User login
Florida medical boards ban transgender care for minors
Florida’s two main medical bodies have voted to stop gender-affirming treatment of children, including the use of puberty blockers, cross-sex hormones, and surgery, other than in minors who are already receiving such care.
The move, which is unprecedented, makes Florida one of several U.S. states to restrict gender-affirming care for adolescents, but the first to do so via an administrative process, through the actions of its Board of Medicine and Board of Osteopathic Medicine.
“I appreciate the integrity of the Boards for ruling in the best interest of children in Florida despite facing tremendous pressure to permit these unproven and risky treatments,” Florida Surgeon General Joseph Ladapo, MD, PhD, said in a statement.
In a statement, The Endocrine Society criticizes the decision as “blatantly discriminatory” and not based on medical evidence.
During a meeting on Oct. 28 that involved testimonies from doctors, parents of transgender children, detransitioners, and patients, board members referred to similar changes in Europe, where some countries have pushed psychotherapy instead of surgery or hormone treatment.
Then, on Nov. 4, the boards each set slightly different instructions, with the Board of Osteopathic Medicine voting to restrict care for new patients but allowing an exception for children enrolled in clinical studies, which “must include long-term longitudinal assessments of the patients’ physiologic and psychologic outcomes,” according to the Florida Department of Health.
The Board of Medicine did not allow the latter.
The proposed rules are open to public comment before finalization.
Arkansas was the first state to enact such a ban on gender-affirming care, with Republican lawmakers in 2021 overriding GOP Gov. Asa Hutchinson’s veto of the legislation. Alabama Republicans in 2022 approved legislation to outlaw gender-affirming medications for transgender youths. Both laws have been paused amid unfolding legal battles, according to Associated Press.
Oklahoma Gov. Kevin Stitt, a Republican, signed a bill in October that bars federal funds earmarked for the University of Oklahoma Medical Center from being used for gender reassignment treatments for minors. Gov. Stitt also called for the legislature to ban some of those gender reassignment treatments statewide when it returns in February.
Top Tennessee Republicans also have vowed to push for strict antitransgender policies. The state already bans doctors from providing gender-confirming hormone treatment to prepubescent minors. To date, no one has legally challenged the law as medical experts maintain no doctor in Tennessee does so.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Florida’s two main medical bodies have voted to stop gender-affirming treatment of children, including the use of puberty blockers, cross-sex hormones, and surgery, other than in minors who are already receiving such care.
The move, which is unprecedented, makes Florida one of several U.S. states to restrict gender-affirming care for adolescents, but the first to do so via an administrative process, through the actions of its Board of Medicine and Board of Osteopathic Medicine.
“I appreciate the integrity of the Boards for ruling in the best interest of children in Florida despite facing tremendous pressure to permit these unproven and risky treatments,” Florida Surgeon General Joseph Ladapo, MD, PhD, said in a statement.
In a statement, The Endocrine Society criticizes the decision as “blatantly discriminatory” and not based on medical evidence.
During a meeting on Oct. 28 that involved testimonies from doctors, parents of transgender children, detransitioners, and patients, board members referred to similar changes in Europe, where some countries have pushed psychotherapy instead of surgery or hormone treatment.
Then, on Nov. 4, the boards each set slightly different instructions, with the Board of Osteopathic Medicine voting to restrict care for new patients but allowing an exception for children enrolled in clinical studies, which “must include long-term longitudinal assessments of the patients’ physiologic and psychologic outcomes,” according to the Florida Department of Health.
The Board of Medicine did not allow the latter.
The proposed rules are open to public comment before finalization.
Arkansas was the first state to enact such a ban on gender-affirming care, with Republican lawmakers in 2021 overriding GOP Gov. Asa Hutchinson’s veto of the legislation. Alabama Republicans in 2022 approved legislation to outlaw gender-affirming medications for transgender youths. Both laws have been paused amid unfolding legal battles, according to Associated Press.
Oklahoma Gov. Kevin Stitt, a Republican, signed a bill in October that bars federal funds earmarked for the University of Oklahoma Medical Center from being used for gender reassignment treatments for minors. Gov. Stitt also called for the legislature to ban some of those gender reassignment treatments statewide when it returns in February.
Top Tennessee Republicans also have vowed to push for strict antitransgender policies. The state already bans doctors from providing gender-confirming hormone treatment to prepubescent minors. To date, no one has legally challenged the law as medical experts maintain no doctor in Tennessee does so.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Florida’s two main medical bodies have voted to stop gender-affirming treatment of children, including the use of puberty blockers, cross-sex hormones, and surgery, other than in minors who are already receiving such care.
The move, which is unprecedented, makes Florida one of several U.S. states to restrict gender-affirming care for adolescents, but the first to do so via an administrative process, through the actions of its Board of Medicine and Board of Osteopathic Medicine.
“I appreciate the integrity of the Boards for ruling in the best interest of children in Florida despite facing tremendous pressure to permit these unproven and risky treatments,” Florida Surgeon General Joseph Ladapo, MD, PhD, said in a statement.
In a statement, The Endocrine Society criticizes the decision as “blatantly discriminatory” and not based on medical evidence.
During a meeting on Oct. 28 that involved testimonies from doctors, parents of transgender children, detransitioners, and patients, board members referred to similar changes in Europe, where some countries have pushed psychotherapy instead of surgery or hormone treatment.
Then, on Nov. 4, the boards each set slightly different instructions, with the Board of Osteopathic Medicine voting to restrict care for new patients but allowing an exception for children enrolled in clinical studies, which “must include long-term longitudinal assessments of the patients’ physiologic and psychologic outcomes,” according to the Florida Department of Health.
The Board of Medicine did not allow the latter.
The proposed rules are open to public comment before finalization.
Arkansas was the first state to enact such a ban on gender-affirming care, with Republican lawmakers in 2021 overriding GOP Gov. Asa Hutchinson’s veto of the legislation. Alabama Republicans in 2022 approved legislation to outlaw gender-affirming medications for transgender youths. Both laws have been paused amid unfolding legal battles, according to Associated Press.
Oklahoma Gov. Kevin Stitt, a Republican, signed a bill in October that bars federal funds earmarked for the University of Oklahoma Medical Center from being used for gender reassignment treatments for minors. Gov. Stitt also called for the legislature to ban some of those gender reassignment treatments statewide when it returns in February.
Top Tennessee Republicans also have vowed to push for strict antitransgender policies. The state already bans doctors from providing gender-confirming hormone treatment to prepubescent minors. To date, no one has legally challenged the law as medical experts maintain no doctor in Tennessee does so.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
DTC telemedicine expands access to gender-affirming therapy
Direct-to-consumer telemedicine services that provide gender-affirming hormone therapy appear to follow evidence-based guidelines and charge about the same as brick-and-mortar medical centers, according to researchers who reviewed the platforms’ websites.
The findings suggest that virtual care “may be a good option” for transgender, nonbinary, and intersex people, who often report difficulty finding physicians they trust, Erin Jesse, MD, a fifth-year urology resident at University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, who is the first author of the study, told this news organization.
Dr. Jesse’s group presented their findings at a joint scientific meeting of the Sexual Medicine Society of North America and the International Society for Sexual Medicine in Miami. The results have not been published in a peer-reviewed journal.
New direct-to-consumer telemedicine companies have emerged with gender-diverse staff and services tailored to the needs of these individuals. They offer “a more inclusive feel” than might be encountered at a physician’s office, Dr. Jesse said.
Confirming that these companies adhere to standards of care and cost-effectiveness “is especially important considering the reduced access to care and potentially increased vulnerability of the gender-diverse population,” she and her colleagues wrote.
From a Google search in March, the team identified six U.S.-based platforms that offer gender-affirming medical therapy: FOLX, True U Clinic, QueerDoc, Queer Med, TransClinique, and Plume.
From information posted on the companies’ websites, the researchers determined that all aligned with the World Professional Association for Transgender Health’s Standards of Care in two areas: use of an informed consent model to ensure that patients have sufficient information and understanding to decide on their own treatment and endorsement of frequent laboratory monitoring of hormone levels in early stages of treatment.
The team also compared the costs listed on the websites for the first year of therapy to the costs of similar care at a tertiary center, as determined using University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center’s online estimator.
The platforms offered various pricing models, including fee-for-service and monthly membership plans ranging from $59 to $139. For individuals without insurance, estimates ranged from $1,022 to $1,428 for oral estradiol and from $1,184 to $1,668 for intramuscular testosterone from the online companies, compared with $1,184 and $1,216, respectively, at the tertiary center.
Although some platforms accept insurance, the researchers were not able to evaluate the cost of using private insurance or Medicaid, Dr. Jesse said. She noted that transgender individuals are more likely to lack insurance than are cisgender patients.
The team also assessed the scope of services. All companies offered legal help with changes to names and gender markers, such as “M” and “F.” Three or more companies offered preexposure prophylaxis to prevent HIV infection, treatment for erectile dysfunction, referrals for surgery, and medical letters of support for surgery.
Two offered puberty blockers, although the researchers were unable to determine the risk of adolescents obtaining treatment without proper assessments, because details of those services are not disclosed on websites, Dr. Jesse said.
An avenue of further research would be to interview patients to learn how platforms operate in practice and whether patients are properly assessed before treatment. “Those sorts of questions we can’t answer just by looking at the websites,” she said.
However, Charlotte Hoffman, JD, senior policy counsel for the National Center for Transgender Equality, an advocacy group, said she does not harbor concerns about patients being treated inappropriately simply because care is virtual. All clinicians who provide gender-affirming care face potential repercussions, such as malpractice lawsuits or state disciplinary action, if they veer from treatment guidelines, she said.
“I don’t necessarily take the premise that telehealth is inherently worse than in-person care as a given,” Ms. Hoffman said.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Ms. Hoffman added, direct-to-consumer telemedicine has expanded access for individuals in rural areas, people with disabilities, and those who live in places where in-person providers of transgender care face public hostility, although individuals without the resources to pay may still be left out.
What might happen to that access if telemedicine restrictions that were loosened during the pandemic are reinstated is unclear, she said.
The researchers and Ms. Hoffman have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Direct-to-consumer telemedicine services that provide gender-affirming hormone therapy appear to follow evidence-based guidelines and charge about the same as brick-and-mortar medical centers, according to researchers who reviewed the platforms’ websites.
The findings suggest that virtual care “may be a good option” for transgender, nonbinary, and intersex people, who often report difficulty finding physicians they trust, Erin Jesse, MD, a fifth-year urology resident at University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, who is the first author of the study, told this news organization.
Dr. Jesse’s group presented their findings at a joint scientific meeting of the Sexual Medicine Society of North America and the International Society for Sexual Medicine in Miami. The results have not been published in a peer-reviewed journal.
New direct-to-consumer telemedicine companies have emerged with gender-diverse staff and services tailored to the needs of these individuals. They offer “a more inclusive feel” than might be encountered at a physician’s office, Dr. Jesse said.
Confirming that these companies adhere to standards of care and cost-effectiveness “is especially important considering the reduced access to care and potentially increased vulnerability of the gender-diverse population,” she and her colleagues wrote.
From a Google search in March, the team identified six U.S.-based platforms that offer gender-affirming medical therapy: FOLX, True U Clinic, QueerDoc, Queer Med, TransClinique, and Plume.
From information posted on the companies’ websites, the researchers determined that all aligned with the World Professional Association for Transgender Health’s Standards of Care in two areas: use of an informed consent model to ensure that patients have sufficient information and understanding to decide on their own treatment and endorsement of frequent laboratory monitoring of hormone levels in early stages of treatment.
The team also compared the costs listed on the websites for the first year of therapy to the costs of similar care at a tertiary center, as determined using University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center’s online estimator.
The platforms offered various pricing models, including fee-for-service and monthly membership plans ranging from $59 to $139. For individuals without insurance, estimates ranged from $1,022 to $1,428 for oral estradiol and from $1,184 to $1,668 for intramuscular testosterone from the online companies, compared with $1,184 and $1,216, respectively, at the tertiary center.
Although some platforms accept insurance, the researchers were not able to evaluate the cost of using private insurance or Medicaid, Dr. Jesse said. She noted that transgender individuals are more likely to lack insurance than are cisgender patients.
The team also assessed the scope of services. All companies offered legal help with changes to names and gender markers, such as “M” and “F.” Three or more companies offered preexposure prophylaxis to prevent HIV infection, treatment for erectile dysfunction, referrals for surgery, and medical letters of support for surgery.
Two offered puberty blockers, although the researchers were unable to determine the risk of adolescents obtaining treatment without proper assessments, because details of those services are not disclosed on websites, Dr. Jesse said.
An avenue of further research would be to interview patients to learn how platforms operate in practice and whether patients are properly assessed before treatment. “Those sorts of questions we can’t answer just by looking at the websites,” she said.
However, Charlotte Hoffman, JD, senior policy counsel for the National Center for Transgender Equality, an advocacy group, said she does not harbor concerns about patients being treated inappropriately simply because care is virtual. All clinicians who provide gender-affirming care face potential repercussions, such as malpractice lawsuits or state disciplinary action, if they veer from treatment guidelines, she said.
“I don’t necessarily take the premise that telehealth is inherently worse than in-person care as a given,” Ms. Hoffman said.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Ms. Hoffman added, direct-to-consumer telemedicine has expanded access for individuals in rural areas, people with disabilities, and those who live in places where in-person providers of transgender care face public hostility, although individuals without the resources to pay may still be left out.
What might happen to that access if telemedicine restrictions that were loosened during the pandemic are reinstated is unclear, she said.
The researchers and Ms. Hoffman have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Direct-to-consumer telemedicine services that provide gender-affirming hormone therapy appear to follow evidence-based guidelines and charge about the same as brick-and-mortar medical centers, according to researchers who reviewed the platforms’ websites.
The findings suggest that virtual care “may be a good option” for transgender, nonbinary, and intersex people, who often report difficulty finding physicians they trust, Erin Jesse, MD, a fifth-year urology resident at University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, who is the first author of the study, told this news organization.
Dr. Jesse’s group presented their findings at a joint scientific meeting of the Sexual Medicine Society of North America and the International Society for Sexual Medicine in Miami. The results have not been published in a peer-reviewed journal.
New direct-to-consumer telemedicine companies have emerged with gender-diverse staff and services tailored to the needs of these individuals. They offer “a more inclusive feel” than might be encountered at a physician’s office, Dr. Jesse said.
Confirming that these companies adhere to standards of care and cost-effectiveness “is especially important considering the reduced access to care and potentially increased vulnerability of the gender-diverse population,” she and her colleagues wrote.
From a Google search in March, the team identified six U.S.-based platforms that offer gender-affirming medical therapy: FOLX, True U Clinic, QueerDoc, Queer Med, TransClinique, and Plume.
From information posted on the companies’ websites, the researchers determined that all aligned with the World Professional Association for Transgender Health’s Standards of Care in two areas: use of an informed consent model to ensure that patients have sufficient information and understanding to decide on their own treatment and endorsement of frequent laboratory monitoring of hormone levels in early stages of treatment.
The team also compared the costs listed on the websites for the first year of therapy to the costs of similar care at a tertiary center, as determined using University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center’s online estimator.
The platforms offered various pricing models, including fee-for-service and monthly membership plans ranging from $59 to $139. For individuals without insurance, estimates ranged from $1,022 to $1,428 for oral estradiol and from $1,184 to $1,668 for intramuscular testosterone from the online companies, compared with $1,184 and $1,216, respectively, at the tertiary center.
Although some platforms accept insurance, the researchers were not able to evaluate the cost of using private insurance or Medicaid, Dr. Jesse said. She noted that transgender individuals are more likely to lack insurance than are cisgender patients.
The team also assessed the scope of services. All companies offered legal help with changes to names and gender markers, such as “M” and “F.” Three or more companies offered preexposure prophylaxis to prevent HIV infection, treatment for erectile dysfunction, referrals for surgery, and medical letters of support for surgery.
Two offered puberty blockers, although the researchers were unable to determine the risk of adolescents obtaining treatment without proper assessments, because details of those services are not disclosed on websites, Dr. Jesse said.
An avenue of further research would be to interview patients to learn how platforms operate in practice and whether patients are properly assessed before treatment. “Those sorts of questions we can’t answer just by looking at the websites,” she said.
