Lazo-Langner A et al. EHA 2019, Abstract S1642.
AMSTERDAM – A new clinical prediction model can determine the risk of venous thromboembolism in patients with leukemia, according to investigators.
The scoring system, which incorporates historical, morphological, and cytologic factors, was internally validated at multiple time points over the course of a year, reported lead author, Alejandro Lazo-Langner, MD, of the University of Western Ontario, London.
“It is important that we can predict or anticipate which patients [with acute leukemia] will develop venous thrombosis so that we can develop preventions and aim for better surveillance strategies,” Dr. Lazo-Langner said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association. Venous thromboembolism (VTE) risk modeling is available for patients with solid tumors, but a similar prognostic tool for leukemia patients has been missing.
To fill this practice gap, Dr. Lazo-Langner and colleagues conducted a retrospective cohort study involving 501 patients with acute leukemia who were diagnosed between 2006 and 2017. Of these patients, 427 (85.2%) had myeloid lineage and 74 (14.8%) had lymphoblastic disease. VTE outcomes of interest included proximal lower- and upper-extremity deep vein thrombosis; pulmonary embolism; and thrombosis of unusual sites, such as splanchnic and cerebral. Patients were followed until last follow-up, VTE, or death. Single variable and multiple variable logistic regression were used sequentially to evaluate and confirm potential predictive factors, with nonparametric bootstrapping for internal validation.
After last follow-up, 77 patients (15.3%) had developed VTE; specifically, 44 patients had upper-extremity deep vein thrombosis, 28 had lower-extremity deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, and 5 had cerebral vein thrombosis. The median time from leukemia diagnosis to VTE was approximately 2 months (64 days). Out of 20 possible predictive factors, 7 were included in the multivariable model, and 3 constitute the final model. These three factors are platelet count greater than 50 x 109/L at time of diagnosis (1 point), lymphoblastic leukemia (2 points), and previous history of venous thromboembolism (3 points).
Dr. Lazo-Langner explained that leukemia patients at high risk of VTE are those with a score of 3 or more points. Using this risk threshold, the investigators found that the overall cumulative incidence of VTE in the high-risk group was 44.0%, compared with 10.5% in the low-risk group. Temporal analysis showed a widening disparity between the two groups, from 3 months (28.8% vs. 6.3%), to 6 months (41.1% vs. 7.9%), and 12 months (42.5% vs. 9.3%).
When asked if treatment type was evaluated, Dr. Lazo-Langner said that treatment type was evaluated but proved unfruitful for the model, which is designed for universal use in leukemia.
“We did include a number of different chemotherapy regimens,” he said. “The problem is, because we included both AML [acute myeloid leukemia] and ALL [acute lymphoblastic leukemia] lineage, and the cornerstone of treatment is different for both lineages. It’s difficult to actually include what kind of chemotherapy [patients had]. For instance, it is known that anthracyclines increase risk of thrombosis, but in both lineages, you use anthracyclines, so you really cannot use that as a predictor.”
Looking to the future, the next step will be validation in other cohorts. If this is successful, then Dr. Lazo-Langner speculated that clinicians could use the scoring system to direct monitoring and treatment. For example, patients with high scores and low platelet counts could receive earlier transfusional support, while all high-risk patients could be placed under more intensive surveillance and given additional education about thrombosis.
“I think recognizing symptoms early is important,” Dr. Lazo-Langner said, “and that would be training not only clinicians, but also nursing personnel and the patients themselves to be aware of the symptoms, so they can actually recognize them sooner.”
The study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Lazo-Langner is an investigator with the Canadian Venous Thromboembolism Clinical Trials and Outcomes Research (CanVECTOR) Network.
SOURCE: Lazo-Langner A et al. EHA 2019, Abstract S1642.
AMSTERDAM – A new clinical prediction model can determine the risk of venous thromboembolism in patients with leukemia, according to investigators.
The scoring system, which incorporates historical, morphological, and cytologic factors, was internally validated at multiple time points over the course of a year, reported lead author, Alejandro Lazo-Langner, MD, of the University of Western Ontario, London.
“It is important that we can predict or anticipate which patients [with acute leukemia] will develop venous thrombosis so that we can develop preventions and aim for better surveillance strategies,” Dr. Lazo-Langner said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association. Venous thromboembolism (VTE) risk modeling is available for patients with solid tumors, but a similar prognostic tool for leukemia patients has been missing.
To fill this practice gap, Dr. Lazo-Langner and colleagues conducted a retrospective cohort study involving 501 patients with acute leukemia who were diagnosed between 2006 and 2017. Of these patients, 427 (85.2%) had myeloid lineage and 74 (14.8%) had lymphoblastic disease. VTE outcomes of interest included proximal lower- and upper-extremity deep vein thrombosis; pulmonary embolism; and thrombosis of unusual sites, such as splanchnic and cerebral. Patients were followed until last follow-up, VTE, or death. Single variable and multiple variable logistic regression were used sequentially to evaluate and confirm potential predictive factors, with nonparametric bootstrapping for internal validation.
After last follow-up, 77 patients (15.3%) had developed VTE; specifically, 44 patients had upper-extremity deep vein thrombosis, 28 had lower-extremity deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, and 5 had cerebral vein thrombosis. The median time from leukemia diagnosis to VTE was approximately 2 months (64 days). Out of 20 possible predictive factors, 7 were included in the multivariable model, and 3 constitute the final model. These three factors are platelet count greater than 50 x 109/L at time of diagnosis (1 point), lymphoblastic leukemia (2 points), and previous history of venous thromboembolism (3 points).
Dr. Lazo-Langner explained that leukemia patients at high risk of VTE are those with a score of 3 or more points. Using this risk threshold, the investigators found that the overall cumulative incidence of VTE in the high-risk group was 44.0%, compared with 10.5% in the low-risk group. Temporal analysis showed a widening disparity between the two groups, from 3 months (28.8% vs. 6.3%), to 6 months (41.1% vs. 7.9%), and 12 months (42.5% vs. 9.3%).
