User login
Gestational hypertension-diabetes combo signals CVD risk
Women who develop transient hypertensive disorders during their pregnancy are at risk for developing subsequent cardiovascular disease (CVD), particularly if this experienced at the same time as gestational diabetes.
In a large population-based study, the adjusted hazard ratios for developing CVD following a gestational hypertensive disorder (GHTD) alone were 1.90 (95% confidence interval, 1.151-2.25) within 5 years and 1.41 (95% CI, 1.12-1.76) after 5 years or more.
When gestational diabetes was added into the mix, however, the risk for CVD after 5 years more than doubled (aHR, 2.43; 95% CI, 1.60-3.67). Risk in the earlier postpartum period was also raised by the combination, but this was not significant (aHR, 1.42; 95% CI, 0.78-2.58).
Having gestational diabetes by itself did not seem to increase the risk for later CVD in the analysis, despite being linked to higher heart disease risk in other studies.
“These are women coming out of a pregnancy – young women of reproductive age – so this is not a group that typically has cardiovascular events,” said Ravi Retnakaran, MD, in an interview, an investigator in the new study, which is published in JAMA Network Open.
“If they are somebody who has both disorders concurrently in their pregnancy, they may be at even greater risk than a woman with one or the other disorder,” added Dr. Retnakaran, who is professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and an endocrinologist at the Leadership Sinai Centre for Diabetes, Mount Sinai Hospital, also in Toronto. “In other words, amongst already high-risk patients. This is identifying a subset at maybe an even higher risk.”
It doesn’t mean that there is a huge absolute risk, Dr. Retnakaran said, but it is showing that there is a heightened risk such that women and their clinicians need to be aware of and potentially the need for greater preventative care in the future.
“It is allowing you to identify future lifetime risk of cardiovascular disease,” he said.
Study rationale and design
GHTD is “a forerunner of hypertension,” and gestational diabetes is “a precursor of diabetes” – each associated with a high risk of developing CVD in the years after pregnancy, the investigators said. While studies have looked at their individual contributions to future CVD risk, not many had looked to see what risks having both may confer in the postpregnancy years.
For the analysis, data on 886,295 women with GHTD (43,861), gestational diabetes (54,061), both (4,975), or neither (783,398) were obtained from several Canadian administrative health databases.
The mean age was around 30 years across the groups, with those with both conditions or gestational diabetes alone more likely to be older than those with GTHD alone or neither condition (32 vs. 29 years, respectively, P < .001).
After a total follow-up period of 12 years, 1,999 CVD events were recorded, most of them (1,162) 5 years after the pregnancy.
Pregnancy is a stress test for the heart
“We know that what we call adverse pregnancy outcomes – things like gestational hypertension, and gestational diabetes, and preeclampsia – are on the rise globally,” Natalie A. Bello, MD, director of hypertension research at the Smidt Heart Institute, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, commented in an interview.
“People who are younger and of childbearing age who are going into pregnancy now are less healthy than they perhaps were in the past,” Dr. Bello suggested, with more hypertension, more obesity, and people being less physically active. “We think that’s translating into some of the pregnancy complications.”
That’s concerning for a number of reasons, said Dr. Bello, who is also the cochair of the American College of Cardiology’s Cardio-Obstetrics Workgroup, and the biggest one perhaps is the stress that these may conditions may be placing on the heart.
“We know that when individuals have an adverse pregnancy outcome like gestational hypertension, or gestational diabetes, their risk for heart disease is increased in the future compared to someone who has an uncomplicated pregnancy,” she said. “So, we sort of say pregnancy is like a stress test for your heart.”
Dr. Bello added that “these situations, these adverse pregnancy outcomes are an indicator for us as physicians, but also they should be for patients as well, to sort of make sure they’re talking to their doctor about their risk factors and modifying them whenever possible.”
The population studied came from quite a racially, ethnically, and economically diverse area of Canada, Dr. Bello pointed out, although because of the nature of an administrative database there wasn’t information on individual level risk factors.
“We don’t know things like smoking, or if individuals were obese when they were pregnant. So, there are some limitations that should be noted,” she said.
Also, the results don’t mean that isolated gestational diabetes “isn’t something we need to be concerned about,” Dr. Bello observed, adding that the study may have been underpowered to look at this association. “It may just be that it will take a longer time for individuals who have gestational diabetes who don’t make lifestyle changes to develop diabetes, and then develop heart disease.”
The main message is that the women who have a co-occurrence of gestational hypertension and gestational diabetes are at particularly high risk of cardiovascular disease in the future,” said Dr. Retnakaran.
“The way to look at it from a patient standpoint is that we are all on different tracks in terms of our cardiometabolic destiny,” and that these data give “some understanding of what kind of tracks they are on for future risk,” Dr. Retnakaran said.
“A history of either gestational hypertension, and/or gestational diabetes should be really a warning sign for physicians and for patients that they have a higher risk of heart disease,” said Dr. Bello.
She added that this is a signal “that we need to do things to modify their risk, because we know that about 80% of heart disease is modifiable and preventable with proper risk factor management.”
The study was funded by the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care. Dr. Retnakaran has received grants and personal fees from Novo Nordisk and Merck, grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, and personal fees from Eli Lily Takeda, and Sanofi. Dr. Bello had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Women who develop transient hypertensive disorders during their pregnancy are at risk for developing subsequent cardiovascular disease (CVD), particularly if this experienced at the same time as gestational diabetes.
In a large population-based study, the adjusted hazard ratios for developing CVD following a gestational hypertensive disorder (GHTD) alone were 1.90 (95% confidence interval, 1.151-2.25) within 5 years and 1.41 (95% CI, 1.12-1.76) after 5 years or more.
When gestational diabetes was added into the mix, however, the risk for CVD after 5 years more than doubled (aHR, 2.43; 95% CI, 1.60-3.67). Risk in the earlier postpartum period was also raised by the combination, but this was not significant (aHR, 1.42; 95% CI, 0.78-2.58).
Having gestational diabetes by itself did not seem to increase the risk for later CVD in the analysis, despite being linked to higher heart disease risk in other studies.
“These are women coming out of a pregnancy – young women of reproductive age – so this is not a group that typically has cardiovascular events,” said Ravi Retnakaran, MD, in an interview, an investigator in the new study, which is published in JAMA Network Open.
“If they are somebody who has both disorders concurrently in their pregnancy, they may be at even greater risk than a woman with one or the other disorder,” added Dr. Retnakaran, who is professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and an endocrinologist at the Leadership Sinai Centre for Diabetes, Mount Sinai Hospital, also in Toronto. “In other words, amongst already high-risk patients. This is identifying a subset at maybe an even higher risk.”
It doesn’t mean that there is a huge absolute risk, Dr. Retnakaran said, but it is showing that there is a heightened risk such that women and their clinicians need to be aware of and potentially the need for greater preventative care in the future.
“It is allowing you to identify future lifetime risk of cardiovascular disease,” he said.
Study rationale and design
GHTD is “a forerunner of hypertension,” and gestational diabetes is “a precursor of diabetes” – each associated with a high risk of developing CVD in the years after pregnancy, the investigators said. While studies have looked at their individual contributions to future CVD risk, not many had looked to see what risks having both may confer in the postpregnancy years.
For the analysis, data on 886,295 women with GHTD (43,861), gestational diabetes (54,061), both (4,975), or neither (783,398) were obtained from several Canadian administrative health databases.
The mean age was around 30 years across the groups, with those with both conditions or gestational diabetes alone more likely to be older than those with GTHD alone or neither condition (32 vs. 29 years, respectively, P < .001).
After a total follow-up period of 12 years, 1,999 CVD events were recorded, most of them (1,162) 5 years after the pregnancy.
Pregnancy is a stress test for the heart
“We know that what we call adverse pregnancy outcomes – things like gestational hypertension, and gestational diabetes, and preeclampsia – are on the rise globally,” Natalie A. Bello, MD, director of hypertension research at the Smidt Heart Institute, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, commented in an interview.
“People who are younger and of childbearing age who are going into pregnancy now are less healthy than they perhaps were in the past,” Dr. Bello suggested, with more hypertension, more obesity, and people being less physically active. “We think that’s translating into some of the pregnancy complications.”
That’s concerning for a number of reasons, said Dr. Bello, who is also the cochair of the American College of Cardiology’s Cardio-Obstetrics Workgroup, and the biggest one perhaps is the stress that these may conditions may be placing on the heart.
“We know that when individuals have an adverse pregnancy outcome like gestational hypertension, or gestational diabetes, their risk for heart disease is increased in the future compared to someone who has an uncomplicated pregnancy,” she said. “So, we sort of say pregnancy is like a stress test for your heart.”
Dr. Bello added that “these situations, these adverse pregnancy outcomes are an indicator for us as physicians, but also they should be for patients as well, to sort of make sure they’re talking to their doctor about their risk factors and modifying them whenever possible.”
The population studied came from quite a racially, ethnically, and economically diverse area of Canada, Dr. Bello pointed out, although because of the nature of an administrative database there wasn’t information on individual level risk factors.
“We don’t know things like smoking, or if individuals were obese when they were pregnant. So, there are some limitations that should be noted,” she said.
Also, the results don’t mean that isolated gestational diabetes “isn’t something we need to be concerned about,” Dr. Bello observed, adding that the study may have been underpowered to look at this association. “It may just be that it will take a longer time for individuals who have gestational diabetes who don’t make lifestyle changes to develop diabetes, and then develop heart disease.”
The main message is that the women who have a co-occurrence of gestational hypertension and gestational diabetes are at particularly high risk of cardiovascular disease in the future,” said Dr. Retnakaran.
“The way to look at it from a patient standpoint is that we are all on different tracks in terms of our cardiometabolic destiny,” and that these data give “some understanding of what kind of tracks they are on for future risk,” Dr. Retnakaran said.
“A history of either gestational hypertension, and/or gestational diabetes should be really a warning sign for physicians and for patients that they have a higher risk of heart disease,” said Dr. Bello.
She added that this is a signal “that we need to do things to modify their risk, because we know that about 80% of heart disease is modifiable and preventable with proper risk factor management.”
The study was funded by the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care. Dr. Retnakaran has received grants and personal fees from Novo Nordisk and Merck, grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, and personal fees from Eli Lily Takeda, and Sanofi. Dr. Bello had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Women who develop transient hypertensive disorders during their pregnancy are at risk for developing subsequent cardiovascular disease (CVD), particularly if this experienced at the same time as gestational diabetes.
In a large population-based study, the adjusted hazard ratios for developing CVD following a gestational hypertensive disorder (GHTD) alone were 1.90 (95% confidence interval, 1.151-2.25) within 5 years and 1.41 (95% CI, 1.12-1.76) after 5 years or more.
When gestational diabetes was added into the mix, however, the risk for CVD after 5 years more than doubled (aHR, 2.43; 95% CI, 1.60-3.67). Risk in the earlier postpartum period was also raised by the combination, but this was not significant (aHR, 1.42; 95% CI, 0.78-2.58).
Having gestational diabetes by itself did not seem to increase the risk for later CVD in the analysis, despite being linked to higher heart disease risk in other studies.
“These are women coming out of a pregnancy – young women of reproductive age – so this is not a group that typically has cardiovascular events,” said Ravi Retnakaran, MD, in an interview, an investigator in the new study, which is published in JAMA Network Open.
“If they are somebody who has both disorders concurrently in their pregnancy, they may be at even greater risk than a woman with one or the other disorder,” added Dr. Retnakaran, who is professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and an endocrinologist at the Leadership Sinai Centre for Diabetes, Mount Sinai Hospital, also in Toronto. “In other words, amongst already high-risk patients. This is identifying a subset at maybe an even higher risk.”
It doesn’t mean that there is a huge absolute risk, Dr. Retnakaran said, but it is showing that there is a heightened risk such that women and their clinicians need to be aware of and potentially the need for greater preventative care in the future.
“It is allowing you to identify future lifetime risk of cardiovascular disease,” he said.
Study rationale and design
GHTD is “a forerunner of hypertension,” and gestational diabetes is “a precursor of diabetes” – each associated with a high risk of developing CVD in the years after pregnancy, the investigators said. While studies have looked at their individual contributions to future CVD risk, not many had looked to see what risks having both may confer in the postpregnancy years.
For the analysis, data on 886,295 women with GHTD (43,861), gestational diabetes (54,061), both (4,975), or neither (783,398) were obtained from several Canadian administrative health databases.
The mean age was around 30 years across the groups, with those with both conditions or gestational diabetes alone more likely to be older than those with GTHD alone or neither condition (32 vs. 29 years, respectively, P < .001).
After a total follow-up period of 12 years, 1,999 CVD events were recorded, most of them (1,162) 5 years after the pregnancy.
Pregnancy is a stress test for the heart
“We know that what we call adverse pregnancy outcomes – things like gestational hypertension, and gestational diabetes, and preeclampsia – are on the rise globally,” Natalie A. Bello, MD, director of hypertension research at the Smidt Heart Institute, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, commented in an interview.
“People who are younger and of childbearing age who are going into pregnancy now are less healthy than they perhaps were in the past,” Dr. Bello suggested, with more hypertension, more obesity, and people being less physically active. “We think that’s translating into some of the pregnancy complications.”
That’s concerning for a number of reasons, said Dr. Bello, who is also the cochair of the American College of Cardiology’s Cardio-Obstetrics Workgroup, and the biggest one perhaps is the stress that these may conditions may be placing on the heart.
“We know that when individuals have an adverse pregnancy outcome like gestational hypertension, or gestational diabetes, their risk for heart disease is increased in the future compared to someone who has an uncomplicated pregnancy,” she said. “So, we sort of say pregnancy is like a stress test for your heart.”
Dr. Bello added that “these situations, these adverse pregnancy outcomes are an indicator for us as physicians, but also they should be for patients as well, to sort of make sure they’re talking to their doctor about their risk factors and modifying them whenever possible.”
The population studied came from quite a racially, ethnically, and economically diverse area of Canada, Dr. Bello pointed out, although because of the nature of an administrative database there wasn’t information on individual level risk factors.
“We don’t know things like smoking, or if individuals were obese when they were pregnant. So, there are some limitations that should be noted,” she said.
Also, the results don’t mean that isolated gestational diabetes “isn’t something we need to be concerned about,” Dr. Bello observed, adding that the study may have been underpowered to look at this association. “It may just be that it will take a longer time for individuals who have gestational diabetes who don’t make lifestyle changes to develop diabetes, and then develop heart disease.”
The main message is that the women who have a co-occurrence of gestational hypertension and gestational diabetes are at particularly high risk of cardiovascular disease in the future,” said Dr. Retnakaran.
“The way to look at it from a patient standpoint is that we are all on different tracks in terms of our cardiometabolic destiny,” and that these data give “some understanding of what kind of tracks they are on for future risk,” Dr. Retnakaran said.
“A history of either gestational hypertension, and/or gestational diabetes should be really a warning sign for physicians and for patients that they have a higher risk of heart disease,” said Dr. Bello.
She added that this is a signal “that we need to do things to modify their risk, because we know that about 80% of heart disease is modifiable and preventable with proper risk factor management.”
The study was funded by the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care. Dr. Retnakaran has received grants and personal fees from Novo Nordisk and Merck, grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, and personal fees from Eli Lily Takeda, and Sanofi. Dr. Bello had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
The TikTok trend that triggered a diabetes drug shortage
Weight loss advice is everywhere you look on social media, but one trend sweeping TikTok has led to shortages of an important diabetes drug.
Ozempic, a weekly injection that helps boost insulin sensitivity in people with type 2 diabetes, also suppresses appetite, which leads to weight loss. Stories of celebrities using the drug off-label to lose a few pounds have led to an explosion of interest. And now people with diabetes – people whose lives could be saved by the drug – are having trouble finding it.
Kim Kardashian and Elon Musk
In the spring, Kim Kardashian pulled off a dramatic weight loss to fit into Marilyn Monroe’s dress for the Met Gala. Soon rumors began to circulate that she’d used Ozempic to do it. Just this week, new Twitter owner Elon Musk tweeted about his own use of Ozempic and its sibling drug, Wegovy.
Variety dubbed Ozempic “the worst kept secret in Hollywood – especially given that its most enthusiastic users are not prediabetic and do not require the drug.” The rich and famous are spending $1,200 to $1,500 a month to get access.
As so often happens, high-profile use sparked a trend. Videos on TikTok hashtagged #ozempic have amassed more than 275 million views, and #ozempicweightloss has more than 110 million.
This raises concerns about who, exactly, is watching these videos, and what message they’re receiving.
“Forty-two percent of Americans have obesity, and even more have overweight. That’s affecting our younger people and our adolescents,” says Caroline Apovian, MD, codirector of the Center for Weight Management and Wellness at the Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. “They’re looking at TikTok and other social media outlets for help.”
A new study shows how damaging this can be: Researchers analyzed 1,000 videos with nutrition, food, and weight-related hashtags, with over 1 billion views combined. They found that nearly all included messages glorifying weight loss and thinness.
At last, an effective weight-loss drug
Ozempic is Danish drug company Novo Nordisk’s brand name for semaglutide, which works by mimicking a naturally occurring hormone known as GLP-1. It travels to your brain and helps you feel full on less food. That leads to weight loss. In one 68-week study, semaglutide helped people lose an average of 15% of their body weight. But it’s not a miracle drug: You still have to change your eating habits and stay physically active.
The FDA approved Ozempic to treat people with type 2 diabetes in 2017. Four years later, Novo Nordisk received the green light for a higher-dose version meant specifically for people with obesity. Wegovy is approved for use only if you have a BMI of at least 27 with one or more weight-related ailments, or a BMI of 30 or more with none.
“These drugs are dominating my practice, because they’re so effective,” says Amanda Velazquez, MD, director of obesity medicine at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles. The drug is considered safe, “so the majority of patients are good candidates.”
More demand than supply
As word spread about how well Ozempic and Wegovy worked, social media posts helped drive even more people to seek out the drugs. Now demand is outpacing the supply – according to the FDA, starter doses of Ozempic will have limited availability through January.
“In Hollywood, people are losing 10 pounds, getting it for $1,500 a month, and depleting stores for people who have such severe obesity that they have congestive heart failure and diabetes,” Dr. Apovian says. “These are people who are going to die, and you’re taking it away just for cosmetic weight loss. That is deplorable.”
In addition to huge demand, Wegovy also had a disruption in its supply chain. Right now, it isn’t available at all in lower doses, which is helping to spike off-label demand for Ozempic. Novo Nordisk expects to have these problems sorted out by the end of the year, with distribution following soon after.
The price of access
With a list price of $1,350 a month, Wegovy costs as much as many mortgages. And Medicaid, Medicare, and many insurance companies don’t cover it. Although obesity is a disease, the insurance industry treats weight loss as more of a vanity issue – so even if you could find the drug, you might not be able to afford it.
“We’re seeing that roughly half the prescriptions we write aren’t being covered,” Dr. Apovian says. “And for the half that are covered, we have to do prior authorization, which takes days, and it’s laborious.” In some instances, she says, insurance companies withdraw authorization after 3 months if they don’t see enough weight coming off.
It’s not like you can take Wegovy for 3 months, lose some weight, and expect it to stay off, either. The medication requires a real commitment, potentially for life. That’s because once the semaglutide leaves your system, your appetite returns. In one study, people regained two-thirds of the weight they’d lost within a year of stopping.
Many see a double standard in the insurance companies’ refusal to cover a drug that could prevent serious illness or death.
“They’re saying it’s not cost-effective to give the 42% of Americans who have a BMI over 30 Wegovy. Did they say this when statins came out?” Dr. Apovian says. “Why are they doing this with antiobesity agents? It’s the culture. The culture isn’t ready to adopt obesity as the disease that it is.”
Unpleasant side effects
Let’s assume you’re one of the lucky ones – your insurance covers Wegovy, and you can actually find some. You might discover that using it is no walk in the park. Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
“The way we counteract that is to start very slowly at a low dose of these medications,” Dr. Apovian says. “We only go up when the patient doesn’t have nausea or it gets better.”
Elise Davenport was excited to try Wegovy. “I did my online research. I’m the type who’s interested in early adoption, tech gadgets and stuff,” says the 40-year-old technical writer. “I wanted to try it because I’d tried so many other things that failed, or hadn’t worked long-term.”
With a BMI over 30, Ms. Davenport qualified for the drug. She signed up for an online program that guaranteed insurance coverage and started taking it in October 2021. At first, the side effects were mild, just a touch of nausea and diarrhea. And the results were impressive. She found it easy to feel satisfied with smaller portions and lost her cravings for sugar and highly processed foods. The weight fell off, roughly 5 pounds a week.
It turns out, that’s too much, too fast. Dr. Apovian and Dr. Velazquez say their patients lose more like 2 pounds each week, with careful monitoring.
By early December, Ms. Davenport’s side effects were ramping up. Because of shortages in lower dosages, the online program wasn’t able to adjust hers right away. She felt nauseated all the time, bad enough that brushing her teeth made her vomit and she had to force herself to eat. Some weeks, she managed less than 500 calories a day. Her sleep patterns became erratic. And then her depression, which medication had kept under control for years, spiraled.
“I remember sitting on the floor of my bathroom crying, thinking I’d rather carry the extra weight,” she says. “I used to take a lot of enjoyment from food, and I had none of that anymore. It was such a joyless experience at that point.”
