User login
On Second Thought: Making Sense of Blood Pressure Guidelines — What Happened in the 1930s Should Stay There
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Blood pressure. If you’re a primary care provider trying to do right by your patients, you might be understandably confused by the current mishmash of guidelines with different blood pressure targets. But as chaotic as things are, at least it’s not the 1930s, when you might hear John Hay give a lecture to the British Medical Association and say, “The greatest danger to a man with high blood pressure lies in its discovery, because then some fool is certain to try and reduce it.”
Yeah, he said that. But what happened in the 1930s stays in the 1930s. And now we can at least agree that we should be treating high blood pressure. But what’s the goal we should be aiming for? This is On Second Thought.
We’ve come a long way since FDR was recording blood pressures of 200 and his doctor prescribed him barbiturates and massage therapy.
That s#$# don’t fly no more. Over the past hundred years, we have become much more aggressive in treating blood pressure. Remember the Oslo study? It defined mild hypertension as a blood pressure between 150 and 180 mm Hg. Now, those numbers send people screaming to the emergency room. So, let’s acknowledge that things are substantially better than they once were. Let’s agree on that and we can start to heal this nation again.
Before we get into the numbers, when we’re treating blood pressure, let’s make a few points about measuring it. Obviously, to treat something, you have to measure it properly. Two recent trials have illustrated that these details matter a lot.
The Cuff(SZ) randomized crossover trial — and it took me a minute to realize that Cuff(SZ) meant cuff size, so bravo, Ishigami et al — showed that picking the wrong cuff size could affect BP measurements by 4.5 points if you were one size off. If you were two sizes too small, you overestimated BP by almost 20 points.
Add on here another recent study, the ARMS crossover randomized clinical trial, looking at how arm position affected BP measures. If the arm was resting on your lap or hanging by your side, that overestimated blood pressure by 4 and 6.5 points. So sometimes you have to remember the fundamentals: cuff size, arm position — it might make the difference between increasing or maintaining the patient’s meds.
But on to the main show. What numbers should we be aiming for? We no longer live in the “BP 200, the president’s going to have a stroke” world of the 1940s, and even a BP of 150 is considered quite high these days. Studies like the MRC trial, INVEST, and SPRINT have pushed BP targets ever lower. SPRINT, in particular, randomized patients to a blood pressure target under 120 systolic vs under 140 systolic, and the under-120 arm won out with fewer cardiovascular events and lower all-cause mortality.
Pretty definitive slam dunk. But the more intensive treatment came with more hypotension, syncope, and kidney injury, because there is no free lunch in medicine. And ditto with BPROAD, just published in The New England Journal of Medicine and presented at the American Heart Association annual meeting. A diabetic population randomized to 120 vs 140 as a BP target showed that more aggressive treatment was better.
Fewer cardiovascular events, like stroke, but no mortality difference, and more hypotension. So a cardiovascular benefit at the cost of more side effects. Now, like all cardiologists, my motto is “Save the heart and screw the kidney.” But if you do care about the other organs in this meat sack that we call a human body, the question you need to wrestle with is, how much do you value cardiovascular protection vs how willing are you to tolerate side effects?
Hypotension may not sound dangerous, but gravity is an unforgiving mistress. If you painstakingly compile the summary of the various BP guidelines for easy perusal, you would notice something critical: One, I have too much free time on my hands; two, the disagreements are not really all that profound.
Arguing about 120 vs 130 vs 140 is not the same as saying, “Drugs schmugs; a good massage will fix what ails you, and here are some addictive sleeping pills for good measure.” Physicians from the 1930s were a little sketchy. So much of this controversy is about how you define high-risk patients and what are the age cutoffs.
Basically, the cardiovascular guidelines say, “Treat them all and let God sort it out” because they care about cardiovascular events and are concerned about cardiovascular endpoints. Whereas general practice guidelines put more emphasis on potential side effects and admittedly tend to treat a not so high-risk population, so they have laxer targets.
A 2014 analysis from the Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration [The Lancet] had a good mathematical way of explaining this problem. Now, lowering blood pressure is obviously a good thing. That prevents heart attacks, strokes, kidney failure, and all that. Please don’t let hypertension denialism become a thing.
Let’s start with the basics. Treating high blood pressure led to a 15% to 18% decrease in cardiovascular events, pretty consistently across all risk categories, and other analyses have found that every 5-point decrease in blood pressure gives you about a 10% decrease in major cardiovascular events on the relative-risk scale.
While the benefits are pretty consistent across all groups, that difference in baseline risk translates into different absolute benefits. In the Lancet paper, when the population was divided into four different groups based on their cardiovascular risk, the absolute risk reduction in the lowest-risk group was 14 fewer cardiovascular events if you treat 1000 patients for 5 years.
With each higher-risk group, it was 20 fewer, 24 fewer, and 38 fewer. At the lowest-risk group, the number needed to treat was 71, 50, 42, and 26 fewer cardiovascular events with 5 years of treatment.
And herein lies the secret to the disagreement: If you have a high-risk patient, there is a big benefit to bringing that blood pressure down from 135 to 130. Whereas for a low-risk patient, it probably doesn’t matter as much. And the cardiovascular benefits are going to be offset by the side effects and the risks for hypotension.
Of course, there’s a simple solution to this dilemma: Just speak to the patient in front of you. Treat high blood pressure, and if your patient’s blood pressure drops or they get dizzy or have fainting spells, then just ease up on the meds. It’s not rocket science; it’s just cardiology.
Arguing about five millimeters of mercury of blood pressure is probably less important from the public health perspective than the fact that tens of millions of people in the United States are unaware that they have hypertension, and even those diagnosed are being inadequately treated.
So, let’s all do better as a medical community. Nobody should have untreated hypertension in this day and age. It’s not the 1930s.
Dr Labos, Cardiologist, Kirkland Medical Center, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Blood pressure. If you’re a primary care provider trying to do right by your patients, you might be understandably confused by the current mishmash of guidelines with different blood pressure targets. But as chaotic as things are, at least it’s not the 1930s, when you might hear John Hay give a lecture to the British Medical Association and say, “The greatest danger to a man with high blood pressure lies in its discovery, because then some fool is certain to try and reduce it.”
Yeah, he said that. But what happened in the 1930s stays in the 1930s. And now we can at least agree that we should be treating high blood pressure. But what’s the goal we should be aiming for? This is On Second Thought.
We’ve come a long way since FDR was recording blood pressures of 200 and his doctor prescribed him barbiturates and massage therapy.
That s#$# don’t fly no more. Over the past hundred years, we have become much more aggressive in treating blood pressure. Remember the Oslo study? It defined mild hypertension as a blood pressure between 150 and 180 mm Hg. Now, those numbers send people screaming to the emergency room. So, let’s acknowledge that things are substantially better than they once were. Let’s agree on that and we can start to heal this nation again.
Before we get into the numbers, when we’re treating blood pressure, let’s make a few points about measuring it. Obviously, to treat something, you have to measure it properly. Two recent trials have illustrated that these details matter a lot.
The Cuff(SZ) randomized crossover trial — and it took me a minute to realize that Cuff(SZ) meant cuff size, so bravo, Ishigami et al — showed that picking the wrong cuff size could affect BP measurements by 4.5 points if you were one size off. If you were two sizes too small, you overestimated BP by almost 20 points.
Add on here another recent study, the ARMS crossover randomized clinical trial, looking at how arm position affected BP measures. If the arm was resting on your lap or hanging by your side, that overestimated blood pressure by 4 and 6.5 points. So sometimes you have to remember the fundamentals: cuff size, arm position — it might make the difference between increasing or maintaining the patient’s meds.
But on to the main show. What numbers should we be aiming for? We no longer live in the “BP 200, the president’s going to have a stroke” world of the 1940s, and even a BP of 150 is considered quite high these days. Studies like the MRC trial, INVEST, and SPRINT have pushed BP targets ever lower. SPRINT, in particular, randomized patients to a blood pressure target under 120 systolic vs under 140 systolic, and the under-120 arm won out with fewer cardiovascular events and lower all-cause mortality.
Pretty definitive slam dunk. But the more intensive treatment came with more hypotension, syncope, and kidney injury, because there is no free lunch in medicine. And ditto with BPROAD, just published in The New England Journal of Medicine and presented at the American Heart Association annual meeting. A diabetic population randomized to 120 vs 140 as a BP target showed that more aggressive treatment was better.
Fewer cardiovascular events, like stroke, but no mortality difference, and more hypotension. So a cardiovascular benefit at the cost of more side effects. Now, like all cardiologists, my motto is “Save the heart and screw the kidney.” But if you do care about the other organs in this meat sack that we call a human body, the question you need to wrestle with is, how much do you value cardiovascular protection vs how willing are you to tolerate side effects?
Hypotension may not sound dangerous, but gravity is an unforgiving mistress. If you painstakingly compile the summary of the various BP guidelines for easy perusal, you would notice something critical: One, I have too much free time on my hands; two, the disagreements are not really all that profound.
Arguing about 120 vs 130 vs 140 is not the same as saying, “Drugs schmugs; a good massage will fix what ails you, and here are some addictive sleeping pills for good measure.” Physicians from the 1930s were a little sketchy. So much of this controversy is about how you define high-risk patients and what are the age cutoffs.
Basically, the cardiovascular guidelines say, “Treat them all and let God sort it out” because they care about cardiovascular events and are concerned about cardiovascular endpoints. Whereas general practice guidelines put more emphasis on potential side effects and admittedly tend to treat a not so high-risk population, so they have laxer targets.
A 2014 analysis from the Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration [The Lancet] had a good mathematical way of explaining this problem. Now, lowering blood pressure is obviously a good thing. That prevents heart attacks, strokes, kidney failure, and all that. Please don’t let hypertension denialism become a thing.
Let’s start with the basics. Treating high blood pressure led to a 15% to 18% decrease in cardiovascular events, pretty consistently across all risk categories, and other analyses have found that every 5-point decrease in blood pressure gives you about a 10% decrease in major cardiovascular events on the relative-risk scale.
While the benefits are pretty consistent across all groups, that difference in baseline risk translates into different absolute benefits. In the Lancet paper, when the population was divided into four different groups based on their cardiovascular risk, the absolute risk reduction in the lowest-risk group was 14 fewer cardiovascular events if you treat 1000 patients for 5 years.
With each higher-risk group, it was 20 fewer, 24 fewer, and 38 fewer. At the lowest-risk group, the number needed to treat was 71, 50, 42, and 26 fewer cardiovascular events with 5 years of treatment.
And herein lies the secret to the disagreement: If you have a high-risk patient, there is a big benefit to bringing that blood pressure down from 135 to 130. Whereas for a low-risk patient, it probably doesn’t matter as much. And the cardiovascular benefits are going to be offset by the side effects and the risks for hypotension.
Of course, there’s a simple solution to this dilemma: Just speak to the patient in front of you. Treat high blood pressure, and if your patient’s blood pressure drops or they get dizzy or have fainting spells, then just ease up on the meds. It’s not rocket science; it’s just cardiology.
Arguing about five millimeters of mercury of blood pressure is probably less important from the public health perspective than the fact that tens of millions of people in the United States are unaware that they have hypertension, and even those diagnosed are being inadequately treated.
So, let’s all do better as a medical community. Nobody should have untreated hypertension in this day and age. It’s not the 1930s.
Dr Labos, Cardiologist, Kirkland Medical Center, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Blood pressure. If you’re a primary care provider trying to do right by your patients, you might be understandably confused by the current mishmash of guidelines with different blood pressure targets. But as chaotic as things are, at least it’s not the 1930s, when you might hear John Hay give a lecture to the British Medical Association and say, “The greatest danger to a man with high blood pressure lies in its discovery, because then some fool is certain to try and reduce it.”
Yeah, he said that. But what happened in the 1930s stays in the 1930s. And now we can at least agree that we should be treating high blood pressure. But what’s the goal we should be aiming for? This is On Second Thought.
We’ve come a long way since FDR was recording blood pressures of 200 and his doctor prescribed him barbiturates and massage therapy.
That s#$# don’t fly no more. Over the past hundred years, we have become much more aggressive in treating blood pressure. Remember the Oslo study? It defined mild hypertension as a blood pressure between 150 and 180 mm Hg. Now, those numbers send people screaming to the emergency room. So, let’s acknowledge that things are substantially better than they once were. Let’s agree on that and we can start to heal this nation again.
Before we get into the numbers, when we’re treating blood pressure, let’s make a few points about measuring it. Obviously, to treat something, you have to measure it properly. Two recent trials have illustrated that these details matter a lot.
The Cuff(SZ) randomized crossover trial — and it took me a minute to realize that Cuff(SZ) meant cuff size, so bravo, Ishigami et al — showed that picking the wrong cuff size could affect BP measurements by 4.5 points if you were one size off. If you were two sizes too small, you overestimated BP by almost 20 points.
Add on here another recent study, the ARMS crossover randomized clinical trial, looking at how arm position affected BP measures. If the arm was resting on your lap or hanging by your side, that overestimated blood pressure by 4 and 6.5 points. So sometimes you have to remember the fundamentals: cuff size, arm position — it might make the difference between increasing or maintaining the patient’s meds.
But on to the main show. What numbers should we be aiming for? We no longer live in the “BP 200, the president’s going to have a stroke” world of the 1940s, and even a BP of 150 is considered quite high these days. Studies like the MRC trial, INVEST, and SPRINT have pushed BP targets ever lower. SPRINT, in particular, randomized patients to a blood pressure target under 120 systolic vs under 140 systolic, and the under-120 arm won out with fewer cardiovascular events and lower all-cause mortality.
Pretty definitive slam dunk. But the more intensive treatment came with more hypotension, syncope, and kidney injury, because there is no free lunch in medicine. And ditto with BPROAD, just published in The New England Journal of Medicine and presented at the American Heart Association annual meeting. A diabetic population randomized to 120 vs 140 as a BP target showed that more aggressive treatment was better.
Fewer cardiovascular events, like stroke, but no mortality difference, and more hypotension. So a cardiovascular benefit at the cost of more side effects. Now, like all cardiologists, my motto is “Save the heart and screw the kidney.” But if you do care about the other organs in this meat sack that we call a human body, the question you need to wrestle with is, how much do you value cardiovascular protection vs how willing are you to tolerate side effects?
Hypotension may not sound dangerous, but gravity is an unforgiving mistress. If you painstakingly compile the summary of the various BP guidelines for easy perusal, you would notice something critical: One, I have too much free time on my hands; two, the disagreements are not really all that profound.
Arguing about 120 vs 130 vs 140 is not the same as saying, “Drugs schmugs; a good massage will fix what ails you, and here are some addictive sleeping pills for good measure.” Physicians from the 1930s were a little sketchy. So much of this controversy is about how you define high-risk patients and what are the age cutoffs.
Basically, the cardiovascular guidelines say, “Treat them all and let God sort it out” because they care about cardiovascular events and are concerned about cardiovascular endpoints. Whereas general practice guidelines put more emphasis on potential side effects and admittedly tend to treat a not so high-risk population, so they have laxer targets.
A 2014 analysis from the Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration [The Lancet] had a good mathematical way of explaining this problem. Now, lowering blood pressure is obviously a good thing. That prevents heart attacks, strokes, kidney failure, and all that. Please don’t let hypertension denialism become a thing.
Let’s start with the basics. Treating high blood pressure led to a 15% to 18% decrease in cardiovascular events, pretty consistently across all risk categories, and other analyses have found that every 5-point decrease in blood pressure gives you about a 10% decrease in major cardiovascular events on the relative-risk scale.
While the benefits are pretty consistent across all groups, that difference in baseline risk translates into different absolute benefits. In the Lancet paper, when the population was divided into four different groups based on their cardiovascular risk, the absolute risk reduction in the lowest-risk group was 14 fewer cardiovascular events if you treat 1000 patients for 5 years.
With each higher-risk group, it was 20 fewer, 24 fewer, and 38 fewer. At the lowest-risk group, the number needed to treat was 71, 50, 42, and 26 fewer cardiovascular events with 5 years of treatment.
