User login
UTI in Primary Care: New Guidelines
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
We often see urinary tract infections in primary care, so these guidelines for the prevention, diagnosis and management of urinary tract infection (UTI) are very helpful to reaffirm our knowledge in the areas where know what we’re doing and update our knowledge in areas of uncertainty. These guidelines are from a new group called the WikiGuidelines group. Ordinarily, I wouldn’t have considered reviewing one of these guidelines, but this one was published in JAMA Network Open. It is evidence based and covers the topic really well.
Diagnosis. Order a urinalysis or a urine culture only if the patient is having symptoms of a UTI. This may seem obvious, but particularly among older individuals, in whom asymptomatic bacteriuria is very common and should not be treated, nonspecific symptoms such as just not feeling well for a day do not warrant obtaining a urinalysis and culture. With no clear way to distinguish between asymptomatic bacteriuria and a true UTI, the first step in making the diagnosis of a UTI accurately is ordering urine studies only in people who have a reasonable chance of having an infection.
The guideline suggests that the diagnosis of UTI should be primarily based on clinical symptoms. A urinalysis can provide further information, but the authors caution us against relying solely on the urinalysis. This is an incredibly important evidence-based recommendation. If you think about it, this supports the common practice of treating UTIs over the phone without having to see the patient or check a urinalysis.
The rationale for this recommendation is that urinalysis is neither a sensitive nor specific test for UTI. The sensitivity of leukocyte esterase is only about 80%, and the specificity is even lower. For positive nitrite on urinalysis, the sensitivity is below 50%, meaning the test would be negative more than half the time when someone actually has a UTI. The specificity of urine nitrate is very high (more than 90%), so if the patient is nitrite positive, they clearly have a UTI. This means that a patient’s report of classic UTI symptoms — urinary burning, frequency, and urgency — is about as good if not a better indicator of a UTI than a urinalysis.
The guidelines also say that in simple uncomplicated cystitis in healthy nonpregnant patients, routine urine cultures are not necessary. A fascinating meta-analysis in JAMA showed that, for women presenting to outpatient clinics with at least two symptoms of UTI and absence of vaginal discharge, there was a greater than 90% likelihood of having acute cystitis. A reminder here, however: If a woman is sexually active and at risk for sexually transmitted infections, then consider testing for STIs as well, because the symptoms of an STI can mimic those of a UTI.
Treatment. Treatment for UTI is usually empiric, with treatment initiated before the culture results are known and with cultures being done only for people with complicated infections, such as pyelonephritis, or with recurrent infections. Decisions about what to use for treatment can be influenced by local patterns of resistance and an individual’s risk factors for antimicrobial resistance. As a general rule, for uncomplicated cystitis, nitrofurantoin for 5 days is a reasonable first-line agent. Evidence of efficacy is good, and the risk for antimicrobial resistance is lower vs using antibiotics for other systemic infections.
Other reasonable first-line agents for uncomplicated cystitis include trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX) for 3 days; fosfomycin (oral) single dose; or a beta-lactam (most commonly a first generation cephalosporin), although evidence for duration is unclear. Also mentioned are two unfamiliar antibiotics: pivmecillinam (a beta-lactam agent recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration [FDA], given for 3 days) and gepotidacin (from a new class of antibiotic that is currently under FDA review). Fluoroquinolones should not usually be first-line agents unless other treatment options are not appropriate.
It’s important to distinguish between uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis. For pyelonephritis (infection of the upper urinary tract), the first decision has to do with setting for care, depending on how sick someone is, and the likelihood of gram-negative bacteremia — all of which help whether the patient needs to be hospitalized for intravenous antibiotics, or can be treated as an outpatient. Determine if they need to be admitted for intravenous antibiotics or whether they can be treated as an outpatient. For outpatient treatment of pyelonephritis, the guideline suggests that TMP-SMX or a first-generation cephalosporin are both reasonable first-line agents, with fluoroquinolones being a reasonable choice as well. Ceftriaxone is recommended for first-line therapy for patients who require intravenous treatment.
People often forget that we can do a lot to prevent UTIs, particularly among women with recurrent UTIs. The prevention of UTIs has both nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic approaches.
Nonpharmacologic prevention. One nonpharmacologic strategy is increasing water intake. A randomized controlled trial in women with recurrent cystitis who drank less than 1.5 L of fluid a day showed that the women randomized to consume an additional 1.5 L of water daily had significantly reduced cystitis frequency — approximately 50%. Because this was the only randomized trial to show this effect, this is not a strong recommendation, but there is very little downside in healthy women, so increasing water intake is a reasonable recommendation.
Another commonly discussed intervention is the use of cranberry products. As it turns out, most prospective studies have shown that cranberry products can reduce the risk for symptomatic UTIs in women with recurrent UTI.
Pharmacologic prevention. For postmenopausal women with recurrent UTI, topical vaginal estrogen has a strong base of evidence — more than 30 randomized trials — supporting its effectiveness in UTI: a 50%-90% reduction in the incidence of recurrent UTIs. Topical estrogen has minimal systemic absorption, and there are no concerning safety signals with respect to either thromboembolic disease or cancer (endometrial or breast).
Methenamine hippurate is also recommended and is FDA-approved for prevention of UTIs. It works by releasing formaldehyde in the urine, leading to bacteriostasis, which is how it leads to a decrease in UTIs. Finally, postcoital or daily administration of TMP-SMX, nitrofurantoin, norfloxacin, and ciprofloxacin all have comparable efficacy for prophylaxis, with a meta-analysis showing a decrease in recurrence rate of approximately 85%. The guideline states that there is insufficient evidence to support the use of either probiotics or D-mannose to prevent UTIs.
This is a wonderful update on a common problem. We all have a lot of clinical experience here.
Dr Skolnik, Department of Family Medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia; Associate Director, Department of Family Medicine, Abington Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Bayer.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
We often see urinary tract infections in primary care, so these guidelines for the prevention, diagnosis and management of urinary tract infection (UTI) are very helpful to reaffirm our knowledge in the areas where know what we’re doing and update our knowledge in areas of uncertainty. These guidelines are from a new group called the WikiGuidelines group. Ordinarily, I wouldn’t have considered reviewing one of these guidelines, but this one was published in JAMA Network Open. It is evidence based and covers the topic really well.
Diagnosis. Order a urinalysis or a urine culture only if the patient is having symptoms of a UTI. This may seem obvious, but particularly among older individuals, in whom asymptomatic bacteriuria is very common and should not be treated, nonspecific symptoms such as just not feeling well for a day do not warrant obtaining a urinalysis and culture. With no clear way to distinguish between asymptomatic bacteriuria and a true UTI, the first step in making the diagnosis of a UTI accurately is ordering urine studies only in people who have a reasonable chance of having an infection.
The guideline suggests that the diagnosis of UTI should be primarily based on clinical symptoms. A urinalysis can provide further information, but the authors caution us against relying solely on the urinalysis. This is an incredibly important evidence-based recommendation. If you think about it, this supports the common practice of treating UTIs over the phone without having to see the patient or check a urinalysis.
The rationale for this recommendation is that urinalysis is neither a sensitive nor specific test for UTI. The sensitivity of leukocyte esterase is only about 80%, and the specificity is even lower. For positive nitrite on urinalysis, the sensitivity is below 50%, meaning the test would be negative more than half the time when someone actually has a UTI. The specificity of urine nitrate is very high (more than 90%), so if the patient is nitrite positive, they clearly have a UTI. This means that a patient’s report of classic UTI symptoms — urinary burning, frequency, and urgency — is about as good if not a better indicator of a UTI than a urinalysis.
The guidelines also say that in simple uncomplicated cystitis in healthy nonpregnant patients, routine urine cultures are not necessary. A fascinating meta-analysis in JAMA showed that, for women presenting to outpatient clinics with at least two symptoms of UTI and absence of vaginal discharge, there was a greater than 90% likelihood of having acute cystitis. A reminder here, however: If a woman is sexually active and at risk for sexually transmitted infections, then consider testing for STIs as well, because the symptoms of an STI can mimic those of a UTI.
Treatment. Treatment for UTI is usually empiric, with treatment initiated before the culture results are known and with cultures being done only for people with complicated infections, such as pyelonephritis, or with recurrent infections. Decisions about what to use for treatment can be influenced by local patterns of resistance and an individual’s risk factors for antimicrobial resistance. As a general rule, for uncomplicated cystitis, nitrofurantoin for 5 days is a reasonable first-line agent. Evidence of efficacy is good, and the risk for antimicrobial resistance is lower vs using antibiotics for other systemic infections.
Other reasonable first-line agents for uncomplicated cystitis include trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX) for 3 days; fosfomycin (oral) single dose; or a beta-lactam (most commonly a first generation cephalosporin), although evidence for duration is unclear. Also mentioned are two unfamiliar antibiotics: pivmecillinam (a beta-lactam agent recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration [FDA], given for 3 days) and gepotidacin (from a new class of antibiotic that is currently under FDA review). Fluoroquinolones should not usually be first-line agents unless other treatment options are not appropriate.
It’s important to distinguish between uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis. For pyelonephritis (infection of the upper urinary tract), the first decision has to do with setting for care, depending on how sick someone is, and the likelihood of gram-negative bacteremia — all of which help whether the patient needs to be hospitalized for intravenous antibiotics, or can be treated as an outpatient. Determine if they need to be admitted for intravenous antibiotics or whether they can be treated as an outpatient. For outpatient treatment of pyelonephritis, the guideline suggests that TMP-SMX or a first-generation cephalosporin are both reasonable first-line agents, with fluoroquinolones being a reasonable choice as well. Ceftriaxone is recommended for first-line therapy for patients who require intravenous treatment.
People often forget that we can do a lot to prevent UTIs, particularly among women with recurrent UTIs. The prevention of UTIs has both nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic approaches.
Nonpharmacologic prevention. One nonpharmacologic strategy is increasing water intake. A randomized controlled trial in women with recurrent cystitis who drank less than 1.5 L of fluid a day showed that the women randomized to consume an additional 1.5 L of water daily had significantly reduced cystitis frequency — approximately 50%. Because this was the only randomized trial to show this effect, this is not a strong recommendation, but there is very little downside in healthy women, so increasing water intake is a reasonable recommendation.
Another commonly discussed intervention is the use of cranberry products. As it turns out, most prospective studies have shown that cranberry products can reduce the risk for symptomatic UTIs in women with recurrent UTI.
Pharmacologic prevention. For postmenopausal women with recurrent UTI, topical vaginal estrogen has a strong base of evidence — more than 30 randomized trials — supporting its effectiveness in UTI: a 50%-90% reduction in the incidence of recurrent UTIs. Topical estrogen has minimal systemic absorption, and there are no concerning safety signals with respect to either thromboembolic disease or cancer (endometrial or breast).
Methenamine hippurate is also recommended and is FDA-approved for prevention of UTIs. It works by releasing formaldehyde in the urine, leading to bacteriostasis, which is how it leads to a decrease in UTIs. Finally, postcoital or daily administration of TMP-SMX, nitrofurantoin, norfloxacin, and ciprofloxacin all have comparable efficacy for prophylaxis, with a meta-analysis showing a decrease in recurrence rate of approximately 85%. The guideline states that there is insufficient evidence to support the use of either probiotics or D-mannose to prevent UTIs.
This is a wonderful update on a common problem. We all have a lot of clinical experience here.
Dr Skolnik, Department of Family Medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia; Associate Director, Department of Family Medicine, Abington Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Bayer.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
We often see urinary tract infections in primary care, so these guidelines for the prevention, diagnosis and management of urinary tract infection (UTI) are very helpful to reaffirm our knowledge in the areas where know what we’re doing and update our knowledge in areas of uncertainty. These guidelines are from a new group called the WikiGuidelines group. Ordinarily, I wouldn’t have considered reviewing one of these guidelines, but this one was published in JAMA Network Open. It is evidence based and covers the topic really well.
Diagnosis. Order a urinalysis or a urine culture only if the patient is having symptoms of a UTI. This may seem obvious, but particularly among older individuals, in whom asymptomatic bacteriuria is very common and should not be treated, nonspecific symptoms such as just not feeling well for a day do not warrant obtaining a urinalysis and culture. With no clear way to distinguish between asymptomatic bacteriuria and a true UTI, the first step in making the diagnosis of a UTI accurately is ordering urine studies only in people who have a reasonable chance of having an infection.
The guideline suggests that the diagnosis of UTI should be primarily based on clinical symptoms. A urinalysis can provide further information, but the authors caution us against relying solely on the urinalysis. This is an incredibly important evidence-based recommendation. If you think about it, this supports the common practice of treating UTIs over the phone without having to see the patient or check a urinalysis.
The rationale for this recommendation is that urinalysis is neither a sensitive nor specific test for UTI. The sensitivity of leukocyte esterase is only about 80%, and the specificity is even lower. For positive nitrite on urinalysis, the sensitivity is below 50%, meaning the test would be negative more than half the time when someone actually has a UTI. The specificity of urine nitrate is very high (more than 90%), so if the patient is nitrite positive, they clearly have a UTI. This means that a patient’s report of classic UTI symptoms — urinary burning, frequency, and urgency — is about as good if not a better indicator of a UTI than a urinalysis.
The guidelines also say that in simple uncomplicated cystitis in healthy nonpregnant patients, routine urine cultures are not necessary. A fascinating meta-analysis in JAMA showed that, for women presenting to outpatient clinics with at least two symptoms of UTI and absence of vaginal discharge, there was a greater than 90% likelihood of having acute cystitis. A reminder here, however: If a woman is sexually active and at risk for sexually transmitted infections, then consider testing for STIs as well, because the symptoms of an STI can mimic those of a UTI.
Treatment. Treatment for UTI is usually empiric, with treatment initiated before the culture results are known and with cultures being done only for people with complicated infections, such as pyelonephritis, or with recurrent infections. Decisions about what to use for treatment can be influenced by local patterns of resistance and an individual’s risk factors for antimicrobial resistance. As a general rule, for uncomplicated cystitis, nitrofurantoin for 5 days is a reasonable first-line agent. Evidence of efficacy is good, and the risk for antimicrobial resistance is lower vs using antibiotics for other systemic infections.
Other reasonable first-line agents for uncomplicated cystitis include trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX) for 3 days; fosfomycin (oral) single dose; or a beta-lactam (most commonly a first generation cephalosporin), although evidence for duration is unclear. Also mentioned are two unfamiliar antibiotics: pivmecillinam (a beta-lactam agent recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration [FDA], given for 3 days) and gepotidacin (from a new class of antibiotic that is currently under FDA review). Fluoroquinolones should not usually be first-line agents unless other treatment options are not appropriate.