Eventually, her dosage was reduced and the symptoms let up, but her primary care doctor encouraged her to stop. By the time she did, in March, she’d lost 55 pounds. So far, she’s gained back about 10.
More than just weight loss
Even though Ms. Davenport’s experience wasn’t a good one, with better monitoring, she’d be willing to try again. For one thing, seeing how easy it was to eat less with medical help helped to undo years of shame.
“Our culture treats obesity like a moral failing. I realized I’d been made to feel that way by doctors and programs – that I wasn’t doing enough,” she says. “This drug made me realize there are legit physiological things going on in my body, things that are often excluded from the conversation.”
Dr. Apovian and Dr. Velazquez say their patients regularly discover similar things.
“Obesity is not a disease of willpower. Medications are not the easy way out,” Dr. Velazquez says. “This is a chronic, relapsing medical condition, and because of that, we should treat it how we treat diabetes, high blood pressure, all these other conditions. We’d never hold back medication for individuals coming in with high blood pressure, tell them to work on willpower and withhold drugs they’d qualify for.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Weight loss advice is everywhere you look on social media, but one trend sweeping TikTok has led to shortages of an important diabetes drug.
Ozempic, a weekly injection that helps boost insulin sensitivity in people with type 2 diabetes, also suppresses appetite, which leads to weight loss. Stories of celebrities using the drug off-label to lose a few pounds have led to an explosion of interest. And now people with diabetes – people whose lives could be saved by the drug – are having trouble finding it.
Kim Kardashian and Elon Musk
In the spring, Kim Kardashian pulled off a dramatic weight loss to fit into Marilyn Monroe’s dress for the Met Gala. Soon rumors began to circulate that she’d used Ozempic to do it. Just this week, new Twitter owner Elon Musk tweeted about his own use of Ozempic and its sibling drug, Wegovy.
Variety dubbed Ozempic “the worst kept secret in Hollywood – especially given that its most enthusiastic users are not prediabetic and do not require the drug.” The rich and famous are spending $1,200 to $1,500 a month to get access.
As so often happens, high-profile use sparked a trend. Videos on TikTok hashtagged #ozempic have amassed more than 275 million views, and #ozempicweightloss has more than 110 million.
This raises concerns about who, exactly, is watching these videos, and what message they’re receiving.
“Forty-two percent of Americans have obesity, and even more have overweight. That’s affecting our younger people and our adolescents,” says Caroline Apovian, MD, codirector of the Center for Weight Management and Wellness at the Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. “They’re looking at TikTok and other social media outlets for help.”
A new study shows how damaging this can be: Researchers analyzed 1,000 videos with nutrition, food, and weight-related hashtags, with over 1 billion views combined. They found that nearly all included messages glorifying weight loss and thinness.
At last, an effective weight-loss drug
Ozempic is Danish drug company Novo Nordisk’s brand name for semaglutide, which works by mimicking a naturally occurring hormone known as GLP-1. It travels to your brain and helps you feel full on less food. That leads to weight loss. In one 68-week study, semaglutide helped people lose an average of 15% of their body weight. But it’s not a miracle drug: You still have to change your eating habits and stay physically active.
The FDA approved Ozempic to treat people with type 2 diabetes in 2017. Four years later, Novo Nordisk received the green light for a higher-dose version meant specifically for people with obesity. Wegovy is approved for use only if you have a BMI of at least 27 with one or more weight-related ailments, or a BMI of 30 or more with none.
“These drugs are dominating my practice, because they’re so effective,” says Amanda Velazquez, MD, director of obesity medicine at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles. The drug is considered safe, “so the majority of patients are good candidates.”
More demand than supply
As word spread about how well Ozempic and Wegovy worked, social media posts helped drive even more people to seek out the drugs. Now demand is outpacing the supply – according to the FDA, starter doses of Ozempic will have limited availability through January.
“In Hollywood, people are losing 10 pounds, getting it for $1,500 a month, and depleting stores for people who have such severe obesity that they have congestive heart failure and diabetes,” Dr. Apovian says. “These are people who are going to die, and you’re taking it away just for cosmetic weight loss. That is deplorable.”
In addition to huge demand, Wegovy also had a disruption in its supply chain. Right now, it isn’t available at all in lower doses, which is helping to spike off-label demand for Ozempic. Novo Nordisk expects to have these problems sorted out by the end of the year, with distribution following soon after.
The price of access
With a list price of $1,350 a month, Wegovy costs as much as many mortgages. And Medicaid, Medicare, and many insurance companies don’t cover it. Although obesity is a disease, the insurance industry treats weight loss as more of a vanity issue – so even if you could find the drug, you might not be able to afford it.
“We’re seeing that roughly half the prescriptions we write aren’t being covered,” Dr. Apovian says. “And for the half that are covered, we have to do prior authorization, which takes days, and it’s laborious.” In some instances, she says, insurance companies withdraw authorization after 3 months if they don’t see enough weight coming off.
It’s not like you can take Wegovy for 3 months, lose some weight, and expect it to stay off, either. The medication requires a real commitment, potentially for life. That’s because once the semaglutide leaves your system, your appetite returns. In one study, people regained two-thirds of the weight they’d lost within a year of stopping.
Many see a double standard in the insurance companies’ refusal to cover a drug that could prevent serious illness or death.
“They’re saying it’s not cost-effective to give the 42% of Americans who have a BMI over 30 Wegovy. Did they say this when statins came out?” Dr. Apovian says. “Why are they doing this with antiobesity agents? It’s the culture. The culture isn’t ready to adopt obesity as the disease that it is.”
Unpleasant side effects
Let’s assume you’re one of the lucky ones – your insurance covers Wegovy, and you can actually find some. You might discover that using it is no walk in the park. Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
“The way we counteract that is to start very slowly at a low dose of these medications,” Dr. Apovian says. “We only go up when the patient doesn’t have nausea or it gets better.”
Elise Davenport was excited to try Wegovy. “I did my online research. I’m the type who’s interested in early adoption, tech gadgets and stuff,” says the 40-year-old technical writer. “I wanted to try it because I’d tried so many other things that failed, or hadn’t worked long-term.”
With a BMI over 30, Ms. Davenport qualified for the drug. She signed up for an online program that guaranteed insurance coverage and started taking it in October 2021. At first, the side effects were mild, just a touch of nausea and diarrhea. And the results were impressive. She found it easy to feel satisfied with smaller portions and lost her cravings for sugar and highly processed foods. The weight fell off, roughly 5 pounds a week.
It turns out, that’s too much, too fast. Dr. Apovian and Dr. Velazquez say their patients lose more like 2 pounds each week, with careful monitoring.
By early December, Ms. Davenport’s side effects were ramping up. Because of shortages in lower dosages, the online program wasn’t able to adjust hers right away. She felt nauseated all the time, bad enough that brushing her teeth made her vomit and she had to force herself to eat. Some weeks, she managed less than 500 calories a day. Her sleep patterns became erratic. And then her depression, which medication had kept under control for years, spiraled.
“I remember sitting on the floor of my bathroom crying, thinking I’d rather carry the extra weight,” she says. “I used to take a lot of enjoyment from food, and I had none of that anymore. It was such a joyless experience at that point.”
Eventually, her dosage was reduced and the symptoms let up, but her primary care doctor encouraged her to stop. By the time she did, in March, she’d lost 55 pounds. So far, she’s gained back about 10.
More than just weight loss
Even though Ms. Davenport’s experience wasn’t a good one, with better monitoring, she’d be willing to try again. For one thing, seeing how easy it was to eat less with medical help helped to undo years of shame.
“Our culture treats obesity like a moral failing. I realized I’d been made to feel that way by doctors and programs – that I wasn’t doing enough,” she says. “This drug made me realize there are legit physiological things going on in my body, things that are often excluded from the conversation.”
Dr. Apovian and Dr. Velazquez say their patients regularly discover similar things.
“Obesity is not a disease of willpower. Medications are not the easy way out,” Dr. Velazquez says. “This is a chronic, relapsing medical condition, and because of that, we should treat it how we treat diabetes, high blood pressure, all these other conditions. We’d never hold back medication for individuals coming in with high blood pressure, tell them to work on willpower and withhold drugs they’d qualify for.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Weight loss advice is everywhere you look on social media, but one trend sweeping TikTok has led to shortages of an important diabetes drug.
Ozempic, a weekly injection that helps boost insulin sensitivity in people with type 2 diabetes, also suppresses appetite, which leads to weight loss. Stories of celebrities using the drug off-label to lose a few pounds have led to an explosion of interest. And now people with diabetes – people whose lives could be saved by the drug – are having trouble finding it.
Kim Kardashian and Elon Musk
In the spring, Kim Kardashian pulled off a dramatic weight loss to fit into Marilyn Monroe’s dress for the Met Gala. Soon rumors began to circulate that she’d used Ozempic to do it. Just this week, new Twitter owner Elon Musk tweeted about his own use of Ozempic and its sibling drug, Wegovy.
Variety dubbed Ozempic “the worst kept secret in Hollywood – especially given that its most enthusiastic users are not prediabetic and do not require the drug.” The rich and famous are spending $1,200 to $1,500 a month to get access.
As so often happens, high-profile use sparked a trend. Videos on TikTok hashtagged #ozempic have amassed more than 275 million views, and #ozempicweightloss has more than 110 million.
This raises concerns about who, exactly, is watching these videos, and what message they’re receiving.
“Forty-two percent of Americans have obesity, and even more have overweight. That’s affecting our younger people and our adolescents,” says Caroline Apovian, MD, codirector of the Center for Weight Management and Wellness at the Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. “They’re looking at TikTok and other social media outlets for help.”
A new study shows how damaging this can be: Researchers analyzed 1,000 videos with nutrition, food, and weight-related hashtags, with over 1 billion views combined. They found that nearly all included messages glorifying weight loss and thinness.
At last, an effective weight-loss drug
Ozempic is Danish drug company Novo Nordisk’s brand name for semaglutide, which works by mimicking a naturally occurring hormone known as GLP-1. It travels to your brain and helps you feel full on less food. That leads to weight loss. In one 68-week study, semaglutide helped people lose an average of 15% of their body weight. But it’s not a miracle drug: You still have to change your eating habits and stay physically active.
The FDA approved Ozempic to treat people with type 2 diabetes in 2017. Four years later, Novo Nordisk received the green light for a higher-dose version meant specifically for people with obesity. Wegovy is approved for use only if you have a BMI of at least 27 with one or more weight-related ailments, or a BMI of 30 or more with none.
“These drugs are dominating my practice, because they’re so effective,” says Amanda Velazquez, MD, director of obesity medicine at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles. The drug is considered safe, “so the majority of patients are good candidates.”
More demand than supply
As word spread about how well Ozempic and Wegovy worked, social media posts helped drive even more people to seek out the drugs. Now demand is outpacing the supply – according to the FDA, starter doses of Ozempic will have limited availability through January.
“In Hollywood, people are losing 10 pounds, getting it for $1,500 a month, and depleting stores for people who have such severe obesity that they have congestive heart failure and diabetes,” Dr. Apovian says. “These are people who are going to die, and you’re taking it away just for cosmetic weight loss. That is deplorable.”
In addition to huge demand, Wegovy also had a disruption in its supply chain. Right now, it isn’t available at all in lower doses, which is helping to spike off-label demand for Ozempic. Novo Nordisk expects to have these problems sorted out by the end of the year, with distribution following soon after.
The price of access
With a list price of $1,350 a month, Wegovy costs as much as many mortgages. And Medicaid, Medicare, and many insurance companies don’t cover it. Although obesity is a disease, the insurance industry treats weight loss as more of a vanity issue – so even if you could find the drug, you might not be able to afford it.
“We’re seeing that roughly half the prescriptions we write aren’t being covered,” Dr. Apovian says. “And for the half that are covered, we have to do prior authorization, which takes days, and it’s laborious.” In some instances, she says, insurance companies withdraw authorization after 3 months if they don’t see enough weight coming off.
It’s not like you can take Wegovy for 3 months, lose some weight, and expect it to stay off, either. The medication requires a real commitment, potentially for life. That’s because once the semaglutide leaves your system, your appetite returns. In one study, people regained two-thirds of the weight they’d lost within a year of stopping.
Many see a double standard in the insurance companies’ refusal to cover a drug that could prevent serious illness or death.
“They’re saying it’s not cost-effective to give the 42% of Americans who have a BMI over 30 Wegovy. Did they say this when statins came out?” Dr. Apovian says. “Why are they doing this with antiobesity agents? It’s the culture. The culture isn’t ready to adopt obesity as the disease that it is.”
Unpleasant side effects
Let’s assume you’re one of the lucky ones – your insurance covers Wegovy, and you can actually find some. You might discover that using it is no walk in the park. Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
“The way we counteract that is to start very slowly at a low dose of these medications,” Dr. Apovian says. “We only go up when the patient doesn’t have nausea or it gets better.”
Elise Davenport was excited to try Wegovy. “I did my online research. I’m the type who’s interested in early adoption, tech gadgets and stuff,” says the 40-year-old technical writer. “I wanted to try it because I’d tried so many other things that failed, or hadn’t worked long-term.”
With a BMI over 30, Ms. Davenport qualified for the drug. She signed up for an online program that guaranteed insurance coverage and started taking it in October 2021. At first, the side effects were mild, just a touch of nausea and diarrhea. And the results were impressive. She found it easy to feel satisfied with smaller portions and lost her cravings for sugar and highly processed foods. The weight fell off, roughly 5 pounds a week.
It turns out, that’s too much, too fast. Dr. Apovian and Dr. Velazquez say their patients lose more like 2 pounds each week, with careful monitoring.
By early December, Ms. Davenport’s side effects were ramping up. Because of shortages in lower dosages, the online program wasn’t able to adjust hers right away. She felt nauseated all the time, bad enough that brushing her teeth made her vomit and she had to force herself to eat. Some weeks, she managed less than 500 calories a day. Her sleep patterns became erratic. And then her depression, which medication had kept under control for years, spiraled.
“I remember sitting on the floor of my bathroom crying, thinking I’d rather carry the extra weight,” she says. “I used to take a lot of enjoyment from food, and I had none of that anymore. It was such a joyless experience at that point.”
Eventually, her dosage was reduced and the symptoms let up, but her primary care doctor encouraged her to stop. By the time she did, in March, she’d lost 55 pounds. So far, she’s gained back about 10.
More than just weight loss
Even though Ms. Davenport’s experience wasn’t a good one, with better monitoring, she’d be willing to try again. For one thing, seeing how easy it was to eat less with medical help helped to undo years of shame.
“Our culture treats obesity like a moral failing. I realized I’d been made to feel that way by doctors and programs – that I wasn’t doing enough,” she says. “This drug made me realize there are legit physiological things going on in my body, things that are often excluded from the conversation.”
Dr. Apovian and Dr. Velazquez say their patients regularly discover similar things.
“Obesity is not a disease of willpower. Medications are not the easy way out,” Dr. Velazquez says. “This is a chronic, relapsing medical condition, and because of that, we should treat it how we treat diabetes, high blood pressure, all these other conditions. We’d never hold back medication for individuals coming in with high blood pressure, tell them to work on willpower and withhold drugs they’d qualify for.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Both potatoes and beans reduced insulin resistance, weight in controlled study
Low energy–density diets that are based either on potatoes or beans similarly reduced insulin resistance in adults with poor blood glucose control, according to a controlled feeding study in 36 individuals.
Potatoes have gotten a bad rap for their high glycemic index, but they have little fat and a low energy density, wrote the study investigators. In fact, “cooling of gelatinized potatoes generates appreciable levels of slowly digested starch (resistant starch type 3) and substantially lowers the blood glucose response that potatoes elicit.”
“There is a view that potatoes are a less healthy plant food, but there is very little empirical data from randomized trials to support this view,” senior investigator John P. Kirwan, PhD, said in an interview.
Dry beans and peas (known as pulses) also contain resistant starch that improves insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance, and multiple studies support pulses as part of a low-glycemic diet to improve glucose control in adults, the researchers explained, but because the density of food often guides how much people eat, they hypothesized that potatoes could substitute for beans and provide similar glucose control benefits.
In a study published in the Journal of Medicinal Food, the researchers randomized 36 adults aged 18-60 years with insulin resistance to 8 weeks of a low energy–density diet (1 kcal/g) high in either potatoes or beans. The baseline body mass index ranged from 25 to 40 kg/m2. Insulin resistance was defined using the homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) with a score greater than 2.
The controlled diet consisted of 50%-55% carbohydrates, 30%-35% fats, and 15%-20% protein. Each meal in the potato group included a side of potatoes, and each meal in the bean group included a side of beans.
The primary outcome was the mean change in blood glucose concentration; the researchers also assessed weight loss.
A total of 14 individuals in the potato group and 17 in the bean group completed the study; but data from the 18 individuals in each group were included in an intent-to-treat analysis.
Among study completers, HOMA-IR in the bean group showed an average decrease of 1.4 from baseline (P = .02 ); a similar decrease of 1.3 occurred in the potato group (P < .05) with no significant difference between the two diets.
Overall compliance with both diets was roughly 88%. Body weight reductions were similar in both groups and significantly reduced from baseline over the study period, with average reductions in intent-to-treat analysis of 5.82 kg in the potato group and 4.0 kg in the bean group. BMI also was significantly reduced from baseline in both potato and bean groups (2.04 kg/m2 and 1.35 kg/m2, respectively). Although baseline differences were not significant, “BMI at baseline was higher and the reduction in response to the treatment was significantly greater in the potato diet compared with the bean diet,” the researchers noted. The effect on blood glucose response was not significantly different between the two groups or from baseline, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the small size, relatively short study period, and controlled nature of the study diet, the researchers noted. “The addition of a typical Western diet would have enhanced our understanding of the effect of low energy–dense diets on metabolic outcomes,” they noted in their discussion.
However, both diets led to a reduction in body weight, and the low energy density of both potato and bean diets promoted weight loss without affecting appetite or requiring calorie restriction, the researchers explained. Therefore, “this weight loss if sustained over time could have a substantial impact on body weight,” they said.
“We hypothesized that there would be equivalence between the potato and bean diet and this hypothesis proved to be correct,” said Dr. Kirwan, of the Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Baton Rouge, La., in an interview.
The take-home message for clinicians is that, though small, the study was very well-controlled, Dr. Kirwan emphasized. “Clinicians ought to consider the health benefits of the potato when it is cooked and served appropriately.”
Looking ahead, larger randomized controlled trials with additional control arms, longer time of at least 12 weeks, and different patient populations are needed, Dr. Kirwan added.
Findings mitigate food myths
The debate continues about whether there are foods that are “good” or “evil;” or foods that one “should not eat” or “should eat,” said Amy Rothberg, MD, associate professor of internal medicine and of nutritional sciences at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, in an interview.
“This study dispels the myth that incorporating a small portion of potato into the diet (although these are not potatoes that are fried, or are topped with cheese, bacon, sour cream, etc.) results in deleterious metabolic outcomes when compared to a diet that is comprised of beans (pulses) as part of a low energy–dense diet,” she explained.
“The diet in both groups was of low energy density, which has been shown to result in fewer calories consumed, weight loss, and improvement in insulin resistance,” so the similarity in results was not so surprising, said Dr. Rothberg.
For the clinical takeaway, Dr. Rothberg agreed with the study authors: “Clinicians may counsel their patients that they can still consume a small potato (with the caveat above regarding cooking methods and toppings) as part of a balanced meal so long as they are keeping their overall calories low and not exceeding their metabolic requirements based on body weight/BMI,” she said.
As for additional research, studies with a longer time frame and a larger and more diverse study population are needed, including populations with common insulin resistance comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes, fatty liver disease, and cardiovascular disease, Dr. Rothberg noted.
Consumer considerations, with caveats
The key message for consumers is that, “based on this very small study of short duration, consuming a small portion of potato as part of an overall balanced, low-energy diet did not produce adverse effects on glucose or insulin when compared to a diet of pulses known to have favorable effects on glucose and insulin,” Dr. Rothberg told this news organization. However, “consumers should note that, although the results from this small study are encouraging, it would be premature to extrapolate the findings from this study to other populations,” she said. Also, keep in mind that the study was supported in part by the Alliance for Potato Research, although the authors stated that none of the funders (Alliance for Potato Research and Education and the National Institutes of Health) had any role in the design, analysis, or writing of the article, she added.
The study was supported in part by the Alliance for Potato Research and Education and the National Institutes of Health, which funds the Louisiana Clinical and Translational Science Center. The researchers and Dr. Rothberg had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Low energy–density diets that are based either on potatoes or beans similarly reduced insulin resistance in adults with poor blood glucose control, according to a controlled feeding study in 36 individuals.
Potatoes have gotten a bad rap for their high glycemic index, but they have little fat and a low energy density, wrote the study investigators. In fact, “cooling of gelatinized potatoes generates appreciable levels of slowly digested starch (resistant starch type 3) and substantially lowers the blood glucose response that potatoes elicit.”
“There is a view that potatoes are a less healthy plant food, but there is very little empirical data from randomized trials to support this view,” senior investigator John P. Kirwan, PhD, said in an interview.
Dry beans and peas (known as pulses) also contain resistant starch that improves insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance, and multiple studies support pulses as part of a low-glycemic diet to improve glucose control in adults, the researchers explained, but because the density of food often guides how much people eat, they hypothesized that potatoes could substitute for beans and provide similar glucose control benefits.
