User login
Personalized cancer vaccine shows early promise across tumor types
The vaccine, PGV-001, was given to 13 patients with solid tumors or multiple myeloma who had a high risk of recurrence after surgery or autologous stem cell transplant.
At last follow-up, four patients were still alive without evidence of disease and had not received subsequent therapy, four were alive and receiving therapy, three had died, and two were lost to follow-up.
Thomas Marron, MD, PhD , of Mount Sinai in New York presented these results in a poster at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021: Week 1 ( Abstract LB048 ). Data in the abstract differ from the data presented.
“While cancer immunotherapy has revolutionized the treatment of cancer, we know that the majority of patients fail to achieve significant clinical response,” Dr. Marron said during his presentation. “One reason for this may be due to lack of preexisting primed T-cell response needed for PD-1 blockade to have a significant effect. To address this, personalized neoantigen vaccines may help prime an improved immune response against tumor cells.”
With this in mind, Dr. Marron and colleagues developed PGV-001, a vaccine consisting of patient-specific synthetic neoantigen peptides given to patients in the adjuvant setting.
Creating a personalized vaccine
The researchers synthesized PGV-001 for 15 patients with advanced malignancies. The patients first underwent tumor and germline DNA sequencing as well as HLA typing. Bulk RNA sequencing was performed on patients’ tumors as well.
Then, the researchers used a computational pipeline called OpenVax to identify candidate neoantigens. This pipeline, developed at Mount Sinai, identified and prioritized candidate neoantigens using predicted MHC class I binding affinity and neoantigen abundance.
OpenVax identified an average of 71.5 neoantigens per patient (range, 7-193). The goal was to synthesize a maximum of 10 peptides per patient, but two patients did not have an adequate number of neoantigens.
Vaccine administration
The peptides were administered over the course of 27 weeks along with poly-ICLC and a tetanus helper peptide. Before receiving their vaccine doses, patients with solid tumors had undergone curative-intent surgery, and those with multiple myeloma had undergone autologous stem cell transplant.
“Most experimental personalized cancer vaccines are administered in the metastatic setting, but prior research indicates that immunotherapies tend to be more effective in patients who have less cancer spread,” principal investigator Nina Bhardwaj, MD, PhD , of Mount Sinai, explained in a press release .
“We have, therefore, developed a neoantigen vaccine that is administered after standard-of-care adjuvant therapy, such as surgery in solid tumors and bone marrow transplant in multiple myeloma, when patients have minimal, typically microscopic, residual disease.”
Feasibility, safety, and immunogenicity
PGV-001 was synthesized for 15 patients and administered to 13 of them. Six of the 13 patients had head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, three had multiple myeloma, two had non–small cell lung cancer, one had breast cancer, and one had urothelial carcinoma.
Eleven patients received all 10 intended doses, and two patients received at least 8 doses.
“The vaccine was well tolerated, with only half of patients experiencing mild, grade 1 adverse events,” Dr. Marron said.
Transient injection site reactions occurred in four patients, and grade 1 fever was reported in one patient.
Immune monitoring is ongoing, but an initial analysis in one patient showed “robust responses” in CD4 and CD8 T cells by intracellular cytokine staining for interferon-gamma, tumor necrosis factor–alpha, and interleukin-2 after in vitro expansion in the presence of vaccine antigens, according to the researchers.
Dr. Marron noted that robust T-cell reactivity was seen at the completion of all 10 doses but was not seen after the 6th dose, and this supports the need for a prolonged dosing schedule.
Survival and subsequent therapy
At a mean follow-up of 880 days, four patients had no evidence of disease and had not received subsequent therapy. This includes one patient with stage IIIA non–small cell lung cancer, one with stage IVA HER-2 positive breast cancer, one with stage II urothelial carcinoma, and one with multiple myeloma.
Four patients were alive and receiving subsequent lines of therapy. Two of these patients had significant responses to anti–PD-1 therapy.
Three patients have died, two of whom had documented recurrence of their malignancy. The last two patients were lost to follow-up without documented recurrence.
“Our results demonstrate that the OpenVax pipeline is a viable approach to generate a safe, personalized cancer vaccine, which could potentially be used to treat a range of tumor types,” Dr. Bhardwaj said.
Trials combining neoantigens identified with the OpenVax platform are ongoing in patients with urothelial carcinoma and glioblastoma multiforme, Dr. Marron said.
The current study ( NCT02721043 ) is sponsored by Dr. Bhardwaj. Dr. Marron and Dr. Bhardwaj reported having no disclosures. Their colleagues disclosed relationships with Bristol Myers Squibb, Sema4, and Related Sciences.
The vaccine, PGV-001, was given to 13 patients with solid tumors or multiple myeloma who had a high risk of recurrence after surgery or autologous stem cell transplant.
At last follow-up, four patients were still alive without evidence of disease and had not received subsequent therapy, four were alive and receiving therapy, three had died, and two were lost to follow-up.
Thomas Marron, MD, PhD , of Mount Sinai in New York presented these results in a poster at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021: Week 1 ( Abstract LB048 ). Data in the abstract differ from the data presented.
“While cancer immunotherapy has revolutionized the treatment of cancer, we know that the majority of patients fail to achieve significant clinical response,” Dr. Marron said during his presentation. “One reason for this may be due to lack of preexisting primed T-cell response needed for PD-1 blockade to have a significant effect. To address this, personalized neoantigen vaccines may help prime an improved immune response against tumor cells.”
With this in mind, Dr. Marron and colleagues developed PGV-001, a vaccine consisting of patient-specific synthetic neoantigen peptides given to patients in the adjuvant setting.
Creating a personalized vaccine
The researchers synthesized PGV-001 for 15 patients with advanced malignancies. The patients first underwent tumor and germline DNA sequencing as well as HLA typing. Bulk RNA sequencing was performed on patients’ tumors as well.
Then, the researchers used a computational pipeline called OpenVax to identify candidate neoantigens. This pipeline, developed at Mount Sinai, identified and prioritized candidate neoantigens using predicted MHC class I binding affinity and neoantigen abundance.
OpenVax identified an average of 71.5 neoantigens per patient (range, 7-193). The goal was to synthesize a maximum of 10 peptides per patient, but two patients did not have an adequate number of neoantigens.
Vaccine administration
The peptides were administered over the course of 27 weeks along with poly-ICLC and a tetanus helper peptide. Before receiving their vaccine doses, patients with solid tumors had undergone curative-intent surgery, and those with multiple myeloma had undergone autologous stem cell transplant.
“Most experimental personalized cancer vaccines are administered in the metastatic setting, but prior research indicates that immunotherapies tend to be more effective in patients who have less cancer spread,” principal investigator Nina Bhardwaj, MD, PhD , of Mount Sinai, explained in a press release .
“We have, therefore, developed a neoantigen vaccine that is administered after standard-of-care adjuvant therapy, such as surgery in solid tumors and bone marrow transplant in multiple myeloma, when patients have minimal, typically microscopic, residual disease.”
Feasibility, safety, and immunogenicity
PGV-001 was synthesized for 15 patients and administered to 13 of them. Six of the 13 patients had head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, three had multiple myeloma, two had non–small cell lung cancer, one had breast cancer, and one had urothelial carcinoma.
Eleven patients received all 10 intended doses, and two patients received at least 8 doses.
“The vaccine was well tolerated, with only half of patients experiencing mild, grade 1 adverse events,” Dr. Marron said.
Transient injection site reactions occurred in four patients, and grade 1 fever was reported in one patient.
Immune monitoring is ongoing, but an initial analysis in one patient showed “robust responses” in CD4 and CD8 T cells by intracellular cytokine staining for interferon-gamma, tumor necrosis factor–alpha, and interleukin-2 after in vitro expansion in the presence of vaccine antigens, according to the researchers.
Dr. Marron noted that robust T-cell reactivity was seen at the completion of all 10 doses but was not seen after the 6th dose, and this supports the need for a prolonged dosing schedule.
Survival and subsequent therapy
At a mean follow-up of 880 days, four patients had no evidence of disease and had not received subsequent therapy. This includes one patient with stage IIIA non–small cell lung cancer, one with stage IVA HER-2 positive breast cancer, one with stage II urothelial carcinoma, and one with multiple myeloma.
Four patients were alive and receiving subsequent lines of therapy. Two of these patients had significant responses to anti–PD-1 therapy.
Three patients have died, two of whom had documented recurrence of their malignancy. The last two patients were lost to follow-up without documented recurrence.
“Our results demonstrate that the OpenVax pipeline is a viable approach to generate a safe, personalized cancer vaccine, which could potentially be used to treat a range of tumor types,” Dr. Bhardwaj said.
Trials combining neoantigens identified with the OpenVax platform are ongoing in patients with urothelial carcinoma and glioblastoma multiforme, Dr. Marron said.
The current study ( NCT02721043 ) is sponsored by Dr. Bhardwaj. Dr. Marron and Dr. Bhardwaj reported having no disclosures. Their colleagues disclosed relationships with Bristol Myers Squibb, Sema4, and Related Sciences.
The vaccine, PGV-001, was given to 13 patients with solid tumors or multiple myeloma who had a high risk of recurrence after surgery or autologous stem cell transplant.
At last follow-up, four patients were still alive without evidence of disease and had not received subsequent therapy, four were alive and receiving therapy, three had died, and two were lost to follow-up.
Thomas Marron, MD, PhD , of Mount Sinai in New York presented these results in a poster at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021: Week 1 ( Abstract LB048 ). Data in the abstract differ from the data presented.
“While cancer immunotherapy has revolutionized the treatment of cancer, we know that the majority of patients fail to achieve significant clinical response,” Dr. Marron said during his presentation. “One reason for this may be due to lack of preexisting primed T-cell response needed for PD-1 blockade to have a significant effect. To address this, personalized neoantigen vaccines may help prime an improved immune response against tumor cells.”
With this in mind, Dr. Marron and colleagues developed PGV-001, a vaccine consisting of patient-specific synthetic neoantigen peptides given to patients in the adjuvant setting.
Creating a personalized vaccine
The researchers synthesized PGV-001 for 15 patients with advanced malignancies. The patients first underwent tumor and germline DNA sequencing as well as HLA typing. Bulk RNA sequencing was performed on patients’ tumors as well.
Then, the researchers used a computational pipeline called OpenVax to identify candidate neoantigens. This pipeline, developed at Mount Sinai, identified and prioritized candidate neoantigens using predicted MHC class I binding affinity and neoantigen abundance.
OpenVax identified an average of 71.5 neoantigens per patient (range, 7-193). The goal was to synthesize a maximum of 10 peptides per patient, but two patients did not have an adequate number of neoantigens.
Vaccine administration
The peptides were administered over the course of 27 weeks along with poly-ICLC and a tetanus helper peptide. Before receiving their vaccine doses, patients with solid tumors had undergone curative-intent surgery, and those with multiple myeloma had undergone autologous stem cell transplant.
“Most experimental personalized cancer vaccines are administered in the metastatic setting, but prior research indicates that immunotherapies tend to be more effective in patients who have less cancer spread,” principal investigator Nina Bhardwaj, MD, PhD , of Mount Sinai, explained in a press release .
“We have, therefore, developed a neoantigen vaccine that is administered after standard-of-care adjuvant therapy, such as surgery in solid tumors and bone marrow transplant in multiple myeloma, when patients have minimal, typically microscopic, residual disease.”
Feasibility, safety, and immunogenicity
PGV-001 was synthesized for 15 patients and administered to 13 of them. Six of the 13 patients had head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, three had multiple myeloma, two had non–small cell lung cancer, one had breast cancer, and one had urothelial carcinoma.
Eleven patients received all 10 intended doses, and two patients received at least 8 doses.
“The vaccine was well tolerated, with only half of patients experiencing mild, grade 1 adverse events,” Dr. Marron said.
Transient injection site reactions occurred in four patients, and grade 1 fever was reported in one patient.
Immune monitoring is ongoing, but an initial analysis in one patient showed “robust responses” in CD4 and CD8 T cells by intracellular cytokine staining for interferon-gamma, tumor necrosis factor–alpha, and interleukin-2 after in vitro expansion in the presence of vaccine antigens, according to the researchers.
Dr. Marron noted that robust T-cell reactivity was seen at the completion of all 10 doses but was not seen after the 6th dose, and this supports the need for a prolonged dosing schedule.
Survival and subsequent therapy
At a mean follow-up of 880 days, four patients had no evidence of disease and had not received subsequent therapy. This includes one patient with stage IIIA non–small cell lung cancer, one with stage IVA HER-2 positive breast cancer, one with stage II urothelial carcinoma, and one with multiple myeloma.
Four patients were alive and receiving subsequent lines of therapy. Two of these patients had significant responses to anti–PD-1 therapy.
Three patients have died, two of whom had documented recurrence of their malignancy. The last two patients were lost to follow-up without documented recurrence.
“Our results demonstrate that the OpenVax pipeline is a viable approach to generate a safe, personalized cancer vaccine, which could potentially be used to treat a range of tumor types,” Dr. Bhardwaj said.
Trials combining neoantigens identified with the OpenVax platform are ongoing in patients with urothelial carcinoma and glioblastoma multiforme, Dr. Marron said.
The current study ( NCT02721043 ) is sponsored by Dr. Bhardwaj. Dr. Marron and Dr. Bhardwaj reported having no disclosures. Their colleagues disclosed relationships with Bristol Myers Squibb, Sema4, and Related Sciences.
FROM AACR 2021
Healthy lifestyle may offset genetic risk in prostate cancer
In men at the highest risk of dying from prostate cancer, having the highest healthy lifestyle scores cut the risk of fatal disease in half, said study author Anna Plym, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard School of Public Health, both in Boston. She presented these findings at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021: Week 1 (Abstract 822).
Dr. Plym noted that about 58% of the variability in prostate cancer risk is accounted for by genetic factors, with common single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) accounting for a substantial proportion of prostate cancer susceptibility.
A recent study showed that a polygenic risk score (PRS) derived by combining information from 269 SNPs was “highly predictive” of prostate cancer, Dr. Plym said. There was a 10-fold gradient in disease risk between the lowest and highest genetic risk deciles, and the pattern was consistent across ethnic groups.
In addition, Dr. Plym noted, previous studies have suggested that a healthy lifestyle reduces lethal prostate cancer risk.
What has remained unclear is whether the risk for both developing prostate cancer and experiencing progression to lethal disease can be offset by adherence to a healthy lifestyle.
To investigate, Dr. Plym and colleagues used the 269-SNP PRS to quantify the genetic risk of prostate cancer in 10,443 men enrolled in the Health Professionals Follow-up Study. The men were divided into quartiles according to genetic risk.
The investigators also classified the men using a validated lifestyle score. For this score, one point was given for each of the following: not currently smoking or having quit 10 or more years ago, body mass index under 30 kg/m2, high vigorous physical activity, high intake of tomatoes and fatty fish, and low intake of processed meat. Patients with 1-2 points were considered the least healthy, those with 3 points were moderately healthy, and those with 4-6 points were the most healthy.
The outcomes assessed were overall prostate cancer and lethal prostate cancer (i.e., metastatic disease or prostate cancer–specific death).
No overall benefit of healthy lifestyle
At a median follow-up of 18 years, 2,111 cases of prostate cancer were observed. And at a median follow-up of 22 years, 238 lethal prostate cancer events occurred.
Men in the highest genetic risk quartile were five times more likely to develop prostate cancer (hazard ratio, 5.39; 95% confidence interval, 4.59-6.34) and three times more likely to develop lethal prostate cancer (HR, 3.43; 95% CI, 2.29-5.14), when compared with men in the lowest genetic risk quartile.
Adherence to a healthy lifestyle did not decrease the risk of prostate cancer overall (HR, 1.01; 95% CI, 0.84-1.22), nor did it affect men in the lower genetic risk quartiles.
However, healthy lifestyle did appear to affect men in the highest genetic risk quartile. Men with the highest healthy lifestyle scores had roughly half the risk of lethal prostate cancer, compared to men with the lowest lifestyle scores (3% vs. 6%).
A counterbalance to genetic risk
Dr. Plym observed that the rate of lethal disease in men with the best lifestyle scores matched the rate for the study population as a whole (3%), suggesting that healthy lifestyle may counterbalance high genetic risk.
She added that previous research has confirmed physical activity as a protective factor, but more study is needed to shed light on the relative benefit of the healthy lifestyle components.
In addition, further research is necessary to explain why the benefit was limited to lethal prostate cancer risk in men with the highest genetic risk.
Dr. Plym speculated that the genetic variants contributing to a high PRS may also be the variants that have the strongest interaction with lifestyle factors. For men with a genetic predisposition to prostate cancer, she added, these findings underscore the potential value of surveillance.
“Our findings add to current evidence suggesting that men with a high genetic risk may benefit from a targeted prostate cancer screening program, aiming at detecting a potentially lethal prostate cancer while it is still curable,” she said.
