User login
EMERGENCY MEDICINE is a practical, peer-reviewed monthly publication and Web site that meets the educational needs of emergency clinicians and urgent care clinicians for their practice.
Urgent recall for Penumbra JET 7 Xtra Flex reperfusion catheters
“All users should stop using this device, and facilities should remove these devices from inventory,” the recall notice, posted on the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website, advises.
The recall covers the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter, which was cleared for use in June 2019, and the JET 7MAX configuration (which includes the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter and MAX delivery device), which was cleared in February of this year.
The recall does not apply to the Penumbra JET 7 reperfusion catheter with standard tip.
The FDA says it has received over 200 medical device reports (MDRs) associated with the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter, including reports of deaths, serious injuries, and malfunctions.
Twenty of these MDRs describe 14 unique patient deaths. Other MDRs describe serious patient injury, such as vessel damage, hemorrhage, and cerebral infarction.
Device malfunctions described in the reports include ballooning, expansion, rupture, breakage or complete separation, and exposure of internal support coils near the distal tip region of the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter.
According to the FDA, bench testing by the manufacturer, in which the catheter distal tip is plugged and pressurized to failure, indicates that the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter is not able to withstand the same burst pressures to failure as the manufacturer’s other large-bore aspiration catheters used to remove thrombus for patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Penumbra’s urgent medical device recall letter advises health care providers and facilities to remove and quarantine all unused devices covered by this recall, to complete the product identification and return form, and to return all products to Penumbra in accordance with instructions provided.
For questions regarding this recall, contact Penumbra customer service by phone at 888-272-4606 or by email at [email protected].
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“All users should stop using this device, and facilities should remove these devices from inventory,” the recall notice, posted on the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website, advises.
The recall covers the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter, which was cleared for use in June 2019, and the JET 7MAX configuration (which includes the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter and MAX delivery device), which was cleared in February of this year.
The recall does not apply to the Penumbra JET 7 reperfusion catheter with standard tip.
The FDA says it has received over 200 medical device reports (MDRs) associated with the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter, including reports of deaths, serious injuries, and malfunctions.
Twenty of these MDRs describe 14 unique patient deaths. Other MDRs describe serious patient injury, such as vessel damage, hemorrhage, and cerebral infarction.
Device malfunctions described in the reports include ballooning, expansion, rupture, breakage or complete separation, and exposure of internal support coils near the distal tip region of the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter.
According to the FDA, bench testing by the manufacturer, in which the catheter distal tip is plugged and pressurized to failure, indicates that the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter is not able to withstand the same burst pressures to failure as the manufacturer’s other large-bore aspiration catheters used to remove thrombus for patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Penumbra’s urgent medical device recall letter advises health care providers and facilities to remove and quarantine all unused devices covered by this recall, to complete the product identification and return form, and to return all products to Penumbra in accordance with instructions provided.
For questions regarding this recall, contact Penumbra customer service by phone at 888-272-4606 or by email at [email protected].
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“All users should stop using this device, and facilities should remove these devices from inventory,” the recall notice, posted on the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website, advises.
The recall covers the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter, which was cleared for use in June 2019, and the JET 7MAX configuration (which includes the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter and MAX delivery device), which was cleared in February of this year.
The recall does not apply to the Penumbra JET 7 reperfusion catheter with standard tip.
The FDA says it has received over 200 medical device reports (MDRs) associated with the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter, including reports of deaths, serious injuries, and malfunctions.
Twenty of these MDRs describe 14 unique patient deaths. Other MDRs describe serious patient injury, such as vessel damage, hemorrhage, and cerebral infarction.
Device malfunctions described in the reports include ballooning, expansion, rupture, breakage or complete separation, and exposure of internal support coils near the distal tip region of the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter.
According to the FDA, bench testing by the manufacturer, in which the catheter distal tip is plugged and pressurized to failure, indicates that the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter is not able to withstand the same burst pressures to failure as the manufacturer’s other large-bore aspiration catheters used to remove thrombus for patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Penumbra’s urgent medical device recall letter advises health care providers and facilities to remove and quarantine all unused devices covered by this recall, to complete the product identification and return form, and to return all products to Penumbra in accordance with instructions provided.
For questions regarding this recall, contact Penumbra customer service by phone at 888-272-4606 or by email at [email protected].
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sac/val heart failure benefit extends to diabetes patients
The beneficial effects of sacubitril/valsartan on reverse cardiac remodeling in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction have been well established, but those benefits haven’t been as clearly demonstrated to carry over to HFrEF patients who also have type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Now, a post-hoc analysis of a pivotal clinical trial reports that those benefits do extend to patients with HFrEF and T2DM.
“It’s really not about a Sophie’s choice of whether you give this or that drug in these patients,” said corresponding author Javed Butler, MD, MPH, MBA. “We really ought to be giving all of these drugs – the angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitors (ARNIs) and sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors – to our patients for the best outcomes.”
The post-hoc analysis, published in JACC: Heart Failure, evaluated 361 patients with T2DM who were enrolled in the PROVE-HF trial of sac/val therapy for HF, published in JAMA.
PROVE-HF evaluated biomarkers, myocardial remodeling, and outcomes through a year of treatment with sac/val. The primary endpoint was the level of changes in natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) concentrations, left-ventricle ejection fraction (LVEF) and overall Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ)-23 scores through 12 months of treatment.
The post hoc study reported that baseline NT-proBNP concentrations were higher in the DM patients (854 pg/mL vs. 706 pg/mL), but at 12 months those levels were 513 and 441 pg/mL, respectively.
LVEF changed similarly from baseline to 12 months in both groups: from 28.3% to 37% in the DM patients and from 28.1% to 38.34% in non-DM patients. Overall KCCQ-23 scores improved similarly in both groups, but longitudinal analyses found modestly higher gains in the T2DM group, 9.3 vs. 8.6 points (P = .07).
“The real reason I wanted to do this study is that I’m a huge fan of all the SGLT-2 inhibitors, and I’m very involved in those trials, and there is right now so much momentum behind SGLT-2 inhibitors that I don’t want people to forget that ARNI is still the base therapy for HF,” said Dr. Butler, chair of cardiovascular research and the department of medicine at the University of Mississippi in Jackson.
He noted that the size of the diabetes cohort in PROVE-HF “is a nonissue” for evaluating power of the post hoc analysis because it tracked key measures in the study population continuously at eight intervals over the 12 months.
The analysis further demonstrates the synergistic effects of ARNI and SGLT-2 inhibitors in patients with T2DM and HF that were also reported in the PARADIGM-HF study, Dr. Butler said.
“We have sort of moved on, saying that SGLT-2 inhibitors have a benefit on the heart, but the reverse is also true: ARNIs are still heart failure drugs, and we don’t think of them as diabetes drugs, but the PARADIGM-HF data showed that there was a substantial reduction in hemoglobin A1c in those who had diabetes,” he said.
The researchers noted that an absence of a control group may contribute to an overestimation of reverse cardiac remodeling in the T2DM patients, and that the PROVE-HF study wasn’t prospectively powered to delineate differences in how sac/val therapy affected patients with or without diabetes. “Future investigations seeking to evaluate differences by T2DM status after sacubitril/valsartan initiation may use our findings to plan prospective sample sizes,” the researchers wrote.
Dr. Butler disclosed financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, Array, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, CVRx, Eli Lilly, G3 Pharmaceutical, Impulse Dynamics, Innolife, Janssen, Luitpold, Medtronic, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Relypsa, Sequana, StealthPeptide and Vifor. Lead author Muhammad Shahzeb Khan, MD, MSc, a professor at the University of Mississippi, has no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Kahn MS et al. JACC: HF. 2020 Dec 9. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2020.09.014.
The beneficial effects of sacubitril/valsartan on reverse cardiac remodeling in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction have been well established, but those benefits haven’t been as clearly demonstrated to carry over to HFrEF patients who also have type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Now, a post-hoc analysis of a pivotal clinical trial reports that those benefits do extend to patients with HFrEF and T2DM.
“It’s really not about a Sophie’s choice of whether you give this or that drug in these patients,” said corresponding author Javed Butler, MD, MPH, MBA. “We really ought to be giving all of these drugs – the angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitors (ARNIs) and sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors – to our patients for the best outcomes.”
The post-hoc analysis, published in JACC: Heart Failure, evaluated 361 patients with T2DM who were enrolled in the PROVE-HF trial of sac/val therapy for HF, published in JAMA.
PROVE-HF evaluated biomarkers, myocardial remodeling, and outcomes through a year of treatment with sac/val. The primary endpoint was the level of changes in natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) concentrations, left-ventricle ejection fraction (LVEF) and overall Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ)-23 scores through 12 months of treatment.
The post hoc study reported that baseline NT-proBNP concentrations were higher in the DM patients (854 pg/mL vs. 706 pg/mL), but at 12 months those levels were 513 and 441 pg/mL, respectively.
LVEF changed similarly from baseline to 12 months in both groups: from 28.3% to 37% in the DM patients and from 28.1% to 38.34% in non-DM patients. Overall KCCQ-23 scores improved similarly in both groups, but longitudinal analyses found modestly higher gains in the T2DM group, 9.3 vs. 8.6 points (P = .07).
“The real reason I wanted to do this study is that I’m a huge fan of all the SGLT-2 inhibitors, and I’m very involved in those trials, and there is right now so much momentum behind SGLT-2 inhibitors that I don’t want people to forget that ARNI is still the base therapy for HF,” said Dr. Butler, chair of cardiovascular research and the department of medicine at the University of Mississippi in Jackson.
He noted that the size of the diabetes cohort in PROVE-HF “is a nonissue” for evaluating power of the post hoc analysis because it tracked key measures in the study population continuously at eight intervals over the 12 months.
The analysis further demonstrates the synergistic effects of ARNI and SGLT-2 inhibitors in patients with T2DM and HF that were also reported in the PARADIGM-HF study, Dr. Butler said.
“We have sort of moved on, saying that SGLT-2 inhibitors have a benefit on the heart, but the reverse is also true: ARNIs are still heart failure drugs, and we don’t think of them as diabetes drugs, but the PARADIGM-HF data showed that there was a substantial reduction in hemoglobin A1c in those who had diabetes,” he said.
The researchers noted that an absence of a control group may contribute to an overestimation of reverse cardiac remodeling in the T2DM patients, and that the PROVE-HF study wasn’t prospectively powered to delineate differences in how sac/val therapy affected patients with or without diabetes. “Future investigations seeking to evaluate differences by T2DM status after sacubitril/valsartan initiation may use our findings to plan prospective sample sizes,” the researchers wrote.
Dr. Butler disclosed financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, Array, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, CVRx, Eli Lilly, G3 Pharmaceutical, Impulse Dynamics, Innolife, Janssen, Luitpold, Medtronic, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Relypsa, Sequana, StealthPeptide and Vifor. Lead author Muhammad Shahzeb Khan, MD, MSc, a professor at the University of Mississippi, has no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Kahn MS et al. JACC: HF. 2020 Dec 9. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2020.09.014.
The beneficial effects of sacubitril/valsartan on reverse cardiac remodeling in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction have been well established, but those benefits haven’t been as clearly demonstrated to carry over to HFrEF patients who also have type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Now, a post-hoc analysis of a pivotal clinical trial reports that those benefits do extend to patients with HFrEF and T2DM.
“It’s really not about a Sophie’s choice of whether you give this or that drug in these patients,” said corresponding author Javed Butler, MD, MPH, MBA. “We really ought to be giving all of these drugs – the angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitors (ARNIs) and sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors – to our patients for the best outcomes.”
The post-hoc analysis, published in JACC: Heart Failure, evaluated 361 patients with T2DM who were enrolled in the PROVE-HF trial of sac/val therapy for HF, published in JAMA.
PROVE-HF evaluated biomarkers, myocardial remodeling, and outcomes through a year of treatment with sac/val. The primary endpoint was the level of changes in natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) concentrations, left-ventricle ejection fraction (LVEF) and overall Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ)-23 scores through 12 months of treatment.
The post hoc study reported that baseline NT-proBNP concentrations were higher in the DM patients (854 pg/mL vs. 706 pg/mL), but at 12 months those levels were 513 and 441 pg/mL, respectively.
LVEF changed similarly from baseline to 12 months in both groups: from 28.3% to 37% in the DM patients and from 28.1% to 38.34% in non-DM patients. Overall KCCQ-23 scores improved similarly in both groups, but longitudinal analyses found modestly higher gains in the T2DM group, 9.3 vs. 8.6 points (P = .07).
“The real reason I wanted to do this study is that I’m a huge fan of all the SGLT-2 inhibitors, and I’m very involved in those trials, and there is right now so much momentum behind SGLT-2 inhibitors that I don’t want people to forget that ARNI is still the base therapy for HF,” said Dr. Butler, chair of cardiovascular research and the department of medicine at the University of Mississippi in Jackson.
He noted that the size of the diabetes cohort in PROVE-HF “is a nonissue” for evaluating power of the post hoc analysis because it tracked key measures in the study population continuously at eight intervals over the 12 months.
The analysis further demonstrates the synergistic effects of ARNI and SGLT-2 inhibitors in patients with T2DM and HF that were also reported in the PARADIGM-HF study, Dr. Butler said.
“We have sort of moved on, saying that SGLT-2 inhibitors have a benefit on the heart, but the reverse is also true: ARNIs are still heart failure drugs, and we don’t think of them as diabetes drugs, but the PARADIGM-HF data showed that there was a substantial reduction in hemoglobin A1c in those who had diabetes,” he said.
The researchers noted that an absence of a control group may contribute to an overestimation of reverse cardiac remodeling in the T2DM patients, and that the PROVE-HF study wasn’t prospectively powered to delineate differences in how sac/val therapy affected patients with or without diabetes. “Future investigations seeking to evaluate differences by T2DM status after sacubitril/valsartan initiation may use our findings to plan prospective sample sizes,” the researchers wrote.
Dr. Butler disclosed financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, Array, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, CVRx, Eli Lilly, G3 Pharmaceutical, Impulse Dynamics, Innolife, Janssen, Luitpold, Medtronic, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Relypsa, Sequana, StealthPeptide and Vifor. Lead author Muhammad Shahzeb Khan, MD, MSc, a professor at the University of Mississippi, has no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Kahn MS et al. JACC: HF. 2020 Dec 9. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2020.09.014.
FROM JACC: HEART FAILURE
ACC/AHA update two atrial fibrillation performance measures
The American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association Task Force on Performance Measures have made two changes to performance measures for adults with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter.
The 2020 Update to the 2016 ACC/AHA Clinical Performance and Quality Measures for Adults With Atrial Fibrillation or Atrial Flutter was published online Dec. 7 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes. It was developed in collaboration with the Heart Rhythm Society.
Both performance measure changes were prompted by, and are in accordance with, the 2019 ACC/AHA/Heart Rhythm Society atrial fibrillation guideline focused update issued in January 2019, and reported by this news organization at that time.
The first change is the clarification that valvular atrial fibrillation is atrial fibrillation with either moderate or severe mitral stenosis or a mechanical heart valve. This change is incorporated into all the performance measures.
The second change, which only applies to the performance measure of anticoagulation prescribed, is the separation of a male and female threshold for the CHA2DS2-VASc score.
This threshold is now a score higher than 1 for men and higher than 2 for women, further demonstrating that the risk for stroke differs for men and women with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter, the ACC/AHA noted in a press release.