In a study published in the Journal of Medicinal Food, the researchers randomized 36 adults aged 18-60 years with insulin resistance to 8 weeks of a low energy–density diet (1 kcal/g) high in either potatoes or beans. The baseline body mass index ranged from 25 to 40 kg/m2. Insulin resistance was defined using the homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) with a score greater than 2.
The controlled diet consisted of 50%-55% carbohydrates, 30%-35% fats, and 15%-20% protein. Each meal in the potato group included a side of potatoes, and each meal in the bean group included a side of beans.
The primary outcome was the mean change in blood glucose concentration; the researchers also assessed weight loss.
A total of 14 individuals in the potato group and 17 in the bean group completed the study; but data from the 18 individuals in each group were included in an intent-to-treat analysis.
Among study completers, HOMA-IR in the bean group showed an average decrease of 1.4 from baseline (P = .02 ); a similar decrease of 1.3 occurred in the potato group (P < .05) with no significant difference between the two diets.
Overall compliance with both diets was roughly 88%. Body weight reductions were similar in both groups and significantly reduced from baseline over the study period, with average reductions in intent-to-treat analysis of 5.82 kg in the potato group and 4.0 kg in the bean group. BMI also was significantly reduced from baseline in both potato and bean groups (2.04 kg/m2 and 1.35 kg/m2, respectively). Although baseline differences were not significant, “BMI at baseline was higher and the reduction in response to the treatment was significantly greater in the potato diet compared with the bean diet,” the researchers noted. The effect on blood glucose response was not significantly different between the two groups or from baseline, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the small size, relatively short study period, and controlled nature of the study diet, the researchers noted. “The addition of a typical Western diet would have enhanced our understanding of the effect of low energy–dense diets on metabolic outcomes,” they noted in their discussion.
However, both diets led to a reduction in body weight, and the low energy density of both potato and bean diets promoted weight loss without affecting appetite or requiring calorie restriction, the researchers explained. Therefore, “this weight loss if sustained over time could have a substantial impact on body weight,” they said.
“We hypothesized that there would be equivalence between the potato and bean diet and this hypothesis proved to be correct,” said Dr. Kirwan, of the Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Baton Rouge, La., in an interview.
The take-home message for clinicians is that, though small, the study was very well-controlled, Dr. Kirwan emphasized. “Clinicians ought to consider the health benefits of the potato when it is cooked and served appropriately.”
Looking ahead, larger randomized controlled trials with additional control arms, longer time of at least 12 weeks, and different patient populations are needed, Dr. Kirwan added.
Findings mitigate food myths
The debate continues about whether there are foods that are “good” or “evil;” or foods that one “should not eat” or “should eat,” said Amy Rothberg, MD, associate professor of internal medicine and of nutritional sciences at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, in an interview.
“This study dispels the myth that incorporating a small portion of potato into the diet (although these are not potatoes that are fried, or are topped with cheese, bacon, sour cream, etc.) results in deleterious metabolic outcomes when compared to a diet that is comprised of beans (pulses) as part of a low energy–dense diet,” she explained.
“The diet in both groups was of low energy density, which has been shown to result in fewer calories consumed, weight loss, and improvement in insulin resistance,” so the similarity in results was not so surprising, said Dr. Rothberg.
For the clinical takeaway, Dr. Rothberg agreed with the study authors: “Clinicians may counsel their patients that they can still consume a small potato (with the caveat above regarding cooking methods and toppings) as part of a balanced meal so long as they are keeping their overall calories low and not exceeding their metabolic requirements based on body weight/BMI,” she said.
As for additional research, studies with a longer time frame and a larger and more diverse study population are needed, including populations with common insulin resistance comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes, fatty liver disease, and cardiovascular disease, Dr. Rothberg noted.
Consumer considerations, with caveats
The key message for consumers is that, “based on this very small study of short duration, consuming a small portion of potato as part of an overall balanced, low-energy diet did not produce adverse effects on glucose or insulin when compared to a diet of pulses known to have favorable effects on glucose and insulin,” Dr. Rothberg told this news organization. However, “consumers should note that, although the results from this small study are encouraging, it would be premature to extrapolate the findings from this study to other populations,” she said. Also, keep in mind that the study was supported in part by the Alliance for Potato Research, although the authors stated that none of the funders (Alliance for Potato Research and Education and the National Institutes of Health) had any role in the design, analysis, or writing of the article, she added.
The study was supported in part by the Alliance for Potato Research and Education and the National Institutes of Health, which funds the Louisiana Clinical and Translational Science Center. The researchers and Dr. Rothberg had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Low energy–density diets that are based either on potatoes or beans similarly reduced insulin resistance in adults with poor blood glucose control, according to a controlled feeding study in 36 individuals.
Potatoes have gotten a bad rap for their high glycemic index, but they have little fat and a low energy density, wrote the study investigators. In fact, “cooling of gelatinized potatoes generates appreciable levels of slowly digested starch (resistant starch type 3) and substantially lowers the blood glucose response that potatoes elicit.”
“There is a view that potatoes are a less healthy plant food, but there is very little empirical data from randomized trials to support this view,” senior investigator John P. Kirwan, PhD, said in an interview.
Dry beans and peas (known as pulses) also contain resistant starch that improves insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance, and multiple studies support pulses as part of a low-glycemic diet to improve glucose control in adults, the researchers explained, but because the density of food often guides how much people eat, they hypothesized that potatoes could substitute for beans and provide similar glucose control benefits.
In a study published in the Journal of Medicinal Food, the researchers randomized 36 adults aged 18-60 years with insulin resistance to 8 weeks of a low energy–density diet (1 kcal/g) high in either potatoes or beans. The baseline body mass index ranged from 25 to 40 kg/m2. Insulin resistance was defined using the homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) with a score greater than 2.
The controlled diet consisted of 50%-55% carbohydrates, 30%-35% fats, and 15%-20% protein. Each meal in the potato group included a side of potatoes, and each meal in the bean group included a side of beans.
The primary outcome was the mean change in blood glucose concentration; the researchers also assessed weight loss.
A total of 14 individuals in the potato group and 17 in the bean group completed the study; but data from the 18 individuals in each group were included in an intent-to-treat analysis.
Among study completers, HOMA-IR in the bean group showed an average decrease of 1.4 from baseline (P = .02 ); a similar decrease of 1.3 occurred in the potato group (P < .05) with no significant difference between the two diets.
Overall compliance with both diets was roughly 88%. Body weight reductions were similar in both groups and significantly reduced from baseline over the study period, with average reductions in intent-to-treat analysis of 5.82 kg in the potato group and 4.0 kg in the bean group. BMI also was significantly reduced from baseline in both potato and bean groups (2.04 kg/m2 and 1.35 kg/m2, respectively). Although baseline differences were not significant, “BMI at baseline was higher and the reduction in response to the treatment was significantly greater in the potato diet compared with the bean diet,” the researchers noted. The effect on blood glucose response was not significantly different between the two groups or from baseline, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the small size, relatively short study period, and controlled nature of the study diet, the researchers noted. “The addition of a typical Western diet would have enhanced our understanding of the effect of low energy–dense diets on metabolic outcomes,” they noted in their discussion.
However, both diets led to a reduction in body weight, and the low energy density of both potato and bean diets promoted weight loss without affecting appetite or requiring calorie restriction, the researchers explained. Therefore, “this weight loss if sustained over time could have a substantial impact on body weight,” they said.
“We hypothesized that there would be equivalence between the potato and bean diet and this hypothesis proved to be correct,” said Dr. Kirwan, of the Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Baton Rouge, La., in an interview.
The take-home message for clinicians is that, though small, the study was very well-controlled, Dr. Kirwan emphasized. “Clinicians ought to consider the health benefits of the potato when it is cooked and served appropriately.”
Looking ahead, larger randomized controlled trials with additional control arms, longer time of at least 12 weeks, and different patient populations are needed, Dr. Kirwan added.
Findings mitigate food myths
The debate continues about whether there are foods that are “good” or “evil;” or foods that one “should not eat” or “should eat,” said Amy Rothberg, MD, associate professor of internal medicine and of nutritional sciences at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, in an interview.
“This study dispels the myth that incorporating a small portion of potato into the diet (although these are not potatoes that are fried, or are topped with cheese, bacon, sour cream, etc.) results in deleterious metabolic outcomes when compared to a diet that is comprised of beans (pulses) as part of a low energy–dense diet,” she explained.
“The diet in both groups was of low energy density, which has been shown to result in fewer calories consumed, weight loss, and improvement in insulin resistance,” so the similarity in results was not so surprising, said Dr. Rothberg.
For the clinical takeaway, Dr. Rothberg agreed with the study authors: “Clinicians may counsel their patients that they can still consume a small potato (with the caveat above regarding cooking methods and toppings) as part of a balanced meal so long as they are keeping their overall calories low and not exceeding their metabolic requirements based on body weight/BMI,” she said.
As for additional research, studies with a longer time frame and a larger and more diverse study population are needed, including populations with common insulin resistance comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes, fatty liver disease, and cardiovascular disease, Dr. Rothberg noted.
Consumer considerations, with caveats
The key message for consumers is that, “based on this very small study of short duration, consuming a small portion of potato as part of an overall balanced, low-energy diet did not produce adverse effects on glucose or insulin when compared to a diet of pulses known to have favorable effects on glucose and insulin,” Dr. Rothberg told this news organization. However, “consumers should note that, although the results from this small study are encouraging, it would be premature to extrapolate the findings from this study to other populations,” she said. Also, keep in mind that the study was supported in part by the Alliance for Potato Research, although the authors stated that none of the funders (Alliance for Potato Research and Education and the National Institutes of Health) had any role in the design, analysis, or writing of the article, she added.
The study was supported in part by the Alliance for Potato Research and Education and the National Institutes of Health, which funds the Louisiana Clinical and Translational Science Center. The researchers and Dr. Rothberg had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF MEDICINAL FOOD
New genetic variant linked to maturity-onset diabetes of the young
A newly discovered genetic variant that is associated with type 2 diabetes (T2D) is responsible for almost 7% of all diabetes cases in Greenland, according to a whole-genome sequencing analysis of 448 Greenlandic Inuit individuals.
The variant, identified as c.1108G>T, “has the largest population impact of any previously reported variant” within the HNF1A gene – a gene that can cause maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY), reported senior author Torben Hansen, MD, PhD, of the University of Copenhagen, and colleagues in The Lancet Regional Health–Europe. The c.1108G>T variant does not cause MODY, but other variants within the HNF1A gene do. However, carriers of this variant, which is present in 1.9% of the Greenlandic Inuit population and has not been found elsewhere, have normal insulin sensitivity, but decreased beta-cell function and a more than fourfold risk of developing type 2 diabetes. “This adds to a previous discovery that about 11% of all diabetes in Greenlandic Inuit is explained by a mutation in the TBC1D4 variant,” Dr. Hansen told this publication. “Thus 1 in 5 patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes in Greenland have a specific mutation explaining their diabetes. In European populations only about 1%-2% of patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes have a known genetic etiology.”
The finding “provides new avenues to subgroup patients, detect diabetes in family members, and pursue precision treatment trials,” noted the authors, although they acknowledged that treatment choices for individuals with this variant still need to be explored. “We know from HNF1A-mutation carriers with European ancestry that they benefit from sulfonylurea treatment,” said Dr. Hansen. “However, we have not yet done treatment studies in Inuit.” The investigators noted that “it is not always the case that variants in HNF1A result in an increased insulin secretory response to sulfonylurea. ... Whether carriers of the c.1108G>T variant could benefit from treatment with sulfonylurea should be pursued within the context of a randomized clinical trial establishing both short- and long-term efficacy of sulfonylurea in these patients.”
A total of 4,497 study participants were randomly sampled from two cross-sectional cohorts in an adult Greenlandic population health survey. Among 448 participants who had whole genome sequencing, 14 known MODY genes were screened for both previously identified as well as novel variants. This identified the c.1108G>T variant, which was then genotyped in the full cohort in order to estimate an allele frequency of 1.3% in the general Greenlandic population, and 1.9% in the Inuit component. The variant was not found in genome sequences of other populations.
The researchers then tested the association of the variant with T2D and showed strong association with T2D (odds ratio, 4.35) and higher hemoglobin A1c levels.
“This is very well-conducted and exciting research that highlights the importance of studying the genetics of diverse populations,” said Miriam Udler, MD, PhD, director of the Massachusetts General Diabetes Genetics Clinic, and assistant professor at Harvard University, both in Boston. “This manuscript builds on prior work from the researchers identifying another genetic variant specific to the Greenlandic Inuit population in the gene TBC1D4,” she added. “About 3.8% of people in this population carry two copies of the TBC1D4 variant and have about a 10-fold increased risk of diabetes. Together the two variants affect 18% of Greenlanders with diabetes.”
With its fourfold increased risk of diabetes, the new variant falls into “an ever-growing category” of “intermediate risk” genetic variants, explained Dr. Udler – “meaning that they have a large impact on diabetes risk, but cannot fully predict whether someone will get diabetes. The contribution of additional risk factors is particularly important for ‘intermediate risk’ genetic variants,” she added. “Thus, clinically, we can tell patients who have variants such as HNF1A c.1108>T that they are at substantial increased risk of diabetes, but that many will not develop diabetes. And for those who do develop diabetes, we are not yet able to advise on particular therapeutic strategies.”
Still, she emphasized, the importance of studying diverse populations with specific genetic risk factors is the end-goal of precision medicine. “An active area of research is determining whether and how to return such information about ‘intermediate risk’ variants to patients who get clinical genetic testing for diabetes, since typically only variants that are very high risk ... are returned in clinical testing reports.” Dr. Udler added that “many more such “intermediate risk’ variants likely exist in all populations, but have yet to be characterized because they are less common than HNF1A c.1108>T; however, ongoing worldwide efforts to increase the sample sizes of human genetic studies will facilitate such discovery.”
The study was funded by Novo Nordisk Foundation, Independent Research Fund Denmark, and Karen Elise Jensen’s Foundation. Dr. Hansen and Dr. Udler had no disclosures.
A newly discovered genetic variant that is associated with type 2 diabetes (T2D) is responsible for almost 7% of all diabetes cases in Greenland, according to a whole-genome sequencing analysis of 448 Greenlandic Inuit individuals.
The variant, identified as c.1108G>T, “has the largest population impact of any previously reported variant” within the HNF1A gene – a gene that can cause maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY), reported senior author Torben Hansen, MD, PhD, of the University of Copenhagen, and colleagues in The Lancet Regional Health–Europe. The c.1108G>T variant does not cause MODY, but other variants within the HNF1A gene do. However, carriers of this variant, which is present in 1.9% of the Greenlandic Inuit population and has not been found elsewhere, have normal insulin sensitivity, but decreased beta-cell function and a more than fourfold risk of developing type 2 diabetes. “This adds to a previous discovery that about 11% of all diabetes in Greenlandic Inuit is explained by a mutation in the TBC1D4 variant,” Dr. Hansen told this publication. “Thus 1 in 5 patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes in Greenland have a specific mutation explaining their diabetes. In European populations only about 1%-2% of patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes have a known genetic etiology.”
The finding “provides new avenues to subgroup patients, detect diabetes in family members, and pursue precision treatment trials,” noted the authors, although they acknowledged that treatment choices for individuals with this variant still need to be explored. “We know from HNF1A-mutation carriers with European ancestry that they benefit from sulfonylurea treatment,” said Dr. Hansen. “However, we have not yet done treatment studies in Inuit.” The investigators noted that “it is not always the case that variants in HNF1A result in an increased insulin secretory response to sulfonylurea. ... Whether carriers of the c.1108G>T variant could benefit from treatment with sulfonylurea should be pursued within the context of a randomized clinical trial establishing both short- and long-term efficacy of sulfonylurea in these patients.”
A total of 4,497 study participants were randomly sampled from two cross-sectional cohorts in an adult Greenlandic population health survey. Among 448 participants who had whole genome sequencing, 14 known MODY genes were screened for both previously identified as well as novel variants. This identified the c.1108G>T variant, which was then genotyped in the full cohort in order to estimate an allele frequency of 1.3% in the general Greenlandic population, and 1.9% in the Inuit component. The variant was not found in genome sequences of other populations.
The researchers then tested the association of the variant with T2D and showed strong association with T2D (odds ratio, 4.35) and higher hemoglobin A1c levels.
“This is very well-conducted and exciting research that highlights the importance of studying the genetics of diverse populations,” said Miriam Udler, MD, PhD, director of the Massachusetts General Diabetes Genetics Clinic, and assistant professor at Harvard University, both in Boston. “This manuscript builds on prior work from the researchers identifying another genetic variant specific to the Greenlandic Inuit population in the gene TBC1D4,” she added. “About 3.8% of people in this population carry two copies of the TBC1D4 variant and have about a 10-fold increased risk of diabetes. Together the two variants affect 18% of Greenlanders with diabetes.”
With its fourfold increased risk of diabetes, the new variant falls into “an ever-growing category” of “intermediate risk” genetic variants, explained Dr. Udler – “meaning that they have a large impact on diabetes risk, but cannot fully predict whether someone will get diabetes. The contribution of additional risk factors is particularly important for ‘intermediate risk’ genetic variants,” she added. “Thus, clinically, we can tell patients who have variants such as HNF1A c.1108>T that they are at substantial increased risk of diabetes, but that many will not develop diabetes. And for those who do develop diabetes, we are not yet able to advise on particular therapeutic strategies.”
Still, she emphasized, the importance of studying diverse populations with specific genetic risk factors is the end-goal of precision medicine. “An active area of research is determining whether and how to return such information about ‘intermediate risk’ variants to patients who get clinical genetic testing for diabetes, since typically only variants that are very high risk ... are returned in clinical testing reports.” Dr. Udler added that “many more such “intermediate risk’ variants likely exist in all populations, but have yet to be characterized because they are less common than HNF1A c.1108>T; however, ongoing worldwide efforts to increase the sample sizes of human genetic studies will facilitate such discovery.”
The study was funded by Novo Nordisk Foundation, Independent Research Fund Denmark, and Karen Elise Jensen’s Foundation. Dr. Hansen and Dr. Udler had no disclosures.
A newly discovered genetic variant that is associated with type 2 diabetes (T2D) is responsible for almost 7% of all diabetes cases in Greenland, according to a whole-genome sequencing analysis of 448 Greenlandic Inuit individuals.
The variant, identified as c.1108G>T, “has the largest population impact of any previously reported variant” within the HNF1A gene – a gene that can cause maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY), reported senior author Torben Hansen, MD, PhD, of the University of Copenhagen, and colleagues in The Lancet Regional Health–Europe. The c.1108G>T variant does not cause MODY, but other variants within the HNF1A gene do. However, carriers of this variant, which is present in 1.9% of the Greenlandic Inuit population and has not been found elsewhere, have normal insulin sensitivity, but decreased beta-cell function and a more than fourfold risk of developing type 2 diabetes. “This adds to a previous discovery that about 11% of all diabetes in Greenlandic Inuit is explained by a mutation in the TBC1D4 variant,” Dr. Hansen told this publication. “Thus 1 in 5 patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes in Greenland have a specific mutation explaining their diabetes. In European populations only about 1%-2% of patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes have a known genetic etiology.”
The finding “provides new avenues to subgroup patients, detect diabetes in family members, and pursue precision treatment trials,” noted the authors, although they acknowledged that treatment choices for individuals with this variant still need to be explored. “We know from HNF1A-mutation carriers with European ancestry that they benefit from sulfonylurea treatment,” said Dr. Hansen. “However, we have not yet done treatment studies in Inuit.” The investigators noted that “it is not always the case that variants in HNF1A result in an increased insulin secretory response to sulfonylurea. ... Whether carriers of the c.1108G>T variant could benefit from treatment with sulfonylurea should be pursued within the context of a randomized clinical trial establishing both short- and long-term efficacy of sulfonylurea in these patients.”
A total of 4,497 study participants were randomly sampled from two cross-sectional cohorts in an adult Greenlandic population health survey. Among 448 participants who had whole genome sequencing, 14 known MODY genes were screened for both previously identified as well as novel variants. This identified the c.1108G>T variant, which was then genotyped in the full cohort in order to estimate an allele frequency of 1.3% in the general Greenlandic population, and 1.9% in the Inuit component. The variant was not found in genome sequences of other populations.
The researchers then tested the association of the variant with T2D and showed strong association with T2D (odds ratio, 4.35) and higher hemoglobin A1c levels.
“This is very well-conducted and exciting research that highlights the importance of studying the genetics of diverse populations,” said Miriam Udler, MD, PhD, director of the Massachusetts General Diabetes Genetics Clinic, and assistant professor at Harvard University, both in Boston. “This manuscript builds on prior work from the researchers identifying another genetic variant specific to the Greenlandic Inuit population in the gene TBC1D4,” she added. “About 3.8% of people in this population carry two copies of the TBC1D4 variant and have about a 10-fold increased risk of diabetes. Together the two variants affect 18% of Greenlanders with diabetes.”
With its fourfold increased risk of diabetes, the new variant falls into “an ever-growing category” of “intermediate risk” genetic variants, explained Dr. Udler – “meaning that they have a large impact on diabetes risk, but cannot fully predict whether someone will get diabetes. The contribution of additional risk factors is particularly important for ‘intermediate risk’ genetic variants,” she added. “Thus, clinically, we can tell patients who have variants such as HNF1A c.1108>T that they are at substantial increased risk of diabetes, but that many will not develop diabetes. And for those who do develop diabetes, we are not yet able to advise on particular therapeutic strategies.”