When asked if treatment type was evaluated, Dr. Lazo-Langner said that treatment type was evaluated but proved unfruitful for the model, which is designed for universal use in leukemia.
“We did include a number of different chemotherapy regimens,” he said. “The problem is, because we included both AML [acute myeloid leukemia] and ALL [acute lymphoblastic leukemia] lineage, and the cornerstone of treatment is different for both lineages. It’s difficult to actually include what kind of chemotherapy [patients had]. For instance, it is known that anthracyclines increase risk of thrombosis, but in both lineages, you use anthracyclines, so you really cannot use that as a predictor.”
Looking to the future, the next step will be validation in other cohorts. If this is successful, then Dr. Lazo-Langner speculated that clinicians could use the scoring system to direct monitoring and treatment. For example, patients with high scores and low platelet counts could receive earlier transfusional support, while all high-risk patients could be placed under more intensive surveillance and given additional education about thrombosis.
“I think recognizing symptoms early is important,” Dr. Lazo-Langner said, “and that would be training not only clinicians, but also nursing personnel and the patients themselves to be aware of the symptoms, so they can actually recognize them sooner.”
The study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Lazo-Langner is an investigator with the Canadian Venous Thromboembolism Clinical Trials and Outcomes Research (CanVECTOR) Network.
SOURCE: Lazo-Langner A et al. EHA 2019, Abstract S1642.
REPORTING FROM EHA CONGRESS
Cell count ratios appear to predict thromboembolism in lymphoma
AMSTERDAM – When predicting the risk of thromboembolism in lymphoma patients receiving chemotherapy, clinicians can rely on a routine diagnostic tool: complete blood count, investigators reported.
A recent study found that high neutrophil to lymphocyte (NLR) and platelet to lymphocyte (PLR) ratios were prognostic for thromboembolism in this setting, reported lead author Vladimir Otasevic, MD, of the Clinical Centre of Serbia in Belgrade.
“Because of the presence of a broad spectrum of risk factors [in patients with lymphoma undergoing chemotherapy], some authors have published risk-assessment models for prediction of thromboembolism,” Dr. Otasevic said during a presentation at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association. While the underlying pathophysiology that precedes thromboembolism is complex, Dr. Otasevic suggested that risk prediction may not have to be, noting that NLR and PLR were recently proposed as risk biomarkers.
To test the utility of these potential biomarkers, Dr. Otasevic and his colleagues retrospectively analyzed data from 484 patients with non-Hodgkin and Hodgkin lymphoma who had undergone at least one cycle of chemotherapy at the Clinic for Hematology, Clinical Centre of Serbia. Patients were followed for venous and arterial thromboembolic events from the time of diagnosis to 3 months beyond their final cycle of chemotherapy. NLR and PLR ratios were calculated from complete blood count. Thromboembolism was diagnosed by radiography, clinical exam, and laboratory evaluation, with probable diagnoses reviewed by an internist and radiologist.
The median patient age was 53 years with a range from 18 to 89 years. Most patients were recently diagnosed with advanced disease (21.1% stage III and 42.5% stage IV). Half of the population had high-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma (50.0%) and slightly more than a quarter had low-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma (28.3%). Low-grade Hodgkin lymphoma was less common (17.4%) and followed distantly by other forms (4.3%).
Thirty-five patients (7.2%) developed thromboembolic events; of these, 30 had venous thromboembolism (6.2%), 6 had arterial thromboembolism (1.2%), and 1 had both. Patients who experienced thromboembolic events had significantly higher NLR and PLR than patients without thromboembolism, and both ratios were significantly associated with one another.
A positive NLR, defined as a ratio of 3.1 or more, was associated with a relative risk of 4.1 for thromboembolism (P less than .001), while a positive PLR, defined as a ratio of 10 or more, was associated with a relative risk of 2.9 (P = .008). Using a multivariate model, a positive NLR was associated with an even higher relative risk (RR = 4.5; P less than .001).
“NLR and PLR demonstrated significant powerfulness in prediction of future risk of [thromboembolism] in lymphoma patients,” the investigators concluded. “Simplicity, effectiveness, modesty, and practicability qualify these new tools for routine [thromboembolism] prognostic assessment.”
Dr. Otasevic said that he and his colleagues have plans to build on these findings with further analysis involving progression-free and overall survival.
The investigators reported no disclosures.
SOURCE: Otasevic V et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S1645.
AMSTERDAM – When predicting the risk of thromboembolism in lymphoma patients receiving chemotherapy, clinicians can rely on a routine diagnostic tool: complete blood count, investigators reported.
A recent study found that high neutrophil to lymphocyte (NLR) and platelet to lymphocyte (PLR) ratios were prognostic for thromboembolism in this setting, reported lead author Vladimir Otasevic, MD, of the Clinical Centre of Serbia in Belgrade.
“Because of the presence of a broad spectrum of risk factors [in patients with lymphoma undergoing chemotherapy], some authors have published risk-assessment models for prediction of thromboembolism,” Dr. Otasevic said during a presentation at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association. While the underlying pathophysiology that precedes thromboembolism is complex, Dr. Otasevic suggested that risk prediction may not have to be, noting that NLR and PLR were recently proposed as risk biomarkers.
To test the utility of these potential biomarkers, Dr. Otasevic and his colleagues retrospectively analyzed data from 484 patients with non-Hodgkin and Hodgkin lymphoma who had undergone at least one cycle of chemotherapy at the Clinic for Hematology, Clinical Centre of Serbia. Patients were followed for venous and arterial thromboembolic events from the time of diagnosis to 3 months beyond their final cycle of chemotherapy. NLR and PLR ratios were calculated from complete blood count. Thromboembolism was diagnosed by radiography, clinical exam, and laboratory evaluation, with probable diagnoses reviewed by an internist and radiologist.