And herein lies the secret to the disagreement: If you have a high-risk patient, there is a big benefit to bringing that blood pressure down from 135 to 130. Whereas for a low-risk patient, it probably doesn’t matter as much. And the cardiovascular benefits are going to be offset by the side effects and the risks for hypotension.
Of course, there’s a simple solution to this dilemma: Just speak to the patient in front of you. Treat high blood pressure, and if your patient’s blood pressure drops or they get dizzy or have fainting spells, then just ease up on the meds. It’s not rocket science; it’s just cardiology.
Arguing about five millimeters of mercury of blood pressure is probably less important from the public health perspective than the fact that tens of millions of people in the United States are unaware that they have hypertension, and even those diagnosed are being inadequately treated.
So, let’s all do better as a medical community. Nobody should have untreated hypertension in this day and age. It’s not the 1930s.
Dr Labos, Cardiologist, Kirkland Medical Center, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
An Epidemiologist’s Guide to Debunking Nutritional Research
You’re invited to a dinner party but you struggle to make small talk. Do not worry; that will invariably crop up over cocktails. Because all journalism has been reduced to listicles, here are four ways to seem clever at dinner parties.
1. The Predinner Cocktails: A Lesson in Reverse Causation
Wine connoisseurs sniff, swirl, and gently swish the wine in their mouths before spitting out and cleansing their palates to better appreciate the subtlety of each vintage. If you’re not an oenophile, no matter. Whenever somebody claims that moderate amounts of alcohol are good for your heart, this is your moment to pounce. Interject yourself in the conversation and tell everybody about reverse causation.
Reverse causation, also known as protopathic bias, involves misinterpreting the directionality of an association. You assume that X leads to Y, when in fact Y leads to X. Temporal paradoxes are useful plot devices in science fiction movies, but they have no place in medical research. In our bland world, cause must precede effect. As such, smoking leads to lung cancer; lung cancer doesn’t make you smoke more.
But with alcohol, directionality is less obvious. Many studies of alcohol and cardiovascular disease have demonstrated a U-shaped association, with risk being lowest among those who drink moderate amounts of alcohol (usually one to two drinks per day) and higher in those who drink more and also those who drink very little.
But one must ask why some people drink little or no alcohol. There is an important difference between former drinkers and never drinkers. Former drinkers cut back for a reason. More likely than not, the reason for this newfound sobriety was medical. A new cancer diagnosis, the emergence of atrial fibrillation, the development of diabetes, or rising blood pressure are all good reasons to reduce or eliminate alcohol. A cross-sectional study will fail to capture that alcohol consumption changes over time — people who now don’t drink may have imbibed alcohol in years past. It was not abstinence that led to an increased risk for heart disease; it was the increased risk for heart disease that led to abstinence.
You see the same phenomenon with the so-called obesity paradox. The idea that being a little overweight is good for you may appeal when you no longer fit into last year’s pants. But people who are underweight are so for a reason. Malnutrition, cachexia from cancer, or some other cause is almost certainly driving up the risk at the left-hand side of the U-shaped curve that makes the middle part seem better than it actually is.
Food consumption changes over time. A cross-sectional survey at one point in time cannot accurately capture past habits and distant exposures, especially for diseases such as heart disease and cancer that develop slowly over time. Studies on alcohol that try to overcome these shortcomings by eliminating former drinkers, or by using Mendelian randomization to better account for past exposure, do not show a cardiovascular benefit for moderate red wine drinking.
2. The Hors D’oeuvres — The Importance of RCTs
Now that you have made yourself the center of attention, it is time to cement your newfound reputation as a font of scientific knowledge. Most self-respecting hosts will serve smoked salmon as an amuse-bouche before the main meal. When someone mentions the health benefits of fish oils, you should take the opportunity to teach them about confounding.
Fish, especially cold-water fish from northern climates, have relatively high amounts of omega-3 fatty acids. Despite the plethora of observational studies suggesting a cardiovascular benefit, it’s now relatively clear that fish oil or omega-3 supplements have no medical benefit.
This will probably come as a shock to the worried well, but many studies, including VITAL and ASCEND, have demonstrated no cardiovascular or cancer benefit to supplementation with omega-3s. The reason is straightforward and explains why hormone replacement therapy, vitamin D, and myriad purported game-changers never panned out. Confounding is hard to overcome in observational research.
Prior to the publication of the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) Study, hormone replacement therapy was routinely prescribed to postmenopausal women because numerous observational studies suggested a cardiovascular benefit. But with the publication of the WHI study, it became clear that much of that “benefit” was due to confounding. The women choosing to take hormones were more health conscious at baseline and healthier overall.
A similar phenomenon occurred during COVID. Patients with low serum vitamin D levels had worse outcomes, prompting many to suggest vitamin D supplementation as a possible treatment. Trials did not support the intervention because we’d overlooked the obvious. People with vitamin D deficiency have underlying health problems that contribute to the vitamin D deficiency. They are probably older, frailer, possibly with a poorer diet. No amount of statistical adjustment can account for all those differences, and some degree of residual confounding will always persist.
The only way to overcome confounding is with randomization. When patients are randomly assigned to one group or another, their baseline differences largely balance out if the randomization was performed properly and the groups were large enough. There is a role for observational research, such as in situations where ethics, cost, and practicality do not allow for a randomized controlled trial. But randomized controlled trials have largely put to rest the purported health benefits of over-the-counter fish oils, omega-3s, and vitamin D.
3. The Main Course — Absolute vs Relative Risk
When you get to the main course, all eyes will now be on you. You will almost certainly be called upon to pronounce on the harms or benefits of red meat consumption. Begin by regaling your guests with a little trivia. Ask them if they know the definition of red meat and white meat. When someone says pork is white meat, you can reveal that “pork, the other white meat,” was a marketing slogan with no scientific underpinning. Now that everyone is lulled into a stupefied silence, tell them that red meat comes from mammals and white meat comes from birds. As they process this revelation, you can now launch into the deeply mathematical concept of absolute vs relative risk.
Many etiquette books will caution against bringing up math at a dinner party. These books are wrong. Everyone finds math interesting if they are primed properly. For example, you can point to a study claiming that berries reduce cardiovascular risk in women. Even if true — and there is reason to be cautious, given the observational nature of the research — we need to understand what the authors meant by a 32% risk reduction. (Side note: It was a reduction in hazard, with a hazard ratio of 0.68 (95% CI, 0.49-0.96), but we won’t dwell on the difference between hazard ratios and risk ratios right now.)
This relative risk reduction has to be interpreted carefully. The authors divided the population into quintiles based on their consumption of anthocyanins (the antioxidant in blueberries and strawberries) and compared the bottom fifth (average consumption, 2.5 mg/d) with the top fifth (average consumption, 25 mg/d). The bottom quintile had 126 myocardial infarctions (MIs) over 324,793 patient-years compared with 59 MIs over 332,143 patient-years. Some quick math shows an approximate reduction from 39 to 18 MIs per 100,000 patient-years. Or to put it another way, you must get 4762 women to increase their berry consumption 10-fold for 1 year to prevent one heart attack. Feel free to show people how you calculated this number. They will be impressed by your head for numbers. It is nothing more than 39 minus 18, divided by 100,000, to get the absolute risk reduction. Take the reciprocal of this (ie, 1 divided by this number) to get the number needed to treat.
Describing risks in absolute terms or using number needed to treat (or harm) can help conceptualize statistics that are sometimes hard to wrap your head around.
4. Dessert — Funding
By the time the coffee is served, everyone will be hanging on to your every word. This is as it should be, and you should not be afraid of your newfound power and influence.
Dessert will probably involve some form of chocolate, possibly in cake format. (Anyone who serves fruit as dessert is not someone you should associate with.) Take the opportunity to tell your follow diners that chocolate is not actually good for you and will not boost brain performance.
The health benefits of chocolate are often repeated but rarely scrutinized. In fact, much of the scientific research purporting to show that chocolate is good for you did not actually study chocolate. It usually involved a cocoa bean extract because the chocolate manufacturing process destroys the supposedly health-promoting antioxidants in the cocoa bean. It is true that dark chocolate has more antioxidants than milk chocolate, and that the addition of milk to chocolate further inactivates the potentially healthy antioxidants. But the amount of sugar and fat that has to be added to chocolate to make it palatable precludes any serious consideration about health benefits. Dark chocolate may have less fat and sugar than milk chocolate, but it still has a lot.
But even the cocoa bean extract doesn’t seem to do much for your heart or your brain. The long-awaited COSMOS study was published with surprisingly little fanfare. The largest randomized controlled trial of chocolate (or rather cocoa bean extract) was supposed to settle the issue definitively.
COSMOS showed no cardiovascular or neurocognitive benefit to the cocoa bean extract. But the health halo of chocolate continues to be bolstered by many studies funded by chocolate manufacturers.
We are appropriately critical of the pharmaceutical industry’s involvement in drug research. However, we should not forget that any private entity is prone to the same self-interest regardless of its product’s tastiness. How many of you knew that there was an avocado lobby funding research? No matter how many industry-funded observational studies using surrogate endpoints are out there telling you that chocolate is healthy, a randomized trial with hard clinical endpoints such as COSMOS should generally win the day.
The Final Goodbyes — Summarizing Your Case
As the party slowly winds down and everyone is saddened that you will soon take your leave, synthesize everything you have taught them over the evening. Like movies, not all studies are good. Some are just bad. They can be prone to reverse causation or confounding, and they may report relative risks when absolute risks would be more telling. Reading research studies critically is essential for separating the wheat from the chaff. With the knowledge you have now imparted to your friends, they will be much better consumers of medical news, especially when it comes to food.
And they will no doubt thank you for it by never inviting you to another dinner party!
Labos, a cardiologist at Hôpital, Notre-Dame, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. He has a degree in epidemiology.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
You’re invited to a dinner party but you struggle to make small talk. Do not worry; that will invariably crop up over cocktails. Because all journalism has been reduced to listicles, here are four ways to seem clever at dinner parties.
1. The Predinner Cocktails: A Lesson in Reverse Causation
Wine connoisseurs sniff, swirl, and gently swish the wine in their mouths before spitting out and cleansing their palates to better appreciate the subtlety of each vintage. If you’re not an oenophile, no matter. Whenever somebody claims that moderate amounts of alcohol are good for your heart, this is your moment to pounce. Interject yourself in the conversation and tell everybody about reverse causation.
Reverse causation, also known as protopathic bias, involves misinterpreting the directionality of an association. You assume that X leads to Y, when in fact Y leads to X. Temporal paradoxes are useful plot devices in science fiction movies, but they have no place in medical research. In our bland world, cause must precede effect. As such, smoking leads to lung cancer; lung cancer doesn’t make you smoke more.
But with alcohol, directionality is less obvious. Many studies of alcohol and cardiovascular disease have demonstrated a U-shaped association, with risk being lowest among those who drink moderate amounts of alcohol (usually one to two drinks per day) and higher in those who drink more and also those who drink very little.
But one must ask why some people drink little or no alcohol. There is an important difference between former drinkers and never drinkers. Former drinkers cut back for a reason. More likely than not, the reason for this newfound sobriety was medical. A new cancer diagnosis, the emergence of atrial fibrillation, the development of diabetes, or rising blood pressure are all good reasons to reduce or eliminate alcohol. A cross-sectional study will fail to capture that alcohol consumption changes over time — people who now don’t drink may have imbibed alcohol in years past. It was not abstinence that led to an increased risk for heart disease; it was the increased risk for heart disease that led to abstinence.
You see the same phenomenon with the so-called obesity paradox. The idea that being a little overweight is good for you may appeal when you no longer fit into last year’s pants. But people who are underweight are so for a reason. Malnutrition, cachexia from cancer, or some other cause is almost certainly driving up the risk at the left-hand side of the U-shaped curve that makes the middle part seem better than it actually is.
Food consumption changes over time. A cross-sectional survey at one point in time cannot accurately capture past habits and distant exposures, especially for diseases such as heart disease and cancer that develop slowly over time. Studies on alcohol that try to overcome these shortcomings by eliminating former drinkers, or by using Mendelian randomization to better account for past exposure, do not show a cardiovascular benefit for moderate red wine drinking.
2. The Hors D’oeuvres — The Importance of RCTs
Now that you have made yourself the center of attention, it is time to cement your newfound reputation as a font of scientific knowledge. Most self-respecting hosts will serve smoked salmon as an amuse-bouche before the main meal. When someone mentions the health benefits of fish oils, you should take the opportunity to teach them about confounding.
Fish, especially cold-water fish from northern climates, have relatively high amounts of omega-3 fatty acids. Despite the plethora of observational studies suggesting a cardiovascular benefit, it’s now relatively clear that fish oil or omega-3 supplements have no medical benefit.
This will probably come as a shock to the worried well, but many studies, including VITAL and ASCEND, have demonstrated no cardiovascular or cancer benefit to supplementation with omega-3s. The reason is straightforward and explains why hormone replacement therapy, vitamin D, and myriad purported game-changers never panned out. Confounding is hard to overcome in observational research.
Prior to the publication of the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) Study, hormone replacement therapy was routinely prescribed to postmenopausal women because numerous observational studies suggested a cardiovascular benefit. But with the publication of the WHI study, it became clear that much of that “benefit” was due to confounding. The women choosing to take hormones were more health conscious at baseline and healthier overall.
A similar phenomenon occurred during COVID. Patients with low serum vitamin D levels had worse outcomes, prompting many to suggest vitamin D supplementation as a possible treatment. Trials did not support the intervention because we’d overlooked the obvious. People with vitamin D deficiency have underlying health problems that contribute to the vitamin D deficiency. They are probably older, frailer, possibly with a poorer diet. No amount of statistical adjustment can account for all those differences, and some degree of residual confounding will always persist.
The only way to overcome confounding is with randomization. When patients are randomly assigned to one group or another, their baseline differences largely balance out if the randomization was performed properly and the groups were large enough. There is a role for observational research, such as in situations where ethics, cost, and practicality do not allow for a randomized controlled trial. But randomized controlled trials have largely put to rest the purported health benefits of over-the-counter fish oils, omega-3s, and vitamin D.
3. The Main Course — Absolute vs Relative Risk
When you get to the main course, all eyes will now be on you. You will almost certainly be called upon to pronounce on the harms or benefits of red meat consumption. Begin by regaling your guests with a little trivia. Ask them if they know the definition of red meat and white meat. When someone says pork is white meat, you can reveal that “pork, the other white meat,” was a marketing slogan with no scientific underpinning. Now that everyone is lulled into a stupefied silence, tell them that red meat comes from mammals and white meat comes from birds. As they process this revelation, you can now launch into the deeply mathematical concept of absolute vs relative risk.
Many etiquette books will caution against bringing up math at a dinner party. These books are wrong. Everyone finds math interesting if they are primed properly. For example, you can point to a study claiming that berries reduce cardiovascular risk in women. Even if true — and there is reason to be cautious, given the observational nature of the research — we need to understand what the authors meant by a 32% risk reduction. (Side note: It was a reduction in hazard, with a hazard ratio of 0.68 (95% CI, 0.49-0.96), but we won’t dwell on the difference between hazard ratios and risk ratios right now.)
This relative risk reduction has to be interpreted carefully. The authors divided the population into quintiles based on their consumption of anthocyanins (the antioxidant in blueberries and strawberries) and compared the bottom fifth (average consumption, 2.5 mg/d) with the top fifth (average consumption, 25 mg/d). The bottom quintile had 126 myocardial infarctions (MIs) over 324,793 patient-years compared with 59 MIs over 332,143 patient-years. Some quick math shows an approximate reduction from 39 to 18 MIs per 100,000 patient-years. Or to put it another way, you must get 4762 women to increase their berry consumption 10-fold for 1 year to prevent one heart attack. Feel free to show people how you calculated this number. They will be impressed by your head for numbers. It is nothing more than 39 minus 18, divided by 100,000, to get the absolute risk reduction. Take the reciprocal of this (ie, 1 divided by this number) to get the number needed to treat.
Describing risks in absolute terms or using number needed to treat (or harm) can help conceptualize statistics that are sometimes hard to wrap your head around.
4. Dessert — Funding
By the time the coffee is served, everyone will be hanging on to your every word. This is as it should be, and you should not be afraid of your newfound power and influence.