“Successful implementation of these updated performance measures by clinicians and healthcare organizations will lead to quality improvement for adult patients with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter,” they said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association Task Force on Performance Measures have made two changes to performance measures for adults with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter.
The 2020 Update to the 2016 ACC/AHA Clinical Performance and Quality Measures for Adults With Atrial Fibrillation or Atrial Flutter was published online Dec. 7 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes. It was developed in collaboration with the Heart Rhythm Society.
Both performance measure changes were prompted by, and are in accordance with, the 2019 ACC/AHA/Heart Rhythm Society atrial fibrillation guideline focused update issued in January 2019, and reported by this news organization at that time.
The first change is the clarification that valvular atrial fibrillation is atrial fibrillation with either moderate or severe mitral stenosis or a mechanical heart valve. This change is incorporated into all the performance measures.
The second change, which only applies to the performance measure of anticoagulation prescribed, is the separation of a male and female threshold for the CHA2DS2-VASc score.
This threshold is now a score higher than 1 for men and higher than 2 for women, further demonstrating that the risk for stroke differs for men and women with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter, the ACC/AHA noted in a press release.
“Successful implementation of these updated performance measures by clinicians and healthcare organizations will lead to quality improvement for adult patients with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter,” they said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association Task Force on Performance Measures have made two changes to performance measures for adults with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter.
The 2020 Update to the 2016 ACC/AHA Clinical Performance and Quality Measures for Adults With Atrial Fibrillation or Atrial Flutter was published online Dec. 7 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes. It was developed in collaboration with the Heart Rhythm Society.
Both performance measure changes were prompted by, and are in accordance with, the 2019 ACC/AHA/Heart Rhythm Society atrial fibrillation guideline focused update issued in January 2019, and reported by this news organization at that time.
The first change is the clarification that valvular atrial fibrillation is atrial fibrillation with either moderate or severe mitral stenosis or a mechanical heart valve. This change is incorporated into all the performance measures.
The second change, which only applies to the performance measure of anticoagulation prescribed, is the separation of a male and female threshold for the CHA2DS2-VASc score.
This threshold is now a score higher than 1 for men and higher than 2 for women, further demonstrating that the risk for stroke differs for men and women with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter, the ACC/AHA noted in a press release.
“Successful implementation of these updated performance measures by clinicians and healthcare organizations will lead to quality improvement for adult patients with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter,” they said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves liraglutide for adolescents with obesity
The Food and Drug Administration’s new indication for liraglutide (Saxenda) for weight loss in adolescents with obesity, announced on Dec. 4, received welcome as a milestone for advancing a field that’s seen no new drug options since 2003 and boosted by 50% the list of agents indicated for weight loss in this age group.
But liraglutide’s track record in adolescents in the key study published earlier in 2020 left some experts unconvinced that liraglutide’s modest effects would have much impact on blunting the expanding cohort of teens who are obese.
“Until now, we’ve had phentermine and orlistat with FDA approval” for adolescents with obesity, and phentermine’s label specifies only patients older than 16 years. “It’s important that the FDA deemed liraglutide’s benefits greater than its risks for adolescents,” said Aaron S. Kelly, PhD, leader of the 82-week, multicenter, randomized study of liraglutide in 251 adolescents with obesity that directly led to the FDA’s action.
“We have results from a strong, published randomized trial, and the green light from the FDA, and that should give clinicians reassurance and confidence to use liraglutide clinically,” said Dr. Kelly, professor of pediatrics and codirector of the Center for Pediatric Obesity Medicine at the University of Minnesota in Minneapolis.
An ‘unimpressive’ drop in BMI
Sonia Caprio, MD, had a more skeptical take on liraglutide’s role with its new indication: “Approval of higher-dose liraglutide is an improvement that reflects a willingness to accept adolescent obesity as a disease that needs treatment with pharmacological agents. However, the study, published in New England Journal of Medicine, was not impressive in terms of weight loss, and more importantly liraglutide was not associated with any significant changes in metabolic markers” such as insulin resistance, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, lipoproteins and triglycerides, and hemoglobin A1c.
The observed average 5% drop in body mass index seen after a year on liraglutide treatment, compared with baseline and relative to no average change from baseline in the placebo arm, was “totally insufficient, and will not diminish any of the metabolic complications in youth with obesity,” commented Dr. Caprio, an endocrinologist and professor of pediatrics at Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
Results from the study led by Dr. Kelly also showed that liraglutide for 56 weeks cut BMI by 5% in 43% of patients, and by 10% in 26%, compared with respective rates of 19% and 8% among those in the placebo-control arm. He took a more expansive view of the potential benefits from weight loss of the caliber demonstrated by liraglutide in the study.
“In general, we wait too long with obesity in children; the earlier the intervention the better. A 3% or 4% reduction in BMI at 12 or 13 years old can pay big dividends down the road” when a typical adolescent trajectory of steadily rising weight can be flattened, he said in an interview.
Bariatric and metabolic surgery, although highly effective and usually safe, is seen by many clinicians, patients, and families as an “intervention of last resort,” and its very low level of uptake in adolescents bears witness to that reputation. It also creates an important niche for safe and effective drugs to fill as an adjunct to lifestyle changes, which are often ineffective when used by themselves. Liraglutide’s main mechanism for weight loss is depressing hunger, Dr. Kelly noted.
Existing meds have limitations
The existing medical treatments, orlistat and phentermine, both have significant drawbacks that limit their use. Orlistat (Xenical, Alli), FDA approved for adolescents 12-16 years old since 2003, limits intestinal fat absorption and as a result often produces unwanted GI effects. Phentermine’s approval for older adolescents dates from 1959 and has a weak evidence base, its label limits it to “short-term” use that’s generally taken to mean a maximum of 12 weeks. And, as a stimulant, phentermine has often been regarded as potentially dangerous, although Dr. Kelly noted that stimulants are well-accepted treatments for other disorders in children and adolescents.
“The earlier we treat obesity in youth, the better, given that it tends to track into adulthood,” agreed Dr. Caprio. “However, it remains to be seen whether weight reduction with a pharmacological agent is going to help prevent the intractable trajectories of weight and its complications. So far, it looks like surgery may be more efficacious,” she said in an interview.
Another drawback for the near future with liraglutide will likely be its cost for many patients, more than $10,000/year at full retail prices for the weight-loss formulation, given that insurers have had a poor record of covering the drug for this indication in adults, both Dr. Caprio and Dr. Kelly noted.
Compliance with liraglutide is also important. Dr. Kelly’s study followed patients for their first 26 weeks off treatment after 56 weeks on the drug, and showed that on average weights rebounded to virtually baseline levels by 6 months after treatment stopped.
Obesity treatment lasts a lifetime
“Obesity is a chronic disease, that requires chronic treatment, just like hypertension,” Dr. Kelly stressed, and cited the rebound seen in his study when liraglutide stopped as further proof of that concept. “All obesity treatment is lifelong,” he maintained.
He highlighted the importance of clinicians discussing with adolescent patients and their families the prospect of potentially remaining on liraglutide treatment for years to maintain weight loss. His experience with the randomized study convinced him that many adolescents with obesity are amenable to daily subcutaneous injection using the pen device that liraglutide comes in, but he acknowledged that some teens find this off-putting.
For the near term, Dr. Kelly foresaw liraglutide treatment of adolescents as something that will mostly be administered to patients who seek care at centers that specialize in obesity management. “I’ll think we’ll eventually see it move to more primary care settings, but that will be down the road.”
The study of liraglutide in adolescents was sponsored by Novo Nordisk, the company that markets liraglutide (Saxenda). Dr. Kelly has been a consultant to Novo Nordisk and also to Orexigen Therapeutics, Vivus, and WW, and he has received research funding from AstraZeneca. Dr. Caprio had no disclosures.
The Food and Drug Administration’s new indication for liraglutide (Saxenda) for weight loss in adolescents with obesity, announced on Dec. 4, received welcome as a milestone for advancing a field that’s seen no new drug options since 2003 and boosted by 50% the list of agents indicated for weight loss in this age group.
But liraglutide’s track record in adolescents in the key study published earlier in 2020 left some experts unconvinced that liraglutide’s modest effects would have much impact on blunting the expanding cohort of teens who are obese.
“Until now, we’ve had phentermine and orlistat with FDA approval” for adolescents with obesity, and phentermine’s label specifies only patients older than 16 years. “It’s important that the FDA deemed liraglutide’s benefits greater than its risks for adolescents,” said Aaron S. Kelly, PhD, leader of the 82-week, multicenter, randomized study of liraglutide in 251 adolescents with obesity that directly led to the FDA’s action.
“We have results from a strong, published randomized trial, and the green light from the FDA, and that should give clinicians reassurance and confidence to use liraglutide clinically,” said Dr. Kelly, professor of pediatrics and codirector of the Center for Pediatric Obesity Medicine at the University of Minnesota in Minneapolis.
An ‘unimpressive’ drop in BMI
Sonia Caprio, MD, had a more skeptical take on liraglutide’s role with its new indication: “Approval of higher-dose liraglutide is an improvement that reflects a willingness to accept adolescent obesity as a disease that needs treatment with pharmacological agents. However, the study, published in New England Journal of Medicine, was not impressive in terms of weight loss, and more importantly liraglutide was not associated with any significant changes in metabolic markers” such as insulin resistance, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, lipoproteins and triglycerides, and hemoglobin A1c.
The observed average 5% drop in body mass index seen after a year on liraglutide treatment, compared with baseline and relative to no average change from baseline in the placebo arm, was “totally insufficient, and will not diminish any of the metabolic complications in youth with obesity,” commented Dr. Caprio, an endocrinologist and professor of pediatrics at Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
Results from the study led by Dr. Kelly also showed that liraglutide for 56 weeks cut BMI by 5% in 43% of patients, and by 10% in 26%, compared with respective rates of 19% and 8% among those in the placebo-control arm. He took a more expansive view of the potential benefits from weight loss of the caliber demonstrated by liraglutide in the study.
“In general, we wait too long with obesity in children; the earlier the intervention the better. A 3% or 4% reduction in BMI at 12 or 13 years old can pay big dividends down the road” when a typical adolescent trajectory of steadily rising weight can be flattened, he said in an interview.
Bariatric and metabolic surgery, although highly effective and usually safe, is seen by many clinicians, patients, and families as an “intervention of last resort,” and its very low level of uptake in adolescents bears witness to that reputation. It also creates an important niche for safe and effective drugs to fill as an adjunct to lifestyle changes, which are often ineffective when used by themselves. Liraglutide’s main mechanism for weight loss is depressing hunger, Dr. Kelly noted.
Existing meds have limitations
The existing medical treatments, orlistat and phentermine, both have significant drawbacks that limit their use. Orlistat (Xenical, Alli), FDA approved for adolescents 12-16 years old since 2003, limits intestinal fat absorption and as a result often produces unwanted GI effects. Phentermine’s approval for older adolescents dates from 1959 and has a weak evidence base, its label limits it to “short-term” use that’s generally taken to mean a maximum of 12 weeks. And, as a stimulant, phentermine has often been regarded as potentially dangerous, although Dr. Kelly noted that stimulants are well-accepted treatments for other disorders in children and adolescents.
“The earlier we treat obesity in youth, the better, given that it tends to track into adulthood,” agreed Dr. Caprio. “However, it remains to be seen whether weight reduction with a pharmacological agent is going to help prevent the intractable trajectories of weight and its complications. So far, it looks like surgery may be more efficacious,” she said in an interview.
Another drawback for the near future with liraglutide will likely be its cost for many patients, more than $10,000/year at full retail prices for the weight-loss formulation, given that insurers have had a poor record of covering the drug for this indication in adults, both Dr. Caprio and Dr. Kelly noted.
Compliance with liraglutide is also important. Dr. Kelly’s study followed patients for their first 26 weeks off treatment after 56 weeks on the drug, and showed that on average weights rebounded to virtually baseline levels by 6 months after treatment stopped.
Obesity treatment lasts a lifetime
“Obesity is a chronic disease, that requires chronic treatment, just like hypertension,” Dr. Kelly stressed, and cited the rebound seen in his study when liraglutide stopped as further proof of that concept. “All obesity treatment is lifelong,” he maintained.
He highlighted the importance of clinicians discussing with adolescent patients and their families the prospect of potentially remaining on liraglutide treatment for years to maintain weight loss. His experience with the randomized study convinced him that many adolescents with obesity are amenable to daily subcutaneous injection using the pen device that liraglutide comes in, but he acknowledged that some teens find this off-putting.
For the near term, Dr. Kelly foresaw liraglutide treatment of adolescents as something that will mostly be administered to patients who seek care at centers that specialize in obesity management. “I’ll think we’ll eventually see it move to more primary care settings, but that will be down the road.”
The study of liraglutide in adolescents was sponsored by Novo Nordisk, the company that markets liraglutide (Saxenda). Dr. Kelly has been a consultant to Novo Nordisk and also to Orexigen Therapeutics, Vivus, and WW, and he has received research funding from AstraZeneca. Dr. Caprio had no disclosures.
The Food and Drug Administration’s new indication for liraglutide (Saxenda) for weight loss in adolescents with obesity, announced on Dec. 4, received welcome as a milestone for advancing a field that’s seen no new drug options since 2003 and boosted by 50% the list of agents indicated for weight loss in this age group.
But liraglutide’s track record in adolescents in the key study published earlier in 2020 left some experts unconvinced that liraglutide’s modest effects would have much impact on blunting the expanding cohort of teens who are obese.
“Until now, we’ve had phentermine and orlistat with FDA approval” for adolescents with obesity, and phentermine’s label specifies only patients older than 16 years. “It’s important that the FDA deemed liraglutide’s benefits greater than its risks for adolescents,” said Aaron S. Kelly, PhD, leader of the 82-week, multicenter, randomized study of liraglutide in 251 adolescents with obesity that directly led to the FDA’s action.
“We have results from a strong, published randomized trial, and the green light from the FDA, and that should give clinicians reassurance and confidence to use liraglutide clinically,” said Dr. Kelly, professor of pediatrics and codirector of the Center for Pediatric Obesity Medicine at the University of Minnesota in Minneapolis.
An ‘unimpressive’ drop in BMI
Sonia Caprio, MD, had a more skeptical take on liraglutide’s role with its new indication: “Approval of higher-dose liraglutide is an improvement that reflects a willingness to accept adolescent obesity as a disease that needs treatment with pharmacological agents. However, the study, published in New England Journal of Medicine, was not impressive in terms of weight loss, and more importantly liraglutide was not associated with any significant changes in metabolic markers” such as insulin resistance, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, lipoproteins and triglycerides, and hemoglobin A1c.
The observed average 5% drop in body mass index seen after a year on liraglutide treatment, compared with baseline and relative to no average change from baseline in the placebo arm, was “totally insufficient, and will not diminish any of the metabolic complications in youth with obesity,” commented Dr. Caprio, an endocrinologist and professor of pediatrics at Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
Results from the study led by Dr. Kelly also showed that liraglutide for 56 weeks cut BMI by 5% in 43% of patients, and by 10% in 26%, compared with respective rates of 19% and 8% among those in the placebo-control arm. He took a more expansive view of the potential benefits from weight loss of the caliber demonstrated by liraglutide in the study.
“In general, we wait too long with obesity in children; the earlier the intervention the better. A 3% or 4% reduction in BMI at 12 or 13 years old can pay big dividends down the road” when a typical adolescent trajectory of steadily rising weight can be flattened, he said in an interview.