The median patient age was 53 years with a range from 18 to 89 years. Most patients were recently diagnosed with advanced disease (21.1% stage III and 42.5% stage IV). Half of the population had high-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma (50.0%) and slightly more than a quarter had low-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma (28.3%). Low-grade Hodgkin lymphoma was less common (17.4%) and followed distantly by other forms (4.3%).
Thirty-five patients (7.2%) developed thromboembolic events; of these, 30 had venous thromboembolism (6.2%), 6 had arterial thromboembolism (1.2%), and 1 had both. Patients who experienced thromboembolic events had significantly higher NLR and PLR than patients without thromboembolism, and both ratios were significantly associated with one another.
A positive NLR, defined as a ratio of 3.1 or more, was associated with a relative risk of 4.1 for thromboembolism (P less than .001), while a positive PLR, defined as a ratio of 10 or more, was associated with a relative risk of 2.9 (P = .008). Using a multivariate model, a positive NLR was associated with an even higher relative risk (RR = 4.5; P less than .001).
“NLR and PLR demonstrated significant powerfulness in prediction of future risk of [thromboembolism] in lymphoma patients,” the investigators concluded. “Simplicity, effectiveness, modesty, and practicability qualify these new tools for routine [thromboembolism] prognostic assessment.”
Dr. Otasevic said that he and his colleagues have plans to build on these findings with further analysis involving progression-free and overall survival.
The investigators reported no disclosures.
SOURCE: Otasevic V et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S1645.
AMSTERDAM – When predicting the risk of thromboembolism in lymphoma patients receiving chemotherapy, clinicians can rely on a routine diagnostic tool: complete blood count, investigators reported.
A recent study found that high neutrophil to lymphocyte (NLR) and platelet to lymphocyte (PLR) ratios were prognostic for thromboembolism in this setting, reported lead author Vladimir Otasevic, MD, of the Clinical Centre of Serbia in Belgrade.
“Because of the presence of a broad spectrum of risk factors [in patients with lymphoma undergoing chemotherapy], some authors have published risk-assessment models for prediction of thromboembolism,” Dr. Otasevic said during a presentation at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association. While the underlying pathophysiology that precedes thromboembolism is complex, Dr. Otasevic suggested that risk prediction may not have to be, noting that NLR and PLR were recently proposed as risk biomarkers.
To test the utility of these potential biomarkers, Dr. Otasevic and his colleagues retrospectively analyzed data from 484 patients with non-Hodgkin and Hodgkin lymphoma who had undergone at least one cycle of chemotherapy at the Clinic for Hematology, Clinical Centre of Serbia. Patients were followed for venous and arterial thromboembolic events from the time of diagnosis to 3 months beyond their final cycle of chemotherapy. NLR and PLR ratios were calculated from complete blood count. Thromboembolism was diagnosed by radiography, clinical exam, and laboratory evaluation, with probable diagnoses reviewed by an internist and radiologist.
The median patient age was 53 years with a range from 18 to 89 years. Most patients were recently diagnosed with advanced disease (21.1% stage III and 42.5% stage IV). Half of the population had high-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma (50.0%) and slightly more than a quarter had low-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma (28.3%). Low-grade Hodgkin lymphoma was less common (17.4%) and followed distantly by other forms (4.3%).
Thirty-five patients (7.2%) developed thromboembolic events; of these, 30 had venous thromboembolism (6.2%), 6 had arterial thromboembolism (1.2%), and 1 had both. Patients who experienced thromboembolic events had significantly higher NLR and PLR than patients without thromboembolism, and both ratios were significantly associated with one another.
A positive NLR, defined as a ratio of 3.1 or more, was associated with a relative risk of 4.1 for thromboembolism (P less than .001), while a positive PLR, defined as a ratio of 10 or more, was associated with a relative risk of 2.9 (P = .008). Using a multivariate model, a positive NLR was associated with an even higher relative risk (RR = 4.5; P less than .001).
“NLR and PLR demonstrated significant powerfulness in prediction of future risk of [thromboembolism] in lymphoma patients,” the investigators concluded. “Simplicity, effectiveness, modesty, and practicability qualify these new tools for routine [thromboembolism] prognostic assessment.”
Dr. Otasevic said that he and his colleagues have plans to build on these findings with further analysis involving progression-free and overall survival.
The investigators reported no disclosures.
SOURCE: Otasevic V et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S1645.
REPORTING FROM EHA CONGRESS
Rivaroxaban tied to higher GI bleeding than other NOACs
SAN DIEGO – Patients on rivaroxaban had significantly higher rates of GI bleeding, compared with those taking apixaban or dabigatran, results from a large population-based study showed.
“This may be due to the fact that rivaroxaban is administered as a single daily dose as opposed to the other two non–vitamin K anticoagulants [NOACs], which are given twice daily,” lead study author Arnar B. Ingason said at the annual Digestive Disease Week. “This may lead to a greater variance in plasma drug concentration, making these patients more susceptible to bleeding.”
Mr. Ingason, a medical student at the University of Iceland, Reykjavik, said that although several studies have compared warfarin with NOACs, it remains unclear which NOAC has the most favorable GI profile. In an effort to improve the research in this area, he and his associates performed a nationwide, population-based study during March 2014–Jan. 2018 to compare the GI bleeding risk of patients receiving rivaroxaban to that of a combined pool of patients receiving either apixaban or dabigatran. They drew from the Icelandic Medicine Registry, which contains all outpatient drug prescriptions in the country. Next, the researchers linked the personal identification numbers of patients to the Landspitali University diagnoses registry, which includes more than 90% of all patients hospitalized for GI bleeding. They used 1:1 nearest neighbor propensity score for matching and Kaplan-Meier survival estimates and Cox regression to compare rates of GI bleeding. The study outcome of interest was any clinically relevant GI bleeding.
Mr. Ingason reported that the baseline characteristics were similar between the rivaroxaban group and the apixaban/dabigatran group. They matched for several variables, including age, sex, Charlson score, the proportion being anticoagulant naive, moderate to severe renal disease, moderate to severe liver disease, any prior bleeding, and any prior thrombotic events.