Charles Swanton, MBPhD, of the Francis Crick Institute and UCL Cancer Institute in London, raised the possibility that competing risk issues could be at play.
If a healthy lifestyle leads to longer life, he asked, does that make it more likely that patients will live long enough to die from their prostate cancer because they are not dying from cardiovascular disease, complications of diabetes, etc.? In that case, is the healthy lifestyle really affecting prostate cancer at all?
Dr. Plym responded that, among those in the highest genetic risk group with an unhealthy lifestyle, the increased risk for prostate cancer exceeded the risk for other illnesses.
This study was funded by the DiNovi Family Foundation, the National Cancer Institute, the William Casey Foundation, the Swedish Society for Medical Research, and the Prostate Cancer Foundation. Dr. Plym declared no conflicts of interest. Dr. Swanton disclosed relationships with numerous companies, including Pfizer, Novartis, and GlaxoSmithKline.
In men at the highest risk of dying from prostate cancer, having the highest healthy lifestyle scores cut the risk of fatal disease in half, said study author Anna Plym, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard School of Public Health, both in Boston. She presented these findings at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021: Week 1 (Abstract 822).
Dr. Plym noted that about 58% of the variability in prostate cancer risk is accounted for by genetic factors, with common single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) accounting for a substantial proportion of prostate cancer susceptibility.
A recent study showed that a polygenic risk score (PRS) derived by combining information from 269 SNPs was “highly predictive” of prostate cancer, Dr. Plym said. There was a 10-fold gradient in disease risk between the lowest and highest genetic risk deciles, and the pattern was consistent across ethnic groups.
In addition, Dr. Plym noted, previous studies have suggested that a healthy lifestyle reduces lethal prostate cancer risk.
What has remained unclear is whether the risk for both developing prostate cancer and experiencing progression to lethal disease can be offset by adherence to a healthy lifestyle.
To investigate, Dr. Plym and colleagues used the 269-SNP PRS to quantify the genetic risk of prostate cancer in 10,443 men enrolled in the Health Professionals Follow-up Study. The men were divided into quartiles according to genetic risk.
The investigators also classified the men using a validated lifestyle score. For this score, one point was given for each of the following: not currently smoking or having quit 10 or more years ago, body mass index under 30 kg/m2, high vigorous physical activity, high intake of tomatoes and fatty fish, and low intake of processed meat. Patients with 1-2 points were considered the least healthy, those with 3 points were moderately healthy, and those with 4-6 points were the most healthy.
The outcomes assessed were overall prostate cancer and lethal prostate cancer (i.e., metastatic disease or prostate cancer–specific death).
No overall benefit of healthy lifestyle
At a median follow-up of 18 years, 2,111 cases of prostate cancer were observed. And at a median follow-up of 22 years, 238 lethal prostate cancer events occurred.
Men in the highest genetic risk quartile were five times more likely to develop prostate cancer (hazard ratio, 5.39; 95% confidence interval, 4.59-6.34) and three times more likely to develop lethal prostate cancer (HR, 3.43; 95% CI, 2.29-5.14), when compared with men in the lowest genetic risk quartile.
Adherence to a healthy lifestyle did not decrease the risk of prostate cancer overall (HR, 1.01; 95% CI, 0.84-1.22), nor did it affect men in the lower genetic risk quartiles.
However, healthy lifestyle did appear to affect men in the highest genetic risk quartile. Men with the highest healthy lifestyle scores had roughly half the risk of lethal prostate cancer, compared to men with the lowest lifestyle scores (3% vs. 6%).
A counterbalance to genetic risk
Dr. Plym observed that the rate of lethal disease in men with the best lifestyle scores matched the rate for the study population as a whole (3%), suggesting that healthy lifestyle may counterbalance high genetic risk.
She added that previous research has confirmed physical activity as a protective factor, but more study is needed to shed light on the relative benefit of the healthy lifestyle components.
In addition, further research is necessary to explain why the benefit was limited to lethal prostate cancer risk in men with the highest genetic risk.
Dr. Plym speculated that the genetic variants contributing to a high PRS may also be the variants that have the strongest interaction with lifestyle factors. For men with a genetic predisposition to prostate cancer, she added, these findings underscore the potential value of surveillance.
“Our findings add to current evidence suggesting that men with a high genetic risk may benefit from a targeted prostate cancer screening program, aiming at detecting a potentially lethal prostate cancer while it is still curable,” she said.
Charles Swanton, MBPhD, of the Francis Crick Institute and UCL Cancer Institute in London, raised the possibility that competing risk issues could be at play.
If a healthy lifestyle leads to longer life, he asked, does that make it more likely that patients will live long enough to die from their prostate cancer because they are not dying from cardiovascular disease, complications of diabetes, etc.? In that case, is the healthy lifestyle really affecting prostate cancer at all?
Dr. Plym responded that, among those in the highest genetic risk group with an unhealthy lifestyle, the increased risk for prostate cancer exceeded the risk for other illnesses.
This study was funded by the DiNovi Family Foundation, the National Cancer Institute, the William Casey Foundation, the Swedish Society for Medical Research, and the Prostate Cancer Foundation. Dr. Plym declared no conflicts of interest. Dr. Swanton disclosed relationships with numerous companies, including Pfizer, Novartis, and GlaxoSmithKline.
In men at the highest risk of dying from prostate cancer, having the highest healthy lifestyle scores cut the risk of fatal disease in half, said study author Anna Plym, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard School of Public Health, both in Boston. She presented these findings at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021: Week 1 (Abstract 822).
Dr. Plym noted that about 58% of the variability in prostate cancer risk is accounted for by genetic factors, with common single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) accounting for a substantial proportion of prostate cancer susceptibility.
A recent study showed that a polygenic risk score (PRS) derived by combining information from 269 SNPs was “highly predictive” of prostate cancer, Dr. Plym said. There was a 10-fold gradient in disease risk between the lowest and highest genetic risk deciles, and the pattern was consistent across ethnic groups.
In addition, Dr. Plym noted, previous studies have suggested that a healthy lifestyle reduces lethal prostate cancer risk.
What has remained unclear is whether the risk for both developing prostate cancer and experiencing progression to lethal disease can be offset by adherence to a healthy lifestyle.
To investigate, Dr. Plym and colleagues used the 269-SNP PRS to quantify the genetic risk of prostate cancer in 10,443 men enrolled in the Health Professionals Follow-up Study. The men were divided into quartiles according to genetic risk.
The investigators also classified the men using a validated lifestyle score. For this score, one point was given for each of the following: not currently smoking or having quit 10 or more years ago, body mass index under 30 kg/m2, high vigorous physical activity, high intake of tomatoes and fatty fish, and low intake of processed meat. Patients with 1-2 points were considered the least healthy, those with 3 points were moderately healthy, and those with 4-6 points were the most healthy.
The outcomes assessed were overall prostate cancer and lethal prostate cancer (i.e., metastatic disease or prostate cancer–specific death).
No overall benefit of healthy lifestyle
At a median follow-up of 18 years, 2,111 cases of prostate cancer were observed. And at a median follow-up of 22 years, 238 lethal prostate cancer events occurred.
Men in the highest genetic risk quartile were five times more likely to develop prostate cancer (hazard ratio, 5.39; 95% confidence interval, 4.59-6.34) and three times more likely to develop lethal prostate cancer (HR, 3.43; 95% CI, 2.29-5.14), when compared with men in the lowest genetic risk quartile.
Adherence to a healthy lifestyle did not decrease the risk of prostate cancer overall (HR, 1.01; 95% CI, 0.84-1.22), nor did it affect men in the lower genetic risk quartiles.
However, healthy lifestyle did appear to affect men in the highest genetic risk quartile. Men with the highest healthy lifestyle scores had roughly half the risk of lethal prostate cancer, compared to men with the lowest lifestyle scores (3% vs. 6%).
A counterbalance to genetic risk
Dr. Plym observed that the rate of lethal disease in men with the best lifestyle scores matched the rate for the study population as a whole (3%), suggesting that healthy lifestyle may counterbalance high genetic risk.
She added that previous research has confirmed physical activity as a protective factor, but more study is needed to shed light on the relative benefit of the healthy lifestyle components.
In addition, further research is necessary to explain why the benefit was limited to lethal prostate cancer risk in men with the highest genetic risk.
Dr. Plym speculated that the genetic variants contributing to a high PRS may also be the variants that have the strongest interaction with lifestyle factors. For men with a genetic predisposition to prostate cancer, she added, these findings underscore the potential value of surveillance.
“Our findings add to current evidence suggesting that men with a high genetic risk may benefit from a targeted prostate cancer screening program, aiming at detecting a potentially lethal prostate cancer while it is still curable,” she said.
Charles Swanton, MBPhD, of the Francis Crick Institute and UCL Cancer Institute in London, raised the possibility that competing risk issues could be at play.
If a healthy lifestyle leads to longer life, he asked, does that make it more likely that patients will live long enough to die from their prostate cancer because they are not dying from cardiovascular disease, complications of diabetes, etc.? In that case, is the healthy lifestyle really affecting prostate cancer at all?
Dr. Plym responded that, among those in the highest genetic risk group with an unhealthy lifestyle, the increased risk for prostate cancer exceeded the risk for other illnesses.
This study was funded by the DiNovi Family Foundation, the National Cancer Institute, the William Casey Foundation, the Swedish Society for Medical Research, and the Prostate Cancer Foundation. Dr. Plym declared no conflicts of interest. Dr. Swanton disclosed relationships with numerous companies, including Pfizer, Novartis, and GlaxoSmithKline.
FROM AACR 2021
Black nonsmokers still at high risk for secondhand smoke exposure
Despite 30+ years of antismoking public policies and dramatic overall decline in secondhand smoke (SHS) exposure, .
No risk-free SHS exposure
Surendranath S. Shastri, MD, of MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and colleagues underscored the U.S. Surgeon General’s determination that there is no risk-free level of SHS exposure in a recent JAMA Internal Medicine Research Letter.
“With the outbreak of the coronavirus disease 2019, which affects lung function, improving smoke-free policies to enhance air quality should be a growing priority,”they wrote.
Dr. Shastri and colleagues looked at 2011-2018 data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), which detailed prevalence of SHS exposure in the U.S. population aged 3 years and older using interviews and biological specimens to test for cotinine levels. For the survey, nonsmokers having serum cotinine levels of 0.05 to 10 ng/mL were considered to have SHS exposure.
While the prevalence of SHS exposure among nonsmokers declined from 87.5% to 25.3% between 1988 and 2012, levels have stagnated since 2012 and racial and economic disparities are evident. Higher smoking rates, less knowledge about health risks, higher workplace exposure, greater likelihood of living in low-income, multi-unit housing, plus having their communities targeted by tobacco companies, may all help explain higher serum levels of cotinine in populations with lower socioeconomic status.
“Multivariable logistic regression identified younger age (odds ratio [OR], 1.88, for 12-19 years, and OR, 2.29, for 3-11 years), non-Hispanic Black race/ethnicity (OR, 2.75), less than high school education (OR, 1.59), and living below the poverty level (OR, 2.61) as risk factors for SHSe in the 2017-2018 cycle, with little change across all data cycles,” the researchers wrote.
Disparities in SHS exposure
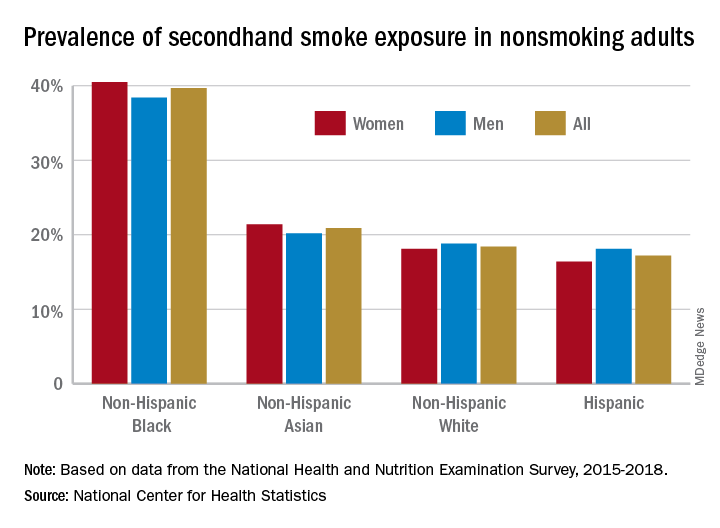
A second report from NHANES data for 2015-2018, published in a National Center for Health Statistics Data Brief (No. 396, February 2021) showed that 20.8% of nonsmoking U.S. adults had SHS exposure, again with greater prevalence among non-Hispanic Black adults (39.7%), than for non-Hispanic White (18.4%), non-Hispanic Asian (20.9%), and Hispanic (17.2%) adults. Exposure was also greater in the younger age groups, with SHS rates for adults aged 18-39 years, 40-59 years, and ≥60 years at 25.6%, 19.1%, and 17.6%, respectively. Lower education (high school or less vs. some college education) and lower income levels were also associated with higher levels of SHS exposure. The investigators noted that among households with smokers, non-Hispanic Black adults are less likely to have complete smoking bans in homes, and among Medicaid or uninsured parents of any race or ethnicity, bans on smoking in family vehicles are less likely.
Overall, the prevalence of SHS exposure declined from 27.7% to 20.7% from 2009 to 2018, but the decreases were mediated by race and income.
SHS exposure in private spaces
A research brief from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on SHS exposure in homes and vehicles in the U.S. among middle and high school students also found a general decline in SHS exposure over 2011-2018 in homes (26.8%-20.9%; P < .001) and vehicles (30.2%-19.8%; P < .001). The findings, derived from the National Youth Tobacco Survey for 2011-2019, showed that no reduction occurred in homes among non-Hispanic Black students. Overall, a significant difference in home SHS exposure was observed by race/ethnicity: non-Hispanic Black (28.4%) and non-Hispanic White (27.4%) students both had a higher prevalence compared with Hispanic (20.0%) and non-Hispanic other (20.2%) students (P < .001).
Progress in reducing SHS exposure in public spaces has been made over the last 2 decades, with 27 states and more than 1,000 municipalities implementing comprehensive smoke-free laws that prohibit smoking in indoor public places, including workplaces, restaurants, and bars. While the prevalence of voluntary smoke-free home (83.7%) and vehicle (78.1%) rules has increased over time, private settings remain major sources of SHS exposure for many people, including youths. “Although SHS exposures have declined,” the authors wrote, “more than 6 million young people remain exposed to SHS in these private settings.”
In reviewing the data, Mary Cataletto, MD, FCCP, clinical professor of pediatrics at NYU Long Island School of Medicine, stated that these studies “highlight the need for implementation of smoke-free policies to reduce exposure to secondhand smoke, especially in homes and cars and with focused advocacy efforts in highly affected communities.”
Panagis Galiatsatos, MD, MHS, assistant professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, emphasized implementation of smoke-free policies but also treatment for smokers. “I’m not at all surprised by these statistics,” he noted in an interview. “Public health policies have helped us to get to where we are now, but there’s a reason that we have plateaued over the last decade. It’s hard to mitigate secondhand smoke exposure because the ones who are smoking now are the most refractory, challenging cases. ... You need good clinical interventions with counseling supported by pharmacological agents to help them if you want to stop secondhand smoke exposure.” He added, “You have to look at current smokers no differently than you look at patients with stage IV cancer – a group that requires a lot of resources to help them get through. Remember, all of them want to quit, but the promise of well-designed, precision-medicine strategies to help them quit has not been kept. Public health policy isn’t going to do it. We need to manage these patients clinically.”
The investigators had no conflict disclosures.
Despite 30+ years of antismoking public policies and dramatic overall decline in secondhand smoke (SHS) exposure, .
No risk-free SHS exposure
Surendranath S. Shastri, MD, of MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and colleagues underscored the U.S. Surgeon General’s determination that there is no risk-free level of SHS exposure in a recent JAMA Internal Medicine Research Letter.
“With the outbreak of the coronavirus disease 2019, which affects lung function, improving smoke-free policies to enhance air quality should be a growing priority,”they wrote.
Dr. Shastri and colleagues looked at 2011-2018 data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), which detailed prevalence of SHS exposure in the U.S. population aged 3 years and older using interviews and biological specimens to test for cotinine levels. For the survey, nonsmokers having serum cotinine levels of 0.05 to 10 ng/mL were considered to have SHS exposure.

While the prevalence of SHS exposure among nonsmokers declined from 87.5% to 25.3% between 1988 and 2012, levels have stagnated since 2012 and racial and economic disparities are evident. Higher smoking rates, less knowledge about health risks, higher workplace exposure, greater likelihood of living in low-income, multi-unit housing, plus having their communities targeted by tobacco companies, may all help explain higher serum levels of cotinine in populations with lower socioeconomic status.