Dessert will probably involve some form of chocolate, possibly in cake format. (Anyone who serves fruit as dessert is not someone you should associate with.) Take the opportunity to tell your follow diners that chocolate is not actually good for you and will not boost brain performance.
The health benefits of chocolate are often repeated but rarely scrutinized. In fact, much of the scientific research purporting to show that chocolate is good for you did not actually study chocolate. It usually involved a cocoa bean extract because the chocolate manufacturing process destroys the supposedly health-promoting antioxidants in the cocoa bean. It is true that dark chocolate has more antioxidants than milk chocolate, and that the addition of milk to chocolate further inactivates the potentially healthy antioxidants. But the amount of sugar and fat that has to be added to chocolate to make it palatable precludes any serious consideration about health benefits. Dark chocolate may have less fat and sugar than milk chocolate, but it still has a lot.
But even the cocoa bean extract doesn’t seem to do much for your heart or your brain. The long-awaited COSMOS study was published with surprisingly little fanfare. The largest randomized controlled trial of chocolate (or rather cocoa bean extract) was supposed to settle the issue definitively.
COSMOS showed no cardiovascular or neurocognitive benefit to the cocoa bean extract. But the health halo of chocolate continues to be bolstered by many studies funded by chocolate manufacturers.
We are appropriately critical of the pharmaceutical industry’s involvement in drug research. However, we should not forget that any private entity is prone to the same self-interest regardless of its product’s tastiness. How many of you knew that there was an avocado lobby funding research? No matter how many industry-funded observational studies using surrogate endpoints are out there telling you that chocolate is healthy, a randomized trial with hard clinical endpoints such as COSMOS should generally win the day.
The Final Goodbyes — Summarizing Your Case
As the party slowly winds down and everyone is saddened that you will soon take your leave, synthesize everything you have taught them over the evening. Like movies, not all studies are good. Some are just bad. They can be prone to reverse causation or confounding, and they may report relative risks when absolute risks would be more telling. Reading research studies critically is essential for separating the wheat from the chaff. With the knowledge you have now imparted to your friends, they will be much better consumers of medical news, especially when it comes to food.
And they will no doubt thank you for it by never inviting you to another dinner party!
Labos, a cardiologist at Hôpital, Notre-Dame, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. He has a degree in epidemiology.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
You’re invited to a dinner party but you struggle to make small talk. Do not worry; that will invariably crop up over cocktails. Because all journalism has been reduced to listicles, here are four ways to seem clever at dinner parties.
1. The Predinner Cocktails: A Lesson in Reverse Causation
Wine connoisseurs sniff, swirl, and gently swish the wine in their mouths before spitting out and cleansing their palates to better appreciate the subtlety of each vintage. If you’re not an oenophile, no matter. Whenever somebody claims that moderate amounts of alcohol are good for your heart, this is your moment to pounce. Interject yourself in the conversation and tell everybody about reverse causation.
Reverse causation, also known as protopathic bias, involves misinterpreting the directionality of an association. You assume that X leads to Y, when in fact Y leads to X. Temporal paradoxes are useful plot devices in science fiction movies, but they have no place in medical research. In our bland world, cause must precede effect. As such, smoking leads to lung cancer; lung cancer doesn’t make you smoke more.
But with alcohol, directionality is less obvious. Many studies of alcohol and cardiovascular disease have demonstrated a U-shaped association, with risk being lowest among those who drink moderate amounts of alcohol (usually one to two drinks per day) and higher in those who drink more and also those who drink very little.
But one must ask why some people drink little or no alcohol. There is an important difference between former drinkers and never drinkers. Former drinkers cut back for a reason. More likely than not, the reason for this newfound sobriety was medical. A new cancer diagnosis, the emergence of atrial fibrillation, the development of diabetes, or rising blood pressure are all good reasons to reduce or eliminate alcohol. A cross-sectional study will fail to capture that alcohol consumption changes over time — people who now don’t drink may have imbibed alcohol in years past. It was not abstinence that led to an increased risk for heart disease; it was the increased risk for heart disease that led to abstinence.
You see the same phenomenon with the so-called obesity paradox. The idea that being a little overweight is good for you may appeal when you no longer fit into last year’s pants. But people who are underweight are so for a reason. Malnutrition, cachexia from cancer, or some other cause is almost certainly driving up the risk at the left-hand side of the U-shaped curve that makes the middle part seem better than it actually is.
Food consumption changes over time. A cross-sectional survey at one point in time cannot accurately capture past habits and distant exposures, especially for diseases such as heart disease and cancer that develop slowly over time. Studies on alcohol that try to overcome these shortcomings by eliminating former drinkers, or by using Mendelian randomization to better account for past exposure, do not show a cardiovascular benefit for moderate red wine drinking.
2. The Hors D’oeuvres — The Importance of RCTs
Now that you have made yourself the center of attention, it is time to cement your newfound reputation as a font of scientific knowledge. Most self-respecting hosts will serve smoked salmon as an amuse-bouche before the main meal. When someone mentions the health benefits of fish oils, you should take the opportunity to teach them about confounding.
Fish, especially cold-water fish from northern climates, have relatively high amounts of omega-3 fatty acids. Despite the plethora of observational studies suggesting a cardiovascular benefit, it’s now relatively clear that fish oil or omega-3 supplements have no medical benefit.
This will probably come as a shock to the worried well, but many studies, including VITAL and ASCEND, have demonstrated no cardiovascular or cancer benefit to supplementation with omega-3s. The reason is straightforward and explains why hormone replacement therapy, vitamin D, and myriad purported game-changers never panned out. Confounding is hard to overcome in observational research.
Prior to the publication of the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) Study, hormone replacement therapy was routinely prescribed to postmenopausal women because numerous observational studies suggested a cardiovascular benefit. But with the publication of the WHI study, it became clear that much of that “benefit” was due to confounding. The women choosing to take hormones were more health conscious at baseline and healthier overall.
A similar phenomenon occurred during COVID. Patients with low serum vitamin D levels had worse outcomes, prompting many to suggest vitamin D supplementation as a possible treatment. Trials did not support the intervention because we’d overlooked the obvious. People with vitamin D deficiency have underlying health problems that contribute to the vitamin D deficiency. They are probably older, frailer, possibly with a poorer diet. No amount of statistical adjustment can account for all those differences, and some degree of residual confounding will always persist.
The only way to overcome confounding is with randomization. When patients are randomly assigned to one group or another, their baseline differences largely balance out if the randomization was performed properly and the groups were large enough. There is a role for observational research, such as in situations where ethics, cost, and practicality do not allow for a randomized controlled trial. But randomized controlled trials have largely put to rest the purported health benefits of over-the-counter fish oils, omega-3s, and vitamin D.
3. The Main Course — Absolute vs Relative Risk
When you get to the main course, all eyes will now be on you. You will almost certainly be called upon to pronounce on the harms or benefits of red meat consumption. Begin by regaling your guests with a little trivia. Ask them if they know the definition of red meat and white meat. When someone says pork is white meat, you can reveal that “pork, the other white meat,” was a marketing slogan with no scientific underpinning. Now that everyone is lulled into a stupefied silence, tell them that red meat comes from mammals and white meat comes from birds. As they process this revelation, you can now launch into the deeply mathematical concept of absolute vs relative risk.
Many etiquette books will caution against bringing up math at a dinner party. These books are wrong. Everyone finds math interesting if they are primed properly. For example, you can point to a study claiming that berries reduce cardiovascular risk in women. Even if true — and there is reason to be cautious, given the observational nature of the research — we need to understand what the authors meant by a 32% risk reduction. (Side note: It was a reduction in hazard, with a hazard ratio of 0.68 (95% CI, 0.49-0.96), but we won’t dwell on the difference between hazard ratios and risk ratios right now.)
This relative risk reduction has to be interpreted carefully. The authors divided the population into quintiles based on their consumption of anthocyanins (the antioxidant in blueberries and strawberries) and compared the bottom fifth (average consumption, 2.5 mg/d) with the top fifth (average consumption, 25 mg/d). The bottom quintile had 126 myocardial infarctions (MIs) over 324,793 patient-years compared with 59 MIs over 332,143 patient-years. Some quick math shows an approximate reduction from 39 to 18 MIs per 100,000 patient-years. Or to put it another way, you must get 4762 women to increase their berry consumption 10-fold for 1 year to prevent one heart attack. Feel free to show people how you calculated this number. They will be impressed by your head for numbers. It is nothing more than 39 minus 18, divided by 100,000, to get the absolute risk reduction. Take the reciprocal of this (ie, 1 divided by this number) to get the number needed to treat.
Describing risks in absolute terms or using number needed to treat (or harm) can help conceptualize statistics that are sometimes hard to wrap your head around.
4. Dessert — Funding
By the time the coffee is served, everyone will be hanging on to your every word. This is as it should be, and you should not be afraid of your newfound power and influence.
Dessert will probably involve some form of chocolate, possibly in cake format. (Anyone who serves fruit as dessert is not someone you should associate with.) Take the opportunity to tell your follow diners that chocolate is not actually good for you and will not boost brain performance.
The health benefits of chocolate are often repeated but rarely scrutinized. In fact, much of the scientific research purporting to show that chocolate is good for you did not actually study chocolate. It usually involved a cocoa bean extract because the chocolate manufacturing process destroys the supposedly health-promoting antioxidants in the cocoa bean. It is true that dark chocolate has more antioxidants than milk chocolate, and that the addition of milk to chocolate further inactivates the potentially healthy antioxidants. But the amount of sugar and fat that has to be added to chocolate to make it palatable precludes any serious consideration about health benefits. Dark chocolate may have less fat and sugar than milk chocolate, but it still has a lot.
But even the cocoa bean extract doesn’t seem to do much for your heart or your brain. The long-awaited COSMOS study was published with surprisingly little fanfare. The largest randomized controlled trial of chocolate (or rather cocoa bean extract) was supposed to settle the issue definitively.
COSMOS showed no cardiovascular or neurocognitive benefit to the cocoa bean extract. But the health halo of chocolate continues to be bolstered by many studies funded by chocolate manufacturers.
We are appropriately critical of the pharmaceutical industry’s involvement in drug research. However, we should not forget that any private entity is prone to the same self-interest regardless of its product’s tastiness. How many of you knew that there was an avocado lobby funding research? No matter how many industry-funded observational studies using surrogate endpoints are out there telling you that chocolate is healthy, a randomized trial with hard clinical endpoints such as COSMOS should generally win the day.
The Final Goodbyes — Summarizing Your Case
As the party slowly winds down and everyone is saddened that you will soon take your leave, synthesize everything you have taught them over the evening. Like movies, not all studies are good. Some are just bad. They can be prone to reverse causation or confounding, and they may report relative risks when absolute risks would be more telling. Reading research studies critically is essential for separating the wheat from the chaff. With the knowledge you have now imparted to your friends, they will be much better consumers of medical news, especially when it comes to food.
And they will no doubt thank you for it by never inviting you to another dinner party!
Labos, a cardiologist at Hôpital, Notre-Dame, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. He has a degree in epidemiology.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
On Second Thought: Aspirin for Primary Prevention — What We Really Know
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Our recommendations vis-à-vis aspirin have evolved at a dizzying pace. The young’uns watching us right now don’t know what things were like in the 1980s. The Reagan era was a wild, heady time where nuclear war was imminent and we didn’t prescribe aspirin to patients.
That only started in 1988, which was a banner year in human history. Not because a number of doves were incinerated by the lighting of the Olympic torch at the Seoul Olympics — look it up if you don’t know what I’m talking about — but because 1988 saw the publication of the ISIS-2 trial, which first showed a mortality benefit to prescribing aspirin post–myocardial infarction (MI).
Giving patients aspirin during or after a heart attack is not controversial. It’s one of the few things in this business that isn’t, but that’s secondary prevention — treating somebody after they develop a disease. Primary prevention, treating them before they have their incident event, is a very different ballgame. Here, things are messy.
For one thing, the doses used have been very inconsistent. We should point out that the reason for 81 mg of aspirin is very arbitrary and is rooted in the old apothecary system of weights and measurements. A standard dose of aspirin was 5 grains, where 20 grains made 1 scruple, 3 scruples made 1 dram, 8 drams made 1 oz, and 12 oz made 1 lb - because screw you, metric system. Therefore, 5 grains was 325 mg of aspirin, and 1 quarter of the standard dose became 81 mg if you rounded out the decimal.
People have tried all kinds of dosing structures with aspirin prophylaxis. The Physicians’ Health Study used a full-dose aspirin, 325 mg every 2 days, while the Hypertension Optimal Treatment (HOT) trial tested 75 mg daily and the Women’s Health Study tested 100 mg, but every other day.
Ironically, almost no one has studied 81 mg every day, which is weird if you think about it. The bigger problem here is not the variability of doses used, but the discrepancy when you look at older vs newer studies.
Older studies, like the Physicians’ Health Study, did show a benefit, at least in the subgroup of patients over age 50 years, which is probably where the “everybody over 50 should be taking an aspirin” idea comes from, at least as near as I can tell.
More recent studies, like the Women’s Health Study, ASPREE, or ASPIRE, didn’t show a benefit. I know what you’re thinking: Newer stuff is always better. That’s why you should never trust anybody over age 40 years. The context of primary prevention studies has changed. In the ‘80s and ‘90s, people smoked more and we didn’t have the same medications that we have today. We talked about all this in the beta-blocker video to explain why beta-blockers don’t seem to have a benefit post MI.
We have a similar issue here. The magnitude of the benefit with aspirin primary prevention has decreased because we’re all just healthier overall. So, yay! Progress! Here’s where the numbers matter. No one is saying that aspirin doesn’t help. It does.
If we look at the 2019 meta-analysis published in JAMA, there is a cardiovascular benefit. The numbers bear that out. I know you’re all here for the math, so here we go. Aspirin reduced the composite cardiovascular endpoint from 65.2 to 60.2 events per 10,000 patient-years; or to put it more meaningfully in absolute risk reduction terms, because that’s my jam, an absolute risk reduction of 0.41%, which means a number needed to treat of 241, which is okay-ish. It’s not super-great, but it may be justifiable for something that costs next to nothing.
The tradeoff is bleeding. Major bleeding increased from 16.4 to 23.1 bleeds per 10,000 patient-years, or an absolute risk increase of 0.47%, which is a number needed to harm of 210. That’s the problem. Aspirin does prevent heart disease. The benefit is small, for sure, but the real problem is that it’s outweighed by the risk of bleeding, so you’re not really coming out ahead.
The real tragedy here is that the public is locked into this idea of everyone over age 50 years should be taking an aspirin. Even today, even though guidelines have recommended against aspirin for primary prevention for some time, data from the National Health Interview Survey sample found that nearly one in three older adults take aspirin for primary prevention when they shouldn’t be. That’s a large number of people. That’s millions of Americans — and Canadians, but nobody cares about us. It’s fine.
That’s the point. We’re not debunking aspirin. It does work. The benefits are just really small in a primary prevention population and offset by the admittedly also really small risks of bleeding. It’s a tradeoff that doesn’t really work in your favor.
But that’s aspirin for cardiovascular disease. When it comes to cancer or DVT prophylaxis, that’s another really interesting story. We might have to save that for another time. Do I know how to tease a sequel or what?
Labos, a cardiologist at Kirkland Medical Center, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Our recommendations vis-à-vis aspirin have evolved at a dizzying pace. The young’uns watching us right now don’t know what things were like in the 1980s. The Reagan era was a wild, heady time where nuclear war was imminent and we didn’t prescribe aspirin to patients.
That only started in 1988, which was a banner year in human history. Not because a number of doves were incinerated by the lighting of the Olympic torch at the Seoul Olympics — look it up if you don’t know what I’m talking about — but because 1988 saw the publication of the ISIS-2 trial, which first showed a mortality benefit to prescribing aspirin post–myocardial infarction (MI).
Giving patients aspirin during or after a heart attack is not controversial. It’s one of the few things in this business that isn’t, but that’s secondary prevention — treating somebody after they develop a disease. Primary prevention, treating them before they have their incident event, is a very different ballgame. Here, things are messy.