However, Charlotte Hoffman, JD, senior policy counsel for the National Center for Transgender Equality, an advocacy group, said she does not harbor concerns about patients being treated inappropriately simply because care is virtual. All clinicians who provide gender-affirming care face potential repercussions, such as malpractice lawsuits or state disciplinary action, if they veer from treatment guidelines, she said.
“I don’t necessarily take the premise that telehealth is inherently worse than in-person care as a given,” Ms. Hoffman said.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Ms. Hoffman added, direct-to-consumer telemedicine has expanded access for individuals in rural areas, people with disabilities, and those who live in places where in-person providers of transgender care face public hostility, although individuals without the resources to pay may still be left out.
What might happen to that access if telemedicine restrictions that were loosened during the pandemic are reinstated is unclear, she said.
The researchers and Ms. Hoffman have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Higher rates of PTSD, BPD in transgender vs. cisgender psych patients
Although mood disorders, depression, and anxiety were the most common diagnoses in both TGD and cisgender patients, “when we compared the diagnostic profiles [of TGD patients] to those of cisgender patients, we found an increased prevalence of PTSD and BPD,” study investigator Mark Zimmerman, MD, professor of psychiatry and human behavior, Brown University, Providence, R.I., told this news organization.
“What we concluded is that psychiatric programs that wish to treat TGD patients should either have or should develop expertise in treating PTSD and BPD, not just mood and anxiety disorders,” Dr. Zimmerman said.
The study was published online September 26 in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
‘Piecemeal literature’
TGD individuals “experience high rates of various forms of psychopathology in general and when compared with cisgender persons,” the investigators note.
They point out that most empirical evidence has relied upon the use of brief, unstructured psychodiagnostic assessment measures and assessment of a “limited constellation of psychiatric symptoms domains,” resulting in a “piecemeal literature wherein each piece of research documents elevations in one – or a few – diagnostic domains.”
Studies pointing to broader psychosocial health variables have often relied upon self-reported measures. In addition, in studies that utilized a structured interview approach, none “used a formal interview procedure to assess psychiatric diagnoses” and most focused only on a “limited number of psychiatric conditions based on self-reports of past diagnosis.”
The goal of the current study was to use semistructured interviews administered by professionals to compare the diagnostic profiles of a samples of TGD and cisgender patients who presented for treatment at a single naturalistic, clinically acute setting – a partial hospital program.
Dr. Zimmerman said that there was an additional motive for conducting the study. “There has been discussion in the field as to whether or not transgender or gender-diverse individuals all have borderline personality disorder, but that hasn’t been our clinical impression.”
Rather, Dr. Zimmerman and colleagues believe TGD people “may have had more difficult childhoods and more difficult adjustments in society because of societal attitudes and have to deal with that stress, whether it be microaggressions or overt bullying and aggression.” The study was designed to investigate this issue.
In addition, studies conducted in primary care programs in individuals seeking gender-affirming surgery have “reported a limited number of psychiatric diagnoses, but we were wondering whether, amongst psychiatric patients specifically, there were differences in diagnostic profiles between transgender and gender-diverse patients and cisgender patients. If so, what might the implications be for providing care for this population?”
TGD not synonymous with borderline
To investigate, the researchers administered semistructured diagnostic interviews for DSM-IV disorders to 2,212 psychiatric patients (66% cisgender women, 30.8% cisgender men, 3.1% TGD; mean [standard deviation] age 36.7 [14.4] years) presenting to the Rhode Island Hospital Department of Psychiatry Partial Hospital Program between April 2014 and January 2021.
Patients also completed a demographic questionnaire including their assigned sex at birth and their current gender identity.
Most patients (44.9%) were single, followed by 23.5% who were married, 14.1% living in a relationship as if married, 12.0% divorced, 3.6% separated, and 1.9% widowed.
Almost three-quarters of participants (73.2%) identified as White, followed by Hispanic (10.7%), Black (6.7%), “other” or a combination of racial/ethnic backgrounds (6.6%), and Asian (2.7%).
There were no differences between cisgender and TGD groups in terms of race or education, but the TGD patients were significantly younger compared with their cisgender counterparts and were significantly more likely to have never been married.
The average number of psychiatric diagnoses in the sample was 3.05 (± 1.73), with TGD patients having a larger number of psychiatric diagnoses than did their cisgender peers (an average of 3.54 ± 1.88 vs. 3.04 ± 1.72, respectively; t = 2.37; P = .02).
Major depressive disorder (MDD) and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) were the most common disorders among both cisgender and TGD patients. However, after controlling for age, the researchers found that TGD patients were significantly more likely than were the cisgender patients to be diagnosed with PTSD and BPD (P < .05 for both).
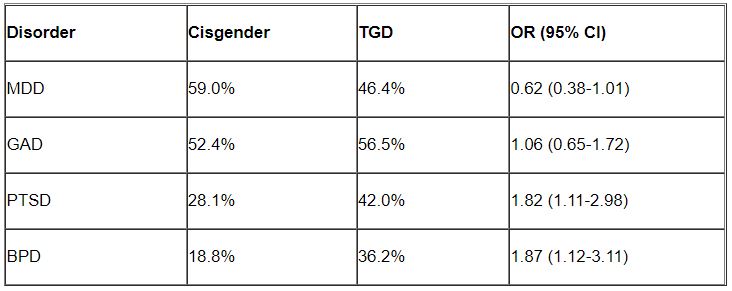
“Of note, only about one-third of the TGD individuals were diagnosed with BPD, so it is important to realize that transgender or gender-diverse identity is not synonymous with BPD, as some have suggested,” noted Dr. Zimmerman, who is also the director of the outpatient division at the Partial Hospital Program, Rhode Island Hospital.
A representative sample?
Commenting on the study, Jack Drescher, MD, distinguished life fellow of the American Psychiatric Association and clinical professor of psychiatry, Columbia University, New York, called the findings “interesting” but noted that a limitation of the study is that it included “a patient population with likely more severe psychiatric illness, since they were all day hospital patients.”
The question is whether similar findings would be obtained in a less severely ill population, said Dr. Drescher, who is also a senior consulting analyst for sexuality and gender at Columbia University and was not involved with the study. “The patients in the study may not be representative of the general population, either cisgender or transgender.”
Dr. Drescher was “not surprised” by the finding regarding PTSD because the finding “is consistent with our understanding of the kinds of traumas that transgender people go through in day-to-day life.”
He noted that some people misunderstand the diagnostic criterion in BPD of identity confusion and think that because people with gender dysphoria may be confused about their identity, it means that all people who are transgender have borderline personality disorder, “but that’s not true.”
Dr. Zimmerman agreed. “The vast majority of individuals with BPD do not have a transgender or gender-diverse identity, and TGD should not be equated with BPD,” he said.
No source of study funding was disclosed. Dr. Zimmerman and coauthors and Dr. Drescher report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although mood disorders, depression, and anxiety were the most common diagnoses in both TGD and cisgender patients, “when we compared the diagnostic profiles [of TGD patients] to those of cisgender patients, we found an increased prevalence of PTSD and BPD,” study investigator Mark Zimmerman, MD, professor of psychiatry and human behavior, Brown University, Providence, R.I., told this news organization.
“What we concluded is that psychiatric programs that wish to treat TGD patients should either have or should develop expertise in treating PTSD and BPD, not just mood and anxiety disorders,” Dr. Zimmerman said.
The study was published online September 26 in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
‘Piecemeal literature’
TGD individuals “experience high rates of various forms of psychopathology in general and when compared with cisgender persons,” the investigators note.
They point out that most empirical evidence has relied upon the use of brief, unstructured psychodiagnostic assessment measures and assessment of a “limited constellation of psychiatric symptoms domains,” resulting in a “piecemeal literature wherein each piece of research documents elevations in one – or a few – diagnostic domains.”
Studies pointing to broader psychosocial health variables have often relied upon self-reported measures. In addition, in studies that utilized a structured interview approach, none “used a formal interview procedure to assess psychiatric diagnoses” and most focused only on a “limited number of psychiatric conditions based on self-reports of past diagnosis.”
The goal of the current study was to use semistructured interviews administered by professionals to compare the diagnostic profiles of a samples of TGD and cisgender patients who presented for treatment at a single naturalistic, clinically acute setting – a partial hospital program.
Dr. Zimmerman said that there was an additional motive for conducting the study. “There has been discussion in the field as to whether or not transgender or gender-diverse individuals all have borderline personality disorder, but that hasn’t been our clinical impression.”
Rather, Dr. Zimmerman and colleagues believe TGD people “may have had more difficult childhoods and more difficult adjustments in society because of societal attitudes and have to deal with that stress, whether it be microaggressions or overt bullying and aggression.” The study was designed to investigate this issue.
In addition, studies conducted in primary care programs in individuals seeking gender-affirming surgery have “reported a limited number of psychiatric diagnoses, but we were wondering whether, amongst psychiatric patients specifically, there were differences in diagnostic profiles between transgender and gender-diverse patients and cisgender patients. If so, what might the implications be for providing care for this population?”
TGD not synonymous with borderline
To investigate, the researchers administered semistructured diagnostic interviews for DSM-IV disorders to 2,212 psychiatric patients (66% cisgender women, 30.8% cisgender men, 3.1% TGD; mean [standard deviation] age 36.7 [14.4] years) presenting to the Rhode Island Hospital Department of Psychiatry Partial Hospital Program between April 2014 and January 2021.
Patients also completed a demographic questionnaire including their assigned sex at birth and their current gender identity.
Most patients (44.9%) were single, followed by 23.5% who were married, 14.1% living in a relationship as if married, 12.0% divorced, 3.6% separated, and 1.9% widowed.
Almost three-quarters of participants (73.2%) identified as White, followed by Hispanic (10.7%), Black (6.7%), “other” or a combination of racial/ethnic backgrounds (6.6%), and Asian (2.7%).
There were no differences between cisgender and TGD groups in terms of race or education, but the TGD patients were significantly younger compared with their cisgender counterparts and were significantly more likely to have never been married.
The average number of psychiatric diagnoses in the sample was 3.05 (± 1.73), with TGD patients having a larger number of psychiatric diagnoses than did their cisgender peers (an average of 3.54 ± 1.88 vs. 3.04 ± 1.72, respectively; t = 2.37; P = .02).
Major depressive disorder (MDD) and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) were the most common disorders among both cisgender and TGD patients. However, after controlling for age, the researchers found that TGD patients were significantly more likely than were the cisgender patients to be diagnosed with PTSD and BPD (P < .05 for both).

“Of note, only about one-third of the TGD individuals were diagnosed with BPD, so it is important to realize that transgender or gender-diverse identity is not synonymous with BPD, as some have suggested,” noted Dr. Zimmerman, who is also the director of the outpatient division at the Partial Hospital Program, Rhode Island Hospital.
A representative sample?
Commenting on the study, Jack Drescher, MD, distinguished life fellow of the American Psychiatric Association and clinical professor of psychiatry, Columbia University, New York, called the findings “interesting” but noted that a limitation of the study is that it included “a patient population with likely more severe psychiatric illness, since they were all day hospital patients.”
The question is whether similar findings would be obtained in a less severely ill population, said Dr. Drescher, who is also a senior consulting analyst for sexuality and gender at Columbia University and was not involved with the study. “The patients in the study may not be representative of the general population, either cisgender or transgender.”
Dr. Drescher was “not surprised” by the finding regarding PTSD because the finding “is consistent with our understanding of the kinds of traumas that transgender people go through in day-to-day life.”
He noted that some people misunderstand the diagnostic criterion in BPD of identity confusion and think that because people with gender dysphoria may be confused about their identity, it means that all people who are transgender have borderline personality disorder, “but that’s not true.”
Dr. Zimmerman agreed. “The vast majority of individuals with BPD do not have a transgender or gender-diverse identity, and TGD should not be equated with BPD,” he said.
No source of study funding was disclosed. Dr. Zimmerman and coauthors and Dr. Drescher report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although mood disorders, depression, and anxiety were the most common diagnoses in both TGD and cisgender patients, “when we compared the diagnostic profiles [of TGD patients] to those of cisgender patients, we found an increased prevalence of PTSD and BPD,” study investigator Mark Zimmerman, MD, professor of psychiatry and human behavior, Brown University, Providence, R.I., told this news organization.
“What we concluded is that psychiatric programs that wish to treat TGD patients should either have or should develop expertise in treating PTSD and BPD, not just mood and anxiety disorders,” Dr. Zimmerman said.
The study was published online September 26 in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
‘Piecemeal literature’
TGD individuals “experience high rates of various forms of psychopathology in general and when compared with cisgender persons,” the investigators note.
They point out that most empirical evidence has relied upon the use of brief, unstructured psychodiagnostic assessment measures and assessment of a “limited constellation of psychiatric symptoms domains,” resulting in a “piecemeal literature wherein each piece of research documents elevations in one – or a few – diagnostic domains.”
Studies pointing to broader psychosocial health variables have often relied upon self-reported measures. In addition, in studies that utilized a structured interview approach, none “used a formal interview procedure to assess psychiatric diagnoses” and most focused only on a “limited number of psychiatric conditions based on self-reports of past diagnosis.”
The goal of the current study was to use semistructured interviews administered by professionals to compare the diagnostic profiles of a samples of TGD and cisgender patients who presented for treatment at a single naturalistic, clinically acute setting – a partial hospital program.
Dr. Zimmerman said that there was an additional motive for conducting the study. “There has been discussion in the field as to whether or not transgender or gender-diverse individuals all have borderline personality disorder, but that hasn’t been our clinical impression.”
Rather, Dr. Zimmerman and colleagues believe TGD people “may have had more difficult childhoods and more difficult adjustments in society because of societal attitudes and have to deal with that stress, whether it be microaggressions or overt bullying and aggression.” The study was designed to investigate this issue.
In addition, studies conducted in primary care programs in individuals seeking gender-affirming surgery have “reported a limited number of psychiatric diagnoses, but we were wondering whether, amongst psychiatric patients specifically, there were differences in diagnostic profiles between transgender and gender-diverse patients and cisgender patients. If so, what might the implications be for providing care for this population?”
TGD not synonymous with borderline
To investigate, the researchers administered semistructured diagnostic interviews for DSM-IV disorders to 2,212 psychiatric patients (66% cisgender women, 30.8% cisgender men, 3.1% TGD; mean [standard deviation] age 36.7 [14.4] years) presenting to the Rhode Island Hospital Department of Psychiatry Partial Hospital Program between April 2014 and January 2021.
Patients also completed a demographic questionnaire including their assigned sex at birth and their current gender identity.
Most patients (44.9%) were single, followed by 23.5% who were married, 14.1% living in a relationship as if married, 12.0% divorced, 3.6% separated, and 1.9% widowed.
Almost three-quarters of participants (73.2%) identified as White, followed by Hispanic (10.7%), Black (6.7%), “other” or a combination of racial/ethnic backgrounds (6.6%), and Asian (2.7%).
There were no differences between cisgender and TGD groups in terms of race or education, but the TGD patients were significantly younger compared with their cisgender counterparts and were significantly more likely to have never been married.
The average number of psychiatric diagnoses in the sample was 3.05 (± 1.73), with TGD patients having a larger number of psychiatric diagnoses than did their cisgender peers (an average of 3.54 ± 1.88 vs. 3.04 ± 1.72, respectively; t = 2.37; P = .02).
Major depressive disorder (MDD) and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) were the most common disorders among both cisgender and TGD patients. However, after controlling for age, the researchers found that TGD patients were significantly more likely than were the cisgender patients to be diagnosed with PTSD and BPD (P < .05 for both).

“Of note, only about one-third of the TGD individuals were diagnosed with BPD, so it is important to realize that transgender or gender-diverse identity is not synonymous with BPD, as some have suggested,” noted Dr. Zimmerman, who is also the director of the outpatient division at the Partial Hospital Program, Rhode Island Hospital.
A representative sample?
Commenting on the study, Jack Drescher, MD, distinguished life fellow of the American Psychiatric Association and clinical professor of psychiatry, Columbia University, New York, called the findings “interesting” but noted that a limitation of the study is that it included “a patient population with likely more severe psychiatric illness, since they were all day hospital patients.”
The question is whether similar findings would be obtained in a less severely ill population, said Dr. Drescher, who is also a senior consulting analyst for sexuality and gender at Columbia University and was not involved with the study. “The patients in the study may not be representative of the general population, either cisgender or transgender.”