“Multivariable logistic regression identified younger age (odds ratio [OR], 1.88, for 12-19 years, and OR, 2.29, for 3-11 years), non-Hispanic Black race/ethnicity (OR, 2.75), less than high school education (OR, 1.59), and living below the poverty level (OR, 2.61) as risk factors for SHSe in the 2017-2018 cycle, with little change across all data cycles,” the researchers wrote.
Disparities in SHS exposure
A second report from NHANES data for 2015-2018, published in a National Center for Health Statistics Data Brief (No. 396, February 2021) showed that 20.8% of nonsmoking U.S. adults had SHS exposure, again with greater prevalence among non-Hispanic Black adults (39.7%), than for non-Hispanic White (18.4%), non-Hispanic Asian (20.9%), and Hispanic (17.2%) adults. Exposure was also greater in the younger age groups, with SHS rates for adults aged 18-39 years, 40-59 years, and ≥60 years at 25.6%, 19.1%, and 17.6%, respectively. Lower education (high school or less vs. some college education) and lower income levels were also associated with higher levels of SHS exposure. The investigators noted that among households with smokers, non-Hispanic Black adults are less likely to have complete smoking bans in homes, and among Medicaid or uninsured parents of any race or ethnicity, bans on smoking in family vehicles are less likely.
Overall, the prevalence of SHS exposure declined from 27.7% to 20.7% from 2009 to 2018, but the decreases were mediated by race and income.
SHS exposure in private spaces
A research brief from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on SHS exposure in homes and vehicles in the U.S. among middle and high school students also found a general decline in SHS exposure over 2011-2018 in homes (26.8%-20.9%; P < .001) and vehicles (30.2%-19.8%; P < .001). The findings, derived from the National Youth Tobacco Survey for 2011-2019, showed that no reduction occurred in homes among non-Hispanic Black students. Overall, a significant difference in home SHS exposure was observed by race/ethnicity: non-Hispanic Black (28.4%) and non-Hispanic White (27.4%) students both had a higher prevalence compared with Hispanic (20.0%) and non-Hispanic other (20.2%) students (P < .001).
Progress in reducing SHS exposure in public spaces has been made over the last 2 decades, with 27 states and more than 1,000 municipalities implementing comprehensive smoke-free laws that prohibit smoking in indoor public places, including workplaces, restaurants, and bars. While the prevalence of voluntary smoke-free home (83.7%) and vehicle (78.1%) rules has increased over time, private settings remain major sources of SHS exposure for many people, including youths. “Although SHS exposures have declined,” the authors wrote, “more than 6 million young people remain exposed to SHS in these private settings.”
In reviewing the data, Mary Cataletto, MD, FCCP, clinical professor of pediatrics at NYU Long Island School of Medicine, stated that these studies “highlight the need for implementation of smoke-free policies to reduce exposure to secondhand smoke, especially in homes and cars and with focused advocacy efforts in highly affected communities.”
Panagis Galiatsatos, MD, MHS, assistant professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, emphasized implementation of smoke-free policies but also treatment for smokers. “I’m not at all surprised by these statistics,” he noted in an interview. “Public health policies have helped us to get to where we are now, but there’s a reason that we have plateaued over the last decade. It’s hard to mitigate secondhand smoke exposure because the ones who are smoking now are the most refractory, challenging cases. ... You need good clinical interventions with counseling supported by pharmacological agents to help them if you want to stop secondhand smoke exposure.” He added, “You have to look at current smokers no differently than you look at patients with stage IV cancer – a group that requires a lot of resources to help them get through. Remember, all of them want to quit, but the promise of well-designed, precision-medicine strategies to help them quit has not been kept. Public health policy isn’t going to do it. We need to manage these patients clinically.”
The investigators had no conflict disclosures.
Despite 30+ years of antismoking public policies and dramatic overall decline in secondhand smoke (SHS) exposure, .
No risk-free SHS exposure
Surendranath S. Shastri, MD, of MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and colleagues underscored the U.S. Surgeon General’s determination that there is no risk-free level of SHS exposure in a recent JAMA Internal Medicine Research Letter.
“With the outbreak of the coronavirus disease 2019, which affects lung function, improving smoke-free policies to enhance air quality should be a growing priority,”they wrote.
Dr. Shastri and colleagues looked at 2011-2018 data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), which detailed prevalence of SHS exposure in the U.S. population aged 3 years and older using interviews and biological specimens to test for cotinine levels. For the survey, nonsmokers having serum cotinine levels of 0.05 to 10 ng/mL were considered to have SHS exposure.

While the prevalence of SHS exposure among nonsmokers declined from 87.5% to 25.3% between 1988 and 2012, levels have stagnated since 2012 and racial and economic disparities are evident. Higher smoking rates, less knowledge about health risks, higher workplace exposure, greater likelihood of living in low-income, multi-unit housing, plus having their communities targeted by tobacco companies, may all help explain higher serum levels of cotinine in populations with lower socioeconomic status.
“Multivariable logistic regression identified younger age (odds ratio [OR], 1.88, for 12-19 years, and OR, 2.29, for 3-11 years), non-Hispanic Black race/ethnicity (OR, 2.75), less than high school education (OR, 1.59), and living below the poverty level (OR, 2.61) as risk factors for SHSe in the 2017-2018 cycle, with little change across all data cycles,” the researchers wrote.
Disparities in SHS exposure
A second report from NHANES data for 2015-2018, published in a National Center for Health Statistics Data Brief (No. 396, February 2021) showed that 20.8% of nonsmoking U.S. adults had SHS exposure, again with greater prevalence among non-Hispanic Black adults (39.7%), than for non-Hispanic White (18.4%), non-Hispanic Asian (20.9%), and Hispanic (17.2%) adults. Exposure was also greater in the younger age groups, with SHS rates for adults aged 18-39 years, 40-59 years, and ≥60 years at 25.6%, 19.1%, and 17.6%, respectively. Lower education (high school or less vs. some college education) and lower income levels were also associated with higher levels of SHS exposure. The investigators noted that among households with smokers, non-Hispanic Black adults are less likely to have complete smoking bans in homes, and among Medicaid or uninsured parents of any race or ethnicity, bans on smoking in family vehicles are less likely.
Overall, the prevalence of SHS exposure declined from 27.7% to 20.7% from 2009 to 2018, but the decreases were mediated by race and income.
SHS exposure in private spaces
A research brief from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on SHS exposure in homes and vehicles in the U.S. among middle and high school students also found a general decline in SHS exposure over 2011-2018 in homes (26.8%-20.9%; P < .001) and vehicles (30.2%-19.8%; P < .001). The findings, derived from the National Youth Tobacco Survey for 2011-2019, showed that no reduction occurred in homes among non-Hispanic Black students. Overall, a significant difference in home SHS exposure was observed by race/ethnicity: non-Hispanic Black (28.4%) and non-Hispanic White (27.4%) students both had a higher prevalence compared with Hispanic (20.0%) and non-Hispanic other (20.2%) students (P < .001).
Progress in reducing SHS exposure in public spaces has been made over the last 2 decades, with 27 states and more than 1,000 municipalities implementing comprehensive smoke-free laws that prohibit smoking in indoor public places, including workplaces, restaurants, and bars. While the prevalence of voluntary smoke-free home (83.7%) and vehicle (78.1%) rules has increased over time, private settings remain major sources of SHS exposure for many people, including youths. “Although SHS exposures have declined,” the authors wrote, “more than 6 million young people remain exposed to SHS in these private settings.”
In reviewing the data, Mary Cataletto, MD, FCCP, clinical professor of pediatrics at NYU Long Island School of Medicine, stated that these studies “highlight the need for implementation of smoke-free policies to reduce exposure to secondhand smoke, especially in homes and cars and with focused advocacy efforts in highly affected communities.”
Panagis Galiatsatos, MD, MHS, assistant professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, emphasized implementation of smoke-free policies but also treatment for smokers. “I’m not at all surprised by these statistics,” he noted in an interview. “Public health policies have helped us to get to where we are now, but there’s a reason that we have plateaued over the last decade. It’s hard to mitigate secondhand smoke exposure because the ones who are smoking now are the most refractory, challenging cases. ... You need good clinical interventions with counseling supported by pharmacological agents to help them if you want to stop secondhand smoke exposure.” He added, “You have to look at current smokers no differently than you look at patients with stage IV cancer – a group that requires a lot of resources to help them get through. Remember, all of them want to quit, but the promise of well-designed, precision-medicine strategies to help them quit has not been kept. Public health policy isn’t going to do it. We need to manage these patients clinically.”
The investigators had no conflict disclosures.
Is the WHO’s HPV vaccination target within reach?
The WHO’s goal is to have HPV vaccines delivered to 90% of all adolescent girls by 2030, part of the organization’s larger goal to “eliminate” cervical cancer, or reduce the annual incidence of cervical cancer to below 4 cases per 100,000 people globally.
Laia Bruni, MD, PhD, of Catalan Institute of Oncology in Barcelona, and colleagues outlined the progress made thus far toward reaching the WHO’s goals in an article published in Preventive Medicine.
The authors noted that cervical cancer caused by HPV is a “major public health problem, especially in low- and middle-income countries (LMIC).”
However, vaccines against HPV have been available since 2006 and have been recommended by the WHO since 2009.
HPV vaccines have been introduced into many national immunization schedules. Among the 194 WHO member states, 107 (55%) had introduced HPV vaccination as of June 2020, according to estimates from the WHO and the United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund (UNICEF).
Still, vaccine introduction and coverages are suboptimal, according to several studies and international agencies.
In their article, Dr. Bruni and colleagues describe the mid-2020 status of HPV vaccine introduction, based on WHO/UNICEF estimates of national HPV immunization coverage from 2010 to 2019.
HPV vaccination by region
The Americas and Europe are by far the WHO regions with the highest rates of HPV vaccination, with 85% and 77% of their countries, respectively, having already introduced HPV vaccination, either partially or nationwide.
In 2019, a record number of introductions, 16, were reported, mostly in LMICs where access has been limited. In prior years, the average had been a relatively steady 7-8 introductions per year.
The percentage of high-income countries (HICs) that have introduced HPV vaccination exceeds 80%. LMICs started introducing HPV vaccination later and at a slower pace, compared with HICs. By the end of 2019, only 41% of LMICs had introduced vaccination. However, of the new introductions in 2019, 87% were in LMICs.
In 2019, the average performance coverage for HPV vaccination programs in 99 countries (both HICs and LMICs) was around 67% for the first vaccine dose and 53% for the final dose.
Median performance coverage was higher in LMICs than in HICs for the first dose (80% and 72%, respectively), but mean dropout rates were higher in LMICs than in HICs (18% and 11%, respectively).
Coverage of more than 90% was achieved for the last dose in only five countries (6%). Twenty-two countries (21%) achieved coverages of 75% or higher, while 35 countries (40%) had final dose coverages of 50% or less.
Global coverage of the final HPV vaccine dose (weighted by population size) was estimated at 15%. According to the authors, that low percentage can be explained by the fact that many of the most populous countries have either not yet introduced HPV vaccination or have low performance.
The countries with highest cervical cancer burden have had limited secondary prevention and have been less likely to provide access to vaccination, the authors noted. However, this trend appears to be reversing, with 14 new LMICs providing HPV vaccination in 2019.
HPV vaccination by sex
By 2019, almost a third of the 107 HPV vaccination programs (n = 33) were “gender neutral,” with girls and boys receiving HPV vaccines. Generally, LMICs targeted younger girls (9-10 years) compared with HICs (11-13 years).
Dr. Bruni and colleagues estimated that 15% of girls and 4% of boys were vaccinated globally with the full course of vaccine. At least one dose was received by 20% of girls and 5% of boys.
From 2010 to 2019, HPV vaccination rates in HICs rose from 42% in girls and 0% in boys to 88% and 44%, respectively. In LMICs, over the same period, rates rose from 4% in girls and 0% in boys to 40% and 5%, respectively.
Obstacles and the path forward
The COVID-19 pandemic has halted HPV vaccine delivery in the majority of countries, Dr. Bruni and colleagues noted. About 70 countries had reported program interruptions by August 2020, and delays to HPV vaccine introductions were anticipated for other countries.
An economic downturn could have further far-reaching effects on plans to introduce HPV vaccines, Dr. Bruni and colleagues observed.
While meeting the 2030 target will be challenging, the authors noted that, in every geographic area, some programs are meeting the 90% target.
“HPV national programs should aim to get 90+% of girls vaccinated before the age of 15,” Dr. Bruni said in an interview. “This is a feasible goal, and some countries have succeeded, such as Norway and Rwanda. Average performance, however, is around 55%, and that shows that it is not an easy task.”
Dr. Bruni underscored the four main actions that should be taken to achieve 90% coverage of HPV vaccination, as outlined in the WHO cervical cancer elimination strategy:
- Secure sufficient and affordable HPV vaccines.
- Increase the quality and coverage of vaccination.
- Improve communication and social mobilization.
- Innovate to improve efficiency of vaccine delivery.
“Addressing vaccine hesitancy adequately is one of the biggest challenges we face, especially for the HPV vaccine,” Dr. Bruni said. “As the WHO document states, understanding social, cultural, societal, and other barriers affecting acceptance and uptake of the vaccine will be critical for overcoming vaccine hesitancy and countering misinformation.”
This research was funded by a grant from Instituto de Salud Carlos III and various other grants. Dr. Bruni and coauthors said they have no relevant disclosures.
The WHO’s goal is to have HPV vaccines delivered to 90% of all adolescent girls by 2030, part of the organization’s larger goal to “eliminate” cervical cancer, or reduce the annual incidence of cervical cancer to below 4 cases per 100,000 people globally.
Laia Bruni, MD, PhD, of Catalan Institute of Oncology in Barcelona, and colleagues outlined the progress made thus far toward reaching the WHO’s goals in an article published in Preventive Medicine.
The authors noted that cervical cancer caused by HPV is a “major public health problem, especially in low- and middle-income countries (LMIC).”
However, vaccines against HPV have been available since 2006 and have been recommended by the WHO since 2009.
HPV vaccines have been introduced into many national immunization schedules. Among the 194 WHO member states, 107 (55%) had introduced HPV vaccination as of June 2020, according to estimates from the WHO and the United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund (UNICEF).
Still, vaccine introduction and coverages are suboptimal, according to several studies and international agencies.
In their article, Dr. Bruni and colleagues describe the mid-2020 status of HPV vaccine introduction, based on WHO/UNICEF estimates of national HPV immunization coverage from 2010 to 2019.
HPV vaccination by region
The Americas and Europe are by far the WHO regions with the highest rates of HPV vaccination, with 85% and 77% of their countries, respectively, having already introduced HPV vaccination, either partially or nationwide.
In 2019, a record number of introductions, 16, were reported, mostly in LMICs where access has been limited. In prior years, the average had been a relatively steady 7-8 introductions per year.
The percentage of high-income countries (HICs) that have introduced HPV vaccination exceeds 80%. LMICs started introducing HPV vaccination later and at a slower pace, compared with HICs. By the end of 2019, only 41% of LMICs had introduced vaccination. However, of the new introductions in 2019, 87% were in LMICs.
In 2019, the average performance coverage for HPV vaccination programs in 99 countries (both HICs and LMICs) was around 67% for the first vaccine dose and 53% for the final dose.
Median performance coverage was higher in LMICs than in HICs for the first dose (80% and 72%, respectively), but mean dropout rates were higher in LMICs than in HICs (18% and 11%, respectively).
Coverage of more than 90% was achieved for the last dose in only five countries (6%). Twenty-two countries (21%) achieved coverages of 75% or higher, while 35 countries (40%) had final dose coverages of 50% or less.
Global coverage of the final HPV vaccine dose (weighted by population size) was estimated at 15%. According to the authors, that low percentage can be explained by the fact that many of the most populous countries have either not yet introduced HPV vaccination or have low performance.
The countries with highest cervical cancer burden have had limited secondary prevention and have been less likely to provide access to vaccination, the authors noted. However, this trend appears to be reversing, with 14 new LMICs providing HPV vaccination in 2019.
HPV vaccination by sex
By 2019, almost a third of the 107 HPV vaccination programs (n = 33) were “gender neutral,” with girls and boys receiving HPV vaccines. Generally, LMICs targeted younger girls (9-10 years) compared with HICs (11-13 years).
Dr. Bruni and colleagues estimated that 15% of girls and 4% of boys were vaccinated globally with the full course of vaccine. At least one dose was received by 20% of girls and 5% of boys.
From 2010 to 2019, HPV vaccination rates in HICs rose from 42% in girls and 0% in boys to 88% and 44%, respectively. In LMICs, over the same period, rates rose from 4% in girls and 0% in boys to 40% and 5%, respectively.
Obstacles and the path forward
The COVID-19 pandemic has halted HPV vaccine delivery in the majority of countries, Dr. Bruni and colleagues noted. About 70 countries had reported program interruptions by August 2020, and delays to HPV vaccine introductions were anticipated for other countries.