For one thing, the doses used have been very inconsistent. We should point out that the reason for 81 mg of aspirin is very arbitrary and is rooted in the old apothecary system of weights and measurements. A standard dose of aspirin was 5 grains, where 20 grains made 1 scruple, 3 scruples made 1 dram, 8 drams made 1 oz, and 12 oz made 1 lb - because screw you, metric system. Therefore, 5 grains was 325 mg of aspirin, and 1 quarter of the standard dose became 81 mg if you rounded out the decimal.
People have tried all kinds of dosing structures with aspirin prophylaxis. The Physicians’ Health Study used a full-dose aspirin, 325 mg every 2 days, while the Hypertension Optimal Treatment (HOT) trial tested 75 mg daily and the Women’s Health Study tested 100 mg, but every other day.
Ironically, almost no one has studied 81 mg every day, which is weird if you think about it. The bigger problem here is not the variability of doses used, but the discrepancy when you look at older vs newer studies.
Older studies, like the Physicians’ Health Study, did show a benefit, at least in the subgroup of patients over age 50 years, which is probably where the “everybody over 50 should be taking an aspirin” idea comes from, at least as near as I can tell.
More recent studies, like the Women’s Health Study, ASPREE, or ASPIRE, didn’t show a benefit. I know what you’re thinking: Newer stuff is always better. That’s why you should never trust anybody over age 40 years. The context of primary prevention studies has changed. In the ‘80s and ‘90s, people smoked more and we didn’t have the same medications that we have today. We talked about all this in the beta-blocker video to explain why beta-blockers don’t seem to have a benefit post MI.
We have a similar issue here. The magnitude of the benefit with aspirin primary prevention has decreased because we’re all just healthier overall. So, yay! Progress! Here’s where the numbers matter. No one is saying that aspirin doesn’t help. It does.
If we look at the 2019 meta-analysis published in JAMA, there is a cardiovascular benefit. The numbers bear that out. I know you’re all here for the math, so here we go. Aspirin reduced the composite cardiovascular endpoint from 65.2 to 60.2 events per 10,000 patient-years; or to put it more meaningfully in absolute risk reduction terms, because that’s my jam, an absolute risk reduction of 0.41%, which means a number needed to treat of 241, which is okay-ish. It’s not super-great, but it may be justifiable for something that costs next to nothing.
The tradeoff is bleeding. Major bleeding increased from 16.4 to 23.1 bleeds per 10,000 patient-years, or an absolute risk increase of 0.47%, which is a number needed to harm of 210. That’s the problem. Aspirin does prevent heart disease. The benefit is small, for sure, but the real problem is that it’s outweighed by the risk of bleeding, so you’re not really coming out ahead.
The real tragedy here is that the public is locked into this idea of everyone over age 50 years should be taking an aspirin. Even today, even though guidelines have recommended against aspirin for primary prevention for some time, data from the National Health Interview Survey sample found that nearly one in three older adults take aspirin for primary prevention when they shouldn’t be. That’s a large number of people. That’s millions of Americans — and Canadians, but nobody cares about us. It’s fine.
That’s the point. We’re not debunking aspirin. It does work. The benefits are just really small in a primary prevention population and offset by the admittedly also really small risks of bleeding. It’s a tradeoff that doesn’t really work in your favor.
But that’s aspirin for cardiovascular disease. When it comes to cancer or DVT prophylaxis, that’s another really interesting story. We might have to save that for another time. Do I know how to tease a sequel or what?
Labos, a cardiologist at Kirkland Medical Center, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Our recommendations vis-à-vis aspirin have evolved at a dizzying pace. The young’uns watching us right now don’t know what things were like in the 1980s. The Reagan era was a wild, heady time where nuclear war was imminent and we didn’t prescribe aspirin to patients.
That only started in 1988, which was a banner year in human history. Not because a number of doves were incinerated by the lighting of the Olympic torch at the Seoul Olympics — look it up if you don’t know what I’m talking about — but because 1988 saw the publication of the ISIS-2 trial, which first showed a mortality benefit to prescribing aspirin post–myocardial infarction (MI).
Giving patients aspirin during or after a heart attack is not controversial. It’s one of the few things in this business that isn’t, but that’s secondary prevention — treating somebody after they develop a disease. Primary prevention, treating them before they have their incident event, is a very different ballgame. Here, things are messy.
For one thing, the doses used have been very inconsistent. We should point out that the reason for 81 mg of aspirin is very arbitrary and is rooted in the old apothecary system of weights and measurements. A standard dose of aspirin was 5 grains, where 20 grains made 1 scruple, 3 scruples made 1 dram, 8 drams made 1 oz, and 12 oz made 1 lb - because screw you, metric system. Therefore, 5 grains was 325 mg of aspirin, and 1 quarter of the standard dose became 81 mg if you rounded out the decimal.
People have tried all kinds of dosing structures with aspirin prophylaxis. The Physicians’ Health Study used a full-dose aspirin, 325 mg every 2 days, while the Hypertension Optimal Treatment (HOT) trial tested 75 mg daily and the Women’s Health Study tested 100 mg, but every other day.
Ironically, almost no one has studied 81 mg every day, which is weird if you think about it. The bigger problem here is not the variability of doses used, but the discrepancy when you look at older vs newer studies.
Older studies, like the Physicians’ Health Study, did show a benefit, at least in the subgroup of patients over age 50 years, which is probably where the “everybody over 50 should be taking an aspirin” idea comes from, at least as near as I can tell.
More recent studies, like the Women’s Health Study, ASPREE, or ASPIRE, didn’t show a benefit. I know what you’re thinking: Newer stuff is always better. That’s why you should never trust anybody over age 40 years. The context of primary prevention studies has changed. In the ‘80s and ‘90s, people smoked more and we didn’t have the same medications that we have today. We talked about all this in the beta-blocker video to explain why beta-blockers don’t seem to have a benefit post MI.
We have a similar issue here. The magnitude of the benefit with aspirin primary prevention has decreased because we’re all just healthier overall. So, yay! Progress! Here’s where the numbers matter. No one is saying that aspirin doesn’t help. It does.
If we look at the 2019 meta-analysis published in JAMA, there is a cardiovascular benefit. The numbers bear that out. I know you’re all here for the math, so here we go. Aspirin reduced the composite cardiovascular endpoint from 65.2 to 60.2 events per 10,000 patient-years; or to put it more meaningfully in absolute risk reduction terms, because that’s my jam, an absolute risk reduction of 0.41%, which means a number needed to treat of 241, which is okay-ish. It’s not super-great, but it may be justifiable for something that costs next to nothing.
The tradeoff is bleeding. Major bleeding increased from 16.4 to 23.1 bleeds per 10,000 patient-years, or an absolute risk increase of 0.47%, which is a number needed to harm of 210. That’s the problem. Aspirin does prevent heart disease. The benefit is small, for sure, but the real problem is that it’s outweighed by the risk of bleeding, so you’re not really coming out ahead.
The real tragedy here is that the public is locked into this idea of everyone over age 50 years should be taking an aspirin. Even today, even though guidelines have recommended against aspirin for primary prevention for some time, data from the National Health Interview Survey sample found that nearly one in three older adults take aspirin for primary prevention when they shouldn’t be. That’s a large number of people. That’s millions of Americans — and Canadians, but nobody cares about us. It’s fine.
That’s the point. We’re not debunking aspirin. It does work. The benefits are just really small in a primary prevention population and offset by the admittedly also really small risks of bleeding. It’s a tradeoff that doesn’t really work in your favor.
But that’s aspirin for cardiovascular disease. When it comes to cancer or DVT prophylaxis, that’s another really interesting story. We might have to save that for another time. Do I know how to tease a sequel or what?
Labos, a cardiologist at Kirkland Medical Center, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Sodium vs Potassium for Lowering Blood Pressure?
A pair of dueling editorials in the journal Hypertension debate whether our focus should be on sodium or its often neglected partner, potassium.
A meta-analysis of 85 trials showed a consistent and linear. It may also depend on where you live and whether your concern is treating individuals or implementing effective food policy.
The Case for Sodium Restriction
Stephen Juraschek, MD, PhD, of the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, co-author of one editorial, told me in a zoom interview that he believes his side of the debate clearly has the stronger argument. Of the two cations in question, there has been infinitely more ink spilled about sodium.
Studies such as INTERSALT, the DASH diet, and TOHP may be the most well-known, but there are many, many intervention studies of sodium restriction’s effect on blood pressure. A meta-analysis of 85 trials of showed a consistent and linear relationship between sodium reduction and blood pressure. In contrast, the evidence base for potassium is more limited and less consistent. There are half as many trials with potassium, and its ability to lower blood pressure may depend on how much sodium is present in the diet.
An outlier in the sodium restriction evidence base is the PURE study, which suggested that extreme sodium restriction could increase cardiovascular mortality, but the trial suffered from two potential issues. First, it used a single spot urine specimen to measure sodium rather than the generally accepted more accurate 24-hour urine collection. A reanalysis of the TOHP study using a spot urine rather than a 24-hour urine collection changed the relationship between sodium intake and mortality and possibly explained the U-shaped association observed in PURE. Second, PURE was an observational cohort and was prone to confounding, or in this case, reverse causation. Why did people who consumed very little salt have an increased risk for cardiovascular disease? It is very possible that people with a high risk for cardiovascular disease were told to consume less salt to begin with. Hence B led to A rather than A leading to B.
The debate on sodium restriction has been bitter at times. Opposing camps formed, and people took sides in the “salt wars.” A group of researchers, termed the Jackson 6, met and decided to end the controversy by running a randomized trial in US prisons (having discounted the options of long-term care homes and military bases). They detailed their plan in an editorial in Hypertension. The study never came to fruition for two reasons: the obvious ethical problems of experimenting on prisoners and the revelation of undisclosed salt industry funding.
More recent studies have mercifully been more conventional. The SSaSS study, a randomized controlled trial of a salt substitute, provided the cardiovascular outcomes data that many were waiting for. And CARDIA-SSBP, a cross-over randomized trial recently presented at the American Heart Association meeting, showed that reducing dietary sodium was on par with medication when it came to lowering blood pressure.
For Dr. Juraschek, the evidence is clear: “If you were going to choose one, I would say the weight of the evidence is still really heavily on the sodium side.”
The Case for Potassium Supplementation
The evidence for salt restriction notwithstanding, Swapnil Hiremath, MD, MPH, from the University of Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, argued in his editorial that potassium supplementation has gotten short shrift. Though he admits the studies for potassium supplementation have been smaller and sometimes rely on observational evidence, the evidence is there. In the distal convoluted tubule, the sodium chloride cotransporter (NCC), aka the potassium switch, is turned on by low potassium levels and leads to sodium reabsorption by the kidney even in settings of high sodium intake (Figure). To nonnephrologists, renal physiology may be a black box. But if you quickly brush up on the mechanism of action of thiazide diuretics, the preceding descriptor will make more sense.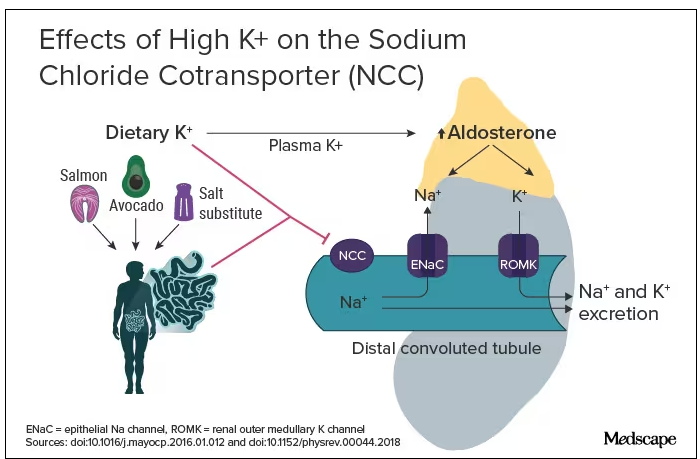
Dr. Hiremath points out that the DASH diet study also got patients to increase their potassium intake by eating more fruits and vegetables. Furthermore, the SSaSS study tested a salt substitute that was 25% potassium (and 75% sodium).
How much blood pressure lowering is due to sodium restriction vs potassium supplementation is a complex question because lowering sodium intake will invariably lead to more potassium intake. “It’s very hard to untangle the relationship,” Dr. Hiremath said in an interview. “It’s sort of synergistic but it’s not completely additive. It’s not as if you add four and four and get eight.” But he maintains there is more evidence regarding the benefit of potassium supplementation than many realize.
Realistic Diets and Taste Issues
“We know that increasing potassium, decreasing sodium is useful. The question is how do we do that?” says Dr. Hiremath. Should we encourage fruit and vegetable consumption in a healthy diet, give potassium supplements, or encourage the use of low-sodium salt substitutes?
Recommending a healthier diet with more fruits and vegetables is a no-brainer. But getting people to do it is hard. In a world where fruit is more expensive than junk food is, economic realities may drive food choice regardless of our best efforts. The 4700 mg of potassium in the DASH eating plan is the equivalent of eleven bananas daily; although not impossible, it would require a substantive shift in eating patterns for most people.
Given that we prescribe iron, vitamin B12, calcium, and vitamin D to patients who need them, why not potassium tablets to help with blood pressure? Granted, there are concerns about inducing hyperkalemia. Also, why not just prescribe a proven anti-hypertensive, such as ramipril, which has the added benefit of helping with renal protection or cardiac remodeling? Dr. Hiremath points out that patients are far less reluctant to take dietary supplements. Medication is something you take when sick. A supplement is seen as “natural” and “healthy” and might be more attractive to people resistant to prescription meds.
Another drawback of oral potassium supplementation is taste. In a Consumer Reports taste test, potassium chloride fared poorly. It was bitter and had a metallic aftertaste. At least one tester wouldn’t ever consume it again. Potassium citrate is slightly more palpable.
Salt substitutes, like the 75:25 ratio of sodium to potassium used in SSaSS, may be as high as you can go for potassium in any low-sodium salt alternative. If you go any higher than that, the taste will just turn people off, suggests Dr. Hiremath.
But SsaSS, which was done in China, may not be relevant to North America. In China, most sodium is added during cooking at home, and the consumption of processed foods is low. For the typical North American, roughly three quarters of the sodium eaten is added to their food by someone else; only about 15% is added during cooking at home or at the dinner table. If you aren’t someone who cooks, buying a salt substitute is probably not going to have much impact.
Given that reality, Dr. Juraschek thinks we need to target the sodium in processed foods. “There’s just so much sodium in so many products,” he says. “When you think about public policy, it’s most expeditious for there to be more regulation about how much is added to our food supply vs trying to get people to consume eight to 12 servings of fruit.”
No Salt War Here
Despite their different editorial takes, Dr. Hiremath and Dr. Juraschek largely agree on the broad strokes of the problem. This isn’t X (or Twitter) after all. Potassium supplementation may be useful in some parts of the world but may not address the underlying problem in countries where processed foods are the source of most dietary sodium.
The CARDIA-SSBP trial showed that a very low–sodium diet had the same blood pressure–lowering effect as a first-line antihypertensive, but most people will not be able to limit themselves to 500 mg of dietary sodium per day. In CARDIA-SSBP, just as in DASH, participants were provided with meals from study kitchens. They were not just told to eat less salt, which would almost certainly have failed.
“We should aim for stuff that is practical and doable rather than aim for stuff that cannot be done,” according to Dr. Hiremath. Whether that should be salt substitutes or policy change may depend on which part of the planet you live on.
One recent positive change may herald the beginning of a policy change, at least in the United States. In March 2023, the US Food and Drug Administration proposed a rule change to allow salt substitutes to be labeled as salt. This would make it easier for food manufacturers to swap out sodium chloride for a low-sodium alternative and reduce the amount of sodium in the US diet without having a large impact on taste and consumer uptake. Both Dr. Hiremath and Dr. Juraschek agree that it may not be enough on its own but that it’s a start.
Christopher Labos is a cardiologist with a degree in epidemiology. He spends most of his time doing things that he doesn’t get paid for, like research, teaching, and podcasting. Occasionally, he finds time to practice cardiology to pay the rent. He realizes that half of his research findings will be disproved in 5 years; he just doesn’t know which half. He is a regular contributor to the Montreal Gazette, CJAD radio, and CTV television in Montreal, and is host of the award-winning podcast The Body of Evidence.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A pair of dueling editorials in the journal Hypertension debate whether our focus should be on sodium or its often neglected partner, potassium.