Dr. Drescher was “not surprised” by the finding regarding PTSD because the finding “is consistent with our understanding of the kinds of traumas that transgender people go through in day-to-day life.”
He noted that some people misunderstand the diagnostic criterion in BPD of identity confusion and think that because people with gender dysphoria may be confused about their identity, it means that all people who are transgender have borderline personality disorder, “but that’s not true.”
Dr. Zimmerman agreed. “The vast majority of individuals with BPD do not have a transgender or gender-diverse identity, and TGD should not be equated with BPD,” he said.
No source of study funding was disclosed. Dr. Zimmerman and coauthors and Dr. Drescher report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PSYCHIATRY
Few transgender teens discontinue hormones in young adulthood
Most adolescents with gender dysphoria who took puberty-blocking drugs for at least 3 months and then progressed to cross-sex hormone treatment were still taking hormones as they entered adulthood, new research of patients at a pioneering Dutch clinic shows.
The study negates past findings that large numbers of youth regret transitioning, say Maria Anna Theodora Catharina van der Loos, MD, and colleagues from the Centre of Expertise on Gender Dysphoria, Amsterdam, in their article published online in The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health. They believe the difference between their findings and those of other studies lies in proper diagnostic evaluation.
“The study aims to demonstrate, with a methodology that is more than adequate, that transgender people who begin their transition in childhood-adolescence do not give up,” Adrián Carrasco Munera, MD, a specialist in family and community medicine and member of the LGTBIQ+ Health Group of the Madrid Society of Family and Community Medicine told the UK Science Media Centre.
The cohort included 720 youth: 220 (31%) were assigned male at birth (AMAB) and 500 (69%) were assigned female at birth (AFAB). At the start of puberty-blocking treatment with a gonadotrophin-releasing hormone agonist, the median age of patients was 14.1 years for AMAB and 16.0 years for AFAB.
Of that cohort, 704 (98%) continued hormone therapy to the end of data collection (Dec. 31, 2018), at which point the median age of patients was 20 years for AMAB and 19 years for AFAB.
Careful consideration of patient needs
All the patients received care at the “Dutch Clinic,” which more than 20 years ago pioneered the approach of giving puberty-blocking drugs to children looking to transition, followed by cross-sex hormones. The study includes the “complete adolescent population” at the facility who met the inclusion criteria.
A similar U.S. study published earlier this year found that 74.4% of individuals who had started gender-affirming hormones before age 18 were still on them 4 years after starting medical treatment.
“However, it is unclear how many of these adolescents [in the U.S. study] used puberty-suppressing treatment before gender-affirming hormone treatment and to what extent they underwent diagnostic evaluation before initiation of medical treatment,” say Dr. van der Loos and colleagues.
She told this news organization that her clinic provides “a thorough diagnostic and mental health assessment” and discussion of fertility preservation prior to any youth being prescribed puberty blockers or cross-sex hormones.
About 40% of adolescents assessed by the gender clinic in Amsterdam go on to receive hormonal treatment.
“The gender identity unit of the Amsterdam UMC is a world leader in all aspects of transgender medicine and is governed by protocolized actions. This is reflected in the quality of the data and methodology of the study, and therefore of its conclusions,” endocrinologist Gilberto Pérez López, MD, Gregorio Marañón General University Hospital, Madrid, told the UK Science Media Centre.
“These findings can and should help and guide the current public and legal debate on the initiation of medical treatment in transgender minors.”
However, he cautioned the study is limited by the fact that the data come from a registry and they looked at only prescriptions issued and not compliance.
Another interesting thing to note in the research is that almost 70% of patients were born girls and they presented at the gender clinics later in adolescence than the natal boys.
“We don’t have a sound reason for this,” Dr. van der Loos noted.
Study limitations
She also acknowledges that the short follow-up data in some individuals make it difficult to draw conclusions about regret, to some extent.
The average use of cross-sex hormones in their study was 3.5 years for males transitioning to females and 2.3 years for females transitioning to males, so on average, this wouldn’t be long enough to see regret, she acknowledged.
Prior research shows that if youth decide to detransition to their natal sex, this can take, on average, 5 years from the start of medical therapy among born females and 7 years among born males.
However, some born males in the study had been taking hormones for 20 years and some natal females for 15 years, said Dr. van der Loos.
Another limitation is that the research only followed individuals until the end of 2018 while some government data estimate that the number of teens identifying as transgender has nearly doubled over the past 5 years.
The authors, Dr. Munera, and Dr. Lopez have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most adolescents with gender dysphoria who took puberty-blocking drugs for at least 3 months and then progressed to cross-sex hormone treatment were still taking hormones as they entered adulthood, new research of patients at a pioneering Dutch clinic shows.
The study negates past findings that large numbers of youth regret transitioning, say Maria Anna Theodora Catharina van der Loos, MD, and colleagues from the Centre of Expertise on Gender Dysphoria, Amsterdam, in their article published online in The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health. They believe the difference between their findings and those of other studies lies in proper diagnostic evaluation.
“The study aims to demonstrate, with a methodology that is more than adequate, that transgender people who begin their transition in childhood-adolescence do not give up,” Adrián Carrasco Munera, MD, a specialist in family and community medicine and member of the LGTBIQ+ Health Group of the Madrid Society of Family and Community Medicine told the UK Science Media Centre.
The cohort included 720 youth: 220 (31%) were assigned male at birth (AMAB) and 500 (69%) were assigned female at birth (AFAB). At the start of puberty-blocking treatment with a gonadotrophin-releasing hormone agonist, the median age of patients was 14.1 years for AMAB and 16.0 years for AFAB.
Of that cohort, 704 (98%) continued hormone therapy to the end of data collection (Dec. 31, 2018), at which point the median age of patients was 20 years for AMAB and 19 years for AFAB.
Careful consideration of patient needs
All the patients received care at the “Dutch Clinic,” which more than 20 years ago pioneered the approach of giving puberty-blocking drugs to children looking to transition, followed by cross-sex hormones. The study includes the “complete adolescent population” at the facility who met the inclusion criteria.
A similar U.S. study published earlier this year found that 74.4% of individuals who had started gender-affirming hormones before age 18 were still on them 4 years after starting medical treatment.
“However, it is unclear how many of these adolescents [in the U.S. study] used puberty-suppressing treatment before gender-affirming hormone treatment and to what extent they underwent diagnostic evaluation before initiation of medical treatment,” say Dr. van der Loos and colleagues.
She told this news organization that her clinic provides “a thorough diagnostic and mental health assessment” and discussion of fertility preservation prior to any youth being prescribed puberty blockers or cross-sex hormones.
About 40% of adolescents assessed by the gender clinic in Amsterdam go on to receive hormonal treatment.
“The gender identity unit of the Amsterdam UMC is a world leader in all aspects of transgender medicine and is governed by protocolized actions. This is reflected in the quality of the data and methodology of the study, and therefore of its conclusions,” endocrinologist Gilberto Pérez López, MD, Gregorio Marañón General University Hospital, Madrid, told the UK Science Media Centre.
“These findings can and should help and guide the current public and legal debate on the initiation of medical treatment in transgender minors.”
However, he cautioned the study is limited by the fact that the data come from a registry and they looked at only prescriptions issued and not compliance.
Another interesting thing to note in the research is that almost 70% of patients were born girls and they presented at the gender clinics later in adolescence than the natal boys.
“We don’t have a sound reason for this,” Dr. van der Loos noted.
Study limitations
She also acknowledges that the short follow-up data in some individuals make it difficult to draw conclusions about regret, to some extent.
The average use of cross-sex hormones in their study was 3.5 years for males transitioning to females and 2.3 years for females transitioning to males, so on average, this wouldn’t be long enough to see regret, she acknowledged.
Prior research shows that if youth decide to detransition to their natal sex, this can take, on average, 5 years from the start of medical therapy among born females and 7 years among born males.
However, some born males in the study had been taking hormones for 20 years and some natal females for 15 years, said Dr. van der Loos.
Another limitation is that the research only followed individuals until the end of 2018 while some government data estimate that the number of teens identifying as transgender has nearly doubled over the past 5 years.
The authors, Dr. Munera, and Dr. Lopez have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most adolescents with gender dysphoria who took puberty-blocking drugs for at least 3 months and then progressed to cross-sex hormone treatment were still taking hormones as they entered adulthood, new research of patients at a pioneering Dutch clinic shows.
The study negates past findings that large numbers of youth regret transitioning, say Maria Anna Theodora Catharina van der Loos, MD, and colleagues from the Centre of Expertise on Gender Dysphoria, Amsterdam, in their article published online in The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health. They believe the difference between their findings and those of other studies lies in proper diagnostic evaluation.
“The study aims to demonstrate, with a methodology that is more than adequate, that transgender people who begin their transition in childhood-adolescence do not give up,” Adrián Carrasco Munera, MD, a specialist in family and community medicine and member of the LGTBIQ+ Health Group of the Madrid Society of Family and Community Medicine told the UK Science Media Centre.
The cohort included 720 youth: 220 (31%) were assigned male at birth (AMAB) and 500 (69%) were assigned female at birth (AFAB). At the start of puberty-blocking treatment with a gonadotrophin-releasing hormone agonist, the median age of patients was 14.1 years for AMAB and 16.0 years for AFAB.
Of that cohort, 704 (98%) continued hormone therapy to the end of data collection (Dec. 31, 2018), at which point the median age of patients was 20 years for AMAB and 19 years for AFAB.
Careful consideration of patient needs
All the patients received care at the “Dutch Clinic,” which more than 20 years ago pioneered the approach of giving puberty-blocking drugs to children looking to transition, followed by cross-sex hormones. The study includes the “complete adolescent population” at the facility who met the inclusion criteria.
A similar U.S. study published earlier this year found that 74.4% of individuals who had started gender-affirming hormones before age 18 were still on them 4 years after starting medical treatment.
“However, it is unclear how many of these adolescents [in the U.S. study] used puberty-suppressing treatment before gender-affirming hormone treatment and to what extent they underwent diagnostic evaluation before initiation of medical treatment,” say Dr. van der Loos and colleagues.
She told this news organization that her clinic provides “a thorough diagnostic and mental health assessment” and discussion of fertility preservation prior to any youth being prescribed puberty blockers or cross-sex hormones.
About 40% of adolescents assessed by the gender clinic in Amsterdam go on to receive hormonal treatment.
“The gender identity unit of the Amsterdam UMC is a world leader in all aspects of transgender medicine and is governed by protocolized actions. This is reflected in the quality of the data and methodology of the study, and therefore of its conclusions,” endocrinologist Gilberto Pérez López, MD, Gregorio Marañón General University Hospital, Madrid, told the UK Science Media Centre.
“These findings can and should help and guide the current public and legal debate on the initiation of medical treatment in transgender minors.”
However, he cautioned the study is limited by the fact that the data come from a registry and they looked at only prescriptions issued and not compliance.
Another interesting thing to note in the research is that almost 70% of patients were born girls and they presented at the gender clinics later in adolescence than the natal boys.
“We don’t have a sound reason for this,” Dr. van der Loos noted.
Study limitations
She also acknowledges that the short follow-up data in some individuals make it difficult to draw conclusions about regret, to some extent.
The average use of cross-sex hormones in their study was 3.5 years for males transitioning to females and 2.3 years for females transitioning to males, so on average, this wouldn’t be long enough to see regret, she acknowledged.
Prior research shows that if youth decide to detransition to their natal sex, this can take, on average, 5 years from the start of medical therapy among born females and 7 years among born males.
However, some born males in the study had been taking hormones for 20 years and some natal females for 15 years, said Dr. van der Loos.
Another limitation is that the research only followed individuals until the end of 2018 while some government data estimate that the number of teens identifying as transgender has nearly doubled over the past 5 years.
The authors, Dr. Munera, and Dr. Lopez have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Caring for the aging transgender patient
The elderly transgender population is rapidly expanding and remains significantly overlooked. Although emerging evidence provides some guidance for medical and surgical treatment for transgender youth, there is still a paucity of research directed at the management of gender-diverse elders.
To a large extent, the challenges that transgender elders face are no different from those experienced by the general elder population. Irrespective of gender identity, patients begin to undergo cognitive and physical changes, encounter difficulties with activities of daily living, suffer the loss of social networks and friends, and face end-of-life issues.1 Attributes that contribute to successful aging in the general population include good health, social engagement and support, and having a positive outlook on life.1 Yet, stigma surrounding gender identity and sexual orientation continues to negatively affect elder transgender people.
Many members of the LGBTQIA+ population have higher rates of obesity, sedentary lifestyle, smoking, cardiovascular disease, substance abuse, depression, suicide, and intimate partner violence than the general same-age cohort.2 Compared with lesbian, gay, and bisexual elders of age-matched cohorts, transgender elders have significantly poorer overall physical health, disability, depressive symptoms, and perceived stress.2
Rates of sexually transmitted infections are also rising in the aging general population and increased by 30% between 2014 and 2017.2 There have been no current studies examining these rates in the LGBTQIA+ population. As providers interact more frequently with these patients, it’s not only essential to screen for conditions such as diabetes, lipid disorders, and sexually transmitted infections, but also to evaluate current gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT) regimens and order appropriate screening tests.
Hormonal therapy for transfeminine patients should be continued as patients age. One of the biggest concerns providers have in continuing hormone therapy is the development of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and increasing thromboembolic risk, both of which tend to occur naturally as patients age. Overall, studies on the prevalence of CVD or stroke in gender-diverse individuals indicate an elevated risk independent of GAHT.3 While the overall rates of thromboembolic events are low in transfeminine populations, estrogen therapy does confer an increased risk. However, most transgender women who have experienced cardiac events or stroke were over the age of 50, had one or more CVD risk factors, or were using synthetic estrogens.3
How these studies affect screening is unclear. Current guidelines recommend using tailored risk-based calculators, which take into consideration the patient’s sex assigned at birth, hormone regimen, length of hormone usage, and additional modifiable risk factors, such as diabetes, obesity, and smoking.3 For transfeminine patients who want to continue GAHT but either develop a venous thromboembolism on estrogen or have increased risk for VTE, providers should consider transitioning them to a transdermal application. Patients who stay on GAHT should be counseled accordingly on the heightened risk of VTE recurrence. It is not unreasonable to consider life-long anticoagulation for patients who remain on estrogen therapy after a VTE.4
While exogenous estrogen exposure is one risk factor for the development of breast cancer in cisgender females, the role of GAHT in breast cancer in transgender women is ambiguous. Therefore, breast screening guidelines should follow current recommendations for cisgender female patients with some caveats. The provider must also take into consideration current estrogen dosage, the age at which hormones were initiated, and whether a patient has undergone an augmentation mammaplasty.3
Both estrogen and testosterone play an important role in bone formation and health. Patients who undergo either medical or surgical interventions that alter sex hormone production, such as GAHT, orchiectomy, or androgen blockade, may be at elevated risk for osteoporosis. Providers should take a thorough medical history to determine patients who may be at risk for osteoporosis and treat them accordingly. Overall, GAHT has a positive effect on bone mineral density. Conversely, gonadectomy, particularly if a patient is not taking GAHT, can decrease bone density. Generally, transgender women, like cisgender women, should undergo DEXA scans starting at the age of 65, with earlier screening considered if they have undergone an orchiectomy and are not currently taking GAHT.3
There is no evidence that GAHT or surgery increases the rate of prostate cancer. Providers should note that the prostate is not removed at the time of gender-affirming surgery and that malignancy or benign prostatic hypertrophy can still occur. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that clinicians have a discussion with cisgender men between the ages of 55 and 69 about the risks and benefits of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening.5 For cisgender men aged 70 and older, the USPSTF recommends against PSA-based screening.5 If digital examination of the prostate is warranted for transfeminine patients, the examination is performed through the neovaginal canal.
Caring for elderly transgender patients is complex. Even though evidence guiding the management of elderly transgender patients is improving, there are still not enough definitive long-term data on this dynamic demographic. Like clinical approaches with hormonal or surgical treatments, caring for transgender elders is also multidisciplinary. Providers should be prepared to work with social workers, geriatric care physicians, endocrinologists, surgeons, and other relevant specialists to assist with potential knowledge gaps. The goals for the aging transgender population are the same as those for cisgender patients – preventing preventable diseases and reducing overall mortality so our patients can enjoy their golden years.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa. Contact her at [email protected].