Still, she emphasized, the importance of studying diverse populations with specific genetic risk factors is the end-goal of precision medicine. “An active area of research is determining whether and how to return such information about ‘intermediate risk’ variants to patients who get clinical genetic testing for diabetes, since typically only variants that are very high risk ... are returned in clinical testing reports.” Dr. Udler added that “many more such “intermediate risk’ variants likely exist in all populations, but have yet to be characterized because they are less common than HNF1A c.1108>T; however, ongoing worldwide efforts to increase the sample sizes of human genetic studies will facilitate such discovery.”
The study was funded by Novo Nordisk Foundation, Independent Research Fund Denmark, and Karen Elise Jensen’s Foundation. Dr. Hansen and Dr. Udler had no disclosures.
FROM THE LANCET REGIONAL HEALTH–EUROPE
Will ICER review aid bid for Medicare to pay for obesity drugs?
A report from a well-respected nonprofit group may bolster efforts to have Medicare, the largest U.S. purchaser of prescription drugs, cover obesity medicines, for which there has been accumulating evidence of significant benefit.
The Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER) released a report last month on obesity medicines, based on extensive review of research done to date and input from clinicians, drug-makers, and members of the public.
Of the treatments reviewed, the ICER report gave the best ratings to two Novo Nordisk products, a B+ for semaglutide (Wegovy) and a B for liraglutide (Saxenda), while also making the case for price cuts. At an annual U.S. net price estimated at $13,618, semaglutide exceeds what ICER considers typical cost-effectiveness thresholds. ICER suggested a benchmark annual price range for semaglutide of between $7,500 and $9,800.
The ICER report also directs insurers in general to provide more generous coverage of obesity medicines, with a specific recommendation for the U.S. Congress to pass a pending bill known as the Treat and Reduce Obesity Act of 2021. The bill would undo a restriction on weight-loss drugs in the Medicare Part D plans, which covered about 49 million people last year. Sen. Tom Carper (D-Del.) and Sen. Bill Cassidy, MD, (R-La.) have repeatedly introduced versions of the bill since 2013.
“In both chambers of Congress and with bipartisan support, we’ve pushed to expand Medicare coverage of additional therapies and medications to treat obesity,” Sen. Cassidy said in an email. “This report confirms what we’ve worked on for nearly a decade – our legislation will help improve lives.”
The current House version of the bill has the backing of more than a third of the members of that chamber, with 113 Democratic and 40 Republican cosponsors. The Senate version has 22 sponsors.
Changing views
The ICER report comes amid a broader change in how clinicians view obesity.
The American Academy of Pediatrics is readying a new Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Treatment of Pediatric Obesity that will mark a major shift in approach. Aaron S. Kelly, PhD, a professor of pediatrics at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, described it as a “sea change,” with obesity now seen as “a chronic, refractory, relapsing disease,” for which watchful waiting is no longer appropriate.
But the field of obesity treatment looked quite different in the early 2000s when Congress worked on a plan to add a pharmacy benefit to Medicare.
The deliberate omission of obesity medicine in the Medicare Part D benefit reflected both the state of science at the time and U.S. experience with a dangerous weight-loss drug combo in the late 1990s.
Initial expectations for weight-loss pills were high after the Food and Drug Administration cleared dexfenfluramine HCl (Redux) in 1996, which was part of the popular fen-phen combination. “Newly Approved Diet Drug Promises to Help Millions of Obese Americans – But Is No Magic Bullet,” read a headline about the Redux approval in The Washington Post
When work began in the 2000s to create a Medicare pharmacy benefit, lawmakers and congressional staff had a pool of about $400 billion available to establish what became the Part D program, Joel White, a former House staffer who helped draft the law, told this news organization in an email exchange.
Given the state of obesity research at the time, it seemed to make sense to exclude weight-loss medications, wrote Mr. White. Mr. White is now chief executive of the consulting firm Horizon, which has clients in the drug industry including the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America.
“Now we know that obesity is a chronic disease of epidemic proportions. Decades of research have produced a series of advances in the way we understand and treat obesity. While scientists and many who work directly with those impacted by this epidemic understand how treatments have advanced, the law lags behind,” Mr. White said.
XXXCurrent payment policies for obesity treatments are based on “outdated information and ongoing misperception,” he noted. “While Part D has been a resounding success, our Medicare approach to obesity is not.”
“In addition, it makes no sense that Medicare covers the most drastic procedure (bariatric surgery) but not less-invasive, effective treatments,” he added. “We should have long ago lifted restrictions based on advances in science and medicine.”
Overcoming the stigma
Scott Kahan, MD, MPH, agreed and hopes that the new ICER report will help more patients secure needed medications, raising a “call to arms” about the need for better coverage of obesity drugs.
Dr. Kahan is director of the National Center for Weight and Wellness, a private clinic in Washington, and chair of the clinical committee for The Obesity Society. He also served as a member of a policy roundtable that ICER convened as part of research on the report on obesity drugs. Dr. Kahan, who also serves on the faculty at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, has received fees from drug makers such as Eli Lilly.
The ICER report may help what Dr. Kahan described as well-founded caution about obesity treatments in general.
“When it comes to weight loss, there are all of these magical treatments that are sold on social media and traditional media. There are a lot of bad actors in terms of people calling themselves experts and gurus and promising all kinds of crazy stuff,” said Dr. Kahan.
And there are long-standing stigmas about obesity, he stressed.
“That underlies a lot of the backward policies, including poor coverage for medications and the noncoverage by Medicare,” Dr. Kahan said. “There’s a societal ingrained set of beliefs and misperceptions and biases. That takes time to unwind, and I think we’re on the way, but we’re not quite there yet.”
Lifestyle changes not enough to tackle obesity
AHIP (formerly America’s Health Insurance Plans) told this news organization its members consider ICER reports when making decisions about which products to cover. “And health plans already cover obesity treatments that they consider medically necessary,” said David Allen, an AHIP spokesperson.
“It is important to note that every treatment does not work for every patient, and many patients experience adverse events and may discontinue treatment,” he added in an email. “Health insurance providers play an important role in helping [health care] providers and patients identify the treatment options that are most likely to be effective as well as affordable.”
Separately, the nonprofit watchdog group Public Citizen cautioned against liraglutide on its Worst Pills, Best Pills website. In its view, the drug is minimally effective and has many dangerous adverse effects, which are even more frequent with the higher-dose weight-loss version (a lower-dose version is approved for type 2 diabetes).
“There is currently no medication that can be used safely to achieve weight loss effortlessly and without dangerous adverse effects,” the group said. “Rather than focus on losing weight by turning to risky drugs, overweight and obese adults seeking to achieve better health should make reasonable and sustainable changes to their lifestyle, such as eating a healthy diet and getting regular exercise.”
Yet, many people find there is little help available for making lifestyle changes, and some patients and physicians say these modifications by themselves are not enough.
“The vast majority of people with obesity cannot achieve sustained weight loss through diet and exercise alone,” said David Rind, MD, chief medical officer of ICER, in an Oct. 20 statement. “As such, obesity, and its resulting physical health, mental health, and social burdens, is not a choice or failing, but a medical condition.”
The focus should now be on assuring that effective medications “are priced in alignment with their benefits so that they are accessible and affordable across U.S. society,” Dr. Rind urges.
‘My own demise with a fork and knife’
ICER sought public feedback on a draft version of the report before finalizing it.
In their comments on ICER’s work, several pharmaceutical researchers and Novo Nordisk questioned the calculations used in making judgments about the value of obesity drugs. In a statement, Novo Nordisk told this news organization that the company’s view is that ICER’s modeling “does not adequately address the real-world complexities of obesity, and consequently underestimates the health and societal impact medical treatments can have.”
Commenters also dug into aspects of ICER’s calculations, including ones that consider quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs). ICER describes QALY as an academic standard for measuring how well all different types of medical treatments can extend or improve patients’ lives. In an explainer on its website, ICER says this metric has served as a fundamental component of cost-effectiveness analyses in the United States and around the world for more than 30 years.
ICER and drug makers have been at odds for some time, with PhRMA having criticized the nonprofit group. A 2020 Reuters article detailed public relations strategies used by firms paid by drug makers to raise questions about ICER’s work. Critics accuse it of allying with insurers.
ICER’s list of its recent financial supporters includes Blue Cross Blue Shield of Massachusetts and the Kaiser Foundation Health Plan, but also many other groups, such as the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, the American Academy of Neurology, and the American College of Rheumatology.
The public comments on the ICER report also include one from an unidentified woman who wrote of her past struggles to lose weight.
She said her health plan wouldn’t cover behavioral programs or semaglutide as a weight-loss drug but did cover it eventually because of signs that she had developed insulin resistance. The patient said the drug worked for her, whereas other approaches to control weight had failed.
“To put it simply, I now experience hunger and satiety in a way that I can only assume people with normal metabolism do. I am 49 years old and approaching the age where serious comorbidities associated with obesity begin to manifest,” the patient wrote.
“I no longer worry about bringing about my own demise with a fork and knife because of misfiring hunger cues.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A report from a well-respected nonprofit group may bolster efforts to have Medicare, the largest U.S. purchaser of prescription drugs, cover obesity medicines, for which there has been accumulating evidence of significant benefit.
The Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER) released a report last month on obesity medicines, based on extensive review of research done to date and input from clinicians, drug-makers, and members of the public.
Of the treatments reviewed, the ICER report gave the best ratings to two Novo Nordisk products, a B+ for semaglutide (Wegovy) and a B for liraglutide (Saxenda), while also making the case for price cuts. At an annual U.S. net price estimated at $13,618, semaglutide exceeds what ICER considers typical cost-effectiveness thresholds. ICER suggested a benchmark annual price range for semaglutide of between $7,500 and $9,800.
The ICER report also directs insurers in general to provide more generous coverage of obesity medicines, with a specific recommendation for the U.S. Congress to pass a pending bill known as the Treat and Reduce Obesity Act of 2021. The bill would undo a restriction on weight-loss drugs in the Medicare Part D plans, which covered about 49 million people last year. Sen. Tom Carper (D-Del.) and Sen. Bill Cassidy, MD, (R-La.) have repeatedly introduced versions of the bill since 2013.
“In both chambers of Congress and with bipartisan support, we’ve pushed to expand Medicare coverage of additional therapies and medications to treat obesity,” Sen. Cassidy said in an email. “This report confirms what we’ve worked on for nearly a decade – our legislation will help improve lives.”
The current House version of the bill has the backing of more than a third of the members of that chamber, with 113 Democratic and 40 Republican cosponsors. The Senate version has 22 sponsors.
Changing views
The ICER report comes amid a broader change in how clinicians view obesity.
The American Academy of Pediatrics is readying a new Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Treatment of Pediatric Obesity that will mark a major shift in approach. Aaron S. Kelly, PhD, a professor of pediatrics at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, described it as a “sea change,” with obesity now seen as “a chronic, refractory, relapsing disease,” for which watchful waiting is no longer appropriate.
But the field of obesity treatment looked quite different in the early 2000s when Congress worked on a plan to add a pharmacy benefit to Medicare.
The deliberate omission of obesity medicine in the Medicare Part D benefit reflected both the state of science at the time and U.S. experience with a dangerous weight-loss drug combo in the late 1990s.
Initial expectations for weight-loss pills were high after the Food and Drug Administration cleared dexfenfluramine HCl (Redux) in 1996, which was part of the popular fen-phen combination. “Newly Approved Diet Drug Promises to Help Millions of Obese Americans – But Is No Magic Bullet,” read a headline about the Redux approval in The Washington Post
When work began in the 2000s to create a Medicare pharmacy benefit, lawmakers and congressional staff had a pool of about $400 billion available to establish what became the Part D program, Joel White, a former House staffer who helped draft the law, told this news organization in an email exchange.
Given the state of obesity research at the time, it seemed to make sense to exclude weight-loss medications, wrote Mr. White. Mr. White is now chief executive of the consulting firm Horizon, which has clients in the drug industry including the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America.
“Now we know that obesity is a chronic disease of epidemic proportions. Decades of research have produced a series of advances in the way we understand and treat obesity. While scientists and many who work directly with those impacted by this epidemic understand how treatments have advanced, the law lags behind,” Mr. White said.
XXXCurrent payment policies for obesity treatments are based on “outdated information and ongoing misperception,” he noted. “While Part D has been a resounding success, our Medicare approach to obesity is not.”
“In addition, it makes no sense that Medicare covers the most drastic procedure (bariatric surgery) but not less-invasive, effective treatments,” he added. “We should have long ago lifted restrictions based on advances in science and medicine.”
Overcoming the stigma
Scott Kahan, MD, MPH, agreed and hopes that the new ICER report will help more patients secure needed medications, raising a “call to arms” about the need for better coverage of obesity drugs.
Dr. Kahan is director of the National Center for Weight and Wellness, a private clinic in Washington, and chair of the clinical committee for The Obesity Society. He also served as a member of a policy roundtable that ICER convened as part of research on the report on obesity drugs. Dr. Kahan, who also serves on the faculty at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, has received fees from drug makers such as Eli Lilly.
The ICER report may help what Dr. Kahan described as well-founded caution about obesity treatments in general.
“When it comes to weight loss, there are all of these magical treatments that are sold on social media and traditional media. There are a lot of bad actors in terms of people calling themselves experts and gurus and promising all kinds of crazy stuff,” said Dr. Kahan.
And there are long-standing stigmas about obesity, he stressed.
“That underlies a lot of the backward policies, including poor coverage for medications and the noncoverage by Medicare,” Dr. Kahan said. “There’s a societal ingrained set of beliefs and misperceptions and biases. That takes time to unwind, and I think we’re on the way, but we’re not quite there yet.”
Lifestyle changes not enough to tackle obesity
AHIP (formerly America’s Health Insurance Plans) told this news organization its members consider ICER reports when making decisions about which products to cover. “And health plans already cover obesity treatments that they consider medically necessary,” said David Allen, an AHIP spokesperson.
“It is important to note that every treatment does not work for every patient, and many patients experience adverse events and may discontinue treatment,” he added in an email. “Health insurance providers play an important role in helping [health care] providers and patients identify the treatment options that are most likely to be effective as well as affordable.”
Separately, the nonprofit watchdog group Public Citizen cautioned against liraglutide on its Worst Pills, Best Pills website. In its view, the drug is minimally effective and has many dangerous adverse effects, which are even more frequent with the higher-dose weight-loss version (a lower-dose version is approved for type 2 diabetes).
“There is currently no medication that can be used safely to achieve weight loss effortlessly and without dangerous adverse effects,” the group said. “Rather than focus on losing weight by turning to risky drugs, overweight and obese adults seeking to achieve better health should make reasonable and sustainable changes to their lifestyle, such as eating a healthy diet and getting regular exercise.”
Yet, many people find there is little help available for making lifestyle changes, and some patients and physicians say these modifications by themselves are not enough.
“The vast majority of people with obesity cannot achieve sustained weight loss through diet and exercise alone,” said David Rind, MD, chief medical officer of ICER, in an Oct. 20 statement. “As such, obesity, and its resulting physical health, mental health, and social burdens, is not a choice or failing, but a medical condition.”
The focus should now be on assuring that effective medications “are priced in alignment with their benefits so that they are accessible and affordable across U.S. society,” Dr. Rind urges.
‘My own demise with a fork and knife’
ICER sought public feedback on a draft version of the report before finalizing it.
In their comments on ICER’s work, several pharmaceutical researchers and Novo Nordisk questioned the calculations used in making judgments about the value of obesity drugs. In a statement, Novo Nordisk told this news organization that the company’s view is that ICER’s modeling “does not adequately address the real-world complexities of obesity, and consequently underestimates the health and societal impact medical treatments can have.”
Commenters also dug into aspects of ICER’s calculations, including ones that consider quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs). ICER describes QALY as an academic standard for measuring how well all different types of medical treatments can extend or improve patients’ lives. In an explainer on its website, ICER says this metric has served as a fundamental component of cost-effectiveness analyses in the United States and around the world for more than 30 years.
ICER and drug makers have been at odds for some time, with PhRMA having criticized the nonprofit group. A 2020 Reuters article detailed public relations strategies used by firms paid by drug makers to raise questions about ICER’s work. Critics accuse it of allying with insurers.
ICER’s list of its recent financial supporters includes Blue Cross Blue Shield of Massachusetts and the Kaiser Foundation Health Plan, but also many other groups, such as the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, the American Academy of Neurology, and the American College of Rheumatology.
The public comments on the ICER report also include one from an unidentified woman who wrote of her past struggles to lose weight.
She said her health plan wouldn’t cover behavioral programs or semaglutide as a weight-loss drug but did cover it eventually because of signs that she had developed insulin resistance. The patient said the drug worked for her, whereas other approaches to control weight had failed.
“To put it simply, I now experience hunger and satiety in a way that I can only assume people with normal metabolism do. I am 49 years old and approaching the age where serious comorbidities associated with obesity begin to manifest,” the patient wrote.
“I no longer worry about bringing about my own demise with a fork and knife because of misfiring hunger cues.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A report from a well-respected nonprofit group may bolster efforts to have Medicare, the largest U.S. purchaser of prescription drugs, cover obesity medicines, for which there has been accumulating evidence of significant benefit.
The Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER) released a report last month on obesity medicines, based on extensive review of research done to date and input from clinicians, drug-makers, and members of the public.
Of the treatments reviewed, the ICER report gave the best ratings to two Novo Nordisk products, a B+ for semaglutide (Wegovy) and a B for liraglutide (Saxenda), while also making the case for price cuts. At an annual U.S. net price estimated at $13,618, semaglutide exceeds what ICER considers typical cost-effectiveness thresholds. ICER suggested a benchmark annual price range for semaglutide of between $7,500 and $9,800.
The ICER report also directs insurers in general to provide more generous coverage of obesity medicines, with a specific recommendation for the U.S. Congress to pass a pending bill known as the Treat and Reduce Obesity Act of 2021. The bill would undo a restriction on weight-loss drugs in the Medicare Part D plans, which covered about 49 million people last year. Sen. Tom Carper (D-Del.) and Sen. Bill Cassidy, MD, (R-La.) have repeatedly introduced versions of the bill since 2013.
“In both chambers of Congress and with bipartisan support, we’ve pushed to expand Medicare coverage of additional therapies and medications to treat obesity,” Sen. Cassidy said in an email. “This report confirms what we’ve worked on for nearly a decade – our legislation will help improve lives.”
The current House version of the bill has the backing of more than a third of the members of that chamber, with 113 Democratic and 40 Republican cosponsors. The Senate version has 22 sponsors.
Changing views
The ICER report comes amid a broader change in how clinicians view obesity.
The American Academy of Pediatrics is readying a new Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Treatment of Pediatric Obesity that will mark a major shift in approach. Aaron S. Kelly, PhD, a professor of pediatrics at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, described it as a “sea change,” with obesity now seen as “a chronic, refractory, relapsing disease,” for which watchful waiting is no longer appropriate.
But the field of obesity treatment looked quite different in the early 2000s when Congress worked on a plan to add a pharmacy benefit to Medicare.
The deliberate omission of obesity medicine in the Medicare Part D benefit reflected both the state of science at the time and U.S. experience with a dangerous weight-loss drug combo in the late 1990s.
Initial expectations for weight-loss pills were high after the Food and Drug Administration cleared dexfenfluramine HCl (Redux) in 1996, which was part of the popular fen-phen combination. “Newly Approved Diet Drug Promises to Help Millions of Obese Americans – But Is No Magic Bullet,” read a headline about the Redux approval in The Washington Post
When work began in the 2000s to create a Medicare pharmacy benefit, lawmakers and congressional staff had a pool of about $400 billion available to establish what became the Part D program, Joel White, a former House staffer who helped draft the law, told this news organization in an email exchange.
Given the state of obesity research at the time, it seemed to make sense to exclude weight-loss medications, wrote Mr. White. Mr. White is now chief executive of the consulting firm Horizon, which has clients in the drug industry including the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America.
“Now we know that obesity is a chronic disease of epidemic proportions. Decades of research have produced a series of advances in the way we understand and treat obesity. While scientists and many who work directly with those impacted by this epidemic understand how treatments have advanced, the law lags behind,” Mr. White said.
XXXCurrent payment policies for obesity treatments are based on “outdated information and ongoing misperception,” he noted. “While Part D has been a resounding success, our Medicare approach to obesity is not.”
“In addition, it makes no sense that Medicare covers the most drastic procedure (bariatric surgery) but not less-invasive, effective treatments,” he added. “We should have long ago lifted restrictions based on advances in science and medicine.”
Overcoming the stigma
Scott Kahan, MD, MPH, agreed and hopes that the new ICER report will help more patients secure needed medications, raising a “call to arms” about the need for better coverage of obesity drugs.
Dr. Kahan is director of the National Center for Weight and Wellness, a private clinic in Washington, and chair of the clinical committee for The Obesity Society. He also served as a member of a policy roundtable that ICER convened as part of research on the report on obesity drugs. Dr. Kahan, who also serves on the faculty at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, has received fees from drug makers such as Eli Lilly.
The ICER report may help what Dr. Kahan described as well-founded caution about obesity treatments in general.