An economic downturn could have further far-reaching effects on plans to introduce HPV vaccines, Dr. Bruni and colleagues observed.
While meeting the 2030 target will be challenging, the authors noted that, in every geographic area, some programs are meeting the 90% target.
“HPV national programs should aim to get 90+% of girls vaccinated before the age of 15,” Dr. Bruni said in an interview. “This is a feasible goal, and some countries have succeeded, such as Norway and Rwanda. Average performance, however, is around 55%, and that shows that it is not an easy task.”
Dr. Bruni underscored the four main actions that should be taken to achieve 90% coverage of HPV vaccination, as outlined in the WHO cervical cancer elimination strategy:
- Secure sufficient and affordable HPV vaccines.
- Increase the quality and coverage of vaccination.
- Improve communication and social mobilization.
- Innovate to improve efficiency of vaccine delivery.
“Addressing vaccine hesitancy adequately is one of the biggest challenges we face, especially for the HPV vaccine,” Dr. Bruni said. “As the WHO document states, understanding social, cultural, societal, and other barriers affecting acceptance and uptake of the vaccine will be critical for overcoming vaccine hesitancy and countering misinformation.”
This research was funded by a grant from Instituto de Salud Carlos III and various other grants. Dr. Bruni and coauthors said they have no relevant disclosures.
The WHO’s goal is to have HPV vaccines delivered to 90% of all adolescent girls by 2030, part of the organization’s larger goal to “eliminate” cervical cancer, or reduce the annual incidence of cervical cancer to below 4 cases per 100,000 people globally.
Laia Bruni, MD, PhD, of Catalan Institute of Oncology in Barcelona, and colleagues outlined the progress made thus far toward reaching the WHO’s goals in an article published in Preventive Medicine.
The authors noted that cervical cancer caused by HPV is a “major public health problem, especially in low- and middle-income countries (LMIC).”
However, vaccines against HPV have been available since 2006 and have been recommended by the WHO since 2009.
HPV vaccines have been introduced into many national immunization schedules. Among the 194 WHO member states, 107 (55%) had introduced HPV vaccination as of June 2020, according to estimates from the WHO and the United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund (UNICEF).
Still, vaccine introduction and coverages are suboptimal, according to several studies and international agencies.
In their article, Dr. Bruni and colleagues describe the mid-2020 status of HPV vaccine introduction, based on WHO/UNICEF estimates of national HPV immunization coverage from 2010 to 2019.
HPV vaccination by region
The Americas and Europe are by far the WHO regions with the highest rates of HPV vaccination, with 85% and 77% of their countries, respectively, having already introduced HPV vaccination, either partially or nationwide.
In 2019, a record number of introductions, 16, were reported, mostly in LMICs where access has been limited. In prior years, the average had been a relatively steady 7-8 introductions per year.
The percentage of high-income countries (HICs) that have introduced HPV vaccination exceeds 80%. LMICs started introducing HPV vaccination later and at a slower pace, compared with HICs. By the end of 2019, only 41% of LMICs had introduced vaccination. However, of the new introductions in 2019, 87% were in LMICs.
In 2019, the average performance coverage for HPV vaccination programs in 99 countries (both HICs and LMICs) was around 67% for the first vaccine dose and 53% for the final dose.
Median performance coverage was higher in LMICs than in HICs for the first dose (80% and 72%, respectively), but mean dropout rates were higher in LMICs than in HICs (18% and 11%, respectively).
Coverage of more than 90% was achieved for the last dose in only five countries (6%). Twenty-two countries (21%) achieved coverages of 75% or higher, while 35 countries (40%) had final dose coverages of 50% or less.
Global coverage of the final HPV vaccine dose (weighted by population size) was estimated at 15%. According to the authors, that low percentage can be explained by the fact that many of the most populous countries have either not yet introduced HPV vaccination or have low performance.
The countries with highest cervical cancer burden have had limited secondary prevention and have been less likely to provide access to vaccination, the authors noted. However, this trend appears to be reversing, with 14 new LMICs providing HPV vaccination in 2019.
HPV vaccination by sex
By 2019, almost a third of the 107 HPV vaccination programs (n = 33) were “gender neutral,” with girls and boys receiving HPV vaccines. Generally, LMICs targeted younger girls (9-10 years) compared with HICs (11-13 years).
Dr. Bruni and colleagues estimated that 15% of girls and 4% of boys were vaccinated globally with the full course of vaccine. At least one dose was received by 20% of girls and 5% of boys.
From 2010 to 2019, HPV vaccination rates in HICs rose from 42% in girls and 0% in boys to 88% and 44%, respectively. In LMICs, over the same period, rates rose from 4% in girls and 0% in boys to 40% and 5%, respectively.
Obstacles and the path forward
The COVID-19 pandemic has halted HPV vaccine delivery in the majority of countries, Dr. Bruni and colleagues noted. About 70 countries had reported program interruptions by August 2020, and delays to HPV vaccine introductions were anticipated for other countries.
An economic downturn could have further far-reaching effects on plans to introduce HPV vaccines, Dr. Bruni and colleagues observed.
While meeting the 2030 target will be challenging, the authors noted that, in every geographic area, some programs are meeting the 90% target.
“HPV national programs should aim to get 90+% of girls vaccinated before the age of 15,” Dr. Bruni said in an interview. “This is a feasible goal, and some countries have succeeded, such as Norway and Rwanda. Average performance, however, is around 55%, and that shows that it is not an easy task.”
Dr. Bruni underscored the four main actions that should be taken to achieve 90% coverage of HPV vaccination, as outlined in the WHO cervical cancer elimination strategy:
- Secure sufficient and affordable HPV vaccines.
- Increase the quality and coverage of vaccination.
- Improve communication and social mobilization.
- Innovate to improve efficiency of vaccine delivery.
“Addressing vaccine hesitancy adequately is one of the biggest challenges we face, especially for the HPV vaccine,” Dr. Bruni said. “As the WHO document states, understanding social, cultural, societal, and other barriers affecting acceptance and uptake of the vaccine will be critical for overcoming vaccine hesitancy and countering misinformation.”
This research was funded by a grant from Instituto de Salud Carlos III and various other grants. Dr. Bruni and coauthors said they have no relevant disclosures.
FROM PREVENTIVE MEDICINE
Routine vaccinations missed by older adults during pandemic
Physicians are going to have to play catch-up when it comes to getting older patients their routine, but important, vaccinations missed during the pandemic.
and have recovered only partially and gradually, according to a report by Kai Hong, PhD, and colleagues at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. “As the pandemic continues,” the investigators stated, “vaccination providers should continue efforts to resolve disruptions in routine adult vaccination.”
The CDC issued guidance recommending postponement of routine adult vaccination in response to the March 13, 2020, COVID-19 national emergency declaration by the U.S. government and also to state and local shelter-in-place orders. Health care facility operations were restricted because of safety concerns around exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The result was a significant drop in routine medical care including adult vaccinations.
The investigators examined Medicare enrollment and claims data to assess the change in weekly receipt of four routine adult vaccines by Medicare beneficiaries aged ≥65 during the pandemic: (13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine [PCV13], 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine [PPSV23], tetanus-diphtheria or tetanus-diphtheria-acellular pertussis vaccine [Td/Tdap], and recombinant zoster vaccine [RZV]). The comparison periods were Jan. 6–July 20, 2019, and Jan. 5–July 18, 2020.
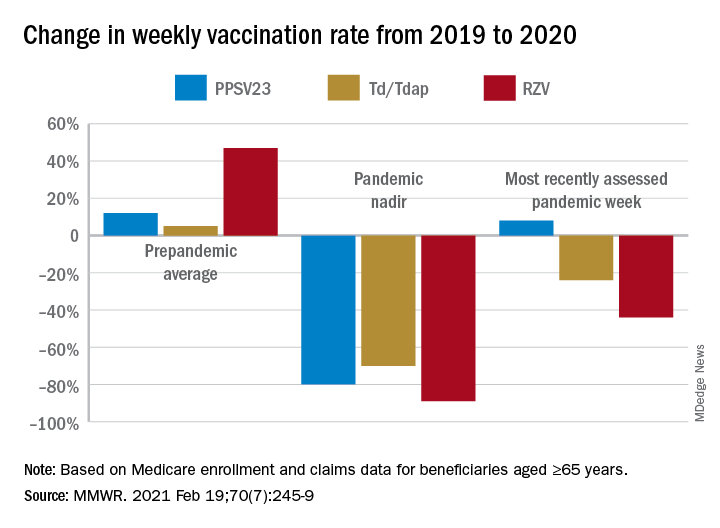
Of the Medicare enrollees in the study sample, 85% were White, 7% Black, 2% Asian, 2% Hispanic, and 4% other racial and ethnic groups. For each of the four vaccines overall, weekly rates of vaccination declined sharply after the emergency declaration, compared with corresponding weeks in 2019. In the period prior to the emergency declaration (Jan. 5–March 14, 2020), weekly percentages of Medicare beneficiaries vaccinated with PPSV23, Td/Tdap, and RZV were consistently higher than rates during the same period in 2019.
After the March 13 declaration, while weekly vaccination rates plummeted 25% for PPSV23 and 62% for RZV in the first week, the greatest weekly declines were during April 5-11, 2020, for PCV13, PPSV23, and Td/Tdap, and during April 12-18, 2020, for RZV. The pandemic weekly vaccination rate nadirs revealed declines of 88% for PCV13, 80% for PPSV23, 70% for Td/Tdap, and 89% for RZV.
Routine vaccinations increased midyear
Vaccination rates recovered gradually. For the most recently assessed pandemic week (July 12-18, 2020), the rate for PPSV23 was 8% higher than in the corresponding period in 2019. Weekly corresponding rates for other examined vaccines, however, remained much lower than in 2019: 44% lower for RZV, 24% lower for Td/Tdap and 43% lower for PCV13. The CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted in June 2019 to stop recommending PCV13 for adults aged ≥65 years and so vaccination with PCV13 among this population declined in 2020, compared with that in 2019.
Another significant drop in the rates of adult vaccinations may have occurred because of the surge in COVID-19 infections in the fall of 2020 and subsequent closures and renewal of lockdown in many localities.
Disparities in routine vaccination trends
Dr. Hong and colleagues noted that their findings are consistent with prior reports of declines in pediatric vaccine ordering, administration, and coverage during the pandemic. While the reductions were similar across all racial and ethnic groups, the magnitudes of recovery varied, with vaccination rates lower among racial and ethnic minority adults than among White adults.
In view of the disproportionate COVID-19 pandemic effects among some racial and ethnic minorities, the investigators recommended monitoring and subsequent early intervention to mitigate similar indirect pandemic effects, such as reduced utilization of other preventive services. “Many members of racial and ethnic minority groups face barriers to routine medical care, which means they have fewer opportunities to receive preventive interventions such as vaccination,” Dr. Hong said in an interview. “When clinicians are following up with patients who have missed vaccinations, it is important for them to remember that patients may face new barriers to vaccination such as loss of income or health insurance, and to work with them to remove those barriers,” he added.
“If vaccination is deferred, older adults and adults with underlying medical conditions who subsequently become infected with a vaccine-preventable disease are at increased risk for complications,” Dr. Hong said. “The most important thing clinicians can do is identify patients who are due for or who have missed vaccinations, and contact them to schedule visits. Immunization Information Systems and electronic health records may be able to support this work. In addition, the vaccination status of all patients should be assessed at every health care visit to reduce missed opportunities for vaccination.”
Physicians are going to have to play catch-up when it comes to getting older patients their routine, but important, vaccinations missed during the pandemic.
and have recovered only partially and gradually, according to a report by Kai Hong, PhD, and colleagues at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. “As the pandemic continues,” the investigators stated, “vaccination providers should continue efforts to resolve disruptions in routine adult vaccination.”
The CDC issued guidance recommending postponement of routine adult vaccination in response to the March 13, 2020, COVID-19 national emergency declaration by the U.S. government and also to state and local shelter-in-place orders. Health care facility operations were restricted because of safety concerns around exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The result was a significant drop in routine medical care including adult vaccinations.
The investigators examined Medicare enrollment and claims data to assess the change in weekly receipt of four routine adult vaccines by Medicare beneficiaries aged ≥65 during the pandemic: (13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine [PCV13], 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine [PPSV23], tetanus-diphtheria or tetanus-diphtheria-acellular pertussis vaccine [Td/Tdap], and recombinant zoster vaccine [RZV]). The comparison periods were Jan. 6–July 20, 2019, and Jan. 5–July 18, 2020.
Of the Medicare enrollees in the study sample, 85% were White, 7% Black, 2% Asian, 2% Hispanic, and 4% other racial and ethnic groups. For each of the four vaccines overall, weekly rates of vaccination declined sharply after the emergency declaration, compared with corresponding weeks in 2019. In the period prior to the emergency declaration (Jan. 5–March 14, 2020), weekly percentages of Medicare beneficiaries vaccinated with PPSV23, Td/Tdap, and RZV were consistently higher than rates during the same period in 2019.
After the March 13 declaration, while weekly vaccination rates plummeted 25% for PPSV23 and 62% for RZV in the first week, the greatest weekly declines were during April 5-11, 2020, for PCV13, PPSV23, and Td/Tdap, and during April 12-18, 2020, for RZV. The pandemic weekly vaccination rate nadirs revealed declines of 88% for PCV13, 80% for PPSV23, 70% for Td/Tdap, and 89% for RZV.
Routine vaccinations increased midyear
Vaccination rates recovered gradually. For the most recently assessed pandemic week (July 12-18, 2020), the rate for PPSV23 was 8% higher than in the corresponding period in 2019. Weekly corresponding rates for other examined vaccines, however, remained much lower than in 2019: 44% lower for RZV, 24% lower for Td/Tdap and 43% lower for PCV13. The CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted in June 2019 to stop recommending PCV13 for adults aged ≥65 years and so vaccination with PCV13 among this population declined in 2020, compared with that in 2019.
Another significant drop in the rates of adult vaccinations may have occurred because of the surge in COVID-19 infections in the fall of 2020 and subsequent closures and renewal of lockdown in many localities.
Disparities in routine vaccination trends
Dr. Hong and colleagues noted that their findings are consistent with prior reports of declines in pediatric vaccine ordering, administration, and coverage during the pandemic. While the reductions were similar across all racial and ethnic groups, the magnitudes of recovery varied, with vaccination rates lower among racial and ethnic minority adults than among White adults.

In view of the disproportionate COVID-19 pandemic effects among some racial and ethnic minorities, the investigators recommended monitoring and subsequent early intervention to mitigate similar indirect pandemic effects, such as reduced utilization of other preventive services. “Many members of racial and ethnic minority groups face barriers to routine medical care, which means they have fewer opportunities to receive preventive interventions such as vaccination,” Dr. Hong said in an interview. “When clinicians are following up with patients who have missed vaccinations, it is important for them to remember that patients may face new barriers to vaccination such as loss of income or health insurance, and to work with them to remove those barriers,” he added.
“If vaccination is deferred, older adults and adults with underlying medical conditions who subsequently become infected with a vaccine-preventable disease are at increased risk for complications,” Dr. Hong said. “The most important thing clinicians can do is identify patients who are due for or who have missed vaccinations, and contact them to schedule visits. Immunization Information Systems and electronic health records may be able to support this work. In addition, the vaccination status of all patients should be assessed at every health care visit to reduce missed opportunities for vaccination.”
Physicians are going to have to play catch-up when it comes to getting older patients their routine, but important, vaccinations missed during the pandemic.
and have recovered only partially and gradually, according to a report by Kai Hong, PhD, and colleagues at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. “As the pandemic continues,” the investigators stated, “vaccination providers should continue efforts to resolve disruptions in routine adult vaccination.”
The CDC issued guidance recommending postponement of routine adult vaccination in response to the March 13, 2020, COVID-19 national emergency declaration by the U.S. government and also to state and local shelter-in-place orders. Health care facility operations were restricted because of safety concerns around exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The result was a significant drop in routine medical care including adult vaccinations.
The investigators examined Medicare enrollment and claims data to assess the change in weekly receipt of four routine adult vaccines by Medicare beneficiaries aged ≥65 during the pandemic: (13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine [PCV13], 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine [PPSV23], tetanus-diphtheria or tetanus-diphtheria-acellular pertussis vaccine [Td/Tdap], and recombinant zoster vaccine [RZV]). The comparison periods were Jan. 6–July 20, 2019, and Jan. 5–July 18, 2020.
Of the Medicare enrollees in the study sample, 85% were White, 7% Black, 2% Asian, 2% Hispanic, and 4% other racial and ethnic groups. For each of the four vaccines overall, weekly rates of vaccination declined sharply after the emergency declaration, compared with corresponding weeks in 2019. In the period prior to the emergency declaration (Jan. 5–March 14, 2020), weekly percentages of Medicare beneficiaries vaccinated with PPSV23, Td/Tdap, and RZV were consistently higher than rates during the same period in 2019.