During the study period, 3,473 patients received rivaroxaban, 1,901 received apixaban, and 1,086 received dabigatran. After propensity score matching, the researchers compared 2,635 patients who received rivaroxaban with 2,365 patients who received either apixaban or dabigatran. They found that patients in the rivaroxaban group had significantly higher rates of GI bleeding, compared with in the apixaban/dabigatran group (1.2 and. 0.6 events per 100 patient-years, respectively). This yielded a hazard ratio of 2.02, “which means that patients receiving rivaroxaban are twice as likely to get GI bleeding compared to patients on apixaban or dabigatran,” Mr. Ingason said. When the researchers examined the entire unmatched cohort of patients, the rivaroxaban group also had significantly higher rates of GI bleeding, compared with the apixaban/dabigatran group (1.0 and 0.6 events per 100 patient-years; HR, 1.75).
Mr. Ingason and his colleagues observed that patients in the rivaroxaban group had higher rates of GI bleeding, compared with the apixaban/dabigatran group, during the entire follow-up period. At the end of year 4, the rivaroxaban group had a 4% cumulative event rate of GI bleeding, compared with 1.8% for the apixaban/dabigatran group, a highly significant difference at P = .0057).
When a meeting attendee asked Mr. Ingason why patients taking apixaban or dabigatran were combined into one group, he said that it was done to increase the power of their study. “Our theory was that rivaroxaban was different because it is administered as a single daily dose, while the others are given twice daily,” he said. The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – Patients on rivaroxaban had significantly higher rates of GI bleeding, compared with those taking apixaban or dabigatran, results from a large population-based study showed.
“This may be due to the fact that rivaroxaban is administered as a single daily dose as opposed to the other two non–vitamin K anticoagulants [NOACs], which are given twice daily,” lead study author Arnar B. Ingason said at the annual Digestive Disease Week. “This may lead to a greater variance in plasma drug concentration, making these patients more susceptible to bleeding.”
Mr. Ingason, a medical student at the University of Iceland, Reykjavik, said that although several studies have compared warfarin with NOACs, it remains unclear which NOAC has the most favorable GI profile. In an effort to improve the research in this area, he and his associates performed a nationwide, population-based study during March 2014–Jan. 2018 to compare the GI bleeding risk of patients receiving rivaroxaban to that of a combined pool of patients receiving either apixaban or dabigatran. They drew from the Icelandic Medicine Registry, which contains all outpatient drug prescriptions in the country. Next, the researchers linked the personal identification numbers of patients to the Landspitali University diagnoses registry, which includes more than 90% of all patients hospitalized for GI bleeding. They used 1:1 nearest neighbor propensity score for matching and Kaplan-Meier survival estimates and Cox regression to compare rates of GI bleeding. The study outcome of interest was any clinically relevant GI bleeding.
Mr. Ingason reported that the baseline characteristics were similar between the rivaroxaban group and the apixaban/dabigatran group. They matched for several variables, including age, sex, Charlson score, the proportion being anticoagulant naive, moderate to severe renal disease, moderate to severe liver disease, any prior bleeding, and any prior thrombotic events.
During the study period, 3,473 patients received rivaroxaban, 1,901 received apixaban, and 1,086 received dabigatran. After propensity score matching, the researchers compared 2,635 patients who received rivaroxaban with 2,365 patients who received either apixaban or dabigatran. They found that patients in the rivaroxaban group had significantly higher rates of GI bleeding, compared with in the apixaban/dabigatran group (1.2 and. 0.6 events per 100 patient-years, respectively). This yielded a hazard ratio of 2.02, “which means that patients receiving rivaroxaban are twice as likely to get GI bleeding compared to patients on apixaban or dabigatran,” Mr. Ingason said. When the researchers examined the entire unmatched cohort of patients, the rivaroxaban group also had significantly higher rates of GI bleeding, compared with the apixaban/dabigatran group (1.0 and 0.6 events per 100 patient-years; HR, 1.75).
Mr. Ingason and his colleagues observed that patients in the rivaroxaban group had higher rates of GI bleeding, compared with the apixaban/dabigatran group, during the entire follow-up period. At the end of year 4, the rivaroxaban group had a 4% cumulative event rate of GI bleeding, compared with 1.8% for the apixaban/dabigatran group, a highly significant difference at P = .0057).
When a meeting attendee asked Mr. Ingason why patients taking apixaban or dabigatran were combined into one group, he said that it was done to increase the power of their study. “Our theory was that rivaroxaban was different because it is administered as a single daily dose, while the others are given twice daily,” he said. The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – Patients on rivaroxaban had significantly higher rates of GI bleeding, compared with those taking apixaban or dabigatran, results from a large population-based study showed.
“This may be due to the fact that rivaroxaban is administered as a single daily dose as opposed to the other two non–vitamin K anticoagulants [NOACs], which are given twice daily,” lead study author Arnar B. Ingason said at the annual Digestive Disease Week. “This may lead to a greater variance in plasma drug concentration, making these patients more susceptible to bleeding.”
Mr. Ingason, a medical student at the University of Iceland, Reykjavik, said that although several studies have compared warfarin with NOACs, it remains unclear which NOAC has the most favorable GI profile. In an effort to improve the research in this area, he and his associates performed a nationwide, population-based study during March 2014–Jan. 2018 to compare the GI bleeding risk of patients receiving rivaroxaban to that of a combined pool of patients receiving either apixaban or dabigatran. They drew from the Icelandic Medicine Registry, which contains all outpatient drug prescriptions in the country. Next, the researchers linked the personal identification numbers of patients to the Landspitali University diagnoses registry, which includes more than 90% of all patients hospitalized for GI bleeding. They used 1:1 nearest neighbor propensity score for matching and Kaplan-Meier survival estimates and Cox regression to compare rates of GI bleeding. The study outcome of interest was any clinically relevant GI bleeding.