Bariatric and metabolic surgery, although highly effective and usually safe, is seen by many clinicians, patients, and families as an “intervention of last resort,” and its very low level of uptake in adolescents bears witness to that reputation. It also creates an important niche for safe and effective drugs to fill as an adjunct to lifestyle changes, which are often ineffective when used by themselves. Liraglutide’s main mechanism for weight loss is depressing hunger, Dr. Kelly noted.
Existing meds have limitations
The existing medical treatments, orlistat and phentermine, both have significant drawbacks that limit their use. Orlistat (Xenical, Alli), FDA approved for adolescents 12-16 years old since 2003, limits intestinal fat absorption and as a result often produces unwanted GI effects. Phentermine’s approval for older adolescents dates from 1959 and has a weak evidence base, its label limits it to “short-term” use that’s generally taken to mean a maximum of 12 weeks. And, as a stimulant, phentermine has often been regarded as potentially dangerous, although Dr. Kelly noted that stimulants are well-accepted treatments for other disorders in children and adolescents.
“The earlier we treat obesity in youth, the better, given that it tends to track into adulthood,” agreed Dr. Caprio. “However, it remains to be seen whether weight reduction with a pharmacological agent is going to help prevent the intractable trajectories of weight and its complications. So far, it looks like surgery may be more efficacious,” she said in an interview.
Another drawback for the near future with liraglutide will likely be its cost for many patients, more than $10,000/year at full retail prices for the weight-loss formulation, given that insurers have had a poor record of covering the drug for this indication in adults, both Dr. Caprio and Dr. Kelly noted.
Compliance with liraglutide is also important. Dr. Kelly’s study followed patients for their first 26 weeks off treatment after 56 weeks on the drug, and showed that on average weights rebounded to virtually baseline levels by 6 months after treatment stopped.
Obesity treatment lasts a lifetime
“Obesity is a chronic disease, that requires chronic treatment, just like hypertension,” Dr. Kelly stressed, and cited the rebound seen in his study when liraglutide stopped as further proof of that concept. “All obesity treatment is lifelong,” he maintained.
He highlighted the importance of clinicians discussing with adolescent patients and their families the prospect of potentially remaining on liraglutide treatment for years to maintain weight loss. His experience with the randomized study convinced him that many adolescents with obesity are amenable to daily subcutaneous injection using the pen device that liraglutide comes in, but he acknowledged that some teens find this off-putting.
For the near term, Dr. Kelly foresaw liraglutide treatment of adolescents as something that will mostly be administered to patients who seek care at centers that specialize in obesity management. “I’ll think we’ll eventually see it move to more primary care settings, but that will be down the road.”
The study of liraglutide in adolescents was sponsored by Novo Nordisk, the company that markets liraglutide (Saxenda). Dr. Kelly has been a consultant to Novo Nordisk and also to Orexigen Therapeutics, Vivus, and WW, and he has received research funding from AstraZeneca. Dr. Caprio had no disclosures.
Calcium burden drives CV risk whether coronary disease is obstructive or not
Coronary artery calcium (CAC) score as a measure of plaque burden more reliably predicts future cardiovascular (CV) risk in patients with suspected coronary disease (CAD) than whether or not the disease is obstructive, a large retrospective study suggests.
Indeed, CV risk went up in tandem with growing plaque burden regardless of whether there was obstructive disease in any coronary artery, defined as a 50% or greater stenosis by computed tomographic angiography (CTA).
The findings argue for plaque burden as measured by CAC score, rather than percent-stenosis severity, for guiding further treatment decisions in such patients, researchers say.
The research was based on more than 20,000 symptomatic patients referred to diagnostic CTA in the Western Denmark Heart Registry who were then followed for about 4 years for major CV events, including death, myocardial infarction, or stroke.
“What we show is that CAC is important for prognosis, and that patients with no stenosis have similar high risk as patients with stenosis when CAC burden is similar,” Martin Bødtker Mortensen, MD, PhD, Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital, said in an interview.
The guidelines “distinguish between primary and secondary prevention patients” based on the presence or absence of obstructive CAD, he said, but “our results challenge this long-held approach. We show that patients with nonobstructive CAD carry similar risk as patients with obstructive CAD.”
In practice, risk tends to be greater in patients with obstructive compared with nonobstructive CAD. But the reason “is simply that they normally have higher atherosclerosis burden,” Dr. Mortensen said. “When you stratify based on atherosclerosis burden, then patients with obstructive and nonobstructive CAD have similar risk.”
The analysis was published online Dec. 7 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology with Mortensen as lead author.
Until recently, it had long been believed that CV-event risk was driven by ischemia – but “ischemia is just a surrogate for the extent of atherosclerotic disease,” Armin Arbab Zadeh, MD, PhD, MPH, who is not connected with the current study, said in an interview.
The finding that CV risk climbs with growing coronary plaque burden “essentially confirms” other recent studies, but with “added value in showing how well the calcium scores, compared to obstructive disease, track with risk. So it’s definitely a nice extension of the evidence,” said Dr. Zadeh, director of cardiac CT at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
“This study clearly shows that there is no ischemia ‘threshold,’ that the risk starts from mild and goes up with the burden of atherosclerotic disease. We were essentially taught wrong for decades.”
Dr. Mortensen said that the new results “are in line with previous studies showing that atherosclerosis burden is very important for risk.” They also help explain why revascularization of patients with stable angina failed to cut the risk of MI or death in trials like COURAGE, FAME-2, and ISCHEMIA. It’s because “stenosis per se explains little of the risk compared to atherosclerosis burden.”
In the current analysis, for example, about 65% of events were in patients who did not show obstructive CAD at CTA. Its 23,759 patients with symptoms suggestive of CAD were referred for CTA from 2008 through 2017; 5,043 (21.2%) were found to have obstructive disease and 18,716 (78.8%) either had no CAD or nonobstructive disease.
About 4.4% of patients experienced a first major CV event over a median follow-up of 4.3 years. Only events occurring later than 90 days after CTA were counted in an effort to exclude any directly related to revascularization, Dr. Mortensen noted.
The risk of events went up proportionally with both CAC score and the number of coronaries with obstructive disease.
The number of major CV events per 1,000 person-years was 6.2 for patients with a CAC score of 0, of whom 87% had no CAD by CTA, 7% had nonobstructive CAD, and 6% had obstructive CAD.
The corresponding rate was 17.5 among patients with a CAC score >100-399 for a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.7 (95% confidence interval [CI] 1.4-2.1) vs. a CAC score of 0.
And it was 42.3 per 1,000 patient-years among patients with CAC score >1000, HR 3.4 (95% CI, 2.5-4.6) vs. a CAC score of 0. Among those with the highest-tier CAC score, none were without CAD by CTA, 17% had nonobstructive disease, and 83% had obstructive CAD.
The major CV event rate rose similarly by number of coronaries with obstructive disease. It was 6.1 per 1,000 person-years in patients with no CAD. But it was 12.3 in those with nonobstructive disease, HR 1.3 (95% CI 1.1-1.6), up to 34.7 in those with triple-vessel obstructive disease, HR 2.9 (95% CI 2.2-3.9), vs. no CAD.
However, in an analysis with stratification by CAC score tier (0, 1-99, 100-399, 400-1,000, and >1,000), obstructive CAD was not associated with increased major CV-event risk in any stratum. The findings were similar in each subgroup with 1-vessel, 2-vessel, or 3-vessel CAD when stratified by CAC score.
Nor did major CV event risk track with obstructive CAD in analyses by age or after excluding all patients who underwent coronary revascularization within 90 days of CTA, the group reported.
“I believe these results support the use of CTA as a first-line test in patients with symptoms suggestive of CAD, as it provides valuable information for both diagnosis and prognosis in symptomatic patients,” Dr. Mortensen said. Those found to have a higher burden of atherosclerosis, he added, should receive aggressive preventive therapy regardless of whether or not they have obstructive disease.
The evidence from this study and others “supports a CTA-based approach” in such patients, Dr. Zadeh said. “And I would go further to say that a stress test is really inadequate,” in that it “detects the disease at such a late stage, you’re missing the opportunity to identify these patients who have atherosclerotic disease while you can do something about it.”
Its continued use as a first-line test, Dr. Zadeh said, “is essentially, in my mind, dismissing the evidence.”
An accompanying editorial Todd C. Villines, MD, and Patricia Rodriguez Lozano, MD, of the University of Virginia, Charlottesville agreed that “it is time that the traditional definitions of primary and secondary prevention evolve to incorporate CAC and CTA measures of patient risk based on coronary artery plaque burden.”
But they pointed out some limitations of the current study.
“The authors compared CAC with ≥50% stenosis, not CAC to comprehensive, contemporary coronary CTA,” and so “did not assess numerous other well-validated measures of coronary plaque burden that are routinely obtained from coronary CTA that typically improve the prognostic accuracy of coronary CTA beyond stenosis alone.” Also not performed was “plaque quantification on coronary CTA, an emerging field of study.”
The editorialists noted that noncontrast CT as used in the study for CAC scoring “is generally not recommended as a standalone test in symptomatic patients. Most studies have shown that coronary CTA, a test that accurately detects stenosis and identifies all types of coronary atherosclerosis (calcified and noncalcified), has significantly higher diagnostic and prognostic accuracy than CAC when performed in symptomatic patients without known coronary artery disease.”
Dr. Mortensen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Villines and Dr. Rodriguez Lozano have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Zadeh disclosed receiving grant support from Canon Medical Systems.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Coronary artery calcium (CAC) score as a measure of plaque burden more reliably predicts future cardiovascular (CV) risk in patients with suspected coronary disease (CAD) than whether or not the disease is obstructive, a large retrospective study suggests.
Indeed, CV risk went up in tandem with growing plaque burden regardless of whether there was obstructive disease in any coronary artery, defined as a 50% or greater stenosis by computed tomographic angiography (CTA).
The findings argue for plaque burden as measured by CAC score, rather than percent-stenosis severity, for guiding further treatment decisions in such patients, researchers say.
The research was based on more than 20,000 symptomatic patients referred to diagnostic CTA in the Western Denmark Heart Registry who were then followed for about 4 years for major CV events, including death, myocardial infarction, or stroke.
“What we show is that CAC is important for prognosis, and that patients with no stenosis have similar high risk as patients with stenosis when CAC burden is similar,” Martin Bødtker Mortensen, MD, PhD, Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital, said in an interview.
The guidelines “distinguish between primary and secondary prevention patients” based on the presence or absence of obstructive CAD, he said, but “our results challenge this long-held approach. We show that patients with nonobstructive CAD carry similar risk as patients with obstructive CAD.”
In practice, risk tends to be greater in patients with obstructive compared with nonobstructive CAD. But the reason “is simply that they normally have higher atherosclerosis burden,” Dr. Mortensen said. “When you stratify based on atherosclerosis burden, then patients with obstructive and nonobstructive CAD have similar risk.”
The analysis was published online Dec. 7 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology with Mortensen as lead author.
Until recently, it had long been believed that CV-event risk was driven by ischemia – but “ischemia is just a surrogate for the extent of atherosclerotic disease,” Armin Arbab Zadeh, MD, PhD, MPH, who is not connected with the current study, said in an interview.
The finding that CV risk climbs with growing coronary plaque burden “essentially confirms” other recent studies, but with “added value in showing how well the calcium scores, compared to obstructive disease, track with risk. So it’s definitely a nice extension of the evidence,” said Dr. Zadeh, director of cardiac CT at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
“This study clearly shows that there is no ischemia ‘threshold,’ that the risk starts from mild and goes up with the burden of atherosclerotic disease. We were essentially taught wrong for decades.”
Dr. Mortensen said that the new results “are in line with previous studies showing that atherosclerosis burden is very important for risk.” They also help explain why revascularization of patients with stable angina failed to cut the risk of MI or death in trials like COURAGE, FAME-2, and ISCHEMIA. It’s because “stenosis per se explains little of the risk compared to atherosclerosis burden.”
In the current analysis, for example, about 65% of events were in patients who did not show obstructive CAD at CTA. Its 23,759 patients with symptoms suggestive of CAD were referred for CTA from 2008 through 2017; 5,043 (21.2%) were found to have obstructive disease and 18,716 (78.8%) either had no CAD or nonobstructive disease.
About 4.4% of patients experienced a first major CV event over a median follow-up of 4.3 years. Only events occurring later than 90 days after CTA were counted in an effort to exclude any directly related to revascularization, Dr. Mortensen noted.
The risk of events went up proportionally with both CAC score and the number of coronaries with obstructive disease.
The number of major CV events per 1,000 person-years was 6.2 for patients with a CAC score of 0, of whom 87% had no CAD by CTA, 7% had nonobstructive CAD, and 6% had obstructive CAD.
The corresponding rate was 17.5 among patients with a CAC score >100-399 for a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.7 (95% confidence interval [CI] 1.4-2.1) vs. a CAC score of 0.
And it was 42.3 per 1,000 patient-years among patients with CAC score >1000, HR 3.4 (95% CI, 2.5-4.6) vs. a CAC score of 0. Among those with the highest-tier CAC score, none were without CAD by CTA, 17% had nonobstructive disease, and 83% had obstructive CAD.
The major CV event rate rose similarly by number of coronaries with obstructive disease. It was 6.1 per 1,000 person-years in patients with no CAD. But it was 12.3 in those with nonobstructive disease, HR 1.3 (95% CI 1.1-1.6), up to 34.7 in those with triple-vessel obstructive disease, HR 2.9 (95% CI 2.2-3.9), vs. no CAD.
However, in an analysis with stratification by CAC score tier (0, 1-99, 100-399, 400-1,000, and >1,000), obstructive CAD was not associated with increased major CV-event risk in any stratum. The findings were similar in each subgroup with 1-vessel, 2-vessel, or 3-vessel CAD when stratified by CAC score.
Nor did major CV event risk track with obstructive CAD in analyses by age or after excluding all patients who underwent coronary revascularization within 90 days of CTA, the group reported.
“I believe these results support the use of CTA as a first-line test in patients with symptoms suggestive of CAD, as it provides valuable information for both diagnosis and prognosis in symptomatic patients,” Dr. Mortensen said. Those found to have a higher burden of atherosclerosis, he added, should receive aggressive preventive therapy regardless of whether or not they have obstructive disease.
The evidence from this study and others “supports a CTA-based approach” in such patients, Dr. Zadeh said. “And I would go further to say that a stress test is really inadequate,” in that it “detects the disease at such a late stage, you’re missing the opportunity to identify these patients who have atherosclerotic disease while you can do something about it.”
Its continued use as a first-line test, Dr. Zadeh said, “is essentially, in my mind, dismissing the evidence.”
An accompanying editorial Todd C. Villines, MD, and Patricia Rodriguez Lozano, MD, of the University of Virginia, Charlottesville agreed that “it is time that the traditional definitions of primary and secondary prevention evolve to incorporate CAC and CTA measures of patient risk based on coronary artery plaque burden.”
But they pointed out some limitations of the current study.
“The authors compared CAC with ≥50% stenosis, not CAC to comprehensive, contemporary coronary CTA,” and so “did not assess numerous other well-validated measures of coronary plaque burden that are routinely obtained from coronary CTA that typically improve the prognostic accuracy of coronary CTA beyond stenosis alone.” Also not performed was “plaque quantification on coronary CTA, an emerging field of study.”