After the March 13 declaration, while weekly vaccination rates plummeted 25% for PPSV23 and 62% for RZV in the first week, the greatest weekly declines were during April 5-11, 2020, for PCV13, PPSV23, and Td/Tdap, and during April 12-18, 2020, for RZV. The pandemic weekly vaccination rate nadirs revealed declines of 88% for PCV13, 80% for PPSV23, 70% for Td/Tdap, and 89% for RZV.
Routine vaccinations increased midyear
Vaccination rates recovered gradually. For the most recently assessed pandemic week (July 12-18, 2020), the rate for PPSV23 was 8% higher than in the corresponding period in 2019. Weekly corresponding rates for other examined vaccines, however, remained much lower than in 2019: 44% lower for RZV, 24% lower for Td/Tdap and 43% lower for PCV13. The CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted in June 2019 to stop recommending PCV13 for adults aged ≥65 years and so vaccination with PCV13 among this population declined in 2020, compared with that in 2019.
Another significant drop in the rates of adult vaccinations may have occurred because of the surge in COVID-19 infections in the fall of 2020 and subsequent closures and renewal of lockdown in many localities.
Disparities in routine vaccination trends
Dr. Hong and colleagues noted that their findings are consistent with prior reports of declines in pediatric vaccine ordering, administration, and coverage during the pandemic. While the reductions were similar across all racial and ethnic groups, the magnitudes of recovery varied, with vaccination rates lower among racial and ethnic minority adults than among White adults.

In view of the disproportionate COVID-19 pandemic effects among some racial and ethnic minorities, the investigators recommended monitoring and subsequent early intervention to mitigate similar indirect pandemic effects, such as reduced utilization of other preventive services. “Many members of racial and ethnic minority groups face barriers to routine medical care, which means they have fewer opportunities to receive preventive interventions such as vaccination,” Dr. Hong said in an interview. “When clinicians are following up with patients who have missed vaccinations, it is important for them to remember that patients may face new barriers to vaccination such as loss of income or health insurance, and to work with them to remove those barriers,” he added.
“If vaccination is deferred, older adults and adults with underlying medical conditions who subsequently become infected with a vaccine-preventable disease are at increased risk for complications,” Dr. Hong said. “The most important thing clinicians can do is identify patients who are due for or who have missed vaccinations, and contact them to schedule visits. Immunization Information Systems and electronic health records may be able to support this work. In addition, the vaccination status of all patients should be assessed at every health care visit to reduce missed opportunities for vaccination.”
FROM MMWR
Researchers identify four small cell lung cancer subtypes and their best therapies
Researchers studying a large set of small cell lung cancer (SCLC) tumor samples have identified four SCLC subtypes, and they propose that matching baseline tumor subtypes to SCLC therapy may enhance the depth and duration of response.
Carl M. Gay, MD, PhD, of University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and colleagues conducted this research and described their findings in Cancer Cell.
The authors noted that survival rates in SCLC remain dismal despite recent modest gains in progression-free survival and overall survival achieved through adding immunotherapy to platinum-based frontline chemotherapy.
Based on transcription factors indicating which genes are activated, prior research had already identified three possible SCLC subtypes. Many SCLC tumors, however, do not fit into one of these three groups, the authors said.
Inflamed gene signature
The four groups were identified using tumor expression data and nonnegative matrix factorization from published sources on 81 SCLC patients, and then validated via the largest SCLC data set available (276 SCLC patients enrolled in the phase 3 IMpower133 trial).
The SCLC subtypes were defined largely by differential expression of transcription factors – subtype SCLC-A by ASCL1, subtype SCLC-N by NEUROD1, and subtype SCLC-P by POU2F3. The fourth subtype, SCLC-I, is characterized by low expression of all three transcription factor signatures and an inflamed gene signature with a high expression of multiple immune genes, including significantly greater levels of genes indicating the presence of CD8-positive cytotoxic T cells.
Because each subtype demonstrates unique vulnerability to investigational therapies, this subtype classification has significant clinical implications.
“We propose that matching baseline tumor subtype to therapy, as well as manipulating subtype switching on therapy, may enhance depth and duration of response for SCLC patients,” the authors stated.
“Our paper shows that the inflamed group has a distinct biology and environment and tends to be more responsive to immunotherapy,” study author Lauren Averett Byers, MD, also of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, stated in a press release. “Identifying the inflamed group is very important because, so far, there have not been any validated biomarkers for small cell lung cancer that predict which patients get the most benefit from immunotherapy.”
In samples from the other three subtypes, SCLC-A was most responsive to BCL2 inhibitors, SCLC-N to Aurora kinase inhibitors, and SCLC-P to PARP inhibitors.
Treatment resistance
The tendency of SCLC to develop treatment resistance, even after an initial response, is a known challenge. Using single-cell RNA sequencing to evaluate tumor evolution, the authors observed a tendency of SCLC-A to switch to SCLC-I after chemotherapy treatment, a possible contributor to treatment resistance.
It will be necessary to verify the study findings through further investigations, particularly regarding the therapeutic vulnerabilities for each group.
“Now we can develop more effective strategies for each group in clinical trials, taking into account that they each have different biology and optimal drug targets,” Dr. Byers said. “As a field, small cell lung cancer is about 15 years behind non–small cell lung cancer’s renaissance of biomarkers and personalized therapies. This represents a huge step in understanding which drugs work best for which patients and gives us a path forward for personalized approaches for small cell lung cancer.”
“Dr. Gay’s work is the latest in a growing series of exciting studies demonstrating the utility of defining subtypes of small cell lung cancer based on expression of master transcriptional regulators,” commented Charles Rudin, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, in an interview.
He added, “While tumors can evolve between some of these categories, the dominant subtype assignment influences therapeutic vulnerabilities. It is an exciting time for those of us engaged in small cell research. Subtyping should help guide more focused and successful clinical trials for patients with small cell lung cancer.”
The authors disclosed multiple relationships with companies. The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute, the University of Texas Southwestern and MD Anderson Cancer Center, and a variety of other governmental and nonprofit groups. Dr. Rudin is principal investigator of the NCI small cell lung cancer research consortium.
Researchers studying a large set of small cell lung cancer (SCLC) tumor samples have identified four SCLC subtypes, and they propose that matching baseline tumor subtypes to SCLC therapy may enhance the depth and duration of response.
Carl M. Gay, MD, PhD, of University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and colleagues conducted this research and described their findings in Cancer Cell.
The authors noted that survival rates in SCLC remain dismal despite recent modest gains in progression-free survival and overall survival achieved through adding immunotherapy to platinum-based frontline chemotherapy.
Based on transcription factors indicating which genes are activated, prior research had already identified three possible SCLC subtypes. Many SCLC tumors, however, do not fit into one of these three groups, the authors said.
Inflamed gene signature
The four groups were identified using tumor expression data and nonnegative matrix factorization from published sources on 81 SCLC patients, and then validated via the largest SCLC data set available (276 SCLC patients enrolled in the phase 3 IMpower133 trial).
The SCLC subtypes were defined largely by differential expression of transcription factors – subtype SCLC-A by ASCL1, subtype SCLC-N by NEUROD1, and subtype SCLC-P by POU2F3. The fourth subtype, SCLC-I, is characterized by low expression of all three transcription factor signatures and an inflamed gene signature with a high expression of multiple immune genes, including significantly greater levels of genes indicating the presence of CD8-positive cytotoxic T cells.
Because each subtype demonstrates unique vulnerability to investigational therapies, this subtype classification has significant clinical implications.
“We propose that matching baseline tumor subtype to therapy, as well as manipulating subtype switching on therapy, may enhance depth and duration of response for SCLC patients,” the authors stated.
“Our paper shows that the inflamed group has a distinct biology and environment and tends to be more responsive to immunotherapy,” study author Lauren Averett Byers, MD, also of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, stated in a press release. “Identifying the inflamed group is very important because, so far, there have not been any validated biomarkers for small cell lung cancer that predict which patients get the most benefit from immunotherapy.”
In samples from the other three subtypes, SCLC-A was most responsive to BCL2 inhibitors, SCLC-N to Aurora kinase inhibitors, and SCLC-P to PARP inhibitors.
Treatment resistance
The tendency of SCLC to develop treatment resistance, even after an initial response, is a known challenge. Using single-cell RNA sequencing to evaluate tumor evolution, the authors observed a tendency of SCLC-A to switch to SCLC-I after chemotherapy treatment, a possible contributor to treatment resistance.
It will be necessary to verify the study findings through further investigations, particularly regarding the therapeutic vulnerabilities for each group.
“Now we can develop more effective strategies for each group in clinical trials, taking into account that they each have different biology and optimal drug targets,” Dr. Byers said. “As a field, small cell lung cancer is about 15 years behind non–small cell lung cancer’s renaissance of biomarkers and personalized therapies. This represents a huge step in understanding which drugs work best for which patients and gives us a path forward for personalized approaches for small cell lung cancer.”
“Dr. Gay’s work is the latest in a growing series of exciting studies demonstrating the utility of defining subtypes of small cell lung cancer based on expression of master transcriptional regulators,” commented Charles Rudin, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, in an interview.
He added, “While tumors can evolve between some of these categories, the dominant subtype assignment influences therapeutic vulnerabilities. It is an exciting time for those of us engaged in small cell research. Subtyping should help guide more focused and successful clinical trials for patients with small cell lung cancer.”
The authors disclosed multiple relationships with companies. The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute, the University of Texas Southwestern and MD Anderson Cancer Center, and a variety of other governmental and nonprofit groups. Dr. Rudin is principal investigator of the NCI small cell lung cancer research consortium.
Researchers studying a large set of small cell lung cancer (SCLC) tumor samples have identified four SCLC subtypes, and they propose that matching baseline tumor subtypes to SCLC therapy may enhance the depth and duration of response.
Carl M. Gay, MD, PhD, of University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and colleagues conducted this research and described their findings in Cancer Cell.
The authors noted that survival rates in SCLC remain dismal despite recent modest gains in progression-free survival and overall survival achieved through adding immunotherapy to platinum-based frontline chemotherapy.
Based on transcription factors indicating which genes are activated, prior research had already identified three possible SCLC subtypes. Many SCLC tumors, however, do not fit into one of these three groups, the authors said.
Inflamed gene signature
The four groups were identified using tumor expression data and nonnegative matrix factorization from published sources on 81 SCLC patients, and then validated via the largest SCLC data set available (276 SCLC patients enrolled in the phase 3 IMpower133 trial).
The SCLC subtypes were defined largely by differential expression of transcription factors – subtype SCLC-A by ASCL1, subtype SCLC-N by NEUROD1, and subtype SCLC-P by POU2F3. The fourth subtype, SCLC-I, is characterized by low expression of all three transcription factor signatures and an inflamed gene signature with a high expression of multiple immune genes, including significantly greater levels of genes indicating the presence of CD8-positive cytotoxic T cells.
Because each subtype demonstrates unique vulnerability to investigational therapies, this subtype classification has significant clinical implications.
“We propose that matching baseline tumor subtype to therapy, as well as manipulating subtype switching on therapy, may enhance depth and duration of response for SCLC patients,” the authors stated.
“Our paper shows that the inflamed group has a distinct biology and environment and tends to be more responsive to immunotherapy,” study author Lauren Averett Byers, MD, also of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, stated in a press release. “Identifying the inflamed group is very important because, so far, there have not been any validated biomarkers for small cell lung cancer that predict which patients get the most benefit from immunotherapy.”
In samples from the other three subtypes, SCLC-A was most responsive to BCL2 inhibitors, SCLC-N to Aurora kinase inhibitors, and SCLC-P to PARP inhibitors.
Treatment resistance
The tendency of SCLC to develop treatment resistance, even after an initial response, is a known challenge. Using single-cell RNA sequencing to evaluate tumor evolution, the authors observed a tendency of SCLC-A to switch to SCLC-I after chemotherapy treatment, a possible contributor to treatment resistance.
It will be necessary to verify the study findings through further investigations, particularly regarding the therapeutic vulnerabilities for each group.
“Now we can develop more effective strategies for each group in clinical trials, taking into account that they each have different biology and optimal drug targets,” Dr. Byers said. “As a field, small cell lung cancer is about 15 years behind non–small cell lung cancer’s renaissance of biomarkers and personalized therapies. This represents a huge step in understanding which drugs work best for which patients and gives us a path forward for personalized approaches for small cell lung cancer.”
“Dr. Gay’s work is the latest in a growing series of exciting studies demonstrating the utility of defining subtypes of small cell lung cancer based on expression of master transcriptional regulators,” commented Charles Rudin, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, in an interview.
He added, “While tumors can evolve between some of these categories, the dominant subtype assignment influences therapeutic vulnerabilities. It is an exciting time for those of us engaged in small cell research. Subtyping should help guide more focused and successful clinical trials for patients with small cell lung cancer.”
The authors disclosed multiple relationships with companies. The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute, the University of Texas Southwestern and MD Anderson Cancer Center, and a variety of other governmental and nonprofit groups. Dr. Rudin is principal investigator of the NCI small cell lung cancer research consortium.
FROM CANCER CELL
COVID-19: Peginterferon lambda may prevent clinical deterioration, shorten viral shedding
and shorten the duration of viral shedding, according to results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (NCT04354259).
Reductions in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) RNA were greater with peginterferon lambda than with placebo from day 3 onward in the phase 2 study led by Jordan J. Feld, MD, of the Toronto Centre for Liver Disease. The findings were reported in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
Fewer side effects
To date in randomized clinical trials, efficacy in treatment of COVID-19 has been shown only for remdesivir and dexamethasone in hospitalized patients, and in an interim analysis of accelerated viral clearance for a monoclonal antibody infusion in outpatients.
Activity against respiratory pathogens has been demonstrated for interferon lambda-1, a type III interferon shown to be involved in innate antiviral responses. Interferons, Dr. Feld and coauthors stated, drive induction of genes with antiviral, antiproliferative and immunoregulatory properties, and early treatment with interferons might halt clinical progression and shorten the duration of viral shedding with reduced onward transmission. In addition, interferon lambdas (type III) use a distinct receptor complex with high expression levels limited to epithelial cells in the lung, liver, and intestine, leading to fewer side effects than other interferons, including avoiding risk of promoting cytokine storm syndrome.
The researchers investigated peginterferon lambda safety and efficacy in treatment of patients with laboratory-confirmed, mild to moderate COVID-19. Sixty patients (median age 46 years, about 60% female, about 50% White) were recruited from outpatient testing centers at six institutions in Toronto, and referred to a single ambulatory site. Patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to a single subcutaneous injection of peginterferon lambda 180 mcg or placebo within 7 days of symptom onset or, if asymptomatic, of their first positive swab. Mean time from symptom onset to injection was about 4.5 days, and about 18.5% were asymptomatic. The primary outcome was the proportion of patients negative for SARS-CoV-2 RNA on day 7 after the injection.
Greater benefit with higher baseline load
A higher baseline SARS-CoV-2 RNA concentration found in the peginterferon lambda group was found to be significantly associated with day 7 clearance (odds ratio [OR] 0.69 [95% confidence interval 0.51-0.87]; P = ·001). In the peginterferon lambda group, also, the mean decline in SARS-CoV-2 RNA was significantly larger than in the placebo group across all time points (days 3, 5, 7, and14). While viral load decline was 0.81 log greater in the treatment group (P = .14) by day 3, viral load decline increased to 1.67 log copies per mL by day 5 (P = .013) and 2.42 log copies per mL by day 7 (P = .0041). At day 14, the viral decline was 1.77 log copies per mL larger in the peginterferon lambda group (P = .048). The investigators pointed out that the difference in viral load decline between groups was greater in patients with high baseline viral load (at or above 106 copies per mL). In the peginterferon lambda high baseline viral load group, the reduction was 7.17 log copies per mL, versus 4.92 log copies per mL in the placebo group (P = .004).
More patients SARS-CoV-2 RNA negative
By day 7, 80% of patients in the peginterferon lambda group were negative for SARS-CoV-2 RNA, compared with 63% in the placebo group (P = .15). After baseline load adjustment, however, the peginterferon lambda treatment was significantly associated with day 7 clearance (OR 4·12 [95% CI 1·15-16·73]; P = .029).
Respiratory symptoms improved faster
Most symptoms in both groups were mild to moderate, without difference in frequency or severity. While symptom improvement was generally similar over time for both groups, respiratory symptoms improved faster with peginterferon lambda, with the effect more pronounced in the high baseline viral load group (OR 5·88 (0·81-42·46; P =. 079).
Laboratory adverse events, similar for both groups, were mild.
“Peginterferon lambda has potential to prevent clinical deterioration and shorten duration of viral shedding,” the investigators concluded.