Mr. Ingason reported that the baseline characteristics were similar between the rivaroxaban group and the apixaban/dabigatran group. They matched for several variables, including age, sex, Charlson score, the proportion being anticoagulant naive, moderate to severe renal disease, moderate to severe liver disease, any prior bleeding, and any prior thrombotic events.
During the study period, 3,473 patients received rivaroxaban, 1,901 received apixaban, and 1,086 received dabigatran. After propensity score matching, the researchers compared 2,635 patients who received rivaroxaban with 2,365 patients who received either apixaban or dabigatran. They found that patients in the rivaroxaban group had significantly higher rates of GI bleeding, compared with in the apixaban/dabigatran group (1.2 and. 0.6 events per 100 patient-years, respectively). This yielded a hazard ratio of 2.02, “which means that patients receiving rivaroxaban are twice as likely to get GI bleeding compared to patients on apixaban or dabigatran,” Mr. Ingason said. When the researchers examined the entire unmatched cohort of patients, the rivaroxaban group also had significantly higher rates of GI bleeding, compared with the apixaban/dabigatran group (1.0 and 0.6 events per 100 patient-years; HR, 1.75).
Mr. Ingason and his colleagues observed that patients in the rivaroxaban group had higher rates of GI bleeding, compared with the apixaban/dabigatran group, during the entire follow-up period. At the end of year 4, the rivaroxaban group had a 4% cumulative event rate of GI bleeding, compared with 1.8% for the apixaban/dabigatran group, a highly significant difference at P = .0057).
When a meeting attendee asked Mr. Ingason why patients taking apixaban or dabigatran were combined into one group, he said that it was done to increase the power of their study. “Our theory was that rivaroxaban was different because it is administered as a single daily dose, while the others are given twice daily,” he said. The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
REPORTING FROM DDW 2019
Antibody hierarchy may drive development of SLE vs. antiphospholipid syndrome
according to study findings presented at the European Congress of Rheumatology.
Spanish researchers found that the number of antiphospholipid (aPL) antibodies present was important for the development of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and that lupus anticoagulant (LA) was the major aPL antibody linked to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)–related organ involvement.
“aPL [antibodies] has been extensively associated with an increased risk of thrombosis and poor pregnancy outcomes, mainly in patients with primary APS,” study investigator Leyre Riancho-Zarrabeitia, MD, PhD, explained in an interview ahead of the congress.
“Moreover, aPL [antibody] positivity in SLE has been proposed to be associated with higher damage accrual and with certain manifestations such as valvular heart disease, pulmonary hypertension, and neuropsychiatric manifestations,” she added.
Anticardiolipin antibodies – notably IgG rather than IgM isotypes – also seemed to play an important role in APS and SLE manifestations, Dr. Riancho-Zarrabeitia, of Hospital Sierrallana, Instituto De Investigación Marqués De Valdecilla, and the University of Cantabria (Spain), noted during her oral presentation.
She reported data on 3,651 patients included in the RELESSER registry between October 2011 and August 2012. This large, multicenter, hospital-based registry retrospectively collects immunologic, clinical and demographic data from unselected adult patients with SLE who are attending 45 Spanish rheumatology services within the country’s national health system.
Over one-third (37.5%) of patients, who had a mean age of 47 years and were mostly (90%) women, were positive for aPL. The most frequent aPL detected was IgG anticardiolipin (aCL) antibodies, seen in 25% of patients, followed by LA in 24%, and IgM aCL in 20%.
Of the aPL-positive patients, 20.6% were positive for only one antibody, 12.1% were positive for two antibodies, and 4.8% were positive for three antibodies.
“All types of aPL were associated with classic APS manifestations,” Dr. Riancho-Zarrabeitia said. The associations were strongest for thrombotic events, such as arterial and venous small-vessel thrombosis and recurrent early pregnancy losses.
aCL antibodies conferred the highest risk for arterial thrombosis, she noted (odds ratio, 5.7), whereas LA conferred the highest risk for venous thrombosis (OR, 4.7). Both IgG and IgM isotypes were associated with thrombotic events, fetal death and recurrent pregnancy loss, but the association was stronger with the IgG isotypes.
Having more than one aPL was particularly associated with a higher risk of these APS manifestations. For example, when one antibody was present the OR for arterial thrombosis was 4.45, but when two or more aPL were detected, the ORs rose to 9.23 and 15.6, respectively.
aCL and LA also were associated with thrombocytopenia and hemolytic anemia, with ORs of around 1-2 and 2-3 respectively. There also were antibody associations with cognitive impairments.
Similar results were seen in patients with SLE. “aPL [antibody] positivity in SLE patients influenced the risk for thrombotic and obstetric manifestations,” Dr. Riancho-Zarrabeitia said. LA and aCL were associated with an increased risk of neuropsychiatric manifestations, and LA was linked to an increased risk for renal disease.
The risk for specific SLE manifestations was again higher with IgG isotypes of aCL, notably an increased risk for cardiac and respiratory events.
While increased antibody numbers generally led to a higher risk of complications, the risk for cutaneous manifestations decreased.
“The load of aPL [antibodies] confers a higher risk for APS,” Dr. Riancho-Zarrabeitia said during her conclusion. “Regarding systemic lupus erythematosus, the number of positive antibodies is directly associated with neurological and ophthalmological manifestations, and inversely associated with cutaneous manifestations.”
What these findings show, said Dr. Riancho-Zarrabeitia in the precongress interview, is that individuals who test positive for aPL antibodies need careful monitoring to prevent and treat severe manifestations. “The next step would be to confirm our findings with a prospective study.”
Dr. Riancho-Zarrabeitia has received travel grants from AbbVie, Pfizer, UCB, Merck, GlaxoSmithKline, Amgen, and Roche.
SOURCE: Riancho-Zarrabeitia L et al. Ann Rheum Dis. Jun 2019;78(Suppl 2):136-7. Abstract OP0124. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-eular.2485.
according to study findings presented at the European Congress of Rheumatology.