The editorialists noted that noncontrast CT as used in the study for CAC scoring “is generally not recommended as a standalone test in symptomatic patients. Most studies have shown that coronary CTA, a test that accurately detects stenosis and identifies all types of coronary atherosclerosis (calcified and noncalcified), has significantly higher diagnostic and prognostic accuracy than CAC when performed in symptomatic patients without known coronary artery disease.”
Dr. Mortensen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Villines and Dr. Rodriguez Lozano have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Zadeh disclosed receiving grant support from Canon Medical Systems.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Coronary artery calcium (CAC) score as a measure of plaque burden more reliably predicts future cardiovascular (CV) risk in patients with suspected coronary disease (CAD) than whether or not the disease is obstructive, a large retrospective study suggests.
Indeed, CV risk went up in tandem with growing plaque burden regardless of whether there was obstructive disease in any coronary artery, defined as a 50% or greater stenosis by computed tomographic angiography (CTA).
The findings argue for plaque burden as measured by CAC score, rather than percent-stenosis severity, for guiding further treatment decisions in such patients, researchers say.
The research was based on more than 20,000 symptomatic patients referred to diagnostic CTA in the Western Denmark Heart Registry who were then followed for about 4 years for major CV events, including death, myocardial infarction, or stroke.
“What we show is that CAC is important for prognosis, and that patients with no stenosis have similar high risk as patients with stenosis when CAC burden is similar,” Martin Bødtker Mortensen, MD, PhD, Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital, said in an interview.
The guidelines “distinguish between primary and secondary prevention patients” based on the presence or absence of obstructive CAD, he said, but “our results challenge this long-held approach. We show that patients with nonobstructive CAD carry similar risk as patients with obstructive CAD.”
In practice, risk tends to be greater in patients with obstructive compared with nonobstructive CAD. But the reason “is simply that they normally have higher atherosclerosis burden,” Dr. Mortensen said. “When you stratify based on atherosclerosis burden, then patients with obstructive and nonobstructive CAD have similar risk.”
The analysis was published online Dec. 7 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology with Mortensen as lead author.
Until recently, it had long been believed that CV-event risk was driven by ischemia – but “ischemia is just a surrogate for the extent of atherosclerotic disease,” Armin Arbab Zadeh, MD, PhD, MPH, who is not connected with the current study, said in an interview.
The finding that CV risk climbs with growing coronary plaque burden “essentially confirms” other recent studies, but with “added value in showing how well the calcium scores, compared to obstructive disease, track with risk. So it’s definitely a nice extension of the evidence,” said Dr. Zadeh, director of cardiac CT at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
“This study clearly shows that there is no ischemia ‘threshold,’ that the risk starts from mild and goes up with the burden of atherosclerotic disease. We were essentially taught wrong for decades.”
Dr. Mortensen said that the new results “are in line with previous studies showing that atherosclerosis burden is very important for risk.” They also help explain why revascularization of patients with stable angina failed to cut the risk of MI or death in trials like COURAGE, FAME-2, and ISCHEMIA. It’s because “stenosis per se explains little of the risk compared to atherosclerosis burden.”
In the current analysis, for example, about 65% of events were in patients who did not show obstructive CAD at CTA. Its 23,759 patients with symptoms suggestive of CAD were referred for CTA from 2008 through 2017; 5,043 (21.2%) were found to have obstructive disease and 18,716 (78.8%) either had no CAD or nonobstructive disease.
About 4.4% of patients experienced a first major CV event over a median follow-up of 4.3 years. Only events occurring later than 90 days after CTA were counted in an effort to exclude any directly related to revascularization, Dr. Mortensen noted.
The risk of events went up proportionally with both CAC score and the number of coronaries with obstructive disease.
The number of major CV events per 1,000 person-years was 6.2 for patients with a CAC score of 0, of whom 87% had no CAD by CTA, 7% had nonobstructive CAD, and 6% had obstructive CAD.
The corresponding rate was 17.5 among patients with a CAC score >100-399 for a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.7 (95% confidence interval [CI] 1.4-2.1) vs. a CAC score of 0.
And it was 42.3 per 1,000 patient-years among patients with CAC score >1000, HR 3.4 (95% CI, 2.5-4.6) vs. a CAC score of 0. Among those with the highest-tier CAC score, none were without CAD by CTA, 17% had nonobstructive disease, and 83% had obstructive CAD.
The major CV event rate rose similarly by number of coronaries with obstructive disease. It was 6.1 per 1,000 person-years in patients with no CAD. But it was 12.3 in those with nonobstructive disease, HR 1.3 (95% CI 1.1-1.6), up to 34.7 in those with triple-vessel obstructive disease, HR 2.9 (95% CI 2.2-3.9), vs. no CAD.
However, in an analysis with stratification by CAC score tier (0, 1-99, 100-399, 400-1,000, and >1,000), obstructive CAD was not associated with increased major CV-event risk in any stratum. The findings were similar in each subgroup with 1-vessel, 2-vessel, or 3-vessel CAD when stratified by CAC score.
Nor did major CV event risk track with obstructive CAD in analyses by age or after excluding all patients who underwent coronary revascularization within 90 days of CTA, the group reported.
“I believe these results support the use of CTA as a first-line test in patients with symptoms suggestive of CAD, as it provides valuable information for both diagnosis and prognosis in symptomatic patients,” Dr. Mortensen said. Those found to have a higher burden of atherosclerosis, he added, should receive aggressive preventive therapy regardless of whether or not they have obstructive disease.
The evidence from this study and others “supports a CTA-based approach” in such patients, Dr. Zadeh said. “And I would go further to say that a stress test is really inadequate,” in that it “detects the disease at such a late stage, you’re missing the opportunity to identify these patients who have atherosclerotic disease while you can do something about it.”
Its continued use as a first-line test, Dr. Zadeh said, “is essentially, in my mind, dismissing the evidence.”
An accompanying editorial Todd C. Villines, MD, and Patricia Rodriguez Lozano, MD, of the University of Virginia, Charlottesville agreed that “it is time that the traditional definitions of primary and secondary prevention evolve to incorporate CAC and CTA measures of patient risk based on coronary artery plaque burden.”
But they pointed out some limitations of the current study.
“The authors compared CAC with ≥50% stenosis, not CAC to comprehensive, contemporary coronary CTA,” and so “did not assess numerous other well-validated measures of coronary plaque burden that are routinely obtained from coronary CTA that typically improve the prognostic accuracy of coronary CTA beyond stenosis alone.” Also not performed was “plaque quantification on coronary CTA, an emerging field of study.”
The editorialists noted that noncontrast CT as used in the study for CAC scoring “is generally not recommended as a standalone test in symptomatic patients. Most studies have shown that coronary CTA, a test that accurately detects stenosis and identifies all types of coronary atherosclerosis (calcified and noncalcified), has significantly higher diagnostic and prognostic accuracy than CAC when performed in symptomatic patients without known coronary artery disease.”
Dr. Mortensen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Villines and Dr. Rodriguez Lozano have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Zadeh disclosed receiving grant support from Canon Medical Systems.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 and risk of clotting: ‘Be proactive about prevention’
The risk of arterial and venous thrombosis in patients with COVID-19 has been a major issue throughout the pandemic, and how best to manage this risk is the subject of a new review article.
The article, by Gregory Dr. Piazza, MD, and David A. Morrow, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, was published online in JAMA on Nov. 23.
“Basically we’re saying: ‘Be proactive about prevention,’” Dr. Piazza told this news organization.
There is growing recognition among those on the frontline that there is an increased risk of thrombosis in COVID-19 patients, Dr. Piazza said. The risk is highest in patients in the intensive care unit, but the risk is also increased in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, even those not in ICU.
“We don’t really know what the risk is in nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients, but we think it’s much lower than in those who are hospitalized,” he said. “We are waiting for data on the optimal way of managing this increased risk of thrombosis in COVID patients, but for the time being, we believe a systematic way of addressing this risk is best, with every patient hospitalized with COVID-19 receiving some type of thromboprophylaxis. This would mainly be with anticoagulation, but in patients in whom anticoagulation is contraindicated, then mechanical methods could be used, such as pneumatic compression boots or compression stockings.”
The authors report thrombotic complication rates of 2.6% in noncritically ill hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and 35.3% in critically ill patients from a recent U.S. registry study.
Autopsy findings of microthrombi in multiple organ systems, including the lungs, heart, and kidneys, suggest that thrombosis may contribute to multisystem organ dysfunction in severe COVID-19, they note. Although the pathophysiology is not fully defined, prothrombotic abnormalities have been identified in patients with COVID-19, including elevated levels of D-dimer, fibrinogen, and factor VIII, they add.
“There are several major questions about which COVID-19 patients to treat with thromboprophylaxis, how to treat them in term of levels of anticoagulation, and there are many ongoing clinical trials to try and answer these questions,” Dr. Piazza commented. “We need results from these randomized trials to provide a better compass for COVID-19 patients at risk of clotting.”
At present, clinicians can follow two different sets of guidelines on the issue, one from the American College of Chest Physicians and the other from the International Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis, the authors note.
“The ACCP guidelines are very conservative and basically follow the evidence base for medical patients, while the ISTH guidelines are more aggressive and recommend increased levels of anticoagulation in both ICU and hospitalized non-ICU patients and also extend prophylaxis after discharge,” Dr. Piazza said.
“There is quite a difference between the two sets of guidelines, which can be a point of confusion,” he added.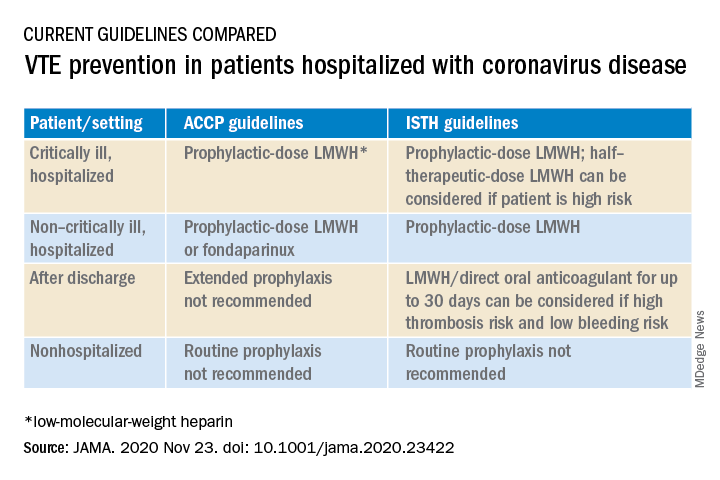
Dr. Piazza notes that at his center every hospitalized COVID patient who does not have a contraindication to anticoagulation receives a standard prophylactic dose of a once-daily low-molecular-weight heparin (for example, enoxaparin 40 mg). A once-daily product is used to minimize infection risk to staff.
While all COVID patients in the ICU should automatically receive some anticoagulation, the optimal dose is an area of active investigation, he explained. “There were several early reports of ICU patients developing blood clots despite receiving standard thromboprophylaxis so perhaps we need to use higher doses. There are trials underway looking at this, and we would advise enrolling patients into these trials.”
If patients can’t be enrolled into trials, and clinicians feel higher anticoagulation levels are needed, Dr. Piazza advises following the ISTH guidance, which allows an intermediate dose of low-molecular-weight heparin (up to 1 mg/kg enoxaparin).
“Some experts are suggesting even higher doses may be needed in some ICU patients, such as the full therapeutic dose, but I worry about the risk of bleeding with such a strategy,” he said.
Dr. Piazza says they do not routinely give anticoagulation after discharge, but if this is desired then patients could be switched to an oral agent, and some of the direct-acting oral anticoagulants are approved for prophylactic use in medically ill patients.
Dr. Piazza points out that whether thromboprophylaxis should be used for nonhospitalized COVID patients who have risk factors for clotting such as a prior history of thrombosis or obesity is a pressing question, and he encourages clinicians to enroll these patients in clinical trials evaluating this issue, such as the PREVENT-HD trial.
“If they can’t enroll patents in a trial, then they have to make a decision whether the patient is high-enough risk to justify off-label use of anticoagulant. There is a case to be made for this, but there is no evidence for or against such action at present,” he noted.
At this time, neither the ISTH nor ACCP recommend measuring D-dimer to screen for venous thromboembolism or to determine intensity of prophylaxis or treatment, the authors note.
“Ongoing investigation will determine optimal preventive regimens in COVID-19 in the intensive care unit, at hospital discharge, and in nonhospitalized patients at high risk for thrombosis,” they conclude.
Dr. Piazza reported grants from Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boston Scientific, Janssen, and Portola, and personal fees from Agile, Amgen, Pfizer, and the Prairie Education and Research Cooperative outside the submitted work. Dr. Morrow reported grants from Abbott Laboratories, Amgen, Anthos Therapeutics, Esai, GlaxoSmithKline, Takeda, and The Medicines Company; grants and personal fees from AstraZeneca, Merck, Novartis, and Roche Diagnostics; and personal fees from Bayer Pharma and InCarda outside the submitted work.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk of arterial and venous thrombosis in patients with COVID-19 has been a major issue throughout the pandemic, and how best to manage this risk is the subject of a new review article.
The article, by Gregory Dr. Piazza, MD, and David A. Morrow, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, was published online in JAMA on Nov. 23.
“Basically we’re saying: ‘Be proactive about prevention,’” Dr. Piazza told this news organization.
There is growing recognition among those on the frontline that there is an increased risk of thrombosis in COVID-19 patients, Dr. Piazza said. The risk is highest in patients in the intensive care unit, but the risk is also increased in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, even those not in ICU.
“We don’t really know what the risk is in nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients, but we think it’s much lower than in those who are hospitalized,” he said. “We are waiting for data on the optimal way of managing this increased risk of thrombosis in COVID patients, but for the time being, we believe a systematic way of addressing this risk is best, with every patient hospitalized with COVID-19 receiving some type of thromboprophylaxis. This would mainly be with anticoagulation, but in patients in whom anticoagulation is contraindicated, then mechanical methods could be used, such as pneumatic compression boots or compression stockings.”
The authors report thrombotic complication rates of 2.6% in noncritically ill hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and 35.3% in critically ill patients from a recent U.S. registry study.
Autopsy findings of microthrombi in multiple organ systems, including the lungs, heart, and kidneys, suggest that thrombosis may contribute to multisystem organ dysfunction in severe COVID-19, they note. Although the pathophysiology is not fully defined, prothrombotic abnormalities have been identified in patients with COVID-19, including elevated levels of D-dimer, fibrinogen, and factor VIII, they add.
“There are several major questions about which COVID-19 patients to treat with thromboprophylaxis, how to treat them in term of levels of anticoagulation, and there are many ongoing clinical trials to try and answer these questions,” Dr. Piazza commented. “We need results from these randomized trials to provide a better compass for COVID-19 patients at risk of clotting.”
At present, clinicians can follow two different sets of guidelines on the issue, one from the American College of Chest Physicians and the other from the International Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis, the authors note.
“The ACCP guidelines are very conservative and basically follow the evidence base for medical patients, while the ISTH guidelines are more aggressive and recommend increased levels of anticoagulation in both ICU and hospitalized non-ICU patients and also extend prophylaxis after discharge,” Dr. Piazza said.
“There is quite a difference between the two sets of guidelines, which can be a point of confusion,” he added.
Dr. Piazza notes that at his center every hospitalized COVID patient who does not have a contraindication to anticoagulation receives a standard prophylactic dose of a once-daily low-molecular-weight heparin (for example, enoxaparin 40 mg). A once-daily product is used to minimize infection risk to staff.