“This clinical trial is important” because it suggests that a single intravenous dose of peginterferon lambda administered to outpatients with a positive SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal swab speeds reduction of SARS-CoV-2 viral load, David L. Bowton, MD, FCCP, professor emeritus, Wake Forest Baptist Health, Winston-Salem, N.C., said in an interview. He observed that the smaller viral load difference observed at day 14 likely reflects host immune responses.
Dr. Bowton also noted that two placebo group baseline characteristics (five placebo group patients with anti-SARS-CoV-2 S protein IgG antibodies; two times more undetectable SARS-CoV-2 RNA at baseline assessment) would tend to reduce differences between the peginterferon lambda and placebo groups. He added that the study findings were concordant with another phase 2 trial of hospitalized COVID-19 patients receiving inhaled interferon beta-1a.
“Thus, interferons may find a place in the treatment of COVID-19 and perhaps other severe viral illnesses,” Dr. Bowton said.
The study was funded by the Toronto COVID-19 Action Initiative, University of Toronto, and the Ontario First COVID-19 Rapid Research Fund, Toronto General & Western Hospital Foundation.
Dr. Bowton had no disclosures. Disclosures for Dr. Feld and coauthors are listed on the Lancet Respiratory Medicine website.
and shorten the duration of viral shedding, according to results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (NCT04354259).
Reductions in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) RNA were greater with peginterferon lambda than with placebo from day 3 onward in the phase 2 study led by Jordan J. Feld, MD, of the Toronto Centre for Liver Disease. The findings were reported in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
Fewer side effects
To date in randomized clinical trials, efficacy in treatment of COVID-19 has been shown only for remdesivir and dexamethasone in hospitalized patients, and in an interim analysis of accelerated viral clearance for a monoclonal antibody infusion in outpatients.
Activity against respiratory pathogens has been demonstrated for interferon lambda-1, a type III interferon shown to be involved in innate antiviral responses. Interferons, Dr. Feld and coauthors stated, drive induction of genes with antiviral, antiproliferative and immunoregulatory properties, and early treatment with interferons might halt clinical progression and shorten the duration of viral shedding with reduced onward transmission. In addition, interferon lambdas (type III) use a distinct receptor complex with high expression levels limited to epithelial cells in the lung, liver, and intestine, leading to fewer side effects than other interferons, including avoiding risk of promoting cytokine storm syndrome.
The researchers investigated peginterferon lambda safety and efficacy in treatment of patients with laboratory-confirmed, mild to moderate COVID-19. Sixty patients (median age 46 years, about 60% female, about 50% White) were recruited from outpatient testing centers at six institutions in Toronto, and referred to a single ambulatory site. Patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to a single subcutaneous injection of peginterferon lambda 180 mcg or placebo within 7 days of symptom onset or, if asymptomatic, of their first positive swab. Mean time from symptom onset to injection was about 4.5 days, and about 18.5% were asymptomatic. The primary outcome was the proportion of patients negative for SARS-CoV-2 RNA on day 7 after the injection.
Greater benefit with higher baseline load
A higher baseline SARS-CoV-2 RNA concentration found in the peginterferon lambda group was found to be significantly associated with day 7 clearance (odds ratio [OR] 0.69 [95% confidence interval 0.51-0.87]; P = ·001). In the peginterferon lambda group, also, the mean decline in SARS-CoV-2 RNA was significantly larger than in the placebo group across all time points (days 3, 5, 7, and14). While viral load decline was 0.81 log greater in the treatment group (P = .14) by day 3, viral load decline increased to 1.67 log copies per mL by day 5 (P = .013) and 2.42 log copies per mL by day 7 (P = .0041). At day 14, the viral decline was 1.77 log copies per mL larger in the peginterferon lambda group (P = .048). The investigators pointed out that the difference in viral load decline between groups was greater in patients with high baseline viral load (at or above 106 copies per mL). In the peginterferon lambda high baseline viral load group, the reduction was 7.17 log copies per mL, versus 4.92 log copies per mL in the placebo group (P = .004).
More patients SARS-CoV-2 RNA negative
By day 7, 80% of patients in the peginterferon lambda group were negative for SARS-CoV-2 RNA, compared with 63% in the placebo group (P = .15). After baseline load adjustment, however, the peginterferon lambda treatment was significantly associated with day 7 clearance (OR 4·12 [95% CI 1·15-16·73]; P = .029).
Respiratory symptoms improved faster
Most symptoms in both groups were mild to moderate, without difference in frequency or severity. While symptom improvement was generally similar over time for both groups, respiratory symptoms improved faster with peginterferon lambda, with the effect more pronounced in the high baseline viral load group (OR 5·88 (0·81-42·46; P =. 079).
Laboratory adverse events, similar for both groups, were mild.
“Peginterferon lambda has potential to prevent clinical deterioration and shorten duration of viral shedding,” the investigators concluded.
“This clinical trial is important” because it suggests that a single intravenous dose of peginterferon lambda administered to outpatients with a positive SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal swab speeds reduction of SARS-CoV-2 viral load, David L. Bowton, MD, FCCP, professor emeritus, Wake Forest Baptist Health, Winston-Salem, N.C., said in an interview. He observed that the smaller viral load difference observed at day 14 likely reflects host immune responses.
Dr. Bowton also noted that two placebo group baseline characteristics (five placebo group patients with anti-SARS-CoV-2 S protein IgG antibodies; two times more undetectable SARS-CoV-2 RNA at baseline assessment) would tend to reduce differences between the peginterferon lambda and placebo groups. He added that the study findings were concordant with another phase 2 trial of hospitalized COVID-19 patients receiving inhaled interferon beta-1a.
“Thus, interferons may find a place in the treatment of COVID-19 and perhaps other severe viral illnesses,” Dr. Bowton said.
The study was funded by the Toronto COVID-19 Action Initiative, University of Toronto, and the Ontario First COVID-19 Rapid Research Fund, Toronto General & Western Hospital Foundation.
Dr. Bowton had no disclosures. Disclosures for Dr. Feld and coauthors are listed on the Lancet Respiratory Medicine website.
and shorten the duration of viral shedding, according to results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (NCT04354259).
Reductions in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) RNA were greater with peginterferon lambda than with placebo from day 3 onward in the phase 2 study led by Jordan J. Feld, MD, of the Toronto Centre for Liver Disease. The findings were reported in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
Fewer side effects
To date in randomized clinical trials, efficacy in treatment of COVID-19 has been shown only for remdesivir and dexamethasone in hospitalized patients, and in an interim analysis of accelerated viral clearance for a monoclonal antibody infusion in outpatients.
Activity against respiratory pathogens has been demonstrated for interferon lambda-1, a type III interferon shown to be involved in innate antiviral responses. Interferons, Dr. Feld and coauthors stated, drive induction of genes with antiviral, antiproliferative and immunoregulatory properties, and early treatment with interferons might halt clinical progression and shorten the duration of viral shedding with reduced onward transmission. In addition, interferon lambdas (type III) use a distinct receptor complex with high expression levels limited to epithelial cells in the lung, liver, and intestine, leading to fewer side effects than other interferons, including avoiding risk of promoting cytokine storm syndrome.
The researchers investigated peginterferon lambda safety and efficacy in treatment of patients with laboratory-confirmed, mild to moderate COVID-19. Sixty patients (median age 46 years, about 60% female, about 50% White) were recruited from outpatient testing centers at six institutions in Toronto, and referred to a single ambulatory site. Patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to a single subcutaneous injection of peginterferon lambda 180 mcg or placebo within 7 days of symptom onset or, if asymptomatic, of their first positive swab. Mean time from symptom onset to injection was about 4.5 days, and about 18.5% were asymptomatic. The primary outcome was the proportion of patients negative for SARS-CoV-2 RNA on day 7 after the injection.
Greater benefit with higher baseline load
A higher baseline SARS-CoV-2 RNA concentration found in the peginterferon lambda group was found to be significantly associated with day 7 clearance (odds ratio [OR] 0.69 [95% confidence interval 0.51-0.87]; P = ·001). In the peginterferon lambda group, also, the mean decline in SARS-CoV-2 RNA was significantly larger than in the placebo group across all time points (days 3, 5, 7, and14). While viral load decline was 0.81 log greater in the treatment group (P = .14) by day 3, viral load decline increased to 1.67 log copies per mL by day 5 (P = .013) and 2.42 log copies per mL by day 7 (P = .0041). At day 14, the viral decline was 1.77 log copies per mL larger in the peginterferon lambda group (P = .048). The investigators pointed out that the difference in viral load decline between groups was greater in patients with high baseline viral load (at or above 106 copies per mL). In the peginterferon lambda high baseline viral load group, the reduction was 7.17 log copies per mL, versus 4.92 log copies per mL in the placebo group (P = .004).
More patients SARS-CoV-2 RNA negative
By day 7, 80% of patients in the peginterferon lambda group were negative for SARS-CoV-2 RNA, compared with 63% in the placebo group (P = .15). After baseline load adjustment, however, the peginterferon lambda treatment was significantly associated with day 7 clearance (OR 4·12 [95% CI 1·15-16·73]; P = .029).
Respiratory symptoms improved faster
Most symptoms in both groups were mild to moderate, without difference in frequency or severity. While symptom improvement was generally similar over time for both groups, respiratory symptoms improved faster with peginterferon lambda, with the effect more pronounced in the high baseline viral load group (OR 5·88 (0·81-42·46; P =. 079).
Laboratory adverse events, similar for both groups, were mild.
“Peginterferon lambda has potential to prevent clinical deterioration and shorten duration of viral shedding,” the investigators concluded.
“This clinical trial is important” because it suggests that a single intravenous dose of peginterferon lambda administered to outpatients with a positive SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal swab speeds reduction of SARS-CoV-2 viral load, David L. Bowton, MD, FCCP, professor emeritus, Wake Forest Baptist Health, Winston-Salem, N.C., said in an interview. He observed that the smaller viral load difference observed at day 14 likely reflects host immune responses.
Dr. Bowton also noted that two placebo group baseline characteristics (five placebo group patients with anti-SARS-CoV-2 S protein IgG antibodies; two times more undetectable SARS-CoV-2 RNA at baseline assessment) would tend to reduce differences between the peginterferon lambda and placebo groups. He added that the study findings were concordant with another phase 2 trial of hospitalized COVID-19 patients receiving inhaled interferon beta-1a.
“Thus, interferons may find a place in the treatment of COVID-19 and perhaps other severe viral illnesses,” Dr. Bowton said.
The study was funded by the Toronto COVID-19 Action Initiative, University of Toronto, and the Ontario First COVID-19 Rapid Research Fund, Toronto General & Western Hospital Foundation.
Dr. Bowton had no disclosures. Disclosures for Dr. Feld and coauthors are listed on the Lancet Respiratory Medicine website.
FROM THE LANCET RESPIRATORY MEDICINE
Many ED visits may be preventable for NSCLC patients
The leading cause of ED visits in the study was the cancer itself, although many visits were unrelated to non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) or cancer therapy.
Less than 10% of ED visits were related to cancer therapy, but visits were much more common among patients receiving chemotherapy than among those receiving immunotherapy or tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs).
Manan P. Shah, MD, and Joel W. Neal, MD, PhD, both of Stanford (Calif. ) University, reported these results in JCO Oncology Practice.
The authors noted that, in the United States, care of patients with cancer, among all diseases, leads to the highest per-person cost. Unplanned hospital visits are among the largest drivers of increased spending in advanced cancer care, accounting for 48% of spending. However, that spending may not be indicative of better quality care, but rather of inefficiency, according to the authors.
One registry spanning 2009-2012 and including more than 400,000 newly diagnosed cancer patients found lung cancer to have the third-highest rate of unplanned hospitalizations (after hepatobiliary and pancreatic cancer). Those findings were published in JCO Oncology Practice in 2018.
While the reason for presentation to the ED is often the cancer or its therapy in this population, there is a paucity of research on the relative contribution of factors leading to unplanned hospital visits.
Common precipitants of medical emergencies in advanced stages of lung cancer include pulmonary embolism, obstructive pneumonia, spinal cord compression caused by metastasis, and tumor progression or pleural effusion leading to respiratory failure.
Lung cancer therapies, such as TKIs, immunotherapy, and cytotoxic chemotherapy, can also cause various medical emergencies arising out of skin reactions, gastrointestinal dysfunction, organ inflammatory processes, and bone marrow suppression.
Identifying drivers of unplanned ED visits
The primary goals of Dr. Shah and Dr. Neal’s study were to understand the drivers of unplanned ED visits and identify potential strategies to prevent them.
Drawing from the Stanford Medicine Research Data Repository, the authors identified 97 NSCLC patients with 173 ED visits at Stanford.
Patients were sorted according to which of the three therapies they had been receiving in the 3 months prior to the unplanned visit – TKIs (n = 47), immunotherapy (n = 24), or chemotherapy (n = 26). Patients receiving a combination of chemotherapy and immunotherapy were classified under the immunotherapy category.
ED visits were divided into four categories: cancer related, therapy related, unrelated to cancer or therapy, and rule-out (when an outpatient provider sent the patient to rule out medico-oncologic emergencies such as pulmonary embolism or cord compression).
If the patient’s main complaint(s) began 2 or more days before presentation, the diagnostics or therapeutics could have been provided in an outpatient setting (e.g., in clinic or urgent care), and the patient was discharged directly from the ED, the encounter was classified as potentially preventable. Among these preventable encounters, those made during business hours were also labeled unnecessary because they could have been managed through the Stanford sick call system for same-day urgent visits.
Leading cause is cancer
Overall, the leading cause of ED visits was NSCLC itself (54%). The patient’s cancer contributed to 61% of ED visits in the TKI group, 49% in the immunotherapy group, and 42% in the chemotherapy group.
Many ED visits were deemed unrelated to cancer or its therapies – 30% in the TKI group, 26% in the immunotherapy group, and 32% in the chemotherapy group.
Rule-out cases contributed to 7% of ED visits in the TKI group, 14% in the immunotherapy group, and 5% in the chemotherapy group.
Overall, 9% of ED visits were therapy related. The smallest proportion of these was observed in the TKI group (2%), which was significantly smaller than in the immunotherapy group (12%), a rate also significantly smaller than in the chemotherapy group (21%, P < .001).
Most unplanned ED visits did not lead to admissions (55%), were for complaints that began 2 or more days prior to presentation (53%), led to diagnostics or therapeutics that could have been administered in an outpatient setting (48%), and were during business hours (52%).
As a result, 24% of visits were classified as preventable, and 10% were deemed unnecessary.
Preventive strategies
“Our study suggests that TKIs lead to fewer emergency room visits than immunotherapy and chemotherapy,” Dr. Shah said in an interview.
“Overall, this may not necessarily change which therapy we prescribe,” he added, “as TKI therapy is often first line for patients with targeted mutations. However, recognizing that those on chemotherapy or immunotherapy are at higher risk for emergency room visits, we may target preventative strategies, for example, nursing phone calls, telemonitoring of symptoms, and frequent video visits toward this high-risk population.”
Dr. Shah and Dr. Neal said it’s “reassuring” that TKIs and immunotherapy are small drivers of unplanned hospital care. However, they also said efforts aimed at reducing chemotherapy-related ED visits are warranted.
The authors speculated that early intervention, extension of ambulatory care, and patient education about outpatient avenues of care could eliminate a significant proportion (at least 20%) of unplanned ED visits by NSCLC patients.
There was no specific funding for this study. Dr. Shah disclosed no conflicts of interest. Dr. Neal disclosed relationships with many companies, including this news organization.
The leading cause of ED visits in the study was the cancer itself, although many visits were unrelated to non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) or cancer therapy.
Less than 10% of ED visits were related to cancer therapy, but visits were much more common among patients receiving chemotherapy than among those receiving immunotherapy or tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs).
Manan P. Shah, MD, and Joel W. Neal, MD, PhD, both of Stanford (Calif. ) University, reported these results in JCO Oncology Practice.
The authors noted that, in the United States, care of patients with cancer, among all diseases, leads to the highest per-person cost. Unplanned hospital visits are among the largest drivers of increased spending in advanced cancer care, accounting for 48% of spending. However, that spending may not be indicative of better quality care, but rather of inefficiency, according to the authors.
One registry spanning 2009-2012 and including more than 400,000 newly diagnosed cancer patients found lung cancer to have the third-highest rate of unplanned hospitalizations (after hepatobiliary and pancreatic cancer). Those findings were published in JCO Oncology Practice in 2018.
While the reason for presentation to the ED is often the cancer or its therapy in this population, there is a paucity of research on the relative contribution of factors leading to unplanned hospital visits.
Common precipitants of medical emergencies in advanced stages of lung cancer include pulmonary embolism, obstructive pneumonia, spinal cord compression caused by metastasis, and tumor progression or pleural effusion leading to respiratory failure.
Lung cancer therapies, such as TKIs, immunotherapy, and cytotoxic chemotherapy, can also cause various medical emergencies arising out of skin reactions, gastrointestinal dysfunction, organ inflammatory processes, and bone marrow suppression.