It’s important to distinguish between uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis. For pyelonephritis (infection of the upper urinary tract), the first decision has to do with setting for care, depending on how sick someone is, and the likelihood of gram-negative bacteremia — all of which help whether the patient needs to be hospitalized for intravenous antibiotics, or can be treated as an outpatient. Determine if they need to be admitted for intravenous antibiotics or whether they can be treated as an outpatient. For outpatient treatment of pyelonephritis, the guideline suggests that TMP-SMX or a first-generation cephalosporin are both reasonable first-line agents, with fluoroquinolones being a reasonable choice as well. Ceftriaxone is recommended for first-line therapy for patients who require intravenous treatment.
People often forget that we can do a lot to prevent UTIs, particularly among women with recurrent UTIs. The prevention of UTIs has both nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic approaches.
Nonpharmacologic prevention. One nonpharmacologic strategy is increasing water intake. A randomized controlled trial in women with recurrent cystitis who drank less than 1.5 L of fluid a day showed that the women randomized to consume an additional 1.5 L of water daily had significantly reduced cystitis frequency — approximately 50%. Because this was the only randomized trial to show this effect, this is not a strong recommendation, but there is very little downside in healthy women, so increasing water intake is a reasonable recommendation.
Another commonly discussed intervention is the use of cranberry products. As it turns out, most prospective studies have shown that cranberry products can reduce the risk for symptomatic UTIs in women with recurrent UTI.
Pharmacologic prevention. For postmenopausal women with recurrent UTI, topical vaginal estrogen has a strong base of evidence — more than 30 randomized trials — supporting its effectiveness in UTI: a 50%-90% reduction in the incidence of recurrent UTIs. Topical estrogen has minimal systemic absorption, and there are no concerning safety signals with respect to either thromboembolic disease or cancer (endometrial or breast).
Methenamine hippurate is also recommended and is FDA-approved for prevention of UTIs. It works by releasing formaldehyde in the urine, leading to bacteriostasis, which is how it leads to a decrease in UTIs. Finally, postcoital or daily administration of TMP-SMX, nitrofurantoin, norfloxacin, and ciprofloxacin all have comparable efficacy for prophylaxis, with a meta-analysis showing a decrease in recurrence rate of approximately 85%. The guideline states that there is insufficient evidence to support the use of either probiotics or D-mannose to prevent UTIs.
This is a wonderful update on a common problem. We all have a lot of clinical experience here.
Dr Skolnik, Department of Family Medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia; Associate Director, Department of Family Medicine, Abington Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Bayer.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New First-Line Therapies for Migraine Prevention
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Today I am going to talk about the position statement from the American Headache Society (AHS) “Calcitonin gene-related peptide [CGRP]–targeting therapies are a first-line option for the prevention of migraine”. This update is of critical importance because about three fourths of people with migraine get their care from a primary care clinician, not from a neurologist or a headache specialist. CGRP-targeting therapies have transformed migraine care at the specialty level, but many in primary care are not yet familiar with this class of medicines. Until this new statement was released, CGRPs were not viewed as first-line agents for migraine. That has now changed.
Two main types of therapy for people with migraine headache are: (1) acute or abortive therapy (when a headache develops, it is treated), and (2) preventive therapy. Preventive therapy is typically used when the patient has headaches on 4 or more days per month. Preventive therapy is aimed at reducing the frequency and severity of headaches. About 40% of patients with migraine qualify for preventive therapy, but only a minority are receiving it.
The armamentarium for preventive therapy of migraines had not changed in a long time — until now. First-line preventive therapy has traditionally consisted of three classes of agents: beta-blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, and topiramate. These medicines were developed for different therapeutic purposes, yet they work for migraines. These drugs may have off-target effects that can make them difficult to tolerate.
Based on new evidence, candesartan — an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) — is now also a first-line drug for migraine. This is good news, because ARBs are a drug class that we have a lot of experience with, are easy to use, and could be an excellent choice for people with concomitant hypertension or chronic kidney disease. The serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (venlafaxine and duloxetine) are also considered first-line agents for migraine treatment.
In the AHS’s new position statement, the two main drug classes are small-molecule CGRP receptor antagonists and monoclonal antibodies.
The role of the neuropeptide CGRP in migraine was originally discovered after finding that blood levels of CGRP were elevated during migraine attacks. This led to the discovery of agents that blocked CGRP, initially for acute treatment of migraine, and then for preventive therapy. Multiple clinical studies show the CGRP targeting therapies to be as or even more effective than traditional first-line agents at decreasing the number of migraine days per month.
The efficacy and safety of these agents have been demonstrated in both randomized trials and in real-world studies. Other important positive endpoints include fewer days of migraine, reduced acute medication use, and improvements in many quality-of-life outcomes. Studies also have shown that CGRP-targeting therapies are well tolerated and safe, with very few serious adverse events.
Furthermore, studies have shown the CGRP targeting therapies are effective in individuals who have failed multiple other first-line therapies. They fit now both as first-line agents and as agents that can be used in difficult-to-treat patients as well as in patients who struggle with acute medication overuse, which is often very challenging.
To quote from the AHS statement,
Side effects are uncommon and can include hypertension, constipation, and Raynaud phenomenon.
The position statement is strong and is based on a lot of evidence and clinical experience. CGRP-targeting therapies are now first-line agents for the prevention of migraine headache. We should learn more about and begin to feel comfortable using this class of agents because they stand to benefit our patients greatly. I’d suggest looking at the table below and picking one new agent to become familiar with so that you can add that agent to your toolbox. 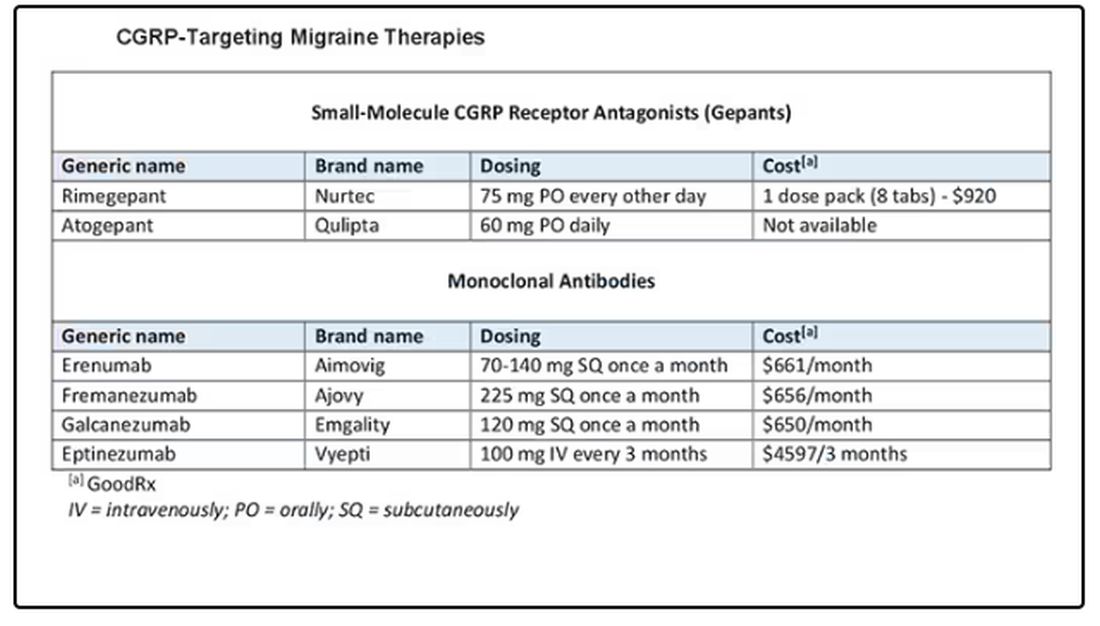
Dr. Skolnik, professor, Department of Family Medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and associate director, Department of Family Medicine, Abington Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Bayer, and Teva.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Today I am going to talk about the position statement from the American Headache Society (AHS) “Calcitonin gene-related peptide [CGRP]–targeting therapies are a first-line option for the prevention of migraine”. This update is of critical importance because about three fourths of people with migraine get their care from a primary care clinician, not from a neurologist or a headache specialist. CGRP-targeting therapies have transformed migraine care at the specialty level, but many in primary care are not yet familiar with this class of medicines. Until this new statement was released, CGRPs were not viewed as first-line agents for migraine. That has now changed.
Two main types of therapy for people with migraine headache are: (1) acute or abortive therapy (when a headache develops, it is treated), and (2) preventive therapy. Preventive therapy is typically used when the patient has headaches on 4 or more days per month. Preventive therapy is aimed at reducing the frequency and severity of headaches. About 40% of patients with migraine qualify for preventive therapy, but only a minority are receiving it.
The armamentarium for preventive therapy of migraines had not changed in a long time — until now. First-line preventive therapy has traditionally consisted of three classes of agents: beta-blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, and topiramate. These medicines were developed for different therapeutic purposes, yet they work for migraines. These drugs may have off-target effects that can make them difficult to tolerate.
Based on new evidence, candesartan — an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) — is now also a first-line drug for migraine. This is good news, because ARBs are a drug class that we have a lot of experience with, are easy to use, and could be an excellent choice for people with concomitant hypertension or chronic kidney disease. The serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (venlafaxine and duloxetine) are also considered first-line agents for migraine treatment.
In the AHS’s new position statement, the two main drug classes are small-molecule CGRP receptor antagonists and monoclonal antibodies.
The role of the neuropeptide CGRP in migraine was originally discovered after finding that blood levels of CGRP were elevated during migraine attacks. This led to the discovery of agents that blocked CGRP, initially for acute treatment of migraine, and then for preventive therapy. Multiple clinical studies show the CGRP targeting therapies to be as or even more effective than traditional first-line agents at decreasing the number of migraine days per month.
The efficacy and safety of these agents have been demonstrated in both randomized trials and in real-world studies. Other important positive endpoints include fewer days of migraine, reduced acute medication use, and improvements in many quality-of-life outcomes. Studies also have shown that CGRP-targeting therapies are well tolerated and safe, with very few serious adverse events.
Furthermore, studies have shown the CGRP targeting therapies are effective in individuals who have failed multiple other first-line therapies. They fit now both as first-line agents and as agents that can be used in difficult-to-treat patients as well as in patients who struggle with acute medication overuse, which is often very challenging.
To quote from the AHS statement,
Side effects are uncommon and can include hypertension, constipation, and Raynaud phenomenon.
The position statement is strong and is based on a lot of evidence and clinical experience. CGRP-targeting therapies are now first-line agents for the prevention of migraine headache. We should learn more about and begin to feel comfortable using this class of agents because they stand to benefit our patients greatly. I’d suggest looking at the table below and picking one new agent to become familiar with so that you can add that agent to your toolbox. 
Dr. Skolnik, professor, Department of Family Medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and associate director, Department of Family Medicine, Abington Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Bayer, and Teva.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Today I am going to talk about the position statement from the American Headache Society (AHS) “Calcitonin gene-related peptide [CGRP]–targeting therapies are a first-line option for the prevention of migraine”. This update is of critical importance because about three fourths of people with migraine get their care from a primary care clinician, not from a neurologist or a headache specialist. CGRP-targeting therapies have transformed migraine care at the specialty level, but many in primary care are not yet familiar with this class of medicines. Until this new statement was released, CGRPs were not viewed as first-line agents for migraine. That has now changed.
Two main types of therapy for people with migraine headache are: (1) acute or abortive therapy (when a headache develops, it is treated), and (2) preventive therapy. Preventive therapy is typically used when the patient has headaches on 4 or more days per month. Preventive therapy is aimed at reducing the frequency and severity of headaches. About 40% of patients with migraine qualify for preventive therapy, but only a minority are receiving it.
The armamentarium for preventive therapy of migraines had not changed in a long time — until now. First-line preventive therapy has traditionally consisted of three classes of agents: beta-blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, and topiramate. These medicines were developed for different therapeutic purposes, yet they work for migraines. These drugs may have off-target effects that can make them difficult to tolerate.
Based on new evidence, candesartan — an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) — is now also a first-line drug for migraine. This is good news, because ARBs are a drug class that we have a lot of experience with, are easy to use, and could be an excellent choice for people with concomitant hypertension or chronic kidney disease. The serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (venlafaxine and duloxetine) are also considered first-line agents for migraine treatment.
In the AHS’s new position statement, the two main drug classes are small-molecule CGRP receptor antagonists and monoclonal antibodies.
The role of the neuropeptide CGRP in migraine was originally discovered after finding that blood levels of CGRP were elevated during migraine attacks. This led to the discovery of agents that blocked CGRP, initially for acute treatment of migraine, and then for preventive therapy. Multiple clinical studies show the CGRP targeting therapies to be as or even more effective than traditional first-line agents at decreasing the number of migraine days per month.
The efficacy and safety of these agents have been demonstrated in both randomized trials and in real-world studies. Other important positive endpoints include fewer days of migraine, reduced acute medication use, and improvements in many quality-of-life outcomes. Studies also have shown that CGRP-targeting therapies are well tolerated and safe, with very few serious adverse events.
Furthermore, studies have shown the CGRP targeting therapies are effective in individuals who have failed multiple other first-line therapies. They fit now both as first-line agents and as agents that can be used in difficult-to-treat patients as well as in patients who struggle with acute medication overuse, which is often very challenging.
To quote from the AHS statement,
Side effects are uncommon and can include hypertension, constipation, and Raynaud phenomenon.
The position statement is strong and is based on a lot of evidence and clinical experience. CGRP-targeting therapies are now first-line agents for the prevention of migraine headache. We should learn more about and begin to feel comfortable using this class of agents because they stand to benefit our patients greatly. I’d suggest looking at the table below and picking one new agent to become familiar with so that you can add that agent to your toolbox. 
Dr. Skolnik, professor, Department of Family Medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and associate director, Department of Family Medicine, Abington Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Bayer, and Teva.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New Vitamin D Recs: Testing, Supplementing, Dosing
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik, and today I’m going to talk about the Endocrine Society Guideline on Vitamin D. The question of who and when to test for vitamin D, and when to prescribe vitamin D, comes up frequently. There have been a lot of studies, and many people I know have opinions about this, but I haven’t seen a lot of clear, evidence-based guidance. This much-needed guideline provides guidance, though I’m not sure that everyone is going to be happy with the recommendations. That said, the society did conduct a comprehensive assessment and systematic review of the evidence that was impressive and well done. For our discussion, I will focus on the recommendations for nonpregnant adults.
The assumption for all of the recommendations is that these are for individuals who are already getting the Institute of Medicine’s recommended amount of vitamin D, which is 600 IU daily for those 50-70 years of age and 800 IU daily for those above 80 years.
For adults aged 18-74 years, who do not have prediabetes, the guidelines suggest against routinely testing for vitamin D deficiency and recommend against routine supplementation. For the older part of this cohort, adults aged 50-74 years, there is abundant randomized trial evidence showing little to no significant differences with vitamin D supplementation on outcomes of fracture, cancer, cardiovascular disease, kidney stones, or mortality. While supplementation is safe, there does not appear to be any benefit to routine supplementation or testing. It is important to note that the trials were done in populations that were meeting the daily recommended intake of vitamin D and who did not have low vitamin D levels at baseline, so individuals who may not be meeting the recommended daily intake though their diet or through sun exposure may consider vitamin D supplementation.