A meta-analysis of 85 trials showed a consistent and linear. It may also depend on where you live and whether your concern is treating individuals or implementing effective food policy.
The Case for Sodium Restriction
Stephen Juraschek, MD, PhD, of the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, co-author of one editorial, told me in a zoom interview that he believes his side of the debate clearly has the stronger argument. Of the two cations in question, there has been infinitely more ink spilled about sodium.
Studies such as INTERSALT, the DASH diet, and TOHP may be the most well-known, but there are many, many intervention studies of sodium restriction’s effect on blood pressure. A meta-analysis of 85 trials of showed a consistent and linear relationship between sodium reduction and blood pressure. In contrast, the evidence base for potassium is more limited and less consistent. There are half as many trials with potassium, and its ability to lower blood pressure may depend on how much sodium is present in the diet.
An outlier in the sodium restriction evidence base is the PURE study, which suggested that extreme sodium restriction could increase cardiovascular mortality, but the trial suffered from two potential issues. First, it used a single spot urine specimen to measure sodium rather than the generally accepted more accurate 24-hour urine collection. A reanalysis of the TOHP study using a spot urine rather than a 24-hour urine collection changed the relationship between sodium intake and mortality and possibly explained the U-shaped association observed in PURE. Second, PURE was an observational cohort and was prone to confounding, or in this case, reverse causation. Why did people who consumed very little salt have an increased risk for cardiovascular disease? It is very possible that people with a high risk for cardiovascular disease were told to consume less salt to begin with. Hence B led to A rather than A leading to B.
The debate on sodium restriction has been bitter at times. Opposing camps formed, and people took sides in the “salt wars.” A group of researchers, termed the Jackson 6, met and decided to end the controversy by running a randomized trial in US prisons (having discounted the options of long-term care homes and military bases). They detailed their plan in an editorial in Hypertension. The study never came to fruition for two reasons: the obvious ethical problems of experimenting on prisoners and the revelation of undisclosed salt industry funding.
More recent studies have mercifully been more conventional. The SSaSS study, a randomized controlled trial of a salt substitute, provided the cardiovascular outcomes data that many were waiting for. And CARDIA-SSBP, a cross-over randomized trial recently presented at the American Heart Association meeting, showed that reducing dietary sodium was on par with medication when it came to lowering blood pressure.
For Dr. Juraschek, the evidence is clear: “If you were going to choose one, I would say the weight of the evidence is still really heavily on the sodium side.”
The Case for Potassium Supplementation
The evidence for salt restriction notwithstanding, Swapnil Hiremath, MD, MPH, from the University of Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, argued in his editorial that potassium supplementation has gotten short shrift. Though he admits the studies for potassium supplementation have been smaller and sometimes rely on observational evidence, the evidence is there. In the distal convoluted tubule, the sodium chloride cotransporter (NCC), aka the potassium switch, is turned on by low potassium levels and leads to sodium reabsorption by the kidney even in settings of high sodium intake (Figure). To nonnephrologists, renal physiology may be a black box. But if you quickly brush up on the mechanism of action of thiazide diuretics, the preceding descriptor will make more sense.
Dr. Hiremath points out that the DASH diet study also got patients to increase their potassium intake by eating more fruits and vegetables. Furthermore, the SSaSS study tested a salt substitute that was 25% potassium (and 75% sodium).
How much blood pressure lowering is due to sodium restriction vs potassium supplementation is a complex question because lowering sodium intake will invariably lead to more potassium intake. “It’s very hard to untangle the relationship,” Dr. Hiremath said in an interview. “It’s sort of synergistic but it’s not completely additive. It’s not as if you add four and four and get eight.” But he maintains there is more evidence regarding the benefit of potassium supplementation than many realize.
Realistic Diets and Taste Issues
“We know that increasing potassium, decreasing sodium is useful. The question is how do we do that?” says Dr. Hiremath. Should we encourage fruit and vegetable consumption in a healthy diet, give potassium supplements, or encourage the use of low-sodium salt substitutes?
Recommending a healthier diet with more fruits and vegetables is a no-brainer. But getting people to do it is hard. In a world where fruit is more expensive than junk food is, economic realities may drive food choice regardless of our best efforts. The 4700 mg of potassium in the DASH eating plan is the equivalent of eleven bananas daily; although not impossible, it would require a substantive shift in eating patterns for most people.
Given that we prescribe iron, vitamin B12, calcium, and vitamin D to patients who need them, why not potassium tablets to help with blood pressure? Granted, there are concerns about inducing hyperkalemia. Also, why not just prescribe a proven anti-hypertensive, such as ramipril, which has the added benefit of helping with renal protection or cardiac remodeling? Dr. Hiremath points out that patients are far less reluctant to take dietary supplements. Medication is something you take when sick. A supplement is seen as “natural” and “healthy” and might be more attractive to people resistant to prescription meds.
Another drawback of oral potassium supplementation is taste. In a Consumer Reports taste test, potassium chloride fared poorly. It was bitter and had a metallic aftertaste. At least one tester wouldn’t ever consume it again. Potassium citrate is slightly more palpable.
Salt substitutes, like the 75:25 ratio of sodium to potassium used in SSaSS, may be as high as you can go for potassium in any low-sodium salt alternative. If you go any higher than that, the taste will just turn people off, suggests Dr. Hiremath.
But SsaSS, which was done in China, may not be relevant to North America. In China, most sodium is added during cooking at home, and the consumption of processed foods is low. For the typical North American, roughly three quarters of the sodium eaten is added to their food by someone else; only about 15% is added during cooking at home or at the dinner table. If you aren’t someone who cooks, buying a salt substitute is probably not going to have much impact.
Given that reality, Dr. Juraschek thinks we need to target the sodium in processed foods. “There’s just so much sodium in so many products,” he says. “When you think about public policy, it’s most expeditious for there to be more regulation about how much is added to our food supply vs trying to get people to consume eight to 12 servings of fruit.”
No Salt War Here
Despite their different editorial takes, Dr. Hiremath and Dr. Juraschek largely agree on the broad strokes of the problem. This isn’t X (or Twitter) after all. Potassium supplementation may be useful in some parts of the world but may not address the underlying problem in countries where processed foods are the source of most dietary sodium.
The CARDIA-SSBP trial showed that a very low–sodium diet had the same blood pressure–lowering effect as a first-line antihypertensive, but most people will not be able to limit themselves to 500 mg of dietary sodium per day. In CARDIA-SSBP, just as in DASH, participants were provided with meals from study kitchens. They were not just told to eat less salt, which would almost certainly have failed.
“We should aim for stuff that is practical and doable rather than aim for stuff that cannot be done,” according to Dr. Hiremath. Whether that should be salt substitutes or policy change may depend on which part of the planet you live on.
One recent positive change may herald the beginning of a policy change, at least in the United States. In March 2023, the US Food and Drug Administration proposed a rule change to allow salt substitutes to be labeled as salt. This would make it easier for food manufacturers to swap out sodium chloride for a low-sodium alternative and reduce the amount of sodium in the US diet without having a large impact on taste and consumer uptake. Both Dr. Hiremath and Dr. Juraschek agree that it may not be enough on its own but that it’s a start.
Christopher Labos is a cardiologist with a degree in epidemiology. He spends most of his time doing things that he doesn’t get paid for, like research, teaching, and podcasting. Occasionally, he finds time to practice cardiology to pay the rent. He realizes that half of his research findings will be disproved in 5 years; he just doesn’t know which half. He is a regular contributor to the Montreal Gazette, CJAD radio, and CTV television in Montreal, and is host of the award-winning podcast The Body of Evidence.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A pair of dueling editorials in the journal Hypertension debate whether our focus should be on sodium or its often neglected partner, potassium.
A meta-analysis of 85 trials showed a consistent and linear. It may also depend on where you live and whether your concern is treating individuals or implementing effective food policy.
The Case for Sodium Restriction
Stephen Juraschek, MD, PhD, of the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, co-author of one editorial, told me in a zoom interview that he believes his side of the debate clearly has the stronger argument. Of the two cations in question, there has been infinitely more ink spilled about sodium.
Studies such as INTERSALT, the DASH diet, and TOHP may be the most well-known, but there are many, many intervention studies of sodium restriction’s effect on blood pressure. A meta-analysis of 85 trials of showed a consistent and linear relationship between sodium reduction and blood pressure. In contrast, the evidence base for potassium is more limited and less consistent. There are half as many trials with potassium, and its ability to lower blood pressure may depend on how much sodium is present in the diet.
An outlier in the sodium restriction evidence base is the PURE study, which suggested that extreme sodium restriction could increase cardiovascular mortality, but the trial suffered from two potential issues. First, it used a single spot urine specimen to measure sodium rather than the generally accepted more accurate 24-hour urine collection. A reanalysis of the TOHP study using a spot urine rather than a 24-hour urine collection changed the relationship between sodium intake and mortality and possibly explained the U-shaped association observed in PURE. Second, PURE was an observational cohort and was prone to confounding, or in this case, reverse causation. Why did people who consumed very little salt have an increased risk for cardiovascular disease? It is very possible that people with a high risk for cardiovascular disease were told to consume less salt to begin with. Hence B led to A rather than A leading to B.
The debate on sodium restriction has been bitter at times. Opposing camps formed, and people took sides in the “salt wars.” A group of researchers, termed the Jackson 6, met and decided to end the controversy by running a randomized trial in US prisons (having discounted the options of long-term care homes and military bases). They detailed their plan in an editorial in Hypertension. The study never came to fruition for two reasons: the obvious ethical problems of experimenting on prisoners and the revelation of undisclosed salt industry funding.
More recent studies have mercifully been more conventional. The SSaSS study, a randomized controlled trial of a salt substitute, provided the cardiovascular outcomes data that many were waiting for. And CARDIA-SSBP, a cross-over randomized trial recently presented at the American Heart Association meeting, showed that reducing dietary sodium was on par with medication when it came to lowering blood pressure.
For Dr. Juraschek, the evidence is clear: “If you were going to choose one, I would say the weight of the evidence is still really heavily on the sodium side.”
The Case for Potassium Supplementation
The evidence for salt restriction notwithstanding, Swapnil Hiremath, MD, MPH, from the University of Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, argued in his editorial that potassium supplementation has gotten short shrift. Though he admits the studies for potassium supplementation have been smaller and sometimes rely on observational evidence, the evidence is there. In the distal convoluted tubule, the sodium chloride cotransporter (NCC), aka the potassium switch, is turned on by low potassium levels and leads to sodium reabsorption by the kidney even in settings of high sodium intake (Figure). To nonnephrologists, renal physiology may be a black box. But if you quickly brush up on the mechanism of action of thiazide diuretics, the preceding descriptor will make more sense.
Dr. Hiremath points out that the DASH diet study also got patients to increase their potassium intake by eating more fruits and vegetables. Furthermore, the SSaSS study tested a salt substitute that was 25% potassium (and 75% sodium).
How much blood pressure lowering is due to sodium restriction vs potassium supplementation is a complex question because lowering sodium intake will invariably lead to more potassium intake. “It’s very hard to untangle the relationship,” Dr. Hiremath said in an interview. “It’s sort of synergistic but it’s not completely additive. It’s not as if you add four and four and get eight.” But he maintains there is more evidence regarding the benefit of potassium supplementation than many realize.
Realistic Diets and Taste Issues
“We know that increasing potassium, decreasing sodium is useful. The question is how do we do that?” says Dr. Hiremath. Should we encourage fruit and vegetable consumption in a healthy diet, give potassium supplements, or encourage the use of low-sodium salt substitutes?
Recommending a healthier diet with more fruits and vegetables is a no-brainer. But getting people to do it is hard. In a world where fruit is more expensive than junk food is, economic realities may drive food choice regardless of our best efforts. The 4700 mg of potassium in the DASH eating plan is the equivalent of eleven bananas daily; although not impossible, it would require a substantive shift in eating patterns for most people.
Given that we prescribe iron, vitamin B12, calcium, and vitamin D to patients who need them, why not potassium tablets to help with blood pressure? Granted, there are concerns about inducing hyperkalemia. Also, why not just prescribe a proven anti-hypertensive, such as ramipril, which has the added benefit of helping with renal protection or cardiac remodeling? Dr. Hiremath points out that patients are far less reluctant to take dietary supplements. Medication is something you take when sick. A supplement is seen as “natural” and “healthy” and might be more attractive to people resistant to prescription meds.
Another drawback of oral potassium supplementation is taste. In a Consumer Reports taste test, potassium chloride fared poorly. It was bitter and had a metallic aftertaste. At least one tester wouldn’t ever consume it again. Potassium citrate is slightly more palpable.
Salt substitutes, like the 75:25 ratio of sodium to potassium used in SSaSS, may be as high as you can go for potassium in any low-sodium salt alternative. If you go any higher than that, the taste will just turn people off, suggests Dr. Hiremath.
But SsaSS, which was done in China, may not be relevant to North America. In China, most sodium is added during cooking at home, and the consumption of processed foods is low. For the typical North American, roughly three quarters of the sodium eaten is added to their food by someone else; only about 15% is added during cooking at home or at the dinner table. If you aren’t someone who cooks, buying a salt substitute is probably not going to have much impact.
Given that reality, Dr. Juraschek thinks we need to target the sodium in processed foods. “There’s just so much sodium in so many products,” he says. “When you think about public policy, it’s most expeditious for there to be more regulation about how much is added to our food supply vs trying to get people to consume eight to 12 servings of fruit.”
No Salt War Here
Despite their different editorial takes, Dr. Hiremath and Dr. Juraschek largely agree on the broad strokes of the problem. This isn’t X (or Twitter) after all. Potassium supplementation may be useful in some parts of the world but may not address the underlying problem in countries where processed foods are the source of most dietary sodium.
The CARDIA-SSBP trial showed that a very low–sodium diet had the same blood pressure–lowering effect as a first-line antihypertensive, but most people will not be able to limit themselves to 500 mg of dietary sodium per day. In CARDIA-SSBP, just as in DASH, participants were provided with meals from study kitchens. They were not just told to eat less salt, which would almost certainly have failed.
“We should aim for stuff that is practical and doable rather than aim for stuff that cannot be done,” according to Dr. Hiremath. Whether that should be salt substitutes or policy change may depend on which part of the planet you live on.
One recent positive change may herald the beginning of a policy change, at least in the United States. In March 2023, the US Food and Drug Administration proposed a rule change to allow salt substitutes to be labeled as salt. This would make it easier for food manufacturers to swap out sodium chloride for a low-sodium alternative and reduce the amount of sodium in the US diet without having a large impact on taste and consumer uptake. Both Dr. Hiremath and Dr. Juraschek agree that it may not be enough on its own but that it’s a start.
Christopher Labos is a cardiologist with a degree in epidemiology. He spends most of his time doing things that he doesn’t get paid for, like research, teaching, and podcasting. Occasionally, he finds time to practice cardiology to pay the rent. He realizes that half of his research findings will be disproved in 5 years; he just doesn’t know which half. He is a regular contributor to the Montreal Gazette, CJAD radio, and CTV television in Montreal, and is host of the award-winning podcast The Body of Evidence.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Multivitamins and dementia: Untangling the COSMOS study web
I have written before about the COSMOS study and its finding that multivitamins (and chocolate) did not improve brain or cardiovascular health. So I was surprised to read that a “new” study found that vitamins can forestall dementia and age-related cognitive decline.
Upon closer look, the new data are neither new nor convincing, at least to me.
Chocolate and multivitamins for CVD and cancer prevention
The large randomized COSMOS trial was supposed to be the definitive study on chocolate that would establish its heart-health benefits without a doubt. Or, rather, the benefits of a cocoa bean extract in pill form given to healthy, older volunteers. The COSMOS study was negative. Chocolate, or the cocoa bean extract they used, did not reduce cardiovascular events.