References
1. Carroll L. Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2017;40:127-40.
2. Selix NW et al. Clinical care of the aging LGBT population. J Nurse Pract. 2020;16(7):349-54.
3. World Professional Association for Transgender Health. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people. 2022;8th version.
4. Shatzel JJ et al. Am J Hematol. 2017;92(2):204-8.
5. Wolf-Gould CS and Wolf-Gould CH. Primary and preventative care for transgender patients. In: Ferrando CA, ed. Comprehensive Care of the Transgender Patient. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2020, p. 114-30.
The elderly transgender population is rapidly expanding and remains significantly overlooked. Although emerging evidence provides some guidance for medical and surgical treatment for transgender youth, there is still a paucity of research directed at the management of gender-diverse elders.
To a large extent, the challenges that transgender elders face are no different from those experienced by the general elder population. Irrespective of gender identity, patients begin to undergo cognitive and physical changes, encounter difficulties with activities of daily living, suffer the loss of social networks and friends, and face end-of-life issues.1 Attributes that contribute to successful aging in the general population include good health, social engagement and support, and having a positive outlook on life.1 Yet, stigma surrounding gender identity and sexual orientation continues to negatively affect elder transgender people.
Many members of the LGBTQIA+ population have higher rates of obesity, sedentary lifestyle, smoking, cardiovascular disease, substance abuse, depression, suicide, and intimate partner violence than the general same-age cohort.2 Compared with lesbian, gay, and bisexual elders of age-matched cohorts, transgender elders have significantly poorer overall physical health, disability, depressive symptoms, and perceived stress.2
Rates of sexually transmitted infections are also rising in the aging general population and increased by 30% between 2014 and 2017.2 There have been no current studies examining these rates in the LGBTQIA+ population. As providers interact more frequently with these patients, it’s not only essential to screen for conditions such as diabetes, lipid disorders, and sexually transmitted infections, but also to evaluate current gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT) regimens and order appropriate screening tests.
Hormonal therapy for transfeminine patients should be continued as patients age. One of the biggest concerns providers have in continuing hormone therapy is the development of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and increasing thromboembolic risk, both of which tend to occur naturally as patients age. Overall, studies on the prevalence of CVD or stroke in gender-diverse individuals indicate an elevated risk independent of GAHT.3 While the overall rates of thromboembolic events are low in transfeminine populations, estrogen therapy does confer an increased risk. However, most transgender women who have experienced cardiac events or stroke were over the age of 50, had one or more CVD risk factors, or were using synthetic estrogens.3
How these studies affect screening is unclear. Current guidelines recommend using tailored risk-based calculators, which take into consideration the patient’s sex assigned at birth, hormone regimen, length of hormone usage, and additional modifiable risk factors, such as diabetes, obesity, and smoking.3 For transfeminine patients who want to continue GAHT but either develop a venous thromboembolism on estrogen or have increased risk for VTE, providers should consider transitioning them to a transdermal application. Patients who stay on GAHT should be counseled accordingly on the heightened risk of VTE recurrence. It is not unreasonable to consider life-long anticoagulation for patients who remain on estrogen therapy after a VTE.4
While exogenous estrogen exposure is one risk factor for the development of breast cancer in cisgender females, the role of GAHT in breast cancer in transgender women is ambiguous. Therefore, breast screening guidelines should follow current recommendations for cisgender female patients with some caveats. The provider must also take into consideration current estrogen dosage, the age at which hormones were initiated, and whether a patient has undergone an augmentation mammaplasty.3
Both estrogen and testosterone play an important role in bone formation and health. Patients who undergo either medical or surgical interventions that alter sex hormone production, such as GAHT, orchiectomy, or androgen blockade, may be at elevated risk for osteoporosis. Providers should take a thorough medical history to determine patients who may be at risk for osteoporosis and treat them accordingly. Overall, GAHT has a positive effect on bone mineral density. Conversely, gonadectomy, particularly if a patient is not taking GAHT, can decrease bone density. Generally, transgender women, like cisgender women, should undergo DEXA scans starting at the age of 65, with earlier screening considered if they have undergone an orchiectomy and are not currently taking GAHT.3
There is no evidence that GAHT or surgery increases the rate of prostate cancer. Providers should note that the prostate is not removed at the time of gender-affirming surgery and that malignancy or benign prostatic hypertrophy can still occur. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that clinicians have a discussion with cisgender men between the ages of 55 and 69 about the risks and benefits of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening.5 For cisgender men aged 70 and older, the USPSTF recommends against PSA-based screening.5 If digital examination of the prostate is warranted for transfeminine patients, the examination is performed through the neovaginal canal.
Caring for elderly transgender patients is complex. Even though evidence guiding the management of elderly transgender patients is improving, there are still not enough definitive long-term data on this dynamic demographic. Like clinical approaches with hormonal or surgical treatments, caring for transgender elders is also multidisciplinary. Providers should be prepared to work with social workers, geriatric care physicians, endocrinologists, surgeons, and other relevant specialists to assist with potential knowledge gaps. The goals for the aging transgender population are the same as those for cisgender patients – preventing preventable diseases and reducing overall mortality so our patients can enjoy their golden years.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa. Contact her at [email protected].
References
1. Carroll L. Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2017;40:127-40.
2. Selix NW et al. Clinical care of the aging LGBT population. J Nurse Pract. 2020;16(7):349-54.
3. World Professional Association for Transgender Health. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people. 2022;8th version.
4. Shatzel JJ et al. Am J Hematol. 2017;92(2):204-8.
5. Wolf-Gould CS and Wolf-Gould CH. Primary and preventative care for transgender patients. In: Ferrando CA, ed. Comprehensive Care of the Transgender Patient. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2020, p. 114-30.
The elderly transgender population is rapidly expanding and remains significantly overlooked. Although emerging evidence provides some guidance for medical and surgical treatment for transgender youth, there is still a paucity of research directed at the management of gender-diverse elders.
To a large extent, the challenges that transgender elders face are no different from those experienced by the general elder population. Irrespective of gender identity, patients begin to undergo cognitive and physical changes, encounter difficulties with activities of daily living, suffer the loss of social networks and friends, and face end-of-life issues.1 Attributes that contribute to successful aging in the general population include good health, social engagement and support, and having a positive outlook on life.1 Yet, stigma surrounding gender identity and sexual orientation continues to negatively affect elder transgender people.
Many members of the LGBTQIA+ population have higher rates of obesity, sedentary lifestyle, smoking, cardiovascular disease, substance abuse, depression, suicide, and intimate partner violence than the general same-age cohort.2 Compared with lesbian, gay, and bisexual elders of age-matched cohorts, transgender elders have significantly poorer overall physical health, disability, depressive symptoms, and perceived stress.2
Rates of sexually transmitted infections are also rising in the aging general population and increased by 30% between 2014 and 2017.2 There have been no current studies examining these rates in the LGBTQIA+ population. As providers interact more frequently with these patients, it’s not only essential to screen for conditions such as diabetes, lipid disorders, and sexually transmitted infections, but also to evaluate current gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT) regimens and order appropriate screening tests.
Hormonal therapy for transfeminine patients should be continued as patients age. One of the biggest concerns providers have in continuing hormone therapy is the development of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and increasing thromboembolic risk, both of which tend to occur naturally as patients age. Overall, studies on the prevalence of CVD or stroke in gender-diverse individuals indicate an elevated risk independent of GAHT.3 While the overall rates of thromboembolic events are low in transfeminine populations, estrogen therapy does confer an increased risk. However, most transgender women who have experienced cardiac events or stroke were over the age of 50, had one or more CVD risk factors, or were using synthetic estrogens.3
How these studies affect screening is unclear. Current guidelines recommend using tailored risk-based calculators, which take into consideration the patient’s sex assigned at birth, hormone regimen, length of hormone usage, and additional modifiable risk factors, such as diabetes, obesity, and smoking.3 For transfeminine patients who want to continue GAHT but either develop a venous thromboembolism on estrogen or have increased risk for VTE, providers should consider transitioning them to a transdermal application. Patients who stay on GAHT should be counseled accordingly on the heightened risk of VTE recurrence. It is not unreasonable to consider life-long anticoagulation for patients who remain on estrogen therapy after a VTE.4
While exogenous estrogen exposure is one risk factor for the development of breast cancer in cisgender females, the role of GAHT in breast cancer in transgender women is ambiguous. Therefore, breast screening guidelines should follow current recommendations for cisgender female patients with some caveats. The provider must also take into consideration current estrogen dosage, the age at which hormones were initiated, and whether a patient has undergone an augmentation mammaplasty.3
Both estrogen and testosterone play an important role in bone formation and health. Patients who undergo either medical or surgical interventions that alter sex hormone production, such as GAHT, orchiectomy, or androgen blockade, may be at elevated risk for osteoporosis. Providers should take a thorough medical history to determine patients who may be at risk for osteoporosis and treat them accordingly. Overall, GAHT has a positive effect on bone mineral density. Conversely, gonadectomy, particularly if a patient is not taking GAHT, can decrease bone density. Generally, transgender women, like cisgender women, should undergo DEXA scans starting at the age of 65, with earlier screening considered if they have undergone an orchiectomy and are not currently taking GAHT.3
There is no evidence that GAHT or surgery increases the rate of prostate cancer. Providers should note that the prostate is not removed at the time of gender-affirming surgery and that malignancy or benign prostatic hypertrophy can still occur. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that clinicians have a discussion with cisgender men between the ages of 55 and 69 about the risks and benefits of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening.5 For cisgender men aged 70 and older, the USPSTF recommends against PSA-based screening.5 If digital examination of the prostate is warranted for transfeminine patients, the examination is performed through the neovaginal canal.
Caring for elderly transgender patients is complex. Even though evidence guiding the management of elderly transgender patients is improving, there are still not enough definitive long-term data on this dynamic demographic. Like clinical approaches with hormonal or surgical treatments, caring for transgender elders is also multidisciplinary. Providers should be prepared to work with social workers, geriatric care physicians, endocrinologists, surgeons, and other relevant specialists to assist with potential knowledge gaps. The goals for the aging transgender population are the same as those for cisgender patients – preventing preventable diseases and reducing overall mortality so our patients can enjoy their golden years.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa. Contact her at [email protected].
References
1. Carroll L. Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2017;40:127-40.
2. Selix NW et al. Clinical care of the aging LGBT population. J Nurse Pract. 2020;16(7):349-54.
3. World Professional Association for Transgender Health. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people. 2022;8th version.
4. Shatzel JJ et al. Am J Hematol. 2017;92(2):204-8.
5. Wolf-Gould CS and Wolf-Gould CH. Primary and preventative care for transgender patients. In: Ferrando CA, ed. Comprehensive Care of the Transgender Patient. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2020, p. 114-30.
Chest reconstruction surgeries up nearly fourfold among adolescents
The number of chest reconstruction surgeries performed for adolescents rose nearly fourfold between 2016 and 2019, researchers report in a study published in JAMA Pediatrics.
“To our knowledge, this study is the largest investigation to date of gender-affirming chest reconstruction in a pediatric population. The results demonstrate substantial increases in gender-affirming chest reconstruction for adolescents,” the authors report.
The researchers, from Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, Tenn., used the Nationwide Ambulatory Surgery Sample to identify youth with gender dysphoria who underwent top surgery to remove, or, in rare cases, to add breasts.
The authors identified 829 chest surgeries. They adjusted the number to a weighted figure of 1,130 patients who underwent chest reconstruction during the study period. Of those, 98.6% underwent masculinizing surgery to remove breasts, and 1.4% underwent feminizing surgery. Roughly 100 individuals received gender-affirming chest surgeries in 2016. In 2019, the number had risen to 489 – a 389% increase, the authors reported.
Approximately 44% of the patients in the study were aged 17 years at the time of surgery, while 5.5% were younger than 14.
Around 78% of the individuals who underwent chest surgeries in 2019 were White, 2.7% were Black, 12.2% were Hispanic, and 2.5% were Asian or Pacific Islander. Half of the patients who underwent surgery had a household income of $82,000 or more, according to the researchers.
“Most transgender adolescents had either public or private health insurance coverage for these procedures, contrasting with the predominance of self-payers reported in earlier studies on transgender adults,” write the researchers, citing a 2018 study of trends in transgender surgery.
Masculinizing chest reconstruction, such as mastectomy, and feminizing chest reconstruction, such as augmentation mammaplasty, can be performed as outpatient procedures or as ambulatory surgeries, according to another study .
The study was supported by a grant from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences Clinical and Translational Science Awards Program. One author has reported receiving grant funding from Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The number of chest reconstruction surgeries performed for adolescents rose nearly fourfold between 2016 and 2019, researchers report in a study published in JAMA Pediatrics.
“To our knowledge, this study is the largest investigation to date of gender-affirming chest reconstruction in a pediatric population. The results demonstrate substantial increases in gender-affirming chest reconstruction for adolescents,” the authors report.
The researchers, from Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, Tenn., used the Nationwide Ambulatory Surgery Sample to identify youth with gender dysphoria who underwent top surgery to remove, or, in rare cases, to add breasts.
The authors identified 829 chest surgeries. They adjusted the number to a weighted figure of 1,130 patients who underwent chest reconstruction during the study period. Of those, 98.6% underwent masculinizing surgery to remove breasts, and 1.4% underwent feminizing surgery. Roughly 100 individuals received gender-affirming chest surgeries in 2016. In 2019, the number had risen to 489 – a 389% increase, the authors reported.
Approximately 44% of the patients in the study were aged 17 years at the time of surgery, while 5.5% were younger than 14.
Around 78% of the individuals who underwent chest surgeries in 2019 were White, 2.7% were Black, 12.2% were Hispanic, and 2.5% were Asian or Pacific Islander. Half of the patients who underwent surgery had a household income of $82,000 or more, according to the researchers.
“Most transgender adolescents had either public or private health insurance coverage for these procedures, contrasting with the predominance of self-payers reported in earlier studies on transgender adults,” write the researchers, citing a 2018 study of trends in transgender surgery.
Masculinizing chest reconstruction, such as mastectomy, and feminizing chest reconstruction, such as augmentation mammaplasty, can be performed as outpatient procedures or as ambulatory surgeries, according to another study .
The study was supported by a grant from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences Clinical and Translational Science Awards Program. One author has reported receiving grant funding from Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The number of chest reconstruction surgeries performed for adolescents rose nearly fourfold between 2016 and 2019, researchers report in a study published in JAMA Pediatrics.
“To our knowledge, this study is the largest investigation to date of gender-affirming chest reconstruction in a pediatric population. The results demonstrate substantial increases in gender-affirming chest reconstruction for adolescents,” the authors report.
The researchers, from Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, Tenn., used the Nationwide Ambulatory Surgery Sample to identify youth with gender dysphoria who underwent top surgery to remove, or, in rare cases, to add breasts.
The authors identified 829 chest surgeries. They adjusted the number to a weighted figure of 1,130 patients who underwent chest reconstruction during the study period. Of those, 98.6% underwent masculinizing surgery to remove breasts, and 1.4% underwent feminizing surgery. Roughly 100 individuals received gender-affirming chest surgeries in 2016. In 2019, the number had risen to 489 – a 389% increase, the authors reported.
Approximately 44% of the patients in the study were aged 17 years at the time of surgery, while 5.5% were younger than 14.
Around 78% of the individuals who underwent chest surgeries in 2019 were White, 2.7% were Black, 12.2% were Hispanic, and 2.5% were Asian or Pacific Islander. Half of the patients who underwent surgery had a household income of $82,000 or more, according to the researchers.
“Most transgender adolescents had either public or private health insurance coverage for these procedures, contrasting with the predominance of self-payers reported in earlier studies on transgender adults,” write the researchers, citing a 2018 study of trends in transgender surgery.
Masculinizing chest reconstruction, such as mastectomy, and feminizing chest reconstruction, such as augmentation mammaplasty, can be performed as outpatient procedures or as ambulatory surgeries, according to another study .
The study was supported by a grant from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences Clinical and Translational Science Awards Program. One author has reported receiving grant funding from Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
The WPATH guidelines for treatment of adolescents with gender dysphoria have changed
The World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) is an interdisciplinary professional and educational organization devoted to transgender health. One of their activities is to produce the Standards of Care (SOC) for treatment of individuals with gender dysphoria. According to WPATH, the SOC “articulate a professional consensus about the psychiatric, psychological, medical, and surgical management of gender dysphoria and help professionals understand the parameters within which they may offer assistance to those with these conditions.” Many clinicians around the world use these guidelines to help them care for patients with gender dysphoria and diverse gender expressions.