For adults with prediabetes, vitamin D supplementation is recommended to reduce the risk for progression from prediabetes to diabetes. This is about 1 in 3 adults in the United States. A number of trials have looked at vitamin D supplementation for adults with prediabetes in addition to lifestyle modification (diet and exercise). Vitamin D decreases the risk for progression from prediabetes to diabetes by approximately 10%-15%. The effect may be greater in those who are over age 60 and who have lower initial vitamin D levels.
Vitamin D in older adults (aged 75 or older) has a separate recommendation. In this age group, low vitamin D levels are common, with up to 20% of older adults having low levels. The guidelines suggest against testing vitamin D in adults aged 75 or over and recommend empiric vitamin D supplementation for all adults aged 75 or older. While observational studies have shown a relationship between low vitamin D levels in this age group and adverse outcomes, including falls, fractures, and respiratory infections, evidence from randomized placebo-controlled trials of vitamin D supplementation have been inconsistent in regard to benefit. That said, a meta-analysis has shown that vitamin D supplementation lowers mortality compared with placebo, with a relative risk of 0.96 (confidence interval, 0.93-1.00). There was no difference in effect according to setting (community vs nursing home), vitamin D dosage, or baseline vitamin D level.
There appeared to be a benefit of low-dose vitamin D supplementation on fall risk, with possibly greater fall risk when high-dose supplementation was used. No significant effect on fracture rate was seen with vitamin D supplementation alone, although there was a decrease in fractures when vitamin D was combined with calcium. In these studies, the median dose of calcium was 1000 mg per day.
Based on the probability of a “slight decrease in all-cause mortality” and its safety, as well as possible benefit to decrease falls, the recommendation is for supplementation for all adults aged 75 or older. Since there was not a consistent difference by vitamin D level, testing is not necessary.
Let’s now discuss dosage. The guidelines recommend daily lower-dose vitamin D over nondaily higher-dose vitamin D. Unfortunately, the guideline does not specify a specific dose of vitamin D. The supplementation dose used in trials of adults aged 75 or older ranged from 400 to 3333 IU daily, with an average dose of 900 IU daily, so it seems to me that a dose of 1000-2000 IU daily is a reasonable choice for older adults. In the prediabetes trials, a higher average dose was used, with a mean of 3500 IU daily, so a higher dose might make sense in this group.
Dr. Skolnik, is a professor in the Department of Family Medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director, Department of Family Medicine, Abington Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania. He disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Bayer, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, and Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik, and today I’m going to talk about the Endocrine Society Guideline on Vitamin D. The question of who and when to test for vitamin D, and when to prescribe vitamin D, comes up frequently. There have been a lot of studies, and many people I know have opinions about this, but I haven’t seen a lot of clear, evidence-based guidance. This much-needed guideline provides guidance, though I’m not sure that everyone is going to be happy with the recommendations. That said, the society did conduct a comprehensive assessment and systematic review of the evidence that was impressive and well done. For our discussion, I will focus on the recommendations for nonpregnant adults.
The assumption for all of the recommendations is that these are for individuals who are already getting the Institute of Medicine’s recommended amount of vitamin D, which is 600 IU daily for those 50-70 years of age and 800 IU daily for those above 80 years.
For adults aged 18-74 years, who do not have prediabetes, the guidelines suggest against routinely testing for vitamin D deficiency and recommend against routine supplementation. For the older part of this cohort, adults aged 50-74 years, there is abundant randomized trial evidence showing little to no significant differences with vitamin D supplementation on outcomes of fracture, cancer, cardiovascular disease, kidney stones, or mortality. While supplementation is safe, there does not appear to be any benefit to routine supplementation or testing. It is important to note that the trials were done in populations that were meeting the daily recommended intake of vitamin D and who did not have low vitamin D levels at baseline, so individuals who may not be meeting the recommended daily intake though their diet or through sun exposure may consider vitamin D supplementation.
For adults with prediabetes, vitamin D supplementation is recommended to reduce the risk for progression from prediabetes to diabetes. This is about 1 in 3 adults in the United States. A number of trials have looked at vitamin D supplementation for adults with prediabetes in addition to lifestyle modification (diet and exercise). Vitamin D decreases the risk for progression from prediabetes to diabetes by approximately 10%-15%. The effect may be greater in those who are over age 60 and who have lower initial vitamin D levels.
Vitamin D in older adults (aged 75 or older) has a separate recommendation. In this age group, low vitamin D levels are common, with up to 20% of older adults having low levels. The guidelines suggest against testing vitamin D in adults aged 75 or over and recommend empiric vitamin D supplementation for all adults aged 75 or older. While observational studies have shown a relationship between low vitamin D levels in this age group and adverse outcomes, including falls, fractures, and respiratory infections, evidence from randomized placebo-controlled trials of vitamin D supplementation have been inconsistent in regard to benefit. That said, a meta-analysis has shown that vitamin D supplementation lowers mortality compared with placebo, with a relative risk of 0.96 (confidence interval, 0.93-1.00). There was no difference in effect according to setting (community vs nursing home), vitamin D dosage, or baseline vitamin D level.
There appeared to be a benefit of low-dose vitamin D supplementation on fall risk, with possibly greater fall risk when high-dose supplementation was used. No significant effect on fracture rate was seen with vitamin D supplementation alone, although there was a decrease in fractures when vitamin D was combined with calcium. In these studies, the median dose of calcium was 1000 mg per day.
Based on the probability of a “slight decrease in all-cause mortality” and its safety, as well as possible benefit to decrease falls, the recommendation is for supplementation for all adults aged 75 or older. Since there was not a consistent difference by vitamin D level, testing is not necessary.
Let’s now discuss dosage. The guidelines recommend daily lower-dose vitamin D over nondaily higher-dose vitamin D. Unfortunately, the guideline does not specify a specific dose of vitamin D. The supplementation dose used in trials of adults aged 75 or older ranged from 400 to 3333 IU daily, with an average dose of 900 IU daily, so it seems to me that a dose of 1000-2000 IU daily is a reasonable choice for older adults. In the prediabetes trials, a higher average dose was used, with a mean of 3500 IU daily, so a higher dose might make sense in this group.
Dr. Skolnik, is a professor in the Department of Family Medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director, Department of Family Medicine, Abington Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania. He disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Bayer, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, and Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik, and today I’m going to talk about the Endocrine Society Guideline on Vitamin D. The question of who and when to test for vitamin D, and when to prescribe vitamin D, comes up frequently. There have been a lot of studies, and many people I know have opinions about this, but I haven’t seen a lot of clear, evidence-based guidance. This much-needed guideline provides guidance, though I’m not sure that everyone is going to be happy with the recommendations. That said, the society did conduct a comprehensive assessment and systematic review of the evidence that was impressive and well done. For our discussion, I will focus on the recommendations for nonpregnant adults.
The assumption for all of the recommendations is that these are for individuals who are already getting the Institute of Medicine’s recommended amount of vitamin D, which is 600 IU daily for those 50-70 years of age and 800 IU daily for those above 80 years.
For adults aged 18-74 years, who do not have prediabetes, the guidelines suggest against routinely testing for vitamin D deficiency and recommend against routine supplementation. For the older part of this cohort, adults aged 50-74 years, there is abundant randomized trial evidence showing little to no significant differences with vitamin D supplementation on outcomes of fracture, cancer, cardiovascular disease, kidney stones, or mortality. While supplementation is safe, there does not appear to be any benefit to routine supplementation or testing. It is important to note that the trials were done in populations that were meeting the daily recommended intake of vitamin D and who did not have low vitamin D levels at baseline, so individuals who may not be meeting the recommended daily intake though their diet or through sun exposure may consider vitamin D supplementation.
For adults with prediabetes, vitamin D supplementation is recommended to reduce the risk for progression from prediabetes to diabetes. This is about 1 in 3 adults in the United States. A number of trials have looked at vitamin D supplementation for adults with prediabetes in addition to lifestyle modification (diet and exercise). Vitamin D decreases the risk for progression from prediabetes to diabetes by approximately 10%-15%. The effect may be greater in those who are over age 60 and who have lower initial vitamin D levels.
Vitamin D in older adults (aged 75 or older) has a separate recommendation. In this age group, low vitamin D levels are common, with up to 20% of older adults having low levels. The guidelines suggest against testing vitamin D in adults aged 75 or over and recommend empiric vitamin D supplementation for all adults aged 75 or older. While observational studies have shown a relationship between low vitamin D levels in this age group and adverse outcomes, including falls, fractures, and respiratory infections, evidence from randomized placebo-controlled trials of vitamin D supplementation have been inconsistent in regard to benefit. That said, a meta-analysis has shown that vitamin D supplementation lowers mortality compared with placebo, with a relative risk of 0.96 (confidence interval, 0.93-1.00). There was no difference in effect according to setting (community vs nursing home), vitamin D dosage, or baseline vitamin D level.
There appeared to be a benefit of low-dose vitamin D supplementation on fall risk, with possibly greater fall risk when high-dose supplementation was used. No significant effect on fracture rate was seen with vitamin D supplementation alone, although there was a decrease in fractures when vitamin D was combined with calcium. In these studies, the median dose of calcium was 1000 mg per day.
Based on the probability of a “slight decrease in all-cause mortality” and its safety, as well as possible benefit to decrease falls, the recommendation is for supplementation for all adults aged 75 or older. Since there was not a consistent difference by vitamin D level, testing is not necessary.
Let’s now discuss dosage. The guidelines recommend daily lower-dose vitamin D over nondaily higher-dose vitamin D. Unfortunately, the guideline does not specify a specific dose of vitamin D. The supplementation dose used in trials of adults aged 75 or older ranged from 400 to 3333 IU daily, with an average dose of 900 IU daily, so it seems to me that a dose of 1000-2000 IU daily is a reasonable choice for older adults. In the prediabetes trials, a higher average dose was used, with a mean of 3500 IU daily, so a higher dose might make sense in this group.
Dr. Skolnik, is a professor in the Department of Family Medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director, Department of Family Medicine, Abington Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania. He disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Bayer, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, and Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Acute Sore Throat in Primary Care: When to Reach for the Antibiotics
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
There is a helpful consensus from experts on the best management of patients with acute sore throat. This is a common problem in primary care, and one for which there is a lot of evidence, opinion, and ultimately overprescribing of antibiotics. This consensus presents a pragmatic clinical approach aimed at decreasing overprescribing, yet detecting which patients are likely to benefit from treatment with antibiotics.
Let’s first go over the evidence that forms the basis for the recommendations, then the recommended approach. First, a sore throat can be caused by many different viruses, as well as group A streptococcus (GAS), the group C streptococcus S dysgalactiae, and fusobacterium. We sometimes think of throat cultures as telling us the definitive etiology of a sore throat. In fact, children commonly are colonized with GAS even when not infected — 35% of the time, when GAS is detected on throat swab in a child, GAS is not the cause of the sore throat. Very few adults are colonized with GAS.
Sore throats are usually self-limited, whether they are treated with antibiotics or not, but occasionally complications can occur. Suppurative complications include peritonsillar abscess, sinusitis and sepsis. Nonsuppurative complications are primarily glomerulonephritis and rheumatic fever, which can lead to rheumatic heart disease.
Antibiotics. Antibiotics have three potential benefits in acute sore throat: to reduce the risk of developing rheumatic heart disease, reduce the duration and severity of symptoms, and treat suppurative complications. The risk for rheumatic heart disease has almost vanished in high-income countries, but not in low-income countries. Thus, antibiotic treatment of acute sore throat due to GAS may benefit those in living in, and those who recently emigrated from, low-income countries.
Patients with suppurative complications should be identified because antibiotics are important for this group. Although antibiotics are prescribed primarily to prevent rheumatic fever in this population, they may be mildly helpful in reducing a patient’s symptoms.
Testing. The sensitivity and specificity of high-quality point-of-care tests (POCTs) are on par with those of cultures, with the advantage that the results are available within minutes. Negative tests reduce unneeded antibiotic prescriptions.
Given this evidence, the authors recommend an approach that puts a lot of emphasis on two major things: the risk for rheumatic fever, and clinical assessment. On the basis of these factors, a decision is made about the utility of POCTs and treatment with antibiotics for GAS. The risk for rheumatic fever is based on epidemiology: If the patient is in a low-income country or has recently immigrated from one, then the risk is high, and if not, the risk is low.
Complicated vs uncomplicated? This is determined by clinical assessment of the severity of the patient’s illness, including general appearance. Uncomplicated sore throat means that the patient:
- Is not getting worse after 3 days of illness
- Has a duration of illness ≤ 5 days or is getting better after day 5
- Has mild to moderate symptom severity (bilateral throat pain, the ability to open the mouth fully, and absence of a sandpaper or scarlatiniform rash or strawberry tongue)
For patients with uncomplicated sore throat and low risk for rheumatic fever, the main goals are to reduce antibiotic use and provide symptomatic relief. For these patients, an assessment such as the Centor score can be done. Those with a low Centor score (0-2) can be treated with analgesics and there is no need for a POCT.
In patients with a higher Centor score, the consensus gives two choices: They can either be tested (and treated if the testing is positive), or it is reasonable to forgo testing and use a wait-and-see strategy, with reevaluation if they are getting worse after day 3 or not improving after day 5 days of their illness. Illnesses that last longer than 5 days with sore throat and fatigue should prompt consideration of alternative diagnoses, such as infectious mononucleosis.
For patients with potentially complicated sore throat — including indicators such as worsening symptoms after 3 days or worsening after initiation of antibiotics, inability to open the mouth fully, unilateral neck pain or swelling, or rigors — should undergo a careful evaluation. The need for further testing in these patients, including labs and imaging, should be decided on a case-by-case basis. If the patient appears seriously ill, don’t rely solely on POCT for GAS, but think about other diagnoses.
Rheumatic fever. The approach is very different in patients at high risk for rheumatic fever. POCT for GAS is recommended irrespective of their clinical score, and antibiotics should be prescribed if it’s positive for GAS. If a POCT is unavailable, then the consensus recommends prescribing antibiotics for all high-risk patients who have acute sore throat.
This approach is sensible and puts a lot of emphasis on clinical evaluation, though it should be noted that this approach is considerably different from that in the 2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines.
Dr. Skolnik, professor, Department of Family Medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director, Department of Family Medicine, Abington Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly and Company, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Bayer.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
There is a helpful consensus from experts on the best management of patients with acute sore throat. This is a common problem in primary care, and one for which there is a lot of evidence, opinion, and ultimately overprescribing of antibiotics. This consensus presents a pragmatic clinical approach aimed at decreasing overprescribing, yet detecting which patients are likely to benefit from treatment with antibiotics.