“When it comes to weight loss, there are all of these magical treatments that are sold on social media and traditional media. There are a lot of bad actors in terms of people calling themselves experts and gurus and promising all kinds of crazy stuff,” said Dr. Kahan.
And there are long-standing stigmas about obesity, he stressed.
“That underlies a lot of the backward policies, including poor coverage for medications and the noncoverage by Medicare,” Dr. Kahan said. “There’s a societal ingrained set of beliefs and misperceptions and biases. That takes time to unwind, and I think we’re on the way, but we’re not quite there yet.”
Lifestyle changes not enough to tackle obesity
AHIP (formerly America’s Health Insurance Plans) told this news organization its members consider ICER reports when making decisions about which products to cover. “And health plans already cover obesity treatments that they consider medically necessary,” said David Allen, an AHIP spokesperson.
“It is important to note that every treatment does not work for every patient, and many patients experience adverse events and may discontinue treatment,” he added in an email. “Health insurance providers play an important role in helping [health care] providers and patients identify the treatment options that are most likely to be effective as well as affordable.”
Separately, the nonprofit watchdog group Public Citizen cautioned against liraglutide on its Worst Pills, Best Pills website. In its view, the drug is minimally effective and has many dangerous adverse effects, which are even more frequent with the higher-dose weight-loss version (a lower-dose version is approved for type 2 diabetes).
“There is currently no medication that can be used safely to achieve weight loss effortlessly and without dangerous adverse effects,” the group said. “Rather than focus on losing weight by turning to risky drugs, overweight and obese adults seeking to achieve better health should make reasonable and sustainable changes to their lifestyle, such as eating a healthy diet and getting regular exercise.”
Yet, many people find there is little help available for making lifestyle changes, and some patients and physicians say these modifications by themselves are not enough.
“The vast majority of people with obesity cannot achieve sustained weight loss through diet and exercise alone,” said David Rind, MD, chief medical officer of ICER, in an Oct. 20 statement. “As such, obesity, and its resulting physical health, mental health, and social burdens, is not a choice or failing, but a medical condition.”
The focus should now be on assuring that effective medications “are priced in alignment with their benefits so that they are accessible and affordable across U.S. society,” Dr. Rind urges.
‘My own demise with a fork and knife’
ICER sought public feedback on a draft version of the report before finalizing it.
In their comments on ICER’s work, several pharmaceutical researchers and Novo Nordisk questioned the calculations used in making judgments about the value of obesity drugs. In a statement, Novo Nordisk told this news organization that the company’s view is that ICER’s modeling “does not adequately address the real-world complexities of obesity, and consequently underestimates the health and societal impact medical treatments can have.”
Commenters also dug into aspects of ICER’s calculations, including ones that consider quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs). ICER describes QALY as an academic standard for measuring how well all different types of medical treatments can extend or improve patients’ lives. In an explainer on its website, ICER says this metric has served as a fundamental component of cost-effectiveness analyses in the United States and around the world for more than 30 years.
ICER and drug makers have been at odds for some time, with PhRMA having criticized the nonprofit group. A 2020 Reuters article detailed public relations strategies used by firms paid by drug makers to raise questions about ICER’s work. Critics accuse it of allying with insurers.
ICER’s list of its recent financial supporters includes Blue Cross Blue Shield of Massachusetts and the Kaiser Foundation Health Plan, but also many other groups, such as the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, the American Academy of Neurology, and the American College of Rheumatology.
The public comments on the ICER report also include one from an unidentified woman who wrote of her past struggles to lose weight.
She said her health plan wouldn’t cover behavioral programs or semaglutide as a weight-loss drug but did cover it eventually because of signs that she had developed insulin resistance. The patient said the drug worked for her, whereas other approaches to control weight had failed.
“To put it simply, I now experience hunger and satiety in a way that I can only assume people with normal metabolism do. I am 49 years old and approaching the age where serious comorbidities associated with obesity begin to manifest,” the patient wrote.
“I no longer worry about bringing about my own demise with a fork and knife because of misfiring hunger cues.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Night lights in the city link to increased risk of diabetes
Higher levels of exposure to outdoor artificial light at night are significantly linked with markers of diabetes and impaired glucose homeostasis, in a new national, cross-sectional study from China.
The results showed a 7% significant increase in diabetes prevalence per quintile exposure to artificial light at night (prevalence ratio, 1.07), report Ruizhi Zheng, PhD, of the Shanghai (China) Jiaotong University School of Medicine, and colleagues. People living in areas with the most exposure to light at night had a 28% higher prevalence of diabetes than those living in places with the lowest exposure (PR, 1.28), the researchers found.
The study was published online in Diabetologia.
Previous animal studies have shown that exposure to light at night may interfere with circadian rhythms and affect glucose homeostasis, the study team note. Other research has demonstrated that chronic exposure to moderate indoor light during sleep elevated the prevalence of diabetes in older adults, compared with those sleeping in a dim setting, the authors add.
“Our findings contribute to the growing literature suggesting that artificial light at night is detrimental to health and demonstrate that artificial light at night may be a potential novel risk factor for diabetes,” they write.
“Considering the coexistence of the diabetes epidemic and the widespread influence of light pollution at night, the positive associations indicate an urgent need for countries and governments to develop effective prevention and intervention policies and to protect people from the adverse health effects of light pollution at night,” the study authors stress.
Gareth Nye, PhD, senior lecturer at the University of Chester, England, agreed that prior research has found an association between metabolic conditions, such as diabetes, and artificial light at night, with most theories as to the cause focusing on the body’s natural circadian cycle.
He said that internal clocks regulate a variety of bodily processes, such as metabolism and hormone synthesis. They also affect sleep patterns by interfering with synthesis of the hormone melatonin, which is essential for sound sleep, Dr. Nye told the UK Science Media Centre.
However, he stressed that much more research is needed before any link can be considered definitive.
Outdoor night light exposure linked to fasting glucose, A1c
The Chinese researchers set out to approximate the relationships between diabetes prevalence and glucose homeostasis with chronic exposure to outdoor light at night.
They assessed 98,658 participants from the China Noncommunicable Disease Surveillance Study across 162 sites. The mean age of participants was 42.7 years. Female participants comprised 49.2% of the study cohort.
Diabetes was defined based on American Diabetes Association criteria. Satellite data were used to determine exposure to outdoor light at night in 2010. The associations between light exposure at night and indicators of glucose homeostasis were investigated.
Prevalence ratios were calculated and adjusted for sex, age, smoking status, education, body mass index, physical activity, household income, family history of diabetes, rural/urban areas, drinking status, and use of lipid-lowering prescription drugs (primarily statins) or antihypertensives.
The findings showed exposure levels to outdoor light at night were positively linked with 2-hour and fasting glucose concentrations, A1c, and insulin resistance (measured using homeostatic model assessment [HOMA]), but negatively related to β-cell function (measured using HOMA).
More research needed
“We advise caution against causal interpretation of the findings and call for further studies involving direct measurement of individual exposure to light at night,” the researchers conclude.
Dr. Nye agreed.
“One issue with this study is that the areas with the highest outdoor artificial light levels are likely to be those in urban areas and bigger cities. It has been known for a long time now that living in an urbanized area increases your risk of obesity through increased access to high-fat and convenience food, less physical activity levels due to transport links, and less social activities. The authors also state this and the fact participants tended to be older,” he noted.
Large datasets are used in this investigation, however, which generally increases the reliability of the data, he observed.
But it is also “unclear as to whether the population here was selected for this study or was retrospectively analyzed, which poses reliability issues, as does the selection of the representative sample, as it is not discussed,” he noted.
Ultimately, there is no confirmed evidence of the link, and until further work is done to directly link light exposure and diabetes in humans, “the link will remain an association only,” he concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Higher levels of exposure to outdoor artificial light at night are significantly linked with markers of diabetes and impaired glucose homeostasis, in a new national, cross-sectional study from China.
The results showed a 7% significant increase in diabetes prevalence per quintile exposure to artificial light at night (prevalence ratio, 1.07), report Ruizhi Zheng, PhD, of the Shanghai (China) Jiaotong University School of Medicine, and colleagues. People living in areas with the most exposure to light at night had a 28% higher prevalence of diabetes than those living in places with the lowest exposure (PR, 1.28), the researchers found.
The study was published online in Diabetologia.
Previous animal studies have shown that exposure to light at night may interfere with circadian rhythms and affect glucose homeostasis, the study team note. Other research has demonstrated that chronic exposure to moderate indoor light during sleep elevated the prevalence of diabetes in older adults, compared with those sleeping in a dim setting, the authors add.
“Our findings contribute to the growing literature suggesting that artificial light at night is detrimental to health and demonstrate that artificial light at night may be a potential novel risk factor for diabetes,” they write.
“Considering the coexistence of the diabetes epidemic and the widespread influence of light pollution at night, the positive associations indicate an urgent need for countries and governments to develop effective prevention and intervention policies and to protect people from the adverse health effects of light pollution at night,” the study authors stress.
Gareth Nye, PhD, senior lecturer at the University of Chester, England, agreed that prior research has found an association between metabolic conditions, such as diabetes, and artificial light at night, with most theories as to the cause focusing on the body’s natural circadian cycle.
He said that internal clocks regulate a variety of bodily processes, such as metabolism and hormone synthesis. They also affect sleep patterns by interfering with synthesis of the hormone melatonin, which is essential for sound sleep, Dr. Nye told the UK Science Media Centre.
However, he stressed that much more research is needed before any link can be considered definitive.
Outdoor night light exposure linked to fasting glucose, A1c
The Chinese researchers set out to approximate the relationships between diabetes prevalence and glucose homeostasis with chronic exposure to outdoor light at night.
They assessed 98,658 participants from the China Noncommunicable Disease Surveillance Study across 162 sites. The mean age of participants was 42.7 years. Female participants comprised 49.2% of the study cohort.
Diabetes was defined based on American Diabetes Association criteria. Satellite data were used to determine exposure to outdoor light at night in 2010. The associations between light exposure at night and indicators of glucose homeostasis were investigated.
Prevalence ratios were calculated and adjusted for sex, age, smoking status, education, body mass index, physical activity, household income, family history of diabetes, rural/urban areas, drinking status, and use of lipid-lowering prescription drugs (primarily statins) or antihypertensives.
The findings showed exposure levels to outdoor light at night were positively linked with 2-hour and fasting glucose concentrations, A1c, and insulin resistance (measured using homeostatic model assessment [HOMA]), but negatively related to β-cell function (measured using HOMA).
More research needed
“We advise caution against causal interpretation of the findings and call for further studies involving direct measurement of individual exposure to light at night,” the researchers conclude.
Dr. Nye agreed.
“One issue with this study is that the areas with the highest outdoor artificial light levels are likely to be those in urban areas and bigger cities. It has been known for a long time now that living in an urbanized area increases your risk of obesity through increased access to high-fat and convenience food, less physical activity levels due to transport links, and less social activities. The authors also state this and the fact participants tended to be older,” he noted.
Large datasets are used in this investigation, however, which generally increases the reliability of the data, he observed.
But it is also “unclear as to whether the population here was selected for this study or was retrospectively analyzed, which poses reliability issues, as does the selection of the representative sample, as it is not discussed,” he noted.
Ultimately, there is no confirmed evidence of the link, and until further work is done to directly link light exposure and diabetes in humans, “the link will remain an association only,” he concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Higher levels of exposure to outdoor artificial light at night are significantly linked with markers of diabetes and impaired glucose homeostasis, in a new national, cross-sectional study from China.
The results showed a 7% significant increase in diabetes prevalence per quintile exposure to artificial light at night (prevalence ratio, 1.07), report Ruizhi Zheng, PhD, of the Shanghai (China) Jiaotong University School of Medicine, and colleagues. People living in areas with the most exposure to light at night had a 28% higher prevalence of diabetes than those living in places with the lowest exposure (PR, 1.28), the researchers found.
The study was published online in Diabetologia.
Previous animal studies have shown that exposure to light at night may interfere with circadian rhythms and affect glucose homeostasis, the study team note. Other research has demonstrated that chronic exposure to moderate indoor light during sleep elevated the prevalence of diabetes in older adults, compared with those sleeping in a dim setting, the authors add.
“Our findings contribute to the growing literature suggesting that artificial light at night is detrimental to health and demonstrate that artificial light at night may be a potential novel risk factor for diabetes,” they write.
“Considering the coexistence of the diabetes epidemic and the widespread influence of light pollution at night, the positive associations indicate an urgent need for countries and governments to develop effective prevention and intervention policies and to protect people from the adverse health effects of light pollution at night,” the study authors stress.
Gareth Nye, PhD, senior lecturer at the University of Chester, England, agreed that prior research has found an association between metabolic conditions, such as diabetes, and artificial light at night, with most theories as to the cause focusing on the body’s natural circadian cycle.
He said that internal clocks regulate a variety of bodily processes, such as metabolism and hormone synthesis. They also affect sleep patterns by interfering with synthesis of the hormone melatonin, which is essential for sound sleep, Dr. Nye told the UK Science Media Centre.
However, he stressed that much more research is needed before any link can be considered definitive.
Outdoor night light exposure linked to fasting glucose, A1c
The Chinese researchers set out to approximate the relationships between diabetes prevalence and glucose homeostasis with chronic exposure to outdoor light at night.
They assessed 98,658 participants from the China Noncommunicable Disease Surveillance Study across 162 sites. The mean age of participants was 42.7 years. Female participants comprised 49.2% of the study cohort.
Diabetes was defined based on American Diabetes Association criteria. Satellite data were used to determine exposure to outdoor light at night in 2010. The associations between light exposure at night and indicators of glucose homeostasis were investigated.
Prevalence ratios were calculated and adjusted for sex, age, smoking status, education, body mass index, physical activity, household income, family history of diabetes, rural/urban areas, drinking status, and use of lipid-lowering prescription drugs (primarily statins) or antihypertensives.
The findings showed exposure levels to outdoor light at night were positively linked with 2-hour and fasting glucose concentrations, A1c, and insulin resistance (measured using homeostatic model assessment [HOMA]), but negatively related to β-cell function (measured using HOMA).
More research needed
“We advise caution against causal interpretation of the findings and call for further studies involving direct measurement of individual exposure to light at night,” the researchers conclude.
Dr. Nye agreed.
“One issue with this study is that the areas with the highest outdoor artificial light levels are likely to be those in urban areas and bigger cities. It has been known for a long time now that living in an urbanized area increases your risk of obesity through increased access to high-fat and convenience food, less physical activity levels due to transport links, and less social activities. The authors also state this and the fact participants tended to be older,” he noted.
Large datasets are used in this investigation, however, which generally increases the reliability of the data, he observed.
But it is also “unclear as to whether the population here was selected for this study or was retrospectively analyzed, which poses reliability issues, as does the selection of the representative sample, as it is not discussed,” he noted.
Ultimately, there is no confirmed evidence of the link, and until further work is done to directly link light exposure and diabetes in humans, “the link will remain an association only,” he concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New recommendations for hyperglycemia management
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik. Today we’re going to talk about the consensus report by the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes on the management of hyperglycemia.
After lifestyle modifications, metformin is no longer the go-to drug for every patient in the management of hyperglycemia. It is recommended that we assess each patient’s personal characteristics in deciding what medication to prescribe. For patients at high cardiorenal risk, refer to the left side of the algorithm and to the right side for all other patients.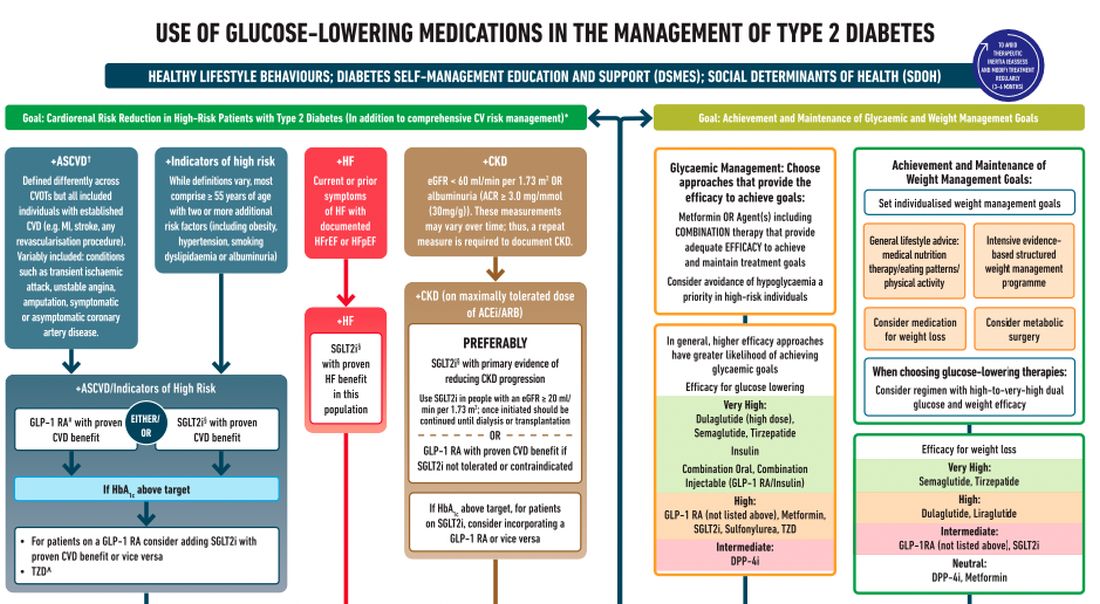
Cardiovascular disease. First, assess whether the patient is at high risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) or already has ASCVD. How is ASCVD defined? Either coronary artery disease (a history of a myocardial infarction [MI] or coronary disease), peripheral vascular disease, stroke, or transient ischemic attack.
What is high risk for ASCVD? Diabetes in someone older than 55 years with two or more additional risk factors. If the patient is at high risk for or has existing ASCVD then it is recommended to prescribe a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonist with proven CVD benefit or an sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor with proven CVD benefit.
For patients at very high risk for ASCVD, it might be reasonable to combine both agents. The recommendation to use these agents holds true whether the patients are at their A1c goals or not. The patient doesn’t need to be on metformin to benefit from these agents. The patient with reduced or preserved ejection fraction heart failure should be taking an SGLT-2 inhibitor.
Chronic kidney disease. Next up, chronic kidney disease (CKD). CKD is defined by an estimated glomerular filtration rate < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or a urine albumin to creatinine ratio > 30. In that case, the patient should be preferentially on an SGLT-2 inhibitor. Patients not able to take an SGLT-2 for some reason should be prescribed a GLP-1 receptor agonist.
If someone doesn’t fit into that high cardiorenal risk category, then we go to the right side of the algorithm. The goal then is achievement and maintenance of glycemic and weight management goals.
Glycemic management. In choosing medicine for glycemic management, metformin is a reasonable choice. You may need to add another agent to metformin to reach the patient’s glycemic goal. If the patient is far away from goal, then a medication with higher efficacy at lowering glucose might be chosen.
Efficacy is listed as:
- Very high efficacy for glucose lowering: dulaglutide at a high dose, semaglutide, tirzepatide, insulin, or combination injectable agents (GLP-1 receptor agonist/insulin combinations).
- High glucose-lowering efficacy: a GLP-1 receptor agonist not already mentioned, metformin, SGLT-2 inhibitors, sulfonylureas, thiazolidinediones.
- Intermediate glucose lowering efficacy: dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors.
Weight management. For weight management, lifestyle modification (diet and exercise) is important. If lifestyle modification alone is insufficient, consider either a medication that specifically helps with weight management or metabolic surgery.
We particularly want to focus on weight management in patients who have complications from obesity. What would those complications be? Sleep apnea, hip or knee pain from arthritis, back pain – that is, biomechanical complications of obesity or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Medications for weight loss are listed by degree of efficacy:
- Very high efficacy for weight loss: semaglutide, tirzepatide.
- High efficacy for weight loss: dulaglutide and liraglutide.
- Intermediate for weight loss: GLP-1 receptor agonist (not listed above), SGLT-2 inhibitor.
- Neutral for weight loss: DPP-4 inhibitors and metformin.
Where does insulin fit in? If patients present with a very high A1c, if they are on other medications and their A1c is still not to goal, or if they are catabolic and losing weight because of their diabetes, then insulin has an important place in management.
These are incredibly important guidelines that provide a clear algorithm for a personalized approach to diabetes management.
Dr. Skolnik is professor, department of family medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director, department of family medicine, Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. He reported conflicts of interest with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Bayer. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik. Today we’re going to talk about the consensus report by the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes on the management of hyperglycemia.
After lifestyle modifications, metformin is no longer the go-to drug for every patient in the management of hyperglycemia. It is recommended that we assess each patient’s personal characteristics in deciding what medication to prescribe. For patients at high cardiorenal risk, refer to the left side of the algorithm and to the right side for all other patients.
Cardiovascular disease. First, assess whether the patient is at high risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) or already has ASCVD. How is ASCVD defined? Either coronary artery disease (a history of a myocardial infarction [MI] or coronary disease), peripheral vascular disease, stroke, or transient ischemic attack.
What is high risk for ASCVD? Diabetes in someone older than 55 years with two or more additional risk factors. If the patient is at high risk for or has existing ASCVD then it is recommended to prescribe a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonist with proven CVD benefit or an sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor with proven CVD benefit.