Identifying drivers of unplanned ED visits
The primary goals of Dr. Shah and Dr. Neal’s study were to understand the drivers of unplanned ED visits and identify potential strategies to prevent them.
Drawing from the Stanford Medicine Research Data Repository, the authors identified 97 NSCLC patients with 173 ED visits at Stanford.
Patients were sorted according to which of the three therapies they had been receiving in the 3 months prior to the unplanned visit – TKIs (n = 47), immunotherapy (n = 24), or chemotherapy (n = 26). Patients receiving a combination of chemotherapy and immunotherapy were classified under the immunotherapy category.
ED visits were divided into four categories: cancer related, therapy related, unrelated to cancer or therapy, and rule-out (when an outpatient provider sent the patient to rule out medico-oncologic emergencies such as pulmonary embolism or cord compression).
If the patient’s main complaint(s) began 2 or more days before presentation, the diagnostics or therapeutics could have been provided in an outpatient setting (e.g., in clinic or urgent care), and the patient was discharged directly from the ED, the encounter was classified as potentially preventable. Among these preventable encounters, those made during business hours were also labeled unnecessary because they could have been managed through the Stanford sick call system for same-day urgent visits.
Leading cause is cancer
Overall, the leading cause of ED visits was NSCLC itself (54%). The patient’s cancer contributed to 61% of ED visits in the TKI group, 49% in the immunotherapy group, and 42% in the chemotherapy group.
Many ED visits were deemed unrelated to cancer or its therapies – 30% in the TKI group, 26% in the immunotherapy group, and 32% in the chemotherapy group.
Rule-out cases contributed to 7% of ED visits in the TKI group, 14% in the immunotherapy group, and 5% in the chemotherapy group.
Overall, 9% of ED visits were therapy related. The smallest proportion of these was observed in the TKI group (2%), which was significantly smaller than in the immunotherapy group (12%), a rate also significantly smaller than in the chemotherapy group (21%, P < .001).
Most unplanned ED visits did not lead to admissions (55%), were for complaints that began 2 or more days prior to presentation (53%), led to diagnostics or therapeutics that could have been administered in an outpatient setting (48%), and were during business hours (52%).
As a result, 24% of visits were classified as preventable, and 10% were deemed unnecessary.
Preventive strategies
“Our study suggests that TKIs lead to fewer emergency room visits than immunotherapy and chemotherapy,” Dr. Shah said in an interview.
“Overall, this may not necessarily change which therapy we prescribe,” he added, “as TKI therapy is often first line for patients with targeted mutations. However, recognizing that those on chemotherapy or immunotherapy are at higher risk for emergency room visits, we may target preventative strategies, for example, nursing phone calls, telemonitoring of symptoms, and frequent video visits toward this high-risk population.”
Dr. Shah and Dr. Neal said it’s “reassuring” that TKIs and immunotherapy are small drivers of unplanned hospital care. However, they also said efforts aimed at reducing chemotherapy-related ED visits are warranted.
The authors speculated that early intervention, extension of ambulatory care, and patient education about outpatient avenues of care could eliminate a significant proportion (at least 20%) of unplanned ED visits by NSCLC patients.
There was no specific funding for this study. Dr. Shah disclosed no conflicts of interest. Dr. Neal disclosed relationships with many companies, including this news organization.
The leading cause of ED visits in the study was the cancer itself, although many visits were unrelated to non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) or cancer therapy.
Less than 10% of ED visits were related to cancer therapy, but visits were much more common among patients receiving chemotherapy than among those receiving immunotherapy or tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs).
Manan P. Shah, MD, and Joel W. Neal, MD, PhD, both of Stanford (Calif. ) University, reported these results in JCO Oncology Practice.
The authors noted that, in the United States, care of patients with cancer, among all diseases, leads to the highest per-person cost. Unplanned hospital visits are among the largest drivers of increased spending in advanced cancer care, accounting for 48% of spending. However, that spending may not be indicative of better quality care, but rather of inefficiency, according to the authors.
One registry spanning 2009-2012 and including more than 400,000 newly diagnosed cancer patients found lung cancer to have the third-highest rate of unplanned hospitalizations (after hepatobiliary and pancreatic cancer). Those findings were published in JCO Oncology Practice in 2018.
While the reason for presentation to the ED is often the cancer or its therapy in this population, there is a paucity of research on the relative contribution of factors leading to unplanned hospital visits.
Common precipitants of medical emergencies in advanced stages of lung cancer include pulmonary embolism, obstructive pneumonia, spinal cord compression caused by metastasis, and tumor progression or pleural effusion leading to respiratory failure.
Lung cancer therapies, such as TKIs, immunotherapy, and cytotoxic chemotherapy, can also cause various medical emergencies arising out of skin reactions, gastrointestinal dysfunction, organ inflammatory processes, and bone marrow suppression.
Identifying drivers of unplanned ED visits
The primary goals of Dr. Shah and Dr. Neal’s study were to understand the drivers of unplanned ED visits and identify potential strategies to prevent them.
Drawing from the Stanford Medicine Research Data Repository, the authors identified 97 NSCLC patients with 173 ED visits at Stanford.
Patients were sorted according to which of the three therapies they had been receiving in the 3 months prior to the unplanned visit – TKIs (n = 47), immunotherapy (n = 24), or chemotherapy (n = 26). Patients receiving a combination of chemotherapy and immunotherapy were classified under the immunotherapy category.
ED visits were divided into four categories: cancer related, therapy related, unrelated to cancer or therapy, and rule-out (when an outpatient provider sent the patient to rule out medico-oncologic emergencies such as pulmonary embolism or cord compression).
If the patient’s main complaint(s) began 2 or more days before presentation, the diagnostics or therapeutics could have been provided in an outpatient setting (e.g., in clinic or urgent care), and the patient was discharged directly from the ED, the encounter was classified as potentially preventable. Among these preventable encounters, those made during business hours were also labeled unnecessary because they could have been managed through the Stanford sick call system for same-day urgent visits.
Leading cause is cancer
Overall, the leading cause of ED visits was NSCLC itself (54%). The patient’s cancer contributed to 61% of ED visits in the TKI group, 49% in the immunotherapy group, and 42% in the chemotherapy group.
Many ED visits were deemed unrelated to cancer or its therapies – 30% in the TKI group, 26% in the immunotherapy group, and 32% in the chemotherapy group.
Rule-out cases contributed to 7% of ED visits in the TKI group, 14% in the immunotherapy group, and 5% in the chemotherapy group.
Overall, 9% of ED visits were therapy related. The smallest proportion of these was observed in the TKI group (2%), which was significantly smaller than in the immunotherapy group (12%), a rate also significantly smaller than in the chemotherapy group (21%, P < .001).
Most unplanned ED visits did not lead to admissions (55%), were for complaints that began 2 or more days prior to presentation (53%), led to diagnostics or therapeutics that could have been administered in an outpatient setting (48%), and were during business hours (52%).
As a result, 24% of visits were classified as preventable, and 10% were deemed unnecessary.
Preventive strategies
“Our study suggests that TKIs lead to fewer emergency room visits than immunotherapy and chemotherapy,” Dr. Shah said in an interview.
“Overall, this may not necessarily change which therapy we prescribe,” he added, “as TKI therapy is often first line for patients with targeted mutations. However, recognizing that those on chemotherapy or immunotherapy are at higher risk for emergency room visits, we may target preventative strategies, for example, nursing phone calls, telemonitoring of symptoms, and frequent video visits toward this high-risk population.”
Dr. Shah and Dr. Neal said it’s “reassuring” that TKIs and immunotherapy are small drivers of unplanned hospital care. However, they also said efforts aimed at reducing chemotherapy-related ED visits are warranted.
The authors speculated that early intervention, extension of ambulatory care, and patient education about outpatient avenues of care could eliminate a significant proportion (at least 20%) of unplanned ED visits by NSCLC patients.
There was no specific funding for this study. Dr. Shah disclosed no conflicts of interest. Dr. Neal disclosed relationships with many companies, including this news organization.
FROM JCO ONCOLOGY PRACTICE
Swedish registry study finds atopic dermatitis significantly associated with autoimmune diseases
in a case control study derived from Swedish national health care registry data.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is known to be associated with other atopic conditions, and there is increasing evidence it is associated with some nonatopic conditions, including some cancers, cardiovascular disease, and neuropsychiatric disorders, according to Lina U. Ivert, MD, of the dermatology and venereology unit at the Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, and coauthors. There are also some data indicating that autoimmune diseases, particularly those involving the skin and gastrointestinal tract, are more common in people with AD.
The aim of their study, published in the British Journal of Dermatology, was to investigate a wide spectrum of autoimmune diseases for associations with AD in a large-scale, population-based study using Swedish registers. Findings could lead to better monitoring of comorbidities and deeper understanding of disease burden and AD pathophysiology, they noted.
Large-scale study
With data from the Swedish Board of Health and Welfare’s National Patient Register on inpatient diagnoses since 1964 and specialist outpatient visits since 2001, the investigators included all patients aged 15 years and older with AD diagnoses (104,832) and matched them with controls from the general population (1,022,435). The authors noted that the large number of people included in the analysis allowed for robust estimates, and underscored that 80% of the AD patients included had received their diagnosis in a dermatology department, which reduces the risk of misclassification.
Association with autoimmune disease
The investigators found an association between AD and autoimmune disease, with an adjusted odds ratio) of 1.97 (95% confidence interval, 1.93-2.01). The association was present with several organ systems, particularly the skin and gastrointestinal tract, and with connective tissue diseases. The strongest associations with autoimmune skin diseases were found for dermatitis herpetiformis (aOR, 9.76; 95% CI, 8.10-11.8), alopecia areata (aOR, 5.11; 95% CI, 4.75-5.49), and chronic urticaria (aOR, 4.82; 95% CI, 4.48-5.19).
AD was associated with gastrointestinal diseases, including celiac disease (aOR, 1.96; 95% CI, 1.84-2.09), Crohn disease (aOR 1.83; CI, 1.71-1.96), and ulcerative colitis (aOR 1.58; 95% CI, 1.49-1.68).
Connective tissue diseases significantly associated with AD included systemic lupus erythematosus (aOR, 1.65; 95% CI, 1.42-1.90), ankylosing spondylitis (aOR, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.29-1.66), and RA (aOR, 1.44; 95% CI,1.34-1.54]). Hematologic or hepatic autoimmune disease associations with AD were not observed.
Stronger association with multiple diseases
The association between AD and two or more autoimmune diseases was significantly stronger than the association between AD and having one autoimmune disease. For example, the OR for AD among people with three to five autoimmune diseases was 3.33 (95% CI, 2.86-3.87), and was stronger in men (OR, 3.96; 95% CI, 2.92-5.37) than in women (OR, 3.14; 95% CI, 2.63-3.74).
Sex differences
In the study overall, the association with AD and autoimmune diseases was stronger in men (aOR, 2.18; 95% CI, 2.10-2.25), compared with women (aOR, 1.89; 95% CI, 1.85-1.93), but this “sex difference was only statistically significant between AD and RA and between AD and Celiac disease,” they noted.
Associations between AD and dermatomyositis, systemic scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus, Hashimoto’s disease, Graves disease, multiple sclerosis, and polymyalgia rheumatica were found only in women. Dr. Ivert and coauthors observed that “women are in general more likely to develop autoimmune diseases, and 80% of patients with autoimmune diseases are women.”
Provocative questions
Commenting on the findings, Jonathan Silverberg, MD, PhD, MPH, associate professor of dermatology, George Washington University, Washington, said, “At a high level, it is important for clinicians to recognize that atopic dermatitis is a systemic immune-mediated disease. AD is associated with higher rates of comorbid autoimmune disease, similar to psoriasis and other chronic inflammatory skin diseases.”
“At this point, there is nothing immediately actionable about these results,” noted Dr. Silverberg, who was not an author of this study. “That said, in my mind, they raise some provocative questions: What is the difference between AD in adults who do versus those who do not get comorbid autoimmune disease? Does AD then present differently? Does it respond to the same therapies? These will have to be the subject of future research.”
The study was funded by the Swedish Asthma and Allergy Association Research Foundation, Hudfonden (the Welander-Finsen Foundation), and the Swedish Society for Dermatology and Venereology. The authors disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Ivert LU et al. Br J Dermatol. 2020 Oct 22. doi: 10.1111/bjd.19624.
in a case control study derived from Swedish national health care registry data.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is known to be associated with other atopic conditions, and there is increasing evidence it is associated with some nonatopic conditions, including some cancers, cardiovascular disease, and neuropsychiatric disorders, according to Lina U. Ivert, MD, of the dermatology and venereology unit at the Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, and coauthors. There are also some data indicating that autoimmune diseases, particularly those involving the skin and gastrointestinal tract, are more common in people with AD.
The aim of their study, published in the British Journal of Dermatology, was to investigate a wide spectrum of autoimmune diseases for associations with AD in a large-scale, population-based study using Swedish registers. Findings could lead to better monitoring of comorbidities and deeper understanding of disease burden and AD pathophysiology, they noted.
Large-scale study
With data from the Swedish Board of Health and Welfare’s National Patient Register on inpatient diagnoses since 1964 and specialist outpatient visits since 2001, the investigators included all patients aged 15 years and older with AD diagnoses (104,832) and matched them with controls from the general population (1,022,435). The authors noted that the large number of people included in the analysis allowed for robust estimates, and underscored that 80% of the AD patients included had received their diagnosis in a dermatology department, which reduces the risk of misclassification.
Association with autoimmune disease
The investigators found an association between AD and autoimmune disease, with an adjusted odds ratio) of 1.97 (95% confidence interval, 1.93-2.01). The association was present with several organ systems, particularly the skin and gastrointestinal tract, and with connective tissue diseases. The strongest associations with autoimmune skin diseases were found for dermatitis herpetiformis (aOR, 9.76; 95% CI, 8.10-11.8), alopecia areata (aOR, 5.11; 95% CI, 4.75-5.49), and chronic urticaria (aOR, 4.82; 95% CI, 4.48-5.19).
AD was associated with gastrointestinal diseases, including celiac disease (aOR, 1.96; 95% CI, 1.84-2.09), Crohn disease (aOR 1.83; CI, 1.71-1.96), and ulcerative colitis (aOR 1.58; 95% CI, 1.49-1.68).
Connective tissue diseases significantly associated with AD included systemic lupus erythematosus (aOR, 1.65; 95% CI, 1.42-1.90), ankylosing spondylitis (aOR, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.29-1.66), and RA (aOR, 1.44; 95% CI,1.34-1.54]). Hematologic or hepatic autoimmune disease associations with AD were not observed.
Stronger association with multiple diseases
The association between AD and two or more autoimmune diseases was significantly stronger than the association between AD and having one autoimmune disease. For example, the OR for AD among people with three to five autoimmune diseases was 3.33 (95% CI, 2.86-3.87), and was stronger in men (OR, 3.96; 95% CI, 2.92-5.37) than in women (OR, 3.14; 95% CI, 2.63-3.74).
Sex differences
In the study overall, the association with AD and autoimmune diseases was stronger in men (aOR, 2.18; 95% CI, 2.10-2.25), compared with women (aOR, 1.89; 95% CI, 1.85-1.93), but this “sex difference was only statistically significant between AD and RA and between AD and Celiac disease,” they noted.
Associations between AD and dermatomyositis, systemic scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus, Hashimoto’s disease, Graves disease, multiple sclerosis, and polymyalgia rheumatica were found only in women. Dr. Ivert and coauthors observed that “women are in general more likely to develop autoimmune diseases, and 80% of patients with autoimmune diseases are women.”
Provocative questions
Commenting on the findings, Jonathan Silverberg, MD, PhD, MPH, associate professor of dermatology, George Washington University, Washington, said, “At a high level, it is important for clinicians to recognize that atopic dermatitis is a systemic immune-mediated disease. AD is associated with higher rates of comorbid autoimmune disease, similar to psoriasis and other chronic inflammatory skin diseases.”
“At this point, there is nothing immediately actionable about these results,” noted Dr. Silverberg, who was not an author of this study. “That said, in my mind, they raise some provocative questions: What is the difference between AD in adults who do versus those who do not get comorbid autoimmune disease? Does AD then present differently? Does it respond to the same therapies? These will have to be the subject of future research.”
The study was funded by the Swedish Asthma and Allergy Association Research Foundation, Hudfonden (the Welander-Finsen Foundation), and the Swedish Society for Dermatology and Venereology. The authors disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Ivert LU et al. Br J Dermatol. 2020 Oct 22. doi: 10.1111/bjd.19624.
in a case control study derived from Swedish national health care registry data.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is known to be associated with other atopic conditions, and there is increasing evidence it is associated with some nonatopic conditions, including some cancers, cardiovascular disease, and neuropsychiatric disorders, according to Lina U. Ivert, MD, of the dermatology and venereology unit at the Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, and coauthors. There are also some data indicating that autoimmune diseases, particularly those involving the skin and gastrointestinal tract, are more common in people with AD.