While all COVID patients in the ICU should automatically receive some anticoagulation, the optimal dose is an area of active investigation, he explained. “There were several early reports of ICU patients developing blood clots despite receiving standard thromboprophylaxis so perhaps we need to use higher doses. There are trials underway looking at this, and we would advise enrolling patients into these trials.”
If patients can’t be enrolled into trials, and clinicians feel higher anticoagulation levels are needed, Dr. Piazza advises following the ISTH guidance, which allows an intermediate dose of low-molecular-weight heparin (up to 1 mg/kg enoxaparin).
“Some experts are suggesting even higher doses may be needed in some ICU patients, such as the full therapeutic dose, but I worry about the risk of bleeding with such a strategy,” he said.
Dr. Piazza says they do not routinely give anticoagulation after discharge, but if this is desired then patients could be switched to an oral agent, and some of the direct-acting oral anticoagulants are approved for prophylactic use in medically ill patients.
Dr. Piazza points out that whether thromboprophylaxis should be used for nonhospitalized COVID patients who have risk factors for clotting such as a prior history of thrombosis or obesity is a pressing question, and he encourages clinicians to enroll these patients in clinical trials evaluating this issue, such as the PREVENT-HD trial.
“If they can’t enroll patents in a trial, then they have to make a decision whether the patient is high-enough risk to justify off-label use of anticoagulant. There is a case to be made for this, but there is no evidence for or against such action at present,” he noted.
At this time, neither the ISTH nor ACCP recommend measuring D-dimer to screen for venous thromboembolism or to determine intensity of prophylaxis or treatment, the authors note.
“Ongoing investigation will determine optimal preventive regimens in COVID-19 in the intensive care unit, at hospital discharge, and in nonhospitalized patients at high risk for thrombosis,” they conclude.
Dr. Piazza reported grants from Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boston Scientific, Janssen, and Portola, and personal fees from Agile, Amgen, Pfizer, and the Prairie Education and Research Cooperative outside the submitted work. Dr. Morrow reported grants from Abbott Laboratories, Amgen, Anthos Therapeutics, Esai, GlaxoSmithKline, Takeda, and The Medicines Company; grants and personal fees from AstraZeneca, Merck, Novartis, and Roche Diagnostics; and personal fees from Bayer Pharma and InCarda outside the submitted work.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk of arterial and venous thrombosis in patients with COVID-19 has been a major issue throughout the pandemic, and how best to manage this risk is the subject of a new review article.
The article, by Gregory Dr. Piazza, MD, and David A. Morrow, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, was published online in JAMA on Nov. 23.
“Basically we’re saying: ‘Be proactive about prevention,’” Dr. Piazza told this news organization.
There is growing recognition among those on the frontline that there is an increased risk of thrombosis in COVID-19 patients, Dr. Piazza said. The risk is highest in patients in the intensive care unit, but the risk is also increased in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, even those not in ICU.
“We don’t really know what the risk is in nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients, but we think it’s much lower than in those who are hospitalized,” he said. “We are waiting for data on the optimal way of managing this increased risk of thrombosis in COVID patients, but for the time being, we believe a systematic way of addressing this risk is best, with every patient hospitalized with COVID-19 receiving some type of thromboprophylaxis. This would mainly be with anticoagulation, but in patients in whom anticoagulation is contraindicated, then mechanical methods could be used, such as pneumatic compression boots or compression stockings.”
The authors report thrombotic complication rates of 2.6% in noncritically ill hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and 35.3% in critically ill patients from a recent U.S. registry study.
Autopsy findings of microthrombi in multiple organ systems, including the lungs, heart, and kidneys, suggest that thrombosis may contribute to multisystem organ dysfunction in severe COVID-19, they note. Although the pathophysiology is not fully defined, prothrombotic abnormalities have been identified in patients with COVID-19, including elevated levels of D-dimer, fibrinogen, and factor VIII, they add.
“There are several major questions about which COVID-19 patients to treat with thromboprophylaxis, how to treat them in term of levels of anticoagulation, and there are many ongoing clinical trials to try and answer these questions,” Dr. Piazza commented. “We need results from these randomized trials to provide a better compass for COVID-19 patients at risk of clotting.”
At present, clinicians can follow two different sets of guidelines on the issue, one from the American College of Chest Physicians and the other from the International Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis, the authors note.
“The ACCP guidelines are very conservative and basically follow the evidence base for medical patients, while the ISTH guidelines are more aggressive and recommend increased levels of anticoagulation in both ICU and hospitalized non-ICU patients and also extend prophylaxis after discharge,” Dr. Piazza said.
“There is quite a difference between the two sets of guidelines, which can be a point of confusion,” he added.
Dr. Piazza notes that at his center every hospitalized COVID patient who does not have a contraindication to anticoagulation receives a standard prophylactic dose of a once-daily low-molecular-weight heparin (for example, enoxaparin 40 mg). A once-daily product is used to minimize infection risk to staff.
While all COVID patients in the ICU should automatically receive some anticoagulation, the optimal dose is an area of active investigation, he explained. “There were several early reports of ICU patients developing blood clots despite receiving standard thromboprophylaxis so perhaps we need to use higher doses. There are trials underway looking at this, and we would advise enrolling patients into these trials.”
If patients can’t be enrolled into trials, and clinicians feel higher anticoagulation levels are needed, Dr. Piazza advises following the ISTH guidance, which allows an intermediate dose of low-molecular-weight heparin (up to 1 mg/kg enoxaparin).
“Some experts are suggesting even higher doses may be needed in some ICU patients, such as the full therapeutic dose, but I worry about the risk of bleeding with such a strategy,” he said.
Dr. Piazza says they do not routinely give anticoagulation after discharge, but if this is desired then patients could be switched to an oral agent, and some of the direct-acting oral anticoagulants are approved for prophylactic use in medically ill patients.
Dr. Piazza points out that whether thromboprophylaxis should be used for nonhospitalized COVID patients who have risk factors for clotting such as a prior history of thrombosis or obesity is a pressing question, and he encourages clinicians to enroll these patients in clinical trials evaluating this issue, such as the PREVENT-HD trial.
“If they can’t enroll patents in a trial, then they have to make a decision whether the patient is high-enough risk to justify off-label use of anticoagulant. There is a case to be made for this, but there is no evidence for or against such action at present,” he noted.
At this time, neither the ISTH nor ACCP recommend measuring D-dimer to screen for venous thromboembolism or to determine intensity of prophylaxis or treatment, the authors note.
“Ongoing investigation will determine optimal preventive regimens in COVID-19 in the intensive care unit, at hospital discharge, and in nonhospitalized patients at high risk for thrombosis,” they conclude.
Dr. Piazza reported grants from Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boston Scientific, Janssen, and Portola, and personal fees from Agile, Amgen, Pfizer, and the Prairie Education and Research Cooperative outside the submitted work. Dr. Morrow reported grants from Abbott Laboratories, Amgen, Anthos Therapeutics, Esai, GlaxoSmithKline, Takeda, and The Medicines Company; grants and personal fees from AstraZeneca, Merck, Novartis, and Roche Diagnostics; and personal fees from Bayer Pharma and InCarda outside the submitted work.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Infant’s COVID-19–related myocardial injury reversed
Reports of signs of heart failure in adults with COVID-19 have been rare – just four such cases have been published since the outbreak started in China – and now a team of pediatric cardiologists in New York have reported a case of acute but reversible myocardial injury in an infant with COVID-19.
and right upper lobe atelectasis.
The 2-month-old infant went home after more than 2 weeks in the hospital with no apparent lingering cardiac effects of the illness and not needing any oral heart failure medications, Madhu Sharma, MD, of the Children’s Hospital and Montefiore in New York and colleagues reported in JACC Case Reports. With close follow-up, the child’s left ventricle size and systolic function have remained normal and mitral regurgitation resolved. The case report didn’t mention the infant’s gender.
But before the straightforward postdischarge course emerged, the infant was in a precarious state, and Dr. Sharma and her team were challenged to diagnose the underlying causes.
The child, who was born about 7 weeks premature, first came to the hospital having turned blue after choking on food. Nonrebreather mask ventilation was initiated in the ED, and an examination detected a holosystolic murmur. A test for COVID-19 was negative, but a later test was positive, and a chest x-ray exhibited cardiomegaly and signs of fluid and inflammation in the lungs.
An electrocardiogram detected sinus tachycardia, ST-segment depression and other anomalies in cardiac function. Further investigation with a transthoracic ECG showed severely depressed left ventricle systolic function with an ejection fraction of 30%, severe mitral regurgitation, and normal right ventricular systolic function.
Treatment included remdesivir and intravenous antibiotics. Through the hospital course, the patient was extubated to noninvasive ventilation, reintubated, put on intravenous steroid (methylprednisolone) and low-molecular-weight heparin, extubated, and tested throughout for cardiac function.
By day 14, left ventricle size and function normalized, and while the mitral regurgitation remained severe, it improved later without HF therapies. Left ventricle ejection fraction had recovered to 60%, and key cardiac biomarkers had normalized. On day 16, milrinone was discontinued, and the care team determined the patient no longer needed oral heart failure therapies.
“Most children with COVID-19 are either asymptomatic or have mild symptoms, but our case shows the potential for reversible myocardial injury in infants with COVID-19,” said Dr. Sharma. “Testing for COVID-19 in children presenting with signs and symptoms of heart failure is very important as we learn more about the impact of this virus.”
Dr. Sharma and coauthors have no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Sharma M et al. JACC Case Rep. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2020.09.031.
Reports of signs of heart failure in adults with COVID-19 have been rare – just four such cases have been published since the outbreak started in China – and now a team of pediatric cardiologists in New York have reported a case of acute but reversible myocardial injury in an infant with COVID-19.
and right upper lobe atelectasis.
The 2-month-old infant went home after more than 2 weeks in the hospital with no apparent lingering cardiac effects of the illness and not needing any oral heart failure medications, Madhu Sharma, MD, of the Children’s Hospital and Montefiore in New York and colleagues reported in JACC Case Reports. With close follow-up, the child’s left ventricle size and systolic function have remained normal and mitral regurgitation resolved. The case report didn’t mention the infant’s gender.
But before the straightforward postdischarge course emerged, the infant was in a precarious state, and Dr. Sharma and her team were challenged to diagnose the underlying causes.
The child, who was born about 7 weeks premature, first came to the hospital having turned blue after choking on food. Nonrebreather mask ventilation was initiated in the ED, and an examination detected a holosystolic murmur. A test for COVID-19 was negative, but a later test was positive, and a chest x-ray exhibited cardiomegaly and signs of fluid and inflammation in the lungs.
An electrocardiogram detected sinus tachycardia, ST-segment depression and other anomalies in cardiac function. Further investigation with a transthoracic ECG showed severely depressed left ventricle systolic function with an ejection fraction of 30%, severe mitral regurgitation, and normal right ventricular systolic function.
Treatment included remdesivir and intravenous antibiotics. Through the hospital course, the patient was extubated to noninvasive ventilation, reintubated, put on intravenous steroid (methylprednisolone) and low-molecular-weight heparin, extubated, and tested throughout for cardiac function.
By day 14, left ventricle size and function normalized, and while the mitral regurgitation remained severe, it improved later without HF therapies. Left ventricle ejection fraction had recovered to 60%, and key cardiac biomarkers had normalized. On day 16, milrinone was discontinued, and the care team determined the patient no longer needed oral heart failure therapies.
“Most children with COVID-19 are either asymptomatic or have mild symptoms, but our case shows the potential for reversible myocardial injury in infants with COVID-19,” said Dr. Sharma. “Testing for COVID-19 in children presenting with signs and symptoms of heart failure is very important as we learn more about the impact of this virus.”
Dr. Sharma and coauthors have no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Sharma M et al. JACC Case Rep. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2020.09.031.
Reports of signs of heart failure in adults with COVID-19 have been rare – just four such cases have been published since the outbreak started in China – and now a team of pediatric cardiologists in New York have reported a case of acute but reversible myocardial injury in an infant with COVID-19.
and right upper lobe atelectasis.
The 2-month-old infant went home after more than 2 weeks in the hospital with no apparent lingering cardiac effects of the illness and not needing any oral heart failure medications, Madhu Sharma, MD, of the Children’s Hospital and Montefiore in New York and colleagues reported in JACC Case Reports. With close follow-up, the child’s left ventricle size and systolic function have remained normal and mitral regurgitation resolved. The case report didn’t mention the infant’s gender.
But before the straightforward postdischarge course emerged, the infant was in a precarious state, and Dr. Sharma and her team were challenged to diagnose the underlying causes.
The child, who was born about 7 weeks premature, first came to the hospital having turned blue after choking on food. Nonrebreather mask ventilation was initiated in the ED, and an examination detected a holosystolic murmur. A test for COVID-19 was negative, but a later test was positive, and a chest x-ray exhibited cardiomegaly and signs of fluid and inflammation in the lungs.
An electrocardiogram detected sinus tachycardia, ST-segment depression and other anomalies in cardiac function. Further investigation with a transthoracic ECG showed severely depressed left ventricle systolic function with an ejection fraction of 30%, severe mitral regurgitation, and normal right ventricular systolic function.
Treatment included remdesivir and intravenous antibiotics. Through the hospital course, the patient was extubated to noninvasive ventilation, reintubated, put on intravenous steroid (methylprednisolone) and low-molecular-weight heparin, extubated, and tested throughout for cardiac function.
By day 14, left ventricle size and function normalized, and while the mitral regurgitation remained severe, it improved later without HF therapies. Left ventricle ejection fraction had recovered to 60%, and key cardiac biomarkers had normalized. On day 16, milrinone was discontinued, and the care team determined the patient no longer needed oral heart failure therapies.
“Most children with COVID-19 are either asymptomatic or have mild symptoms, but our case shows the potential for reversible myocardial injury in infants with COVID-19,” said Dr. Sharma. “Testing for COVID-19 in children presenting with signs and symptoms of heart failure is very important as we learn more about the impact of this virus.”
Dr. Sharma and coauthors have no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Sharma M et al. JACC Case Rep. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2020.09.031.
FROM JACC CASE REPORTS
Key clinical point: Children presenting with COVID-19 should be tested for heart failure.
Major finding: A 2-month-old infant with COVID-19 had acute but reversible myocardial injury.
Study details: Single case report.
Disclosures: Dr. Sharma, MD, has no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
Source: Sharma M et al. JACC Case Rep. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2020.09.031.
Noninvasive, low-cost CGM for type 2 diabetes coming in U.S. and EU
A novel lower-cost noninvasive continuous glucose monitor (CGM) combined with a digital education/guidance program is set to launch in the United States and Europe this month for use in type 2 diabetes.
With the goal of improving management, or even reversing the condition, Neumara’s SugarBEAT device is thought to be the world’s first noninvasive CGM.
Its cost is anticipated to be far lower than traditional CGM, and it’s aimed at a different patient population: those with type 2 diabetes or prediabetes who may or may not be performing fingerstick glucose monitoring, but if they are, they still aren’t using the information to guide management.
“This isn’t about handing out devices and letting patients get on about it on their own accord. This is really about supporting those individuals,” Faz Chowdhury, MD, Nemaura’s chief executive officer, said in an interview.
He pointed to studies showing improvements in glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes who were instructed to perform fingerstick blood glucose testing seven times a day for 3-4 days a month and given advice about how to respond to the data.