The most recent SOC, version 8, were released on Sept. 15, 2022, after a 2-year postponement because of the pandemic. These new standards represent the first update to the SOC since version 7, which was released in 2012. Given how recent this update is, this column will attempt to summarize the changes in the new guidelines that affect children and adolescents.
One of the major differences between SOC versions 7 and 8 is that version 8 now includes a chapter specifically dedicated to the care of adolescents. Version 7 lumped children and adolescents together into one chapter. This is an important distinction for SOC 8, as it highlights that care for prepubertal youth is simply social in nature and distinct from that of pubertal adolescents. Social transition includes things such as using an affirmed name/pronouns and changing hair style and clothes. It does not include medications of any kind. Allowing these youth the time and space to explore the natural gender diversity of childhood leads to improved psychological outcomes over time and reduces adversity. Psychological support, where indicated, should be offered to gender-diverse children and their families to explore the persistence, consistence, and insistence of that child’s gender identity.
Once a child reaches puberty, medications may come into play as part of an adolescent’s transition. SOC 7 had established a minimum age of 16 before any partially reversible medications (testosterone, estrogen) were started as part of a patient’s medical transition. Starting with SOC 8, a minimum age has been removed for the initiation of gender-affirming hormone therapy. However, a patient must still have begun their natal puberty before any medication is started. A specific age was removed to acknowledge that maturity in adolescents occurs on a continuum and at different ages. SOC 8 guidelines continue to recommend that the individual’s emotional, cognitive, and psychosocial development be taken into account when determining their ability to provide consent for treatment. These individuals should still undergo a comprehensive assessment, as described below.
Similar to SOC 7, SOC 8 continues to stress the importance of a comprehensive, multidisciplinary evaluation of those adolescents who seek medical therapy as part of their transition. This allows for the exploration of additional coexisting causes of gender dysphoria, such as anxiety, depression, or other mental health conditions. If these exist, then they must be appropriately treated before any gender-affirming medical treatment is initiated. Assessments should be performed by clinicians who have training and expertise with the developmental trajectory of adolescents, as well as with common mental health conditions. These assessments are also critical, as SOC 8 acknowledges a rise in the number of adolescents who may not have had gender-diverse expression in childhood.
SOC 8 and the Endocrine Society Guidelines (see references) provide physicians and other health care professionals with a road map for addressing the needs of transgender and gender-diverse persons. By referencing these guidelines when taking care of these patients, physicians and other health care professionals will know that they are providing the most up-to-date, evidence-based care.
Dr. M. Brett Cooper is an assistant professor of pediatrics at University of Texas Southwestern, Dallas, and an adolescent medicine specialist at Children’s Medical Center Dallas.
References
SOC 8: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/26895269.2022.2100644
SOC 7: https://www.wpath.org/media/cms/Documents/SOC%20v7/SOC%20V7_English2012.pdf?_t=1613669341
Endocrine Society Gender Affirming Care Guidelines: https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/102/11/3869/4157558?login=false
The World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) is an interdisciplinary professional and educational organization devoted to transgender health. One of their activities is to produce the Standards of Care (SOC) for treatment of individuals with gender dysphoria. According to WPATH, the SOC “articulate a professional consensus about the psychiatric, psychological, medical, and surgical management of gender dysphoria and help professionals understand the parameters within which they may offer assistance to those with these conditions.” Many clinicians around the world use these guidelines to help them care for patients with gender dysphoria and diverse gender expressions.
The most recent SOC, version 8, were released on Sept. 15, 2022, after a 2-year postponement because of the pandemic. These new standards represent the first update to the SOC since version 7, which was released in 2012. Given how recent this update is, this column will attempt to summarize the changes in the new guidelines that affect children and adolescents.
One of the major differences between SOC versions 7 and 8 is that version 8 now includes a chapter specifically dedicated to the care of adolescents. Version 7 lumped children and adolescents together into one chapter. This is an important distinction for SOC 8, as it highlights that care for prepubertal youth is simply social in nature and distinct from that of pubertal adolescents. Social transition includes things such as using an affirmed name/pronouns and changing hair style and clothes. It does not include medications of any kind. Allowing these youth the time and space to explore the natural gender diversity of childhood leads to improved psychological outcomes over time and reduces adversity. Psychological support, where indicated, should be offered to gender-diverse children and their families to explore the persistence, consistence, and insistence of that child’s gender identity.
Once a child reaches puberty, medications may come into play as part of an adolescent’s transition. SOC 7 had established a minimum age of 16 before any partially reversible medications (testosterone, estrogen) were started as part of a patient’s medical transition. Starting with SOC 8, a minimum age has been removed for the initiation of gender-affirming hormone therapy. However, a patient must still have begun their natal puberty before any medication is started. A specific age was removed to acknowledge that maturity in adolescents occurs on a continuum and at different ages. SOC 8 guidelines continue to recommend that the individual’s emotional, cognitive, and psychosocial development be taken into account when determining their ability to provide consent for treatment. These individuals should still undergo a comprehensive assessment, as described below.
Similar to SOC 7, SOC 8 continues to stress the importance of a comprehensive, multidisciplinary evaluation of those adolescents who seek medical therapy as part of their transition. This allows for the exploration of additional coexisting causes of gender dysphoria, such as anxiety, depression, or other mental health conditions. If these exist, then they must be appropriately treated before any gender-affirming medical treatment is initiated. Assessments should be performed by clinicians who have training and expertise with the developmental trajectory of adolescents, as well as with common mental health conditions. These assessments are also critical, as SOC 8 acknowledges a rise in the number of adolescents who may not have had gender-diverse expression in childhood.
SOC 8 and the Endocrine Society Guidelines (see references) provide physicians and other health care professionals with a road map for addressing the needs of transgender and gender-diverse persons. By referencing these guidelines when taking care of these patients, physicians and other health care professionals will know that they are providing the most up-to-date, evidence-based care.
Dr. M. Brett Cooper is an assistant professor of pediatrics at University of Texas Southwestern, Dallas, and an adolescent medicine specialist at Children’s Medical Center Dallas.
References
SOC 8: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/26895269.2022.2100644
SOC 7: https://www.wpath.org/media/cms/Documents/SOC%20v7/SOC%20V7_English2012.pdf?_t=1613669341
Endocrine Society Gender Affirming Care Guidelines: https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/102/11/3869/4157558?login=false
The World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) is an interdisciplinary professional and educational organization devoted to transgender health. One of their activities is to produce the Standards of Care (SOC) for treatment of individuals with gender dysphoria. According to WPATH, the SOC “articulate a professional consensus about the psychiatric, psychological, medical, and surgical management of gender dysphoria and help professionals understand the parameters within which they may offer assistance to those with these conditions.” Many clinicians around the world use these guidelines to help them care for patients with gender dysphoria and diverse gender expressions.
The most recent SOC, version 8, were released on Sept. 15, 2022, after a 2-year postponement because of the pandemic. These new standards represent the first update to the SOC since version 7, which was released in 2012. Given how recent this update is, this column will attempt to summarize the changes in the new guidelines that affect children and adolescents.
One of the major differences between SOC versions 7 and 8 is that version 8 now includes a chapter specifically dedicated to the care of adolescents. Version 7 lumped children and adolescents together into one chapter. This is an important distinction for SOC 8, as it highlights that care for prepubertal youth is simply social in nature and distinct from that of pubertal adolescents. Social transition includes things such as using an affirmed name/pronouns and changing hair style and clothes. It does not include medications of any kind. Allowing these youth the time and space to explore the natural gender diversity of childhood leads to improved psychological outcomes over time and reduces adversity. Psychological support, where indicated, should be offered to gender-diverse children and their families to explore the persistence, consistence, and insistence of that child’s gender identity.
Once a child reaches puberty, medications may come into play as part of an adolescent’s transition. SOC 7 had established a minimum age of 16 before any partially reversible medications (testosterone, estrogen) were started as part of a patient’s medical transition. Starting with SOC 8, a minimum age has been removed for the initiation of gender-affirming hormone therapy. However, a patient must still have begun their natal puberty before any medication is started. A specific age was removed to acknowledge that maturity in adolescents occurs on a continuum and at different ages. SOC 8 guidelines continue to recommend that the individual’s emotional, cognitive, and psychosocial development be taken into account when determining their ability to provide consent for treatment. These individuals should still undergo a comprehensive assessment, as described below.
Similar to SOC 7, SOC 8 continues to stress the importance of a comprehensive, multidisciplinary evaluation of those adolescents who seek medical therapy as part of their transition. This allows for the exploration of additional coexisting causes of gender dysphoria, such as anxiety, depression, or other mental health conditions. If these exist, then they must be appropriately treated before any gender-affirming medical treatment is initiated. Assessments should be performed by clinicians who have training and expertise with the developmental trajectory of adolescents, as well as with common mental health conditions. These assessments are also critical, as SOC 8 acknowledges a rise in the number of adolescents who may not have had gender-diverse expression in childhood.
SOC 8 and the Endocrine Society Guidelines (see references) provide physicians and other health care professionals with a road map for addressing the needs of transgender and gender-diverse persons. By referencing these guidelines when taking care of these patients, physicians and other health care professionals will know that they are providing the most up-to-date, evidence-based care.
Dr. M. Brett Cooper is an assistant professor of pediatrics at University of Texas Southwestern, Dallas, and an adolescent medicine specialist at Children’s Medical Center Dallas.
References
SOC 8: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/26895269.2022.2100644
SOC 7: https://www.wpath.org/media/cms/Documents/SOC%20v7/SOC%20V7_English2012.pdf?_t=1613669341
Endocrine Society Gender Affirming Care Guidelines: https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/102/11/3869/4157558?login=false
Cardiac biomarkers track with hormone therapy in transgender people
Cardiac biomarkers vary according to sex hormones in healthy transgender adults, just as in cisgender individuals, a new cross-sectional study suggests.
Previous research in the general population has shown that females have a lower 99th percentile upper reference limit for high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) than males, whereas N-terminal prohormone brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) concentrations are higher in females than males across all ages after puberty.
“That trend is similar for people that have been on gender-affirming hormones, saying that sex hormones are playing a role in how cardiac turnover happens in a healthy state,” study author Dina M. Greene, PhD, University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview.
Although the number of transgender people seeking gender-affirming care is increasing, studies are limited and largely retrospective cohorts, she noted. The scientific literature evaluating and defining cardiac biomarker concentrations is “currently absent.”
The American Heart Association’s recent scientific statement on the cardiovascular health of transgender and gender diverse (TGD) people says mounting evidence points to worse CV health in TGD people and that part of this excess risk is driven by significant psychosocial stressors across the lifespan. “In addition, the use of gender-affirming hormone therapy may be associated with cardiometabolic changes, but health research in this area remains limited and, at times, contradictory.”
For the present study, Dr. Greene and colleagues reached out to LGBTQ-oriented primary care and internal medicine clinics in Seattle and Iowa City to recruit 79 transgender men prescribed testosterone (mean age, 28.8 years) and 93 transgender women (mean age, 35.1 years) prescribed estradiol for at least 12 months. The mean duration of hormone therapy was 4.8 and 3.5 years, respectively.
The median estradiol concentration was 51 pg/mL in transgender men and 207 pg/mL in transgender women. Median testosterone concentrations were 4.6 ng/mL and 0.4 ng/mL, respectively.
The cardiac biomarkers were measured with the ARCHITECT STAT (Abbott Diagnostics) and ACCESS (Beckman Coulter) high-sensitivity troponin I assays, the Elecsys Troponin T Gen 5 STAT assay (Roche Diagnostics), and the Elecsys ProBNP II immunoassay (Roche Diagnostics).
As reported in JAMA Cardiology, the median hs-cTnI level on the ARCHITECT STAT assay was 0.9 ng/L (range, 0.6-1.7) in transgender men and 0.6 ng/L (range, 0.3-1.0) in transgender women. The pattern was consistent across the two other assays.
In contrast, the median NT-proBNP level was 17 ng/L (range, 13-27) in transgender men and 49 ng/L (range, 32-86) in transgender women.
“It seems that sex hormone concentration is a stronger driver of baseline cardiac troponin and NT-proBNP concentrations relative to sex assigned at birth,” Dr. Greene said.
The observed differences in hs-cTn concentrations “are likely physiological and not pathological,” given that concentrations between healthy cisgender people are also apparent and not thought to portend adverse events, the authors noted.
Teasing out the clinical implications of sex-specific hs-cTn upper reference limits for ruling in acute myocardial infarction (MI), however, is complicated by biological and social factors that contribute to poorer outcomes in women, despite lower baseline levels, they added. “Ultimately, the psychosocial benefits of gender-affirming hormones are substantial, and informed consent is likely the ideal method to balance the undetermined risks.”
Dr. Greene pointed out that the study wasn’t powered to accurately calculate gender-specific hs-cTn 99th percentiles or reference intervals for NT-proBNP and assessed the biomarkers at a single time point.
For the transgender person presenting with chest pain, she said, the clinical implications are not yet known, but the data suggest that when sex-specific 99th percentiles for hs-cTn are used, the numeric value associated with the affirmed gender, rather than the sex assigned at birth, may be the appropriate URL.
“It really depends on what the triage pathway is and if that pathway has differences for people of different sexes and how often people get serial measurements,” Dr. Greene said. “Within this population, it’s very important to look at those serial measurements because for people that are not cismen, those 99th percentiles when they’re non–sex specific, are going to favor in detection of a heart attack. So, you need to look at the second value to make sure there hasn’t been a change over time.”
The observed differences in the distribution of NT-proBNP concentrations is similar to that in the cisgender population, Dr. Greene noted. But these differences do not lead to sex-specific diagnostic thresholds because of the significant elevations present in overt heart failure and cardiovascular disease. “For NT-proBNP, it’s not as important. People don’t usually have a little bit of heart failure, they have heart failure, where people have small MIs.”
Dr. Greene said she would like to see larger trials looking at biomarker measurements and cardiac imaging before hormone therapy but that the biggest issue is the need for inclusion of transgender people in all cardiovascular trials.
“The sample sizes are never going to be as big as we get for cisgender people for a number of reasons but ensuring that it’s something that’s being asked on intake and monitored over time so we can understand how transgender people fit into the general population for cardiac disease,” Dr. Greene said. “And so, we can normalize that they exist. I keep driving this point home, but this is the biggest thing right now when it’s such a political issue.”
The study was supported in part by the department of laboratory medicine at the University of Washington, the department of pathology at the University of Iowa, and a grant from Abbott Diagnostics for in-kind high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I reagent. One coauthor reported financial relationships with Siemens Healthineers, Roche Diagnostics, Beckman Coulter, Becton, Dickinson, Abbott Diagnostics, Quidel Diagnostics, Sphingotech, and PixCell Medical. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiac biomarkers vary according to sex hormones in healthy transgender adults, just as in cisgender individuals, a new cross-sectional study suggests.
Previous research in the general population has shown that females have a lower 99th percentile upper reference limit for high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) than males, whereas N-terminal prohormone brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) concentrations are higher in females than males across all ages after puberty.
“That trend is similar for people that have been on gender-affirming hormones, saying that sex hormones are playing a role in how cardiac turnover happens in a healthy state,” study author Dina M. Greene, PhD, University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview.
Although the number of transgender people seeking gender-affirming care is increasing, studies are limited and largely retrospective cohorts, she noted. The scientific literature evaluating and defining cardiac biomarker concentrations is “currently absent.”
The American Heart Association’s recent scientific statement on the cardiovascular health of transgender and gender diverse (TGD) people says mounting evidence points to worse CV health in TGD people and that part of this excess risk is driven by significant psychosocial stressors across the lifespan. “In addition, the use of gender-affirming hormone therapy may be associated with cardiometabolic changes, but health research in this area remains limited and, at times, contradictory.”
For the present study, Dr. Greene and colleagues reached out to LGBTQ-oriented primary care and internal medicine clinics in Seattle and Iowa City to recruit 79 transgender men prescribed testosterone (mean age, 28.8 years) and 93 transgender women (mean age, 35.1 years) prescribed estradiol for at least 12 months. The mean duration of hormone therapy was 4.8 and 3.5 years, respectively.