For patients at very high risk for ASCVD, it might be reasonable to combine both agents. The recommendation to use these agents holds true whether the patients are at their A1c goals or not. The patient doesn’t need to be on metformin to benefit from these agents. The patient with reduced or preserved ejection fraction heart failure should be taking an SGLT-2 inhibitor.
Chronic kidney disease. Next up, chronic kidney disease (CKD). CKD is defined by an estimated glomerular filtration rate < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or a urine albumin to creatinine ratio > 30. In that case, the patient should be preferentially on an SGLT-2 inhibitor. Patients not able to take an SGLT-2 for some reason should be prescribed a GLP-1 receptor agonist.
If someone doesn’t fit into that high cardiorenal risk category, then we go to the right side of the algorithm. The goal then is achievement and maintenance of glycemic and weight management goals.
Glycemic management. In choosing medicine for glycemic management, metformin is a reasonable choice. You may need to add another agent to metformin to reach the patient’s glycemic goal. If the patient is far away from goal, then a medication with higher efficacy at lowering glucose might be chosen.
Efficacy is listed as:
- Very high efficacy for glucose lowering: dulaglutide at a high dose, semaglutide, tirzepatide, insulin, or combination injectable agents (GLP-1 receptor agonist/insulin combinations).
- High glucose-lowering efficacy: a GLP-1 receptor agonist not already mentioned, metformin, SGLT-2 inhibitors, sulfonylureas, thiazolidinediones.
- Intermediate glucose lowering efficacy: dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors.
Weight management. For weight management, lifestyle modification (diet and exercise) is important. If lifestyle modification alone is insufficient, consider either a medication that specifically helps with weight management or metabolic surgery.
We particularly want to focus on weight management in patients who have complications from obesity. What would those complications be? Sleep apnea, hip or knee pain from arthritis, back pain – that is, biomechanical complications of obesity or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Medications for weight loss are listed by degree of efficacy:
- Very high efficacy for weight loss: semaglutide, tirzepatide.
- High efficacy for weight loss: dulaglutide and liraglutide.
- Intermediate for weight loss: GLP-1 receptor agonist (not listed above), SGLT-2 inhibitor.
- Neutral for weight loss: DPP-4 inhibitors and metformin.
Where does insulin fit in? If patients present with a very high A1c, if they are on other medications and their A1c is still not to goal, or if they are catabolic and losing weight because of their diabetes, then insulin has an important place in management.
These are incredibly important guidelines that provide a clear algorithm for a personalized approach to diabetes management.
Dr. Skolnik is professor, department of family medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director, department of family medicine, Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. He reported conflicts of interest with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Bayer. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik. Today we’re going to talk about the consensus report by the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes on the management of hyperglycemia.
After lifestyle modifications, metformin is no longer the go-to drug for every patient in the management of hyperglycemia. It is recommended that we assess each patient’s personal characteristics in deciding what medication to prescribe. For patients at high cardiorenal risk, refer to the left side of the algorithm and to the right side for all other patients.
Cardiovascular disease. First, assess whether the patient is at high risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) or already has ASCVD. How is ASCVD defined? Either coronary artery disease (a history of a myocardial infarction [MI] or coronary disease), peripheral vascular disease, stroke, or transient ischemic attack.
What is high risk for ASCVD? Diabetes in someone older than 55 years with two or more additional risk factors. If the patient is at high risk for or has existing ASCVD then it is recommended to prescribe a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonist with proven CVD benefit or an sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor with proven CVD benefit.
For patients at very high risk for ASCVD, it might be reasonable to combine both agents. The recommendation to use these agents holds true whether the patients are at their A1c goals or not. The patient doesn’t need to be on metformin to benefit from these agents. The patient with reduced or preserved ejection fraction heart failure should be taking an SGLT-2 inhibitor.
Chronic kidney disease. Next up, chronic kidney disease (CKD). CKD is defined by an estimated glomerular filtration rate < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or a urine albumin to creatinine ratio > 30. In that case, the patient should be preferentially on an SGLT-2 inhibitor. Patients not able to take an SGLT-2 for some reason should be prescribed a GLP-1 receptor agonist.
If someone doesn’t fit into that high cardiorenal risk category, then we go to the right side of the algorithm. The goal then is achievement and maintenance of glycemic and weight management goals.
Glycemic management. In choosing medicine for glycemic management, metformin is a reasonable choice. You may need to add another agent to metformin to reach the patient’s glycemic goal. If the patient is far away from goal, then a medication with higher efficacy at lowering glucose might be chosen.
Efficacy is listed as:
- Very high efficacy for glucose lowering: dulaglutide at a high dose, semaglutide, tirzepatide, insulin, or combination injectable agents (GLP-1 receptor agonist/insulin combinations).
- High glucose-lowering efficacy: a GLP-1 receptor agonist not already mentioned, metformin, SGLT-2 inhibitors, sulfonylureas, thiazolidinediones.
- Intermediate glucose lowering efficacy: dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors.
Weight management. For weight management, lifestyle modification (diet and exercise) is important. If lifestyle modification alone is insufficient, consider either a medication that specifically helps with weight management or metabolic surgery.
We particularly want to focus on weight management in patients who have complications from obesity. What would those complications be? Sleep apnea, hip or knee pain from arthritis, back pain – that is, biomechanical complications of obesity or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Medications for weight loss are listed by degree of efficacy:
- Very high efficacy for weight loss: semaglutide, tirzepatide.
- High efficacy for weight loss: dulaglutide and liraglutide.
- Intermediate for weight loss: GLP-1 receptor agonist (not listed above), SGLT-2 inhibitor.
- Neutral for weight loss: DPP-4 inhibitors and metformin.
Where does insulin fit in? If patients present with a very high A1c, if they are on other medications and their A1c is still not to goal, or if they are catabolic and losing weight because of their diabetes, then insulin has an important place in management.
These are incredibly important guidelines that provide a clear algorithm for a personalized approach to diabetes management.
Dr. Skolnik is professor, department of family medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director, department of family medicine, Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. He reported conflicts of interest with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Bayer. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients complain some obesity care startups offer pills, and not much else
Many Americans turn to the latest big idea to lose weight – fad diets, fitness crazes, dodgy herbs and pills, bariatric surgery, just to name a few. They’re rarely the magic solution people dream of.
Now a wave of startups offer access to a new category of drugs coupled with intensive behavioral coaching online. But already concerns are emerging.
These startups, spurred by hundreds of millions of dollars in funding from blue-chip venture capital firms, have signed up well over 100,000 patients and could reach millions more. These patients pay hundreds, if not thousands, of dollars to access new drugs, called glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) agonists, along with online coaching to encourage healthy habits.
The startups initially positioned themselves in lofty terms. “This is the last weight-loss program you’ll try,” said a 2020 marketing analysis by startup Calibrate Health, in messaging designed to reach one of its target demographics, the “working mom.” (Company spokesperson Michelle Wellington said the document does not reflect Calibrate’s current marketing strategy.)
But while doctors and patients are intrigued by the new model, some customers complain online that reality is short of the buildup: They say they got canned advice and unresponsive clinicians – and some report they couldn’t get the newest drugs.
Calibrate Health, a New York City–based startup, reported earlier in 2022 it had served 20,000 people. Another startup, Found, headquartered in San Francisco, has served 135,000 patients since July 2020, CEO Sarah Jones Simmer said in an interview. Calibrate costs patients nearly $1,600 a year, not counting the price of drugs, which can hit nearly $1,500 monthly without insurance, according to drug price savings site GoodRx. (Insurers reimburse for GLP-1agonists in limited circumstances, patients said.) Found offers a 6-month plan for nearly $600, a company spokesperson said. (That price includes generic drugs, but not the newer GLP-1 agonists, like Wegovy.)
The two companies are beneficiaries of over $200 million in combined venture funding, according to tracking by Crunchbase, a repository of venture capital investments. The firms say they’re on the vanguard of weight care, both citing the influence of biology and other scientific factors as key ingredients to their approaches.
There’s potentially a big market for these startups. Just over 4 in 10 Americans are obese, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, driving up their risk for cardiovascular conditions and type 2 diabetes. Effective medical treatments are elusive and hard to access.
Centers that provide this specialty care “are overwhelmed,” said Fatima Stanford, MD, an obesity medicine specialist at Massachusetts General in Boston, a teaching hospital affiliated with Harvard. Her own clinic has a wait list of 3,000.
Dr. Stanford, who said she has advised several of these telemedicine startups, is bullish on their potential.
Scott Butsch, MD, director of obesity medicine at the Cleveland Clinic, said the startups can offer care with less judgment and stigma than in-person peers. They’re also more convenient.
Dr. Butsch, who learned about the model through consultancies, patients, and colleagues, wonders whether the startups are operating “to strategically find which patients respond to which drug.” He said they should coordinate well with behavioral specialists, as antidepressants or other medications may be driving weight gain. “Obesity is a complex disease and requires treatments that match its complexity. I think programs that do not have a multidisciplinary team are less comprehensive and, in the long term, less effective.”
The startups market a two-pronged product: first, the new class of GLP-1 agonists. While these medications are effective at provoking weight loss, Wegovy, one of two in this class specifically approved for this purpose, is in short supply because of manufacturing difficulties, according to its maker, Novo Nordisk. Others in the category can be prescribed off label. But doctors generally aren’t familiar with the medications, Stanford said. In theory, the startups can bridge some of those gaps: They offer more specialized, knowledgeable clinicians.
Then there’s the other prong: behavioral changes. The companies use televisits and online messaging with nutritionists or coaches to help patients incorporate new diet and exercise habits. The weight loss figures achieved by participants in clinical trials for the new drugs – up to 15% of body mass – were tied to such changes, according to Novo Nordisk.
Social media sites are bursting with these startups’ ads, everywhere from podcasts to Instagram. A search of Meta’s ad library finds 40,000 ads on Facebook and Instagram between the two firms.
The ads complement people’s own postings on social media: Numerous Facebook groups are devoted to the new type of drugs – some even focused on helping patients manage side effects, like changes in their bowel movements. The buzz is quantifiable: On TikTok, mentions of the new GLP-1 agonists tripled from last June to this June, according to an analysis by investment bankers at Morgan Stanley.
There’s now a feverish, expectant appetite for these medications among the startups’ clientele. Patients often complained that their friends had obtained a drug they weren’t offered, recalled Alexandra Coults, a former pharmacist consultant for Found. Ms. Coults said patients may have perceived some sort of bait-and-switch when in reality clinical reasons – like drug contraindications – guide prescribing decisions.
Patient expectations influence care, Ms. Coults said. Customers came in with ideas shaped by the culture of fad diets and New Year’s resolutions. “Quite a few people would sign up for 1 month and not continue.”
In interviews with KHN and in online complaints, patients also questioned the quality of care they received. Some said intake – which began by filling out a form and proceeded to an online visit with a doctor – was perfunctory. Once medication began, they said, requests for counseling about side effects were slow to be answered.
Jess Garrant, a Found patient, recalled that after she was prescribed zonisamide, a generic anticonvulsant that has shown some ability to help with weight loss, she felt “absolutely weird.”
“I was up all night and my thoughts were racing,” she wrote in a blog post. She developed sores in her mouth.
She sought advice and help from Found physicians, but their replies “weren’t quick.” Nonemergency communications are routed through the company’s portal.
It took a week to complete a switch of medications and have a new prescription arrive at her home, she said. Meanwhile, she said, she went to an urgent care clinic for the mouth sores.
Found frequently prescribes generic medications – often off label – rather than just the new GLP-1 agonists, company executives said in an interview. Found said older generics like zonisamide are more accessible than the GLP-1 agonists advertised on social media and their own website. Both Dr. Butsch and Dr. Stanford said they’ve prescribed zonisamide successfully. Dr. Butsch said ramping up dosage rapidly can increase the risk of side effects.
But Kim Boyd, MD, chief medical officer of competitor Calibrate, said the older drugs “just haven’t worked.”
Patients of both companies have critiqued online and in interviews the startups’ behavioral care – which experts across the board maintain is integral to successful weight loss treatment. But some patients felt they simply had canned advice.
Other patients said they had ups and downs with their coaches. Dana Crom, an attorney, said she had gone through many coaches with Calibrate. Some were good, effective cheerleaders; others, not so good. But when kinks in the program arose, she said, the coach wasn’t able to help her navigate them. While the coach can report trouble with medications or the app, it appears those reports are no more effective than messages sent through the portal, Ms. Crom said.
And what about when her yearlong subscription ends? Ms. Crom said she’d consider continuing with Calibrate.
Relationships with coaches, given the need to change behavior, are a critical element of the business models. Patients’ results depend “on how adherent they are to lifestyle changes,” said Found’s chief medical officer, Rehka Kumar, MD.
While the startups offer care to a larger geographic footprint, it’s not clear whether the demographics of their patient populations are different from those of the traditional bricks-and-mortar model. Calibrate’s patients are overwhelmingly White; over 8 in 10 have at least an undergraduate degree; and over 8 in 10 are women, according to the company.
And its earlier marketing strategies reflected that. The September 2020 “segmentation” document laid out three types of customers the company could hope to attract: perimenopausal or menopausal women, with income ranging from $75,000 to $150,000 a year; working mothers, with a similar income; and “men.”
Isabelle Kenyon, Calibrate’s CEO, said the company now hopes to expand its reach to partner with large employers, and that will help diversify its patients.
Patients will need to be convinced that the model – more affordable, more accessible – works for them. For her part, Ms. Garrant, who no longer is using Found, reflected on her experience, writing in her blog post that she was hoping for more follow-up and a more personal approach. “I don’t think it’s a helpful way to lose weight,” she said.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Many Americans turn to the latest big idea to lose weight – fad diets, fitness crazes, dodgy herbs and pills, bariatric surgery, just to name a few. They’re rarely the magic solution people dream of.
Now a wave of startups offer access to a new category of drugs coupled with intensive behavioral coaching online. But already concerns are emerging.
These startups, spurred by hundreds of millions of dollars in funding from blue-chip venture capital firms, have signed up well over 100,000 patients and could reach millions more. These patients pay hundreds, if not thousands, of dollars to access new drugs, called glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) agonists, along with online coaching to encourage healthy habits.
The startups initially positioned themselves in lofty terms. “This is the last weight-loss program you’ll try,” said a 2020 marketing analysis by startup Calibrate Health, in messaging designed to reach one of its target demographics, the “working mom.” (Company spokesperson Michelle Wellington said the document does not reflect Calibrate’s current marketing strategy.)
But while doctors and patients are intrigued by the new model, some customers complain online that reality is short of the buildup: They say they got canned advice and unresponsive clinicians – and some report they couldn’t get the newest drugs.
Calibrate Health, a New York City–based startup, reported earlier in 2022 it had served 20,000 people. Another startup, Found, headquartered in San Francisco, has served 135,000 patients since July 2020, CEO Sarah Jones Simmer said in an interview. Calibrate costs patients nearly $1,600 a year, not counting the price of drugs, which can hit nearly $1,500 monthly without insurance, according to drug price savings site GoodRx. (Insurers reimburse for GLP-1agonists in limited circumstances, patients said.) Found offers a 6-month plan for nearly $600, a company spokesperson said. (That price includes generic drugs, but not the newer GLP-1 agonists, like Wegovy.)
The two companies are beneficiaries of over $200 million in combined venture funding, according to tracking by Crunchbase, a repository of venture capital investments. The firms say they’re on the vanguard of weight care, both citing the influence of biology and other scientific factors as key ingredients to their approaches.
There’s potentially a big market for these startups. Just over 4 in 10 Americans are obese, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, driving up their risk for cardiovascular conditions and type 2 diabetes. Effective medical treatments are elusive and hard to access.
Centers that provide this specialty care “are overwhelmed,” said Fatima Stanford, MD, an obesity medicine specialist at Massachusetts General in Boston, a teaching hospital affiliated with Harvard. Her own clinic has a wait list of 3,000.
Dr. Stanford, who said she has advised several of these telemedicine startups, is bullish on their potential.
Scott Butsch, MD, director of obesity medicine at the Cleveland Clinic, said the startups can offer care with less judgment and stigma than in-person peers. They’re also more convenient.
Dr. Butsch, who learned about the model through consultancies, patients, and colleagues, wonders whether the startups are operating “to strategically find which patients respond to which drug.” He said they should coordinate well with behavioral specialists, as antidepressants or other medications may be driving weight gain. “Obesity is a complex disease and requires treatments that match its complexity. I think programs that do not have a multidisciplinary team are less comprehensive and, in the long term, less effective.”
The startups market a two-pronged product: first, the new class of GLP-1 agonists. While these medications are effective at provoking weight loss, Wegovy, one of two in this class specifically approved for this purpose, is in short supply because of manufacturing difficulties, according to its maker, Novo Nordisk. Others in the category can be prescribed off label. But doctors generally aren’t familiar with the medications, Stanford said. In theory, the startups can bridge some of those gaps: They offer more specialized, knowledgeable clinicians.
Then there’s the other prong: behavioral changes. The companies use televisits and online messaging with nutritionists or coaches to help patients incorporate new diet and exercise habits. The weight loss figures achieved by participants in clinical trials for the new drugs – up to 15% of body mass – were tied to such changes, according to Novo Nordisk.
Social media sites are bursting with these startups’ ads, everywhere from podcasts to Instagram. A search of Meta’s ad library finds 40,000 ads on Facebook and Instagram between the two firms.
The ads complement people’s own postings on social media: Numerous Facebook groups are devoted to the new type of drugs – some even focused on helping patients manage side effects, like changes in their bowel movements. The buzz is quantifiable: On TikTok, mentions of the new GLP-1 agonists tripled from last June to this June, according to an analysis by investment bankers at Morgan Stanley.
There’s now a feverish, expectant appetite for these medications among the startups’ clientele. Patients often complained that their friends had obtained a drug they weren’t offered, recalled Alexandra Coults, a former pharmacist consultant for Found. Ms. Coults said patients may have perceived some sort of bait-and-switch when in reality clinical reasons – like drug contraindications – guide prescribing decisions.
Patient expectations influence care, Ms. Coults said. Customers came in with ideas shaped by the culture of fad diets and New Year’s resolutions. “Quite a few people would sign up for 1 month and not continue.”
In interviews with KHN and in online complaints, patients also questioned the quality of care they received. Some said intake – which began by filling out a form and proceeded to an online visit with a doctor – was perfunctory. Once medication began, they said, requests for counseling about side effects were slow to be answered.
Jess Garrant, a Found patient, recalled that after she was prescribed zonisamide, a generic anticonvulsant that has shown some ability to help with weight loss, she felt “absolutely weird.”
“I was up all night and my thoughts were racing,” she wrote in a blog post. She developed sores in her mouth.
She sought advice and help from Found physicians, but their replies “weren’t quick.” Nonemergency communications are routed through the company’s portal.
It took a week to complete a switch of medications and have a new prescription arrive at her home, she said. Meanwhile, she said, she went to an urgent care clinic for the mouth sores.
Found frequently prescribes generic medications – often off label – rather than just the new GLP-1 agonists, company executives said in an interview. Found said older generics like zonisamide are more accessible than the GLP-1 agonists advertised on social media and their own website. Both Dr. Butsch and Dr. Stanford said they’ve prescribed zonisamide successfully. Dr. Butsch said ramping up dosage rapidly can increase the risk of side effects.
But Kim Boyd, MD, chief medical officer of competitor Calibrate, said the older drugs “just haven’t worked.”
Patients of both companies have critiqued online and in interviews the startups’ behavioral care – which experts across the board maintain is integral to successful weight loss treatment. But some patients felt they simply had canned advice.
Other patients said they had ups and downs with their coaches. Dana Crom, an attorney, said she had gone through many coaches with Calibrate. Some were good, effective cheerleaders; others, not so good. But when kinks in the program arose, she said, the coach wasn’t able to help her navigate them. While the coach can report trouble with medications or the app, it appears those reports are no more effective than messages sent through the portal, Ms. Crom said.
And what about when her yearlong subscription ends? Ms. Crom said she’d consider continuing with Calibrate.
Relationships with coaches, given the need to change behavior, are a critical element of the business models. Patients’ results depend “on how adherent they are to lifestyle changes,” said Found’s chief medical officer, Rehka Kumar, MD.
While the startups offer care to a larger geographic footprint, it’s not clear whether the demographics of their patient populations are different from those of the traditional bricks-and-mortar model. Calibrate’s patients are overwhelmingly White; over 8 in 10 have at least an undergraduate degree; and over 8 in 10 are women, according to the company.
And its earlier marketing strategies reflected that. The September 2020 “segmentation” document laid out three types of customers the company could hope to attract: perimenopausal or menopausal women, with income ranging from $75,000 to $150,000 a year; working mothers, with a similar income; and “men.”
Isabelle Kenyon, Calibrate’s CEO, said the company now hopes to expand its reach to partner with large employers, and that will help diversify its patients.
Patients will need to be convinced that the model – more affordable, more accessible – works for them. For her part, Ms. Garrant, who no longer is using Found, reflected on her experience, writing in her blog post that she was hoping for more follow-up and a more personal approach. “I don’t think it’s a helpful way to lose weight,” she said.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Many Americans turn to the latest big idea to lose weight – fad diets, fitness crazes, dodgy herbs and pills, bariatric surgery, just to name a few. They’re rarely the magic solution people dream of.