Spanish researchers found that the number of antiphospholipid (aPL) antibodies present was important for the development of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and that lupus anticoagulant (LA) was the major aPL antibody linked to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)–related organ involvement.
“aPL [antibodies] has been extensively associated with an increased risk of thrombosis and poor pregnancy outcomes, mainly in patients with primary APS,” study investigator Leyre Riancho-Zarrabeitia, MD, PhD, explained in an interview ahead of the congress.
“Moreover, aPL [antibody] positivity in SLE has been proposed to be associated with higher damage accrual and with certain manifestations such as valvular heart disease, pulmonary hypertension, and neuropsychiatric manifestations,” she added.
Anticardiolipin antibodies – notably IgG rather than IgM isotypes – also seemed to play an important role in APS and SLE manifestations, Dr. Riancho-Zarrabeitia, of Hospital Sierrallana, Instituto De Investigación Marqués De Valdecilla, and the University of Cantabria (Spain), noted during her oral presentation.
She reported data on 3,651 patients included in the RELESSER registry between October 2011 and August 2012. This large, multicenter, hospital-based registry retrospectively collects immunologic, clinical and demographic data from unselected adult patients with SLE who are attending 45 Spanish rheumatology services within the country’s national health system.
Over one-third (37.5%) of patients, who had a mean age of 47 years and were mostly (90%) women, were positive for aPL. The most frequent aPL detected was IgG anticardiolipin (aCL) antibodies, seen in 25% of patients, followed by LA in 24%, and IgM aCL in 20%.
Of the aPL-positive patients, 20.6% were positive for only one antibody, 12.1% were positive for two antibodies, and 4.8% were positive for three antibodies.
“All types of aPL were associated with classic APS manifestations,” Dr. Riancho-Zarrabeitia said. The associations were strongest for thrombotic events, such as arterial and venous small-vessel thrombosis and recurrent early pregnancy losses.
aCL antibodies conferred the highest risk for arterial thrombosis, she noted (odds ratio, 5.7), whereas LA conferred the highest risk for venous thrombosis (OR, 4.7). Both IgG and IgM isotypes were associated with thrombotic events, fetal death and recurrent pregnancy loss, but the association was stronger with the IgG isotypes.
Having more than one aPL was particularly associated with a higher risk of these APS manifestations. For example, when one antibody was present the OR for arterial thrombosis was 4.45, but when two or more aPL were detected, the ORs rose to 9.23 and 15.6, respectively.
aCL and LA also were associated with thrombocytopenia and hemolytic anemia, with ORs of around 1-2 and 2-3 respectively. There also were antibody associations with cognitive impairments.
Similar results were seen in patients with SLE. “aPL [antibody] positivity in SLE patients influenced the risk for thrombotic and obstetric manifestations,” Dr. Riancho-Zarrabeitia said. LA and aCL were associated with an increased risk of neuropsychiatric manifestations, and LA was linked to an increased risk for renal disease.
The risk for specific SLE manifestations was again higher with IgG isotypes of aCL, notably an increased risk for cardiac and respiratory events.
While increased antibody numbers generally led to a higher risk of complications, the risk for cutaneous manifestations decreased.
“The load of aPL [antibodies] confers a higher risk for APS,” Dr. Riancho-Zarrabeitia said during her conclusion. “Regarding systemic lupus erythematosus, the number of positive antibodies is directly associated with neurological and ophthalmological manifestations, and inversely associated with cutaneous manifestations.”
What these findings show, said Dr. Riancho-Zarrabeitia in the precongress interview, is that individuals who test positive for aPL antibodies need careful monitoring to prevent and treat severe manifestations. “The next step would be to confirm our findings with a prospective study.”
Dr. Riancho-Zarrabeitia has received travel grants from AbbVie, Pfizer, UCB, Merck, GlaxoSmithKline, Amgen, and Roche.
SOURCE: Riancho-Zarrabeitia L et al. Ann Rheum Dis. Jun 2019;78(Suppl 2):136-7. Abstract OP0124. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-eular.2485.
according to study findings presented at the European Congress of Rheumatology.
Spanish researchers found that the number of antiphospholipid (aPL) antibodies present was important for the development of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and that lupus anticoagulant (LA) was the major aPL antibody linked to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)–related organ involvement.
“aPL [antibodies] has been extensively associated with an increased risk of thrombosis and poor pregnancy outcomes, mainly in patients with primary APS,” study investigator Leyre Riancho-Zarrabeitia, MD, PhD, explained in an interview ahead of the congress.
“Moreover, aPL [antibody] positivity in SLE has been proposed to be associated with higher damage accrual and with certain manifestations such as valvular heart disease, pulmonary hypertension, and neuropsychiatric manifestations,” she added.
Anticardiolipin antibodies – notably IgG rather than IgM isotypes – also seemed to play an important role in APS and SLE manifestations, Dr. Riancho-Zarrabeitia, of Hospital Sierrallana, Instituto De Investigación Marqués De Valdecilla, and the University of Cantabria (Spain), noted during her oral presentation.
She reported data on 3,651 patients included in the RELESSER registry between October 2011 and August 2012. This large, multicenter, hospital-based registry retrospectively collects immunologic, clinical and demographic data from unselected adult patients with SLE who are attending 45 Spanish rheumatology services within the country’s national health system.
Over one-third (37.5%) of patients, who had a mean age of 47 years and were mostly (90%) women, were positive for aPL. The most frequent aPL detected was IgG anticardiolipin (aCL) antibodies, seen in 25% of patients, followed by LA in 24%, and IgM aCL in 20%.
Of the aPL-positive patients, 20.6% were positive for only one antibody, 12.1% were positive for two antibodies, and 4.8% were positive for three antibodies.