The median estradiol concentration was 51 pg/mL in transgender men and 207 pg/mL in transgender women. Median testosterone concentrations were 4.6 ng/mL and 0.4 ng/mL, respectively.
The cardiac biomarkers were measured with the ARCHITECT STAT (Abbott Diagnostics) and ACCESS (Beckman Coulter) high-sensitivity troponin I assays, the Elecsys Troponin T Gen 5 STAT assay (Roche Diagnostics), and the Elecsys ProBNP II immunoassay (Roche Diagnostics).
As reported in JAMA Cardiology, the median hs-cTnI level on the ARCHITECT STAT assay was 0.9 ng/L (range, 0.6-1.7) in transgender men and 0.6 ng/L (range, 0.3-1.0) in transgender women. The pattern was consistent across the two other assays.
In contrast, the median NT-proBNP level was 17 ng/L (range, 13-27) in transgender men and 49 ng/L (range, 32-86) in transgender women.
“It seems that sex hormone concentration is a stronger driver of baseline cardiac troponin and NT-proBNP concentrations relative to sex assigned at birth,” Dr. Greene said.
The observed differences in hs-cTn concentrations “are likely physiological and not pathological,” given that concentrations between healthy cisgender people are also apparent and not thought to portend adverse events, the authors noted.
Teasing out the clinical implications of sex-specific hs-cTn upper reference limits for ruling in acute myocardial infarction (MI), however, is complicated by biological and social factors that contribute to poorer outcomes in women, despite lower baseline levels, they added. “Ultimately, the psychosocial benefits of gender-affirming hormones are substantial, and informed consent is likely the ideal method to balance the undetermined risks.”
Dr. Greene pointed out that the study wasn’t powered to accurately calculate gender-specific hs-cTn 99th percentiles or reference intervals for NT-proBNP and assessed the biomarkers at a single time point.
For the transgender person presenting with chest pain, she said, the clinical implications are not yet known, but the data suggest that when sex-specific 99th percentiles for hs-cTn are used, the numeric value associated with the affirmed gender, rather than the sex assigned at birth, may be the appropriate URL.
“It really depends on what the triage pathway is and if that pathway has differences for people of different sexes and how often people get serial measurements,” Dr. Greene said. “Within this population, it’s very important to look at those serial measurements because for people that are not cismen, those 99th percentiles when they’re non–sex specific, are going to favor in detection of a heart attack. So, you need to look at the second value to make sure there hasn’t been a change over time.”
The observed differences in the distribution of NT-proBNP concentrations is similar to that in the cisgender population, Dr. Greene noted. But these differences do not lead to sex-specific diagnostic thresholds because of the significant elevations present in overt heart failure and cardiovascular disease. “For NT-proBNP, it’s not as important. People don’t usually have a little bit of heart failure, they have heart failure, where people have small MIs.”
Dr. Greene said she would like to see larger trials looking at biomarker measurements and cardiac imaging before hormone therapy but that the biggest issue is the need for inclusion of transgender people in all cardiovascular trials.
“The sample sizes are never going to be as big as we get for cisgender people for a number of reasons but ensuring that it’s something that’s being asked on intake and monitored over time so we can understand how transgender people fit into the general population for cardiac disease,” Dr. Greene said. “And so, we can normalize that they exist. I keep driving this point home, but this is the biggest thing right now when it’s such a political issue.”
The study was supported in part by the department of laboratory medicine at the University of Washington, the department of pathology at the University of Iowa, and a grant from Abbott Diagnostics for in-kind high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I reagent. One coauthor reported financial relationships with Siemens Healthineers, Roche Diagnostics, Beckman Coulter, Becton, Dickinson, Abbott Diagnostics, Quidel Diagnostics, Sphingotech, and PixCell Medical. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiac biomarkers vary according to sex hormones in healthy transgender adults, just as in cisgender individuals, a new cross-sectional study suggests.
Previous research in the general population has shown that females have a lower 99th percentile upper reference limit for high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) than males, whereas N-terminal prohormone brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) concentrations are higher in females than males across all ages after puberty.
“That trend is similar for people that have been on gender-affirming hormones, saying that sex hormones are playing a role in how cardiac turnover happens in a healthy state,” study author Dina M. Greene, PhD, University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview.
Although the number of transgender people seeking gender-affirming care is increasing, studies are limited and largely retrospective cohorts, she noted. The scientific literature evaluating and defining cardiac biomarker concentrations is “currently absent.”
The American Heart Association’s recent scientific statement on the cardiovascular health of transgender and gender diverse (TGD) people says mounting evidence points to worse CV health in TGD people and that part of this excess risk is driven by significant psychosocial stressors across the lifespan. “In addition, the use of gender-affirming hormone therapy may be associated with cardiometabolic changes, but health research in this area remains limited and, at times, contradictory.”
For the present study, Dr. Greene and colleagues reached out to LGBTQ-oriented primary care and internal medicine clinics in Seattle and Iowa City to recruit 79 transgender men prescribed testosterone (mean age, 28.8 years) and 93 transgender women (mean age, 35.1 years) prescribed estradiol for at least 12 months. The mean duration of hormone therapy was 4.8 and 3.5 years, respectively.
The median estradiol concentration was 51 pg/mL in transgender men and 207 pg/mL in transgender women. Median testosterone concentrations were 4.6 ng/mL and 0.4 ng/mL, respectively.
The cardiac biomarkers were measured with the ARCHITECT STAT (Abbott Diagnostics) and ACCESS (Beckman Coulter) high-sensitivity troponin I assays, the Elecsys Troponin T Gen 5 STAT assay (Roche Diagnostics), and the Elecsys ProBNP II immunoassay (Roche Diagnostics).
As reported in JAMA Cardiology, the median hs-cTnI level on the ARCHITECT STAT assay was 0.9 ng/L (range, 0.6-1.7) in transgender men and 0.6 ng/L (range, 0.3-1.0) in transgender women. The pattern was consistent across the two other assays.
In contrast, the median NT-proBNP level was 17 ng/L (range, 13-27) in transgender men and 49 ng/L (range, 32-86) in transgender women.
“It seems that sex hormone concentration is a stronger driver of baseline cardiac troponin and NT-proBNP concentrations relative to sex assigned at birth,” Dr. Greene said.
The observed differences in hs-cTn concentrations “are likely physiological and not pathological,” given that concentrations between healthy cisgender people are also apparent and not thought to portend adverse events, the authors noted.
Teasing out the clinical implications of sex-specific hs-cTn upper reference limits for ruling in acute myocardial infarction (MI), however, is complicated by biological and social factors that contribute to poorer outcomes in women, despite lower baseline levels, they added. “Ultimately, the psychosocial benefits of gender-affirming hormones are substantial, and informed consent is likely the ideal method to balance the undetermined risks.”
Dr. Greene pointed out that the study wasn’t powered to accurately calculate gender-specific hs-cTn 99th percentiles or reference intervals for NT-proBNP and assessed the biomarkers at a single time point.
For the transgender person presenting with chest pain, she said, the clinical implications are not yet known, but the data suggest that when sex-specific 99th percentiles for hs-cTn are used, the numeric value associated with the affirmed gender, rather than the sex assigned at birth, may be the appropriate URL.
“It really depends on what the triage pathway is and if that pathway has differences for people of different sexes and how often people get serial measurements,” Dr. Greene said. “Within this population, it’s very important to look at those serial measurements because for people that are not cismen, those 99th percentiles when they’re non–sex specific, are going to favor in detection of a heart attack. So, you need to look at the second value to make sure there hasn’t been a change over time.”
The observed differences in the distribution of NT-proBNP concentrations is similar to that in the cisgender population, Dr. Greene noted. But these differences do not lead to sex-specific diagnostic thresholds because of the significant elevations present in overt heart failure and cardiovascular disease. “For NT-proBNP, it’s not as important. People don’t usually have a little bit of heart failure, they have heart failure, where people have small MIs.”
Dr. Greene said she would like to see larger trials looking at biomarker measurements and cardiac imaging before hormone therapy but that the biggest issue is the need for inclusion of transgender people in all cardiovascular trials.
“The sample sizes are never going to be as big as we get for cisgender people for a number of reasons but ensuring that it’s something that’s being asked on intake and monitored over time so we can understand how transgender people fit into the general population for cardiac disease,” Dr. Greene said. “And so, we can normalize that they exist. I keep driving this point home, but this is the biggest thing right now when it’s such a political issue.”
The study was supported in part by the department of laboratory medicine at the University of Washington, the department of pathology at the University of Iowa, and a grant from Abbott Diagnostics for in-kind high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I reagent. One coauthor reported financial relationships with Siemens Healthineers, Roche Diagnostics, Beckman Coulter, Becton, Dickinson, Abbott Diagnostics, Quidel Diagnostics, Sphingotech, and PixCell Medical. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA CARDIOLOGY
Best practices for an LGBTQ+ friendly medical space
While rainbow-colored flags may wave proudly from hotel balconies and sports arenas, LGBTQ+ patients might still feel some discrimination in the medical space, according to a Center for American Progress survey.
“Despite health care being considered a basic human right by the World Health Organization, it’s common for LGBTQ+ folks to face difficulties not only when trying to access care but also within the walls of the doctor’s office or hospital,” says Samantha Estevez, MD, a reproductive endocrinology and infertility fellow in New York.
In Medscape’s Physicians’ Views on LGBTQ+ Rights Issues Report 2022: Strong Emotions, Contrary Opinions, physicians were asked whether they see disparities in the care LGBTQ+ patients receive in comparison with the care that non-LGBTQ+ patients receive. About 35% of physicians said LGBTQ+ patients receive a different level of care; 52% of respondents younger than 45 said so.
It’s an issue unlikely to be resolved without the medical community’s awareness. With insights from four LGBTQ+ clinicians, here are several steps physicians can take to close the disparity gap.
Update intake forms
Many patient medical forms are populated with checkboxes. These forms may make it easier for patients to share their medical information and for practices to collect data. But unfortunately, they don’t allow for patients to fill in contextual information.
“It’s extremely important for health care professionals to understand the people they are serving,” says Nicholas Grant, PhD, ABPP, president of GLMA: Health Professionals Advancing LGBTQ+ Equality. Dr. Grant is a board-certified clinical psychologist in Hawaii. “The more accurate we are with our information gathering and paperwork, the more accurate we will be at serving our LGBTQ+ communities.”
Dr. Grant recommends asking open-ended questions, such as the following:
- What is your gender identity?
- What was your assigned sex at birth?
- What pronouns do you prefer?
- What gender(s) are your sexual partners?
However, Frances Grimstad, MD, a Boston-based ob/gyn and GLMA board member, adds this advice: Before revising intake forms, consider their purpose.
“As an ob/gyn, information about a patient’s sexual orientation and their sexual activity is beneficial for my care,” says Dr. Grimstad. “But that information may not be relevant for a physical therapy clinic where most patients are coming in with knee injuries. So, you shouldn’t just place items on your intake forms by default. Instead, clinicians should consider what is relevant to the encounter you’re having and how you are going to use the information.”
Change signage
Take stock of posters and brochures in the office and signs outside restrooms. If they communicate traditional gender roles, then it may be time for a change.
“It’s important to ensure representation of all types of people and families in your office,” says Chase Anderson, MD, an assistant professor of child and adolescent psychiatry in San Francisco.
Hang posters with images of diverse families. Display brochures that address LGBTQ+ health concerns when warranted. And for restrooms, replace traditional binary images with gender-neutral ones. You can also add signage about each bathroom’s purpose, suggests Dr. Grimstad.
“Let’s not just de-gender bathrooms,” she says. “Let’s hang signs that tell if the bathroom has multiple stalls, urinals, or handicap access. Let signage focus on the functions of each bathroom, not gender.”
Ask for feedback
Feedback forms give LBGTQ+ patients a platform to share concerns. For example, consider an email with a linked document that all patients can fill out anonymously. Ask questions such as the following:
- Did you feel affirmed during your appointment? If so, how? If not, how can we improve?
- Did we use the proper pronouns?
- Did signage make you feel like you were in a safe space? What didn’t make you feel safe?
Set up a system with team members to process feedback and implement changes.
Also, if you have a large-scale practice, consider forming an LGBTQ+ community advisory board. “They can offer feedback about your practice’s clinical structure,” Dr. Grimstad tells Medscape.
Hire diverse employees
Building a diverse and inclusive workforce is critical to serving the LBGTQ+ community. Team members should reflect your patient population.
“Diversity isn’t a monolith,” says Dr. Grimstad. “It isn’t just racial diversity, or sexual or gender diversity. Even in a town which appears homogeneous in one area of diversity, such as a majority White town, it’s important to remember all the other facets of diversity that exist, such as gender, sexual orientation, cultural diversity.”
A diverse team may offer a surprising boost to your practice. According to a study published in the Journal of the National Medical Association, patient outcomes improve when a more diverse team provides care. In fact, diverse teams fare better in innovation, communication, risk assessment, and financial performance.
Dr. Anderson also recommends allowing team members “to be themselves.” For example, let employees wear their hair in whatever way they prefer or display their tattoos.
“This signals to patients that if staff members can be themselves here, patients can be themselves here, too,” says Dr. Anderson.
Provide training
Medical staff may sometimes feel uncomfortable serving LBGTQ+ patients because of their own biases, attitudes, or lack of knowledge about the community. Regular training can ease their discomfort.
“Make sure all health professionals are trained and educated on the needs of LGBTQ+ patients,” says Dr. Grant. “Understanding their health needs is the provider’s responsibility.”
For basic information, Dr. Anderson recommends visiting The Trevor Project, an organization that serves LGBTQ+ youth. “They’re really good at keeping up with changing verbiage and trends,” says Dr. Anderson.
To strengthen community connections, Dr. Grimstad recommends using trainers from your local area if possible. Do a Google search to find an LGBTQ+ center nearby or in the closest major city. Invite them to staff meetings or ask them to organize a workshop.
By implementing these strategies, you can start building a bridge between your practice and the LGBTQ+ community and provide better care for them as patients.
“Whether it’s knowing about PrEP ... or ensuring staff members are trained in caring for patients with any general or sexual identity, we as doctors and medical professionals must continue to move forward and serve our LGBTQ+ patients in big and small ways,” says Dr. Estevez.
For in-depth training, check the following organizations:
National LGBTQIA+ Health Education Center at the Fenway Institute provides educational programs and resources to health care organizations.
GLMA has a top 10 health issues webpage that doctors can use to educate themselves and staff members on the LGBTQ+ community’s most urgent health needs.
Alliance for Full Acceptance offers LGBTQ cultural competency training, including a 1-hour awareness class and a 3-hour inclusivity workshop for clinicians.
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has compiled a list of training curricula for behavioral health counselors and primary care providers.
UCSF’s Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, and Transgender Resource Center has a list of training and educational materials for medical professionals.
Equality California Institute offers both in-person and virtual training covering basic terminology, data on LGBTQ+ health issues, and how to create an inclusive environment.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
While rainbow-colored flags may wave proudly from hotel balconies and sports arenas, LGBTQ+ patients might still feel some discrimination in the medical space, according to a Center for American Progress survey.
“Despite health care being considered a basic human right by the World Health Organization, it’s common for LGBTQ+ folks to face difficulties not only when trying to access care but also within the walls of the doctor’s office or hospital,” says Samantha Estevez, MD, a reproductive endocrinology and infertility fellow in New York.
In Medscape’s Physicians’ Views on LGBTQ+ Rights Issues Report 2022: Strong Emotions, Contrary Opinions, physicians were asked whether they see disparities in the care LGBTQ+ patients receive in comparison with the care that non-LGBTQ+ patients receive. About 35% of physicians said LGBTQ+ patients receive a different level of care; 52% of respondents younger than 45 said so.
It’s an issue unlikely to be resolved without the medical community’s awareness. With insights from four LGBTQ+ clinicians, here are several steps physicians can take to close the disparity gap.
Update intake forms
Many patient medical forms are populated with checkboxes. These forms may make it easier for patients to share their medical information and for practices to collect data. But unfortunately, they don’t allow for patients to fill in contextual information.
“It’s extremely important for health care professionals to understand the people they are serving,” says Nicholas Grant, PhD, ABPP, president of GLMA: Health Professionals Advancing LGBTQ+ Equality. Dr. Grant is a board-certified clinical psychologist in Hawaii. “The more accurate we are with our information gathering and paperwork, the more accurate we will be at serving our LGBTQ+ communities.”