Let’s first go over the evidence that forms the basis for the recommendations, then the recommended approach. First, a sore throat can be caused by many different viruses, as well as group A streptococcus (GAS), the group C streptococcus S dysgalactiae, and fusobacterium. We sometimes think of throat cultures as telling us the definitive etiology of a sore throat. In fact, children commonly are colonized with GAS even when not infected — 35% of the time, when GAS is detected on throat swab in a child, GAS is not the cause of the sore throat. Very few adults are colonized with GAS.
Sore throats are usually self-limited, whether they are treated with antibiotics or not, but occasionally complications can occur. Suppurative complications include peritonsillar abscess, sinusitis and sepsis. Nonsuppurative complications are primarily glomerulonephritis and rheumatic fever, which can lead to rheumatic heart disease.
Antibiotics. Antibiotics have three potential benefits in acute sore throat: to reduce the risk of developing rheumatic heart disease, reduce the duration and severity of symptoms, and treat suppurative complications. The risk for rheumatic heart disease has almost vanished in high-income countries, but not in low-income countries. Thus, antibiotic treatment of acute sore throat due to GAS may benefit those in living in, and those who recently emigrated from, low-income countries.
Patients with suppurative complications should be identified because antibiotics are important for this group. Although antibiotics are prescribed primarily to prevent rheumatic fever in this population, they may be mildly helpful in reducing a patient’s symptoms.
Testing. The sensitivity and specificity of high-quality point-of-care tests (POCTs) are on par with those of cultures, with the advantage that the results are available within minutes. Negative tests reduce unneeded antibiotic prescriptions.
Given this evidence, the authors recommend an approach that puts a lot of emphasis on two major things: the risk for rheumatic fever, and clinical assessment. On the basis of these factors, a decision is made about the utility of POCTs and treatment with antibiotics for GAS. The risk for rheumatic fever is based on epidemiology: If the patient is in a low-income country or has recently immigrated from one, then the risk is high, and if not, the risk is low.
Complicated vs uncomplicated? This is determined by clinical assessment of the severity of the patient’s illness, including general appearance. Uncomplicated sore throat means that the patient:
- Is not getting worse after 3 days of illness
- Has a duration of illness ≤ 5 days or is getting better after day 5
- Has mild to moderate symptom severity (bilateral throat pain, the ability to open the mouth fully, and absence of a sandpaper or scarlatiniform rash or strawberry tongue)
For patients with uncomplicated sore throat and low risk for rheumatic fever, the main goals are to reduce antibiotic use and provide symptomatic relief. For these patients, an assessment such as the Centor score can be done. Those with a low Centor score (0-2) can be treated with analgesics and there is no need for a POCT.
In patients with a higher Centor score, the consensus gives two choices: They can either be tested (and treated if the testing is positive), or it is reasonable to forgo testing and use a wait-and-see strategy, with reevaluation if they are getting worse after day 3 or not improving after day 5 days of their illness. Illnesses that last longer than 5 days with sore throat and fatigue should prompt consideration of alternative diagnoses, such as infectious mononucleosis.
For patients with potentially complicated sore throat — including indicators such as worsening symptoms after 3 days or worsening after initiation of antibiotics, inability to open the mouth fully, unilateral neck pain or swelling, or rigors — should undergo a careful evaluation. The need for further testing in these patients, including labs and imaging, should be decided on a case-by-case basis. If the patient appears seriously ill, don’t rely solely on POCT for GAS, but think about other diagnoses.
Rheumatic fever. The approach is very different in patients at high risk for rheumatic fever. POCT for GAS is recommended irrespective of their clinical score, and antibiotics should be prescribed if it’s positive for GAS. If a POCT is unavailable, then the consensus recommends prescribing antibiotics for all high-risk patients who have acute sore throat.
This approach is sensible and puts a lot of emphasis on clinical evaluation, though it should be noted that this approach is considerably different from that in the 2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines.
Dr. Skolnik, professor, Department of Family Medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director, Department of Family Medicine, Abington Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly and Company, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Bayer.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
There is a helpful consensus from experts on the best management of patients with acute sore throat. This is a common problem in primary care, and one for which there is a lot of evidence, opinion, and ultimately overprescribing of antibiotics. This consensus presents a pragmatic clinical approach aimed at decreasing overprescribing, yet detecting which patients are likely to benefit from treatment with antibiotics.
Let’s first go over the evidence that forms the basis for the recommendations, then the recommended approach. First, a sore throat can be caused by many different viruses, as well as group A streptococcus (GAS), the group C streptococcus S dysgalactiae, and fusobacterium. We sometimes think of throat cultures as telling us the definitive etiology of a sore throat. In fact, children commonly are colonized with GAS even when not infected — 35% of the time, when GAS is detected on throat swab in a child, GAS is not the cause of the sore throat. Very few adults are colonized with GAS.
Sore throats are usually self-limited, whether they are treated with antibiotics or not, but occasionally complications can occur. Suppurative complications include peritonsillar abscess, sinusitis and sepsis. Nonsuppurative complications are primarily glomerulonephritis and rheumatic fever, which can lead to rheumatic heart disease.
Antibiotics. Antibiotics have three potential benefits in acute sore throat: to reduce the risk of developing rheumatic heart disease, reduce the duration and severity of symptoms, and treat suppurative complications. The risk for rheumatic heart disease has almost vanished in high-income countries, but not in low-income countries. Thus, antibiotic treatment of acute sore throat due to GAS may benefit those in living in, and those who recently emigrated from, low-income countries.
Patients with suppurative complications should be identified because antibiotics are important for this group. Although antibiotics are prescribed primarily to prevent rheumatic fever in this population, they may be mildly helpful in reducing a patient’s symptoms.
Testing. The sensitivity and specificity of high-quality point-of-care tests (POCTs) are on par with those of cultures, with the advantage that the results are available within minutes. Negative tests reduce unneeded antibiotic prescriptions.
Given this evidence, the authors recommend an approach that puts a lot of emphasis on two major things: the risk for rheumatic fever, and clinical assessment. On the basis of these factors, a decision is made about the utility of POCTs and treatment with antibiotics for GAS. The risk for rheumatic fever is based on epidemiology: If the patient is in a low-income country or has recently immigrated from one, then the risk is high, and if not, the risk is low.
Complicated vs uncomplicated? This is determined by clinical assessment of the severity of the patient’s illness, including general appearance. Uncomplicated sore throat means that the patient:
- Is not getting worse after 3 days of illness
- Has a duration of illness ≤ 5 days or is getting better after day 5
- Has mild to moderate symptom severity (bilateral throat pain, the ability to open the mouth fully, and absence of a sandpaper or scarlatiniform rash or strawberry tongue)
For patients with uncomplicated sore throat and low risk for rheumatic fever, the main goals are to reduce antibiotic use and provide symptomatic relief. For these patients, an assessment such as the Centor score can be done. Those with a low Centor score (0-2) can be treated with analgesics and there is no need for a POCT.
In patients with a higher Centor score, the consensus gives two choices: They can either be tested (and treated if the testing is positive), or it is reasonable to forgo testing and use a wait-and-see strategy, with reevaluation if they are getting worse after day 3 or not improving after day 5 days of their illness. Illnesses that last longer than 5 days with sore throat and fatigue should prompt consideration of alternative diagnoses, such as infectious mononucleosis.
For patients with potentially complicated sore throat — including indicators such as worsening symptoms after 3 days or worsening after initiation of antibiotics, inability to open the mouth fully, unilateral neck pain or swelling, or rigors — should undergo a careful evaluation. The need for further testing in these patients, including labs and imaging, should be decided on a case-by-case basis. If the patient appears seriously ill, don’t rely solely on POCT for GAS, but think about other diagnoses.
Rheumatic fever. The approach is very different in patients at high risk for rheumatic fever. POCT for GAS is recommended irrespective of their clinical score, and antibiotics should be prescribed if it’s positive for GAS. If a POCT is unavailable, then the consensus recommends prescribing antibiotics for all high-risk patients who have acute sore throat.
This approach is sensible and puts a lot of emphasis on clinical evaluation, though it should be noted that this approach is considerably different from that in the 2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines.
Dr. Skolnik, professor, Department of Family Medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director, Department of Family Medicine, Abington Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly and Company, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Bayer.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
What’s Changed in Asthma Treatment? Quite a Bit
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik, and today I am going to talk about the 2023 update to the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. We treat a lot of asthma, and there are some important changes, particularly around the use of albuterol. There are two main guidelines when it comes to asthma, the Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) guideline and the US National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Guidelines. While I had the privilege of serving on the expert working group for the US guidelines, what I like about the GINA guidelines is that they are updated annually, and so they really help us keep up with rapid changes in the field.
Today, I’m going to focus on assessment and treatment.
Four Questions to Assess Asthma Control
Because over half of patients with asthma are not well controlled, it is important to assess control at every asthma visit. Asthma control has two domains: symptom control and the risk for future exacerbations. It is not enough to simply ask, “How is your asthma?” because many patients overrate their control and live with ongoing symptoms. There are many assessment tools; the Asthma Control Test (ACT) focuses on symptoms, and the new Asthma Impairment and Risk Questionnaire (AIRQ) assesses both symptoms and risk for exacerbations. The GINA assessment is probably the easiest to implement, with just four questions relevant to the past 4 weeks:
- Have you had daytime symptoms more than twice in one week?
- Have you had any night waking due to asthma?
- Have you needed short-acting beta-agonist (SABA), such as albuterol, rescue more than twice in one week?
- Have you had any activity limitation due to asthma?
Well-controlled asthma is defined as a negative response to all four of these questions, partly controlled asthma is one or two “yes” answers, and uncontrolled asthma is three to four positive responses. You can’t modify a patient’s therapy if you don’t know whether their asthma is well or poorly controlled. You’ll notice that these questions focus on symptom control. It is important also to ask about risk factors for exacerbations, particularly previous exacerbations.
Asthma Treatment Changes
The goals of treatment are control of symptoms and avoidance of exacerbations. The GINA guidelines emphasize that even patients with mild asthma can have severe or fatal exacerbations.
GINA recommends two management tracks. The preferred track uses inhaled corticosteroid (ICS)-formoterol as both maintenance and reliever therapy (MART). Track 2, without the use of ICS-formoterol for MART, is also offered, recognizing that the use of ICS-formoterol for MART is not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. There is an easy-to-follow stepped-care diagram that is worth looking at; it’s on page 66 of the GINA guideline PDF.
For patients who have symptoms less than twice a month, begin with Step 1 therapy:
- Track 1: as-needed low-dose ICS-formoterol.
- Track 2: treatment with albuterol; also use ICS whenever albuterol is used.
For patients with symptoms more than twice a month (but not most days of the week) treatment can start with Step 2 therapy:
- Track 1: as-needed low-dose ICS-formoterol
- Track 2: daily low-dose ICS plus as-needed SABA
An option for rescue therapy for Track 2 across all steps of therapy is to use an ICS whenever a SABA is used for rescue to reduce the likelihood of exacerbation.
For patients with more severe asthma symptoms most days of the week, or whose asthma is waking them from sleep one or more times weekly, then you can start with Step 3 therapy as follows:
- Track 1: low dose ICS-formoterol as MART
- Track 2: low-dose ICS with long-acting beta-agonist (LABA) for maintenance, plus as needed SABA or as needed ICS-SABA
That’s going to cover most of our patients. As we see people back, if escalation of therapy is needed, then Step 4 therapy is:
- Track 1: medium-dose ICS-formoterol as MART
- Track 2: medium-dose ICS-LABA plus as needed SABA or as-needed ICS-SABA
For patients who remain uncontrolled, it’s important to realize that Step 5 gives you the option to add a long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA). In my experience this can be very helpful. We can also consider going to high-dose ICS-LABS for maintenance. At this step, the patient usually has pretty severe, uncontrolled asthma and we can think about checking eosinophil counts, ordering pulmonary function tests, and referring to our specialist colleagues for consideration of biologic therapy.
It is important to see patients back regularly, and to assess asthma control. If a patient is not well controlled or has had exacerbations, consider stepping up therapy, or changing from albuterol alone as rescue to albuterol plus ICS for rescue. If they have been well controlled for a long time, consider de-escalation of therapy among patients on one of the higher therapy steps.
Dr. Skolnik has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) on the advisory board for AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly and Company, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck; and Bayer; serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly and Company, GlaxoSmithKline. Received research grant from Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, and Bayer; and received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly and Company, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Bayer.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik, and today I am going to talk about the 2023 update to the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. We treat a lot of asthma, and there are some important changes, particularly around the use of albuterol. There are two main guidelines when it comes to asthma, the Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) guideline and the US National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Guidelines. While I had the privilege of serving on the expert working group for the US guidelines, what I like about the GINA guidelines is that they are updated annually, and so they really help us keep up with rapid changes in the field.
Today, I’m going to focus on assessment and treatment.
Four Questions to Assess Asthma Control
Because over half of patients with asthma are not well controlled, it is important to assess control at every asthma visit. Asthma control has two domains: symptom control and the risk for future exacerbations. It is not enough to simply ask, “How is your asthma?” because many patients overrate their control and live with ongoing symptoms. There are many assessment tools; the Asthma Control Test (ACT) focuses on symptoms, and the new Asthma Impairment and Risk Questionnaire (AIRQ) assesses both symptoms and risk for exacerbations. The GINA assessment is probably the easiest to implement, with just four questions relevant to the past 4 weeks:
- Have you had daytime symptoms more than twice in one week?
- Have you had any night waking due to asthma?
- Have you needed short-acting beta-agonist (SABA), such as albuterol, rescue more than twice in one week?
- Have you had any activity limitation due to asthma?
Well-controlled asthma is defined as a negative response to all four of these questions, partly controlled asthma is one or two “yes” answers, and uncontrolled asthma is three to four positive responses. You can’t modify a patient’s therapy if you don’t know whether their asthma is well or poorly controlled. You’ll notice that these questions focus on symptom control. It is important also to ask about risk factors for exacerbations, particularly previous exacerbations.
Asthma Treatment Changes
The goals of treatment are control of symptoms and avoidance of exacerbations. The GINA guidelines emphasize that even patients with mild asthma can have severe or fatal exacerbations.
GINA recommends two management tracks. The preferred track uses inhaled corticosteroid (ICS)-formoterol as both maintenance and reliever therapy (MART). Track 2, without the use of ICS-formoterol for MART, is also offered, recognizing that the use of ICS-formoterol for MART is not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. There is an easy-to-follow stepped-care diagram that is worth looking at; it’s on page 66 of the GINA guideline PDF.
For patients who have symptoms less than twice a month, begin with Step 1 therapy:
- Track 1: as-needed low-dose ICS-formoterol.
- Track 2: treatment with albuterol; also use ICS whenever albuterol is used.
For patients with symptoms more than twice a month (but not most days of the week) treatment can start with Step 2 therapy:
- Track 1: as-needed low-dose ICS-formoterol
- Track 2: daily low-dose ICS plus as-needed SABA
An option for rescue therapy for Track 2 across all steps of therapy is to use an ICS whenever a SABA is used for rescue to reduce the likelihood of exacerbation.