And yet for all the prepublication importance attached to COSMOS, it is scarcely mentioned. Had it been positive, rest assured that Mars, the candy bar company that cofunded the research, and other interested parties would have been shouting it from the rooftops. As it is, they’re already spinning it.
Which brings us to the multivitamin component. COSMOS actually had a 2 × 2 design. In other words, there were four groups in this study: chocolate plus multivitamin, chocolate plus placebo, placebo plus multivitamin, and placebo plus placebo. This type of study design allows you to study two different interventions simultaneously, provided that they are independent and do not interact with each other. In addition to the primary cardiovascular endpoint, they also studied a cancer endpoint.
The multivitamin supplement didn’t reduce cardiovascular events either. Nor did it affect cancer outcomes. The main COSMOS study was negative and reinforced what countless other studies have proven: Taking a daily multivitamin does not reduce your risk of having a heart attack or developing cancer.
But wait, there’s more: COSMOS-Mind
But no researcher worth his salt studies just one or two endpoints in a study. The participants also underwent neurologic and memory testing. These results were reported separately in the COSMOS-Mind study.
COSMOS-Mind is often described as a separate (or “new”) study. In reality, it included the same participants from the original COSMOS trial and measured yet another primary outcome of cognitive performance on a series of tests administered by telephone. Although there is nothing inherently wrong with studying multiple outcomes in your patient population (after all, that salami isn’t going to slice itself), they cannot all be primary outcomes. Some, by necessity, must be secondary hypothesis–generating outcomes. If you test enough endpoints, multiple hypothesis testing dictates that eventually you will get a positive result simply by chance.
There was a time when the neurocognitive outcomes of COSMOS would have been reported in the same paper as the cardiovascular outcomes, but that time seems to have passed us by. Researchers live or die by the number of their publications, and there is an inherent advantage to squeezing as many publications as possible from the same dataset. Though, to be fair, the journal would probably have asked them to split up the paper as well.
In brief, the cocoa extract again fell short in COSMOS-Mind, but the multivitamin arm did better on the composite cognitive outcome. It was a fairly small difference – a 0.07-point improvement on the z-score at the 3-year mark (the z-score is the mean divided by the standard deviation). Much was also made of the fact that the improvement seemed to vary by prior history of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Those with a history of CVD had a 0.11-point improvement, whereas those without had a 0.06-point improvement. The authors couldn’t offer a definitive explanation for these findings. Any argument that multivitamins improve cardiovascular health and therefore prevent vascular dementia has to contend with the fact that the main COSMOS study didn’t show a cardiovascular benefit for vitamins. Speculation that you are treating nutritional deficiencies is exactly that: speculation.
A more salient question is: What does a 0.07-point improvement on the z-score mean clinically? This study didn’t assess whether a multivitamin supplement prevented dementia or allowed people to live independently for longer. In fairness, that would have been exceptionally difficult to do and would have required a much longer study.
Their one attempt to quantify the cognitive benefit clinically was a calculation about normal age-related decline. Test scores were 0.045 points lower for every 1-year increase in age among participants (their mean age was 73 years). So the authors contend that a 0.07-point increase, or the 0.083-point increase that they found at year 3, corresponds to 1.8 years of age-related decline forestalled. Whether this is an appropriate assumption, I leave for the reader to decide.
COSMOS-Web and replication
The results of COSMOS-Mind were seemingly bolstered by the recent publication of COSMOS-Web. Although I’ve seen this study described as having replicated the results of COSMOS-Mind, that description is a bit misleading. This was yet another ancillary COSMOS study; more than half of the 2,262 participants in COSMOS-Mind were also included in COSMOS-Web. Replicating results in the same people isn’t true replication.
The main difference between COSMOS-Mind and COSMOS-Web is that the former used a telephone interview to administer the cognitive tests and the latter used the Internet. They also had different endpoints, with COSMOS-Web looking at immediate recall rather than a global test composite.
COSMOS-Web was a positive study in that patients getting the multivitamin supplement did better on the test for immediate memory recall (remembering a list of 20 words), though they didn’t improve on tests of memory retention, executive function, or novel object recognition (basically a test where subjects have to identify matching geometric patterns and then recall them later). They were able to remember an additional 0.71 word on average, compared with 0.44 word in the placebo group. (For the record, it found no benefit for the cocoa extract).
Everybody does better on memory tests the second time around because practice makes perfect, hence the improvement in the placebo group. This benefit at 1 year did not survive to the end of follow-up at 3 years, in contrast to COSMOS-Mind, where the benefit was not apparent at 1 year and seen only at year 3. A history of cardiovascular disease didn’t seem to affect the results in COSMOS-Web as it did in COSMOS-Mind. As far as replications go, COSMOS-Web has some very non-negligible differences, compared with COSMOS-Mind. This incongruity, especially given the overlap in the patient populations is hard to reconcile. If COSMOS-Web was supposed to assuage any doubts that persisted after COSMOS-Mind, it hasn’t for me.
One of these studies is not like the others
Finally, although the COSMOS trial and all its ancillary study analyses suggest a neurocognitive benefit to multivitamin supplementation, it’s not the first study to test the matter. The Age-Related Eye Disease Study looked at vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, zinc, and copper. There was no benefit on any of the six cognitive tests administered to patients. The Women’s Health Study, the Women’s Antioxidant Cardiovascular Study and PREADViSE have all failed to show any benefit to the various vitamins and minerals they studied. A meta-analysis of 11 trials found no benefit to B vitamins in slowing cognitive aging.
The claim that COSMOS is the “first” study to test the hypothesis hinges on some careful wordplay. Prior studies tested specific vitamins, not a multivitamin. In the discussion of the paper, these other studies are critiqued for being short term. But the Physicians’ Health Study II did in fact study a multivitamin and assessed cognitive performance on average 2.5 years after randomization. It found no benefit. The authors of COSMOS-Web critiqued the 2.5-year wait to perform cognitive testing, saying it would have missed any short-term benefits. Although, given that they simultaneously praised their 3 years of follow-up, the criticism is hard to fully accept or even understand.
Whether follow-up is short or long, uses individual vitamins or a multivitamin, the results excluding COSMOS are uniformly negative.
Do enough tests in the same population, and something will rise above the noise just by chance. When you get a positive result in your research, it’s always exciting. But when a slew of studies that came before you are negative, you aren’t groundbreaking. You’re an outlier.
Dr. Labos is a cardiologist at Hôpital Notre-Dame, Montreal. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
I have written before about the COSMOS study and its finding that multivitamins (and chocolate) did not improve brain or cardiovascular health. So I was surprised to read that a “new” study found that vitamins can forestall dementia and age-related cognitive decline.
Upon closer look, the new data are neither new nor convincing, at least to me.
Chocolate and multivitamins for CVD and cancer prevention
The large randomized COSMOS trial was supposed to be the definitive study on chocolate that would establish its heart-health benefits without a doubt. Or, rather, the benefits of a cocoa bean extract in pill form given to healthy, older volunteers. The COSMOS study was negative. Chocolate, or the cocoa bean extract they used, did not reduce cardiovascular events.
And yet for all the prepublication importance attached to COSMOS, it is scarcely mentioned. Had it been positive, rest assured that Mars, the candy bar company that cofunded the research, and other interested parties would have been shouting it from the rooftops. As it is, they’re already spinning it.
Which brings us to the multivitamin component. COSMOS actually had a 2 × 2 design. In other words, there were four groups in this study: chocolate plus multivitamin, chocolate plus placebo, placebo plus multivitamin, and placebo plus placebo. This type of study design allows you to study two different interventions simultaneously, provided that they are independent and do not interact with each other. In addition to the primary cardiovascular endpoint, they also studied a cancer endpoint.
The multivitamin supplement didn’t reduce cardiovascular events either. Nor did it affect cancer outcomes. The main COSMOS study was negative and reinforced what countless other studies have proven: Taking a daily multivitamin does not reduce your risk of having a heart attack or developing cancer.
But wait, there’s more: COSMOS-Mind
But no researcher worth his salt studies just one or two endpoints in a study. The participants also underwent neurologic and memory testing. These results were reported separately in the COSMOS-Mind study.
COSMOS-Mind is often described as a separate (or “new”) study. In reality, it included the same participants from the original COSMOS trial and measured yet another primary outcome of cognitive performance on a series of tests administered by telephone. Although there is nothing inherently wrong with studying multiple outcomes in your patient population (after all, that salami isn’t going to slice itself), they cannot all be primary outcomes. Some, by necessity, must be secondary hypothesis–generating outcomes. If you test enough endpoints, multiple hypothesis testing dictates that eventually you will get a positive result simply by chance.
There was a time when the neurocognitive outcomes of COSMOS would have been reported in the same paper as the cardiovascular outcomes, but that time seems to have passed us by. Researchers live or die by the number of their publications, and there is an inherent advantage to squeezing as many publications as possible from the same dataset. Though, to be fair, the journal would probably have asked them to split up the paper as well.
In brief, the cocoa extract again fell short in COSMOS-Mind, but the multivitamin arm did better on the composite cognitive outcome. It was a fairly small difference – a 0.07-point improvement on the z-score at the 3-year mark (the z-score is the mean divided by the standard deviation). Much was also made of the fact that the improvement seemed to vary by prior history of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Those with a history of CVD had a 0.11-point improvement, whereas those without had a 0.06-point improvement. The authors couldn’t offer a definitive explanation for these findings. Any argument that multivitamins improve cardiovascular health and therefore prevent vascular dementia has to contend with the fact that the main COSMOS study didn’t show a cardiovascular benefit for vitamins. Speculation that you are treating nutritional deficiencies is exactly that: speculation.
A more salient question is: What does a 0.07-point improvement on the z-score mean clinically? This study didn’t assess whether a multivitamin supplement prevented dementia or allowed people to live independently for longer. In fairness, that would have been exceptionally difficult to do and would have required a much longer study.
Their one attempt to quantify the cognitive benefit clinically was a calculation about normal age-related decline. Test scores were 0.045 points lower for every 1-year increase in age among participants (their mean age was 73 years). So the authors contend that a 0.07-point increase, or the 0.083-point increase that they found at year 3, corresponds to 1.8 years of age-related decline forestalled. Whether this is an appropriate assumption, I leave for the reader to decide.
COSMOS-Web and replication
The results of COSMOS-Mind were seemingly bolstered by the recent publication of COSMOS-Web. Although I’ve seen this study described as having replicated the results of COSMOS-Mind, that description is a bit misleading. This was yet another ancillary COSMOS study; more than half of the 2,262 participants in COSMOS-Mind were also included in COSMOS-Web. Replicating results in the same people isn’t true replication.
The main difference between COSMOS-Mind and COSMOS-Web is that the former used a telephone interview to administer the cognitive tests and the latter used the Internet. They also had different endpoints, with COSMOS-Web looking at immediate recall rather than a global test composite.
COSMOS-Web was a positive study in that patients getting the multivitamin supplement did better on the test for immediate memory recall (remembering a list of 20 words), though they didn’t improve on tests of memory retention, executive function, or novel object recognition (basically a test where subjects have to identify matching geometric patterns and then recall them later). They were able to remember an additional 0.71 word on average, compared with 0.44 word in the placebo group. (For the record, it found no benefit for the cocoa extract).
Everybody does better on memory tests the second time around because practice makes perfect, hence the improvement in the placebo group. This benefit at 1 year did not survive to the end of follow-up at 3 years, in contrast to COSMOS-Mind, where the benefit was not apparent at 1 year and seen only at year 3. A history of cardiovascular disease didn’t seem to affect the results in COSMOS-Web as it did in COSMOS-Mind. As far as replications go, COSMOS-Web has some very non-negligible differences, compared with COSMOS-Mind. This incongruity, especially given the overlap in the patient populations is hard to reconcile. If COSMOS-Web was supposed to assuage any doubts that persisted after COSMOS-Mind, it hasn’t for me.
One of these studies is not like the others
Finally, although the COSMOS trial and all its ancillary study analyses suggest a neurocognitive benefit to multivitamin supplementation, it’s not the first study to test the matter. The Age-Related Eye Disease Study looked at vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, zinc, and copper. There was no benefit on any of the six cognitive tests administered to patients. The Women’s Health Study, the Women’s Antioxidant Cardiovascular Study and PREADViSE have all failed to show any benefit to the various vitamins and minerals they studied. A meta-analysis of 11 trials found no benefit to B vitamins in slowing cognitive aging.
The claim that COSMOS is the “first” study to test the hypothesis hinges on some careful wordplay. Prior studies tested specific vitamins, not a multivitamin. In the discussion of the paper, these other studies are critiqued for being short term. But the Physicians’ Health Study II did in fact study a multivitamin and assessed cognitive performance on average 2.5 years after randomization. It found no benefit. The authors of COSMOS-Web critiqued the 2.5-year wait to perform cognitive testing, saying it would have missed any short-term benefits. Although, given that they simultaneously praised their 3 years of follow-up, the criticism is hard to fully accept or even understand.
Whether follow-up is short or long, uses individual vitamins or a multivitamin, the results excluding COSMOS are uniformly negative.
Do enough tests in the same population, and something will rise above the noise just by chance. When you get a positive result in your research, it’s always exciting. But when a slew of studies that came before you are negative, you aren’t groundbreaking. You’re an outlier.
Dr. Labos is a cardiologist at Hôpital Notre-Dame, Montreal. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
I have written before about the COSMOS study and its finding that multivitamins (and chocolate) did not improve brain or cardiovascular health. So I was surprised to read that a “new” study found that vitamins can forestall dementia and age-related cognitive decline.
Upon closer look, the new data are neither new nor convincing, at least to me.
Chocolate and multivitamins for CVD and cancer prevention
The large randomized COSMOS trial was supposed to be the definitive study on chocolate that would establish its heart-health benefits without a doubt. Or, rather, the benefits of a cocoa bean extract in pill form given to healthy, older volunteers. The COSMOS study was negative. Chocolate, or the cocoa bean extract they used, did not reduce cardiovascular events.
And yet for all the prepublication importance attached to COSMOS, it is scarcely mentioned. Had it been positive, rest assured that Mars, the candy bar company that cofunded the research, and other interested parties would have been shouting it from the rooftops. As it is, they’re already spinning it.
Which brings us to the multivitamin component. COSMOS actually had a 2 × 2 design. In other words, there were four groups in this study: chocolate plus multivitamin, chocolate plus placebo, placebo plus multivitamin, and placebo plus placebo. This type of study design allows you to study two different interventions simultaneously, provided that they are independent and do not interact with each other. In addition to the primary cardiovascular endpoint, they also studied a cancer endpoint.
The multivitamin supplement didn’t reduce cardiovascular events either. Nor did it affect cancer outcomes. The main COSMOS study was negative and reinforced what countless other studies have proven: Taking a daily multivitamin does not reduce your risk of having a heart attack or developing cancer.
But wait, there’s more: COSMOS-Mind
But no researcher worth his salt studies just one or two endpoints in a study. The participants also underwent neurologic and memory testing. These results were reported separately in the COSMOS-Mind study.
COSMOS-Mind is often described as a separate (or “new”) study. In reality, it included the same participants from the original COSMOS trial and measured yet another primary outcome of cognitive performance on a series of tests administered by telephone. Although there is nothing inherently wrong with studying multiple outcomes in your patient population (after all, that salami isn’t going to slice itself), they cannot all be primary outcomes. Some, by necessity, must be secondary hypothesis–generating outcomes. If you test enough endpoints, multiple hypothesis testing dictates that eventually you will get a positive result simply by chance.
There was a time when the neurocognitive outcomes of COSMOS would have been reported in the same paper as the cardiovascular outcomes, but that time seems to have passed us by. Researchers live or die by the number of their publications, and there is an inherent advantage to squeezing as many publications as possible from the same dataset. Though, to be fair, the journal would probably have asked them to split up the paper as well.
In brief, the cocoa extract again fell short in COSMOS-Mind, but the multivitamin arm did better on the composite cognitive outcome. It was a fairly small difference – a 0.07-point improvement on the z-score at the 3-year mark (the z-score is the mean divided by the standard deviation). Much was also made of the fact that the improvement seemed to vary by prior history of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Those with a history of CVD had a 0.11-point improvement, whereas those without had a 0.06-point improvement. The authors couldn’t offer a definitive explanation for these findings. Any argument that multivitamins improve cardiovascular health and therefore prevent vascular dementia has to contend with the fact that the main COSMOS study didn’t show a cardiovascular benefit for vitamins. Speculation that you are treating nutritional deficiencies is exactly that: speculation.