Dr. Grant recommends asking open-ended questions, such as the following:
- What is your gender identity?
- What was your assigned sex at birth?
- What pronouns do you prefer?
- What gender(s) are your sexual partners?
However, Frances Grimstad, MD, a Boston-based ob/gyn and GLMA board member, adds this advice: Before revising intake forms, consider their purpose.
“As an ob/gyn, information about a patient’s sexual orientation and their sexual activity is beneficial for my care,” says Dr. Grimstad. “But that information may not be relevant for a physical therapy clinic where most patients are coming in with knee injuries. So, you shouldn’t just place items on your intake forms by default. Instead, clinicians should consider what is relevant to the encounter you’re having and how you are going to use the information.”
Change signage
Take stock of posters and brochures in the office and signs outside restrooms. If they communicate traditional gender roles, then it may be time for a change.
“It’s important to ensure representation of all types of people and families in your office,” says Chase Anderson, MD, an assistant professor of child and adolescent psychiatry in San Francisco.
Hang posters with images of diverse families. Display brochures that address LGBTQ+ health concerns when warranted. And for restrooms, replace traditional binary images with gender-neutral ones. You can also add signage about each bathroom’s purpose, suggests Dr. Grimstad.
“Let’s not just de-gender bathrooms,” she says. “Let’s hang signs that tell if the bathroom has multiple stalls, urinals, or handicap access. Let signage focus on the functions of each bathroom, not gender.”
Ask for feedback
Feedback forms give LBGTQ+ patients a platform to share concerns. For example, consider an email with a linked document that all patients can fill out anonymously. Ask questions such as the following:
- Did you feel affirmed during your appointment? If so, how? If not, how can we improve?
- Did we use the proper pronouns?
- Did signage make you feel like you were in a safe space? What didn’t make you feel safe?
Set up a system with team members to process feedback and implement changes.
Also, if you have a large-scale practice, consider forming an LGBTQ+ community advisory board. “They can offer feedback about your practice’s clinical structure,” Dr. Grimstad tells Medscape.
Hire diverse employees
Building a diverse and inclusive workforce is critical to serving the LBGTQ+ community. Team members should reflect your patient population.
“Diversity isn’t a monolith,” says Dr. Grimstad. “It isn’t just racial diversity, or sexual or gender diversity. Even in a town which appears homogeneous in one area of diversity, such as a majority White town, it’s important to remember all the other facets of diversity that exist, such as gender, sexual orientation, cultural diversity.”
A diverse team may offer a surprising boost to your practice. According to a study published in the Journal of the National Medical Association, patient outcomes improve when a more diverse team provides care. In fact, diverse teams fare better in innovation, communication, risk assessment, and financial performance.
Dr. Anderson also recommends allowing team members “to be themselves.” For example, let employees wear their hair in whatever way they prefer or display their tattoos.
“This signals to patients that if staff members can be themselves here, patients can be themselves here, too,” says Dr. Anderson.
Provide training
Medical staff may sometimes feel uncomfortable serving LBGTQ+ patients because of their own biases, attitudes, or lack of knowledge about the community. Regular training can ease their discomfort.
“Make sure all health professionals are trained and educated on the needs of LGBTQ+ patients,” says Dr. Grant. “Understanding their health needs is the provider’s responsibility.”
For basic information, Dr. Anderson recommends visiting The Trevor Project, an organization that serves LGBTQ+ youth. “They’re really good at keeping up with changing verbiage and trends,” says Dr. Anderson.
To strengthen community connections, Dr. Grimstad recommends using trainers from your local area if possible. Do a Google search to find an LGBTQ+ center nearby or in the closest major city. Invite them to staff meetings or ask them to organize a workshop.
By implementing these strategies, you can start building a bridge between your practice and the LGBTQ+ community and provide better care for them as patients.
“Whether it’s knowing about PrEP ... or ensuring staff members are trained in caring for patients with any general or sexual identity, we as doctors and medical professionals must continue to move forward and serve our LGBTQ+ patients in big and small ways,” says Dr. Estevez.
For in-depth training, check the following organizations:
National LGBTQIA+ Health Education Center at the Fenway Institute provides educational programs and resources to health care organizations.
GLMA has a top 10 health issues webpage that doctors can use to educate themselves and staff members on the LGBTQ+ community’s most urgent health needs.
Alliance for Full Acceptance offers LGBTQ cultural competency training, including a 1-hour awareness class and a 3-hour inclusivity workshop for clinicians.
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has compiled a list of training curricula for behavioral health counselors and primary care providers.
UCSF’s Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, and Transgender Resource Center has a list of training and educational materials for medical professionals.
Equality California Institute offers both in-person and virtual training covering basic terminology, data on LGBTQ+ health issues, and how to create an inclusive environment.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
While rainbow-colored flags may wave proudly from hotel balconies and sports arenas, LGBTQ+ patients might still feel some discrimination in the medical space, according to a Center for American Progress survey.
“Despite health care being considered a basic human right by the World Health Organization, it’s common for LGBTQ+ folks to face difficulties not only when trying to access care but also within the walls of the doctor’s office or hospital,” says Samantha Estevez, MD, a reproductive endocrinology and infertility fellow in New York.
In Medscape’s Physicians’ Views on LGBTQ+ Rights Issues Report 2022: Strong Emotions, Contrary Opinions, physicians were asked whether they see disparities in the care LGBTQ+ patients receive in comparison with the care that non-LGBTQ+ patients receive. About 35% of physicians said LGBTQ+ patients receive a different level of care; 52% of respondents younger than 45 said so.
It’s an issue unlikely to be resolved without the medical community’s awareness. With insights from four LGBTQ+ clinicians, here are several steps physicians can take to close the disparity gap.
Update intake forms
Many patient medical forms are populated with checkboxes. These forms may make it easier for patients to share their medical information and for practices to collect data. But unfortunately, they don’t allow for patients to fill in contextual information.
“It’s extremely important for health care professionals to understand the people they are serving,” says Nicholas Grant, PhD, ABPP, president of GLMA: Health Professionals Advancing LGBTQ+ Equality. Dr. Grant is a board-certified clinical psychologist in Hawaii. “The more accurate we are with our information gathering and paperwork, the more accurate we will be at serving our LGBTQ+ communities.”
Dr. Grant recommends asking open-ended questions, such as the following:
- What is your gender identity?
- What was your assigned sex at birth?
- What pronouns do you prefer?
- What gender(s) are your sexual partners?
However, Frances Grimstad, MD, a Boston-based ob/gyn and GLMA board member, adds this advice: Before revising intake forms, consider their purpose.
“As an ob/gyn, information about a patient’s sexual orientation and their sexual activity is beneficial for my care,” says Dr. Grimstad. “But that information may not be relevant for a physical therapy clinic where most patients are coming in with knee injuries. So, you shouldn’t just place items on your intake forms by default. Instead, clinicians should consider what is relevant to the encounter you’re having and how you are going to use the information.”
Change signage
Take stock of posters and brochures in the office and signs outside restrooms. If they communicate traditional gender roles, then it may be time for a change.
“It’s important to ensure representation of all types of people and families in your office,” says Chase Anderson, MD, an assistant professor of child and adolescent psychiatry in San Francisco.
Hang posters with images of diverse families. Display brochures that address LGBTQ+ health concerns when warranted. And for restrooms, replace traditional binary images with gender-neutral ones. You can also add signage about each bathroom’s purpose, suggests Dr. Grimstad.
“Let’s not just de-gender bathrooms,” she says. “Let’s hang signs that tell if the bathroom has multiple stalls, urinals, or handicap access. Let signage focus on the functions of each bathroom, not gender.”
Ask for feedback
Feedback forms give LBGTQ+ patients a platform to share concerns. For example, consider an email with a linked document that all patients can fill out anonymously. Ask questions such as the following:
- Did you feel affirmed during your appointment? If so, how? If not, how can we improve?
- Did we use the proper pronouns?
- Did signage make you feel like you were in a safe space? What didn’t make you feel safe?
Set up a system with team members to process feedback and implement changes.
Also, if you have a large-scale practice, consider forming an LGBTQ+ community advisory board. “They can offer feedback about your practice’s clinical structure,” Dr. Grimstad tells Medscape.
Hire diverse employees
Building a diverse and inclusive workforce is critical to serving the LBGTQ+ community. Team members should reflect your patient population.
“Diversity isn’t a monolith,” says Dr. Grimstad. “It isn’t just racial diversity, or sexual or gender diversity. Even in a town which appears homogeneous in one area of diversity, such as a majority White town, it’s important to remember all the other facets of diversity that exist, such as gender, sexual orientation, cultural diversity.”
A diverse team may offer a surprising boost to your practice. According to a study published in the Journal of the National Medical Association, patient outcomes improve when a more diverse team provides care. In fact, diverse teams fare better in innovation, communication, risk assessment, and financial performance.
Dr. Anderson also recommends allowing team members “to be themselves.” For example, let employees wear their hair in whatever way they prefer or display their tattoos.
“This signals to patients that if staff members can be themselves here, patients can be themselves here, too,” says Dr. Anderson.
Provide training
Medical staff may sometimes feel uncomfortable serving LBGTQ+ patients because of their own biases, attitudes, or lack of knowledge about the community. Regular training can ease their discomfort.
“Make sure all health professionals are trained and educated on the needs of LGBTQ+ patients,” says Dr. Grant. “Understanding their health needs is the provider’s responsibility.”
For basic information, Dr. Anderson recommends visiting The Trevor Project, an organization that serves LGBTQ+ youth. “They’re really good at keeping up with changing verbiage and trends,” says Dr. Anderson.
To strengthen community connections, Dr. Grimstad recommends using trainers from your local area if possible. Do a Google search to find an LGBTQ+ center nearby or in the closest major city. Invite them to staff meetings or ask them to organize a workshop.
By implementing these strategies, you can start building a bridge between your practice and the LGBTQ+ community and provide better care for them as patients.
“Whether it’s knowing about PrEP ... or ensuring staff members are trained in caring for patients with any general or sexual identity, we as doctors and medical professionals must continue to move forward and serve our LGBTQ+ patients in big and small ways,” says Dr. Estevez.
For in-depth training, check the following organizations:
National LGBTQIA+ Health Education Center at the Fenway Institute provides educational programs and resources to health care organizations.
GLMA has a top 10 health issues webpage that doctors can use to educate themselves and staff members on the LGBTQ+ community’s most urgent health needs.
Alliance for Full Acceptance offers LGBTQ cultural competency training, including a 1-hour awareness class and a 3-hour inclusivity workshop for clinicians.
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has compiled a list of training curricula for behavioral health counselors and primary care providers.
UCSF’s Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, and Transgender Resource Center has a list of training and educational materials for medical professionals.
Equality California Institute offers both in-person and virtual training covering basic terminology, data on LGBTQ+ health issues, and how to create an inclusive environment.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Digital mental health training acceptable to boarding teens
ANAHEIM, CALIF. – A modular digital intervention to teach mental health skills to youth awaiting transfer to psychiatric care appeared feasible to implement and acceptable to teens and their parents, according to a study presented at the American Academy of Pediatrics National Conference.
“This program has the potential to teach evidence-based mental health skills to youth during boarding, providing a head start on recovery prior to psychiatric hospitalization,” study coauthor Samantha House, DO, MPH, section chief of pediatric hospital medicine at Dartmouth Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, N.H., told attendees.
Mental health boarding has become increasingly common as psychiatric care resources have been stretched by a crisis in pediatric mental health that began even before the COVID pandemic. Since youth often don’t receive evidence-based therapies while boarding, Dr. House and her coauthor, JoAnna K. Leyenaar, MD, PhD, MPH, developed a pilot program called I-CARE, which stands for Improving Care, Accelerating Recovery and Education.
I-CARE is a digital health intervention that combines videos on a tablet with workbook exercises that teach mental health skills. The seven modules include an introduction and one each on schedule-making, safety planning, psychoeducation, behavioral activation, relaxation skills, and mindfulness skills. Licensed nursing assistants who have received a 6-hour training from a clinical psychologist administer the program and provide safety supervision during boarding.
“I-CARE was designed to be largely self-directed, supported by ‘coaches’ who are not mental health professionals,” Dr. Leyenaar, vice chair of research in the department of pediatrics and an associate professor of pediatrics at Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H., said in an interview. With this model, the program requires minimal additional resources beyond the tablets and workbooks, and is designed for implementation in settings with few or no mental health professionals, she said.
Cora Breuner, MD, MPH, a professor of pediatrics at the University of Washington, Seattle, and an attending physician at Seattle Children’s Hospital, was not involved in the study but was excited to see it.
“I think it’s a really good idea, and I like that it’s being studied,” Dr. Breuner said in an interview. She said the health care and public health system has let down an entire population who data had shown were experiencing mental health problems.
“We knew before the pandemic that behavioral health issues were creeping up slowly with anxiety, depression, suicidal ideation, and, of course, substance use disorders and eating disorders, and not a lot was being done about it,” Dr. Breuner said, and the pandemic exacerbated those issues. ”I don’t know why no one realized that this was going to be the downstream effect of having no socialization for kids for 18 months and limited resources for those who we need desperately to provide care for,” especially BIPOC [Black, Indigenous, and people of color] kids and underresourced kids.
That sentiment is exactly what inspired the creation of the program, according to Dr. Leyenaar.
The I-CARE program was implemented at Dartmouth Hitchcock Medical Center in November 2021 for adolescents aged 12-17 who were boarding because of suicidality or self-harm. The program and study excluded youth with psychosis and other cognitive or behavioral conditions that didn’t fit with the skills taught by the module training.
The researchers qualitatively evaluated the I-CARE program in youth who were offered at least two I-CARE modules and with parents present during boarding.
Twenty-four youth, with a median age of 14, were offered the I-CARE program between November 2021 and April 2022 while boarding for a median 8 days. Most of the patients were female (79%), and a third were transgender or gender diverse. Most were White (83%), and about two-thirds had Medicaid (62.5%). The most common diagnoses among the participants were major depressive disorder (71%) and generalized anxiety disorder (46%). Others included PTSD (29%), restrictive eating disorder (21%), and bipolar disorder (12.5%).
All offered the program completed the first module, and 79% participated in additional modules. The main reason for discontinuation was transfer to another facility, but a few youth either refused to engage with the program or felt they knew the material well enough that they weren’t benefiting from it.
The evaluation involved 16 youth, seven parents, and 17 clinicians. On a Likert scale, the composite score for the program’s appropriateness – suitability, applicability, and meeting needs – was an average 3.7, with a higher rating from clinicians (4.3) and caregivers (3.5) than youth (2.8).
“Some youth felt the intervention was better suited for a younger audience or those with less familiarity with mental health skills, but they acknowledged that the intervention would be helpful and appropriate for others,” Dr. House, who is also an assistant professor of pediatrics at Geisel School of Medicine, said.
Youth rated the acceptability of the program more highly (3.6) and all three groups found it easy to use, with an average feasibility score of 4 across the board. The program’s acceptability received an average score of 4 from parents and clinicians.
”Teens seem to particularly value the psychoeducation module that explains the relationship between thoughts and feelings, as well as the opportunity to develop a personalized safety plan,” Dr. Leyenaar said.
Among the challenges expressed by the participating teens were that the loud sounds and beeping in the hospital made it difficult to practice mindfulness and that they often had to wait for staff to be available to do I-CARE.
“I feel like not many people have been trained yet,” one teen said, “so to have more nurses available to do I-CARE would be helpful.”
Another participant found the coaches helpful. “Sometimes they were my nurse, sometimes they were someone I never met before. … and also, they were all really, really nice,” the teen said.
Another teen regarded the material as “really surface-level mental health stuff” that they thought “could be helpful to other people who are here for the first time.” But others found the content more beneficial.
“The videos were helpful. … I was worried that they weren’t going to be very informative, but they did make sense to me,” one participant said. “They weren’t overcomplicating things. … They weren’t saying anything I didn’t understand, so that was good.”
The researchers next plan to conduct a multisite study to determine the program’s effectiveness in improving health outcomes and reducing suicidal ideation. Dr. House and Dr. Leyenaar are looking at ways to refine the program.
”We may narrow the age range for participants, with an upper age limit of 16, since some older teens said that the modules were best suited for a younger audience,” Dr. Leyenaar said. “We are also discussing how to best support youth who are readmitted to our hospital and have participated in I-CARE previously.”