For patients with more severe asthma symptoms most days of the week, or whose asthma is waking them from sleep one or more times weekly, then you can start with Step 3 therapy as follows:
- Track 1: low dose ICS-formoterol as MART
- Track 2: low-dose ICS with long-acting beta-agonist (LABA) for maintenance, plus as needed SABA or as needed ICS-SABA
That’s going to cover most of our patients. As we see people back, if escalation of therapy is needed, then Step 4 therapy is:
- Track 1: medium-dose ICS-formoterol as MART
- Track 2: medium-dose ICS-LABA plus as needed SABA or as-needed ICS-SABA
For patients who remain uncontrolled, it’s important to realize that Step 5 gives you the option to add a long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA). In my experience this can be very helpful. We can also consider going to high-dose ICS-LABS for maintenance. At this step, the patient usually has pretty severe, uncontrolled asthma and we can think about checking eosinophil counts, ordering pulmonary function tests, and referring to our specialist colleagues for consideration of biologic therapy.
It is important to see patients back regularly, and to assess asthma control. If a patient is not well controlled or has had exacerbations, consider stepping up therapy, or changing from albuterol alone as rescue to albuterol plus ICS for rescue. If they have been well controlled for a long time, consider de-escalation of therapy among patients on one of the higher therapy steps.
Dr. Skolnik has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) on the advisory board for AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly and Company, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck; and Bayer; serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly and Company, GlaxoSmithKline. Received research grant from Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, and Bayer; and received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly and Company, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Bayer.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik, and today I am going to talk about the 2023 update to the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. We treat a lot of asthma, and there are some important changes, particularly around the use of albuterol. There are two main guidelines when it comes to asthma, the Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) guideline and the US National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Guidelines. While I had the privilege of serving on the expert working group for the US guidelines, what I like about the GINA guidelines is that they are updated annually, and so they really help us keep up with rapid changes in the field.
Today, I’m going to focus on assessment and treatment.
Four Questions to Assess Asthma Control
Because over half of patients with asthma are not well controlled, it is important to assess control at every asthma visit. Asthma control has two domains: symptom control and the risk for future exacerbations. It is not enough to simply ask, “How is your asthma?” because many patients overrate their control and live with ongoing symptoms. There are many assessment tools; the Asthma Control Test (ACT) focuses on symptoms, and the new Asthma Impairment and Risk Questionnaire (AIRQ) assesses both symptoms and risk for exacerbations. The GINA assessment is probably the easiest to implement, with just four questions relevant to the past 4 weeks:
- Have you had daytime symptoms more than twice in one week?
- Have you had any night waking due to asthma?
- Have you needed short-acting beta-agonist (SABA), such as albuterol, rescue more than twice in one week?
- Have you had any activity limitation due to asthma?
Well-controlled asthma is defined as a negative response to all four of these questions, partly controlled asthma is one or two “yes” answers, and uncontrolled asthma is three to four positive responses. You can’t modify a patient’s therapy if you don’t know whether their asthma is well or poorly controlled. You’ll notice that these questions focus on symptom control. It is important also to ask about risk factors for exacerbations, particularly previous exacerbations.
Asthma Treatment Changes
The goals of treatment are control of symptoms and avoidance of exacerbations. The GINA guidelines emphasize that even patients with mild asthma can have severe or fatal exacerbations.
GINA recommends two management tracks. The preferred track uses inhaled corticosteroid (ICS)-formoterol as both maintenance and reliever therapy (MART). Track 2, without the use of ICS-formoterol for MART, is also offered, recognizing that the use of ICS-formoterol for MART is not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. There is an easy-to-follow stepped-care diagram that is worth looking at; it’s on page 66 of the GINA guideline PDF.
For patients who have symptoms less than twice a month, begin with Step 1 therapy:
- Track 1: as-needed low-dose ICS-formoterol.
- Track 2: treatment with albuterol; also use ICS whenever albuterol is used.
For patients with symptoms more than twice a month (but not most days of the week) treatment can start with Step 2 therapy:
- Track 1: as-needed low-dose ICS-formoterol
- Track 2: daily low-dose ICS plus as-needed SABA
An option for rescue therapy for Track 2 across all steps of therapy is to use an ICS whenever a SABA is used for rescue to reduce the likelihood of exacerbation.
For patients with more severe asthma symptoms most days of the week, or whose asthma is waking them from sleep one or more times weekly, then you can start with Step 3 therapy as follows:
- Track 1: low dose ICS-formoterol as MART
- Track 2: low-dose ICS with long-acting beta-agonist (LABA) for maintenance, plus as needed SABA or as needed ICS-SABA
That’s going to cover most of our patients. As we see people back, if escalation of therapy is needed, then Step 4 therapy is:
- Track 1: medium-dose ICS-formoterol as MART
- Track 2: medium-dose ICS-LABA plus as needed SABA or as-needed ICS-SABA
For patients who remain uncontrolled, it’s important to realize that Step 5 gives you the option to add a long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA). In my experience this can be very helpful. We can also consider going to high-dose ICS-LABS for maintenance. At this step, the patient usually has pretty severe, uncontrolled asthma and we can think about checking eosinophil counts, ordering pulmonary function tests, and referring to our specialist colleagues for consideration of biologic therapy.
It is important to see patients back regularly, and to assess asthma control. If a patient is not well controlled or has had exacerbations, consider stepping up therapy, or changing from albuterol alone as rescue to albuterol plus ICS for rescue. If they have been well controlled for a long time, consider de-escalation of therapy among patients on one of the higher therapy steps.
Dr. Skolnik has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) on the advisory board for AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly and Company, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck; and Bayer; serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly and Company, GlaxoSmithKline. Received research grant from Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, and Bayer; and received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly and Company, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Bayer.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
What not to prescribe to older adults and what to use instead
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
These criteria have been updated and revised approximately every 5 years since 1991 and serve to alert us to medications for which the risk-benefit ratio is not as good in older adults as in the rest of the population.
These are important criteria because medications are metabolized differently in older adults and have different effects compared with younger patients. For the sake of these criteria, older adults are 65 years of age or older. That said, we know that everyone from 65 to 100 is not the same. As people age, they develop more comorbidities, they become more frail, and they are more sensitive to the effects and side effects of drugs.
The guidance covers potentially inappropriate medications for older adults. The word “potentially” is important because this is guidance. As clinicians, we make decisions involving individuals. This guidance should be used with judgment, integrating the clinical context of the individual patient.
There is a lot in this guidance. I am going to try to cover what I feel are the most important points.
Aspirin. Since the risk for major bleeding increases with age, for primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, the harm can be greater than the benefit in older adults, so aspirin should not be used for primary prevention. Aspirin remains indicated for secondary prevention in individuals with established cardiovascular disease.
Warfarin. For treatment of atrial fibrillation or venous thromboembolism (deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism), warfarin should be avoided if possible. Warfarin has a higher risk for major bleeding, particularly intracranial bleeding, than direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs); therefore the latter are preferred. Rivaroxaban should be avoided, as it has a higher risk for major bleeding in older adults than the other DOACs. Apixaban is preferred over dabigatran. If a patient is well controlled on warfarin, you can consider continuing that treatment.
Antipsychotics. These include first- and second-generation antipsychotics such as aripiprazole, haloperidol, olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone, and others. The guidance says to avoid these agents except for FDA-approved indications such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and adjuvant treatment of depression. Use of these antipsychotics can increase risk for stroke, heart attack, and mortality. Essentially, the guidance says do not use these medications lightly for the treatment of agitated dementia. For those of us with older patients, this can get tricky because agitated dementia is a difficult issue for which there are no good effective medications. The Beers guidance recognizes this in saying that these medications should be avoided unless behavioral interventions have failed. So, there are times where you may need to use these medicines, but use them judiciously.
For patients with dementia, anticholinergics, antipsychotics, and benzodiazepines should be avoided if possible.
Benzodiazepines. Benzodiazepines should also be avoided because older adults have increased sensitivity to their effects due to slower metabolism and clearance of these medications, which can lead to a much longer half-life and higher serum level. In older adults, benzodiazepines increase the risk for cognitive impairment, delirium, falls, fractures, and even motor accidents. The same concerns affect the group of non-benzodiazepine sleeping medicines known as “Z-drugs.”
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Used frequently in our practices, NSAIDs are nevertheless on the list. As we think through the risk-benefit ratio of using NSAIDs in older adults, we often underappreciate the risks of these agents. Upper gastrointestinal ulcers with bleeding occur in approximately 1% of patients treated for 3-6 months with an NSAID and in 2%-4% of patients treated for a year. NSAIDs also increase the risk for renal impairment and cardiovascular disease.
Other medications to avoid (if possible). These include:
Sulfonylureas, due to a high risk for hypoglycemia. A short-acting sulfonylurea, such as glipizide, should be used if one is needed.
Proton pump inhibitors should not be used long-term if it can be avoided.
Digoxin should not be first-line treatment for atrial fibrillation or heart failure. Decreased renal clearance in older adults can lead to toxic levels of digoxin, particularly during acute illnesses. Avoid doses > 0.125 mg/day.
Nitrofurantoin should be avoided when the patient’s creatinine clearance is < 30 or for long-term suppressive therapy.
Avoid combining medications that have high anticholinergic side effects, such as scopolamine, diphenhydramine, oxybutynin, cyclobenzaprine, and others.
It is always important to understand the benefits and the risks of the drugs we prescribe. It is also important to remember that older adults are a particularly vulnerable population. The Beers criteria provide important guidance, which we can then use to make decisions about medicines for individual patients.
Dr. Skolnik is a professor in the department of family medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director in the department of family medicine at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. He disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, GSK, Merck, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, and Teva.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
These criteria have been updated and revised approximately every 5 years since 1991 and serve to alert us to medications for which the risk-benefit ratio is not as good in older adults as in the rest of the population.
These are important criteria because medications are metabolized differently in older adults and have different effects compared with younger patients. For the sake of these criteria, older adults are 65 years of age or older. That said, we know that everyone from 65 to 100 is not the same. As people age, they develop more comorbidities, they become more frail, and they are more sensitive to the effects and side effects of drugs.
The guidance covers potentially inappropriate medications for older adults. The word “potentially” is important because this is guidance. As clinicians, we make decisions involving individuals. This guidance should be used with judgment, integrating the clinical context of the individual patient.
There is a lot in this guidance. I am going to try to cover what I feel are the most important points.
Aspirin. Since the risk for major bleeding increases with age, for primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, the harm can be greater than the benefit in older adults, so aspirin should not be used for primary prevention. Aspirin remains indicated for secondary prevention in individuals with established cardiovascular disease.
Warfarin. For treatment of atrial fibrillation or venous thromboembolism (deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism), warfarin should be avoided if possible. Warfarin has a higher risk for major bleeding, particularly intracranial bleeding, than direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs); therefore the latter are preferred. Rivaroxaban should be avoided, as it has a higher risk for major bleeding in older adults than the other DOACs. Apixaban is preferred over dabigatran. If a patient is well controlled on warfarin, you can consider continuing that treatment.
Antipsychotics. These include first- and second-generation antipsychotics such as aripiprazole, haloperidol, olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone, and others. The guidance says to avoid these agents except for FDA-approved indications such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and adjuvant treatment of depression. Use of these antipsychotics can increase risk for stroke, heart attack, and mortality. Essentially, the guidance says do not use these medications lightly for the treatment of agitated dementia. For those of us with older patients, this can get tricky because agitated dementia is a difficult issue for which there are no good effective medications. The Beers guidance recognizes this in saying that these medications should be avoided unless behavioral interventions have failed. So, there are times where you may need to use these medicines, but use them judiciously.
For patients with dementia, anticholinergics, antipsychotics, and benzodiazepines should be avoided if possible.
Benzodiazepines. Benzodiazepines should also be avoided because older adults have increased sensitivity to their effects due to slower metabolism and clearance of these medications, which can lead to a much longer half-life and higher serum level. In older adults, benzodiazepines increase the risk for cognitive impairment, delirium, falls, fractures, and even motor accidents. The same concerns affect the group of non-benzodiazepine sleeping medicines known as “Z-drugs.”
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Used frequently in our practices, NSAIDs are nevertheless on the list. As we think through the risk-benefit ratio of using NSAIDs in older adults, we often underappreciate the risks of these agents. Upper gastrointestinal ulcers with bleeding occur in approximately 1% of patients treated for 3-6 months with an NSAID and in 2%-4% of patients treated for a year. NSAIDs also increase the risk for renal impairment and cardiovascular disease.
Other medications to avoid (if possible). These include:
Sulfonylureas, due to a high risk for hypoglycemia. A short-acting sulfonylurea, such as glipizide, should be used if one is needed.
Proton pump inhibitors should not be used long-term if it can be avoided.
Digoxin should not be first-line treatment for atrial fibrillation or heart failure. Decreased renal clearance in older adults can lead to toxic levels of digoxin, particularly during acute illnesses. Avoid doses > 0.125 mg/day.
Nitrofurantoin should be avoided when the patient’s creatinine clearance is < 30 or for long-term suppressive therapy.
Avoid combining medications that have high anticholinergic side effects, such as scopolamine, diphenhydramine, oxybutynin, cyclobenzaprine, and others.
It is always important to understand the benefits and the risks of the drugs we prescribe. It is also important to remember that older adults are a particularly vulnerable population. The Beers criteria provide important guidance, which we can then use to make decisions about medicines for individual patients.
Dr. Skolnik is a professor in the department of family medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director in the department of family medicine at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. He disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, GSK, Merck, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, and Teva.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
These criteria have been updated and revised approximately every 5 years since 1991 and serve to alert us to medications for which the risk-benefit ratio is not as good in older adults as in the rest of the population.
These are important criteria because medications are metabolized differently in older adults and have different effects compared with younger patients. For the sake of these criteria, older adults are 65 years of age or older. That said, we know that everyone from 65 to 100 is not the same. As people age, they develop more comorbidities, they become more frail, and they are more sensitive to the effects and side effects of drugs.
The guidance covers potentially inappropriate medications for older adults. The word “potentially” is important because this is guidance. As clinicians, we make decisions involving individuals. This guidance should be used with judgment, integrating the clinical context of the individual patient.
There is a lot in this guidance. I am going to try to cover what I feel are the most important points.
Aspirin. Since the risk for major bleeding increases with age, for primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, the harm can be greater than the benefit in older adults, so aspirin should not be used for primary prevention. Aspirin remains indicated for secondary prevention in individuals with established cardiovascular disease.
Warfarin. For treatment of atrial fibrillation or venous thromboembolism (deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism), warfarin should be avoided if possible. Warfarin has a higher risk for major bleeding, particularly intracranial bleeding, than direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs); therefore the latter are preferred. Rivaroxaban should be avoided, as it has a higher risk for major bleeding in older adults than the other DOACs. Apixaban is preferred over dabigatran. If a patient is well controlled on warfarin, you can consider continuing that treatment.