“All types of aPL were associated with classic APS manifestations,” Dr. Riancho-Zarrabeitia said. The associations were strongest for thrombotic events, such as arterial and venous small-vessel thrombosis and recurrent early pregnancy losses.
aCL antibodies conferred the highest risk for arterial thrombosis, she noted (odds ratio, 5.7), whereas LA conferred the highest risk for venous thrombosis (OR, 4.7). Both IgG and IgM isotypes were associated with thrombotic events, fetal death and recurrent pregnancy loss, but the association was stronger with the IgG isotypes.
Having more than one aPL was particularly associated with a higher risk of these APS manifestations. For example, when one antibody was present the OR for arterial thrombosis was 4.45, but when two or more aPL were detected, the ORs rose to 9.23 and 15.6, respectively.
aCL and LA also were associated with thrombocytopenia and hemolytic anemia, with ORs of around 1-2 and 2-3 respectively. There also were antibody associations with cognitive impairments.
Similar results were seen in patients with SLE. “aPL [antibody] positivity in SLE patients influenced the risk for thrombotic and obstetric manifestations,” Dr. Riancho-Zarrabeitia said. LA and aCL were associated with an increased risk of neuropsychiatric manifestations, and LA was linked to an increased risk for renal disease.
The risk for specific SLE manifestations was again higher with IgG isotypes of aCL, notably an increased risk for cardiac and respiratory events.
While increased antibody numbers generally led to a higher risk of complications, the risk for cutaneous manifestations decreased.
“The load of aPL [antibodies] confers a higher risk for APS,” Dr. Riancho-Zarrabeitia said during her conclusion. “Regarding systemic lupus erythematosus, the number of positive antibodies is directly associated with neurological and ophthalmological manifestations, and inversely associated with cutaneous manifestations.”
What these findings show, said Dr. Riancho-Zarrabeitia in the precongress interview, is that individuals who test positive for aPL antibodies need careful monitoring to prevent and treat severe manifestations. “The next step would be to confirm our findings with a prospective study.”
Dr. Riancho-Zarrabeitia has received travel grants from AbbVie, Pfizer, UCB, Merck, GlaxoSmithKline, Amgen, and Roche.
SOURCE: Riancho-Zarrabeitia L et al. Ann Rheum Dis. Jun 2019;78(Suppl 2):136-7. Abstract OP0124. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-eular.2485.
REPORTING FROM EULAR 2019 CONGRESS
Subsegmental PEs overtreated despite link with patient harm
Background: CT pulmonary angiography (CTPA) often detects distal, subsegmental pulmonary embolisms (SSPE) for which there is unclear clinical significance. For these isolated SSPEs, the 2016 CHEST guidelines recommend clinical surveillance in lieu of treatment. Such clinical surveillance has not been associated with an increased recurrence of venous thromboembolism (VTE) over 3 months.
Study design: Retrospective review.
Setting: Tertiary care center in Quebec.
Synopsis: A review of all CTPAs at McGill University in Montreal, from 2014-2016 yielded 222 acute pulmonary emboli (PEs), 71 of which were SSPEs without associated Doppler imaging positive for deep vein thrombosis. Of those 71, 62 (87%) were systemically anticoagulated, compared with 135/143 (94%) of the more proximal PEs. The adverse events of both groups of anticoagulated patients were common and similar. Over the following 3 months, 26 patients in the SSPE group visited the ED or were readmitted (42%; 95% confidence interval, 30%-55%), 21 had a drop in hemoglobin level of 2 g/dL or greater and/or received a blood transfusion (34%; 95% CI, 22%-47%), and 10 died from causes unrelated to VTE (16%; 95% CI, 8%-28%). Limitations of this study included the small number of participants and short time to follow-up.
Bottom line: Although SSPEs have unknown clinical significance, they are being treated with systemic anticoagulation at a similar rate to more proximal PEs and are associated with patient harm.
Citation: Raslan IA et al. Rates of overtreatment and treatment-related adverse effects among patients with subsegmental pulmonary embolism. JAMA Intern Med. 2018 Sep 1;178(9):1272-4.
Dr. Shaw is an assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, University of New Mexico.
Background: CT pulmonary angiography (CTPA) often detects distal, subsegmental pulmonary embolisms (SSPE) for which there is unclear clinical significance. For these isolated SSPEs, the 2016 CHEST guidelines recommend clinical surveillance in lieu of treatment. Such clinical surveillance has not been associated with an increased recurrence of venous thromboembolism (VTE) over 3 months.
Study design: Retrospective review.
Setting: Tertiary care center in Quebec.
Synopsis: A review of all CTPAs at McGill University in Montreal, from 2014-2016 yielded 222 acute pulmonary emboli (PEs), 71 of which were SSPEs without associated Doppler imaging positive for deep vein thrombosis. Of those 71, 62 (87%) were systemically anticoagulated, compared with 135/143 (94%) of the more proximal PEs. The adverse events of both groups of anticoagulated patients were common and similar. Over the following 3 months, 26 patients in the SSPE group visited the ED or were readmitted (42%; 95% confidence interval, 30%-55%), 21 had a drop in hemoglobin level of 2 g/dL or greater and/or received a blood transfusion (34%; 95% CI, 22%-47%), and 10 died from causes unrelated to VTE (16%; 95% CI, 8%-28%). Limitations of this study included the small number of participants and short time to follow-up.
Bottom line: Although SSPEs have unknown clinical significance, they are being treated with systemic anticoagulation at a similar rate to more proximal PEs and are associated with patient harm.
Citation: Raslan IA et al. Rates of overtreatment and treatment-related adverse effects among patients with subsegmental pulmonary embolism. JAMA Intern Med. 2018 Sep 1;178(9):1272-4.
Dr. Shaw is an assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, University of New Mexico.
Background: CT pulmonary angiography (CTPA) often detects distal, subsegmental pulmonary embolisms (SSPE) for which there is unclear clinical significance. For these isolated SSPEs, the 2016 CHEST guidelines recommend clinical surveillance in lieu of treatment. Such clinical surveillance has not been associated with an increased recurrence of venous thromboembolism (VTE) over 3 months.