Dr. Breuner said she would be interested to see, in future studies of the program, whether it reduced the likelihood of inpatient psychiatric stay, the length of psychiatric stay after admission, or the risk of readmission. She also wondered if the program might be offered in languages other than English, whether a version might be specifically designed for BIPOC youth, and whether the researchers had considered offering the intervention to caregivers as well.
The modules are teaching the kids but should they also be teaching the parents? Dr. Breuner wondered. A lot of times, she said, the parents are bringing these kids in because they don’t know what to do and can’t deal with them anymore. Offering modules on the same skills to caregivers would also enable the caregivers to reinforce and reteach the skills to their children, especially if the youth struggled to really take in what the modules were trying to teach.
Dr. Leyenaar said she expects buy-in for a program like this would be high at other institutions, but it’s premature to scale it up until they’ve conducted at least another clinical trial on its effectiveness. The biggest potential barrier to buy-in that Dr. Breuner perceived would be cost.
“It’s always difficult when it costs money” since the hospital needs to train the clinicians who provide the care, Dr. Breuner said, but it’s possible those costs could be offset if the program reduces the risk of readmission or return to the emergency department.
While the overall risk of harms from the intervention are low, Dr. Breuner said it is important to be conscious that the intervention may not necessarily be appropriate for all youth.
“There’s always risk when there’s a trauma background, and you have to be very careful, especially with mindfulness training,” Dr. Breuner said. For those with a history of abuse or other adverse childhood experiences “for someone to get into a very calm, still place can actually be counterproductive.”
Dr. Breuner especially appreciated that the researchers involved the youth and caregivers in the evaluation process. “That the parents expressed positive attitudes is really incredible,” she said.
Dr. House, Dr. Leyenaar, and Dr. Breuner had no disclosures. No external funding was noted for the study.
ANAHEIM, CALIF. – A modular digital intervention to teach mental health skills to youth awaiting transfer to psychiatric care appeared feasible to implement and acceptable to teens and their parents, according to a study presented at the American Academy of Pediatrics National Conference.
“This program has the potential to teach evidence-based mental health skills to youth during boarding, providing a head start on recovery prior to psychiatric hospitalization,” study coauthor Samantha House, DO, MPH, section chief of pediatric hospital medicine at Dartmouth Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, N.H., told attendees.
Mental health boarding has become increasingly common as psychiatric care resources have been stretched by a crisis in pediatric mental health that began even before the COVID pandemic. Since youth often don’t receive evidence-based therapies while boarding, Dr. House and her coauthor, JoAnna K. Leyenaar, MD, PhD, MPH, developed a pilot program called I-CARE, which stands for Improving Care, Accelerating Recovery and Education.
I-CARE is a digital health intervention that combines videos on a tablet with workbook exercises that teach mental health skills. The seven modules include an introduction and one each on schedule-making, safety planning, psychoeducation, behavioral activation, relaxation skills, and mindfulness skills. Licensed nursing assistants who have received a 6-hour training from a clinical psychologist administer the program and provide safety supervision during boarding.
“I-CARE was designed to be largely self-directed, supported by ‘coaches’ who are not mental health professionals,” Dr. Leyenaar, vice chair of research in the department of pediatrics and an associate professor of pediatrics at Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H., said in an interview. With this model, the program requires minimal additional resources beyond the tablets and workbooks, and is designed for implementation in settings with few or no mental health professionals, she said.
Cora Breuner, MD, MPH, a professor of pediatrics at the University of Washington, Seattle, and an attending physician at Seattle Children’s Hospital, was not involved in the study but was excited to see it.
“I think it’s a really good idea, and I like that it’s being studied,” Dr. Breuner said in an interview. She said the health care and public health system has let down an entire population who data had shown were experiencing mental health problems.
“We knew before the pandemic that behavioral health issues were creeping up slowly with anxiety, depression, suicidal ideation, and, of course, substance use disorders and eating disorders, and not a lot was being done about it,” Dr. Breuner said, and the pandemic exacerbated those issues. ”I don’t know why no one realized that this was going to be the downstream effect of having no socialization for kids for 18 months and limited resources for those who we need desperately to provide care for,” especially BIPOC [Black, Indigenous, and people of color] kids and underresourced kids.
That sentiment is exactly what inspired the creation of the program, according to Dr. Leyenaar.
The I-CARE program was implemented at Dartmouth Hitchcock Medical Center in November 2021 for adolescents aged 12-17 who were boarding because of suicidality or self-harm. The program and study excluded youth with psychosis and other cognitive or behavioral conditions that didn’t fit with the skills taught by the module training.
The researchers qualitatively evaluated the I-CARE program in youth who were offered at least two I-CARE modules and with parents present during boarding.
Twenty-four youth, with a median age of 14, were offered the I-CARE program between November 2021 and April 2022 while boarding for a median 8 days. Most of the patients were female (79%), and a third were transgender or gender diverse. Most were White (83%), and about two-thirds had Medicaid (62.5%). The most common diagnoses among the participants were major depressive disorder (71%) and generalized anxiety disorder (46%). Others included PTSD (29%), restrictive eating disorder (21%), and bipolar disorder (12.5%).
All offered the program completed the first module, and 79% participated in additional modules. The main reason for discontinuation was transfer to another facility, but a few youth either refused to engage with the program or felt they knew the material well enough that they weren’t benefiting from it.
The evaluation involved 16 youth, seven parents, and 17 clinicians. On a Likert scale, the composite score for the program’s appropriateness – suitability, applicability, and meeting needs – was an average 3.7, with a higher rating from clinicians (4.3) and caregivers (3.5) than youth (2.8).
“Some youth felt the intervention was better suited for a younger audience or those with less familiarity with mental health skills, but they acknowledged that the intervention would be helpful and appropriate for others,” Dr. House, who is also an assistant professor of pediatrics at Geisel School of Medicine, said.
Youth rated the acceptability of the program more highly (3.6) and all three groups found it easy to use, with an average feasibility score of 4 across the board. The program’s acceptability received an average score of 4 from parents and clinicians.
”Teens seem to particularly value the psychoeducation module that explains the relationship between thoughts and feelings, as well as the opportunity to develop a personalized safety plan,” Dr. Leyenaar said.
Among the challenges expressed by the participating teens were that the loud sounds and beeping in the hospital made it difficult to practice mindfulness and that they often had to wait for staff to be available to do I-CARE.
“I feel like not many people have been trained yet,” one teen said, “so to have more nurses available to do I-CARE would be helpful.”
Another participant found the coaches helpful. “Sometimes they were my nurse, sometimes they were someone I never met before. … and also, they were all really, really nice,” the teen said.
Another teen regarded the material as “really surface-level mental health stuff” that they thought “could be helpful to other people who are here for the first time.” But others found the content more beneficial.
“The videos were helpful. … I was worried that they weren’t going to be very informative, but they did make sense to me,” one participant said. “They weren’t overcomplicating things. … They weren’t saying anything I didn’t understand, so that was good.”
The researchers next plan to conduct a multisite study to determine the program’s effectiveness in improving health outcomes and reducing suicidal ideation. Dr. House and Dr. Leyenaar are looking at ways to refine the program.
”We may narrow the age range for participants, with an upper age limit of 16, since some older teens said that the modules were best suited for a younger audience,” Dr. Leyenaar said. “We are also discussing how to best support youth who are readmitted to our hospital and have participated in I-CARE previously.”
Dr. Breuner said she would be interested to see, in future studies of the program, whether it reduced the likelihood of inpatient psychiatric stay, the length of psychiatric stay after admission, or the risk of readmission. She also wondered if the program might be offered in languages other than English, whether a version might be specifically designed for BIPOC youth, and whether the researchers had considered offering the intervention to caregivers as well.
The modules are teaching the kids but should they also be teaching the parents? Dr. Breuner wondered. A lot of times, she said, the parents are bringing these kids in because they don’t know what to do and can’t deal with them anymore. Offering modules on the same skills to caregivers would also enable the caregivers to reinforce and reteach the skills to their children, especially if the youth struggled to really take in what the modules were trying to teach.
Dr. Leyenaar said she expects buy-in for a program like this would be high at other institutions, but it’s premature to scale it up until they’ve conducted at least another clinical trial on its effectiveness. The biggest potential barrier to buy-in that Dr. Breuner perceived would be cost.
“It’s always difficult when it costs money” since the hospital needs to train the clinicians who provide the care, Dr. Breuner said, but it’s possible those costs could be offset if the program reduces the risk of readmission or return to the emergency department.
While the overall risk of harms from the intervention are low, Dr. Breuner said it is important to be conscious that the intervention may not necessarily be appropriate for all youth.
“There’s always risk when there’s a trauma background, and you have to be very careful, especially with mindfulness training,” Dr. Breuner said. For those with a history of abuse or other adverse childhood experiences “for someone to get into a very calm, still place can actually be counterproductive.”
Dr. Breuner especially appreciated that the researchers involved the youth and caregivers in the evaluation process. “That the parents expressed positive attitudes is really incredible,” she said.
Dr. House, Dr. Leyenaar, and Dr. Breuner had no disclosures. No external funding was noted for the study.
ANAHEIM, CALIF. – A modular digital intervention to teach mental health skills to youth awaiting transfer to psychiatric care appeared feasible to implement and acceptable to teens and their parents, according to a study presented at the American Academy of Pediatrics National Conference.
“This program has the potential to teach evidence-based mental health skills to youth during boarding, providing a head start on recovery prior to psychiatric hospitalization,” study coauthor Samantha House, DO, MPH, section chief of pediatric hospital medicine at Dartmouth Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, N.H., told attendees.
Mental health boarding has become increasingly common as psychiatric care resources have been stretched by a crisis in pediatric mental health that began even before the COVID pandemic. Since youth often don’t receive evidence-based therapies while boarding, Dr. House and her coauthor, JoAnna K. Leyenaar, MD, PhD, MPH, developed a pilot program called I-CARE, which stands for Improving Care, Accelerating Recovery and Education.
I-CARE is a digital health intervention that combines videos on a tablet with workbook exercises that teach mental health skills. The seven modules include an introduction and one each on schedule-making, safety planning, psychoeducation, behavioral activation, relaxation skills, and mindfulness skills. Licensed nursing assistants who have received a 6-hour training from a clinical psychologist administer the program and provide safety supervision during boarding.
“I-CARE was designed to be largely self-directed, supported by ‘coaches’ who are not mental health professionals,” Dr. Leyenaar, vice chair of research in the department of pediatrics and an associate professor of pediatrics at Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H., said in an interview. With this model, the program requires minimal additional resources beyond the tablets and workbooks, and is designed for implementation in settings with few or no mental health professionals, she said.
Cora Breuner, MD, MPH, a professor of pediatrics at the University of Washington, Seattle, and an attending physician at Seattle Children’s Hospital, was not involved in the study but was excited to see it.
“I think it’s a really good idea, and I like that it’s being studied,” Dr. Breuner said in an interview. She said the health care and public health system has let down an entire population who data had shown were experiencing mental health problems.
“We knew before the pandemic that behavioral health issues were creeping up slowly with anxiety, depression, suicidal ideation, and, of course, substance use disorders and eating disorders, and not a lot was being done about it,” Dr. Breuner said, and the pandemic exacerbated those issues. ”I don’t know why no one realized that this was going to be the downstream effect of having no socialization for kids for 18 months and limited resources for those who we need desperately to provide care for,” especially BIPOC [Black, Indigenous, and people of color] kids and underresourced kids.
That sentiment is exactly what inspired the creation of the program, according to Dr. Leyenaar.
The I-CARE program was implemented at Dartmouth Hitchcock Medical Center in November 2021 for adolescents aged 12-17 who were boarding because of suicidality or self-harm. The program and study excluded youth with psychosis and other cognitive or behavioral conditions that didn’t fit with the skills taught by the module training.
The researchers qualitatively evaluated the I-CARE program in youth who were offered at least two I-CARE modules and with parents present during boarding.
Twenty-four youth, with a median age of 14, were offered the I-CARE program between November 2021 and April 2022 while boarding for a median 8 days. Most of the patients were female (79%), and a third were transgender or gender diverse. Most were White (83%), and about two-thirds had Medicaid (62.5%). The most common diagnoses among the participants were major depressive disorder (71%) and generalized anxiety disorder (46%). Others included PTSD (29%), restrictive eating disorder (21%), and bipolar disorder (12.5%).
All offered the program completed the first module, and 79% participated in additional modules. The main reason for discontinuation was transfer to another facility, but a few youth either refused to engage with the program or felt they knew the material well enough that they weren’t benefiting from it.
The evaluation involved 16 youth, seven parents, and 17 clinicians. On a Likert scale, the composite score for the program’s appropriateness – suitability, applicability, and meeting needs – was an average 3.7, with a higher rating from clinicians (4.3) and caregivers (3.5) than youth (2.8).
“Some youth felt the intervention was better suited for a younger audience or those with less familiarity with mental health skills, but they acknowledged that the intervention would be helpful and appropriate for others,” Dr. House, who is also an assistant professor of pediatrics at Geisel School of Medicine, said.
Youth rated the acceptability of the program more highly (3.6) and all three groups found it easy to use, with an average feasibility score of 4 across the board. The program’s acceptability received an average score of 4 from parents and clinicians.
”Teens seem to particularly value the psychoeducation module that explains the relationship between thoughts and feelings, as well as the opportunity to develop a personalized safety plan,” Dr. Leyenaar said.
Among the challenges expressed by the participating teens were that the loud sounds and beeping in the hospital made it difficult to practice mindfulness and that they often had to wait for staff to be available to do I-CARE.
“I feel like not many people have been trained yet,” one teen said, “so to have more nurses available to do I-CARE would be helpful.”
Another participant found the coaches helpful. “Sometimes they were my nurse, sometimes they were someone I never met before. … and also, they were all really, really nice,” the teen said.
Another teen regarded the material as “really surface-level mental health stuff” that they thought “could be helpful to other people who are here for the first time.” But others found the content more beneficial.
“The videos were helpful. … I was worried that they weren’t going to be very informative, but they did make sense to me,” one participant said. “They weren’t overcomplicating things. … They weren’t saying anything I didn’t understand, so that was good.”
The researchers next plan to conduct a multisite study to determine the program’s effectiveness in improving health outcomes and reducing suicidal ideation. Dr. House and Dr. Leyenaar are looking at ways to refine the program.
”We may narrow the age range for participants, with an upper age limit of 16, since some older teens said that the modules were best suited for a younger audience,” Dr. Leyenaar said. “We are also discussing how to best support youth who are readmitted to our hospital and have participated in I-CARE previously.”
Dr. Breuner said she would be interested to see, in future studies of the program, whether it reduced the likelihood of inpatient psychiatric stay, the length of psychiatric stay after admission, or the risk of readmission. She also wondered if the program might be offered in languages other than English, whether a version might be specifically designed for BIPOC youth, and whether the researchers had considered offering the intervention to caregivers as well.
The modules are teaching the kids but should they also be teaching the parents? Dr. Breuner wondered. A lot of times, she said, the parents are bringing these kids in because they don’t know what to do and can’t deal with them anymore. Offering modules on the same skills to caregivers would also enable the caregivers to reinforce and reteach the skills to their children, especially if the youth struggled to really take in what the modules were trying to teach.
Dr. Leyenaar said she expects buy-in for a program like this would be high at other institutions, but it’s premature to scale it up until they’ve conducted at least another clinical trial on its effectiveness. The biggest potential barrier to buy-in that Dr. Breuner perceived would be cost.
“It’s always difficult when it costs money” since the hospital needs to train the clinicians who provide the care, Dr. Breuner said, but it’s possible those costs could be offset if the program reduces the risk of readmission or return to the emergency department.
While the overall risk of harms from the intervention are low, Dr. Breuner said it is important to be conscious that the intervention may not necessarily be appropriate for all youth.
“There’s always risk when there’s a trauma background, and you have to be very careful, especially with mindfulness training,” Dr. Breuner said. For those with a history of abuse or other adverse childhood experiences “for someone to get into a very calm, still place can actually be counterproductive.”
Dr. Breuner especially appreciated that the researchers involved the youth and caregivers in the evaluation process. “That the parents expressed positive attitudes is really incredible,” she said.
Dr. House, Dr. Leyenaar, and Dr. Breuner had no disclosures. No external funding was noted for the study.
AT AAP 2022