A more salient question is: What does a 0.07-point improvement on the z-score mean clinically? This study didn’t assess whether a multivitamin supplement prevented dementia or allowed people to live independently for longer. In fairness, that would have been exceptionally difficult to do and would have required a much longer study.
Their one attempt to quantify the cognitive benefit clinically was a calculation about normal age-related decline. Test scores were 0.045 points lower for every 1-year increase in age among participants (their mean age was 73 years). So the authors contend that a 0.07-point increase, or the 0.083-point increase that they found at year 3, corresponds to 1.8 years of age-related decline forestalled. Whether this is an appropriate assumption, I leave for the reader to decide.
COSMOS-Web and replication
The results of COSMOS-Mind were seemingly bolstered by the recent publication of COSMOS-Web. Although I’ve seen this study described as having replicated the results of COSMOS-Mind, that description is a bit misleading. This was yet another ancillary COSMOS study; more than half of the 2,262 participants in COSMOS-Mind were also included in COSMOS-Web. Replicating results in the same people isn’t true replication.
The main difference between COSMOS-Mind and COSMOS-Web is that the former used a telephone interview to administer the cognitive tests and the latter used the Internet. They also had different endpoints, with COSMOS-Web looking at immediate recall rather than a global test composite.
COSMOS-Web was a positive study in that patients getting the multivitamin supplement did better on the test for immediate memory recall (remembering a list of 20 words), though they didn’t improve on tests of memory retention, executive function, or novel object recognition (basically a test where subjects have to identify matching geometric patterns and then recall them later). They were able to remember an additional 0.71 word on average, compared with 0.44 word in the placebo group. (For the record, it found no benefit for the cocoa extract).
Everybody does better on memory tests the second time around because practice makes perfect, hence the improvement in the placebo group. This benefit at 1 year did not survive to the end of follow-up at 3 years, in contrast to COSMOS-Mind, where the benefit was not apparent at 1 year and seen only at year 3. A history of cardiovascular disease didn’t seem to affect the results in COSMOS-Web as it did in COSMOS-Mind. As far as replications go, COSMOS-Web has some very non-negligible differences, compared with COSMOS-Mind. This incongruity, especially given the overlap in the patient populations is hard to reconcile. If COSMOS-Web was supposed to assuage any doubts that persisted after COSMOS-Mind, it hasn’t for me.
One of these studies is not like the others
Finally, although the COSMOS trial and all its ancillary study analyses suggest a neurocognitive benefit to multivitamin supplementation, it’s not the first study to test the matter. The Age-Related Eye Disease Study looked at vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, zinc, and copper. There was no benefit on any of the six cognitive tests administered to patients. The Women’s Health Study, the Women’s Antioxidant Cardiovascular Study and PREADViSE have all failed to show any benefit to the various vitamins and minerals they studied. A meta-analysis of 11 trials found no benefit to B vitamins in slowing cognitive aging.
The claim that COSMOS is the “first” study to test the hypothesis hinges on some careful wordplay. Prior studies tested specific vitamins, not a multivitamin. In the discussion of the paper, these other studies are critiqued for being short term. But the Physicians’ Health Study II did in fact study a multivitamin and assessed cognitive performance on average 2.5 years after randomization. It found no benefit. The authors of COSMOS-Web critiqued the 2.5-year wait to perform cognitive testing, saying it would have missed any short-term benefits. Although, given that they simultaneously praised their 3 years of follow-up, the criticism is hard to fully accept or even understand.
Whether follow-up is short or long, uses individual vitamins or a multivitamin, the results excluding COSMOS are uniformly negative.
Do enough tests in the same population, and something will rise above the noise just by chance. When you get a positive result in your research, it’s always exciting. But when a slew of studies that came before you are negative, you aren’t groundbreaking. You’re an outlier.
Dr. Labos is a cardiologist at Hôpital Notre-Dame, Montreal. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Conflicting blood pressure targets: Déjà vu all over again
Stop me if you’ve heard this before. There’s a controversy over blood pressure targets. Some argue for 140/90 mm Hg, others for 130/80 mm Hg, and some super ambitious folks think that we should aim for 120/80 mm Hg. If this sounds familiar, it should. We did it in 2017. It’s unclear what, if anything, we learned from the experience. On the upside, it’s not as bad as it was 100 years ago.
When high blood pressure was a ‘good’ thing
Back then, many believed that you needed higher blood pressure as you got older to push the blood through your progressively stiffened and hardened arteries. Hence the name “essential” hypertension. The concern was that lowering blood pressure would hypoperfuse your organs and be dangerous. In the 1930s, John Hay told an audience at a British Medical Association lecture: “The greatest danger to a man with high blood pressure lies in its discovery, because then some fool is certain to try and reduce it.”
The 1900s were a simpler time when people had fatal strokes in their 50s, and their families were consoled by the knowledge that they had lived a good life.
If our thinking around blood pressure had evolved slightly faster, perhaps President Roosevelt wouldn’t have died of a stroke during World War II as his doctors watched his systolic blood pressure climb above 200 mm Hg and suggested massages and barbiturates to take the edge off.
The current controversy
Not that long ago, 180 mm Hg was considered mild hypertension. Now, we are arguing about a systolic blood pressure of 140 versus 130 mm Hg.
The American Academy of Family Physicians takes the view that 140/90 mm Hg is good enough for most people. Their most recent clinical practice guideline, based primarily on two 2020 Cochrane Reviews of blood pressure targets in patients with and without cardiovascular disease, did not find any mortality benefit for a lower blood pressure threshold.
This puts the AAFP guideline in conflict with the 2017 guideline issued jointly by the American College of Cardiology, American Heart Association, and nine other groups, which recommended a target of 130/80 mm Hg for pretty much everyone. Though they say greater than 140/90 mm Hg should be the threshold for low-risk patients or for starting therapy post stroke, we often forget those nuances. The main point of contention is that the AAFP guideline was looking for a mortality benefit, whereas the ACC/AHA/everyone else guideline was looking at preventing cardiovascular events. The latter guideline was driven mainly by the results of the SPRINT trial. ACC/AHA argue for more aggressive targets to prevent the things that cardiologists care about, namely heart attacks.
The AAFP guideline conceded that more aggressive control will result in fewer myocardial infarctions but warn that it comes with more adverse events. Treating 1,000 patients to this lower target would theoretically prevent four MIs, possibly prevent three strokes, but result in 30 adverse events.
In the end, what we are seeing here is not so much a debate over the evidence as a debate over priorities. Interventions that don’t improve mortality can be questioned in terms of their cost effectiveness. But you probably don’t want to have a heart attack (even a nonfatal one). And you certainly don’t want to have a stroke. However, lower blood pressure targets inevitably require more medications. Notwithstanding the economic costs, the dangers of polypharmacy, medication interactions, side effects, and syncope leading to falls cannot be ignored. Falls are not benign adverse events, especially in older adults.
The counter argument is that physicians are human and often let things slide. Set the target at 140/90 mm Hg, and many physicians won’t jump on a systolic blood pressure of 144 mm Hg. Set the target at 130 mm Hg, and maybe they’ll be more likely to react. There’s a fine line between permissiveness and complacency.
If you zoom out and look at the multitude of blood pressure guidelines, you start to notice an important fact. There is not much daylight between them. There are subtle differences in what constitutes high risk and different definitions of older (older should be defined as 10 years older than the reader’s current age). But otherwise, the blood pressure targets are not that different.
Does that final 10 mm Hg really matter when barriers to care mean that tens of millions in the United States are unaware they have hypertension? Even among those diagnosed, many are either untreated or inadequately treated.
With this context, perhaps the most insightful thing that can be said about the blood pressure guideline controversy is that it’s not all that controversial. We can likely all agree that we need to be better at treating hypertension and that creative solutions to reach underserved communities are necessary.
Arguing about 140/90 mm Hg or 130/80 mm Hg is less important than acknowledging that we should be aggressive in screening for and treating hypertension. We should acknowledge that beyond a certain point any cardiovascular benefit comes at the cost of hypotension and side effects. That tipping point will be different for different groups, and probably at a higher set point in older patients.
Individualizing care isn’t difficult. We do it all the time. We just shouldn’t be letting people walk around with untreated hypertension. It’s not the 1900s anymore.
Dr. Labos is a cardiologist at Hôpital Notre-Dame, Montreal. He reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Stop me if you’ve heard this before. There’s a controversy over blood pressure targets. Some argue for 140/90 mm Hg, others for 130/80 mm Hg, and some super ambitious folks think that we should aim for 120/80 mm Hg. If this sounds familiar, it should. We did it in 2017. It’s unclear what, if anything, we learned from the experience. On the upside, it’s not as bad as it was 100 years ago.
When high blood pressure was a ‘good’ thing
Back then, many believed that you needed higher blood pressure as you got older to push the blood through your progressively stiffened and hardened arteries. Hence the name “essential” hypertension. The concern was that lowering blood pressure would hypoperfuse your organs and be dangerous. In the 1930s, John Hay told an audience at a British Medical Association lecture: “The greatest danger to a man with high blood pressure lies in its discovery, because then some fool is certain to try and reduce it.”
The 1900s were a simpler time when people had fatal strokes in their 50s, and their families were consoled by the knowledge that they had lived a good life.
If our thinking around blood pressure had evolved slightly faster, perhaps President Roosevelt wouldn’t have died of a stroke during World War II as his doctors watched his systolic blood pressure climb above 200 mm Hg and suggested massages and barbiturates to take the edge off.
The current controversy
Not that long ago, 180 mm Hg was considered mild hypertension. Now, we are arguing about a systolic blood pressure of 140 versus 130 mm Hg.
The American Academy of Family Physicians takes the view that 140/90 mm Hg is good enough for most people. Their most recent clinical practice guideline, based primarily on two 2020 Cochrane Reviews of blood pressure targets in patients with and without cardiovascular disease, did not find any mortality benefit for a lower blood pressure threshold.
This puts the AAFP guideline in conflict with the 2017 guideline issued jointly by the American College of Cardiology, American Heart Association, and nine other groups, which recommended a target of 130/80 mm Hg for pretty much everyone. Though they say greater than 140/90 mm Hg should be the threshold for low-risk patients or for starting therapy post stroke, we often forget those nuances. The main point of contention is that the AAFP guideline was looking for a mortality benefit, whereas the ACC/AHA/everyone else guideline was looking at preventing cardiovascular events. The latter guideline was driven mainly by the results of the SPRINT trial. ACC/AHA argue for more aggressive targets to prevent the things that cardiologists care about, namely heart attacks.
The AAFP guideline conceded that more aggressive control will result in fewer myocardial infarctions but warn that it comes with more adverse events. Treating 1,000 patients to this lower target would theoretically prevent four MIs, possibly prevent three strokes, but result in 30 adverse events.
In the end, what we are seeing here is not so much a debate over the evidence as a debate over priorities. Interventions that don’t improve mortality can be questioned in terms of their cost effectiveness. But you probably don’t want to have a heart attack (even a nonfatal one). And you certainly don’t want to have a stroke. However, lower blood pressure targets inevitably require more medications. Notwithstanding the economic costs, the dangers of polypharmacy, medication interactions, side effects, and syncope leading to falls cannot be ignored. Falls are not benign adverse events, especially in older adults.
The counter argument is that physicians are human and often let things slide. Set the target at 140/90 mm Hg, and many physicians won’t jump on a systolic blood pressure of 144 mm Hg. Set the target at 130 mm Hg, and maybe they’ll be more likely to react. There’s a fine line between permissiveness and complacency.
If you zoom out and look at the multitude of blood pressure guidelines, you start to notice an important fact. There is not much daylight between them. There are subtle differences in what constitutes high risk and different definitions of older (older should be defined as 10 years older than the reader’s current age). But otherwise, the blood pressure targets are not that different.
Does that final 10 mm Hg really matter when barriers to care mean that tens of millions in the United States are unaware they have hypertension? Even among those diagnosed, many are either untreated or inadequately treated.
With this context, perhaps the most insightful thing that can be said about the blood pressure guideline controversy is that it’s not all that controversial. We can likely all agree that we need to be better at treating hypertension and that creative solutions to reach underserved communities are necessary.
Arguing about 140/90 mm Hg or 130/80 mm Hg is less important than acknowledging that we should be aggressive in screening for and treating hypertension. We should acknowledge that beyond a certain point any cardiovascular benefit comes at the cost of hypotension and side effects. That tipping point will be different for different groups, and probably at a higher set point in older patients.
Individualizing care isn’t difficult. We do it all the time. We just shouldn’t be letting people walk around with untreated hypertension. It’s not the 1900s anymore.
Dr. Labos is a cardiologist at Hôpital Notre-Dame, Montreal. He reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Stop me if you’ve heard this before. There’s a controversy over blood pressure targets. Some argue for 140/90 mm Hg, others for 130/80 mm Hg, and some super ambitious folks think that we should aim for 120/80 mm Hg. If this sounds familiar, it should. We did it in 2017. It’s unclear what, if anything, we learned from the experience. On the upside, it’s not as bad as it was 100 years ago.
When high blood pressure was a ‘good’ thing
Back then, many believed that you needed higher blood pressure as you got older to push the blood through your progressively stiffened and hardened arteries. Hence the name “essential” hypertension. The concern was that lowering blood pressure would hypoperfuse your organs and be dangerous. In the 1930s, John Hay told an audience at a British Medical Association lecture: “The greatest danger to a man with high blood pressure lies in its discovery, because then some fool is certain to try and reduce it.”
The 1900s were a simpler time when people had fatal strokes in their 50s, and their families were consoled by the knowledge that they had lived a good life.
If our thinking around blood pressure had evolved slightly faster, perhaps President Roosevelt wouldn’t have died of a stroke during World War II as his doctors watched his systolic blood pressure climb above 200 mm Hg and suggested massages and barbiturates to take the edge off.
The current controversy
Not that long ago, 180 mm Hg was considered mild hypertension. Now, we are arguing about a systolic blood pressure of 140 versus 130 mm Hg.
The American Academy of Family Physicians takes the view that 140/90 mm Hg is good enough for most people. Their most recent clinical practice guideline, based primarily on two 2020 Cochrane Reviews of blood pressure targets in patients with and without cardiovascular disease, did not find any mortality benefit for a lower blood pressure threshold.
This puts the AAFP guideline in conflict with the 2017 guideline issued jointly by the American College of Cardiology, American Heart Association, and nine other groups, which recommended a target of 130/80 mm Hg for pretty much everyone. Though they say greater than 140/90 mm Hg should be the threshold for low-risk patients or for starting therapy post stroke, we often forget those nuances. The main point of contention is that the AAFP guideline was looking for a mortality benefit, whereas the ACC/AHA/everyone else guideline was looking at preventing cardiovascular events. The latter guideline was driven mainly by the results of the SPRINT trial. ACC/AHA argue for more aggressive targets to prevent the things that cardiologists care about, namely heart attacks.
The AAFP guideline conceded that more aggressive control will result in fewer myocardial infarctions but warn that it comes with more adverse events. Treating 1,000 patients to this lower target would theoretically prevent four MIs, possibly prevent three strokes, but result in 30 adverse events.
In the end, what we are seeing here is not so much a debate over the evidence as a debate over priorities. Interventions that don’t improve mortality can be questioned in terms of their cost effectiveness. But you probably don’t want to have a heart attack (even a nonfatal one). And you certainly don’t want to have a stroke. However, lower blood pressure targets inevitably require more medications. Notwithstanding the economic costs, the dangers of polypharmacy, medication interactions, side effects, and syncope leading to falls cannot be ignored. Falls are not benign adverse events, especially in older adults.
The counter argument is that physicians are human and often let things slide. Set the target at 140/90 mm Hg, and many physicians won’t jump on a systolic blood pressure of 144 mm Hg. Set the target at 130 mm Hg, and maybe they’ll be more likely to react. There’s a fine line between permissiveness and complacency.