The aim of their study, published in the British Journal of Dermatology, was to investigate a wide spectrum of autoimmune diseases for associations with AD in a large-scale, population-based study using Swedish registers. Findings could lead to better monitoring of comorbidities and deeper understanding of disease burden and AD pathophysiology, they noted.
Large-scale study
With data from the Swedish Board of Health and Welfare’s National Patient Register on inpatient diagnoses since 1964 and specialist outpatient visits since 2001, the investigators included all patients aged 15 years and older with AD diagnoses (104,832) and matched them with controls from the general population (1,022,435). The authors noted that the large number of people included in the analysis allowed for robust estimates, and underscored that 80% of the AD patients included had received their diagnosis in a dermatology department, which reduces the risk of misclassification.
Association with autoimmune disease
The investigators found an association between AD and autoimmune disease, with an adjusted odds ratio) of 1.97 (95% confidence interval, 1.93-2.01). The association was present with several organ systems, particularly the skin and gastrointestinal tract, and with connective tissue diseases. The strongest associations with autoimmune skin diseases were found for dermatitis herpetiformis (aOR, 9.76; 95% CI, 8.10-11.8), alopecia areata (aOR, 5.11; 95% CI, 4.75-5.49), and chronic urticaria (aOR, 4.82; 95% CI, 4.48-5.19).
AD was associated with gastrointestinal diseases, including celiac disease (aOR, 1.96; 95% CI, 1.84-2.09), Crohn disease (aOR 1.83; CI, 1.71-1.96), and ulcerative colitis (aOR 1.58; 95% CI, 1.49-1.68).
Connective tissue diseases significantly associated with AD included systemic lupus erythematosus (aOR, 1.65; 95% CI, 1.42-1.90), ankylosing spondylitis (aOR, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.29-1.66), and RA (aOR, 1.44; 95% CI,1.34-1.54]). Hematologic or hepatic autoimmune disease associations with AD were not observed.
Stronger association with multiple diseases
The association between AD and two or more autoimmune diseases was significantly stronger than the association between AD and having one autoimmune disease. For example, the OR for AD among people with three to five autoimmune diseases was 3.33 (95% CI, 2.86-3.87), and was stronger in men (OR, 3.96; 95% CI, 2.92-5.37) than in women (OR, 3.14; 95% CI, 2.63-3.74).
Sex differences
In the study overall, the association with AD and autoimmune diseases was stronger in men (aOR, 2.18; 95% CI, 2.10-2.25), compared with women (aOR, 1.89; 95% CI, 1.85-1.93), but this “sex difference was only statistically significant between AD and RA and between AD and Celiac disease,” they noted.
Associations between AD and dermatomyositis, systemic scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus, Hashimoto’s disease, Graves disease, multiple sclerosis, and polymyalgia rheumatica were found only in women. Dr. Ivert and coauthors observed that “women are in general more likely to develop autoimmune diseases, and 80% of patients with autoimmune diseases are women.”
Provocative questions
Commenting on the findings, Jonathan Silverberg, MD, PhD, MPH, associate professor of dermatology, George Washington University, Washington, said, “At a high level, it is important for clinicians to recognize that atopic dermatitis is a systemic immune-mediated disease. AD is associated with higher rates of comorbid autoimmune disease, similar to psoriasis and other chronic inflammatory skin diseases.”
“At this point, there is nothing immediately actionable about these results,” noted Dr. Silverberg, who was not an author of this study. “That said, in my mind, they raise some provocative questions: What is the difference between AD in adults who do versus those who do not get comorbid autoimmune disease? Does AD then present differently? Does it respond to the same therapies? These will have to be the subject of future research.”
The study was funded by the Swedish Asthma and Allergy Association Research Foundation, Hudfonden (the Welander-Finsen Foundation), and the Swedish Society for Dermatology and Venereology. The authors disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Ivert LU et al. Br J Dermatol. 2020 Oct 22. doi: 10.1111/bjd.19624.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF DERMATOLOGY
In high-risk first relapse ALL, blinatumomab seen superior to consolidation chemo
Blinatumomab was superior to high-risk consolidation (HC) 3 chemotherapy in a phase 3 clinical trial among children with high-risk first-relapse acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), according to Franco Locatelli, MD, PhD, Ospedale Pediatrico Bambino Gesú and Sapienza, Rome.
Blinatumomab constitutes a new standard of care because of superior event-free survival (EFS) and other comparative benefits, including fewer and less severe toxicities, he said in a presentation at theannual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, which was held virtually.
About 15% of children with B-cell precursor (BCP) ALL relapse after standard treatment. Prognosis depends largely on time from diagnosis to relapse and the site of relapse. After relapse, when a second morphological complete remission (M1 marrow) is achieved, most are candidates for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (alloHSCT), Dr. Locatelli noted. Immuno-oncotherapy with blinatumomab, a bispecific T-cell–engager molecule, has been shown to be efficacious in children with relapsed/refractory BCP-ALL.
In the open-label, controlled trial, investigators randomized children with M1 (<5% blasts) or M2 (<25% and 5% or greater blasts) marrow 1:1 after induction therapy and cycles of HC1 and HC2 chemotherapy to a third consolidation course with blinatumomab (15 µg/m2/day for 4 weeks) or HC3 (dexamethasone, vincristine, daunorubicin, methotrexate, ifosfamide, PEG-asparaginase); intrathecal chemotherapy (methotrexate/cytarabine/prednisolone) was administered before treatment. Patients achieving a second complete morphological remission (M1 marrow) after blinatumomab or HC3 proceeded to alloHSCT. EFS was the primary endpoint (from randomization until relapse date or M2 marrow after a complete response [CR], failure to achieve CR at end of treatment, second malignancy, or death from any cause).
Investigators had enrolled 108 (54 received HC3; 54 received blinatumomab) out of a target of about 202 patients when the data-monitoring committee recommended termination because of blinatumomab benefit observed at the first interim analysis. Median age was around 5.5 years (1-17), with the mean time from first diagnosis to relapse at approximately 22 months.
Dr. Locatelli reported events for 18/54 (33.3%) in the blinatumomab arm and 31/54 (57.4%) in the HC3 arm, with a median EFS of “not reached” and 7.4 months, respectively. The risk of relapse with blinatumomab was reduced by 64% versus HC3 (hazard ratio, 0.36; 95% confidence interval, 0.19-0.66, P < .001). Overall survival (OS) favored blinatumomab over HC3, as well, with a hazard ratio of 0.43 (95% CI, 0.18-1.01). Minimal residual disease (MRD) remission (MRD < 10-4) was seen in 43/46 (93.5%) blinatumomab-randomized and 25/46 (54.3%) HC3-randomized patients.
Relapses occurred more often in the HC3 group (blinatumomab 13, 24%; HC3 29, 54%) overall, and at each of the assessments at 6 months, 12 months, and 24 months. Also, MRD remissions by PCR (polymerase chain reaction) were superior in the blinatumomab arm overall (90% versus 54%) and according to baseline MRD status with strikingly divergent rates in those with MRD greater than or equal to 104 at baseline (93% blinatumomab/24% HC3). Rates were relatively similar in patients with MRD less than 104 at baseline (85% blinatumomab/87% HC3).
Grade 3 or greater treatment-emergent adverse events were reported by 30/53 (57%) and 41/51 (80%) patients in the blinatumomab and HC3 groups, respectively, with several markedly lower in the blinatumomab group (neutropenia/neutrophil count decrease 17 versus 31; anemia 15 versus 41; febrile neutropenia 4 versus 26). As expected, grade 3 or greater neurologic events occurred more frequently with blinatumomab than with HC3 (48% versus 29%); no grade 3 or greater cytokine release syndrome events were reported.
Tallying the blinatumomab benefits (superior EFS and MRD negativity prior to alloHSCT, improved OS, fewer relapses, fewer and less severe toxicities), Dr. Locatelli concluded, “Blinatumomab constitutes a new standard of care in children with high-risk first-relapse ALL.”
In the postpresentation discussion, Dr. Locatelli underscored the blinatumomab benefit versus a third course of chemotherapy: “Monotherapy with blinatumomab was able to present a higher proportion of patients in CR2 who could proceed to transplant.”
Dr. Locatelli disclosed relationships with multiple companies.
SOURCE: Locatelli F et al. ASH 2020, Abstract 268.
Blinatumomab was superior to high-risk consolidation (HC) 3 chemotherapy in a phase 3 clinical trial among children with high-risk first-relapse acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), according to Franco Locatelli, MD, PhD, Ospedale Pediatrico Bambino Gesú and Sapienza, Rome.
Blinatumomab constitutes a new standard of care because of superior event-free survival (EFS) and other comparative benefits, including fewer and less severe toxicities, he said in a presentation at theannual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, which was held virtually.
About 15% of children with B-cell precursor (BCP) ALL relapse after standard treatment. Prognosis depends largely on time from diagnosis to relapse and the site of relapse. After relapse, when a second morphological complete remission (M1 marrow) is achieved, most are candidates for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (alloHSCT), Dr. Locatelli noted. Immuno-oncotherapy with blinatumomab, a bispecific T-cell–engager molecule, has been shown to be efficacious in children with relapsed/refractory BCP-ALL.
In the open-label, controlled trial, investigators randomized children with M1 (<5% blasts) or M2 (<25% and 5% or greater blasts) marrow 1:1 after induction therapy and cycles of HC1 and HC2 chemotherapy to a third consolidation course with blinatumomab (15 µg/m2/day for 4 weeks) or HC3 (dexamethasone, vincristine, daunorubicin, methotrexate, ifosfamide, PEG-asparaginase); intrathecal chemotherapy (methotrexate/cytarabine/prednisolone) was administered before treatment. Patients achieving a second complete morphological remission (M1 marrow) after blinatumomab or HC3 proceeded to alloHSCT. EFS was the primary endpoint (from randomization until relapse date or M2 marrow after a complete response [CR], failure to achieve CR at end of treatment, second malignancy, or death from any cause).
Investigators had enrolled 108 (54 received HC3; 54 received blinatumomab) out of a target of about 202 patients when the data-monitoring committee recommended termination because of blinatumomab benefit observed at the first interim analysis. Median age was around 5.5 years (1-17), with the mean time from first diagnosis to relapse at approximately 22 months.
Dr. Locatelli reported events for 18/54 (33.3%) in the blinatumomab arm and 31/54 (57.4%) in the HC3 arm, with a median EFS of “not reached” and 7.4 months, respectively. The risk of relapse with blinatumomab was reduced by 64% versus HC3 (hazard ratio, 0.36; 95% confidence interval, 0.19-0.66, P < .001). Overall survival (OS) favored blinatumomab over HC3, as well, with a hazard ratio of 0.43 (95% CI, 0.18-1.01). Minimal residual disease (MRD) remission (MRD < 10-4) was seen in 43/46 (93.5%) blinatumomab-randomized and 25/46 (54.3%) HC3-randomized patients.
Relapses occurred more often in the HC3 group (blinatumomab 13, 24%; HC3 29, 54%) overall, and at each of the assessments at 6 months, 12 months, and 24 months. Also, MRD remissions by PCR (polymerase chain reaction) were superior in the blinatumomab arm overall (90% versus 54%) and according to baseline MRD status with strikingly divergent rates in those with MRD greater than or equal to 104 at baseline (93% blinatumomab/24% HC3). Rates were relatively similar in patients with MRD less than 104 at baseline (85% blinatumomab/87% HC3).
Grade 3 or greater treatment-emergent adverse events were reported by 30/53 (57%) and 41/51 (80%) patients in the blinatumomab and HC3 groups, respectively, with several markedly lower in the blinatumomab group (neutropenia/neutrophil count decrease 17 versus 31; anemia 15 versus 41; febrile neutropenia 4 versus 26). As expected, grade 3 or greater neurologic events occurred more frequently with blinatumomab than with HC3 (48% versus 29%); no grade 3 or greater cytokine release syndrome events were reported.
Tallying the blinatumomab benefits (superior EFS and MRD negativity prior to alloHSCT, improved OS, fewer relapses, fewer and less severe toxicities), Dr. Locatelli concluded, “Blinatumomab constitutes a new standard of care in children with high-risk first-relapse ALL.”
In the postpresentation discussion, Dr. Locatelli underscored the blinatumomab benefit versus a third course of chemotherapy: “Monotherapy with blinatumomab was able to present a higher proportion of patients in CR2 who could proceed to transplant.”
Dr. Locatelli disclosed relationships with multiple companies.
SOURCE: Locatelli F et al. ASH 2020, Abstract 268.
Blinatumomab was superior to high-risk consolidation (HC) 3 chemotherapy in a phase 3 clinical trial among children with high-risk first-relapse acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), according to Franco Locatelli, MD, PhD, Ospedale Pediatrico Bambino Gesú and Sapienza, Rome.
Blinatumomab constitutes a new standard of care because of superior event-free survival (EFS) and other comparative benefits, including fewer and less severe toxicities, he said in a presentation at theannual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, which was held virtually.
About 15% of children with B-cell precursor (BCP) ALL relapse after standard treatment. Prognosis depends largely on time from diagnosis to relapse and the site of relapse. After relapse, when a second morphological complete remission (M1 marrow) is achieved, most are candidates for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (alloHSCT), Dr. Locatelli noted. Immuno-oncotherapy with blinatumomab, a bispecific T-cell–engager molecule, has been shown to be efficacious in children with relapsed/refractory BCP-ALL.
In the open-label, controlled trial, investigators randomized children with M1 (<5% blasts) or M2 (<25% and 5% or greater blasts) marrow 1:1 after induction therapy and cycles of HC1 and HC2 chemotherapy to a third consolidation course with blinatumomab (15 µg/m2/day for 4 weeks) or HC3 (dexamethasone, vincristine, daunorubicin, methotrexate, ifosfamide, PEG-asparaginase); intrathecal chemotherapy (methotrexate/cytarabine/prednisolone) was administered before treatment. Patients achieving a second complete morphological remission (M1 marrow) after blinatumomab or HC3 proceeded to alloHSCT. EFS was the primary endpoint (from randomization until relapse date or M2 marrow after a complete response [CR], failure to achieve CR at end of treatment, second malignancy, or death from any cause).
Investigators had enrolled 108 (54 received HC3; 54 received blinatumomab) out of a target of about 202 patients when the data-monitoring committee recommended termination because of blinatumomab benefit observed at the first interim analysis. Median age was around 5.5 years (1-17), with the mean time from first diagnosis to relapse at approximately 22 months.
Dr. Locatelli reported events for 18/54 (33.3%) in the blinatumomab arm and 31/54 (57.4%) in the HC3 arm, with a median EFS of “not reached” and 7.4 months, respectively. The risk of relapse with blinatumomab was reduced by 64% versus HC3 (hazard ratio, 0.36; 95% confidence interval, 0.19-0.66, P < .001). Overall survival (OS) favored blinatumomab over HC3, as well, with a hazard ratio of 0.43 (95% CI, 0.18-1.01). Minimal residual disease (MRD) remission (MRD < 10-4) was seen in 43/46 (93.5%) blinatumomab-randomized and 25/46 (54.3%) HC3-randomized patients.
Relapses occurred more often in the HC3 group (blinatumomab 13, 24%; HC3 29, 54%) overall, and at each of the assessments at 6 months, 12 months, and 24 months. Also, MRD remissions by PCR (polymerase chain reaction) were superior in the blinatumomab arm overall (90% versus 54%) and according to baseline MRD status with strikingly divergent rates in those with MRD greater than or equal to 104 at baseline (93% blinatumomab/24% HC3). Rates were relatively similar in patients with MRD less than 104 at baseline (85% blinatumomab/87% HC3).
Grade 3 or greater treatment-emergent adverse events were reported by 30/53 (57%) and 41/51 (80%) patients in the blinatumomab and HC3 groups, respectively, with several markedly lower in the blinatumomab group (neutropenia/neutrophil count decrease 17 versus 31; anemia 15 versus 41; febrile neutropenia 4 versus 26). As expected, grade 3 or greater neurologic events occurred more frequently with blinatumomab than with HC3 (48% versus 29%); no grade 3 or greater cytokine release syndrome events were reported.
Tallying the blinatumomab benefits (superior EFS and MRD negativity prior to alloHSCT, improved OS, fewer relapses, fewer and less severe toxicities), Dr. Locatelli concluded, “Blinatumomab constitutes a new standard of care in children with high-risk first-relapse ALL.”
In the postpresentation discussion, Dr. Locatelli underscored the blinatumomab benefit versus a third course of chemotherapy: “Monotherapy with blinatumomab was able to present a higher proportion of patients in CR2 who could proceed to transplant.”
Dr. Locatelli disclosed relationships with multiple companies.
SOURCE: Locatelli F et al. ASH 2020, Abstract 268.
FROM ASH 2020