Antipsychotics. These include first- and second-generation antipsychotics such as aripiprazole, haloperidol, olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone, and others. The guidance says to avoid these agents except for FDA-approved indications such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and adjuvant treatment of depression. Use of these antipsychotics can increase risk for stroke, heart attack, and mortality. Essentially, the guidance says do not use these medications lightly for the treatment of agitated dementia. For those of us with older patients, this can get tricky because agitated dementia is a difficult issue for which there are no good effective medications. The Beers guidance recognizes this in saying that these medications should be avoided unless behavioral interventions have failed. So, there are times where you may need to use these medicines, but use them judiciously.
For patients with dementia, anticholinergics, antipsychotics, and benzodiazepines should be avoided if possible.
Benzodiazepines. Benzodiazepines should also be avoided because older adults have increased sensitivity to their effects due to slower metabolism and clearance of these medications, which can lead to a much longer half-life and higher serum level. In older adults, benzodiazepines increase the risk for cognitive impairment, delirium, falls, fractures, and even motor accidents. The same concerns affect the group of non-benzodiazepine sleeping medicines known as “Z-drugs.”
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Used frequently in our practices, NSAIDs are nevertheless on the list. As we think through the risk-benefit ratio of using NSAIDs in older adults, we often underappreciate the risks of these agents. Upper gastrointestinal ulcers with bleeding occur in approximately 1% of patients treated for 3-6 months with an NSAID and in 2%-4% of patients treated for a year. NSAIDs also increase the risk for renal impairment and cardiovascular disease.
Other medications to avoid (if possible). These include:
Sulfonylureas, due to a high risk for hypoglycemia. A short-acting sulfonylurea, such as glipizide, should be used if one is needed.
Proton pump inhibitors should not be used long-term if it can be avoided.
Digoxin should not be first-line treatment for atrial fibrillation or heart failure. Decreased renal clearance in older adults can lead to toxic levels of digoxin, particularly during acute illnesses. Avoid doses > 0.125 mg/day.
Nitrofurantoin should be avoided when the patient’s creatinine clearance is < 30 or for long-term suppressive therapy.
Avoid combining medications that have high anticholinergic side effects, such as scopolamine, diphenhydramine, oxybutynin, cyclobenzaprine, and others.
It is always important to understand the benefits and the risks of the drugs we prescribe. It is also important to remember that older adults are a particularly vulnerable population. The Beers criteria provide important guidance, which we can then use to make decisions about medicines for individual patients.
Dr. Skolnik is a professor in the department of family medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director in the department of family medicine at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. He disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, GSK, Merck, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, and Teva.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Mammography breast density reporting: What it means for clinicians
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Today, I’m going to talk about the 2023 Food and Drug Administration regulation that requires breast density to be reported on all mammogram results nationwide, and for that report to go to both clinicians and patients. Previously this was the rule in some states, but not in others. This is important because 40%-50% of women have dense breasts. I’m going to discuss what that means for you, and for our patients.
First
Breast density describes the appearance of the breast on mammography. Appearance varies on the basis of breast tissue composition, with fibroglandular tissue being more dense than fatty tissue. Breast density is important because it relates to both the risk for cancer and the ability of mammography to detect cancer.
Breast density is defined and classified according to the American College of Radiology’s BI-RADS four-category scale. Categories 1 and 2 refer to breast tissue that is not dense, accounting for about 50% of the population. Categories 3 and 4 describe heterogeneously dense and extremely dense breast tissue, which occur in approximately 40% and 50% of women, respectively. When speaking about dense breast tissue readings on mammography, we are referring to categories 3 and 4.
Women with dense breast tissue have an increased risk of developing breast cancer and are less likely to have early breast cancer detected on mammography.
Let’s go over the details by category:
For women in categories 1 and 2 (considered not dense breast tissue), the sensitivity of mammography for detecting early breast cancer is 80%-90%. In categories 3 and 4, the sensitivity of mammography drops to 60%-70%.
Compared with women with average breast density, the risk of developing breast cancer is 20% higher in women with BI-RADS category 3 breasts, and more than twice as high (relative risk, 2.1) in those with BI-RADS category 4 breasts. Thus, the risk of developing breast cancer is higher, but the sensitivity of the test is lower.
The clinical question is, what should we do about this? For women who have a normal mammogram with dense breasts, should follow-up testing be done, and if so, what test? The main follow-up testing options are either ultrasound or MRI, usually ultrasound. Additional testing will detect additional cancers that were not picked up on the initial mammogram and will also lead to additional biopsies for false-positive tests from the additional testing.
An American College of Gynecology and Obstetrics practice advisory nicely summarizes the evidence and clarifies that this decision is made in the context of a lack of published evidence demonstrating improved outcomes, specifically no reduction in breast cancer mortality, with supplemental testing. The official ACOG stance is that they “do not recommend routine use of alternative or adjunctive tests to screening mammography in women with dense breasts who are asymptomatic and have no additional risk factors.”
This is an area where it is important to understand the data. We are all going to be getting test results back that indicate level of breast density, and those test results will also be sent to our patients, so we are going to be asked about this by interested patients. Should this be something that we talk to patients about, utilizing shared decision-making to decide about whether follow-up testing is necessary in women with dense breasts? That is something each clinician will need to decide, and knowing the data is a critically important step in that decision.
Neil Skolnik, MD, is a professor, department of family medicine, at Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director, department of family medicine, Abington (Pennsylvania) Jefferson Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Today, I’m going to talk about the 2023 Food and Drug Administration regulation that requires breast density to be reported on all mammogram results nationwide, and for that report to go to both clinicians and patients. Previously this was the rule in some states, but not in others. This is important because 40%-50% of women have dense breasts. I’m going to discuss what that means for you, and for our patients.
First
Breast density describes the appearance of the breast on mammography. Appearance varies on the basis of breast tissue composition, with fibroglandular tissue being more dense than fatty tissue. Breast density is important because it relates to both the risk for cancer and the ability of mammography to detect cancer.
Breast density is defined and classified according to the American College of Radiology’s BI-RADS four-category scale. Categories 1 and 2 refer to breast tissue that is not dense, accounting for about 50% of the population. Categories 3 and 4 describe heterogeneously dense and extremely dense breast tissue, which occur in approximately 40% and 50% of women, respectively. When speaking about dense breast tissue readings on mammography, we are referring to categories 3 and 4.
Women with dense breast tissue have an increased risk of developing breast cancer and are less likely to have early breast cancer detected on mammography.
Let’s go over the details by category:
For women in categories 1 and 2 (considered not dense breast tissue), the sensitivity of mammography for detecting early breast cancer is 80%-90%. In categories 3 and 4, the sensitivity of mammography drops to 60%-70%.
Compared with women with average breast density, the risk of developing breast cancer is 20% higher in women with BI-RADS category 3 breasts, and more than twice as high (relative risk, 2.1) in those with BI-RADS category 4 breasts. Thus, the risk of developing breast cancer is higher, but the sensitivity of the test is lower.
The clinical question is, what should we do about this? For women who have a normal mammogram with dense breasts, should follow-up testing be done, and if so, what test? The main follow-up testing options are either ultrasound or MRI, usually ultrasound. Additional testing will detect additional cancers that were not picked up on the initial mammogram and will also lead to additional biopsies for false-positive tests from the additional testing.
An American College of Gynecology and Obstetrics practice advisory nicely summarizes the evidence and clarifies that this decision is made in the context of a lack of published evidence demonstrating improved outcomes, specifically no reduction in breast cancer mortality, with supplemental testing. The official ACOG stance is that they “do not recommend routine use of alternative or adjunctive tests to screening mammography in women with dense breasts who are asymptomatic and have no additional risk factors.”
This is an area where it is important to understand the data. We are all going to be getting test results back that indicate level of breast density, and those test results will also be sent to our patients, so we are going to be asked about this by interested patients. Should this be something that we talk to patients about, utilizing shared decision-making to decide about whether follow-up testing is necessary in women with dense breasts? That is something each clinician will need to decide, and knowing the data is a critically important step in that decision.
Neil Skolnik, MD, is a professor, department of family medicine, at Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director, department of family medicine, Abington (Pennsylvania) Jefferson Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Today, I’m going to talk about the 2023 Food and Drug Administration regulation that requires breast density to be reported on all mammogram results nationwide, and for that report to go to both clinicians and patients. Previously this was the rule in some states, but not in others. This is important because 40%-50% of women have dense breasts. I’m going to discuss what that means for you, and for our patients.
First
Breast density describes the appearance of the breast on mammography. Appearance varies on the basis of breast tissue composition, with fibroglandular tissue being more dense than fatty tissue. Breast density is important because it relates to both the risk for cancer and the ability of mammography to detect cancer.
Breast density is defined and classified according to the American College of Radiology’s BI-RADS four-category scale. Categories 1 and 2 refer to breast tissue that is not dense, accounting for about 50% of the population. Categories 3 and 4 describe heterogeneously dense and extremely dense breast tissue, which occur in approximately 40% and 50% of women, respectively. When speaking about dense breast tissue readings on mammography, we are referring to categories 3 and 4.
Women with dense breast tissue have an increased risk of developing breast cancer and are less likely to have early breast cancer detected on mammography.
Let’s go over the details by category:
For women in categories 1 and 2 (considered not dense breast tissue), the sensitivity of mammography for detecting early breast cancer is 80%-90%. In categories 3 and 4, the sensitivity of mammography drops to 60%-70%.
Compared with women with average breast density, the risk of developing breast cancer is 20% higher in women with BI-RADS category 3 breasts, and more than twice as high (relative risk, 2.1) in those with BI-RADS category 4 breasts. Thus, the risk of developing breast cancer is higher, but the sensitivity of the test is lower.
The clinical question is, what should we do about this? For women who have a normal mammogram with dense breasts, should follow-up testing be done, and if so, what test? The main follow-up testing options are either ultrasound or MRI, usually ultrasound. Additional testing will detect additional cancers that were not picked up on the initial mammogram and will also lead to additional biopsies for false-positive tests from the additional testing.
An American College of Gynecology and Obstetrics practice advisory nicely summarizes the evidence and clarifies that this decision is made in the context of a lack of published evidence demonstrating improved outcomes, specifically no reduction in breast cancer mortality, with supplemental testing. The official ACOG stance is that they “do not recommend routine use of alternative or adjunctive tests to screening mammography in women with dense breasts who are asymptomatic and have no additional risk factors.”
This is an area where it is important to understand the data. We are all going to be getting test results back that indicate level of breast density, and those test results will also be sent to our patients, so we are going to be asked about this by interested patients. Should this be something that we talk to patients about, utilizing shared decision-making to decide about whether follow-up testing is necessary in women with dense breasts? That is something each clinician will need to decide, and knowing the data is a critically important step in that decision.
Neil Skolnik, MD, is a professor, department of family medicine, at Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director, department of family medicine, Abington (Pennsylvania) Jefferson Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HFpEF: New guidelines are pertinent for primary care
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik. The incidence of HFpEF is increasing, yet it’s underrecognized. Now that there are evidence-based treatment approaches that improve outcomes, we’ve started to look for this condition and are diagnosing it more often. HFpEF is commonly encountered in primary care.
We should be thinking about HFpEF when we see adults with shortness of breath and/or fatigue and reduced exercise capacity, particularly in the settings of obesity, hypertension, or diabetes. It may not be simple deconditioning; it could be HFpEF.
I’ll organize this discussion into three topics: when to think about HFpEF, how to diagnosis it. and how to treat it.
When to think about HFpEF. When we see a person with risk factors (e.g., older age, obesity, diabetes, hypertension) experiencing dyspnea or fatigue with physical activity, their symptoms are not always from simple deconditioning. HFpEF should be on our differential as well as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Making the diagnosis. HFpEF is defined as a clinical diagnosis of HR with left ventricular EF (LVEF) greater than 50%. Remember, in HF with reduced EF (HFrEF), the EF is less than 40%, and the EF in midrange HF is 40%-50%. See this recent HF review for more details on reduced and midrange ejection fractions.
For practical purposes, to diagnose HFpEF, check for an elevated N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) (> 125 pg/mL) and evidence of diastolic dysfunction on echocardiogram. Be aware that patients with obesity and HFpEF have lower BNP concentrations than those without obesity, and one professional society has suggested that a 50% reduction in BNP cutoff values should be used when making the diagnosis in patients with obesity.
Of course, we evaluate for other causes of dyspnea and/or edema including lung (most commonly COPD), liver, or kidney disease. When the diagnosis of HFpEF is made, consider whether further evaluation is warranted for specific underlying causes of HFpEF, such as amyloidosis, sarcoid, hemochromatosis, or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Treatment. The evolution of the management of HFpEF has been intriguing. I recommend that people take a look at the guidelines and read the supporting trials. Finding effective therapies has taken longer than it did for HFrEF, but finally, an effective therapy for HFpEF is available.
To quote the guidelines, diuretics should be used “judiciously as needed” to reduce pulmonary congestion and improve symptoms. But here’s the big deal. The mainstays of treatment for HFpEF are the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on the basis of the findings of two trials: DELIVER (dapagliflozin) and EMPEROR-Preserved (empagliflozin), both of which have shown very impressive levels of benefit.
Both trials lasted a little over 2 years and found a statistically significant approximately 30% decline in HF hospitalizations and a numerical reduction of about 10% in cardiovascular death, which was statistically significant in meta-analysis. That’s over 2 years! That’s a large level of effect. They also showed improvements in symptoms and health status. Therefore, SGLT2 inhibitors are first-line treatment for all individuals with HFpEF, currently graded as a Class 2a (moderate) recommendation, but likely soon to be upgraded to Class 1 (strong) recommendation.
After the SGLT2 inhibitors, treatment is based on evidence which is not as strong and the recommendations are graded as Class 2b (weak) recommendations. In men with an LVEF less than 55%-60% and for women with any EF, use of a mineralocorticoid antagonist (MRA), an angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor, or if an ARN inhibitor is not feasible, an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) may be considered.
Nonpharmacologic management is also important. Exercise and weight loss (if the patient is overweight) can improve symptoms and quality of life. A new intervention, an implantable ambulatory pulmonary artery sensor, called CardioMEMS, has been evaluated in two trials, showing a decrease in HF hospitalizations. This may be considered for those who experience hospitalizations for HF and continue to experience New York Heart Association functional Class 3 symptoms despite optimal guideline-directed medical therapy or those who have lability in volume status or other medical problems (such as obesity or COPD) that make it difficult to tell whether their symptoms are from HFpEF or a comorbid condition.
In summary:
- Have a low threshold to evaluate for HFpEF in any patients who have shortness of breath, fatigue with exertion, or fluid overload.
- Initially evaluate with an NT-proBNP level and an echocardiogram.
- First-line treatment is an evidence-based SGLT2 inhibitor along with exercise and perhaps weight loss if needed. A loop diuretic can be used as needed to control volume status. Then you can consider, based on symptoms and details discussed above, an MRA, ARN inhibitor, or ARB.