If you zoom out and look at the multitude of blood pressure guidelines, you start to notice an important fact. There is not much daylight between them. There are subtle differences in what constitutes high risk and different definitions of older (older should be defined as 10 years older than the reader’s current age). But otherwise, the blood pressure targets are not that different.
Does that final 10 mm Hg really matter when barriers to care mean that tens of millions in the United States are unaware they have hypertension? Even among those diagnosed, many are either untreated or inadequately treated.
With this context, perhaps the most insightful thing that can be said about the blood pressure guideline controversy is that it’s not all that controversial. We can likely all agree that we need to be better at treating hypertension and that creative solutions to reach underserved communities are necessary.
Arguing about 140/90 mm Hg or 130/80 mm Hg is less important than acknowledging that we should be aggressive in screening for and treating hypertension. We should acknowledge that beyond a certain point any cardiovascular benefit comes at the cost of hypotension and side effects. That tipping point will be different for different groups, and probably at a higher set point in older patients.
Individualizing care isn’t difficult. We do it all the time. We just shouldn’t be letting people walk around with untreated hypertension. It’s not the 1900s anymore.
Dr. Labos is a cardiologist at Hôpital Notre-Dame, Montreal. He reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is it time to stop treating high triglycerides?
The publication of the PROMINENT trial, where pemafibrate successfully lowered high levels but was not associated with a lower risk for cardiovascular events, reinforced the point. Is it time to stop measuring and treating high triglycerides?
There may be noncardiovascular reasons to treat hypertriglyceridemia. Pancreatitis is the most cited one, given that the risk for pancreatitis increases with increasing triglyceride levels, especially in patients with a prior episode.
There may also be practical reasons to lower trigs. Because most cholesterol panels use the Friedewald equation to calculate low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) rather than measuring it directly, very high triglyceride levels can invalidate the calculation and return error messages on lab reports.
But we now have alternatives to measuring LDL-C, including non–high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and apolipoprotein B (apoB), that better predict risk and are usable even in the setting of nonfasting samples when triglycerides are elevated.
Independent cardiovascular risk factor?
If we are going to measure and treat high triglycerides for cardiovascular reasons, the relevant question is, are high triglycerides an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease?
Proponents have a broad swath of supportive literature to point at. Multiple studies have shown an association between triglyceride levels and cardiovascular risk. The evidence even extends beyond traditional epidemiologic analyses, to genetic studies that should be free from some of the problems seen in observational cohorts.
But it is difficult to be certain whether these associations are causal or merely confounding. An unhealthy diet will increase triglycerides, as will alcohol. Patients with diabetes or metabolic syndrome have high triglycerides. So do patients with nephrotic syndrome or hypothyroidism, or hypertensive patients taking thiazide diuretics. Adjusting for these baseline factors is possible but imperfect, and residual confounding is always an issue. An analysis of the Reykjavik and the EPIC-Norfolk studies found an association between triglyceride levels and cardiovascular risk. That risk was attenuated, but not eliminated, when adjusted for traditional risk factors such as age, smoking, blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol.
Randomized trials of triglyceride-lowering therapies would help resolve the question of whether hypertriglyceridemia contributes to coronary disease or simply identifies high-risk patients. Early trials seemed to support the idea of a causal link. The Helsinki Heart Study randomized patients to gemfibrozil or placebo and found a 34% relative risk reduction in coronary artery disease with the fibrate. But gemfibrozil didn’t only reduce triglycerides. It also increased HDL-C and lowered LDL-C relative to placebo, which may explain the observed benefit.
Gemfibrozil is rarely used today because we can achieve much greater LDL-C reductions with statins, as well as ezetimibe and PCSK9 inhibitors. The success of these drugs may not leave any room for triglyceride-lowering medications.
The pre- vs. post-statin era
In the 2005 FIELD study, participants were randomized to receive fenofibrate or placebo. Although patients weren’t taking statin at study entry, 17% of the placebo group started taking one during the trial. Fenofibrate wasn’t associated with a reduction in the primary endpoint, a combination of coronary heart disease death or nonfatal myocardial infarction (MI). Among the many secondary endpoints, nonfatal MI was lower but cardiovascular mortality was not in the fibrate-treated patients. In the same vein, the 2010 ACCORD study randomized patients to receive simvastatin plus fenofibrate or simvastatin alone. The composite primary outcome of MI, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality was not lowered nor were any secondary outcomes with the combination therapy. In the statin era, triglyceride-lowering therapies have not shown much benefit.
The final nail in the coffin may very well be the aforementioned PROMINENT trial. The new agent, pemafibrate, fared no better than its predecessor fenofibrate. Pemafibrate had no impact on the study’s primary composite outcome of nonfatal MI, stroke, coronary revascularization, or cardiovascular death despite being very effective at lowering triglycerides (by more than 25%). Patients treated with pemafibrate had increased LDL-C and apoB compared with the placebo group. When you realize that, the results of the study are not very surprising.
Some point to the results of REDUCE-IT as proof that triglycerides are still a valid target for pharmacotherapy. The debate on whether REDUCE-IT tested a good drug or a bad placebo is one for another day. The salient point for today is that the benefits of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) were seen regardless of either baseline or final triglyceride level. EPA may lower cardiac risk, but there is no widespread consensus that it does so by lowering triglycerides. There may be other mechanisms at work.
You could still argue that high triglycerides have value as a risk prediction tool even if their role as a target for drug therapy is questionable. There was a time when medications to lower triglycerides had a benefit. But this is the post-statin era, and that time has passed.
If you see patients with high triglycerides, treating them with triglyceride-lowering medication probably isn’t going to reduce their cardiovascular risk. Dietary interventions, encouraging exercise, and reducing alcohol consumption are better options. Not only will they lead to lower cholesterol levels, but they’ll lower cardiovascular risk, too.
Dr. Labos is a cardiologist at Hôpital Notre-Dame, Montreal, with a degree in epidemiology. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. He spends most of his time doing things that he doesn’t get paid for, like research, teaching, and podcasting. Occasionally he finds time to practice cardiology to pay the rent. He realizes that half of his research findings will be disproved in 5 years; he just doesn’t know which half. He is a regular contributor to the Montreal Gazette, CJAD radio, and CTV television in Montreal and is host of the award-winning podcast The Body of Evidence. The Body of Evidence.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The publication of the PROMINENT trial, where pemafibrate successfully lowered high levels but was not associated with a lower risk for cardiovascular events, reinforced the point. Is it time to stop measuring and treating high triglycerides?
There may be noncardiovascular reasons to treat hypertriglyceridemia. Pancreatitis is the most cited one, given that the risk for pancreatitis increases with increasing triglyceride levels, especially in patients with a prior episode.
There may also be practical reasons to lower trigs. Because most cholesterol panels use the Friedewald equation to calculate low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) rather than measuring it directly, very high triglyceride levels can invalidate the calculation and return error messages on lab reports.
But we now have alternatives to measuring LDL-C, including non–high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and apolipoprotein B (apoB), that better predict risk and are usable even in the setting of nonfasting samples when triglycerides are elevated.
Independent cardiovascular risk factor?
If we are going to measure and treat high triglycerides for cardiovascular reasons, the relevant question is, are high triglycerides an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease?
Proponents have a broad swath of supportive literature to point at. Multiple studies have shown an association between triglyceride levels and cardiovascular risk. The evidence even extends beyond traditional epidemiologic analyses, to genetic studies that should be free from some of the problems seen in observational cohorts.
But it is difficult to be certain whether these associations are causal or merely confounding. An unhealthy diet will increase triglycerides, as will alcohol. Patients with diabetes or metabolic syndrome have high triglycerides. So do patients with nephrotic syndrome or hypothyroidism, or hypertensive patients taking thiazide diuretics. Adjusting for these baseline factors is possible but imperfect, and residual confounding is always an issue. An analysis of the Reykjavik and the EPIC-Norfolk studies found an association between triglyceride levels and cardiovascular risk. That risk was attenuated, but not eliminated, when adjusted for traditional risk factors such as age, smoking, blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol.
Randomized trials of triglyceride-lowering therapies would help resolve the question of whether hypertriglyceridemia contributes to coronary disease or simply identifies high-risk patients. Early trials seemed to support the idea of a causal link. The Helsinki Heart Study randomized patients to gemfibrozil or placebo and found a 34% relative risk reduction in coronary artery disease with the fibrate. But gemfibrozil didn’t only reduce triglycerides. It also increased HDL-C and lowered LDL-C relative to placebo, which may explain the observed benefit.
Gemfibrozil is rarely used today because we can achieve much greater LDL-C reductions with statins, as well as ezetimibe and PCSK9 inhibitors. The success of these drugs may not leave any room for triglyceride-lowering medications.
The pre- vs. post-statin era
In the 2005 FIELD study, participants were randomized to receive fenofibrate or placebo. Although patients weren’t taking statin at study entry, 17% of the placebo group started taking one during the trial. Fenofibrate wasn’t associated with a reduction in the primary endpoint, a combination of coronary heart disease death or nonfatal myocardial infarction (MI). Among the many secondary endpoints, nonfatal MI was lower but cardiovascular mortality was not in the fibrate-treated patients. In the same vein, the 2010 ACCORD study randomized patients to receive simvastatin plus fenofibrate or simvastatin alone. The composite primary outcome of MI, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality was not lowered nor were any secondary outcomes with the combination therapy. In the statin era, triglyceride-lowering therapies have not shown much benefit.
The final nail in the coffin may very well be the aforementioned PROMINENT trial. The new agent, pemafibrate, fared no better than its predecessor fenofibrate. Pemafibrate had no impact on the study’s primary composite outcome of nonfatal MI, stroke, coronary revascularization, or cardiovascular death despite being very effective at lowering triglycerides (by more than 25%). Patients treated with pemafibrate had increased LDL-C and apoB compared with the placebo group. When you realize that, the results of the study are not very surprising.
Some point to the results of REDUCE-IT as proof that triglycerides are still a valid target for pharmacotherapy. The debate on whether REDUCE-IT tested a good drug or a bad placebo is one for another day. The salient point for today is that the benefits of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) were seen regardless of either baseline or final triglyceride level. EPA may lower cardiac risk, but there is no widespread consensus that it does so by lowering triglycerides. There may be other mechanisms at work.
You could still argue that high triglycerides have value as a risk prediction tool even if their role as a target for drug therapy is questionable. There was a time when medications to lower triglycerides had a benefit. But this is the post-statin era, and that time has passed.
If you see patients with high triglycerides, treating them with triglyceride-lowering medication probably isn’t going to reduce their cardiovascular risk. Dietary interventions, encouraging exercise, and reducing alcohol consumption are better options. Not only will they lead to lower cholesterol levels, but they’ll lower cardiovascular risk, too.
Dr. Labos is a cardiologist at Hôpital Notre-Dame, Montreal, with a degree in epidemiology. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. He spends most of his time doing things that he doesn’t get paid for, like research, teaching, and podcasting. Occasionally he finds time to practice cardiology to pay the rent. He realizes that half of his research findings will be disproved in 5 years; he just doesn’t know which half. He is a regular contributor to the Montreal Gazette, CJAD radio, and CTV television in Montreal and is host of the award-winning podcast The Body of Evidence. The Body of Evidence.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The publication of the PROMINENT trial, where pemafibrate successfully lowered high levels but was not associated with a lower risk for cardiovascular events, reinforced the point. Is it time to stop measuring and treating high triglycerides?
There may be noncardiovascular reasons to treat hypertriglyceridemia. Pancreatitis is the most cited one, given that the risk for pancreatitis increases with increasing triglyceride levels, especially in patients with a prior episode.
There may also be practical reasons to lower trigs. Because most cholesterol panels use the Friedewald equation to calculate low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) rather than measuring it directly, very high triglyceride levels can invalidate the calculation and return error messages on lab reports.
But we now have alternatives to measuring LDL-C, including non–high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and apolipoprotein B (apoB), that better predict risk and are usable even in the setting of nonfasting samples when triglycerides are elevated.
Independent cardiovascular risk factor?
If we are going to measure and treat high triglycerides for cardiovascular reasons, the relevant question is, are high triglycerides an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease?
Proponents have a broad swath of supportive literature to point at. Multiple studies have shown an association between triglyceride levels and cardiovascular risk. The evidence even extends beyond traditional epidemiologic analyses, to genetic studies that should be free from some of the problems seen in observational cohorts.
But it is difficult to be certain whether these associations are causal or merely confounding. An unhealthy diet will increase triglycerides, as will alcohol. Patients with diabetes or metabolic syndrome have high triglycerides. So do patients with nephrotic syndrome or hypothyroidism, or hypertensive patients taking thiazide diuretics. Adjusting for these baseline factors is possible but imperfect, and residual confounding is always an issue. An analysis of the Reykjavik and the EPIC-Norfolk studies found an association between triglyceride levels and cardiovascular risk. That risk was attenuated, but not eliminated, when adjusted for traditional risk factors such as age, smoking, blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol.
Randomized trials of triglyceride-lowering therapies would help resolve the question of whether hypertriglyceridemia contributes to coronary disease or simply identifies high-risk patients. Early trials seemed to support the idea of a causal link. The Helsinki Heart Study randomized patients to gemfibrozil or placebo and found a 34% relative risk reduction in coronary artery disease with the fibrate. But gemfibrozil didn’t only reduce triglycerides. It also increased HDL-C and lowered LDL-C relative to placebo, which may explain the observed benefit.
Gemfibrozil is rarely used today because we can achieve much greater LDL-C reductions with statins, as well as ezetimibe and PCSK9 inhibitors. The success of these drugs may not leave any room for triglyceride-lowering medications.
The pre- vs. post-statin era
In the 2005 FIELD study, participants were randomized to receive fenofibrate or placebo. Although patients weren’t taking statin at study entry, 17% of the placebo group started taking one during the trial. Fenofibrate wasn’t associated with a reduction in the primary endpoint, a combination of coronary heart disease death or nonfatal myocardial infarction (MI). Among the many secondary endpoints, nonfatal MI was lower but cardiovascular mortality was not in the fibrate-treated patients. In the same vein, the 2010 ACCORD study randomized patients to receive simvastatin plus fenofibrate or simvastatin alone. The composite primary outcome of MI, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality was not lowered nor were any secondary outcomes with the combination therapy. In the statin era, triglyceride-lowering therapies have not shown much benefit.
The final nail in the coffin may very well be the aforementioned PROMINENT trial. The new agent, pemafibrate, fared no better than its predecessor fenofibrate. Pemafibrate had no impact on the study’s primary composite outcome of nonfatal MI, stroke, coronary revascularization, or cardiovascular death despite being very effective at lowering triglycerides (by more than 25%). Patients treated with pemafibrate had increased LDL-C and apoB compared with the placebo group. When you realize that, the results of the study are not very surprising.
Some point to the results of REDUCE-IT as proof that triglycerides are still a valid target for pharmacotherapy. The debate on whether REDUCE-IT tested a good drug or a bad placebo is one for another day. The salient point for today is that the benefits of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) were seen regardless of either baseline or final triglyceride level. EPA may lower cardiac risk, but there is no widespread consensus that it does so by lowering triglycerides. There may be other mechanisms at work.
You could still argue that high triglycerides have value as a risk prediction tool even if their role as a target for drug therapy is questionable. There was a time when medications to lower triglycerides had a benefit. But this is the post-statin era, and that time has passed.
If you see patients with high triglycerides, treating them with triglyceride-lowering medication probably isn’t going to reduce their cardiovascular risk. Dietary interventions, encouraging exercise, and reducing alcohol consumption are better options. Not only will they lead to lower cholesterol levels, but they’ll lower cardiovascular risk, too.
Dr. Labos is a cardiologist at Hôpital Notre-Dame, Montreal, with a degree in epidemiology. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. He spends most of his time doing things that he doesn’t get paid for, like research, teaching, and podcasting. Occasionally he finds time to practice cardiology to pay the rent. He realizes that half of his research findings will be disproved in 5 years; he just doesn’t know which half. He is a regular contributor to the Montreal Gazette, CJAD radio, and CTV television in Montreal and is host of the award-winning podcast The Body of Evidence. The Body of Evidence.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.