“This is well established. We’re saying we can make that process a lot more scalable and affordable and convenient for the patient. ... The behavior change side is digitized,” Dr. Chowdhury said. “We want to provide a program to help people reverse their diabetes or at least stabilize it as much as possible.”
Nicholas Argento, MD, diabetes technology director at Maryland Endocrine and Diabetes, Columbia, said in an interview: “It’s interesting. They’re taking a very different approach. I think there’s a lot of validity to what they’re looking at because we have great CGMs right now, but because of the price point it’s not accessible to a lot of people.
“I think they’re onto something that could prove to be useful to a larger group of patients,” he added.
Worn a few days per month and accurate despite being noninvasive
Instead of inserting a catheter under the skin with a needle, as do current CGMs, the device comprises a small rechargeable transmitter and adhesive patch with a sensor that sits on the top of the skin, typically the upper arm. Glucose molecules are drawn out of the interstitial fluid just below the skin and into a chamber where the transmitter measures the glucose level and transmits the data every 5 minutes via Bluetooth to a smartphone app.
Despite this noninvasive approach, the device appears to be about as accurate as traditional CGMs, with comparable mean absolute relative difference (MARD) from a gold standard glucose measure of about 11%-12% with once-daily calibration versus 10%-11% for the Abbott FreeStyle Libre.
Unlike traditional CGMs, SugarBEAT is meant to be worn for only 14 hours at a time during the day and for 2-4 days per month rather than every day.
It’s not aimed at patients with type 1 diabetes or those with type 2 diabetes who are at high risk for hypoglycemia. It requires once-daily fingerstick calibration and is not indicated to replace fingersticks for treatment decisions.
SugarBEAT received a CE Mark in Europe as a Class IIb medical device in May 2019. That version provides real-time glucose values visible to the wearer. In the United States the company submitted a premarketing approval application for the device to the Food and Drug Administration in July 2020, which awaits a decision.
However, FDA is allowing it to enter the U.S. market as a “wellness” device that won’t deliver real-time values for now but instead will generate retroactive reports available to the physician and the patient.
And last month, U.K.-based Neumara launched the BEATdiabetes site, which allows users to sign in and link to the device once it becomes available.
The site provides “scientifically validated, personalized coaching” based on a program developed at the Joslin Diabetes Clinic in Syracuse, N.Y., and will ultimately include monitoring of other cardiovascular risk factors with digital connectivity to a variety of wearables.
Fingerstick monitoring in type 2 diabetes is only so useful
“Fingerstick monitoring for type 2 diabetes is only so useful,” Dr. Argento said in an interview.
“It’s difficult to get people to monitor in a meaningful way.” If patients perform them only in the morning or at other sporadic times of the day, he said, “Then you get a one-dimensional picture ... and they don’t know what to do with the information anyway, so they stop doing it.”
In contrast, with SugarBEAT and BEATDiabetes, “I think it does address a need that fingerstick monitoring doesn’t.”
Dr. Argento did express a few caveats about the device, however. For one, it still requires one fingerstick a day for calibration. “If people don’t like needles, that might be a disincentive.”
Also, despite the apparently comparable mean absolute relative difference with that of conventional CGMs, that measure can still “hide” values that may be consistently either above or below target range.
“MARD is like A1c in that it’s useful but limited. ... It doesn’t tell you about variability or systemic bias,” he said.
Dr. Argento also said that he’d like to see data on the lag time between the interstitial fluid and blood glucose measures with this noninvasive method as compared with that of a subcutaneous catheter.
However, he acknowledged that these potentials for error would be less important for patients with type 2 diabetes who aren’t generally taking medications that increase their risk for hypoglycemia.
In all, he said, “stay tuned. I think this is part of a movement going away from point-in-time to looking at trends and wearables and data to enrich decision-making…There are still some unanswered questions I have but I think they’re onto a concept that’s useful for a broader population.”
Dr. Chowdhury is an employee of Neumara. Dr. Argento consults for Senseonics and Dexcom, and is also a speaker for Dexcom.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A novel lower-cost noninvasive continuous glucose monitor (CGM) combined with a digital education/guidance program is set to launch in the United States and Europe this month for use in type 2 diabetes.
With the goal of improving management, or even reversing the condition, Neumara’s SugarBEAT device is thought to be the world’s first noninvasive CGM.
Its cost is anticipated to be far lower than traditional CGM, and it’s aimed at a different patient population: those with type 2 diabetes or prediabetes who may or may not be performing fingerstick glucose monitoring, but if they are, they still aren’t using the information to guide management.
“This isn’t about handing out devices and letting patients get on about it on their own accord. This is really about supporting those individuals,” Faz Chowdhury, MD, Nemaura’s chief executive officer, said in an interview.
He pointed to studies showing improvements in glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes who were instructed to perform fingerstick blood glucose testing seven times a day for 3-4 days a month and given advice about how to respond to the data.
“This is well established. We’re saying we can make that process a lot more scalable and affordable and convenient for the patient. ... The behavior change side is digitized,” Dr. Chowdhury said. “We want to provide a program to help people reverse their diabetes or at least stabilize it as much as possible.”
Nicholas Argento, MD, diabetes technology director at Maryland Endocrine and Diabetes, Columbia, said in an interview: “It’s interesting. They’re taking a very different approach. I think there’s a lot of validity to what they’re looking at because we have great CGMs right now, but because of the price point it’s not accessible to a lot of people.
“I think they’re onto something that could prove to be useful to a larger group of patients,” he added.
Worn a few days per month and accurate despite being noninvasive
Instead of inserting a catheter under the skin with a needle, as do current CGMs, the device comprises a small rechargeable transmitter and adhesive patch with a sensor that sits on the top of the skin, typically the upper arm. Glucose molecules are drawn out of the interstitial fluid just below the skin and into a chamber where the transmitter measures the glucose level and transmits the data every 5 minutes via Bluetooth to a smartphone app.
Despite this noninvasive approach, the device appears to be about as accurate as traditional CGMs, with comparable mean absolute relative difference (MARD) from a gold standard glucose measure of about 11%-12% with once-daily calibration versus 10%-11% for the Abbott FreeStyle Libre.
Unlike traditional CGMs, SugarBEAT is meant to be worn for only 14 hours at a time during the day and for 2-4 days per month rather than every day.
It’s not aimed at patients with type 1 diabetes or those with type 2 diabetes who are at high risk for hypoglycemia. It requires once-daily fingerstick calibration and is not indicated to replace fingersticks for treatment decisions.
SugarBEAT received a CE Mark in Europe as a Class IIb medical device in May 2019. That version provides real-time glucose values visible to the wearer. In the United States the company submitted a premarketing approval application for the device to the Food and Drug Administration in July 2020, which awaits a decision.
However, FDA is allowing it to enter the U.S. market as a “wellness” device that won’t deliver real-time values for now but instead will generate retroactive reports available to the physician and the patient.
And last month, U.K.-based Neumara launched the BEATdiabetes site, which allows users to sign in and link to the device once it becomes available.
The site provides “scientifically validated, personalized coaching” based on a program developed at the Joslin Diabetes Clinic in Syracuse, N.Y., and will ultimately include monitoring of other cardiovascular risk factors with digital connectivity to a variety of wearables.
Fingerstick monitoring in type 2 diabetes is only so useful
“Fingerstick monitoring for type 2 diabetes is only so useful,” Dr. Argento said in an interview.
“It’s difficult to get people to monitor in a meaningful way.” If patients perform them only in the morning or at other sporadic times of the day, he said, “Then you get a one-dimensional picture ... and they don’t know what to do with the information anyway, so they stop doing it.”
In contrast, with SugarBEAT and BEATDiabetes, “I think it does address a need that fingerstick monitoring doesn’t.”
Dr. Argento did express a few caveats about the device, however. For one, it still requires one fingerstick a day for calibration. “If people don’t like needles, that might be a disincentive.”
Also, despite the apparently comparable mean absolute relative difference with that of conventional CGMs, that measure can still “hide” values that may be consistently either above or below target range.
“MARD is like A1c in that it’s useful but limited. ... It doesn’t tell you about variability or systemic bias,” he said.
Dr. Argento also said that he’d like to see data on the lag time between the interstitial fluid and blood glucose measures with this noninvasive method as compared with that of a subcutaneous catheter.
However, he acknowledged that these potentials for error would be less important for patients with type 2 diabetes who aren’t generally taking medications that increase their risk for hypoglycemia.
In all, he said, “stay tuned. I think this is part of a movement going away from point-in-time to looking at trends and wearables and data to enrich decision-making…There are still some unanswered questions I have but I think they’re onto a concept that’s useful for a broader population.”
Dr. Chowdhury is an employee of Neumara. Dr. Argento consults for Senseonics and Dexcom, and is also a speaker for Dexcom.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A novel lower-cost noninvasive continuous glucose monitor (CGM) combined with a digital education/guidance program is set to launch in the United States and Europe this month for use in type 2 diabetes.
With the goal of improving management, or even reversing the condition, Neumara’s SugarBEAT device is thought to be the world’s first noninvasive CGM.
Its cost is anticipated to be far lower than traditional CGM, and it’s aimed at a different patient population: those with type 2 diabetes or prediabetes who may or may not be performing fingerstick glucose monitoring, but if they are, they still aren’t using the information to guide management.
“This isn’t about handing out devices and letting patients get on about it on their own accord. This is really about supporting those individuals,” Faz Chowdhury, MD, Nemaura’s chief executive officer, said in an interview.
He pointed to studies showing improvements in glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes who were instructed to perform fingerstick blood glucose testing seven times a day for 3-4 days a month and given advice about how to respond to the data.
“This is well established. We’re saying we can make that process a lot more scalable and affordable and convenient for the patient. ... The behavior change side is digitized,” Dr. Chowdhury said. “We want to provide a program to help people reverse their diabetes or at least stabilize it as much as possible.”
Nicholas Argento, MD, diabetes technology director at Maryland Endocrine and Diabetes, Columbia, said in an interview: “It’s interesting. They’re taking a very different approach. I think there’s a lot of validity to what they’re looking at because we have great CGMs right now, but because of the price point it’s not accessible to a lot of people.
“I think they’re onto something that could prove to be useful to a larger group of patients,” he added.
Worn a few days per month and accurate despite being noninvasive
Instead of inserting a catheter under the skin with a needle, as do current CGMs, the device comprises a small rechargeable transmitter and adhesive patch with a sensor that sits on the top of the skin, typically the upper arm. Glucose molecules are drawn out of the interstitial fluid just below the skin and into a chamber where the transmitter measures the glucose level and transmits the data every 5 minutes via Bluetooth to a smartphone app.
Despite this noninvasive approach, the device appears to be about as accurate as traditional CGMs, with comparable mean absolute relative difference (MARD) from a gold standard glucose measure of about 11%-12% with once-daily calibration versus 10%-11% for the Abbott FreeStyle Libre.
Unlike traditional CGMs, SugarBEAT is meant to be worn for only 14 hours at a time during the day and for 2-4 days per month rather than every day.
It’s not aimed at patients with type 1 diabetes or those with type 2 diabetes who are at high risk for hypoglycemia. It requires once-daily fingerstick calibration and is not indicated to replace fingersticks for treatment decisions.
SugarBEAT received a CE Mark in Europe as a Class IIb medical device in May 2019. That version provides real-time glucose values visible to the wearer. In the United States the company submitted a premarketing approval application for the device to the Food and Drug Administration in July 2020, which awaits a decision.
However, FDA is allowing it to enter the U.S. market as a “wellness” device that won’t deliver real-time values for now but instead will generate retroactive reports available to the physician and the patient.
And last month, U.K.-based Neumara launched the BEATdiabetes site, which allows users to sign in and link to the device once it becomes available.
The site provides “scientifically validated, personalized coaching” based on a program developed at the Joslin Diabetes Clinic in Syracuse, N.Y., and will ultimately include monitoring of other cardiovascular risk factors with digital connectivity to a variety of wearables.
Fingerstick monitoring in type 2 diabetes is only so useful
“Fingerstick monitoring for type 2 diabetes is only so useful,” Dr. Argento said in an interview.
“It’s difficult to get people to monitor in a meaningful way.” If patients perform them only in the morning or at other sporadic times of the day, he said, “Then you get a one-dimensional picture ... and they don’t know what to do with the information anyway, so they stop doing it.”
In contrast, with SugarBEAT and BEATDiabetes, “I think it does address a need that fingerstick monitoring doesn’t.”
Dr. Argento did express a few caveats about the device, however. For one, it still requires one fingerstick a day for calibration. “If people don’t like needles, that might be a disincentive.”
Also, despite the apparently comparable mean absolute relative difference with that of conventional CGMs, that measure can still “hide” values that may be consistently either above or below target range.
“MARD is like A1c in that it’s useful but limited. ... It doesn’t tell you about variability or systemic bias,” he said.
Dr. Argento also said that he’d like to see data on the lag time between the interstitial fluid and blood glucose measures with this noninvasive method as compared with that of a subcutaneous catheter.
However, he acknowledged that these potentials for error would be less important for patients with type 2 diabetes who aren’t generally taking medications that increase their risk for hypoglycemia.
In all, he said, “stay tuned. I think this is part of a movement going away from point-in-time to looking at trends and wearables and data to enrich decision-making…There are still some unanswered questions I have but I think they’re onto a concept that’s useful for a broader population.”
Dr. Chowdhury is an employee of Neumara. Dr. Argento consults for Senseonics and Dexcom, and is also a speaker for Dexcom.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New AHA scientific statement on menopause and CVD risk
Changes in hormones, body composition, lipids, and vascular health during the menopause transition can increase a woman’s chance of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD) after menopause, the American Heart Association said in a scientific statement.
“This statement aims to raise awareness of both healthcare providers and women about the menopause transition as a time of increasing heart disease risk,” Samar R. El Khoudary, PhD, MPH, who chaired the writing group, said in an interview.
“As such, it emphasizes the importance of monitoring women’s health during midlife and targeting this stage as a critical window for applying early intervention strategies that aim to maintain a healthy heart and reduce the risk of heart disease,” said Dr. El Khoudary, of the University of Pittsburgh.
The statement was published online Nov. 30 in Circulation.
Evolution in knowledge
During the past 20 years, knowledge of how menopause might contribute to CVD has evolved “dramatically,” Dr. El Khoudary noted. The accumulated data consistently point to the menopause transition as a time of change in heart health.
“Importantly,” she said, the latest AHA guidelines for CVD prevention in women, published in 2011, do not include data now available on the menopause transition as a time of increased CVD risk.
“As such, there is a compelling need to discuss the implications of the accumulating body of literature on this topic,” said Dr. El Khoudary.
The statement provides a contemporary synthesis of the existing data on menopause and how it relates to CVD, the leading cause of death of U.S. women.
Earlier age at natural menopause has generally been found to be a marker of greater CVD risk. Iatrogenically induced menopause (bilateral oophorectomy) during the premenopausal period is also associated with higher CVD risk, the data suggest.
Vasomotor symptoms are associated with worse levels of CVD risk factors and measures of subclinical atherosclerosis. Sleep disturbance has also been linked to greater risk for subclinical CVD and worse CV health indexes in women during midlife.
Increases in central/visceral fat and decreases in lean muscle mass are more pronounced during the menopause transition. This increased central adiposity is associated with increased risk for mortality, even among those with normal body mass index, the writing group found.