This is important information for a diagnosis that is common in primary care, HFpEF, and for which we now have impressive, effective treatment.
Dr. Skolnik is a professor in the department of family medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the department of family medicine at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. He disclosed conflicts of interest with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim; Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik. The incidence of HFpEF is increasing, yet it’s underrecognized. Now that there are evidence-based treatment approaches that improve outcomes, we’ve started to look for this condition and are diagnosing it more often. HFpEF is commonly encountered in primary care.
We should be thinking about HFpEF when we see adults with shortness of breath and/or fatigue and reduced exercise capacity, particularly in the settings of obesity, hypertension, or diabetes. It may not be simple deconditioning; it could be HFpEF.
I’ll organize this discussion into three topics: when to think about HFpEF, how to diagnosis it. and how to treat it.
When to think about HFpEF. When we see a person with risk factors (e.g., older age, obesity, diabetes, hypertension) experiencing dyspnea or fatigue with physical activity, their symptoms are not always from simple deconditioning. HFpEF should be on our differential as well as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Making the diagnosis. HFpEF is defined as a clinical diagnosis of HR with left ventricular EF (LVEF) greater than 50%. Remember, in HF with reduced EF (HFrEF), the EF is less than 40%, and the EF in midrange HF is 40%-50%. See this recent HF review for more details on reduced and midrange ejection fractions.
For practical purposes, to diagnose HFpEF, check for an elevated N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) (> 125 pg/mL) and evidence of diastolic dysfunction on echocardiogram. Be aware that patients with obesity and HFpEF have lower BNP concentrations than those without obesity, and one professional society has suggested that a 50% reduction in BNP cutoff values should be used when making the diagnosis in patients with obesity.
Of course, we evaluate for other causes of dyspnea and/or edema including lung (most commonly COPD), liver, or kidney disease. When the diagnosis of HFpEF is made, consider whether further evaluation is warranted for specific underlying causes of HFpEF, such as amyloidosis, sarcoid, hemochromatosis, or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Treatment. The evolution of the management of HFpEF has been intriguing. I recommend that people take a look at the guidelines and read the supporting trials. Finding effective therapies has taken longer than it did for HFrEF, but finally, an effective therapy for HFpEF is available.
To quote the guidelines, diuretics should be used “judiciously as needed” to reduce pulmonary congestion and improve symptoms. But here’s the big deal. The mainstays of treatment for HFpEF are the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on the basis of the findings of two trials: DELIVER (dapagliflozin) and EMPEROR-Preserved (empagliflozin), both of which have shown very impressive levels of benefit.
Both trials lasted a little over 2 years and found a statistically significant approximately 30% decline in HF hospitalizations and a numerical reduction of about 10% in cardiovascular death, which was statistically significant in meta-analysis. That’s over 2 years! That’s a large level of effect. They also showed improvements in symptoms and health status. Therefore, SGLT2 inhibitors are first-line treatment for all individuals with HFpEF, currently graded as a Class 2a (moderate) recommendation, but likely soon to be upgraded to Class 1 (strong) recommendation.
After the SGLT2 inhibitors, treatment is based on evidence which is not as strong and the recommendations are graded as Class 2b (weak) recommendations. In men with an LVEF less than 55%-60% and for women with any EF, use of a mineralocorticoid antagonist (MRA), an angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor, or if an ARN inhibitor is not feasible, an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) may be considered.
Nonpharmacologic management is also important. Exercise and weight loss (if the patient is overweight) can improve symptoms and quality of life. A new intervention, an implantable ambulatory pulmonary artery sensor, called CardioMEMS, has been evaluated in two trials, showing a decrease in HF hospitalizations. This may be considered for those who experience hospitalizations for HF and continue to experience New York Heart Association functional Class 3 symptoms despite optimal guideline-directed medical therapy or those who have lability in volume status or other medical problems (such as obesity or COPD) that make it difficult to tell whether their symptoms are from HFpEF or a comorbid condition.
In summary:
- Have a low threshold to evaluate for HFpEF in any patients who have shortness of breath, fatigue with exertion, or fluid overload.
- Initially evaluate with an NT-proBNP level and an echocardiogram.
- First-line treatment is an evidence-based SGLT2 inhibitor along with exercise and perhaps weight loss if needed. A loop diuretic can be used as needed to control volume status. Then you can consider, based on symptoms and details discussed above, an MRA, ARN inhibitor, or ARB.
This is important information for a diagnosis that is common in primary care, HFpEF, and for which we now have impressive, effective treatment.
Dr. Skolnik is a professor in the department of family medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the department of family medicine at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. He disclosed conflicts of interest with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim; Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik. The incidence of HFpEF is increasing, yet it’s underrecognized. Now that there are evidence-based treatment approaches that improve outcomes, we’ve started to look for this condition and are diagnosing it more often. HFpEF is commonly encountered in primary care.
We should be thinking about HFpEF when we see adults with shortness of breath and/or fatigue and reduced exercise capacity, particularly in the settings of obesity, hypertension, or diabetes. It may not be simple deconditioning; it could be HFpEF.
I’ll organize this discussion into three topics: when to think about HFpEF, how to diagnosis it. and how to treat it.
When to think about HFpEF. When we see a person with risk factors (e.g., older age, obesity, diabetes, hypertension) experiencing dyspnea or fatigue with physical activity, their symptoms are not always from simple deconditioning. HFpEF should be on our differential as well as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Making the diagnosis. HFpEF is defined as a clinical diagnosis of HR with left ventricular EF (LVEF) greater than 50%. Remember, in HF with reduced EF (HFrEF), the EF is less than 40%, and the EF in midrange HF is 40%-50%. See this recent HF review for more details on reduced and midrange ejection fractions.
For practical purposes, to diagnose HFpEF, check for an elevated N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) (> 125 pg/mL) and evidence of diastolic dysfunction on echocardiogram. Be aware that patients with obesity and HFpEF have lower BNP concentrations than those without obesity, and one professional society has suggested that a 50% reduction in BNP cutoff values should be used when making the diagnosis in patients with obesity.
Of course, we evaluate for other causes of dyspnea and/or edema including lung (most commonly COPD), liver, or kidney disease. When the diagnosis of HFpEF is made, consider whether further evaluation is warranted for specific underlying causes of HFpEF, such as amyloidosis, sarcoid, hemochromatosis, or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Treatment. The evolution of the management of HFpEF has been intriguing. I recommend that people take a look at the guidelines and read the supporting trials. Finding effective therapies has taken longer than it did for HFrEF, but finally, an effective therapy for HFpEF is available.
To quote the guidelines, diuretics should be used “judiciously as needed” to reduce pulmonary congestion and improve symptoms. But here’s the big deal. The mainstays of treatment for HFpEF are the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on the basis of the findings of two trials: DELIVER (dapagliflozin) and EMPEROR-Preserved (empagliflozin), both of which have shown very impressive levels of benefit.
Both trials lasted a little over 2 years and found a statistically significant approximately 30% decline in HF hospitalizations and a numerical reduction of about 10% in cardiovascular death, which was statistically significant in meta-analysis. That’s over 2 years! That’s a large level of effect. They also showed improvements in symptoms and health status. Therefore, SGLT2 inhibitors are first-line treatment for all individuals with HFpEF, currently graded as a Class 2a (moderate) recommendation, but likely soon to be upgraded to Class 1 (strong) recommendation.
After the SGLT2 inhibitors, treatment is based on evidence which is not as strong and the recommendations are graded as Class 2b (weak) recommendations. In men with an LVEF less than 55%-60% and for women with any EF, use of a mineralocorticoid antagonist (MRA), an angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor, or if an ARN inhibitor is not feasible, an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) may be considered.
Nonpharmacologic management is also important. Exercise and weight loss (if the patient is overweight) can improve symptoms and quality of life. A new intervention, an implantable ambulatory pulmonary artery sensor, called CardioMEMS, has been evaluated in two trials, showing a decrease in HF hospitalizations. This may be considered for those who experience hospitalizations for HF and continue to experience New York Heart Association functional Class 3 symptoms despite optimal guideline-directed medical therapy or those who have lability in volume status or other medical problems (such as obesity or COPD) that make it difficult to tell whether their symptoms are from HFpEF or a comorbid condition.
In summary:
- Have a low threshold to evaluate for HFpEF in any patients who have shortness of breath, fatigue with exertion, or fluid overload.
- Initially evaluate with an NT-proBNP level and an echocardiogram.
- First-line treatment is an evidence-based SGLT2 inhibitor along with exercise and perhaps weight loss if needed. A loop diuretic can be used as needed to control volume status. Then you can consider, based on symptoms and details discussed above, an MRA, ARN inhibitor, or ARB.
This is important information for a diagnosis that is common in primary care, HFpEF, and for which we now have impressive, effective treatment.
Dr. Skolnik is a professor in the department of family medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the department of family medicine at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. He disclosed conflicts of interest with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim; Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Osteoporosis and osteopenia: Latest treatment recommendations
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik. Today’s topic is the new osteoporosis treatment guidelines issued by the American College of Physicians (ACP). The focus of the guidelines is treatment of osteoporosis. But first, I want to discuss screening.
In its 2018 statement, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) says that osteoporosis should be screened for in women older than 65 years of age, and those who are younger who are at increased risk based on a risk assessment tool (usually the FRAX tool). There is not enough evidence to weigh in for or against screening men. The other large organization that weighs in on screening is the Bone Health & Osteoporosis Foundation, which agrees with the USPSTF, but in addition says that we should be screening men over age 70 and men who are younger (age 50 to 69) who have risk factors. We should also screen anyone who has a fracture after low impact or no trauma.
Let’s now go on to the ACP treatment guidelines. Osteoporosis is defined as bone mineral density at the femoral neck or the lumbar spine, or both, with a T score less than -2.5.
For postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, you should use a bisphosphonate as first-line treatment to reduce the risk for future fractures. This is given a strong recommendation based on a high certainty of evidence. Bisphosphonates vs. placebo over 3 years leads to one fewer hip fracture per 150 patients treated and one fewer vertebral fracture per 50 people treated.
All the other recommendations in the guidelines are considered “conditional recommendations” that are correct for most people. But whether they make sense for an individual patient depends upon other details, as well as their values and preferences. For instance, treatment of osteoporosis in men is given a conditional recommendation, not because the evidence suggests that it’s not as effective, but because there is not as much evidence. Initial treatment for a man with osteoporosis is with bisphosphonates. Men do get osteoporosis and account for about 30% of hip fractures. This is not a surprise to anyone who takes care of older adults.
For postmenopausal women or men who you would want to treat but who can’t tolerate a bisphosphonate, then the recommendation is to use a RANK ligand inhibitor. Denosumab can be used as second-line treatment to reduce the risk for fractures. Remember, bisphosphonates and denosumab are antiresorptive drugs, meaning they slow the progression of osteoporosis. The anabolic drugs, on the other hand, such as the sclerostin inhibitor romosozumab and recombinant human parathyroid hormone (PTH) teriparatide, increase bone density. The anabolic agents should be used only in women with primary osteoporosis who are at very high risk for fractures, and use of these agents always needs to be followed by an antiresorptive agent, because otherwise there’s a risk for rebound osteoporosis and an increased risk for vertebral fractures.
Now, how about osteopenia? The guidelines recommend that for women over 65 with osteopenia, use an individualized approach influenced by the level of risk for fracture, including increased age, low body weight, current smoking, hip fracture in a parent, fall risk, and a personal history of fracture. The guidelines note that increasing the duration of bisphosphonate therapy beyond 3-5 years does reduce the risk for new vertebral fractures, but it doesn’t reduce the risk for other fractures and it increases the risk for osteonecrosis of the jaw and atypical hip fractures. Therefore, the guidelines say that we should use bisphosphonates only for 3-5 years unless someone is at extremely high risk. It’s also important to note that there’s a fivefold higher risk for atypical femoral fractures among Asian women.
Don’t forget about adequate vitamin D and calcium. And most importantly, don’t forget about exercise, particularly exercise aimed at improving balance and quadriceps strength, which helps prevent falls.
Dr. Skolnik is professor, department of family medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director, department of family medicine, Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. He disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, and Teva.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik. Today’s topic is the new osteoporosis treatment guidelines issued by the American College of Physicians (ACP). The focus of the guidelines is treatment of osteoporosis. But first, I want to discuss screening.
In its 2018 statement, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) says that osteoporosis should be screened for in women older than 65 years of age, and those who are younger who are at increased risk based on a risk assessment tool (usually the FRAX tool). There is not enough evidence to weigh in for or against screening men. The other large organization that weighs in on screening is the Bone Health & Osteoporosis Foundation, which agrees with the USPSTF, but in addition says that we should be screening men over age 70 and men who are younger (age 50 to 69) who have risk factors. We should also screen anyone who has a fracture after low impact or no trauma.
Let’s now go on to the ACP treatment guidelines. Osteoporosis is defined as bone mineral density at the femoral neck or the lumbar spine, or both, with a T score less than -2.5.
For postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, you should use a bisphosphonate as first-line treatment to reduce the risk for future fractures. This is given a strong recommendation based on a high certainty of evidence. Bisphosphonates vs. placebo over 3 years leads to one fewer hip fracture per 150 patients treated and one fewer vertebral fracture per 50 people treated.
All the other recommendations in the guidelines are considered “conditional recommendations” that are correct for most people. But whether they make sense for an individual patient depends upon other details, as well as their values and preferences. For instance, treatment of osteoporosis in men is given a conditional recommendation, not because the evidence suggests that it’s not as effective, but because there is not as much evidence. Initial treatment for a man with osteoporosis is with bisphosphonates. Men do get osteoporosis and account for about 30% of hip fractures. This is not a surprise to anyone who takes care of older adults.
For postmenopausal women or men who you would want to treat but who can’t tolerate a bisphosphonate, then the recommendation is to use a RANK ligand inhibitor. Denosumab can be used as second-line treatment to reduce the risk for fractures. Remember, bisphosphonates and denosumab are antiresorptive drugs, meaning they slow the progression of osteoporosis. The anabolic drugs, on the other hand, such as the sclerostin inhibitor romosozumab and recombinant human parathyroid hormone (PTH) teriparatide, increase bone density. The anabolic agents should be used only in women with primary osteoporosis who are at very high risk for fractures, and use of these agents always needs to be followed by an antiresorptive agent, because otherwise there’s a risk for rebound osteoporosis and an increased risk for vertebral fractures.
Now, how about osteopenia? The guidelines recommend that for women over 65 with osteopenia, use an individualized approach influenced by the level of risk for fracture, including increased age, low body weight, current smoking, hip fracture in a parent, fall risk, and a personal history of fracture. The guidelines note that increasing the duration of bisphosphonate therapy beyond 3-5 years does reduce the risk for new vertebral fractures, but it doesn’t reduce the risk for other fractures and it increases the risk for osteonecrosis of the jaw and atypical hip fractures. Therefore, the guidelines say that we should use bisphosphonates only for 3-5 years unless someone is at extremely high risk. It’s also important to note that there’s a fivefold higher risk for atypical femoral fractures among Asian women.