Now a wave of startups offer access to a new category of drugs coupled with intensive behavioral coaching online. But already concerns are emerging.
These startups, spurred by hundreds of millions of dollars in funding from blue-chip venture capital firms, have signed up well over 100,000 patients and could reach millions more. These patients pay hundreds, if not thousands, of dollars to access new drugs, called glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) agonists, along with online coaching to encourage healthy habits.
The startups initially positioned themselves in lofty terms. “This is the last weight-loss program you’ll try,” said a 2020 marketing analysis by startup Calibrate Health, in messaging designed to reach one of its target demographics, the “working mom.” (Company spokesperson Michelle Wellington said the document does not reflect Calibrate’s current marketing strategy.)
But while doctors and patients are intrigued by the new model, some customers complain online that reality is short of the buildup: They say they got canned advice and unresponsive clinicians – and some report they couldn’t get the newest drugs.
Calibrate Health, a New York City–based startup, reported earlier in 2022 it had served 20,000 people. Another startup, Found, headquartered in San Francisco, has served 135,000 patients since July 2020, CEO Sarah Jones Simmer said in an interview. Calibrate costs patients nearly $1,600 a year, not counting the price of drugs, which can hit nearly $1,500 monthly without insurance, according to drug price savings site GoodRx. (Insurers reimburse for GLP-1agonists in limited circumstances, patients said.) Found offers a 6-month plan for nearly $600, a company spokesperson said. (That price includes generic drugs, but not the newer GLP-1 agonists, like Wegovy.)
The two companies are beneficiaries of over $200 million in combined venture funding, according to tracking by Crunchbase, a repository of venture capital investments. The firms say they’re on the vanguard of weight care, both citing the influence of biology and other scientific factors as key ingredients to their approaches.
There’s potentially a big market for these startups. Just over 4 in 10 Americans are obese, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, driving up their risk for cardiovascular conditions and type 2 diabetes. Effective medical treatments are elusive and hard to access.
Centers that provide this specialty care “are overwhelmed,” said Fatima Stanford, MD, an obesity medicine specialist at Massachusetts General in Boston, a teaching hospital affiliated with Harvard. Her own clinic has a wait list of 3,000.
Dr. Stanford, who said she has advised several of these telemedicine startups, is bullish on their potential.
Scott Butsch, MD, director of obesity medicine at the Cleveland Clinic, said the startups can offer care with less judgment and stigma than in-person peers. They’re also more convenient.
Dr. Butsch, who learned about the model through consultancies, patients, and colleagues, wonders whether the startups are operating “to strategically find which patients respond to which drug.” He said they should coordinate well with behavioral specialists, as antidepressants or other medications may be driving weight gain. “Obesity is a complex disease and requires treatments that match its complexity. I think programs that do not have a multidisciplinary team are less comprehensive and, in the long term, less effective.”
The startups market a two-pronged product: first, the new class of GLP-1 agonists. While these medications are effective at provoking weight loss, Wegovy, one of two in this class specifically approved for this purpose, is in short supply because of manufacturing difficulties, according to its maker, Novo Nordisk. Others in the category can be prescribed off label. But doctors generally aren’t familiar with the medications, Stanford said. In theory, the startups can bridge some of those gaps: They offer more specialized, knowledgeable clinicians.
Then there’s the other prong: behavioral changes. The companies use televisits and online messaging with nutritionists or coaches to help patients incorporate new diet and exercise habits. The weight loss figures achieved by participants in clinical trials for the new drugs – up to 15% of body mass – were tied to such changes, according to Novo Nordisk.
Social media sites are bursting with these startups’ ads, everywhere from podcasts to Instagram. A search of Meta’s ad library finds 40,000 ads on Facebook and Instagram between the two firms.
The ads complement people’s own postings on social media: Numerous Facebook groups are devoted to the new type of drugs – some even focused on helping patients manage side effects, like changes in their bowel movements. The buzz is quantifiable: On TikTok, mentions of the new GLP-1 agonists tripled from last June to this June, according to an analysis by investment bankers at Morgan Stanley.
There’s now a feverish, expectant appetite for these medications among the startups’ clientele. Patients often complained that their friends had obtained a drug they weren’t offered, recalled Alexandra Coults, a former pharmacist consultant for Found. Ms. Coults said patients may have perceived some sort of bait-and-switch when in reality clinical reasons – like drug contraindications – guide prescribing decisions.
Patient expectations influence care, Ms. Coults said. Customers came in with ideas shaped by the culture of fad diets and New Year’s resolutions. “Quite a few people would sign up for 1 month and not continue.”
In interviews with KHN and in online complaints, patients also questioned the quality of care they received. Some said intake – which began by filling out a form and proceeded to an online visit with a doctor – was perfunctory. Once medication began, they said, requests for counseling about side effects were slow to be answered.
Jess Garrant, a Found patient, recalled that after she was prescribed zonisamide, a generic anticonvulsant that has shown some ability to help with weight loss, she felt “absolutely weird.”
“I was up all night and my thoughts were racing,” she wrote in a blog post. She developed sores in her mouth.
She sought advice and help from Found physicians, but their replies “weren’t quick.” Nonemergency communications are routed through the company’s portal.
It took a week to complete a switch of medications and have a new prescription arrive at her home, she said. Meanwhile, she said, she went to an urgent care clinic for the mouth sores.
Found frequently prescribes generic medications – often off label – rather than just the new GLP-1 agonists, company executives said in an interview. Found said older generics like zonisamide are more accessible than the GLP-1 agonists advertised on social media and their own website. Both Dr. Butsch and Dr. Stanford said they’ve prescribed zonisamide successfully. Dr. Butsch said ramping up dosage rapidly can increase the risk of side effects.
But Kim Boyd, MD, chief medical officer of competitor Calibrate, said the older drugs “just haven’t worked.”
Patients of both companies have critiqued online and in interviews the startups’ behavioral care – which experts across the board maintain is integral to successful weight loss treatment. But some patients felt they simply had canned advice.
Other patients said they had ups and downs with their coaches. Dana Crom, an attorney, said she had gone through many coaches with Calibrate. Some were good, effective cheerleaders; others, not so good. But when kinks in the program arose, she said, the coach wasn’t able to help her navigate them. While the coach can report trouble with medications or the app, it appears those reports are no more effective than messages sent through the portal, Ms. Crom said.
And what about when her yearlong subscription ends? Ms. Crom said she’d consider continuing with Calibrate.
Relationships with coaches, given the need to change behavior, are a critical element of the business models. Patients’ results depend “on how adherent they are to lifestyle changes,” said Found’s chief medical officer, Rehka Kumar, MD.
While the startups offer care to a larger geographic footprint, it’s not clear whether the demographics of their patient populations are different from those of the traditional bricks-and-mortar model. Calibrate’s patients are overwhelmingly White; over 8 in 10 have at least an undergraduate degree; and over 8 in 10 are women, according to the company.
And its earlier marketing strategies reflected that. The September 2020 “segmentation” document laid out three types of customers the company could hope to attract: perimenopausal or menopausal women, with income ranging from $75,000 to $150,000 a year; working mothers, with a similar income; and “men.”
Isabelle Kenyon, Calibrate’s CEO, said the company now hopes to expand its reach to partner with large employers, and that will help diversify its patients.
Patients will need to be convinced that the model – more affordable, more accessible – works for them. For her part, Ms. Garrant, who no longer is using Found, reflected on her experience, writing in her blog post that she was hoping for more follow-up and a more personal approach. “I don’t think it’s a helpful way to lose weight,” she said.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
‘Key cause’ of type 2 diabetes identified
Understanding of the key mechanisms underlying the progression of type 2 diabetes has been advanced by new research from Oxford (England) University suggesting potential ways to “slow the seemingly inexorable decline in beta-cell function in T2D”.
The study in mice elucidated a “key cause” of T2D by showing that
Scientists already knew that chronic hyperglycemia leads to a progressive decline in beta-cell function and, conversely, that the failure of pancreatic beta-cells to produce insulin results in chronically elevated blood glucose. However, the exact cause of beta-cell failure in T2D has remained unclear. T2D typically presents in later adult life, and by the time of diagnosis as much as 50% of beta-cell function has been lost.
In the United Kingdom there are nearly 5 million people diagnosed with T2D, which costs the National Health Service some £10 billion annually.
Glucose metabolites, rather than glucose itself, drives failure of cells to release insulin
The new study, published in Nature Communications, used both an animal model of diabetes and in vitro culture of beta-cells in a high glucose medium. In both cases the researchers showed, for the first time, that it is glucose metabolites, rather than glucose itself, that drives the failure of beta-cells to release insulin and is key to the progression of type 2 diabetes.
Senior researcher Frances Ashcroft, PhD, of the department of physiology, anatomy and genetics at the University of Oxford said: “This suggests a potential way in which the decline in beta-cell function in T2D might be slowed or prevented.”
Blood glucose concentration is controlled within narrow limits, the team explained. When it is too low for more than few minutes, consciousness is rapidly lost because the brain is starved of fuel. However chronic elevation of blood glucose leads to the serious complications found in poorly controlled diabetes, such as retinopathy, nephropathy, peripheral neuropathy, and cardiac disease. Insulin, released from pancreatic beta-cells when blood glucose levels rise, is the only hormone that can lower the blood glucose concentration, and insufficient secretion results in diabetes. In T2D, the beta-cells are still present (unlike in T1D), but they have a reduced insulin content and the coupling between glucose and insulin release is impaired.
Vicious spiral of hyperglycemia and beta-cell damage
Previous work by the same team had shown that chronic hyperglycemia damages the ability of the beta-cell to produce insulin and to release it when blood glucose levels rise. This suggested that “prolonged hyperglycemia sets off a vicious spiral in which an increase in blood glucose leads to beta-cell damage and less insulin secretion - which causes an even greater increase in blood glucose and a further decline in beta-cell function,” the team explained.
Lead researcher Elizabeth Haythorne, PhD, said: “We realized that we next needed to understand how glucose damages beta-cell function, so we can think about how we might stop it and so slow the seemingly inexorable decline in beta-cell function in T2D.”
In the new study, they showed that altered glycolysis in T2D occurs, in part, through marked up-regulation of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1), a protein complex involved in control of cell growth, dysregulation of which underlies a variety of human diseases, including diabetes. Up-regulation of mTORC1 led to changes in metabolic gene expression, oxidative phosphorylation and insulin secretion. Furthermore, they demonstrated that reducing the rate at which glucose is metabolized and at which its metabolites build up could prevent the effects of chronic hyperglycemia and the ensuing beta-cell failure.
“High blood glucose levels cause an increased rate of glucose metabolism in the beta-cell, which leads to a metabolic bottleneck and the pooling of upstream metabolites,” the team said. “These metabolites switch off the insulin gene, so less insulin is made, as well as switching off numerous genes involved in metabolism and stimulus-secretion coupling. Consequently, the beta-cells become glucose blind and no longer respond to changes in blood glucose with insulin secretion.”
Blocking metabolic enzyme could maintain insulin secretion
The team attempted to block the first step in glucose metabolism, and therefore prevent the gene changes from taking place, by blocking the enzyme glucokinase, which regulates the process. They found that this could maintain glucose-stimulated insulin secretion even in the presence of chronic hyperglycemia.
“Our results support the idea that progressive impairment of beta-cell metabolism, induced by increasing hyperglycemia, speeds T2D development, and suggest that reducing glycolysis at the level of glucokinase may slow this progression,” they said.
Dr. Ashcroft said: “This is potentially a useful way to try to prevent beta-cell decline in diabetes. Because glucose metabolism normally stimulates insulin secretion, it was previously hypothesized that increasing glucose metabolism would enhance insulin secretion in T2D and glucokinase activators were trialled, with varying results.
“Our data suggests that glucokinase activators could have an adverse effect and, somewhat counter-intuitively, that a glucokinase inhibitor might be a better strategy to treat T2D. Of course, it would be important to reduce glucose flux in T2D to that found in people without diabetes – and no further. But there is a very long way to go before we can tell if this approach would be useful for treating beta-cell decline in T2D.
“In the meantime, the key message from our study if you have type 2 diabetes is that it is important to keep your blood glucose well controlled.”
This study was funded by the UK Medical Research Council, the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council, the John Fell Fund, and the Nuffield Benefaction for Medicine/Wellcome Institutional Strategic Support Fund. The authors declared no competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
Understanding of the key mechanisms underlying the progression of type 2 diabetes has been advanced by new research from Oxford (England) University suggesting potential ways to “slow the seemingly inexorable decline in beta-cell function in T2D”.
The study in mice elucidated a “key cause” of T2D by showing that
Scientists already knew that chronic hyperglycemia leads to a progressive decline in beta-cell function and, conversely, that the failure of pancreatic beta-cells to produce insulin results in chronically elevated blood glucose. However, the exact cause of beta-cell failure in T2D has remained unclear. T2D typically presents in later adult life, and by the time of diagnosis as much as 50% of beta-cell function has been lost.
In the United Kingdom there are nearly 5 million people diagnosed with T2D, which costs the National Health Service some £10 billion annually.
Glucose metabolites, rather than glucose itself, drives failure of cells to release insulin
The new study, published in Nature Communications, used both an animal model of diabetes and in vitro culture of beta-cells in a high glucose medium. In both cases the researchers showed, for the first time, that it is glucose metabolites, rather than glucose itself, that drives the failure of beta-cells to release insulin and is key to the progression of type 2 diabetes.
Senior researcher Frances Ashcroft, PhD, of the department of physiology, anatomy and genetics at the University of Oxford said: “This suggests a potential way in which the decline in beta-cell function in T2D might be slowed or prevented.”
Blood glucose concentration is controlled within narrow limits, the team explained. When it is too low for more than few minutes, consciousness is rapidly lost because the brain is starved of fuel. However chronic elevation of blood glucose leads to the serious complications found in poorly controlled diabetes, such as retinopathy, nephropathy, peripheral neuropathy, and cardiac disease. Insulin, released from pancreatic beta-cells when blood glucose levels rise, is the only hormone that can lower the blood glucose concentration, and insufficient secretion results in diabetes. In T2D, the beta-cells are still present (unlike in T1D), but they have a reduced insulin content and the coupling between glucose and insulin release is impaired.
Vicious spiral of hyperglycemia and beta-cell damage
Previous work by the same team had shown that chronic hyperglycemia damages the ability of the beta-cell to produce insulin and to release it when blood glucose levels rise. This suggested that “prolonged hyperglycemia sets off a vicious spiral in which an increase in blood glucose leads to beta-cell damage and less insulin secretion - which causes an even greater increase in blood glucose and a further decline in beta-cell function,” the team explained.
Lead researcher Elizabeth Haythorne, PhD, said: “We realized that we next needed to understand how glucose damages beta-cell function, so we can think about how we might stop it and so slow the seemingly inexorable decline in beta-cell function in T2D.”
In the new study, they showed that altered glycolysis in T2D occurs, in part, through marked up-regulation of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1), a protein complex involved in control of cell growth, dysregulation of which underlies a variety of human diseases, including diabetes. Up-regulation of mTORC1 led to changes in metabolic gene expression, oxidative phosphorylation and insulin secretion. Furthermore, they demonstrated that reducing the rate at which glucose is metabolized and at which its metabolites build up could prevent the effects of chronic hyperglycemia and the ensuing beta-cell failure.
“High blood glucose levels cause an increased rate of glucose metabolism in the beta-cell, which leads to a metabolic bottleneck and the pooling of upstream metabolites,” the team said. “These metabolites switch off the insulin gene, so less insulin is made, as well as switching off numerous genes involved in metabolism and stimulus-secretion coupling. Consequently, the beta-cells become glucose blind and no longer respond to changes in blood glucose with insulin secretion.”
Blocking metabolic enzyme could maintain insulin secretion
The team attempted to block the first step in glucose metabolism, and therefore prevent the gene changes from taking place, by blocking the enzyme glucokinase, which regulates the process. They found that this could maintain glucose-stimulated insulin secretion even in the presence of chronic hyperglycemia.
“Our results support the idea that progressive impairment of beta-cell metabolism, induced by increasing hyperglycemia, speeds T2D development, and suggest that reducing glycolysis at the level of glucokinase may slow this progression,” they said.
Dr. Ashcroft said: “This is potentially a useful way to try to prevent beta-cell decline in diabetes. Because glucose metabolism normally stimulates insulin secretion, it was previously hypothesized that increasing glucose metabolism would enhance insulin secretion in T2D and glucokinase activators were trialled, with varying results.
“Our data suggests that glucokinase activators could have an adverse effect and, somewhat counter-intuitively, that a glucokinase inhibitor might be a better strategy to treat T2D. Of course, it would be important to reduce glucose flux in T2D to that found in people without diabetes – and no further. But there is a very long way to go before we can tell if this approach would be useful for treating beta-cell decline in T2D.
“In the meantime, the key message from our study if you have type 2 diabetes is that it is important to keep your blood glucose well controlled.”
This study was funded by the UK Medical Research Council, the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council, the John Fell Fund, and the Nuffield Benefaction for Medicine/Wellcome Institutional Strategic Support Fund. The authors declared no competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
Understanding of the key mechanisms underlying the progression of type 2 diabetes has been advanced by new research from Oxford (England) University suggesting potential ways to “slow the seemingly inexorable decline in beta-cell function in T2D”.
The study in mice elucidated a “key cause” of T2D by showing that
Scientists already knew that chronic hyperglycemia leads to a progressive decline in beta-cell function and, conversely, that the failure of pancreatic beta-cells to produce insulin results in chronically elevated blood glucose. However, the exact cause of beta-cell failure in T2D has remained unclear. T2D typically presents in later adult life, and by the time of diagnosis as much as 50% of beta-cell function has been lost.
In the United Kingdom there are nearly 5 million people diagnosed with T2D, which costs the National Health Service some £10 billion annually.
Glucose metabolites, rather than glucose itself, drives failure of cells to release insulin
The new study, published in Nature Communications, used both an animal model of diabetes and in vitro culture of beta-cells in a high glucose medium. In both cases the researchers showed, for the first time, that it is glucose metabolites, rather than glucose itself, that drives the failure of beta-cells to release insulin and is key to the progression of type 2 diabetes.
Senior researcher Frances Ashcroft, PhD, of the department of physiology, anatomy and genetics at the University of Oxford said: “This suggests a potential way in which the decline in beta-cell function in T2D might be slowed or prevented.”
Blood glucose concentration is controlled within narrow limits, the team explained. When it is too low for more than few minutes, consciousness is rapidly lost because the brain is starved of fuel. However chronic elevation of blood glucose leads to the serious complications found in poorly controlled diabetes, such as retinopathy, nephropathy, peripheral neuropathy, and cardiac disease. Insulin, released from pancreatic beta-cells when blood glucose levels rise, is the only hormone that can lower the blood glucose concentration, and insufficient secretion results in diabetes. In T2D, the beta-cells are still present (unlike in T1D), but they have a reduced insulin content and the coupling between glucose and insulin release is impaired.
Vicious spiral of hyperglycemia and beta-cell damage
Previous work by the same team had shown that chronic hyperglycemia damages the ability of the beta-cell to produce insulin and to release it when blood glucose levels rise. This suggested that “prolonged hyperglycemia sets off a vicious spiral in which an increase in blood glucose leads to beta-cell damage and less insulin secretion - which causes an even greater increase in blood glucose and a further decline in beta-cell function,” the team explained.
Lead researcher Elizabeth Haythorne, PhD, said: “We realized that we next needed to understand how glucose damages beta-cell function, so we can think about how we might stop it and so slow the seemingly inexorable decline in beta-cell function in T2D.”
In the new study, they showed that altered glycolysis in T2D occurs, in part, through marked up-regulation of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1), a protein complex involved in control of cell growth, dysregulation of which underlies a variety of human diseases, including diabetes. Up-regulation of mTORC1 led to changes in metabolic gene expression, oxidative phosphorylation and insulin secretion. Furthermore, they demonstrated that reducing the rate at which glucose is metabolized and at which its metabolites build up could prevent the effects of chronic hyperglycemia and the ensuing beta-cell failure.
“High blood glucose levels cause an increased rate of glucose metabolism in the beta-cell, which leads to a metabolic bottleneck and the pooling of upstream metabolites,” the team said. “These metabolites switch off the insulin gene, so less insulin is made, as well as switching off numerous genes involved in metabolism and stimulus-secretion coupling. Consequently, the beta-cells become glucose blind and no longer respond to changes in blood glucose with insulin secretion.”
Blocking metabolic enzyme could maintain insulin secretion
The team attempted to block the first step in glucose metabolism, and therefore prevent the gene changes from taking place, by blocking the enzyme glucokinase, which regulates the process. They found that this could maintain glucose-stimulated insulin secretion even in the presence of chronic hyperglycemia.
“Our results support the idea that progressive impairment of beta-cell metabolism, induced by increasing hyperglycemia, speeds T2D development, and suggest that reducing glycolysis at the level of glucokinase may slow this progression,” they said.
Dr. Ashcroft said: “This is potentially a useful way to try to prevent beta-cell decline in diabetes. Because glucose metabolism normally stimulates insulin secretion, it was previously hypothesized that increasing glucose metabolism would enhance insulin secretion in T2D and glucokinase activators were trialled, with varying results.