Increases in lipid levels (LDL cholesterol and apolipoprotein B), metabolic syndrome risk, and vascular remodeling at midlife are driven by the menopause transition more than aging, whereas increases in blood pressure, insulin level, and glucose level are likely more influenced by chronological aging, they reported.
Lifestyle interventions
The writing group noted that, because of the increase in overall life expectancy in the United States, a significant proportion of women will spend up to 40% of their lives after menopause.
Yet data suggest that only 7.2% of women transitioning to menopause are meeting physical activity guidelines and that fewer than 20% of those women are consistently maintaining a healthy diet.
Limited data from randomized, controlled trials suggest that a multidimensional lifestyle intervention during the menopause transition can prevent weight gain and reduce blood pressure and levels of triglycerides, blood glucose, and insulin and reduce the incidence of subclinical carotid atherosclerosis, they pointed out.
“Novel data” indicate a reversal in the associations of HDL cholesterol with CVD risk over the menopause transition, suggesting that higher HDL cholesterol levels may not consistently reflect good cardiovascular health in middle-aged women, the group noted.
There are also data suggesting that starting menopause hormone therapy when younger than 60 years or within 10 years of menopause is associated with reduced CVD risk.
The group said further research is needed into the cardiometabolic effects of menopause hormone therapy, including effects associated with form, route, and duration of administration, in women traversing menopause.
They also noted that data for the primary and secondary prevention of atherosclerotic CVD and improved survival with lipid-lowering interventions “remain elusive” for women and that further study is needed to develop evidence-based recommendations tailored specifically to women.
The research had no commercial funding. Dr. El Khoudary has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Changes in hormones, body composition, lipids, and vascular health during the menopause transition can increase a woman’s chance of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD) after menopause, the American Heart Association said in a scientific statement.
“This statement aims to raise awareness of both healthcare providers and women about the menopause transition as a time of increasing heart disease risk,” Samar R. El Khoudary, PhD, MPH, who chaired the writing group, said in an interview.
“As such, it emphasizes the importance of monitoring women’s health during midlife and targeting this stage as a critical window for applying early intervention strategies that aim to maintain a healthy heart and reduce the risk of heart disease,” said Dr. El Khoudary, of the University of Pittsburgh.
The statement was published online Nov. 30 in Circulation.
Evolution in knowledge
During the past 20 years, knowledge of how menopause might contribute to CVD has evolved “dramatically,” Dr. El Khoudary noted. The accumulated data consistently point to the menopause transition as a time of change in heart health.
“Importantly,” she said, the latest AHA guidelines for CVD prevention in women, published in 2011, do not include data now available on the menopause transition as a time of increased CVD risk.
“As such, there is a compelling need to discuss the implications of the accumulating body of literature on this topic,” said Dr. El Khoudary.
The statement provides a contemporary synthesis of the existing data on menopause and how it relates to CVD, the leading cause of death of U.S. women.
Earlier age at natural menopause has generally been found to be a marker of greater CVD risk. Iatrogenically induced menopause (bilateral oophorectomy) during the premenopausal period is also associated with higher CVD risk, the data suggest.
Vasomotor symptoms are associated with worse levels of CVD risk factors and measures of subclinical atherosclerosis. Sleep disturbance has also been linked to greater risk for subclinical CVD and worse CV health indexes in women during midlife.
Increases in central/visceral fat and decreases in lean muscle mass are more pronounced during the menopause transition. This increased central adiposity is associated with increased risk for mortality, even among those with normal body mass index, the writing group found.
Increases in lipid levels (LDL cholesterol and apolipoprotein B), metabolic syndrome risk, and vascular remodeling at midlife are driven by the menopause transition more than aging, whereas increases in blood pressure, insulin level, and glucose level are likely more influenced by chronological aging, they reported.
Lifestyle interventions
The writing group noted that, because of the increase in overall life expectancy in the United States, a significant proportion of women will spend up to 40% of their lives after menopause.
Yet data suggest that only 7.2% of women transitioning to menopause are meeting physical activity guidelines and that fewer than 20% of those women are consistently maintaining a healthy diet.
Limited data from randomized, controlled trials suggest that a multidimensional lifestyle intervention during the menopause transition can prevent weight gain and reduce blood pressure and levels of triglycerides, blood glucose, and insulin and reduce the incidence of subclinical carotid atherosclerosis, they pointed out.
“Novel data” indicate a reversal in the associations of HDL cholesterol with CVD risk over the menopause transition, suggesting that higher HDL cholesterol levels may not consistently reflect good cardiovascular health in middle-aged women, the group noted.
There are also data suggesting that starting menopause hormone therapy when younger than 60 years or within 10 years of menopause is associated with reduced CVD risk.
The group said further research is needed into the cardiometabolic effects of menopause hormone therapy, including effects associated with form, route, and duration of administration, in women traversing menopause.
They also noted that data for the primary and secondary prevention of atherosclerotic CVD and improved survival with lipid-lowering interventions “remain elusive” for women and that further study is needed to develop evidence-based recommendations tailored specifically to women.
The research had no commercial funding. Dr. El Khoudary has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Changes in hormones, body composition, lipids, and vascular health during the menopause transition can increase a woman’s chance of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD) after menopause, the American Heart Association said in a scientific statement.
“This statement aims to raise awareness of both healthcare providers and women about the menopause transition as a time of increasing heart disease risk,” Samar R. El Khoudary, PhD, MPH, who chaired the writing group, said in an interview.
“As such, it emphasizes the importance of monitoring women’s health during midlife and targeting this stage as a critical window for applying early intervention strategies that aim to maintain a healthy heart and reduce the risk of heart disease,” said Dr. El Khoudary, of the University of Pittsburgh.
The statement was published online Nov. 30 in Circulation.
Evolution in knowledge
During the past 20 years, knowledge of how menopause might contribute to CVD has evolved “dramatically,” Dr. El Khoudary noted. The accumulated data consistently point to the menopause transition as a time of change in heart health.
“Importantly,” she said, the latest AHA guidelines for CVD prevention in women, published in 2011, do not include data now available on the menopause transition as a time of increased CVD risk.
“As such, there is a compelling need to discuss the implications of the accumulating body of literature on this topic,” said Dr. El Khoudary.
The statement provides a contemporary synthesis of the existing data on menopause and how it relates to CVD, the leading cause of death of U.S. women.
Earlier age at natural menopause has generally been found to be a marker of greater CVD risk. Iatrogenically induced menopause (bilateral oophorectomy) during the premenopausal period is also associated with higher CVD risk, the data suggest.
Vasomotor symptoms are associated with worse levels of CVD risk factors and measures of subclinical atherosclerosis. Sleep disturbance has also been linked to greater risk for subclinical CVD and worse CV health indexes in women during midlife.
Increases in central/visceral fat and decreases in lean muscle mass are more pronounced during the menopause transition. This increased central adiposity is associated with increased risk for mortality, even among those with normal body mass index, the writing group found.
Increases in lipid levels (LDL cholesterol and apolipoprotein B), metabolic syndrome risk, and vascular remodeling at midlife are driven by the menopause transition more than aging, whereas increases in blood pressure, insulin level, and glucose level are likely more influenced by chronological aging, they reported.
Lifestyle interventions
The writing group noted that, because of the increase in overall life expectancy in the United States, a significant proportion of women will spend up to 40% of their lives after menopause.
Yet data suggest that only 7.2% of women transitioning to menopause are meeting physical activity guidelines and that fewer than 20% of those women are consistently maintaining a healthy diet.
Limited data from randomized, controlled trials suggest that a multidimensional lifestyle intervention during the menopause transition can prevent weight gain and reduce blood pressure and levels of triglycerides, blood glucose, and insulin and reduce the incidence of subclinical carotid atherosclerosis, they pointed out.
“Novel data” indicate a reversal in the associations of HDL cholesterol with CVD risk over the menopause transition, suggesting that higher HDL cholesterol levels may not consistently reflect good cardiovascular health in middle-aged women, the group noted.
There are also data suggesting that starting menopause hormone therapy when younger than 60 years or within 10 years of menopause is associated with reduced CVD risk.
The group said further research is needed into the cardiometabolic effects of menopause hormone therapy, including effects associated with form, route, and duration of administration, in women traversing menopause.
They also noted that data for the primary and secondary prevention of atherosclerotic CVD and improved survival with lipid-lowering interventions “remain elusive” for women and that further study is needed to develop evidence-based recommendations tailored specifically to women.
The research had no commercial funding. Dr. El Khoudary has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
First SGLT1/2 inhibitor shows ‘spectacular’ phase 3 safety and efficacy in T2D
Sotagliflozin, a novel type of sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibitor, showed the diverse benefits this drug class provides along some new twists in a pair of international pivotal trials that together enrolled nearly 12,000 patients with type 2 diabetes.
Unprecedented benefits were seen for the first time with a drug, sotagliflozin (Zynquista) that produces both sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition as well as SGLT1 inhibition.
They included a big reduction in both MIs and strokes; an ability to meaningfully reduce hyperglycemia in patients with severe renal dysfunction with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 25-29 mL/min per 1.73 m2; an ability to safely and effectively start in patients still hospitalized (but stable) for an acute heart failure episode; and a striking 37% relative risk reduction in cardiovascular death, heart failure hospitalizations, or an urgent outpatient visit for heart failure in 739 of the patients enrolled in both trials who had heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
These studies produced for the first time evidence from controlled, prospective, randomized trials that a drug could improve the outcome of HFpEF patients.
All these novel outcomes came on top of the usual benefits clinicians have generally seen across the SGLT2 inhibitors already on the U.S. market: reductions in cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalizations among all patients with type 2 diabetes, preservation of renal function, and hemoglobin A1c lowering among T2D patients with eGFR levels of at least 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
“The data look spectacular,” summed up Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, who presented the results from the two trials, SOLOIST-WHF and SCORED, in talks at the virtual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association.
“I think sotagliflozin has the potential to be the best in class” based on the several added attributes shown in the two trials, he said in an interview. “We’ve shown that it is very safe, well tolerated, and effective.”
The primary results were a significant 33% relative risk reduction with sotagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo in the rate of total cardiovascular deaths, hospitalizations for heart failure, or urgent outpatient visits for heart failure during just over 9 months of median follow-up among patients with T2D recently hospitalized for heart failure in SOLOIST-WFH. And a significant 26% relative risk reduction with sotagliflozin for the same endpoint after a median follow-up of just over 14 months in SCORED, which enrolled patients with T2D and chronic kidney disease.
“Sotagliflozin adds to the SGLT2 inhibitor story,” and the SOLOIST-WHF results “may shift our focus to vulnerable, acute heart failure patients with an opportunity to treat during the transition phase,” when these patients leave the hospital, commented Jane E. Wilcox, MD, the study’s designated discussant and a heart failure cardiologist at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago.
A dual SGLT inhibitor
What sets sotagliflozin apart from the SGLT2 inhibitors is that it not only inhibits that protein but also SGTL1, which primarily resides in the gastrointestinal tract and is the main route for gut absorption of glucose. Dr. Bhatt said that he was unaware of any other SGLT1/2 inhibitors currently in advanced clinical testing.
The activity of sotagliflozin against the SGLT1 protein likely explains its ability to cut A1c levels in patients with severe renal dysfunction, a condition that stymies glucose lowering by SGLT2 inhibitors. In SCORED, which randomized 10,584 patients with T2D at 750 study sites in 44 countries, 813 patients (8%) had an eGFR of 25-29 mL/min per 1.73 m2 at enrollment. Sotagliflozin treatment led to an average 0.6% cut in A1c in this subgroup, and by the same average amount among the patients with GFRs of 30-60 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
“This is a huge finding for endocrinologists and primary care physicians” who treat patients with T2D who have severe renal dysfunction, said Dr. Bhatt, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School in Boston. “It’s a good enough reason by itself to approve this drug.”
The same mechanism may also be behind another unexpected finding in SCORED. Treatment with sotagliflozin cut the rate of total episodes of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, or nonfatal stroke by an absolute 1.6%, compared with placebo, and by a relative 23%. This benefit was largely driven by a 32% relative risk reduction total in MIs, and a 34% relative risk reduction in total stroke, both significant differences.
“No SGLT2 inhibitor has shown a reduction in stroke, and the MI signals have been mixed. The sizable MI and stroke effects are unique to sotagliflozin,” compared with the SGLT2 inhibitors, and likely reflect one or more mechanisms that result from blocked gut SGLT1 and a cut in GI glucose uptake, said Dr. Bhatt. “Probably some novel mechanism we don’t fully understand.”
First-ever HFpEF benefit
In contrast to these two benefits that are probably unique to drugs that inhibit the SGLT1 protein, sotagliflozin showed two other notable and unprecedented benefits that are likely generalizable to the SGLT2 inhibitors.
First is the striking benefit for HFpEF. Neither SOLOIST, which enrolled 1,222 patients with T2D and just hospitalized for worsening heart failure, nor SCORED, which enrolled patients with T2D and chronic kidney disease based exclusively on an eGFR of 25-60 mL/min per 1.73 m2, excluded patients with HFpEF, defined as heart failure patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction of at least 50%. The two studies together included a total of 739 of these patients, and they split fairly evenly between treatment with sotagliflozin or placebo.
The combined analysis showed that the incidence rate for the primary endpoint in both SOLOIST and SCORED was 59% with placebo and 39% with sotagliflozin, an absolute event reduction of 11.6 events/100 patient-years, and a significant 37% relative risk reduction, with a number needed to treat to prevent 1 event per year event of 9.
Although this observation comes from a nonprespecified combined analysis, “to me this result seems real, and I think it’s a class effect that I’m willing to extrapolate to the SGLT2 inhibitors,” Dr. Bhatt said. “It will change my practice,” he added, by spurring him to more aggressively prescribe an SGLT2 inhibitor to a patient with T2D and HFpEF.
“I think there has been some hesitation to use SGLT2 inhibitors in T2D patients with HFpEF” because of the paucity of data in this population, even though labeling and society recommendations do not rule it out. “I hope this finding will move that needle, and also generally improve SGLT2 inhibitor uptake, which has been low,” he said.
Also safe soon after acute heart failure decompensation
The other finding likely generalizable to SGLT2 inhibitors stems from the design of SOLOIST-WHF, which tested the efficacy and safety of starting sotagliflozin in patients with T2D as soon as they were stable after hospitalization for acute heart failure decompensation.
“Showing safety and efficacy when started in the hospital is pretty meaningful, because its tells patients that this drug is important and they should stay on it,” which should improve adherence, predicted Dr. Bhatt, who is also executive director of Interventional Cardiovascular Programs at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. “That’s the ultimate treatment path to prevent patients from falling through the cracks” and failing to receive an SGLT2 inhibitor.
SOLOIST-WHF enrolled patients hospitalized for worsening heart failure who also required intravenous diuretic treatment but had become stable enough to transition to an oral diuretic and come off oxygen. During a median follow-up of just over 9 months (both SOLOIST-WHF and SCORED ended sooner than planned because of a change in drug company sponsorship), treatment with sotagliflozin cut the primary endpoint by a relative 33%, compared with placebo, and with an absolute reduction of 25 events per 100 patient-years for a number needed to treat of 4. Sotagliflozin produced a strikingly high level of treatment efficiency driven by the high event rate in these recently decompensated patients. The benefit also appeared quickly, with a significant cut in events discernible within 28 days.
Extrapolating this finding to the SGLT2 inhibitors is “not a huge leap of faith,” Dr. Bhatt said.