Don’t forget about adequate vitamin D and calcium. And most importantly, don’t forget about exercise, particularly exercise aimed at improving balance and quadriceps strength, which helps prevent falls.
Dr. Skolnik is professor, department of family medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director, department of family medicine, Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. He disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, and Teva.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik. Today’s topic is the new osteoporosis treatment guidelines issued by the American College of Physicians (ACP). The focus of the guidelines is treatment of osteoporosis. But first, I want to discuss screening.
In its 2018 statement, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) says that osteoporosis should be screened for in women older than 65 years of age, and those who are younger who are at increased risk based on a risk assessment tool (usually the FRAX tool). There is not enough evidence to weigh in for or against screening men. The other large organization that weighs in on screening is the Bone Health & Osteoporosis Foundation, which agrees with the USPSTF, but in addition says that we should be screening men over age 70 and men who are younger (age 50 to 69) who have risk factors. We should also screen anyone who has a fracture after low impact or no trauma.
Let’s now go on to the ACP treatment guidelines. Osteoporosis is defined as bone mineral density at the femoral neck or the lumbar spine, or both, with a T score less than -2.5.
For postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, you should use a bisphosphonate as first-line treatment to reduce the risk for future fractures. This is given a strong recommendation based on a high certainty of evidence. Bisphosphonates vs. placebo over 3 years leads to one fewer hip fracture per 150 patients treated and one fewer vertebral fracture per 50 people treated.
All the other recommendations in the guidelines are considered “conditional recommendations” that are correct for most people. But whether they make sense for an individual patient depends upon other details, as well as their values and preferences. For instance, treatment of osteoporosis in men is given a conditional recommendation, not because the evidence suggests that it’s not as effective, but because there is not as much evidence. Initial treatment for a man with osteoporosis is with bisphosphonates. Men do get osteoporosis and account for about 30% of hip fractures. This is not a surprise to anyone who takes care of older adults.
For postmenopausal women or men who you would want to treat but who can’t tolerate a bisphosphonate, then the recommendation is to use a RANK ligand inhibitor. Denosumab can be used as second-line treatment to reduce the risk for fractures. Remember, bisphosphonates and denosumab are antiresorptive drugs, meaning they slow the progression of osteoporosis. The anabolic drugs, on the other hand, such as the sclerostin inhibitor romosozumab and recombinant human parathyroid hormone (PTH) teriparatide, increase bone density. The anabolic agents should be used only in women with primary osteoporosis who are at very high risk for fractures, and use of these agents always needs to be followed by an antiresorptive agent, because otherwise there’s a risk for rebound osteoporosis and an increased risk for vertebral fractures.
Now, how about osteopenia? The guidelines recommend that for women over 65 with osteopenia, use an individualized approach influenced by the level of risk for fracture, including increased age, low body weight, current smoking, hip fracture in a parent, fall risk, and a personal history of fracture. The guidelines note that increasing the duration of bisphosphonate therapy beyond 3-5 years does reduce the risk for new vertebral fractures, but it doesn’t reduce the risk for other fractures and it increases the risk for osteonecrosis of the jaw and atypical hip fractures. Therefore, the guidelines say that we should use bisphosphonates only for 3-5 years unless someone is at extremely high risk. It’s also important to note that there’s a fivefold higher risk for atypical femoral fractures among Asian women.
Don’t forget about adequate vitamin D and calcium. And most importantly, don’t forget about exercise, particularly exercise aimed at improving balance and quadriceps strength, which helps prevent falls.
Dr. Skolnik is professor, department of family medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director, department of family medicine, Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. He disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, and Teva.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The new blood pressure target in primary care
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik. There are very few things that we treat more often than hypertension, so you’d think the guidelines would have been clear a long time ago. Less than 10 years ago, in 2014, JNC 8 (Eighth Joint National Committee) recommended target blood pressure for individuals under 60 to be less than 140/90, and for those older than 60, less than 150/90.
Then, based primarily on the SPRINT trial (which included only people with or at significantly elevated risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease), in 2017 the American Heart Association’s hypertension guidelines lowered the target BP to less than 130/80 for most individuals. It’s a little more nuanced than that, but most of us don’t remember the nuance. I’ve written about my reservations with that statement in the AHA’s journal, Circulation.
Now the American Academy of Family Physicians has updated its recommendations, and they recommend a BP less than 140/90. This is not a small change, as it often takes additional medication to achieve lower BP targets, and additional medicines lead to additional adverse effects. I’m going share with you some details from the new guideline, and then I’m going share my opinion about it.
The AAFP guideline applies to adults with hypertension, with or without cardiovascular disease. In the comprehensive literature review, the trials ran for an average of 3.7 years, and about 75% of the patients in the trials did not have preexisting cardiovascular disease.
The key to their recommendations is that target BPs lower than 140/90 did not show a statistically significant decrease in total mortality. In regard to serious adverse events, though, lower targets led to a nominal increase that didn’t reach statistical significance. Serious adverse events were defined as death or events that required hospitalization or resulted in significant disability. In regard to all other adverse events, including syncope and hypotension, there was a significant increase, with a relative risk of 1.44 (a 44% increase in adverse events). This reflected an absolute risk increase of 3%, compared with the standard target group (specifically 9.8% vs. 6.8%), with a number needed to harm of 33 over 3.7 years.
Another potential harm of low BP targets was the need for an average of one additional medicine to reach lower BP targets. One systematic review cited an eightfold higher withdrawal rate because of adverse events in the lower-target BP groups.
The AAFP guidelines said that, in the comprehensive review of the literature, while there was no difference in mortality or stroke with lower BP targets, a small additional benefit was observed in myocardial infarction – a 16% lower incidence, with a number needed to treat of 137 over 3.7 years.
So that’s the background. Let me now go over the specifics of the AAFP recommendations.
AAFP gives a strong recommendation for a standard BP target of less than 140/90. They go on to say – and grade this next statement as a weak recommendation – that, while treating to a lower BP target does not provide additional mortality benefit, a target BP of less than 135/85 can be considered to lower the risk for MI, noting that lower BP may increase harms. They state that the lower BP target could be considered based on patient preferences and values.
The AAFP guideline is incredibly helpful. The difference in the recommendations of two large societies – American Heart Association and AAFP — stems from two things. I believe that AHA focused on the composite endpoints in trials such as SPRINT, which included only high-risk patients, and the AAFP uses mortality as the driving endpoint in a broader group of patients that included both high- and lower-risk patients.
In addition, it appears that the two organizations weigh adverse events differently in coming to their conclusions. Clearly, we see more adverse events when aiming for a lower BP level, and in my experience, patients care a lot about adverse events.
Interestingly, the International Society of Hypertension recommends an “essential” BP target of less than 140/90 for most individuals, and for those under 65, they provide the option of an “optimal” BP of less than 130/80. Remember that for certain comorbidities there are also other guidelines out there. The American Diabetes Association this year revised its target BP to less than 130/80 for people with diabetes; for prevention of recurrent stroke, guidelines from the AHA/American Stroke Association in 2021 recommend BP less than 130/80, and the International Society for Hypertension as well as the AHA recommends a BP of less than 130/80 for those with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
To repeat, though, the main topic for today is that as a general target, the AAFP guidelines recommend a BP less than 140/90.
Dr. Skolnik is professor, department of family medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director, department of family medicine, Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. He disclosed conflicts of interest with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
*This article was updated on 2/7/2023.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik. There are very few things that we treat more often than hypertension, so you’d think the guidelines would have been clear a long time ago. Less than 10 years ago, in 2014, JNC 8 (Eighth Joint National Committee) recommended target blood pressure for individuals under 60 to be less than 140/90, and for those older than 60, less than 150/90.
Then, based primarily on the SPRINT trial (which included only people with or at significantly elevated risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease), in 2017 the American Heart Association’s hypertension guidelines lowered the target BP to less than 130/80 for most individuals. It’s a little more nuanced than that, but most of us don’t remember the nuance. I’ve written about my reservations with that statement in the AHA’s journal, Circulation.
Now the American Academy of Family Physicians has updated its recommendations, and they recommend a BP less than 140/90. This is not a small change, as it often takes additional medication to achieve lower BP targets, and additional medicines lead to additional adverse effects. I’m going share with you some details from the new guideline, and then I’m going share my opinion about it.
The AAFP guideline applies to adults with hypertension, with or without cardiovascular disease. In the comprehensive literature review, the trials ran for an average of 3.7 years, and about 75% of the patients in the trials did not have preexisting cardiovascular disease.
The key to their recommendations is that target BPs lower than 140/90 did not show a statistically significant decrease in total mortality. In regard to serious adverse events, though, lower targets led to a nominal increase that didn’t reach statistical significance. Serious adverse events were defined as death or events that required hospitalization or resulted in significant disability. In regard to all other adverse events, including syncope and hypotension, there was a significant increase, with a relative risk of 1.44 (a 44% increase in adverse events). This reflected an absolute risk increase of 3%, compared with the standard target group (specifically 9.8% vs. 6.8%), with a number needed to harm of 33 over 3.7 years.
Another potential harm of low BP targets was the need for an average of one additional medicine to reach lower BP targets. One systematic review cited an eightfold higher withdrawal rate because of adverse events in the lower-target BP groups.
The AAFP guidelines said that, in the comprehensive review of the literature, while there was no difference in mortality or stroke with lower BP targets, a small additional benefit was observed in myocardial infarction – a 16% lower incidence, with a number needed to treat of 137 over 3.7 years.
So that’s the background. Let me now go over the specifics of the AAFP recommendations.
AAFP gives a strong recommendation for a standard BP target of less than 140/90. They go on to say – and grade this next statement as a weak recommendation – that, while treating to a lower BP target does not provide additional mortality benefit, a target BP of less than 135/85 can be considered to lower the risk for MI, noting that lower BP may increase harms. They state that the lower BP target could be considered based on patient preferences and values.
The AAFP guideline is incredibly helpful. The difference in the recommendations of two large societies – American Heart Association and AAFP — stems from two things. I believe that AHA focused on the composite endpoints in trials such as SPRINT, which included only high-risk patients, and the AAFP uses mortality as the driving endpoint in a broader group of patients that included both high- and lower-risk patients.
In addition, it appears that the two organizations weigh adverse events differently in coming to their conclusions. Clearly, we see more adverse events when aiming for a lower BP level, and in my experience, patients care a lot about adverse events.
Interestingly, the International Society of Hypertension recommends an “essential” BP target of less than 140/90 for most individuals, and for those under 65, they provide the option of an “optimal” BP of less than 130/80. Remember that for certain comorbidities there are also other guidelines out there. The American Diabetes Association this year revised its target BP to less than 130/80 for people with diabetes; for prevention of recurrent stroke, guidelines from the AHA/American Stroke Association in 2021 recommend BP less than 130/80, and the International Society for Hypertension as well as the AHA recommends a BP of less than 130/80 for those with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
To repeat, though, the main topic for today is that as a general target, the AAFP guidelines recommend a BP less than 140/90.
Dr. Skolnik is professor, department of family medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director, department of family medicine, Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. He disclosed conflicts of interest with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
*This article was updated on 2/7/2023.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik. There are very few things that we treat more often than hypertension, so you’d think the guidelines would have been clear a long time ago. Less than 10 years ago, in 2014, JNC 8 (Eighth Joint National Committee) recommended target blood pressure for individuals under 60 to be less than 140/90, and for those older than 60, less than 150/90.
Then, based primarily on the SPRINT trial (which included only people with or at significantly elevated risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease), in 2017 the American Heart Association’s hypertension guidelines lowered the target BP to less than 130/80 for most individuals. It’s a little more nuanced than that, but most of us don’t remember the nuance. I’ve written about my reservations with that statement in the AHA’s journal, Circulation.
Now the American Academy of Family Physicians has updated its recommendations, and they recommend a BP less than 140/90. This is not a small change, as it often takes additional medication to achieve lower BP targets, and additional medicines lead to additional adverse effects. I’m going share with you some details from the new guideline, and then I’m going share my opinion about it.
The AAFP guideline applies to adults with hypertension, with or without cardiovascular disease. In the comprehensive literature review, the trials ran for an average of 3.7 years, and about 75% of the patients in the trials did not have preexisting cardiovascular disease.
The key to their recommendations is that target BPs lower than 140/90 did not show a statistically significant decrease in total mortality. In regard to serious adverse events, though, lower targets led to a nominal increase that didn’t reach statistical significance. Serious adverse events were defined as death or events that required hospitalization or resulted in significant disability. In regard to all other adverse events, including syncope and hypotension, there was a significant increase, with a relative risk of 1.44 (a 44% increase in adverse events). This reflected an absolute risk increase of 3%, compared with the standard target group (specifically 9.8% vs. 6.8%), with a number needed to harm of 33 over 3.7 years.
Another potential harm of low BP targets was the need for an average of one additional medicine to reach lower BP targets. One systematic review cited an eightfold higher withdrawal rate because of adverse events in the lower-target BP groups.
The AAFP guidelines said that, in the comprehensive review of the literature, while there was no difference in mortality or stroke with lower BP targets, a small additional benefit was observed in myocardial infarction – a 16% lower incidence, with a number needed to treat of 137 over 3.7 years.
So that’s the background. Let me now go over the specifics of the AAFP recommendations.
AAFP gives a strong recommendation for a standard BP target of less than 140/90. They go on to say – and grade this next statement as a weak recommendation – that, while treating to a lower BP target does not provide additional mortality benefit, a target BP of less than 135/85 can be considered to lower the risk for MI, noting that lower BP may increase harms. They state that the lower BP target could be considered based on patient preferences and values.
The AAFP guideline is incredibly helpful. The difference in the recommendations of two large societies – American Heart Association and AAFP — stems from two things. I believe that AHA focused on the composite endpoints in trials such as SPRINT, which included only high-risk patients, and the AAFP uses mortality as the driving endpoint in a broader group of patients that included both high- and lower-risk patients.
In addition, it appears that the two organizations weigh adverse events differently in coming to their conclusions. Clearly, we see more adverse events when aiming for a lower BP level, and in my experience, patients care a lot about adverse events.
Interestingly, the International Society of Hypertension recommends an “essential” BP target of less than 140/90 for most individuals, and for those under 65, they provide the option of an “optimal” BP of less than 130/80. Remember that for certain comorbidities there are also other guidelines out there. The American Diabetes Association this year revised its target BP to less than 130/80 for people with diabetes; for prevention of recurrent stroke, guidelines from the AHA/American Stroke Association in 2021 recommend BP less than 130/80, and the International Society for Hypertension as well as the AHA recommends a BP of less than 130/80 for those with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
To repeat, though, the main topic for today is that as a general target, the AAFP guidelines recommend a BP less than 140/90.
Dr. Skolnik is professor, department of family medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director, department of family medicine, Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. He disclosed conflicts of interest with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
*This article was updated on 2/7/2023.