Study design: Retrospective review.
Setting: Tertiary care center in Quebec.
Synopsis: A review of all CTPAs at McGill University in Montreal, from 2014-2016 yielded 222 acute pulmonary emboli (PEs), 71 of which were SSPEs without associated Doppler imaging positive for deep vein thrombosis. Of those 71, 62 (87%) were systemically anticoagulated, compared with 135/143 (94%) of the more proximal PEs. The adverse events of both groups of anticoagulated patients were common and similar. Over the following 3 months, 26 patients in the SSPE group visited the ED or were readmitted (42%; 95% confidence interval, 30%-55%), 21 had a drop in hemoglobin level of 2 g/dL or greater and/or received a blood transfusion (34%; 95% CI, 22%-47%), and 10 died from causes unrelated to VTE (16%; 95% CI, 8%-28%). Limitations of this study included the small number of participants and short time to follow-up.
Bottom line: Although SSPEs have unknown clinical significance, they are being treated with systemic anticoagulation at a similar rate to more proximal PEs and are associated with patient harm.
Citation: Raslan IA et al. Rates of overtreatment and treatment-related adverse effects among patients with subsegmental pulmonary embolism. JAMA Intern Med. 2018 Sep 1;178(9):1272-4.
Dr. Shaw is an assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, University of New Mexico.
FDA: Faulty hematology analyzers face class I recall
The Food and Drug Administration is alerting laboratories and providers to a class I recall on Beckman Coulter hematology analyzers because of the potential for inaccurate platelet count results.
A class I recall indicates reasonable probability of serious adverse health consequences or death associated with use, according to the FDA.
The recall is related to the devices’ platelet analyzing function; among other uses, these devices help assess patients fitness for surgery, so a faulty reading on platelet counts could result in increased risk for life-threatening bleeding during a procedure in patients who have unidentified severe thrombocytopenia, according to a statement from the agency.
“Because this may cause serious injury, or even death, to a patient, we are urging health care professionals to be aware of the potential for inaccurate diagnostic results with these analyzers and to take appropriate actions including the use of alternative diagnostic testing or confirming analyzer results with manual scanning or estimate of platelets,” Tim Stenzel, MD, PhD, director of the Office of In Vitro Diagnostics and Radiological Health in the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, said in the statement.
The recall applies to the UniCel DxH 800 Coulter Cellular Analysis System, UniCel DxH 600 Coulter Cellular Analysis System, and UniCel DxH 900 Coulter Cellular Analysis System. The faulty devices were first identified in 2018, and the manufacturer released an urgent medical device correction letter at that time. The company has more recently released a software patch for the devices, but the FDA has not yet assessed whether it resolves the problem. The agency has released detailed actions and recommendations related to these devices.
At this time, the FDA is unaware of any serious adverse events that have been directly linked to these devices, but the agency recommends that any events be reported through its MedWatch reporting system.
The Food and Drug Administration is alerting laboratories and providers to a class I recall on Beckman Coulter hematology analyzers because of the potential for inaccurate platelet count results.
A class I recall indicates reasonable probability of serious adverse health consequences or death associated with use, according to the FDA.
The recall is related to the devices’ platelet analyzing function; among other uses, these devices help assess patients fitness for surgery, so a faulty reading on platelet counts could result in increased risk for life-threatening bleeding during a procedure in patients who have unidentified severe thrombocytopenia, according to a statement from the agency.
“Because this may cause serious injury, or even death, to a patient, we are urging health care professionals to be aware of the potential for inaccurate diagnostic results with these analyzers and to take appropriate actions including the use of alternative diagnostic testing or confirming analyzer results with manual scanning or estimate of platelets,” Tim Stenzel, MD, PhD, director of the Office of In Vitro Diagnostics and Radiological Health in the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, said in the statement.
The recall applies to the UniCel DxH 800 Coulter Cellular Analysis System, UniCel DxH 600 Coulter Cellular Analysis System, and UniCel DxH 900 Coulter Cellular Analysis System. The faulty devices were first identified in 2018, and the manufacturer released an urgent medical device correction letter at that time. The company has more recently released a software patch for the devices, but the FDA has not yet assessed whether it resolves the problem. The agency has released detailed actions and recommendations related to these devices.
At this time, the FDA is unaware of any serious adverse events that have been directly linked to these devices, but the agency recommends that any events be reported through its MedWatch reporting system.
The Food and Drug Administration is alerting laboratories and providers to a class I recall on Beckman Coulter hematology analyzers because of the potential for inaccurate platelet count results.
A class I recall indicates reasonable probability of serious adverse health consequences or death associated with use, according to the FDA.
The recall is related to the devices’ platelet analyzing function; among other uses, these devices help assess patients fitness for surgery, so a faulty reading on platelet counts could result in increased risk for life-threatening bleeding during a procedure in patients who have unidentified severe thrombocytopenia, according to a statement from the agency.
“Because this may cause serious injury, or even death, to a patient, we are urging health care professionals to be aware of the potential for inaccurate diagnostic results with these analyzers and to take appropriate actions including the use of alternative diagnostic testing or confirming analyzer results with manual scanning or estimate of platelets,” Tim Stenzel, MD, PhD, director of the Office of In Vitro Diagnostics and Radiological Health in the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, said in the statement.
The recall applies to the UniCel DxH 800 Coulter Cellular Analysis System, UniCel DxH 600 Coulter Cellular Analysis System, and UniCel DxH 900 Coulter Cellular Analysis System. The faulty devices were first identified in 2018, and the manufacturer released an urgent medical device correction letter at that time. The company has more recently released a software patch for the devices, but the FDA has not yet assessed whether it resolves the problem. The agency has released detailed actions and recommendations related to these devices.
At this time, the FDA is unaware of any serious adverse events that have been directly linked to these devices, but the agency recommends that any events be reported through its MedWatch reporting system.