“Our data suggests that glucokinase activators could have an adverse effect and, somewhat counter-intuitively, that a glucokinase inhibitor might be a better strategy to treat T2D. Of course, it would be important to reduce glucose flux in T2D to that found in people without diabetes – and no further. But there is a very long way to go before we can tell if this approach would be useful for treating beta-cell decline in T2D.
“In the meantime, the key message from our study if you have type 2 diabetes is that it is important to keep your blood glucose well controlled.”
This study was funded by the UK Medical Research Council, the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council, the John Fell Fund, and the Nuffield Benefaction for Medicine/Wellcome Institutional Strategic Support Fund. The authors declared no competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
FROM NATURE COMMUNICATIONS
Statins boost glycemia slightly, but CVD benefits prevail
CHICAGO – A new, expanded meta-analysis confirmed the long-known effect that statin treatment has on raising blood glucose levels and causing incident diabetes, but it also documented that these effects are small and any risk they pose to statin users is dwarfed by the cholesterol-lowering effect of statins and their ability to reduce risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
This meta-analysis of 23 trials with a total of more than 150,000 participants showed that statin therapy significantly increased the risk for new-onset diabetes and worsening glycemia, driven by a “very small but generalized increase in glucose,” with a greater effect from high-intensity statin regimens and a similar but somewhat more muted effect from low- and moderate-intensity statin treatment, David Preiss, MBChB, PhD, reported at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
Dr. Preiss also stressed that despite this, “the cardiovascular benefits of statin therapy remain substantial and profound” in people regardless of whether they have diabetes, prediabetes, or normoglycemia when they start statin treatment, noting that the impact of even high-intensity statin treatment is “absolutely tiny” increases in hemoglobin A1c and blood glucose.
“This does not detract from the substantial benefit of statin treatment,” declared Dr. Preiss, a metabolic medicine specialist and endocrinologist at Oxford (England) University.
Small glycemia increases ‘nudge’ some into diabetes
The data Dr. Preiss reported showed that high-intensity statin treatment (atorvastatin at a daily dose of at least 40 mg, or rosuvastatin at a daily dose of at least 20 mg) led to an average increase in A1c levels of 0.08 percentage points among people without diabetes when their treatment began and 0.24 percentage points among people already diagnosed with diabetes. Blood glucose levels rose by an average of 0.04 mmol/L (less than 1 mg/d) in those without diabetes, and by an average 0.22 mmol/L (about 4 mg/dL) in those with diabetes. People who received low- or moderate-intensity statin regimens had significant but smaller increases.
“We’re not talking about people going from no diabetes to frank diabetes. We’re talking about [statins] nudging a very small number of people across a diabetes threshold,” an A1c of 6.5% that is set somewhat arbitrarily based on an increased risk for developing retinopathy, Dr. Preiss said. ”A person just needs to lose a [daily] can of Coke’s worth of weight to eliminate any apparent diabetes risk,” he noted.
Benefit outweighs risks by three- to sevenfold
Dr. Preiss presented two other examples of what his findings showed to illustrate the relatively small risk posed by statin therapy compared with its potential benefits. Treating 10,000 people for 5 years with a high-intensity statin regimen in those with established ASCVD (secondary prevention) would result in an increment of 150 extra people developing diabetes because of the hyperglycemic effect of statins, compared with an expected prevention of 1,000 ASCVD events. Among 10,000 people at high ASCVD risk and taking a high-intensity statin regimen for primary prevention 5 years of treatment would result in roughly 130 extra cases of incident diabetes while preventing about 500 ASCVD events.
In addition, applying the new risk estimates to the people included in the UK Biobank database, whose median A1c is 5.5%, showed that a high-intensity statin regimen could be expected to raise the prevalence of those with an A1c of 6.5% or greater from 4.5% to 5.7%.
Several preventive cardiologists who heard the report and were not involved with the analysis agreed with Dr. Preiss that the benefits of statin treatment substantially offset this confirmed hyperglycemic effect.
Risk ‘more than counterbalanced by benefit’
“He clearly showed that the small hyperglycemia risk posed by statin use is more than counterbalanced by its benefit for reducing ASCVD events,” commented Neil J. Stone, MD, a cardiologist and professor of medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago. “I agree that, for those with prediabetes who are on the road to diabetes with or without a statin, the small increase in glucose with a statin should not dissuade statin usage because the benefit is so large. Rather, it should focus efforts to improve diet, increase physical activity, and keep weight controlled.”
Dr. Stone also noted in an interview that in the JUPITER trial, which examined the effects of a daily 20-mg dose of rosuvastatin (Crestor), a high-intensity regimen, study participants with diabetes risk factors who were assigned to rosuvastatin had an onset of diabetes that was earlier than people assigned to placebo by only about 5.4 weeks, yet this group had evidence of significant benefit.
“I agree with Dr. Preiss that the benefits of statins in reducing heart attack, stroke, and cardiovascular death far outweigh their modest effects on glycemia,” commented Brendan M. Everett, MD, a cardiologist and preventive medicine specialist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. “This is particularly true for those with preexisting prediabetes or diabetes, who have an elevated risk of atherosclerotic events and thus stand to derive more significant benefit from statins. The benefits of lowering LDL cholesterol with a statin for preventing seriously morbid, and potentially fatal, cardiovascular events far outweigh the extremely modest, or even negligible, increases in the risk of diabetes that could be seen with the extremely small increases in A1c,” Dr. Everett said in an interview.
The new findings “reaffirm that there is a increased risk [from statins] but the most important point is that it is a very, very tiny difference in A1c,” commented Marc S. Sabatine, MD, a cardiologist and professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “These data have been known for quite some time, but this analysis was done in a more rigorous way.” The finding of “a small increase in risk for diabetes is really because diabetes has a biochemical threshold and statin treatment nudges some people a little past a line that is semi-arbitrary. It’s important to be cognizant of this, but it in no way dissuades me from treating patients aggressively with statins to reduce their ASCVD risk. I would monitor their A1c levels, and if they go higher and can’t be controlled with lifestyle we have plenty of medications that can control it,” he said in an interview.
No difference by statin type
The meta-analysis used data from 13 placebo-controlled statin trials that together involved 123,940 participants and had an average 4.3 years of follow-up, and four trials that compared one statin with another and collectively involved 30,734 participants with an average 4.9 years of follow-up.
The analyses showed that high-intensity statin treatment increased the rate of incident diabetes by a significant 36% relative to controls and increased the rate of worsening glycemia by a significant 24% compared with controls. Low- or moderate-intensity statin regimens increased incident diabetes by a significant 10% and raised the incidence of worsening glycemia by a significant 10% compared with controls, Dr. Preiss reported.
These effects did not significantly differ by type of statin (the study included people treated with atorvastatin, fluvastatin, lovastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin, and simvastatin), nor across a variety of subgroups based on age, sex, race, body mass index, diabetes risk, renal function, cholesterol levels, or cardiovascular disease. The effect was also consistent regardless of the duration of treatment.
Dr. Preiss also downplayed the magnitude of the apparent difference in risk posed by high-intensity and less intense statin regimens. “I suspect the apparent heterogeneity is true, but not quite as big as what we see,” he said.
The mechanisms by which statins have this effect remain unclear, but evidence suggests that it may be a direct effect of the main action of statins, inhibition of the HMG-CoA reductase enzyme.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Preiss and Dr. Stone had no disclosures. Dr. Everett has been a consultant to Eli Lilly, Gilead, Ipsen, Janssen, and Provention. Dr. Sabatine has been a consultant to Althera, Amgen, Anthos Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Beren Therapeutics, Bristol-Myers Squibb, DalCor, Dr Reddy’s Laboratories, Fibrogen, Intarcia, Merck, Moderna, Novo Nordisk, and Silence Therapeutics.
CHICAGO – A new, expanded meta-analysis confirmed the long-known effect that statin treatment has on raising blood glucose levels and causing incident diabetes, but it also documented that these effects are small and any risk they pose to statin users is dwarfed by the cholesterol-lowering effect of statins and their ability to reduce risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
This meta-analysis of 23 trials with a total of more than 150,000 participants showed that statin therapy significantly increased the risk for new-onset diabetes and worsening glycemia, driven by a “very small but generalized increase in glucose,” with a greater effect from high-intensity statin regimens and a similar but somewhat more muted effect from low- and moderate-intensity statin treatment, David Preiss, MBChB, PhD, reported at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
Dr. Preiss also stressed that despite this, “the cardiovascular benefits of statin therapy remain substantial and profound” in people regardless of whether they have diabetes, prediabetes, or normoglycemia when they start statin treatment, noting that the impact of even high-intensity statin treatment is “absolutely tiny” increases in hemoglobin A1c and blood glucose.
“This does not detract from the substantial benefit of statin treatment,” declared Dr. Preiss, a metabolic medicine specialist and endocrinologist at Oxford (England) University.
Small glycemia increases ‘nudge’ some into diabetes
The data Dr. Preiss reported showed that high-intensity statin treatment (atorvastatin at a daily dose of at least 40 mg, or rosuvastatin at a daily dose of at least 20 mg) led to an average increase in A1c levels of 0.08 percentage points among people without diabetes when their treatment began and 0.24 percentage points among people already diagnosed with diabetes. Blood glucose levels rose by an average of 0.04 mmol/L (less than 1 mg/d) in those without diabetes, and by an average 0.22 mmol/L (about 4 mg/dL) in those with diabetes. People who received low- or moderate-intensity statin regimens had significant but smaller increases.
“We’re not talking about people going from no diabetes to frank diabetes. We’re talking about [statins] nudging a very small number of people across a diabetes threshold,” an A1c of 6.5% that is set somewhat arbitrarily based on an increased risk for developing retinopathy, Dr. Preiss said. ”A person just needs to lose a [daily] can of Coke’s worth of weight to eliminate any apparent diabetes risk,” he noted.
Benefit outweighs risks by three- to sevenfold
Dr. Preiss presented two other examples of what his findings showed to illustrate the relatively small risk posed by statin therapy compared with its potential benefits. Treating 10,000 people for 5 years with a high-intensity statin regimen in those with established ASCVD (secondary prevention) would result in an increment of 150 extra people developing diabetes because of the hyperglycemic effect of statins, compared with an expected prevention of 1,000 ASCVD events. Among 10,000 people at high ASCVD risk and taking a high-intensity statin regimen for primary prevention 5 years of treatment would result in roughly 130 extra cases of incident diabetes while preventing about 500 ASCVD events.
In addition, applying the new risk estimates to the people included in the UK Biobank database, whose median A1c is 5.5%, showed that a high-intensity statin regimen could be expected to raise the prevalence of those with an A1c of 6.5% or greater from 4.5% to 5.7%.
Several preventive cardiologists who heard the report and were not involved with the analysis agreed with Dr. Preiss that the benefits of statin treatment substantially offset this confirmed hyperglycemic effect.
Risk ‘more than counterbalanced by benefit’
“He clearly showed that the small hyperglycemia risk posed by statin use is more than counterbalanced by its benefit for reducing ASCVD events,” commented Neil J. Stone, MD, a cardiologist and professor of medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago. “I agree that, for those with prediabetes who are on the road to diabetes with or without a statin, the small increase in glucose with a statin should not dissuade statin usage because the benefit is so large. Rather, it should focus efforts to improve diet, increase physical activity, and keep weight controlled.”
Dr. Stone also noted in an interview that in the JUPITER trial, which examined the effects of a daily 20-mg dose of rosuvastatin (Crestor), a high-intensity regimen, study participants with diabetes risk factors who were assigned to rosuvastatin had an onset of diabetes that was earlier than people assigned to placebo by only about 5.4 weeks, yet this group had evidence of significant benefit.
“I agree with Dr. Preiss that the benefits of statins in reducing heart attack, stroke, and cardiovascular death far outweigh their modest effects on glycemia,” commented Brendan M. Everett, MD, a cardiologist and preventive medicine specialist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. “This is particularly true for those with preexisting prediabetes or diabetes, who have an elevated risk of atherosclerotic events and thus stand to derive more significant benefit from statins. The benefits of lowering LDL cholesterol with a statin for preventing seriously morbid, and potentially fatal, cardiovascular events far outweigh the extremely modest, or even negligible, increases in the risk of diabetes that could be seen with the extremely small increases in A1c,” Dr. Everett said in an interview.
The new findings “reaffirm that there is a increased risk [from statins] but the most important point is that it is a very, very tiny difference in A1c,” commented Marc S. Sabatine, MD, a cardiologist and professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “These data have been known for quite some time, but this analysis was done in a more rigorous way.” The finding of “a small increase in risk for diabetes is really because diabetes has a biochemical threshold and statin treatment nudges some people a little past a line that is semi-arbitrary. It’s important to be cognizant of this, but it in no way dissuades me from treating patients aggressively with statins to reduce their ASCVD risk. I would monitor their A1c levels, and if they go higher and can’t be controlled with lifestyle we have plenty of medications that can control it,” he said in an interview.
No difference by statin type
The meta-analysis used data from 13 placebo-controlled statin trials that together involved 123,940 participants and had an average 4.3 years of follow-up, and four trials that compared one statin with another and collectively involved 30,734 participants with an average 4.9 years of follow-up.
The analyses showed that high-intensity statin treatment increased the rate of incident diabetes by a significant 36% relative to controls and increased the rate of worsening glycemia by a significant 24% compared with controls. Low- or moderate-intensity statin regimens increased incident diabetes by a significant 10% and raised the incidence of worsening glycemia by a significant 10% compared with controls, Dr. Preiss reported.
These effects did not significantly differ by type of statin (the study included people treated with atorvastatin, fluvastatin, lovastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin, and simvastatin), nor across a variety of subgroups based on age, sex, race, body mass index, diabetes risk, renal function, cholesterol levels, or cardiovascular disease. The effect was also consistent regardless of the duration of treatment.
Dr. Preiss also downplayed the magnitude of the apparent difference in risk posed by high-intensity and less intense statin regimens. “I suspect the apparent heterogeneity is true, but not quite as big as what we see,” he said.
The mechanisms by which statins have this effect remain unclear, but evidence suggests that it may be a direct effect of the main action of statins, inhibition of the HMG-CoA reductase enzyme.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Preiss and Dr. Stone had no disclosures. Dr. Everett has been a consultant to Eli Lilly, Gilead, Ipsen, Janssen, and Provention. Dr. Sabatine has been a consultant to Althera, Amgen, Anthos Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Beren Therapeutics, Bristol-Myers Squibb, DalCor, Dr Reddy’s Laboratories, Fibrogen, Intarcia, Merck, Moderna, Novo Nordisk, and Silence Therapeutics.
CHICAGO – A new, expanded meta-analysis confirmed the long-known effect that statin treatment has on raising blood glucose levels and causing incident diabetes, but it also documented that these effects are small and any risk they pose to statin users is dwarfed by the cholesterol-lowering effect of statins and their ability to reduce risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
This meta-analysis of 23 trials with a total of more than 150,000 participants showed that statin therapy significantly increased the risk for new-onset diabetes and worsening glycemia, driven by a “very small but generalized increase in glucose,” with a greater effect from high-intensity statin regimens and a similar but somewhat more muted effect from low- and moderate-intensity statin treatment, David Preiss, MBChB, PhD, reported at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
Dr. Preiss also stressed that despite this, “the cardiovascular benefits of statin therapy remain substantial and profound” in people regardless of whether they have diabetes, prediabetes, or normoglycemia when they start statin treatment, noting that the impact of even high-intensity statin treatment is “absolutely tiny” increases in hemoglobin A1c and blood glucose.
“This does not detract from the substantial benefit of statin treatment,” declared Dr. Preiss, a metabolic medicine specialist and endocrinologist at Oxford (England) University.
Small glycemia increases ‘nudge’ some into diabetes
The data Dr. Preiss reported showed that high-intensity statin treatment (atorvastatin at a daily dose of at least 40 mg, or rosuvastatin at a daily dose of at least 20 mg) led to an average increase in A1c levels of 0.08 percentage points among people without diabetes when their treatment began and 0.24 percentage points among people already diagnosed with diabetes. Blood glucose levels rose by an average of 0.04 mmol/L (less than 1 mg/d) in those without diabetes, and by an average 0.22 mmol/L (about 4 mg/dL) in those with diabetes. People who received low- or moderate-intensity statin regimens had significant but smaller increases.
“We’re not talking about people going from no diabetes to frank diabetes. We’re talking about [statins] nudging a very small number of people across a diabetes threshold,” an A1c of 6.5% that is set somewhat arbitrarily based on an increased risk for developing retinopathy, Dr. Preiss said. ”A person just needs to lose a [daily] can of Coke’s worth of weight to eliminate any apparent diabetes risk,” he noted.
Benefit outweighs risks by three- to sevenfold
Dr. Preiss presented two other examples of what his findings showed to illustrate the relatively small risk posed by statin therapy compared with its potential benefits. Treating 10,000 people for 5 years with a high-intensity statin regimen in those with established ASCVD (secondary prevention) would result in an increment of 150 extra people developing diabetes because of the hyperglycemic effect of statins, compared with an expected prevention of 1,000 ASCVD events. Among 10,000 people at high ASCVD risk and taking a high-intensity statin regimen for primary prevention 5 years of treatment would result in roughly 130 extra cases of incident diabetes while preventing about 500 ASCVD events.
In addition, applying the new risk estimates to the people included in the UK Biobank database, whose median A1c is 5.5%, showed that a high-intensity statin regimen could be expected to raise the prevalence of those with an A1c of 6.5% or greater from 4.5% to 5.7%.
Several preventive cardiologists who heard the report and were not involved with the analysis agreed with Dr. Preiss that the benefits of statin treatment substantially offset this confirmed hyperglycemic effect.
Risk ‘more than counterbalanced by benefit’
“He clearly showed that the small hyperglycemia risk posed by statin use is more than counterbalanced by its benefit for reducing ASCVD events,” commented Neil J. Stone, MD, a cardiologist and professor of medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago. “I agree that, for those with prediabetes who are on the road to diabetes with or without a statin, the small increase in glucose with a statin should not dissuade statin usage because the benefit is so large. Rather, it should focus efforts to improve diet, increase physical activity, and keep weight controlled.”
Dr. Stone also noted in an interview that in the JUPITER trial, which examined the effects of a daily 20-mg dose of rosuvastatin (Crestor), a high-intensity regimen, study participants with diabetes risk factors who were assigned to rosuvastatin had an onset of diabetes that was earlier than people assigned to placebo by only about 5.4 weeks, yet this group had evidence of significant benefit.
“I agree with Dr. Preiss that the benefits of statins in reducing heart attack, stroke, and cardiovascular death far outweigh their modest effects on glycemia,” commented Brendan M. Everett, MD, a cardiologist and preventive medicine specialist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. “This is particularly true for those with preexisting prediabetes or diabetes, who have an elevated risk of atherosclerotic events and thus stand to derive more significant benefit from statins. The benefits of lowering LDL cholesterol with a statin for preventing seriously morbid, and potentially fatal, cardiovascular events far outweigh the extremely modest, or even negligible, increases in the risk of diabetes that could be seen with the extremely small increases in A1c,” Dr. Everett said in an interview.
The new findings “reaffirm that there is a increased risk [from statins] but the most important point is that it is a very, very tiny difference in A1c,” commented Marc S. Sabatine, MD, a cardiologist and professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “These data have been known for quite some time, but this analysis was done in a more rigorous way.” The finding of “a small increase in risk for diabetes is really because diabetes has a biochemical threshold and statin treatment nudges some people a little past a line that is semi-arbitrary. It’s important to be cognizant of this, but it in no way dissuades me from treating patients aggressively with statins to reduce their ASCVD risk. I would monitor their A1c levels, and if they go higher and can’t be controlled with lifestyle we have plenty of medications that can control it,” he said in an interview.
No difference by statin type
The meta-analysis used data from 13 placebo-controlled statin trials that together involved 123,940 participants and had an average 4.3 years of follow-up, and four trials that compared one statin with another and collectively involved 30,734 participants with an average 4.9 years of follow-up.
The analyses showed that high-intensity statin treatment increased the rate of incident diabetes by a significant 36% relative to controls and increased the rate of worsening glycemia by a significant 24% compared with controls. Low- or moderate-intensity statin regimens increased incident diabetes by a significant 10% and raised the incidence of worsening glycemia by a significant 10% compared with controls, Dr. Preiss reported.
These effects did not significantly differ by type of statin (the study included people treated with atorvastatin, fluvastatin, lovastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin, and simvastatin), nor across a variety of subgroups based on age, sex, race, body mass index, diabetes risk, renal function, cholesterol levels, or cardiovascular disease. The effect was also consistent regardless of the duration of treatment.
Dr. Preiss also downplayed the magnitude of the apparent difference in risk posed by high-intensity and less intense statin regimens. “I suspect the apparent heterogeneity is true, but not quite as big as what we see,” he said.
The mechanisms by which statins have this effect remain unclear, but evidence suggests that it may be a direct effect of the main action of statins, inhibition of the HMG-CoA reductase enzyme.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Preiss and Dr. Stone had no disclosures. Dr. Everett has been a consultant to Eli Lilly, Gilead, Ipsen, Janssen, and Provention. Dr. Sabatine has been a consultant to Althera, Amgen, Anthos Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Beren Therapeutics, Bristol-Myers Squibb, DalCor, Dr Reddy’s Laboratories, Fibrogen, Intarcia, Merck, Moderna, Novo Nordisk, and Silence Therapeutics.
AT AHA 2022