“There is a role for sotagliflozin in acute heart failure. It showed benefit in these high-risk, transition-phase patients,” said Dr. Wilcox.
Simultaneously with Dr. Bhatt’s presentation, results of SOLOIST-WHF and SCORED were published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The trials were sponsored initially by Sanofi, and more recently by Lexicon. Dr. Bhatt has received research funding from both companies, and also from several other companies. He also is an adviser to several companies. Dr. Wilcox has been a consultant to Boehringer Ingelheim and Medtronic.
Sotagliflozin, a novel type of sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibitor, showed the diverse benefits this drug class provides along some new twists in a pair of international pivotal trials that together enrolled nearly 12,000 patients with type 2 diabetes.
Unprecedented benefits were seen for the first time with a drug, sotagliflozin (Zynquista) that produces both sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition as well as SGLT1 inhibition.
They included a big reduction in both MIs and strokes; an ability to meaningfully reduce hyperglycemia in patients with severe renal dysfunction with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 25-29 mL/min per 1.73 m2; an ability to safely and effectively start in patients still hospitalized (but stable) for an acute heart failure episode; and a striking 37% relative risk reduction in cardiovascular death, heart failure hospitalizations, or an urgent outpatient visit for heart failure in 739 of the patients enrolled in both trials who had heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
These studies produced for the first time evidence from controlled, prospective, randomized trials that a drug could improve the outcome of HFpEF patients.
All these novel outcomes came on top of the usual benefits clinicians have generally seen across the SGLT2 inhibitors already on the U.S. market: reductions in cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalizations among all patients with type 2 diabetes, preservation of renal function, and hemoglobin A1c lowering among T2D patients with eGFR levels of at least 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
“The data look spectacular,” summed up Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, who presented the results from the two trials, SOLOIST-WHF and SCORED, in talks at the virtual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association.
“I think sotagliflozin has the potential to be the best in class” based on the several added attributes shown in the two trials, he said in an interview. “We’ve shown that it is very safe, well tolerated, and effective.”
The primary results were a significant 33% relative risk reduction with sotagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo in the rate of total cardiovascular deaths, hospitalizations for heart failure, or urgent outpatient visits for heart failure during just over 9 months of median follow-up among patients with T2D recently hospitalized for heart failure in SOLOIST-WFH. And a significant 26% relative risk reduction with sotagliflozin for the same endpoint after a median follow-up of just over 14 months in SCORED, which enrolled patients with T2D and chronic kidney disease.
“Sotagliflozin adds to the SGLT2 inhibitor story,” and the SOLOIST-WHF results “may shift our focus to vulnerable, acute heart failure patients with an opportunity to treat during the transition phase,” when these patients leave the hospital, commented Jane E. Wilcox, MD, the study’s designated discussant and a heart failure cardiologist at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago.
A dual SGLT inhibitor
What sets sotagliflozin apart from the SGLT2 inhibitors is that it not only inhibits that protein but also SGTL1, which primarily resides in the gastrointestinal tract and is the main route for gut absorption of glucose. Dr. Bhatt said that he was unaware of any other SGLT1/2 inhibitors currently in advanced clinical testing.
The activity of sotagliflozin against the SGLT1 protein likely explains its ability to cut A1c levels in patients with severe renal dysfunction, a condition that stymies glucose lowering by SGLT2 inhibitors. In SCORED, which randomized 10,584 patients with T2D at 750 study sites in 44 countries, 813 patients (8%) had an eGFR of 25-29 mL/min per 1.73 m2 at enrollment. Sotagliflozin treatment led to an average 0.6% cut in A1c in this subgroup, and by the same average amount among the patients with GFRs of 30-60 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
“This is a huge finding for endocrinologists and primary care physicians” who treat patients with T2D who have severe renal dysfunction, said Dr. Bhatt, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School in Boston. “It’s a good enough reason by itself to approve this drug.”
The same mechanism may also be behind another unexpected finding in SCORED. Treatment with sotagliflozin cut the rate of total episodes of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, or nonfatal stroke by an absolute 1.6%, compared with placebo, and by a relative 23%. This benefit was largely driven by a 32% relative risk reduction total in MIs, and a 34% relative risk reduction in total stroke, both significant differences.
“No SGLT2 inhibitor has shown a reduction in stroke, and the MI signals have been mixed. The sizable MI and stroke effects are unique to sotagliflozin,” compared with the SGLT2 inhibitors, and likely reflect one or more mechanisms that result from blocked gut SGLT1 and a cut in GI glucose uptake, said Dr. Bhatt. “Probably some novel mechanism we don’t fully understand.”
First-ever HFpEF benefit
In contrast to these two benefits that are probably unique to drugs that inhibit the SGLT1 protein, sotagliflozin showed two other notable and unprecedented benefits that are likely generalizable to the SGLT2 inhibitors.
First is the striking benefit for HFpEF. Neither SOLOIST, which enrolled 1,222 patients with T2D and just hospitalized for worsening heart failure, nor SCORED, which enrolled patients with T2D and chronic kidney disease based exclusively on an eGFR of 25-60 mL/min per 1.73 m2, excluded patients with HFpEF, defined as heart failure patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction of at least 50%. The two studies together included a total of 739 of these patients, and they split fairly evenly between treatment with sotagliflozin or placebo.
The combined analysis showed that the incidence rate for the primary endpoint in both SOLOIST and SCORED was 59% with placebo and 39% with sotagliflozin, an absolute event reduction of 11.6 events/100 patient-years, and a significant 37% relative risk reduction, with a number needed to treat to prevent 1 event per year event of 9.
Although this observation comes from a nonprespecified combined analysis, “to me this result seems real, and I think it’s a class effect that I’m willing to extrapolate to the SGLT2 inhibitors,” Dr. Bhatt said. “It will change my practice,” he added, by spurring him to more aggressively prescribe an SGLT2 inhibitor to a patient with T2D and HFpEF.
“I think there has been some hesitation to use SGLT2 inhibitors in T2D patients with HFpEF” because of the paucity of data in this population, even though labeling and society recommendations do not rule it out. “I hope this finding will move that needle, and also generally improve SGLT2 inhibitor uptake, which has been low,” he said.
Also safe soon after acute heart failure decompensation
The other finding likely generalizable to SGLT2 inhibitors stems from the design of SOLOIST-WHF, which tested the efficacy and safety of starting sotagliflozin in patients with T2D as soon as they were stable after hospitalization for acute heart failure decompensation.
“Showing safety and efficacy when started in the hospital is pretty meaningful, because its tells patients that this drug is important and they should stay on it,” which should improve adherence, predicted Dr. Bhatt, who is also executive director of Interventional Cardiovascular Programs at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. “That’s the ultimate treatment path to prevent patients from falling through the cracks” and failing to receive an SGLT2 inhibitor.
SOLOIST-WHF enrolled patients hospitalized for worsening heart failure who also required intravenous diuretic treatment but had become stable enough to transition to an oral diuretic and come off oxygen. During a median follow-up of just over 9 months (both SOLOIST-WHF and SCORED ended sooner than planned because of a change in drug company sponsorship), treatment with sotagliflozin cut the primary endpoint by a relative 33%, compared with placebo, and with an absolute reduction of 25 events per 100 patient-years for a number needed to treat of 4. Sotagliflozin produced a strikingly high level of treatment efficiency driven by the high event rate in these recently decompensated patients. The benefit also appeared quickly, with a significant cut in events discernible within 28 days.
Extrapolating this finding to the SGLT2 inhibitors is “not a huge leap of faith,” Dr. Bhatt said.
“There is a role for sotagliflozin in acute heart failure. It showed benefit in these high-risk, transition-phase patients,” said Dr. Wilcox.
Simultaneously with Dr. Bhatt’s presentation, results of SOLOIST-WHF and SCORED were published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The trials were sponsored initially by Sanofi, and more recently by Lexicon. Dr. Bhatt has received research funding from both companies, and also from several other companies. He also is an adviser to several companies. Dr. Wilcox has been a consultant to Boehringer Ingelheim and Medtronic.
Sotagliflozin, a novel type of sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibitor, showed the diverse benefits this drug class provides along some new twists in a pair of international pivotal trials that together enrolled nearly 12,000 patients with type 2 diabetes.
Unprecedented benefits were seen for the first time with a drug, sotagliflozin (Zynquista) that produces both sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition as well as SGLT1 inhibition.
They included a big reduction in both MIs and strokes; an ability to meaningfully reduce hyperglycemia in patients with severe renal dysfunction with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 25-29 mL/min per 1.73 m2; an ability to safely and effectively start in patients still hospitalized (but stable) for an acute heart failure episode; and a striking 37% relative risk reduction in cardiovascular death, heart failure hospitalizations, or an urgent outpatient visit for heart failure in 739 of the patients enrolled in both trials who had heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
These studies produced for the first time evidence from controlled, prospective, randomized trials that a drug could improve the outcome of HFpEF patients.
All these novel outcomes came on top of the usual benefits clinicians have generally seen across the SGLT2 inhibitors already on the U.S. market: reductions in cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalizations among all patients with type 2 diabetes, preservation of renal function, and hemoglobin A1c lowering among T2D patients with eGFR levels of at least 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
“The data look spectacular,” summed up Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, who presented the results from the two trials, SOLOIST-WHF and SCORED, in talks at the virtual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association.
“I think sotagliflozin has the potential to be the best in class” based on the several added attributes shown in the two trials, he said in an interview. “We’ve shown that it is very safe, well tolerated, and effective.”
The primary results were a significant 33% relative risk reduction with sotagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo in the rate of total cardiovascular deaths, hospitalizations for heart failure, or urgent outpatient visits for heart failure during just over 9 months of median follow-up among patients with T2D recently hospitalized for heart failure in SOLOIST-WFH. And a significant 26% relative risk reduction with sotagliflozin for the same endpoint after a median follow-up of just over 14 months in SCORED, which enrolled patients with T2D and chronic kidney disease.
“Sotagliflozin adds to the SGLT2 inhibitor story,” and the SOLOIST-WHF results “may shift our focus to vulnerable, acute heart failure patients with an opportunity to treat during the transition phase,” when these patients leave the hospital, commented Jane E. Wilcox, MD, the study’s designated discussant and a heart failure cardiologist at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago.
A dual SGLT inhibitor
What sets sotagliflozin apart from the SGLT2 inhibitors is that it not only inhibits that protein but also SGTL1, which primarily resides in the gastrointestinal tract and is the main route for gut absorption of glucose. Dr. Bhatt said that he was unaware of any other SGLT1/2 inhibitors currently in advanced clinical testing.
The activity of sotagliflozin against the SGLT1 protein likely explains its ability to cut A1c levels in patients with severe renal dysfunction, a condition that stymies glucose lowering by SGLT2 inhibitors. In SCORED, which randomized 10,584 patients with T2D at 750 study sites in 44 countries, 813 patients (8%) had an eGFR of 25-29 mL/min per 1.73 m2 at enrollment. Sotagliflozin treatment led to an average 0.6% cut in A1c in this subgroup, and by the same average amount among the patients with GFRs of 30-60 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
“This is a huge finding for endocrinologists and primary care physicians” who treat patients with T2D who have severe renal dysfunction, said Dr. Bhatt, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School in Boston. “It’s a good enough reason by itself to approve this drug.”
The same mechanism may also be behind another unexpected finding in SCORED. Treatment with sotagliflozin cut the rate of total episodes of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, or nonfatal stroke by an absolute 1.6%, compared with placebo, and by a relative 23%. This benefit was largely driven by a 32% relative risk reduction total in MIs, and a 34% relative risk reduction in total stroke, both significant differences.
“No SGLT2 inhibitor has shown a reduction in stroke, and the MI signals have been mixed. The sizable MI and stroke effects are unique to sotagliflozin,” compared with the SGLT2 inhibitors, and likely reflect one or more mechanisms that result from blocked gut SGLT1 and a cut in GI glucose uptake, said Dr. Bhatt. “Probably some novel mechanism we don’t fully understand.”
First-ever HFpEF benefit
In contrast to these two benefits that are probably unique to drugs that inhibit the SGLT1 protein, sotagliflozin showed two other notable and unprecedented benefits that are likely generalizable to the SGLT2 inhibitors.
First is the striking benefit for HFpEF. Neither SOLOIST, which enrolled 1,222 patients with T2D and just hospitalized for worsening heart failure, nor SCORED, which enrolled patients with T2D and chronic kidney disease based exclusively on an eGFR of 25-60 mL/min per 1.73 m2, excluded patients with HFpEF, defined as heart failure patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction of at least 50%. The two studies together included a total of 739 of these patients, and they split fairly evenly between treatment with sotagliflozin or placebo.
The combined analysis showed that the incidence rate for the primary endpoint in both SOLOIST and SCORED was 59% with placebo and 39% with sotagliflozin, an absolute event reduction of 11.6 events/100 patient-years, and a significant 37% relative risk reduction, with a number needed to treat to prevent 1 event per year event of 9.
Although this observation comes from a nonprespecified combined analysis, “to me this result seems real, and I think it’s a class effect that I’m willing to extrapolate to the SGLT2 inhibitors,” Dr. Bhatt said. “It will change my practice,” he added, by spurring him to more aggressively prescribe an SGLT2 inhibitor to a patient with T2D and HFpEF.
“I think there has been some hesitation to use SGLT2 inhibitors in T2D patients with HFpEF” because of the paucity of data in this population, even though labeling and society recommendations do not rule it out. “I hope this finding will move that needle, and also generally improve SGLT2 inhibitor uptake, which has been low,” he said.
Also safe soon after acute heart failure decompensation
The other finding likely generalizable to SGLT2 inhibitors stems from the design of SOLOIST-WHF, which tested the efficacy and safety of starting sotagliflozin in patients with T2D as soon as they were stable after hospitalization for acute heart failure decompensation.
“Showing safety and efficacy when started in the hospital is pretty meaningful, because its tells patients that this drug is important and they should stay on it,” which should improve adherence, predicted Dr. Bhatt, who is also executive director of Interventional Cardiovascular Programs at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. “That’s the ultimate treatment path to prevent patients from falling through the cracks” and failing to receive an SGLT2 inhibitor.
SOLOIST-WHF enrolled patients hospitalized for worsening heart failure who also required intravenous diuretic treatment but had become stable enough to transition to an oral diuretic and come off oxygen. During a median follow-up of just over 9 months (both SOLOIST-WHF and SCORED ended sooner than planned because of a change in drug company sponsorship), treatment with sotagliflozin cut the primary endpoint by a relative 33%, compared with placebo, and with an absolute reduction of 25 events per 100 patient-years for a number needed to treat of 4. Sotagliflozin produced a strikingly high level of treatment efficiency driven by the high event rate in these recently decompensated patients. The benefit also appeared quickly, with a significant cut in events discernible within 28 days.
Extrapolating this finding to the SGLT2 inhibitors is “not a huge leap of faith,” Dr. Bhatt said.
“There is a role for sotagliflozin in acute heart failure. It showed benefit in these high-risk, transition-phase patients,” said Dr. Wilcox.
Simultaneously with Dr. Bhatt’s presentation, results of SOLOIST-WHF and SCORED were published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The trials were sponsored initially by Sanofi, and more recently by Lexicon. Dr. Bhatt has received research funding from both companies, and also from several other companies. He also is an adviser to several companies. Dr. Wilcox has been a consultant to Boehringer Ingelheim and Medtronic.
FROM AHA 2020